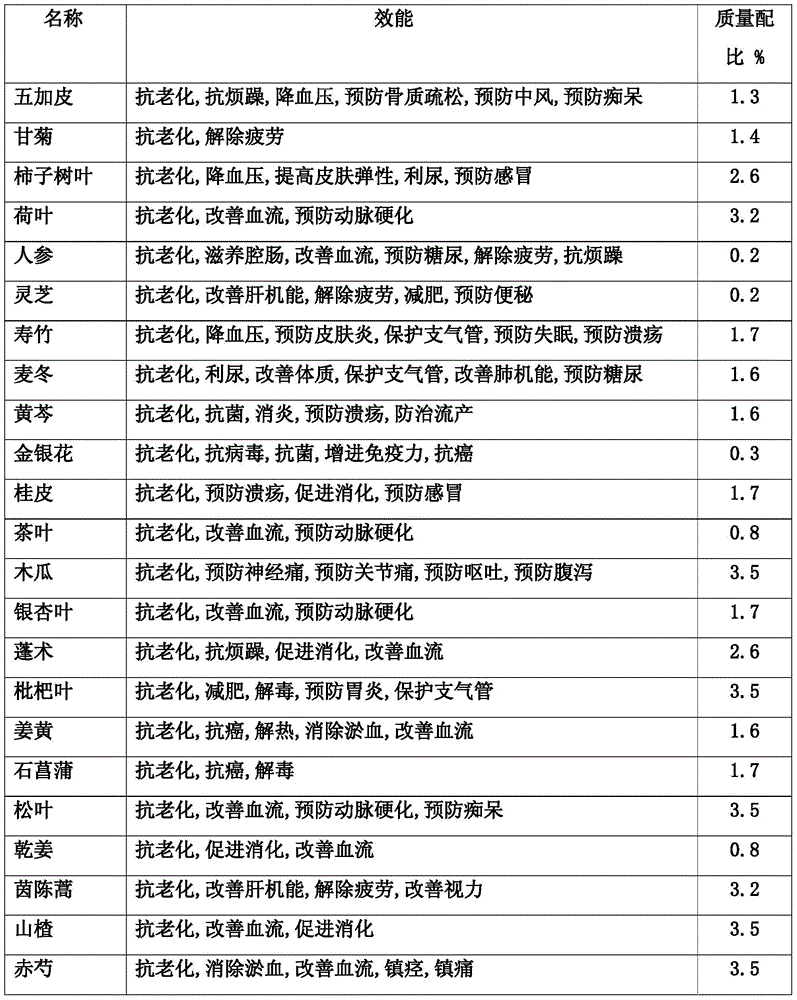
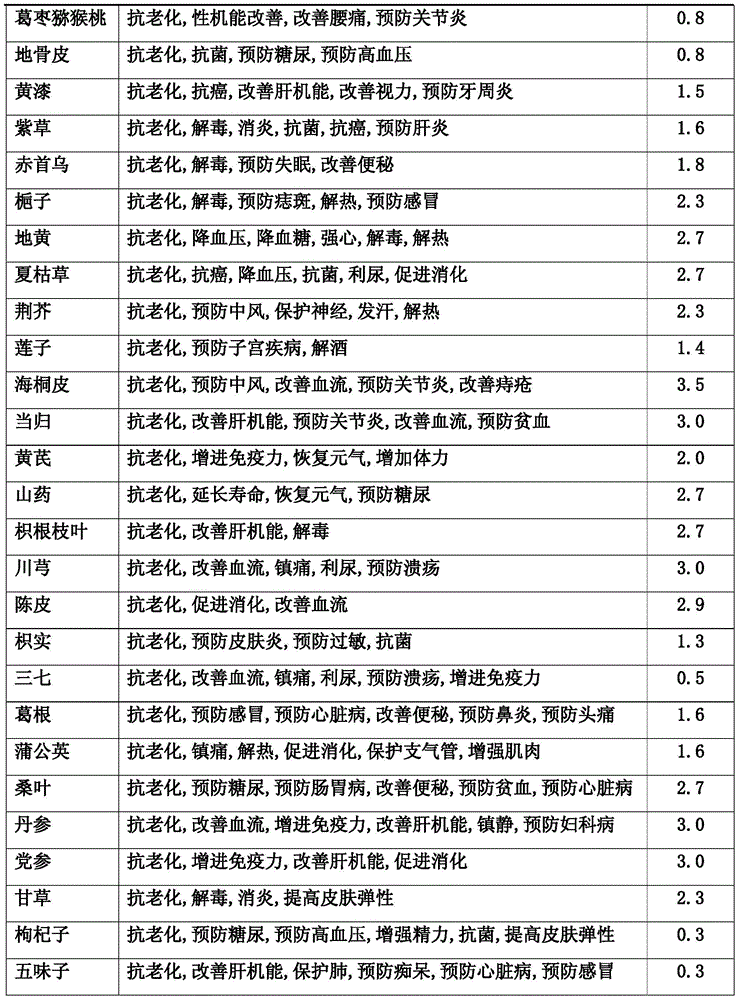
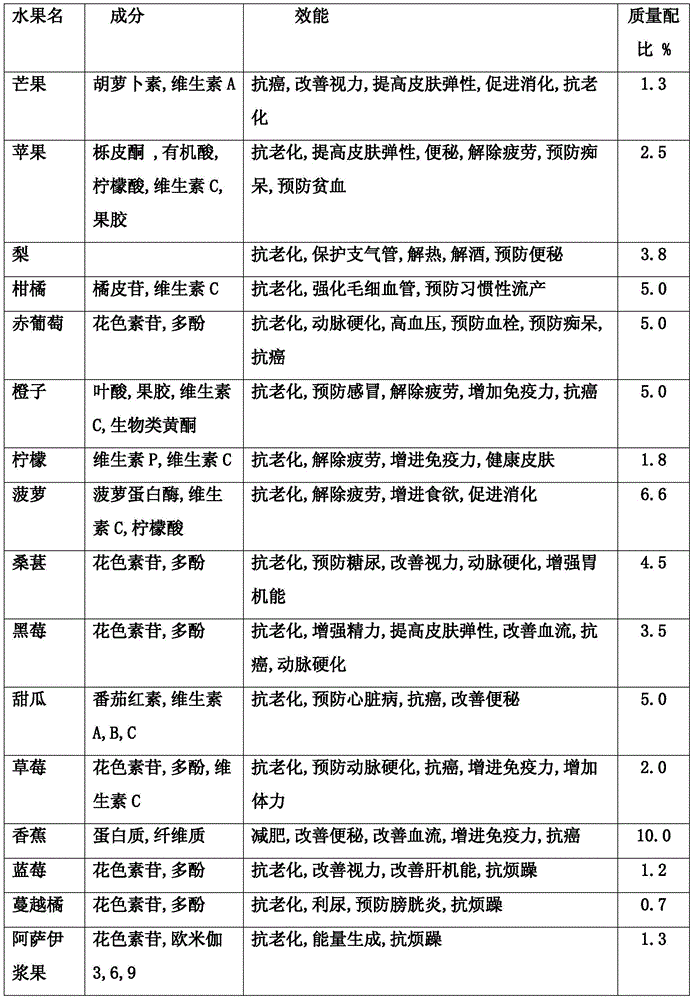
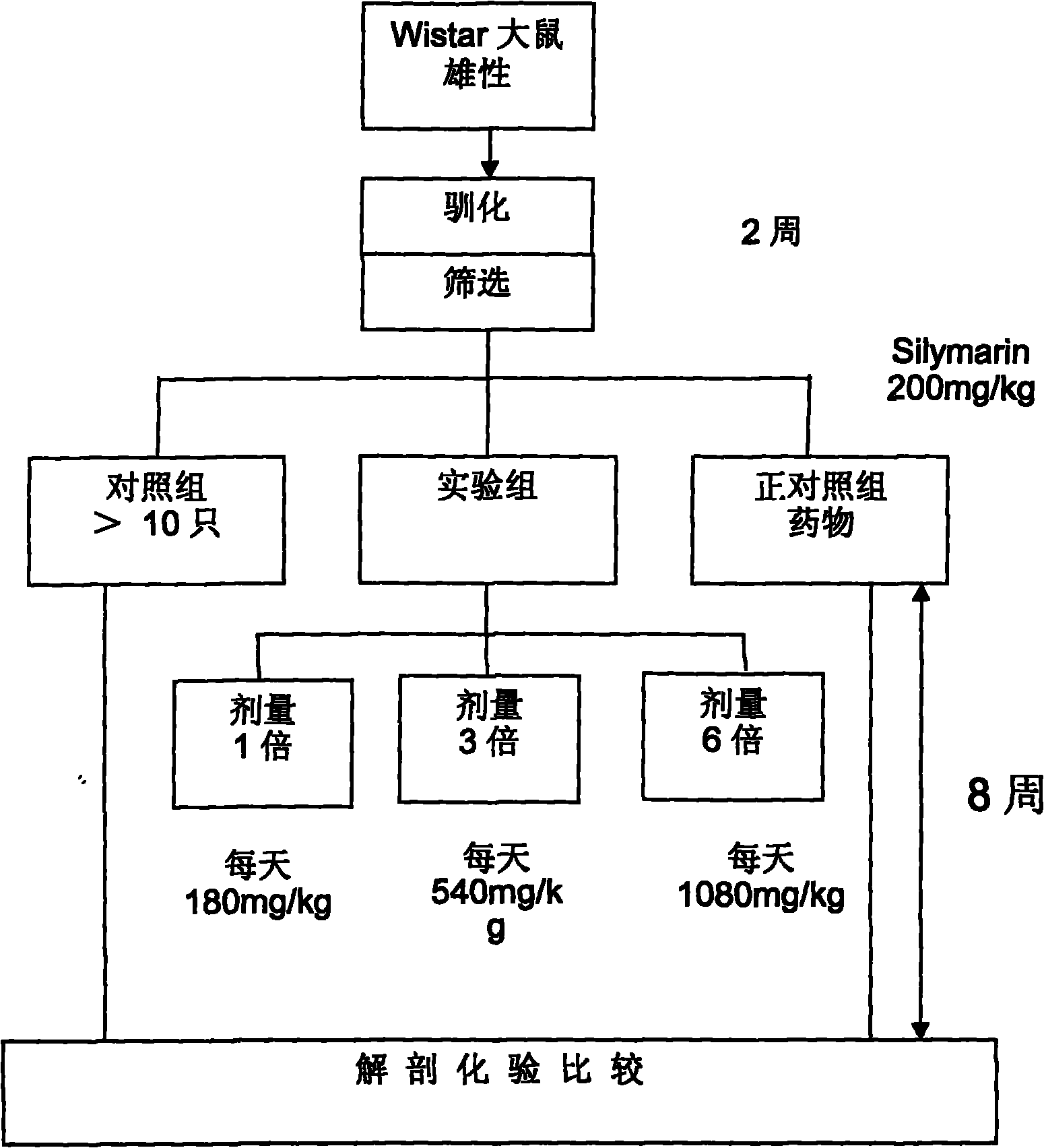
Patents
Literature
88 results about "Phagocyte" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Phagocytes are cells that protect the body by ingesting harmful foreign particles, bacteria, and dead or dying cells. Their name comes from the Greek phagein, "to eat" or "devour", and "-cyte", the suffix in biology denoting "cell", from the Greek kutos, "hollow vessel". They are essential for fighting infections and for subsequent immunity. Phagocytes are important throughout the animal kingdom and are highly developed within vertebrates. One litre of human blood contains about six billion phagocytes. They were discovered in 1882 by Ilya Ilyich Mechnikov while he was studying starfish larvae. Mechnikov was awarded the 1908 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine for his discovery. Phagocytes occur in many species; some amoebae behave like macrophage phagocytes, which suggests that phagocytes appeared early in the evolution of life.
Plant additive premixed forage for aquatic culture and bait therefrom
InactiveCN1644077AQuality improvementEnhance phagocytosisClimate change adaptationAnimal feeding stuffHerbAnimal Foraging
A vegetative additive for the mixed feed used to culture quatic animals is proportionally prepared from adhesive, allicin, and 8 Chinese-medicinal materials including dandelion herb, phellodendron bark, scutellaria root, liquorice root, etc. Its advantage is high effect to kill bacteria and virus and promote the development of immune organs.
Owner:冯绍宽
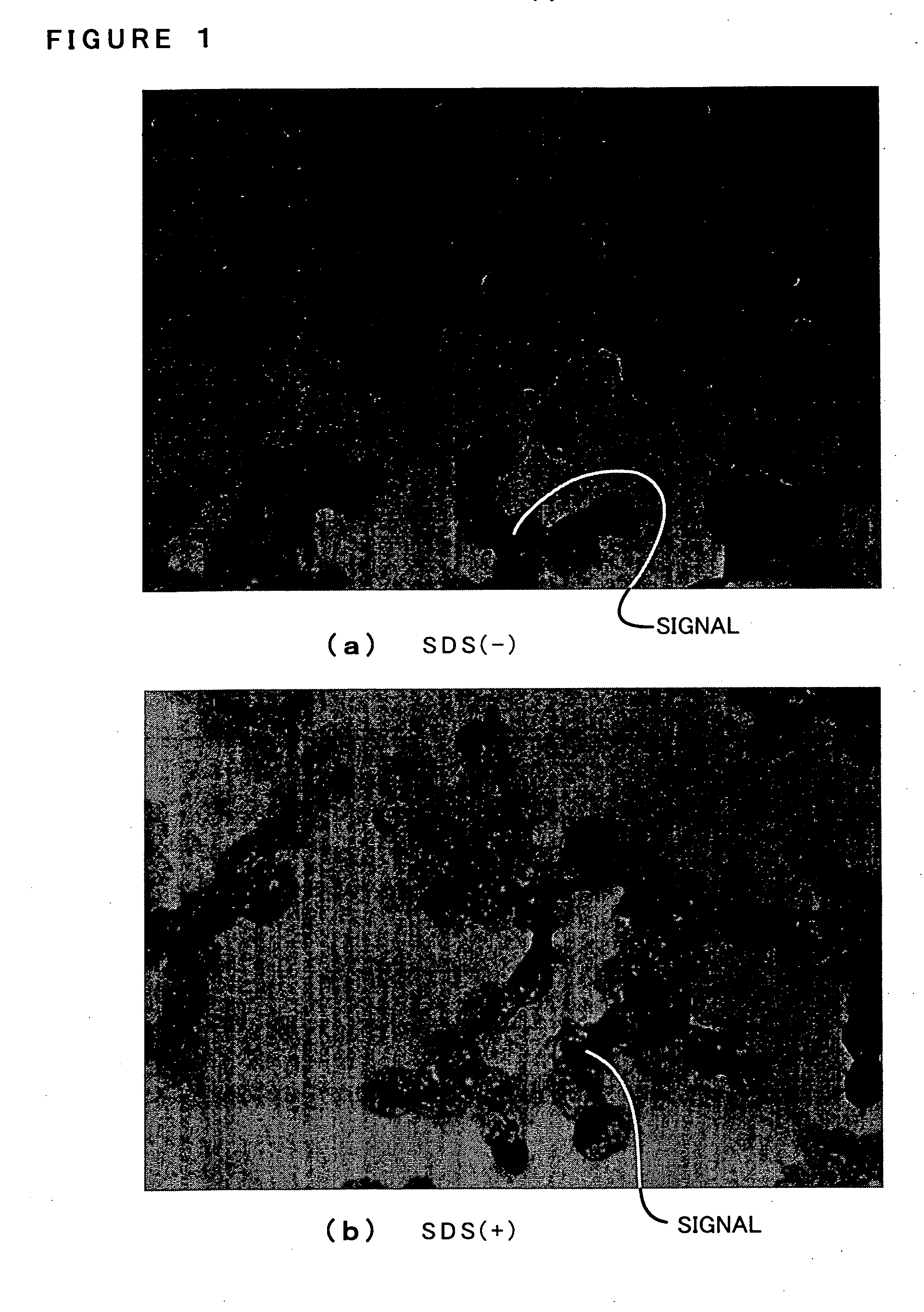
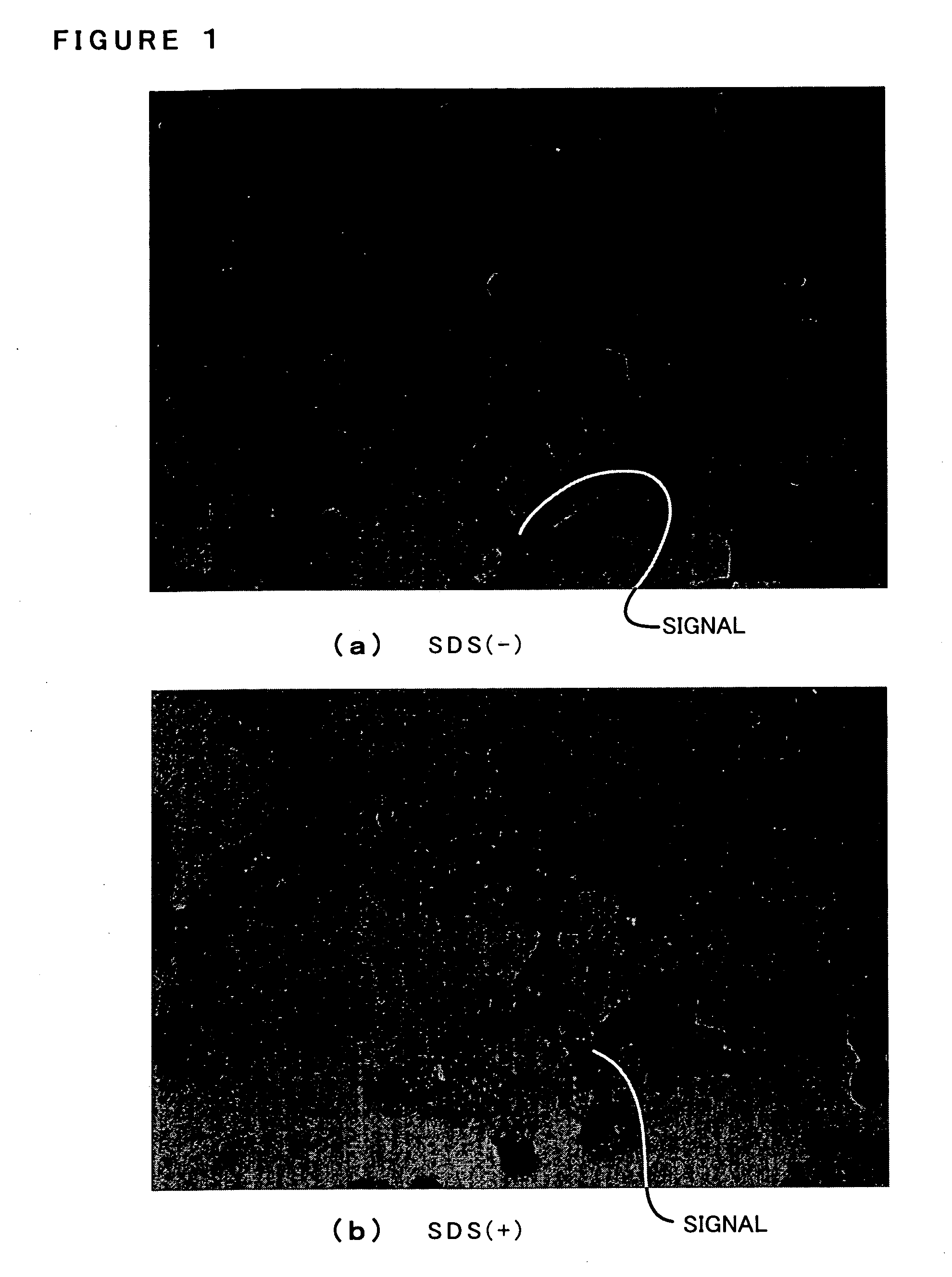
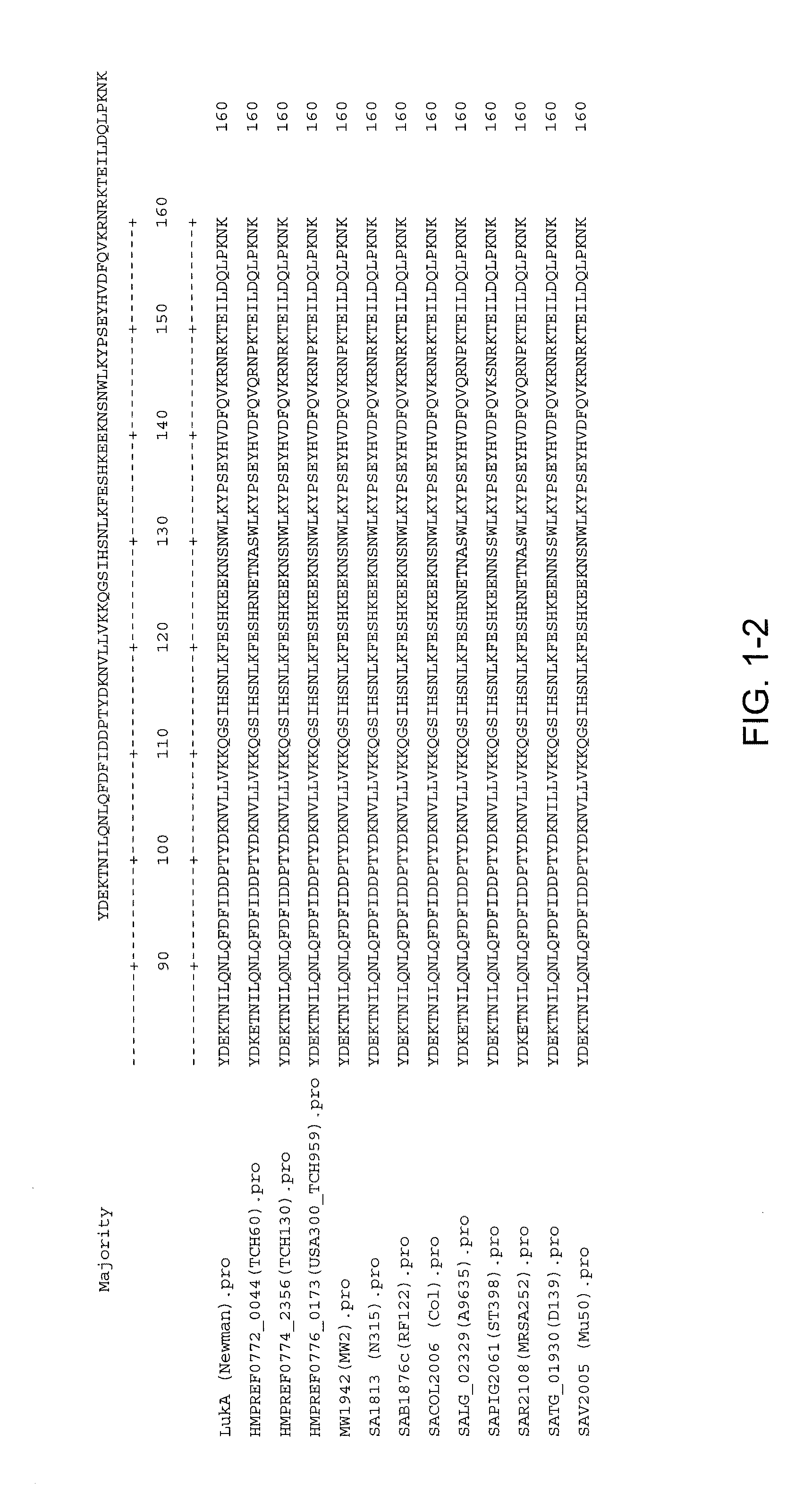
Staphylococcus aureus leukocidins, therapeutic compositions, and uses thereof
ActiveUS20110274693A1Reduce in quantityReduce severityAntibacterial agentsPeptide/protein ingredientsPhagocyteWhite blood cell
Disclosed herein are isolated and purified Staphylococcus aureus bi-component leukocidin, referred to herein as LukAB, and its components LukA and LukB, antibodies specific to LukA, antibodies specific to LukB, therapeutic compositions containing LukA and / or LukB, or anti-LukA and / or anti-LukB antibodies, uses of the compositions to treat acute inflammatory conditions or S. aureus infection, methods for identifying inhibitors of LukAB-mediated cytotoxicity of human phagocytes, and methods for using LukAB as a marker to predict severity of S. aureus infection.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
Mononuclear phagocytes and their use to promote axonal regeneration
InactiveUS6267955B1Increase capacityEnhance phagocytic activityBiocideNervous disorderPhagocyteDisease
Methods and compositions are disclosed for the use of allogeneic mononuclear phagocytes to promote axonal regeneration in the central nervous system of a mammal. In one embodiment, allogeneic mononuclear phagocytes are cultured together with stimulatory tissue, such as skin, dermis or at least one nerve segment, and are subsequently administered into the central nervous system of a mammal at or near a site of injury or disease. In an alternative embodiment, autologous monocytes, preferably stimulated autologous monocytes, are administered into the central nervous system of a mammal at or near a site of injury or disease. CNS administration of mononuclear phagocytes may optionally be combined with administration of an adjuvant factor (e.g. aFGF) to the CNS, anti-inflammatory therapy of the mammal, or both. Methods for screening stimulatory tissue and cells and methods and compositions for cryopreserved allogeneic mononuclear phagocytes are also disclosed.
Owner:YEDA RES & DEV CO LTD
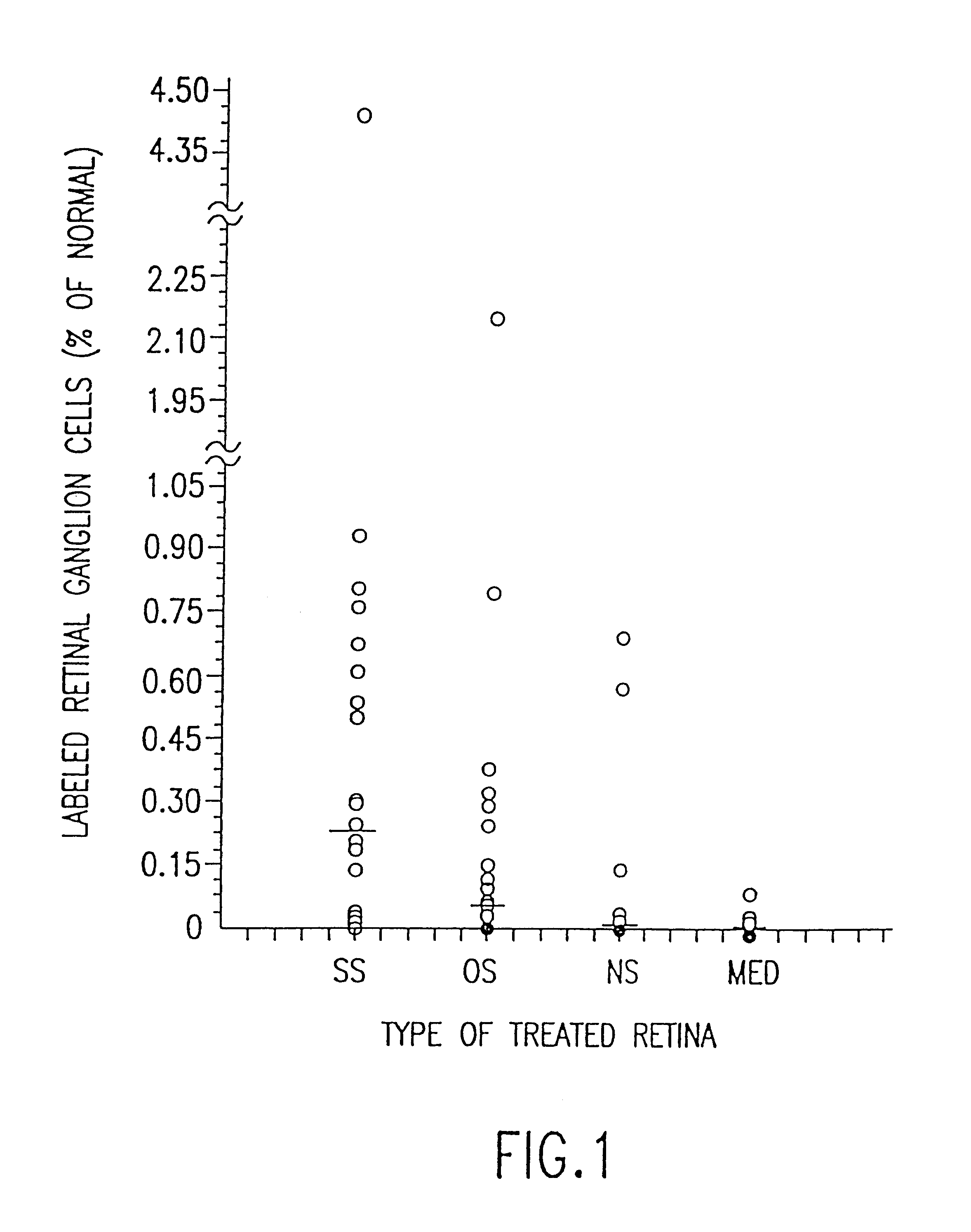
Methods and compositions for treating secondary tissue damage and other inflammatory conditions and disorders
InactiveUS7157418B1Enhance and aid in survivalPrevent proliferationAntibacterial agentsBiocidePhagocyteDendritic cell
Conjugates containing as a ligand a chemokine receptor targeting agents, such as chemokines, and a targeted agent, such as a toxin are provided. These conjugates are used to treat inflammatory responses associated with activation, proliferation and migration of immune effector cells, including leukocyte cell types, neutrophiles, macrophages, and eosinophils. The conjugates provided herein are used to lessen or inhibit these processes to prevent or at least lessen the resulting secondary effects. In particular, the conjugates are used to target toxins to receptors on secondary tissue damage-promoting cells. The ligand moiety can be selected to deliver the cell toxin to such secondary tissue damage-promoting cells as mononuclear phagocytes, leukocytes, natural killer cells, dendritic cells, and T and B lymphocytes, thereby suppressing the proliferation, migration, or physiological activity of such cells. Among preferred conjugates are fusion proteins having a chemokine, or a biologically active fragment thereof, as the ligand moiety linked to a cell toxin via a peptide linker of from 2 to about 60 amino acid residues.
Owner:OSPREY PHARMA USA INC
Method for detecting and identifying microorganism causative of infection
InactiveUS7651837B2Microbiological testing/measurementPreparing sample for investigationPhagocytePathogenic microorganism
Causative microorganisms of infectious diseases are detected and / or identified rapidly and with high sensitivity by taking phagocytes from clinical specimens containing active phagocytes, immobilizing the phagocytes so taken, treating the phagocytes to improve cell membrane permeabilities thereof, further treating the phagocytes to bare DNA in the causative microorganisms which might exist in the phagocytes, and detecting the causative microorganisms with DNA probes which can hybridize with such DNA under stringent conditions.
Owner:FUSO PHARMA INDS
Method of inhibiting overactivity of phagocytes or lymphocytes in an individual
InactiveUS20030100514A1Reduce formationReduce riskBiocideHydroxy compound active ingredientsPhagocyteEnterolactone
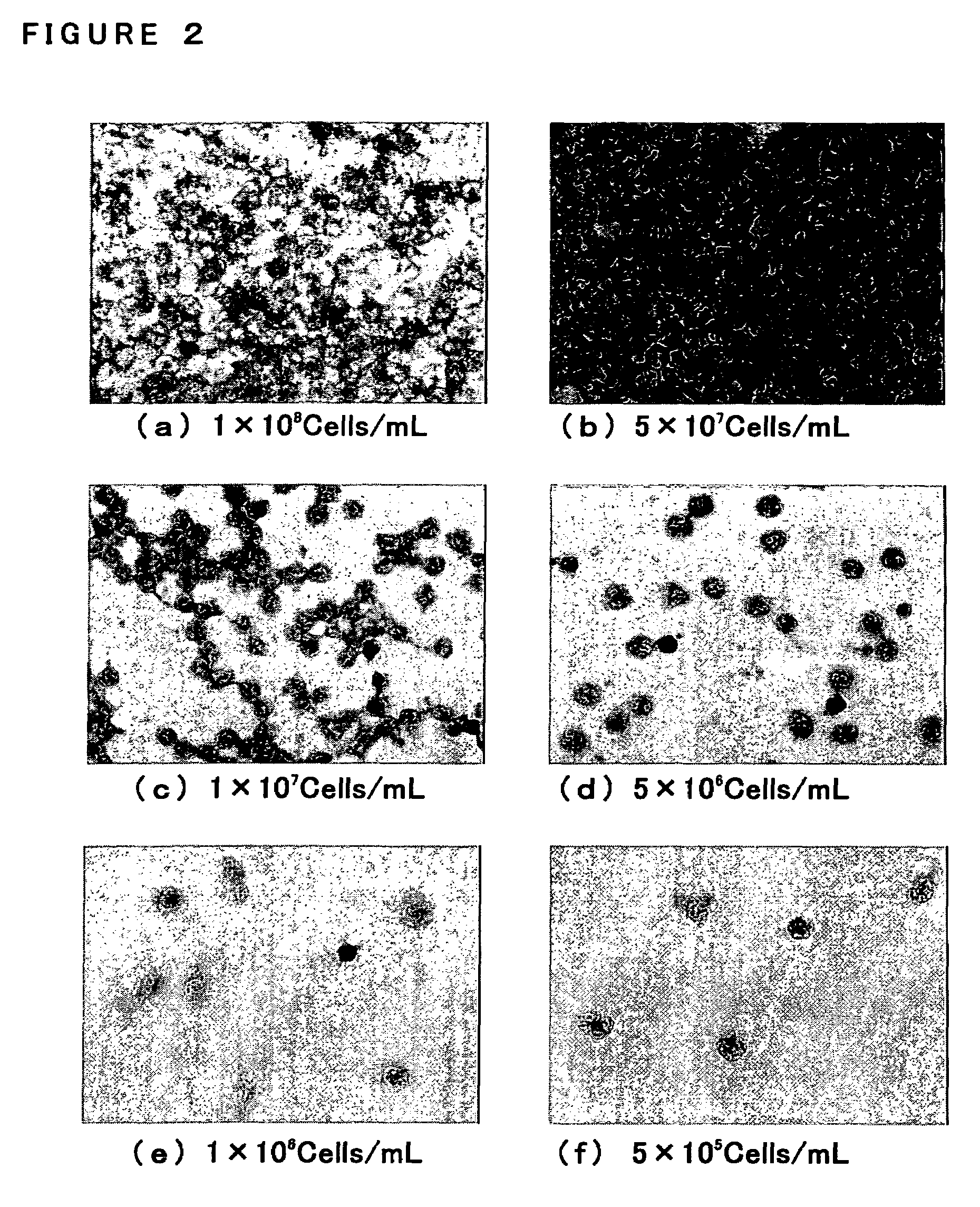
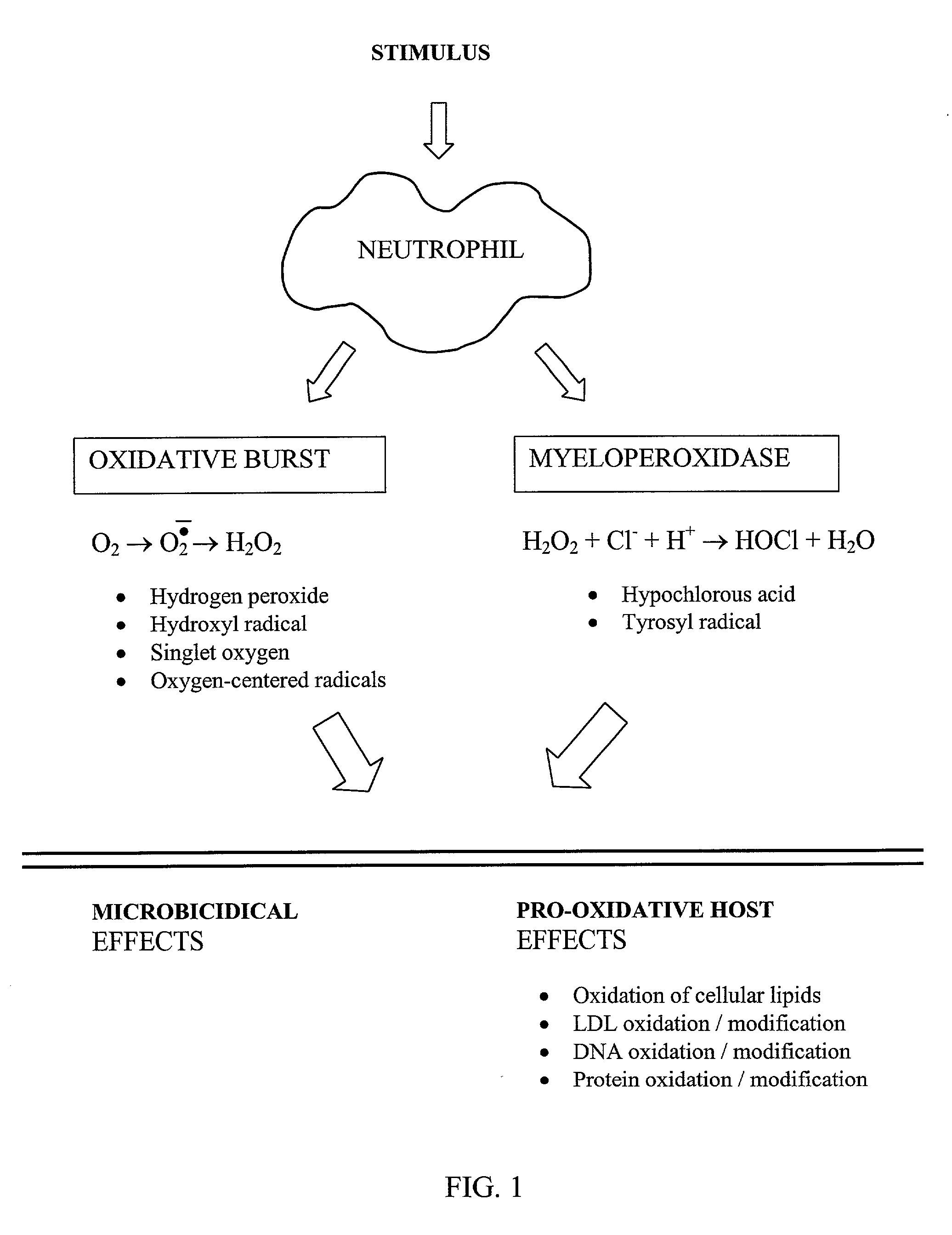
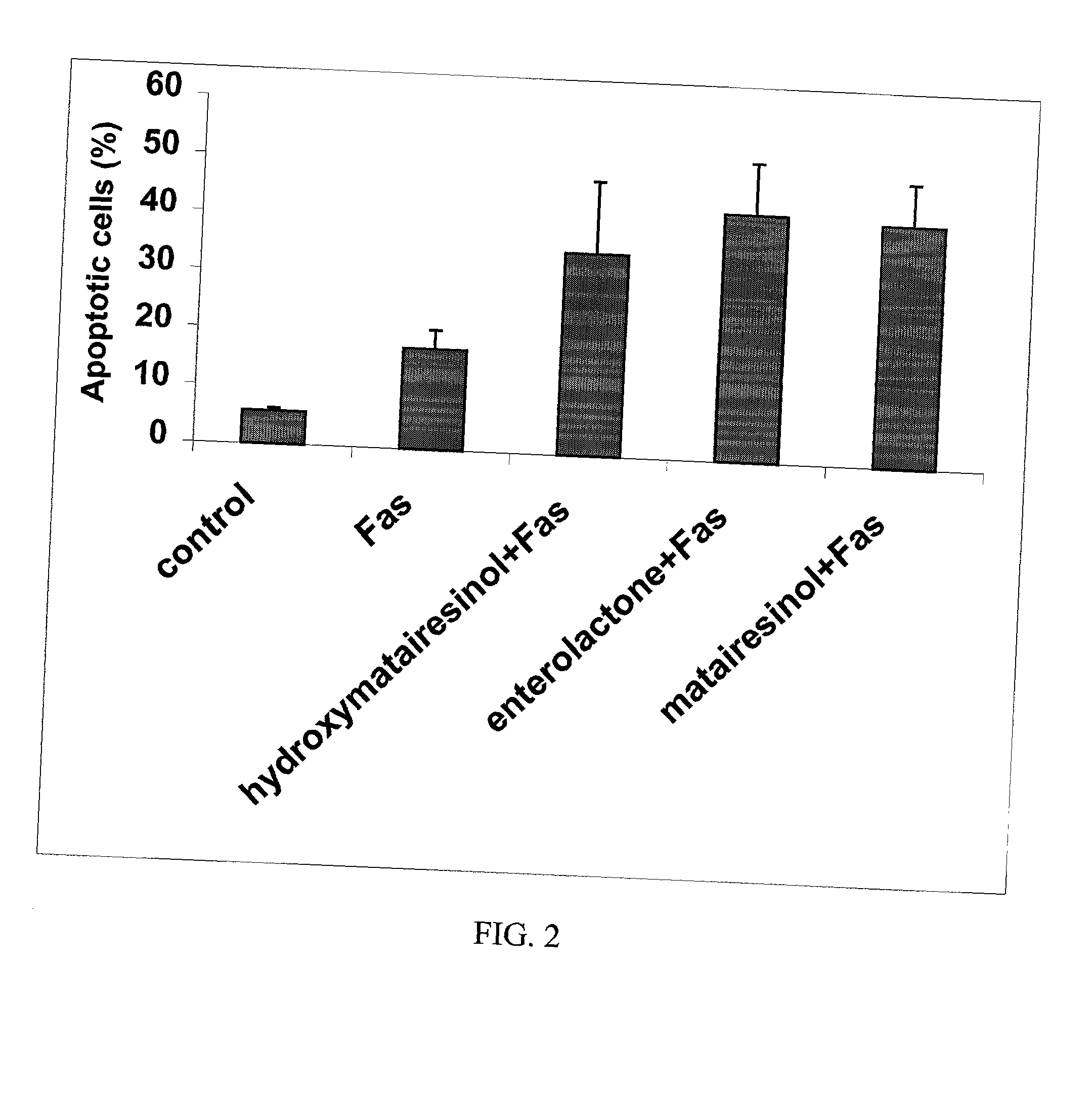
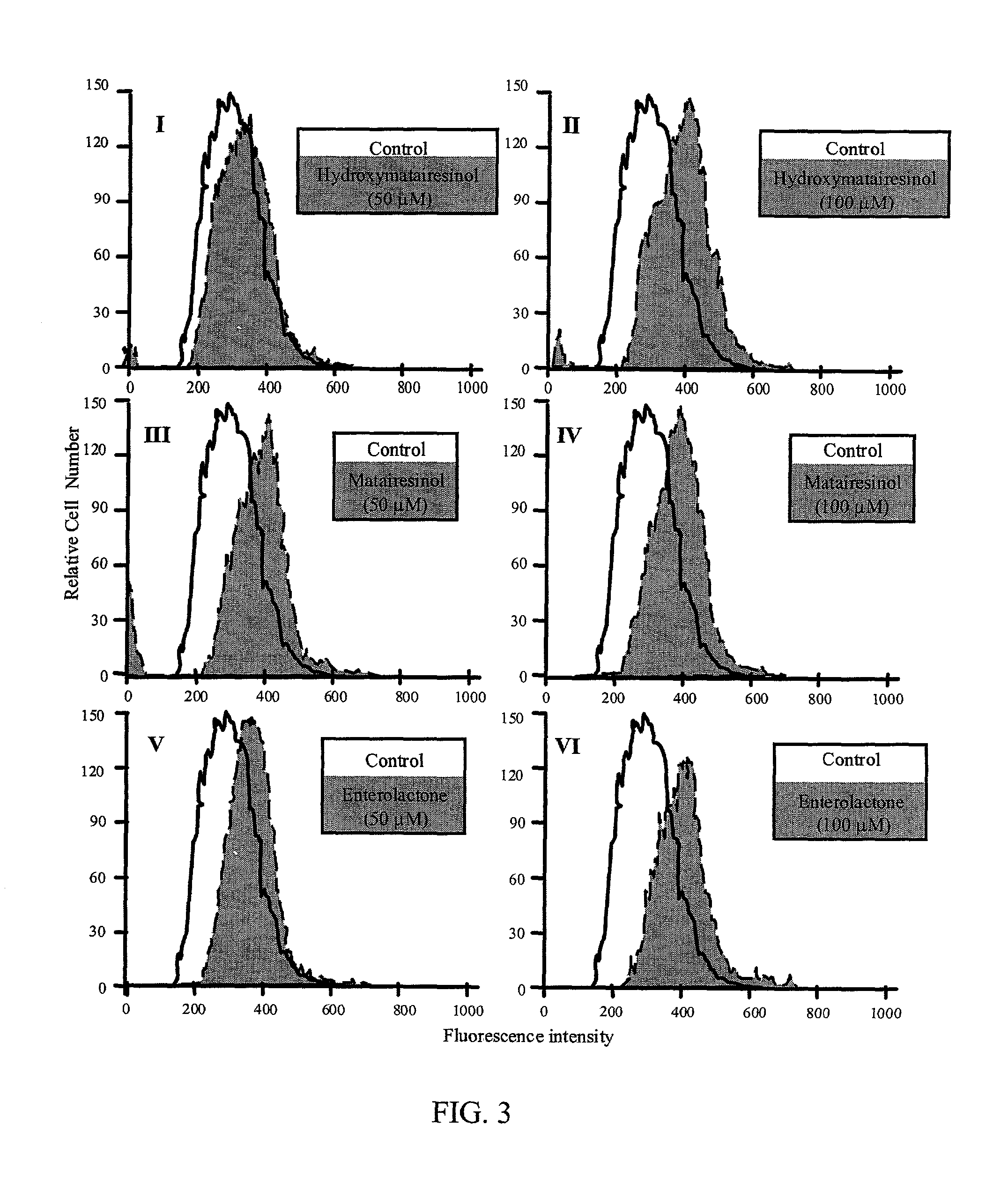
This invention relates to a method of inhibiting the overactivity of phagocytes or lymphocytes in an individual by administering to said individual an effective amount of a lignan, wherein i) the phagocytes are neutrophils and the lignan is hydroxymatairesinol or matairesinol or mixtures thereof, or ii) the phagocytes are cells of myeloid origin and the lignan is enterolactone or hydroxymatairesinol or mixtures thereof, or iii) the lymphocytes are T-lymphocytes and the lignan is hydroxymatairesinol, matairesinol or enterolactone or mixtures thereof. Furthermore, this invention concerns a method of treating or preventing an acute ischemia-reperfusion injury or a chronic condition, caused by overactivity of phagocytes or lymphocytes in an individual, said method comprising decreasing the activity of phagocytes in an individual by administering to said individual an effective amount of a lignan.
Owner:HORMOS NUTRACEUTICAL
Methods of Detecting A Neurological Condition Via Analysis of Circulating Phagocytes
ActiveUS20100055722A1Decreased level of biomarkerMicrobiological testing/measurementPeptide preparation methodsPhagocyteBiomarker (petroleum)
The present invention features methods of monitoring or detecting a neurological or inflammatory condition in a patient. The method comprises (1) obtaining from the patient a fluid sample from outside of a brain tissue of the patient, wherein the fluid sample contains a circulating phagocyte, and (2) detecting for one or more biomarkers (e.g., a panel of biomarkers) inside the phagocyte, wherein the biomarker is associated with the respective neurological or inflammatory condition.
Owner:MSDX
Cytotoxic conjugates comprising a chemokine receptor targeting agent
InactiveUS7166702B1Enhance and aid in survivalPrevent proliferationPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifChemokinesPhagocyteDendritic cell
Owner:OSPREY PHARMA USA INC
Method for extracting ganoderma lucidum fruitbody polysaccharide using ultrahigh pressure
InactiveCN101357951AHigh yieldReduce extraction timeAntinoxious agentsImmunological disordersPhagocyteMicroorganism
The invention discloses a method for extracting ganoderma lucidum fruit body polysaccharides by using superpressure; the ganoderma lucidum fruit body polysaccharides are new endogenetic active materials extracted from the ganoderma lucidum fruit bodies. The ingredients of the ganoderma lucidum polysaccharides can improve the phagocytosis of phagocytes, the humoral immunity and cellular immune function, which can improve the SOD activity of superoxide dismutases in red blood cells in human bodies. However, the ganoderma lucidum cells are compact, and the polysaccharides are difficult to be extracted from ganoderma lucidum. The methods of extraction which are most used currently are defective. The method for extracting ganoderma lucidum fruit body polysaccharides comprises the steps of selecting ganoderma lucidum fruit bodies, adding extracting solution, sealing and immersing the ganoderma lucidum fruit bodies in the extracting solution, treating the ganoderma lucidum fruit bodies under superpressure, filtration and condensation, drying the condensed filtrate, getting the polysaccharides from the ganoderma lucidum fruit bodies. High temperature does not occur during the extraction; active ingredients in the ganoderma lucidum fruit bodies can be preserved; the extraction takes little time with high yield and low impurity content. In addition, some microbes can be killed through pressurization to complete extraction and sterilization at one step. The method for extracting ganoderma lucidum fruit body polysaccharides overwhelms the defects of the prior methods for extracting polysaccharides from ganoderma lucidum.
Owner:INFINITUS (CHINA) CO LTD +2
Compositions of mononuclear phagocytes useful for promoting axonal regeneration
InactiveUS6117424AIncrease capacityEnhance phagocytic activityBiocideOrganic active ingredientsDiseasePhagocyte
Methods and compositions for the use of allogeneic mononuclear phagocytes to promote axonal regeneration in the central nervous system of a mammal are disclosed. In one embodiment, allogeneic mononuclear phagocytes are cultured together with stimulatory tissue, such as dermis or at least one nerve segment, and are subsequently administered into the central nervous system of a mammal at or near a site of injury or disease. In an alternative embodiment, autologous monocytes, preferably stimulated autologous monocytes, are administered into the central nervous system of a mammal at or near a site of injury or disease. Methods for identifying stimulatory tissue and cells and methods and compositions for cryopreserved allogeneic mononuclear phagocytes are also disclosed.
Owner:YEDA RES & DEV CO LTD
Method for detecting infectious agents using computer controlled automated image analysis
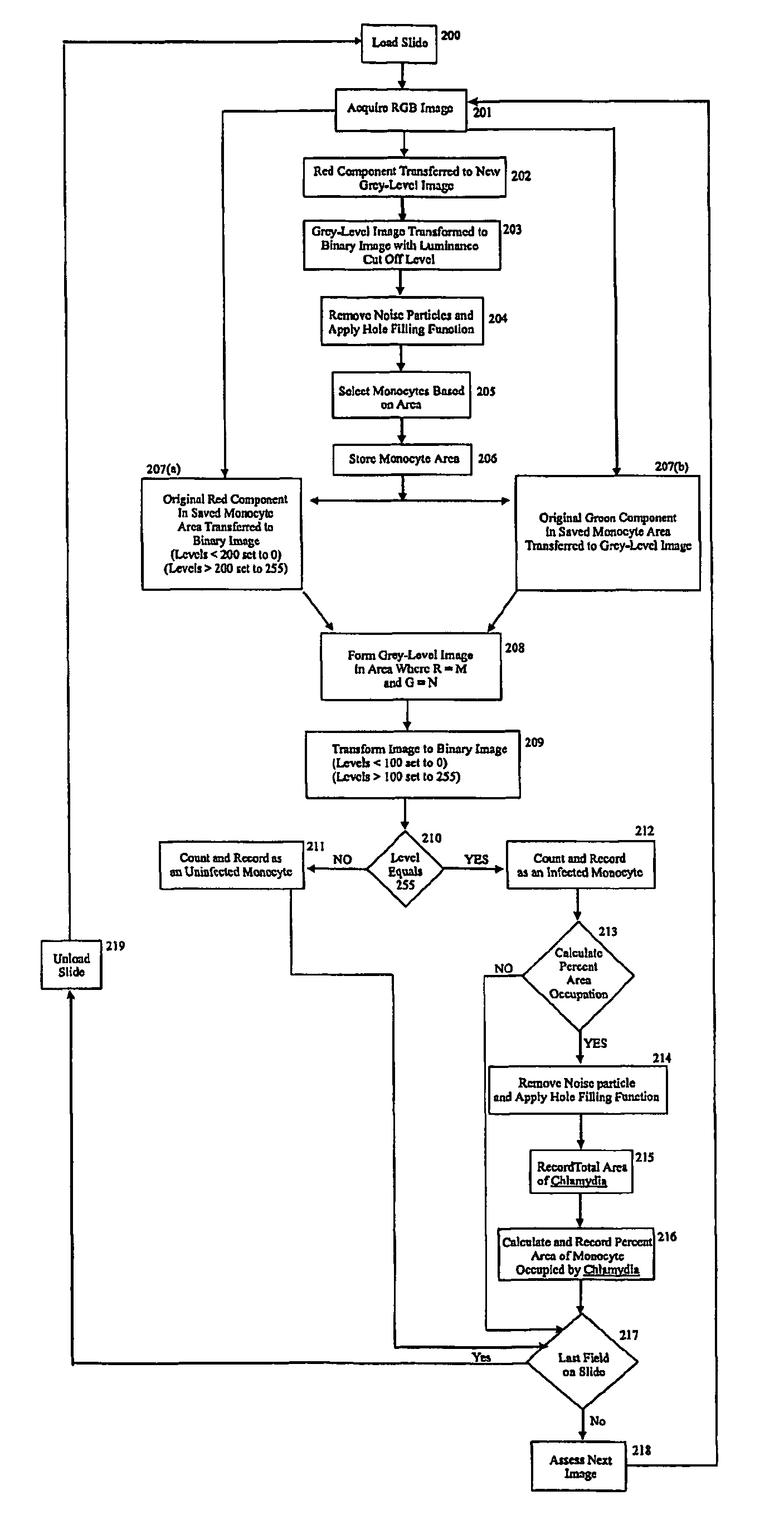
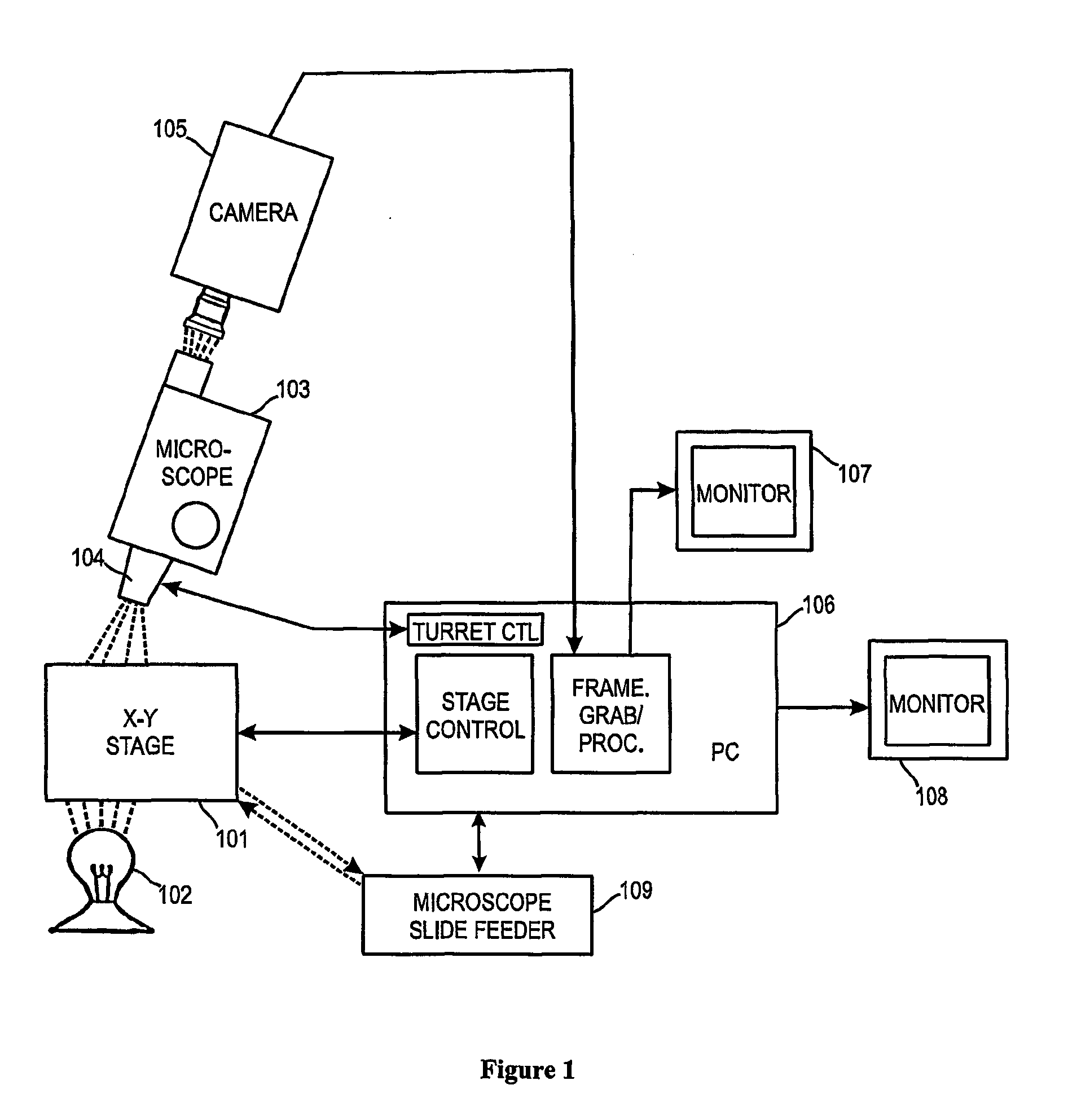
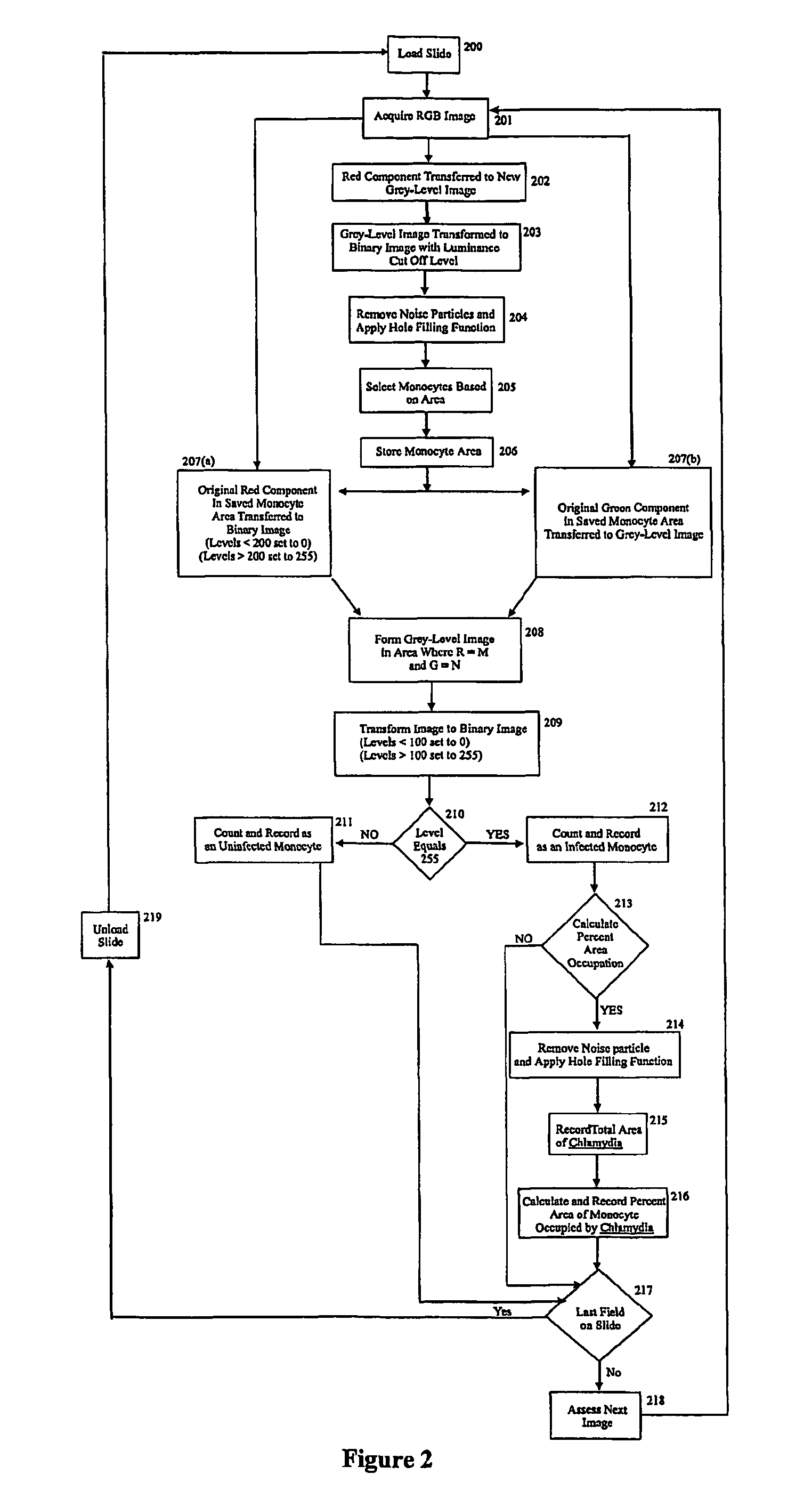
InactiveUS20060239533A1Detection signalReduce signal noiseImage enhancementImage analysisPhagocytePlant cell
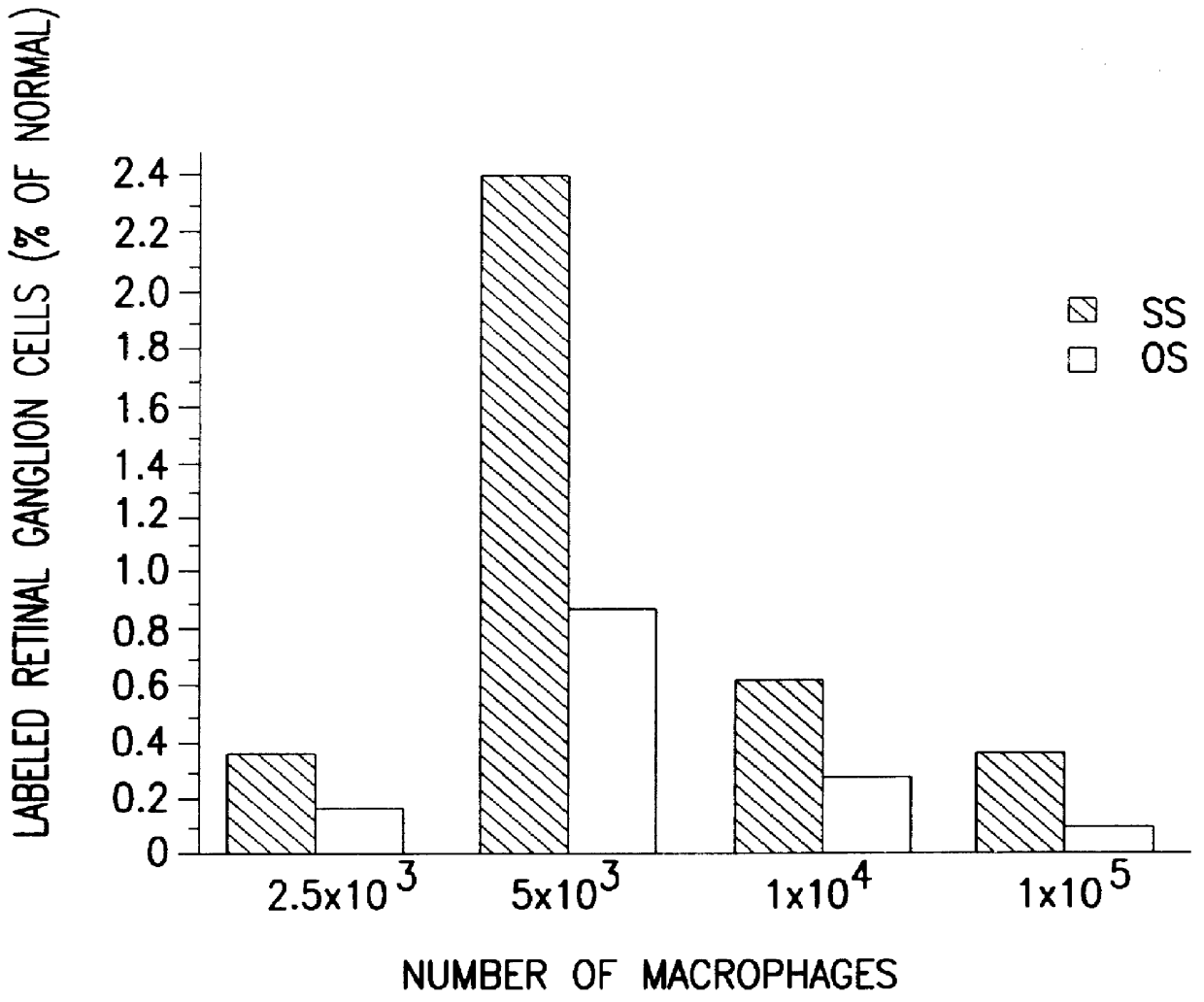
Computer controlled methods, systems and apparatus for detecting an infectious agent in a host cell, an animal cell, or plant cell, a body fluid or tissue sample to provide information useful to diagnose a disease or prognosticate disease susceptibility, extent or outcome are provided. In one illustrative embodiment, the infected animal cell is a Chlamydia infected mononuclear phagocyte in a blood sample. In another illustrative embodiment, the infected body fluid is a blood sample infected with “fee floating”Chlamydia. Detection and preferably, quantification of such an infected mononuclear phagocyte(s) or blood sample provides information useful in diagnosing or prognosticating susceptibility, extent or outcome of patients suspected of suffering from vascular, coronary or central nervous disease(s) or disorder(s).
Owner:IKONISYS INC
Detection of surface-associated human leukocyte elastase
InactiveUS6858400B2Microbiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisPhagocyteBinding site
In order to accurately and reliably quantitate HLE on the plasma membranes of the lymphocytes and mononuclear phagocytes, a test sample containing the lymphocytes and mononuclear phagocytes is initially treated with a first antiserum specific for CD4 receptors on the plasma membrane or with a second antiserum specific for chemokine receptors on the plasma membrane. Once the CD4 or chemokine receptors have been rendered non-reactive (competitive) relative to the HLE receptors (also “binding sites”) on the plasma membrane, the test sample is contacted with an immunoreagent specific for interaction with one or more of the HLE receptors on the plasma membranes of the lymphocytes and mononuclear phagocytes. The immunoreagent forms a complex with the HLE binding sites and produces a characteristic physical change in the lymphocytes and mononuclear phagocytes that can be monitored by any one of a number of standard techniques, (e.g., confocal laser scanning microscopy and flow cytometry).
Owner:BRISTOW CYNTHIA L
Process for evaluating phagocytotic function and use thereof
InactiveUS20070059687A1Microbiological testing/measurementArtificial cell constructsPhagocyteMicroorganism
A digested phagocyte prepared by contacting in vitro a phagocyte with a foreign microorganism and isolating the phagocyte so contacted; a process for producing the same; and a process and a kit in which these are utilized are disclosed. An experimental model, which enables in vitro evaluation of a phagocytotic function of phagocytes, is provided.
Owner:FUSO PHARMA INDS
Lysin-deficient bacteriophages having reduced immunogenicity
InactiveUS6896882B2Reduce gapBlocking can be undesirableAntibacterial agentsBiocidePhagocyteBacteroides
The present invention features therapeutic bacteriophage deficient in the lysin protein (“Lys minus” phage). Lys minus bacteriophage are incapable of facilitating efficient lysis of the bacterial host since the enzymatic activity of the lysin of the phage is needed for breaking down the peptidoglycan layer of the bacterial cell wall. Lys minus bacteriophage retain activity in invasion of its appropriate bacterial host, destruction of the bacterial genome, and replication, which are sufficient to inhibit bacterial growth and replication. Therefore, the therapeutic Lys minus phage stops the spread of infection by the bacterial pathogen without lysis of the bacterium. This approach is attractive as it also prevents the release of the phage progeny, thus reducing or eliminating the potential for generation of immune responses against the phage. The incapacitated bacterial pathogen is then removed by the normal defense systems such as phagocytes and macrophages.
Owner:BACTOCLEAR HLDG PTE LTD
Visfatin and uses thereof
InactiveUS20090010876A1High activityAvoid developmentOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsHuman animalPhagocyte
The invention is directed to methods for treating, inhibiting or prevent the incidence of vascular disease in a subject or in a non-human animal by administering visfatin. Particularly, the invention provides for methods to prevent phagocyte cell death due to ER-stress by the administration of visfatin. The invention also encompasses methods for identifying a visfatin polypeptide or a visfatin nucleic acid capable of treating a vascular disease as well as pharmaceutical compositions comprising visfatin.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
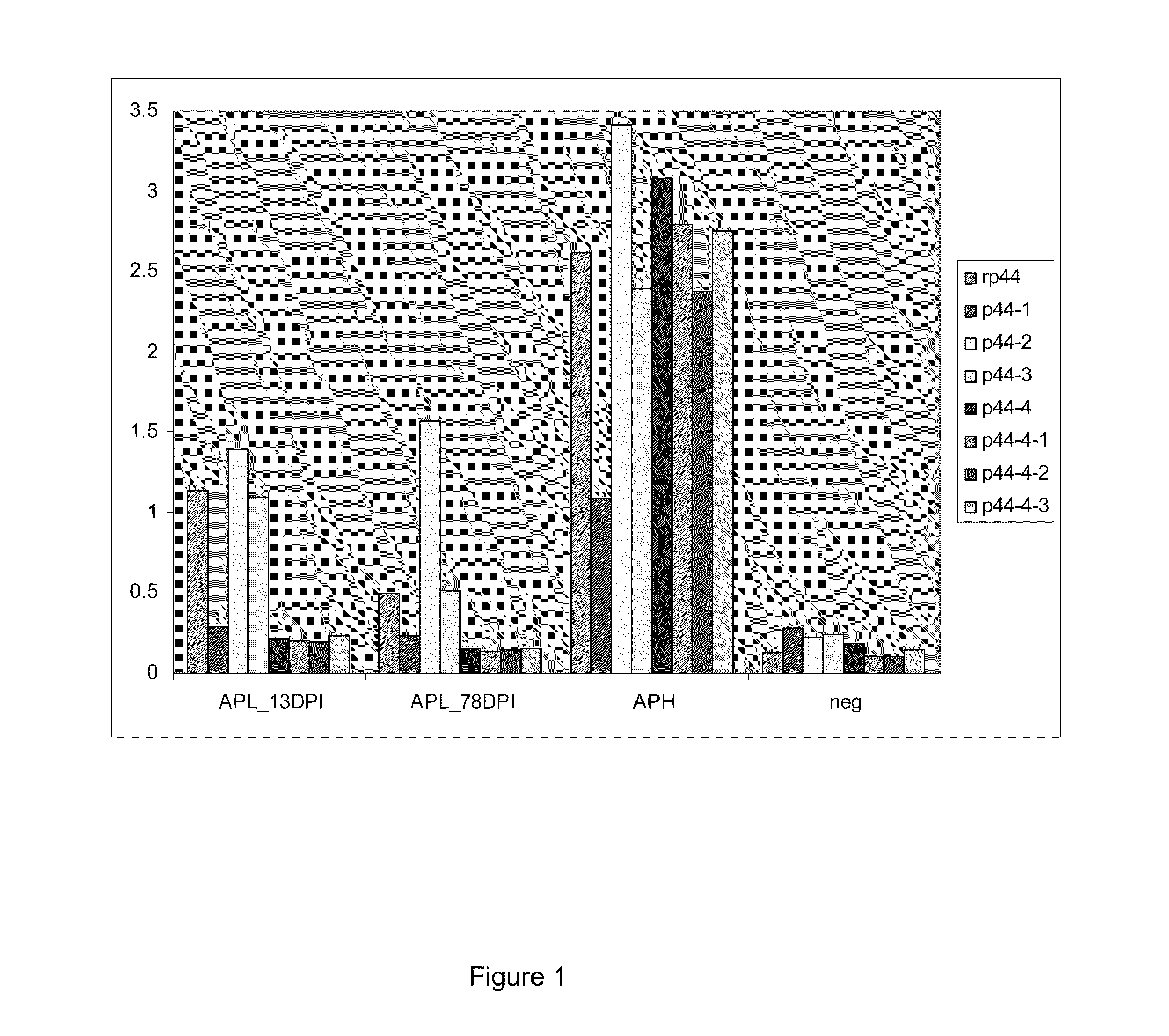
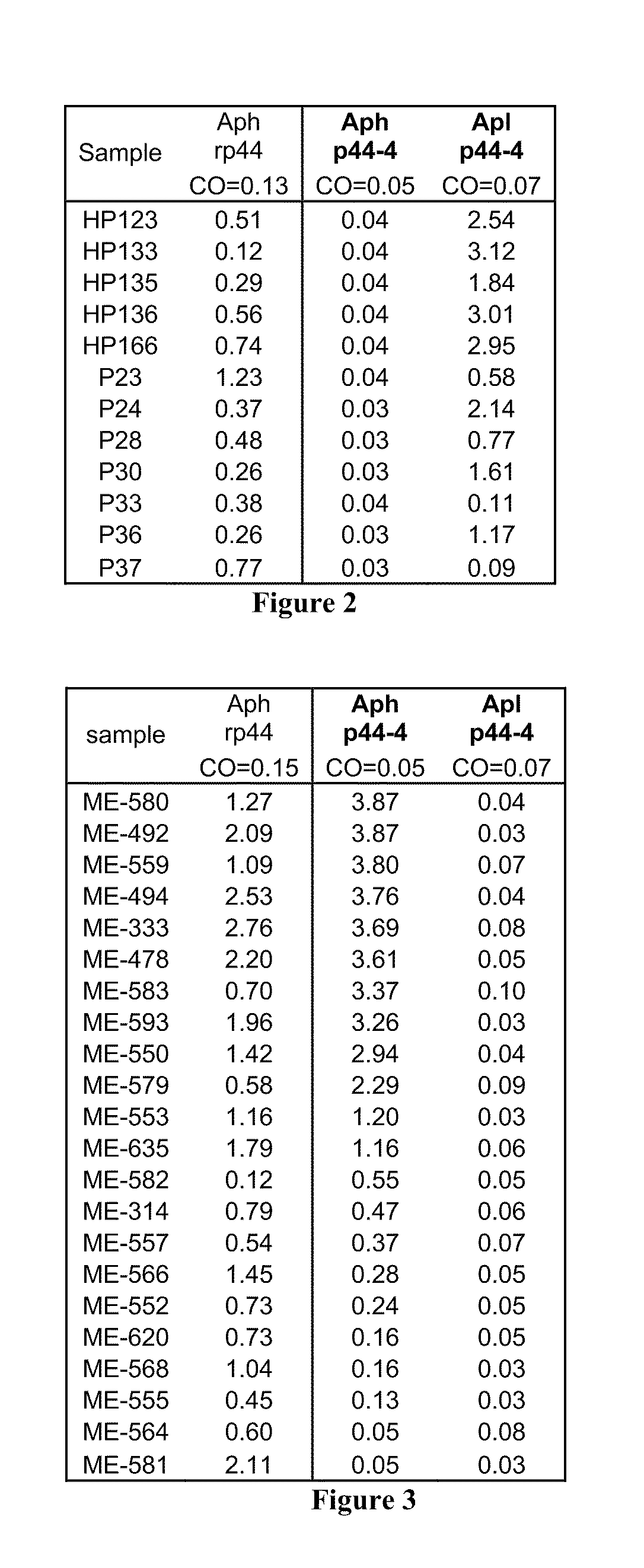
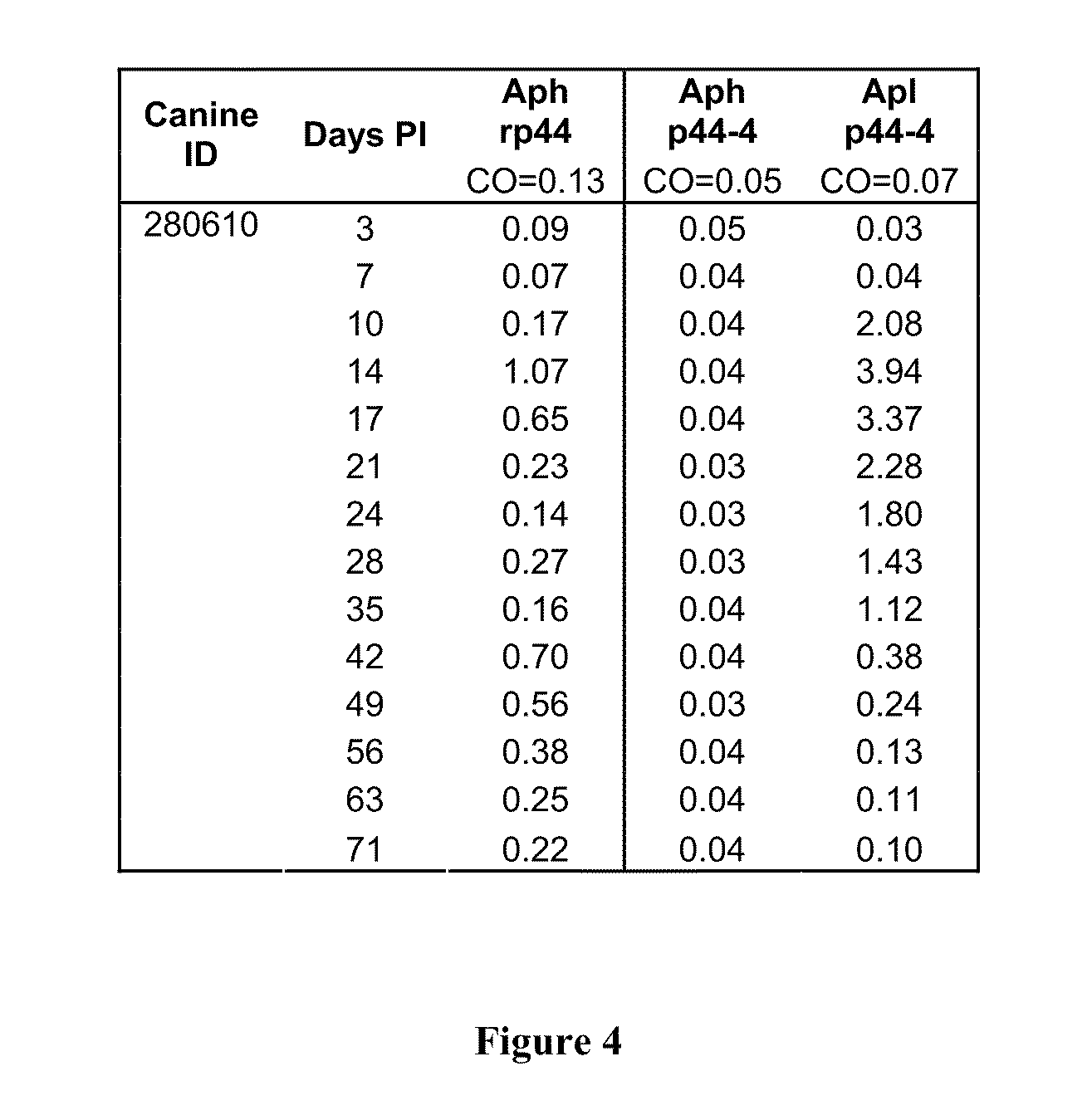
Anaplasma phagocytophilum (Aph) antigens and antibodies specific for Anaplasma
ActiveUS8158370B2Enhance immune responseImprove purification effectAntibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsPhagocyteAntigen
The invention provides methods and compositions for the detection and treatment of Anaplasma phagocytophilum and Anaplasma platys infection.
Owner:IDEXX LABORATORIES
Method for evaluation of function of phagocyte
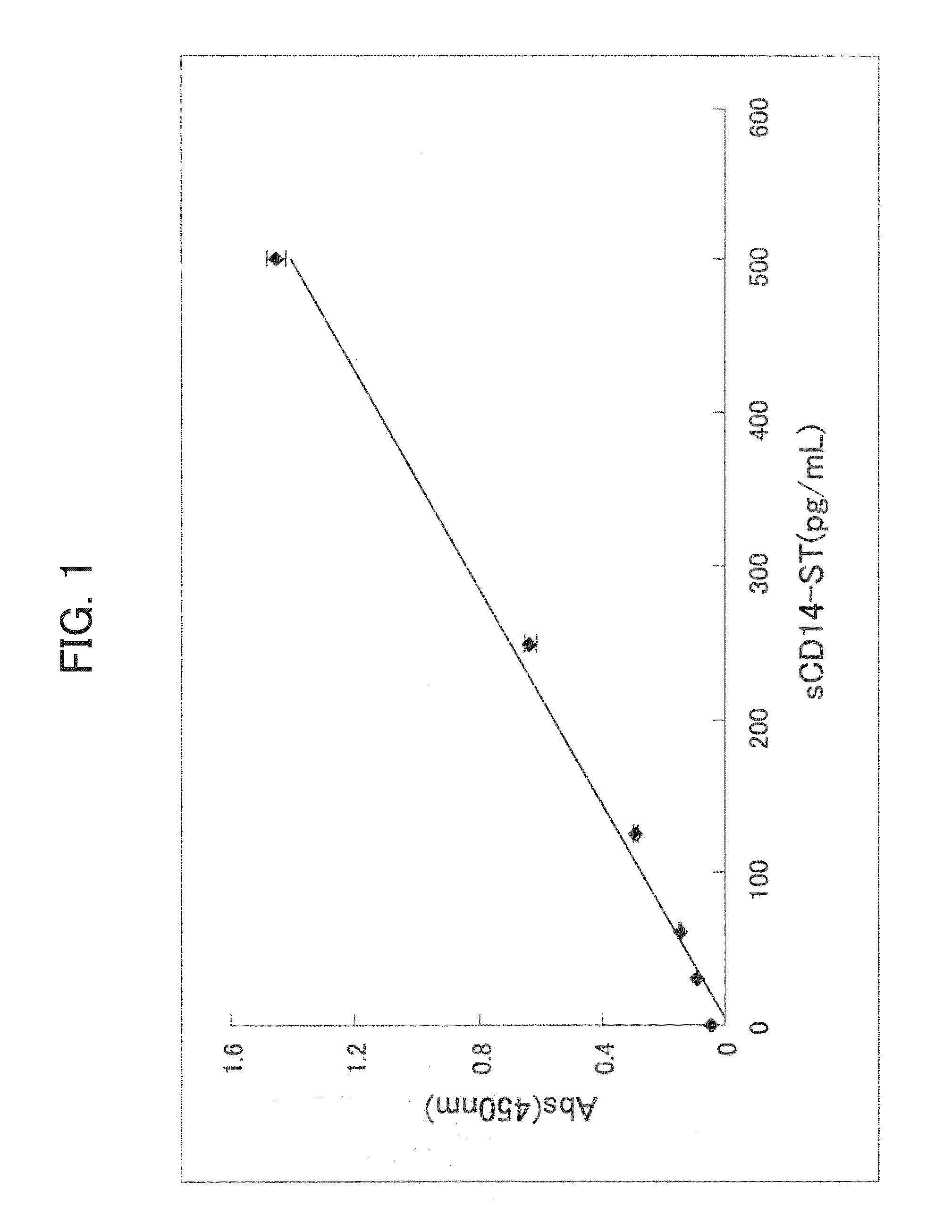
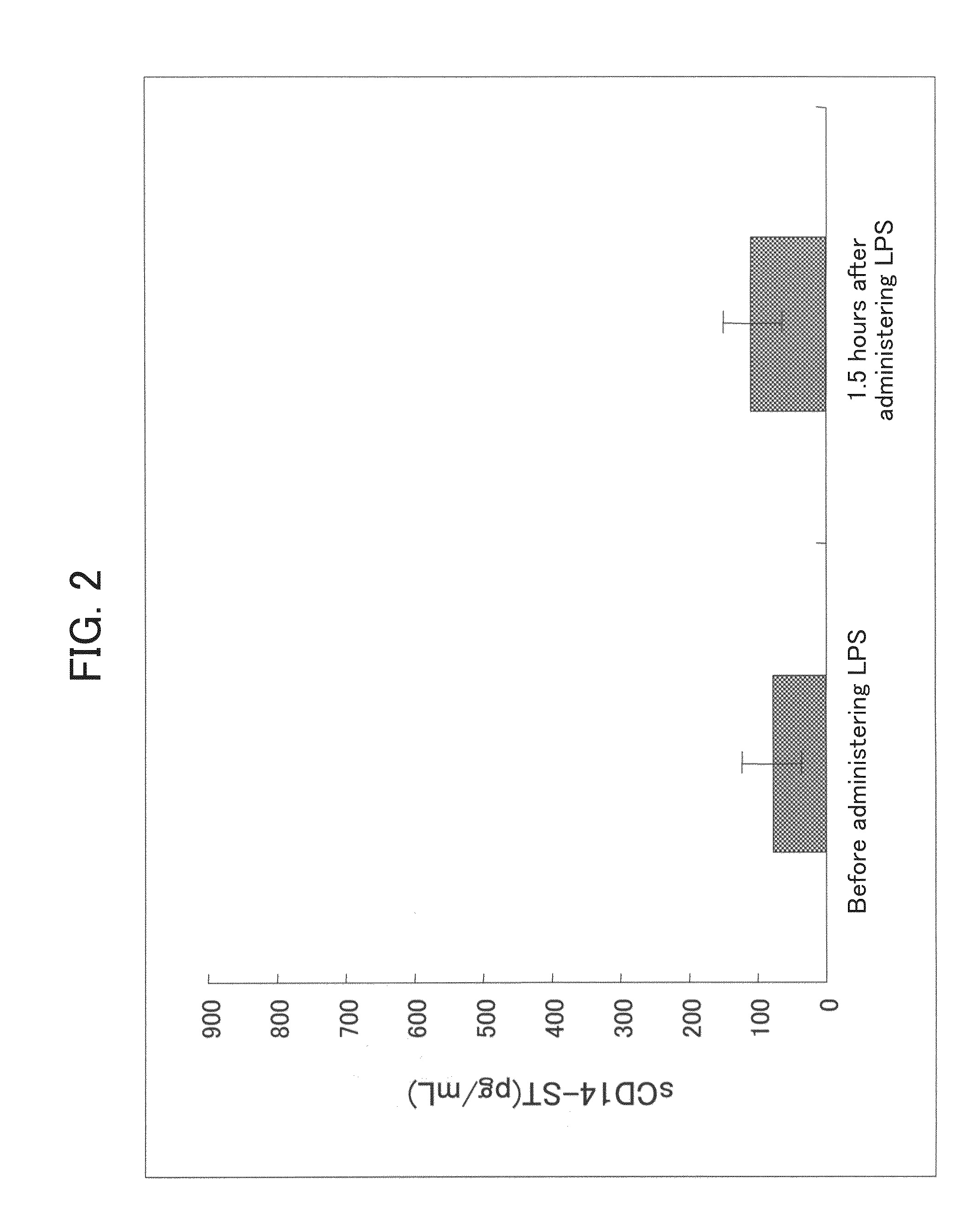
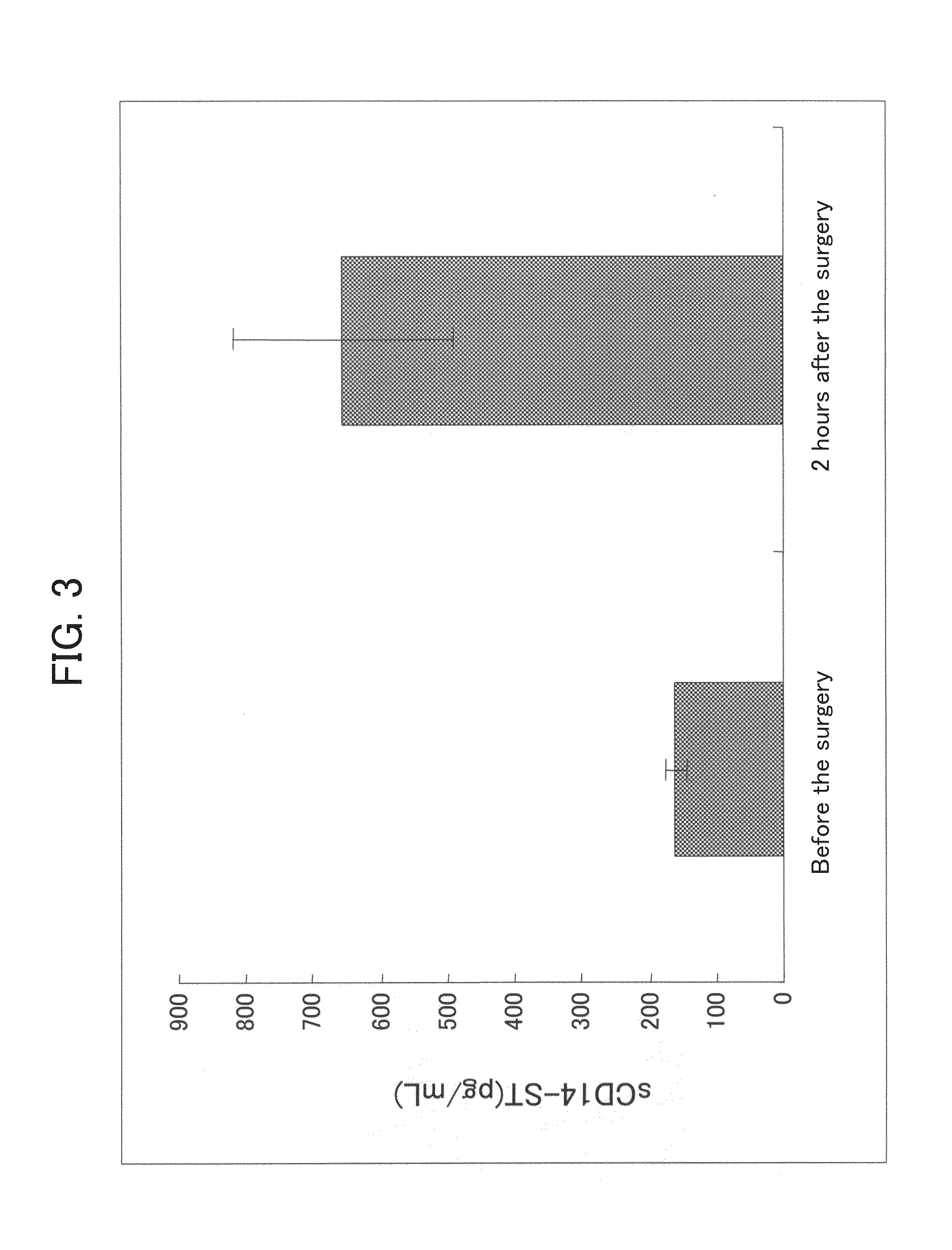
ActiveUS20110086381A1Specific and convenient assayEasy to detectCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsMicrobiological testing/measurementDiseasePhagocytosis
A novel convenient method for evaluating the function of a phagocyte is provided. The method assays sCD14-ST, which is a humoral factor specifically produced in phagocytosis by the phagocyte and which is stable enough for use in an assay. Also provided is a method for detecting diseases associated with the phagocytosis by the phagocyte.
Owner:MOCHIDA PHARM CO LTD
Novel Peptides and Methods Using Same
ActiveUS20140140926A1Treating and ameliorating and preventing inflammatory diseaseTreat and ameliorates and prevents inflammatory diseaseBiocidePeptide-nucleic acidsPhagocyteDisease cause
The present invention includes a method of modulating the phagocytic activity of at least one phagocyte in a subject. The present invention also includes a method of providing a composition resistant to phagocytosis to a subject. The present invention further includes a method of treating, ameliorating or preventing an inflammatory disease in a subject.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
Compositions and methods for delivering pharmaceutically active agents using nanoparticulates
The present invention is directed to methods and pharmaceutical compositions, e.g., nanoparticulate drug delivery vehicles, for delivering pharmaceutically active agents to tissues and areas containing mononuclear phagocytes e.g., macrophages in order to treat inflammatory diseases or disorders, e.g., a mononuclear phagocyte-associated disease or disorder, infected biological areas or tissue, injured tissue, or disease tissue. The inflamed, infected, injured, or diseased tissue can be accessible through the blood stream, using a nanoparticulate drug delivery vehicle injected into vascular beds (such as for example arterial and venous beds). Alternatively, the nanoparticulate drug delivery vehicle and pharmaceutically active agent of the invention may be administered locally, to treat specific areas or tissues, e.g., inflamed, infected, injured, or diseased tissue. In one embodiment, the nanoparticulate drug delivery vehicle is formulated as a contrast agent. Accordingly, imaging of the target area or tissue may be carried out prior to, during, or after administration of the nanoparticulate drug delivery vehicle.
Owner:NANOSCAN IMAGING
Compositions and methods for detection of antibodies specific for Anaplasma phagocytophilum (Aph) and Anaplasma platys (Apl)
The invention provides methods and compositions for the detection and treatment of Anaplasma phagocytophilum and Anaplasma platys infection.
Owner:IDEXX LABORATORIES
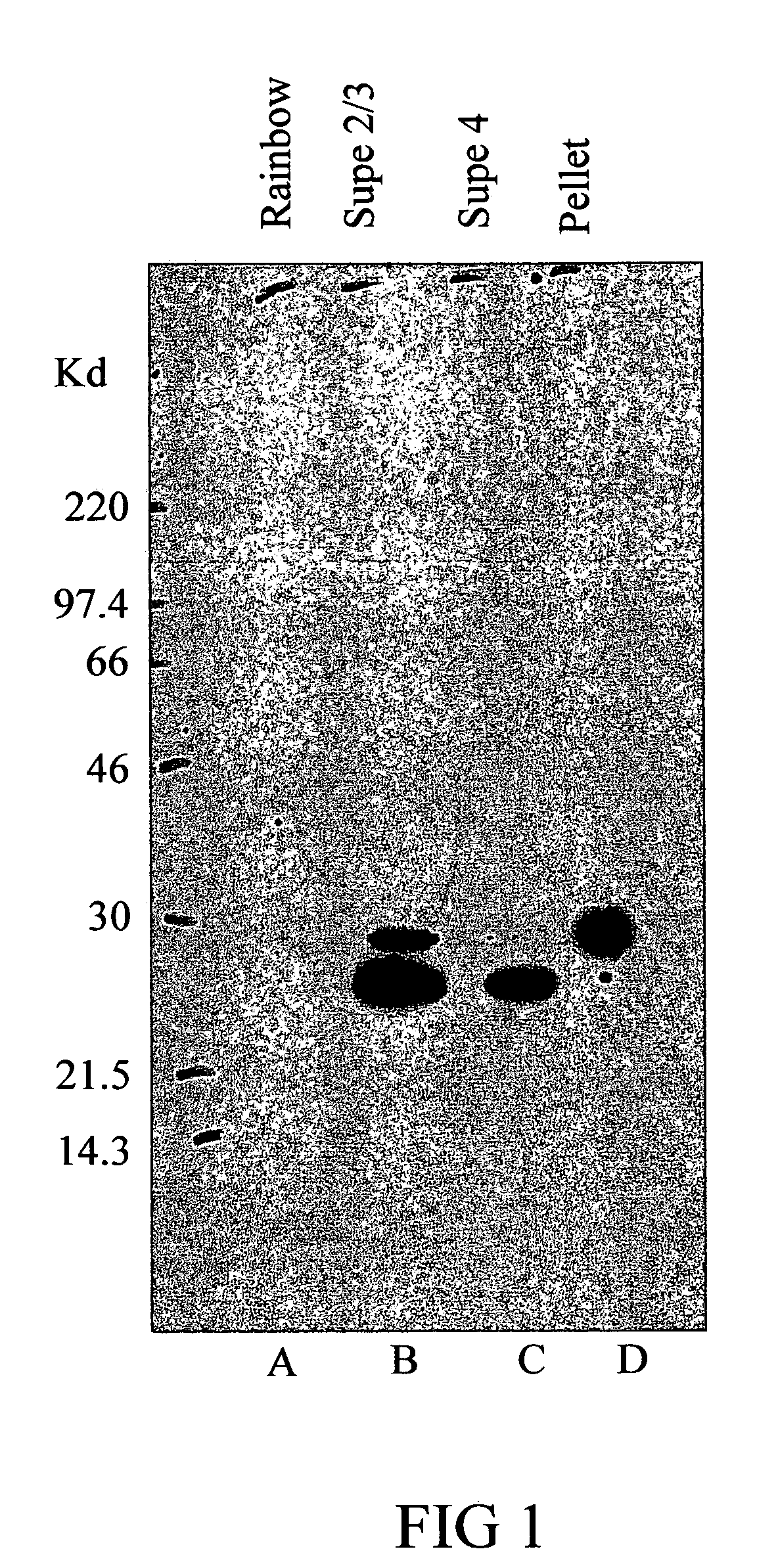
Polynucleotides and polypeptides of Anaplasma phagocytophilum and methods of using the same
InactiveUS7304139B2Simplifies diagnosisEasy to identifyBacteriaPeptide/protein ingredientsPhagocyteWhole Organism
We have successfully sequenced and cloned the gene expressing the Major Surface Protein 5 (MSP5) of A. phagocytophilum. The recombinant MSP5 (rMSP5) protein has been tested using sera from humans and dogs infected with A. phacytophilum. The polypeptide has been found to be immunogenic and useful as a diagnostic test antigen. The polypeptide antigen of the subject invention can provide the basis of a diagnostic assay that would allow the rapid, in-house, laboratory diagnosis of infection with A. phagocytophilum using a sample (e.g., serum, plasma, or whole blood) from an infected human or animal. Additionally, the subject invention provides methods of detecting the presence of A. phagocytophilum in biological or environmental samples utilizing antibodies provided by the subject invention. Furthermore, the use of the single antigen in the diagnosis of this important disease offers many advantages including enhanced test specificity, ease of testing and consistency of results using synthetically produced test antigens instead of cultured, whole organisms.
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC +1
Bovine derived anti-staphylococcus aureus fusion antibody scFv-Fc and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN109021109AGrowth inhibitionHas antibacterial activity in vitroAntibacterial agentsHybrid immunoglobulinsAntigenPhagocyte
The invention discloses a bovine derived anti-staphylococcus aureus fusion antibody scFv-Fc and a preparation method thereof. The fusion antibody scFv-Fc at least has a light chain variable region ofthe amino acid sequence shown as SEQ ID No:1, a heavy chain variable region of the amino acid sequence shown as SEQ ID No:2, an intermediate connecting peptide between the light chain variable regionand the heavy chain variable region, and a Fc fragment of the amino acid sequence shown as SEQ ID No:3. The ELISA result shows that the fusion antibody can be specifically bound to a staphylococcus aureus antigen; in in-vitro bacteriostatic test, the fusion antibody can completely inhibit the growth of staphylococcus aureus within 24h; moreover, the fusion antibody can mediate dairy cow peripheralblood phagocytes in terms of playing the role of conditioning phagocytosis. The fusion antibody can be used in related reagents or drugs for diagnosis, prevention and treatment of staphylococcus aureus cow mastitis.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
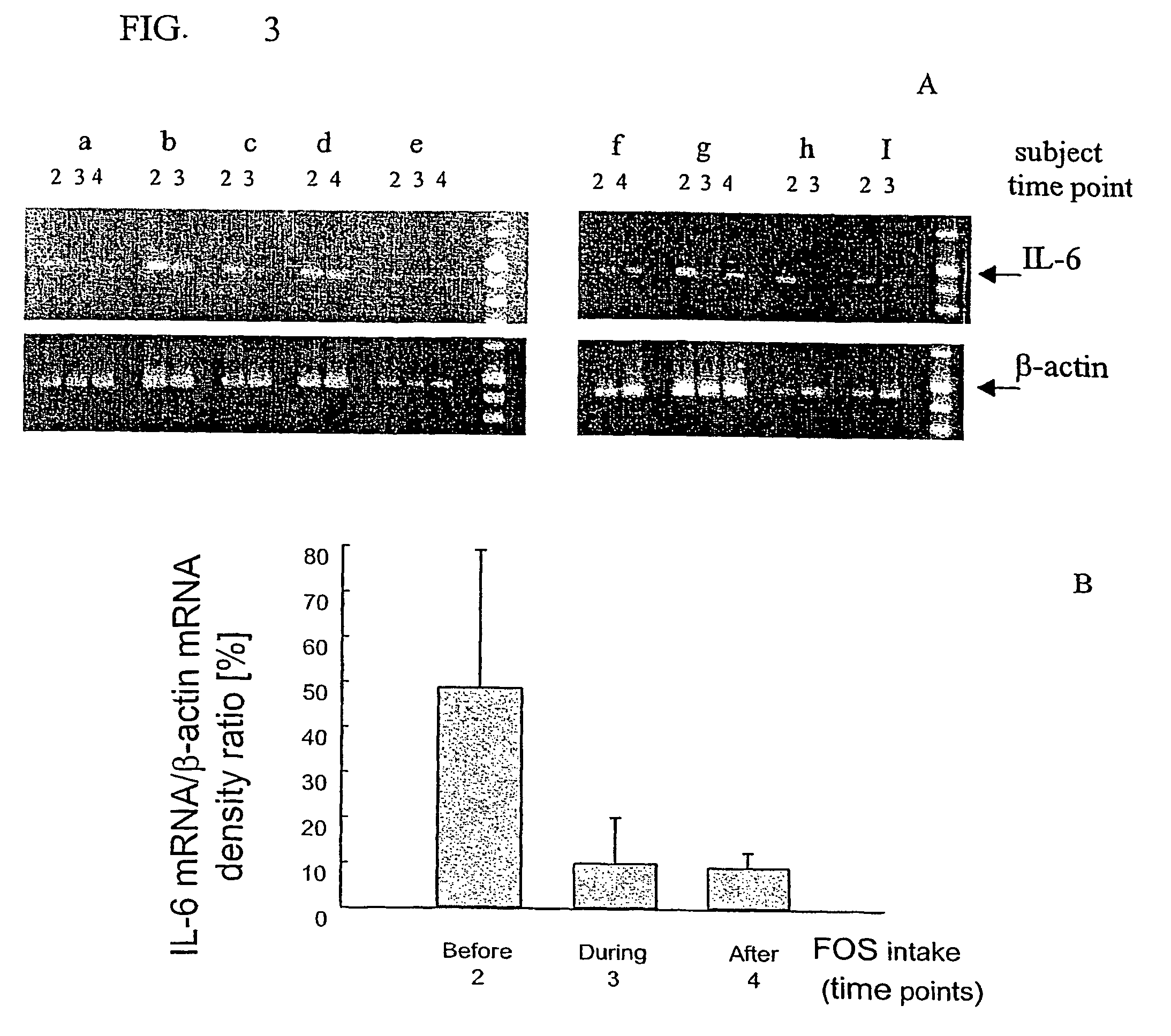
Composition comprising a prebiotic for decreasing inflammatory process and abnormal activation of non-specific immune parameters
ActiveUS8092608B2Reduce inflammationReduce expressionOrganic active ingredientsBiocidePhagocyteAdjuvant
The present invention relates to a composition comprising prebiotic (prebiotic adjuvant) for decreasing inflammatory process by improving the homeostasis of non-specific immune parameters and of lymphocyte subpopulations. It also relates to the use of a prebiotic formulation in the manufacture of a medicament or a food or petfood composition for decreasing inflammatory process and / or abnormal activation of non-specific immune parameters, such as phagocytes.
Owner:NESTEC SA
Methods of Modulating Inflammatory Reactions by Modulating Xanthine Oxidoreductase Activity
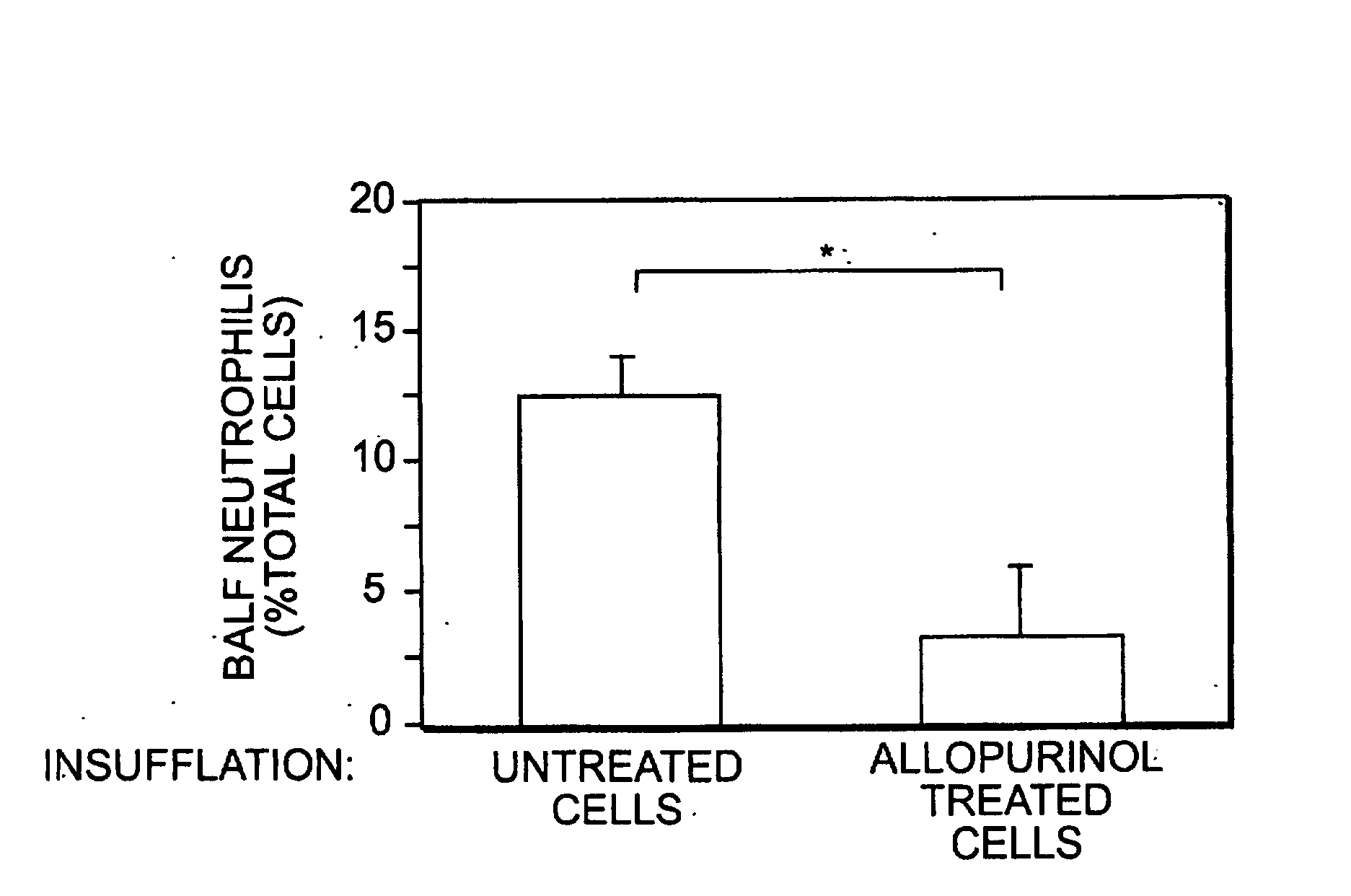
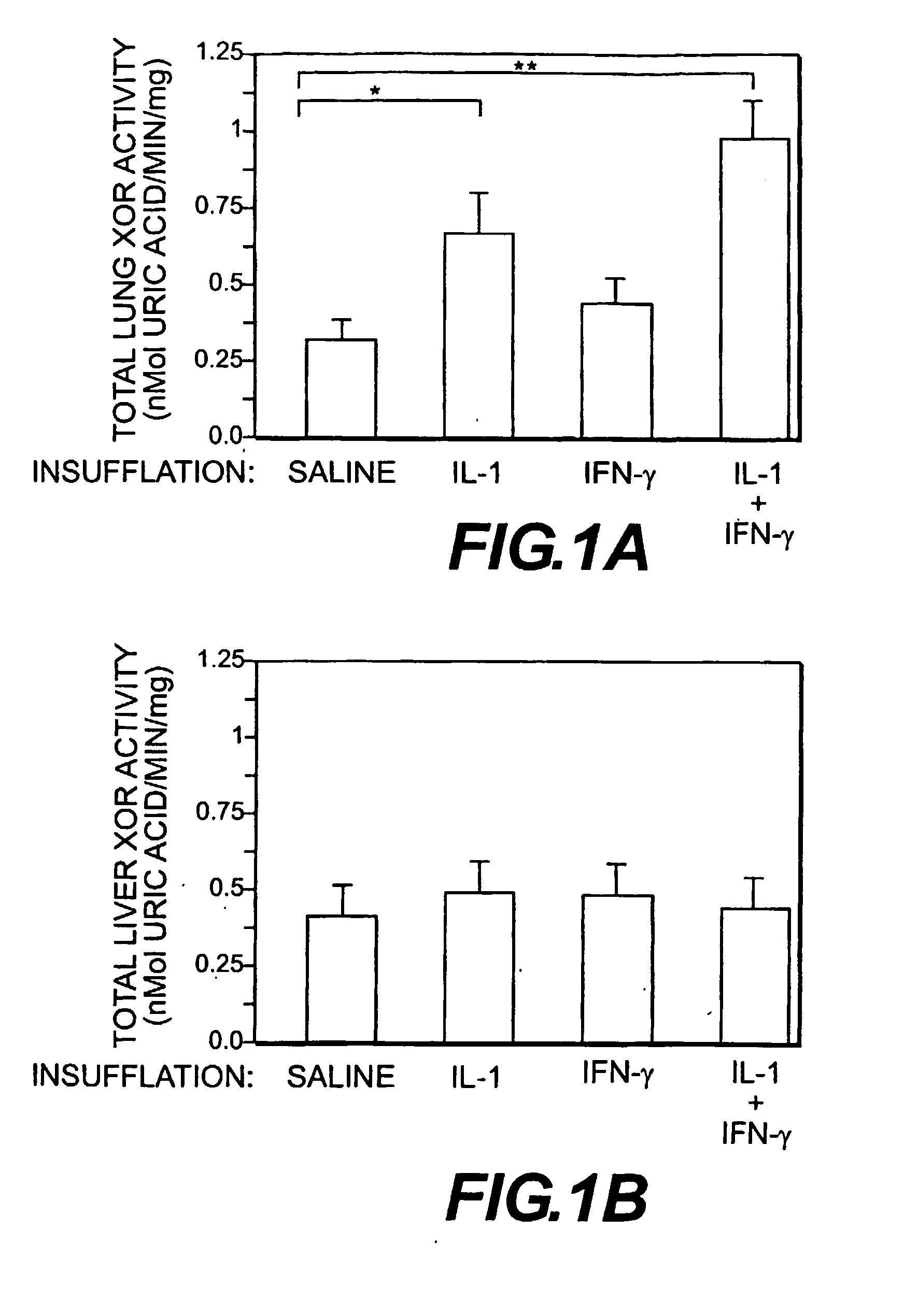
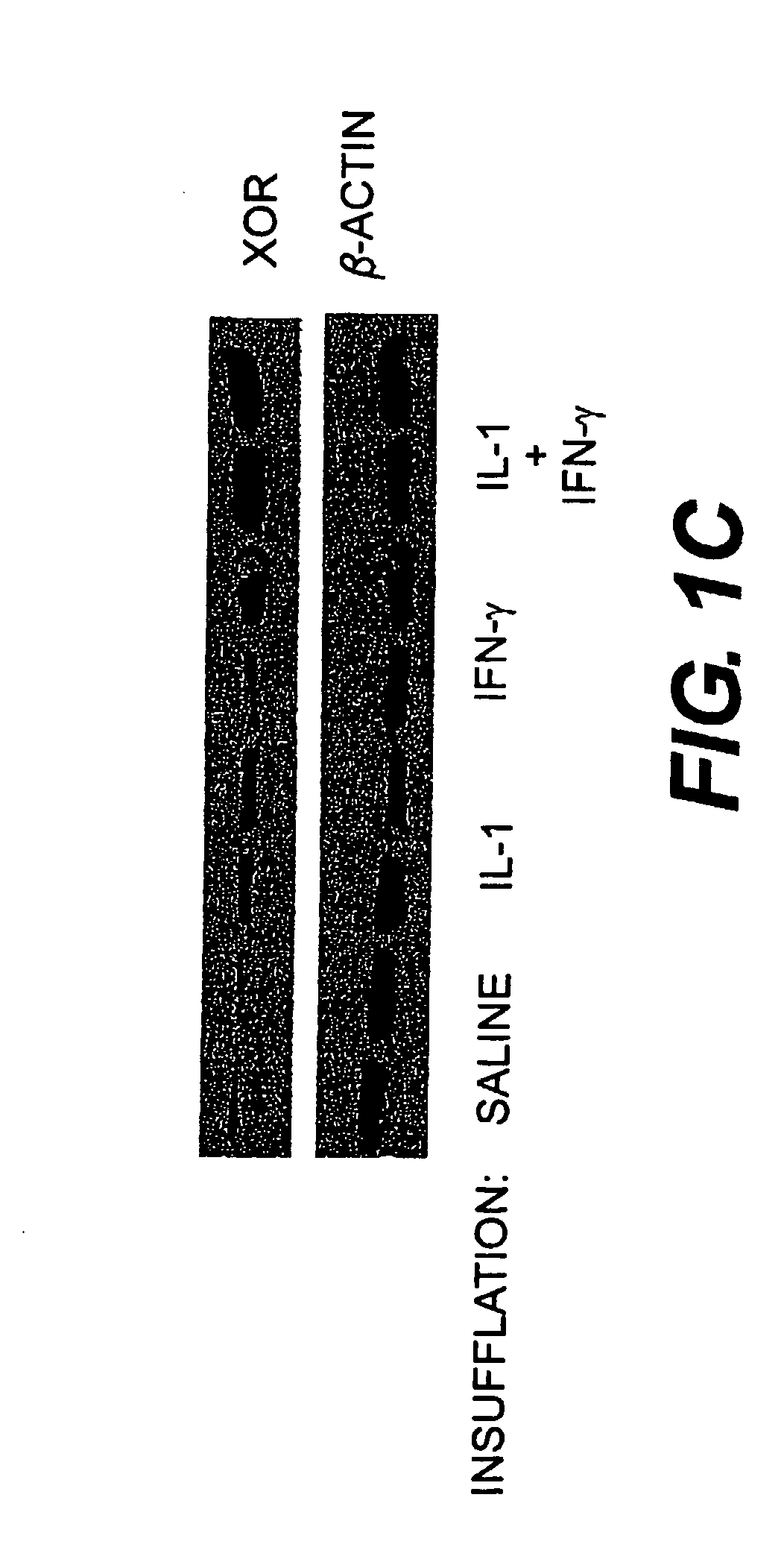
Evidence is presented that inflammation and injury involves activation of xanthine oxidoreductase (XOR) in the newly recruited mononuclear phagocytes (MNP). XOR has been shown to be increased predominantly in the MNP that increase rapidly in the lungs of rats that develop acute lung injury (ALI) following intratracheal cytokine insufflation. XOR was recovered from the MNP largely converted to its oxygen radical generating, reversible O-form, and alveolar MNP exhibited increased oxidative stress as evidenced by increased nitrotyrosine staining. Cytokine insufflation also increased alveolar cell apoptosis. A functional role for XOR in cytokine induced inflammation was demonstrated. Tungsten and allopurinol decreased MNP XOR induction, nitrotyrosine staining, inflammatory cell infiltration, and alveolar cell apoptosis. Transfer of control or allopurinol treated MNP into rat lungs and confirmed a specific role for MNP XOR in promoting lung inflammation. These data indicate that XOR can contribute to lung inflammation by its expression and conversion in a highly mobile inflammatory cell population.
Owner:WEBB WARING INST
Method for detecting and identifying microorganism causative of infection
InactiveUS20060234219A1Microbiological testing/measurementGenetic engineeringPhagocytePathogenic microorganism
Causative microorganisms of infectious diseases are detected and / or identified rapidly and high-sensitively by taking phagocytes from the clinical specimens containing active phagocytes, immobilizing the phagocytes so taken, treating the phagocytes to improve cell membrane permeabilities thereof, further treating the phagocytes to bare DNA in the causative microorganisms which might be existed in the phagocytes, and detecting the causative microorganisms with DNA probes which can hybridize with such DNA under stringent conditions.
Owner:FUSO PHARMA INDS
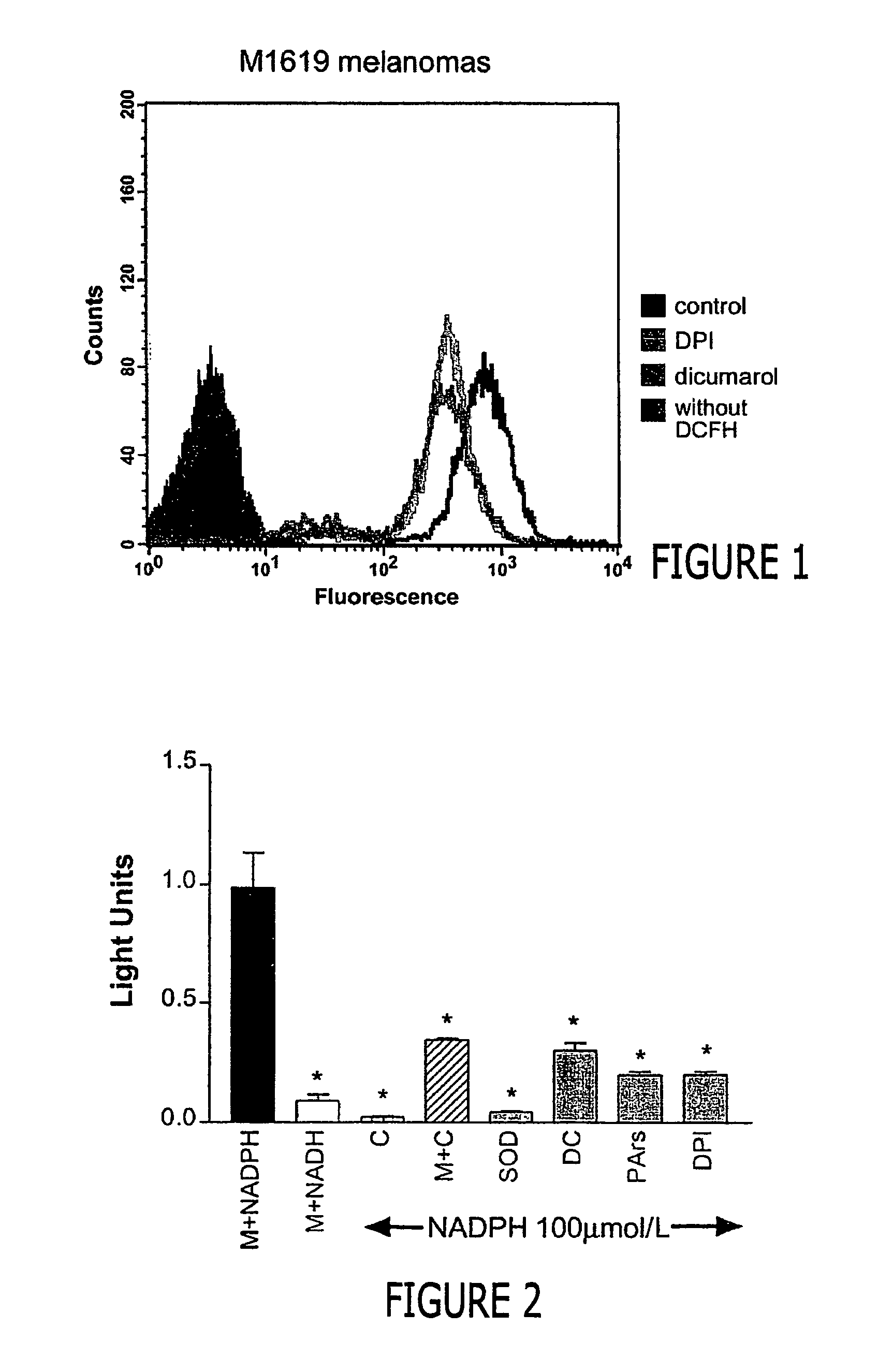
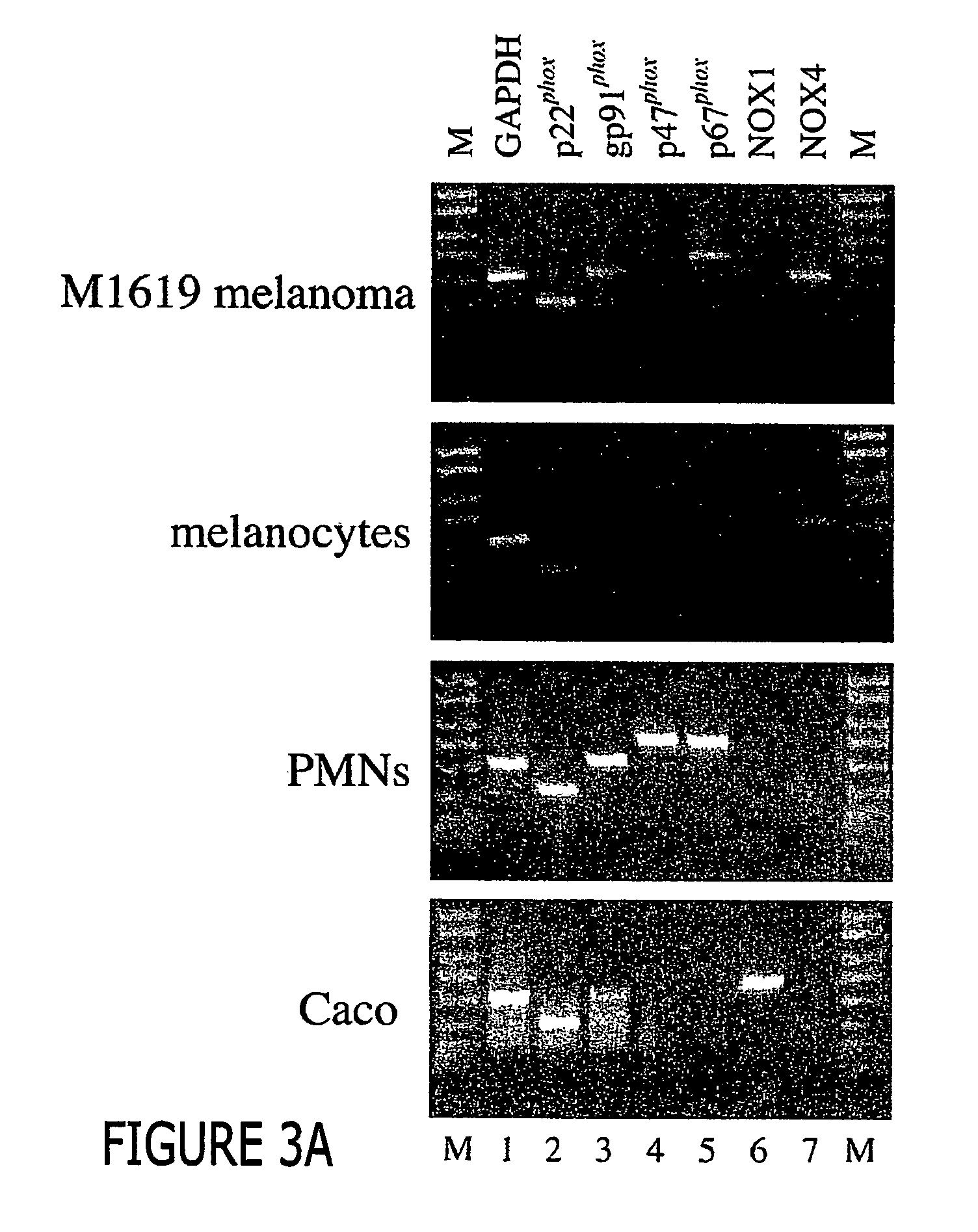
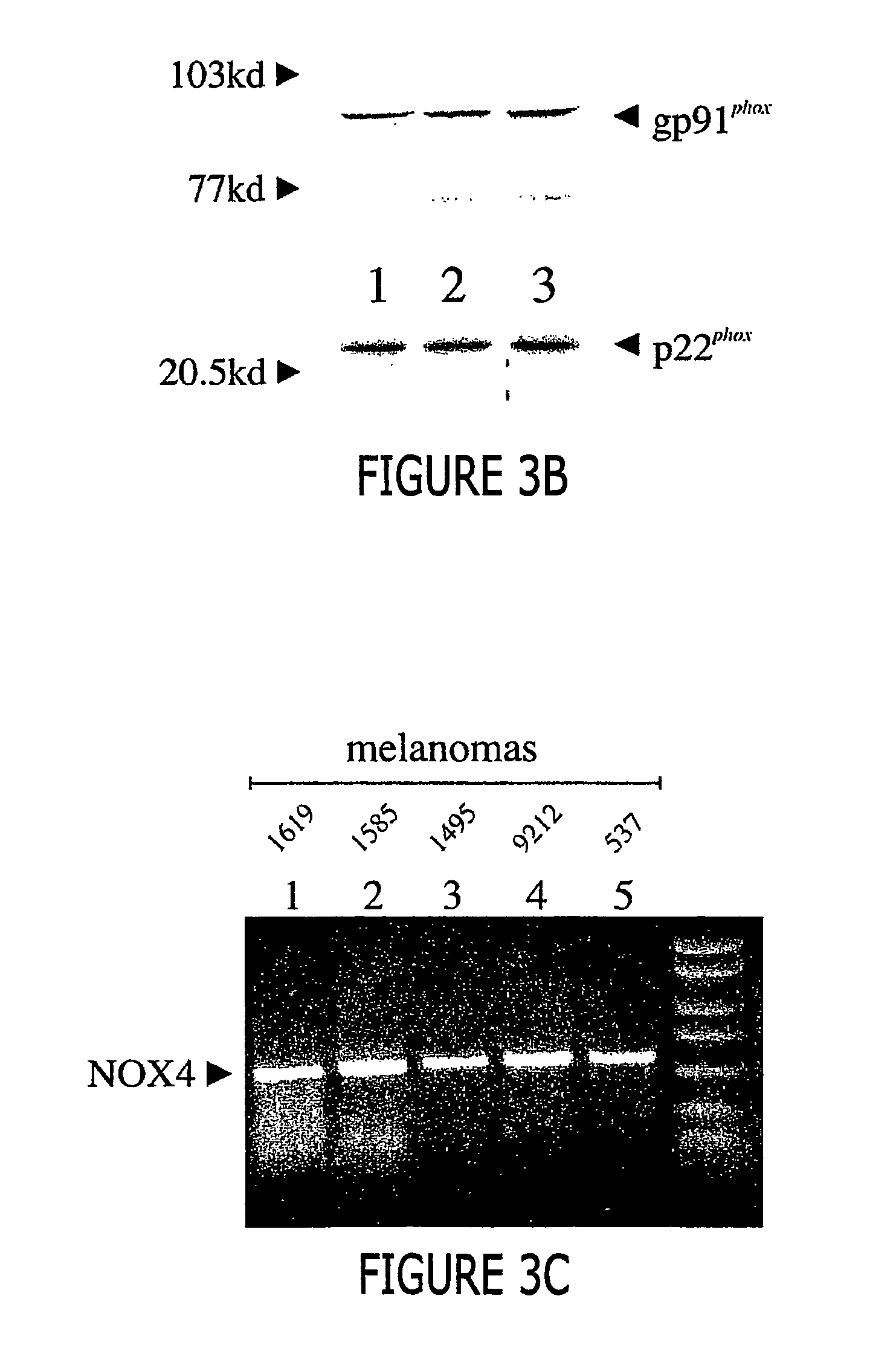
Regulation of NAD(P)H oxidase growth and transcription in melanoma cells
Malignant melanoma cells spontaneously generate reactive oxygen species (ROS) that promote constitutive activation of the transcription factor nuclear factor-kB (NF-kB). Although antioxidants and inhibitors of NAD(P)H oxidases significantly reduce constitutive NF-kB activation and suppress cell proliferation, the nature of the enzyme responsible for ROS production in melanoma cells has not been determined. To address this issue, we now have characterized the source of ROS production in melanoma cells. ROS are generated by isolated, cytosol-free melanoma plasma membranes, with inhibition by NAD(P)H oxidase inhibitors. The p22phox, gp91phox and p67phox components of the human phagocyte NAD(P)H oxidase, and the 91phox homolog NOX4 were demon-strated in melanomas by RT-PCR and sequencing, and protein product for both p22phox and gp91phox were detected in cell membranes by immunoassay. Normal human epidermal melanocytes expressed only p22phox and NOX4. Melanoma proliferation was reduced by NAD(P)H oxidase inhibitors and by transfection of antisense but not sense oligonucleotides for p22phox and NOX4. Also, the flavoprotein inhibitor diphenylene iodonium inhibited constitutive DNA binding of nuclear protein to the NF-kB and cyclic-AMP response element consensus oligonucleotides, without affecting DNA binding activity to AP-1 or OCT-1.
Owner:THE UNIV OF UTAH
Multi-component compounded functional solid drink for enhancing human immunity and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN109221864AImprove immunityPromote regenerationMilk preparationFood ingredient functionsPhagocyteVitamin C
The invention belongs to the field of functional foods and relates to a multi-component compounded functional solid drink for enhancing human immunity and a preparation method thereof. The functionalsolid drink comprises 20-30 parts of sorbitol, 15-25 parts of dried skim milk, 10-25 parts of resistant dextrin, 5-20 parts of xylooligosaccharide, 5-15 parts of yeast beta-glucan, 1-10 parts of bovine colostrum powder, 1-10 parts of orange powder, 1-10 parts of soybean peptide, 1-10 parts of fish collagen powder, 0.1-1 part of casein phosphopeptides, 0.1-1 part of composite amino acid powder and0.01-1 part of vitamin C. The functional solid drink is capable of improving human immunity from six aspects of stimulating immune cell regeneration, promoting mitosis of phagocyte, providing immunityactive factors, providing basic constitution substances for establishing cells of bodies, replenishing vitamin C and regulating intestinal tract health, and is high in security and remarkable in effect. The functional solid drink is prepared by using a modern process, multiple components are compounded, the components play a role of synergism, and the human immunity can be well improved; and compared with a conventional product in the market, the functional solid drink has a comprehensive replenishing function and good advantages.
Owner:杭州千岛湖标普健康食品有限公司
Destruction of spores through glycoconjugate enhanced phagocytosis
InactiveUS20080213316A1Increased activationAvoid cell deathBacterial antigen ingredientsBacteriaPhagocyteBacteroides
Methods for enhancing destruction and killing of bacterial spores via phagocytosis, where phagocytosis of bacterial spores is enhanced by using a glycoconjugate. In one embodiment, the method includes the steps of modifying a surface of a bacterial spore to increase adherence to a phagocyte; and ingesting the adherence-increased spore with the phagocyte, thereby destructing and killing the spore by blocking spore-induced phagocyte cell death, while increasing phagocyte activation level and production of antimicrobial and cytocidal agents such as NO and inflammatory cytokines. The adherence of spore to a phagocyte is increased after the surface thereof is coated with a glycoconjugate to form a glycoconjugate-coated spores. The glycoconjugate-coated spores also increase ingestion of the spores by phagocytes and facilitate phagosome-lysosome fusion, which in turn results in destruction and killing of bacterial spores via phagocytosis. The method enhances adherence, ingestion, destruction and killing of bacterial spores via phagocytes, which otherwise may be resistant to phagocytosis.
Owner:TARASENKO OLGA
A plant extracted immune-enhancing refined substance and a preparation method thereof
InactiveCN104886571AGood for healthNatural extract food ingredientsFood ingredient functionsPhagocyteSide effect
The present invention discloses a plant extracted immune-enhancing refined substance and a preparation method thereof, and belongs to the technical field of bioactive substance preparation. The refined substance consists of aronia melanocarpa extract (52%), radix ginseng rubra extract (16%), mixed Chinese herbal medicine extract (16%) and mixed fruit extract (16%) in mass percentage. Mixed extract of the above-mentioned aronia melanocarpa extract, radix ginseng rubra extract, mixed Chinese herbal medicine extract and mixed fruit extract is used to prepare the pharmaceutical refined substance with an immune-enhancing effect. In conclusion, the refined substance can impact granular leukocytes and phagocytes with bactericidal function and cells with virucidal function to produce media immunity and humoral immunity. The refined substance is safe without any side effects, and has the effect on recovering and enhancing immune function; and long-term taking the refined substance provides effects on resisting senility and ageing, and maintaining exuberant energy and stamina for middle-aged and elderly people.
Owner:安徽广生堂生物科技有限公司
Application of antradiacomphora extract capsule for protecting liver and promoting body immune regulation function
InactiveCN101785793AEnhance immune regulation functionHigh activityFungi medical ingredientsBiological testingAbnormal tissue growthPhagocyte
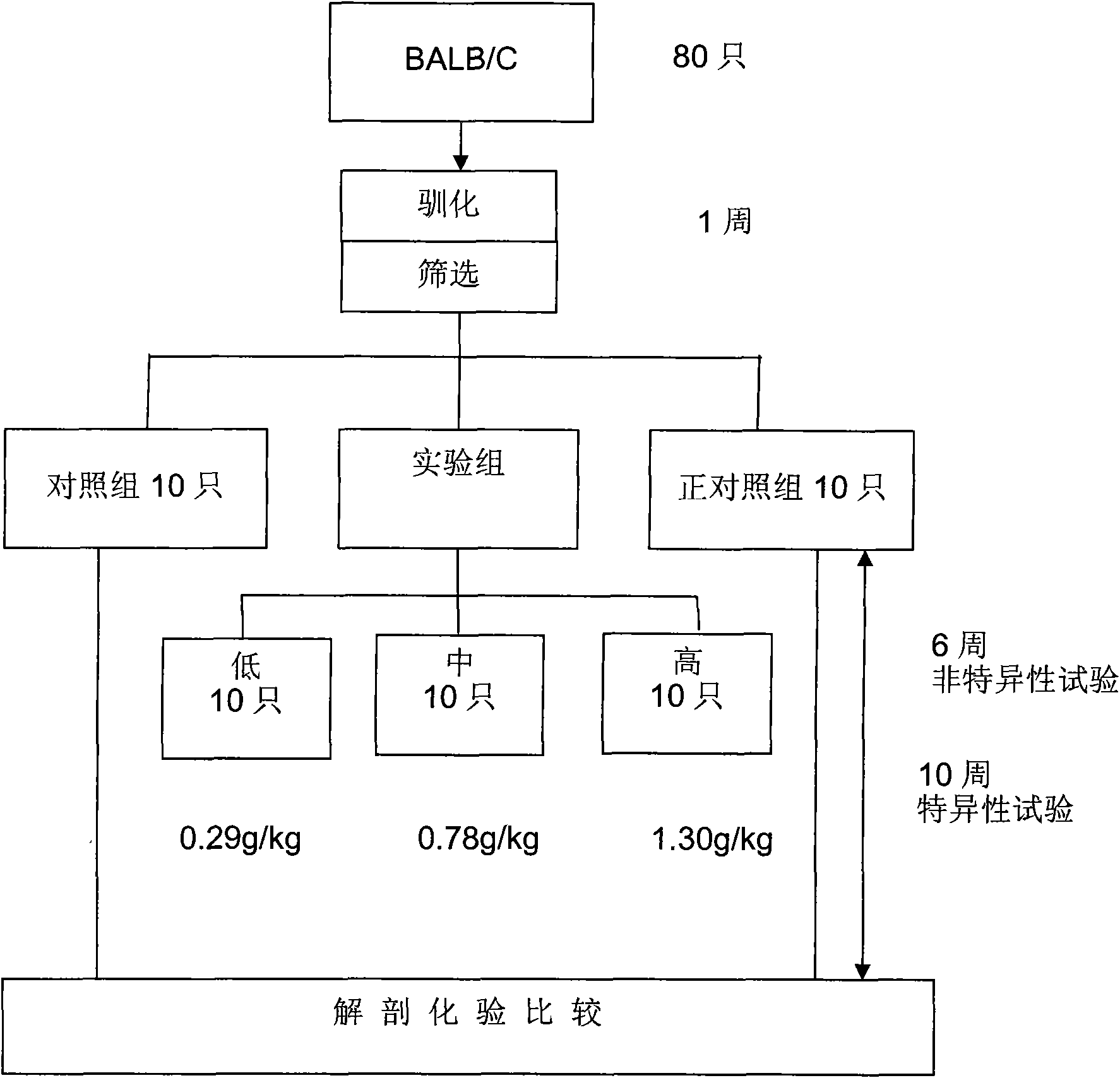
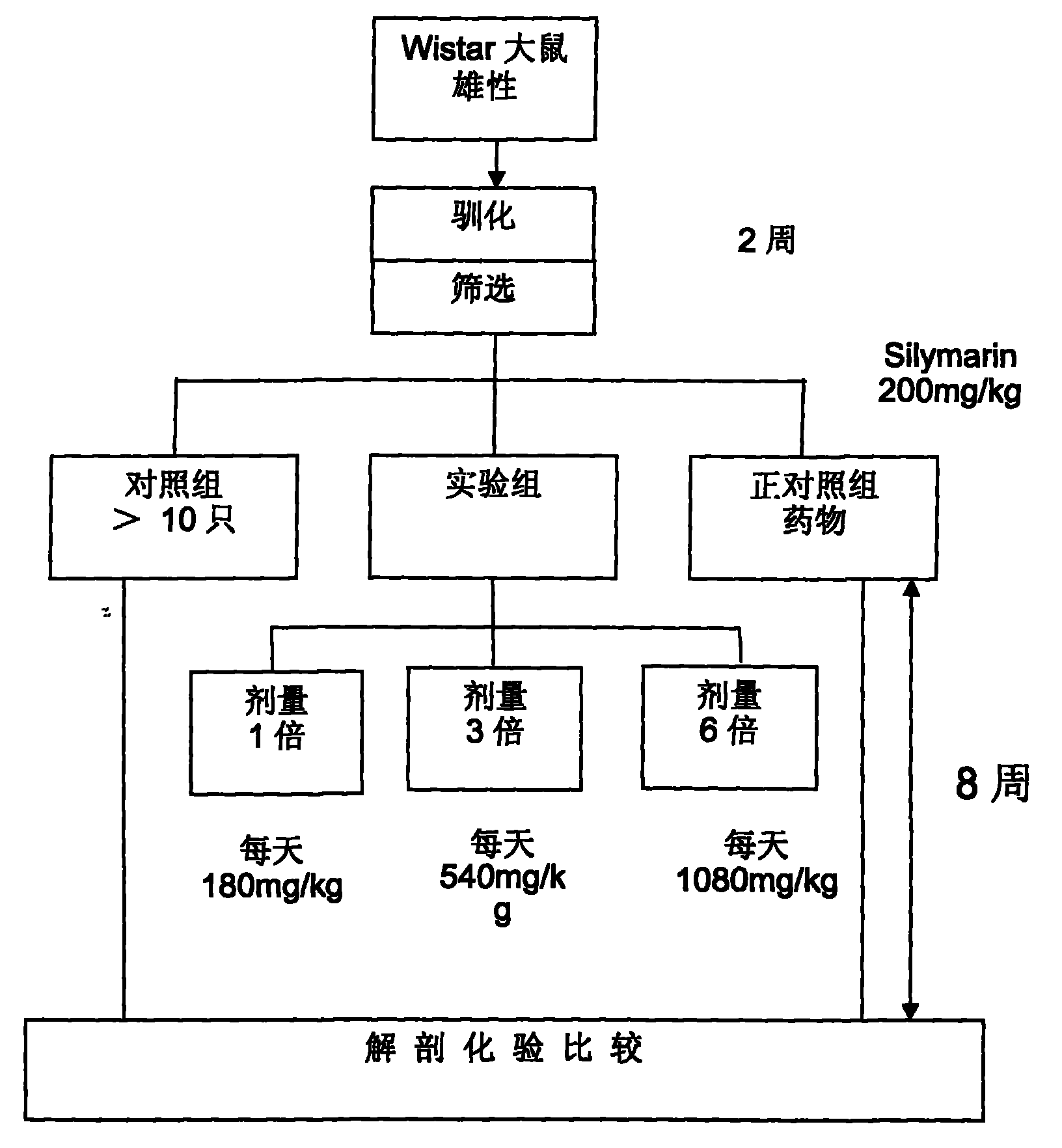
The invention tests liver protection and immune regulation functions by feeding a rat and a mouse with an antradiacomphora capsule which is prepared by adopting a special process and solid-state culture, wherein a liver protection test comprises the following steps of: inducing chronic hepatitis of the rat by using carbon tetrachloride twice a week for eight weeks, and measuring GPT and GOT, water content of liver, spleen and liver, liver protein and hydroxyproline content. The antradiacomphora capsule can lighten the rat chronic hepatitis induced by the carbon tetrachloride. A specific immunity test: the test matter is fed to the BALB / c mouse and egg albumen is injected, thereby accelerating the immune cell proliferation capacity and the effect of the immune regulation function generated by an antibody with serological specificity. A non-specific immunity test comprises the following step of: doing an oral test for consecutive six weeks by means of the BALB / c mouse. The invention accelerates the abdominal cavity phagocyte activity, regulates the anti-tumor cytohormone secretion and promotes the effect of the immune regulation function generated by a serological antibody.
Owner:WEI CHENG BIOTECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com