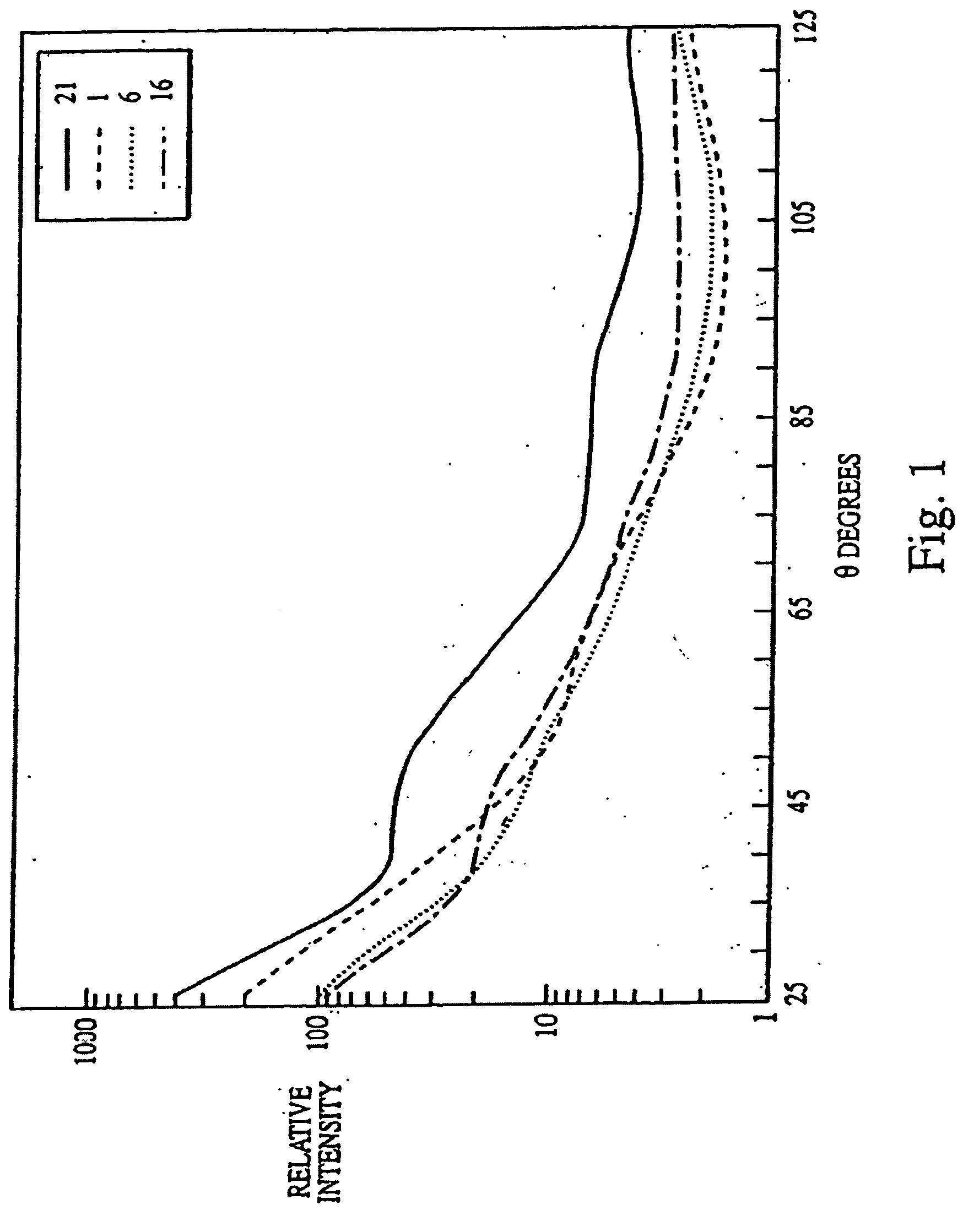
Patents
Literature
200 results about "Bacterial spore" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A bacterial spore is a spore or spore-like structure produced by bacteria. These include endospores, Akinetes, and spores produced by Actinobacteria and Azotobacter. Spore formation in bacteria is not a method of reproduction but simply a method of surviving unfavourable conditions. They have a number of features: They can tolerate extreme dryness. Some cannot be killed even at subzero temperatures. Some can spread poisonous chemicals, such as the Cry toxin synthesised by Bacillus thuringiensis Bacterial spores are extremely resistant. Spores of tetanus and anthrax, for example, can survive in the soil for many years. The origin of these spores was discovered in the 19th century, when a biologist noticed, under the microscope, a small, round, bright body inside bacterial cells. This survived even when the bacteria were boiled for five minutes. This killed the bacteria, but not the spores. They germinated when conditions were right. Because spores are so resistant, they are highly transmissible. This makes them a very problematic aspect of spore-forming pathogens such as Clostridium difficile.
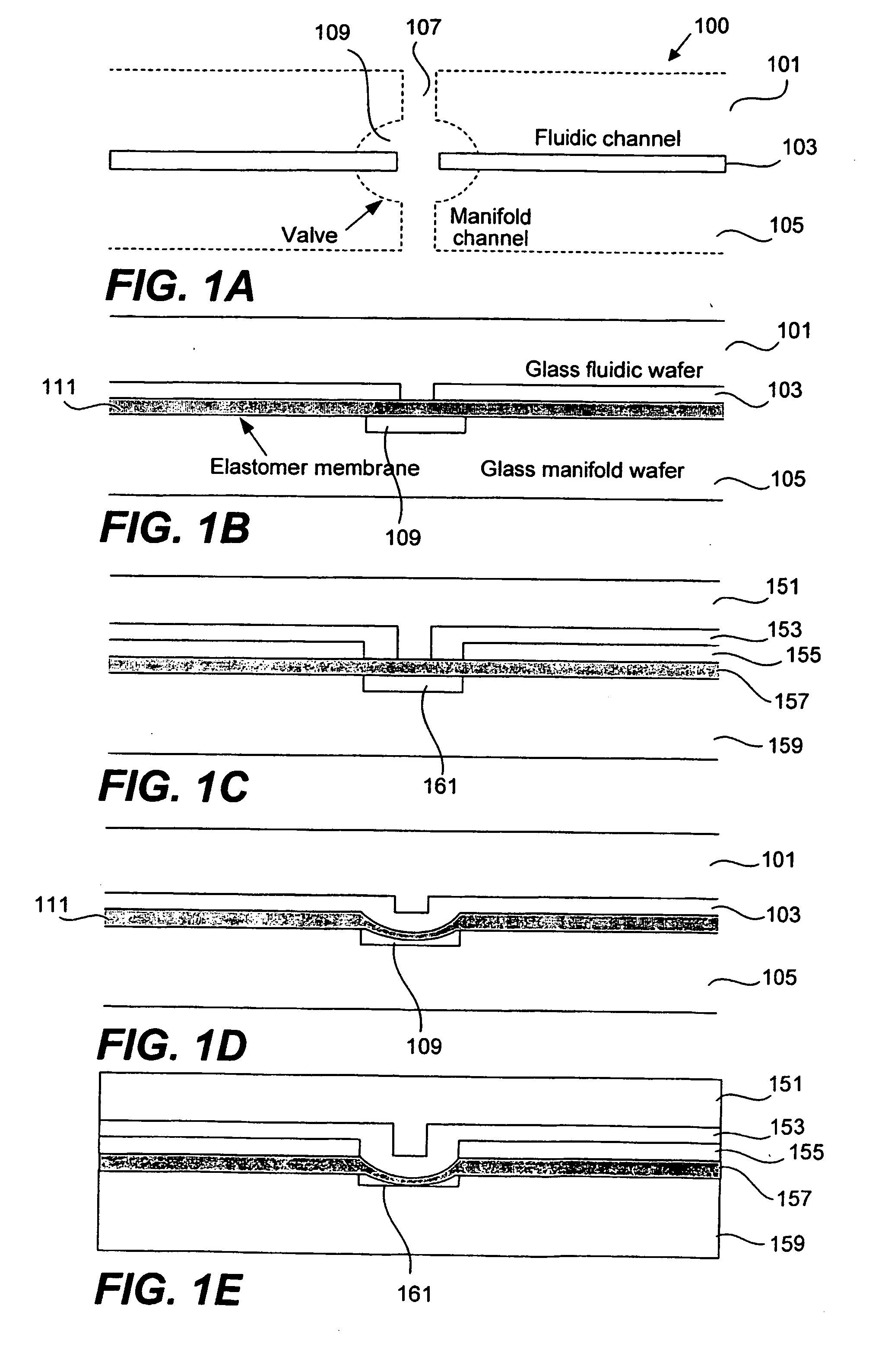
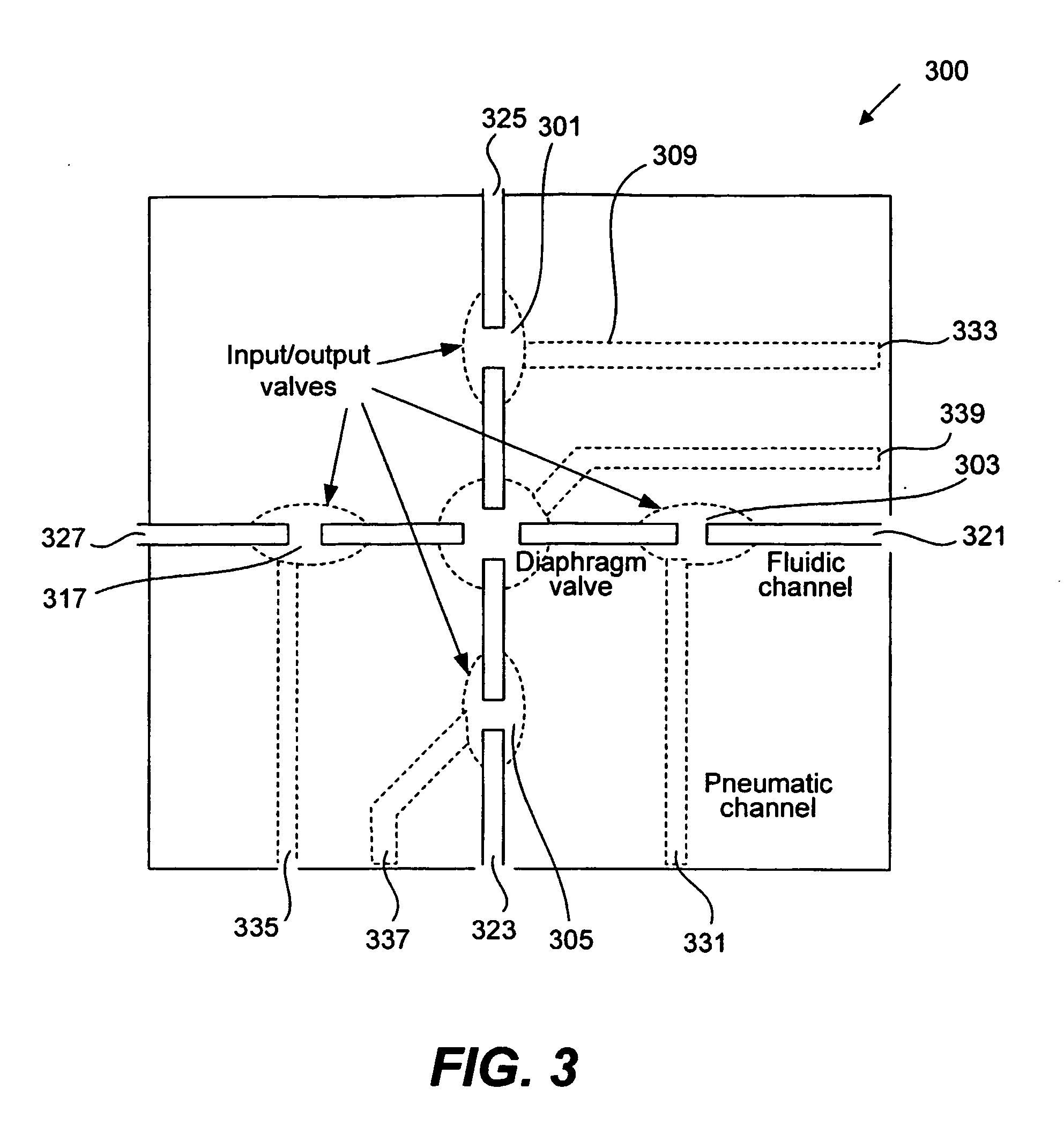
Methods and apparatus for pathogen detection and analysis
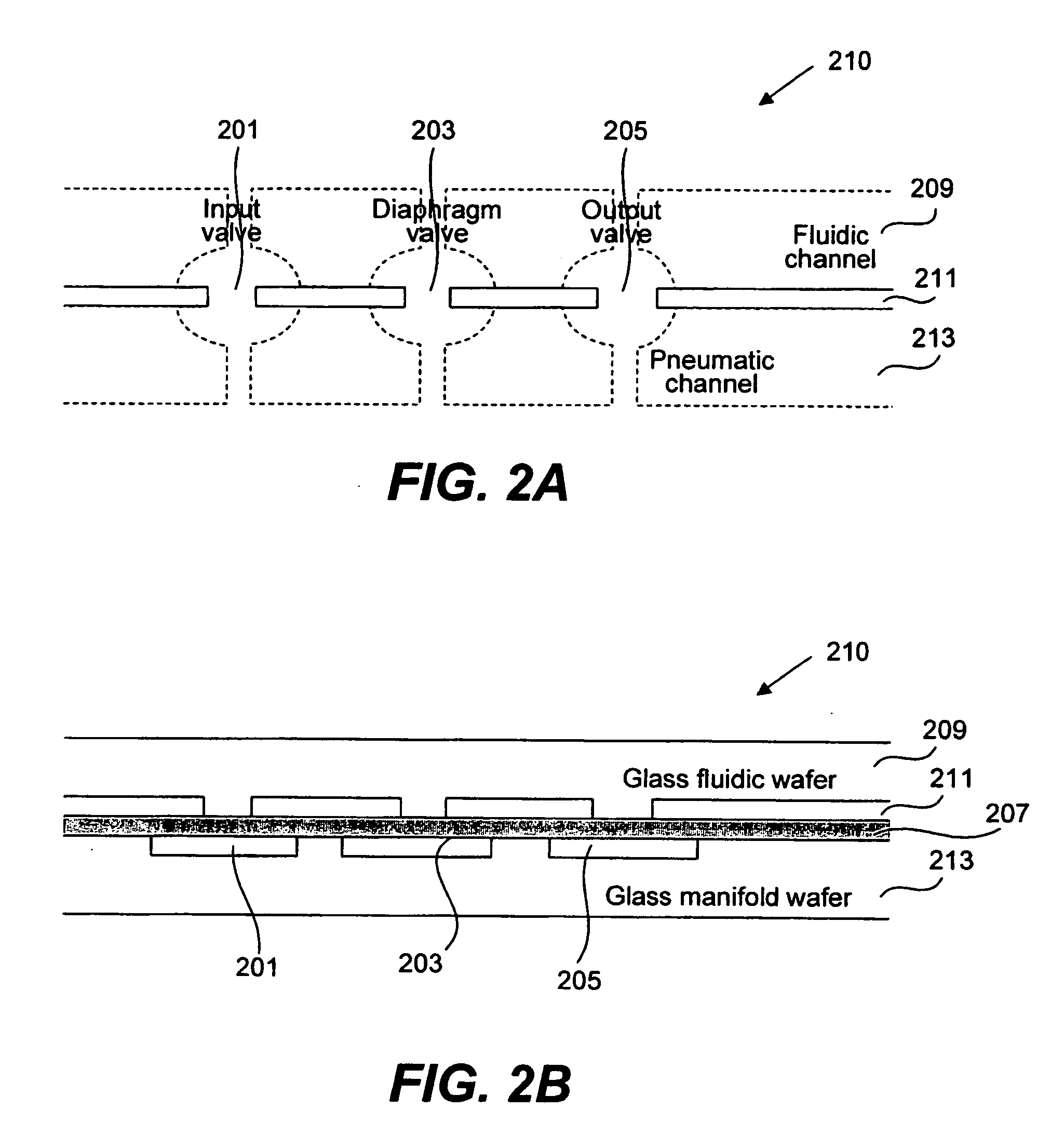
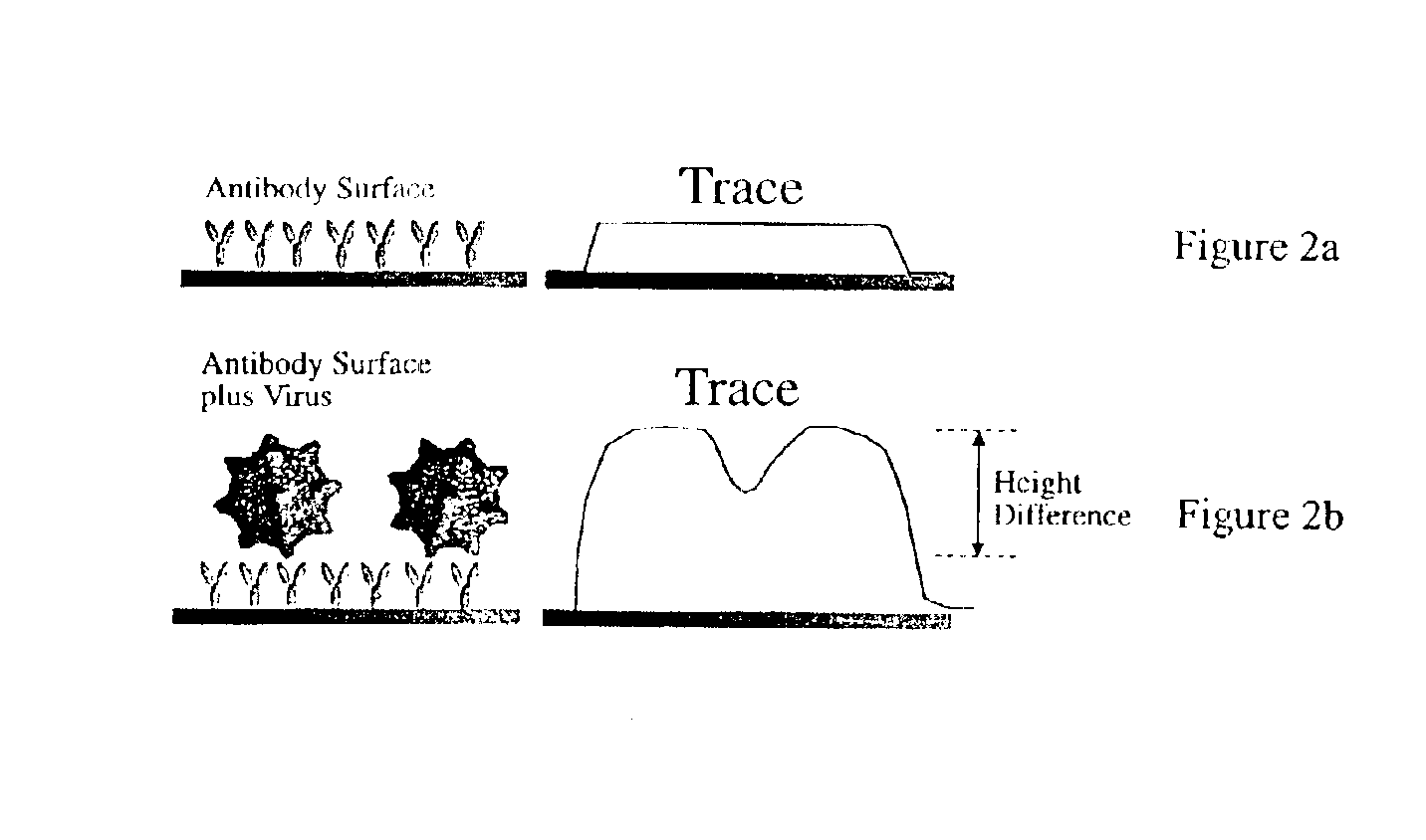
Methods and apparatus for implementing microfluidic analysis devices are provided. A monolithic elastomer membrane associated with an integrated pneumatic manifold allows the placement and actuation of dense arrays of a variety of fluid control structures, such as structures for isolating, routing, merging, splitting, and storing volumes of fluid. The fluid control structures can be used to implement a pathogen detection and analysis system including integrated immunoaffinity capture and analysis, such as polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and capillary electrophoresis (CE) analysis. An analyte solution can be input into the device and pumped through a series of immunoaffinity capture matrices in microfabricated chambers having antibodies targeted to the various classes of microbiological organisms such as bacteria, viruses and bacterial spores. The immunoaffinity chambers can capture, purify, and concentrate the target for further analysis steps.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Method and a product for the rapid decontamination and sterilization of bacterial endospores
The present invention is directed to a method for the disinfection and sterilization of material and surfaces contaminated with one or more members selected from the group consisting of bacteria and bacterial spores, comprising the steps of: (a) providing a biocidal fluid containing a mixture of effective amounts of a germinant and a germicide; and (b) contacting the material and surfaces contaminated with one or more members selected from the group consisting of bacteria and bacterial spores, with the biocidal fluid of step (a) for a time sufficient for disinfecting and sterilizing said material. The invention also provides a sterilizing composition suitable for killing and rendering spores lifeless comprising: (a) an effective amount of a germinating agent; (b) an effective amount of a germicide.
Owner:BAUGH CLARENCE L +2
Sterialization methods and apparatus which employ additive-containing supercritical carbon dioxide sterilant
ActiveUS7108832B2Enhances mass transfer and sterilizationImprove sterilizationSamplingOther chemical processesSporePressure cycling
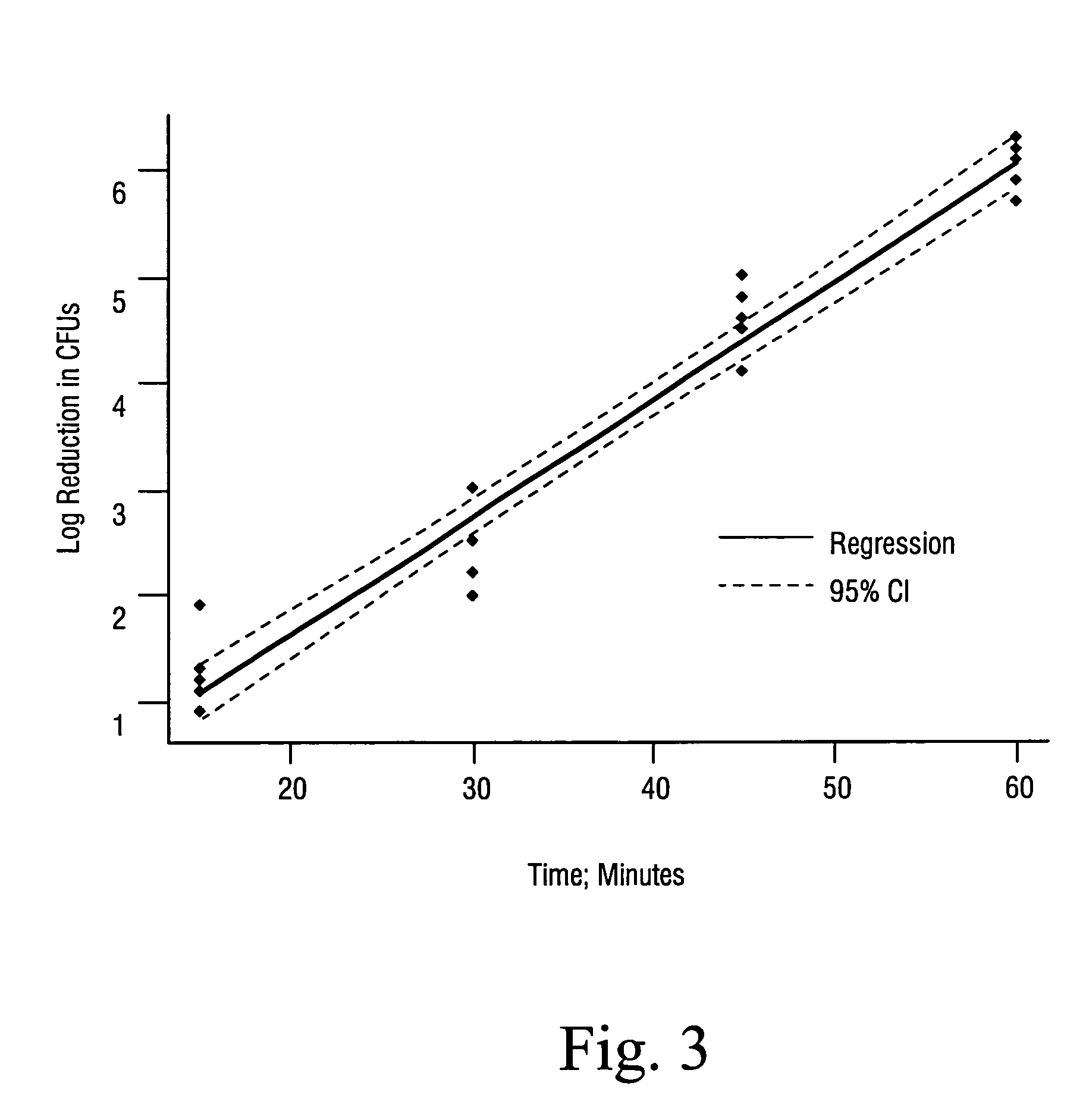
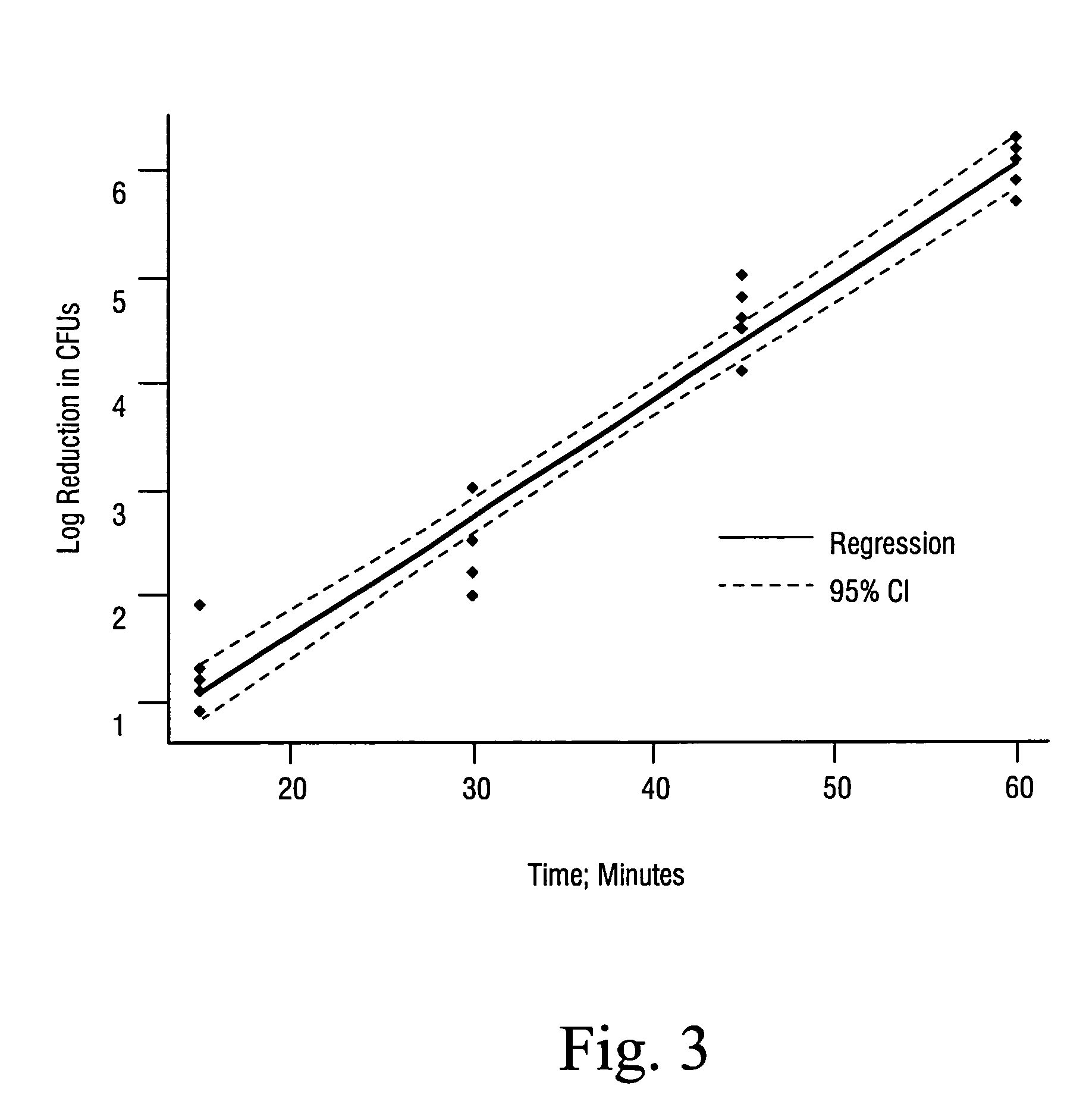
Sterilization methods and apparatus are effective to achieve a 6-log reduction in CFUs of industry standard bacteria and bacterial spores, i.e., B. stearothermophilus and B. subtilis spores, by subjecting sterilizable materials to a chemical additive-containing carbon dioxide sterilant fluid at or near its supercritical pressure and temperature conditions. Most preferably, the chemical additive-containing supercritical carbon dioxide sterilant fluid is agitated during sterilization, e.g., via mechanical agitation or via pressure cycling.
Owner:NOVASTERILIS
Universal method and composition for the rapid lysis of cells for the release of nucleic acids and their detection
InactiveUS7494771B2Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleic acid testSolid particle
This invention describes a rapid (10 to 15 minutes), simple, flexible and efficient method of nucleic acids extraction for nucleic acid testing assays. This method has the following basic steps: i) mechanical cell lysis using solid particles in the presence of a chelating agent, followed by ii) controlling the presence and / or activity of NAT assays inhibitors. This method is applicable to various biological samples and universal for microorganisms, as one can use it to extract nucleic acids from test samples containing target viruses, bacteria, bacterial spores, fungi, parasites or other eukaryotic cells, including animal and human cells.
Owner:ART RECH & TECH AVANCEES INC ART ADVANCED RES TECH INC +1
Electrochemically treated water, method and device for the production thereof, and the use thereof as a disinfection agent
The present invention relates to electrochemically treated water, obtainable by means of a method that is characterized by the following steps: a) electrolyzing water and b) reducing the concentrations of the oxidants created in step a). The electrochemically treated water obtained in this manner is characterized by a disinfecting effect on bacteria, bacterial spores, fungi, fungal spores, viruses, prions, or mixtures thereof. The invention further relates to water, characterized in that the same has a disinfecting effect on bacteria, bacterial spores, fungi, fungal spores, viruses, algae, prions, or mixtures thereof, that it is substantially free of disinfection agents with the exception of the oxidants related to the disinfection agents, and that it has a total concentration of oxidants of less than 20 ppm.
Owner:AQUAGROUP AG
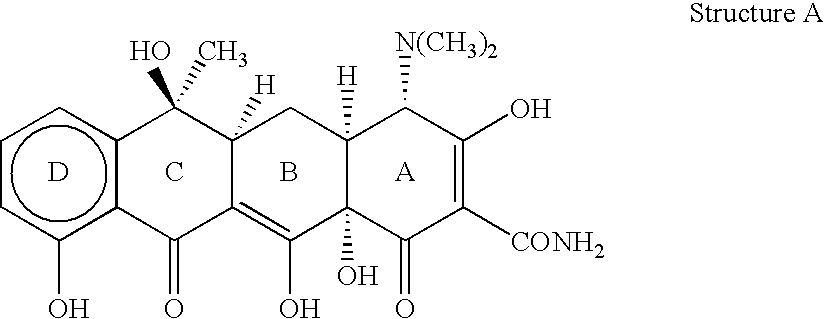
Use of non-antibacterial tetracycline formulations for inhibiting bacterial spores
The invention relates to a method for inhibiting bacterial spores from becoming infectious vegetative cells in a mammal in need thereof. In another embodiment, invention relates to a method for inhibiting outgrowth of bacterial spores in a mammal in need thereof. The method comprises administering to the mammal an effective amount of a non-antibacterial tetracycline formulation. In one embodiment, the non-antibacterial tetracycline formulation comprises an antibacterial tetracycline in a sub-antibacterial amount. In another embodiment, the non-antibacterial tetracycline formulation comprises a non-antibacterial tetracycline.
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK
Particle impedance sensor
Apparatuses and methods for analyzing particles using an impedance sensor. A flow-through impedance sensor may use two in-line electrodes driven in counter phase. A common sensor electrode may be used to, for example, detect impedance and determine trajectories through the sensor area. The sensor may be used in a wide variety of applications, including but not limited to use with microfluidic devices for determining particle characteristics such as position, velocity, size, and concentration as well as detection of bacterial spores and other biological agents of potential use in warfare and bio-terrorism.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Double-channel real-time bioaerosol monitoring method and device thereof
InactiveCN101858847AReduce false alarm rateShort detection cycleWithdrawing sample devicesFluorescence/phosphorescencePhysicsFluorescence
The invention provides a double-channel real-time bioaerosol monitoring method and a device thereof. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps: (1) concentrating atmospheric aerosol particles; (2) carrying out double-channel ultraviolet induced fluorescence detection; (3) data-processing; (4) cleaning the surface of an enrichment board of the particles and regenerating; and (5) repeatedly carrying out a new round of loop detection. The device comprises an aerosol-particles concentration unit, a double-channel ultraviolet induced fluorescence detection unit, a particle enrichment board regeneration mechanism, a rotary table and a control system. The invention can measure the density and the change of bio-particles such as bacteria, spores, viruses and the like in an ambient atmosphere in real time so as to achieve an early warning function on bioaerosol content in the atmosphere.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Device and method of use for detection and characterization of pathogens and biological materials
The present invention includes a method and apparatus for the detection of a target material. The method and apparatus includes providing a substrate with a surface and forming a domains of deposited materials thereon. The deposited material can be placed on the surface and bound directly and non-specifically to the surface, or it may be specifically or non-specifically bound to the surface. The deposited material has an affinity for a specific target material. The domains thus created are termed affinity domains or deposition domains. Multiple affinity domains of deposited materials can be deposited on a single surface, creating a plurality of specific binding affinity domains for a plurality of target materials. Target materials may include, for example, pathogens or pathogenic markers such as viruses, bacteria, bacterial spores, parasites, prions, fungi, mold or pollen spores. The device thus created is incubated with a test solution, gas or other supporting environment suspected of containing one or more of the target materials. Specific binding interactions between the target materials and a particular affinity domain occurs and is detected by various methods.
Owner:BIOFORCE NANOSCI
Composition having bacteristatic and bactericidal activity against bacterial spores and vegetative cells and process for treating foods therewith
InactiveUS6991820B2Excellent bacteristaticHigh bactericidal activityMeat/fish preservation by coatingPre-baking dough/flour preservationBacteroidesMetabolite
Antibacterial compositions effective against both gram positive and gram negative vegetative bacteria plus harmful gram positive sporeforming bacteria include propionibacterial metabolites in combination with two or more of the following: a lantibiotic; a lytic enzyme; and an organic acid or its salt. Methods of use are provided, as well as food products treated with these antibacterial compositions.
Owner:DUPONT NUTRITION BIOSCIENCES APS
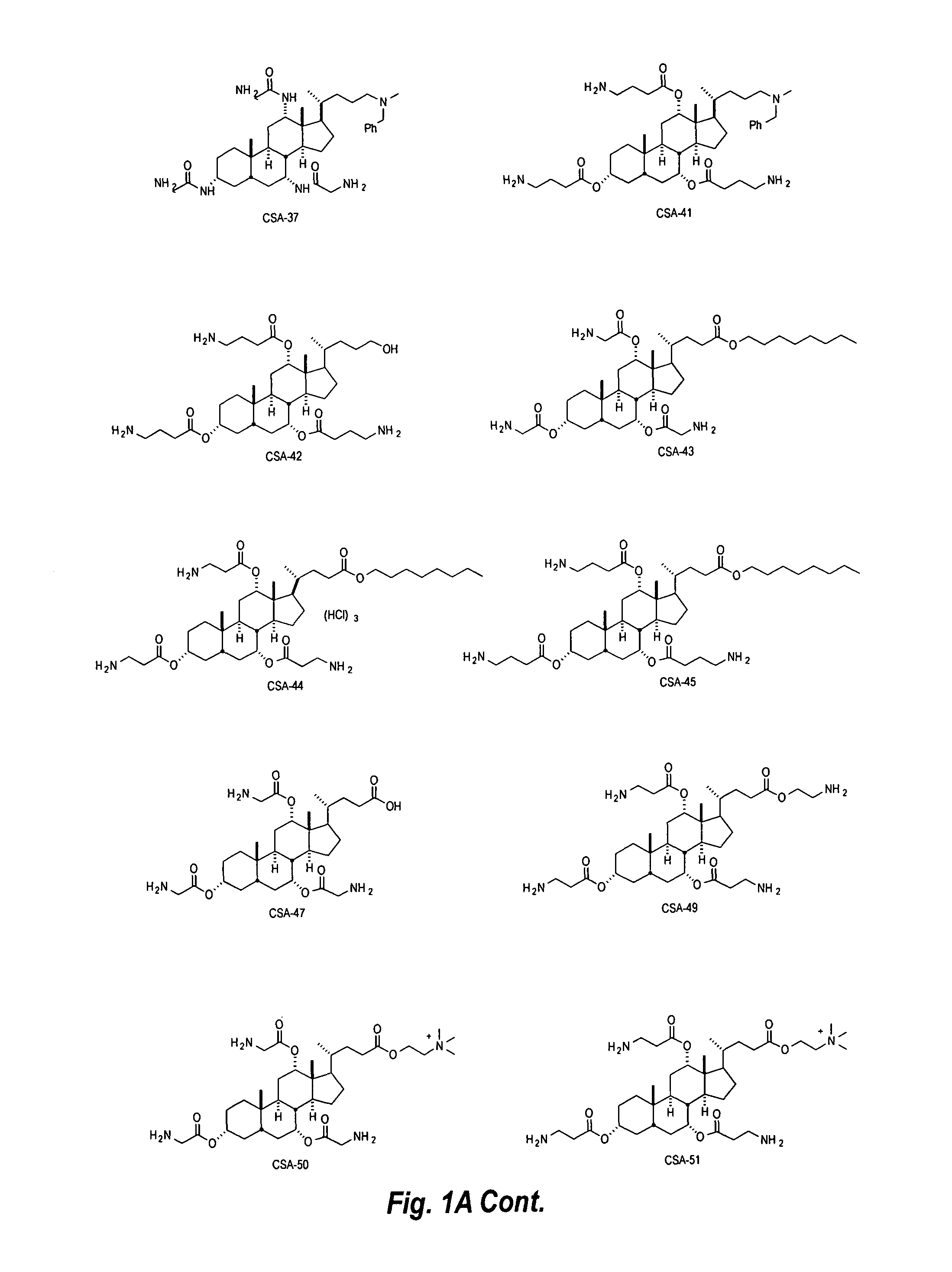
Novel Chemistries, Solutions, and Dispersal Systems for Decontamination of Chemical and Biological Systems
InactiveUS20100179368A1Sufficient perhydrolysisGood solubilization effectBiocideDead animal preservationOrganophosphateVirus
The present invention relates generally to chemical and biological decontamination solutions and methods of using them. The invention is useful for decontaminating a wide range of compounds and organisms. In particular, the systems, methods, solutions, and formulations of the invention can be used to remove and / or neutralize organophosphates and other toxic chemicals, bacteria, bacterial spores, fungi, molds and viruses.
Owner:L 3 SERVICES
High temperature flow-through device for rapid solubilization and analysis
InactiveUS7592139B2Dissolve fastFast preparationBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsLysisBiological materials
Devices and methods for thermally lysing of biological material, for example vegetative bacterial cells and bacterial spores, are provided. Hot solution methods for solubilizing bacterial spores are described. Systems for direct analysis are disclosed including thermal lysers coupled to sample preparation stations. Integrated systems capable of performing sample lysis, labeling and protein fingerprint analysis of biological material, for example, vegetative bacterial cells, bacterial spores and viruses are provided.
Owner:SANDIA NAT LAB
Methods, compositions and kits for biological indicator of sterilization
A novel biological indicator system to detect the effectiveness of a sterilization treatment and methods for assessing the viability of and / or changes in bacterial spores exposed to a sterilization or disinfection method by multiangle light scattering thereby detecting a change in the spores as indicators of spore viability and the efficacy of the sterilization or disinfection method.
Owner:ICF TECH
Bacterial spore compositions for industrial uses
ActiveUS20160040119A1Reduce mortalityIncrease weightAntibacterial agentsBio-organic fraction processingSporeMicroorganism
In one aspect, the present invention is directed to a plant or plant part coated with a composition comprising a bacterial spore and a germinative compound. In another aspect the present invention is directed to a method of enhancing the growth of a plant or plant part comprising coating such plant or plant part with such a composition. In yet another aspect, the present invention is directed to a composition comprising a bacterial spore and a germinative compound where such components are maintained in an inactive form. The present invention also relates to use of the compositions in wastewater treatment, environmental remediation, oil recovery, aquaculture systems, and direct fed microbials.
Owner:ENVERA
Sterilization methods and apparatus which employ additive-containing supercritical carbon dioxide sterilant
ActiveUS20050025667A1Enhances mass transfer and sterilizationImprove sterilizationSamplingOther chemical processesSporePressure cycling
Sterilization methods and apparatus are effective to achieve a 6-log reduction in CFUs of industry standard bacteria and bacterial spores, i.e., B. stearothermophilus and B. subtilis spores, by subjecting sterilizable materials to a chemical additive-containing carbon dioxide sterilant fluid at or near its supercritical pressure and temperature conditions. Most preferably, the chemical additive-containing supercritical carbon dioxide sterilant fluid is agitated during sterilization, e.g., via mechanical agitation or via pressure cycling.
Owner:NOVASTERILIS
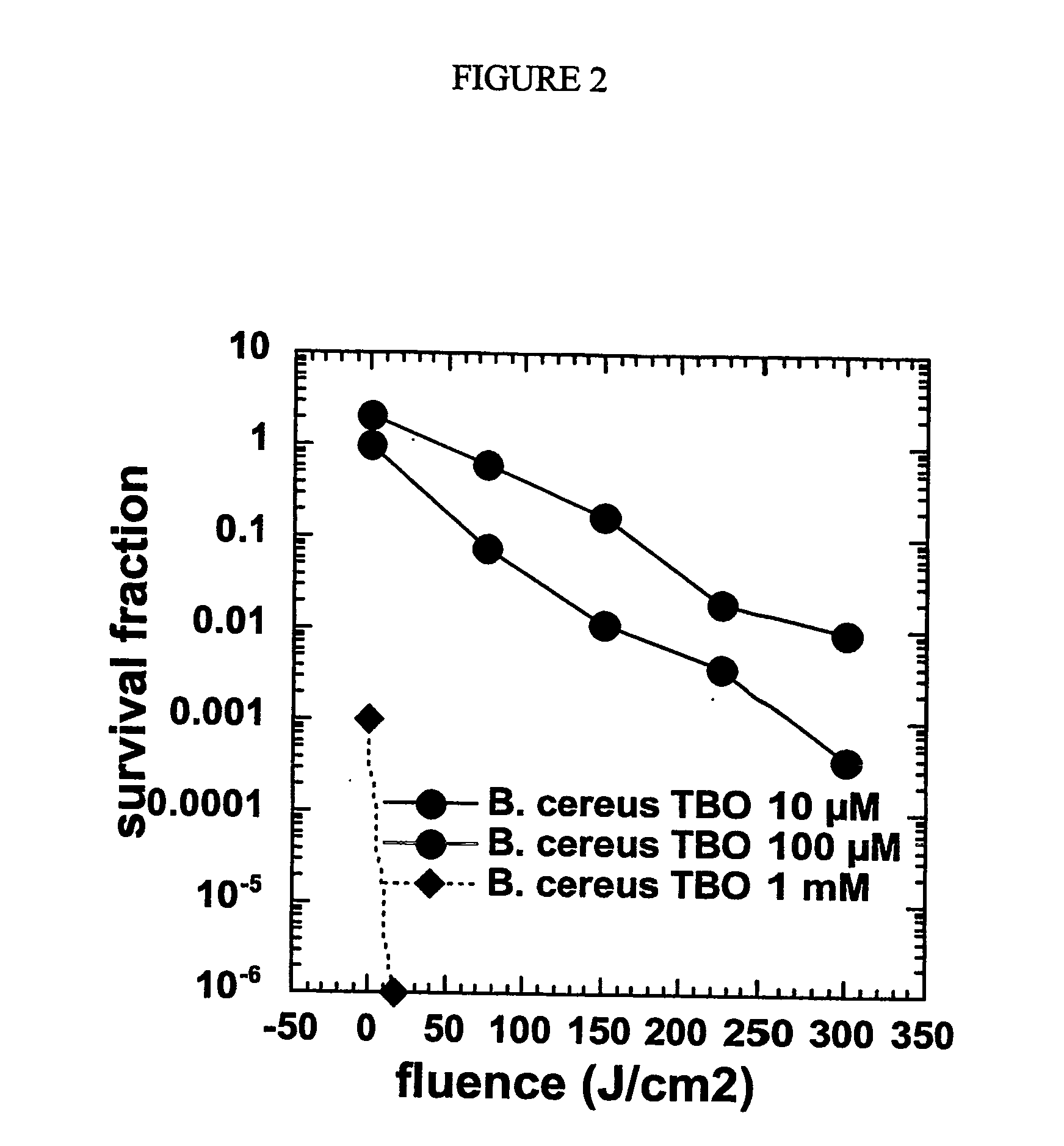
Photodynamic inactivation of bacterial spores
The present invention relates the use photosensitizers to inactivate bacterial spores of bacterial species including Bacillus anthracis. Methods of the present invention are useful in the decontamination and treatment of living animals and in the decontamination of inanimate objects and substances.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
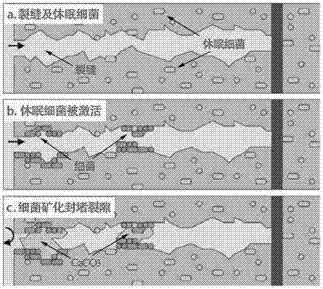
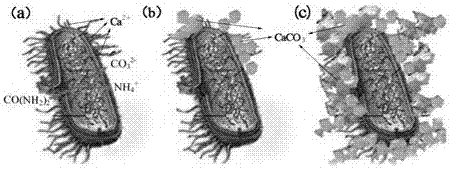
Microbial seal-healing capsule for coal mine air leakage plugging as well as preparation method and application of microbial seal-healing capsule
InactiveCN107973542AImplement automatic detectionAchieve automatic healingMicroparticleCalcium carbonate precipitation
The invention discloses a microbial seal-healing capsule for coal mine air leakage plugging as well as a preparation method and application of the microbial seal-healing capsule. Dry powder of bacterial spores is uniformly dispersed in water, a suitable substrate is selected according to the kinds of the bacterial spores, the substrate is added into a uniformly-dispersed mixed solution according to a certain ratio of the bacterial spores to the substrate and is uniformly stirred to be agglomerated, the agglomerated mixture is slowly added into a multifunctional granulator and is extruded, a cooling system is started, the temperature of the material is maintained, and the extruded strip-shaped substance is added into a rounder for rounding and is sieved and dried to obtain microparticles; and the microbial seal-healing capsule is prepared from the microparticles and a wall material by using a vacuum impregnation method or an interfacial polymerization method, the microbial seal-healingcapsule and a main material for air leakage plugging are mixed to be used, once concrete is cracked, the spores inside the material can be activated to normally metabolize, and calcium carbonate is continuously induced to be precipitated, so that the self-repair of cracks is realized.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Methods, compositions and kits for biological indicator of sterilization
InactiveUS20060183183A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsSporeDisinfection methods
A novel biological indicator system to detect the effectiveness of a sterilization treatment and methods for assessing the viability of and / or changes in bacterial spores exposed to a sterilization or disinfection method by multiangle light scattering thereby detecting a change in the spores as indicators of spore viability and the efficacy of the sterilization or disinfection method.
Owner:ICF TECH
Aerosols incorporating ceragenin compounds and methods of use thereof
Aerosols that include ceragenin compounds (i.e., ceragenin-containing aerosols), methods for delivering such aerosols, and devices for delivering such aerosols. Ceragenins can be used to kill a broad range of microbes (e.g., bacteria, viruses, fungi, bacterial spores, fungal spores, and the like), yet they are thought to be completely non-toxic to humans and other higher eukaryotes. Aerosols can penetrate into the nooks and crannies of a space and kill microbes that may lurk in a space. In addition, ceragenins have a extended mode of action, which allows them to continue killing microbes in a space for an extended period of time.
Owner:BRIGHAM YOUNG UNIV
Novel Chemistries, Solutions, and Dispersal Systems for Decontamination of Chemical and Biological Systems
InactiveUS20120108878A1Improve solubilityReduce surface tensionBiocideDead animal preservationVirusOrganophosphate
The present invention relates generally to chemical and biological decontamination solutions and methods of using them. The invention is useful for decontaminating a wide range of compounds and organisms. In particular, the systems, methods, solutions, and formulations of the invention can be used to remove and / or neutralize organophosphates and other toxic chemicals, bacteria, bacterial spores, fungi, molds and viruses.
Owner:L 3 SERVICES
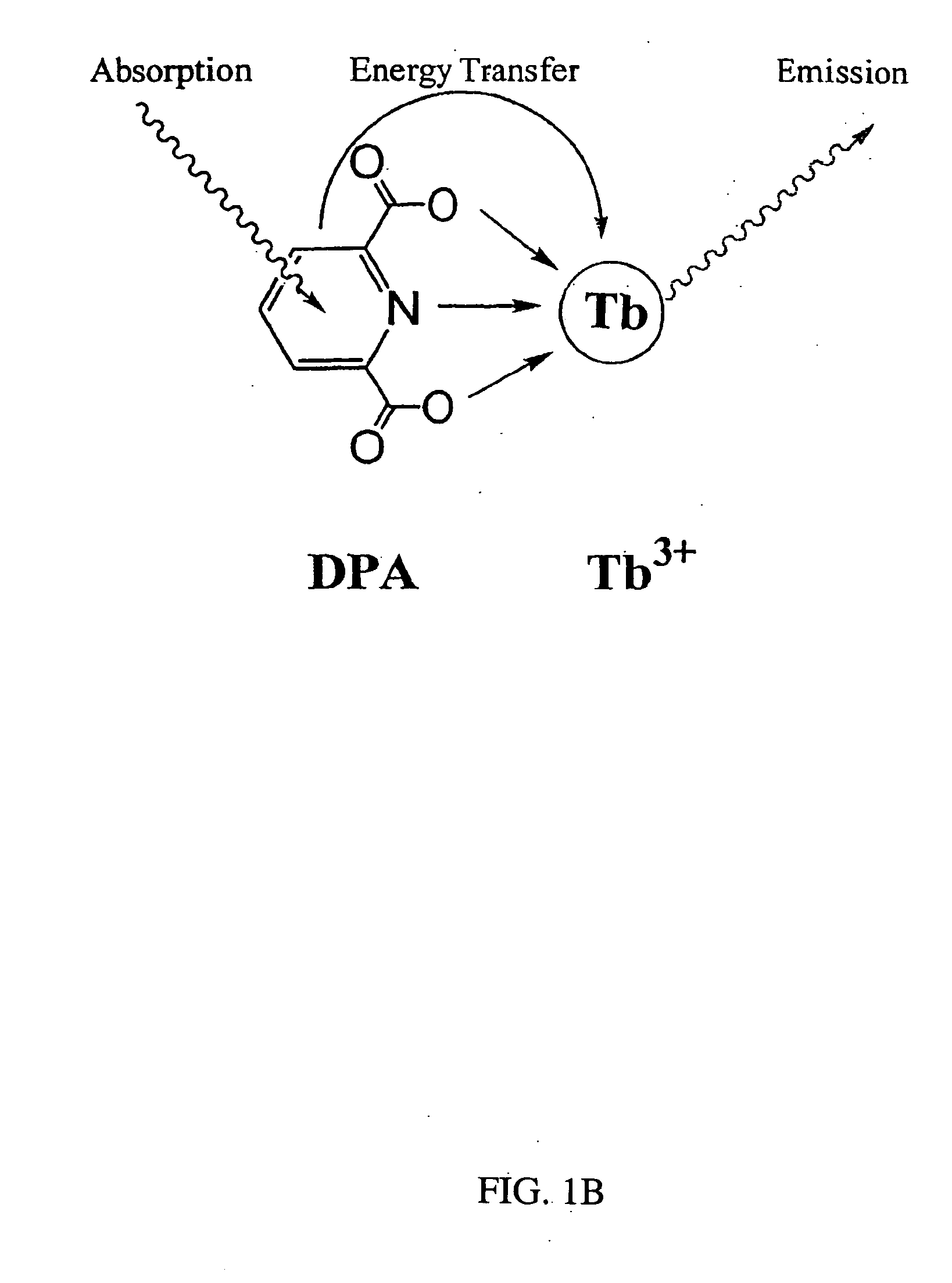
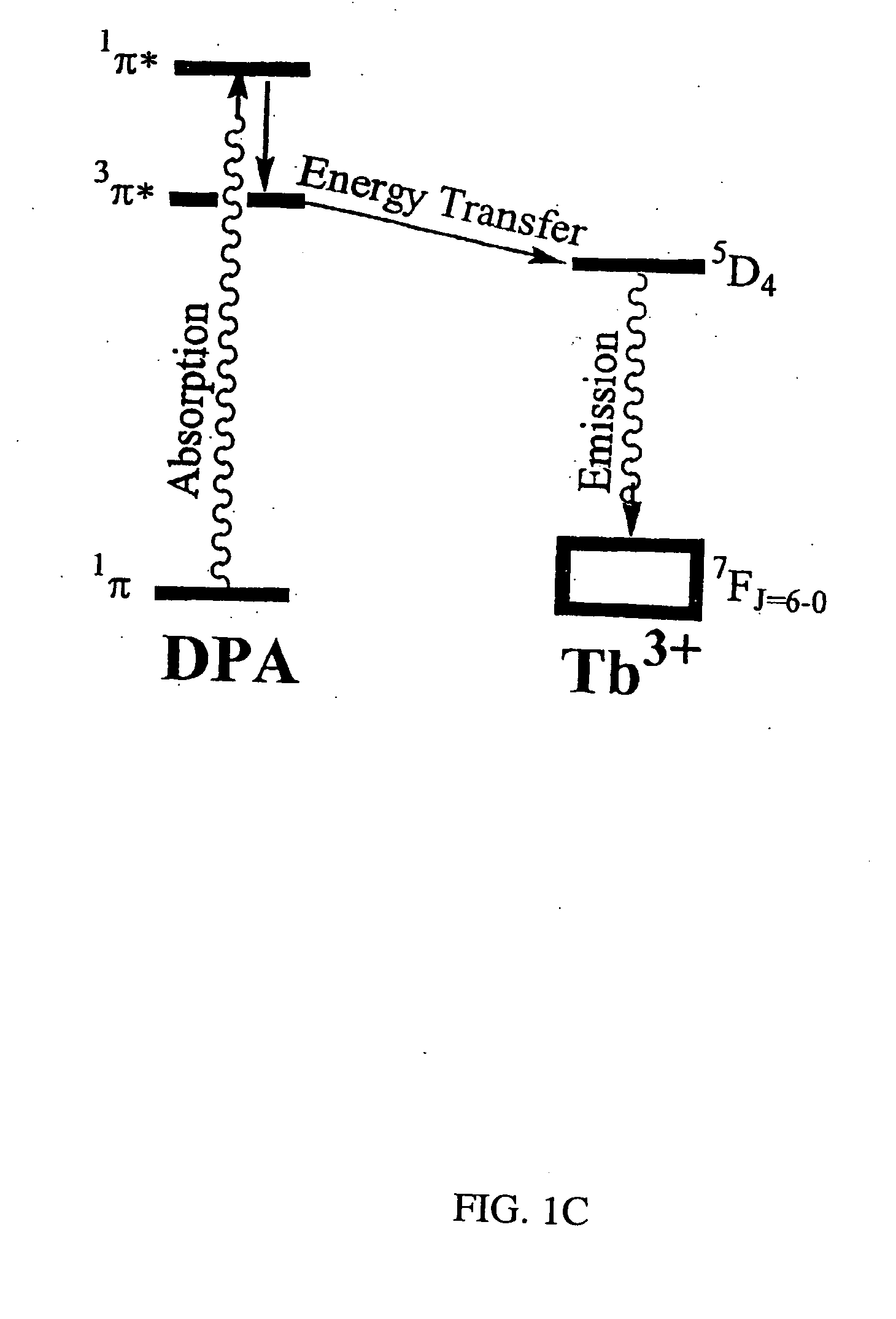
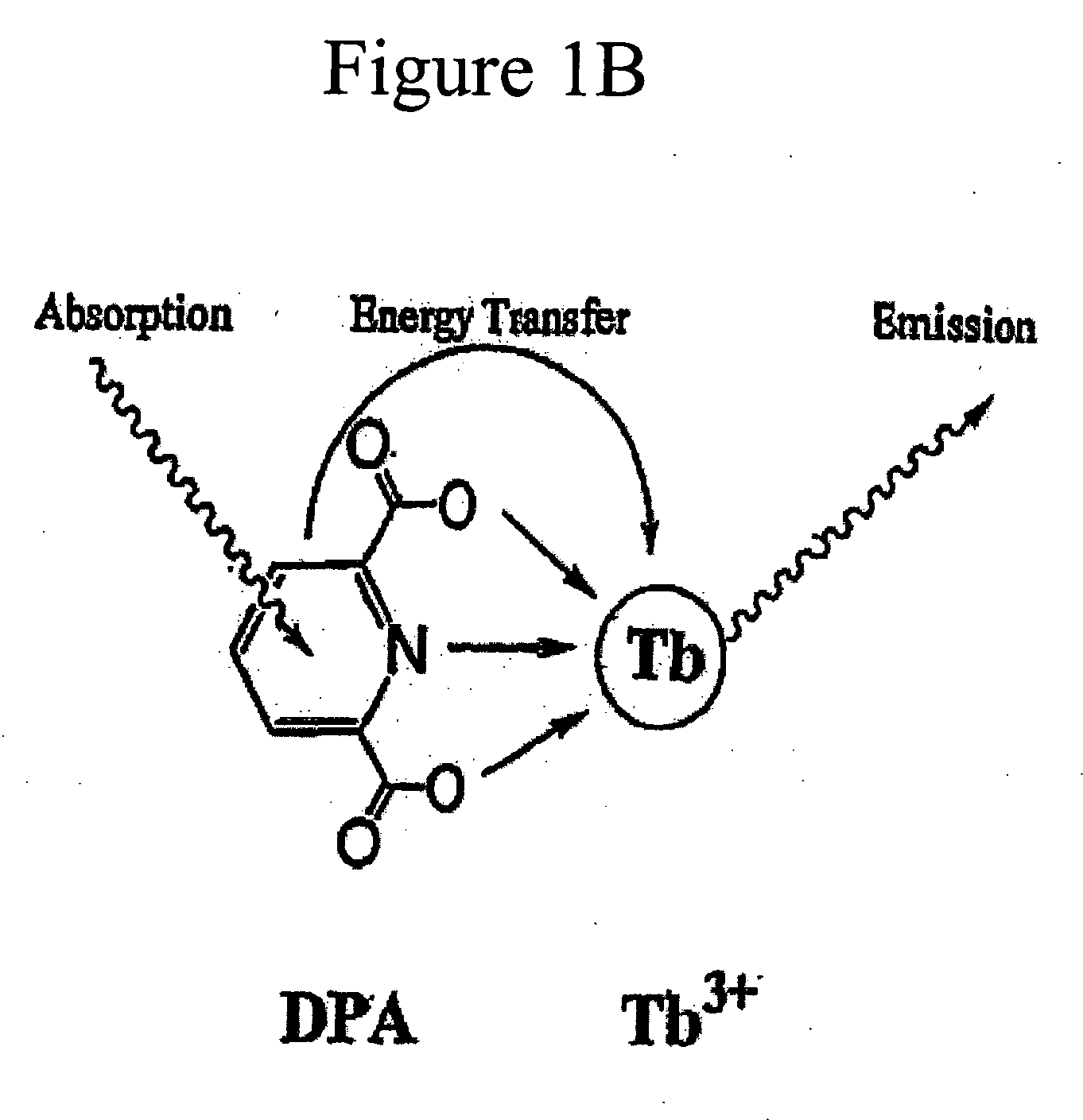
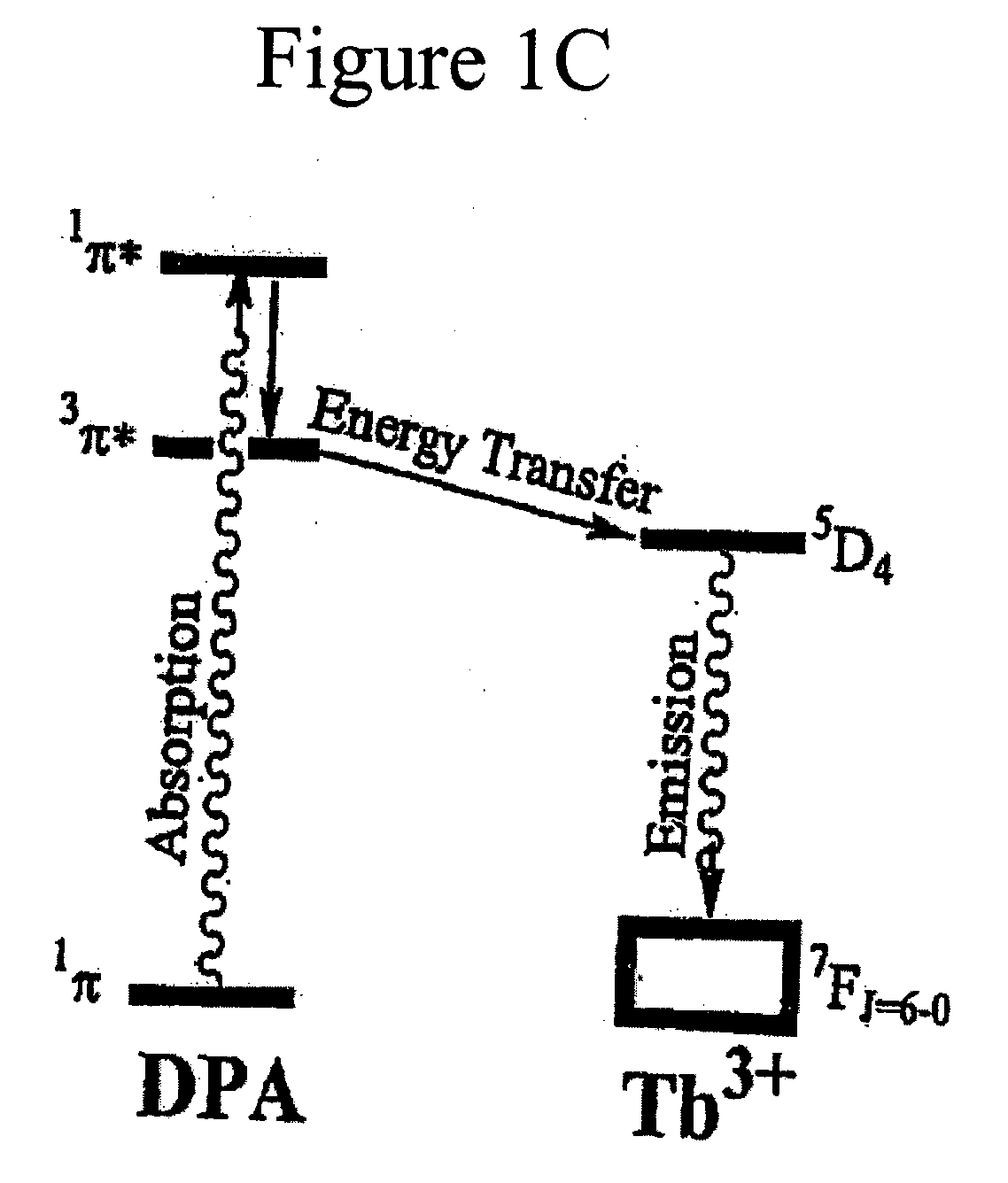
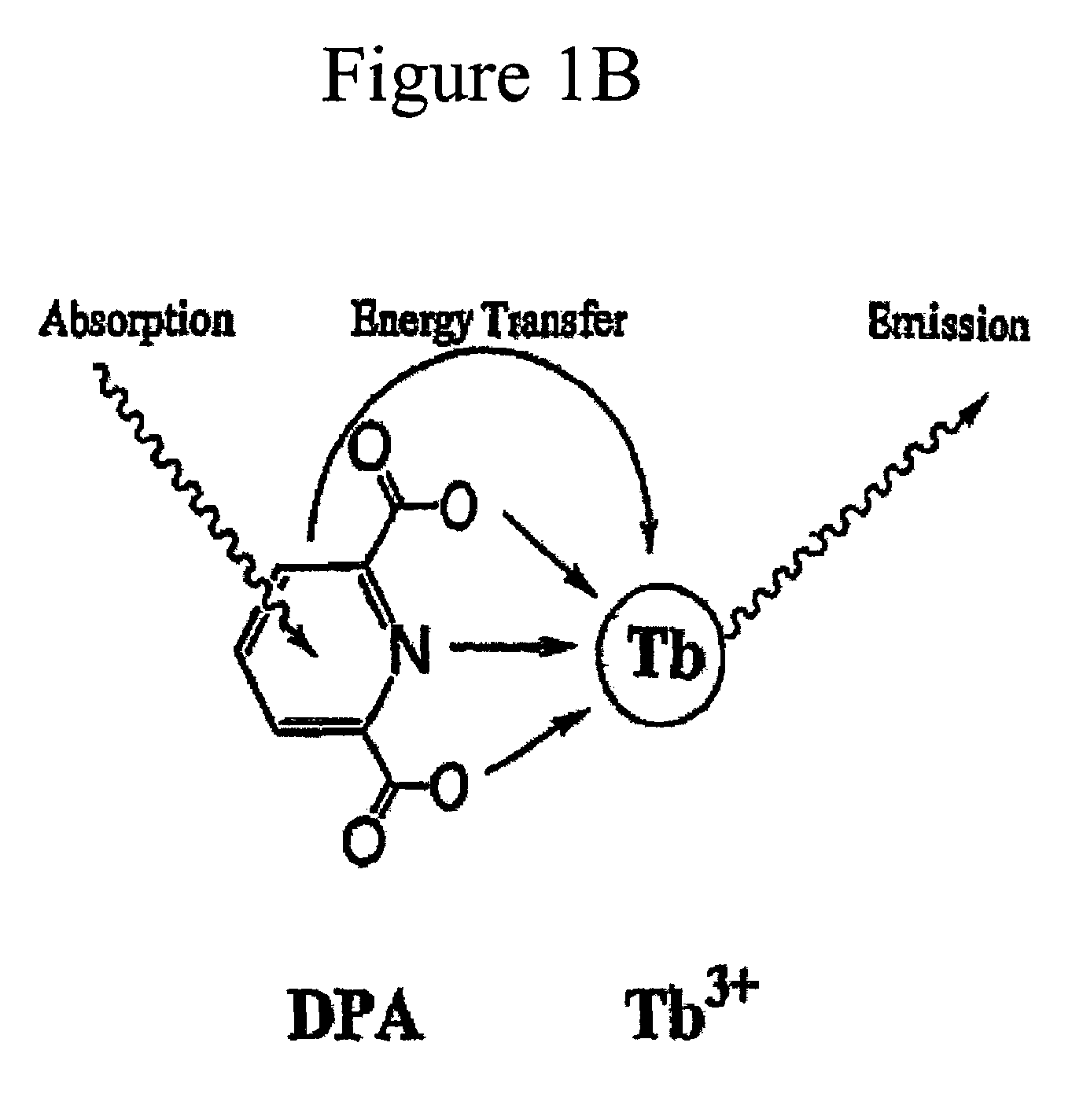
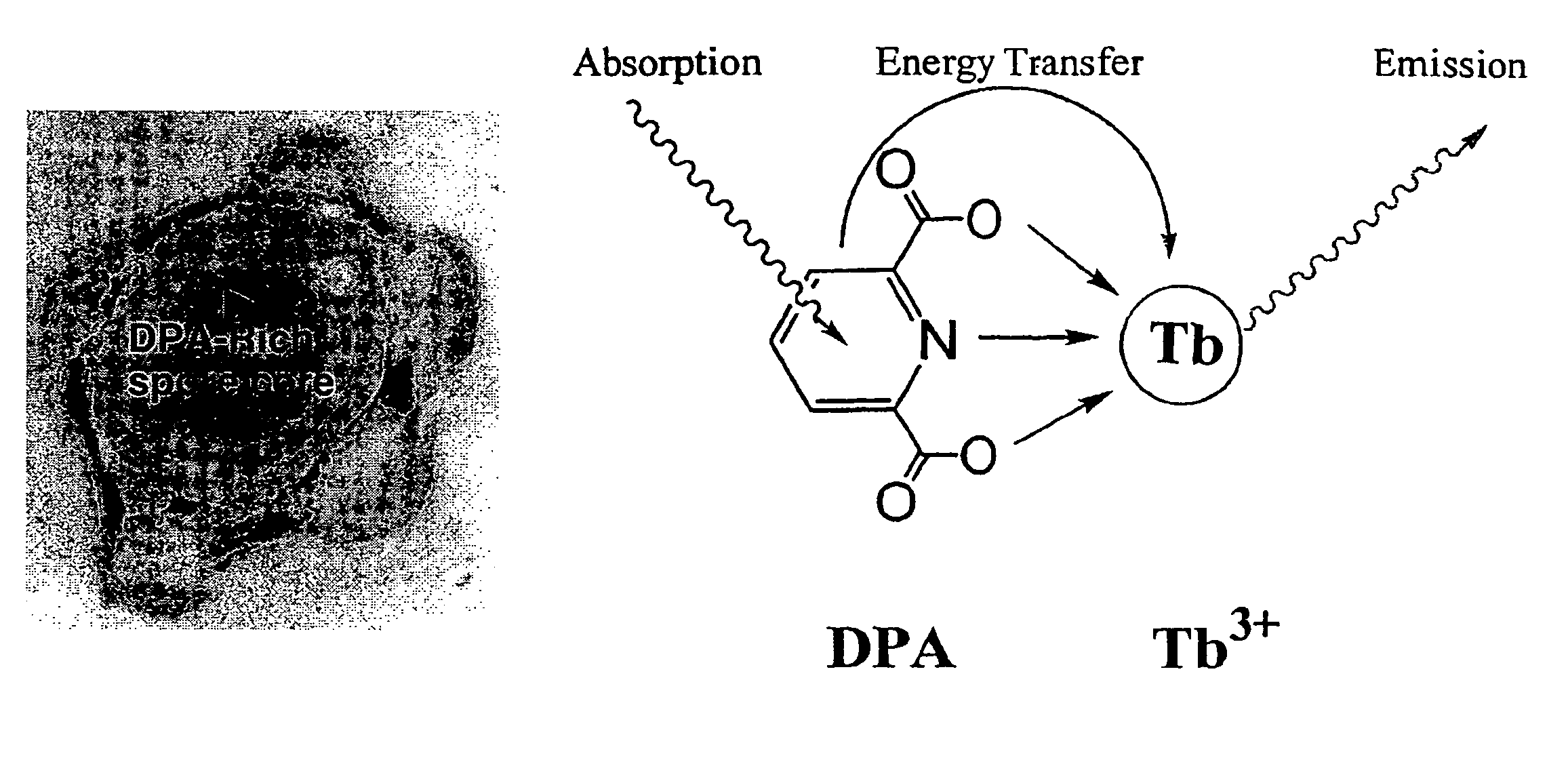
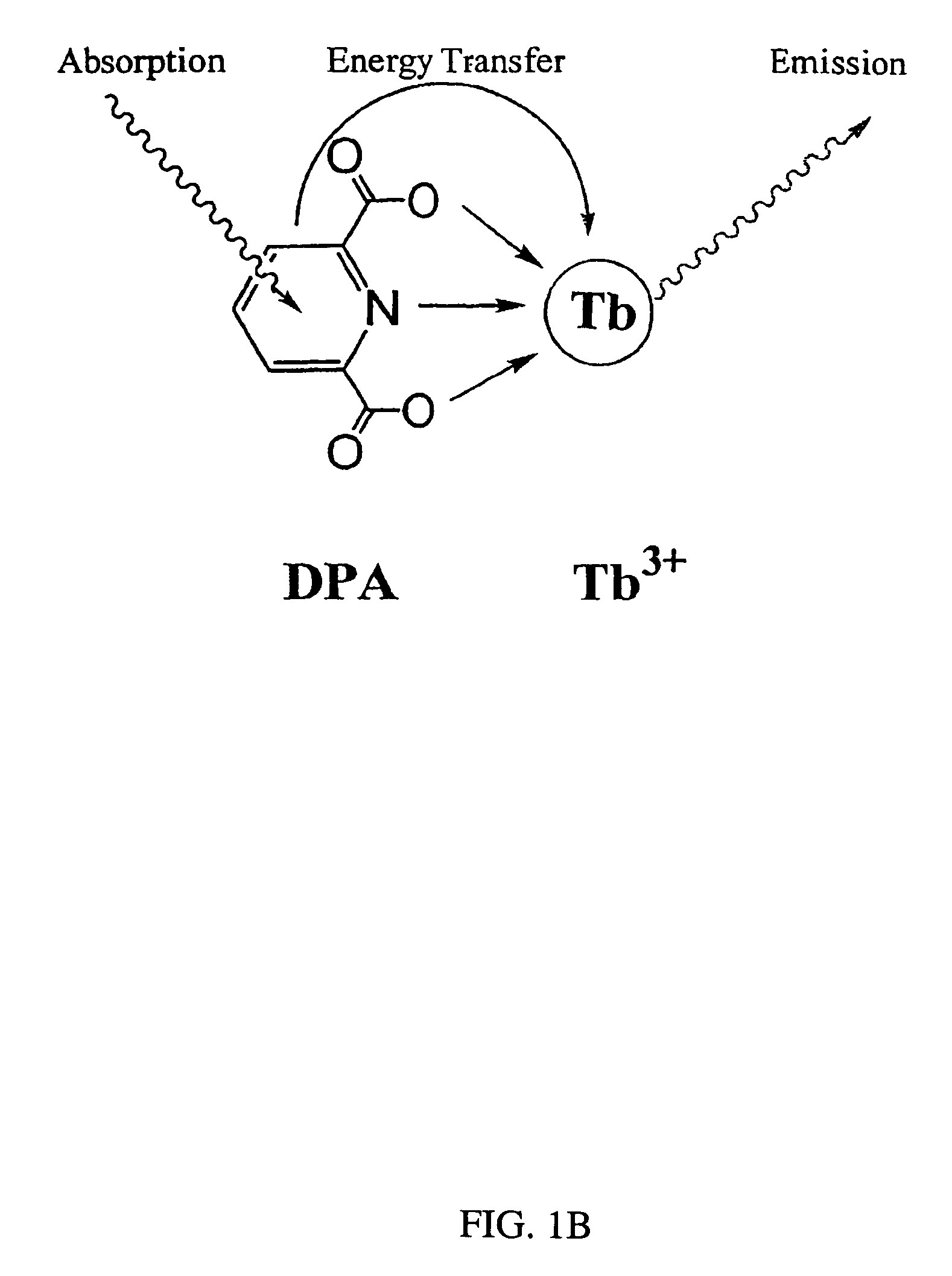
Method and apparatus for detecting and quantifying bacterial spores on a surface
ActiveUS20050136508A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsLanthanideLuminescence
A method and an apparatus for detecting and quantifying bacterial spores on a surface. In accordance with the method: a matrix including lanthanide ions is provided on the surface containing the bacterial spores; functionalized aromatic molecules are released from the bacterial spores on the surface; a complex of the lanthanide ion and the aromatic molecule is formed on the surface; the complex of the lanthanide ion and the aromatic molecule is excited to generate a characteristic luminescence of the complex on the surface; and the bacterial spores exhibiting the luminescence of the complex on the surface are detected and quantified.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Method for whole surrounding surface display of target proteins using bacterial exosporium
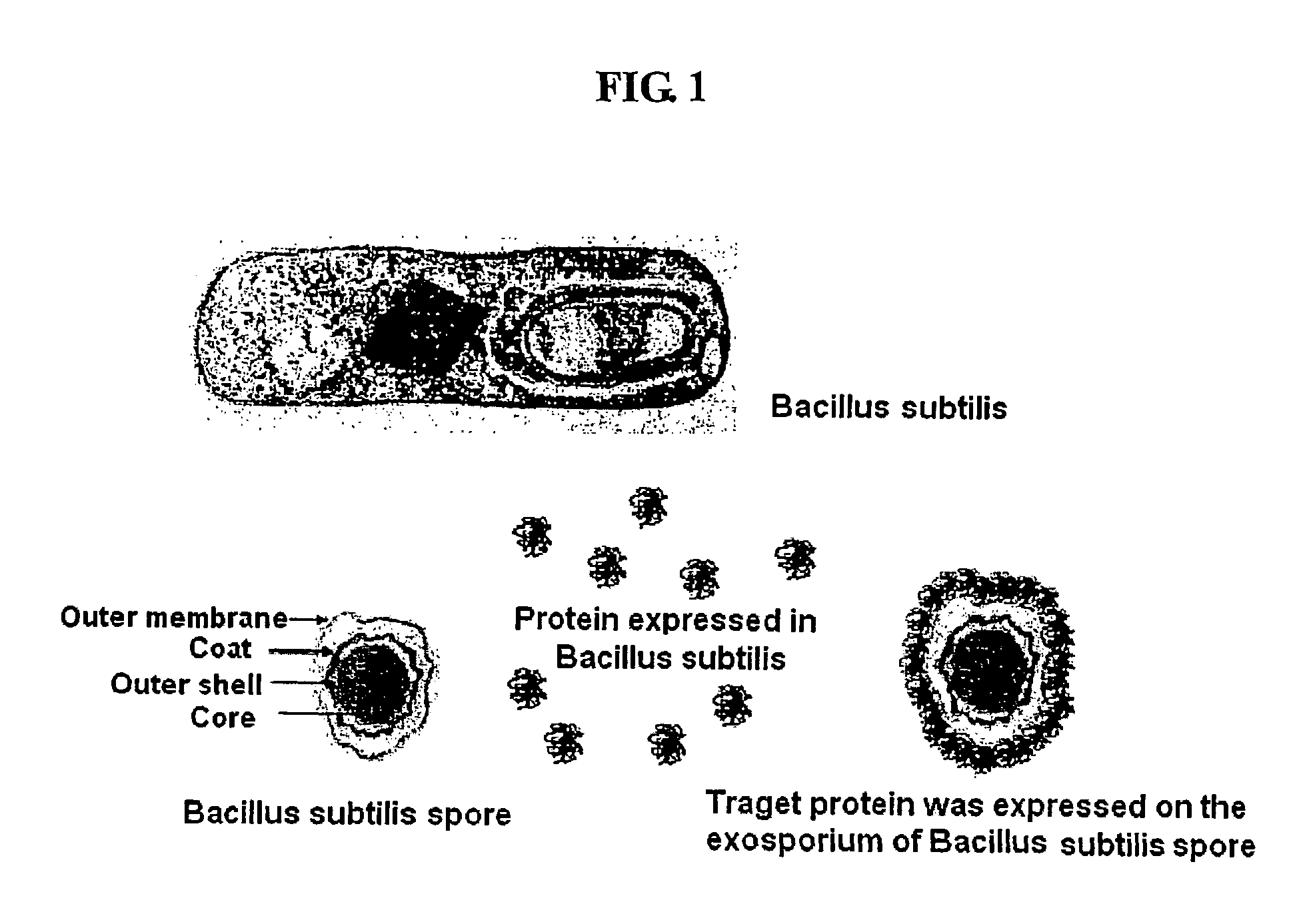
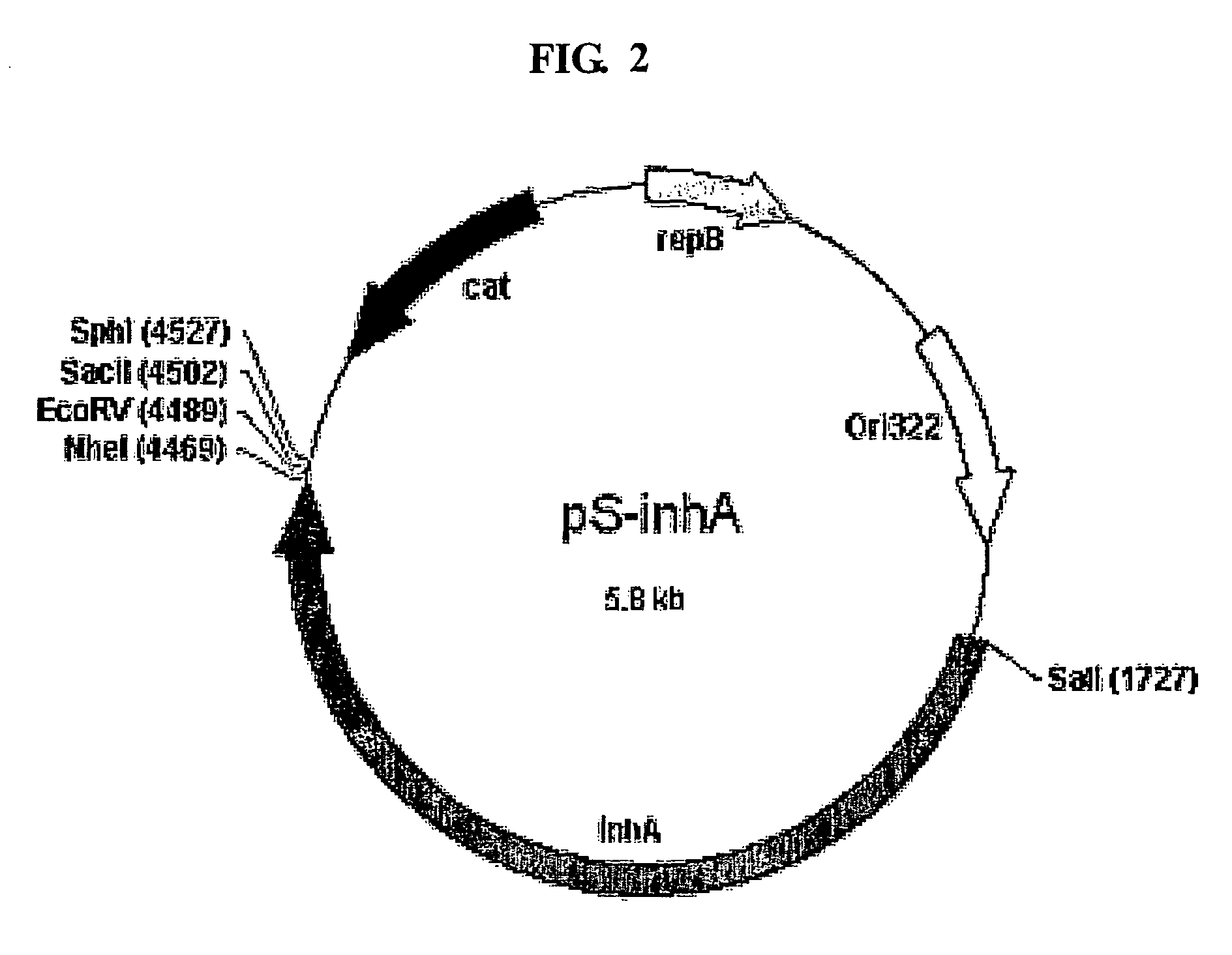
InactiveUS8030064B2Fast conductionAddressing slow performanceBacteriaPeptide/protein ingredientsSurface displayScreening method
The present invention relates to a method for expressing a target protein on an exosporium forming the outermost surface of bacterial spores. More particularly, the present invention relates to a method for expressing a target protein on the surface of cells and spores using an exosporium as a matrix for surface expression, and methods for the production of a protein array, the production of antibodies, the separation of a certain substance from a mixture, bioconversion, and the improvement of a target protein, which are characterized by using the cells or spores having the target protein that was expressed on the surface by the above expression method. The method for expressing the target protein on the surface of the spore outer membrane of the gene carriers according to the present invention has effects in that a variety of the target proteins can be expressed and the level of surface expression of the target protein is increased compared to the existing technology, and also the structural stability of the gene carriers having the target protein expressed on their surface, the viability of the host, and the rapidity of the screening method, are greatly increased.
Owner:KOREA ADVANCED INST OF SCI & TECH +1
Method and apparatus for sterilizing and disinfecting air and surfaces and protecting a zone from external microbial contamination
ActiveUS20170304472A1Short action timeEffective treatmentFouling preventionFruits/vegetable preservation by irradiation/electric treatmentParticulatesToxic material
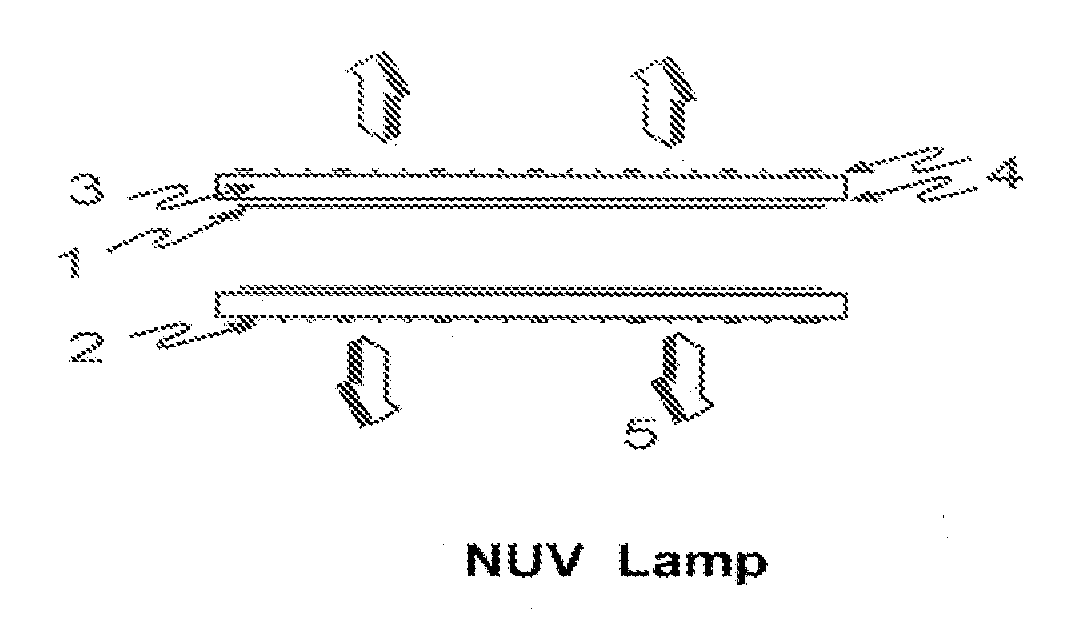
This invention relates to a method, process and apparatus for disinfecting and sterilizing all types of surfaces contaminated with microorganisms and toxic substances to render both inactive. Furthermore, this invention relates to both a method and apparatus for disinfecting and / or sterilizing breathable air and then using this air to protect a confined space from external contamination. The apparatus consists of a new ultra-violet (NUV) source that is more effective than mercury based 254 nm light for destroying DNA of virus, bacteria, spores and cists. It is most effective in breaking chemical bonds in toxic gases and Biotoxins that are useful to terrorists. It is combined with other apparatus that remove particulates and byproducts sometimes produced by the NUV source and maintains positive pressure of the confined space so as to prevent the influx of air from outside the protected zone.
Owner:NEISTER S EDWARD
Method and apparatus for detecting and quantifying bacterial spores on a surface
ActiveUS20060292664A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsPhysical chemistryLanthanide
A method and an apparatus for detecting and quantifying bacterial spores on a surface. In accordance with the method: bacterial spores are transferred from a place of origin to a test surface, the test surface comprises lanthanide ions. Aromatic molecules are released from the bacterial spores; a complex of the lanthanide ions and aromatic molecules is formed on the test surface, the complex is excited to generate a characteristic luminescence on the test surface; the luminescence on the test surface is detected and quantified.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
High pressure processing of juice containing probiotics
The objective of the invention is to provide an improved method of making healthier juice products inoculated with probiotics, wherein the juice includes but is not limited to apple juice, coconut water, coconut milk, orange juice and / or carrot juice. The present invention relates to a method of pressure treating a juice containing probiotics. Vegetative cells of harmful microorganisms and enzymes are inactivated by applying high pressure while maintaining the activity of the probiotics. The juice preferably is dairy-free. The juice could be any dairy-free juice, such as a fruit juice, a vegetable juice, or their combination. Fruit and / or vegetable juice are prepared by any traditional methods, including but not limited to, washing, extracting by optionally treating with enzyme(s), centrifuging and packing. Probiotics, e.g., probiotics from bacterial spores, such as the spores of Bacillus coagulans and / or Lactobacillus plantarum, stay alive and active in the fruit or vegetable juice after high pressure pasteurization, as well as during the product shelf life.
Owner:CHIC GRP
Method and apparatus for detecting and quantifying bacterial spores on a surface
ActiveUS7611862B2Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsPhysical chemistryLuminescence
A method and an apparatus for detecting and quantifying bacterial spores on a surface. In accordance with the method: bacterial spores are transferred from a place of origin to a test surface, the test surface comprises lanthanide ions. Aromatic molecules are released from the bacterial spores; a complex of the lanthanide ions and aromatic molecules is formed on the test surface, the complex is excited to generate a characteristic luminescence on the test surface; the luminescence on the test surface is detected and quantified.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Method and apparatus for detecting and quantifying bacterial spores on a surface
ActiveUS7608419B2Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsLanthanideLuminescence
A method and an apparatus for detecting and quantifying bacterial spores on a surface. In accordance with the method: a matrix including lanthanide ions is provided on the surface containing the bacterial spores; functionalized aromatic molecules are released from the bacterial spores on the surface; a complex of the lanthanide ion and the aromatic molecule is formed on the surface; the complex of the lanthanide ion and the aromatic molecule is excited to generate a characteristic luminescence of the complex on the surface; and the bacterial spores exhibiting the luminescence of the complex on the surface are detected and quantified.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
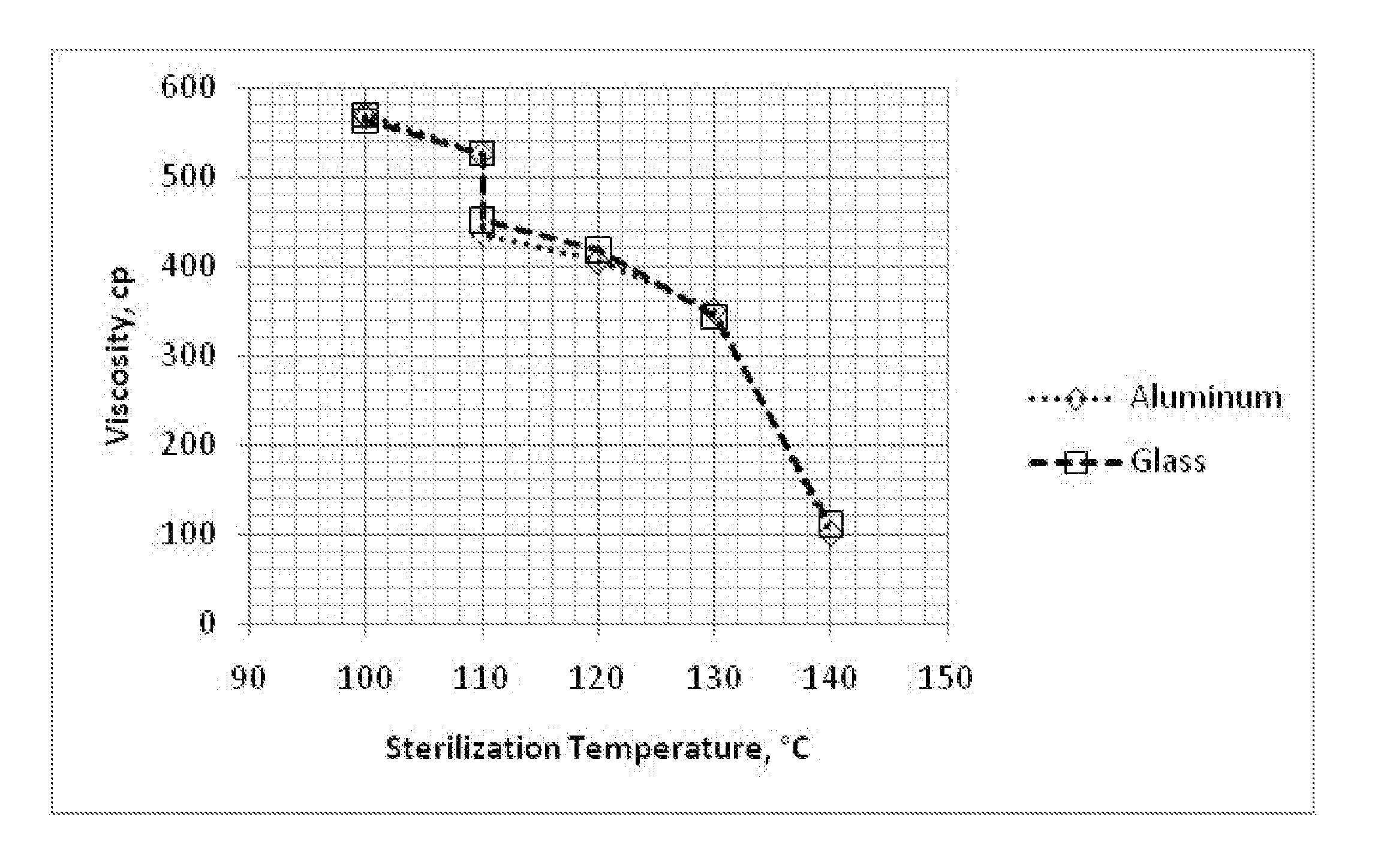
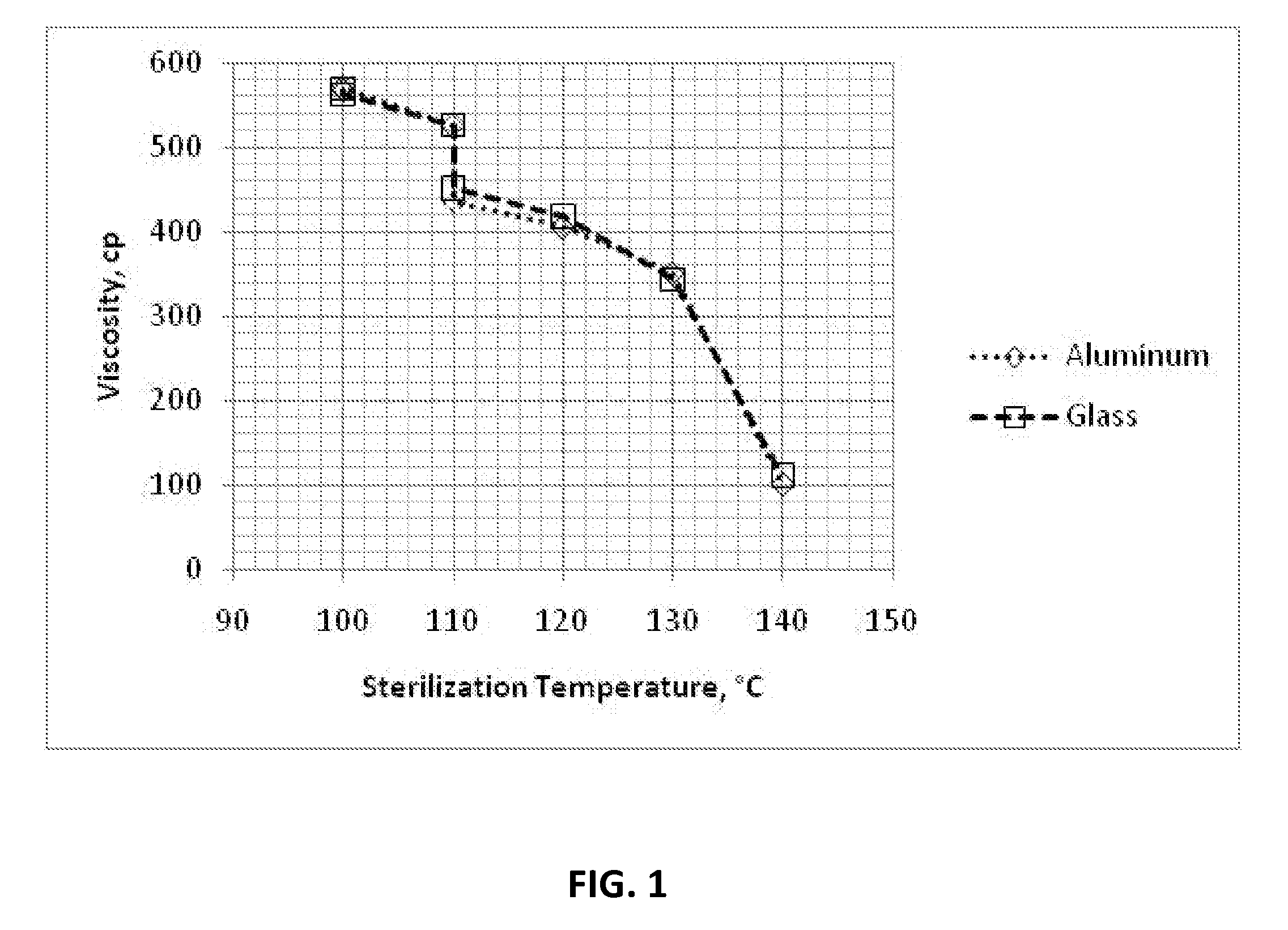
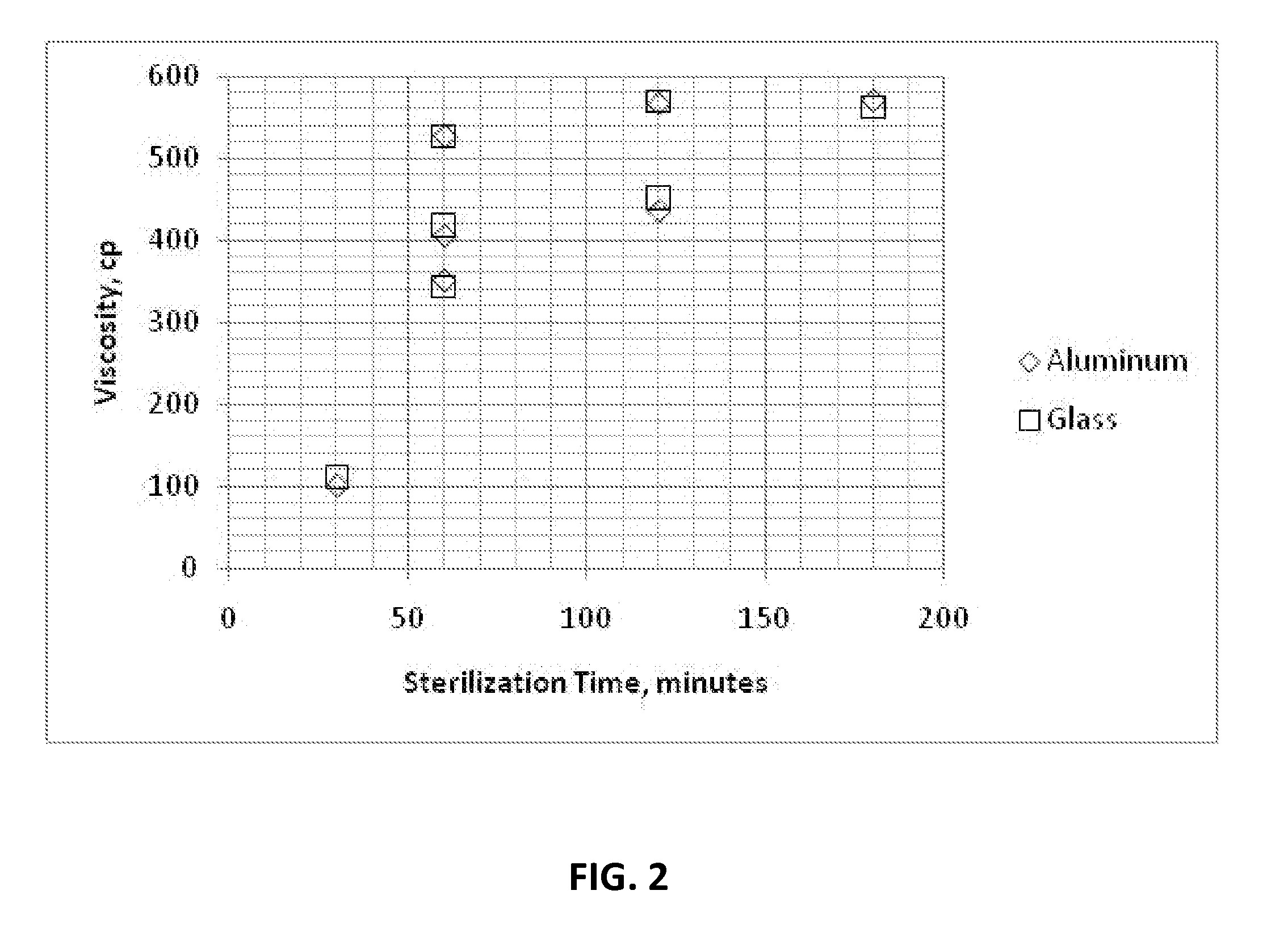
Cyanoacrylate Adhesive Compositions and Devices and Process for Sterilization Thereof
The viscosity of 2-cyanoacrylate monomer based adhesives is increased by combining the monomers with suitable thickeners according to a certain process. The resulting formulations may be heat sterilized without degrading the viscosity or causing premature polymerization. The effectiveness of the sterilization process is assayed by disposing bacterial spores in the formulation, exposing it to a dry heat sterilization process, transferring it to a sterile aldose solution, transferring and exposing the sample to a nutrient medium which supports germination and growth of viable spores, incubating the samples, and determining the presence or absence of growth.
Owner:CLAST TRADING
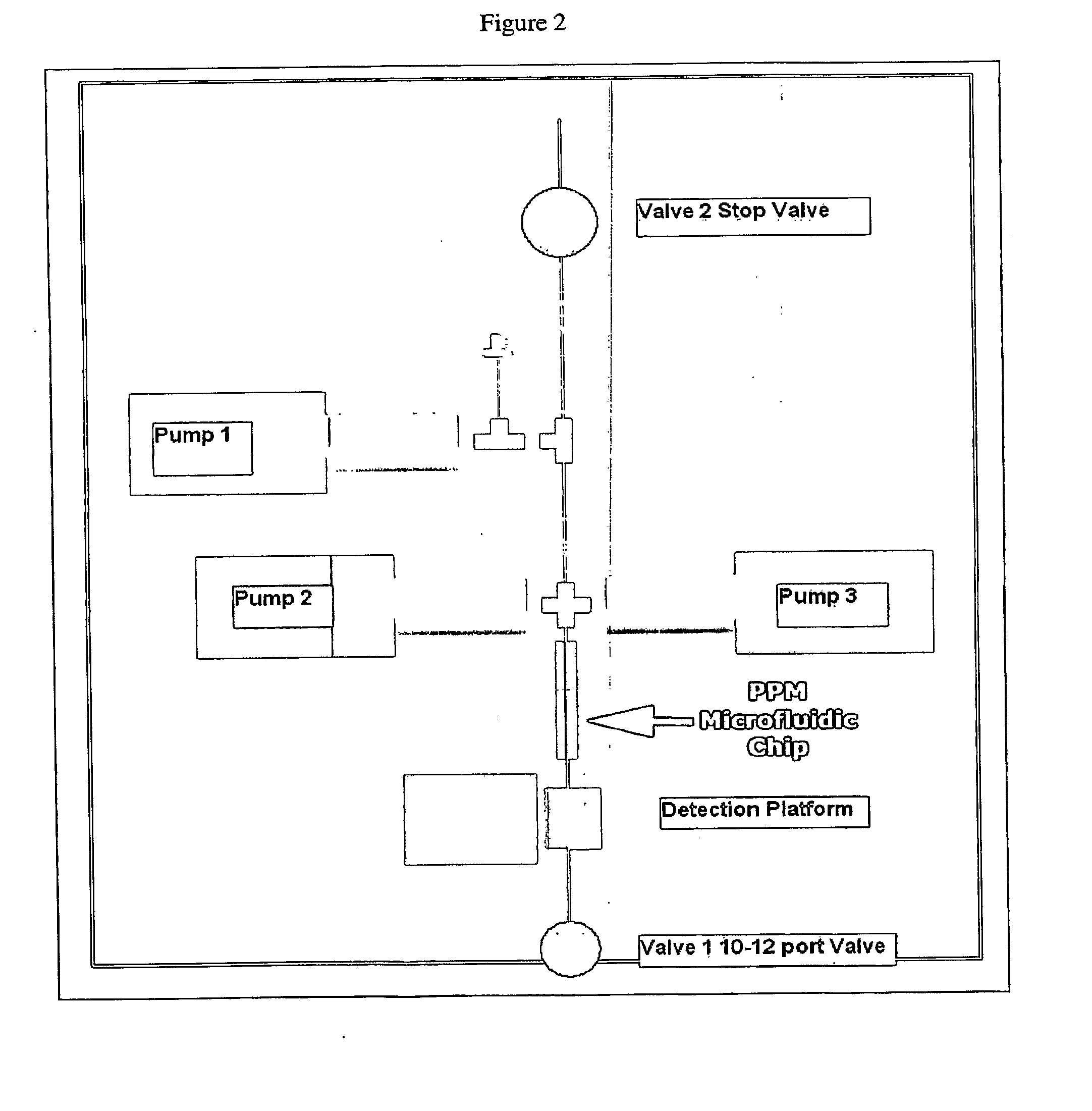
Pcr-free sample preparation and detection systems for high speed biologic analysis and identification
InactiveUS20100216657A1Great reagent stabilityPrevent degradationNucleotide librariesLibrary screeningPersonal protective equipmentBiology
Provided herein are biologic sample preparation and analysis systems that are rapid, portable, robust detection system for multiplexed detection of bio-threats, and which can be ruggedized to operate in harsh environments. A new method of detection called Combinatorial Probe Analysis (CPA), which provides an exponential increase in detection reliability, has been incorporated into these systems. This type of analysis greatly reduces false positives and false negatives; in addition it is reusable and eliminates special storage requirements for reagents. Specific technical advancements in the optimization of hybridization assays for nucleic acid detection on porous polymer monoliths (PPM) are also disclosed. Performing rapid and complete solubilization of viruses, vegetative bacteria and bacterial spores with an ultra high temperature solubilization protocol is also described. The systems provided herein provides the ability to perform rapid highly multiplexed analysis of a variety of bioagents, including bacteria viruses, and protein biotoxins. The systems and assays described herein are perform completely automated sample preparation and analysis, in a time frame of five minutes or less. The assay is simple in design allowing users in personal protective equipment to easily operate the system. The disclosed systems are robust, simple to use, and address the goals of the first responder community.
Owner:FLUIDIGM CORP
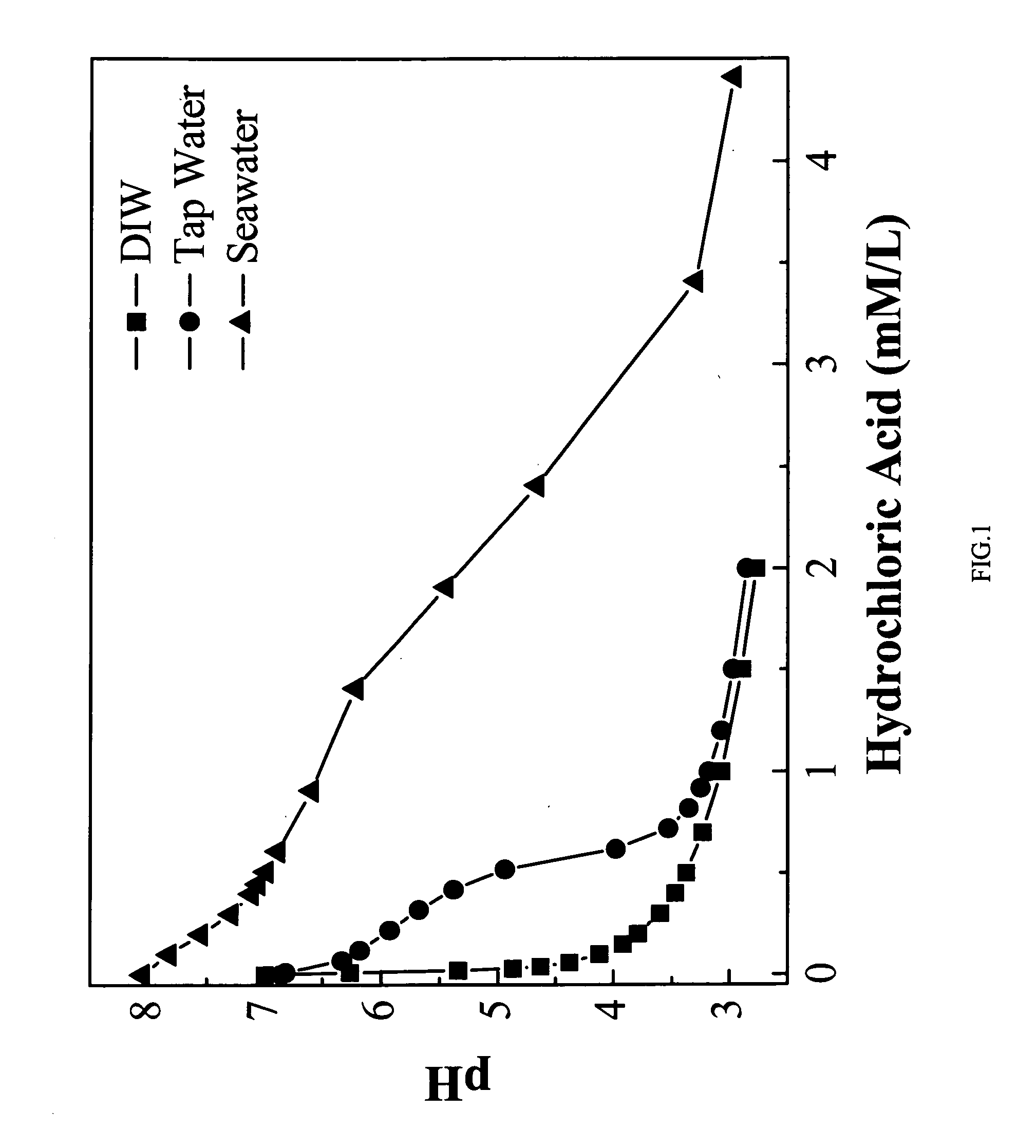
Sterilization effects of acidic ozone water
ActiveUS20120164024A1Short timeHigh ozone concentrationWater treatment parameter controlSeawater treatmentSeawaterChemistry
This invention is directed to a sterilization method of contaminated areas with biological agents by making use of the acidic ozone water that very effectively kills spores of Bacillus atrophaeus, thereby demonstrating the capability of sterilizing a large surface-area in a very short time and reinstating the contaminated environment as free from toxic biological agents. The effective sterilization of the acidic ozone water is due to synergic benefits derived from the combination of ozone and acidity. The acidic ozone water can also effectively kill other ordinary microbes of viruses, bacteria, and fungi, hence being applicable to agriculture, seafood and livestock industries for the preservation of various products as well as being useful in hospitals or other germ infested areas for disinfections. Particularly, the acidity and ozone in the seawater sterilize microbes effectively, demonstrating a potential for the sterilization of a large amount of seawater in a short time. After the decontamination process, the acidic ozone water disintegrates into water and oxygen without any trace of harmful materials to the environment.
Owner:UHM HAN SUP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com