Molecular Signature of the Pten Tumor Suppressor
a tumor suppressor and molecular signature technology, applied in the field of gene identification, can solve problems such as not being reported, and achieve the effect of predicting the effectiveness and/or responsiveness of a therapeuti
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Random Forest Deals Effectively with Microarray Data
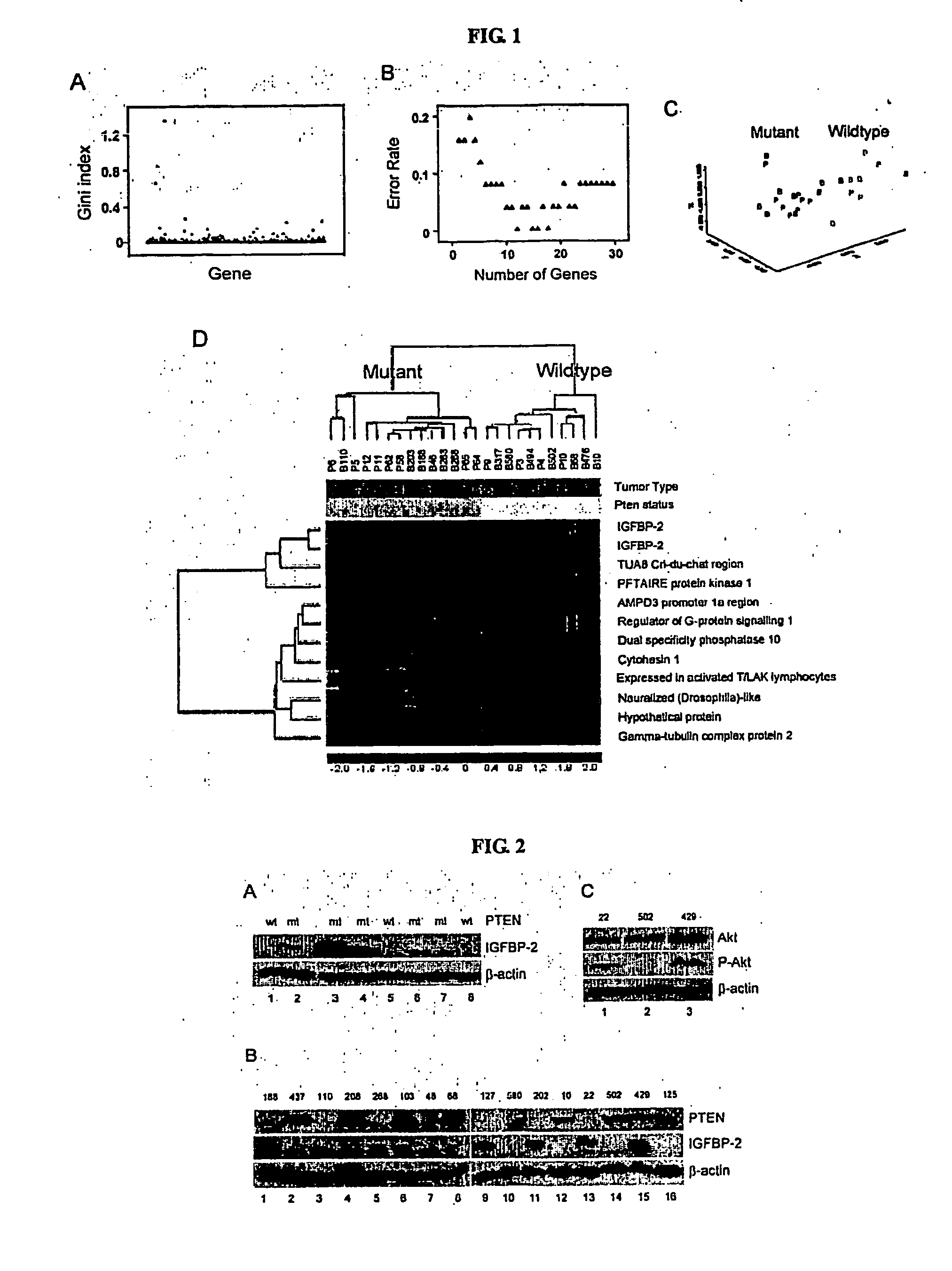
[0077] We have used microarray technology to identify overexpression of androgen receptor as the general mechanism for hormone refractory prostate cancer. The data indicate that overexpression of androgen receptor is a diagnostic and therapeutic target for hormone refractory prostate cancer and can be used as a screening method for hormone refractory prostate cancer drug development (FIG. 7). This is consistent with microarray technology being a useful tool for a variety of purposes. However, it has been difficult in identifying molecular signatures for signal transduction pathways. One of the reasons is that microarray experiments are usually performed on a relatively few samples, therefore, data analysis on these experiments requires specific statistical tools. In this report, we described a novel unsupervised learning algorithm, called Random Forest, to identify a molecular signature for the signaling pathway of PTEN. This stat...
example 2
Molecular Signature of the PTEN Tumor Suppressor
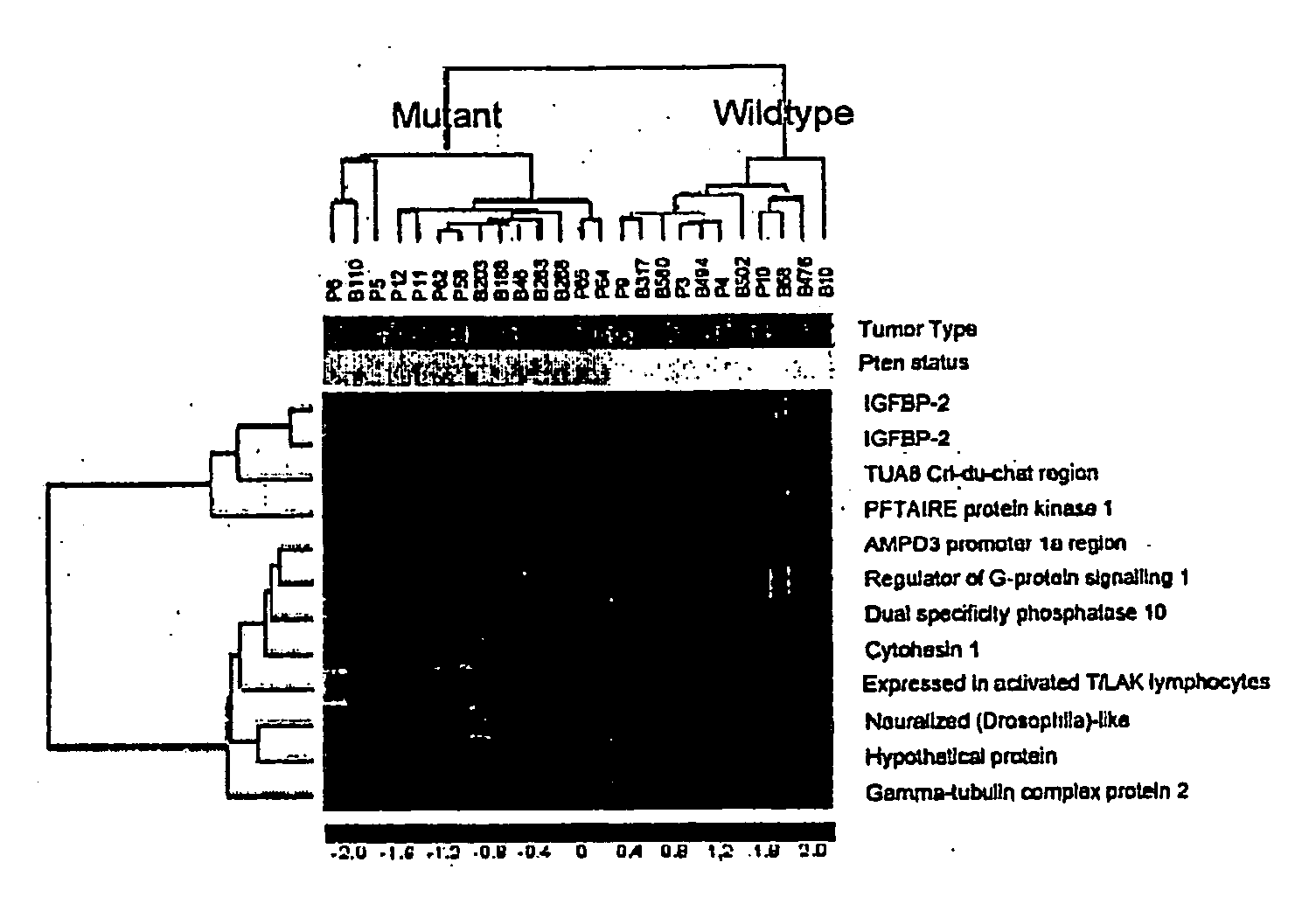
[0078] To identify transcriptional targets associate with the PTEN tumor suppressor function, we compared the gene expression profiles of 11 tissue samples that have the wild-type PTEN gene to those of 14 samples that have mutated PTEN gene (table 1). These 25 samples include 12 advanced prostate cancer xenografts and 13 glioblastoma tissue samples. The PTEN status of the prostate cancer xenografts were characterized previously (21) and those of the glioblastoma were determined by western blot and genomic DNA sequence analysis. Six of the glioblastoma samples do not express the PTEN protein and, therefore, were defined as PTEN mutant samples. The other seven samples have the wild-type PTEN because they express the PTEN protein and they do not carry point mutation, which was determined by genomic DNA sequence analysis. We used both prostate cancer and glioblastoma tissue samples in order to increase a tissue-independent signature assoc...
example 3
Elevated Levels of IGFBP2 Expression in PTEN Mutant Tumors
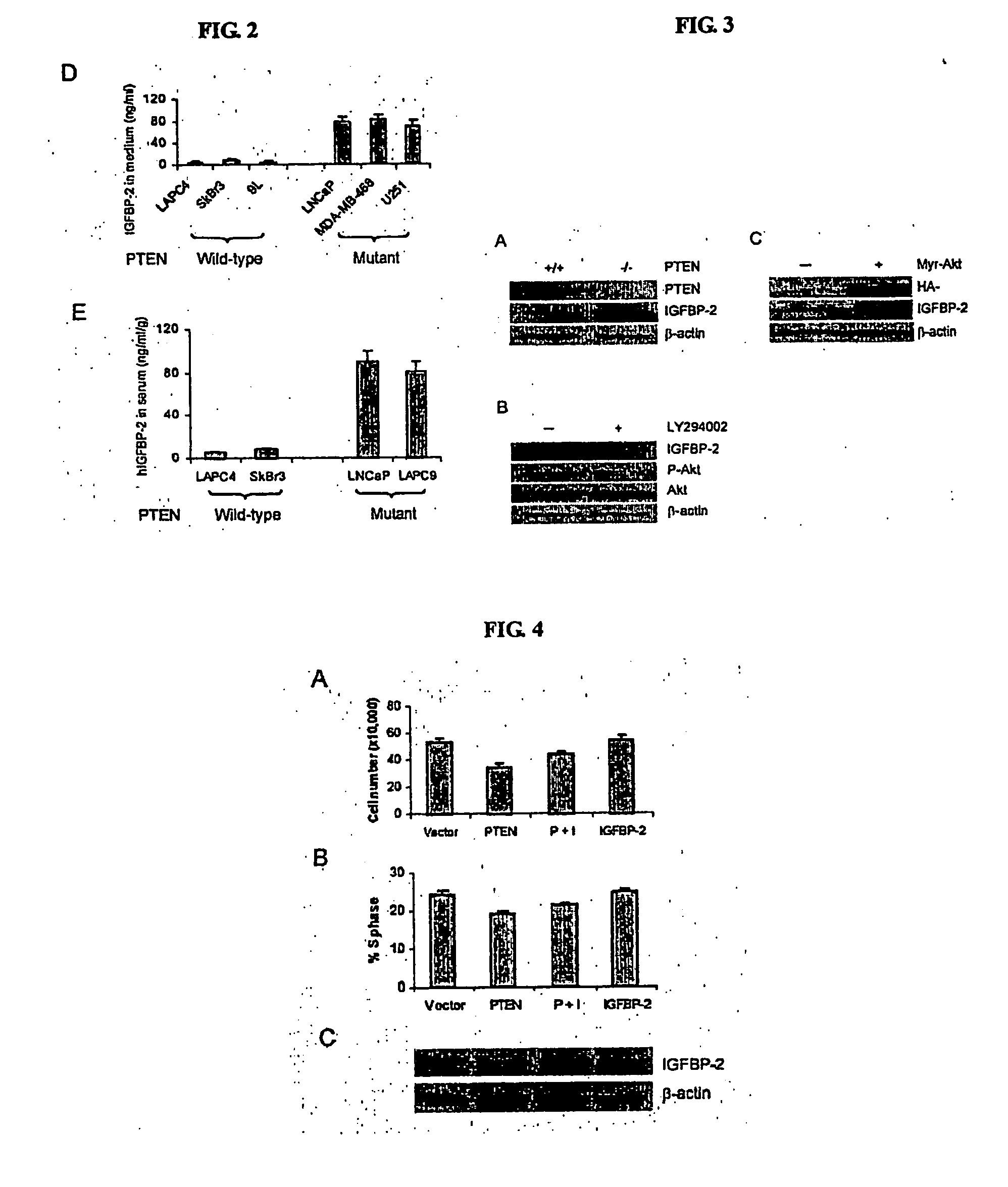
[0080] Having identified several genes whose expression patterns correlate with the PTEN status, we wish to investigate biochemical regulation and biological role of one of these genes in PTEN function. Because both probe sets in the microarray were identified and both have the highest power in predicting the PTEN status, IGFBP2 was chosen for further study. As the first step, we confirmed the relationship between PTEN mutations and IGFBP2 expression by western blot analysis using whole tissue lysates from prostate cancer xenografts. IGFBP2 protein was detected in PTEN mutated xenografts LAPC9, LUCaP 35, and LNCaP but not in PTEN wild-type tumors LAPC4 and LUCaP23 (FIG. 2A, table 1), consistent with the microarray analysis.
[0081] The relationship was extended to other tumors that were not included in the microarray analysis. IGFBP2 was highly expressed in PTEN mutated tumors LAPC3, LAPC12, and LUCaP41, but was not detected ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Digital information | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Digital information | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Cell growth | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com