Patents
Literature
339 results about "Tumor formation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
To summarize, there are four major phases of tumor formation. Each phase can take years to complete. The first one alone usually takes anywhere from 15 to 30 years. The first phase occurs when normal cells mutate into tumor cells and begin dividing out-of-control. This may take place over successive generations of cells.
Compositions and methods for controlling stem cell and tumor cell differentiation, growth, and formation
InactiveUS20050214257A1Small sizeEnhance tumor formationAntibacterial agentsBiocideAmphiphileTumor cells
The present invention relates to the use of self-assembling peptide amphiphiles to prevent tumor formation by transplanted stem cells. The present invention further relates to the use of self-assembling peptide amphiphiles to treat cancers.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN UNIV
Recombinant influenza viruses expressing tumor-associated antigens as antitumor agents
InactiveUS6884414B1Quick changeAvoid problemsSsRNA viruses negative-senseBiocideTumor reductionIn vivo
The present invention relates to the engineering of recombinant influenza viruses that express tumor-associated antigens. Expression of tumor-associated antigens by these viruses can be achieved by engineering specific epitopes into influenza virus proteins, or by engineering viral genes that encode a viral protein and the specific antigen as independent polypeptides. Tumor-bearing patients can be immunized with the recombinant influenza viruses alone, or in combination with another treatment, to induce an immune response that leads to tumor reduction. The recombinant viruses can also be used to vaccinate high risk tumor-free patients to prevent tumor formation in vivo.
Owner:MT SINAI SCHOOL OF MEDICINE +1
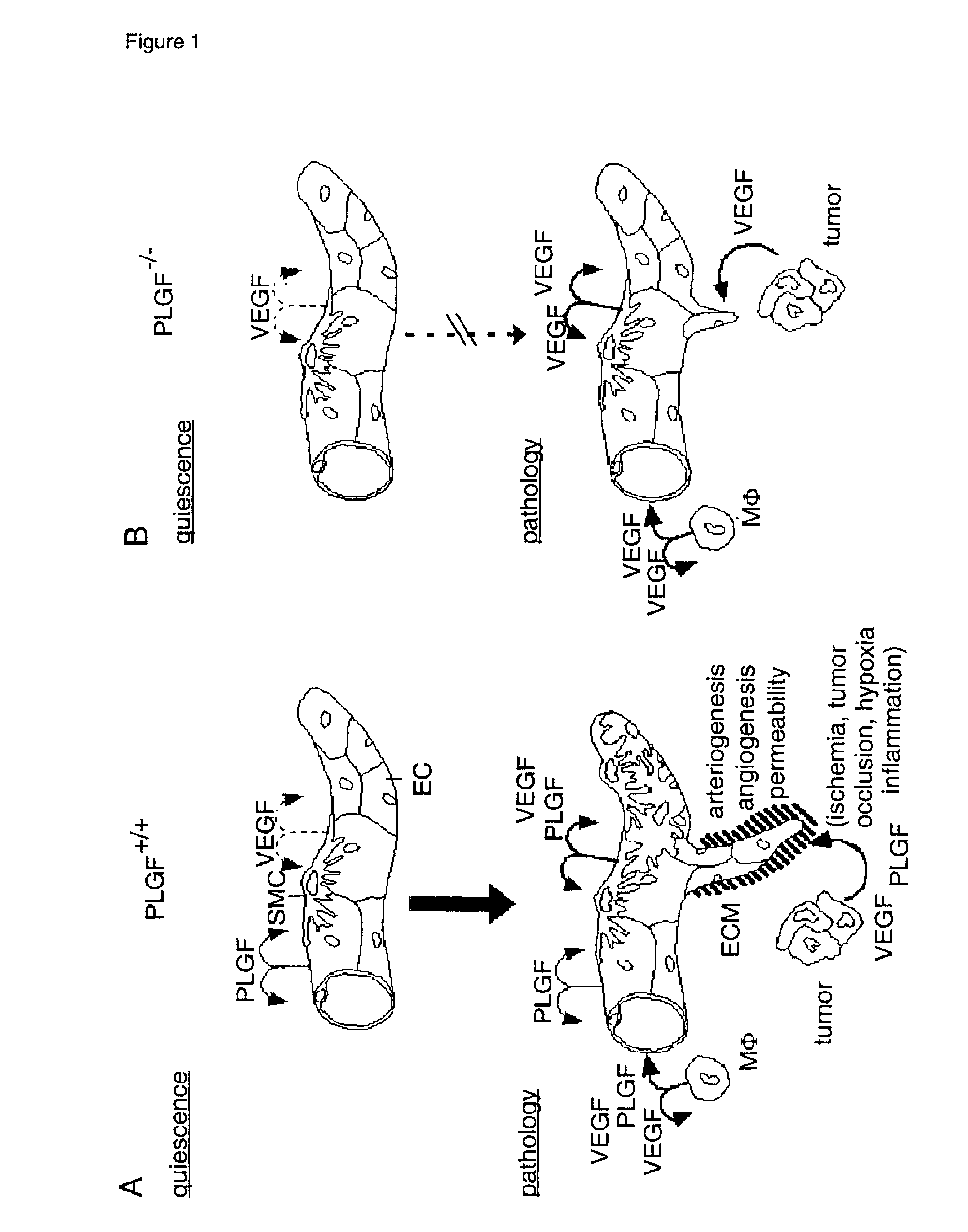
Inhibitors of placental growth factor for the treatment of pathological angiogenesis, pathological arteriogenesis, inflammation, tumor formation and/or vascular leakage
InactiveUS20030180286A1Improve angiogenesisIncrease vascular permeabilitySenses disorderAntipyreticStress inducedIschemic retinopathy
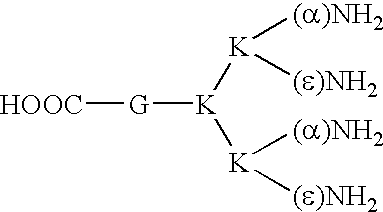
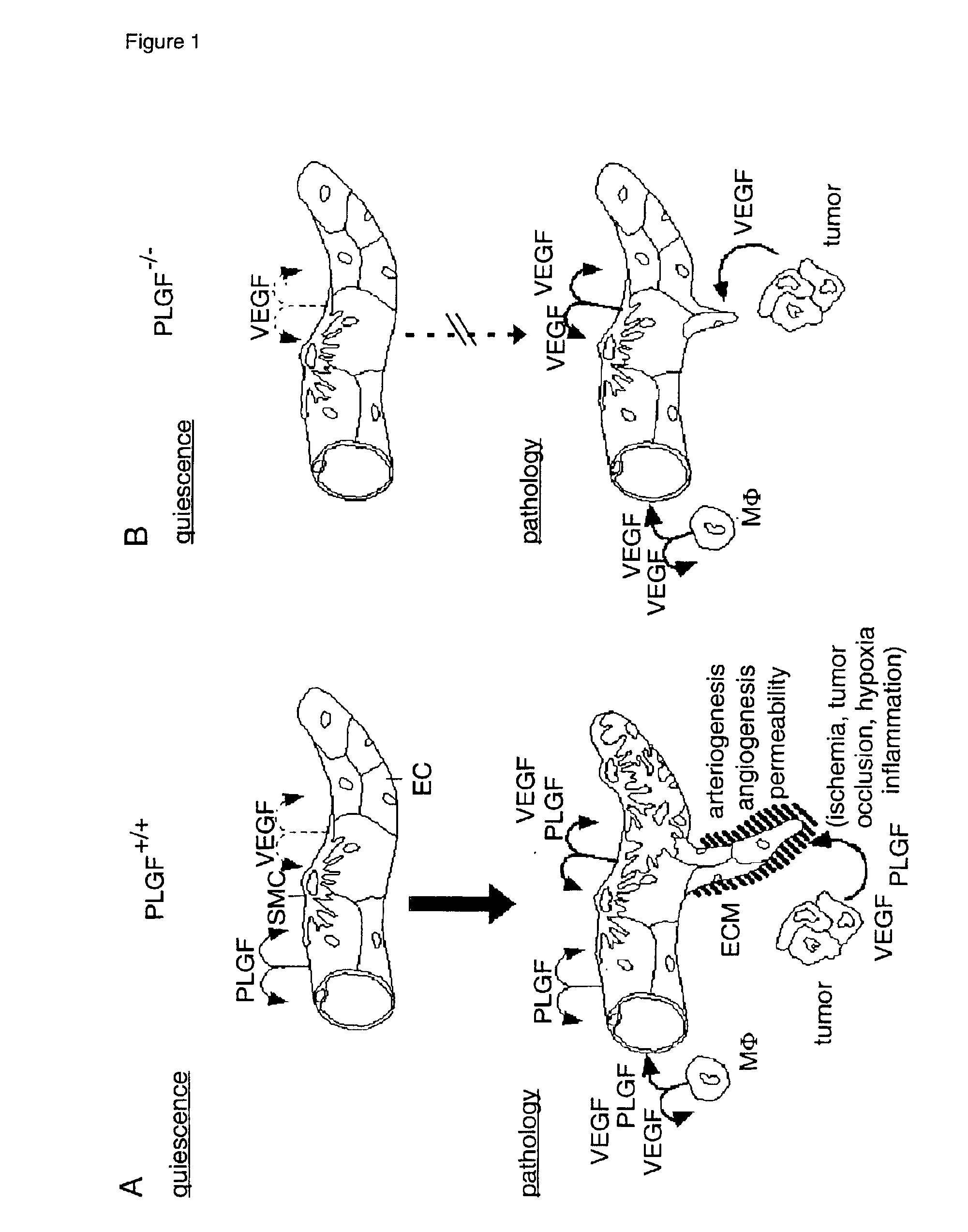
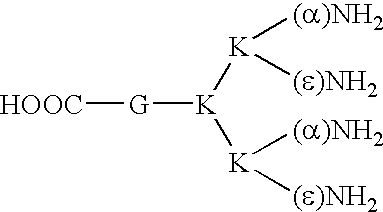
The present invention relates to the field of pathological angiogenesis and arteriogenesis. in particular, a stress induced phenotype in a transgenic mouse (PIGF- / -) that does not produce Placental Growth Factor (PIGF) and that demonstrates an impaired vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)-dependent response. PIGF-deficiency has a negative influence on diverse pathological processes of angiogenesis, arteriogenesis and vascular leakage comprising ischemic retinopathy, tumour formation, pulmonary hypertension, vascular leakage (oedema formation) and inflammatory disorders. Molecules that can inhibit the binding of PIGF to its receptor (VEGFR-1), such as monoclonal antibodies and tetrameric peptides. Further, the use of these molecules to treat the latter pathological processes.
Owner:VLAAMS INTERUNIVERSITAIR INST VOOR BIOTECHNOLOGIE VZW +1
Recombinant influenza viruses expressing tumor-associated antigens as antitumor agents
InactiveUS20040253273A1Prevent tumor formationQuick changeSsRNA viruses negative-senseAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsTumor reductionEpitope
The present invention relates to the engineering of recombinant influenza viruses that express tumor-associated antigens. Expression of tumor-associated antigens by these viruses can be achieved by engineering specific epitopes into influenza virus proteins, or by engineering viral genes that encode a viral protein and the specific antigen as independent polypeptides. Tumor-bearing patients can be immunized with the recombinant influenza viruses alone, or in combination with another treatment, to induce an immune response that leads to tumor reduction. The recombinant viruses can also be used to vaccinate high risk tumor-free patients to prevent tumor formation in vivo.
Owner:PALESO PETER +2
Method for selecting clone of induced pluripotent stem cells
InactiveUS20120129172A1Efficiently identifying and selectingImprove securityMicrobiological testing/measurementGenetically modified cellsIn vivoLiving body
To efficiently identify and select a clone from clones of induced pluripotent stem cells (iPS cell) having low tumor formation rate in vivo when allowed to differentiate and transplanted in a living body, iPS cells of the clones are induced to differentiate, undifferentiated cells among the cells after the induction of differentiation are detected, and a clone having the content of the undifferentiated cell below a control is selected.
Owner:KYOTO UNIV
Bicyclic, nitrogen-containing compounds modulating CXCR4 and/or CCXCKR2
The present invention is directed to novel compounds and pharmaceutical compositions that inhibit the binding of the SDF-1 chemokine to the chemokine receptor CXCR4 and / or the binding of the SDF-1 or I-TAC chemokines to the chemokine receptor CCXCKR2 (CXCR7). These compounds are useful in preventing tumor cell proliferation, tumor formation, metastasis, inflammatory diseases, treatment of HIV infectivity, treatment of stem cell differentiation and mobilization disorders, and ocular disorders.
Owner:CHEMOCENTRYX INC
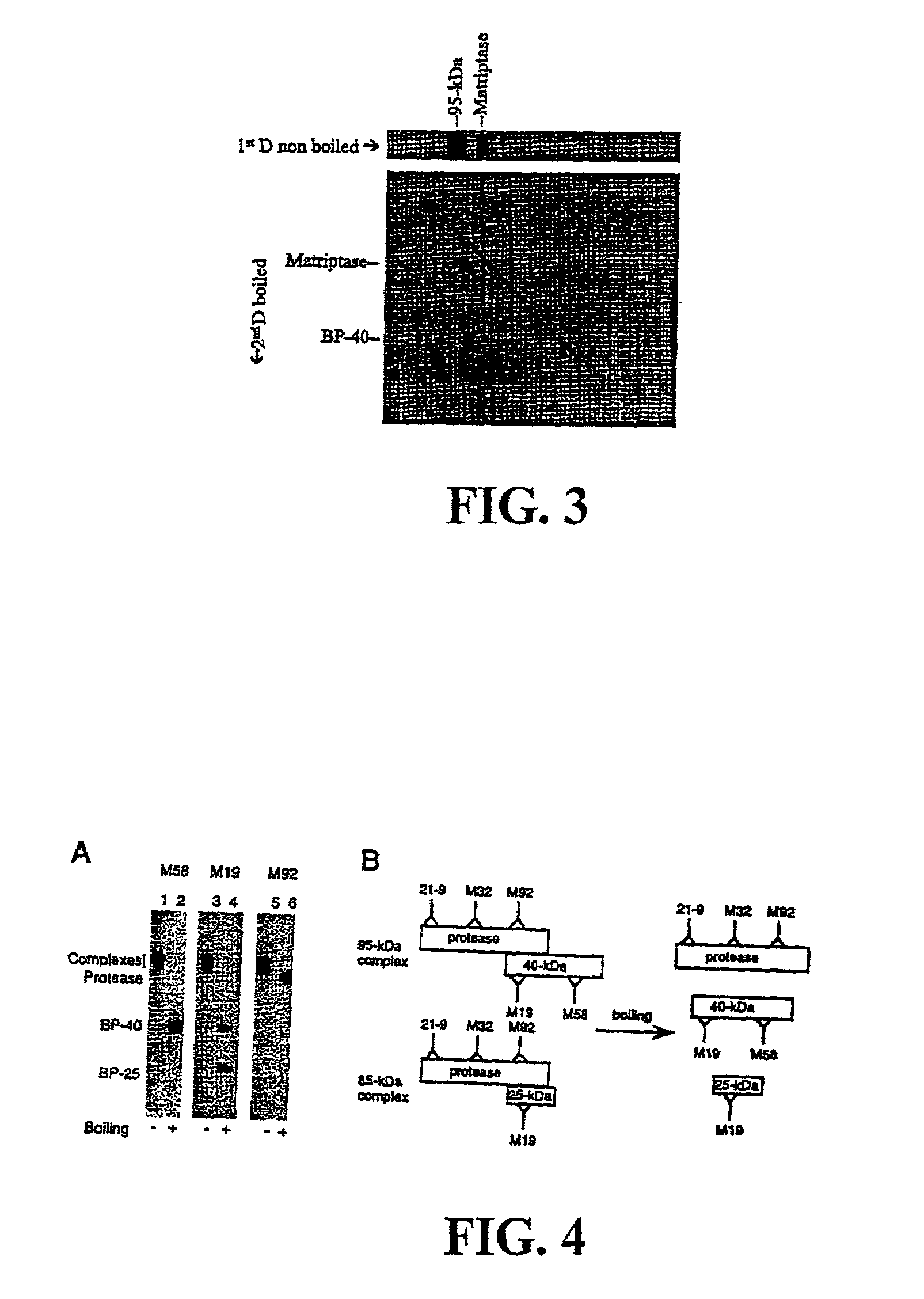
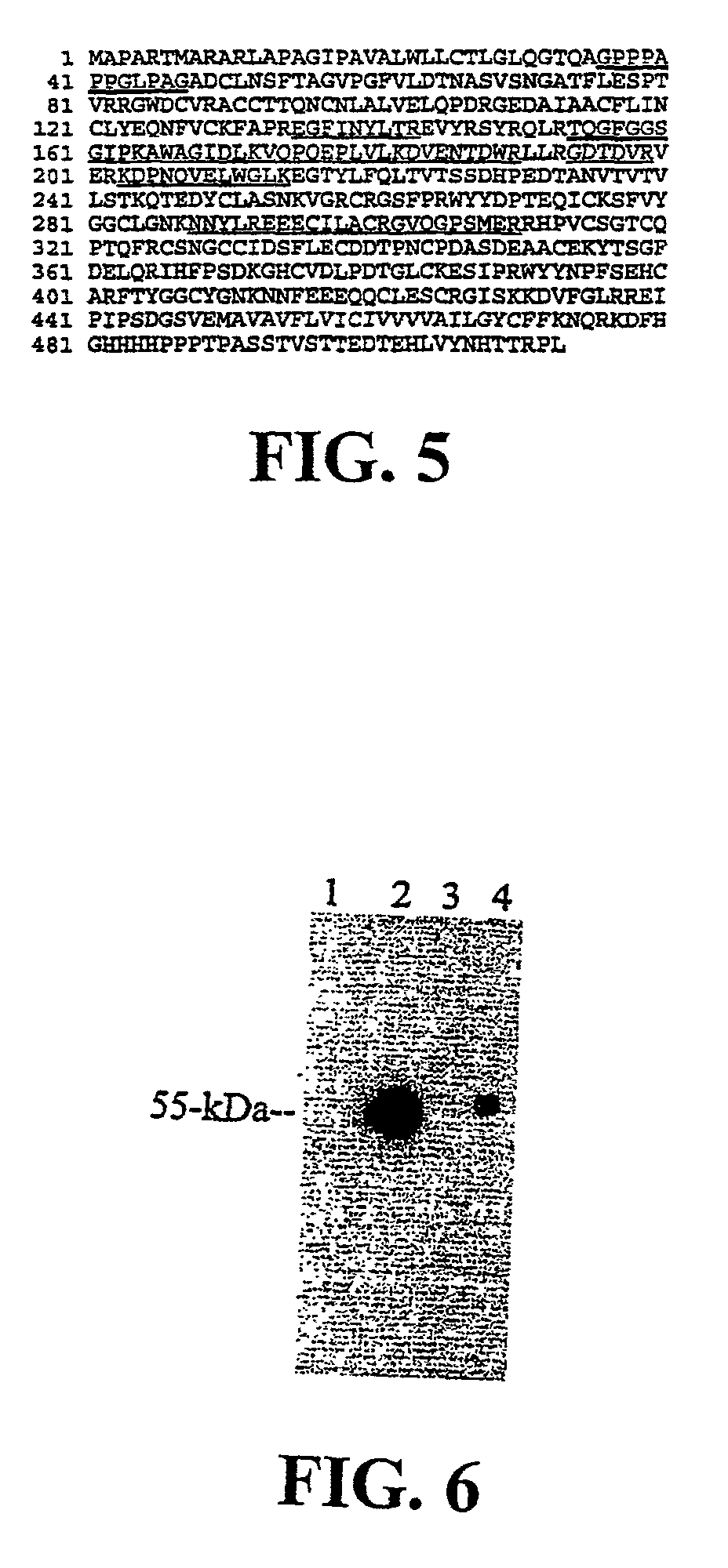
Matriptase, a serine protease and its applications
The invention is directed to a method of detecting a malignancy or a pre-malignant lesion in breast or other tissue, or a pathologic condition, by detecting the presence of single-chain or two-chain forms of matriptase in the tissue. The invention is further directed to a method of treating malignancies, which have the phenotype of matriptase production by administering a tumor formation inhibiting effective amount of concentrate of Bowman-Birk inhibitor (BBIC), or other matriptase inhibitor. The invention also is directed to nucleic acids encoding a matriptase protein or fragments thereof, and their use for structure elucidation and modeling to identify other inhibitors of matriptase, as well as to methods of identifying matriptase modulating agents, including activators and inhibitors.
Owner:GEORGETOWN UNIV
Benzyl and pyridinyl derivatives as modulators of the hedgehog signaling pathway
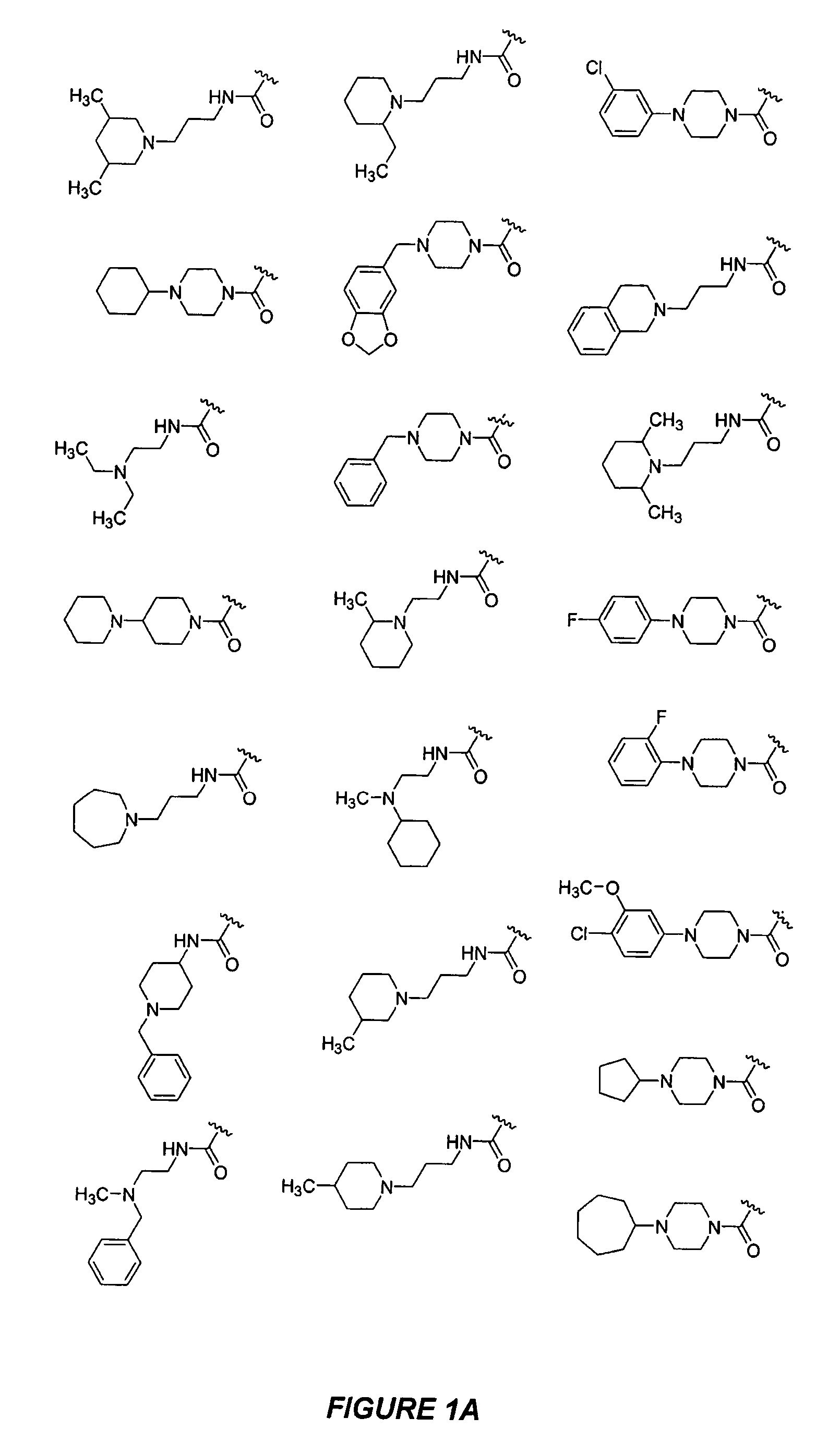
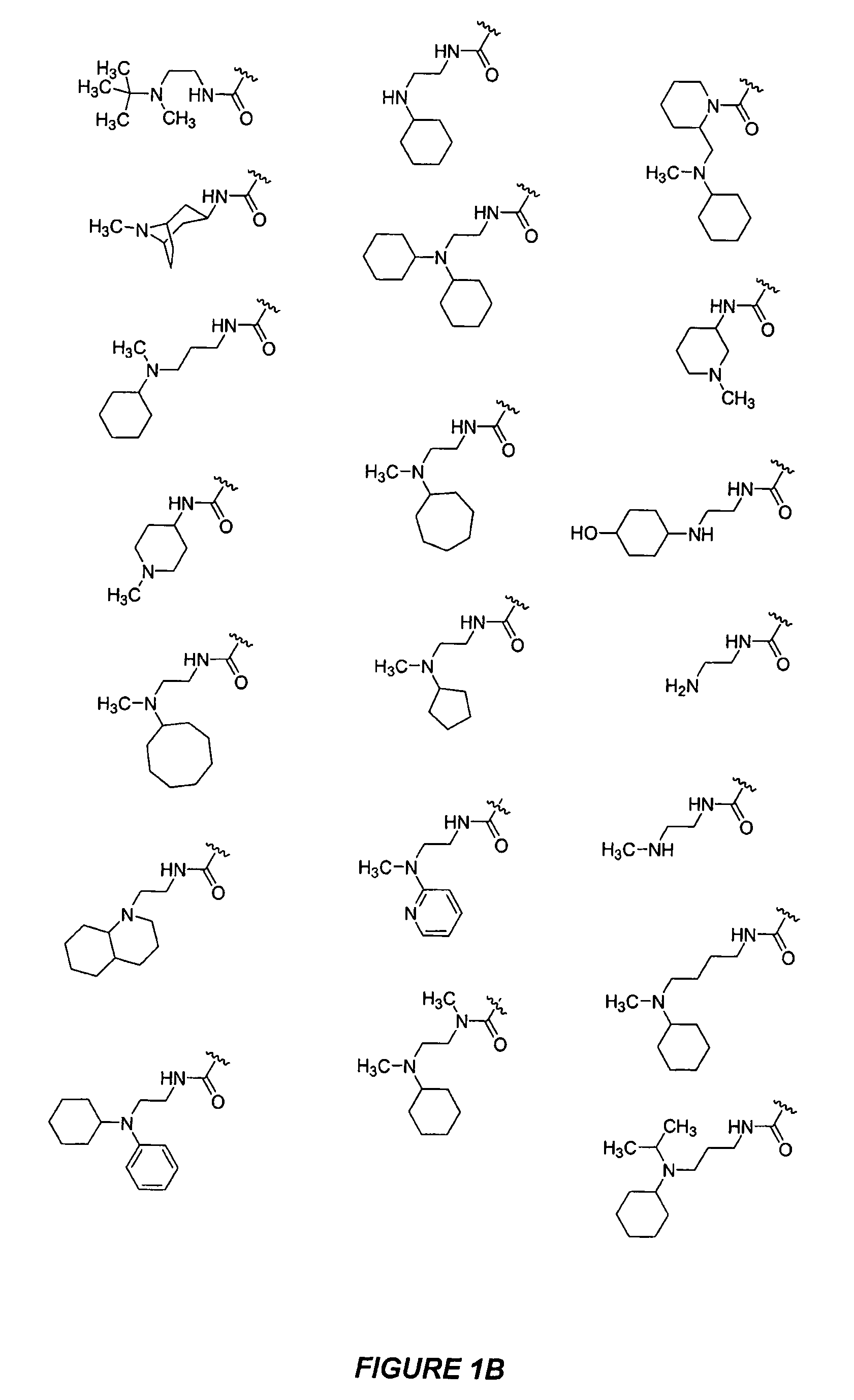
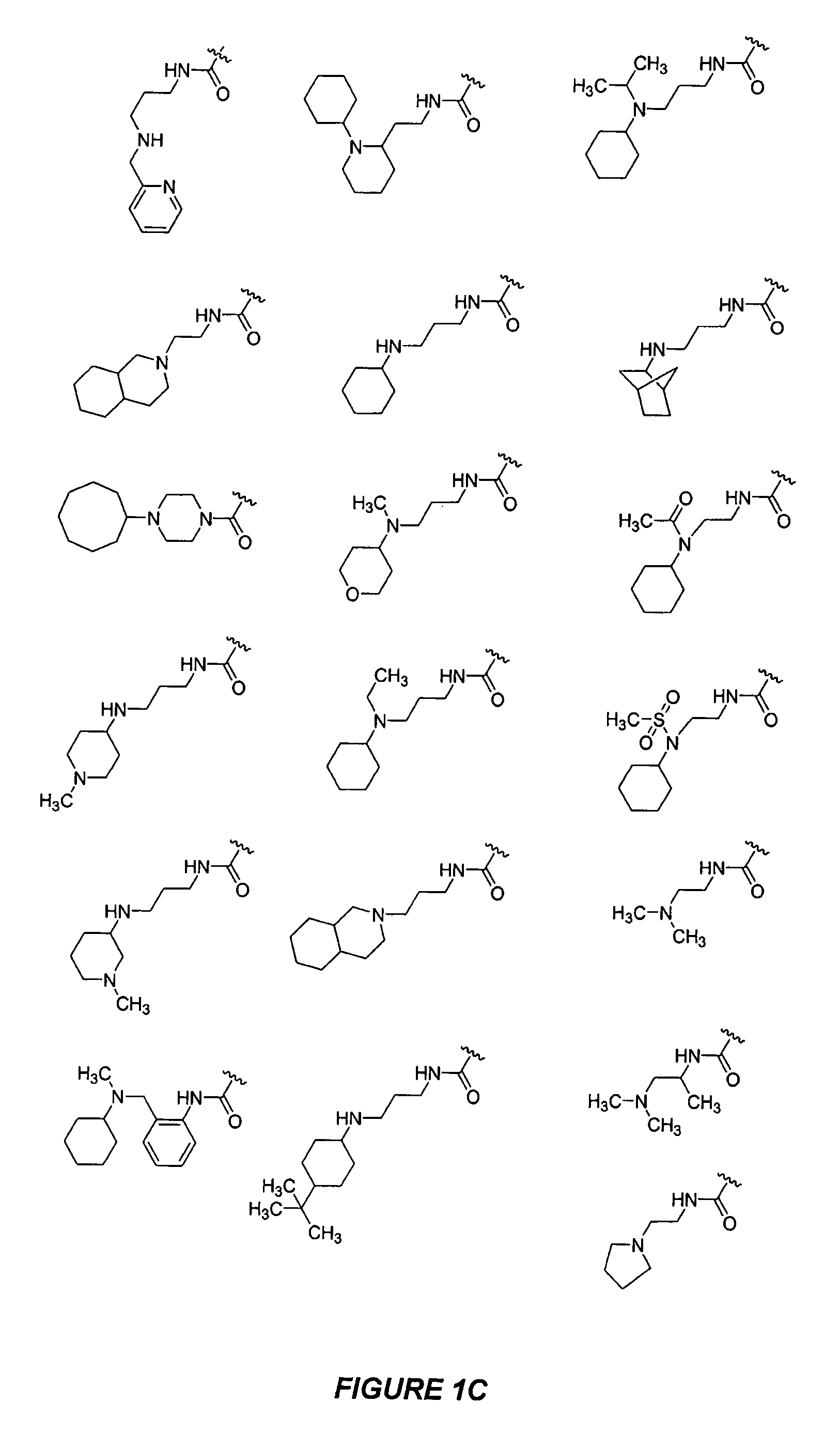
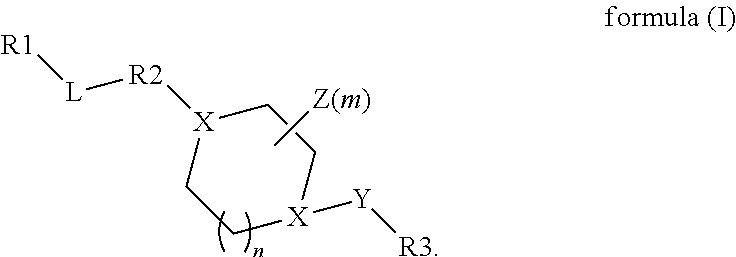
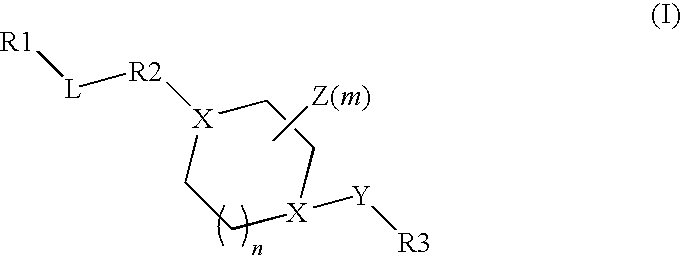
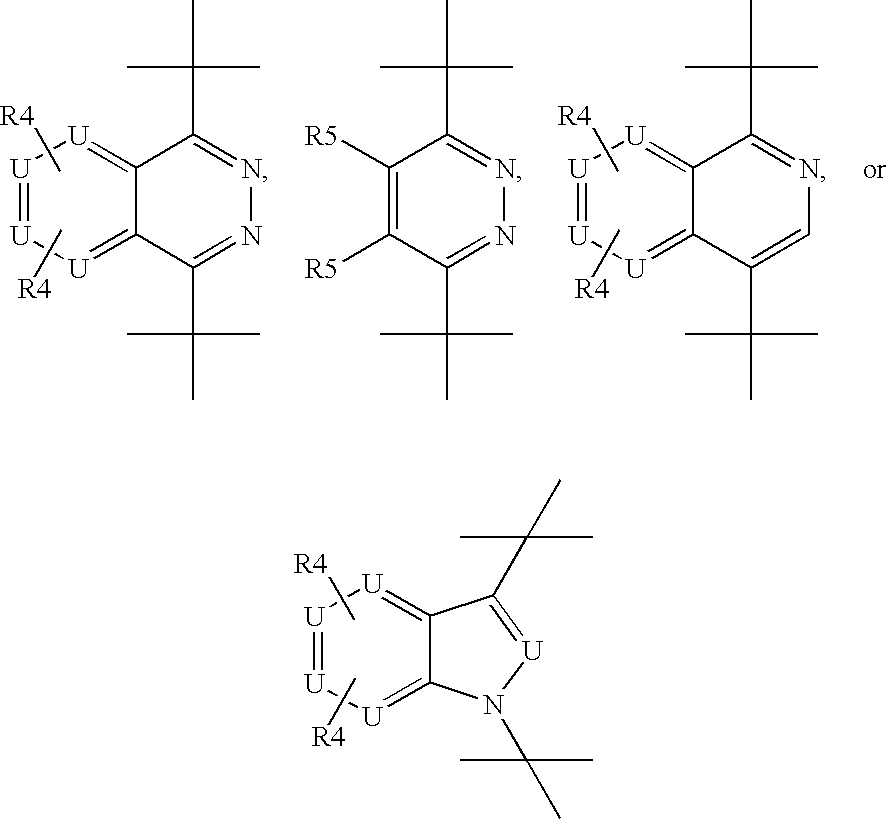
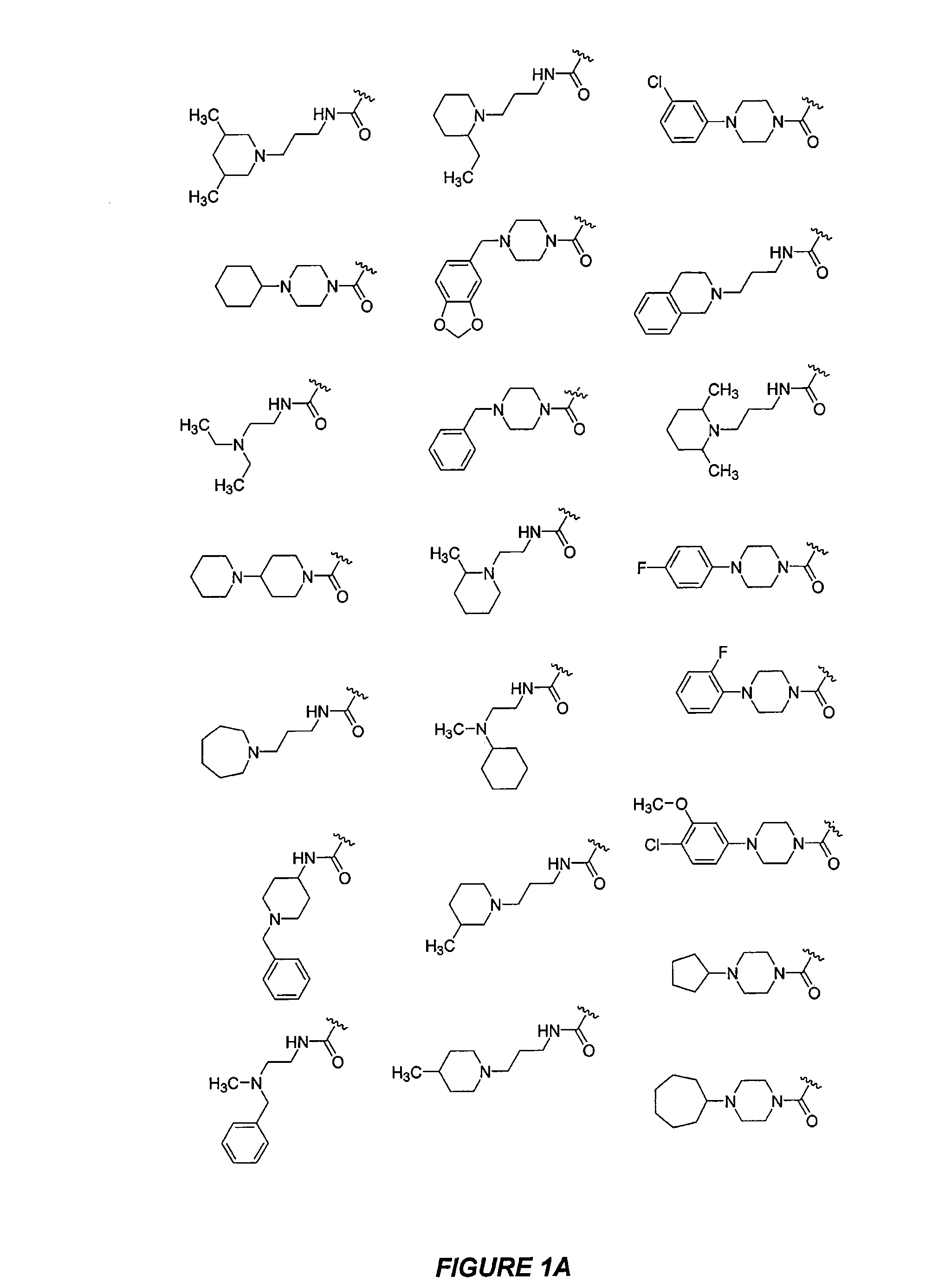
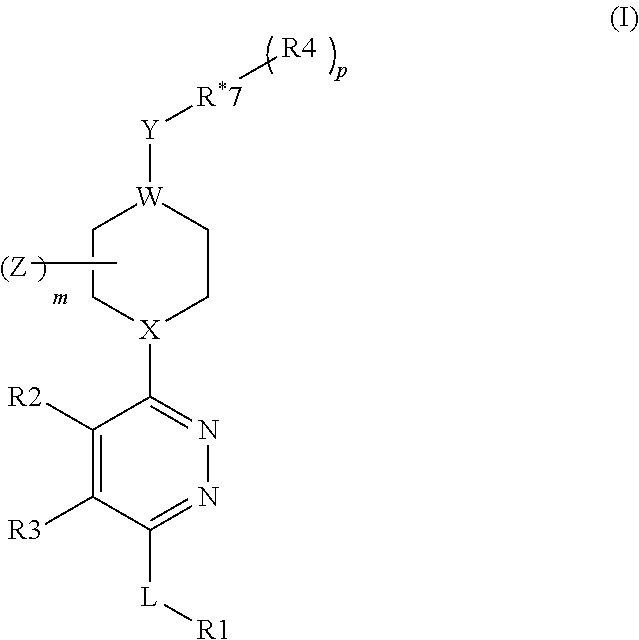
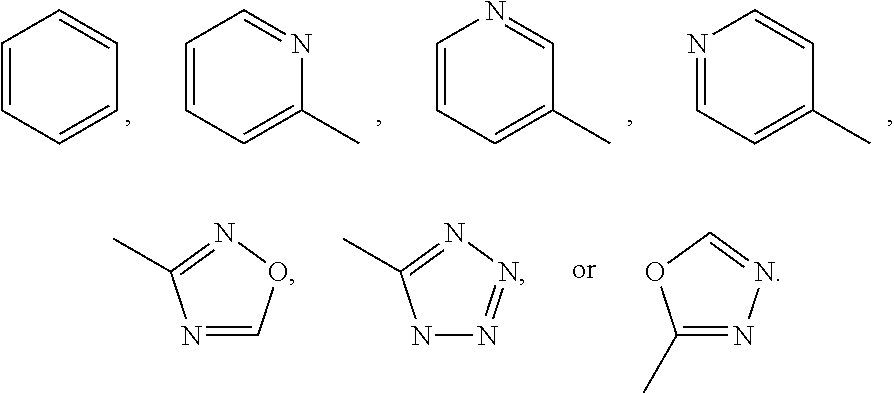
The present disclosure relates to compounds relating to the diagnosis and treatment of pathologies relating to the Hedgehog pathway, including but not limited to tumor formation, cancer, neoplasia, and non-malignant hyperproliferative disorders; specifically relating to compounds of formula I:
Owner:NOVARTIS AG
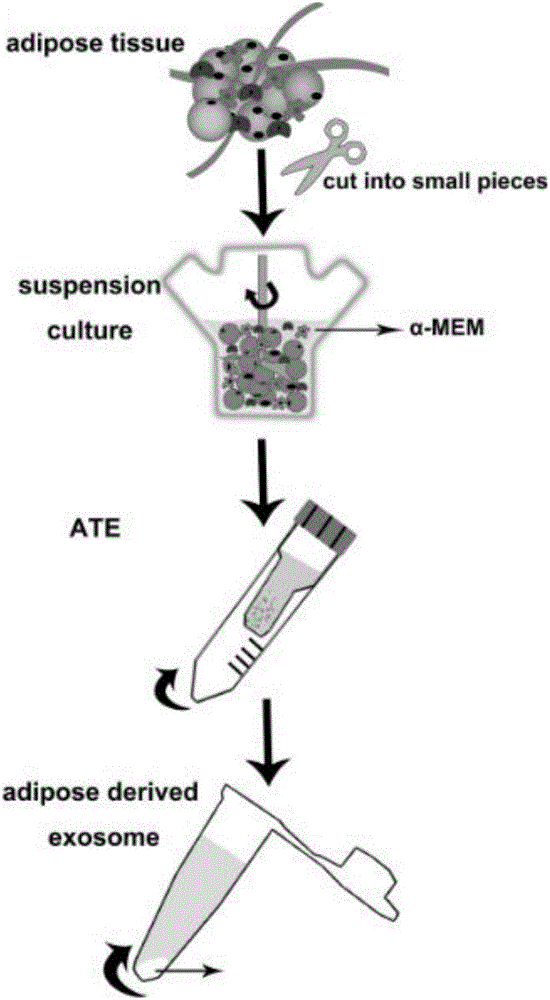
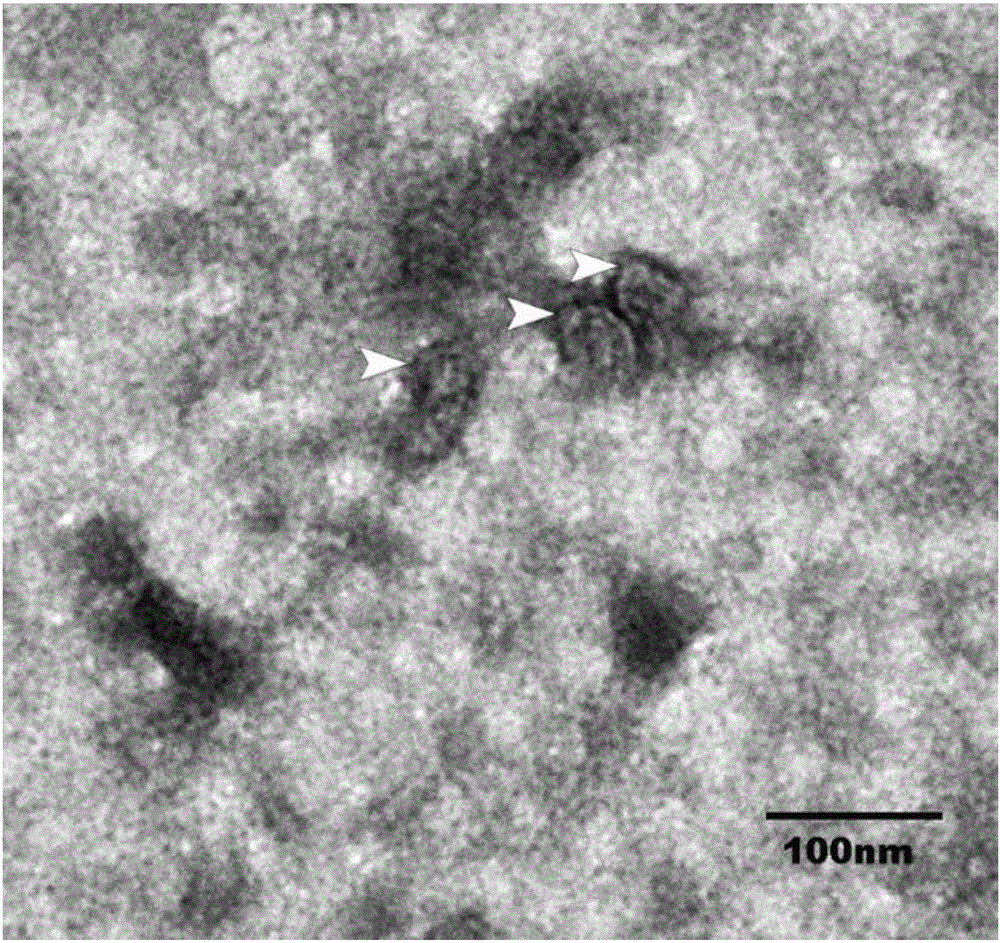
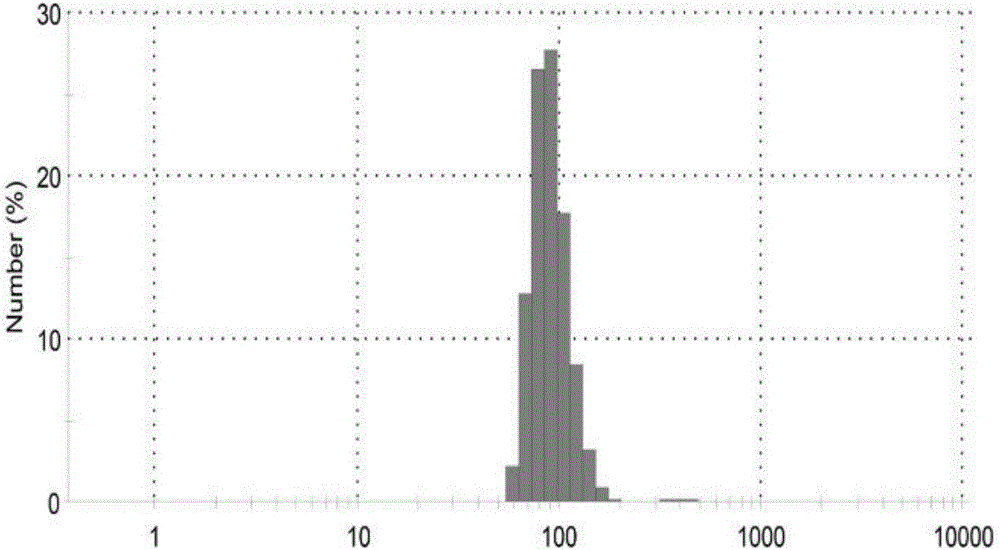
Adipose tissue source exosome gel, preparation method and application
ActiveCN106676065AAvoid time consumingAvoid potential malignant cancer and other disadvantagesArtificial cell constructsSkeletal/connective tissue cellsNude mouseExosome
The invention belongs to the technical field of tissue engineering and particularly relates to adipose tissue source exosome gel, a preparation method and application. The adipose tissue source exosome gel is characterized by comprising an adipose tissue exosome and a solvent in a mass-volume ratio of (1-3):1, wherein an aquogel is served as the solvent. The preparation method comprises the following steps: treating an adipose tissue, acquiring an adipose tissue extract, acquiring the adipose tissue source exosome and preparing the adipose tissue source exosome gel. The adipose tissue source exosome gel is mainly used for promoting the fat regeneration. The invention particularly relates to the exosome extracted from the adipose tissue. When the exosome is applied to the nude mouse body, a new mature adipose tissue can be generated. The defects of insufficient seed cell resource, potential malignant transformation and tumor formation of the traditional tissue engineering can be overcome; the exosome has the advantage of easiness in storage and transportation; a new thought is supplied for acquiring the fat for the tissue engineering.
Owner:成都世联康健生物科技有限公司
CXCR4 modulators
The present invention is directed to novel compounds and pharmaceutical compositions that inhibit the binding of the SDF-1 chemokine to the chemokine receptor CXCR4 and / or the binding of the SDF-1 or I-TAC chemokines to the chemokine receptor CCXCKR2 (CXCR7). These compounds are useful in preventing tumor cell proliferation, tumor formation, metastasis, inflammatory diseases, treatment of HIV infectivity, treatment of stem cell differentiation and mobilization disorders, and ocular disorders.
Owner:CHEMOCENTRYX INC
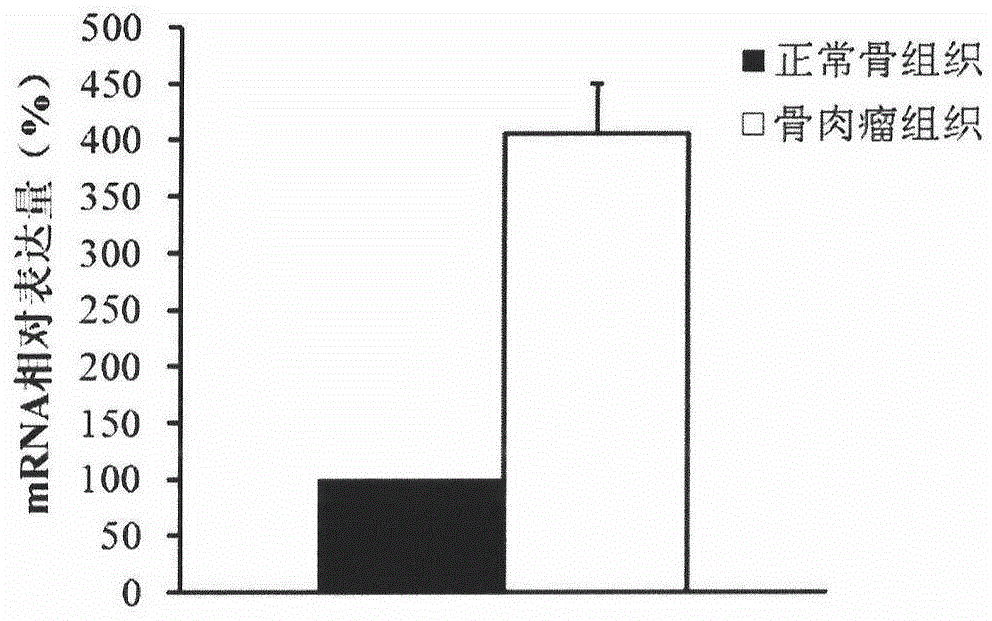
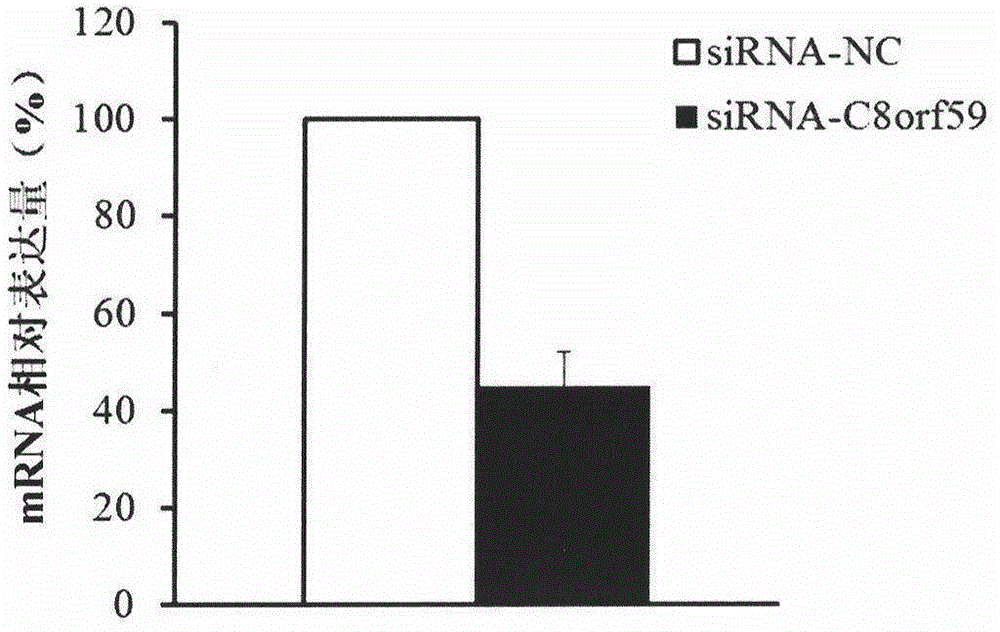
New drug target for osteosarcoma
ActiveCN104651509AEasy diagnosisOrganic active ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementOsteosarcoma cell lineApoptosis
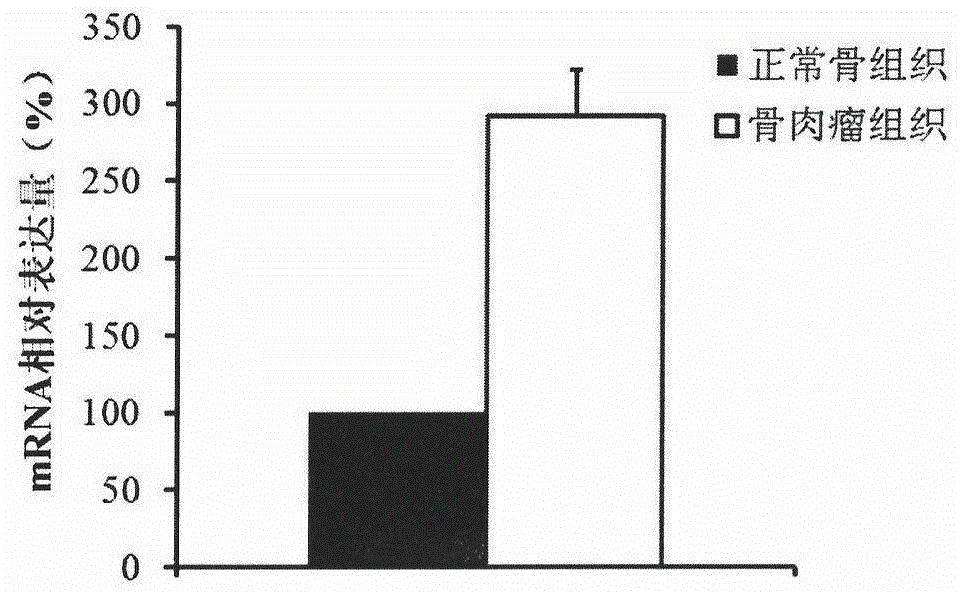
The invention discloses application of C8orf59 gene in preparing drugs for diagnosing and treating osteosarcoma. The experiment proves that the expression level of the C8orf59 gene in osteosarcoma tissues is obviously higher than that in normal tissues, and therefore, the C8orf59 gene can be used as a specific marker for diagnosing osteosarcoma, so that the osteosarcoma diagnosis is more accurate and faster. The expression of the C8orf59 gene in the osteosarcoma cell line can be disturbed to obviously inhibit the cell proliferation, migration, invasion and tumor formation capacity and accelerate apoptosis. Therefore, the C8orf59 gene has potential application value for gene therapy of osteosarcoma, and is hopeful to be used for treating osteosarcoma and developing new anti-osteosarcoma drugs on such basis, thereby making contribution for preventing and treating osteosarcoma in clinic.
Owner:QINGDAO MEDINTELL BIOMEDICAL CO LTD
Organic Compounds as Smo Inhibitors
InactiveUS20100041663A1Inhibition of activationBiocideSenses disorderAbnormal tissue growthNon malignant
The present invention relates generally to novel compounds relating to the diagnosis and treatment of pathologies relating to the Hedgehog pathway, including but not limited to tumor formation, cancer, neoplasia, and non-malignant hyperproliferative disorders. The present invention includes novel compounds, novel compositions, methods of their use and methods of their manufacture, where such compounds are generally pharmacologically useful as agents in therapies whose mechanism of action involve methods of inhibiting tumorigenesis, tumor growth and tumor survival using agents that inhibit the Hedgehog and Smo signaling pathway.
Owner:NOVARTIS AG
Fushion protein of melittin with gene mutant interleukin -2
The invention discloses a fusion protein of melittin and human mutant interleukin-2, which is characterized in that, a linker peptide gene is used to link the encoding genes of human mutant IL-2 and melittin. The invention can be used to screen cloning capable of improving CD8+T cell mediated CTL reactivity of the body after the tumor formation, the fusion protein can be used fine genetic medicament for the treatment of tumors.
Owner:QINGDAO UNIV
Wortmannin analogs and methods of using same
Novel Wortmannin analogs and their use in inhibiting inhibiting PI-3-kinase activity in mammals as well as tumor formation in a subject are described herein.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF PITTSBURGH +1
Use of the Pro-Peptide Domain of Lysyl Oxidase as a Therapeutic Agent
A therapeutic composition that includes an active portion of the lysyl oxidase pro-peptide in a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier substance and methods of using such a therapeutic composition are disclosed. The active agent does not have lysyl oxidase enzymatic activity. Preferably, the active polypeptide is active in inhibiting cell growth in soft agar and active in inhibiting tumor formation. In addition, the active polypeptide preferably comprises an active portion of the amino acid sequence given in SEQ ID NO.: 1 or SEQ ID NO.: 2, or conservative substitions thereof. Alternatively, the active polypeptide comprises a polypeptide comprising an active portion of an amino acid sequence selected from the group consisting of SEQ ID NOs.: 3-8, or conservative substitions thereof.
Owner:TRACKMAN PHILIP C +3
Use of anti-α5β1 antibodies to inhibit cancer cell proliferation
InactiveUS7662384B2Prevent proliferationPeptide/protein ingredientsImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsAntiangiogenesis TherapyAntiendomysial antibodies
The present invention provides methods for direct killing of cancer cells using anti-α5β1 antibodies. Generally, the method comprises contacting a cancer cell that expresses α5β1 on its surface with an anti-α5β1 antibody, and thereby inducing the death of the cancer cell. The methods of the invention may be employed at an early stage of cancer development in a patient to prevent tumor establishment. In addition, the methods may be used to treat previously formed tumors especially in cancer that have not proven susceptible to anti-angiogenesis therapy. The methods may be employed as a combination therapy of anti-α5β1 antibodies together with cancer chemotherapeutic agents or other molecular-based cancer therapeutic agents.
Owner:ABBOTT BIOTHERAPEUTICS CORP
Method for preparing biological composite artificial trachea and application thereof
ActiveCN105056302APorous structureAvoid dependenceAdditive manufacturing apparatusTubular organ implantsCartilage cellsForeign matter
The invention provides a biological artificial trachea and a preparation method thereof in combination with a 3D printing technology. Materials adopted for the biological artificial trachea simultaneously have flexibility and a certain mechanical strength, so that physical and mechanical properties of the trachea serving as a hollow organ in the chest are met. The artificial trachea is porous and loosened in structure and favorable for nutrient diffusion and ingrowth of autologous vessels. In addition, seed cells obtained by expansion of airway epithelial cells and cartilage cells of a receptor are printed on the trachea wall, and patients' rejection reaction to cells is avoided. Besides, the seed cells are composed of mature cells in terminal differentiation, the induced differentiation problem and the tumor formation risk caused by the use of stem cells can be avoided. The spatial distribution of the cells is accurately controllable in printing, and the restorative process is accelerated according to the histology regular distribution. Finally, a trachea support can be degraded in vivo, complications caused by the fact that foreign matter remains in vivo are reduced, and the risk of taking out the foreign matter through a second operation is avoided.
Owner:SHANGHAI PULMONARY HOSPITAL +1
Use of anti-alpha5beta1 antibodies to inhibit cancer cell proliferation
InactiveUS20050260210A1Prevent proliferationPeptide/protein ingredientsImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsAbnormal tissue growthAntiangiogenesis Therapy
The present invention provides methods for direct killing of cancer cells using anti-α5β1 antibodies. Generally, the method comprises contacting a cancer cell that expresses α5β1 on its surface with an anti-α5β1 antibody, and thereby inducing the death of the cancer cell. The methods of the invention may be employed at an early stage of cancer development in a patient to prevent tumor establishment. In addition, the methods may be used to treat previously formed tumors especially in cancer that have not proven susceptible to anti-angiogenesis therapy. The methods may be employed as a combination therapy of anti-α5β1 antibodies together with cancer chemotherapeutic agents or other molecular-based cancer therapeutic agents.
Owner:ABBOTT BIOTHERAPEUTICS CORP
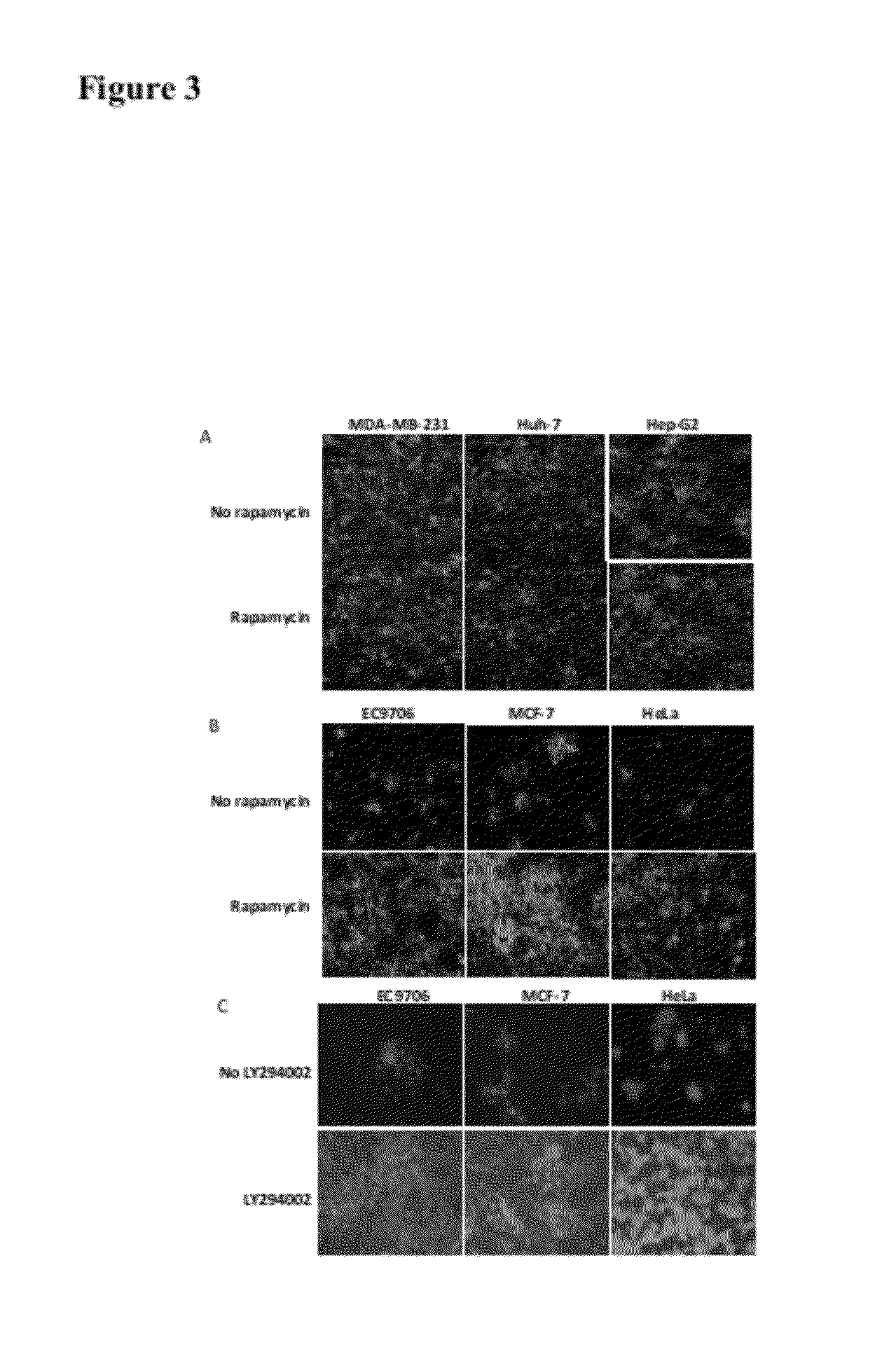
Method for increasing the replication of oncolytic HSVs in highly resistant tumor cells using mTOR pathway and PI3K inhibitors
InactiveUS20120100109A1Reduce healingImproved prognosisBiocideOrganic active ingredientsTherapy resistantWilms' tumor
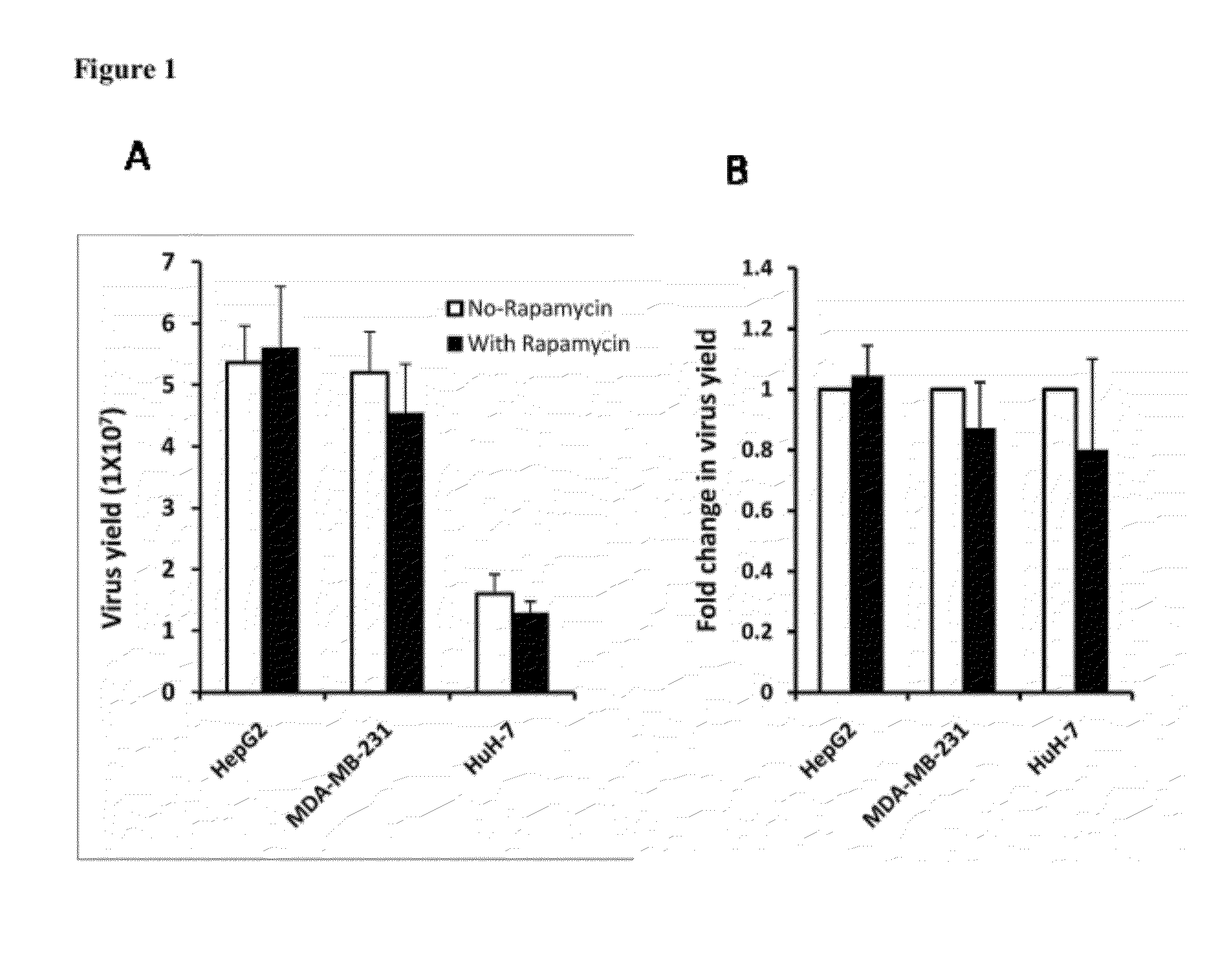
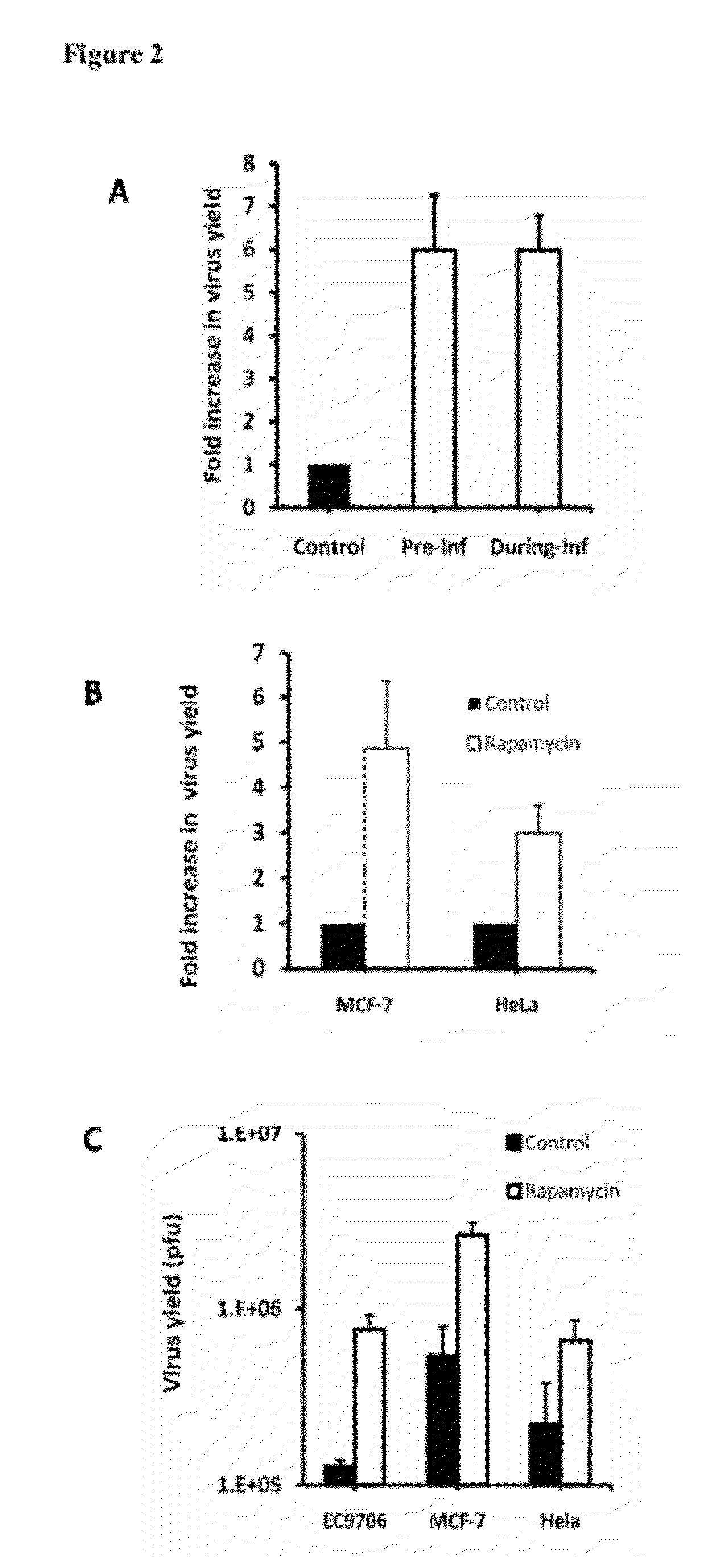
The present invention is directed to the administration of an HSV derived oncolytic virus and a PI3K / AKT / mTOR pathway inhibitor to treat various types of resistant tumors. Therapy-resistant tumor formation is one of the main causes for treatment failure in the clinic. The treatment methods and compositions disclosed herein sensitize resistant tumors to the treatment of herpes simplex virus (HSV)-based oncolytic virotherapy. Pre or co-treatment of resistant tumor cells with the mTOR inhibitor, rapamycin, or certain PI3K inhibitors, such as LY294002, can efficiently sensitize the tumors to HSV derived oncolytic viruses, whereby the replication and spread of the viruses are dramatically enhanced.
Owner:HOUSTON SYST UNIV OF
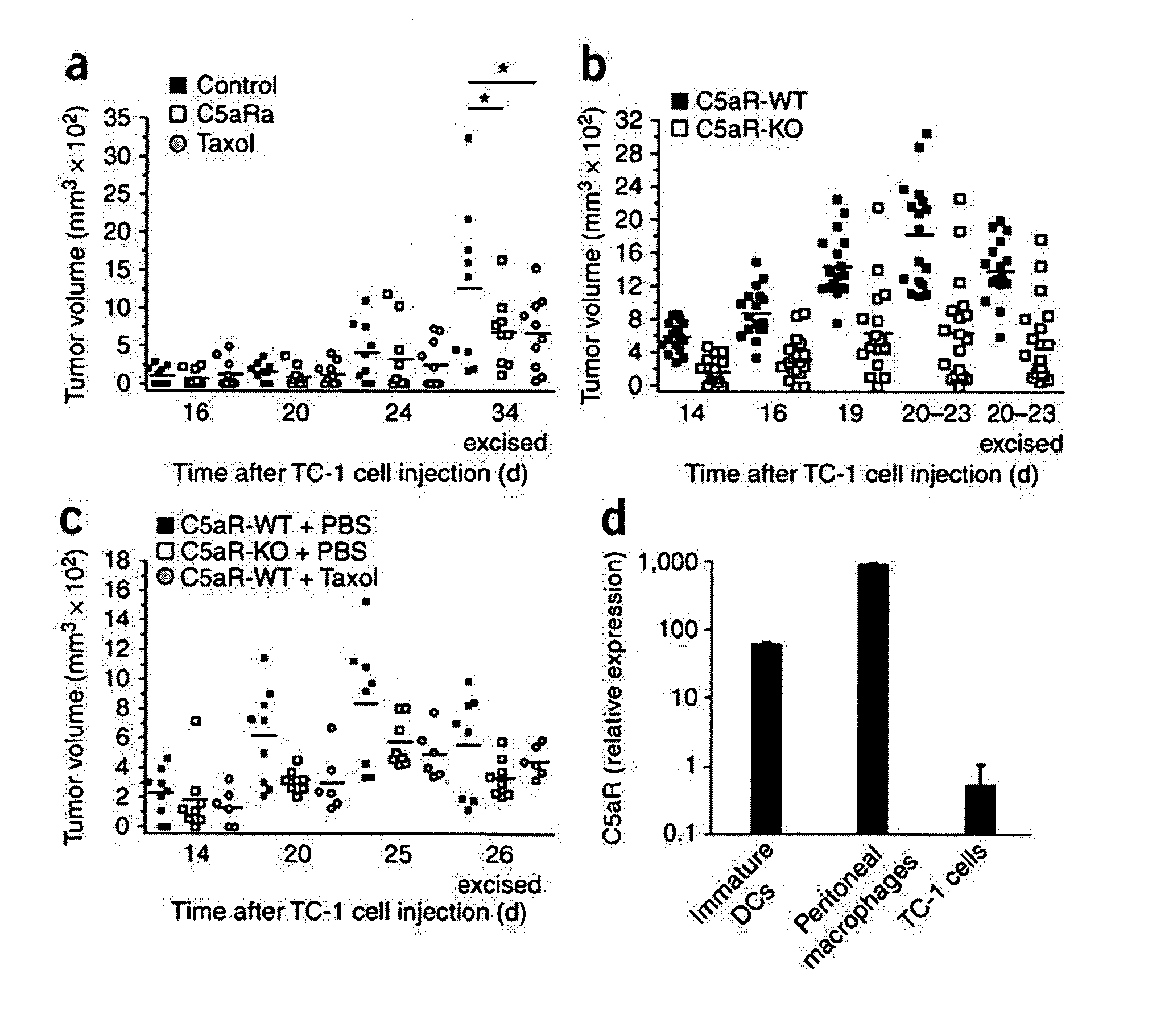
Complement inhibitors as therapeutic agents for treatment of cancer
ActiveUS20110044983A1Preventing and reducing and delaying growth of tumorOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsTumor microenvironmentOncology
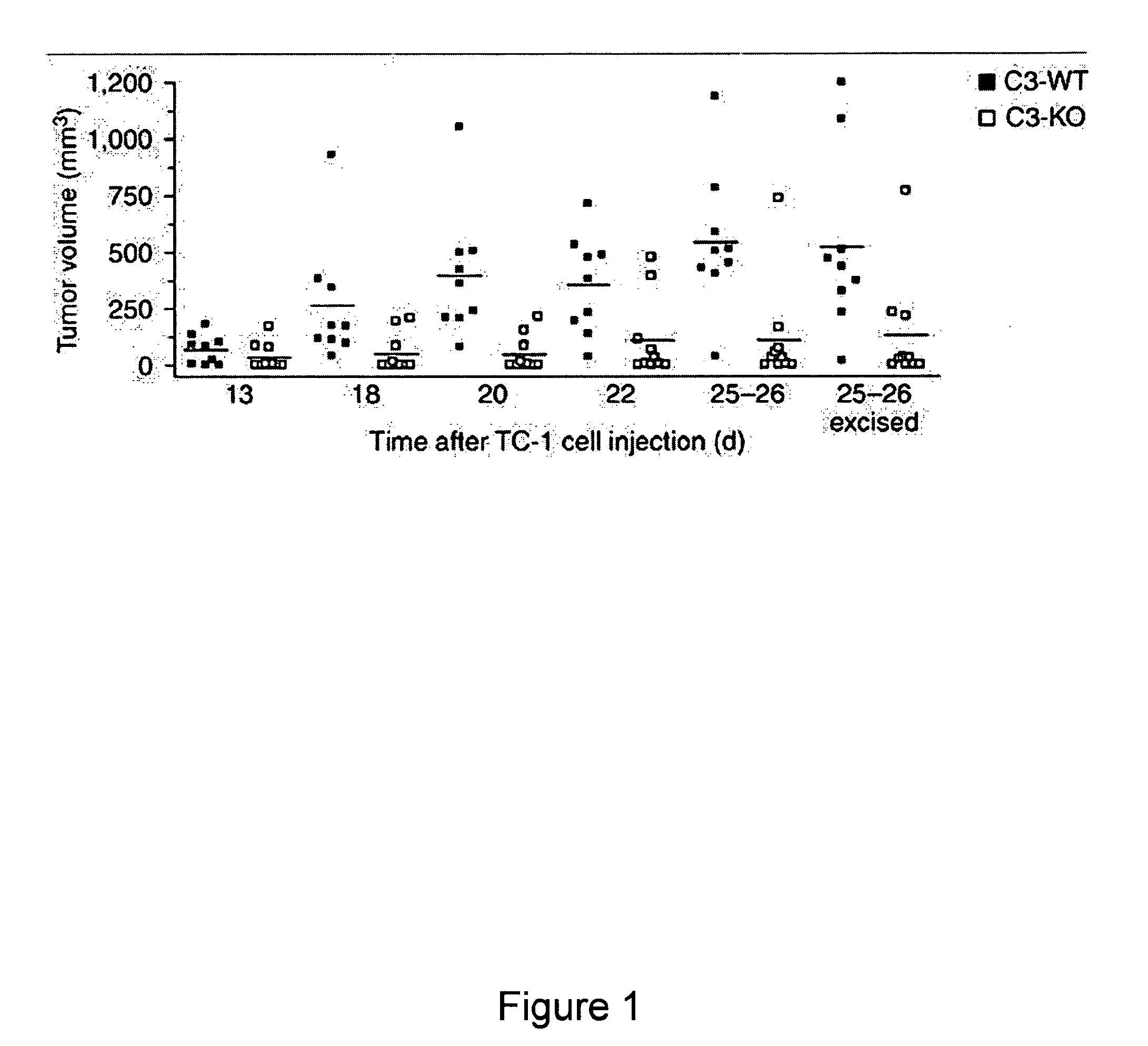
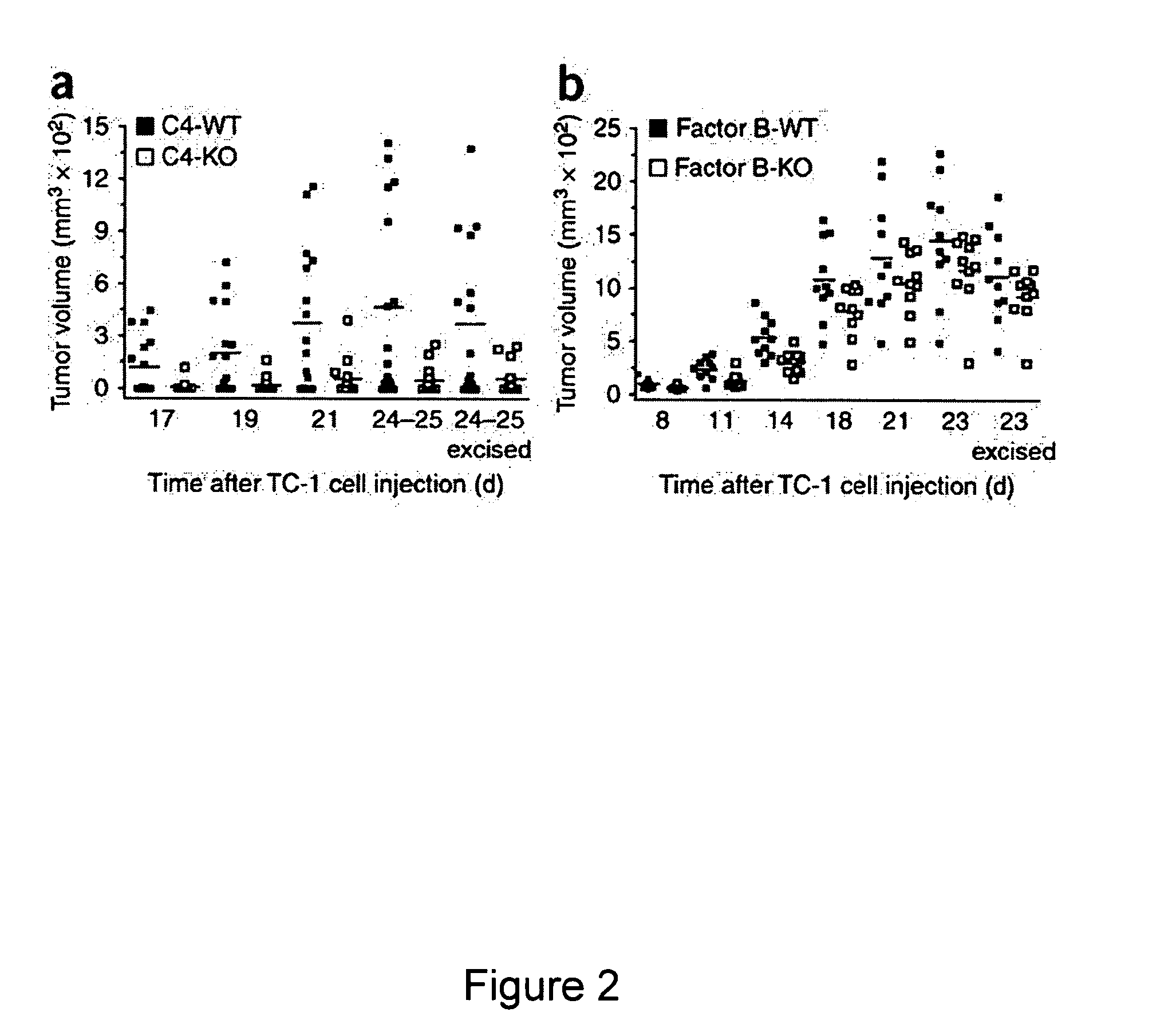
Methods for treating, preventing or delaying onset of tumor formation and other forms of cancer are disclosed. The methods involve administration of a complement inhibitor to inhibit C5a receptor signaling in the tumor microenvironment.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
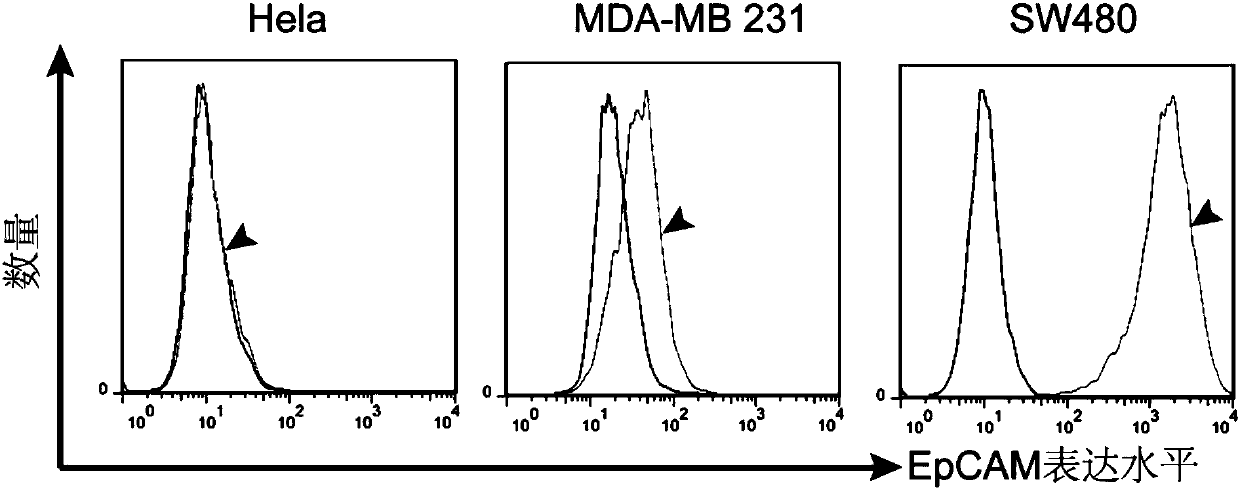
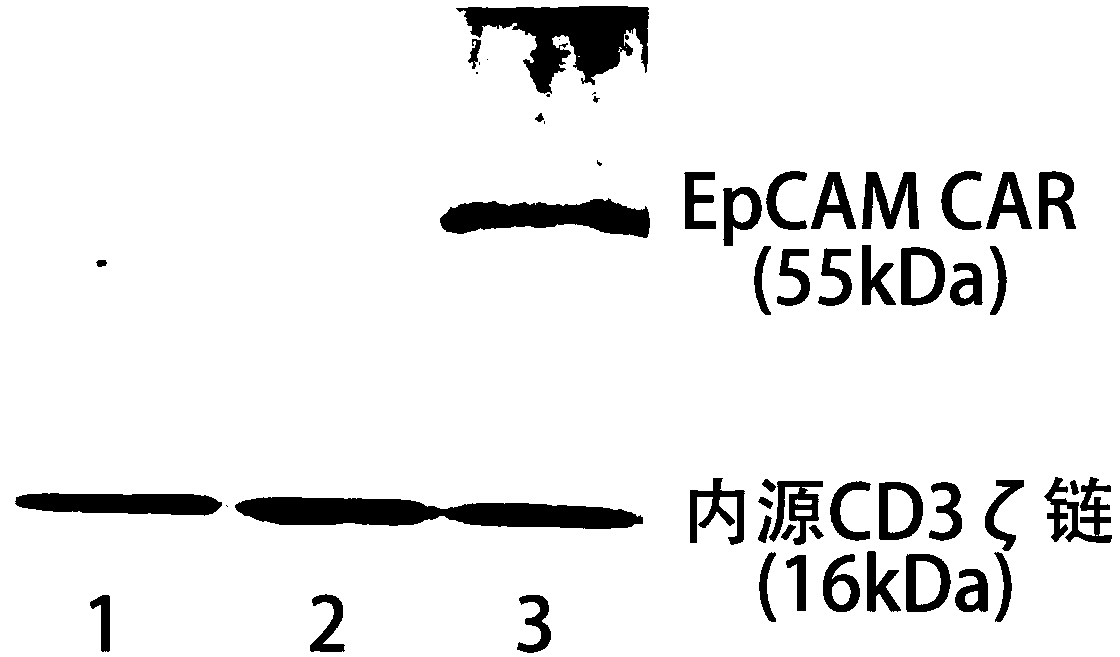
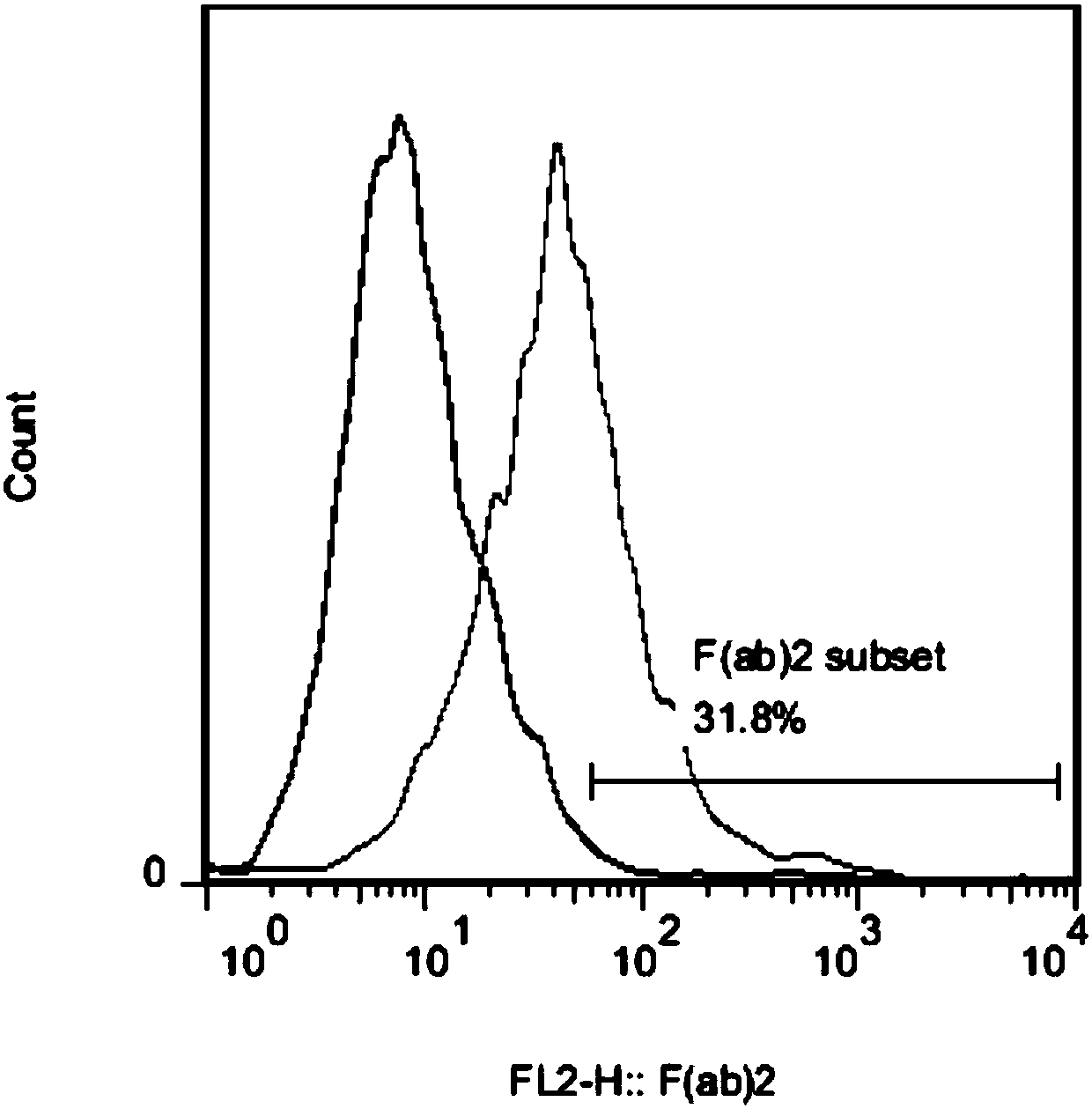
Human EpCAM targeted genetically engineered lymphocyte, preparation method and use thereof
ActiveCN107602703AInhibition formationInhibit tumor growthPeptide/protein ingredientsMammal material medical ingredientsSingle-Chain AntibodiesCytotoxicity
The invention relates to the genetic engineering field, in particular to a human EpCAM targeted genetically engineered lymphocyte, a preparation method and use thereof. Technically, the invention aimsto provide a new effective means for immunotherapy of tumors. The technical scheme for solving the technical problem of the invention firstly provides a single-chain antibody capable of recognizing human EpCAM, a chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) containing the single-chain antibody, a vector carrying the chimeric antigen receptor, and a lymphocyte modified by the chimeric antigen receptor. After specific recognition of EpCAM overexpressed tumor cells, the EpCAM targeted chimeric antigen receptor modified lymphocyte provided by the invention can play an anti-tumor role through cytokine releaseand cytotoxicity, and can remarkably tumor formation, tumor growth and lung metastasis in vivo, thus having good application prospect.
Owner:WEST VAC BIOPHARMA CO LTD
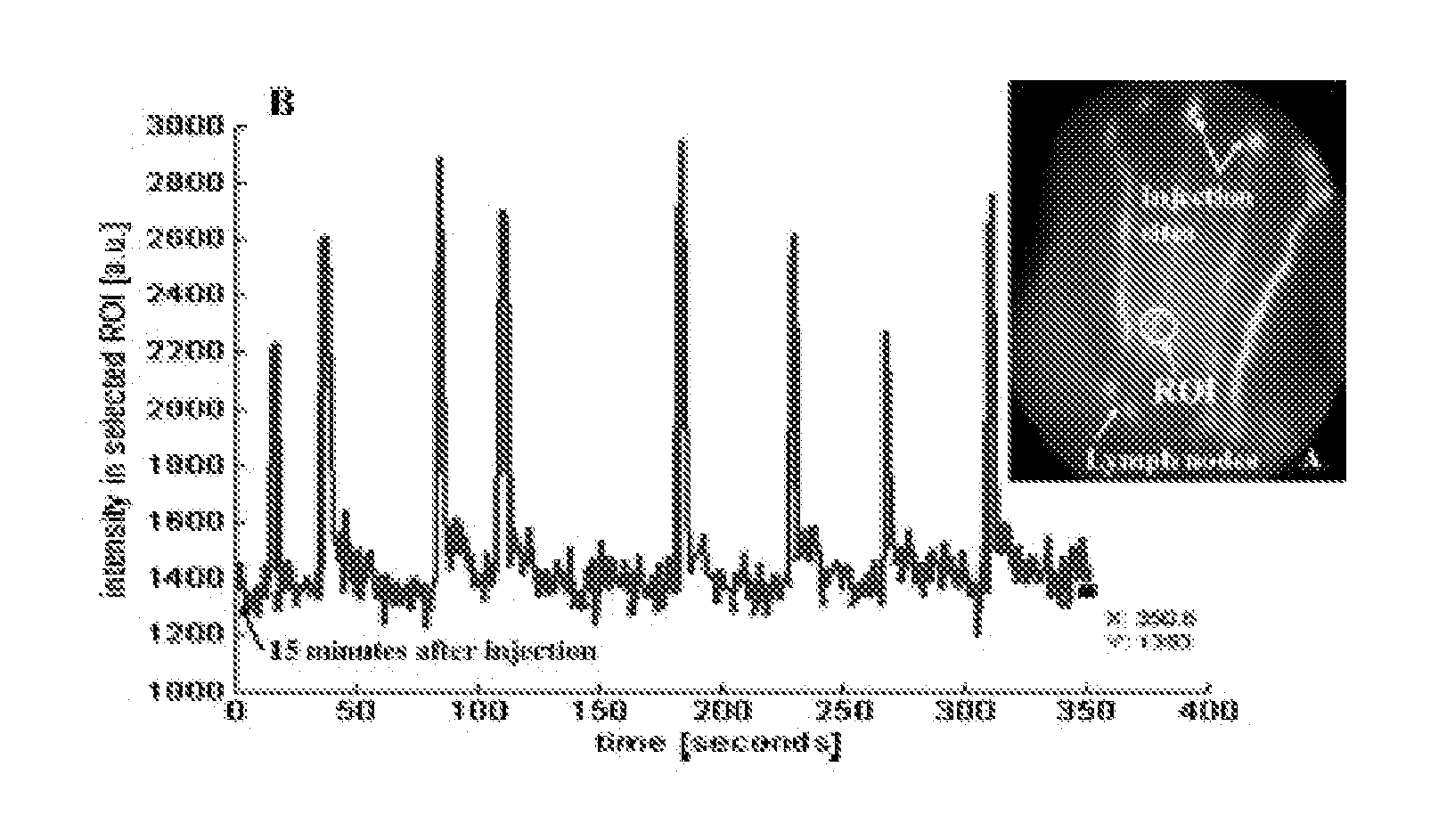
Imaging agents for functional imaging of lymphatic structures
InactiveUS20080056999A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsDiagnostics using lightLymphatic SpreadImaging agent
Novel imaging agents targeted to a lymph vascular cell receptor and a hyaluranon cell receptor are disclosed. The disclosed imaging agents incorporate biological molecules such as hyaluronic acid which bind to the receptors. Lymph vascular cell receptor expression may be related to the beginnings of tumor formation. As such, embodiments of the imaging agents may be used to stain lymph structures for detailed imaging of lymph architecture as well as serving as potential markers for tumor angiogenesis, tumor metastases, etc.
Owner:BAYLOR COLLEGE OF MEDICINE
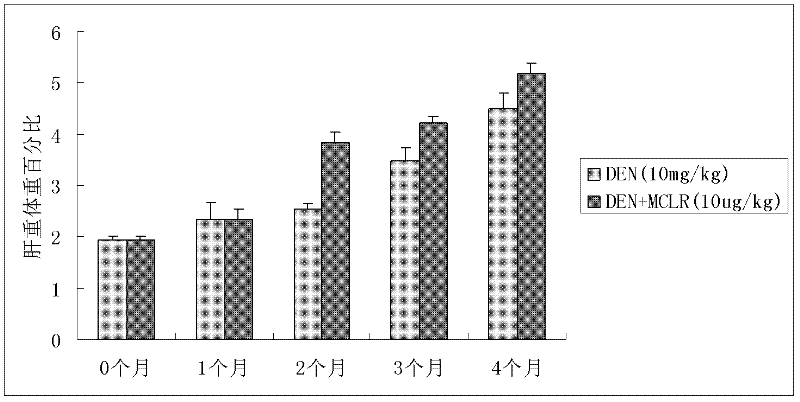
Method for establishing microcystin MC-LR promoted diethyl nitrosamine DEN induced rat liver cancer model
InactiveCN102524180ACyclic peptide ingredientsVeterinary instrumentsIntraperitoneal routeProcess mechanism
The invention discloses a method for inducing a rat liver cancer model by injecting diethyl nitrosamine DEN in coordination with microcystin MC-LR into a rat body through intraperitoneal injection. Indexes such as liver weight to body weight ratio, liver appearance, liver histopathological slicing and GST-Pi (Glutathione S-transferase) protein expression level clearly show liver cell injury phase, liver cell hyperplasia-hepatocirrhosis phase and liver cell carcinomatous change process in a rat liver cancer occurring process, and find that the liver cancer model induced by the DEN in coordination with the microcystin MC-LR has a more obvious effect at the same time than that induced by DEN independently; the tumor formation time is shorter; and the model is an ideal model for researching occurrence of the liver cancer of a human body. The model has the characteristic of clearly showing each stage for occurrence of the liver cancer and contributing to research of a liver cancer occurrence process mechanism, detection of precancerous lesion and development of treatment medicaments.
Owner:ANHUI UNIVERSITY
Inhibitors of placental growth factor for the treatment of pathological angiogenesis, pathological arteriogenesis, inflammation, tumor formation and/or vascular leakage
The present invention relates to the field of pathological angiogenesis and arteriogenesis and, in particular, to a stress-induced phenotype in a transgenic mouse (PIGF− / −) that does not produce Placental Growth Factor (PIGF) and that demonstrates an impaired vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)-dependent response. PIGF deficiency has a negative influence on diverse pathological processes of angiogenesis, arteriogenesis and vascular leakage comprising ischemic retinopathy, tumor formation, pulmonary hypertension, vascular leakage (edema formation) and inflammatory disorders. The invention thus relates to molecules that can inhibit the binding of PIGF to its receptor (VEGFR-1), such as monoclonal antibodies and tetrameric peptides, and to the use of these molecules to treat the above-mentioned pathological processes.
Owner:VLAAMS INTERUNIVERSITAIR INST VOOR BIOTECHNOLOGIE VZW +1
Method for establishing colorectal cancer patient-derived xenograft model through three-dimensional culture system based on thermo-sensitive biogel
ActiveCN108148811AEnhance tumorigenic abilityGood subcutaneous tumor formation abilityCell culture supports/coating3D cultureMature technologyStem cell culture
The invention relates to a three-dimensional culture system based on thermo-sensitive biogel. The three-dimensional culture system is prepared by combining the following reagents: thermo-sensitive biogel, digestive fluid required for separating and culturing tumor cells, a basal culture medium and a human intestinal stem cell culture medium. The invention also provides a method for establishing acolorectal cancer patient-derived xenograft model through the three-dimensional culture system based on thermo-sensitive biogel. The three-dimensional culture system has the advantages that colorectalcancer cells can be further amplified and grown in the three-dimensional culture system based on thermo-sensitive biogel, and the tumor formation capability of the colorectal cancer cells in the immune deficient mice can be enhanced. Polyclonal tumor cells cultured in the system have high subcutaneous tumor formation capability in nude mice. The three-dimensional culture system has the advantagesof simple preparation method and mature technology, and is capable of greatly reducing the time and the cost for establishing the human-derived colorectal cancer xenograft model.
Owner:ZHONGSHAN HOSPITAL FUDAN UNIV
Three-dimensional transglutaminase-crosslinked hydrogel for tumor engineering
InactiveUS20160178611A1Microbiological testing/measurementBiological testingHeterograftsDelivery vehicle
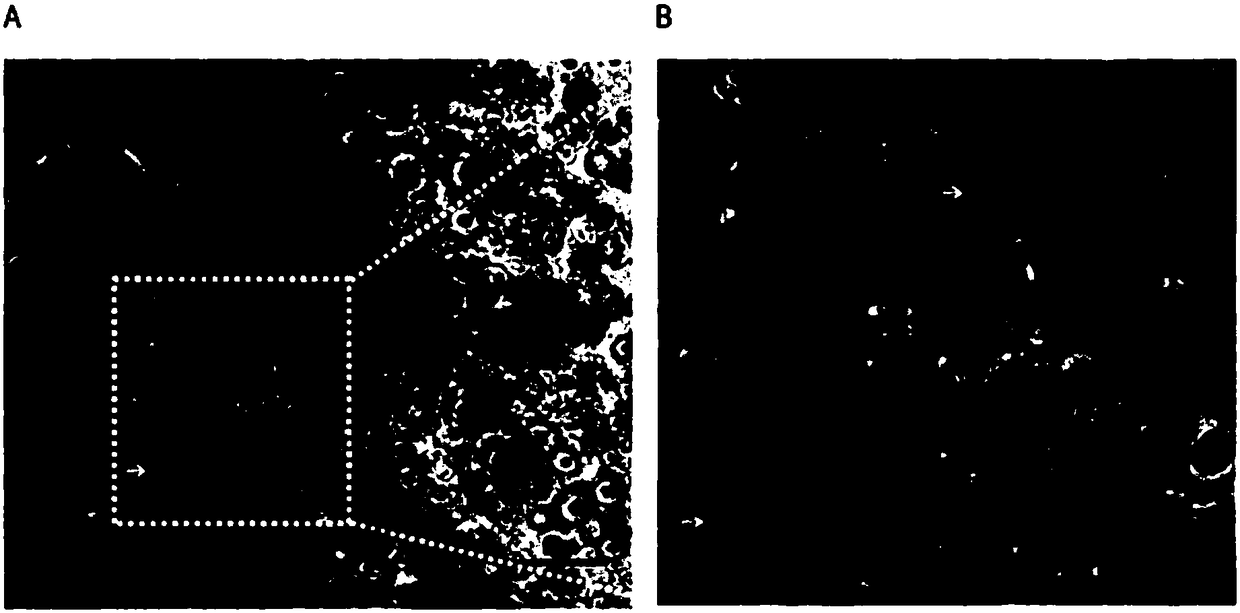
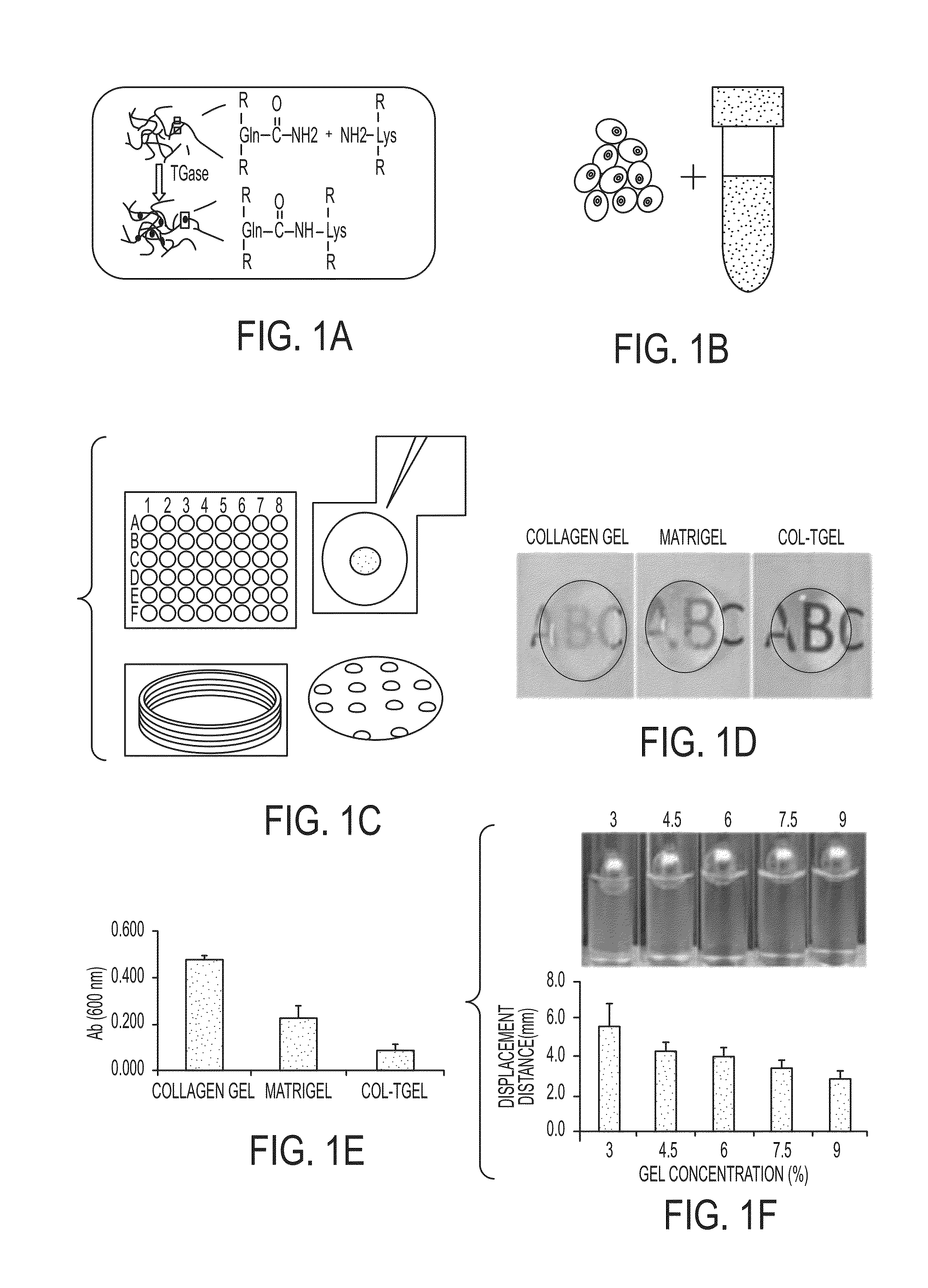
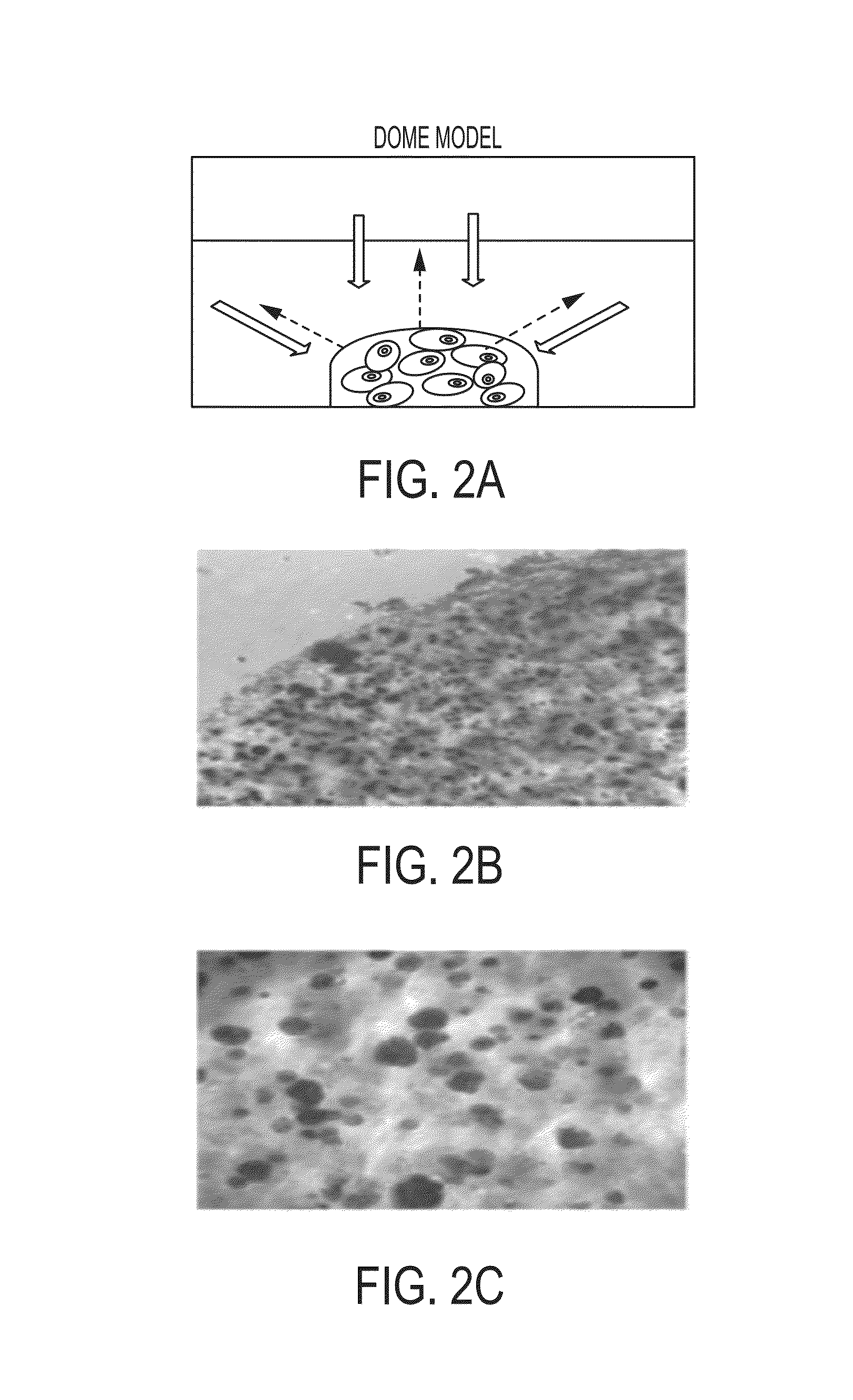
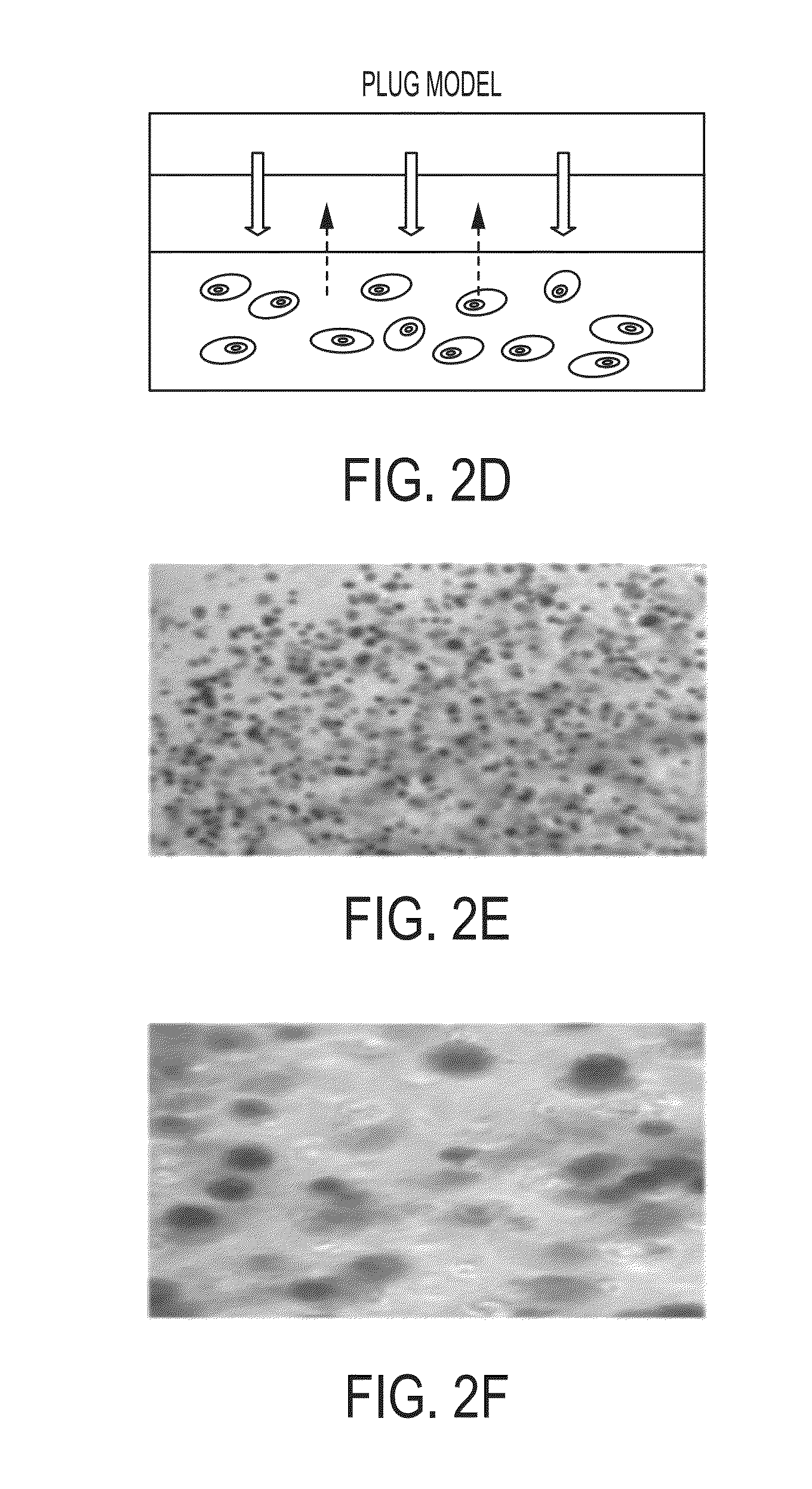
Development of a physiologically relevant 3D model system for cancer research and drug development represents quite a challenge. We have adopted a 3D culture system based on a transglutaminase-crosslinked gelatin gel (Col-Tgel) to mimic tumor 3D microenvironment. The system has several unique advantages over other alternatives which include cell-matrix interaction sites provided by collagen derived peptides, a 3D construct suitable for reproducing the solid tumor microenvironment including multicellular tumor spheroids and metabolic gradients. In addition the controllable gel stiffness provides a wide range of mechanical restrictions; and compatibility with imaging based screening due to its transparent properties. In addition the Col-Tgel provides a cure-in-situ delivery vehicle for tumor xenograft formation in animals with a high take rate. Overall, this unique 3D system could provide a platform to accurately mimic in vivo situations to study tumor formation and progression both in vitro and in vivo, as well as for screening antineoplastic drugs and assessing the occurrence of drug resistance related to cancer cell stress.
Owner:HAN BO +1
Method and apparatus for recognizing abnormal tissue using the detection of early increase in microvascular blood content
The present invention, in one aspect, relates to a method of and apparatus for examining a target for tumors or lesions using what is referred to as ''Early Increase in microvascular Blood Supply'' (EIBS) that exists in tissues that are close to, but are not themselves, the abnormal tissue and in tissues that precede the development of such lesions or tumors. While the abnormal tissue can be a lesion or tumor, the abnofmal tissue can also be tissue that precedes formation of a lesion or tumor, such as a precancerous adenoma, aberrant crypt foci, tissues that precede the development of dysplastic lesions that themselves do not yet exhibit dysplastic phenotype, and tissues in the vicinity of these lesions or pre-dysplastic tissues.
Owner:NORTHSHORE UNIV HEALTHSYST +1
Antiestrogenic glyceollins suppress human breast and ovarian carcinoma proliferation and tumorigenesis
InactiveUS20060246162A1Preventing minimizing development growthOrganic active ingredientsBiocideStress inducedPhytochemical
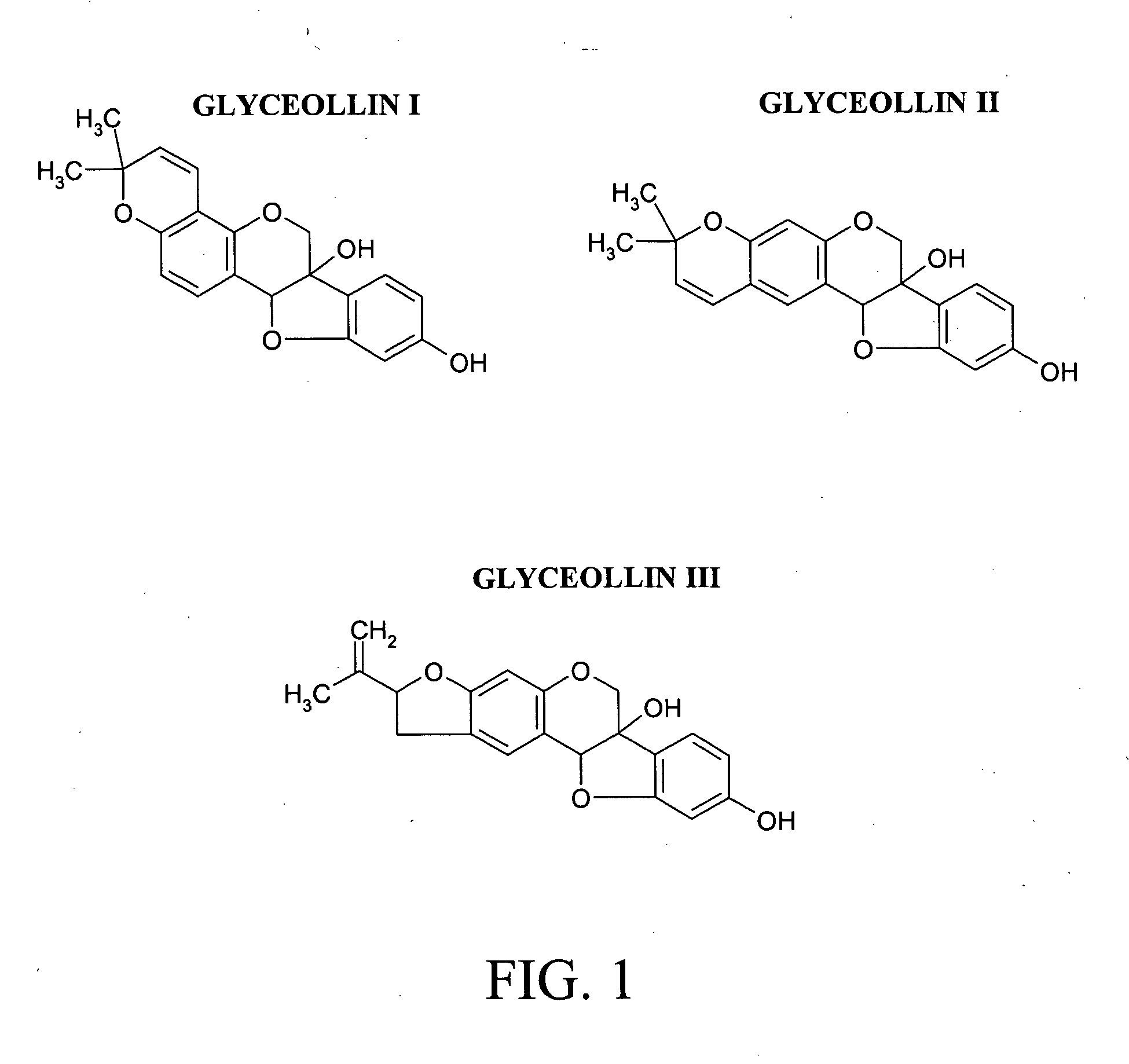
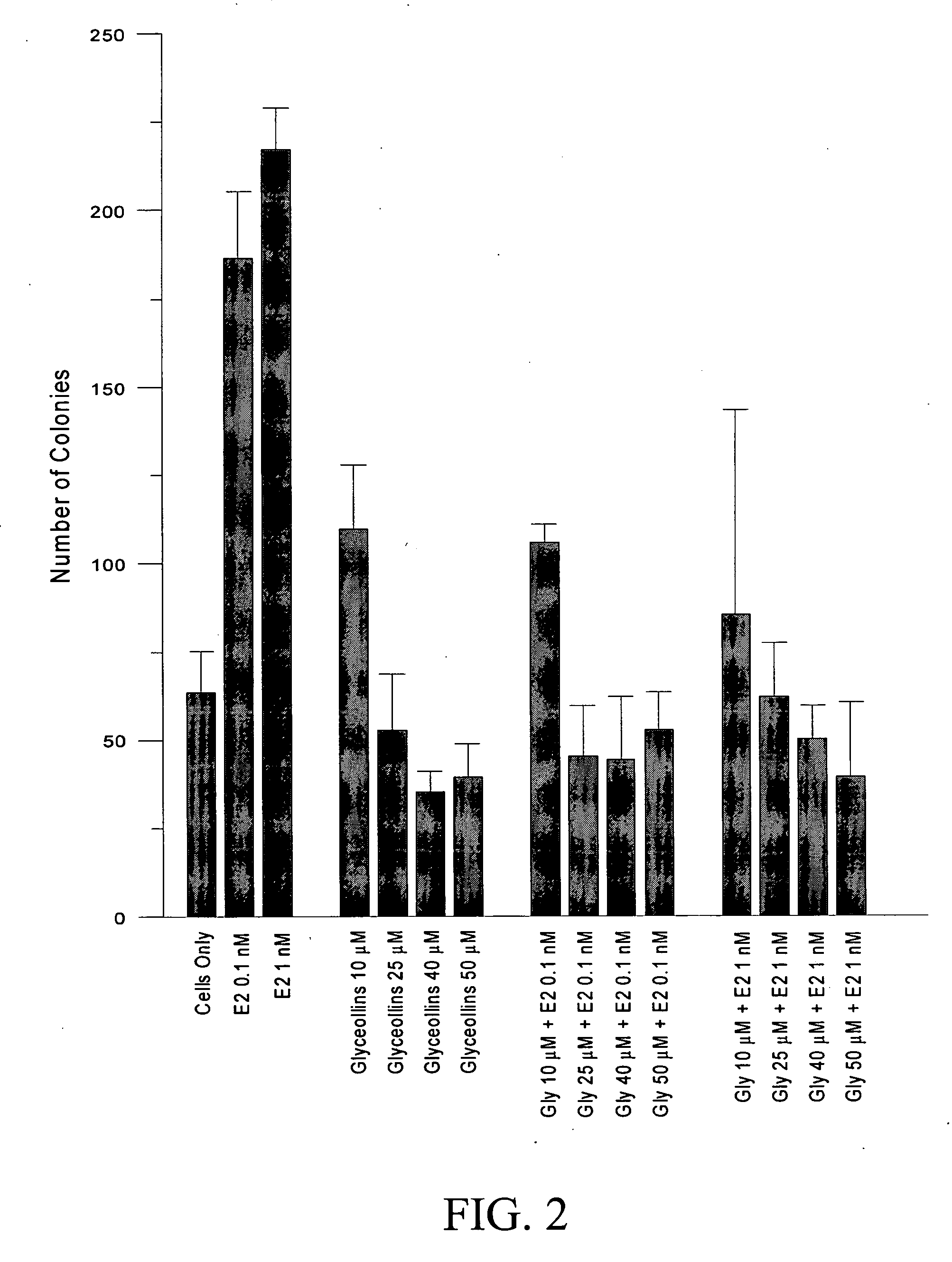
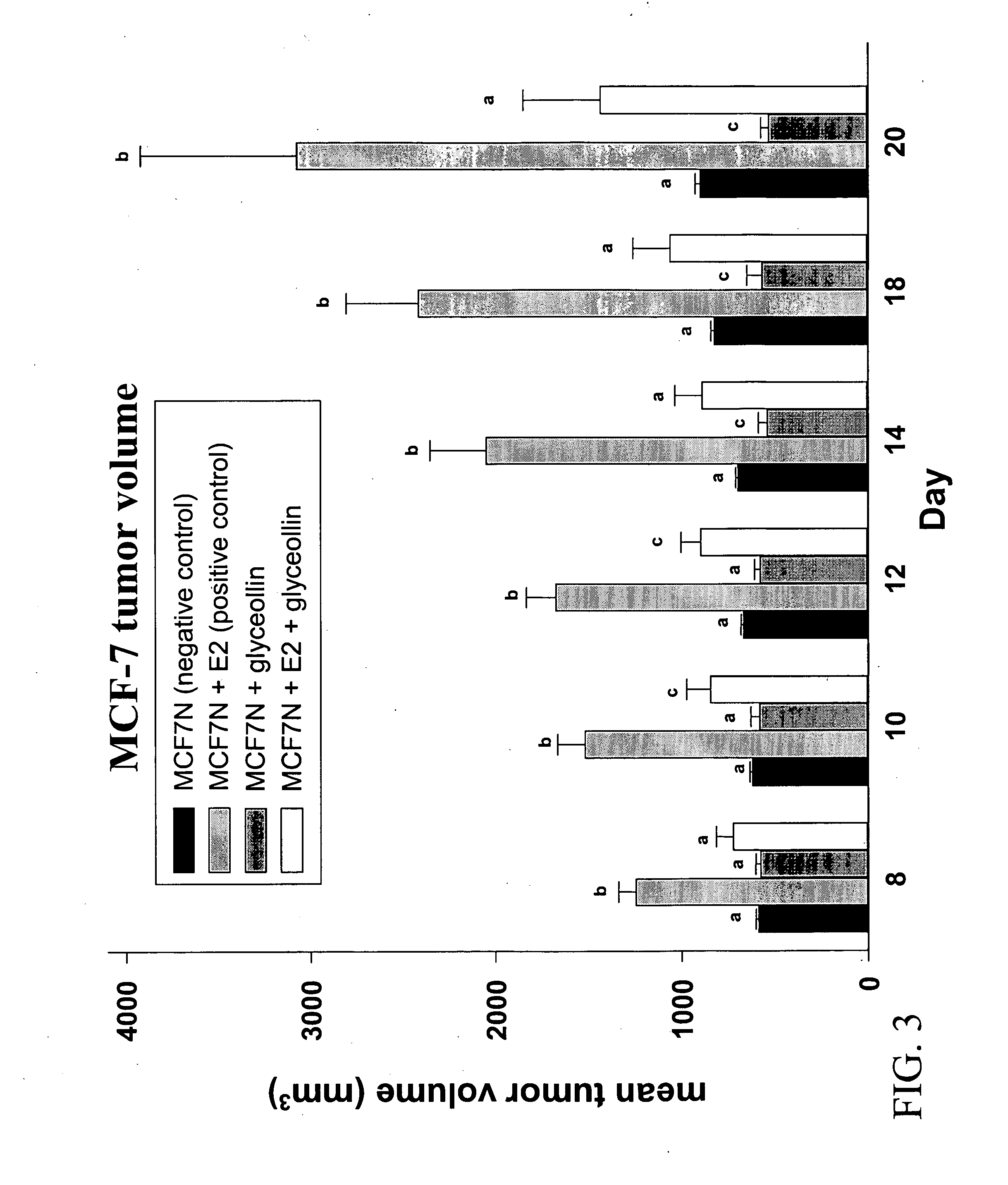
The flavonoid family of phytochemicals, particularly those derived from soy, has received attention regarding their hormonal activity and their effects on human health and disease. The types and amounts of these compounds in soy and other plants are controlled by both constitutive expression and stress-induced biosynthesis. The health benefits of soy may therefore be dependent upon the amounts of the various hormonally active phytochemicals present. We have identified increased biosynthesis of the isoflavonoid phytoalexin compounds, Glyceollins I, II and III, in soy plants grown under stressed conditions (elicited soy), which exhibit marked anti-estrogenic effects on ER function. Here we demonstrate that specific glyceollins, isolated from elicited soy, displayed anti-estrogenic activity, suppressing basal and estrogen stimulated colony formation of ER-positive estrogen dependent breast cancer cells and inhibiting ER-dependent gene expression of progesterone receptor (PgR) and stromal derived factor-1 (SDF1 / CXCL12). Examining the effects of glyceollin on in vivo tumor formation / growth we demonstrate the ability of glyceollins to significantly suppress basal and estrogen-stimulated tumor growth of ER-positive MCF-7 breast and BG-1 ovarian carcinoma cells in ovariectomized female nude mice. We further demonstrate that the effects of glyceollins on suppression of tumor growth correlate with inhibition of estrogen stimulated PgR expression. In contrast to the uterotropic activity of tamoxifen the glyceollins displayed no uterine agonist activity. The Glyceollin (I-III) compounds may represent an important component of the health effects of soy as well as represent novel anti-estrogens useful in the prevention or treatment of breast and ovarian carcinoma.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF AGRI THE
Immunodeficient mouse model constructed by utilizing NK/T lymphoma cell strain
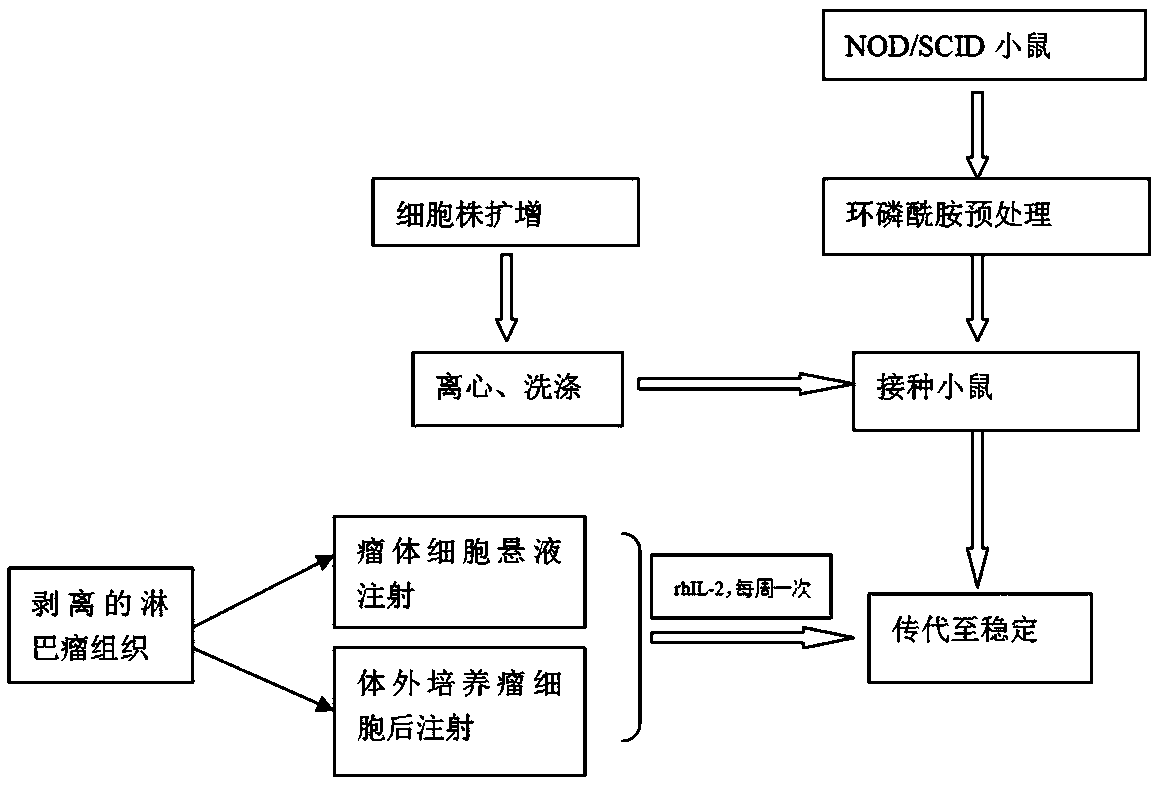
PendingCN108753831ATumor fastHigh tumor formation rateCompounds screening/testingMicroinjection basedCulture fluidCell strain
The application belongs to the technical field of construction of animal tumor models, and particularly relates to a stably passaged immunodeficient mouse model constructed by utilizing an NK / T lymphoma cell strain and a construction method of the model. The method comprises the following steps: pretreating an innoculation object and a lymphoma cell strain respectively, preparing tumor suspensionfor injecting into a mouse, enabling tumor cells to passage and the like. The immunodeficient mouse model can be used for drug screening or therapeutic effect evaluation in medical science. The construction method for constructing the lymphoma animal model by utilizing the NK / T lymphoma cell strain, which is provided by the application, utilizes the fixing effect of matrigel, can be used for fixing lymphoma cells beneath skin, so that the tumor formation rate of the mouse is ensured, and the technical advantages of fast tumor formation and high tumor formation rate are manifested; on the otherhand, in the process of passage, the method cooperates with the cryopreserved operation of a relevant tumor tissue culture solution, and the lymphoma animal model for passage can be recovered at anymoment and directly constructed.
Owner:THE FIRST AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF ZHENGZHOU UNIV
In-vivo tumor engineering human oophoroma tumor model established on basis of collagen aquogel
InactiveCN103497931ASimple methodGood repeatabilityTumor/cancer cellsAnimal husbandryCancer cellMalignancy
The invention discloses application research of an in-vivo tumor engineering human oophoroma tumor model established on the basis of an injectable collagen aquogel composite human oophoroma cells in a noninvasive subcutaneous injection form to a nude mouse. The injectable collagen aquogel stent used as a substrate material is compounded with human oophoroma cell SKOV3 to noninvasively establish the in-vivo tumor engineering human oophoroma tumor model at the nude mouse subcutaneous tissues; and compared with the traditional human oophoroma tumor model established in an independent cell injection mode under the condition of no stent material, the detection on the tumor model indicates that the malignancy of the human oophoroma tumor established on the basis of the injectable collagen aquogel is higher, and is more approximate to that of the human oophoroma tumor, and the in-vivo tumor model established in such a mode has smaller trauma possibility. The tumor model established by the method has higher tumor formation rate (up to 95%), which is about 15% higher than the traditional mode, thereby providing a more reliable tumor model for further research.
Owner:GUANGXI MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com