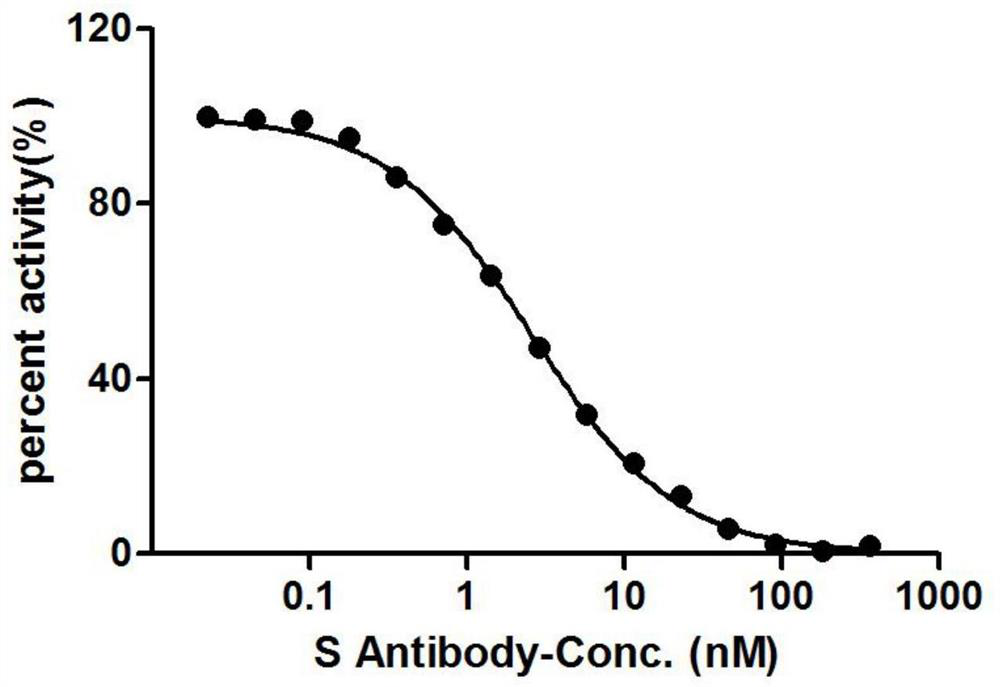
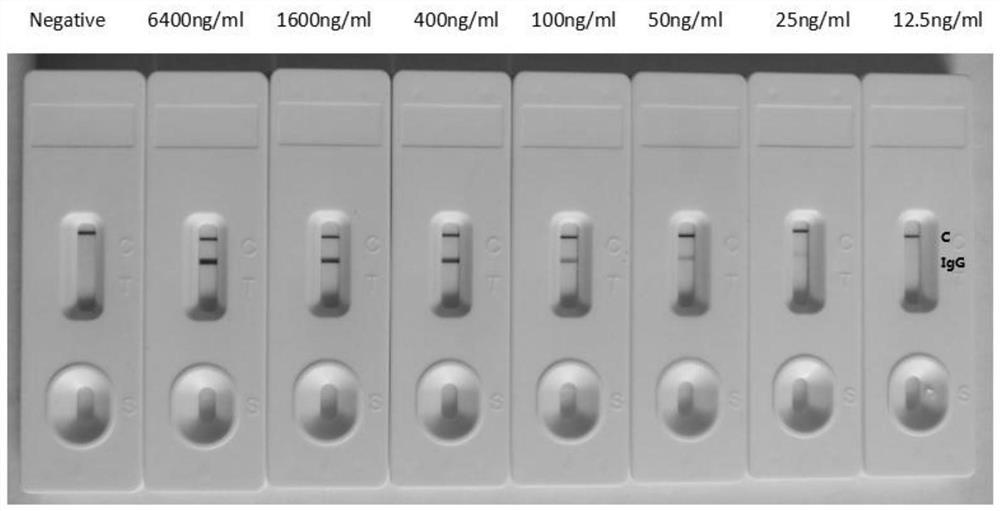
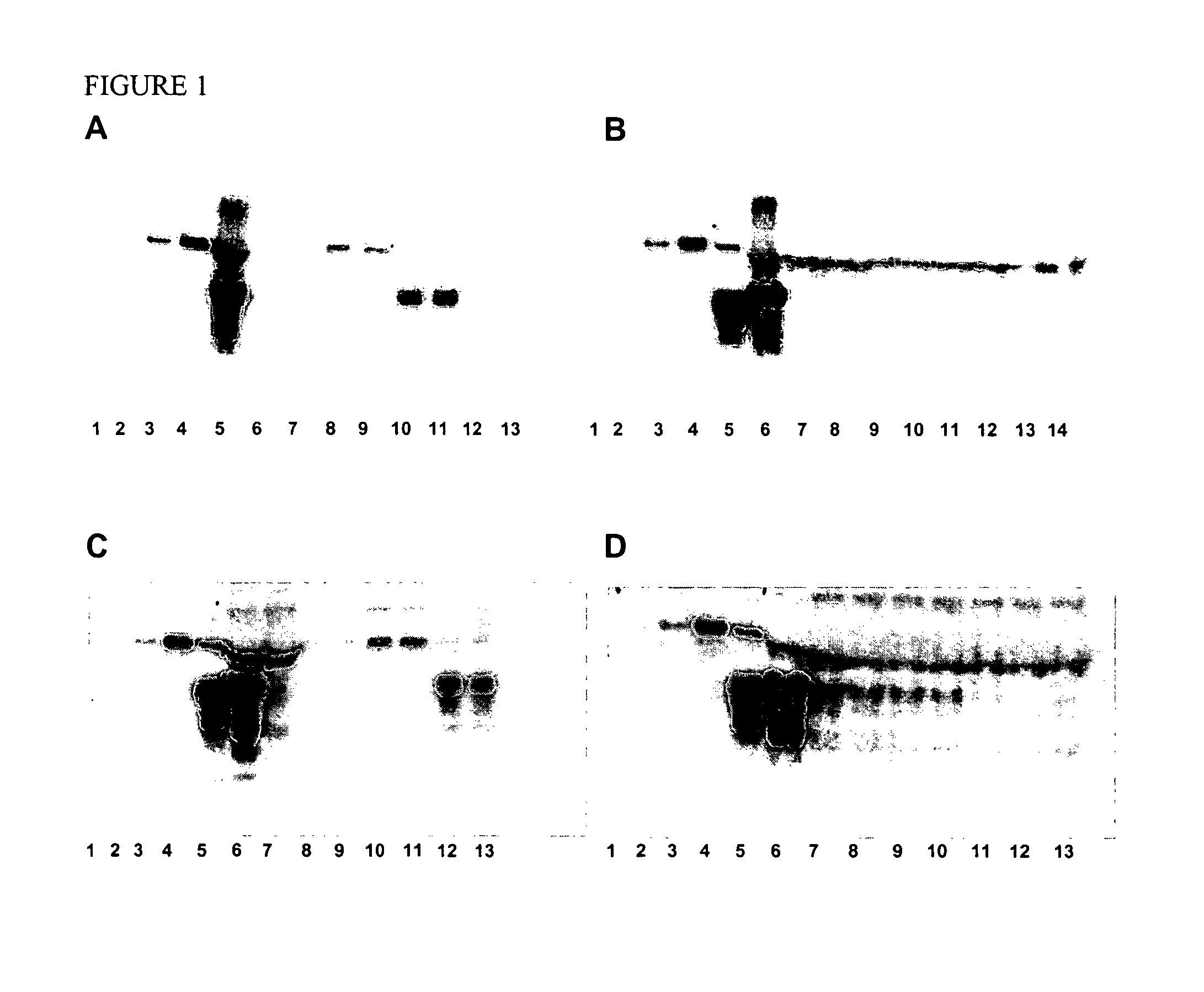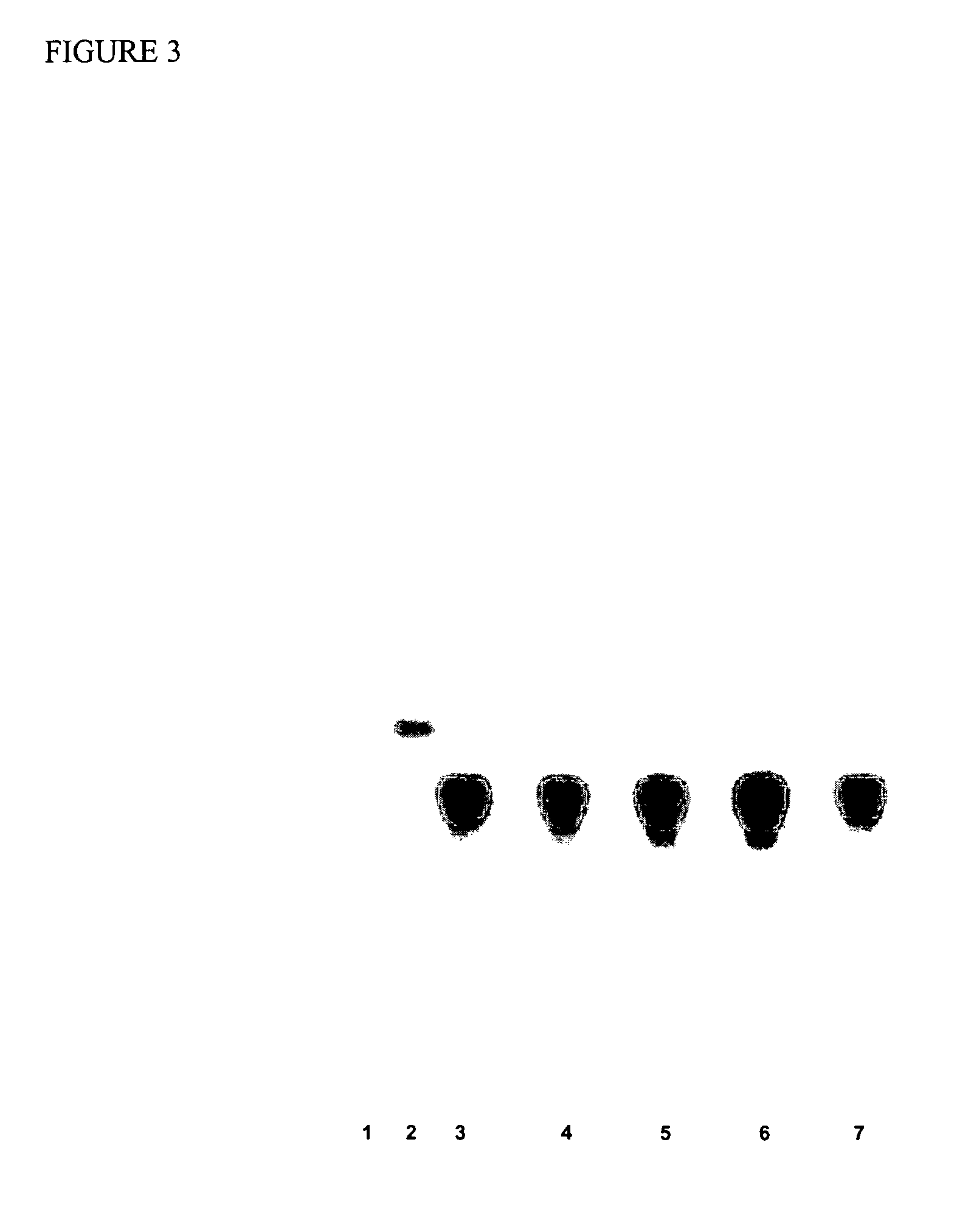Patents
Literature
649 results about "Viral protein" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A viral protein is both a component and a product of a virus. Viral proteins are grouped according to their functions, and groups of viral proteins include structural proteins, nonstructural proteins, regulatory, and accessory proteins. Viruses are non-living and they do not have the means to reproduce on their own. They depend on their host cell's metabolism for energy, enzymes, and precursors, in order to reproduce. As such, viruses do not code for many of their own viral proteins, but rather, they use the host cell's machinery to produce the viral proteins they require for replication.
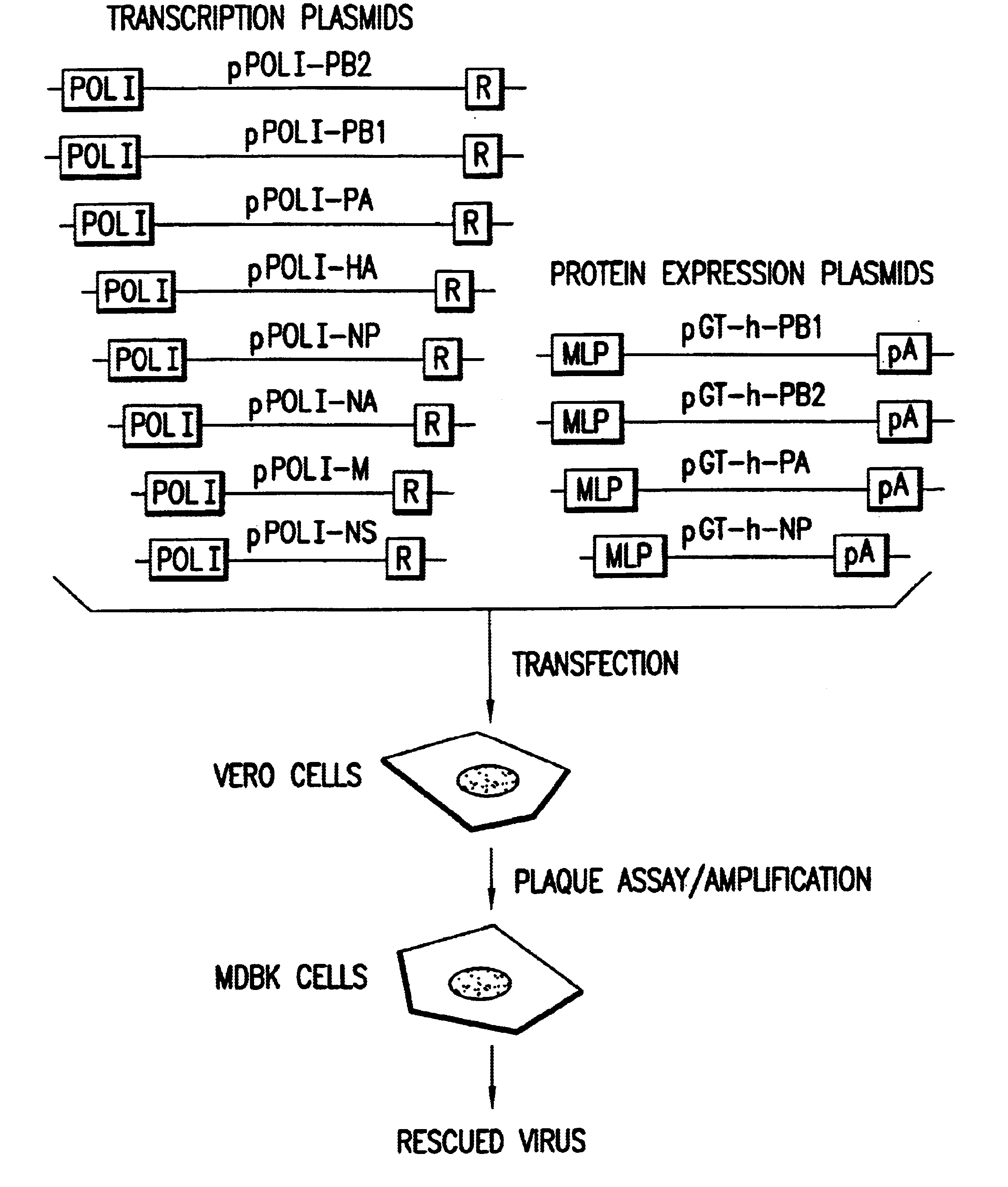
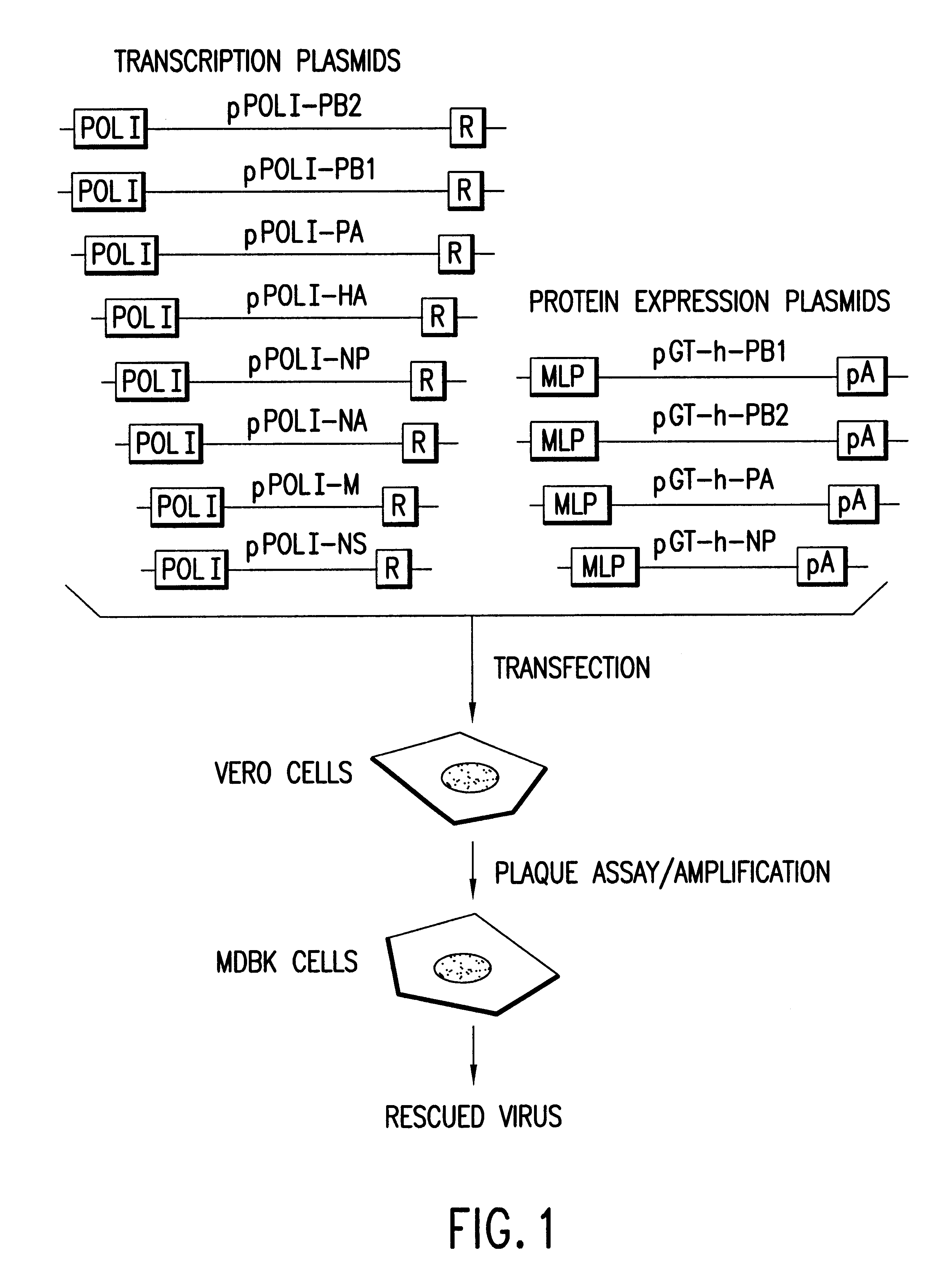
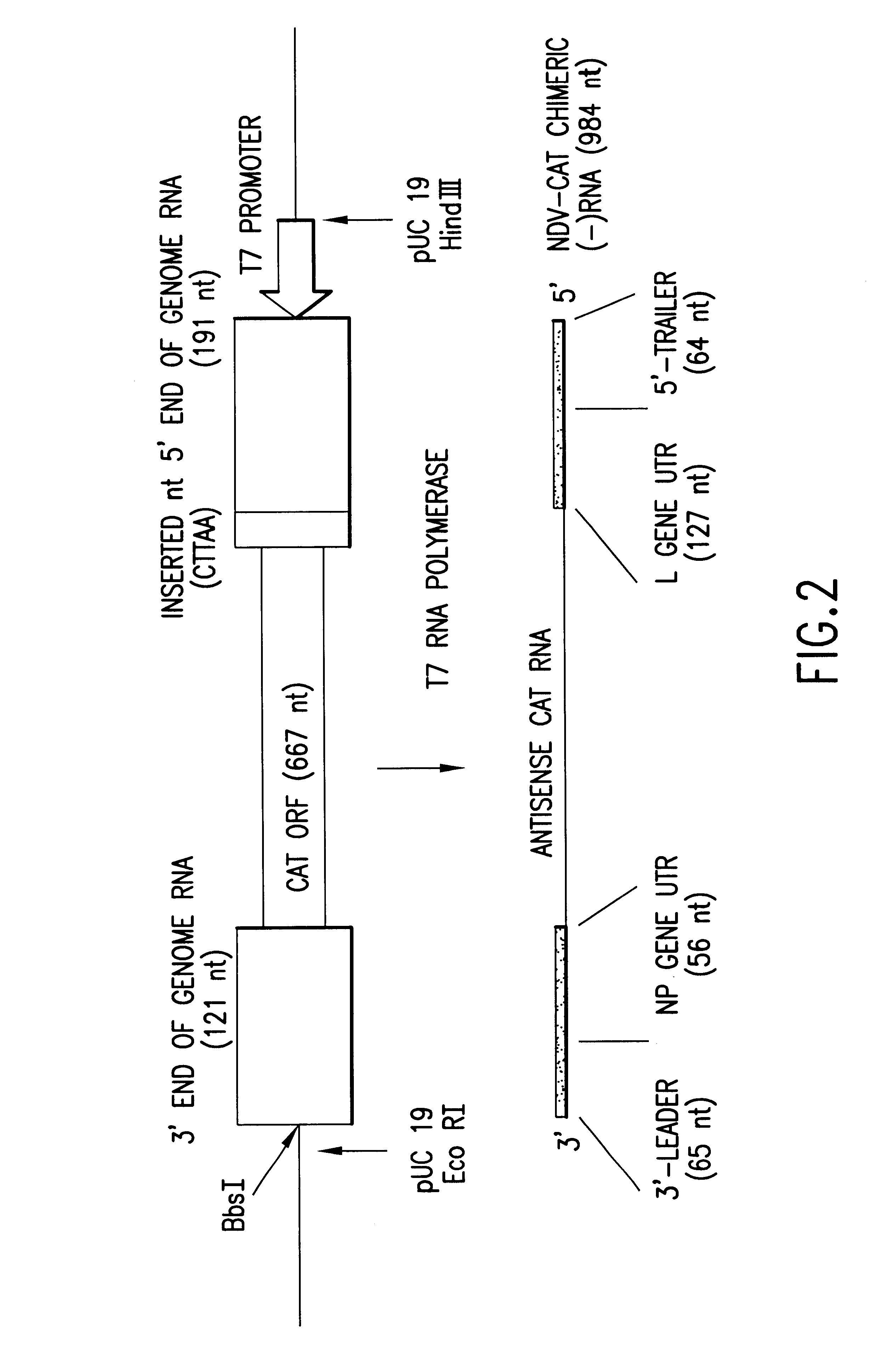
Helper-free rescue of recombinant negative strand RNA virus
Owner:MT SINAI SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Helper-free rescue of recombinant negative strand RNA viruses
InactiveUS6544785B1SsRNA viruses negative-senseGenetic material ingredientsNegative strandNucleic acid sequence
The present invention relates methods of generating infectious negative-strand virus in host cells by an entirely vector-based system without the aid of a helper virus. In particular, the present invention relates methods of generating infectious recombinant negative-strand RNA viruses intracellularly in the absence of helper virus from expression vectors comprising cDNAs encoding the viral proteins necessary to form ribonucleoprotein complexes (RNPs) and expression vectors comprising cDNA for genomic viral RNA(s) (vRNAs) or the corresponding cRNA(s). The present invention also relates to methods of generating infectious recombinant negative-strand RNA viruses which have mutations in viral genes and / or which express, package and / or present peptides or polypeptides encoded by heterologous nucleic acid sequences. The present invention further relates the use of the recombinant negative-strand RNA viruses or chimeric negative-strand RNA viruses of the invention in vaccine formulations and pharmaceutical compositions.
Owner:MT SINAI SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Screening methods to identify agents that selectively inhibit hepatitis C virus replication
InactiveUS6030785APrevent dimerizationBlock viral inhibitionFungiSsRNA viruses positive-senseCellular defenseViral infection
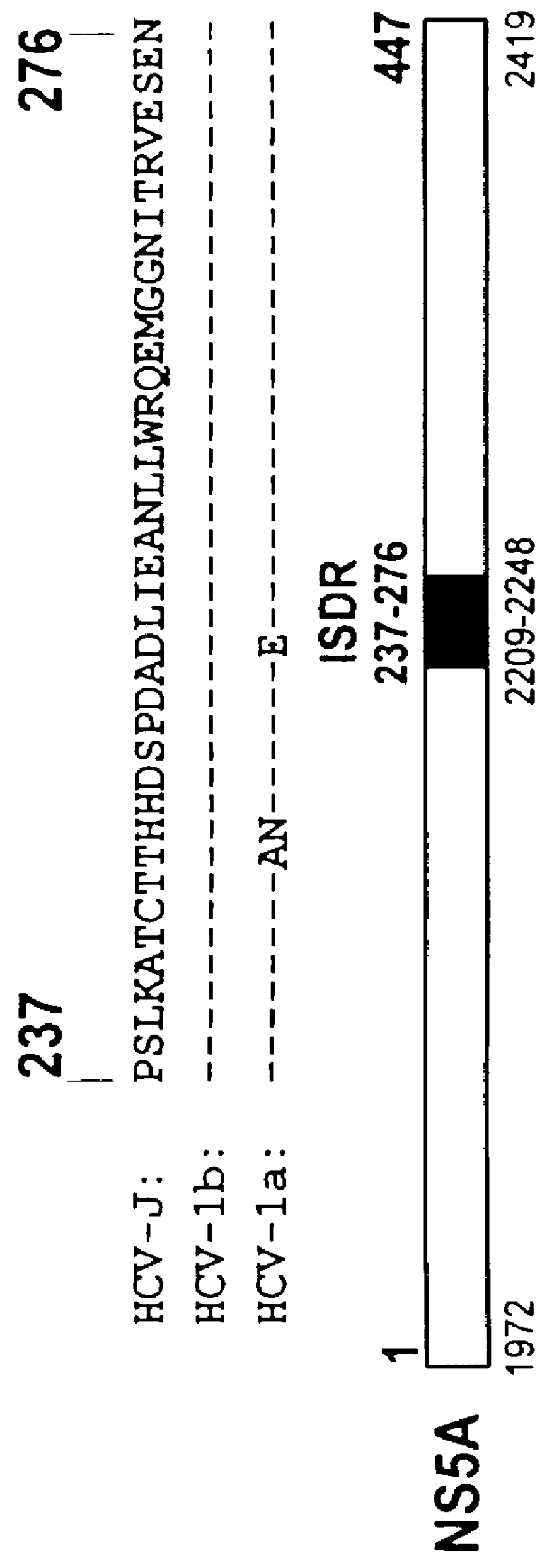
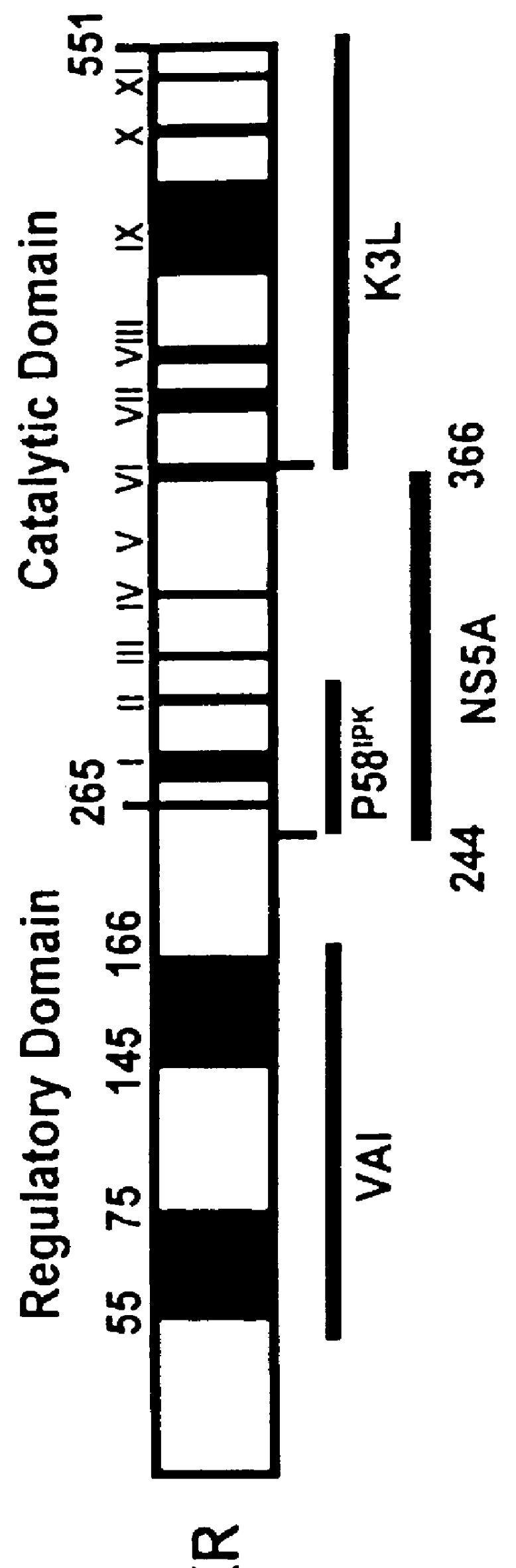
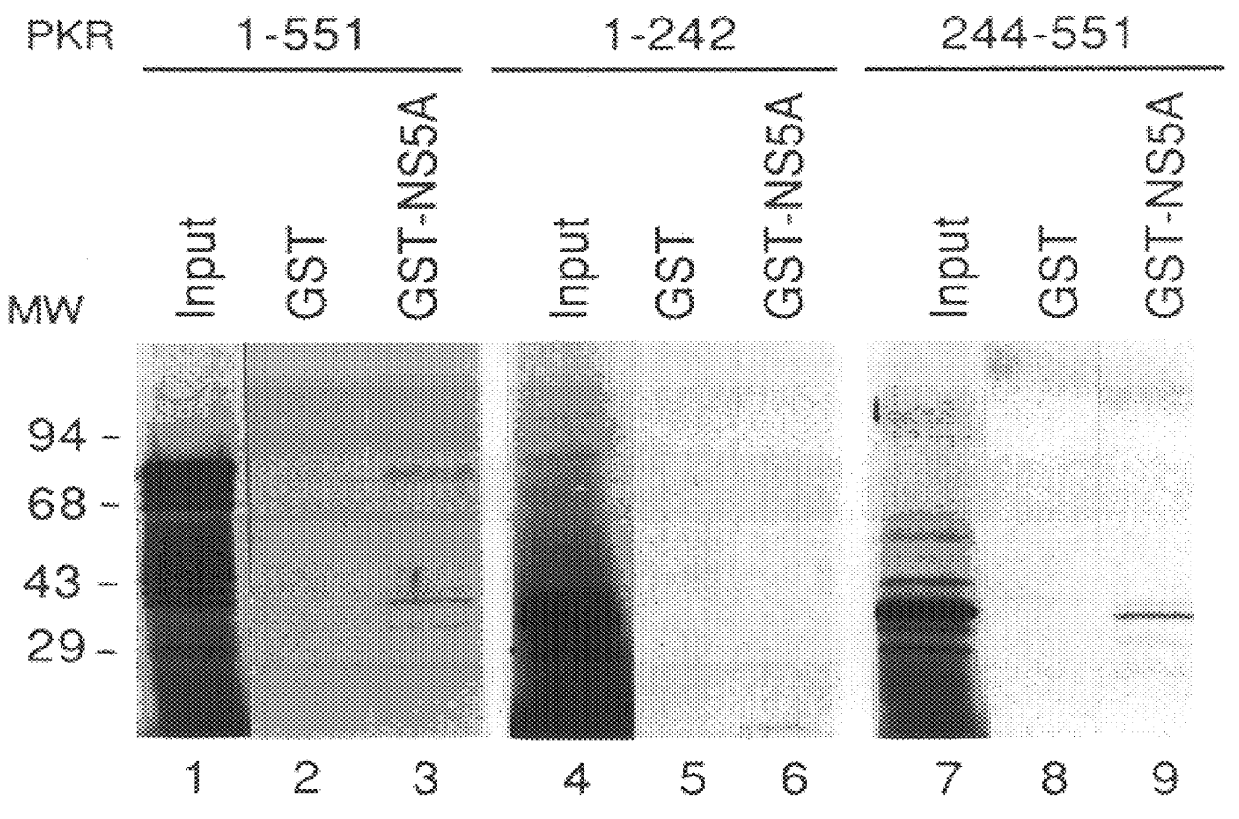
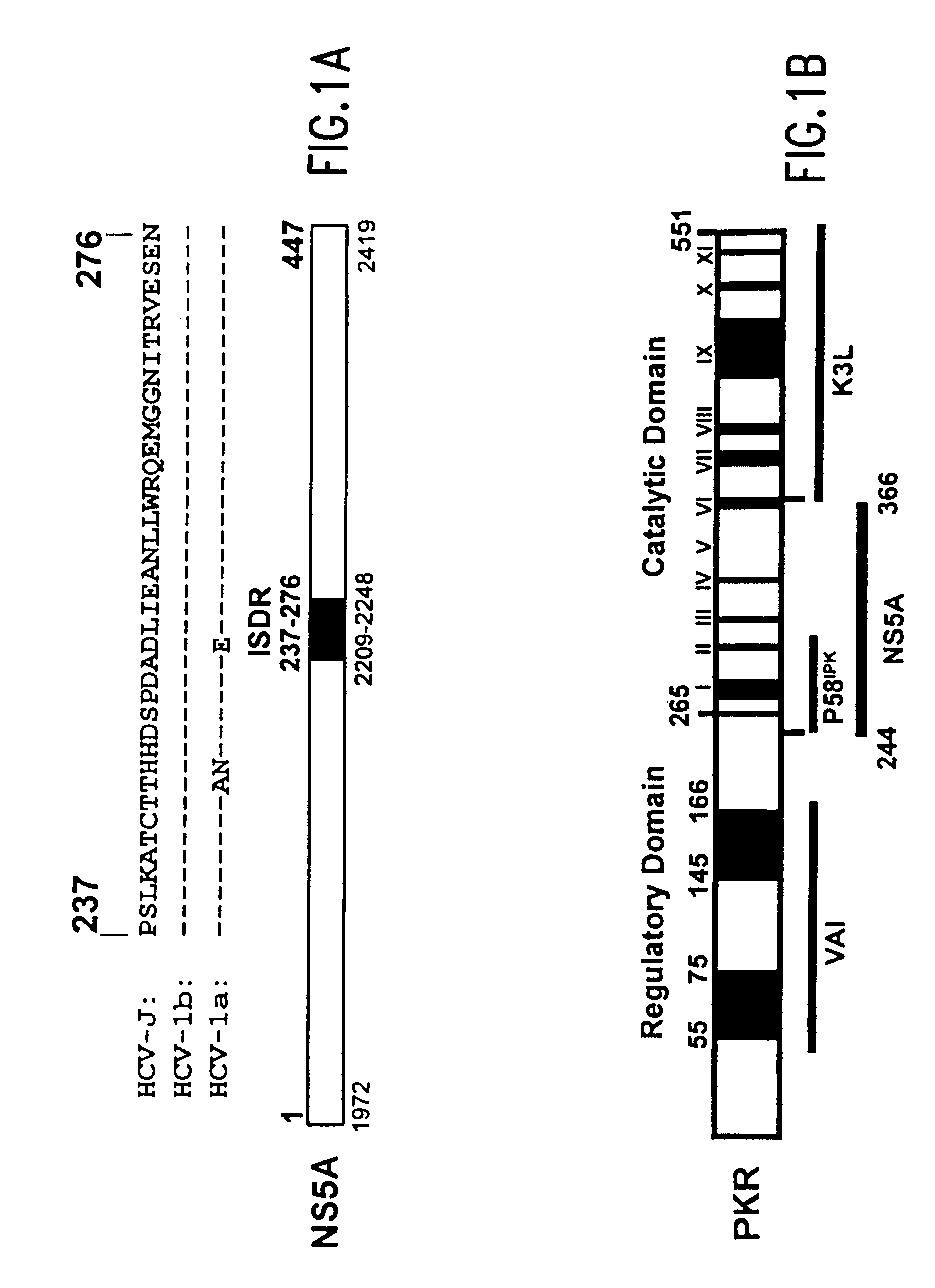
The present invention relates to novel methods for identifying antiviral agents which selectively interfere with viral proteins that override the interferon(IFN)-induced cellular defense mechanisms against viral infection. In particular, the present invention relates to screening assays that identify agents which selectively inhibit the interaction between viral proteins containing an interferon sensitivity determining region (ISDR) and IFN-induced PKR protein kinase. The present invention more particularly relates to screening assays that identify agents which selectively inhibit the interaction between hepatitis C virus (HCV) nonstructural 5A protein (NS5A), which contains an ISDR, and IFN-induced PKR protein kinase. The interaction between the viral ISDR and IFN-induced PKR protein kinase results in the override of IFN-induced cellular defense mechanisms to combat viral infection. Therefore the agents identified using the assays of the invention may have utility as antiviral agents.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON
Interferon inducing genetically engineered attenuated viruses
InactiveUS6468544B1Reduce in quantityReduced characteristicsSsRNA viruses negative-senseVectorsGenetic engineeringRecombinant DNA
The present invention relates to genetically engineered attenuated viruses and methods for their production. In particular, the present invention relates to engineering live attenuated viruses which contain a modified NS gene segment. Recombinant DNA techniques can be utilized to engineer site specific mutations into one or more noncoding regions of the viral genome which result in the down-regulation of one or more viral genes. Alternatively, recombinant DNA techniques can be used to engineer a mutation, including but not limited to an insertion, deletion, or substitution of an amino acid residue(s) or an epitope(s) into a coding region of the viral genome so that altered or chimeric viral proteins are expressed by the engineered virus.
Owner:MT SINAI SCHOOL OF MEDICINE +1
Method and kit for extracting prion protein
InactiveUS6150172AMethod is fastThe testing process is simplePeptide preparation methodsDepsipeptidesIonic strengthSheep brain
A method for extracting prion protein from a biological material, e.g., an animal tissue or product. In a specific example, abnormal prion protein is extracted from homogenized sheep brain with hexafluoro-2-propanol. The hexafluoro-2-propanol is separated from the aqueous brain preparation by increasing the ionic strength of the aqueous solution. Prion protein in the organic extract can be further purified, or the extract can be tested, e.g., by immunoassay, for the presence of prion protein, and more particularly abnormal prion protein. The extraction process permits testing for the presence of abnormal prior protein, e.g., for diagnosis of transmissible spongiform encephalopathies (TSE).
Owner:US SEC AGRI
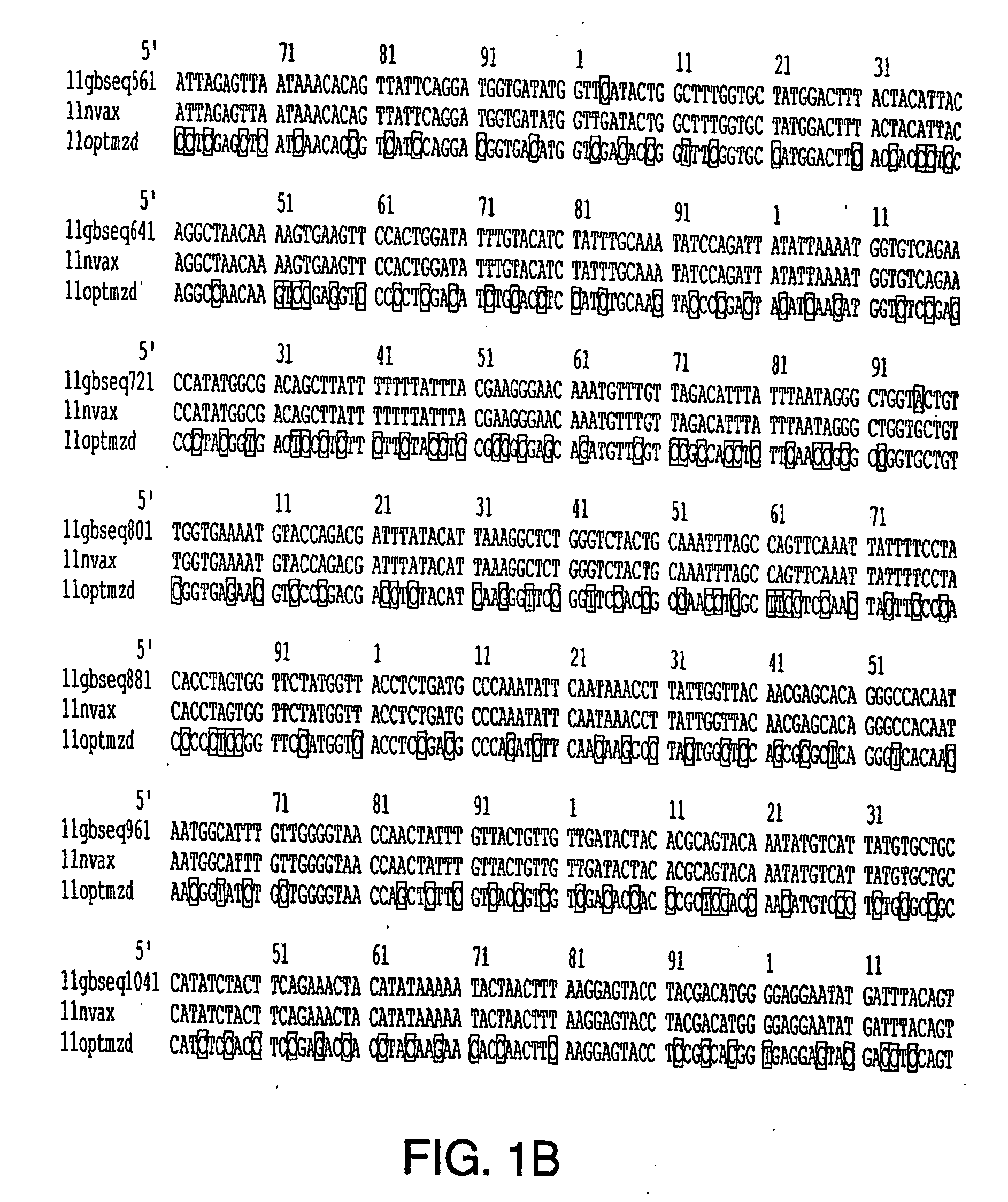
Optimization of gene sequences of chimeric virus-like particles for expression in insect cells
InactiveUS20050118191A1Minimize the numberSequence minimizedAnimal cellsViral antigen ingredientsDiagnostic testTGE VACCINE
Owner:NOVAVAX
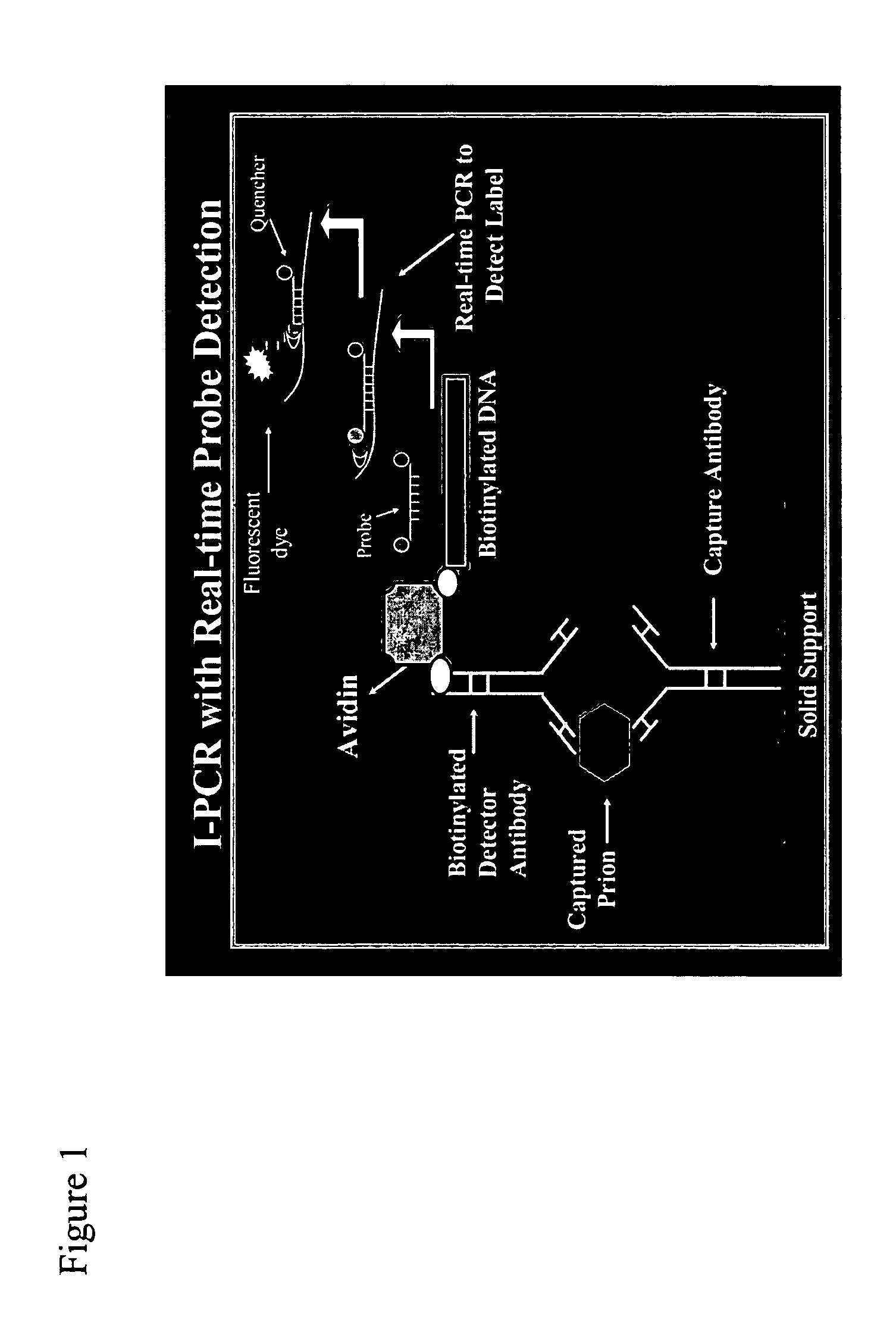
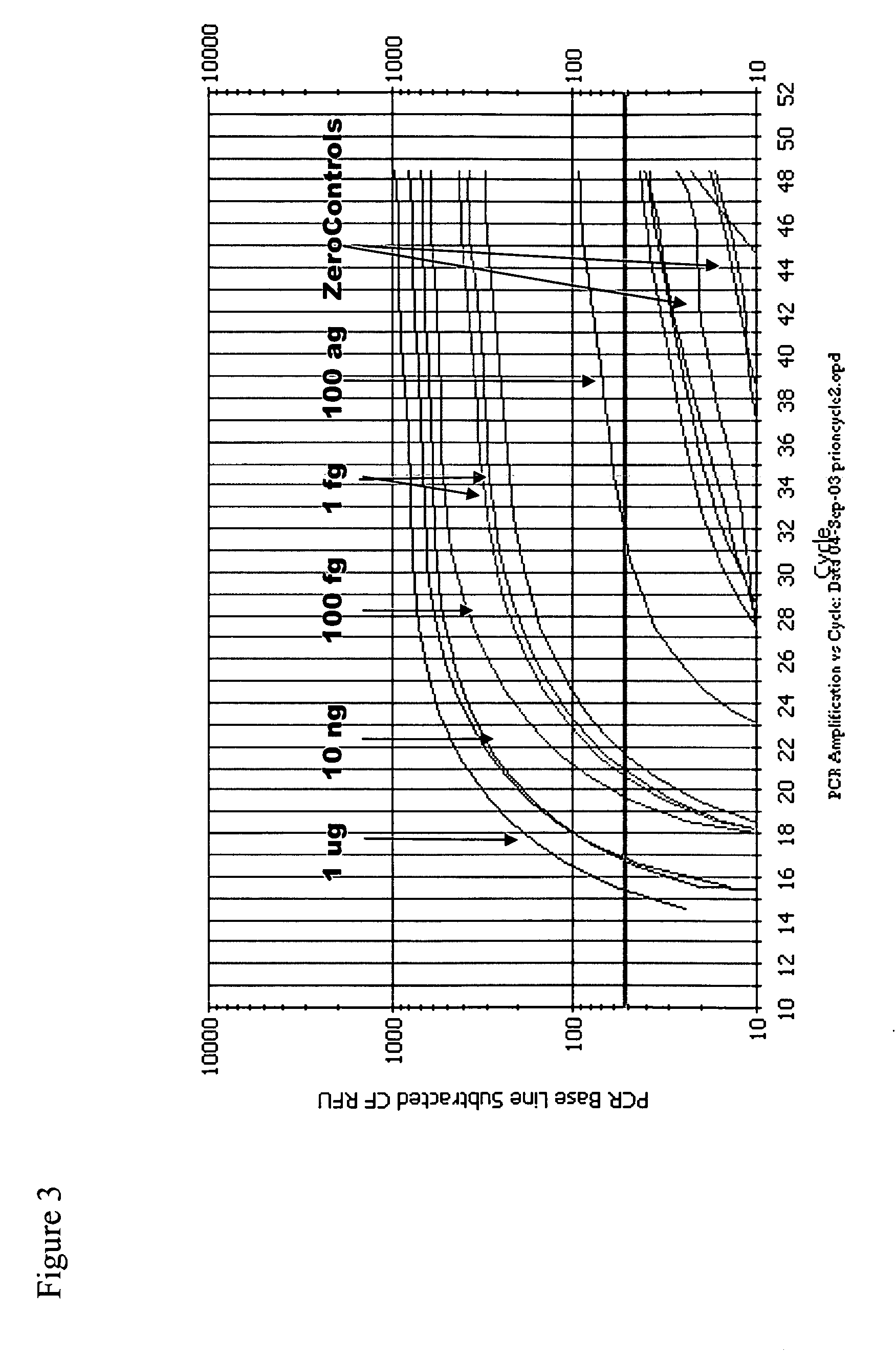
Immuno-PCR method for the detection of a biomolecule in a test sample
InactiveUS20050239108A1Simple and highly sensitiveSimple and highly methodMicrobiological testing/measurementAssay labelsHuman bodyNucleic acid amplification technique
The invention relates to methods and kits for detecting and / or monitoring biological molecules in a test sample. For example, the invention relates to methods and kits for detecting and / or monitoring HIV p24 antigen in human body fluid, biological toxins such as ricin or botulism in an environmental or biological sample, and prion protein from human, deer or bovine, such as PrPSC, in a biological sample. The antigen detection signal is boosted by amplification of a polynucleotide linked to a detector molecule using methods for nucleic acid amplification technology.
Owner:UNIV OF MARLAND BALTIMORE +1
Recombinant influenza viruses expressing tumor-associated antigens as antitumor agents
InactiveUS6884414B1Quick changeAvoid problemsSsRNA viruses negative-senseBiocideTumor reductionIn vivo
The present invention relates to the engineering of recombinant influenza viruses that express tumor-associated antigens. Expression of tumor-associated antigens by these viruses can be achieved by engineering specific epitopes into influenza virus proteins, or by engineering viral genes that encode a viral protein and the specific antigen as independent polypeptides. Tumor-bearing patients can be immunized with the recombinant influenza viruses alone, or in combination with another treatment, to induce an immune response that leads to tumor reduction. The recombinant viruses can also be used to vaccinate high risk tumor-free patients to prevent tumor formation in vivo.
Owner:MT SINAI SCHOOL OF MEDICINE +1
Methods for the inhibition of epstein-barr virus transmission employing anti-viral peptides capable of abrogating viral fusion and transmission
InactiveUS6518013B1SsRNA viruses negative-sensePeptide/protein ingredientsCell membraneViral life cycle
Fusion of the viral envelope, or infected cell membranes with uninfected cell membranes, is an essential step in the viral life cycle. Recent studies involving the human immunodeficiency virus type 1(HIV-1) demonstrated that synthetic peptides (designated DP-107 and DP-178) derived from potential helical regions of the transmembrane (TM) protein, gp41, were potent inhibitors of viral fusion and infection. A computerized antiviral searching technology (C.A.S.T.) that detects related structural motifs (e.g., ALLMOTI 5, 107x178x4, and PLZIP) in other viral proteins was employed to identify similar regions in the Epstein-Barr virus (EBV). Several conserved heptad repeat domains that are predicted to form coiled-coil structures with antiviral activity were identified in the EBV genome. Synthetic peptides of 16 to 39 amino acids derived from these regions were prepared and their antiviral activities assessed in a suitable in vitro screening assay. These peptides proved to be potent inhibitors of EBV fusion. Based upon their structural and functional equivalence to the known HIV-1 inhibitors DP-107 and DP-178, these peptides should provide a novel approach to the development of targeted therapies for the treatment of EBV infections.
Owner:TRIMERIS
RNA respiratory syncytial virus vaccines
InactiveUS6060308AFaster replicationImprove efficiencySsRNA viruses negative-senseBiocideF proteinViral Vaccine
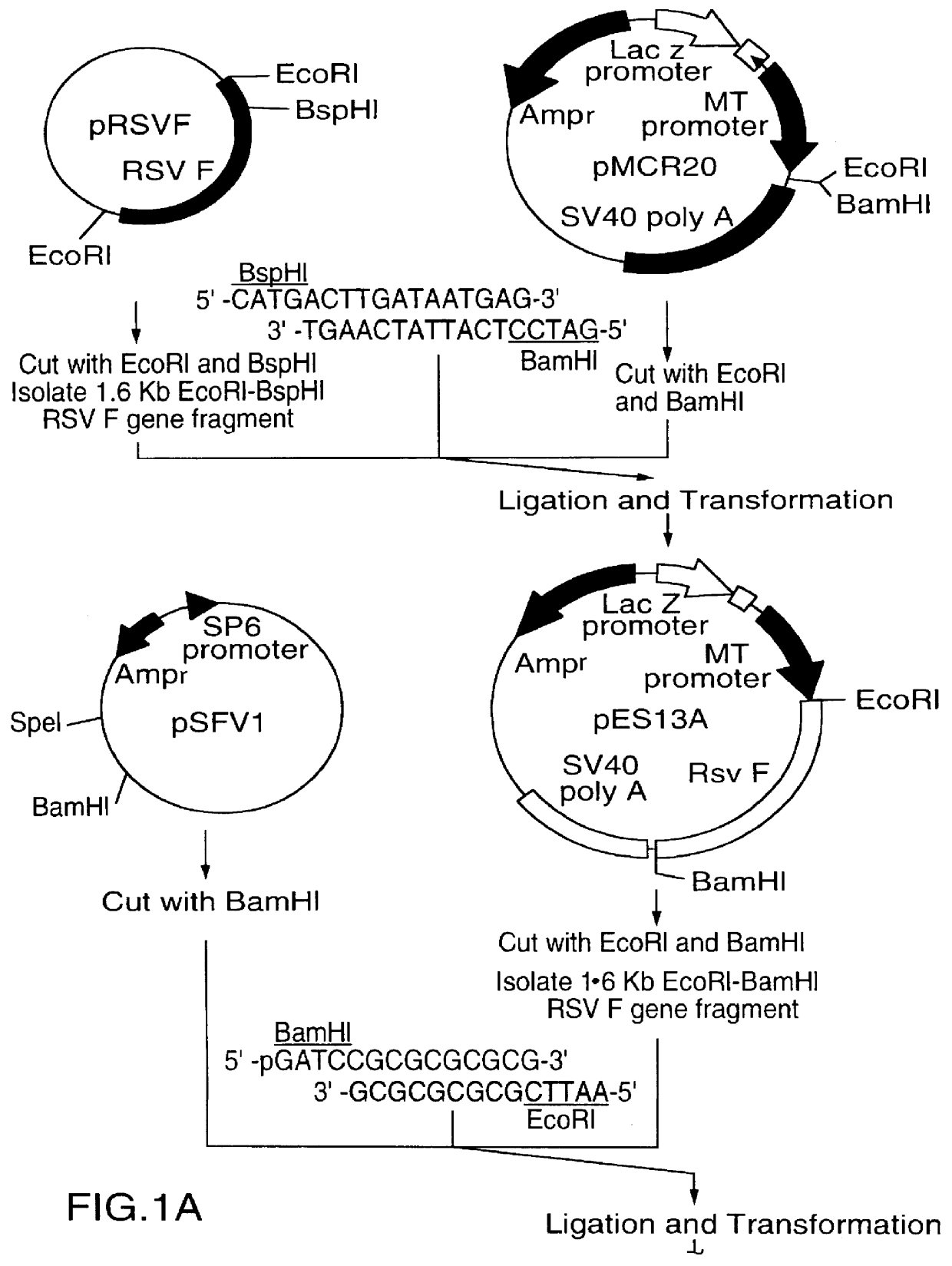
A vector comprising a first DNA sequence which is complementary to at least part of an alphavirus RNA genome and having the complement of complete alphavirus DNA genome replication regions, a second DNA sequence encoding a paramyxovirus protein, particularly a respiratory syncytial virus fusion (RSV F) protein or a RSV F protein fragment that generates antibodies that specifically react with RSV F protein, the first and second DNA sequences being under the transcriptional control of a promoter is described. Such vector may be used to produce an RNA transcript which may be used to immunize a host, including a human host, to protect the host against disease caused by paramyxovirus, particularly respiratory syncytial virus, by administration to the host.
Owner:CONNAUGHT LAB
Method to measure and characterize microvesicles in the human body fluids
InactiveUS20090220944A1Low efficiencySimple yet reliableMicrobiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisHuman bodyNon invasive
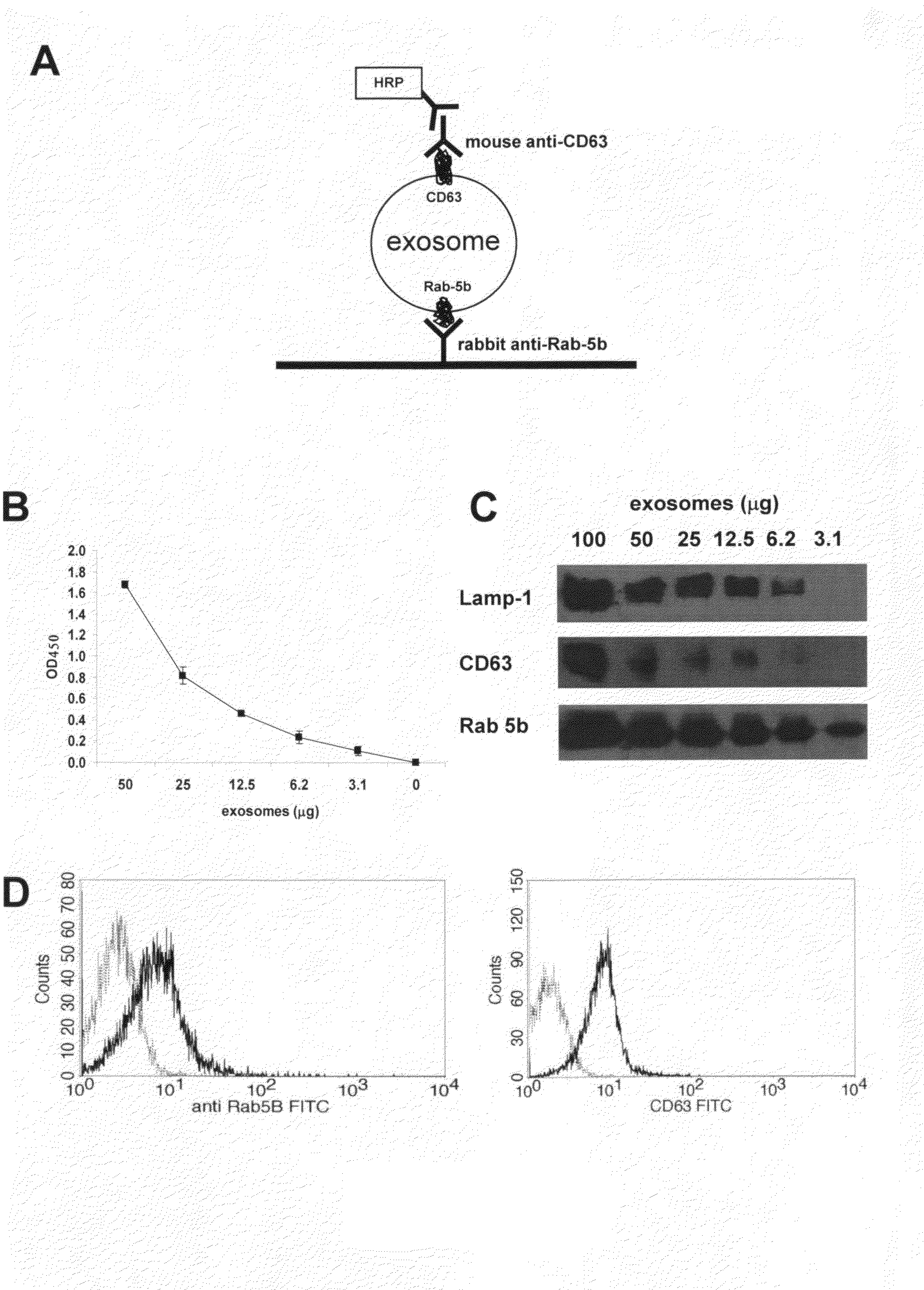
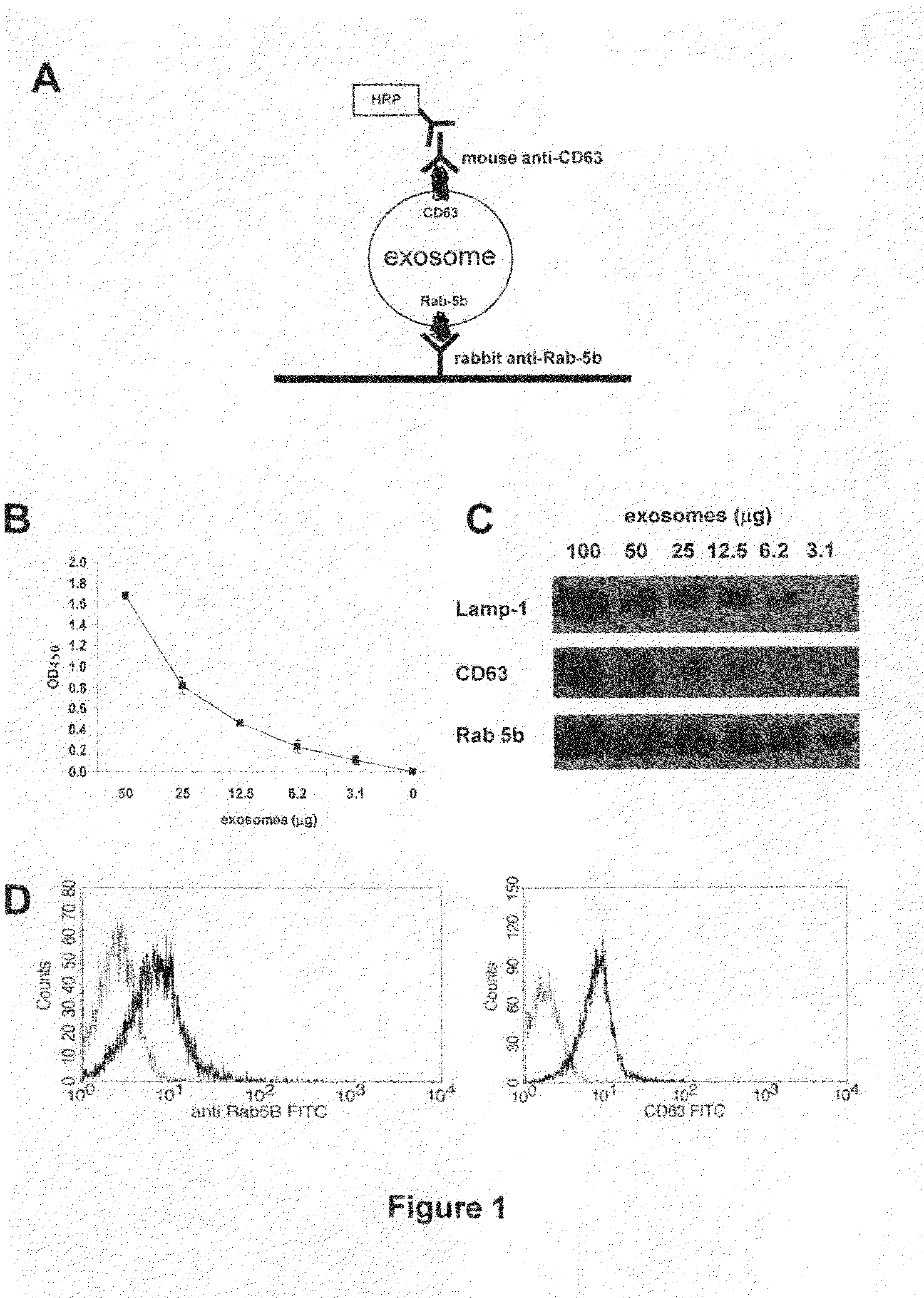
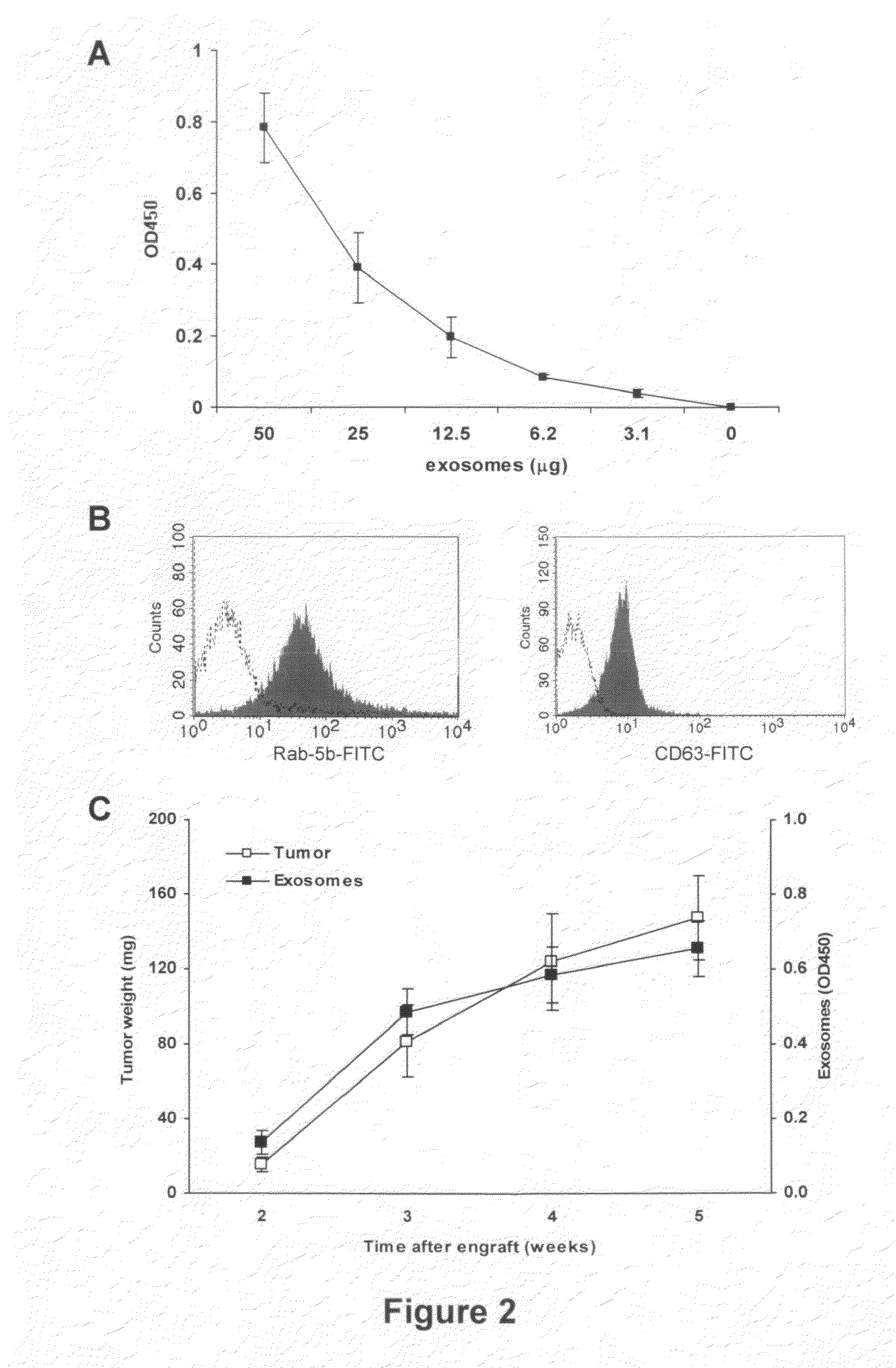
This disclosure provides a method to capture, detect, characterize and quantify human exosomes in small volumes of human body fluids by using a sandwich ELISA test. This method allows a full characterization of an exosome preparation, thus providing a tool to distinguish a disease-related condition from a healthy state, by the use of a non-invasive assay. In fact, this method may be useful in screening, diagnosis and prognosis of tumors, with a simple plasma sample. At the same time measurement of circulating exosomes may provide information on the level of tumor mass present in a patient. The method provided here is suitable to evaluate presence of some infectious and / or transmissible agents, such as viral proteins or prion proteins, within circulating exosomes.
Owner:EXOSOMICS SPA
Baculoviral vectors comprising repeated coding sequences with differential codon biases
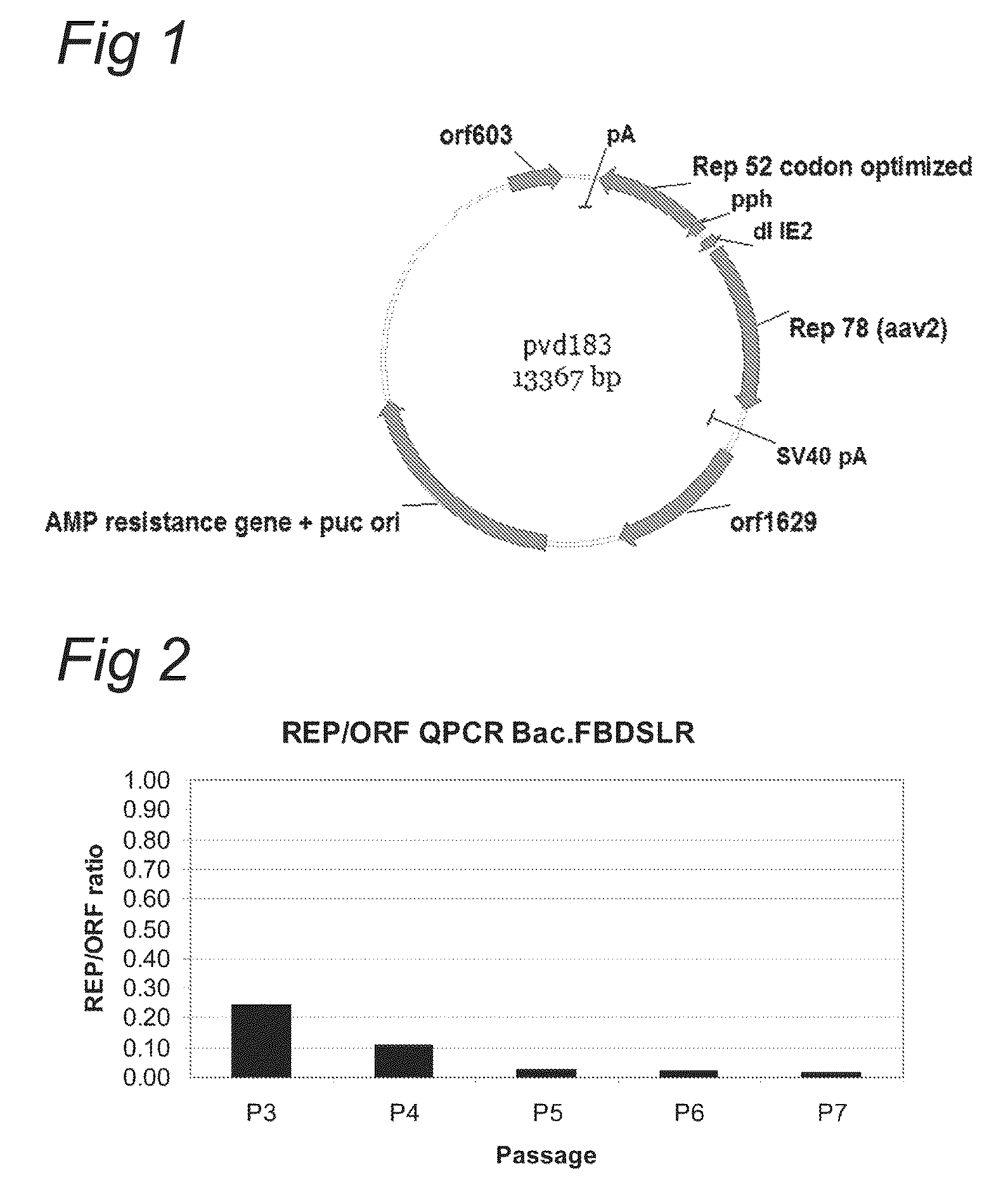
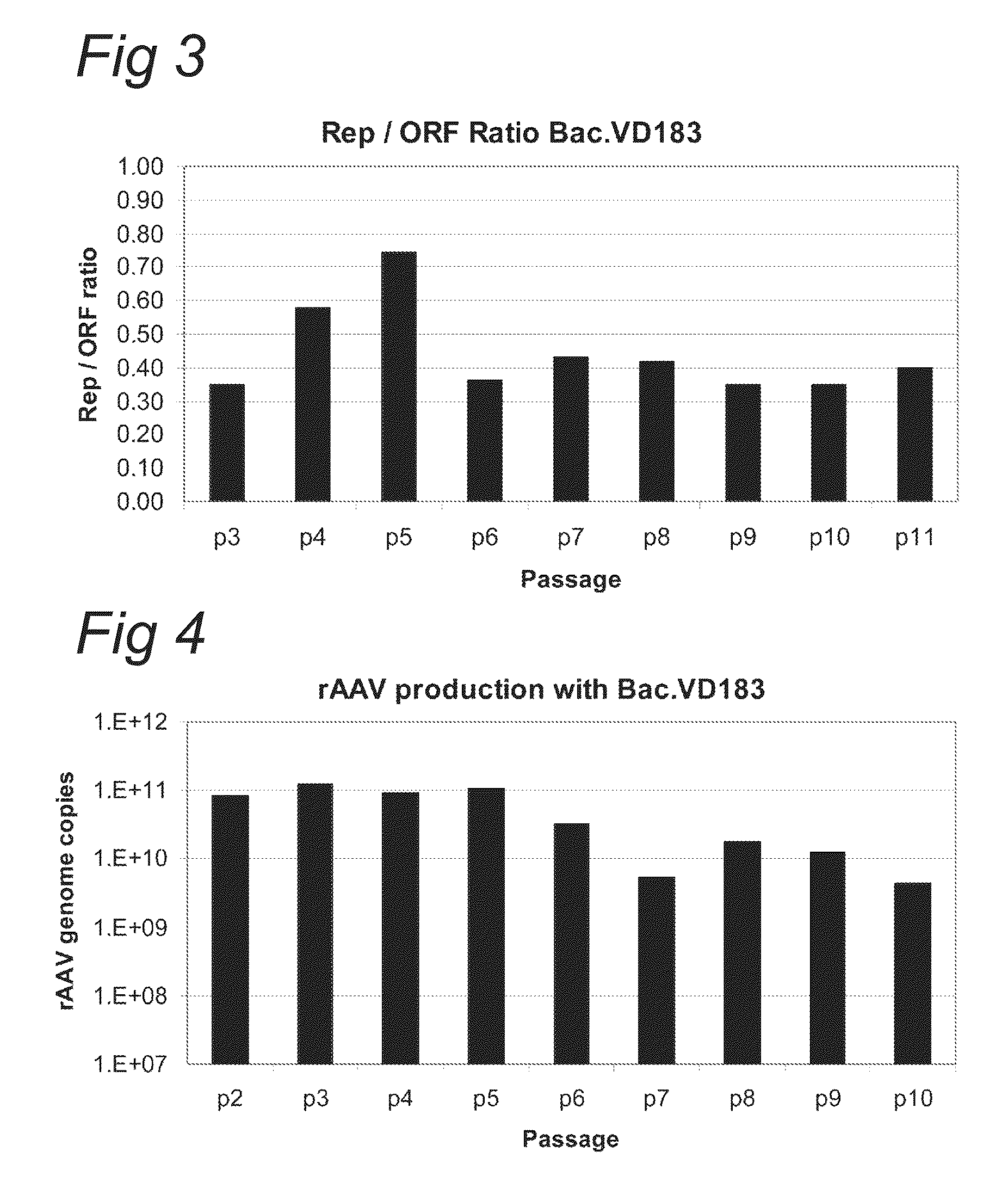
ActiveUS8697417B2Improve stabilityReduced expression levelAnimal cellsSugar derivativesViral vectorParvovirus
The present invention relates to production of proteins in insect cells whereby repeated coding sequences are used in baculoviral vectors. In particular the invention relates to the production of parvoviral vectors that may be used in gene therapy and to improvements in expression of the viral rep proteins that increase the productivity of parvoviral vectors.
Owner:UNIQURE IP BV
SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing antibody detection kit
PendingCN111562369AGood repeatabilityStrong specificityImmunoassaysImmunodiagnosticsProtein s antigen
The invention relates to an SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing antibody detection kit. The SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing antibody detection kit comprises a solid phase carrier, an S protein antigen of SARS-CoV-2 and acompetitive substance. The competitive substance is marked with a signal substance and can be specifically combined with the new coronavirus S protein antigen. Whether a tested person is infected bythe new coronavirus or not and whether infection risks exist or not are judged by detecting a neutralizing antibody through an immunodiagnosis technology, and the method is reliable in theory, practical and feasible and can be completed only in a secondary biosafety laboratory.
Owner:威海威高生物科技有限公司
Optimization of expression of parvoviral rep and cap proteins in insect cells
The present invention relates to the improved production of recombinant parvoviral virions in insect cells. In particular, the invention relates to an improved process for the production of recombinant parvoviral virions in insect cells, wherein the full / empty parvoviral virion ratio is increased. The invention also relates to the production of parvoviral vectors that may be used in gene therapy and to improvements in expression of the viral Rep proteins that increase the productivity of parvoviral vectors.
Owner:UNIQURE IP BV
Two-step immunization procedure against the pyramyxoviridae family of viruses using recombinant virus and subunit protein preparation
InactiveUS6180398B1Improve the level ofSlow and sustained releaseSsRNA viruses negative-senseViral antigen ingredientsDiseaseProtection sex
An immunization strategy to provide protection against disease caused by infection with a paramyxoviridae virus, specifically respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) and parainfluenza virus, is described. A priming intranasal administration of a recombinant virus expressing at least one RSV or PIV protein or immunogenic sequence there first is made to the host followed by a booster administration of at least one purified RSV or PIV protein or immunogenic fragment thereof, which may be adjuvanted with alum. This immunization strategy provides a safe and effective means of controlling RSV and PIV infections. The strategy leads to a stronger protective immune response than other strategies and to the induction of a more balanced Th-1 / Th-2 type response than previously attained. Novel recombinant poxviruses are provided containing nucleic acid encoding a paramyxovirus protein or immunogenic fragment thereof is a non-essential region of the poxvirus genome, specifically NYVAC-F and ALVAC-F, which produce the F glycoprotein of RSV.
Owner:CONNAUGHT LAB +1
Screening methods to identify agents that selectively inhibit hepatitis C virus replication
InactiveUS6326151B1Prevent dimerizationBlock viral inhibitionFungiSsRNA viruses positive-senseCellular defenseViral infection
The present invention relates to novel methods for identifying antiviral agents which selectively interfere with viral proteins that override the interferon(IFN)-induced cellular defense mechanisms against viral infection. In particular, the present invention relates to screening assays that identify agents which selectively inhibit the interaction between viral proteins containing an interferon sensitivity determining region (ISDR) and IFN-induced PKR protein kinase. The present invention more particularly relates to screening assays that identify agents which selectively inhibit the interaction between hepatitis C virus (HCV) nonstructural 5A protein (NS5A), which contains an ISDR, and IFN-induced PKR protein kinase. The interaction between the viral ISDR and IFN-induced PKR protein kinase results in the override of IFN-induced cellular defense mechanisms to combat viral infection. Therefore the agents identified using the assays of the invention may have utility as antiviral agents.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON
Imaging methods and compositions comprising fluorescent dyes associated with viral components for nerve imaging
Disclosed herein are compositions and methods for imaging nerve cells. The composition comprises a fluorescent dye; and a viral component selected from a neurotropic, replication-defective virus, a viral protein of a neurotropic virus, and a capsid of a neurotropic virus. Although the fluorescent dye in itself cannot penetrate nerve cells, the fluorescent dye is bound to the viral component to form a dye / viral component complex that is capable of penetrating nerve cells.
Owner:STRYKER CORP
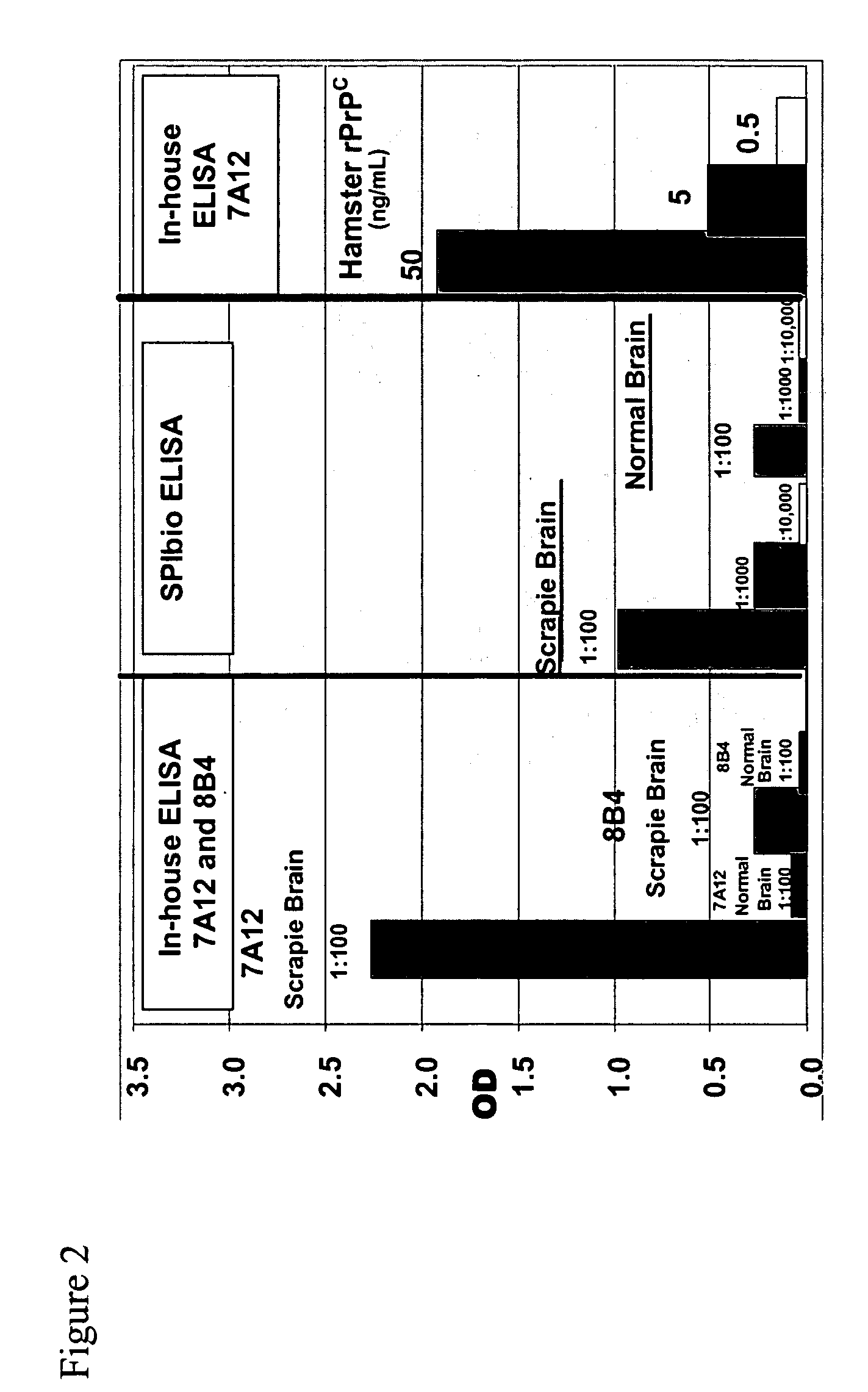
Prion protein binding materials and methods of use
ActiveUS7393658B2Viral antigen ingredientsBiological testingHamsterProteinaceous infectious particle
Prion protein binding materials and methods for using the binding materials to detect or remove a prion protein from a sample, such as a biological fluid or an environmental sample. The binding materials are capable of binding to one or more forms of prion protein including cellular prion protein (PrPc), infectious prion protein (PrPsc), recombinant prion protein (PrPr), and proteinase resistant prion protein (PrPres). Prions from various species, including humans and hamsters, are bound by the binding materials.
Owner:PATHOGEN REMOVAL & DIAGNOSTIC TECH +1
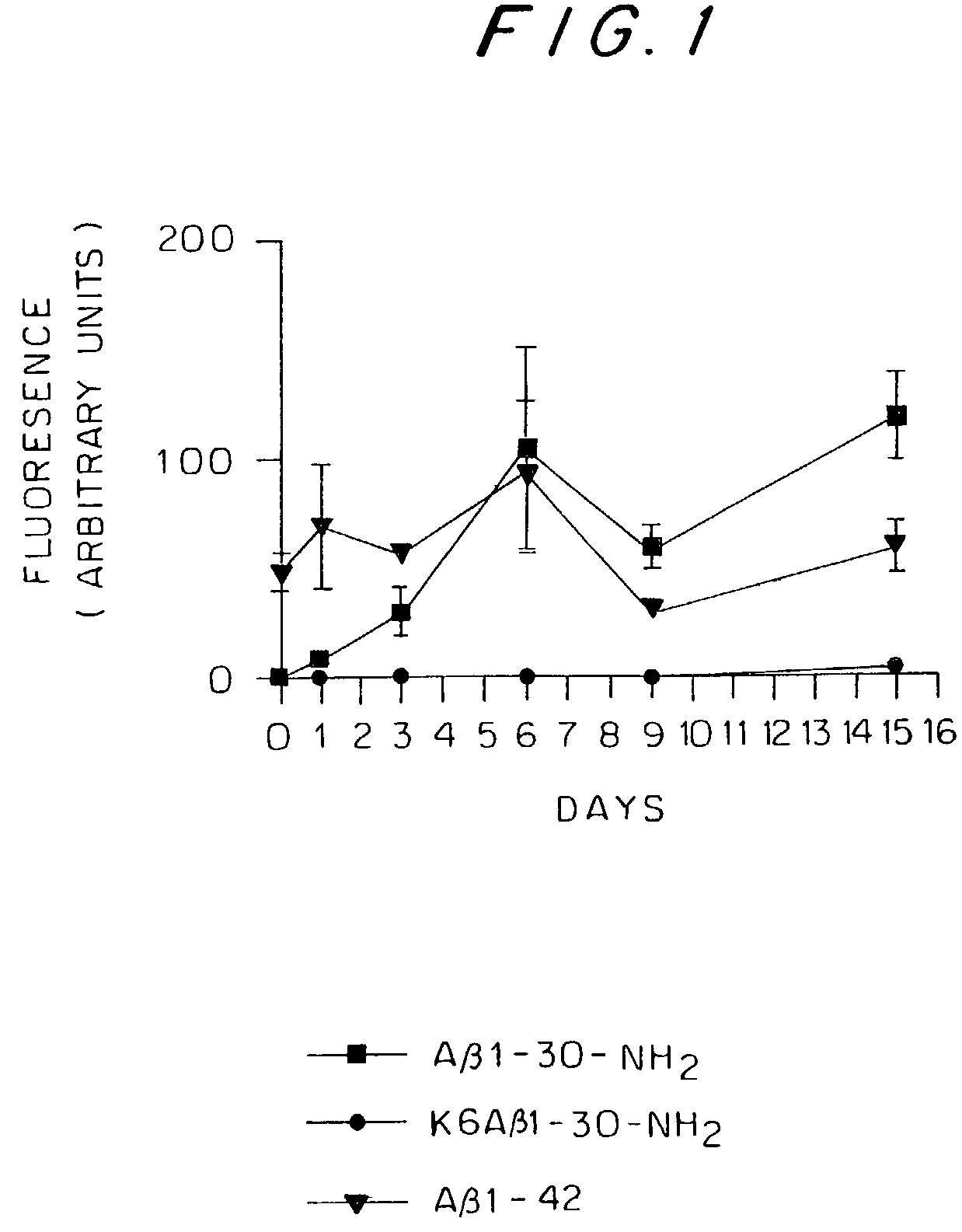
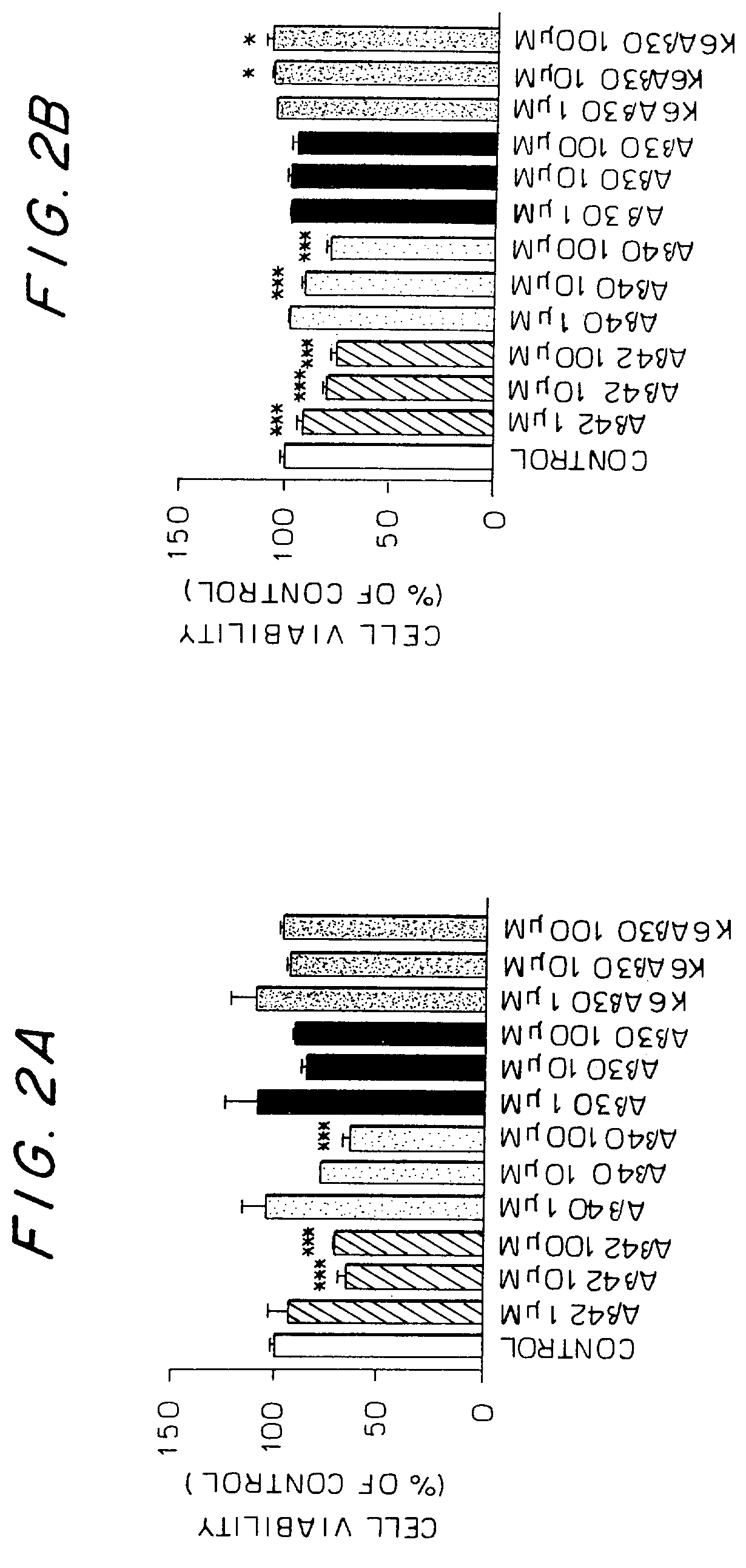
Synthetic immunogenic but non-deposit-forming polypeptides and peptides homologous to amyloid beta, prion protein, amylin, alpha-synuclein, or polyglutamine repeats for induction of an immune response thereto
InactiveUS7479482B2Reduce formationAvoid formingHormone peptidesNervous disorderPassive ImmunizationsAmyloid beta
The present invention relates to immunogenic but non-depositing-forming polypeptides or peptides homologous to amyloid β, prion, amylin or α-synuclein which can be used alone or conjugated to an immunostimulatory molecule in an immunizing composition for inducing an immune response to amyloid β peptides and amyloid deposits, to prion protein and prion deposits, to amylin and amylin deposits, to α-synuclein and deposits containing α-synuclein, or to polyglutamine repeats and deposits of proteins containing polyglutamine repeats. Described are also antibodies directed against such peptides, their generation, and their use in methods of passive immunization to such peptides and deposits.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
Recombinant influenza viruses expressing tumor-associated antigens as antitumor agents
InactiveUS20040253273A1Prevent tumor formationQuick changeSsRNA viruses negative-senseAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsTumor reductionEpitope
The present invention relates to the engineering of recombinant influenza viruses that express tumor-associated antigens. Expression of tumor-associated antigens by these viruses can be achieved by engineering specific epitopes into influenza virus proteins, or by engineering viral genes that encode a viral protein and the specific antigen as independent polypeptides. Tumor-bearing patients can be immunized with the recombinant influenza viruses alone, or in combination with another treatment, to induce an immune response that leads to tumor reduction. The recombinant viruses can also be used to vaccinate high risk tumor-free patients to prevent tumor formation in vivo.
Owner:PALESO PETER +2
Nanobody against SARS-COV-2 virus S protein RBD structure domain and use thereof
InactiveCN111825762AAvoid infectionStrong specificityImmunoglobulins against virusesAntiviralsViral ReceptorPharmaceutical drug
The invention provides a nanobody against a SARS-COV-2 virus S protein RBD structure domain. The nanobody can recognize the RBD structure domain of SARS-COV-2 virus S protein, and includes one or moreof nanobody1-nanobody19. The nanobody can specifically bind to an S protein RBD region of SARS-COV-2 and block the binding of the virus to a cell receptor ACE2, and EC50 of the binding of the antibody to RBD is 0.4212ng / ml-325.24ng / ml. The nanobody competes with viral receptor ACE2 protein, and the IC50 is 2.433nm-100.02nm. The invention further provides use of the nanobody and recombinant antibody thereof in preparing drugs for inhibiting SARS-COV-2 virus infection, and preparing a SARS-COV-2 virus detection reagent or kit.
Owner:CUSABIO TECH LLC
Prion protein binding materials and methods of use
ActiveUS7510848B2Bacterial antigen ingredientsViral antigen ingredientsHamsterProteinaceous infectious particle
Prion protein binding materials and methods for using the binding materials to detect or remove a prion protein from a sample, such as a biological fluid or an environmental sample. The binding materials are capable of binding to one or more forms of prion protein including cellular prion protein (PrPc), infectious prion protein (PrPsc), recombinant prion protein (PrPr), and proteinase resistant prion protein (PrPres). Prions from various species, including humans and hamsters, are bound by the binding materials.
Owner:PATHOGEN REMOVAL & DIAGNOSTIC TECH +1
Engineered lectins for viral inactivation
ActiveUS20090297516A1Easy to neutralizeGood curative effectAntibacterial agentsBiocideHalf-lifeComplement-dependent cytotoxicity
Engineered lectins and methods of using such reagents for both preventing and treating a broad array of viral infections are provided. The lectins of the invention are engineered in two ways, first through the enhancement of the natural mode of action of lectins against viruses through linked multimerization, and second through the creation of a new class of reagents, hereinafter referred to as a “lectibody” or “lectibodies”, that engage host immune function in addition to simply binding glycosylated viral proteins via the combination of a lectin and the Fc region of an antibody in order to drive Fc-mediated effector functions including ADCC (antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity), increased half-life, complement-dependent cytotoxicity (CDC), and antibody-dependent cell-mediated phagocytosis (ADCP) in response to a lectin-mediated carbohydrate-binding event.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Oral smallpox vaccine production and methods to evaluate safety, efficacy, and potency of orally delivered vaccine
InactiveUS20040175398A1Efficient responseSafety and efficacyViral antigen ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementHuman useDiagnostic test
This invention relates to methods and systems for generating a safe and effective oral smallpox vaccine for humans using a genetically defective strain of vaccinia virus to confer immunity following oral delivery of the vaccine. This invention is one that expands on current use of vaccinia virus propagation developed for gene therapy applications, and pharmaceuticals and nutraceuticals packaging and formualtion technologies. The vaccine invention can be delivered as a live virus with the ability to express viral proteins but unable to achieve complete, lytic virus replication, or it may be derived from such a virus, contain additional immunogens, or be delivered as viral antigens. Furthermore, the invention establishes innovative methods for formulation and packaging and for preclinical testing of the vaccine invention for safety, efficacy and potency with the use of human intestinal and other test cells and diagnostic test systems and kits.
Owner:INCELLS
Bacterial polysaccharide-protein conjugate vaccine and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to a bacterial polysaccharide-protein conjugate vaccine with immunogenicity, in particular to a conjugate vaccine which is formed by connecting a recombinant rotavirus protein with a bacterial polysaccharide by using a covalent bond, a nucleotide sequence for coding the recombinant rotavirus protein, a recombinant expression system, a protein expressed by the recombinant expression system, a preparation method of the conjugate vaccine and a pneumococcus polysaccharide-recombinant rotavirus protein conjugate vaccine. The bacterial polysaccharide is connected with a recombinant rotavirus surface protein through a covalent bond. The recombinant rotavirus protein is selected from a partial or complete amino acid sequence of a P-gene rotavirus protein and a partial or complete amino acid sequence of a G-gene rotavirus protein.
Owner:普大生物科技(泰州)有限公司
Prion-specific peptide reagents
InactiveUS20050118645A1Nervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsProteinaceous infectious particleAntibody
Owner:NOVARTIS VACCINES & DIAGNOSTICS INC
Prion free nanoparticle compositions and methods of making thereof
The present invention provides prion-free compositions comprising nanoparticles comprising albumin and substantially water insoluble drugs. Also provided are methods of making prion-free compositions and methods of removing prion proteins from the nanoparticle compositions. Methods of using the compositions, as well as kits useful for carrying out the methods are also provided.
Owner:ABRAXIS BIOSCI LLC
Compositions and methods for treating viral infections
InactiveUS6043347AImprove hydrophobicityEasy to fixPeptide/protein ingredientsVirus peptidesEpitopeImmunodeficiency virus
Methods and compositions for treatment, diagnosis, and prevention of a virus comprise administering to a patient antibodies which react with regions of viral proteins and result in neutralization of infectivity and inactivation of functionally essential events in the life cycle of the virus. The antibodies recognize viral epitopes which fail to elicit an immune response in man when encountered through infection or naturally through the environment. In a preferred embodiment, the invention provides compositions and methods useful in the treatment and diagnosis of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infections.
Owner:TECH HLDG +1
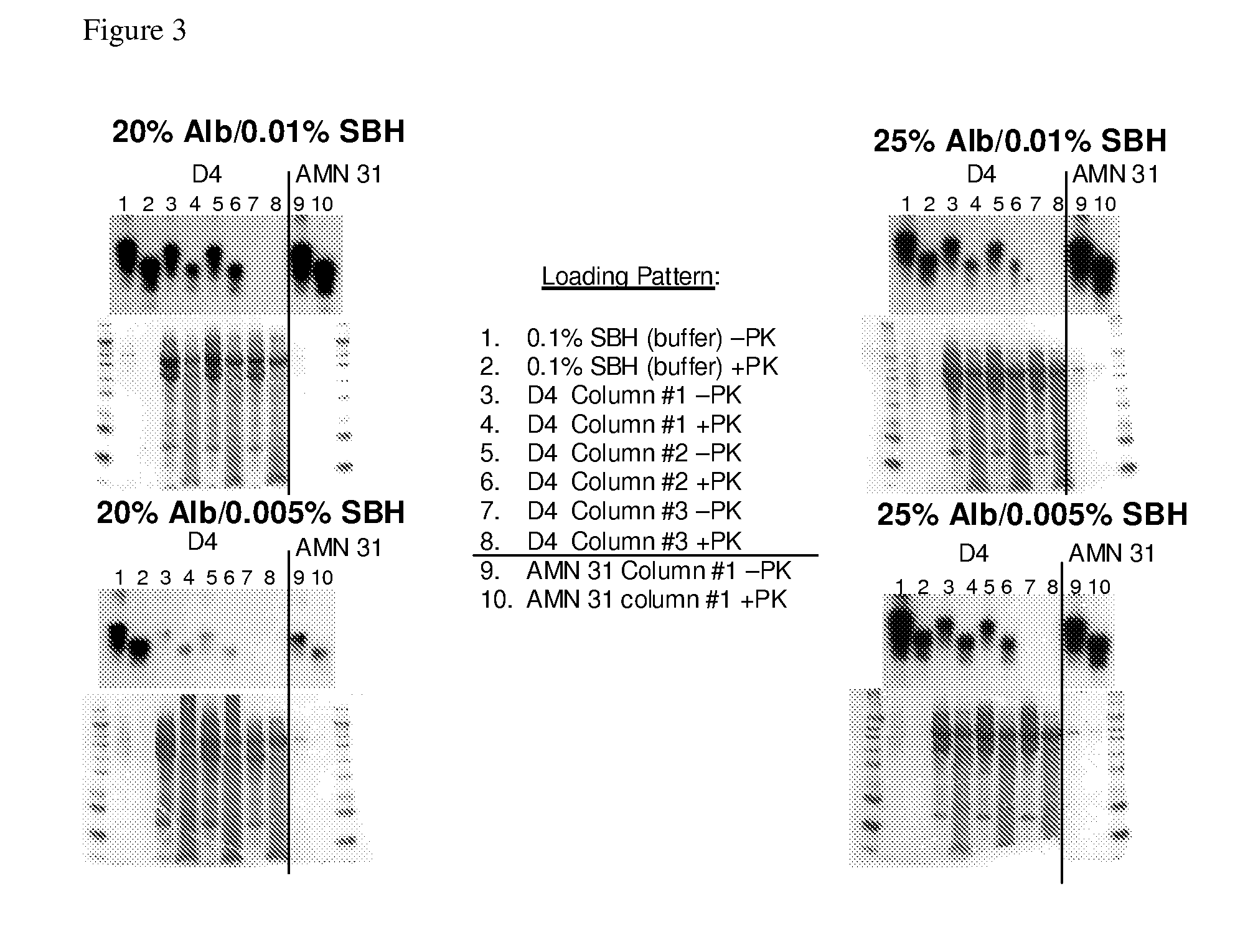
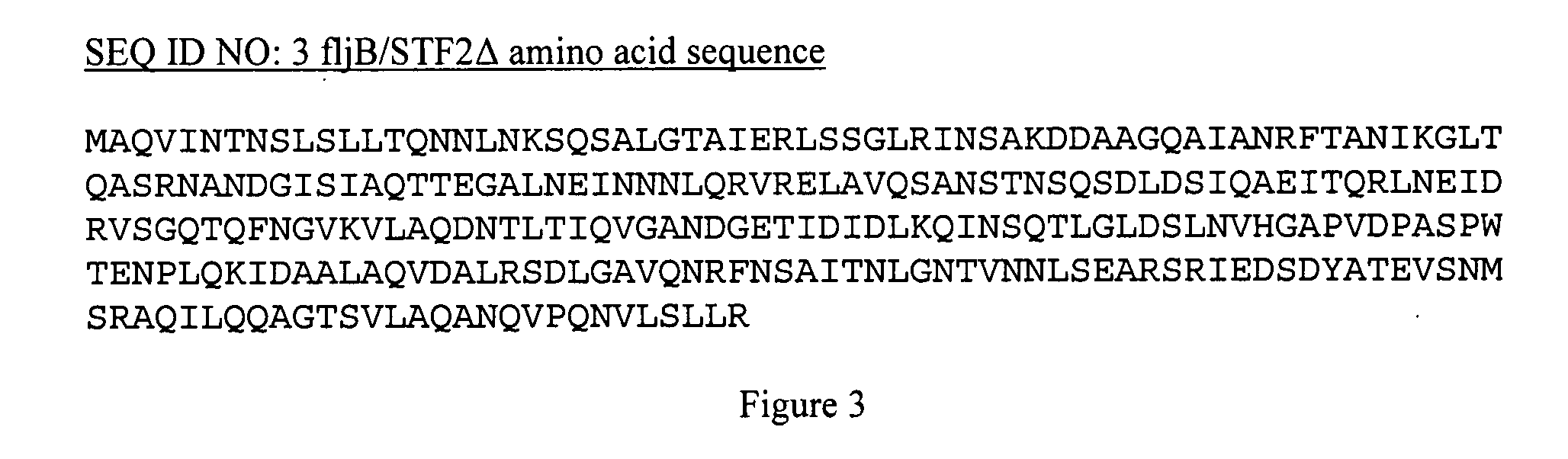
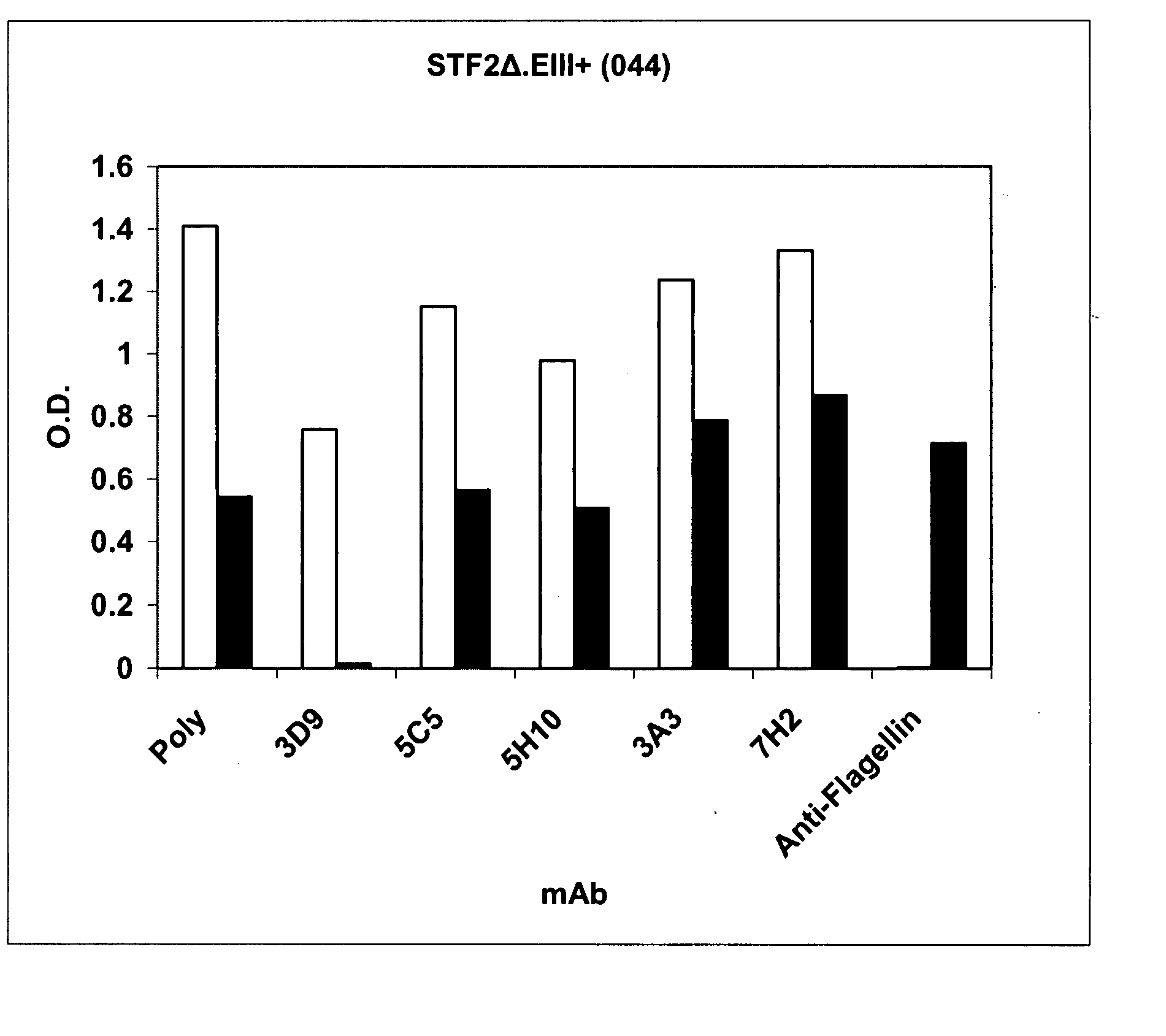
Compositions of influenza viral proteins and methods of use thereof
InactiveUS20090162400A1Increase productionStimulate immune responseSsRNA viruses negative-senseSsRNA viruses positive-senseIntegral membrane proteinPathogen-Associated Molecular Pattern Molecules
Compositions, fusion proteins and polypeptides comprise at least one pathogen-associated molecular pattern and at least a portion of at least one integral membrane protein of an influenza viral antigen. The compositions, fusion proteins and polypeptides are used to stimulate an immune response in a subject.
Owner:VAXINNATE
Compositions comprising pathogen-associated molecular patterns and antigens and methods of use thereof
InactiveUS20080063657A1Stimulate immune responseImprove immunitySsRNA viruses positive-sensePeptide/protein ingredientsAntigenYellow fever
Compositions comprise at least a portion of an antigen and at least a portion of a flagellin that lacks a hinge region. Compositions, fusion proteins and polypeptides comprise at least a portion of at least one pathogen-associated molecular pattern and at least a portion of at least one viral protein. The viral protein of the compositions, fusion proteins and polypeptides of the invention are flaviviral proteins, including a West Nile flaviviral protein, a Dengue flaviviral protein, a Langat flaviviral protein, a Kunjin flaviviral protein, a Murray Valley encephalitis flaviviral protein, a Japanese encephalitis flaviviral protein, a Tick-borne encephalitis flaviviral protein, a Yellow fever flaviviral protein and a hepatitis C flaviviral protein. The compositions, fusion proteins and polypeptides are used to stimulate an immune response and protective immunity in a subject.
Owner:VAXINNATE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com