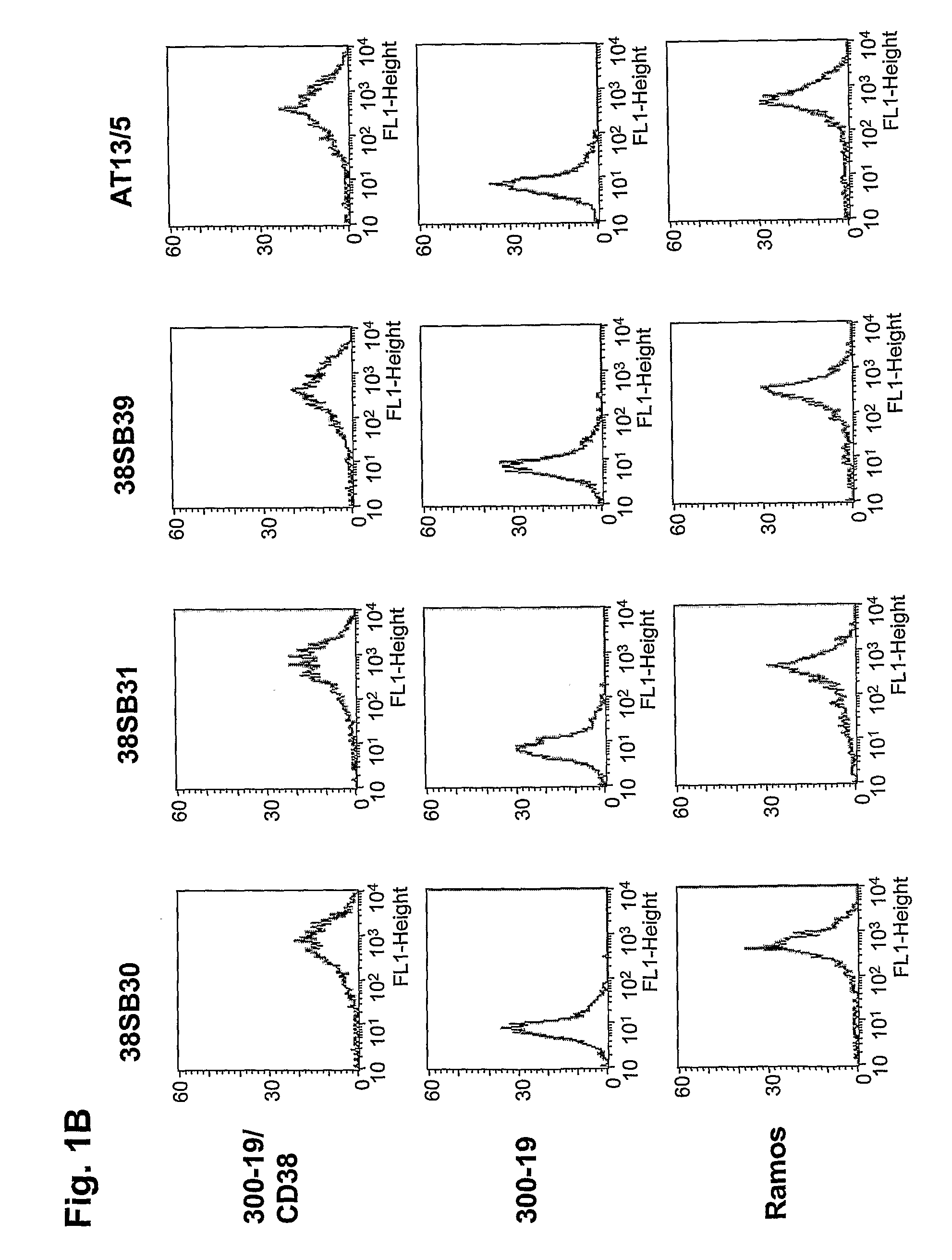
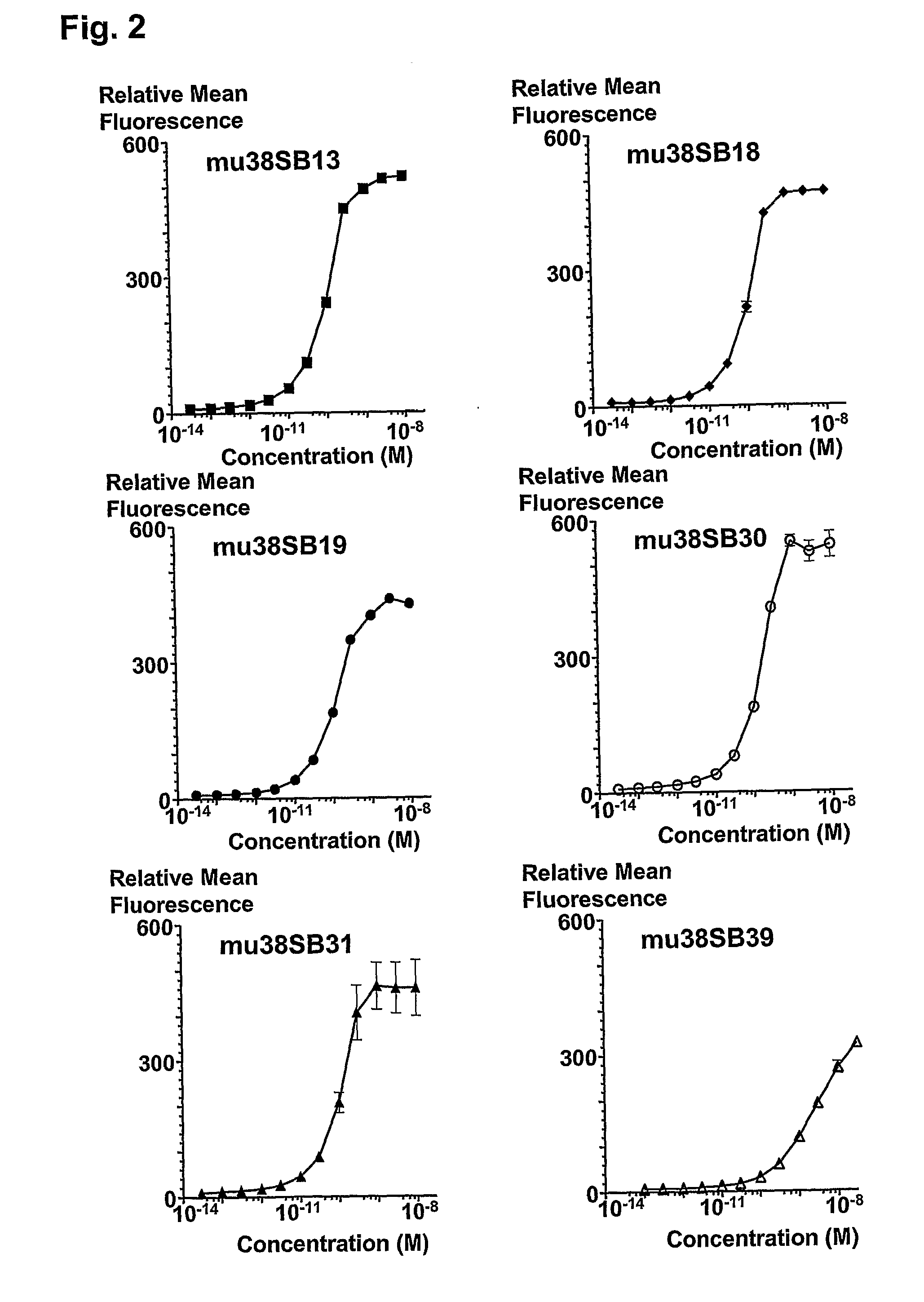
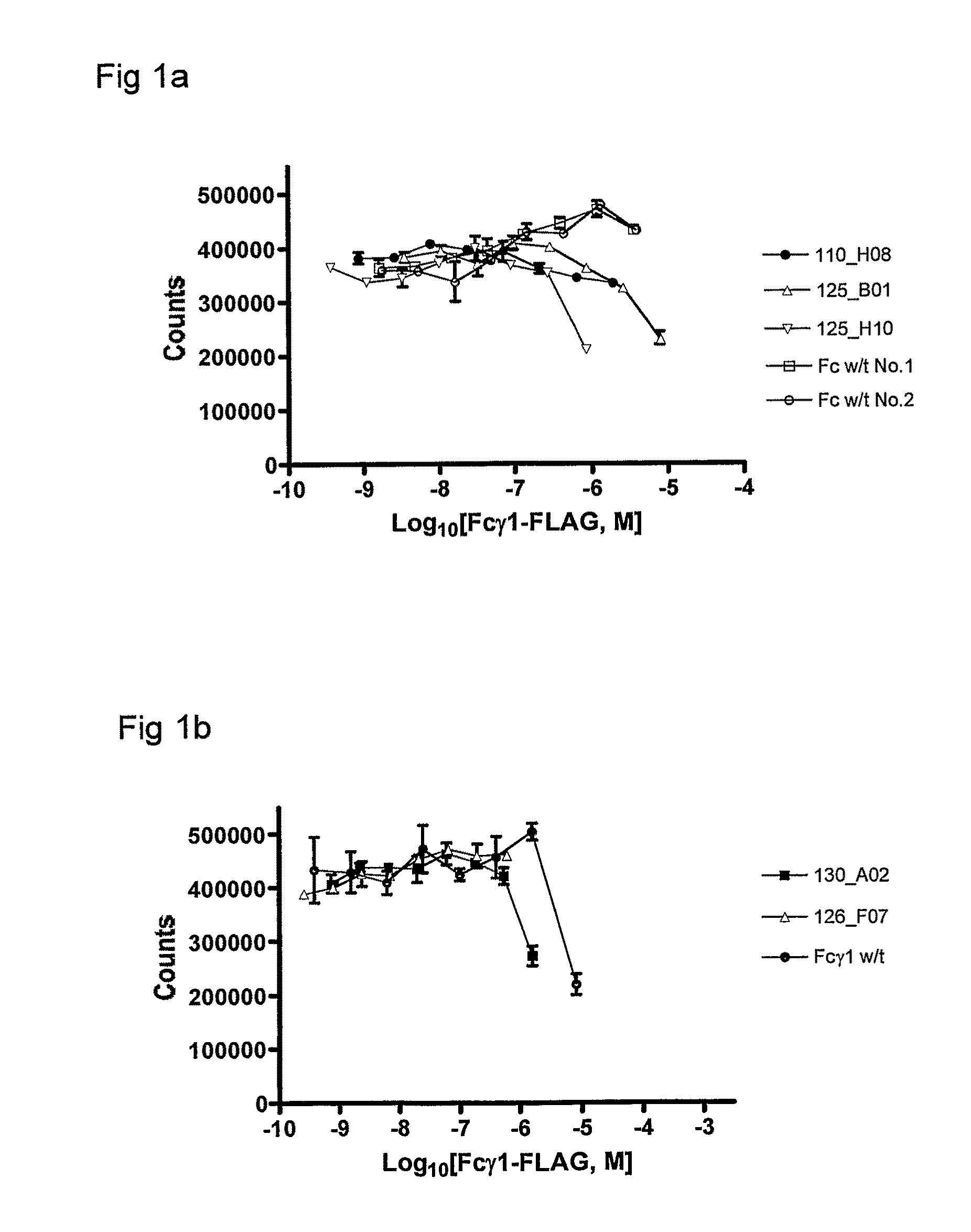
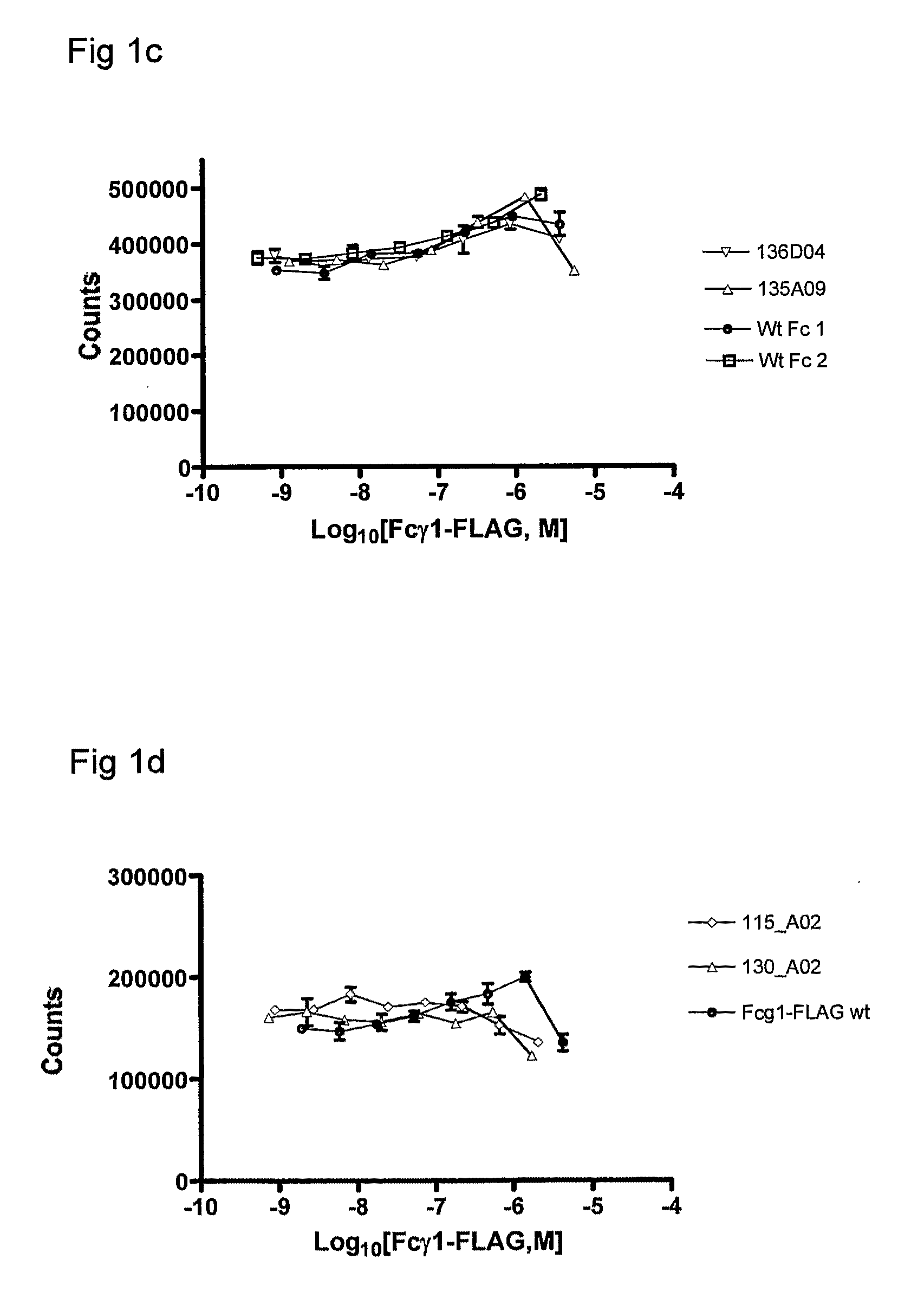
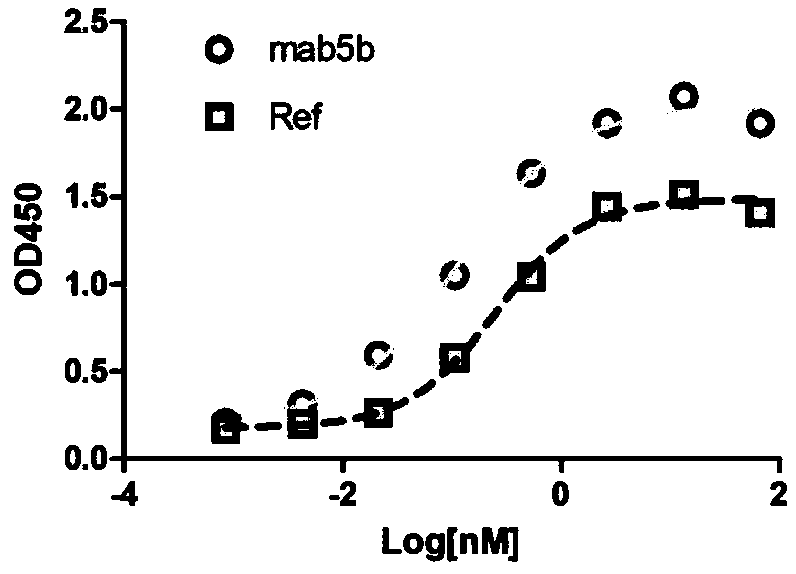
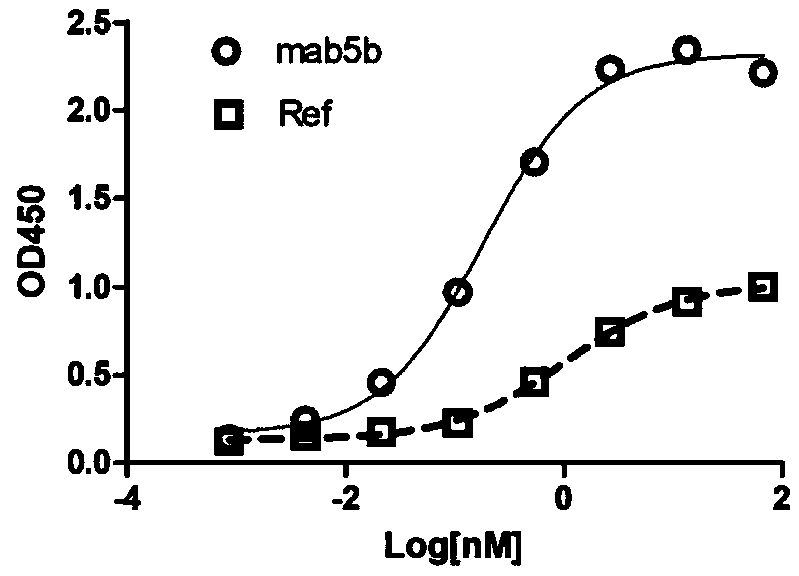
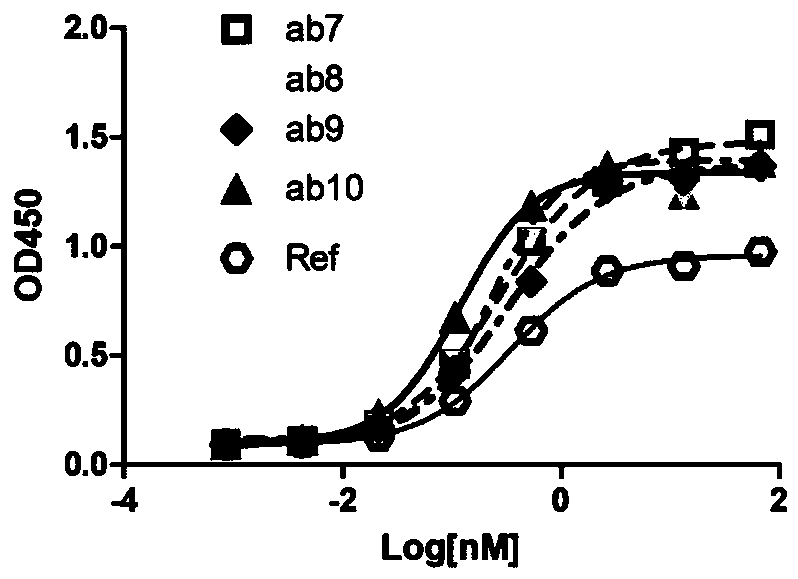
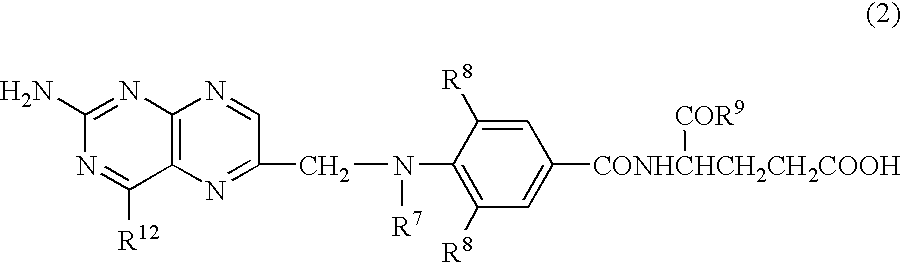
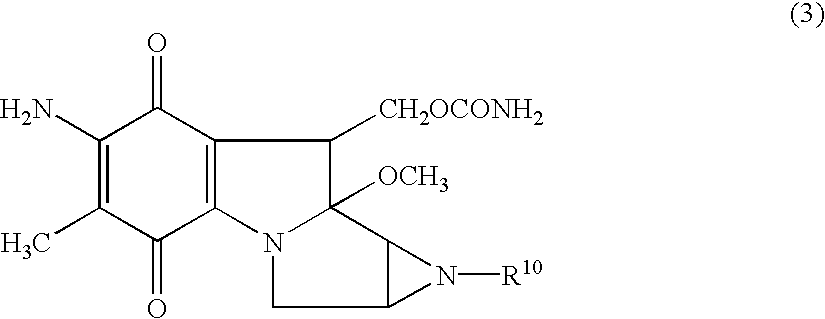
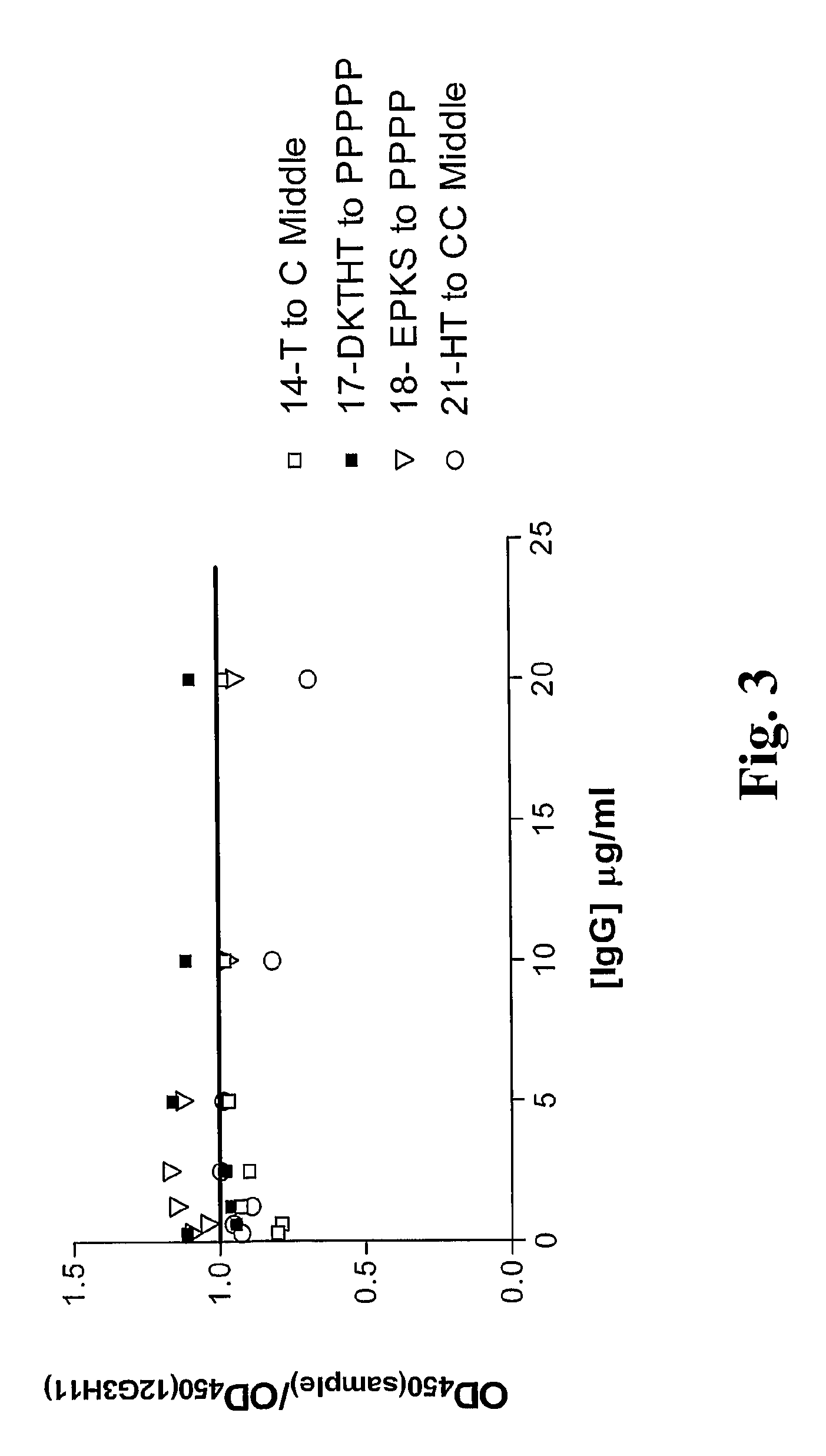
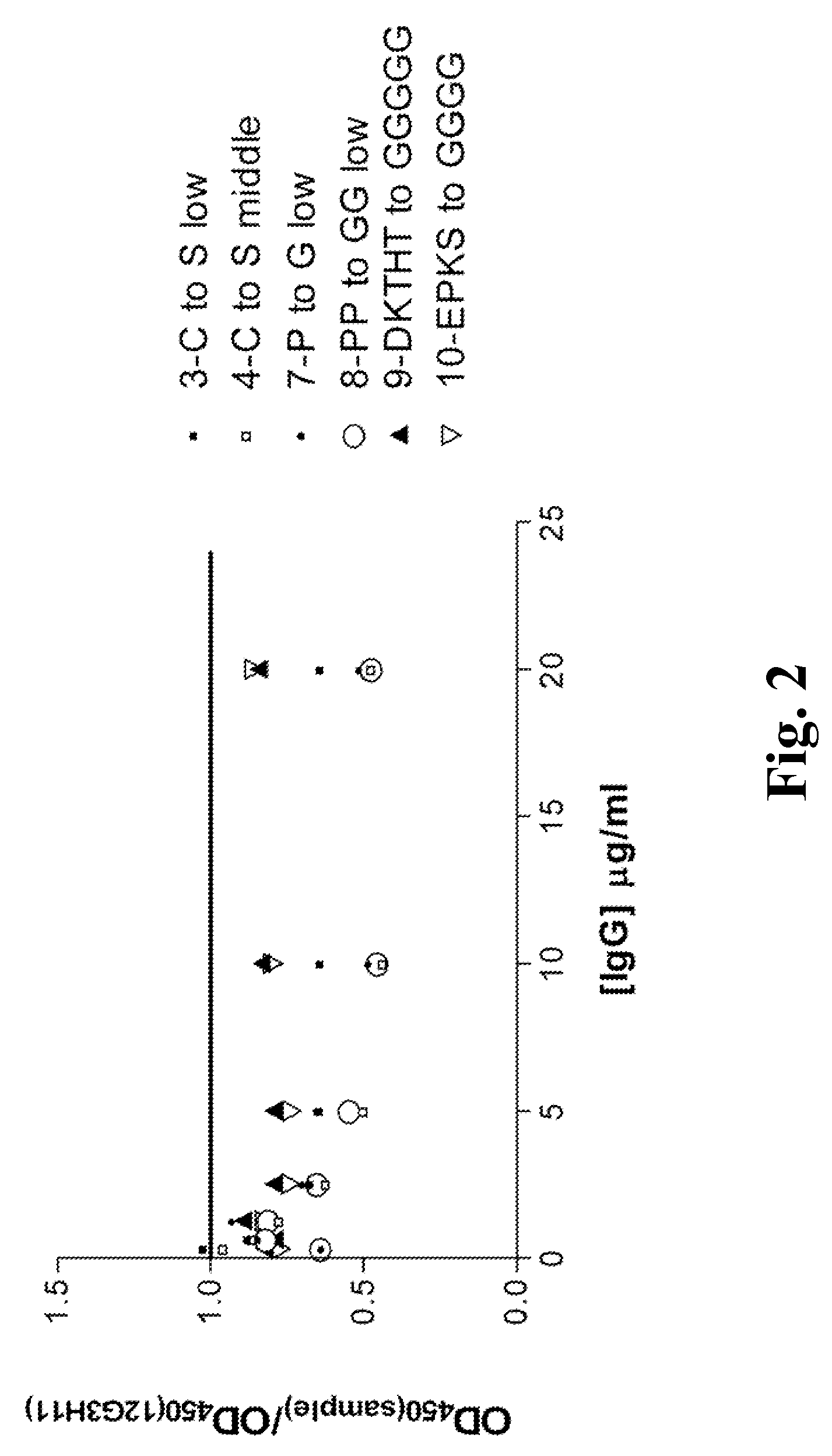
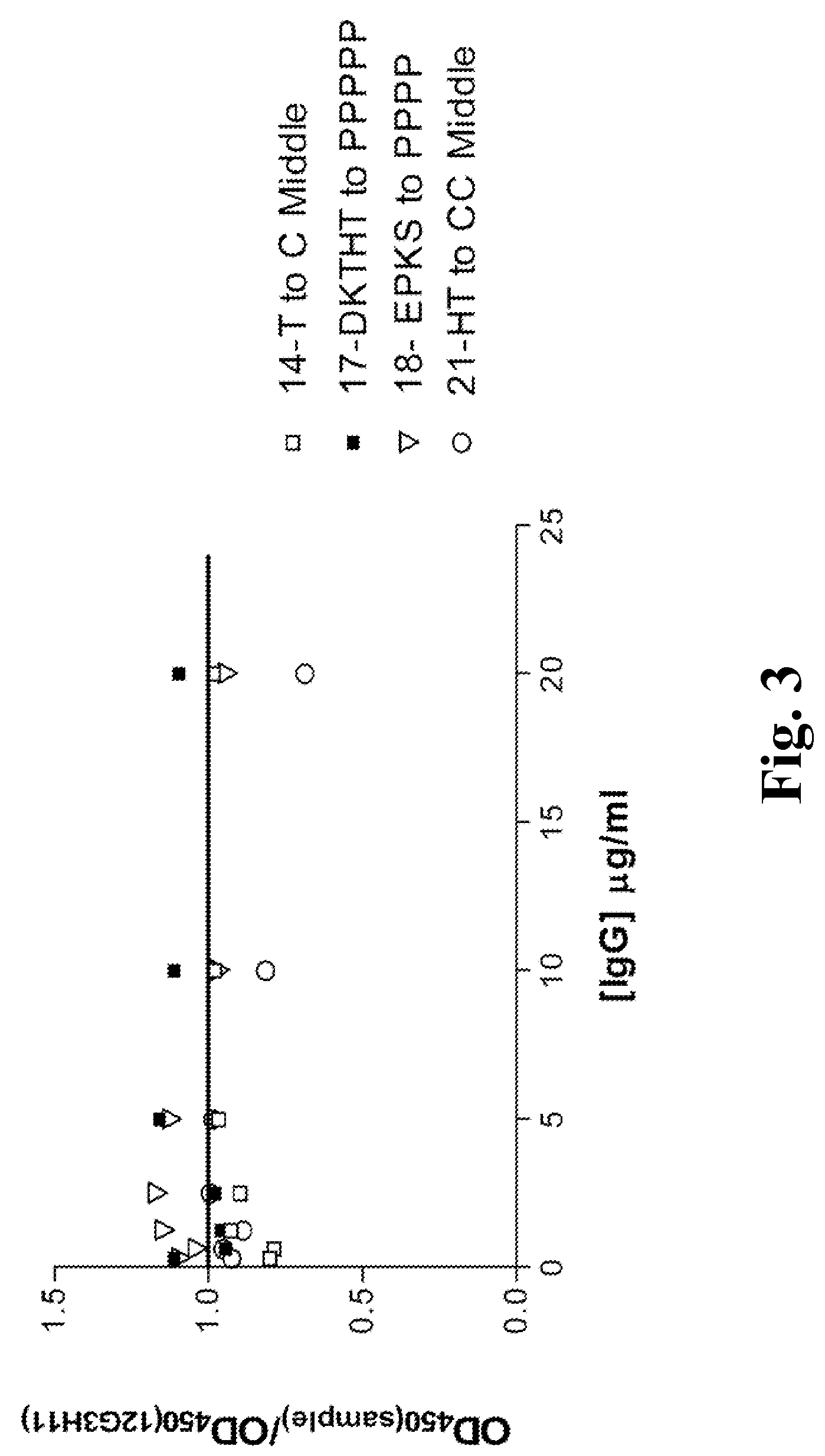
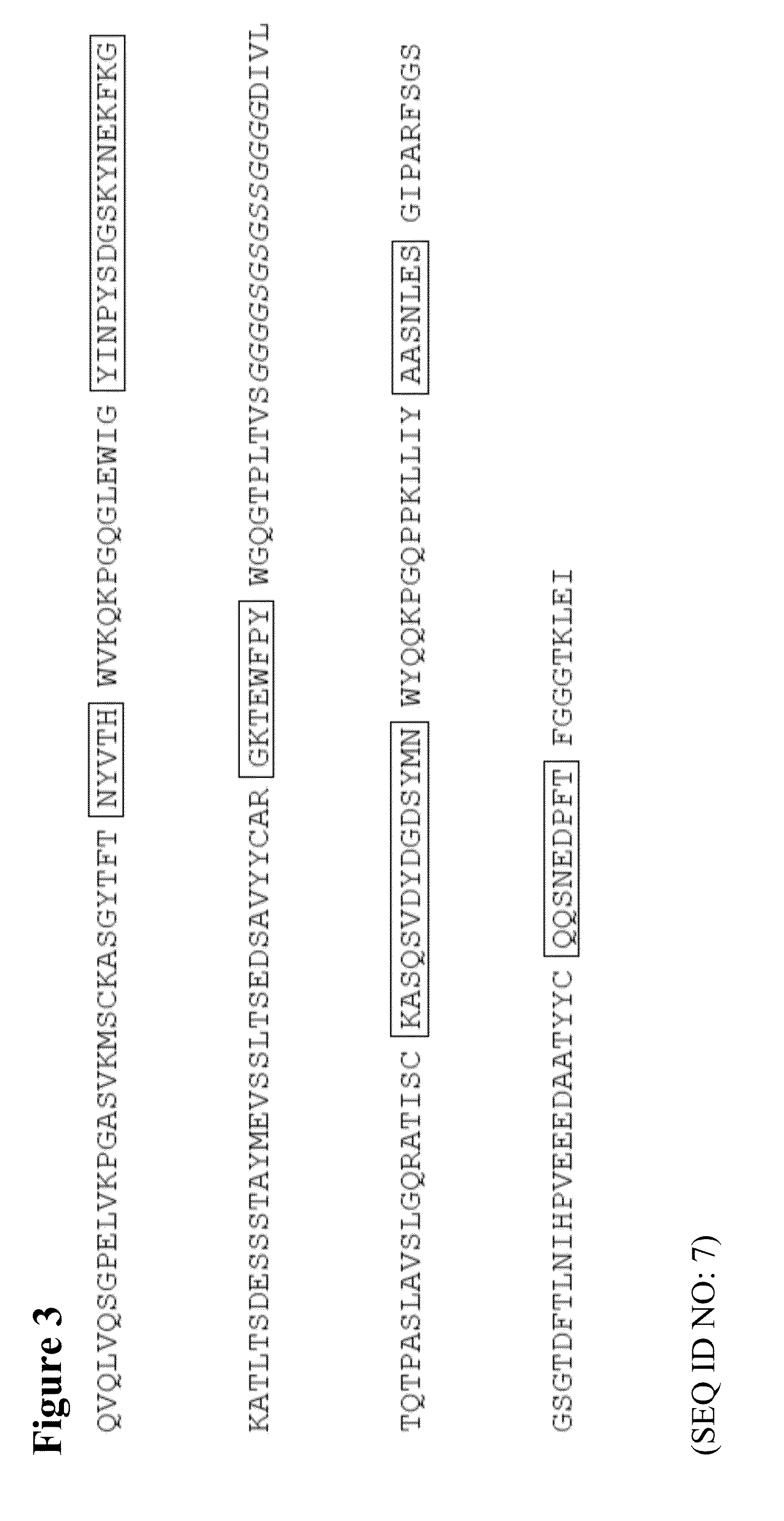
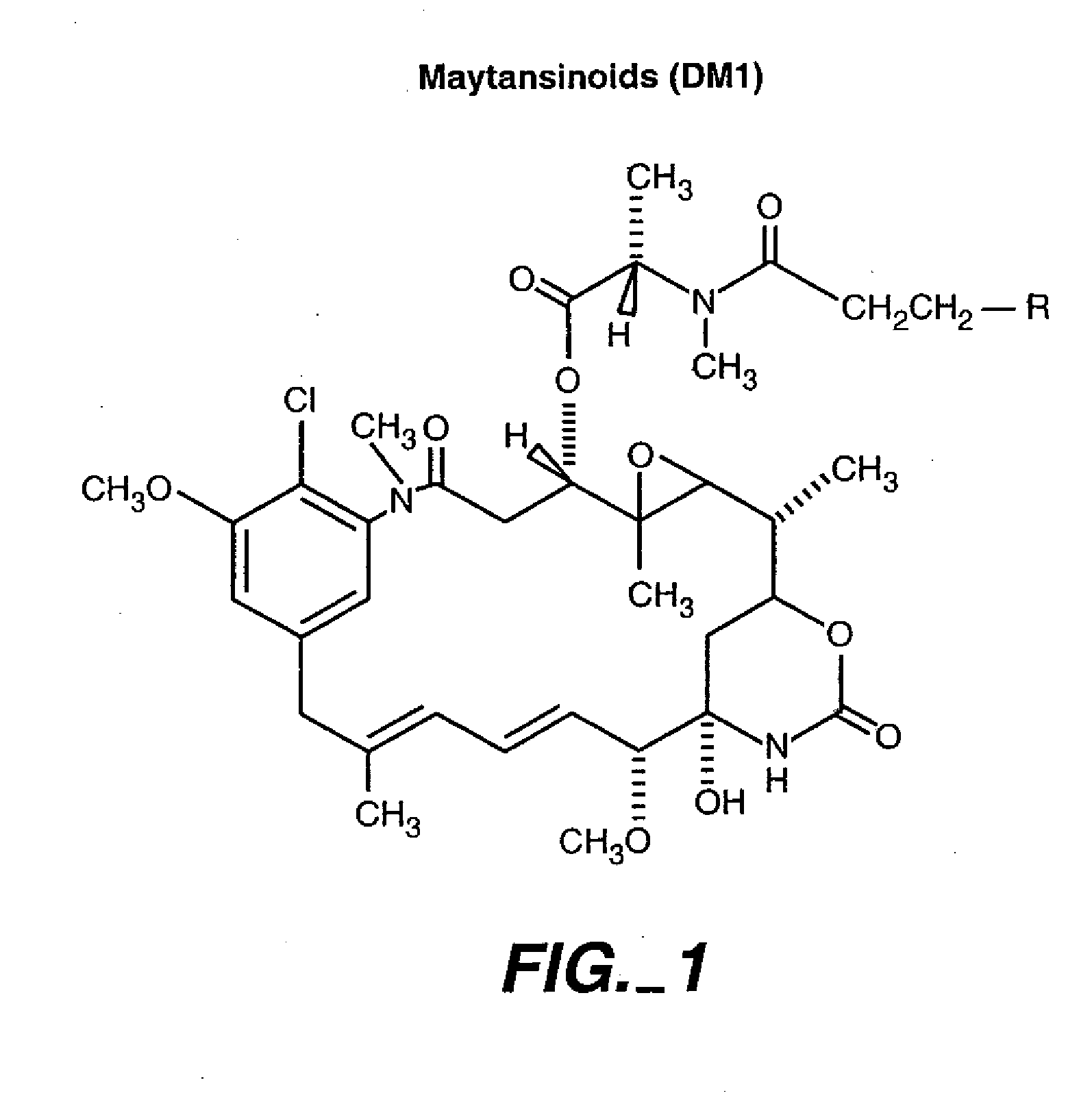
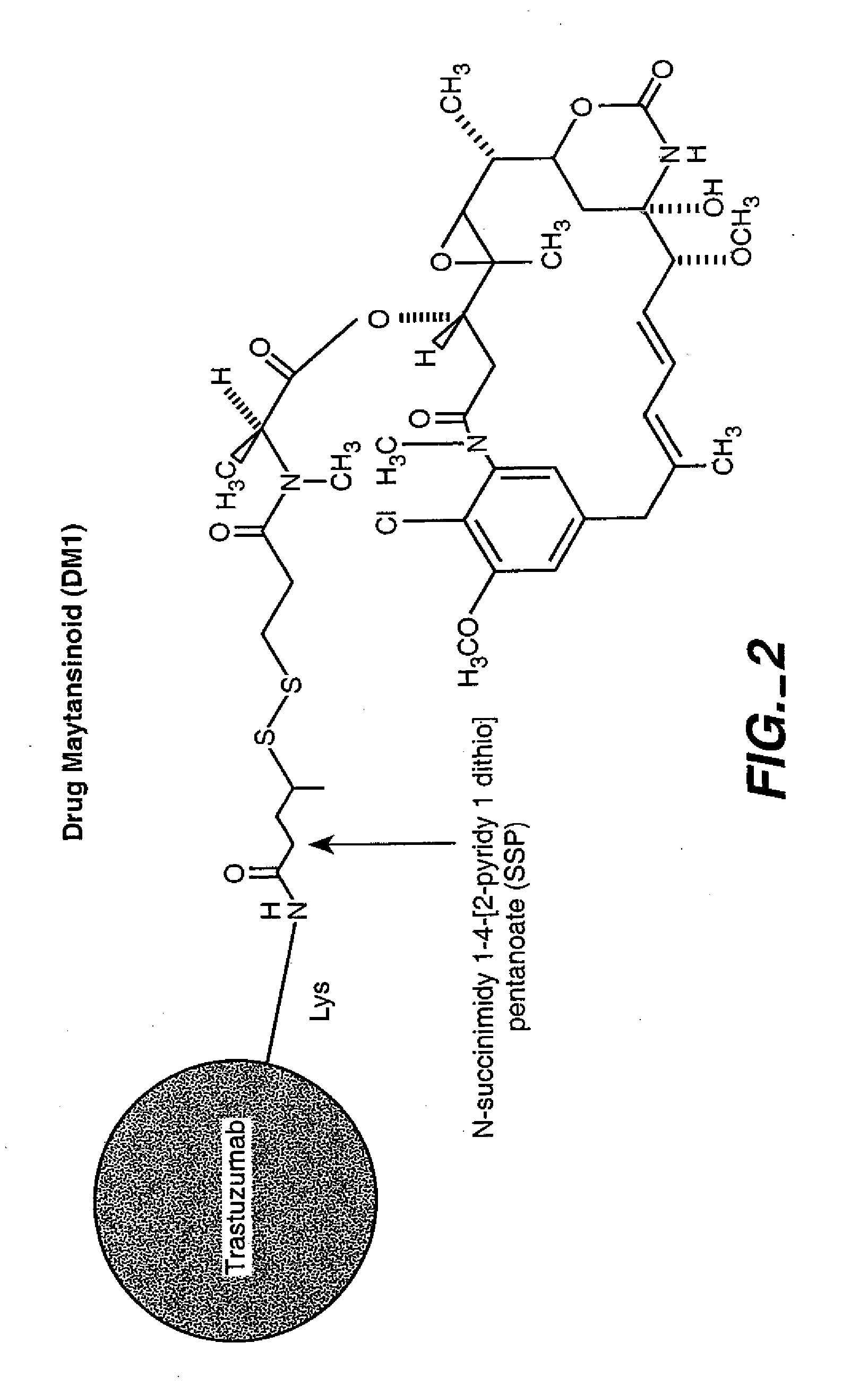
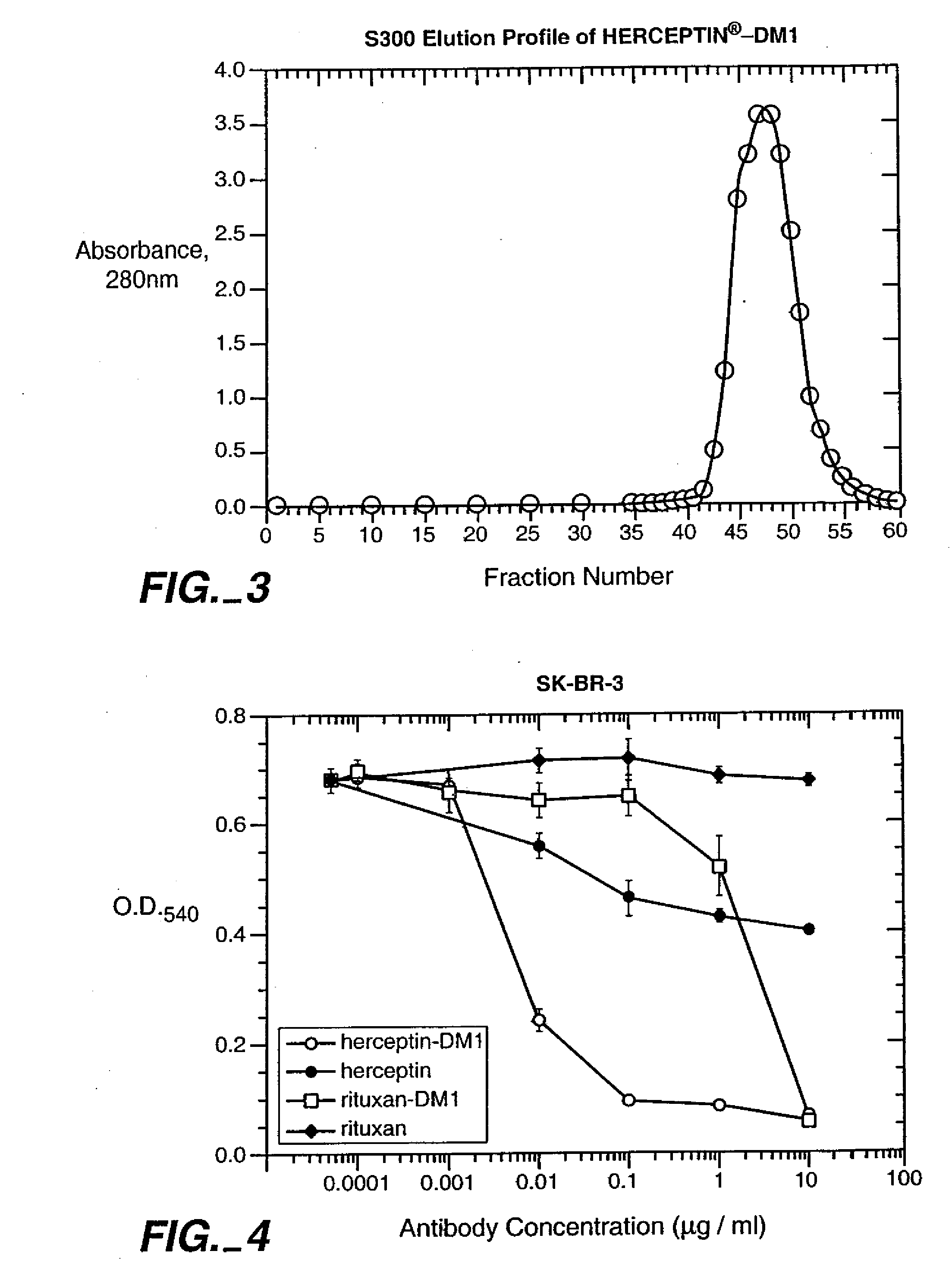
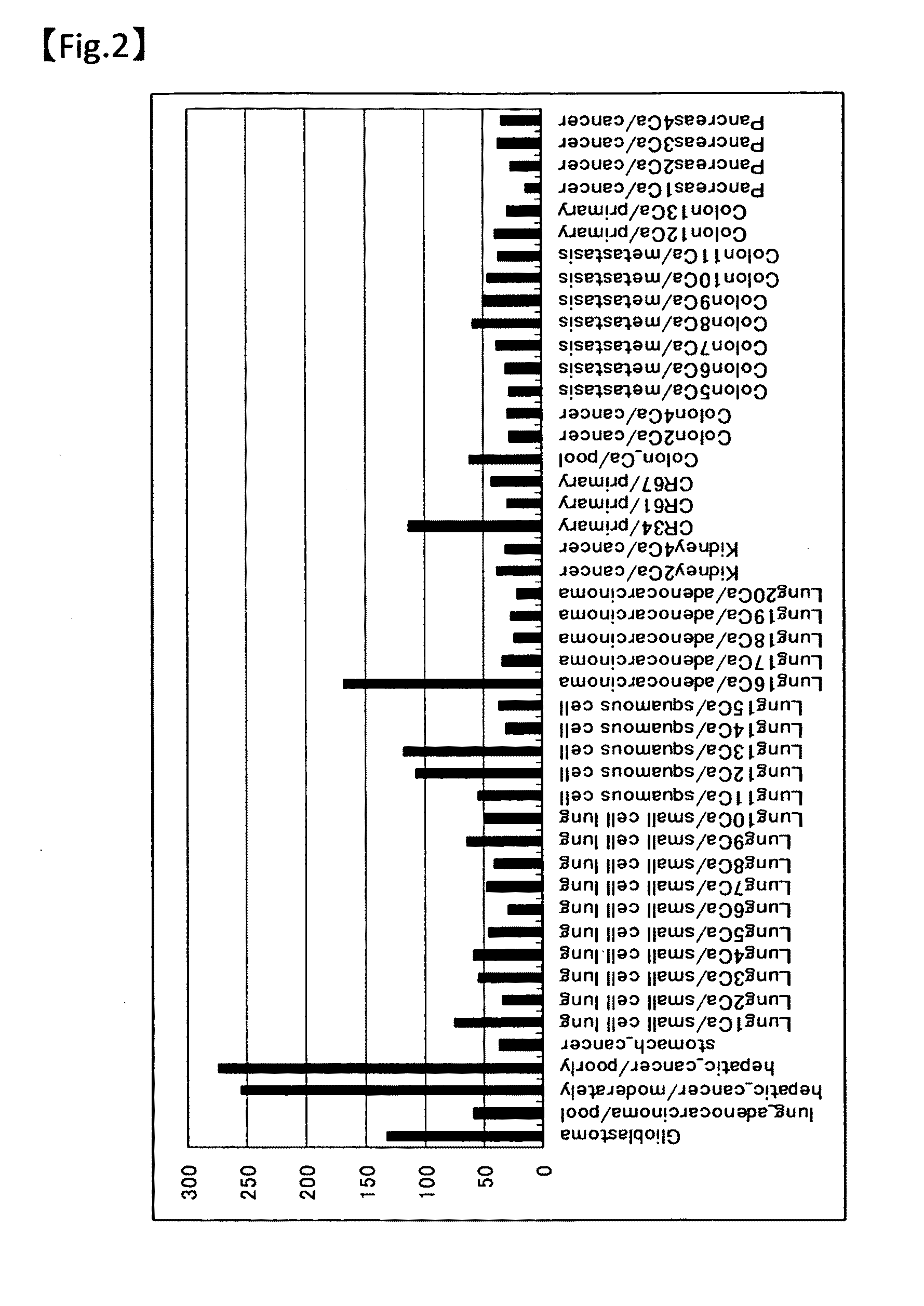
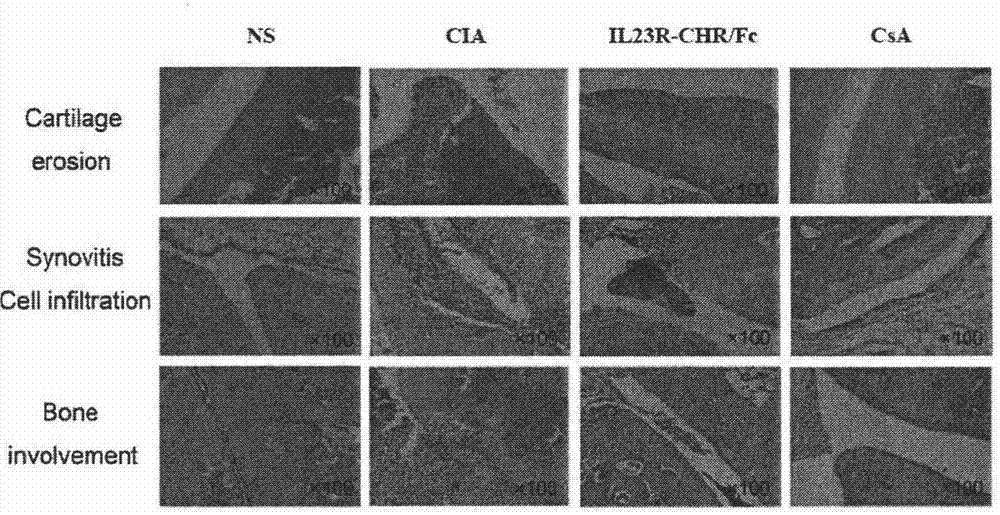
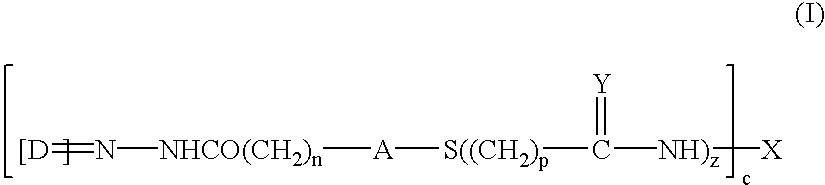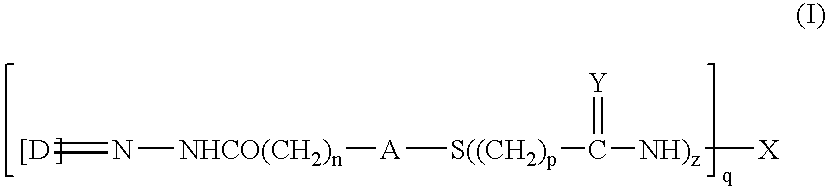Patents
Literature
61 results about "Complement-dependent cytotoxicity" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
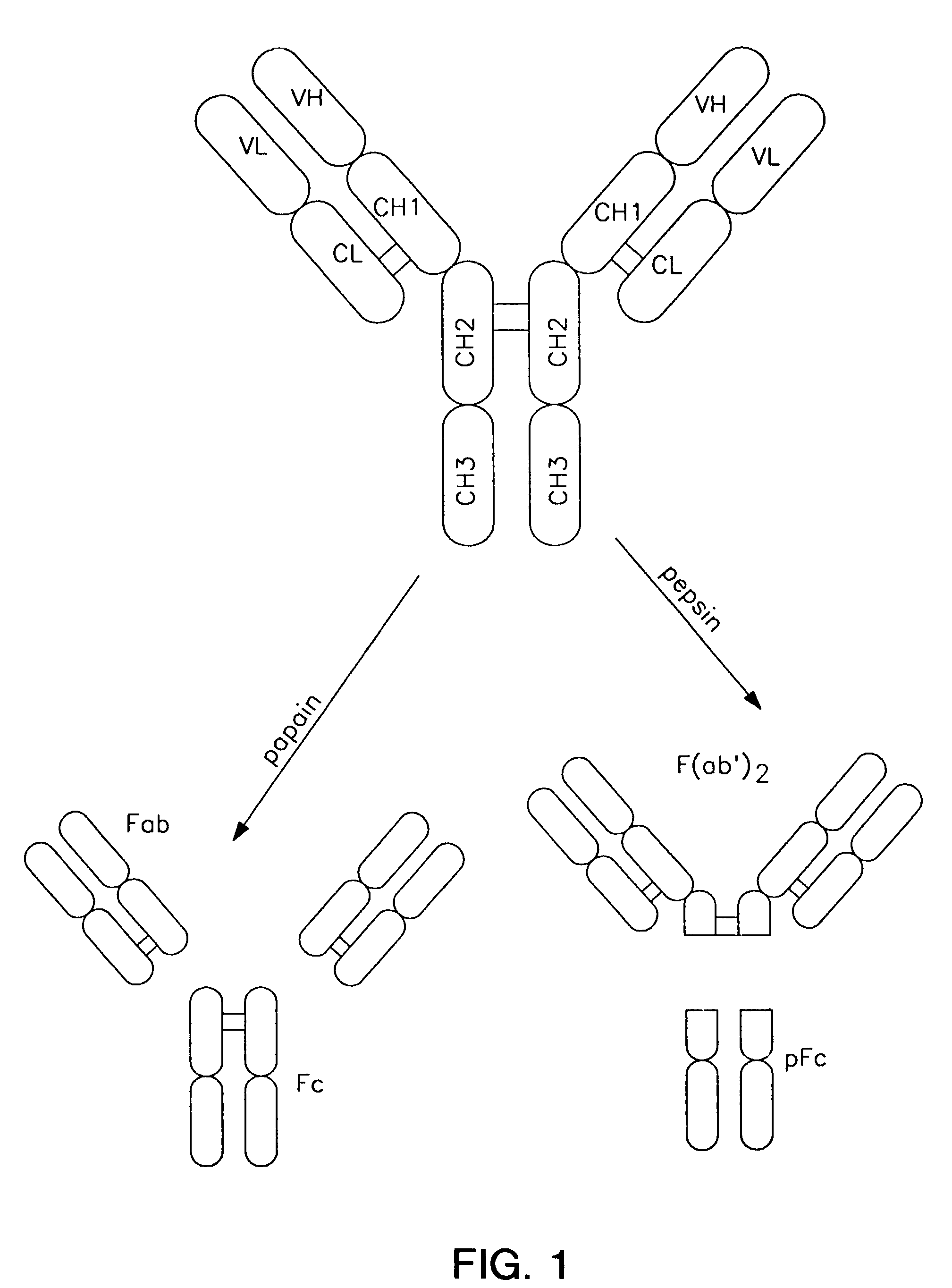
Complement-dependent cytotoxicity (CDC) is an effector function of IgG and IgM antibodies. When they are bound to surface antigen on target cell (e.g. bacterial or viral infected cell), the classical complement pathway is triggered by bonding protein C1q to these antibodies, resulting in formation of a membrane attack complex (MAC) and target cell lysis.
Polypeptide variants
InactiveUS7297775B2Peptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsAmino acid substitutionComplement-dependent cytotoxicity
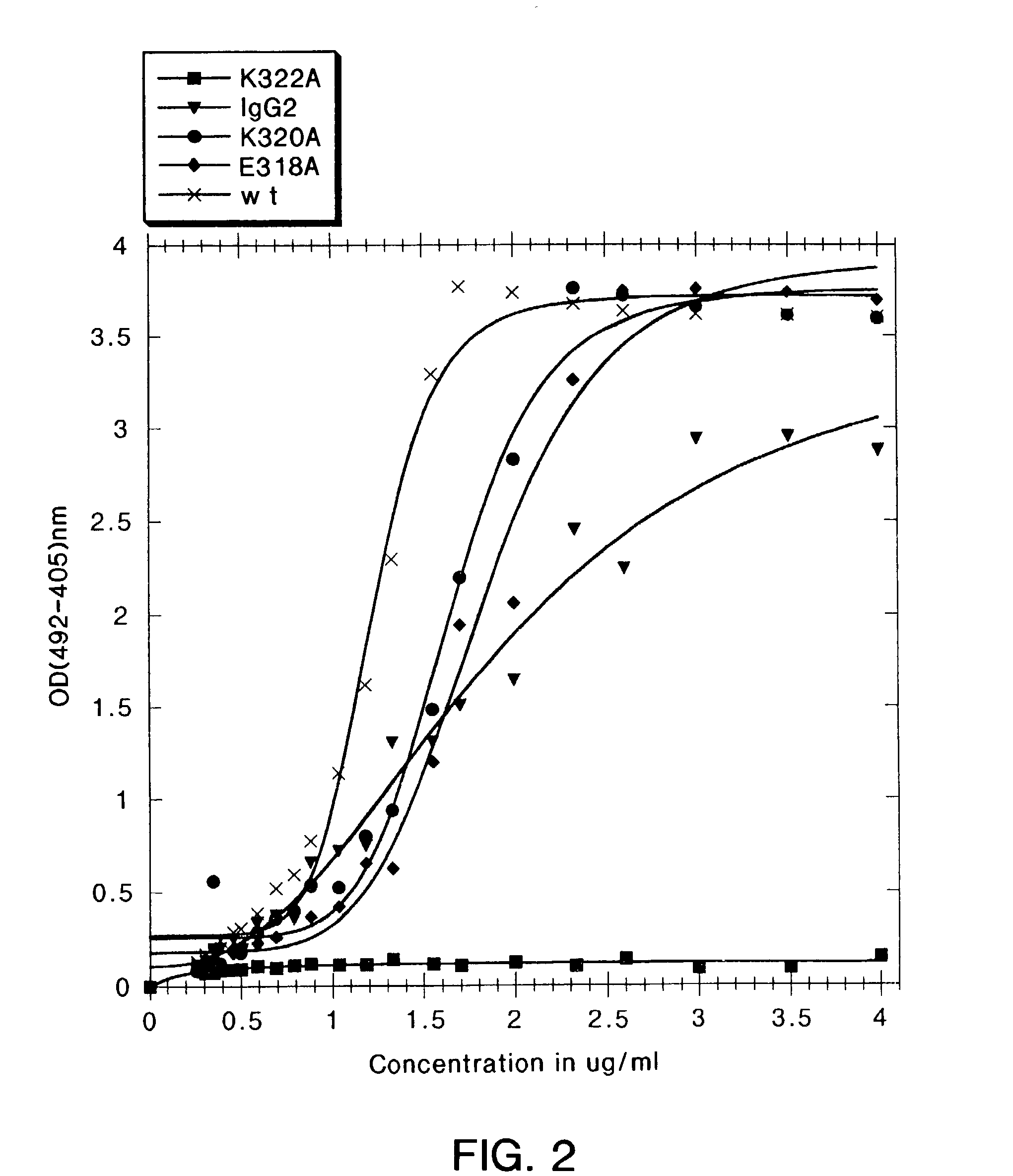
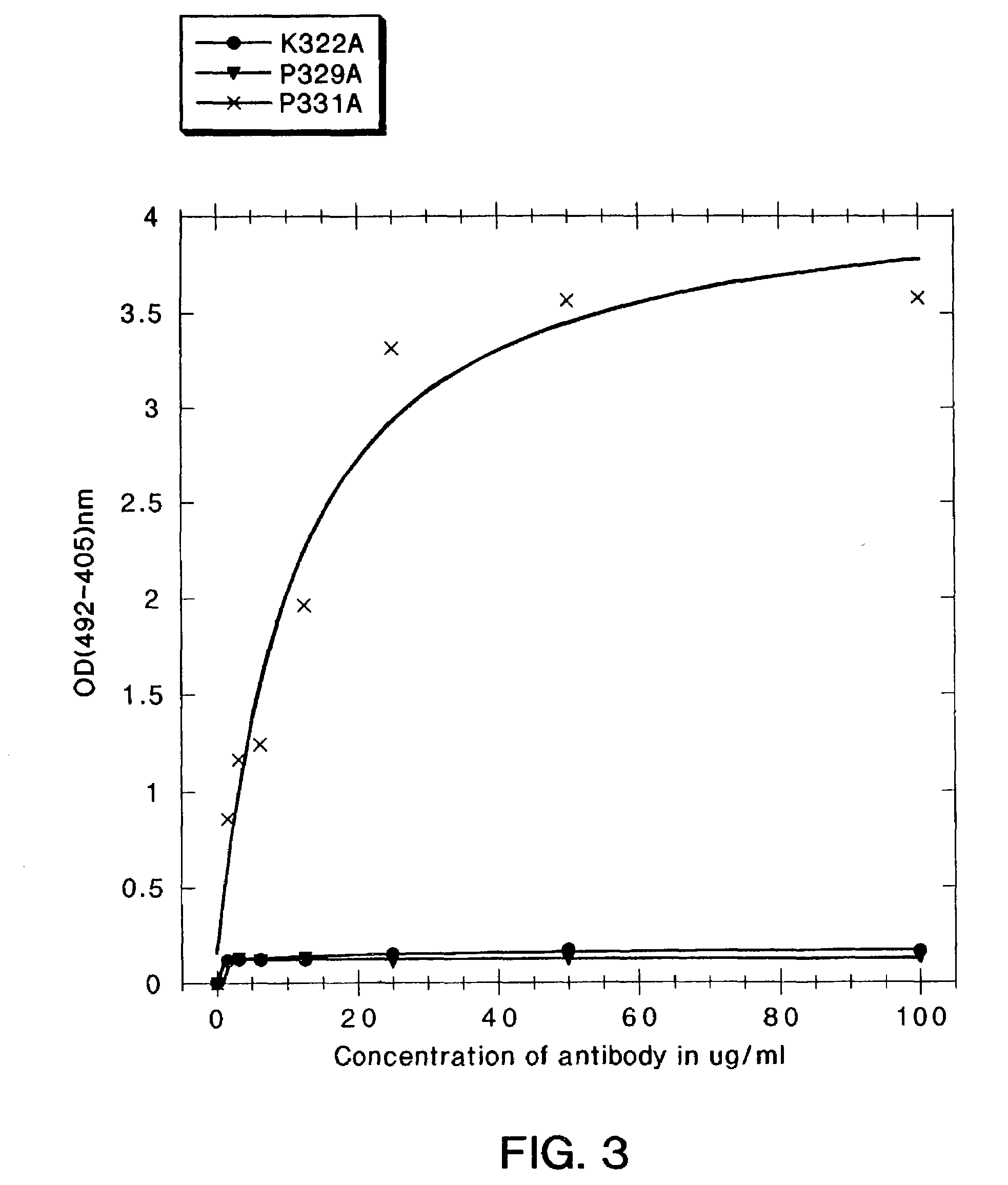
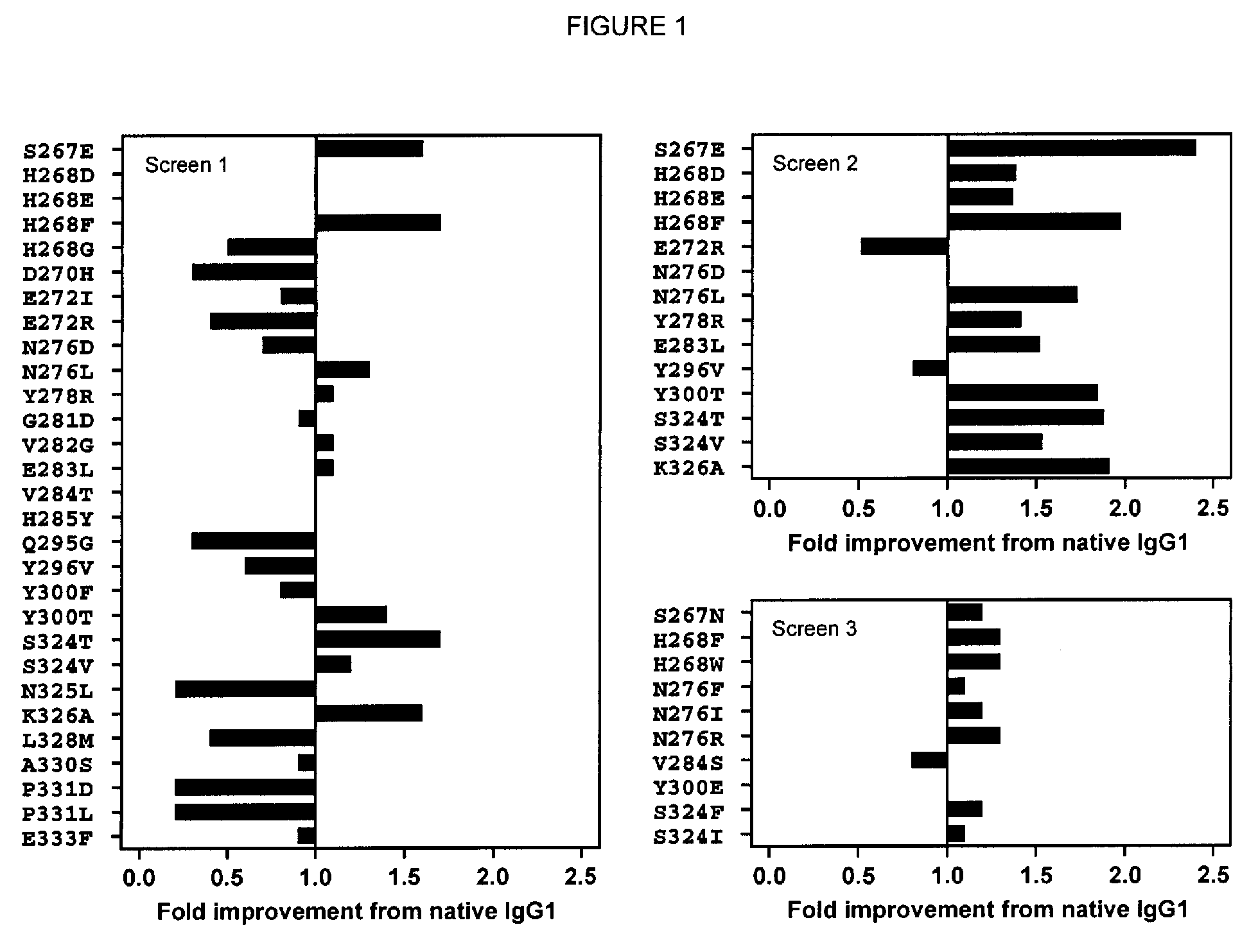
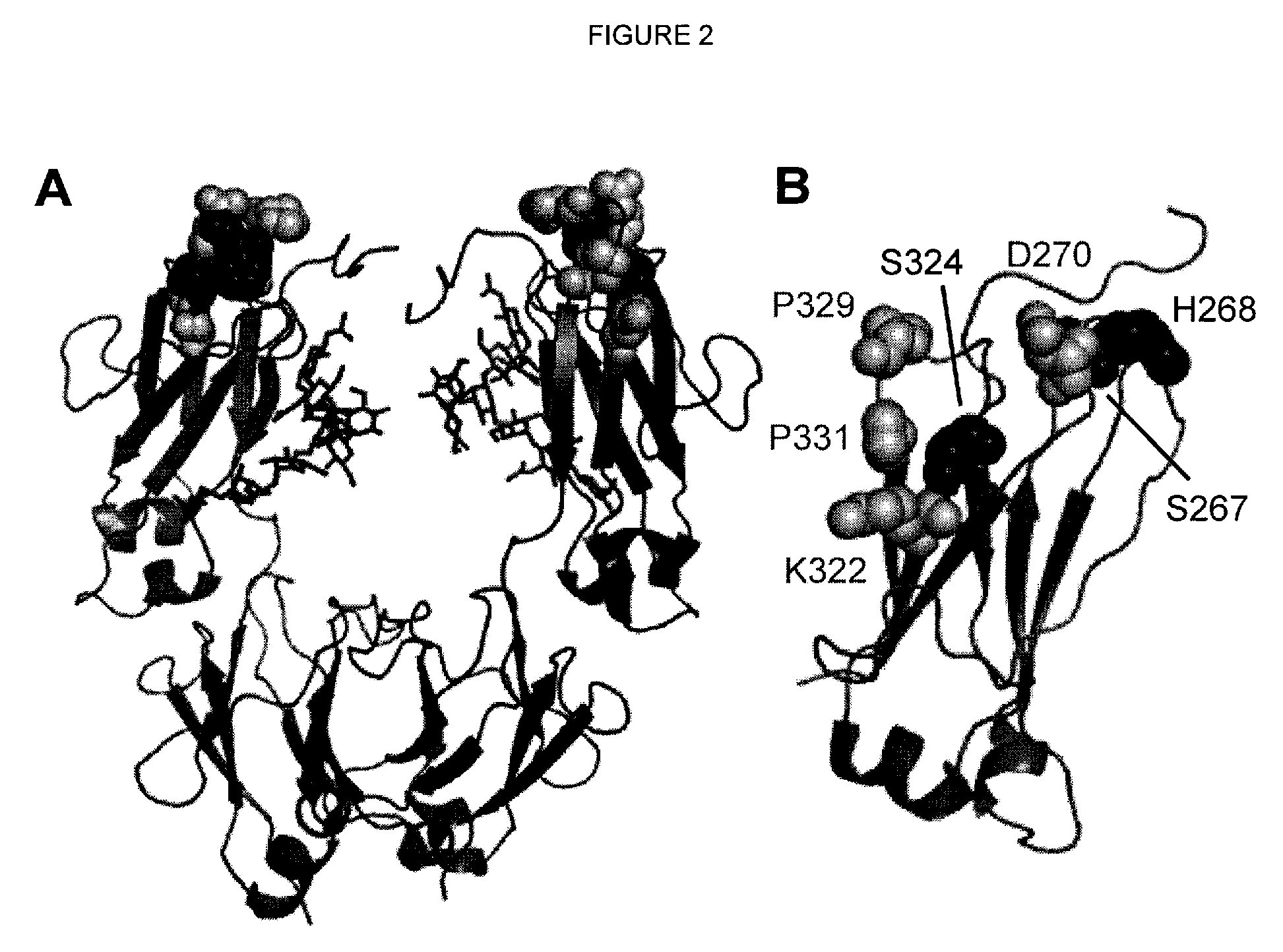
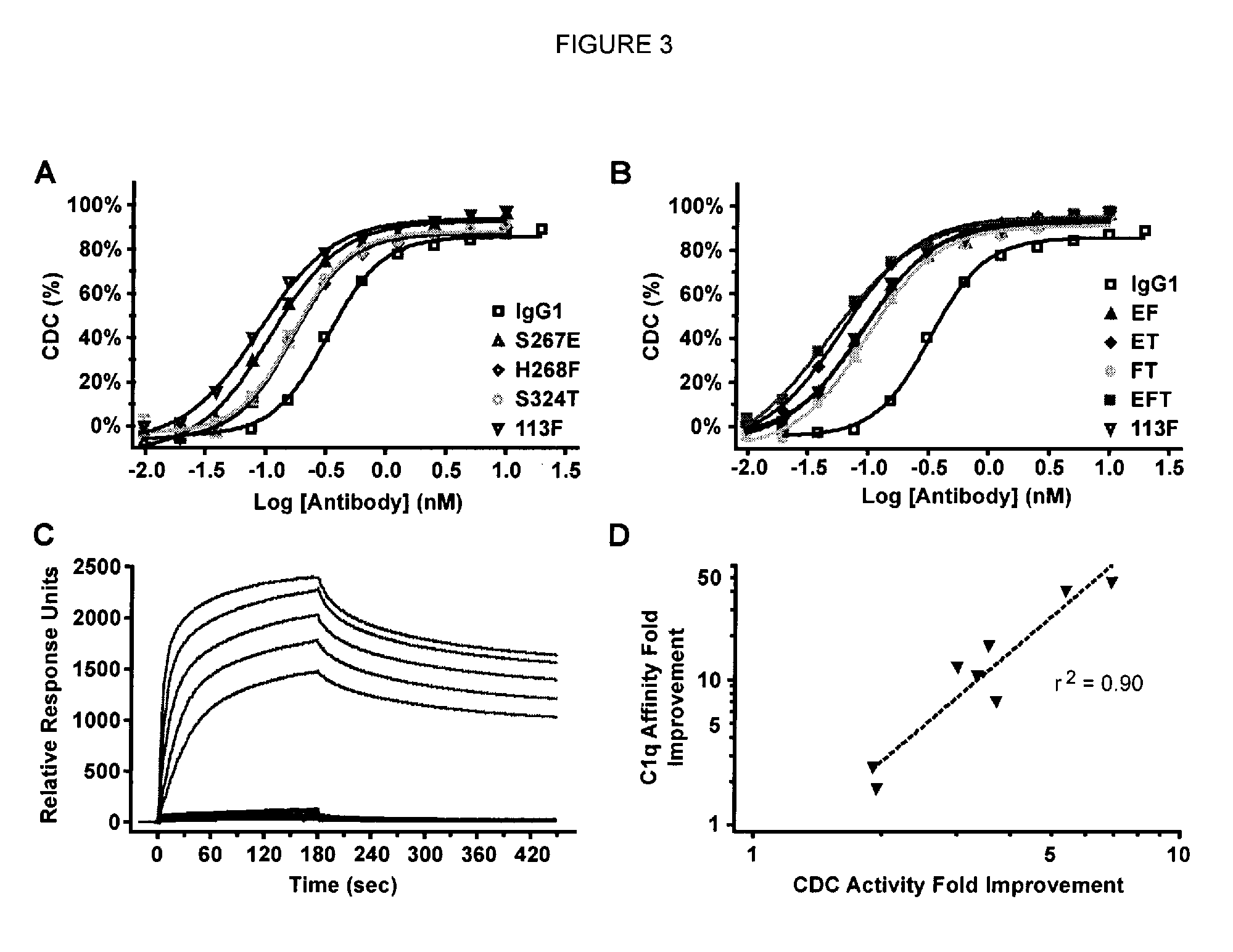
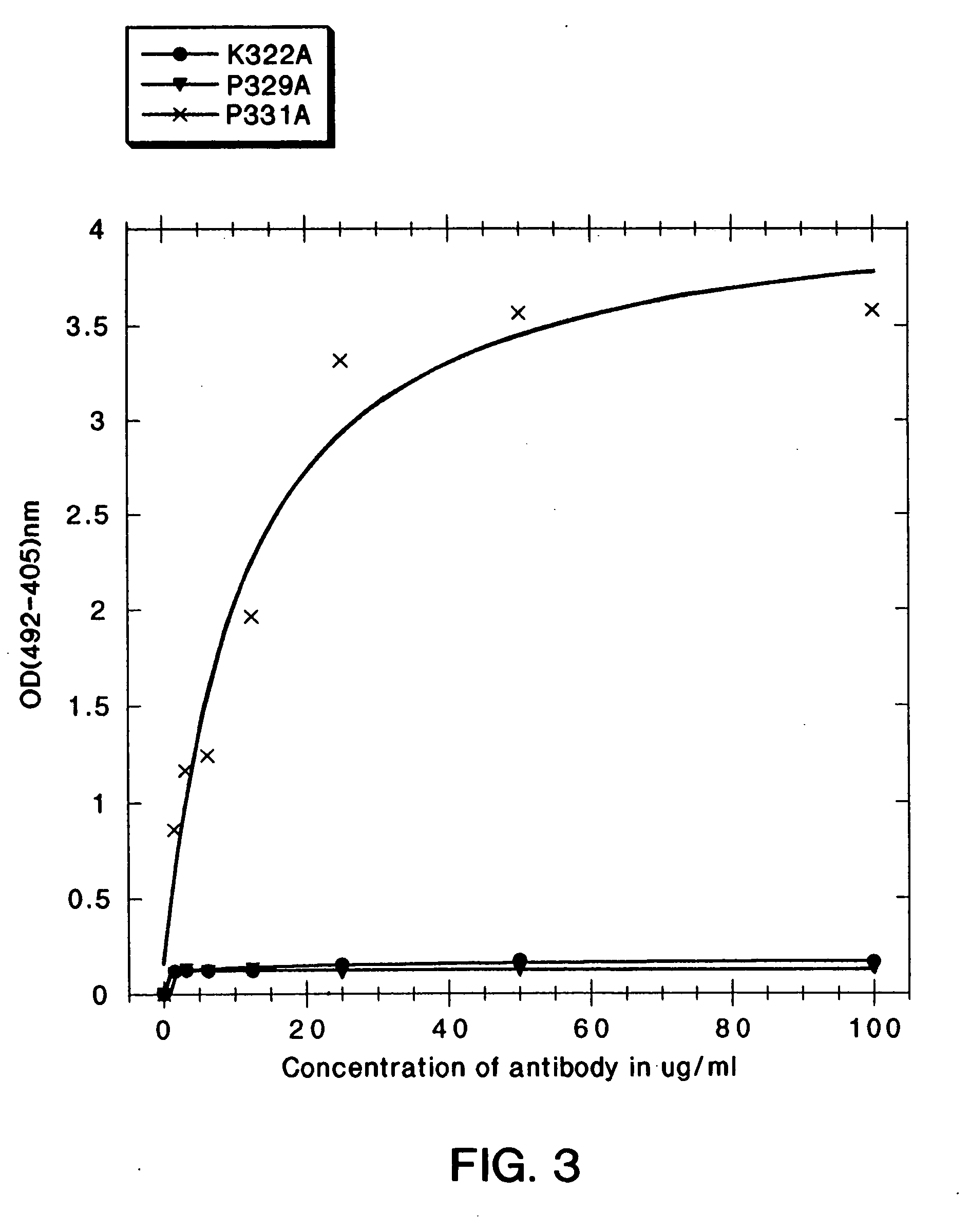
A variant of a polypeptide comprising a human IgG Fc region is described, which variant comprises an amino acid substitution at one or more of amino acid positions 270, 322, 326, 327, 329, 331, 333 or 334 of the human IgG Fc region. Such variants display altered effector function. For example, C1q binding and / or complement dependent cytotoxicity (CDC) activity may be altered in the variant polypeptide. The application also discloses a variant of a parent polypeptide comprising a human IgG Fc region, which variant has a better binding affinity for human C1q than the parent polypeptide.
Owner:GENENTECH INC
Novel Anti-cd38 antibodies for the treatment of cancer
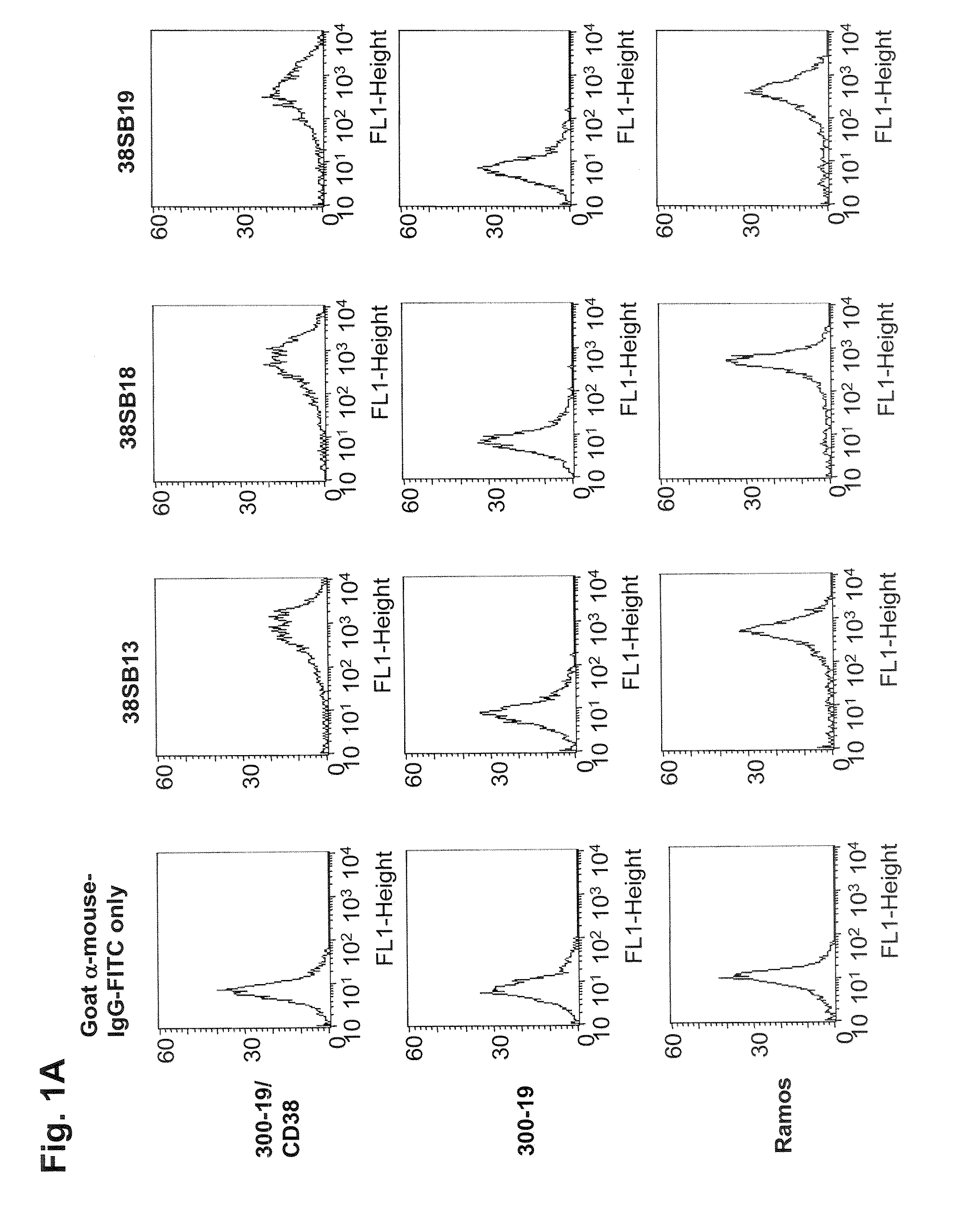
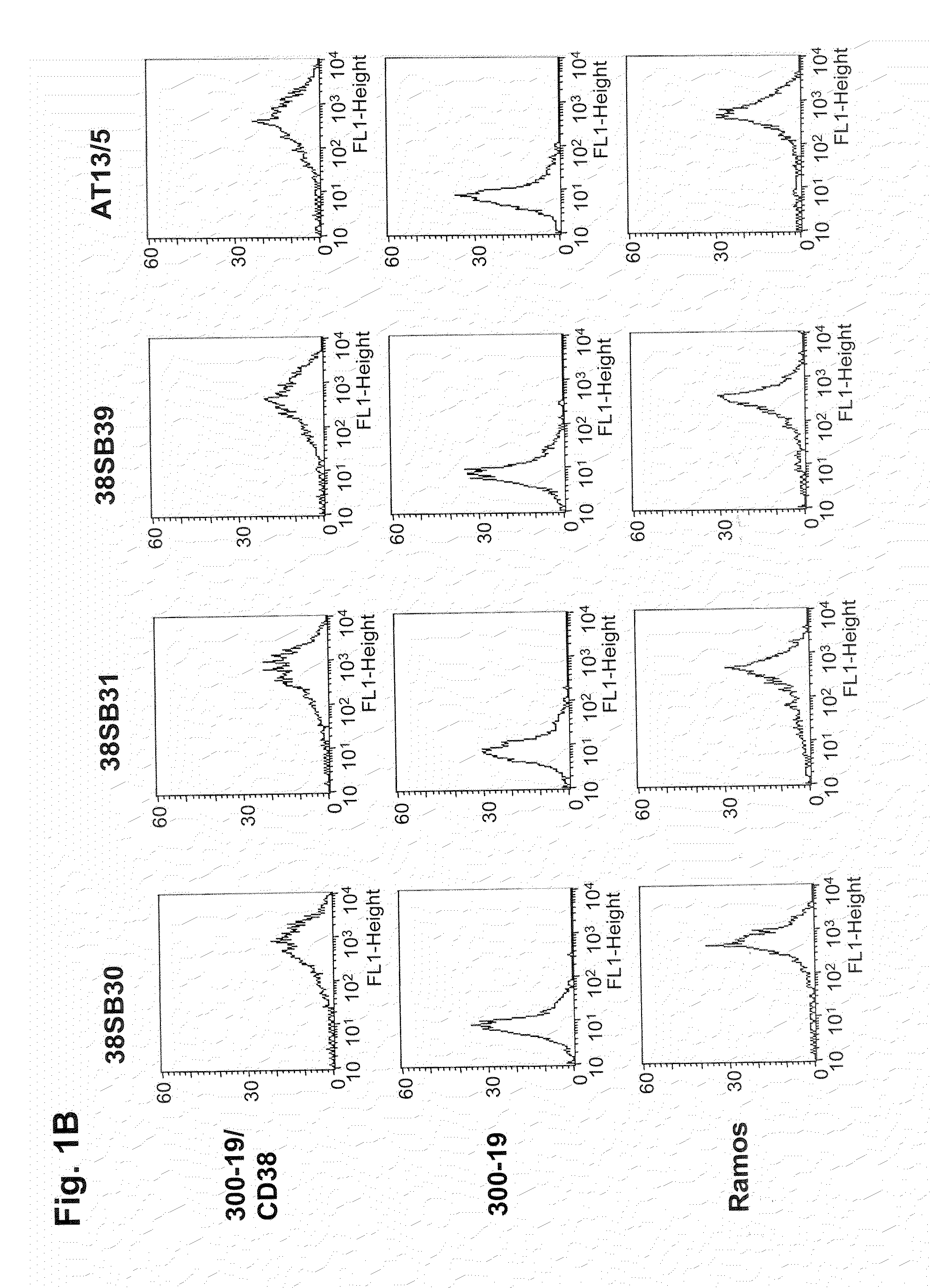
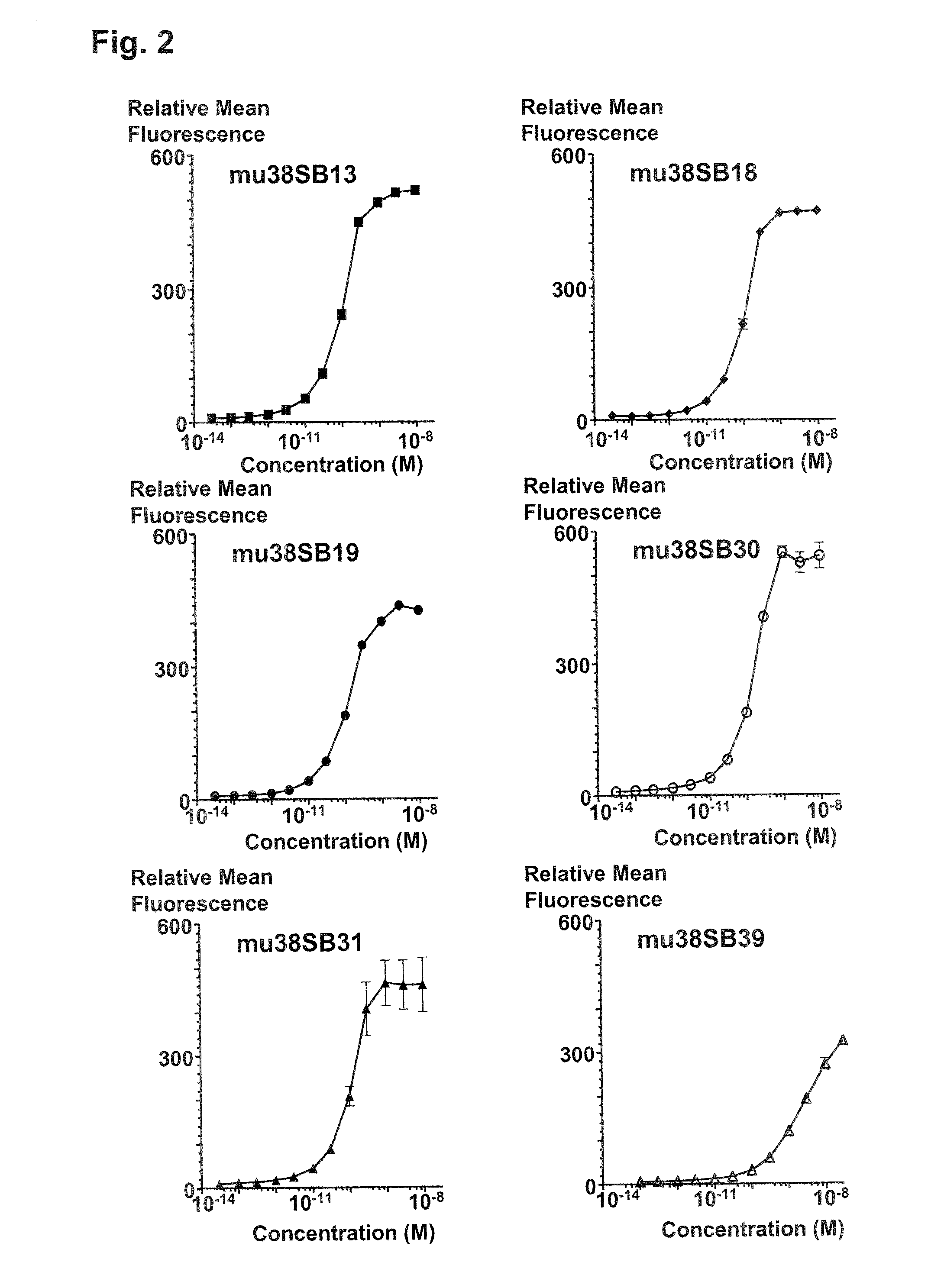
ActiveUS20090304710A1Improve propertiesLess immunogenicSenses disorderAntipyreticComplement-dependent cytotoxicityAntibody fragments
Antibodies, humanized antibodies, resurfaced antibodies, antibody fragments, derivatized antibodies, and conjugates of same with cytotoxic agents, which specifically bind to CD38, are capable of killing CD38+ cells by apoptosis, antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC), and / or complement-dependent cytotoxicity (CDC). Said antibodies and fragments thereof may be used in the treatment of tumors that express CD38 protein, such as multiple myeloma, chronic lymphocytic leukemia, chronic myelogenous leukemia, acute myelogenous leukemia, or acute lymphocytic leukemia, or the treatment of autoimmune and inflammatory diseases such as systemic lupus, rheumatoid arthritis, multiple sclerosis, erythematosus, and asthma. Said derivatized antibodies may be used in the diagnosis and imaging of tumors that express elevated levels of CD38. Also provided are cytotoxic conjugates comprising a cell binding agent and a cytotoxic agent, therapeutic compositions comprising the conjugate, methods for using the conjugates in the inhibition of cell growth and the treatment of disease, and a kit comprising the cytotoxic conjugate. In particular, the cell binding agent is a monoclonal antibody, and epitope-binding fragments thereof, that recognizes and binds the CD38 protein.
Owner:SANOFI AVENTIS US LLC
Polypeptide Variants
InactiveUS20100184959A1High sequence homologyFunction increasePeptide librariesLibrary screeningComplement-dependent cytotoxicityAntibody
The present invention relates to methods for selecting, obtaining or producing Fc variant polypeptides which show altered recognition for an Fc ligand (e.g., FcγR, CIq). Additionally, the Fc variant polypeptides may have altered antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC) and / or complement dependent cytotoxicity (CDC) activity. The invention further provides methods and protocols for the application of said Fc variant polypeptides particularly for therapeutic purposes.
Owner:MEDIMMUNE LTD
EPH receptor Fc variants with enhanced antibody dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity activity
InactiveUS20060039904A1Altered binding affinityHigh binding affinityCompound screeningApoptosis detectionComplement-dependent cytotoxicityReceptor
The present invention relates to novel Fc variants that immuno-specifically bind to an Eph receptor. The Fc variants comprise a binding region that immunospecifically binds to an Eph receptor and an Fc region that further comprises at least one novel amino acid residue which may provide for enhanced effector function. More specifically, this invention provides Fc variants that have modified binding affinity to one or more Fc ligand (e.g., FcγR, C1q). Additionally, the Fc variants have altered antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC) and / or complement dependent cytotoxicity (CDC) activity. The invention further provides methods and protocols for the application of said Fc variants that immunospecifically bind to an Eph receptor, particularly for therapeutic purposes.
Owner:MEDIMMUNE LLC
Methods for the identification of polypeptide antigens associated with disorders involving aberrant cell proliferation and compositions useful for the treatment of such disorders
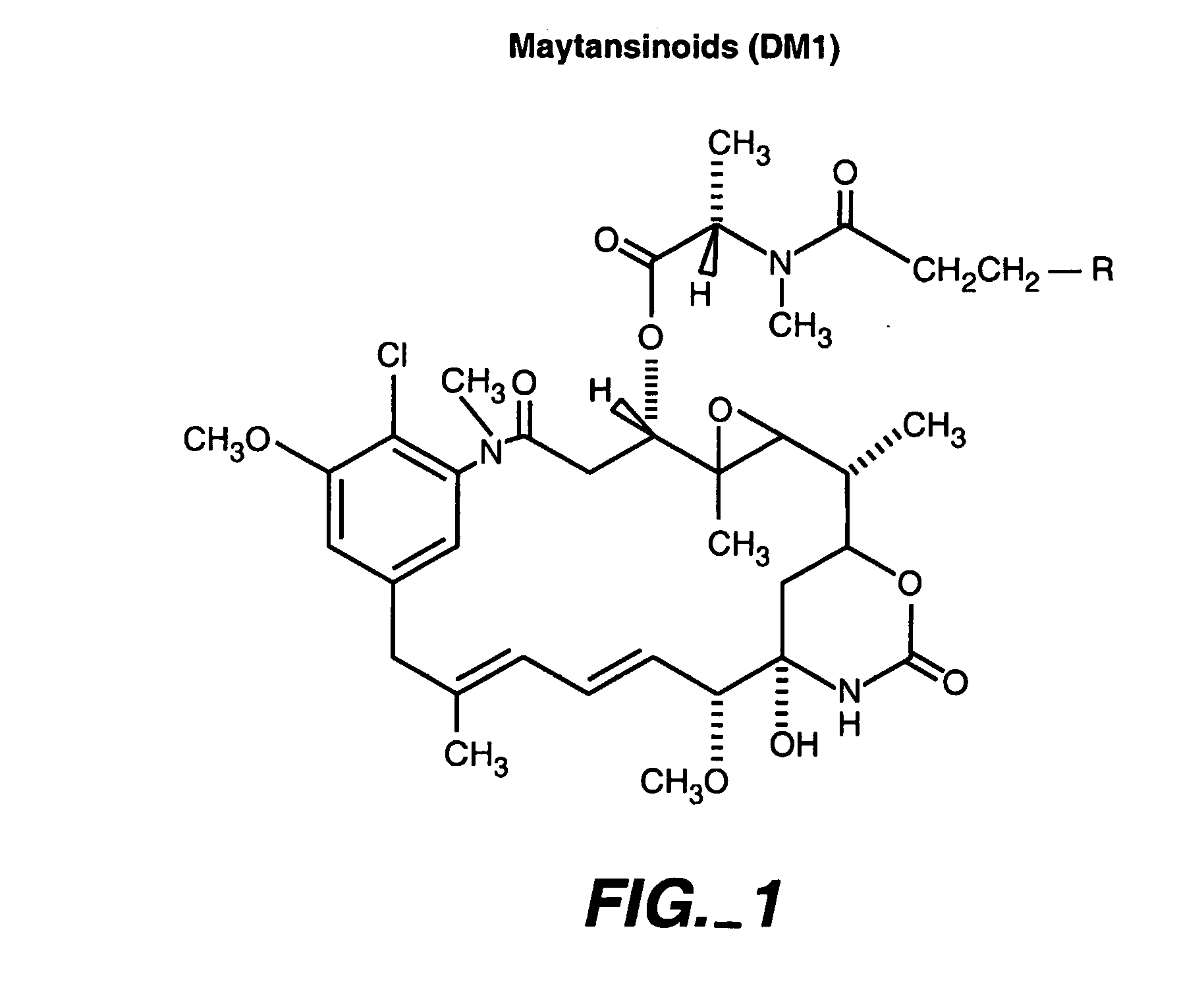
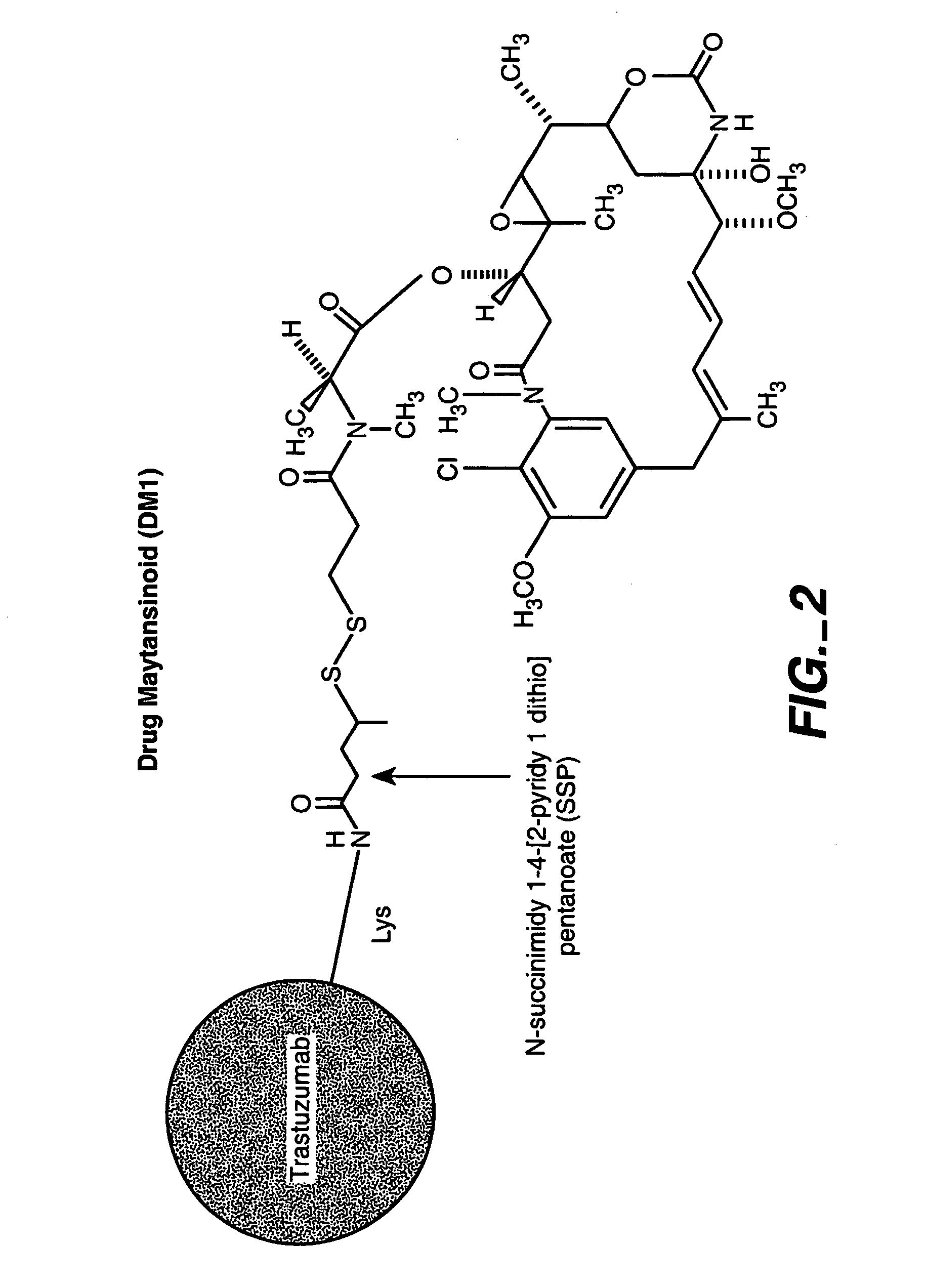
Methods and compositions for the development of effective cancer therapies using mitotic inhibitors which have limited general toxicity to normal, non-cancerous cells and tissues are provided. The methods and compositions utilize cytotoxic compounds comprised of a cell-binding agent (e.g., antibodies) conjugated to an anti-mitotic compound (e.g., maytansinoids). The invention further provides antibodies which are substantially incapable of inducing antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC) and / or complement dependent cytotoxicity (CDC), thereby ensuring that the therapeutic effect is mediated primarily by the anti-mitotic component of the cytotoxic compound, rather than by indirect cell killing via ADCC and / or CDC. The antibodies of the invention further are capable of differentiating between polypeptide antigens which are more highly expressed on proliferating cancer cells as compared to proliferating non-cancer cells.
Owner:GENENTECH INC
Integrin antagonists with enhanced antibody dependent cell-mediated cytoxicity activity
InactiveUS20060040325A1Enhance ADCCAltered binding affinityCompound screeningApoptosis detectionIntegrin antagonistComplement-dependent cytotoxicity
The present invention relates to novel Fc variants of antibodies that immunospecifically binds to Integrin αvβ3. The Fc variants comprise a variable region that immunospecifically binds to Integrin αvβ3 and a Fc region that further comprises at least one novel amino acid residue which may provide for enhanced effector function. More specifically, this invention provides Fc variants that have modified binding affinity to one or more FcγR and / or C1q. Additionally, the Fc variants have altered antibody dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC) and / or complement dependent cytotoxicity (CDC) activity. The invention further provides methods and protocols for the application of said Fc variants of an antibody that immunospecifically binds to Integrin αvβ3, particularly for therapeutic purposes.
Owner:MEDIMMUNE LLC
Modulation of antibody effector function by hinge domain engineering
ActiveUS20090221803A1Enhance prophylacticGood treatment effectAntibacterial agentsSenses disorderComplement-dependent cytotoxicityAntigen binding
The present invention relates to novel molecules (Fc variants) comprising at least one antigen binding region and an Fc region that further comprises a modified hinge which alters the binding of Fc to one or more Fc ligand (e.g., FcγRs) and / or modulates effector function. More specifically, this invention provides Fc variants that have modified binding affinity to one or more FcγR and / or CIq. Additionally, the Fc variants have altered antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC) and / or complement dependent cytotoxicity (CDC) activity. The invention further provides methods and protocols for the application of said Fc variants particularly for therapeutic purposes.
Owner:MEDIMMUNE LLC
Antibody variants with enhanced complement activity
The present invention relates to novel Fc variants that comprise at least one novel amino acid residue which may provide for enhanced effector function. More specifically, this invention provides Fc variants that have modified binding affinity to one or more Fc receptor or ligand (e.g., Fc gamma R, C1q). Additionally, the Fc variants have altered complement dependent cytotoxicity (CDC) activity and / or antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC). The invention further provides methods and protocols for the application of said Fc variants, particularly for therapeutic purposes.
Owner:XENCOR INC
Specific Anti-cd38 antibodies for treating human cancers
InactiveUS20150118251A1Low costOrganic active ingredientsImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsHuman cancerComplement-dependent cytotoxicity
The present disclosure concerns an antibody that specifically binds CD38 which is capable of killing a CD38+ cell by induction of apoptosis, antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC), and complement-dependent cytotoxicity. The disclosed antibody may be used as a medicament or in the making of a medicament, wherein the antibody is to be administered to a human subject in a safe therapeutic dose of about 20 mg / kg or below. In one embodiment, the medicament is for treating CD38+ multiple Myeloma in humans.
Owner:SANOFI SA
Novel antibody molecule aiming at human CLDN18.2, antigen binding fragment and medical application thereof
ActiveCN110606891AHigh binding activityInanimate material medical ingredientsImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsComplement-dependent cytotoxicityAntigen Binding Fragment
The invention discloses an anti-human CLDN18.2 antibody as well as an antigen binding fragment and a medical application thereof. Specifically, the present invention relates to a murine antibody comprising a CDR region of the anti-human CLDN18.2 antibody, a chimeric antibody and a humanized antibody, a fully humanized antibody, an antibody-dependent cytotoxicity (ADCC) comprising the antibody andthe antigen binding fragment thereof, complement dependent cytotoxicity (CDC), the killing effect on CLDN18.2 positive cells, the effect of inhibiting the growth of CLDN18.2 positive tumors, the in-vivo drug effect, a medicine containing the anti-human CLDN18.2 antibody and the antigen binding fragment thereof, a composition of the medicine thereof, and an application of the medicine in tumor treatment, in particular to treatment of CLDN18.2 positive tumor patients..
Owner:L&L BIOPHARMA CO LTD
Engineered lectins for viral inactivation
ActiveUS20090297516A1Easy to neutralizeGood curative effectAntibacterial agentsBiocideHalf-lifeComplement-dependent cytotoxicity
Engineered lectins and methods of using such reagents for both preventing and treating a broad array of viral infections are provided. The lectins of the invention are engineered in two ways, first through the enhancement of the natural mode of action of lectins against viruses through linked multimerization, and second through the creation of a new class of reagents, hereinafter referred to as a “lectibody” or “lectibodies”, that engage host immune function in addition to simply binding glycosylated viral proteins via the combination of a lectin and the Fc region of an antibody in order to drive Fc-mediated effector functions including ADCC (antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity), increased half-life, complement-dependent cytotoxicity (CDC), and antibody-dependent cell-mediated phagocytosis (ADCP) in response to a lectin-mediated carbohydrate-binding event.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Polypeptide variants
InactiveUS20060194954A1Weak affinityPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsAmino acid substitutionComplement-dependent cytotoxicity
A variant of a polypeptide comprising a human IgG Fc region is described, which variant comprises an amino acid substitution at one or more of amino acid positions 270, 322, 326, 327, 329, 331, 333 or 334 of the human IgG Fc region. Such variants display altered effector function. For example, C1q binding and / or complement dependent cytotoxicity (CDC) activity may be altered in the variant polypeptide. The application also discloses a variant of a parent polypeptide comprising a human IgG Fc region, which variant has a better binding affinity for human C1q than the parent polypeptide
Owner:GENENTECH INC
Novel Anti-cd38 antibodies for the treatment of cancer
InactiveUS20110262454A1Improved propertyLess immunogenicSenses disorderAntipyreticDiseaseComplement-dependent cytotoxicity
Antibodies, humanized antibodies, resurfaced antibodies, antibody fragments, derivatized antibodies, and conjugates of same with cytotoxic agents, which specifically bind to CD38, are capable of killing CD38+ cells by apoptosis, antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC), and / or complement-dependent cytotoxicity (CDC). Said antibodies and fragments thereof may be used in the treatment of tumors that express CD38 protein, such as multiple myeloma, chronic lymphocytic leukemia, chronic myelogenous leukemia, acute myelogenous leukemia, or acute lymphocytic leukemia, or the treatment of autoimmune and inflammatory diseases such as systemic lupus, rheumatoid arthritis, multiple sclerosis, erythematosus, and asthma. Said derivatized antibodies may be used in the diagnosis and imaging of tumors that express elevated levels of CD38. Also provided are cytotoxic conjugates comprising a cell binding agent and a cytotoxic agent, therapeutic compositions comprising the conjugate, methods for using the conjugates in the inhibition of cell growth and the treatment of disease, and a kit comprising the cytotoxic conjugate. In particular, the cell binding agent is a monoclonal antibody, and epitope-binding fragments thereof, that recognizes and binds the CD38 protein.
Owner:SANOFI SA
Eph receptor Fc variants with enhanced antibody dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity activity
InactiveUS7659374B2Altered binding affinityHigh binding affinityCompound screeningApoptosis detectionComplement-dependent cytotoxicityImmunologic specificity
The present invention relates to novel Fc variants that immuno-specifically bind to an Eph receptor. The Fc variants comprise a binding region that immunospecifically binds to an Eph receptor and an Fc region that further comprises at least one novel amino acid residue which may provide for enhanced effector function. More specifically, this invention provides Fc variants that have modified binding affinity to one or more Fc ligand (e.g., FcγR, C1q). Additionally, the Fc variants have altered antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC) and / or complement dependent cytotoxicity (CDC) activity. The invention further provides methods and protocols for the application of said Fc variants that immunospecifically bind to an Eph receptor, particularly for therapeutic purposes.
Owner:MEDIMMUNE LLC
Novel antibodies reactive with human carcinomas
InactiveUS20040043029A1Low immunogenicityImprove antibody based therapyPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsAntibody fragmentsAntibody conjugate
The present invention relates to novel antibodies, antibody fragments and antibody conjugates and single-chain immunotoxins reactive with human carcinoma cells. More particularly, the antibodies, conjugates and single-chain immunotoxins of the invention include: a murine monoclonal antibody, BR96; a human / murine chimeric antibody, ChiBR96; a F(ab')2 fragment of BR96; ChiBR96-PE, ChiBR96-LysPE40, ChiBR96 F(ab')2-LysPE40 and ChiBR96 Fab'-LysPE40 conjugates and recombinant BR96 sFv-PE40 immunotoxin. These molecules are reactive with a cell membrane antigen on the surface of human carcinomas. The BR96 antibody and its functional equivalents, displays a high degree of selectivity for carcinoma cells and possess the ability to mediate antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity and complement-dependent cytotoxicity activity. In addition, the antibodies of the invention internalize within the carcinoma cells to which they bind and are therefore particularly useful for therapeutic applications, for example, as the antibody component of antibody-drug or antibody-toxin conjugates. The antibodies also have a unique feature in that they are cytotoxic when used in the unmodified form, at specified concentrations.
Owner:BRISTOL MYERS SQUIBB CO
Modulation of antibody effector function by hinge domain engineering
ActiveUS8008443B2Altered binding affinityHigh binding affinityAntibacterial agentsSenses disorderComplement-dependent cytotoxicityAntigen binding
The present invention relates to novel molecules (Fc variants) comprising at least one antigen binding region and an Fc region that further comprises a modified hinge which alters the binding of Fc to one or more Fc ligand (e.g., FcγRs) and / or modulates effector function. More specifically, this invention provides Fc variants that have modified binding affinity to one or more FcγR and / or CIq. Additionally, the Fc variants have altered antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC) and / or complement dependent cytotoxicity (CDC) activity. The invention further provides methods and protocols for the application of said Fc variants particularly for therapeutic purposes.
Owner:MEDIMMUNE LLC
Hinge domain engineering
InactiveUS20110077383A1Improve stabilityAltered bindingImmunoglobulinsFermentationComplement-dependent cytotoxicityAntigen binding
The present invention relates to novel molecules (Fc variants) comprising at least one antigen binding region and an Fc region that further comprises a modified hinge which improves stability and / or alters the binding of Fc to one or more metal ion and / or one or more Fc ligand (e.g., FcγRs) and / or modulates effector function. More specifically, this invention provides Fc variants that are less susceptible to metal ion-mediated cleavage and / or have modified binding affinity to one or more FcγR and / or C1q. Additionally, the Fc variants have altered antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC) and / or complement dependent cytotoxicity (CDC) activity. Furthermore, the modified hinge of the Fc variants retains a similar flexibility to the wild type hinge. The invention further provides methods and protocols for the application of said Fc variants particularly for therapeutic purposes.
Owner:MEDIMMUNE LLC
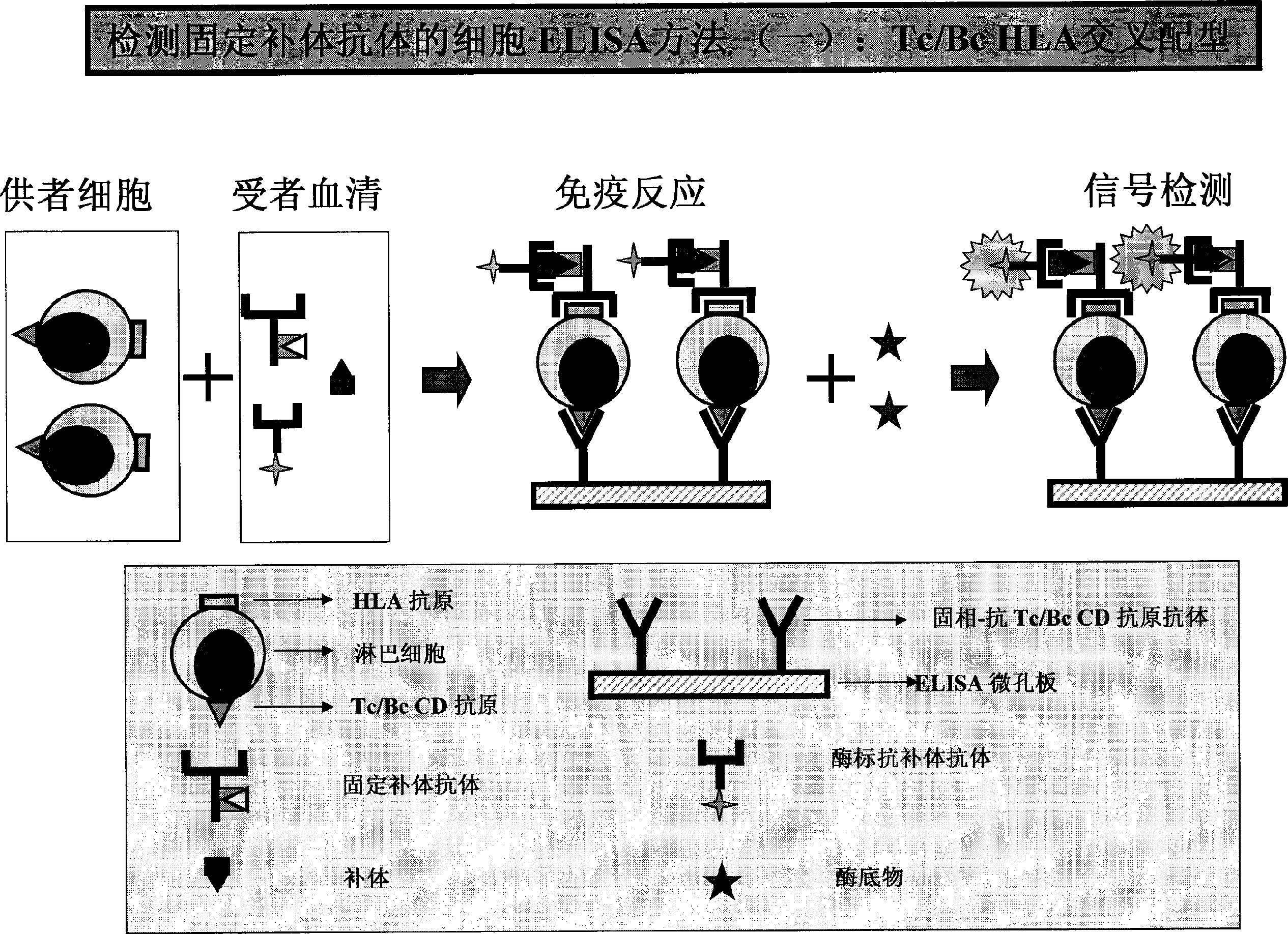
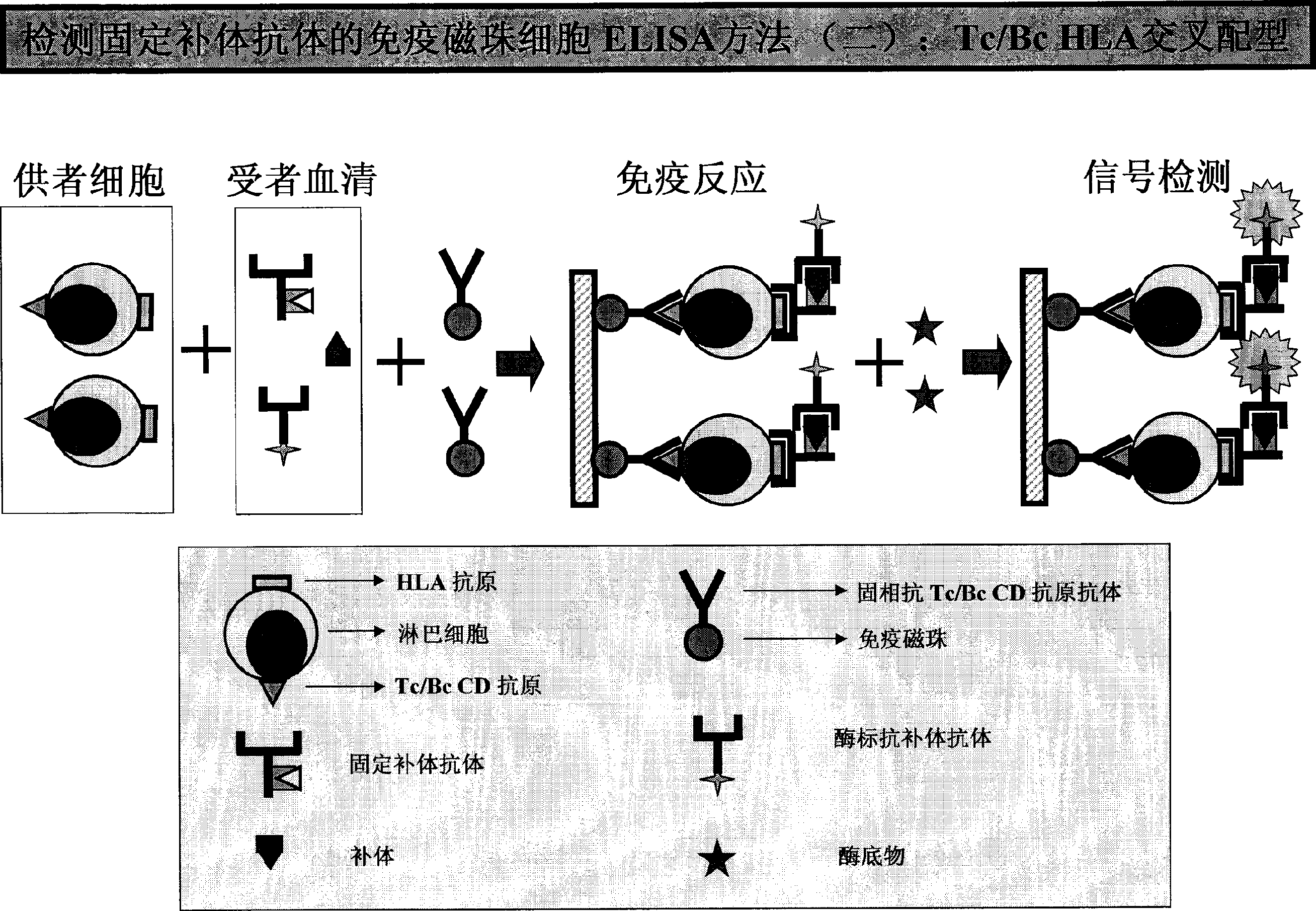
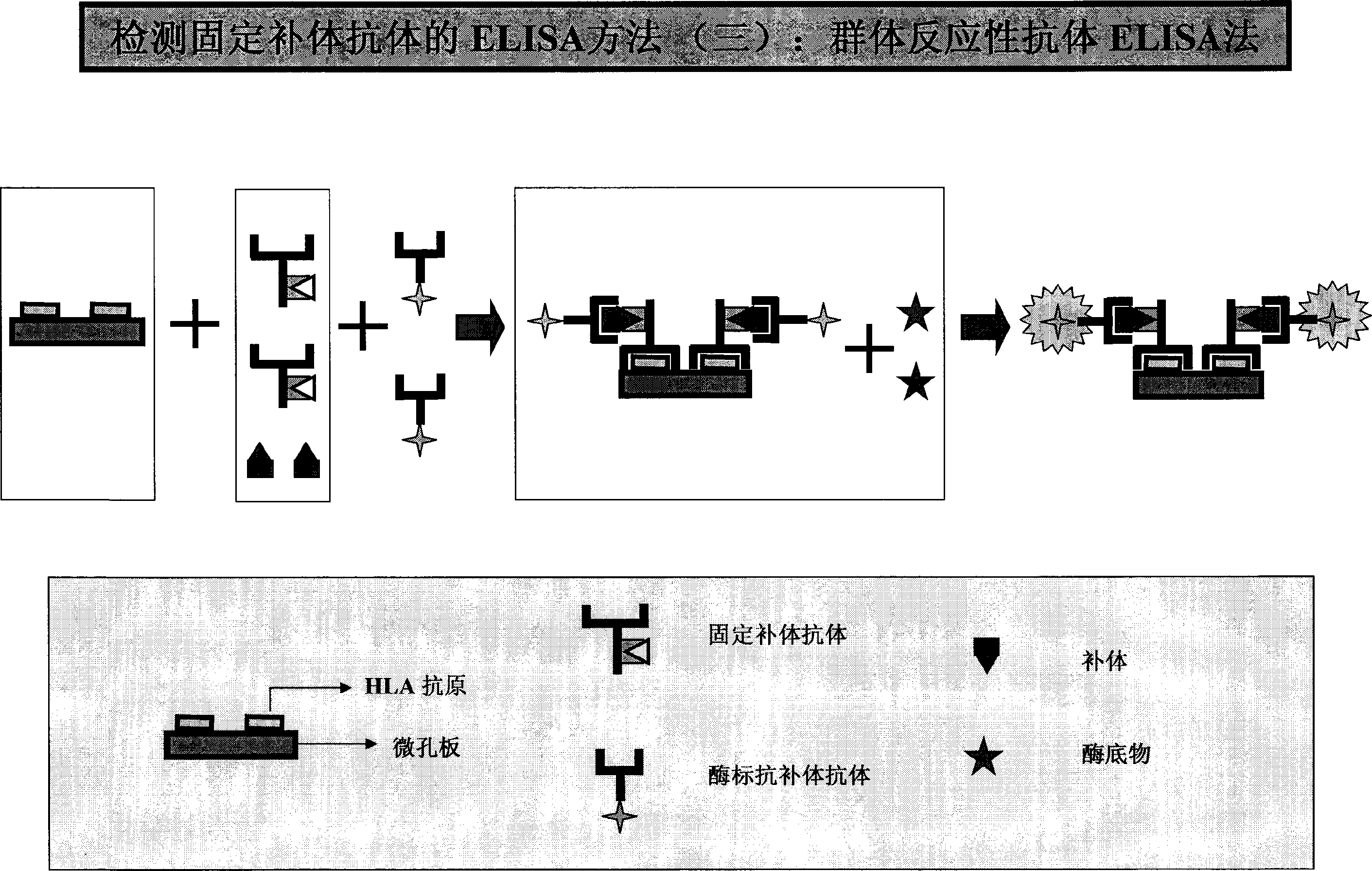
HLA complement-dependent cytotoxcity antibody detection method using ELIA as basis and its kit
InactiveCN1444044AShort reaction timeHigh sensitivityBiological testingComplement-dependent cytotoxicityCytotoxic antibody
According to the complement-dependent cytotoxicity (CDC) reaction principle in the immunology said invention creates an in-vitro enzyme-linked immunoreactino method for assaying HLA complement fixingantibodies (CFAbs) and its kit. The reaction system is formed from solid-phase HLA antigen or target cell with HLA antigen and liquid-phase enzyme-labelled ligand. CFAbs in the tested sample and solid-phase HLA antigen or HLA antigen of target cell are combined, and simultaneously fixed and existed in enzyme-labelled complement or the enzyme-labelled complement anti body is combined with complement fixed in HLA antigen-CFAb composite, then the correspondent enzyme substrate can be added to produce zymolygical color development reaction.
Owner:PEL FREEZ BIOTECH BEIJING
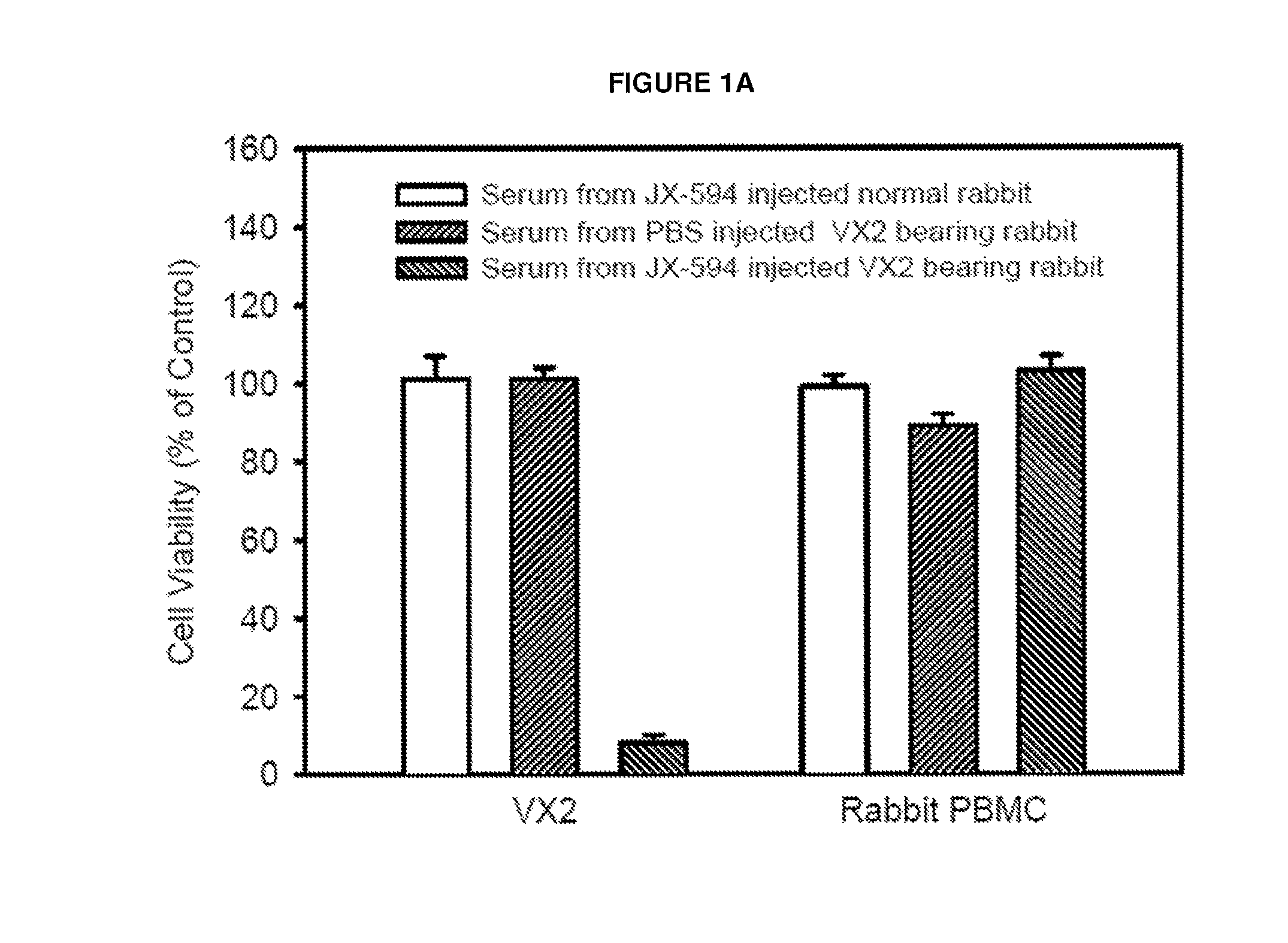
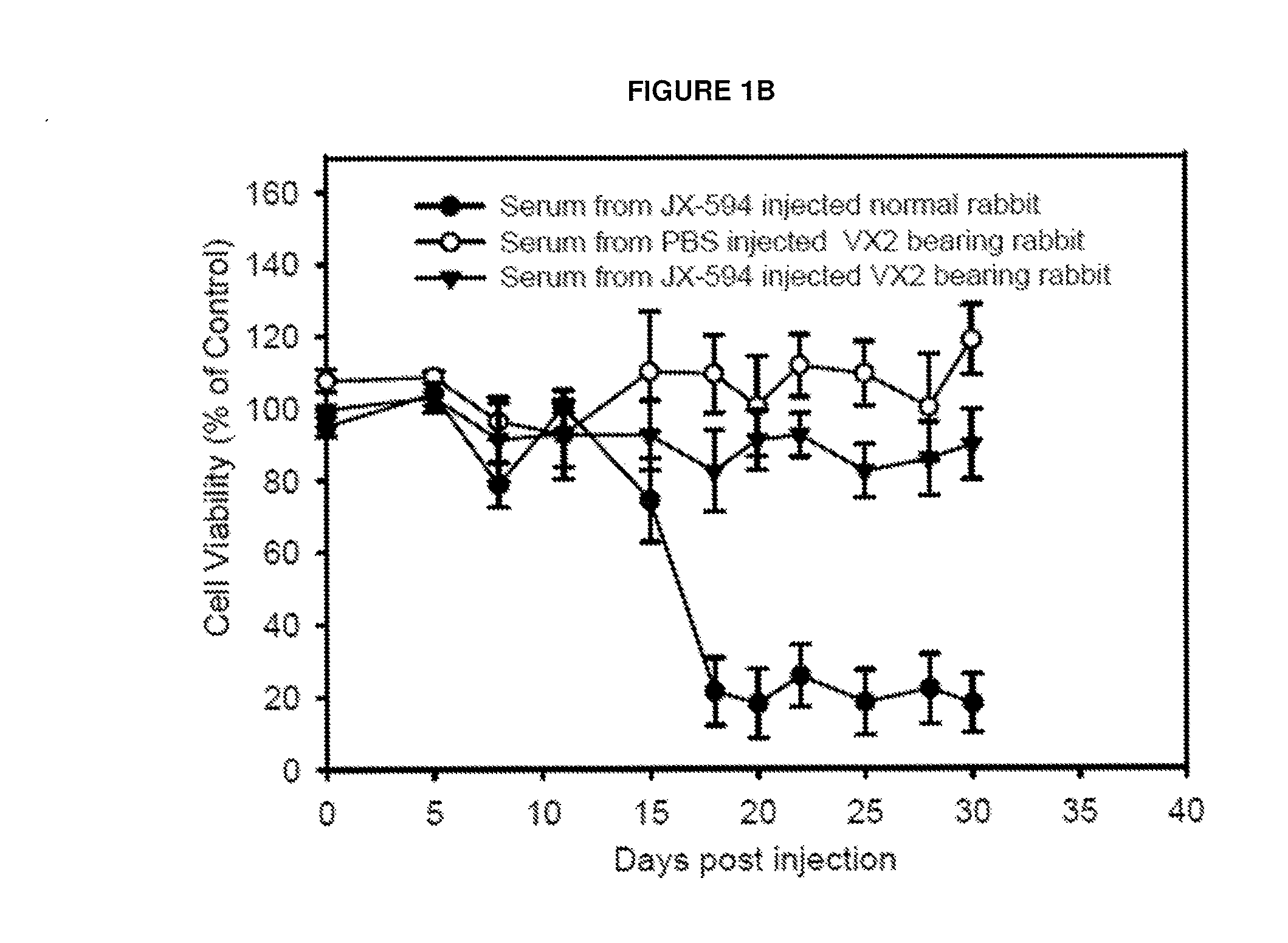
Generation of antibodies to tumor antigens and generation of tumor specific complement dependent cytotoxicity by administration of oncolytic vaccinia virus
The present invention relates to methods and compositions for use in inducing tumor-specific antibody mediated complement-dependent cytotoxic response in an animal having a tumor comprising administering to said animal a composition comprising a replication competent oncolytic virus wherein administration of the composition induces in the animal production of antibodies that mediate a CDC response specific to said tumor.
Owner:SILLAJEN +1
Therapeutic Agent And Diagnostic Agent For Cholangiocarcinoma
InactiveUS20080008710A1Easy to reachDifficult to reachDigestive systemImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsGrowth retardantDiagnostic agent
Disclosed is a cholangiocarcinoma cell growth inhibitor comprising an anti-glypican-3 antibody as an active ingredient. Preferably, the anti-glypican-3 antibody has a cytotoxic activity such as an antibody-dependent cytotoxic (ADCC) activity and a complement-dependent cytotoxic (CDC) activity. Also disclosed is a diagnostic agent for diagnosis of cholangiocarcinoma comprising an anti-glypican-3 antibody.
Owner:CHUGAI PHARMA CO LTD +3
Anti-cd22 Anti-idiotypic antibodies and uses thereof
ActiveUS20150175711A1Not applyBiological material analysisArtificial cell constructsComplement-dependent cytotoxicityAntibody fragments
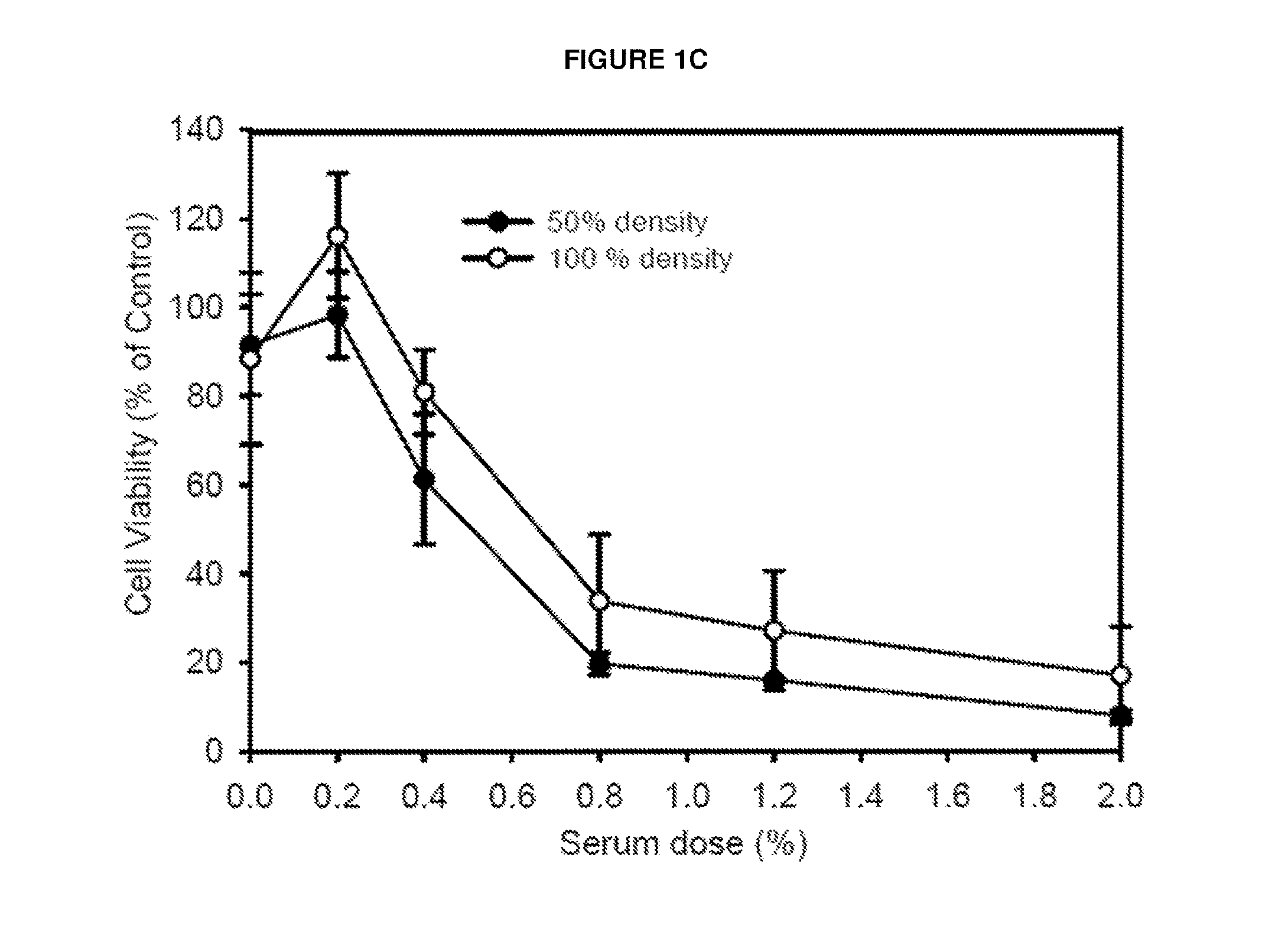
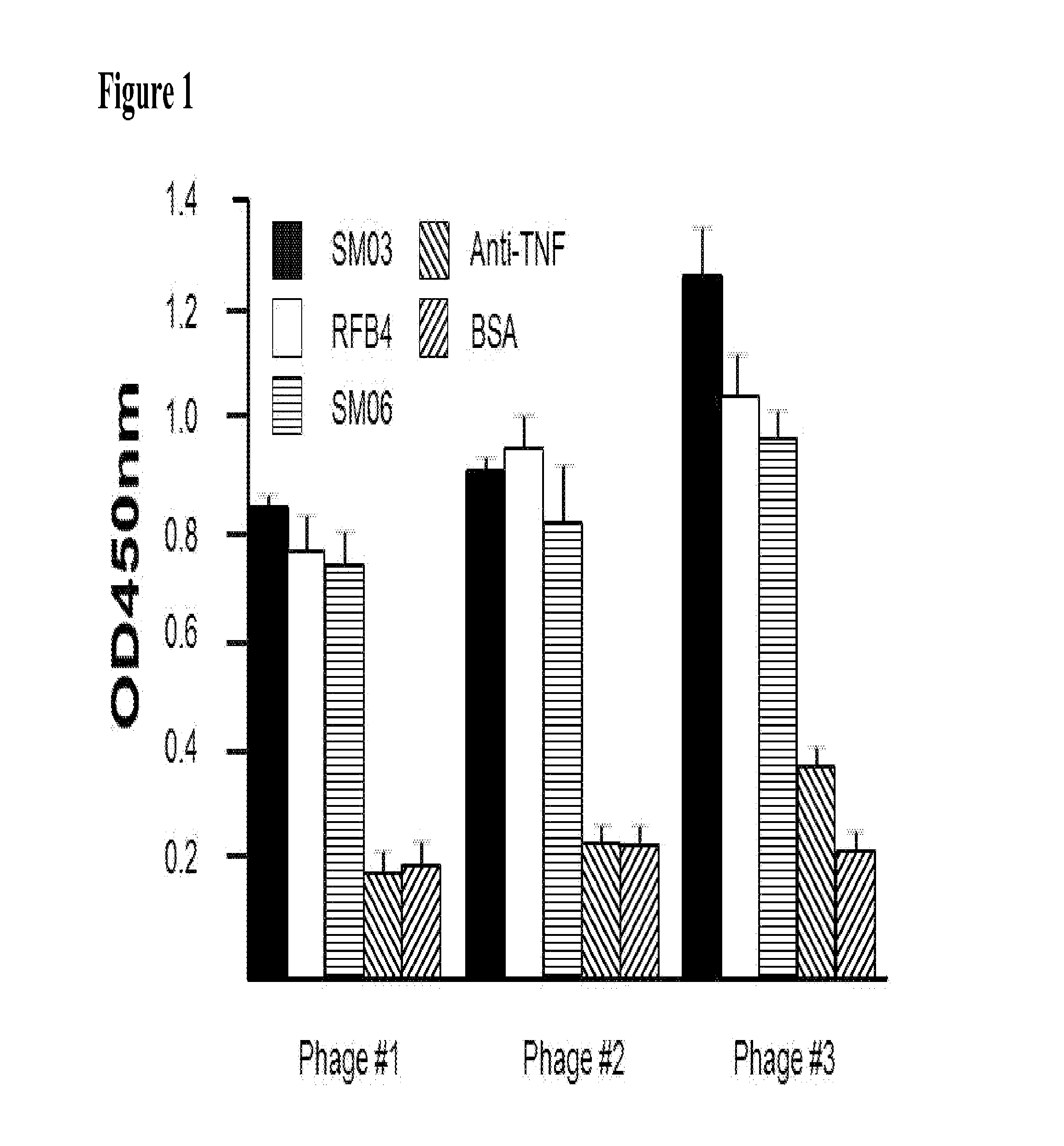
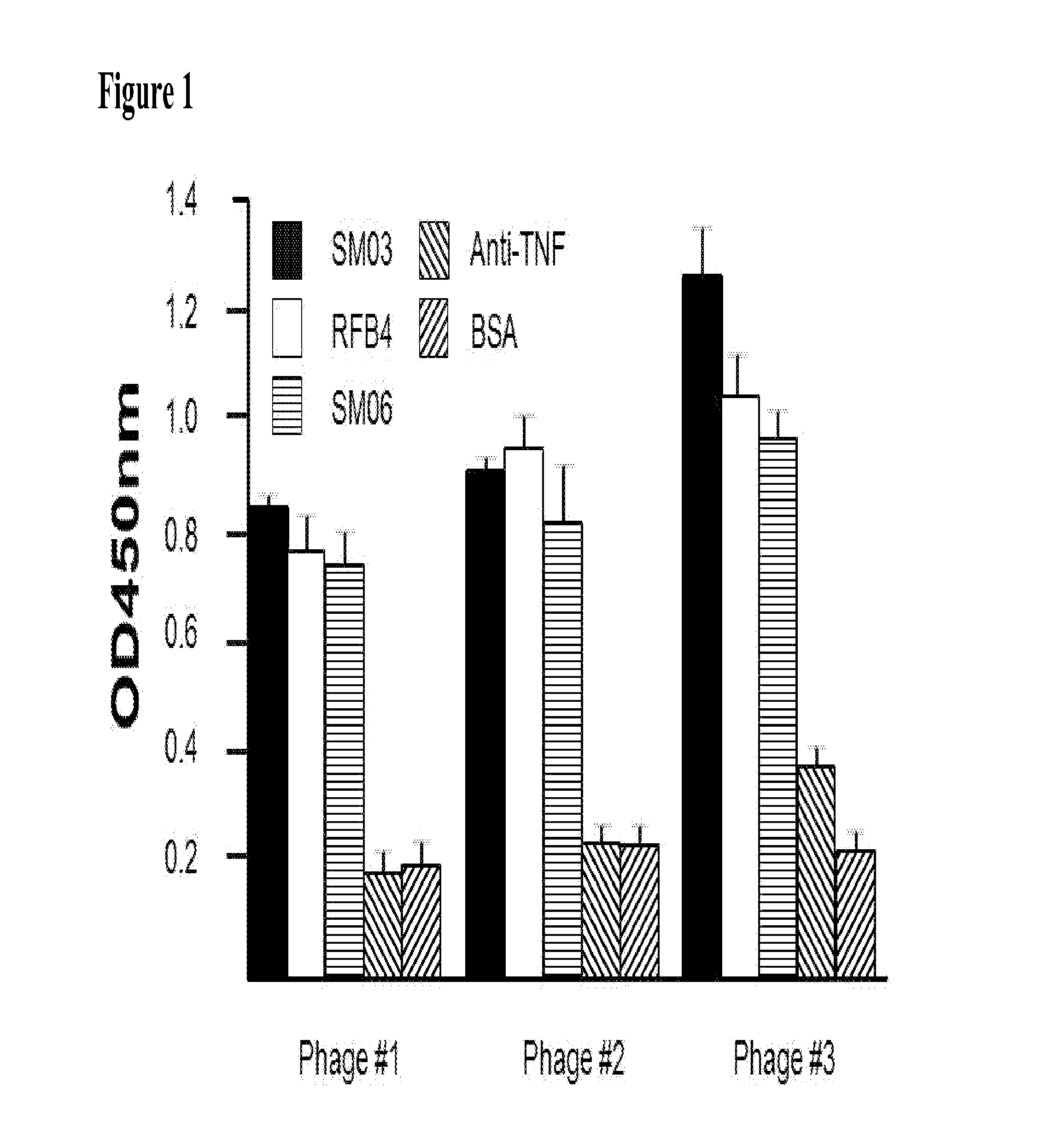
The present invention describes the generation of an anti-idiotype single-chain Fv (scFv) antibody specific for the murine (RFB4), chimeric (SM03) and humanized (SM06) versions of an anti-CD22 antibody (the anti-CD22 antibodies). The present invention further describes the construction of a murine IgG2a / kappa immunoglobulin carrying the variable region sequences of the anti-idiotype scFv sequences. Additionally, the present invention provides a cell line capable of producing an anti-idiotype murine antibody specific for the anti-CD22 antibodies. The present invention is directed against a method for identifying and evaluating the activities and concentration of the anti-CD22 antibodies. Additionally, the present invention provides a method for evaluating serum concentration of the anti-CD22 antibodies that are being used clinically. The present invention is also directed against a method to detect HAMA, HACA and HAHA responses in patients treated with the anti-CD22 antibodies. Specifically, the present invention is directed against the establishment of a cell line expressing surface concentration of the antibody of the invention; the said cell line expressing surface anti-idiotype antibodies or antibody fragments will be used as the target cell line for evaluating the functional activities of the anti-CD22 antibodies via complement dependent cytotoxicity (CDC) and / or antibody dependent cell cytotoxicity (ADCC) activities.
Owner:SINOMAB BIOSCI
Methods for the identification of polypeptide antigens associated with disorders involving aberrant cell proliferation and compositions useful for the treatment of such disorders
Methods and compositions for the development of effective cancer therapies using mitotic inhibitors which have limited general toxicity to normal, non-cancerous cells and tissues are provided. The methods and compositions utilize cytotoxic compounds comprised of a cell-binding agent (e.g., antibodies) conjugated to an anti-mitotic compound (e.g., maytansinoids). The invention further provides antibodies which are substantially incapable of inducing antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC) and / or complement dependent cytotoxicity (CDC), thereby ensuring that the therapeutic effect is mediated primarily by the anti-mitotic component of the cytotoxic compound, rather than by indirect cell killing via ADCC and / or CDC. The antibodies of the invention further are capable of differentiating between polypeptide antigens which are more highly expressed on proliferating cancer cells as compared to proliferating non-cancer cells.
Owner:LEVINSON ARTHUR D
Anti-CD22 anti-idiotypic antibodies and uses thereof
ActiveUS9371396B2Biological material analysisImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsComplement-dependent cytotoxicityAntibody fragments
The present invention describes the generation of an anti-idiotype single-chain Fv (scFv) antibody specific for the murine (RFB4), chimeric (SM03) and humanized (SM06) versions of an anti-CD22 antibody (the anti-CD22 antibodies). The present invention further describes the construction of a murine IgG2a / kappa immunoglobulin carrying the variable region sequences of the anti-idiotype scFv sequences. Additionally, the present invention provides a cell line capable of producing an anti-idiotype murine antibody specific for the anti-CD22 antibodies. The present invention is directed against a method for identifying and evaluating the activities and concentration of the anti-CD22 antibodies. Additionally, the present invention provides a method for evaluating serum concentration of the anti-CD22 antibodies that are being used clinically. The present invention is also directed against a method to detect HAMA, HACA and HAHA responses in patients treated with the anti-CD22 antibodies. Specifically, the present invention is directed against the establishment of a cell line expressing surface concentration of the antibody of the invention; the said cell line expressing surface anti-idiotype antibodies or antibody fragments will be used as the target cell line for evaluating the functional activities of the anti-CD22 antibodies via complement dependent cytotoxicity (CDC) and / or antibody dependent cell cytotoxicity (ADCC) activities.
Owner:SINOMAB BIOSCI
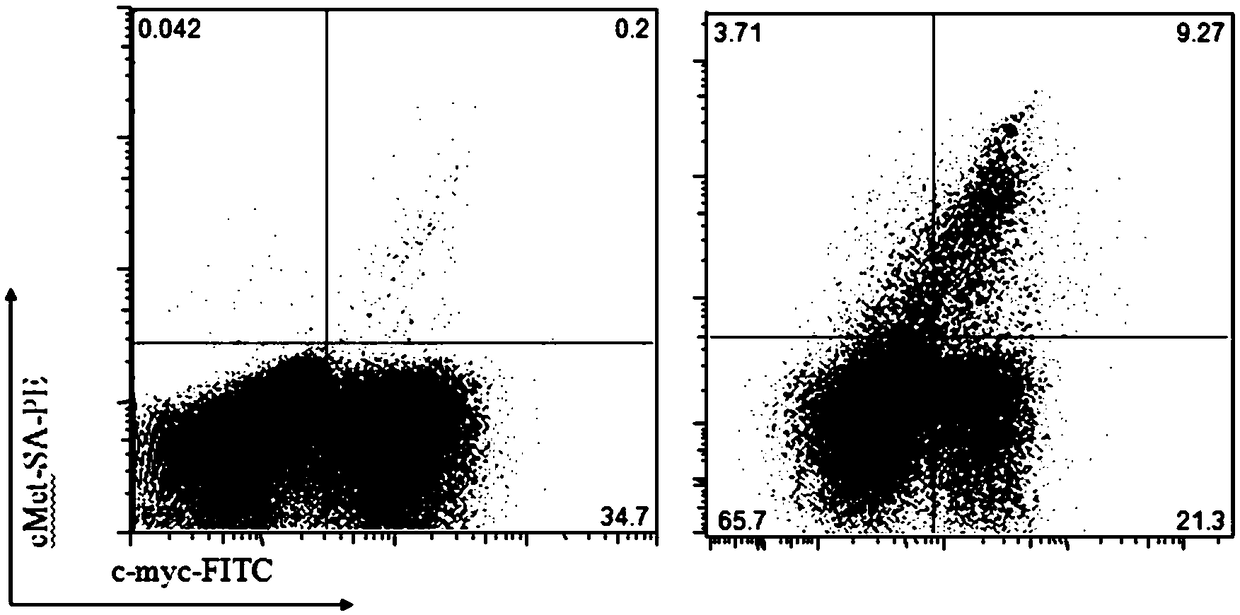
Human single chain variable fragments antibody for recognizing human c-Met proteins, diagnostic reagent and CAR-T cell preparation thereof
InactiveCN108707198AStrong specificityGood target for tumor therapyImmunoglobulin superfamilyAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsHuman tumorSingle-Chain Antibodies
The invention relates to a nucleotide sequence and an amino acid sequence, which can specifically recognize human c-Met proteins, of a single chain antibody. Based on the single chain antibody, a fusion protein for specifically recognizing tumor cells with positive c-Met can be acquired. In vitro experiments prove that the fusion protein can mediate complement-dependent cytotoxicity effect and antibody-dependent cytotoxicity effect; the fusion protein can kill the tumor cells when being injected into a tumor-bearing mouse; and based on the single chain antibody, a chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) for recognizing the c-Met is constructed, and CAR-T cells are prepared and amplified. The c-Met CAR-T cells can specifically recognize human tumor cells with the positive c-Met and are effectivelykilled in vitro and expresses the treatment effects of specifically recognizing the c-Met and inhibiting growth of the tumor cells when being injected into the tumor-bearing mouse.
Owner:李永海
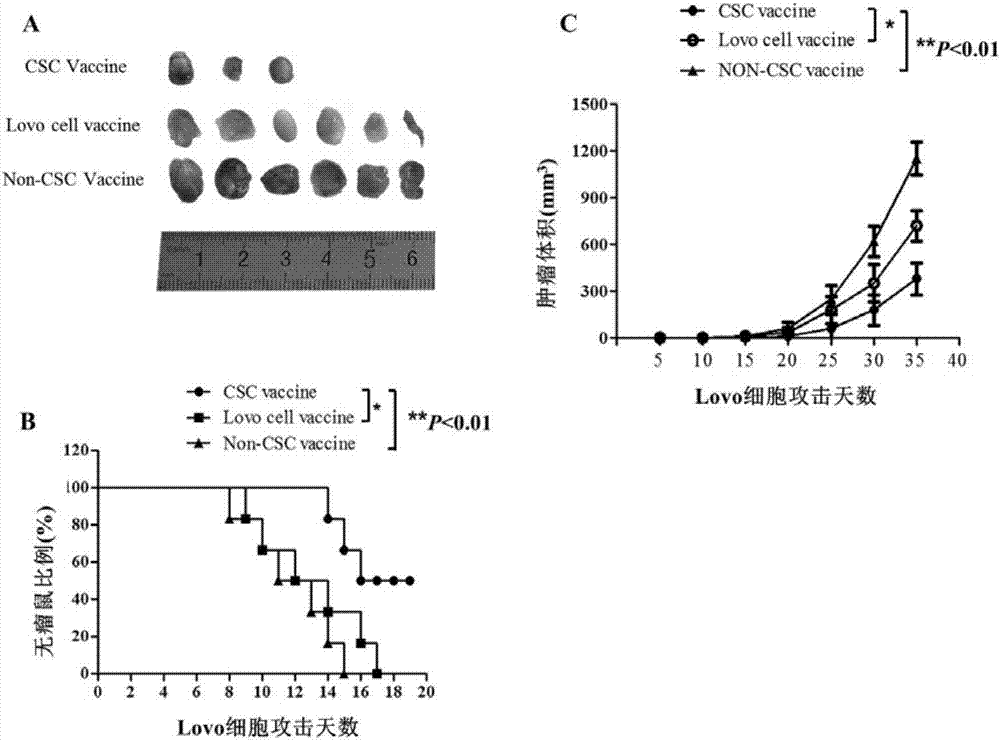
Colorectal cancer stem cell vaccine preparation method and application
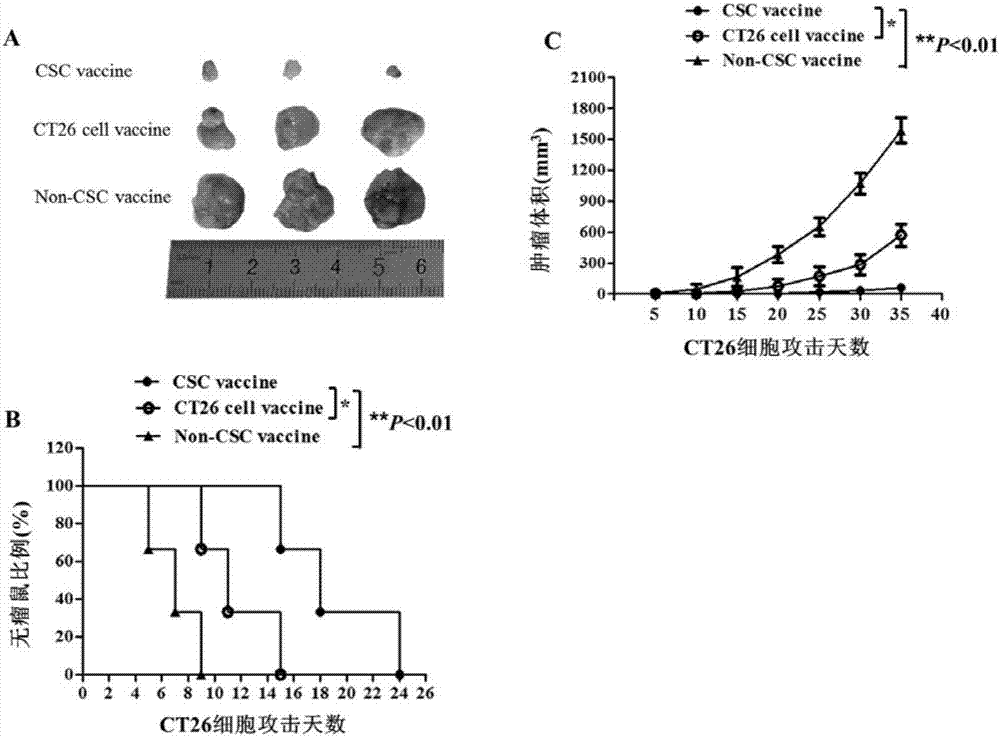
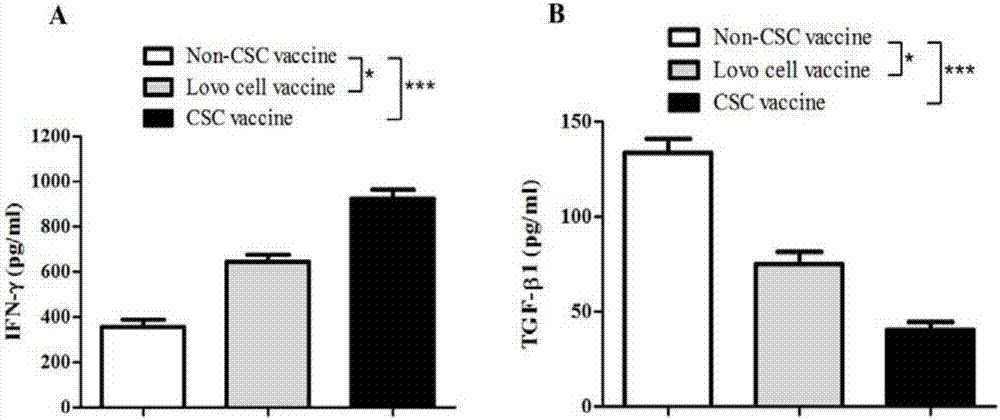
InactiveCN107158367AEnhance immune functionHigh activityCell dissociation methodsCancer antigen ingredientsMedicineComplement-dependent cytotoxicity
The invention discloses a colorectal cancer stem cell vaccine preparation method and application. Postoperative tumor tissue cells derived from patients with colorectal cancer, human colorectal cancer cell lines Lovo or mouse colorectal cancer cell lines CT26 are prepared into CD133+ colorectal cancer stem cell vaccines by a repeated freezing-thawing method. The CD133+ colorectal cancer stem cell vaccines can reduce immunized mouse serum TGF-beta level, IFN-gamma level is improved, killing activity of NK (natural killer) cells and CDC (complement-dependent cytotoxicity) activity are enhanced, immunized mice resist colorectal cancer cell attack, immune cells are induced to selectively kill CD133+ colorectal cancer stem cells, and further tumor growth is inhibited.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Novel antibody conjugates reactive with human carcinomas
InactiveUS20060018914A1Peptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsCancer cellAntibody conjugate
Owner:BRISTOL MYERS SQUIBB CO
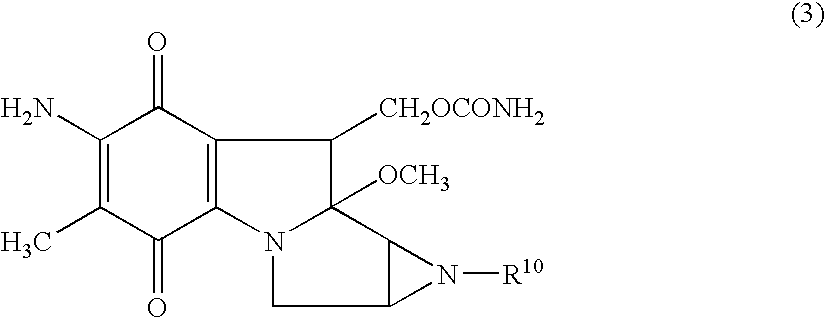
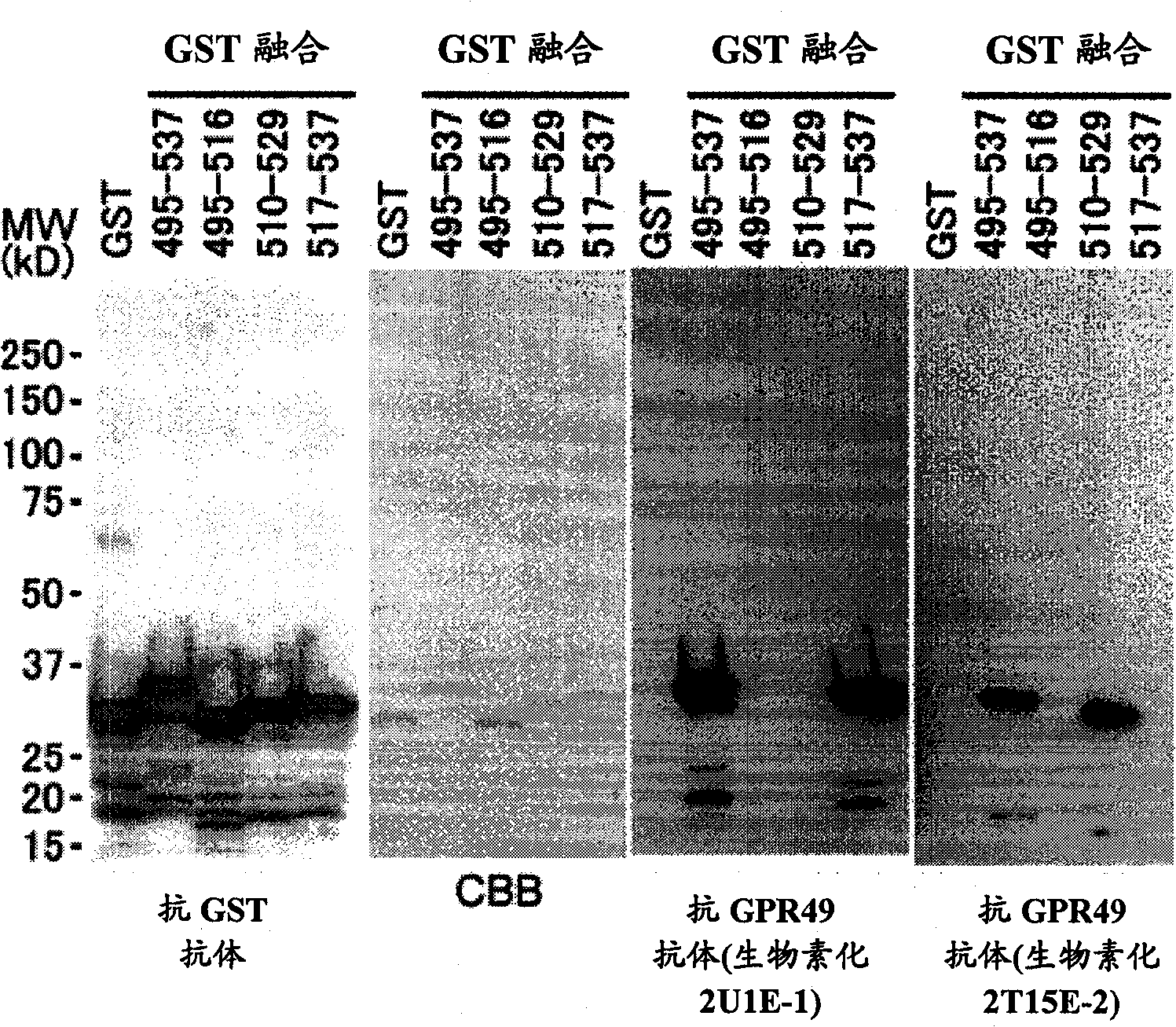
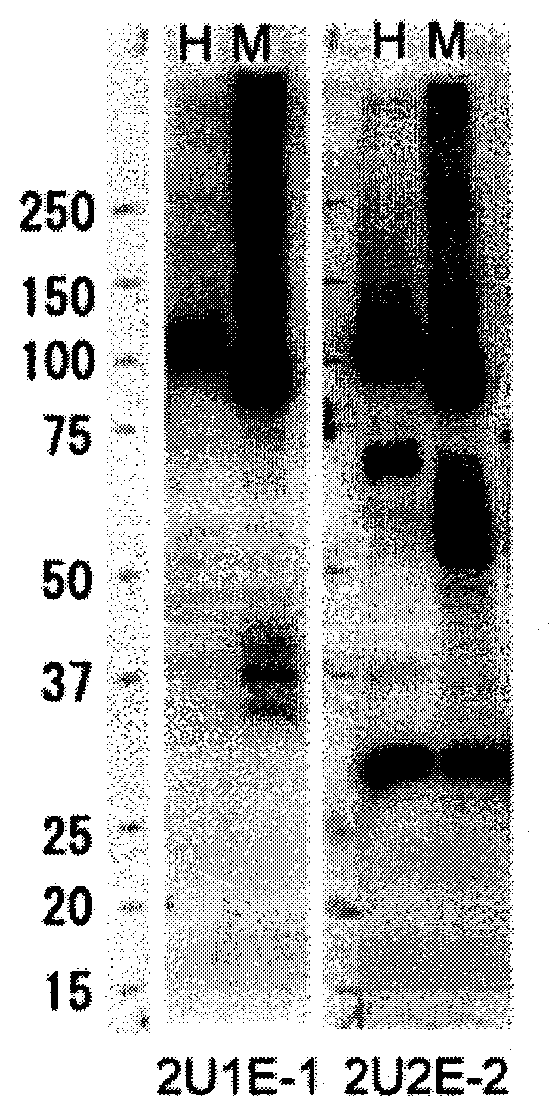
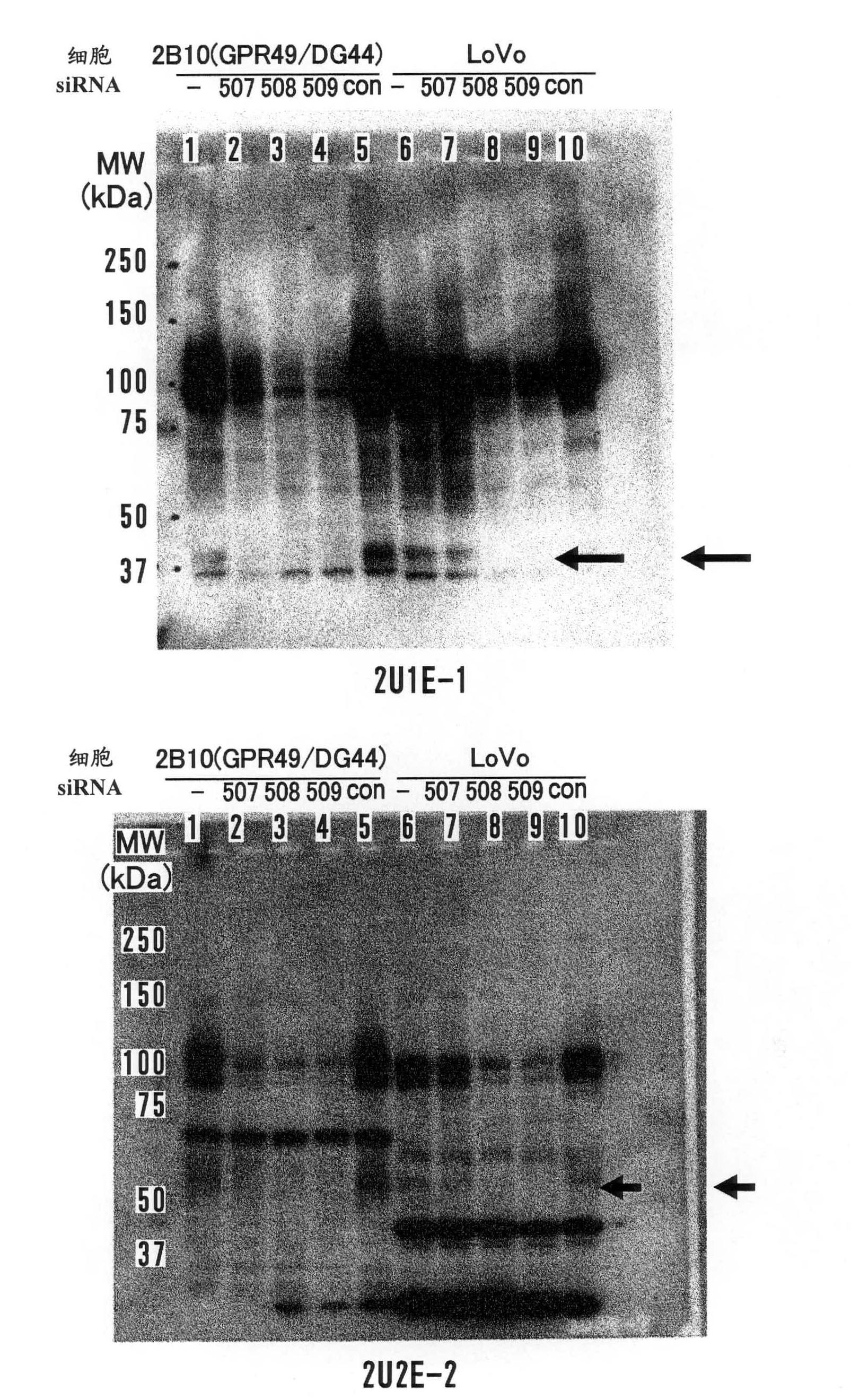
Diagnosis and treatment of cancer using anti-GPR49 antibody
InactiveCN102112492AEffective diagnosisIn-vivo radioactive preparationsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsComplement-dependent cytotoxicityHepatocellular carcinoma
Disclosed is an antibody which can bind to GPR49 protein and which has a cell proliferation-inhibiting activity against a cell capable of producing GPR49 protein. The cell proliferation-inhibiting activity may be a cytotoxic activity such as an antibody-dependent cytotoxicity or a complement-dependent cytotoxicity. Also disclosed are: a pharmaceutical composition; a cell proliferation inhibitor; and an anti-cancer agent, each of which comprises the antibody as an active ingredient. The cancer may be gastric cancer, colorectal cancer, hepatocellular cancer, lung cancer, prostate cancer, ovarian cancer, Ewing sarcoma, or glioma. Further disclosed are: a method for the diagnosis of cancer by detecting GPR49 protein or the expression of a gene encoding GPR49 protein; and a diagnosis agent and a kit for use in the method.
Owner:CHUGAI PHARMA CO LTD
Diagnosis and Treatment of Cancer Using Anti-LGR7 Antibody
InactiveUS20120014870A1Library screeningImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsOvarian Clear Cell AdenocarcinomaComplement-dependent cytotoxicity
With dedicated research, the present inventors discovered that not only the LGR7 gene but also the LGR7 protein are highly expressed in clear cell adenocarcinoma cells of ovarian cancer. Furthermore, the present inventors found that anti-LGR7 antibodies have antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC) activity and complement-dependent cytotoxicity (CDC) activity against LGR7-expressing cells. From the above findings, the present inventors discovered that the anti-LGR7 antibodies are useful for diagnosis, prevention, and treatment of primary and metastatic ovarian clear cell adenocarcinoma.
Owner:CHUGAI PHARMA CO LTD +1
Diagnosis and treatment of cancer by using Anti-prg-3 antibody
InactiveUS20100111851A1LevelImprove the level ofIn-vivo radioactive preparationsMicrobiological testing/measurementAnticarcinogenCancer type
The present invention discloses an antibody capable of binding to the PRG-3 protein and inhibiting the growth of cells expressing the PRG-3 protein. The growth inhibitory activity is cytotoxic activity, such as antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity and complement-dependent cytotoxicity. The present invention also discloses a pharmaceutical composition, cell growth inhibitor, and an anticancer agent comprising the antibody of the present invention as an active ingredient. Examples of the type of cancer include hepatocellular carcinoma, lung cancer, colon cancer, and glioblastoma. In addition, the present invention discloses a method for diagnosing cancer by detecting expression of the PRG-3 protein or the gene encoding the PRG-3 protein, as well as a diagnostic agent and kit for use in the method.
Owner:THE UNIV OF TOKYO +1
Novel IL23 antagonist
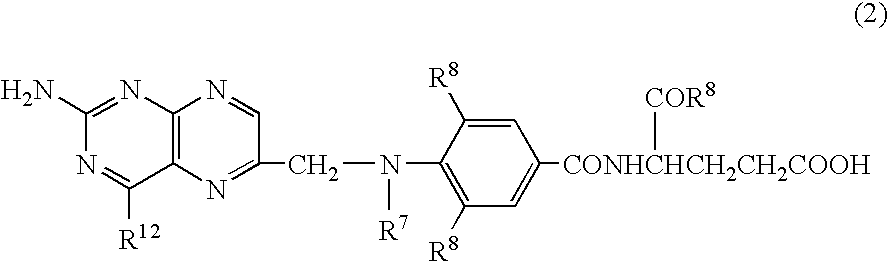
The invention relates to a recombinant human IL (Interleukin)-23 receptor extracellular region / Fc fusion protein capable of combining with IL-23 and antagonizing a function of IL-23. The fusion protein is characterized in that a fusion protein encoding gene is rich in mammalian cell preferred codons, and is highly expressed by a CHO (Chinese Hamster Ovary) stable transfection cell strain. The protein is formed by fusion of a gene optimized IL-23R-CHR active fragment and a human immune globulin molecule Fc fragment; the defects that the half-life period of the prokaryotic expression IL-23R-CHR fragment is short, the stability is poor and endotoxin is difficult to remove are overcome; the biological activity of IL-23-CHR is reserved; in addition, the fusion protein does not have ADCC (Antibody Dependent Cellular Cytotoxicity) and CDC (Complement Dependent Cytotoxicity) effects, so that the fusion protein is more suitable for treatment of chronic diseases such as an autoimmune disease and a chronic infection; and the contents of molecular design, expression, purification, construction of a stable expression cell strain and disease treatment and the like of the fusion protein are included.
Owner:CHINA PHARM UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com