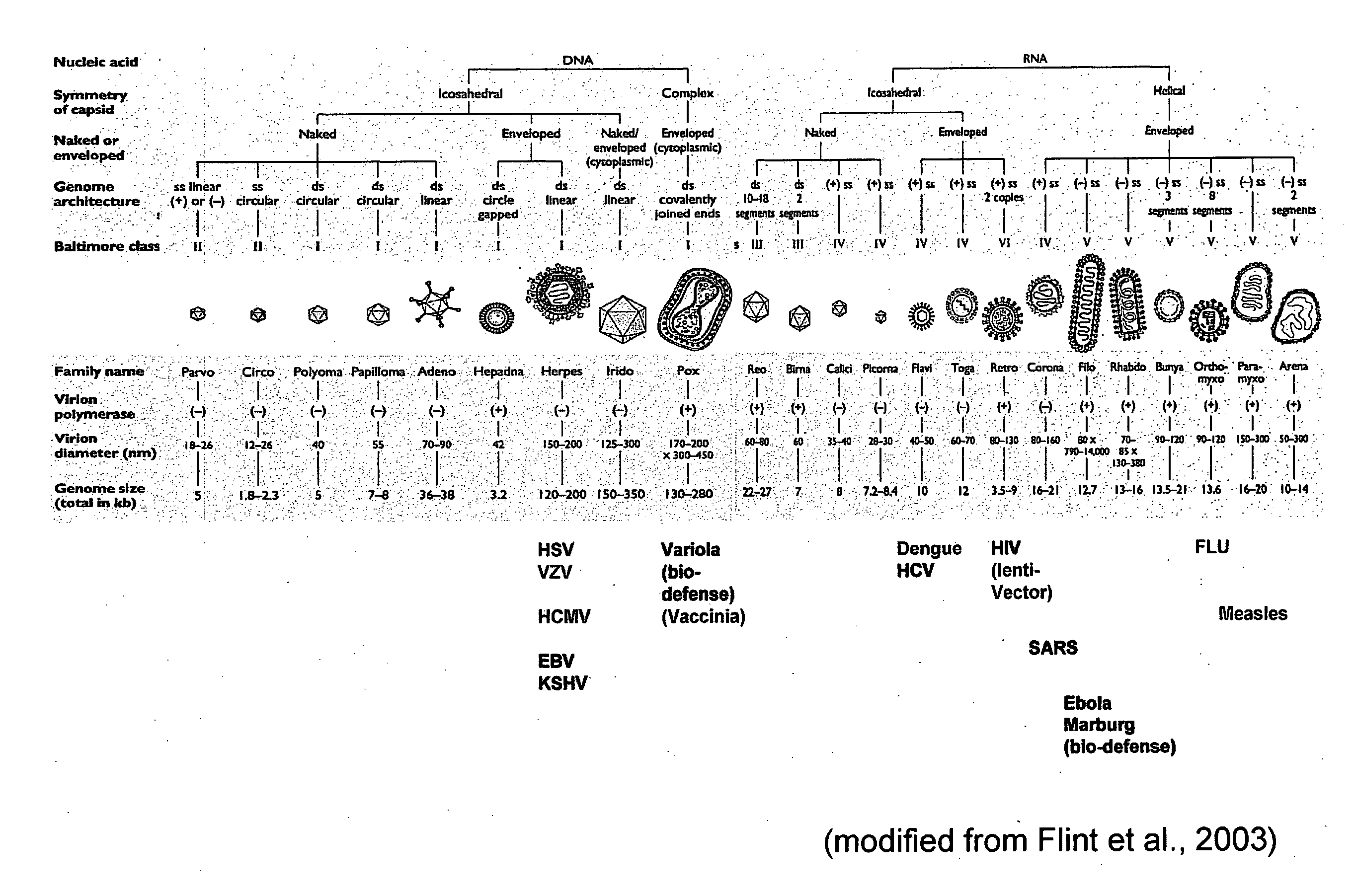
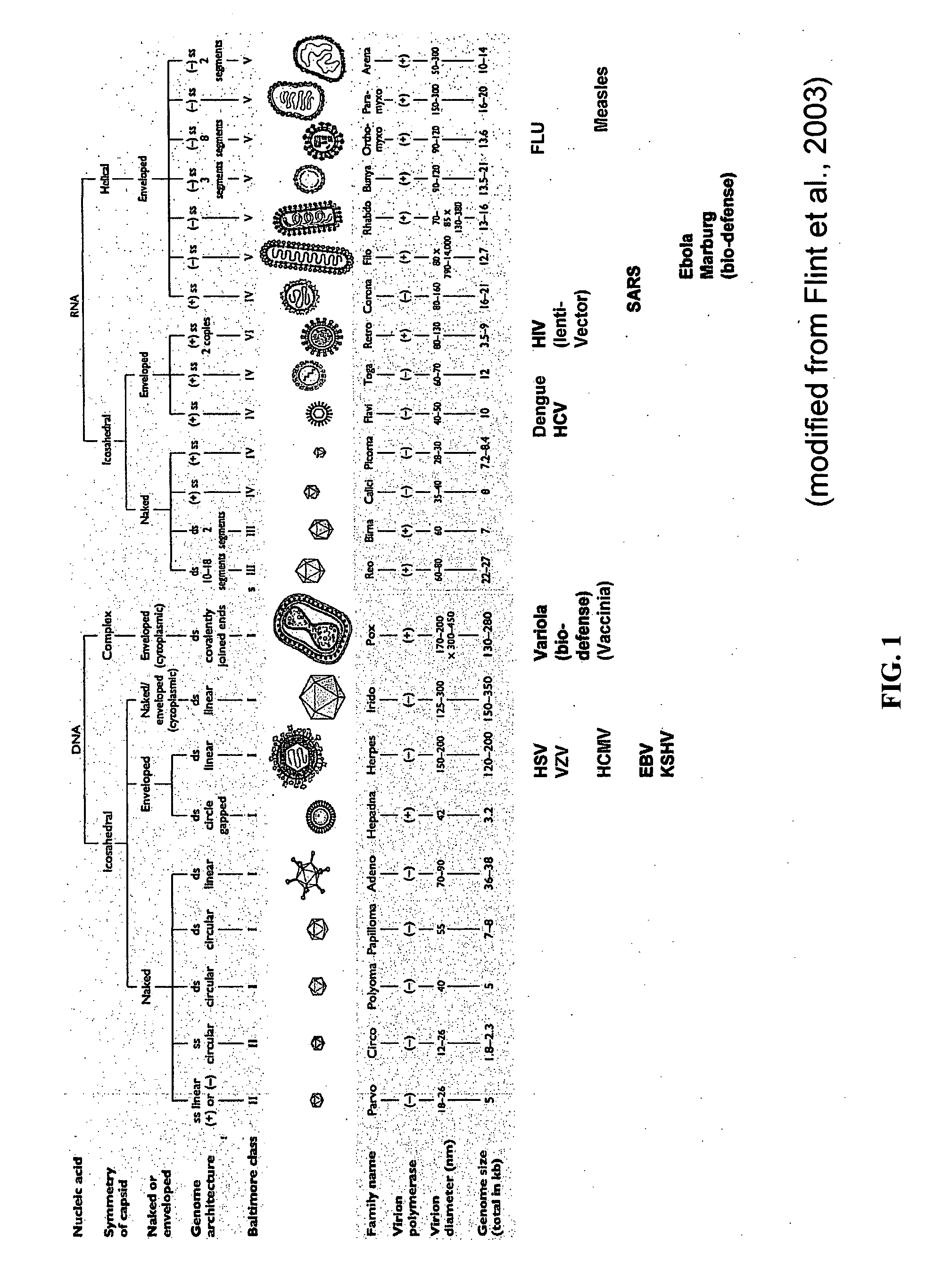
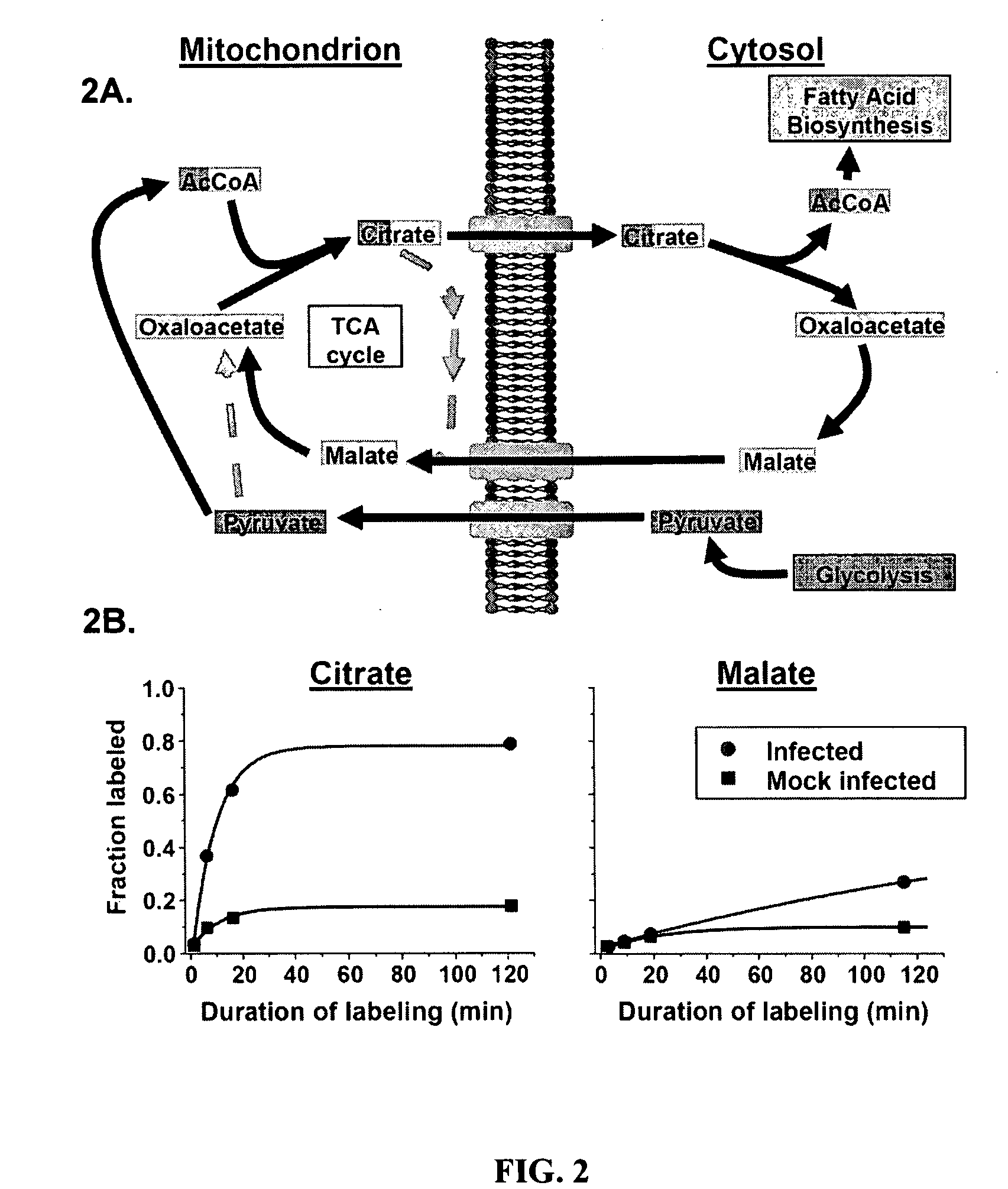
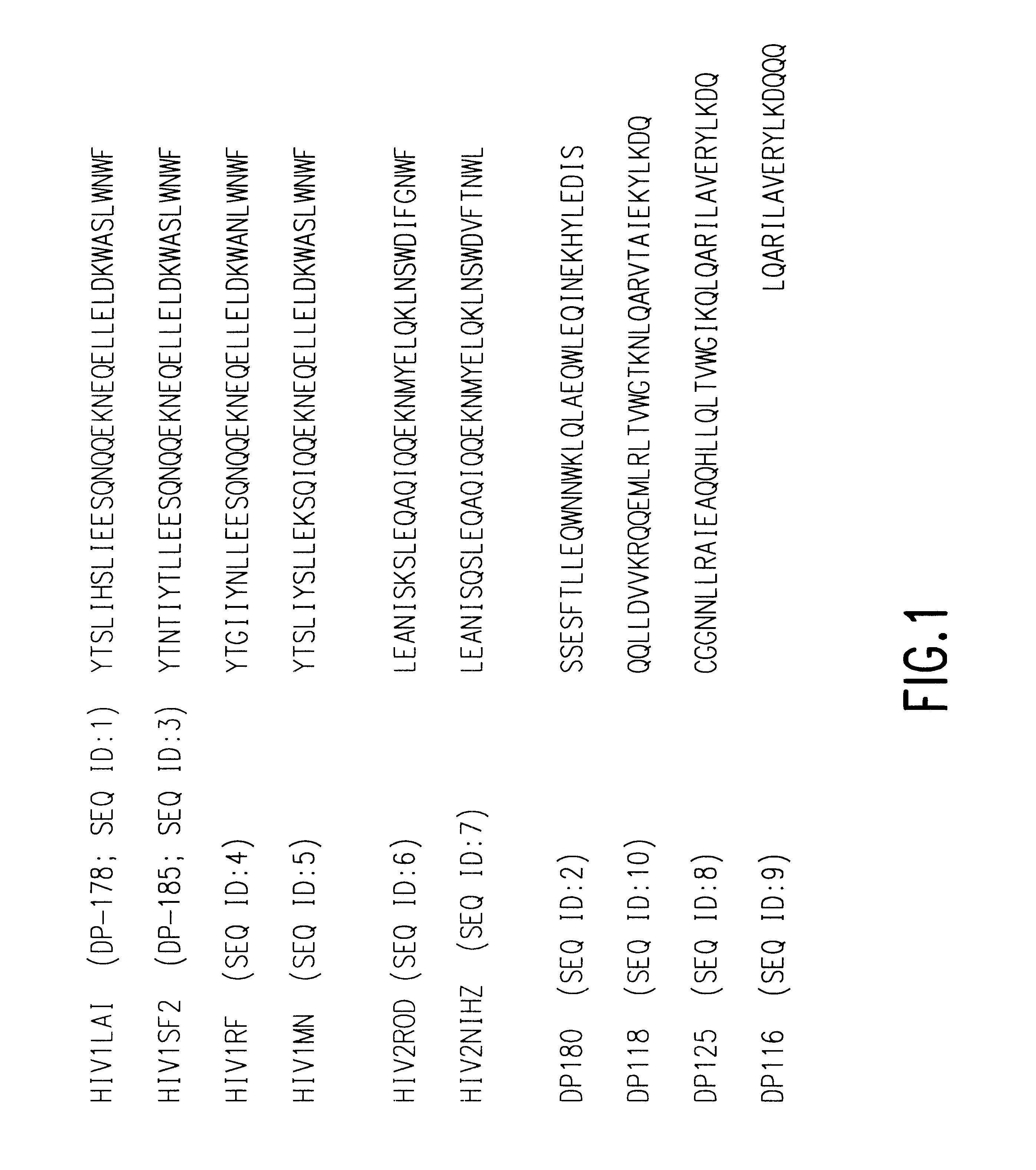
Patents
Literature
35 results about "Uninfected cell" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
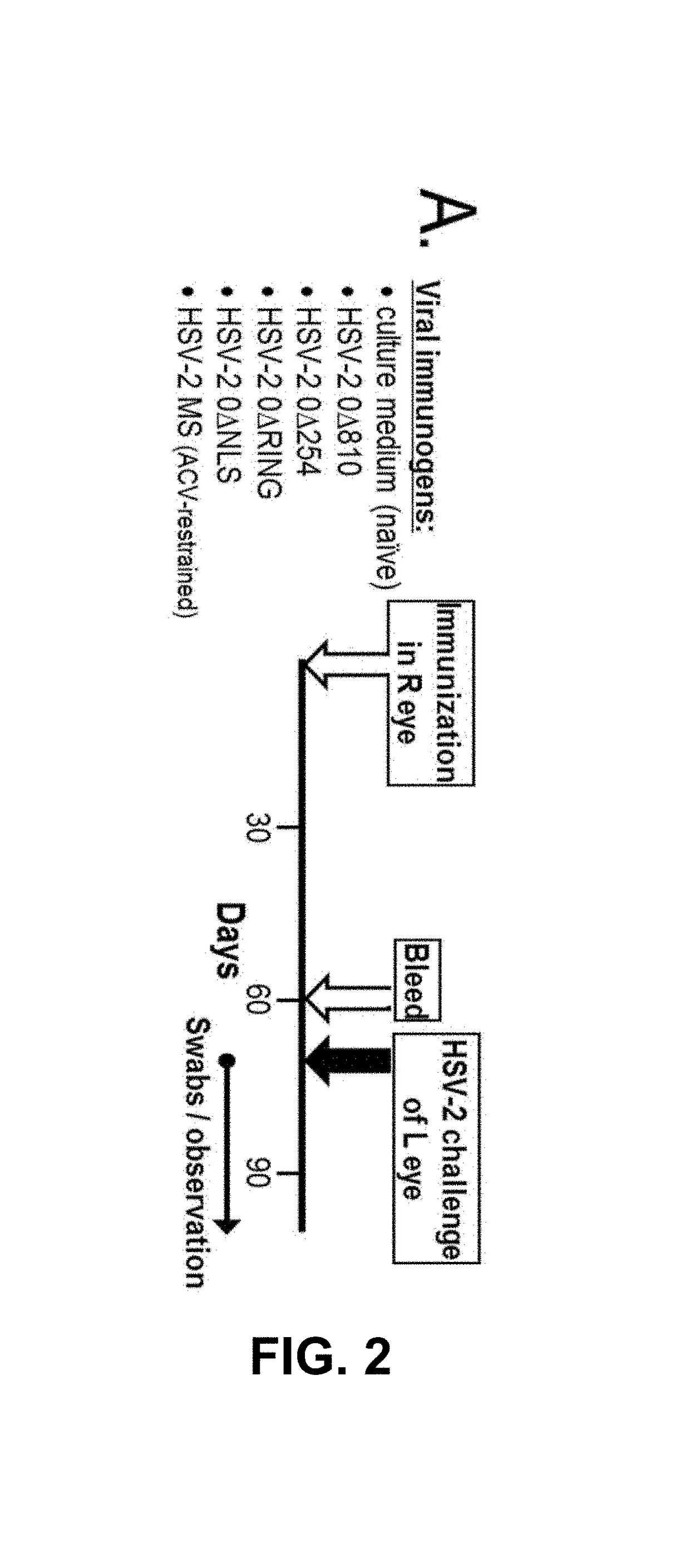
Measles virus peptides with antifusogenic and antiviral activities
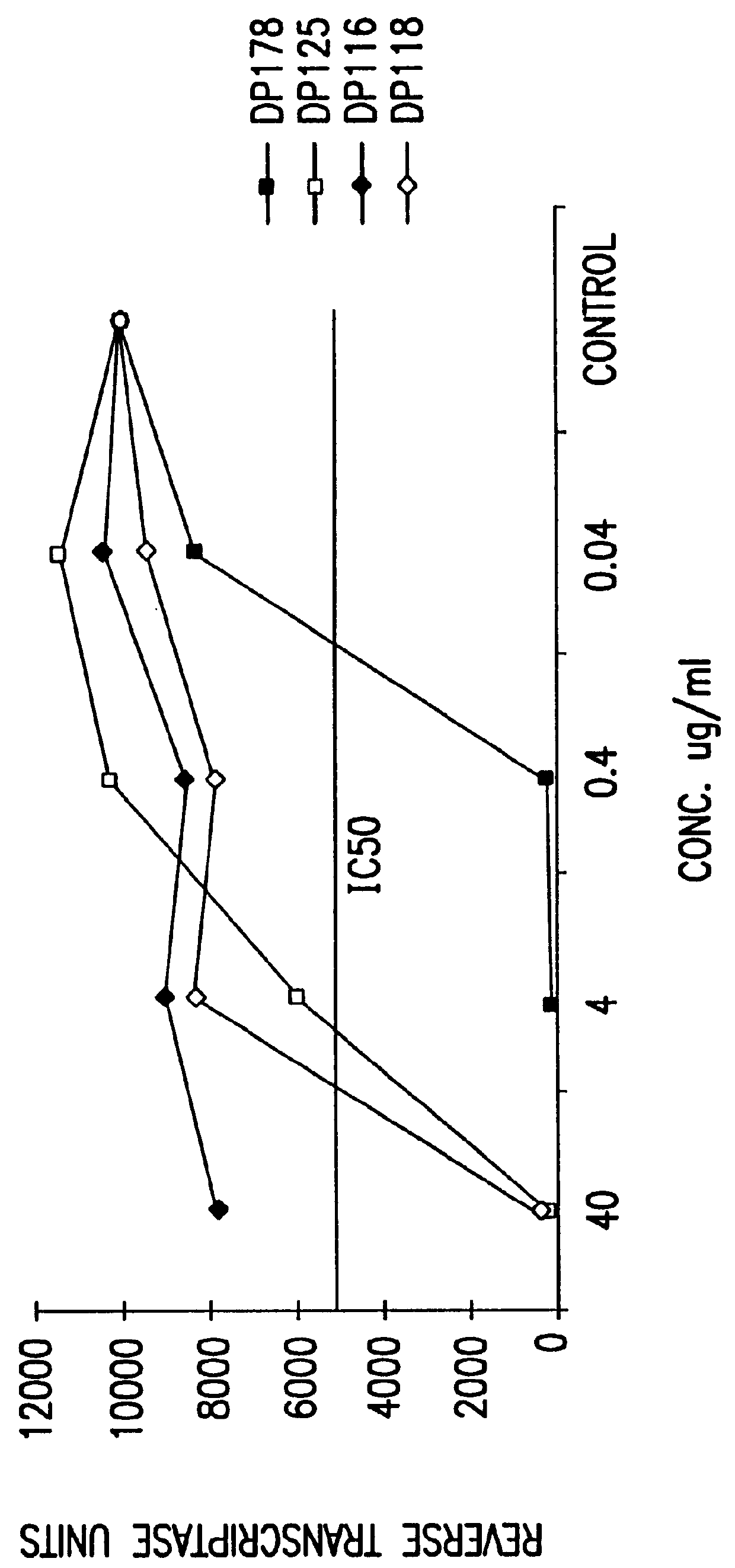
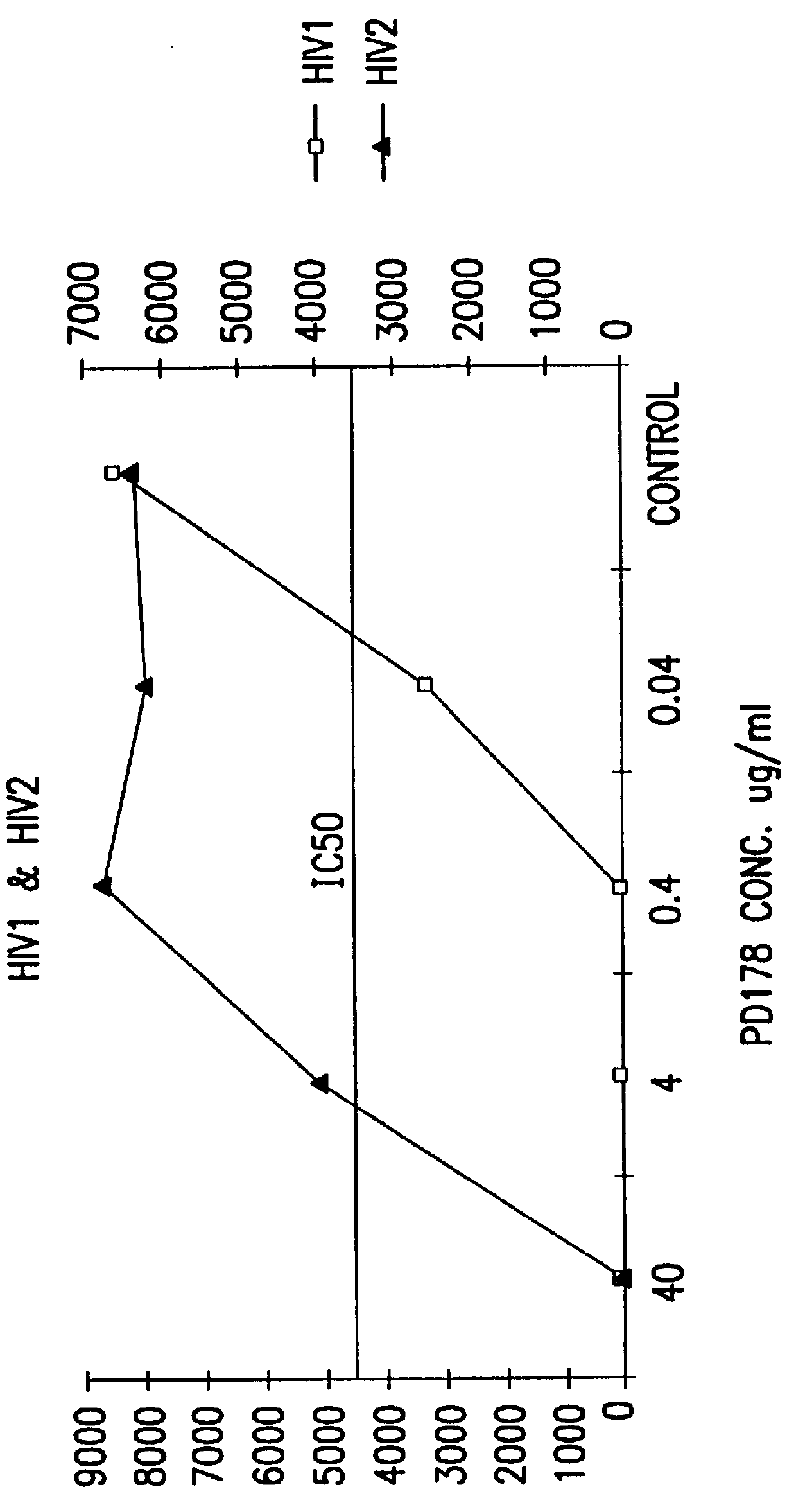
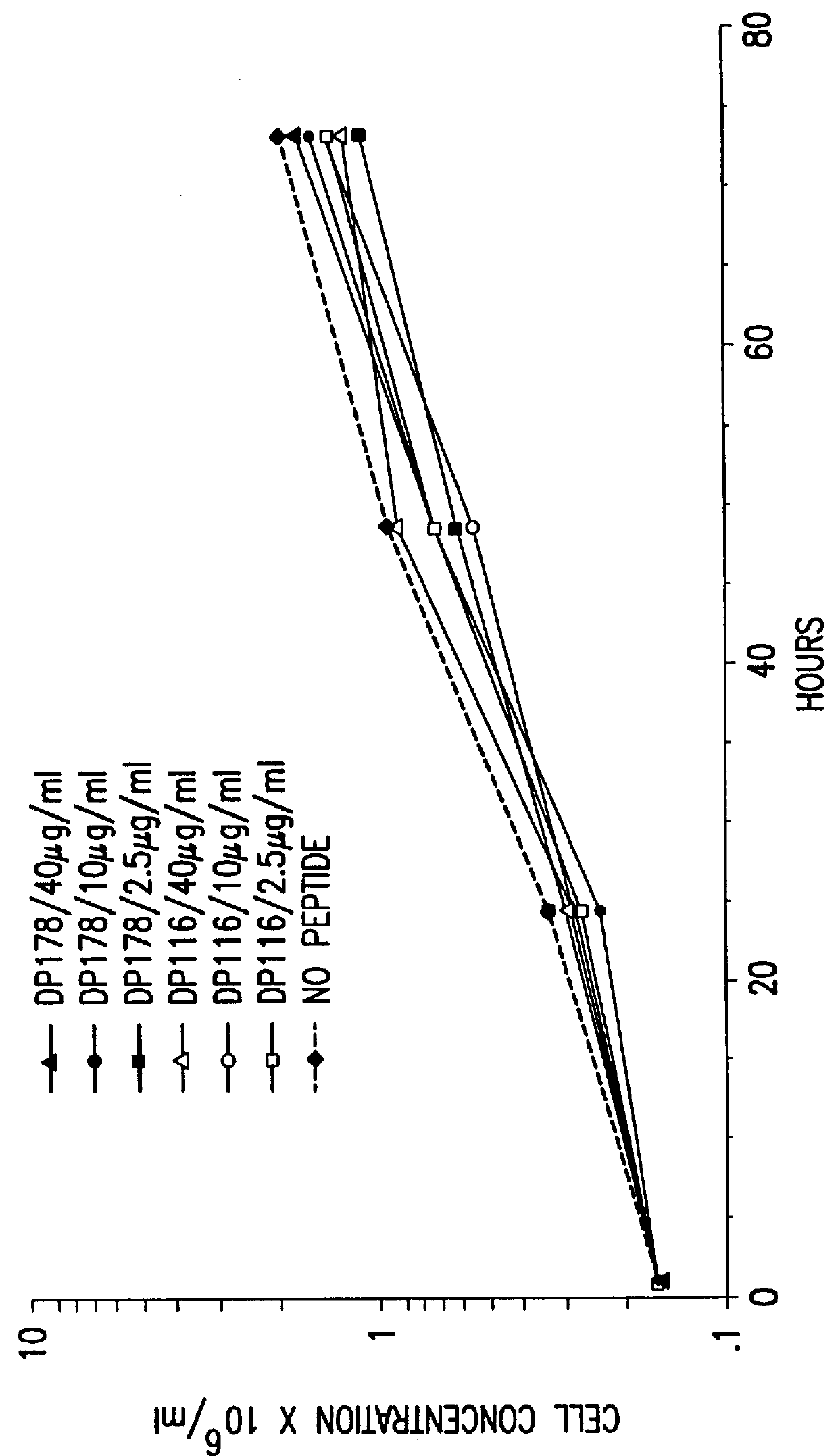
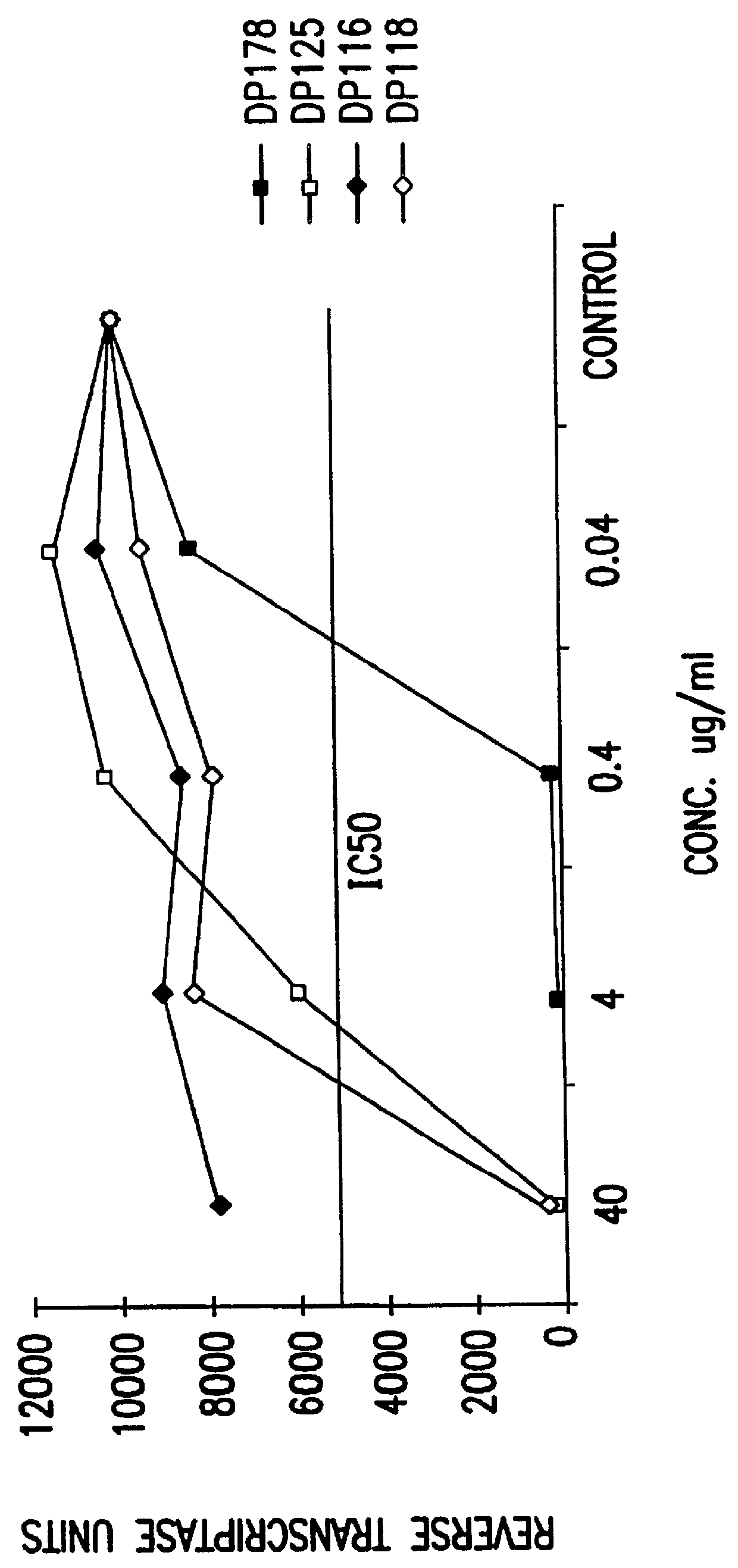
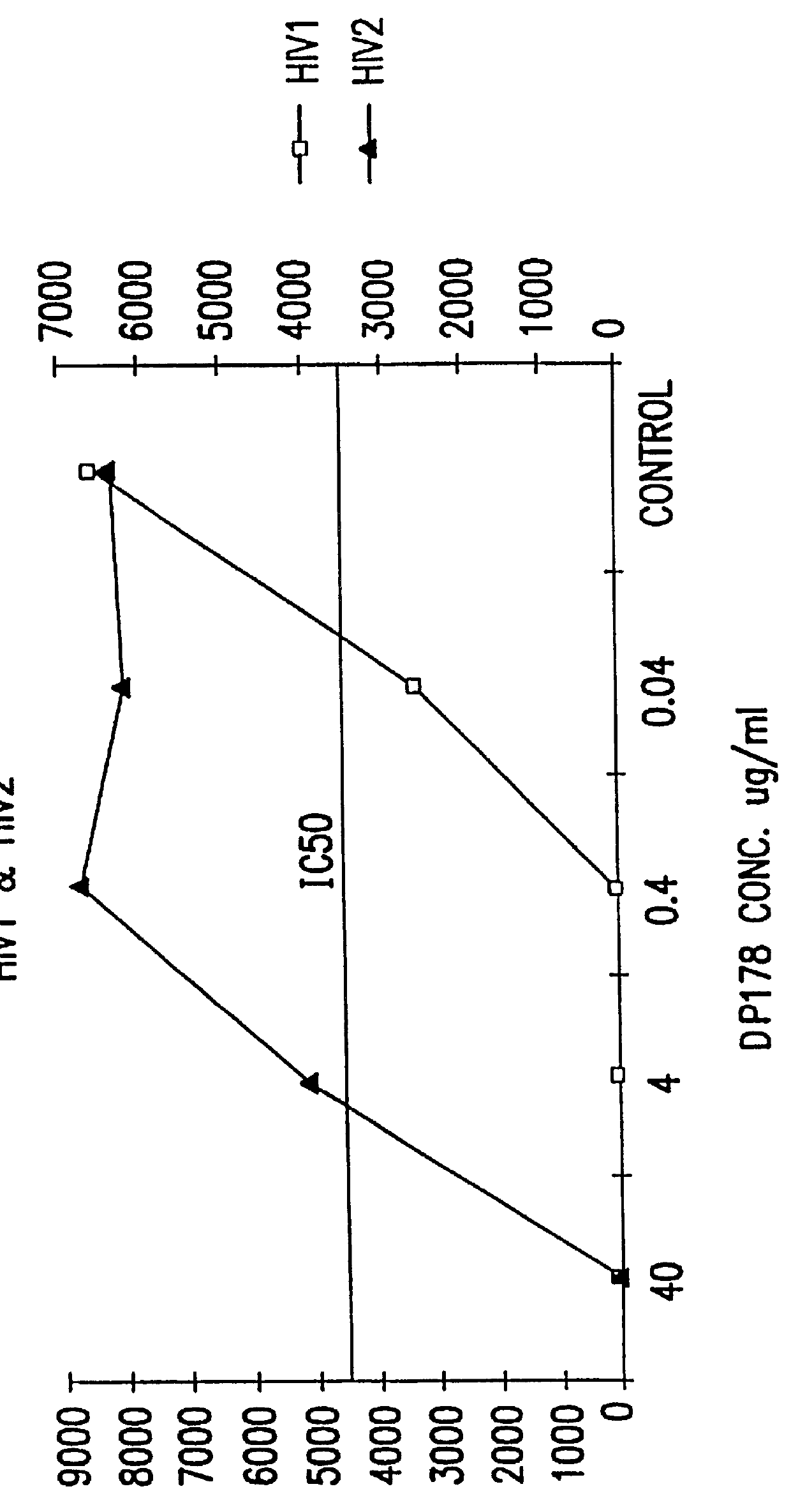
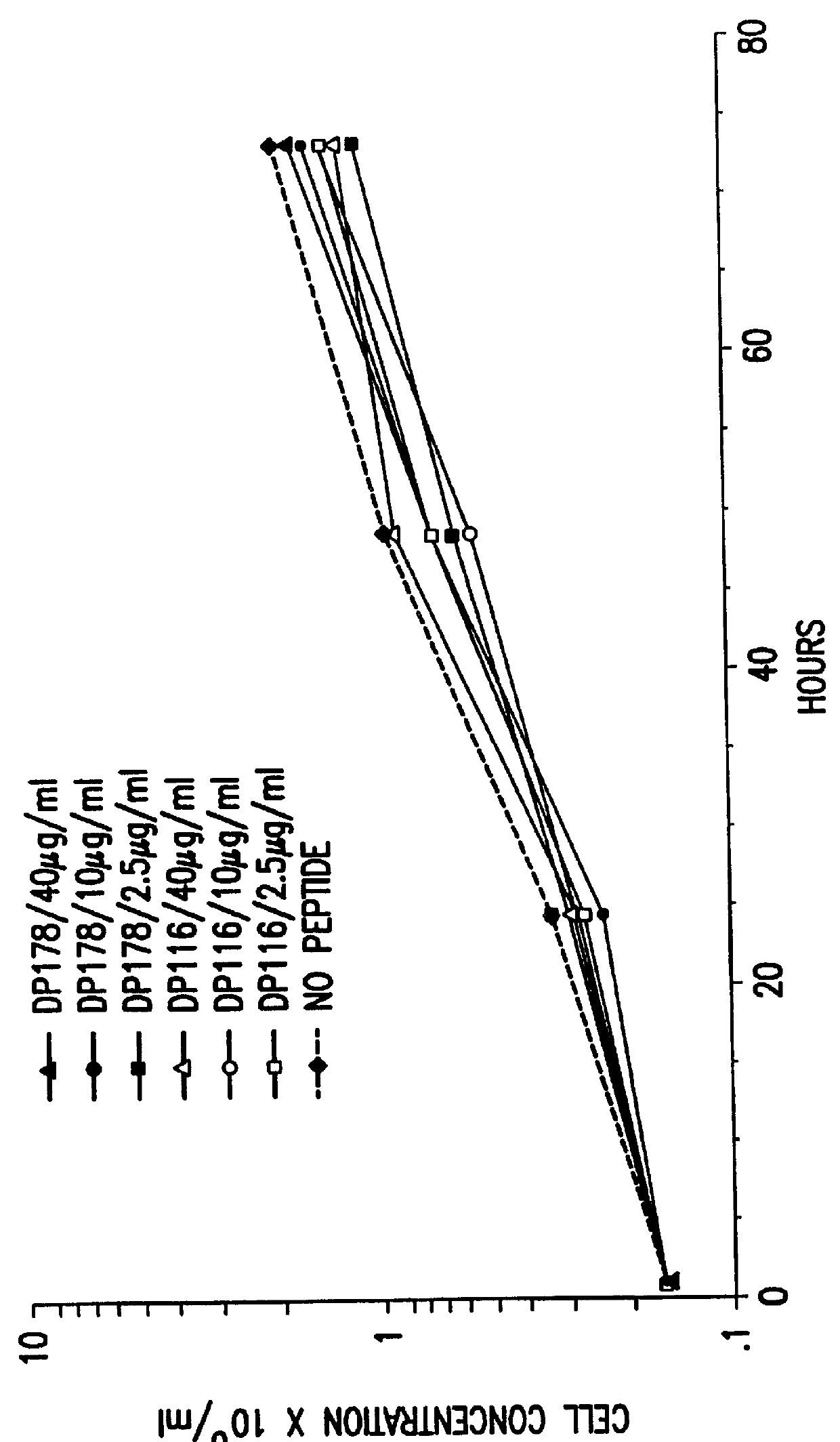
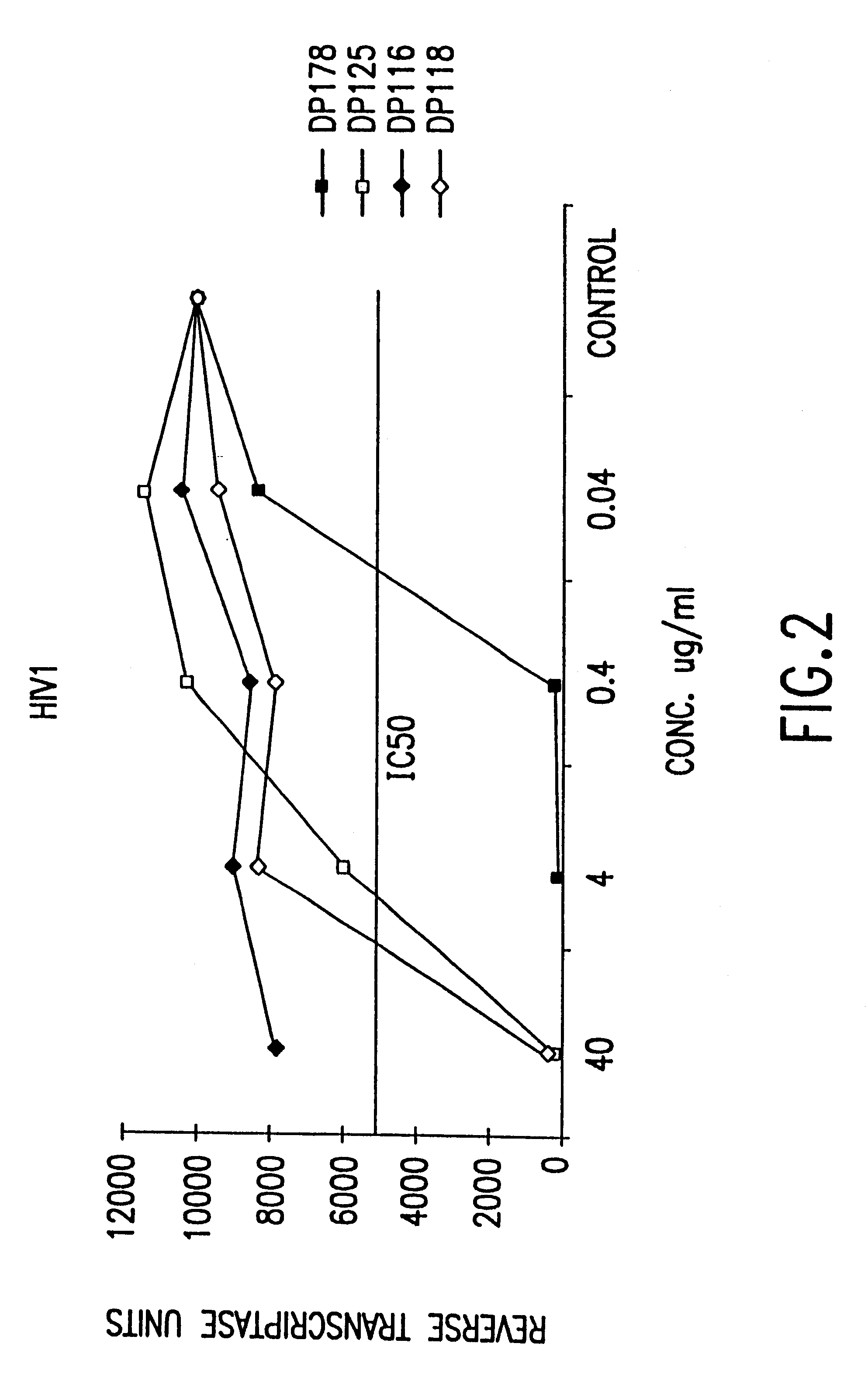
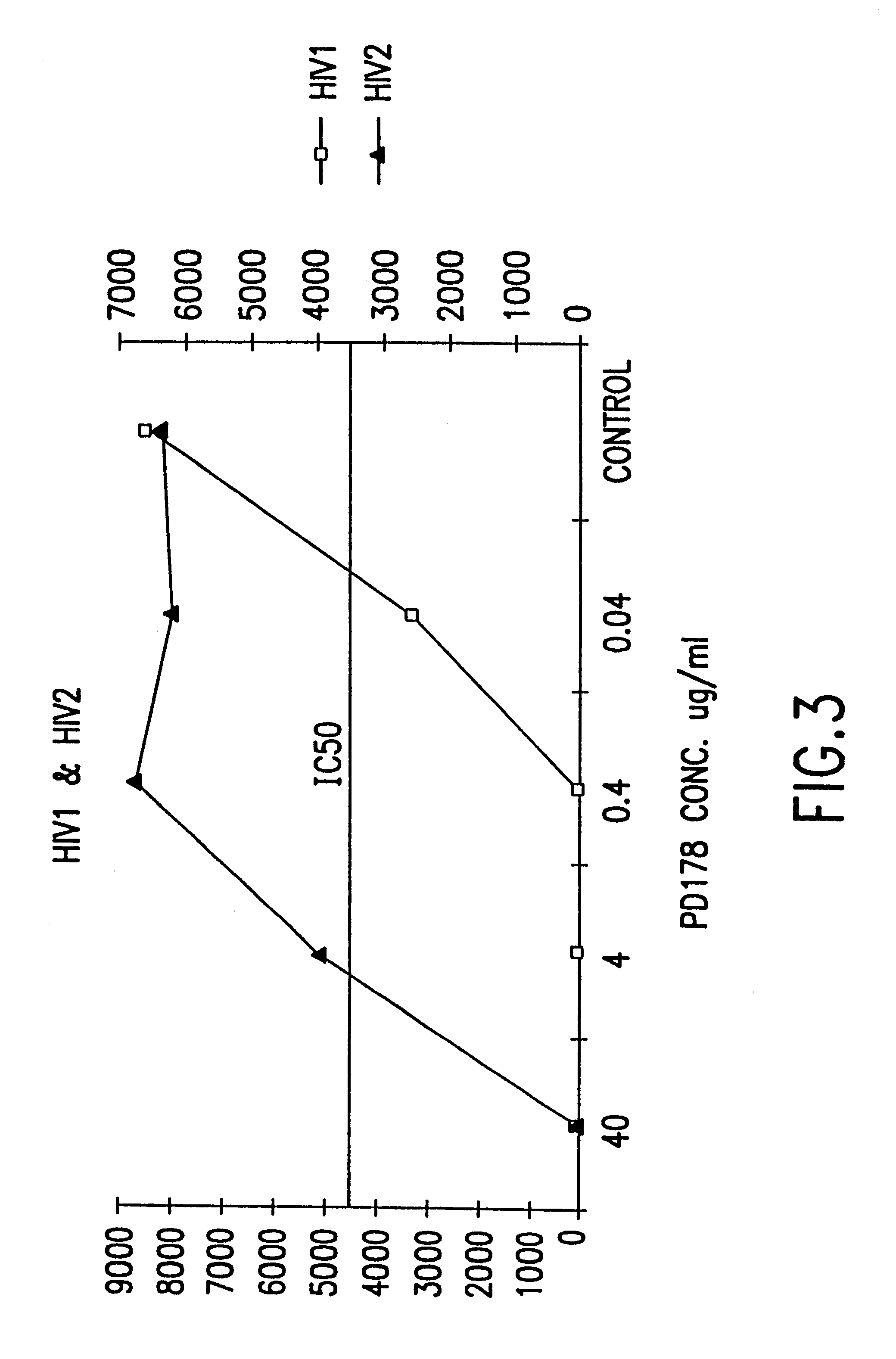
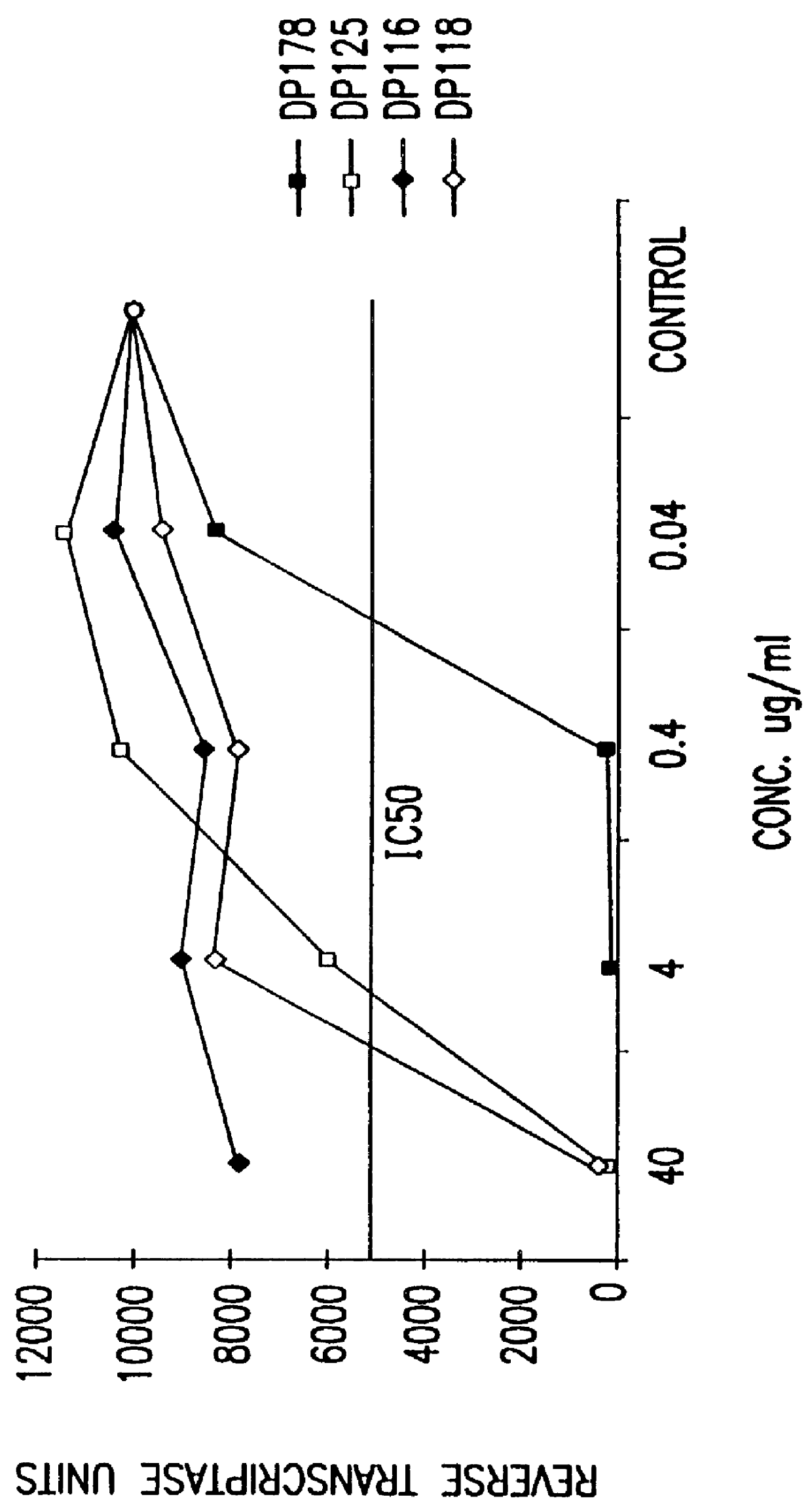
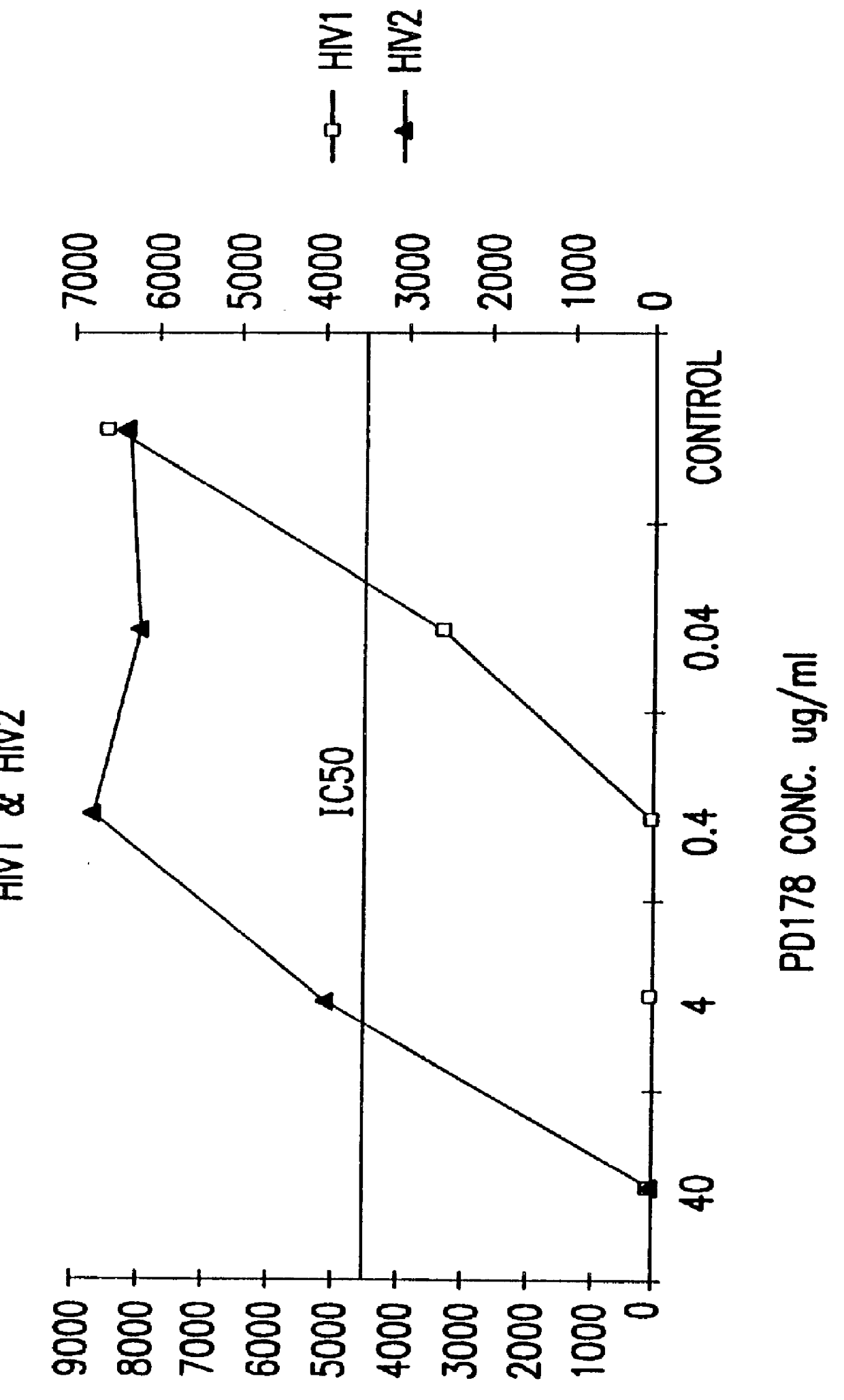
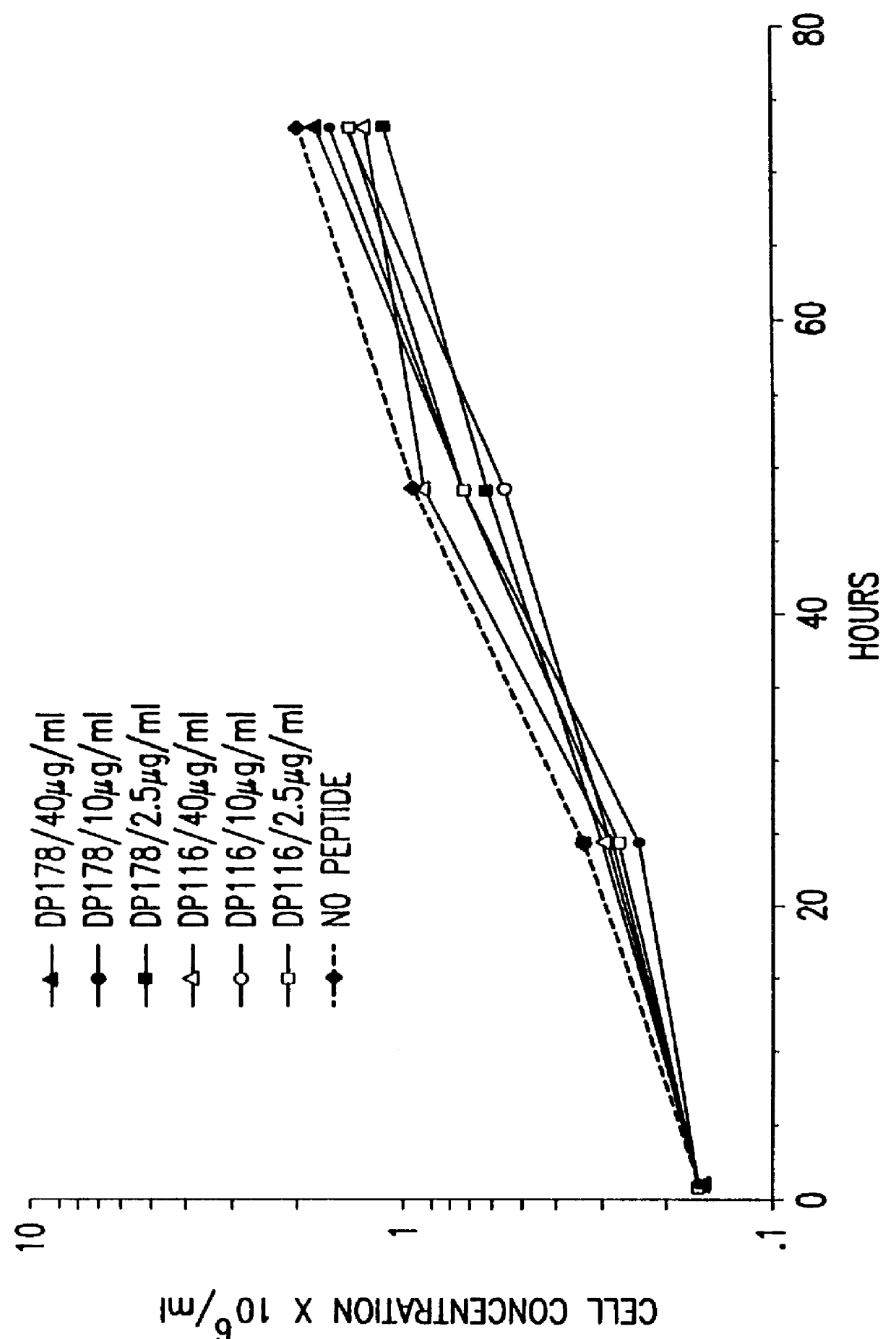
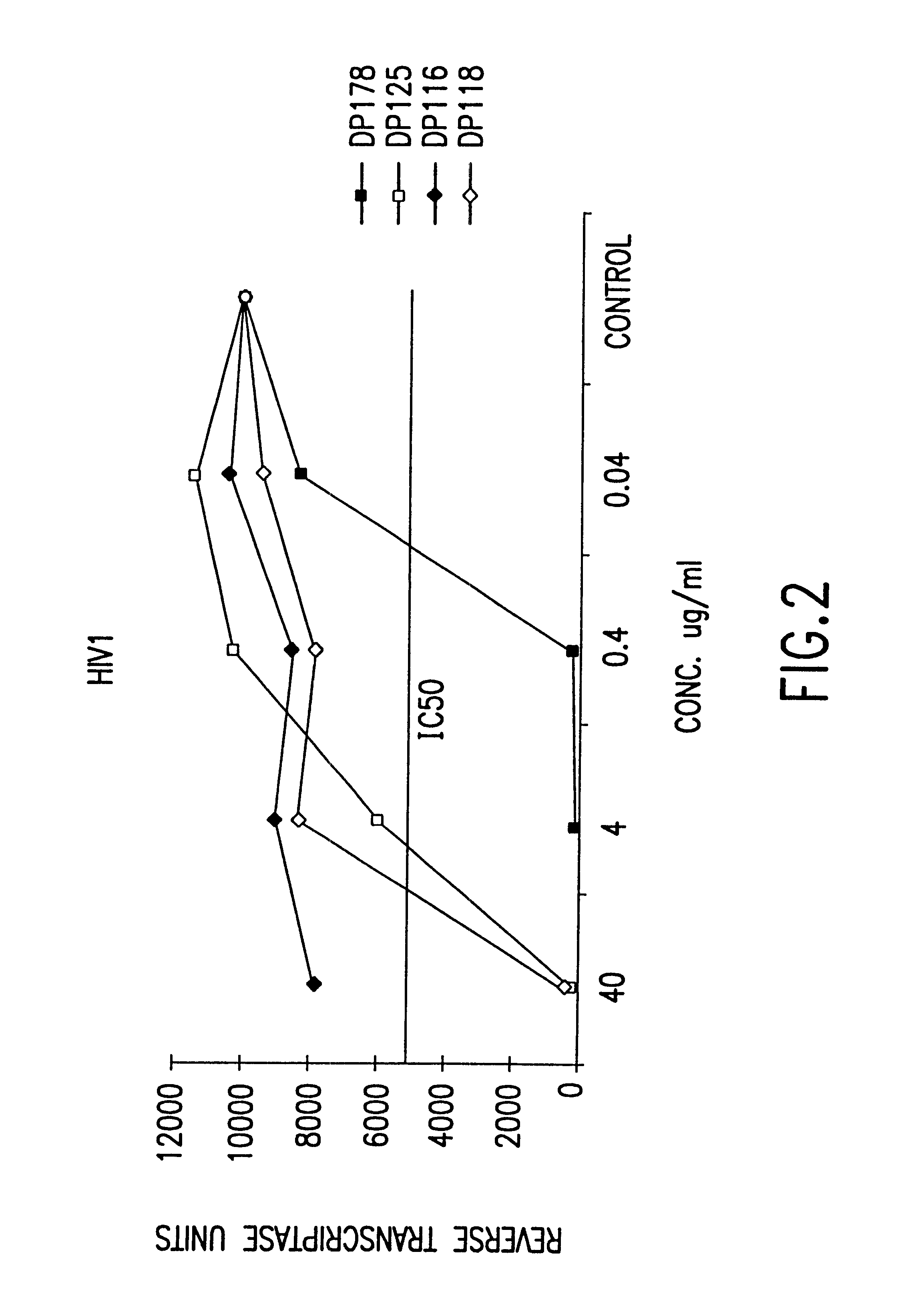
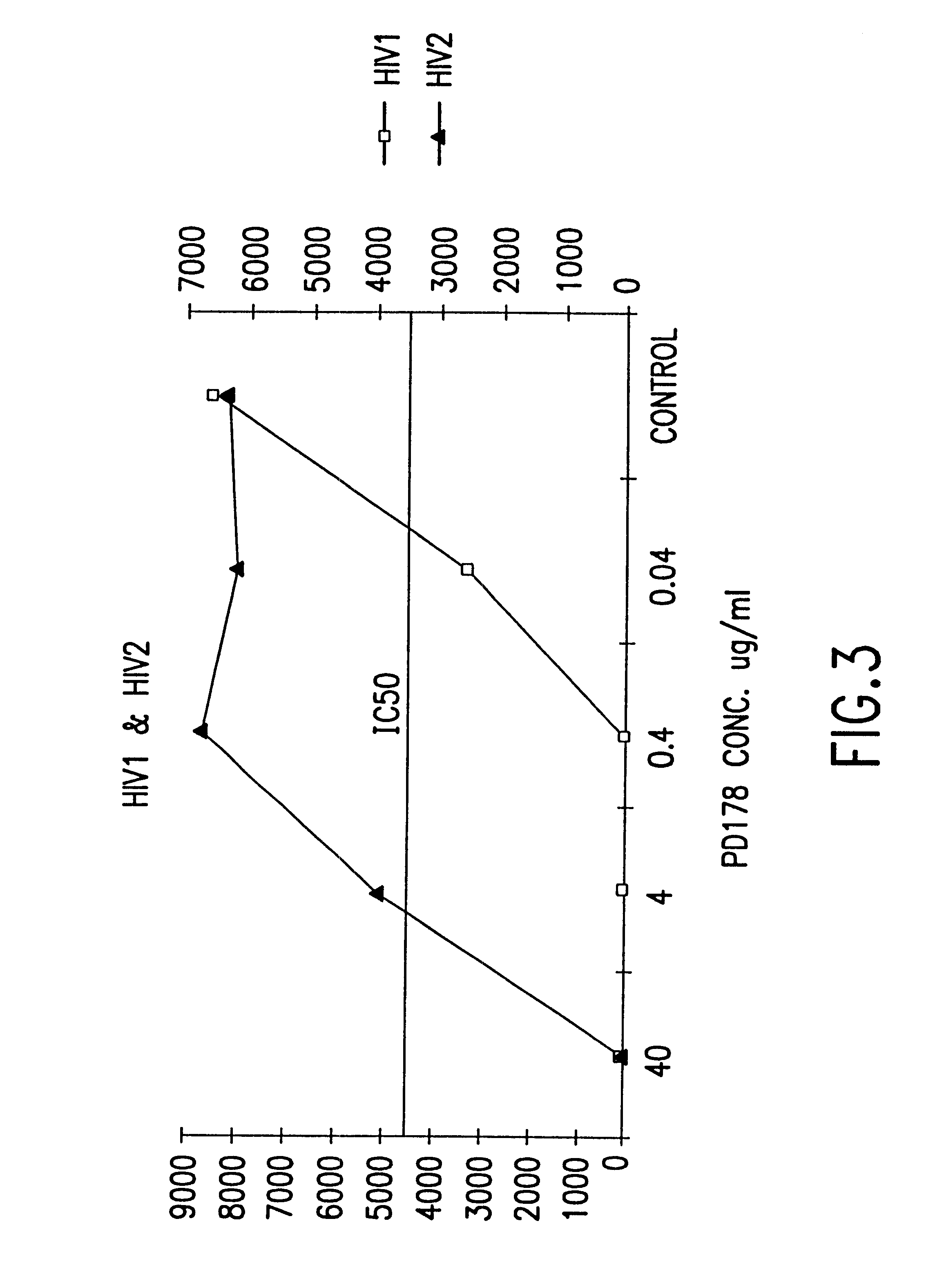
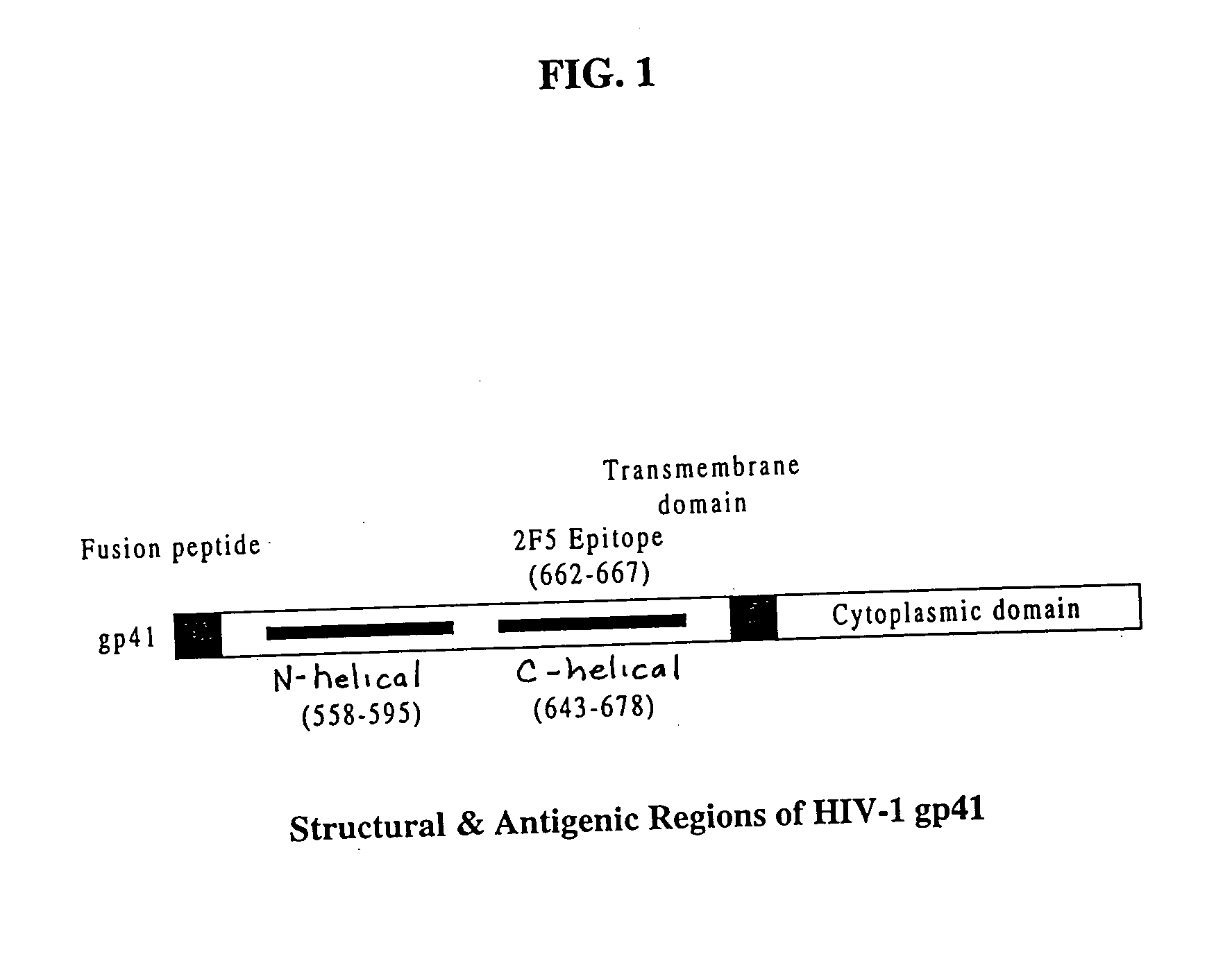
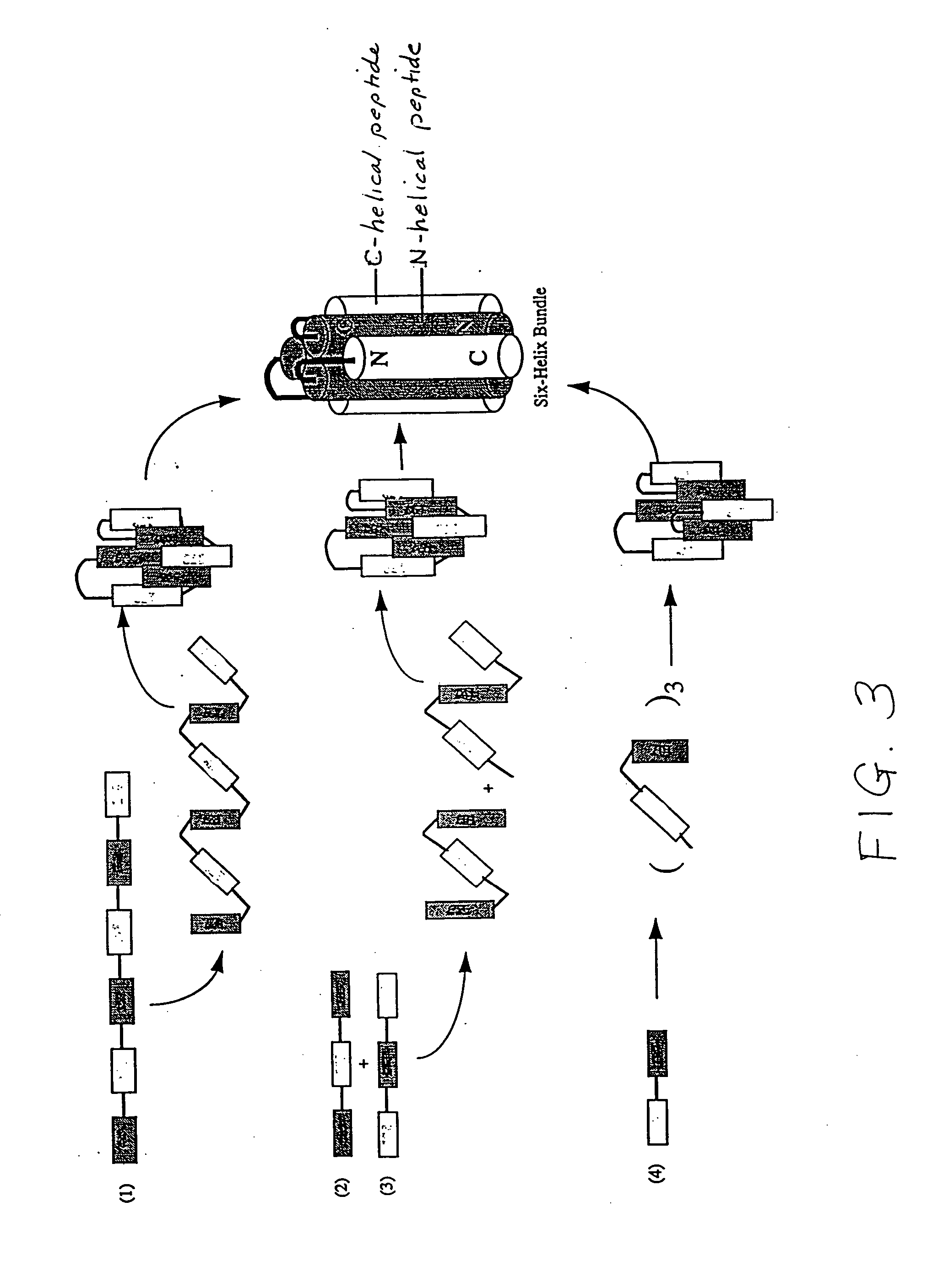
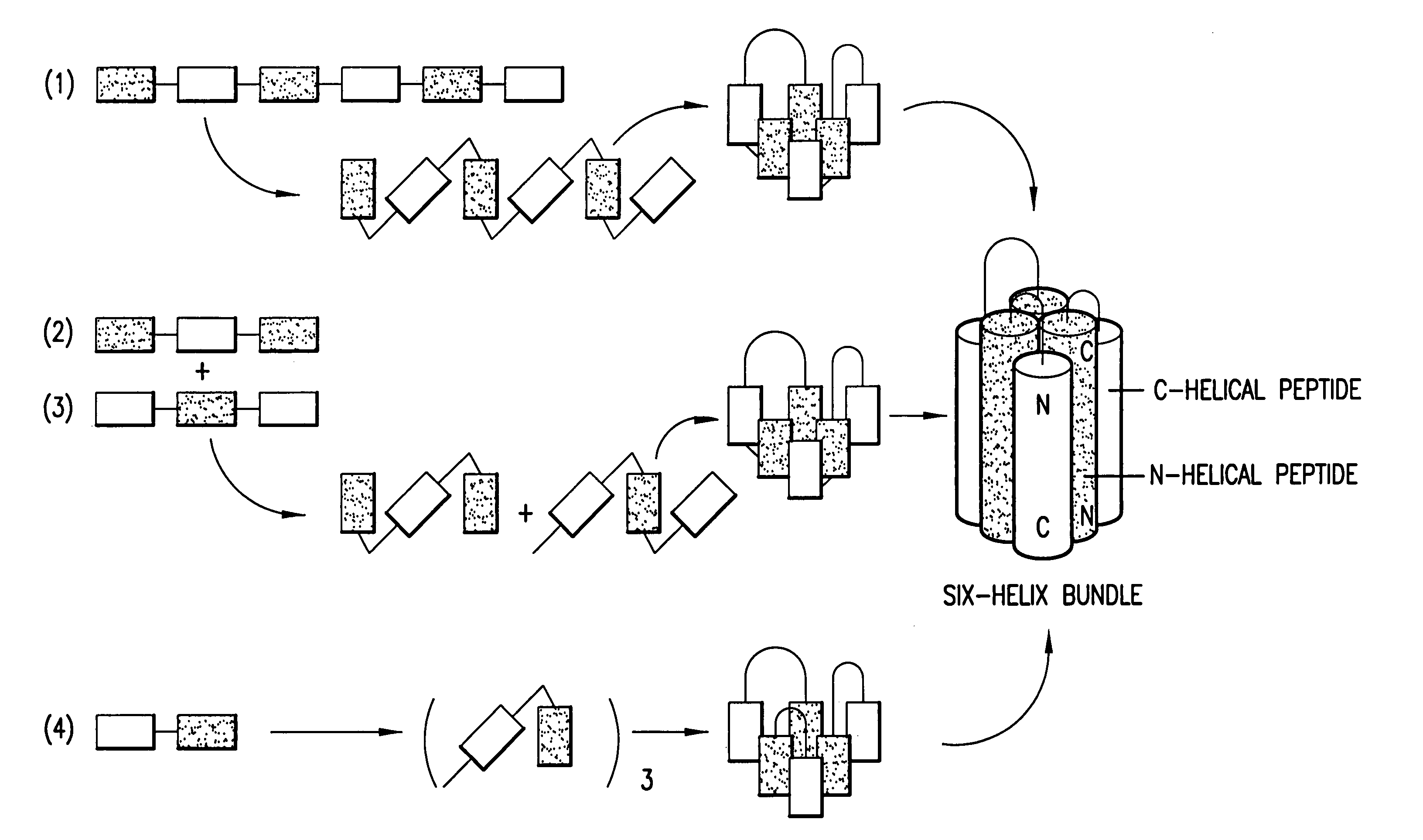
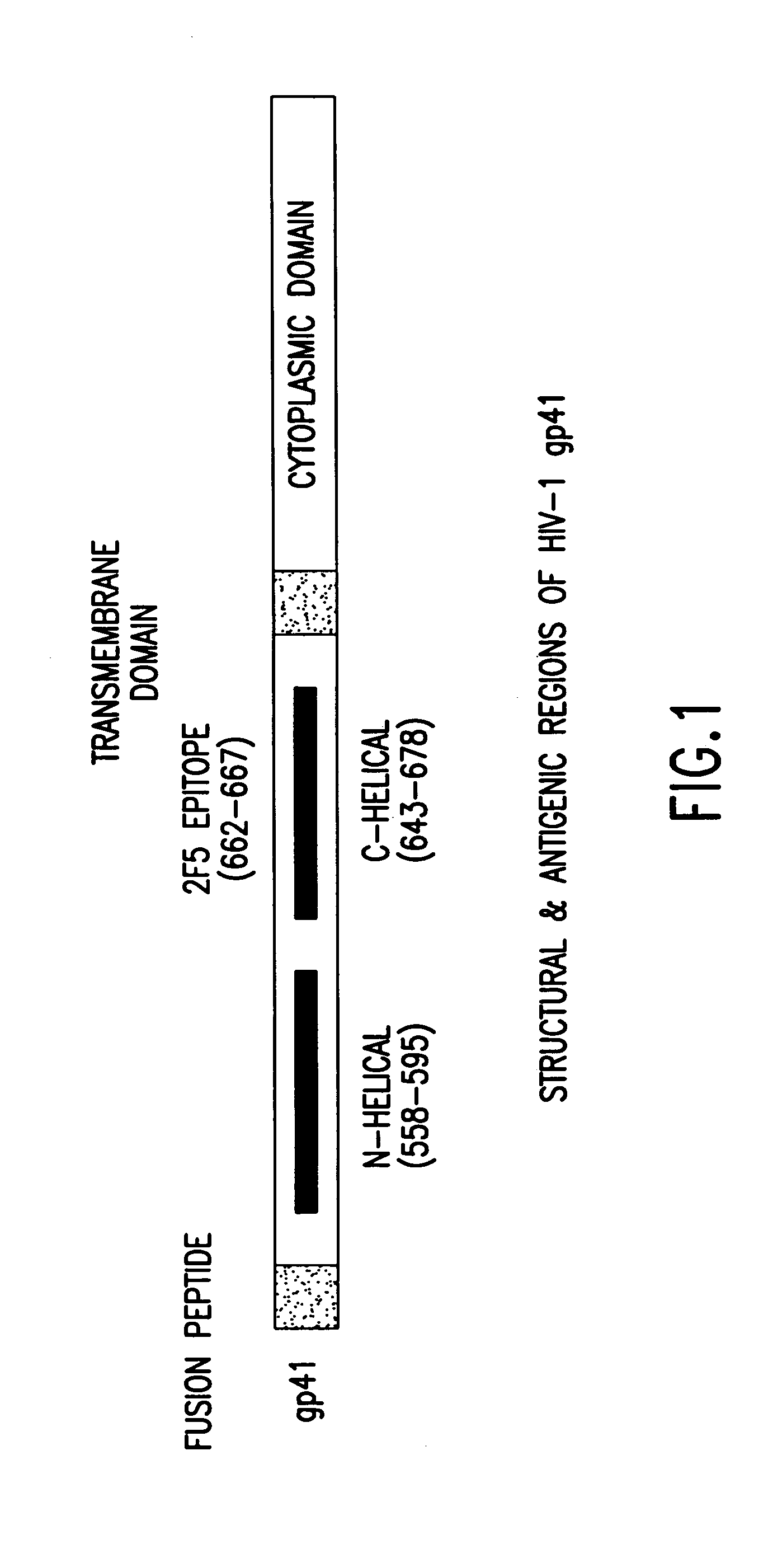
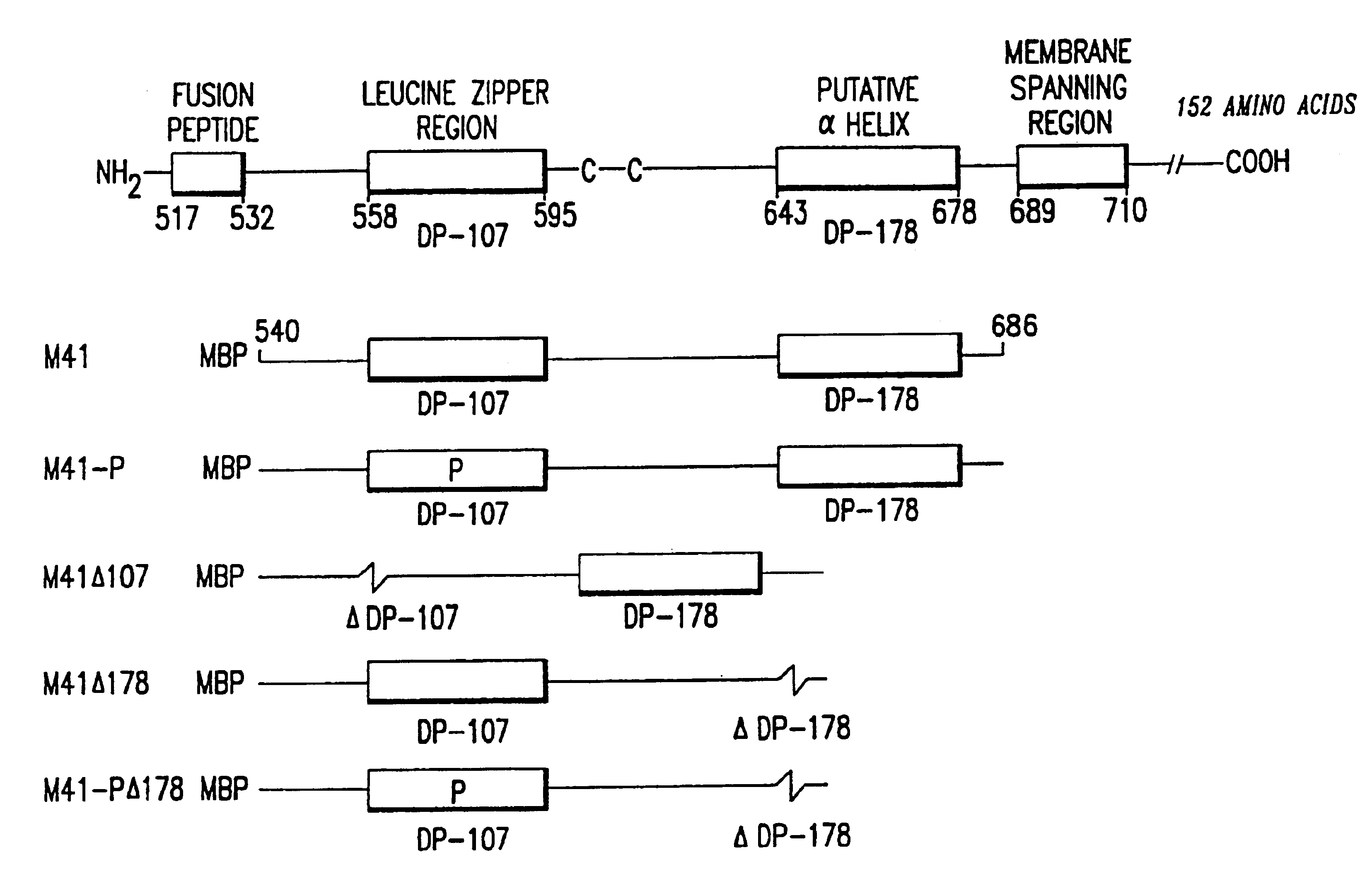
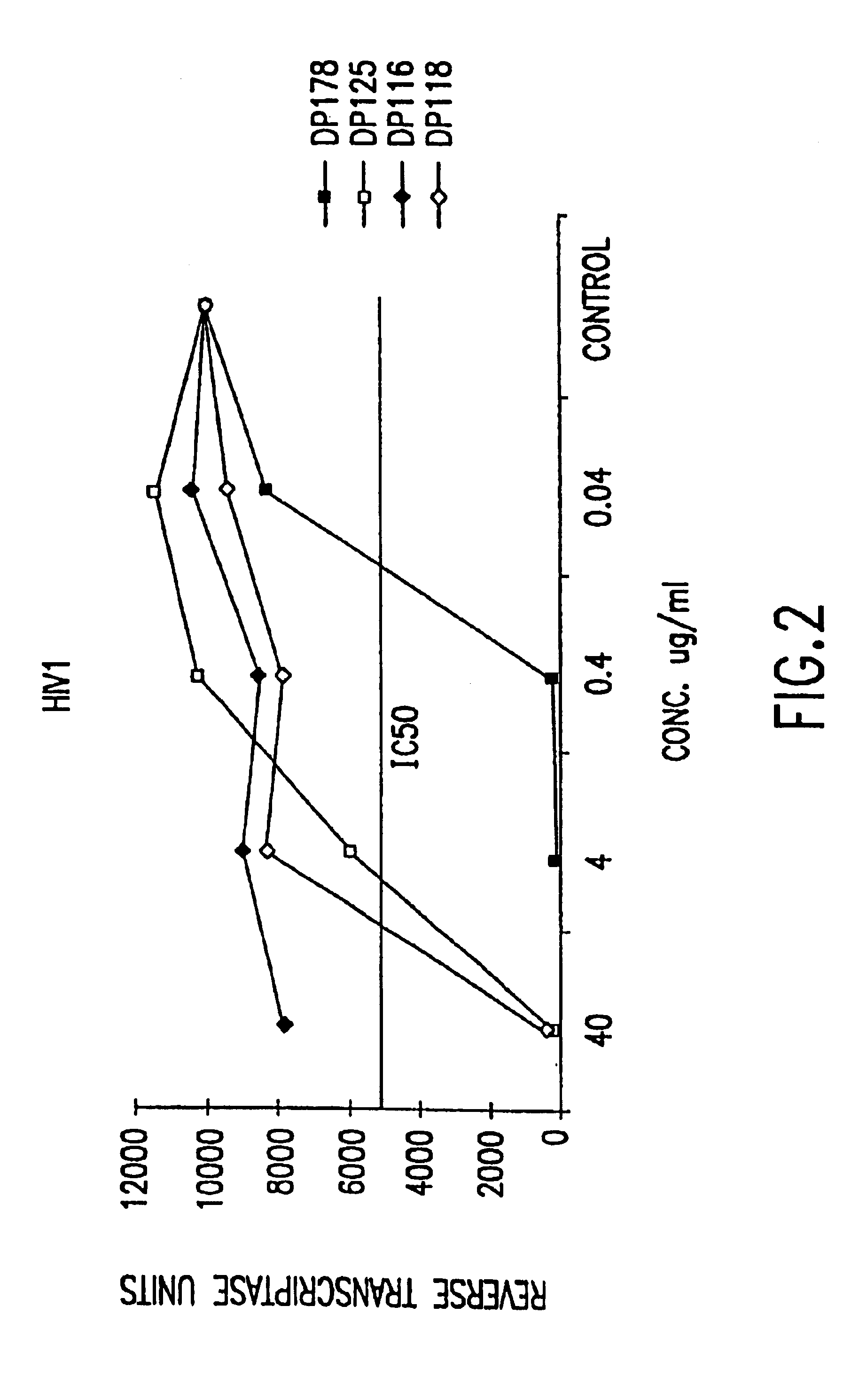
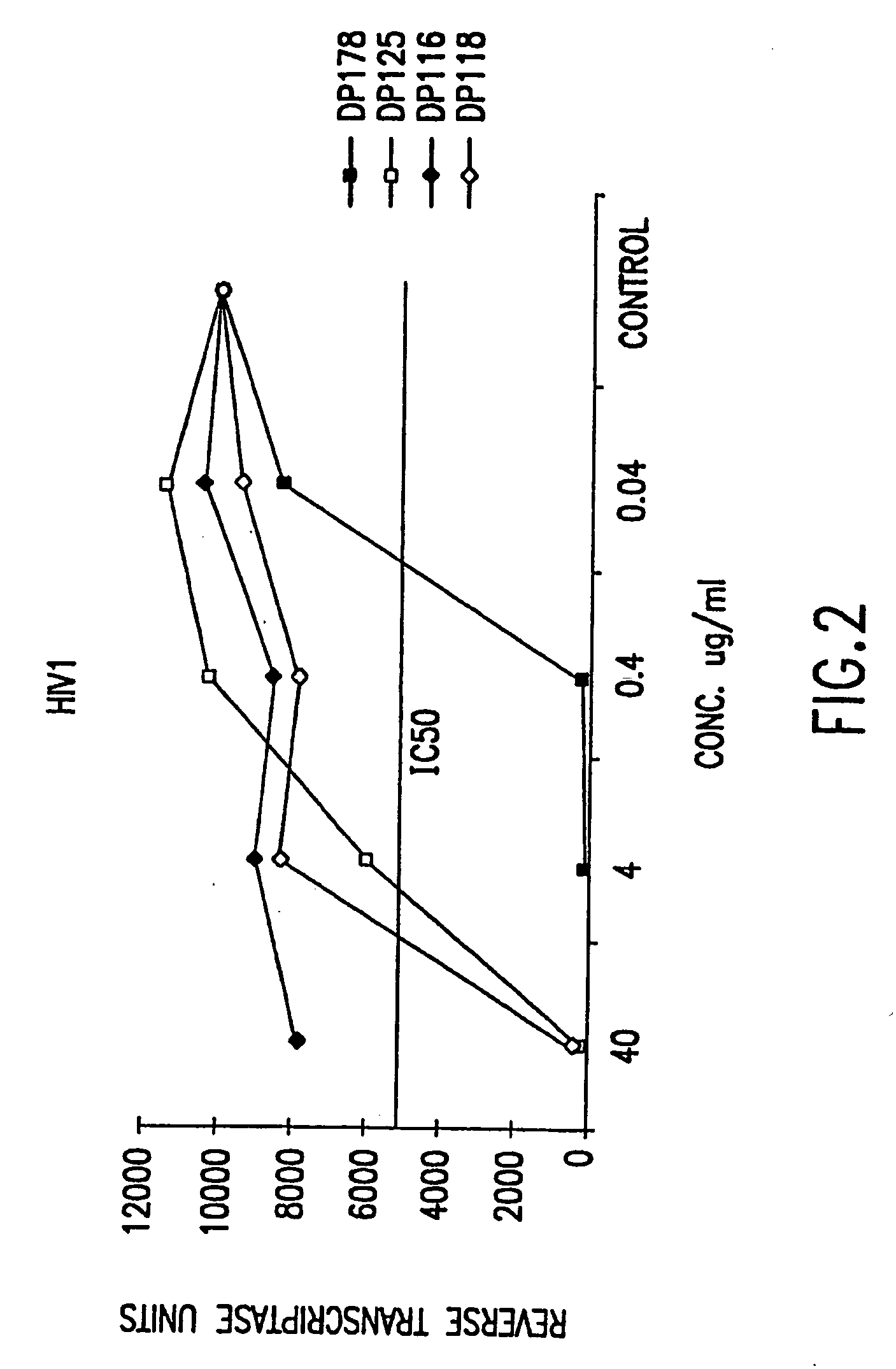
The present invention relates to peptides which exhibit potent anti-retroviral activity. The peptides of the invention comprise DP178 (SEQ ID:1) peptide corresponding to amino acids 638 to 673 of the HIV-1LAI gp41 protein, and fragments, analogs and homologs of DP178. The invention further relates to the uses of such peptides as inhibitory of human and non-human retroviral, especially HIV, transmission to uninfected cells.
Owner:TRIMERIS
Synthetic peptide inhibitors of HIV transmission
The present invention relates to peptides which exhibit potent anti-retroviral activity. The peptides of the invention comprise DP-178 (SEQ ID:1) ptide corresponding to amino acids 638 to 673 of the HIV-1LAI gp41 protein, and fragments, analogs and homologs of DP-178. The invention further relates to the uses of such peptides as inhibitory of human and non-human retroviral, especially HIV, transmission to uninfected cells.
Owner:DUKE UNIV
Methods for the inhibition of epstein-barr virus transmission employing anti-viral peptides capable of abrogating viral fusion and transmission
InactiveUS6518013B1SsRNA viruses negative-sensePeptide/protein ingredientsCell membraneViral life cycle
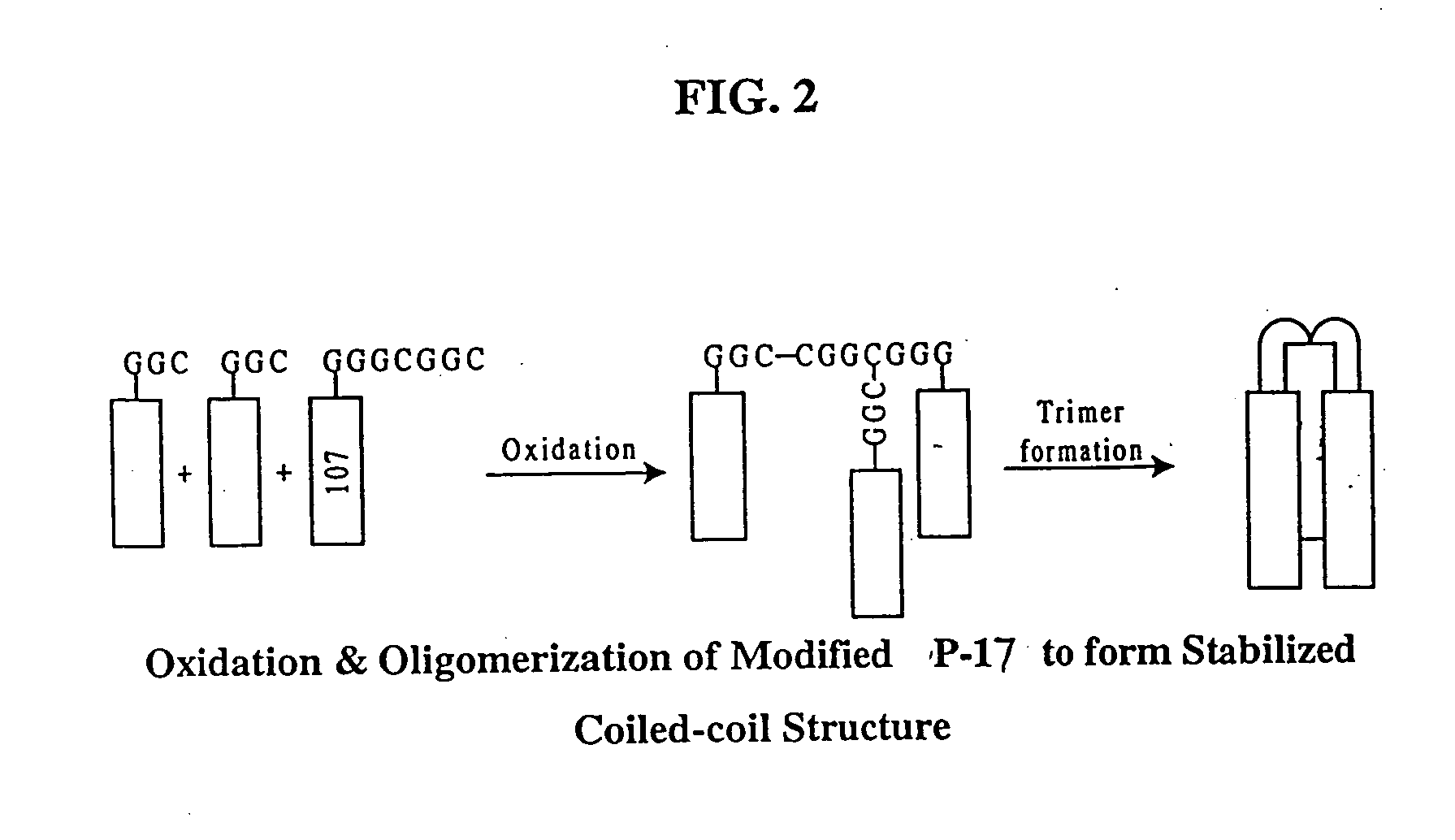
Fusion of the viral envelope, or infected cell membranes with uninfected cell membranes, is an essential step in the viral life cycle. Recent studies involving the human immunodeficiency virus type 1(HIV-1) demonstrated that synthetic peptides (designated DP-107 and DP-178) derived from potential helical regions of the transmembrane (TM) protein, gp41, were potent inhibitors of viral fusion and infection. A computerized antiviral searching technology (C.A.S.T.) that detects related structural motifs (e.g., ALLMOTI 5, 107x178x4, and PLZIP) in other viral proteins was employed to identify similar regions in the Epstein-Barr virus (EBV). Several conserved heptad repeat domains that are predicted to form coiled-coil structures with antiviral activity were identified in the EBV genome. Synthetic peptides of 16 to 39 amino acids derived from these regions were prepared and their antiviral activities assessed in a suitable in vitro screening assay. These peptides proved to be potent inhibitors of EBV fusion. Based upon their structural and functional equivalence to the known HIV-1 inhibitors DP-107 and DP-178, these peptides should provide a novel approach to the development of targeted therapies for the treatment of EBV infections.
Owner:TRIMERIS
Screening assays for compounds that inhibit membrane fusion-associated events
The present invention relates to peptides which exhibit potent anti-retroviral activity. The peptides of the invention comprise DP178 (SEQ ID:1) peptide corresponding to amino acids 638 to 673 of the HIV-1LAI gp41 protein, and fragments, analogs and homologs of DP178. The invention further relates to the uses of such peptides as inhibitory of human and non-human retroviral, especially HIV, transmission to uninfected cells.
Owner:TRIMERIS
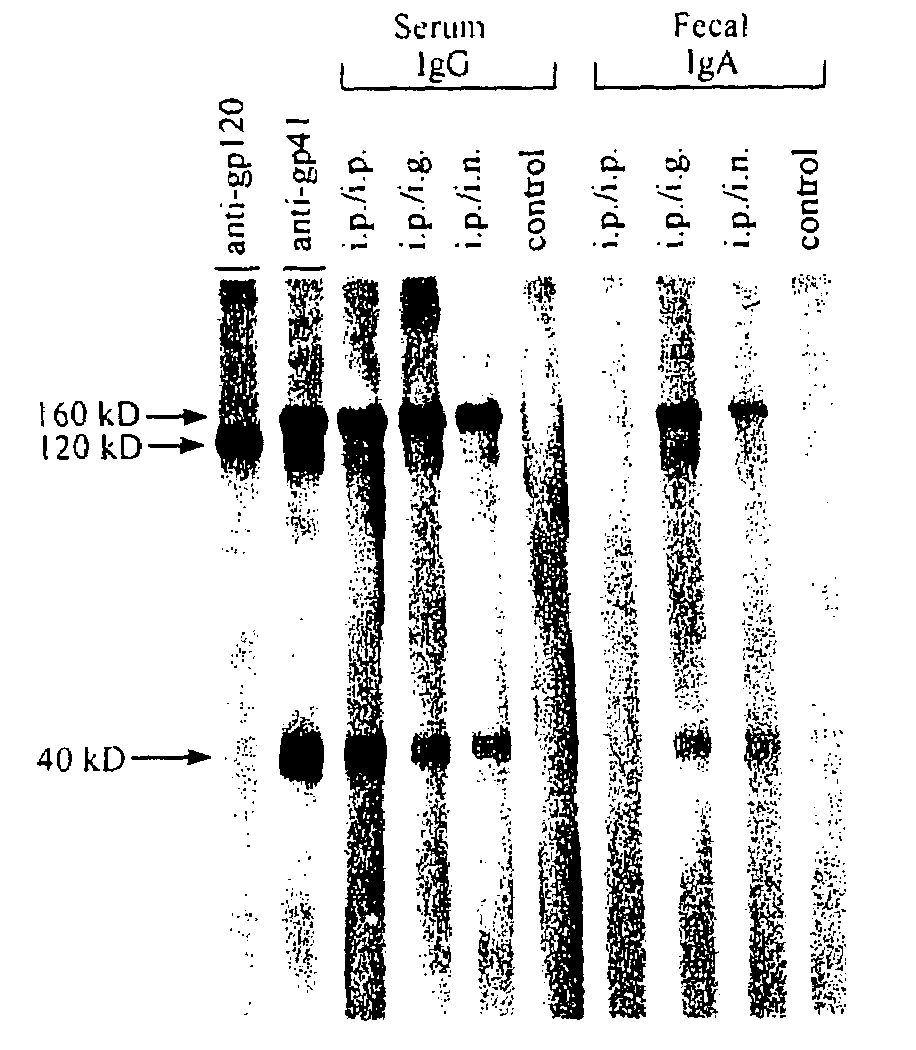
Fusion protein construct and method for inducing HIV-specific serum IgG and secretory IgA antibodies in-vivo
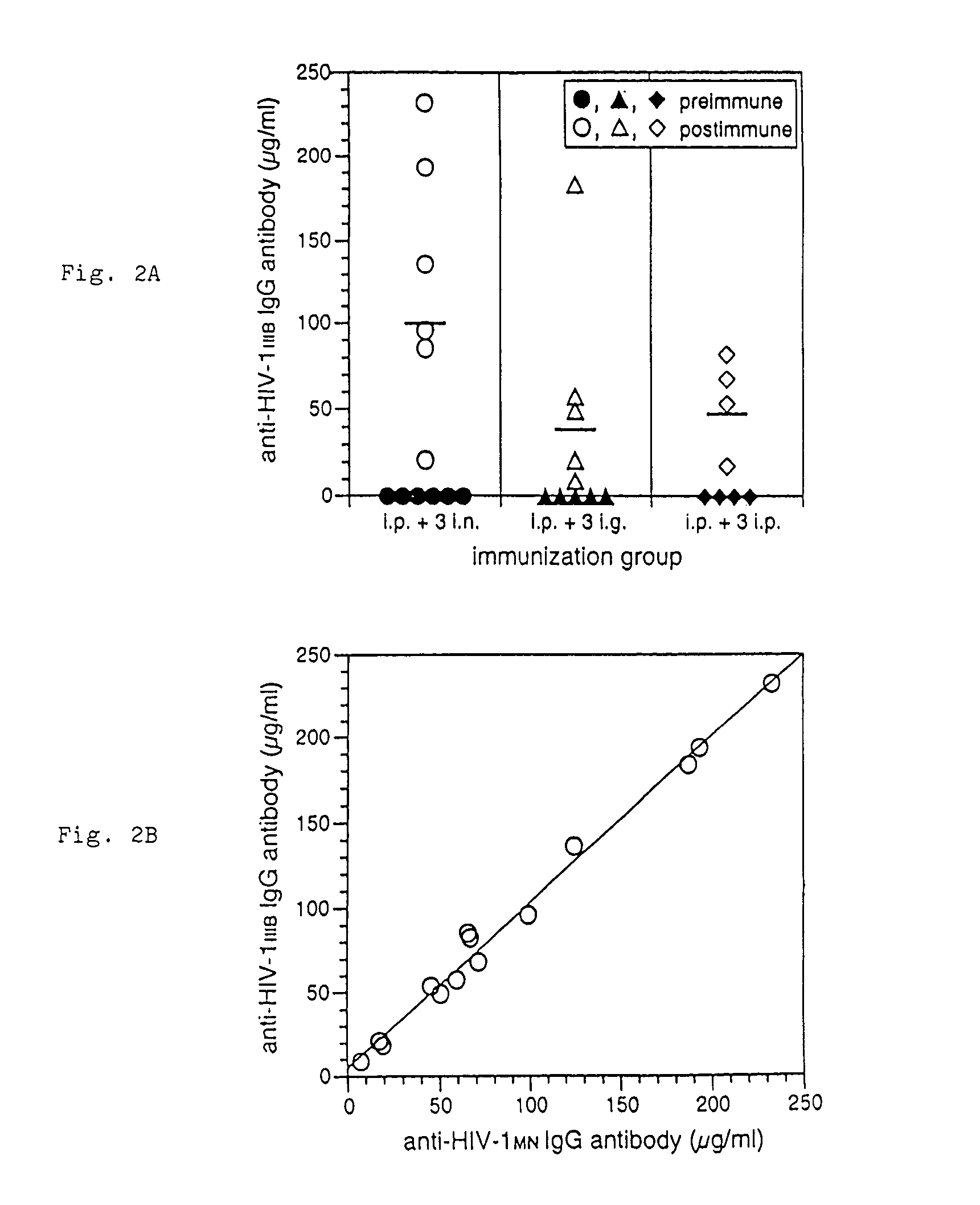
The present invention provides a fusion protein construct (gp41HA) consisting of the ectodomain of the HIV-1IIIB envelope glycoprotein gp41 fused to a fragment of the influenza virus HA2 hemagglutinin protein. Immunization in-vivo via an intraperitoneal prime followed by intranasal or intragastric boosts with gp41HA induces high concentrations of serum IgG antibodies and fecal IgA antibodies that reacted with gp41 in HIV-1IIIB viral lysate and are cross-reactive with gp41 in HIV-1MN lysate. Followup analyses by indirect immunofluorescence showed that both serum IgG and fecal IgA recognized human peripheral blood mononuclear cells infected with either syncytium-inducing (SI) or non-syncytium-inducing (NSI) North American HIV-1 field isolates, but not uninfected cells.
Owner:CHILDRENS MEDICAL CENT CORP
Hiv inhibiting proteins
InactiveUS20060241027A1High activityProlong half-life in vivoBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsHiv transmissionAlbumin
The invention relates to proteins comprising HIV fusion inhibiting peptides, such as T-20 and / or T-1249 peptides (including, but not limited to, fragments and variants thereof), which exhibit anti-retroviral activity, fused to albumin (including, but nbot limited to fragments or variants of albumin). These fusion proteins are herein collectively referred to as “albumin fusion proteins of the invention.” These fusion proteins exhibit extended shelf-life and / or extended or therapeutic activity. The invention encompasses therapeutic albumin fusion proteins, compositions, pharmaceutical compositions, formulations and kits. The invention also encompasses nucleic acid molecules encoding the albumin fusion proteins of the invention, as well as vectors containing these nucleic acids, host cells transformed with these nucleic acids and vectors, and methods of making the albumin fusion proteins of the invention using these nucleic acids, vectors, and / or host cells. The invention also relates to compositions and methods for inhibiting HIV-induced cell fusion. The invention further relates to compositions and methods for inhibiting HIV transmission to uninfected cells.
Owner:NOVOZYMES BIOPHARMA DK AS
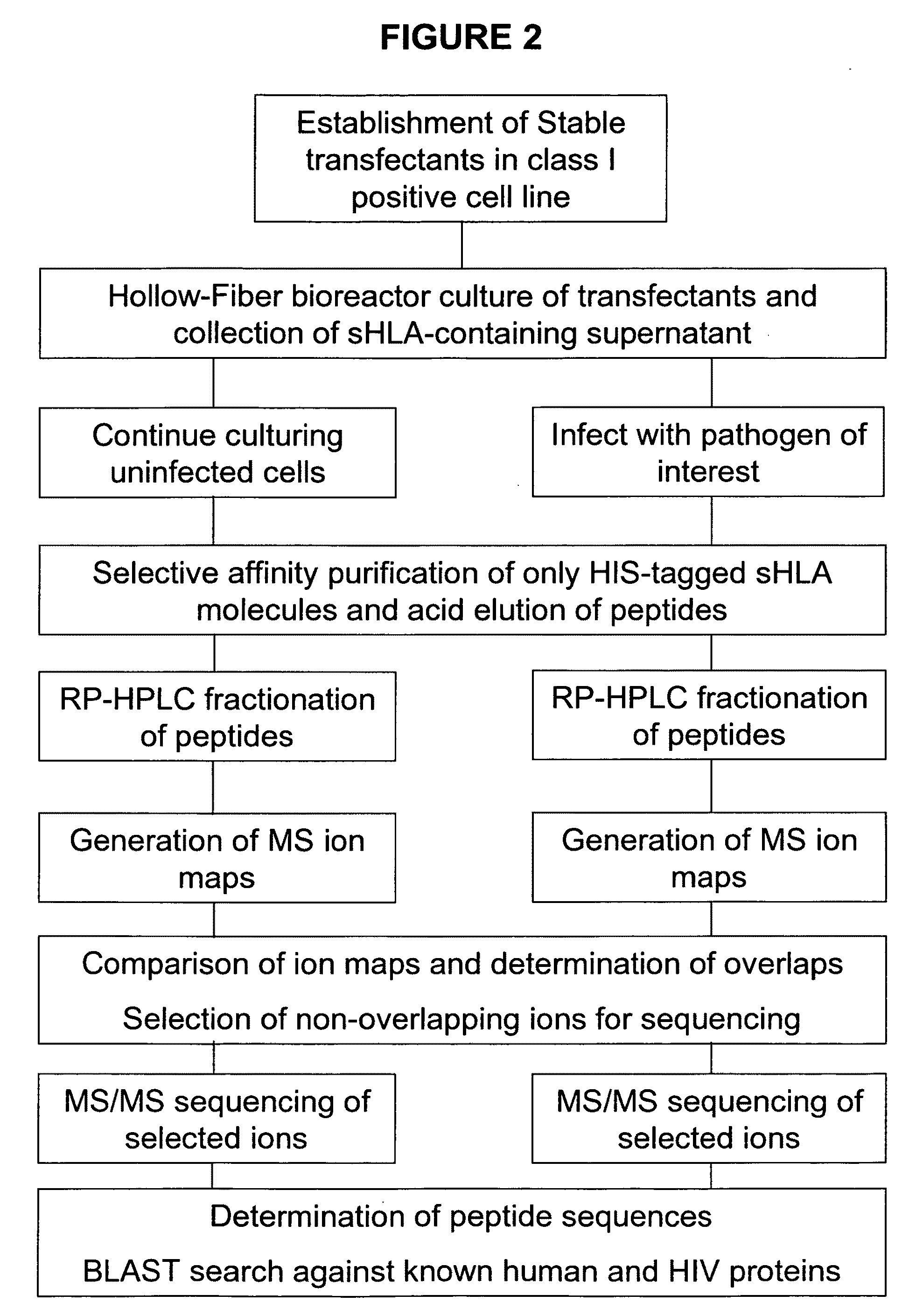
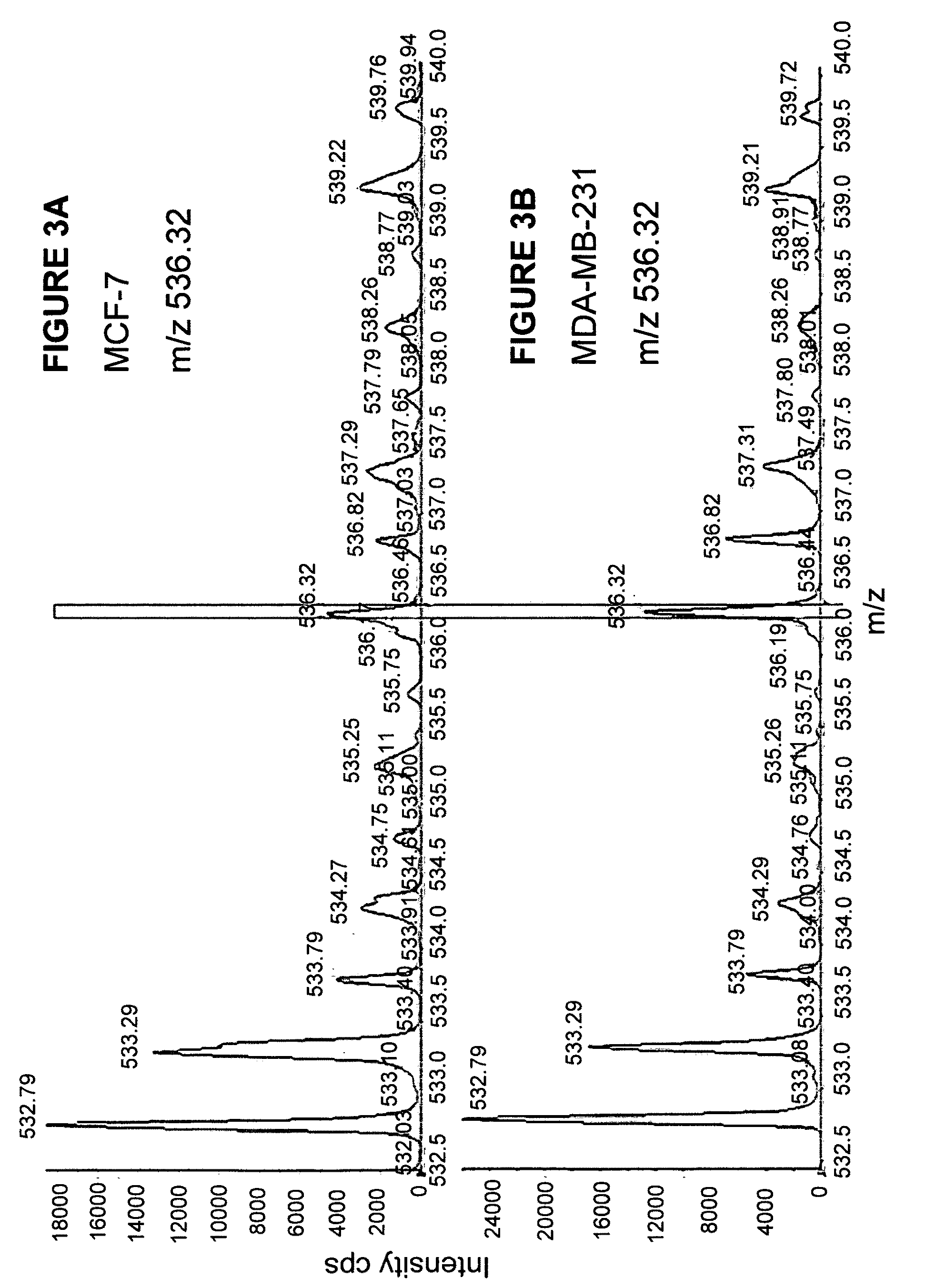
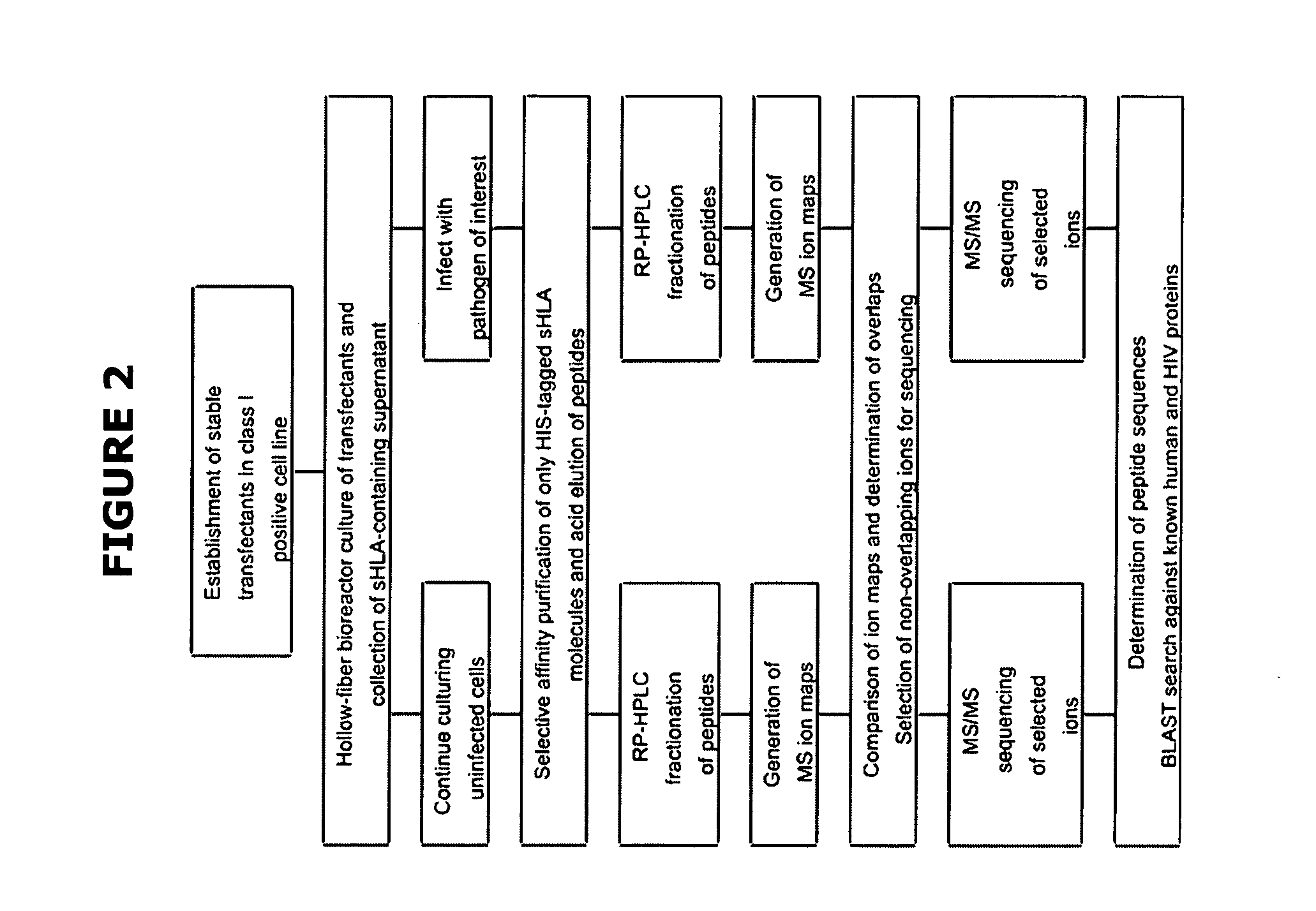
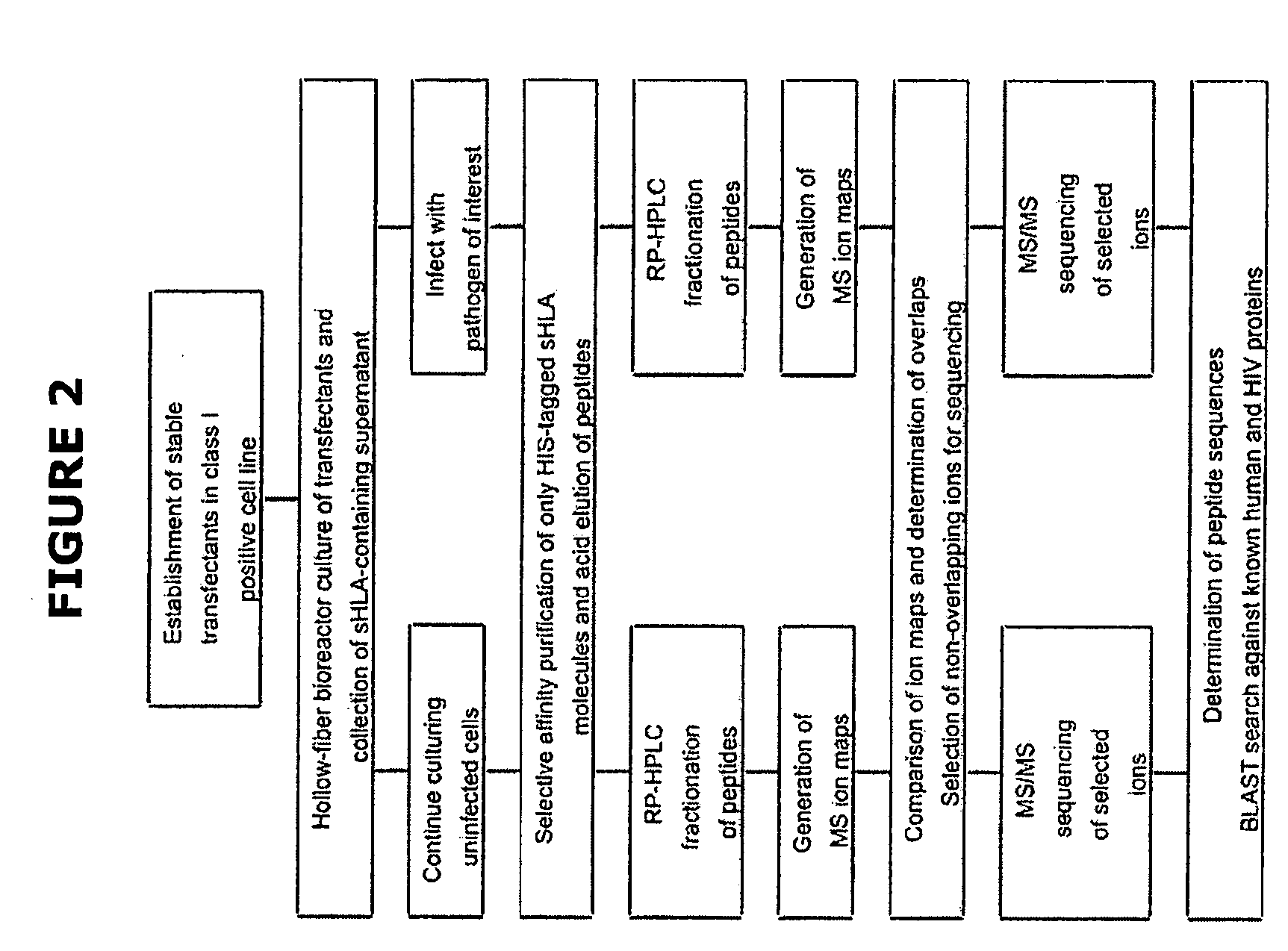
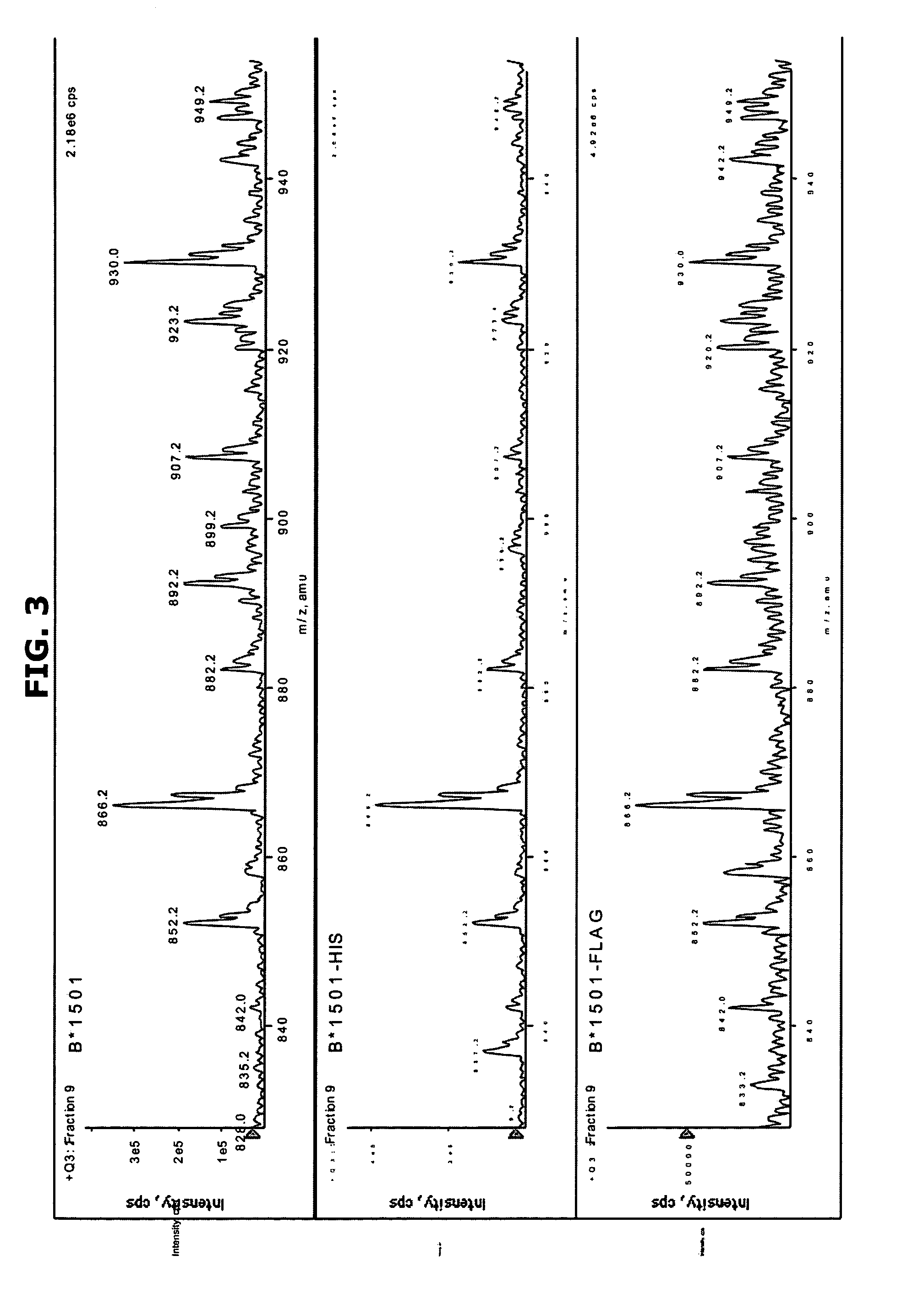
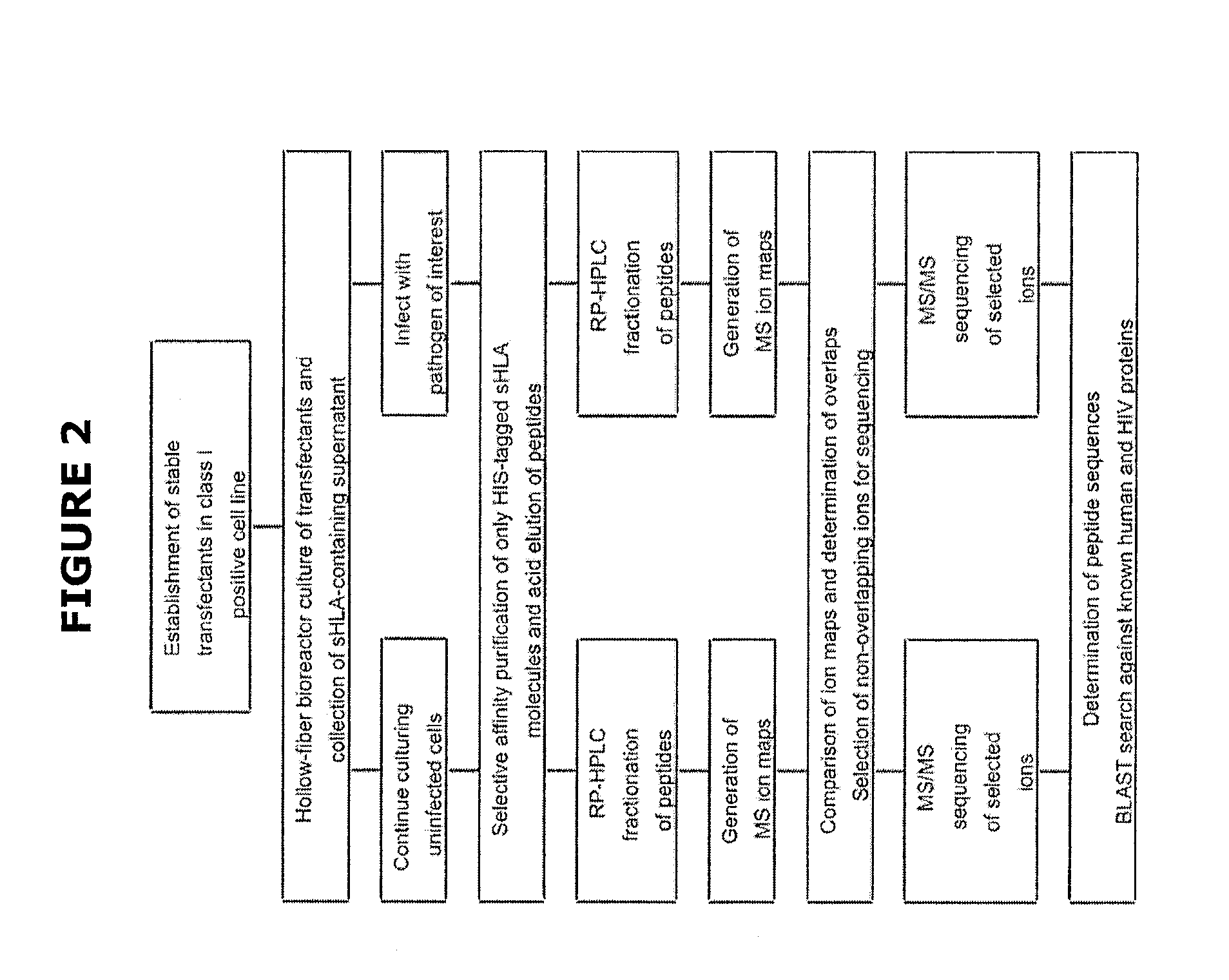
Comparative ligand mapping from MHC class I positive cells
The present invention relates generally to a methodology for the isolation, purification and identification of peptide ligands presented by MHC positive cells. In particular, the methodology of the present invention relates to the isolation, purification and identification of these peptide ligands from soluble class I and class II MHC molecules which may be from uninfected, infected, or tumorigenic cells. The methodology of the present invention broadly allows for these peptide ligands and their cognate source proteins thereof to be identified and used as markers for infected versus uninfected cells and / or tumorigenic versus nontumorigenic cells, with said identification being useful for marking or targeting a cell for therapeutic treatment or priming the immune response against infected / tumorigenic cells.
Owner:THE BOARD OF RGT UNIV OF OKLAHOMA
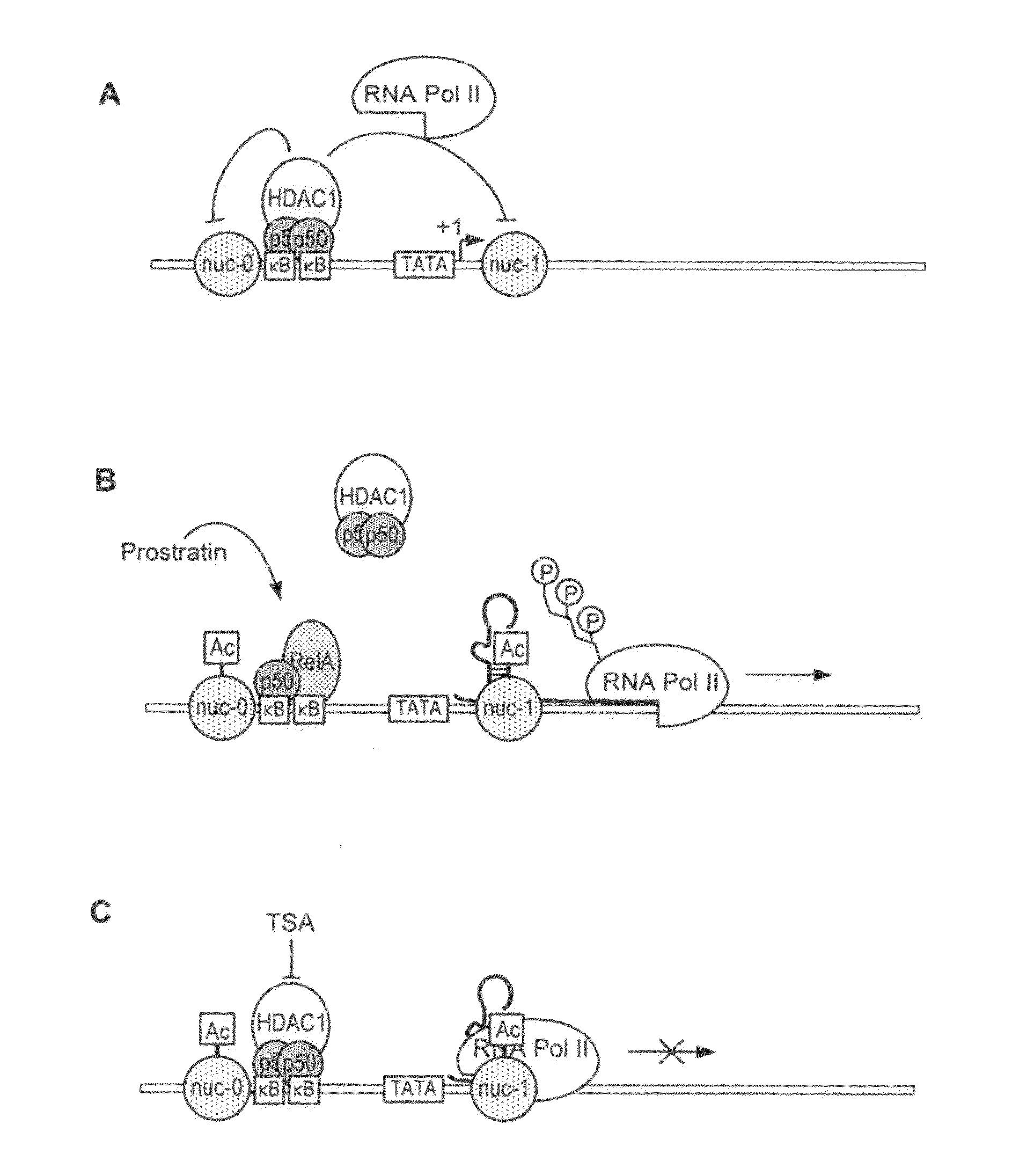
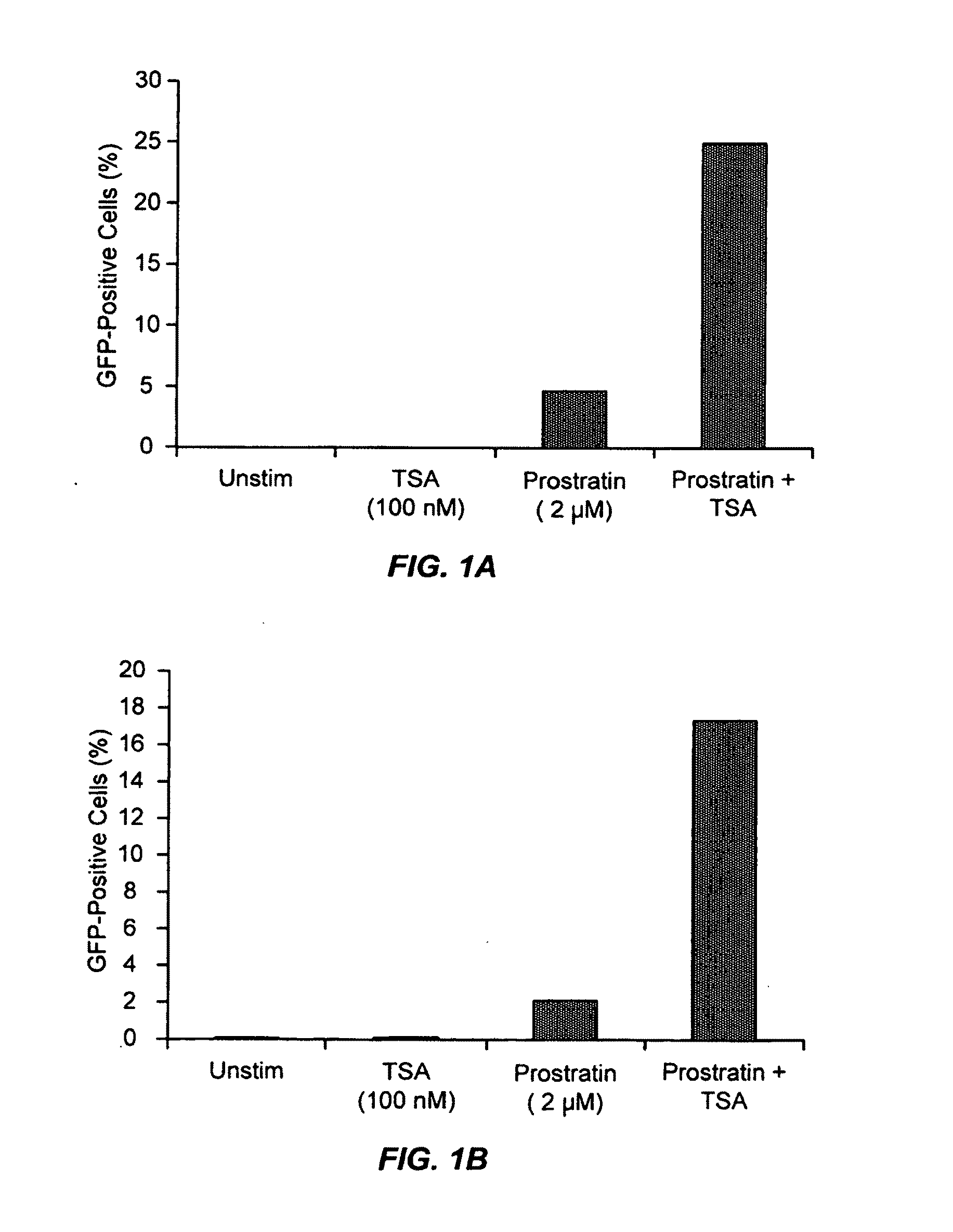
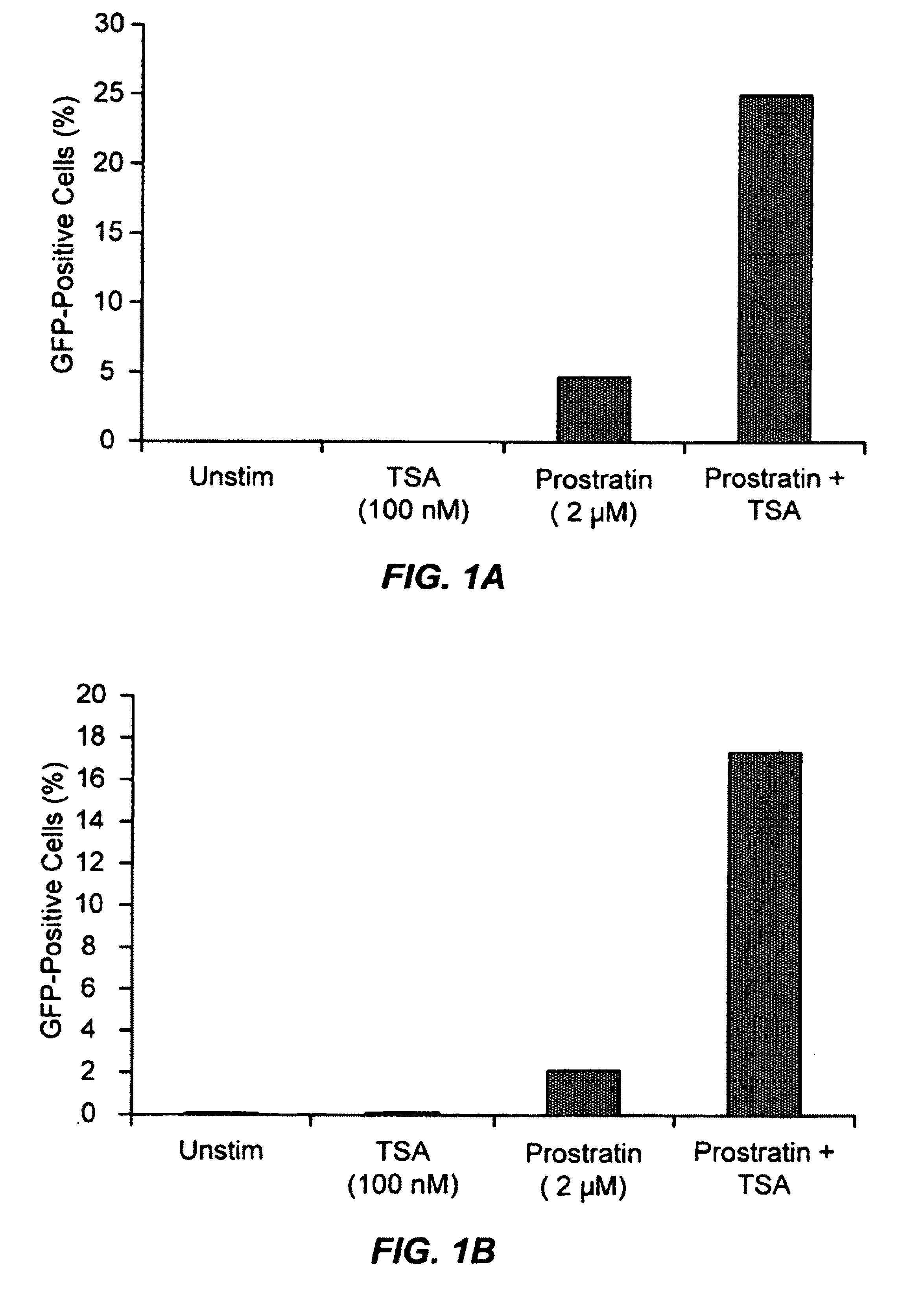
Methods and compositions for the synergistic activation of latent HIV
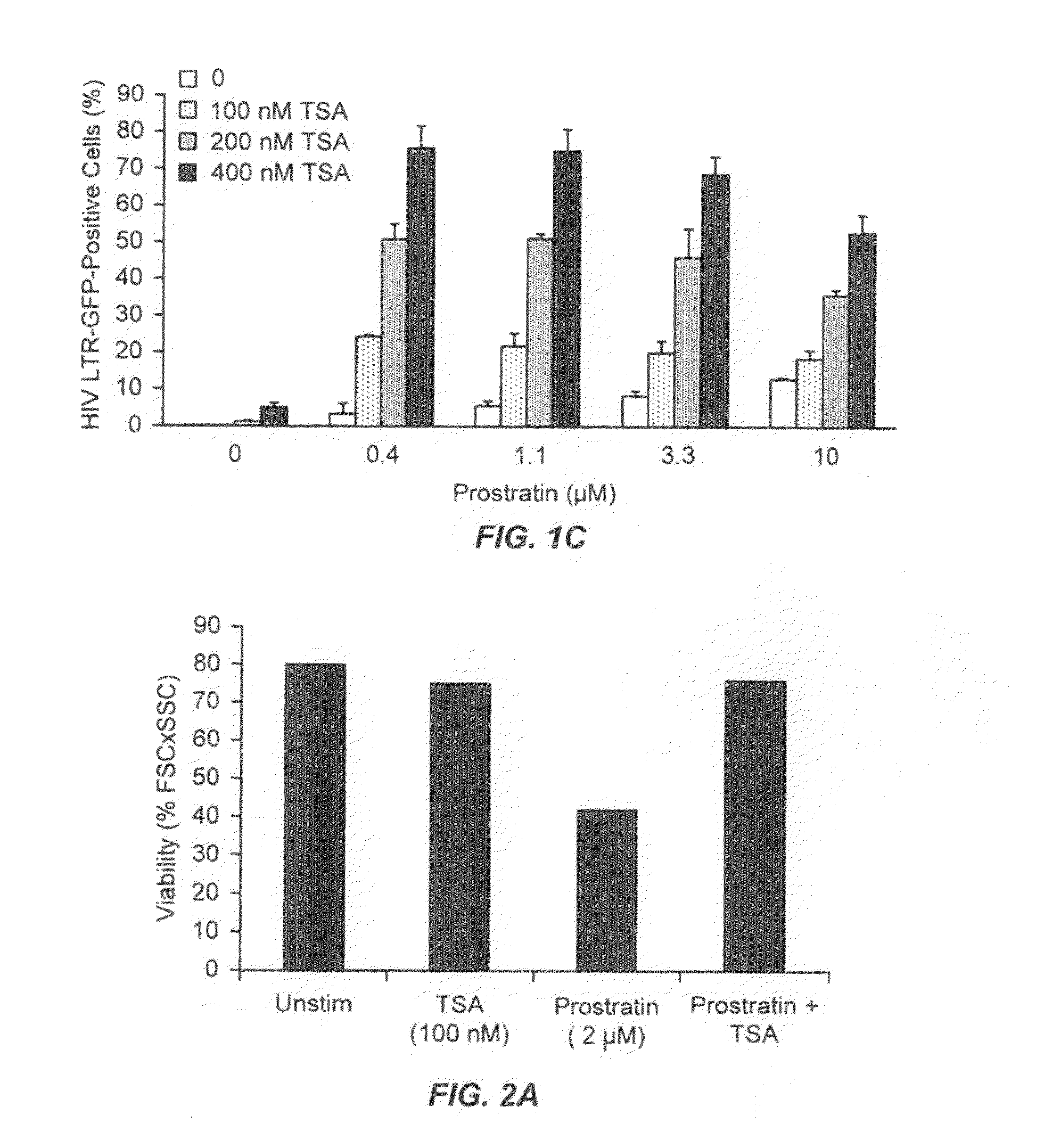
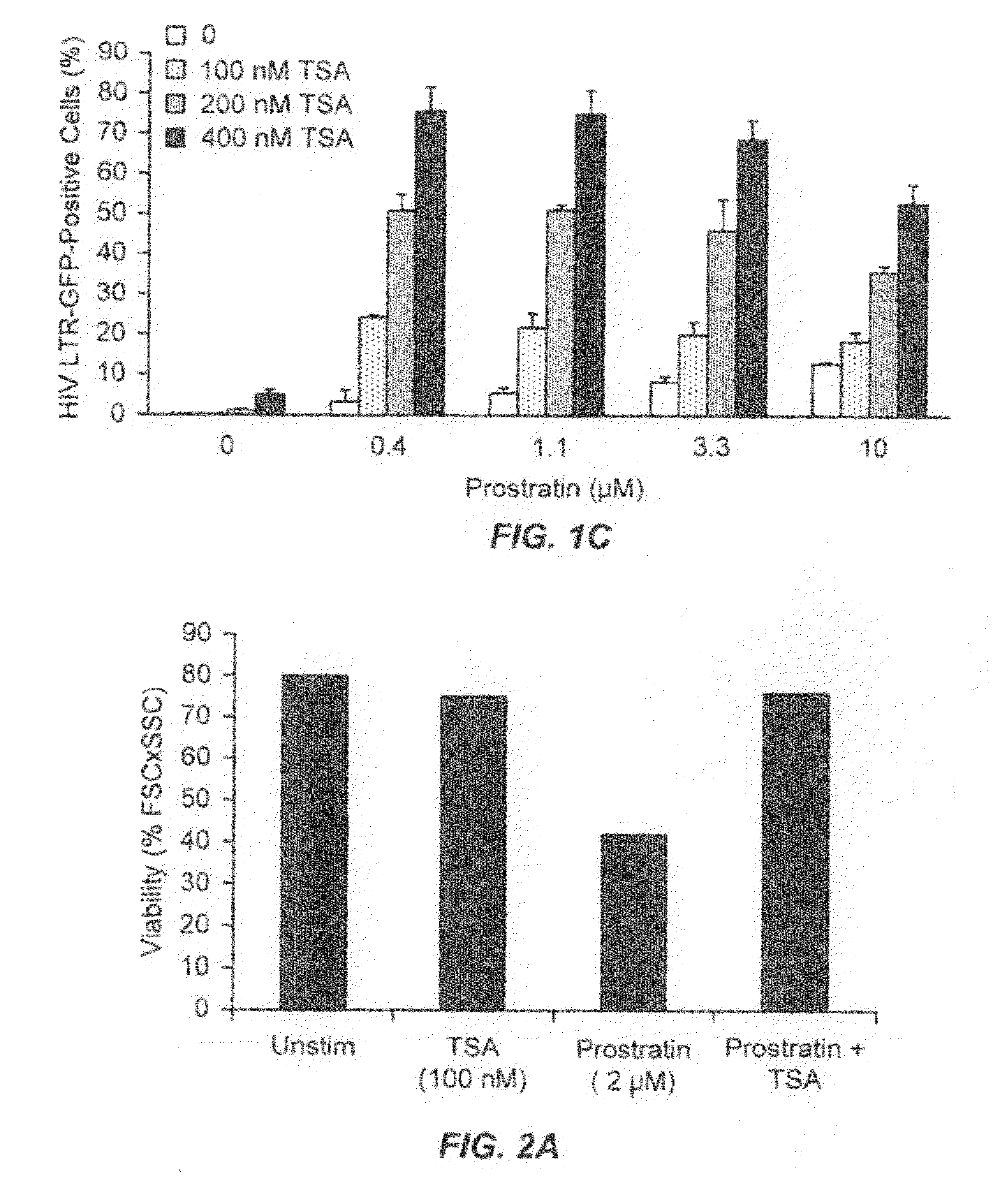
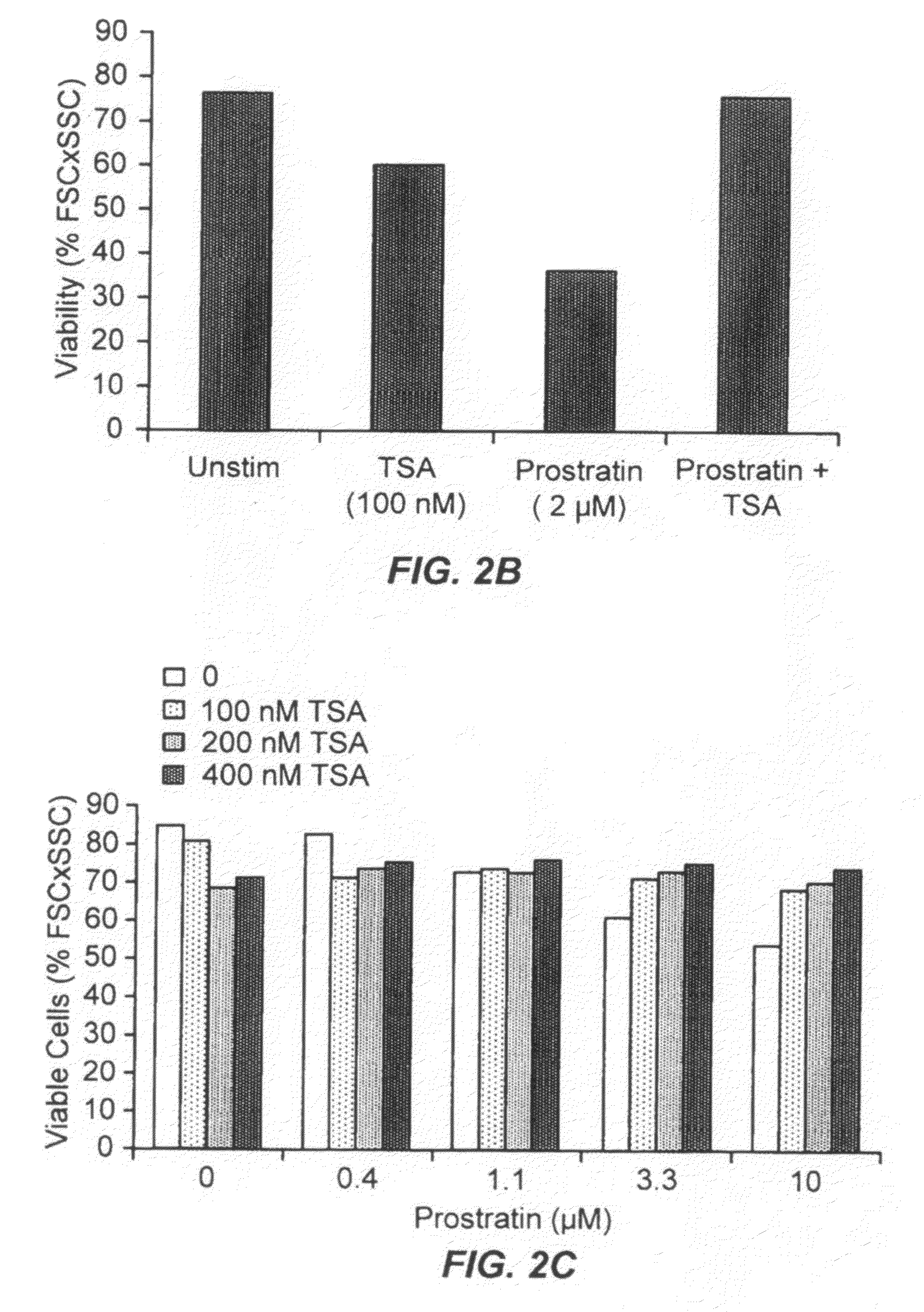
The present invention provides methods and compositions useful for the elimination of latent HIV reservoirs that persist despite HAART. The methods and compositions overcome this latent barrier by inducing the replication of HIV in latently infected T cells while preventing the spread of the newly produced virions to uninfected cells by providing HAART simultaneously. Compositions of the invention comprise an activator of latent HIV expression, such as prostratin, and an inhibitor of histone deacetylase, such as TSA. A surprising finding of this invention is that the inhibitor of the histone deacetylase synergizes the effect of prostratin thus, allowing administering to a patient a lower, non-toxic dose of prostratin.
Owner:THE J DAVID GLADSTONE INST A TESTAMENTARY TRUST ESTABLISHED UNDER THE WILL OF J DAVID GLADS
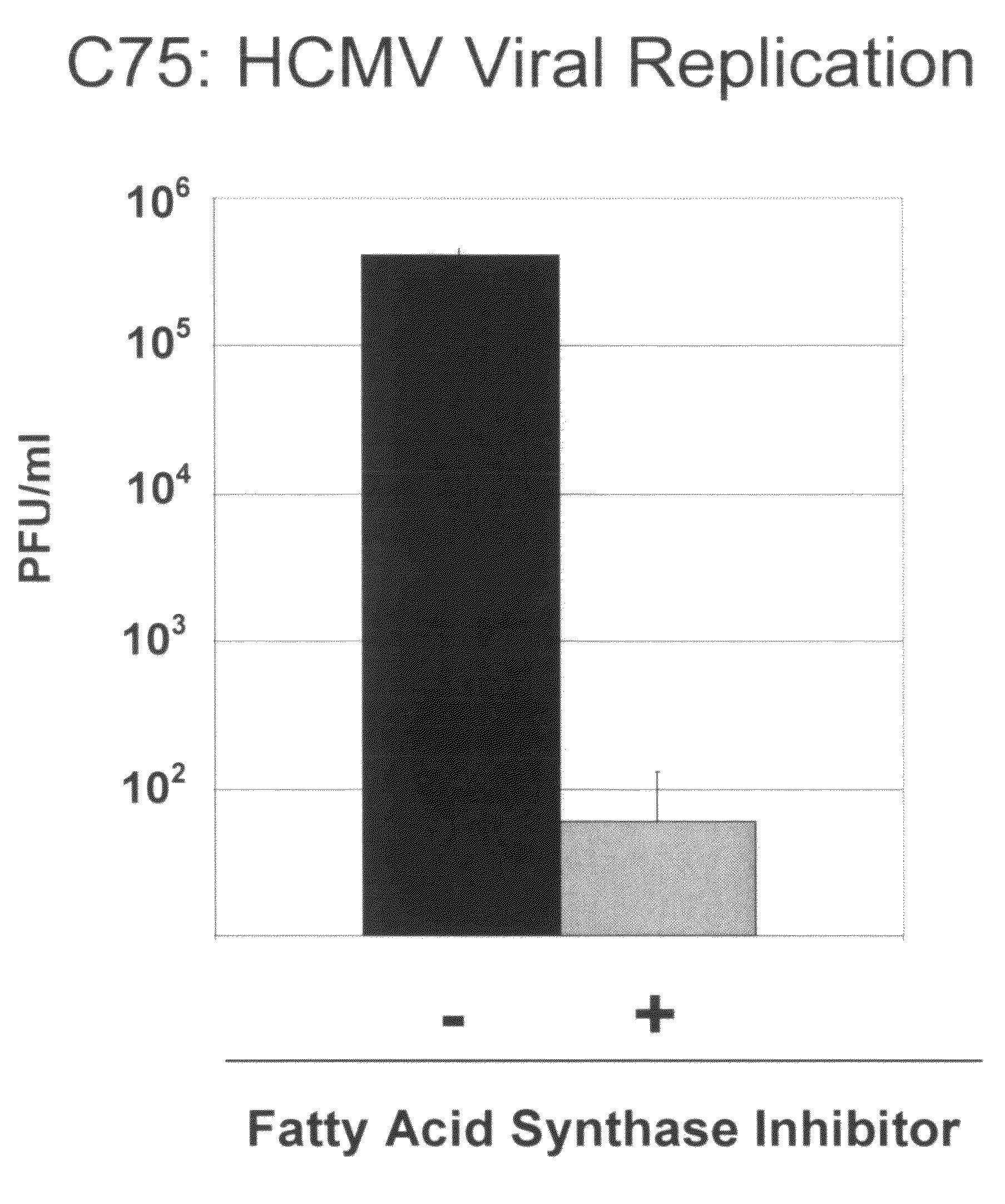
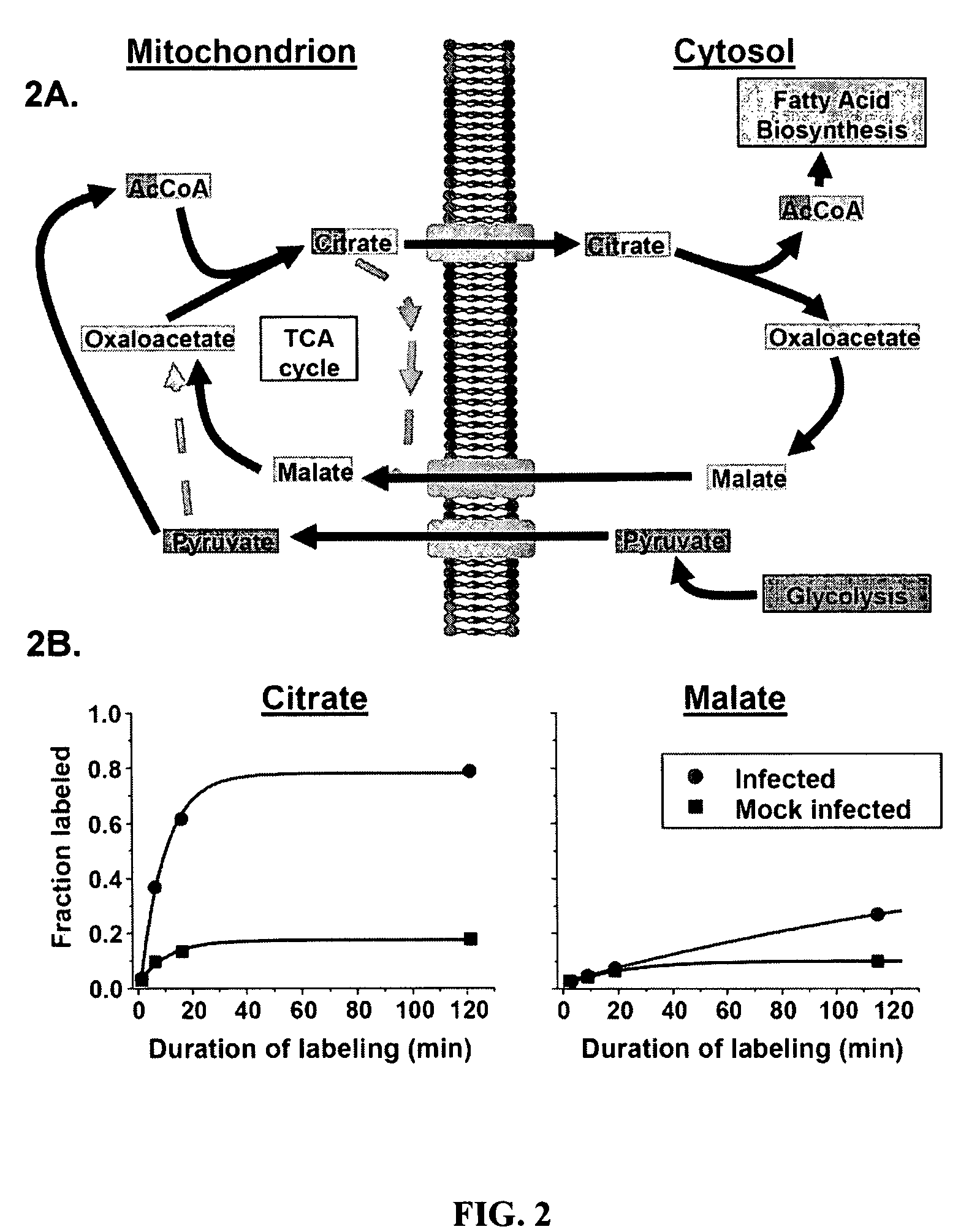
Treatment of viral infections by modulation of host cell metabolic pathways
InactiveUS8158677B2Reduce severityImprove survivalBiocideDigestive systemCritical control pointMetabolite
Owner:THE TRUSTEES FOR PRINCETON UNIV
Treatment of viral infections by modulation of host cell metabolic pathways
InactiveUS20090239830A1Reduction and amelioration of severityShorten the construction periodBiocideDigestive systemCritical control pointAntiviral drug
Alterations of certain metabolite concentrations and fluxes that occur in response to viral infection are described. Host cell enzymes in the involved metabolic pathways are selected as targets for intervention; i.e., to restore metabolic flux to disadvantage viral replication, or to further derange metabolic flux resulting in “suicide” of viral-infected cells (but not uninfected cells) in order to limit viral propagation. While any of the enzymes in the relevant metabolic pathway can be selected, pivotal enzymes at key control points in these metabolic pathways are preferred as candidate antiviral drug targets. Inhibitors of these enzymes are used to reverse, or redirect, the effects of the viral infection. Drug candidates are tested for antiviral activity using screening assays in vitro and host cells, as well as in animal models. Animal models are then used to test efficacy of candidate compounds in preventing and treating viral infections. The antiviral activity of enzyme inhibitors is demonstrated.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES FOR PRINCETON UNIV
Methods for the inhibition of respiratory syncytial virus transmission
Fusion of the viral envelope, or infected cell membranes with uninfected cell membranes, is an essential step in the viral life cycle. Recent studies involving the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) demonstrated that synthetic peptides (designated DP-107 and DP-178) derived from potential helical regions of the transmembrane (TM) protein, gp41, were potent inhibitors of viral fusion and infection. A computerized antiviral searching technology (C.A.S.T.) that detects related structural motifs (e.g., ALLMOTI5, 107x178x4, and PLZIP) in other viral proteins was employed to identify similar regions in the respiratory syncytial virus (RSV). Several conserved heptad repeat domains that are predicted to form coiled-coil structures with antiviral activity were identified in the RSV genome. Synthetic peptides of 16 to 39 amino acids derived from these regions were prepared and their antiviral activities assessed in a suitable in vitro screening assay. These peptides proved to be potent inhibitors of RSV fusion. Based upon their structural and functional equivalence to the known HIV-1 inhibitors DP-107 and DP-178, these peptides should provide a novel approach to the development of targeted therapies for the treatment of RSV infections.
Owner:TRIMERIS
Methods of eliciting broadly neutralizing antibodies targeting HIV-1 gp41
The present invention is directed to the induction and characterization of a humoral immune response targeting "entry-relevant" gp41 structures. In its broadest aspect, the present invention is directed to methods of raising a neutralizing antibody response to a broad spectrum of HIV strains and isolates. The present invention targets particular molecular conformations or structures that occur at the cell surface of HIV during viral entry into host cells. Such a humoral response can be generated in vivo as a prophylactic measure in individuals to reduce or inhibit the ability of HIV to infect uninfected cells in the individual's body. Such a response can also be employed to raise antibodies against "entry relevant" gp41 structures. These antibodies can be employed for therapeutic uses, and as tools for further illuminating the mechanism of HIV cell entry.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA +1
Methods of eliciting broadly neutralizing antibodies targeting HIV-1 gp41
The present invention is directed to the induction and characterization of a humoral immune response targeting “entry-relevant” gp41 structures. In its broadest aspect, the present invention is directed to methods of raising a neutralizing antibody response to a broad spectrum of HIV strains and isolates. The present invention targets particular molecular conformations or structures that occur at the cell surface of HIV during viral entry into host cells. Such a humoral response can be generated in vivo as a prophylactic measure in individuals to reduce or inhibit the ability of HIV to infect uninfected cells in the individual's body. Such a response can also be employed to raise antibodies against “entry relevant” gp41 structures. These antibodies can be employed for therapeutic uses, and as tools for further illuminating the mechanism of HIV cell entry.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA +1
Methods and compositions for inhibition of membrane fusion-associated events, including HIV transmission
The present invention relates to peptides which exhibit potent anti-retroviral activity. The peptides of the invention comprise DP178 (SEQ ID:1) peptide corresponding to amino acids 638 to 673 of the HIV-1LAI gp41 protein, and fragments, analogs and homologs of DP178. The invention further relates to the uses of such peptides as inhibitory of human and non-human retroviral, especially HIV, transmission to uninfected cells.
Owner:TRIMERIS
Comparative ligand mapping from MHC class 1 positive cells
The present invention relates generally to a methodology for the isolation, purification and identification of peptide ligands presented by MHC positive cells. In particular, the methodology of the present invention relates to the isolation, purification and identification of these peptide ligands from soluble class I and class II MHC molecules which may be from uninfected, infected, or tumorigenic cells. The methodology of the present invention broadly allows for these peptide ligands and their cognate source proteins thereof to be identified and used as markers for infected versus uninfected cells and / or tumorigenic versus nontumorigenic cells with said identification being useful for marking or targeting a cell for therapeutic treatment or priming the immune response against infected cells.
Owner:THE BOARD OF RGT UNIV OF OKLAHOMA
Therapeutic administration of a modified alpha1 proteinase inhibitor
InactiveUS20020004477A1Prevent and inhibitGrowth inhibitionOrganic active ingredientsBiocideSerum igeAlpha1-proteinase inhibitor
A method for the treatment of asymtomatic HIV seropositive individuals to inhibit onset of an AIDS infection and, for suppression of propagation of HIV infections in individuals with a fully developed AIDS infection. The method consists of administering a therapeutic effective amount of a modified {acute over (alpha)}1Proteinase Inhibitor (m{acute over (alpha)}1PI) to an individual within the effected population so as to inhibit and / or prevent {acute over (alpha)} PI facilitated HIV entry into healthy / uninfected cells.
Owner:BRISTOW CYNTHIA L
Nucleic acids encoding DP-178 and other viral fusion inhibitor peptides useful for treating aids
InactiveUS20070202127A1Avoid virus infectionSsRNA viruses negative-sensePeptide/protein ingredientsTherapy HIVUninfected cell
The present invention relates to peptides which exhibit potent anti-retroviral activity. The peptides of the invention comprise DP178 (SEQ ID:1) peptide corresponding to amino acids 638 to 673 of the HIV-1LAI gp41 protein, and fragments, analogs and homologs of DP178. The invention further relates to the uses of such peptides as inhibitory of human and non-human retroviral, especially HIV, transmission to uninfected cells.
Owner:DUKE UNIV +1
Chinese herbal medicine feed additive for preventing freshwater salmon from enteritis and application thereof
InactiveCN107348137AImprove disease resistancePrevent enteritisAnthropod material medical ingredientsDigestive systemBiotechnologyFlos chrysanthemi
The invention discloses a Chinese herbal medicine feed additive for preventing a freshwater salmon from enteritis and application thereof. The additive is prepared from the following components in parts by weight: 16 parts to 20 parts of herba polygoni hydropiperis, 15 parts to 18 parts of radix isatidis, 13 parts to 18 parts of radix rehmanniae preparata, 15 parts to 20 parts of galla chinensis, 10 parts to 13 parts of herba verbenae, 8 parts to 12 parts of flos chrysanthemi indici, 10 parts to 13 parts of radix glycyrrhizae, 8 parts to 13 parts of herba andrographis, 3 parts to 6 parts of honeysuckle flowers, and 5 parts to 8 parts of radix scutellariae. The Chinese herbal medicine feed additive has the beneficial effects that by utilizing the additive, uninfected cells in an intestinal tract of the salmon can be induced to produce cell factors, so that the expression of the cell factors can be more enhanced and extended in infected cells, the disease resistant capability of the freshwater salmon to enteritis viruses can be enhanced, and an aim of preventing the enteritis is fulfilled; and the feed of the additive disclosed by the invention is mixed, and the addition of other anti-biological drugs is not needed any longer, and therefore, the feed additive has the effects of clearing away heat and removing toxic substances, and sterilizing and resisting bacteria.
Owner:TONGHUA NORMAL UNIV
Comparative ligand mapping from MHC class I positive cells
InactiveUS20070099182A1Peptide/protein ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementMHC class IPeptide ligand
The present invention relates generally to a methodology for the isolation, purification and identification of peptide ligands presented by MHC positive cells. In particular, the methodology of the present invention relates to the isolation, purification and identification of these peptide ligands from soluble class I and class 11 MHC molecules which may be from uninfected, infected, or tumorigenic cells. The methodology of the present invention broadly allows for these peptide ligands and their cognate source proteins thereof to be identified and used as markers for infected versus uninfected cells and / or tumorigenic versus nontumorigenic cells, with said identification being useful for marking or targeting a cell for therapeutic treatment or priming the immune response against infected cells.
Owner:THE BOARD OF RGT UNIV OF OKLAHOMA
Methods and compositions for the synergistic activation of latent HIV
The present invention provides methods and compositions useful for the elimination of latent HIV reservoirs that persist despite HAART. The methods and compositions overcome this latent barrier by inducing the replication of HIV in latently infected T cells while preventing the spread of the newly produced virions to uninfected cells by providing HAART simultaneously. Compositions of the invention comprise an activator of latent HIV expression, such as prostratin, and an inhibitor of histone deacetylase, such as TSA. A surprising finding of this invention is that the inhibitor of the histone deacetylase synergizes the effect of prostratin thus, allowing administering to a patient a lower, non-toxic dose of prostratin.
Owner:THE J DAVID GLADSTONE INST A TESTAMENTARY TRUST ESTABLISHED UNDER THE WILL OF J DAVID GLADS
Method for Screening of Agents for the Prevention of Hepatitis C Virus Infection with Cell Culture Tool
InactiveUS20110117541A1Improve discovery efficiencyAvoid spreadingMicrobiological testing/measurementBiochemistry apparatusCryopreservationImproved method
The invention relates to an improved method of screening of anti-HCV agents that may have an efficacy for prevention of hepatitis C virus. The method involves the isolation and cryopreservation of HCV-infected hepatocytes from multiple infected individuals. The isolated and cryopreserved hepatocytes are stored in a cryopreservation bank made up of HCV-infected hepatocytes representing the different genotypes of HCV. These stored hepatocytes then are co-cultured in a culture medium with uninfected hepatocytes, and anti-HCV screening of the hepatocytes is done by subjecting HCV infected hepatocytes and uninfected hepatocytes in parallel to the actions of different anti-HCV compounds at various concentrations. An effective anti-HCV agent will lead to prevention of increase in concentration of HCV content of uninfected cells in the co-culture.
Owner:DISCOVERY LIFE SCI LLC
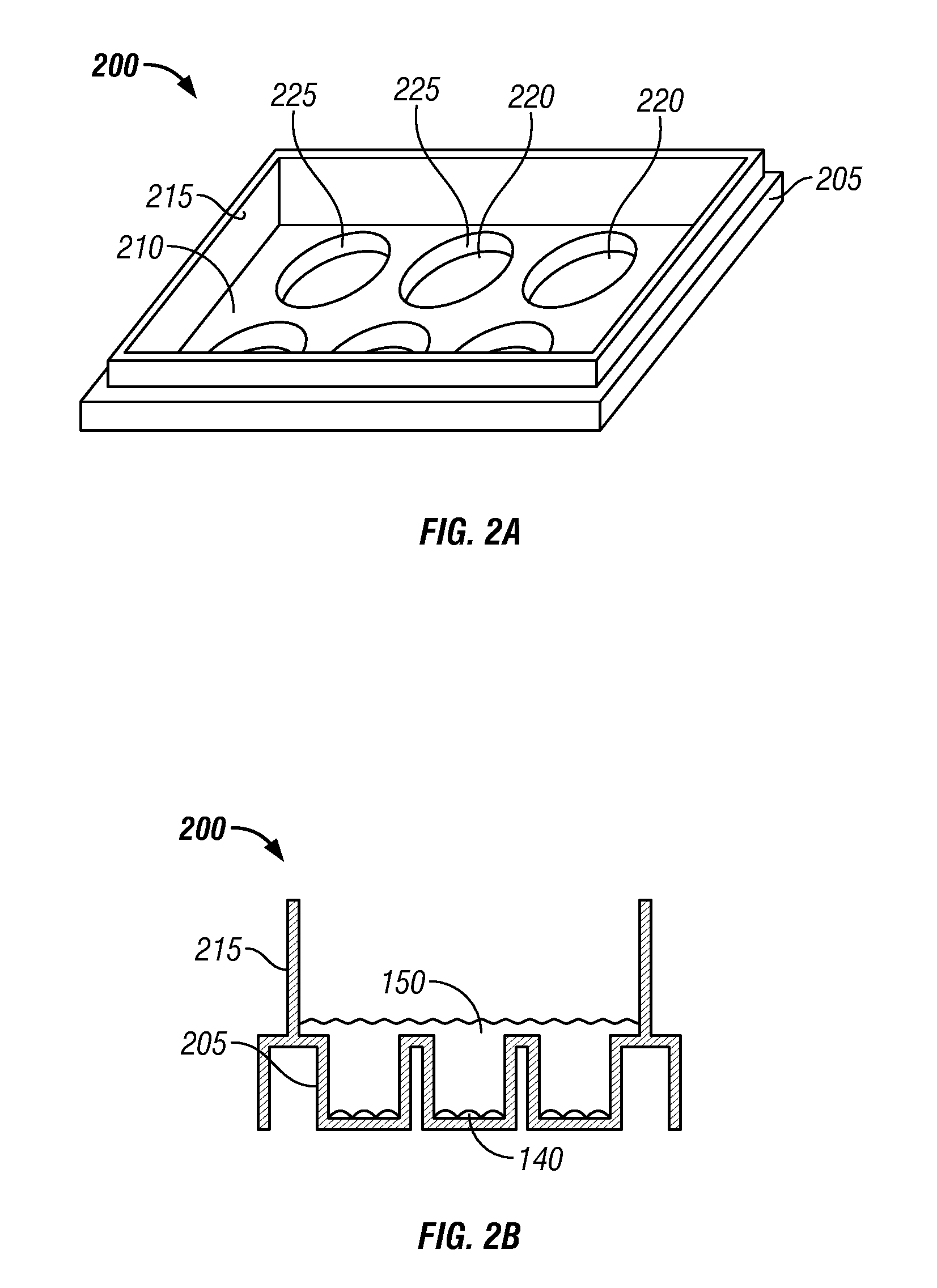
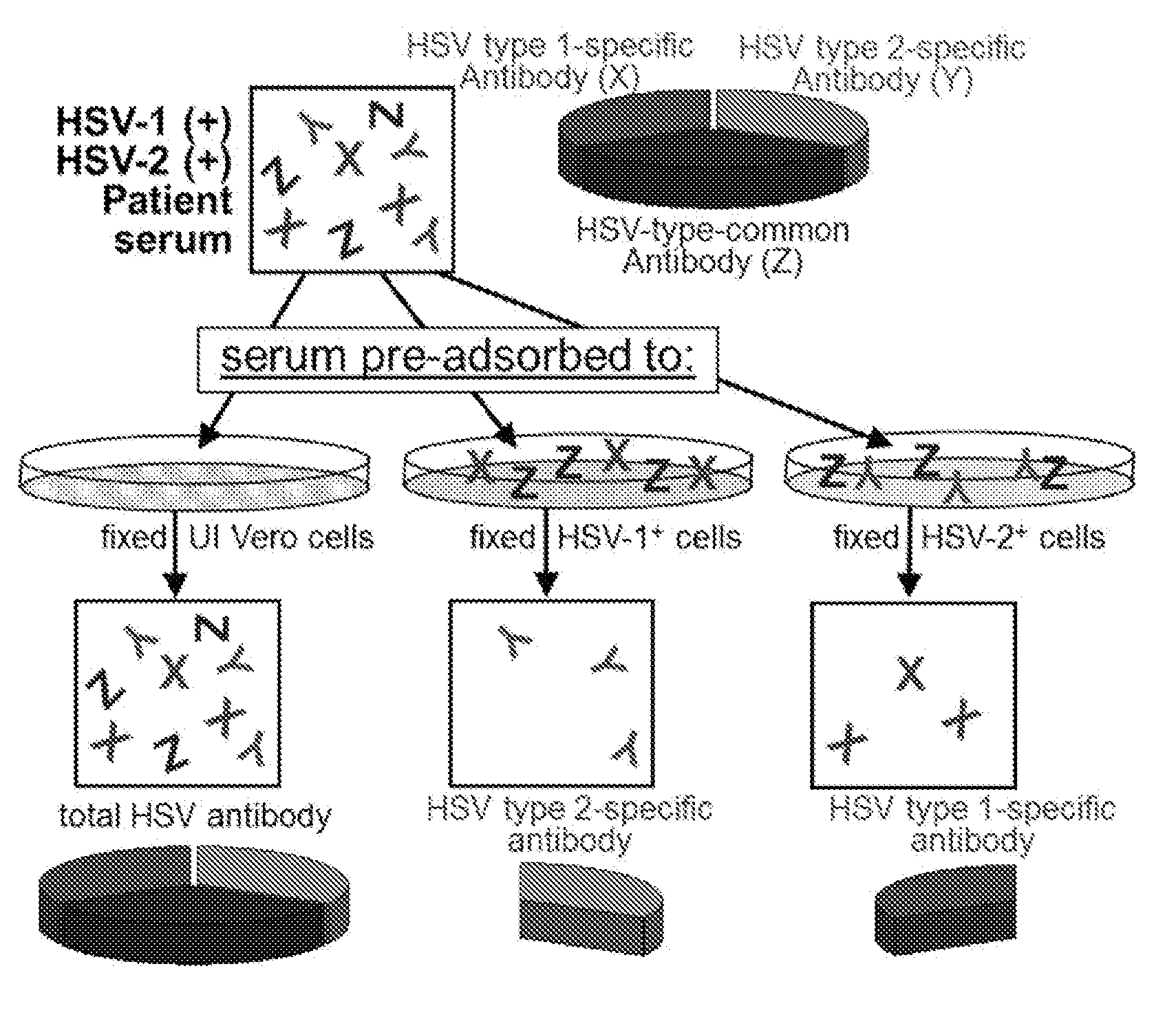
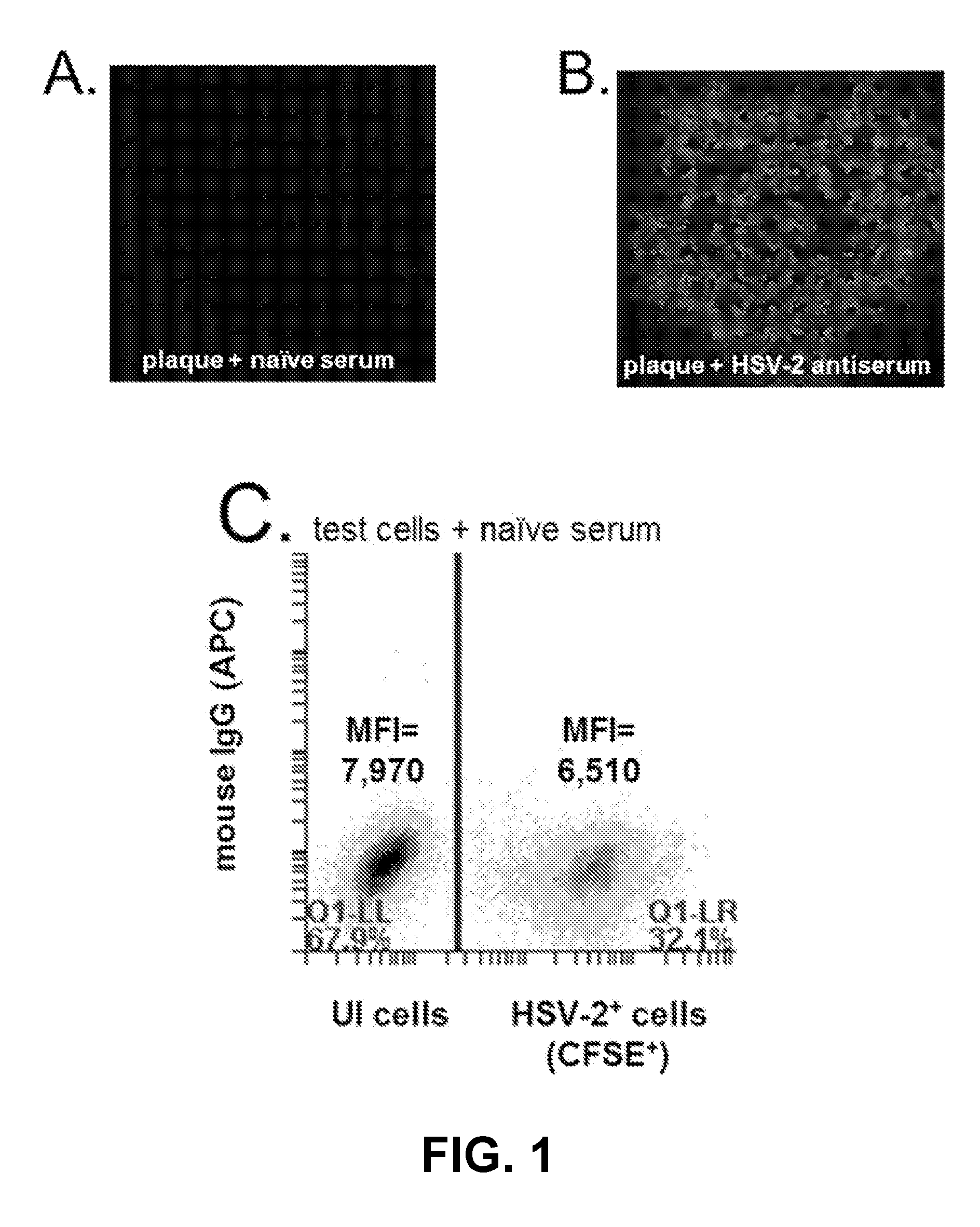
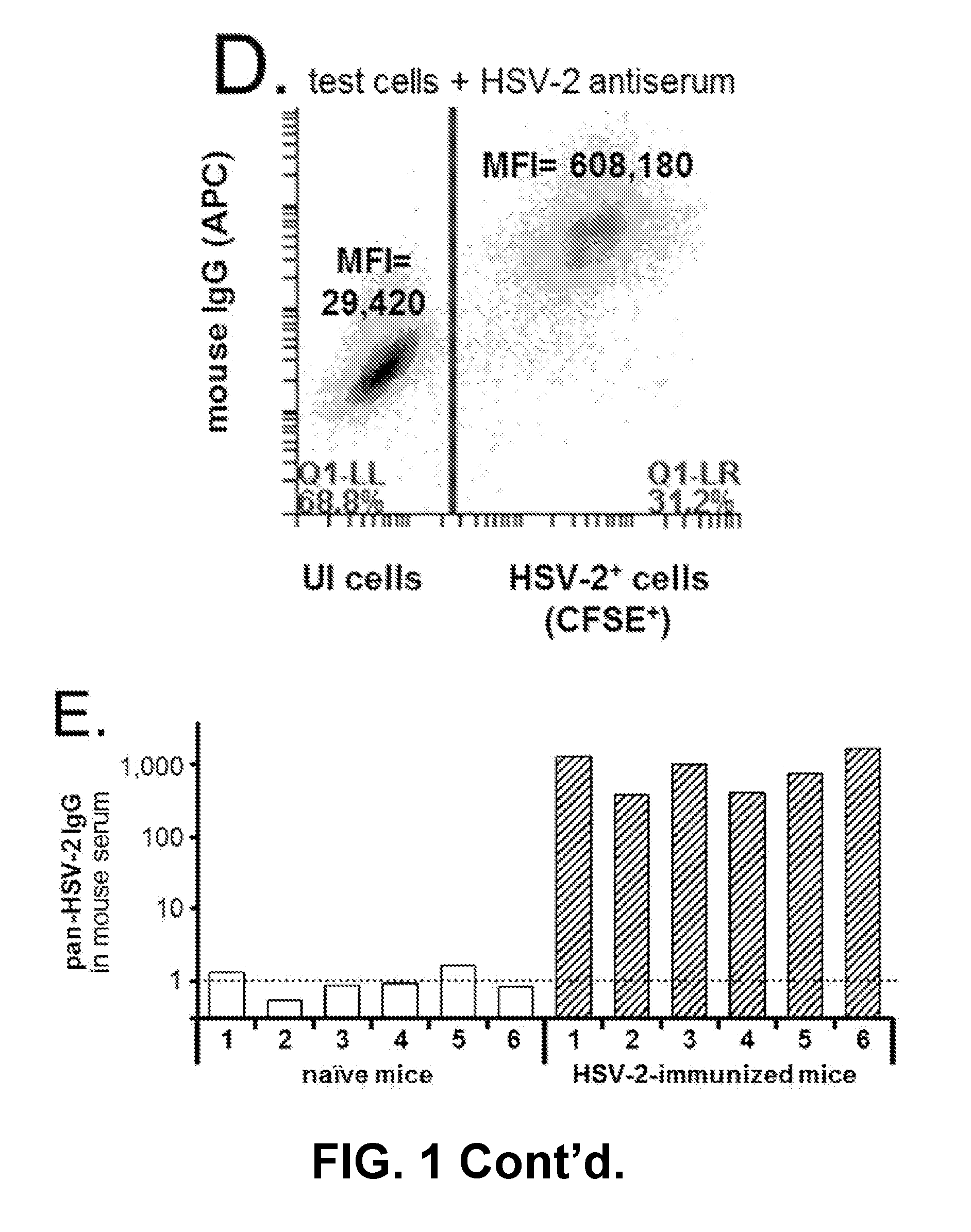
Rapid and sensitive serological assay to determine if patients are infected with herpes simplex virus type 1 hsv-1 and/or type 2 hsv-2
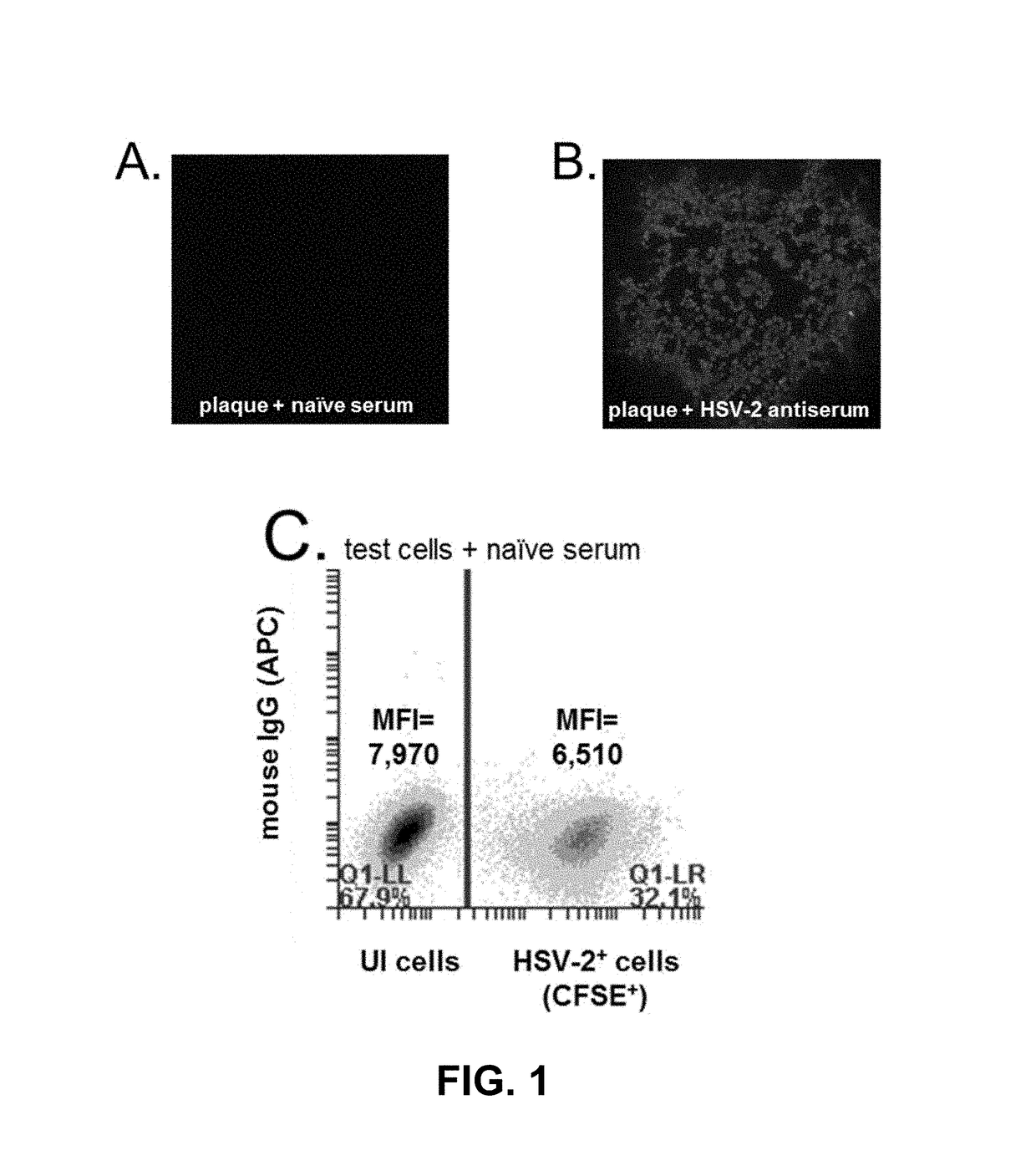
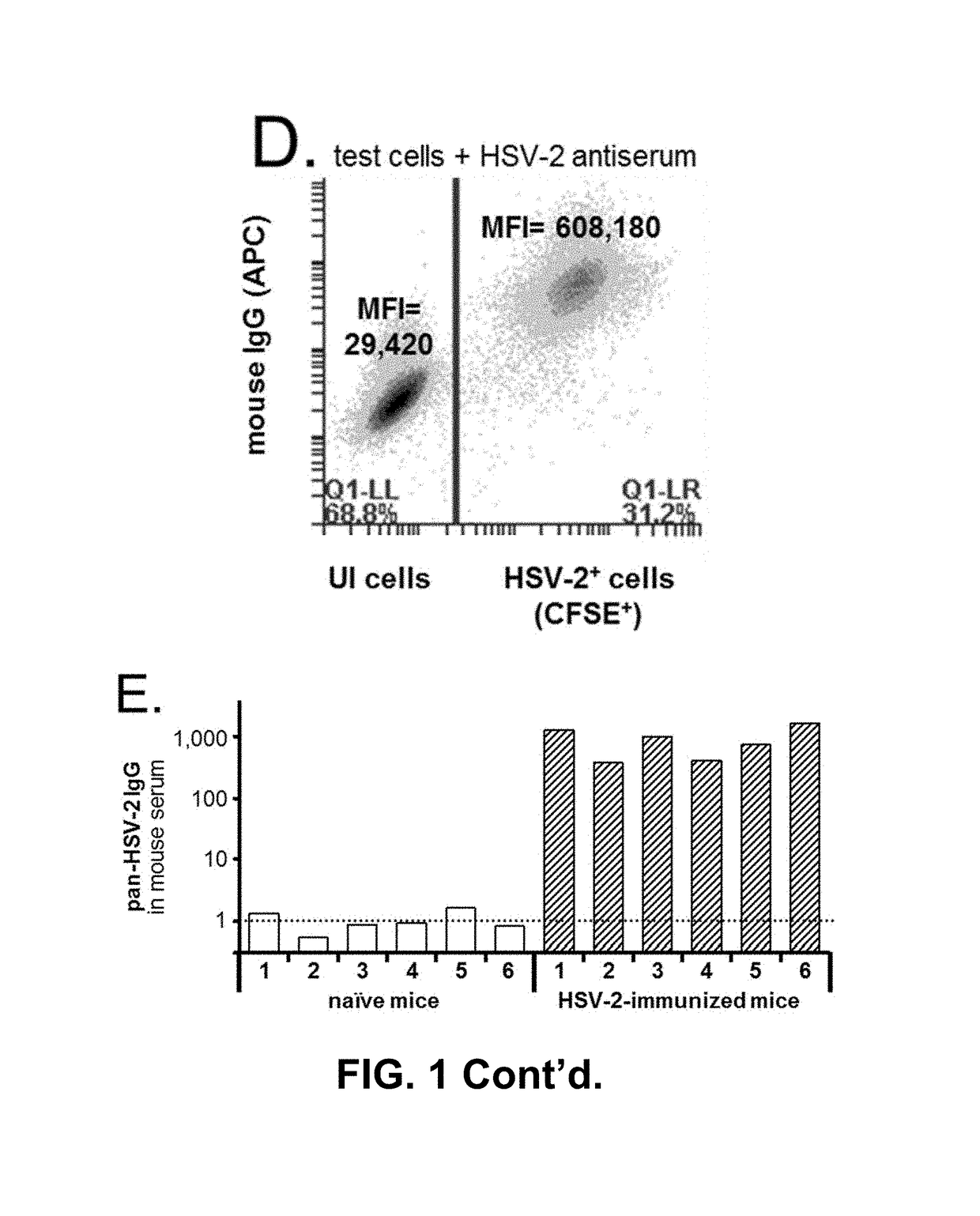
An assay for infection with one or more herpes simplex viruses that comprises a) dividing an antibody-containing serum sample into at least three serum subsamples, and b) separately incubating each with a physical matrix of cell antigens from i) uninfected cells, (ii) HSV-1-infected cells, or (iii) HSV-2-infected cells to form at least three serum subsample admixtures so that antibodies present in each admixture can immunoreact to form matrix-bound antibodies and at least three preadsorbed serum subsample portions. Each preadsorbed serum subsample portion is incubated with a mixture of matrix-bound antigens from cells uninfected by HSV-1 or HSV-2, infected by each of HSV-1 and by HSV-2 to permit antibodies to immunoreact with antigens present to form three matrix-bound immunoreactants. The amount of each immunoreaction is determined, and reaction amounts are prognostic for whether the subject whose serum was tested is infected by one, both, or neither of HSV-1 and HSV-2.
Owner:SOUTHERN ILLINOIS UNIVERSITY
Compounds for preventing or treating viral infections and methods of use thereof
Described herein are compounds and methods that prevent the viral infection of cells. The compounds and methods described herein minimize viral resistance and maximize the number of targeted viruses.Additionally, the compounds and methods minimize the toxicity toward uninfected cells.
Owner:艾伯塔大学校董
Fusobacterium nucleatum related oral epithelial cell tumor biomarker and screening application
The invention discloses a fusobacterium nucleatum related oral epithelial cell tumor biomarker and screening application. The biomarker comprises 15 lncRNAs (long non-coding RNAs) such as AC118757.1,AL162727.1 and AC090844.3. During screening, the human immortalized oral epithelial cells HIOECs are resuscitated and cultured; a fusobacterium nucleatum model strain ATCC25586 is resuscitated; an in-vitro model of the fusobacterium nucleatum infected HIOECs cells is constructed; total RNA of HIOECs infected by fusobacterium nucleatum and uninfected HIOECs cells are extracted respectively to carryout high-throughput sequencing on lncRNA and mRNA transcriptomes, differentially expressed mRNA and lncRNA are screened to further determine a core gene; and the lncRNA participating in differentialexpression of a core gene is screened by constructing an lncRNA-core gene co-expression network. An analysis result can lay a good foundation for further research of fusobacterium nucleatum in the process of affecting malignant transformation and tumors.
Owner:HOSPITAL OF STOMATOLOGY CHINA MEDICAL UNIV
Comparative ligand mapping from MHC positive cells
The present invention relates generally to a methodology for the isolation, purification and identification of peptide ligands presented by MHC positive cells. In particular, the methodology of the present invention relates to the isolation, purification and identification of these peptide ligands from soluble class I and class II MHC molecules which may be uninfected, infected, or tumorgenic. The methodology of the present invention broadly allows for these peptide ligands and their comcomittant source proteins thereof to be identified and used as markers for infected versus uninfected cells and / or tumorgenic versus nontumorgenic cells with said identification being useful for marking or targeting a cell for therapeutic treatment or priming the immune response against infected cells.
Owner:THE BOARD OF RGT UNIV OF OKLAHOMA
Transformed shigella
A method for modifying a wild strain of an entero-invasive Shigella to produce a modified strain of Shigella that can be used for making a vaccine against the wild strain of Shigella. The genome of the wild strain of Shigella is transformed so that it cannot substantially invade cells of a human host and cannot spread substantially within infected cells and from infected to uninfected cells of the host and cannot produce toxins which will kill substantial numbers of the host's infected, as well as uninfected, cells. A first gene of the wild strain of Shigella, coding for a protein necessary for the Shigella to invade cells of the host, and a second gene, coding for a protein necessary for the Shigella to spread within infected cells and between the infected and uninfected cells of the host, are mutagenized.
Owner:INST PASTEUR
Transformed Shigella
A method for modifying a wild strain of an entero-invasive Shigella to produce a modified strain of Shigella that can be used for making a vaccine against the wild strain of Shigella. The genome of the wild strain of Shigella is transformed so that it cannot substantially invade cells of a human host and cannot spread substantially within infected cells and from infected to uninfected cells of the host and cannot produce toxins which will kill substantial numbers of the host's infected, as well as uninfected, cells. A first gene of the wild strain of Shigella, coding for a protein necessary for the Shigella to invade cells of the host, and a second gene, coding for a protein necessary for the Shigella to spread within infected cells and between the infected and uninfected cells of the host, are mutagenized.
Owner:INST PASTEUR +1
Preparation method of artificial antibody
PendingCN114835803AAvoid side effectsImprove permeabilityOrganic active ingredientsImmunoglobulins against virusesReceptorMicrosatellite
Owner:杭州痴创生物科技有限公司
Rapid and sensitive serological assay to determine if patients are infected with herpes simplex virus type 1 HSV-1 and/or type 2 HSV-2
An assay for infection with one or more herpes simplex viruses that comprises a) dividing an antibody-containing serum sample into at least three serum subsamples, and b) separately incubating each with a physical matrix of cell antigens from i) uninfected cells, (ii) HSV-1-infected cells, or (iii) HSV-2-infected cells to form at least three serum subsample admixtures so that antibodies present in each admixture can immunoreact to form matrix-bound antibodies and at least three preadsorbed serum subsample portions. Each preadsorbed serum subsample portion is incubated with a mixture of matrix-bound antigens from cells uninfected by HSV-1 or HSV-2, infected by each of HSV-1 and by HSV-2 to permit antibodies to immunoreact with antigens present to form three matrix-bound immunoreactants. The amount of each immunoreaction is determined, and reaction amounts are prognostic for whether the subject whose serum was tested is infected by one, both, or neither of HSV-1 and HSV-2.
Owner:SOUTHERN ILLINOIS UNIVERSITY
Comparative ligand mapping from mhc class i positive cells
The present invention relates generally to a methodology for the isolation, purification and identification of peptide ligands presented by MHC positive cells. In particular, the methodology of the present invention relates to the isolation, purification and identification of these peptide ligands from soluble class I and class II MHC molecules which may be from uninfected, infected, or tumorigenic cells. The methodology of the present invention broadly allows for these peptide ligands and their cognate source proteins thereof to be identified and used as markers for infected versus uninfected cells and / or tumorigenic versus nontumorigenic cells, with said identification being useful for marking or targeting a cell for therapeutic treatment or priming the immune response against infected / tumorigenic cells.
Owner:HILDEBRAND WILLIAM H +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com