Preparation method of artificial antibody
A technology of artificial antibodies and mutated strains, applied in the field of biopharmaceuticals for the prevention and treatment of infectious diseases, can solve problems such as difficulty in passing through cell membranes, large molecular weight, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
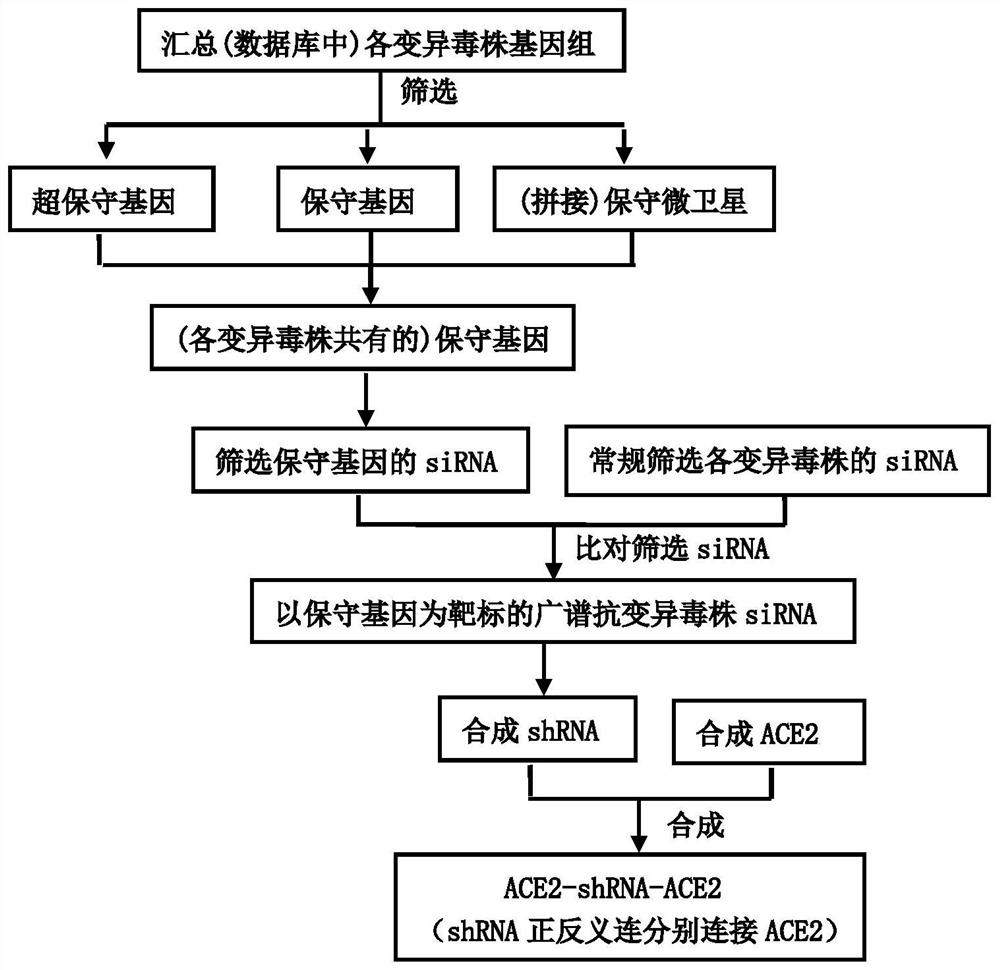
[0034] Combine below figure 1 , 2 And 3, the specific implementation method of the present invention is described in detail, but these exemplary descriptions do not constitute any limitation to the protection scope defined by the claims of the present invention.
[0035] 1. Design siRNA targeting ultra-conserved genes, conserved genes or conserved microsatellites
[0036] 1. Design of ultra-conserved genes, conserved genes and conserved microsatellites
[0037] such as technical lines figure 1 As shown, the whole genome (cDNA) sequence of betacoronavirus (especially the novel coronavirus and its variant strains) was downloaded from the Genbank database (http: / / www.NCBI.nlm.nih.gov / genome / ), and found in Search for the longest common subsequence in the whole genome sequence to obtain ultra-conserved genes or conserved genes; use Clustal W software to perform sequence alignment on the whole genome downloaded from the Genbank database, detect the similarity between different s...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com