Patents
Literature
42 results about "Integral membrane protein" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
An integral membrane protein (IMP) is a type of membrane protein that is permanently attached to the biological membrane. All transmembrane proteins are IMPs, but not all IMPs are transmembrane proteins. IMPs comprise a significant fraction of the proteins encoded in an organism's genome. Proteins that cross the membrane are surrounded by annular lipids, which are defined as lipids that are in direct contact with a membrane protein. Such proteins can only be separated from the membranes by using detergents, nonpolar solvents, or sometimes denaturing agents.
Compositions and methods for producing recombinant proteins
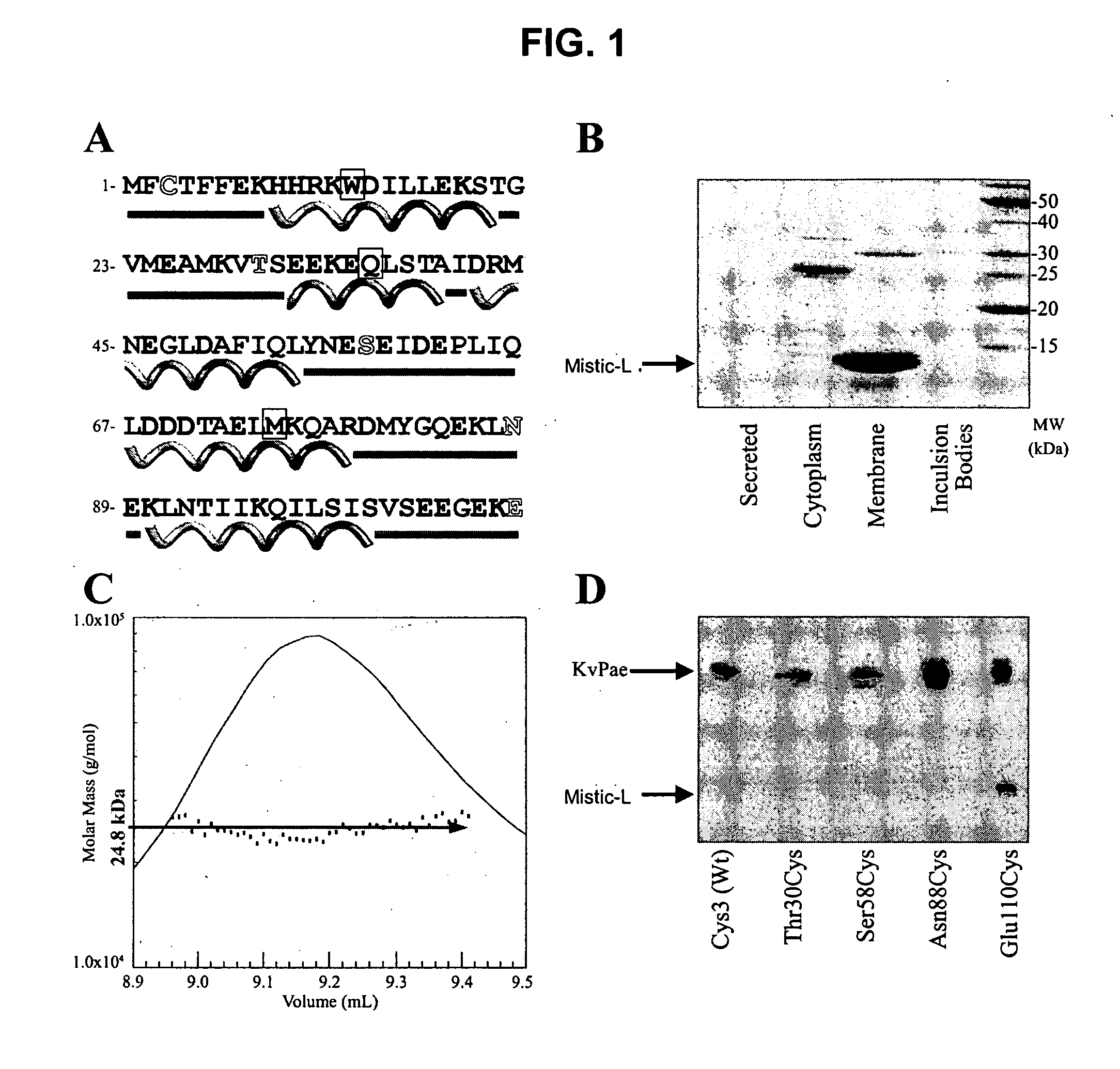
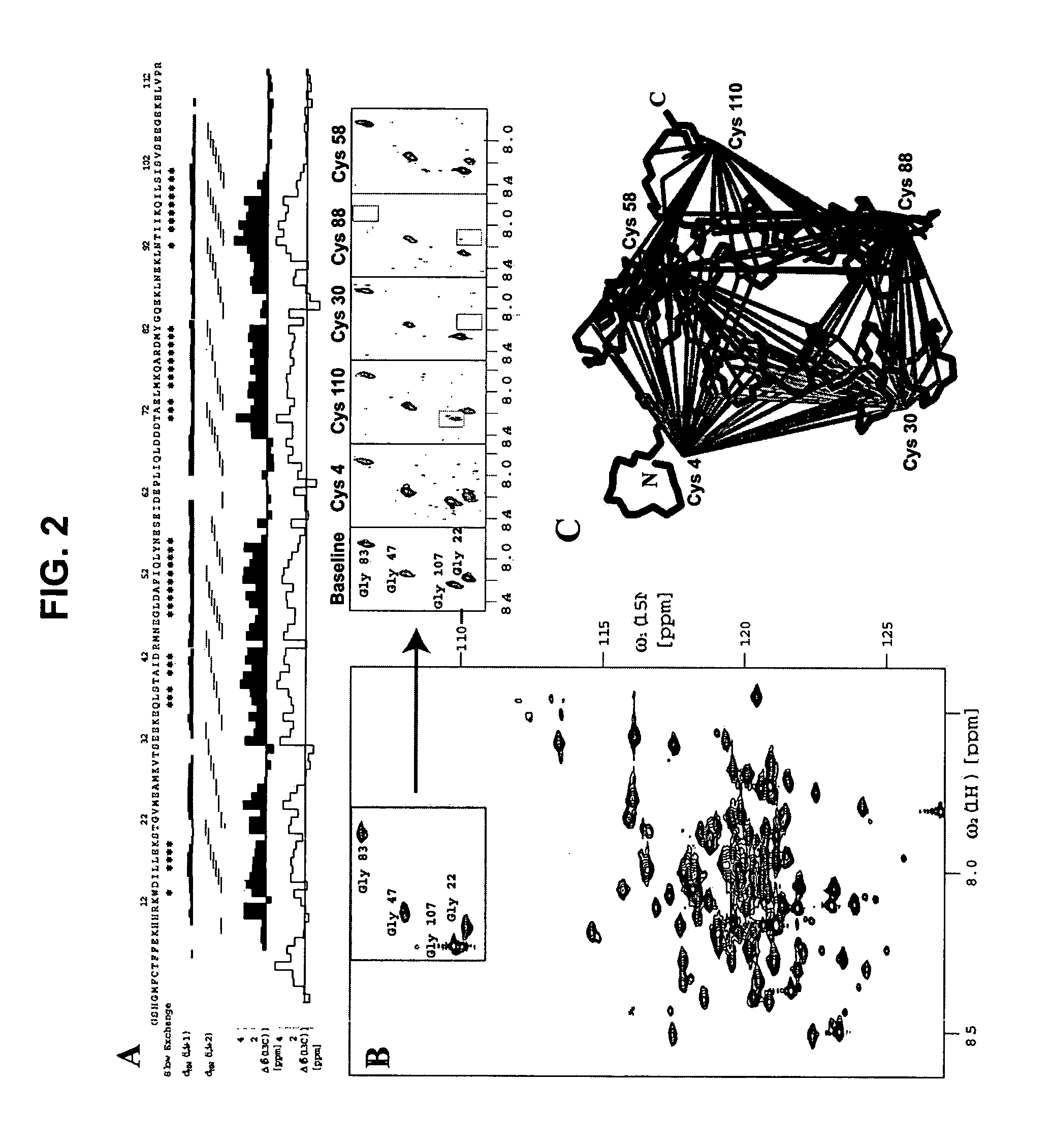
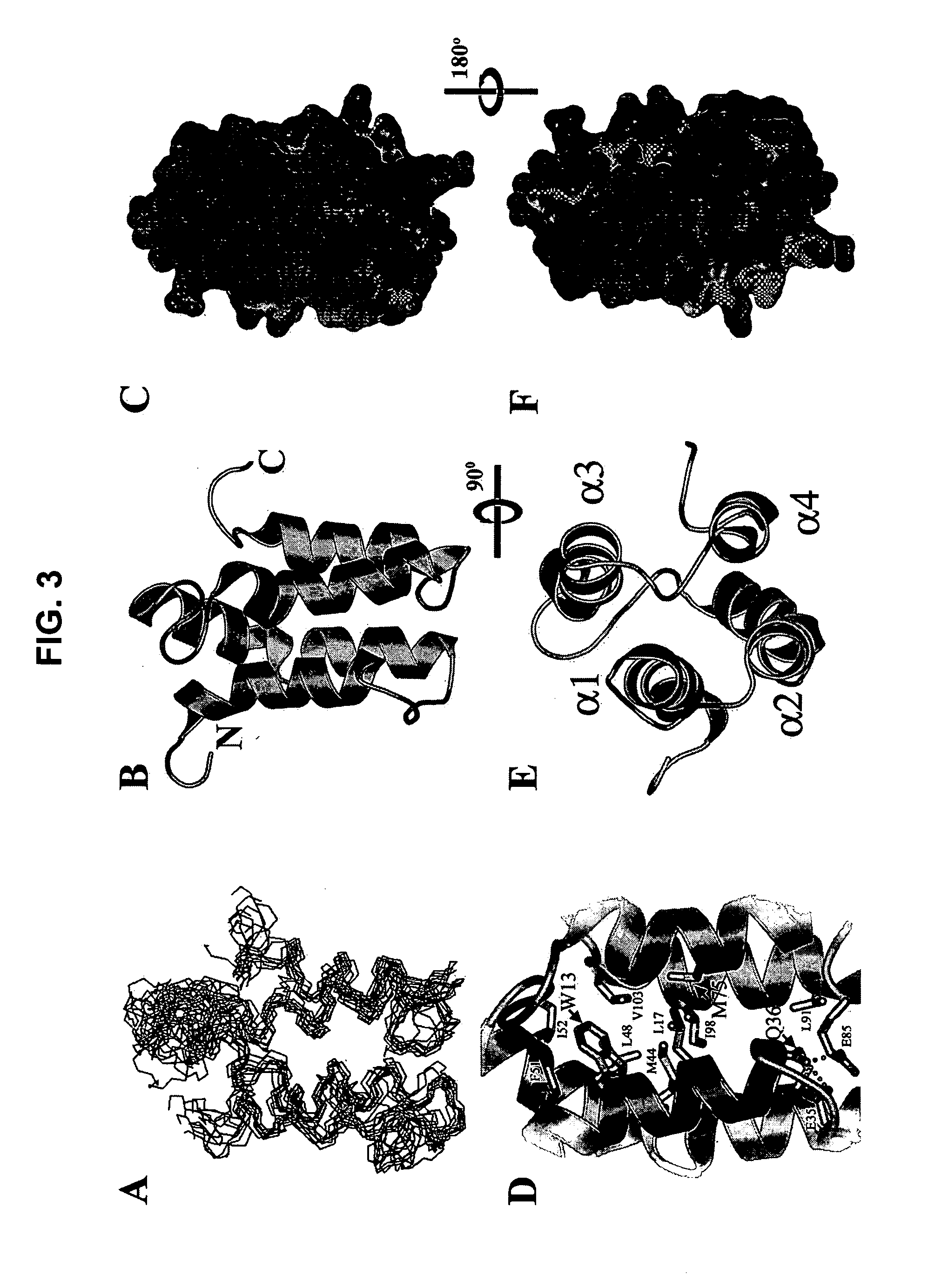
A class of integral membrane proteins, referred to as Mistic polypeptides, their variants, fusion proteins including a Mistic polypeptide domain, and nucleic acid molecules encoding Mistic polypeptides and Mistic fusion proteins are disclosed herein. Also described are methods of using Mistic polypeptides and Mistic fusion proteins to produce and / or isolate recombinant proteins (including without limitation classes of eukaryotic proteins that have previously been intractable to recombinant bacterial expression, such as, eukaryotic integral membrane proteins).
Owner:SALK INST FOR BIOLOGICAL STUDIES
Compositions of influenza viral proteins and methods of use thereof
InactiveUS20090162400A1Increase productionStimulate immune responseSsRNA viruses negative-senseSsRNA viruses positive-senseIntegral membrane proteinPathogen-Associated Molecular Pattern Molecules
Compositions, fusion proteins and polypeptides comprise at least one pathogen-associated molecular pattern and at least a portion of at least one integral membrane protein of an influenza viral antigen. The compositions, fusion proteins and polypeptides are used to stimulate an immune response in a subject.
Owner:VAXINNATE
Biocompatible implants and methods of making and attaching the same
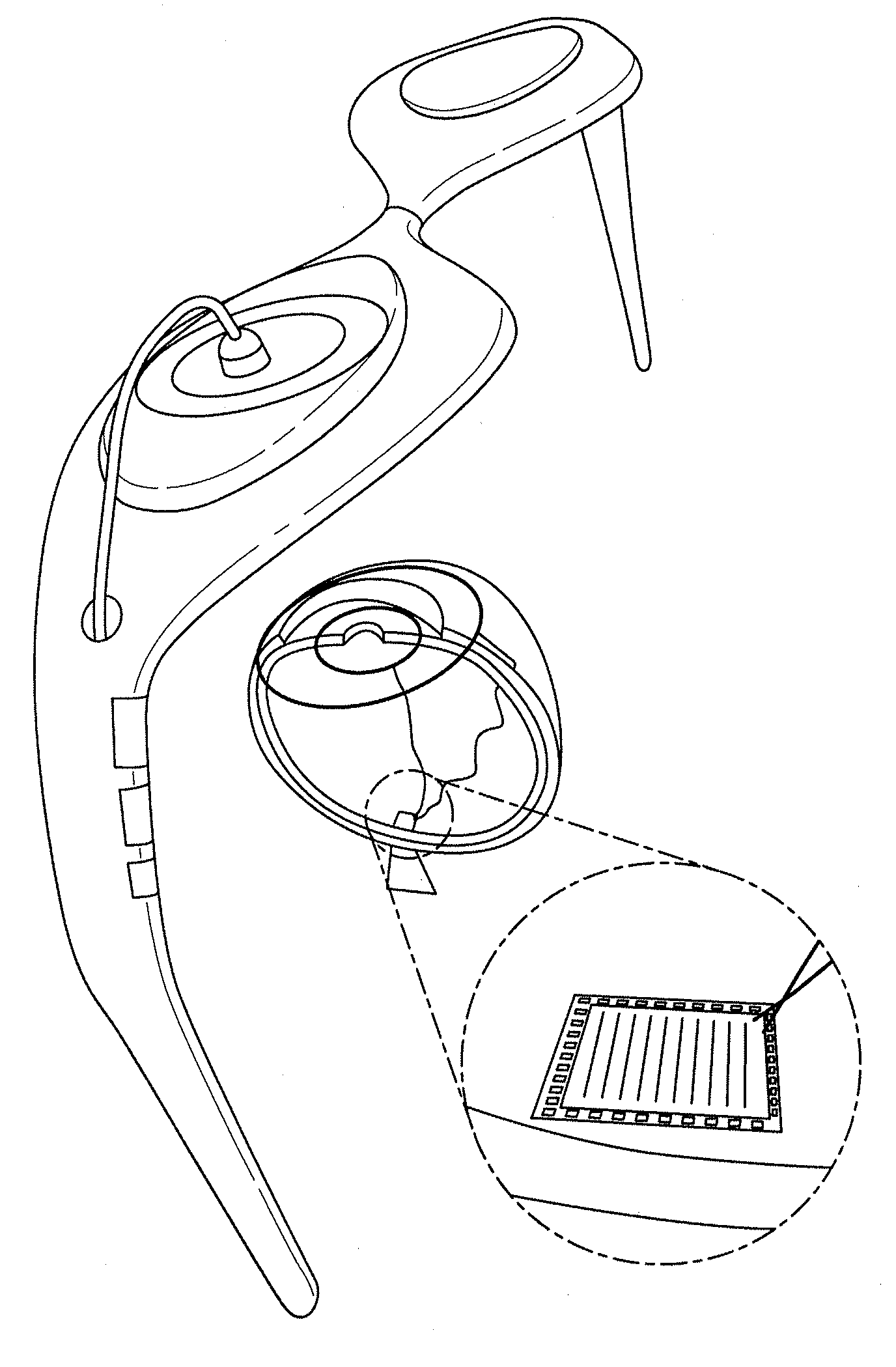
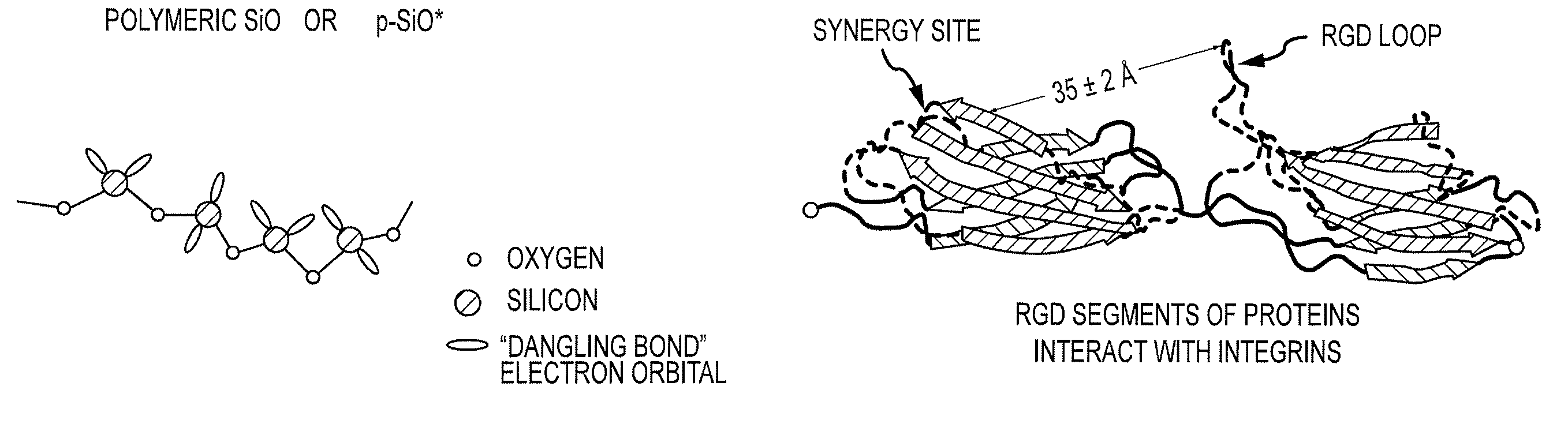
The invention provides a biocompatible silicone implant that can be securely affixed to living tissue through interaction with integral membrane proteins (integrins). A silicone article containing a laser-activated surface is utilized to make the implant. One example is an implantable prosthesis to treat blindness caused by outer retinal degenerative diseases. The device bypasses damaged photoreceptors and electrically stimulates the undamaged neurons of the retina. Electrical stimulation is achieved using a silicone microelectrode array (MEA). A safe, protein adhesive is used in attaching the MEA to the retinal surface and assist in alleviating focal pressure effects. Methods of making and attaching such implants are also provided.
Owner:DOHENY EYE INST
Compositions comprising antigen-complexes, method of making same as well as methods of using the antigen-complexes for vaccination
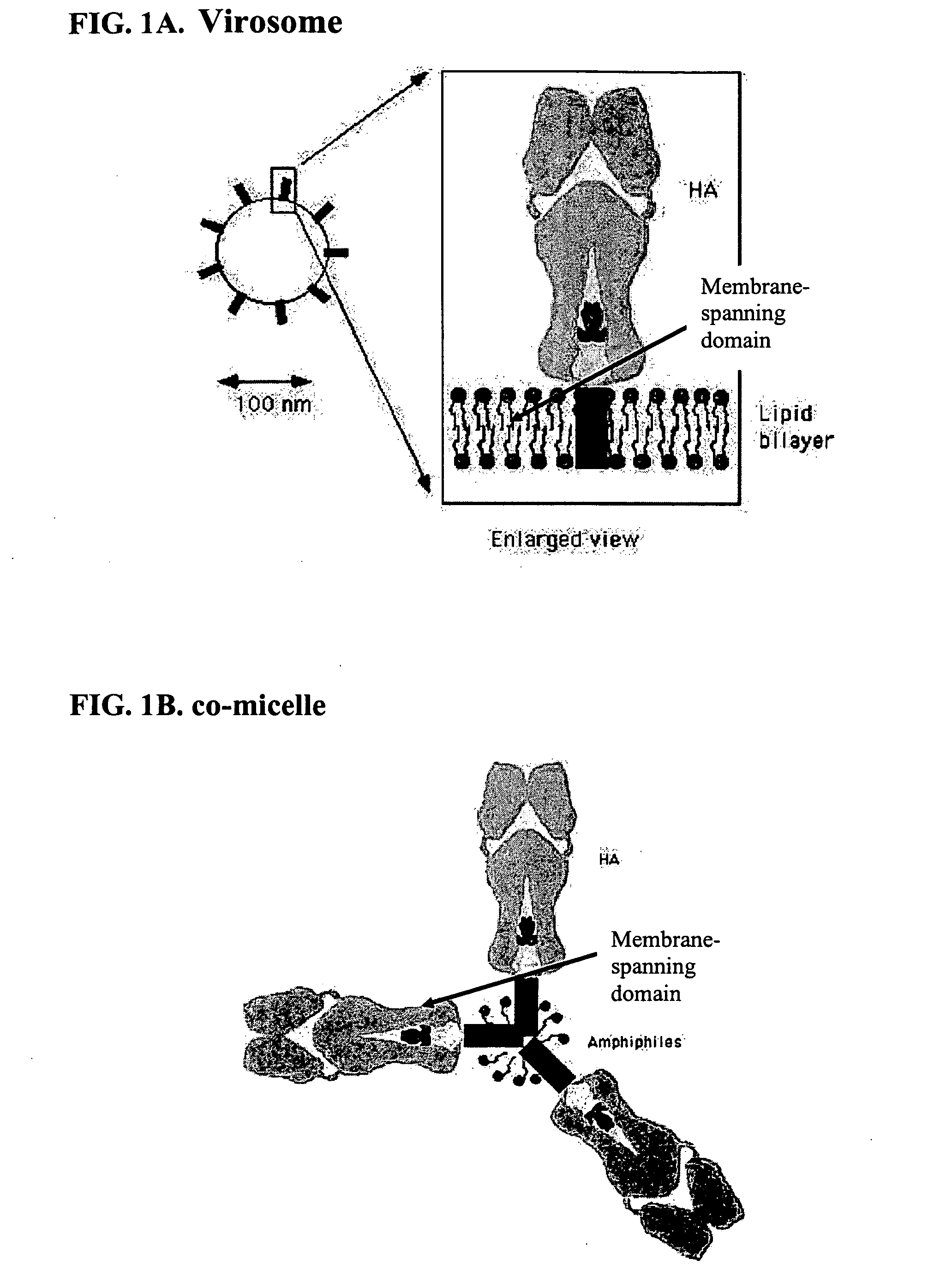
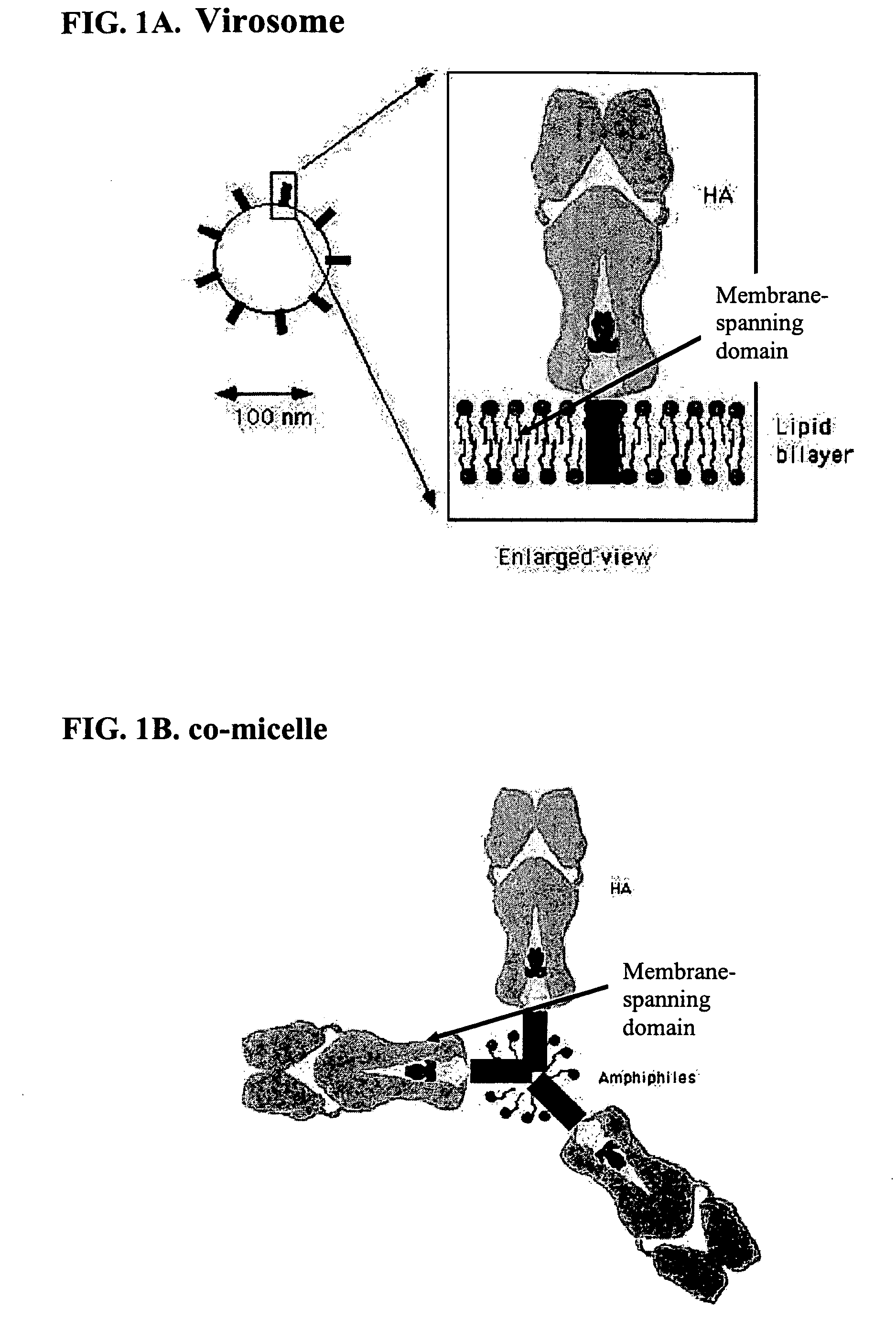
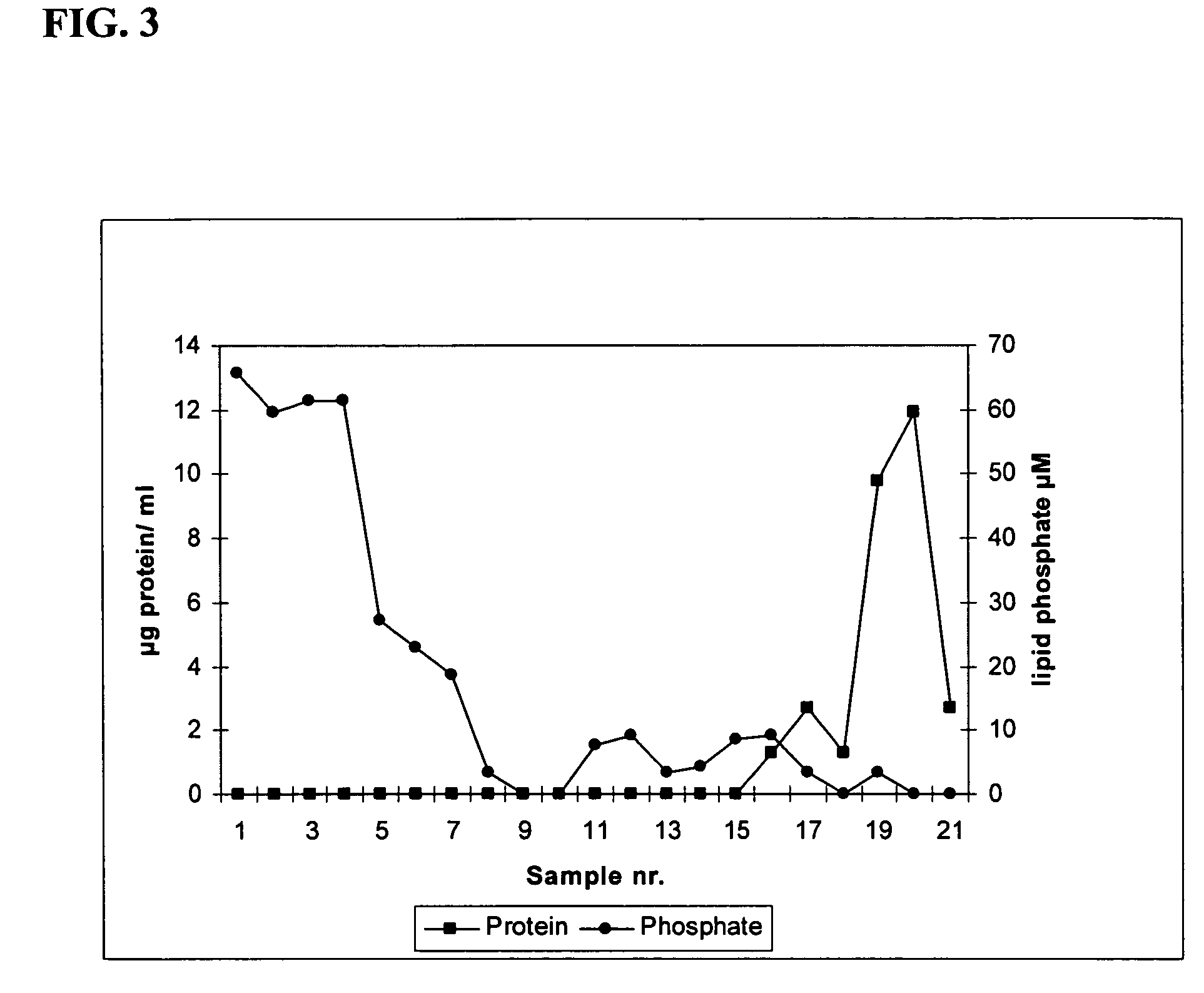
The present invention provides methods and means for preparing vaccines that are capable of eliciting strong immune responses, especially through intranasal delivery. The invention discloses particles, referred to as “co-micelles,” in which antigens are present that interact through hydrophobic interactions with certain specific types of amphiphilic compounds, wherein the amphiphilic compounds have adjuvant activity and wherein the antigens are preferably antigenic surface proteins, such as integral membrane proteins from infectious agents like viruses.
Owner:BESTEWIL HOLDING BV
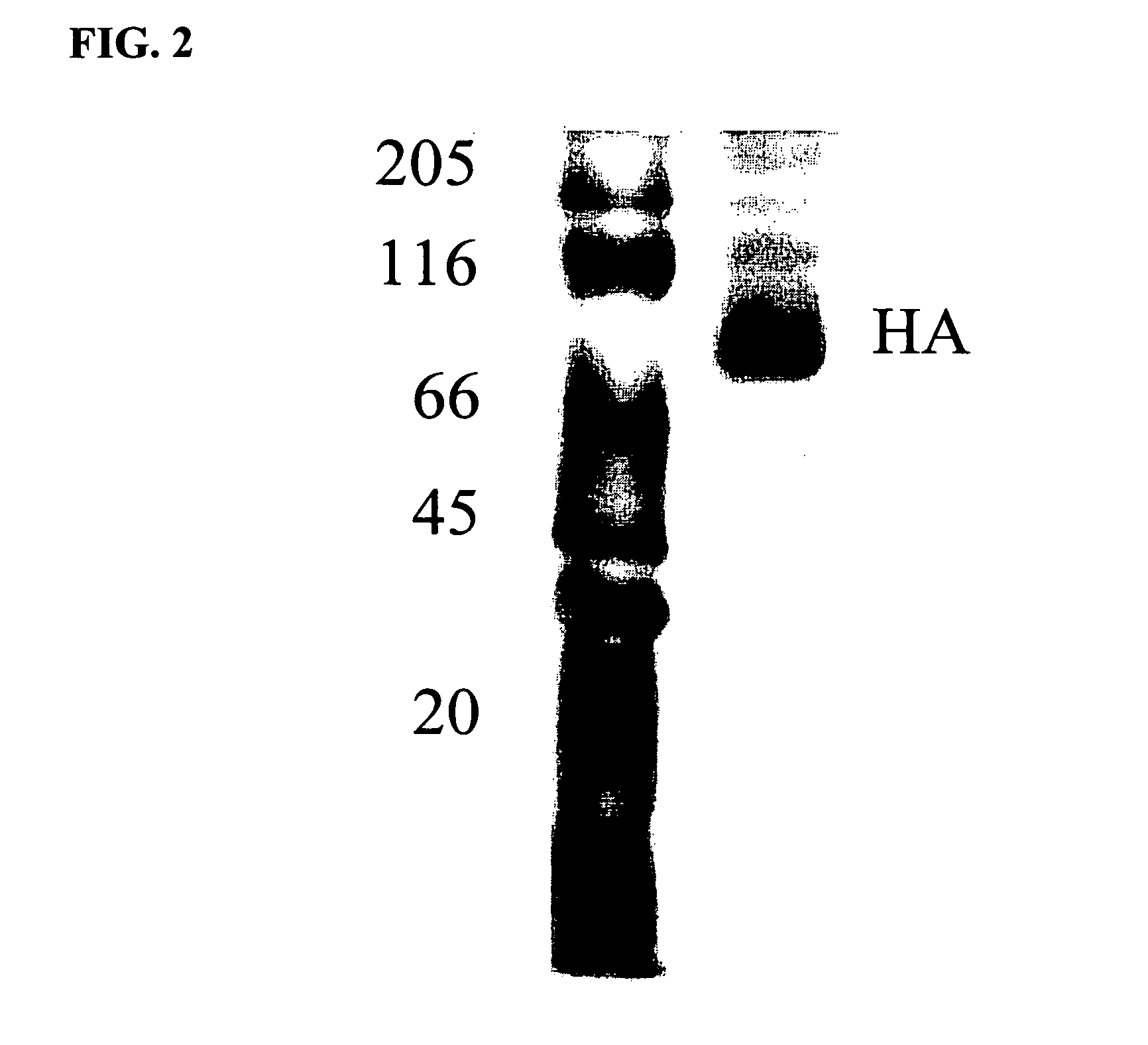
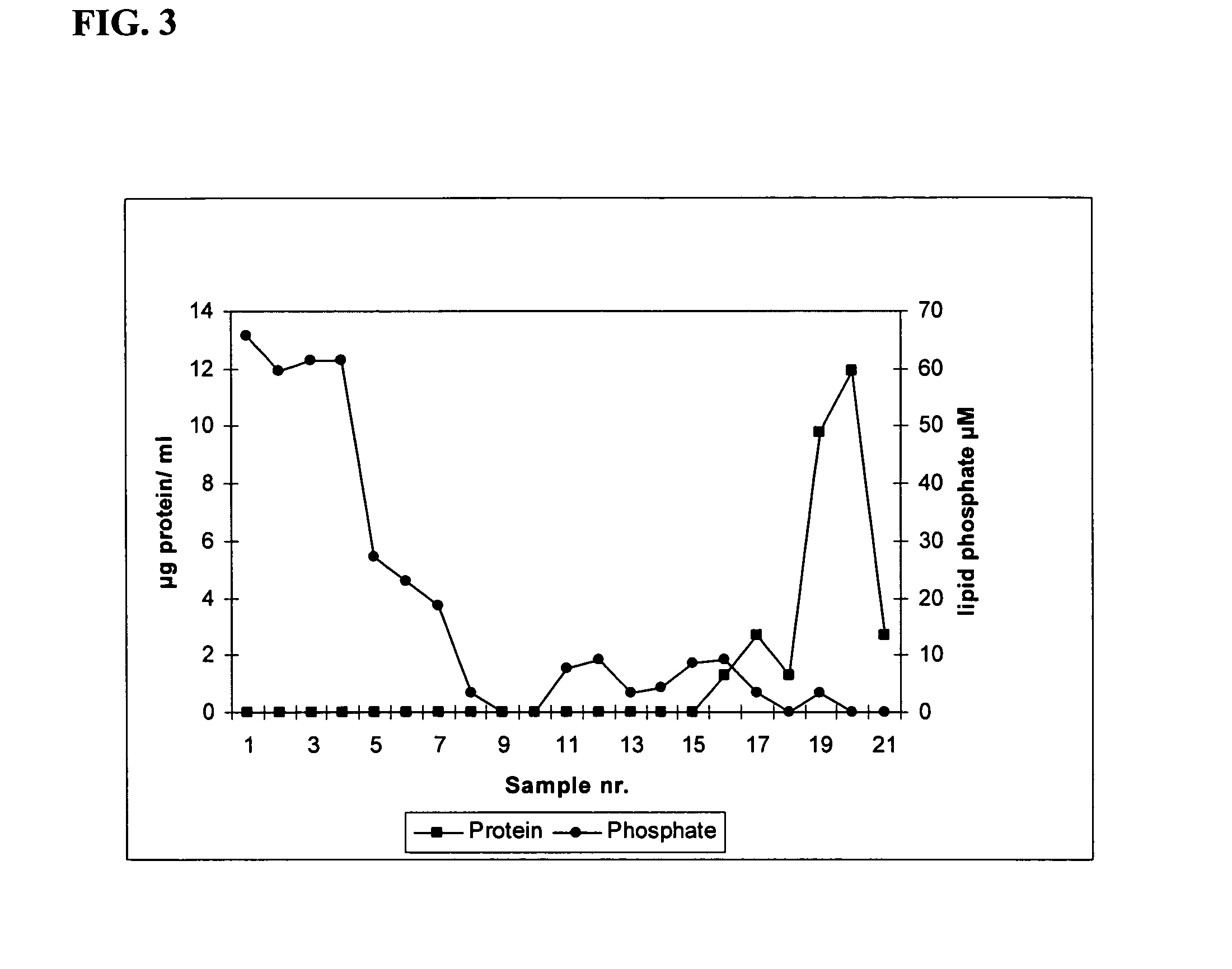
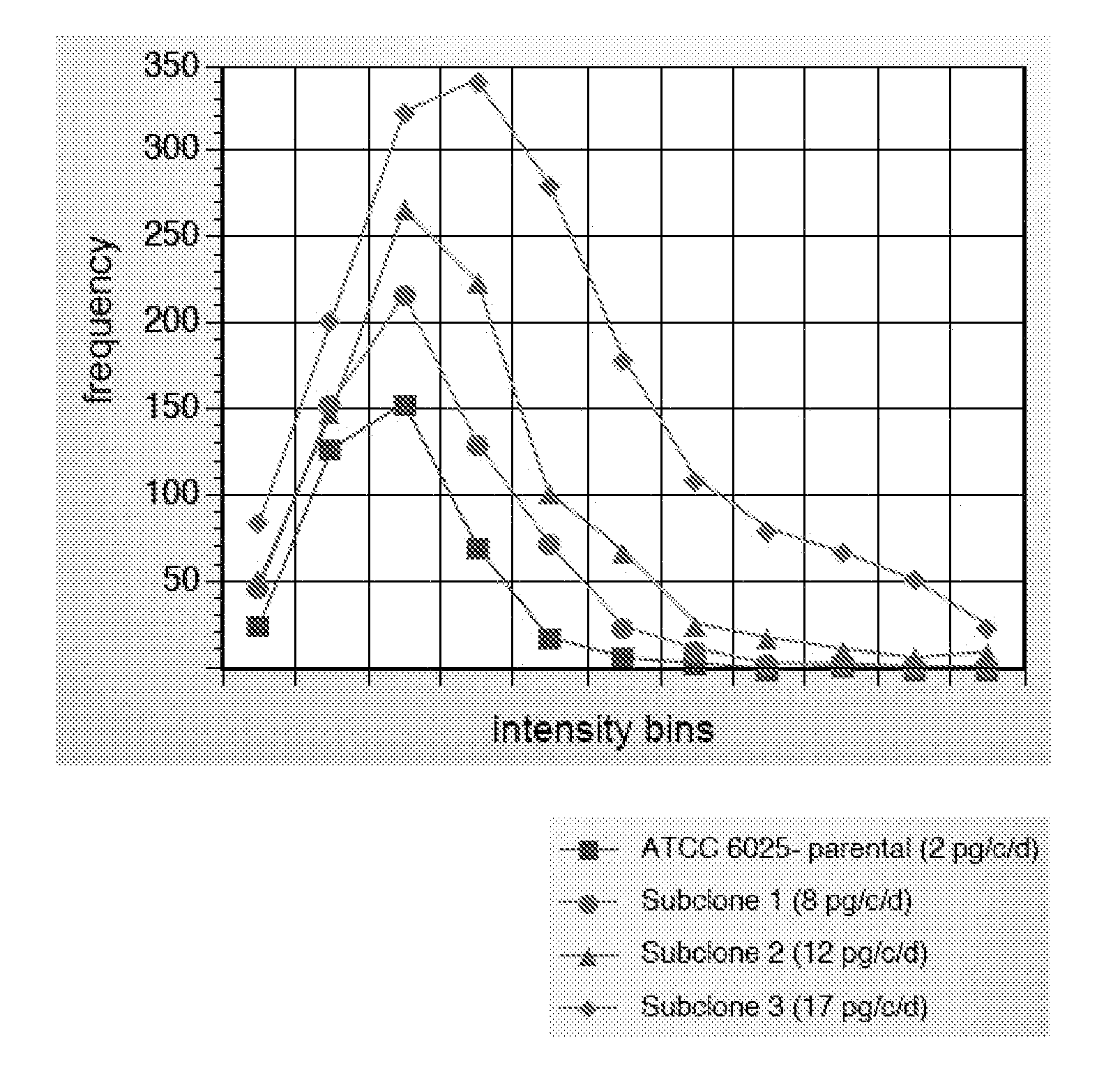
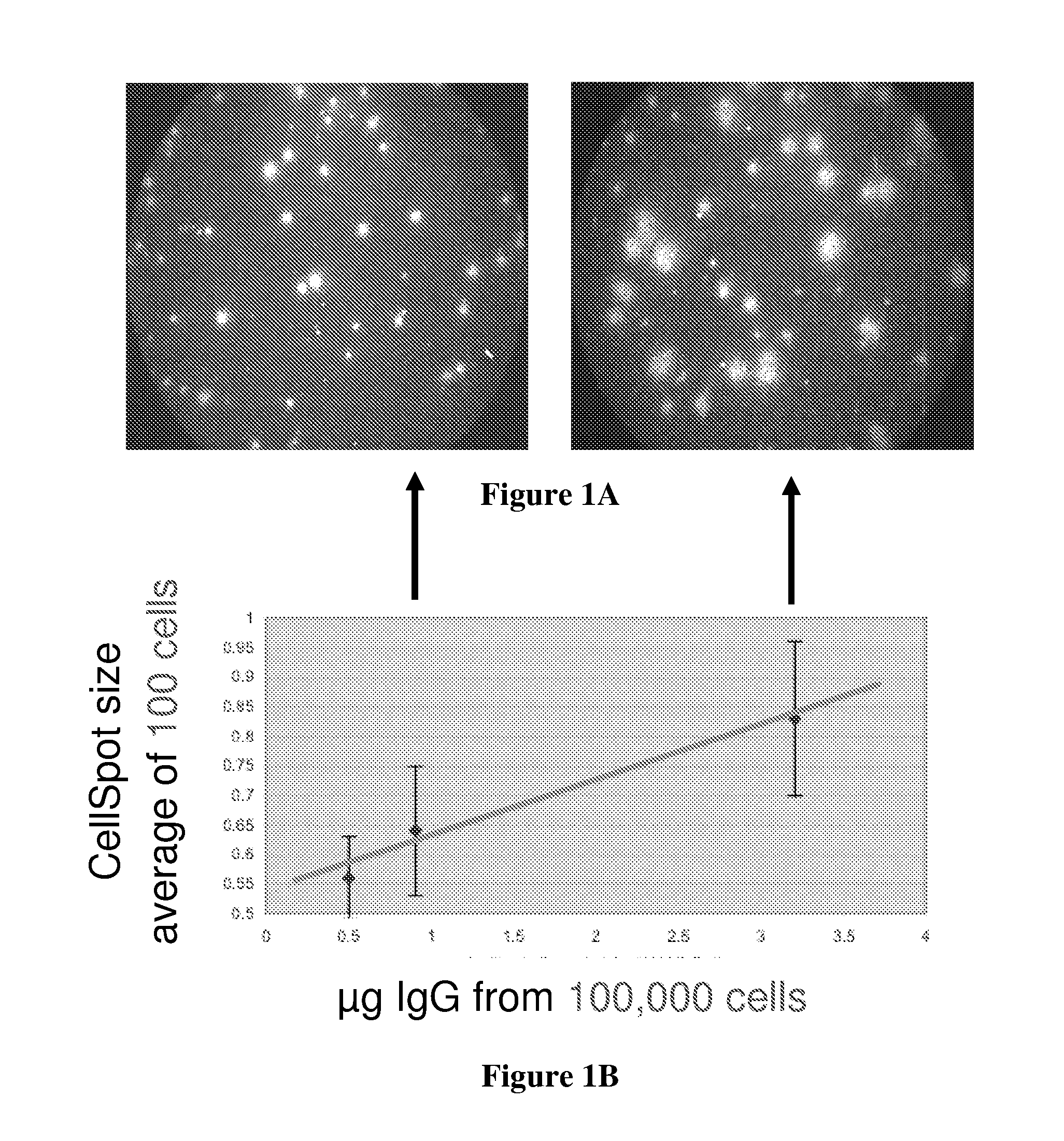
Cellspot applications
InactiveUS20080038755A1Improving immunogenicityImprove efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementArtificial cell constructsIntegral membrane proteinApplication procedure
A multiplicity of applications of the CellSpot™ assay method are described. Among these applications are extension to integral membrane protein probes, extension to secretion from bacterial cells, identification of antibodies with enhanced affinity, identification of clones with increased secretion levels, and use of massively parallel screening to identify rare efficacious antibodies.
Owner:TRELLIS BIOSCIENCE LLC
Compositions comprising antigen-complexes, method of making same as well as methods of using the antigen-complexes for vaccination
The present invention provides methods and means for preparing vaccines that are capable of eliciting strong immune responses, especially through intranasal delivery. The invention discloses particles, referred to as “co-micelles,” in which antigens are present that interact through hydrophobic interactions with certain specific types of amphiphilic compounds, wherein the amphiphilic compounds have adjuvant activity and wherein the antigens are preferably antigenic surface proteins, such as integral membrane proteins from infectious agents like viruses.
Owner:BESTEWIL HOLDING BV
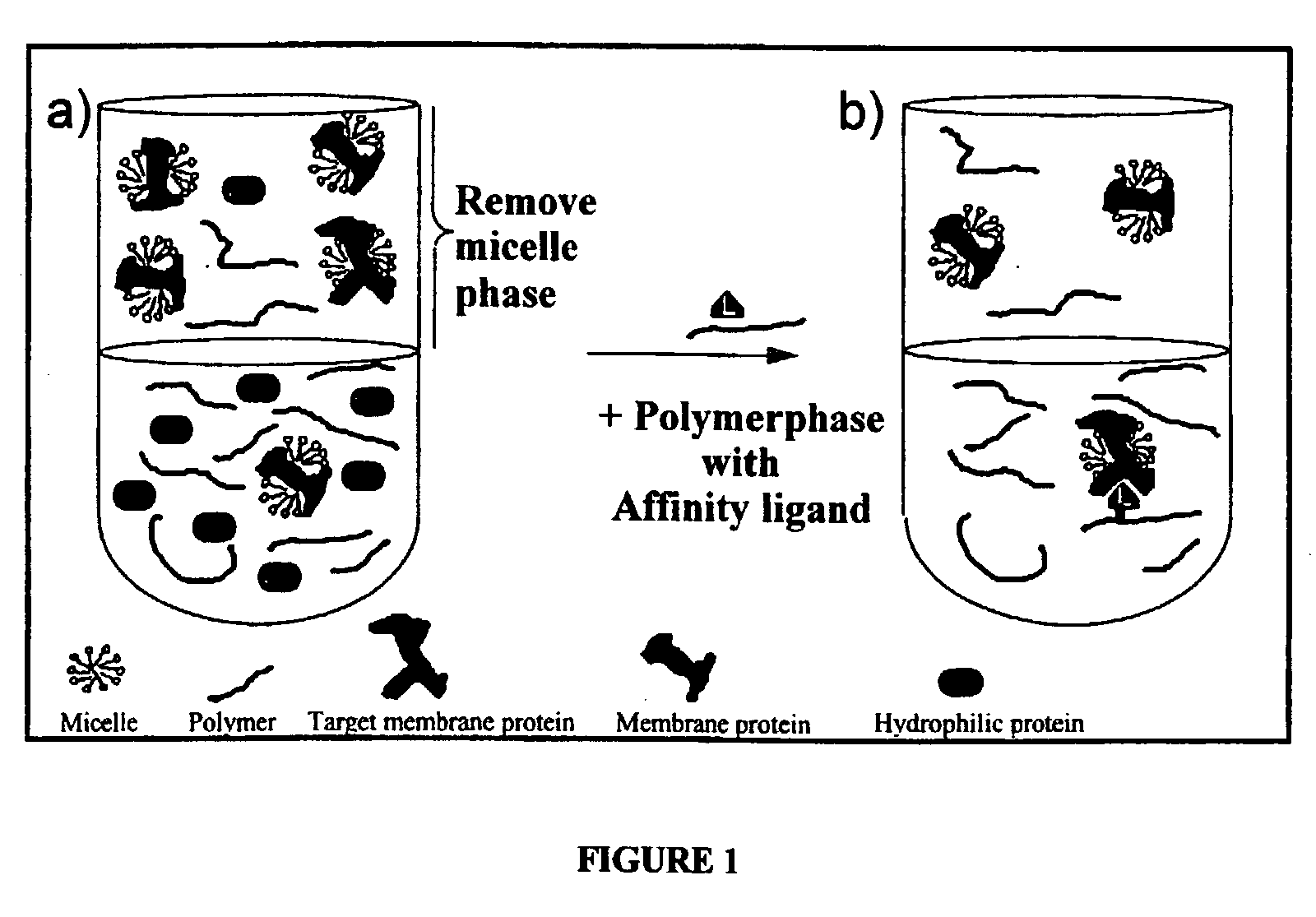
Method for the isolation of hydrophobic proteins
InactiveUS20030049819A1High selectivityHigh resolutionDepsipeptidesPeptide preparation methodsCrystallographyIntegral membrane protein
A method for separating one or more hydrophobic proteins, for instance membrane proteins such as integral membrane proteins, from a mixture of proteins. The method is characterized in that said mixture is partitioned in a phase system comprising a micelle-enriched aqueous phase (micelle-phase) and a polymer-enriched aqueous phase (polymer phase). At least part of the polymer of the polymer phase carries an affinity ligand that is capable of binding to an affinity structure on at least one of said one or more hydrophobic proteins.
Owner:GE HEALTHCARE BIO SCI CORP
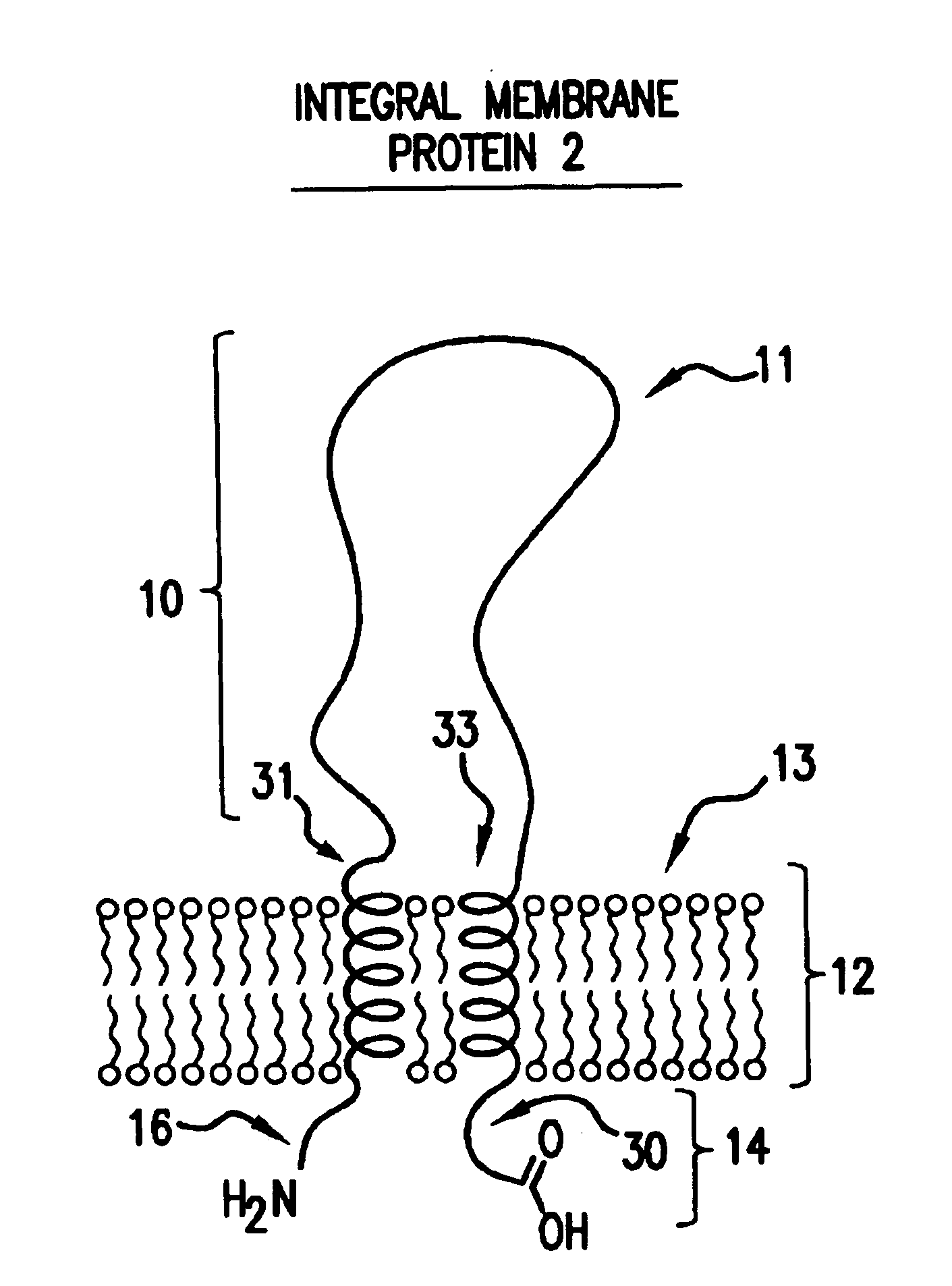
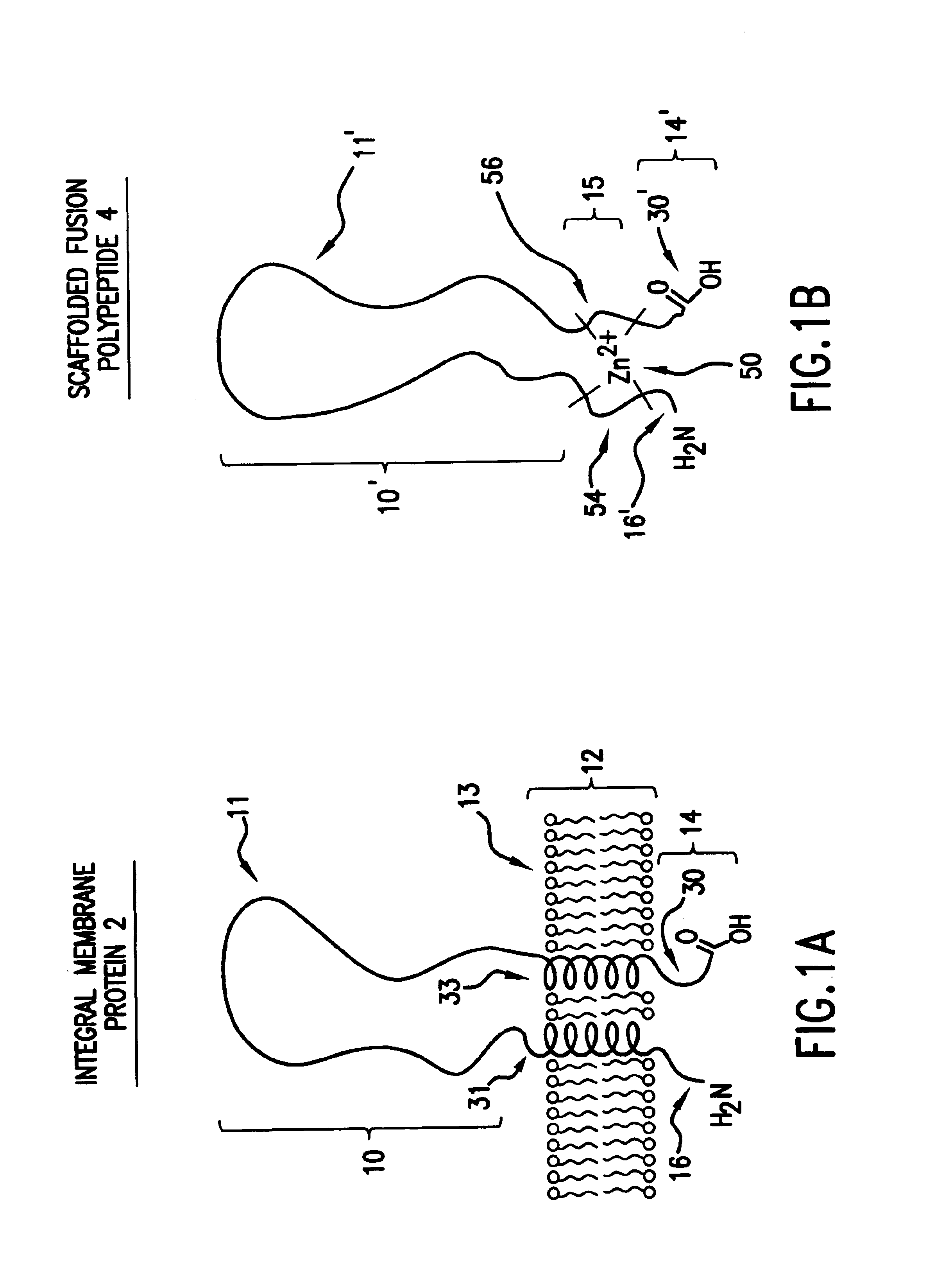
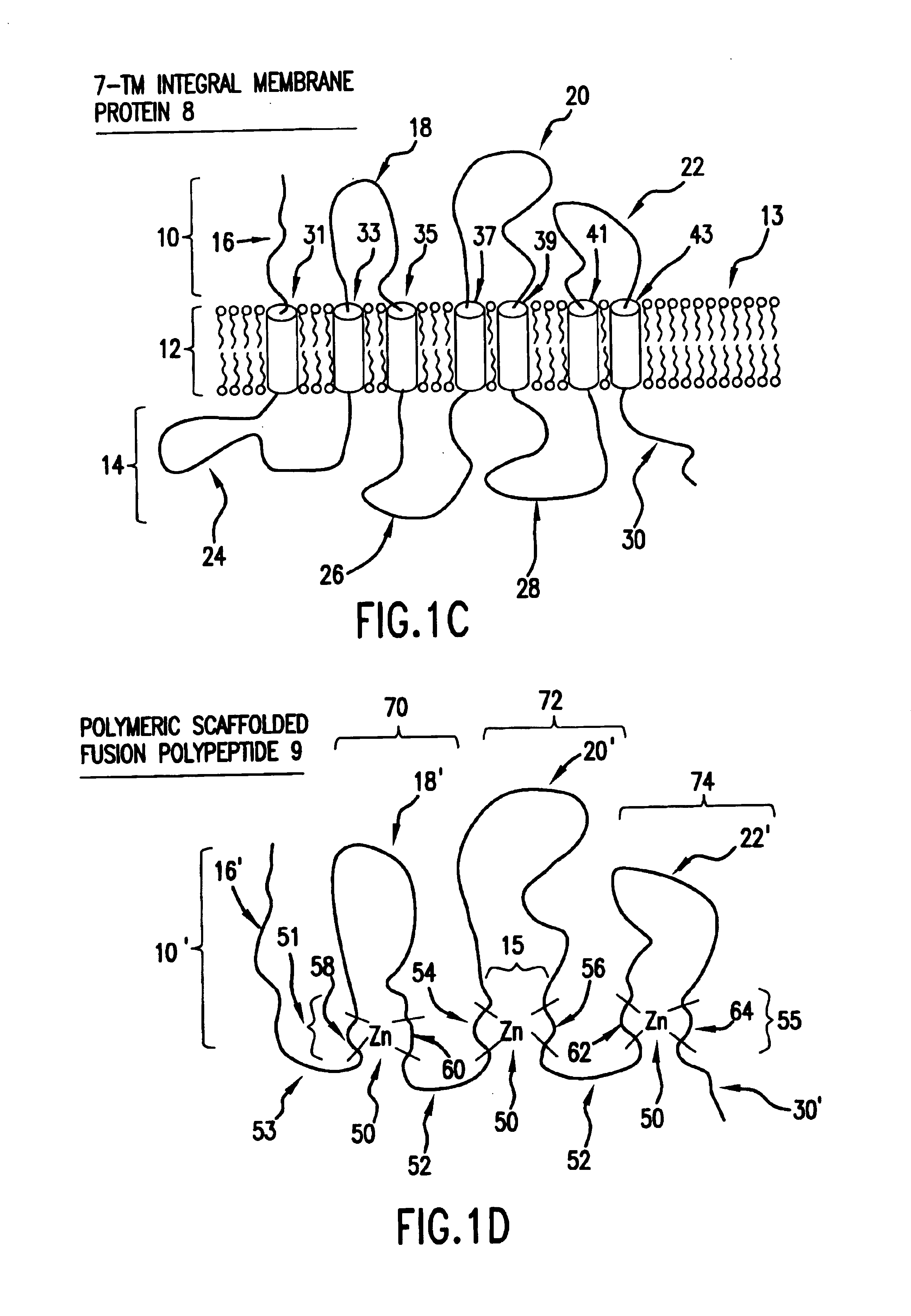
Scaffolded fusion polypeptides and compositions and methods for making the same
InactiveUS6872548B2Improve solubilityGood flexibilityFusion with DNA-binding domainPeptide/protein ingredientsIntegral membrane proteinDrug biological activity
The present invention provides soluble forms of integral membrane proteins, or domains or portions thereof, that retain the biological activity of the integral membrane protein, domain or portion from which they are designed or derived and that can readily be expressed in high yield.
Owner:HUMAN GENOME SCI INC
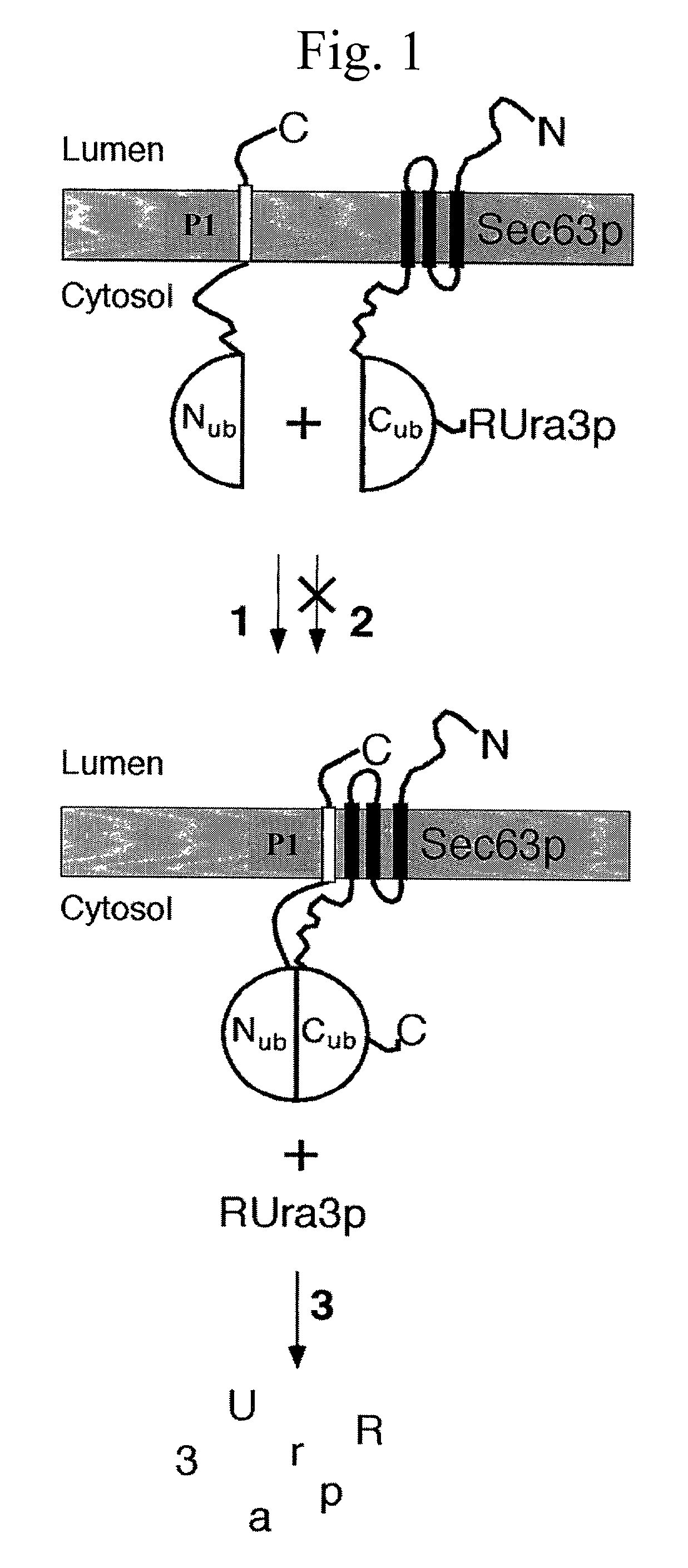
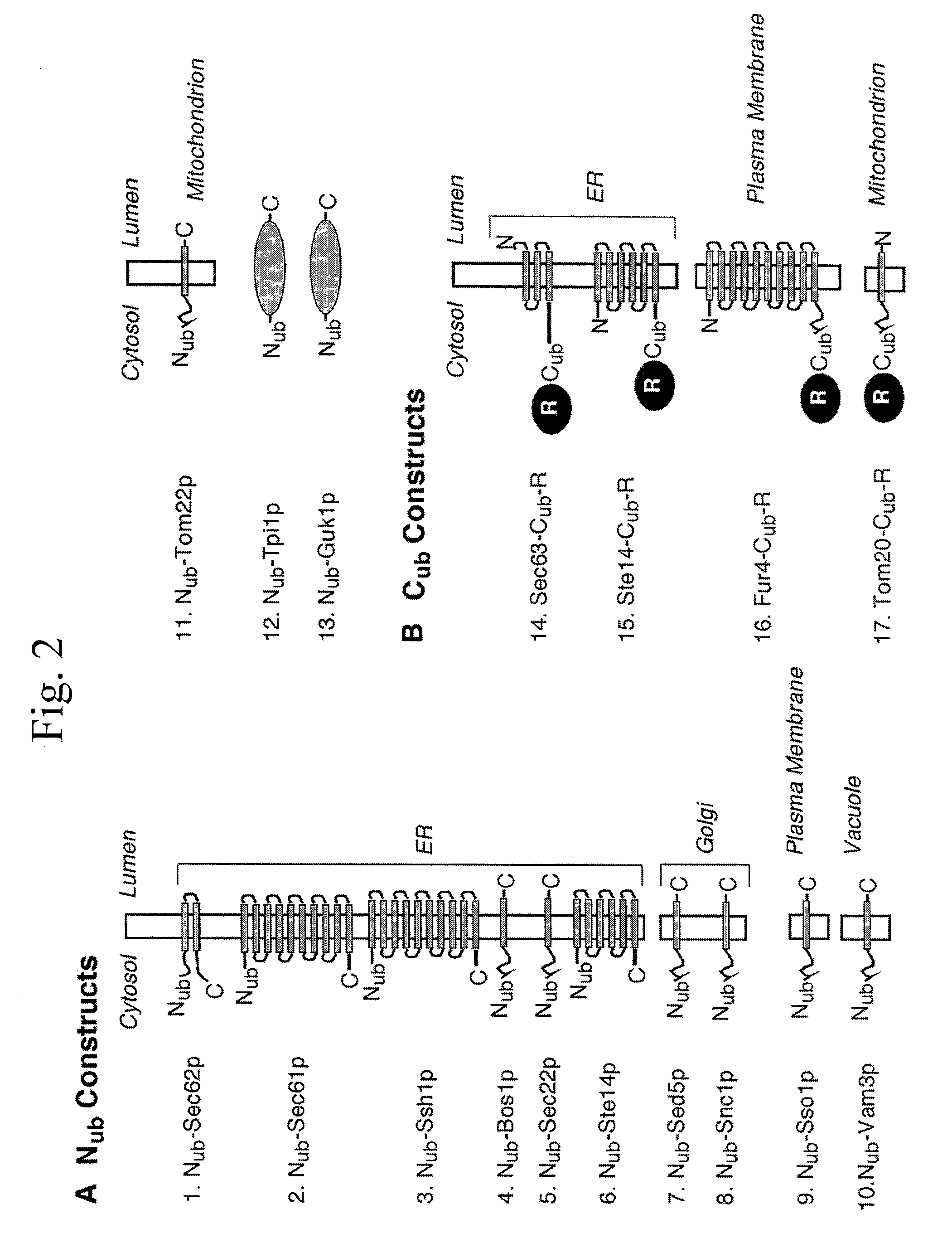
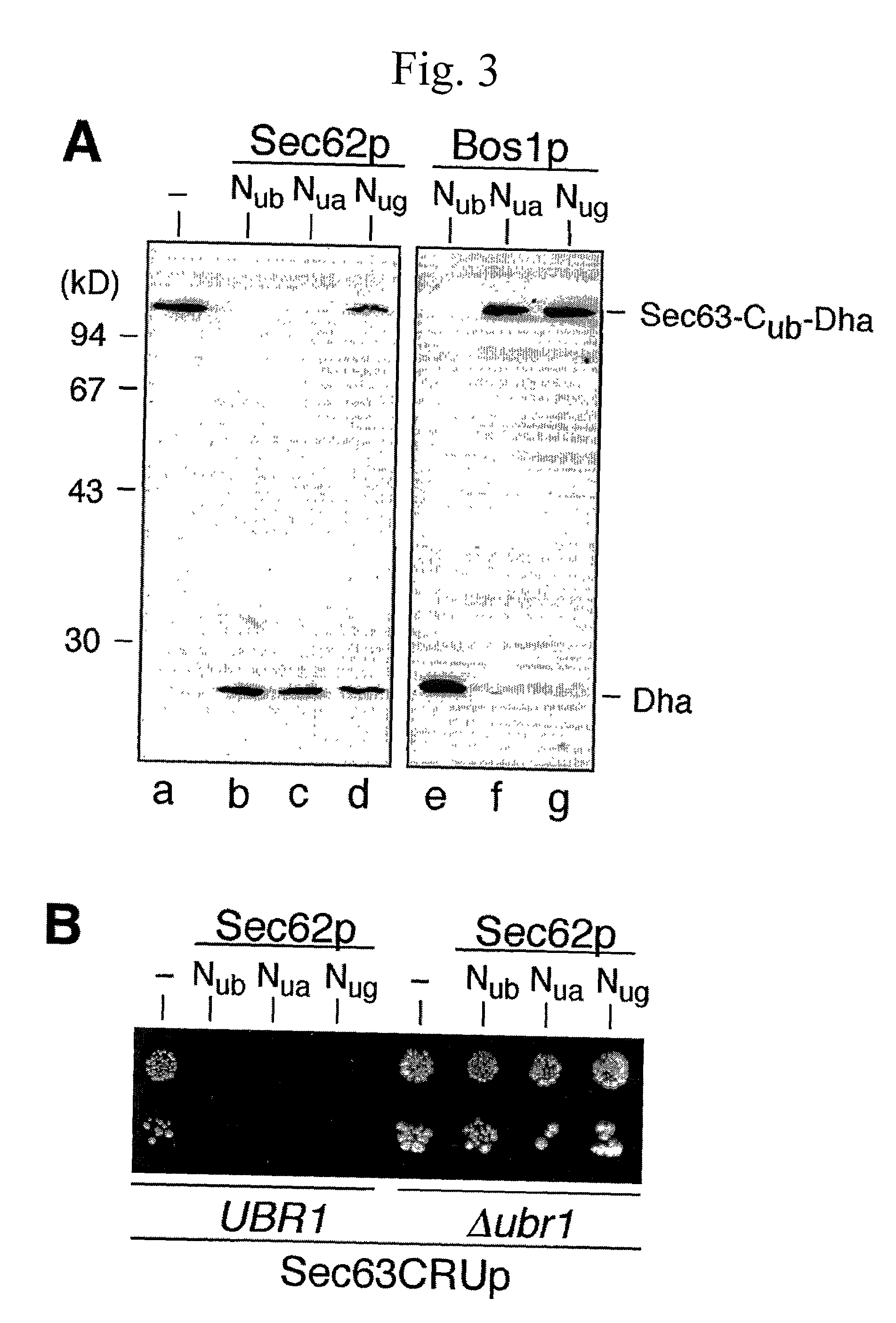
Split- ubiquitin based reporter systems and methods of their use
InactiveUS20040170970A1Increased cleavageReduce splitCompound screeningApoptosis detectionProtein targetADAMTS Proteins
Methods and reagents for the detection and selection of two interacting-polypeptides, especially integral membrane proteins and transcription factors, by monitoring the reassembly of ubiquitin amino-terminal and carboxy-terminal chimeric polypeptide fragments are disclosed. Negative selection against an N-end rule-labilized marker released following ubiquitin reassembly allows direct selection of the interacting polypeptide pair. Methods to identify agonists and antagonists for certain protein-protein interactions; methods and reagents / kits for identifying proteins that binds a target protein are also provided. The dynamic and adaptable nature of the assay allows adaptation to a number of applications-such as probing the molecular environment of cellular membrane proteins in vivo.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH +1
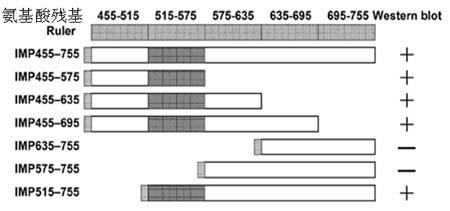
Detection method of lactobacillus micro integral membrane protein active fragments
ActiveCN102375062AMaintain integrityStrong specificityMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansBacteria peptidesMutated proteinIntegral membrane protein
The invention relates to a detection method of lactobacillus micro integral membrane protein active fragments. According to the invention, first, 6 N-terminal deleted or C-terminal deleted mutant proteins are established; mucin marked by HRP is adopted as a marked first antibody, and western bolt (WB) and Coomassie brilliant blue staining detections are carried out; WB results and Coomassie brilliant blue staining results are compared, such that the positions of the active fragments in the lactobacillus micro integral membrane protein sequence are obtained.
Owner:SHANGHAI SIXTH PEOPLES HOSPITAL
Use Of A Compound For Enhancing The Expression Of Membrane Proteins On The Cell Surface
InactiveUS20100129343A1High expressionLower Level RequirementsOrganic active ingredientsSugar derivativesDiseaseIntegral membrane protein
Owner:AXENTIS PHARMA
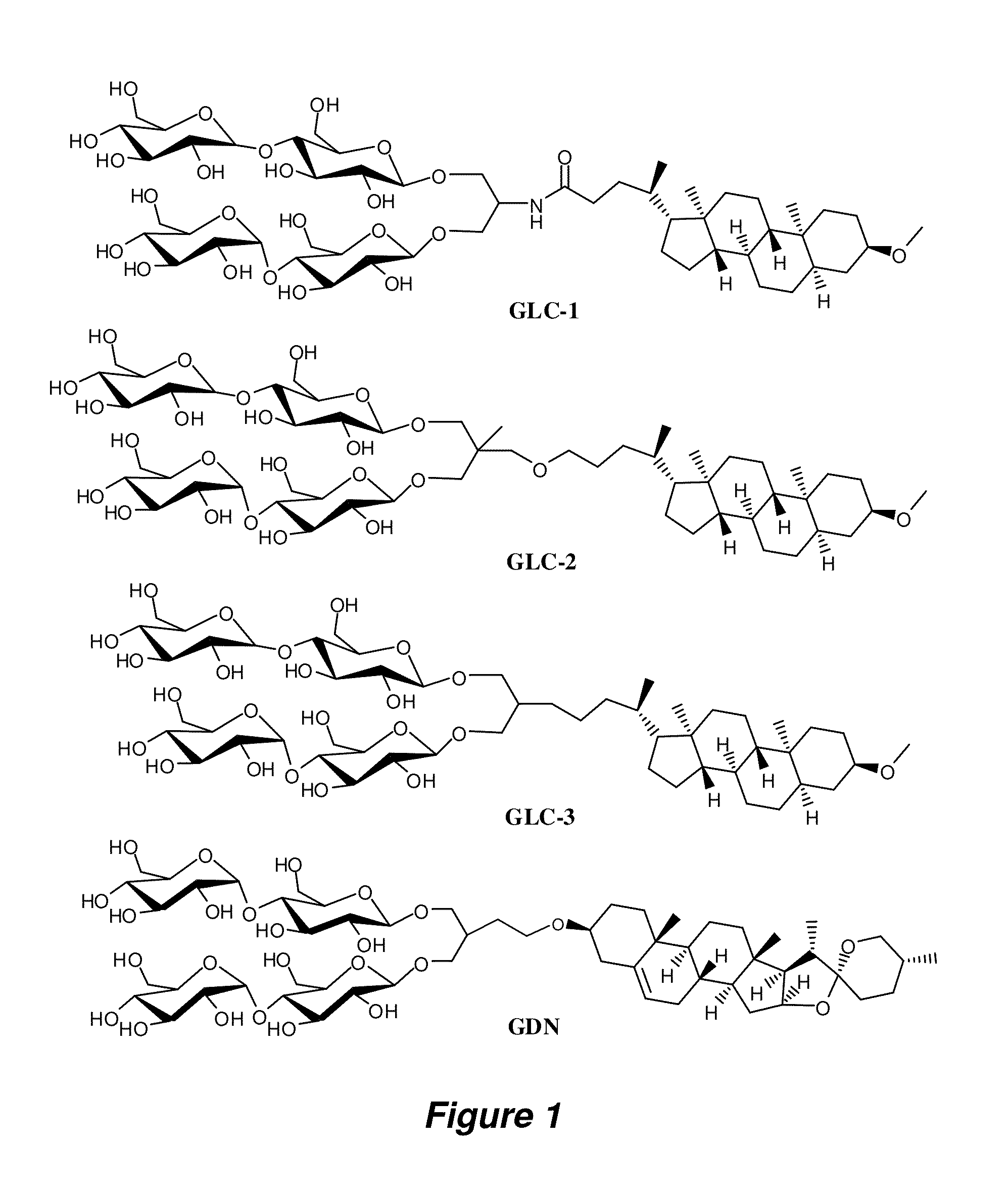
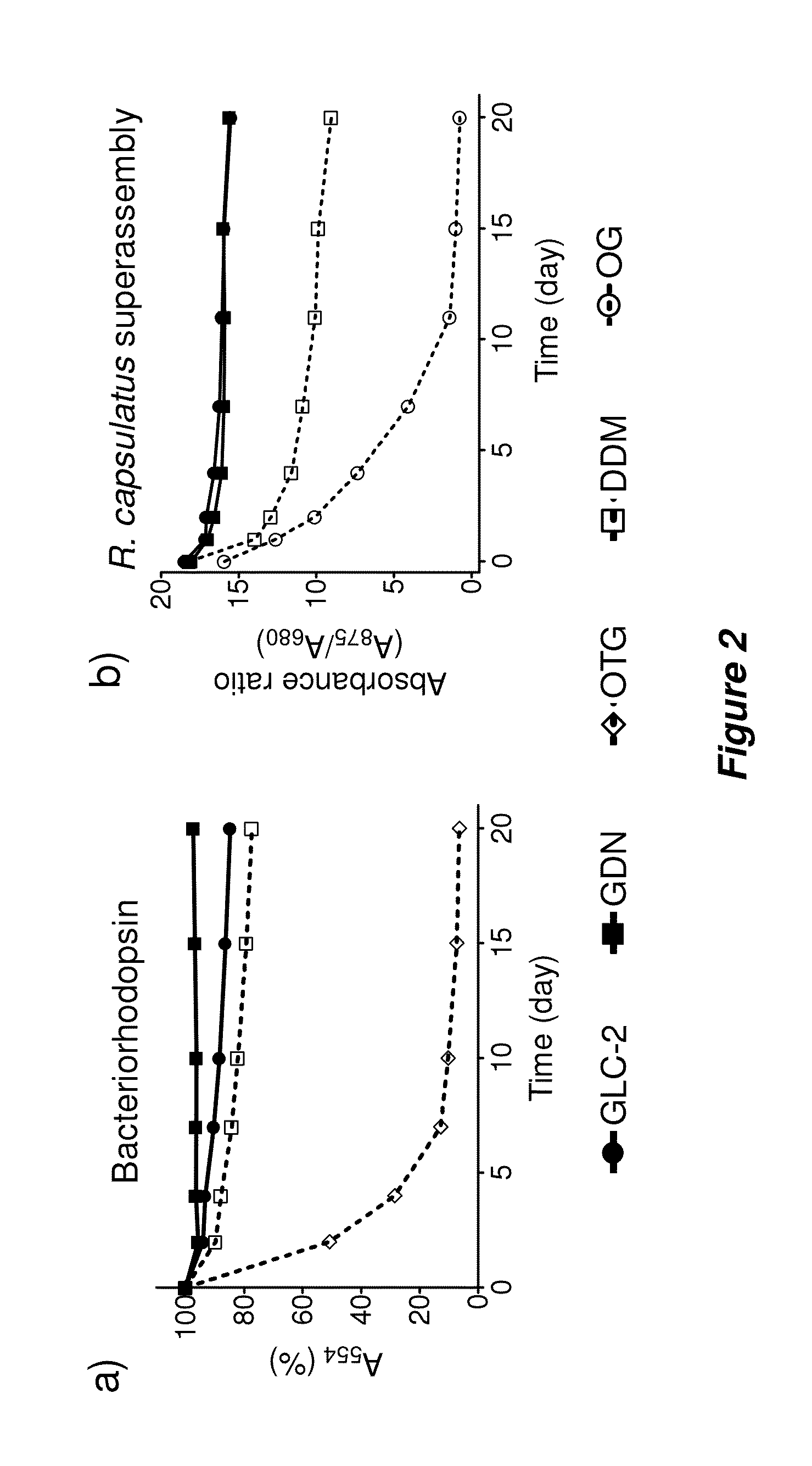
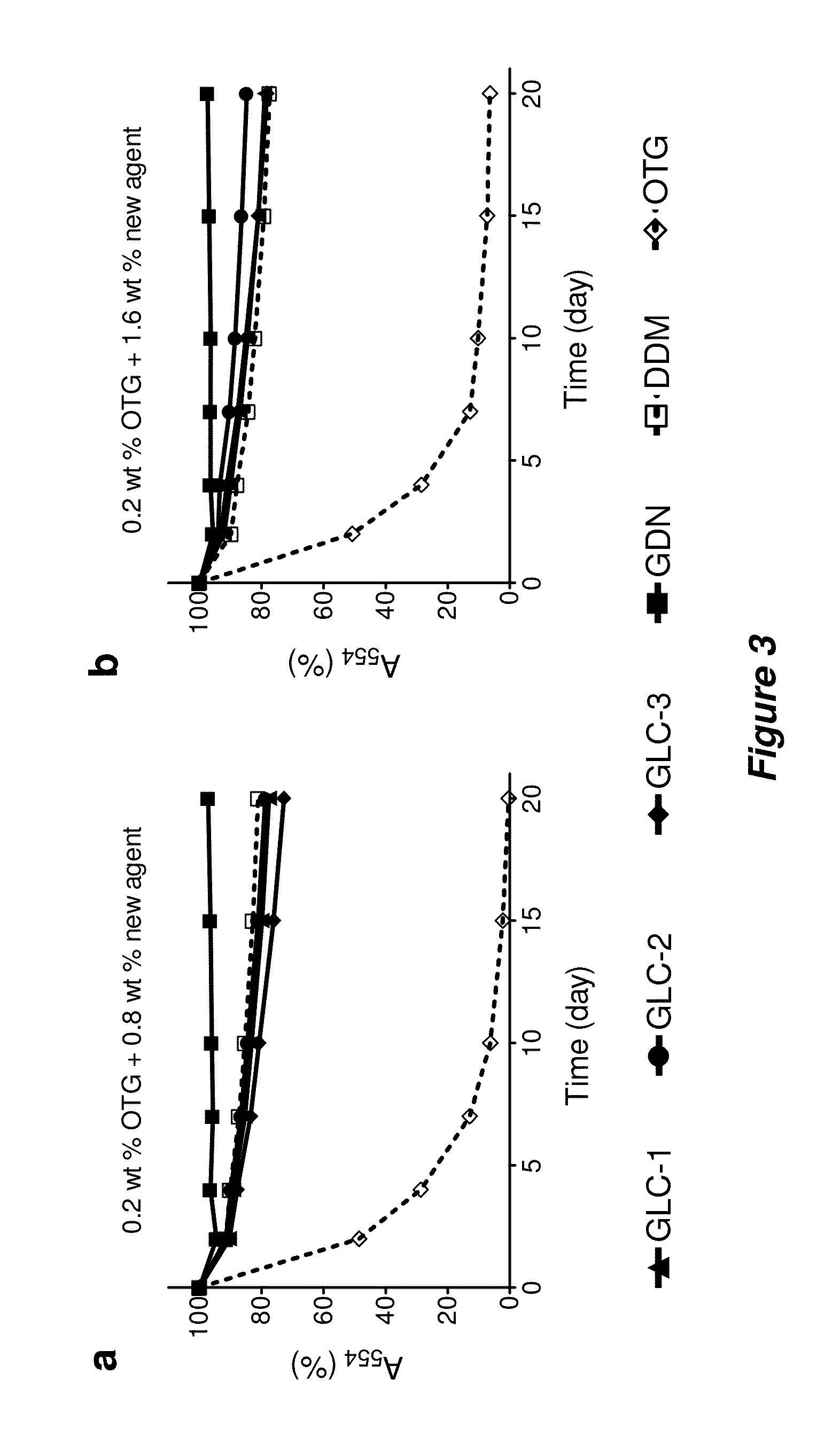
Amphiphilic compounds
ActiveUS20130266656A1Peptide/protein ingredientsOther chemical processesIntegral membrane proteinCell Membrane Proteins
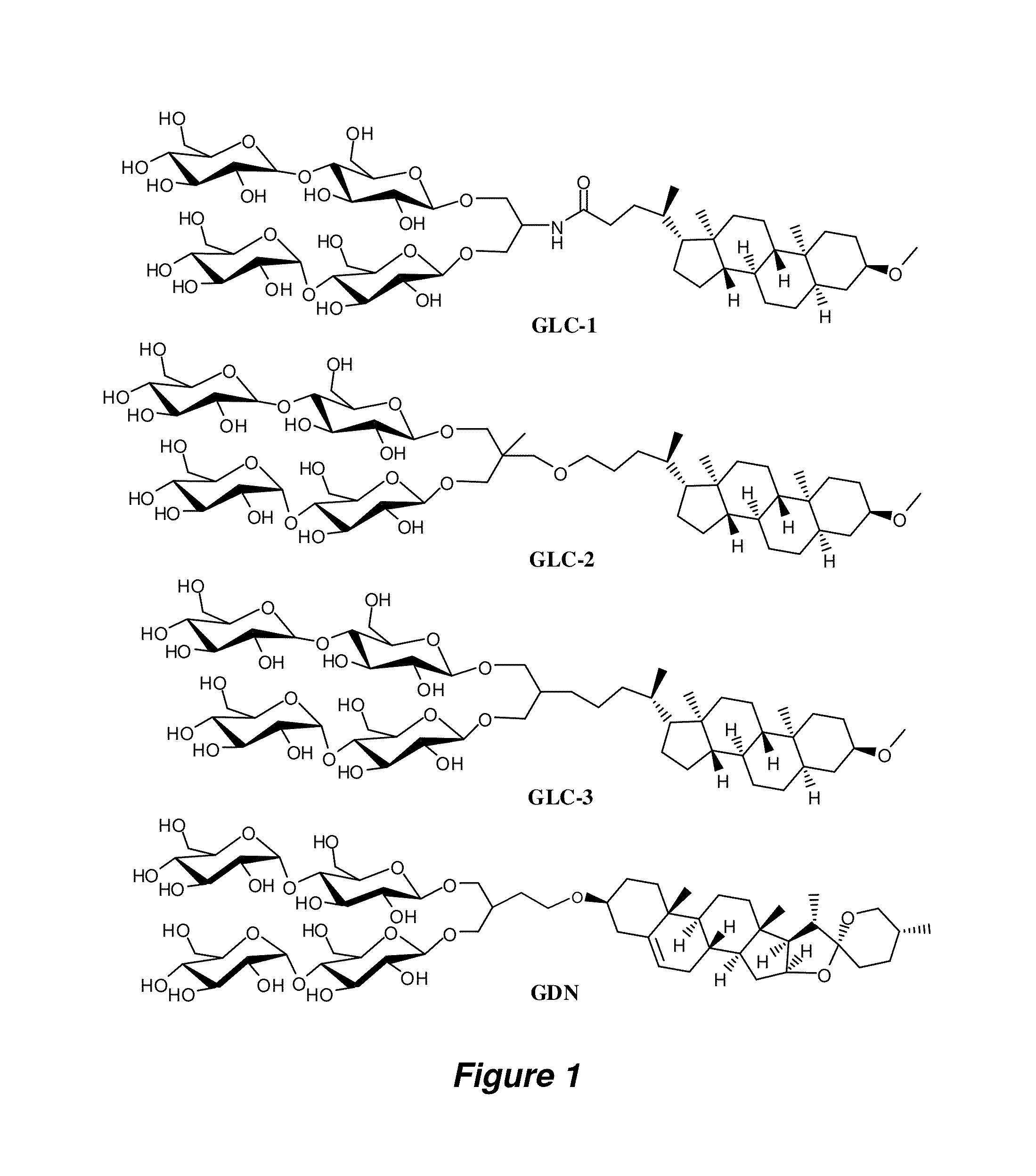
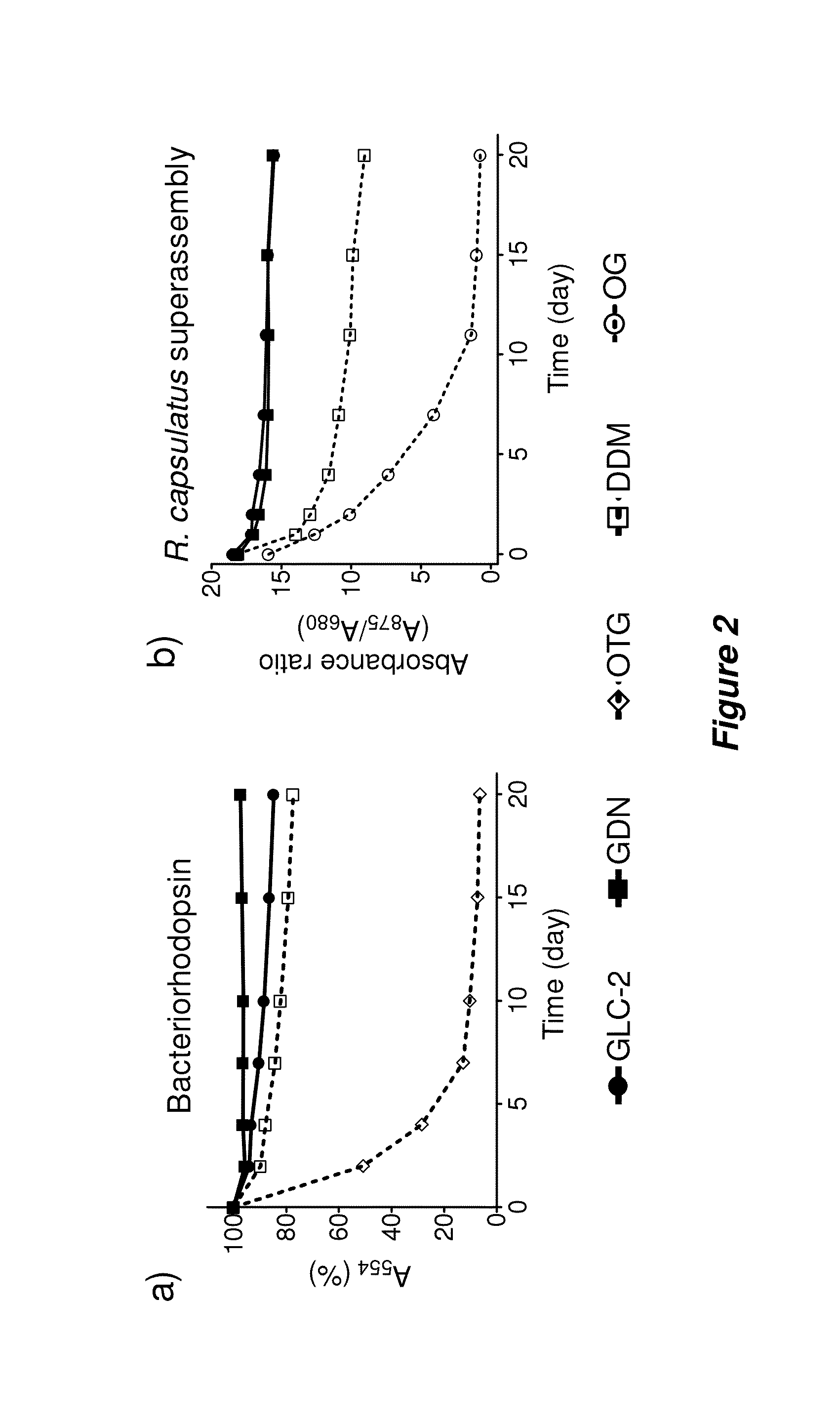
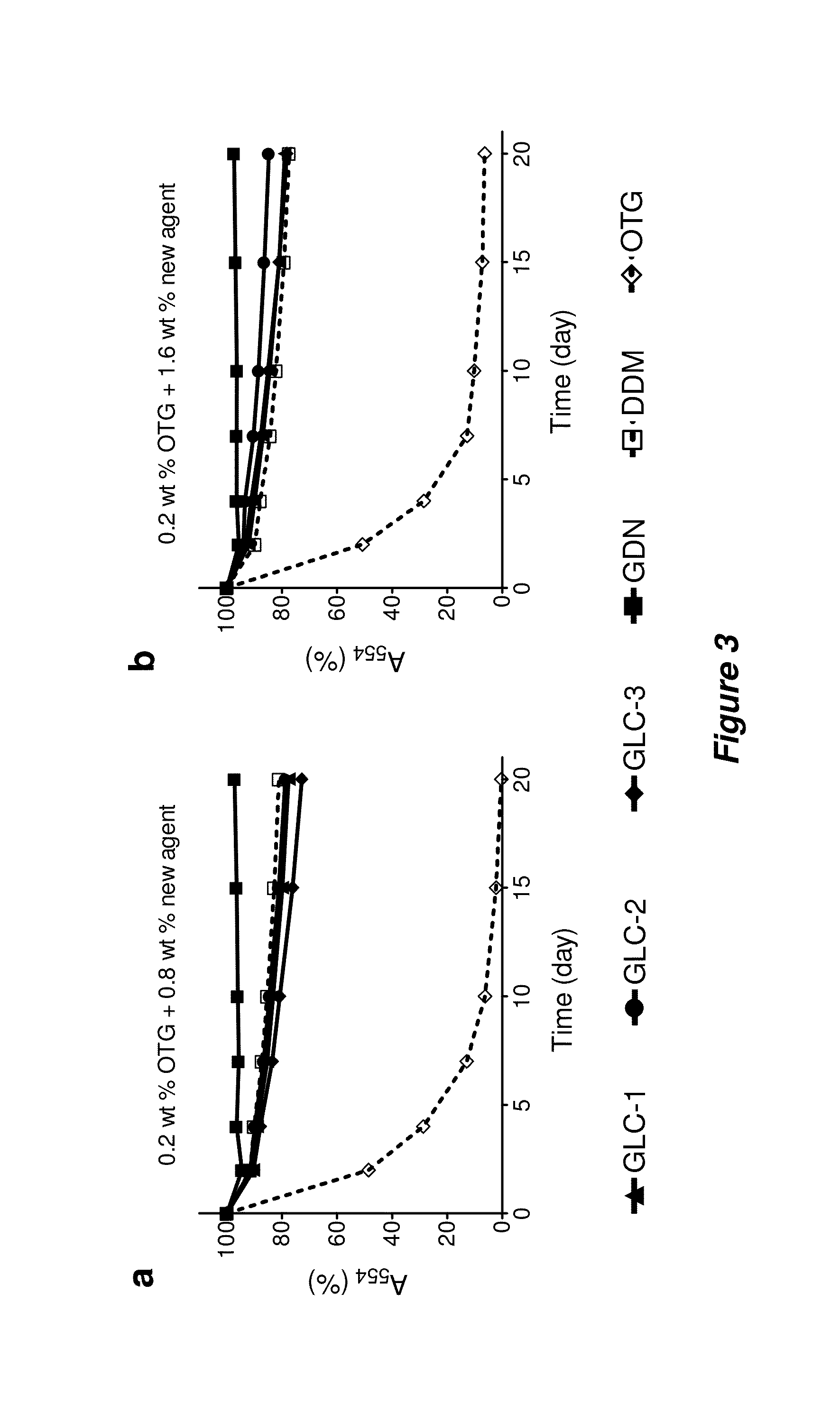
Bringing membrane proteins into aqueous solution generally requires the use of detergents or other amphiphilic agents. The invention provides a new class of amphiphiles, each of which includes a multi-fused ring system as a lipophilic group. These new amphiphiles confer enhanced stability to a range of membrane proteins in solution relative to conventional detergents, leading to improved structural and functional stability of membrane proteins, including integral membrane proteins. Accordingly, the invention provides new amphiphiles for biochemical manipulations and characterization of membrane proteins. These amphiphiles display favorable behavior with membrane proteins and can be used to aid the solubilization, isolation, purification, stabilization, crystallization, and / or structural determination of membrane proteins.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV +1
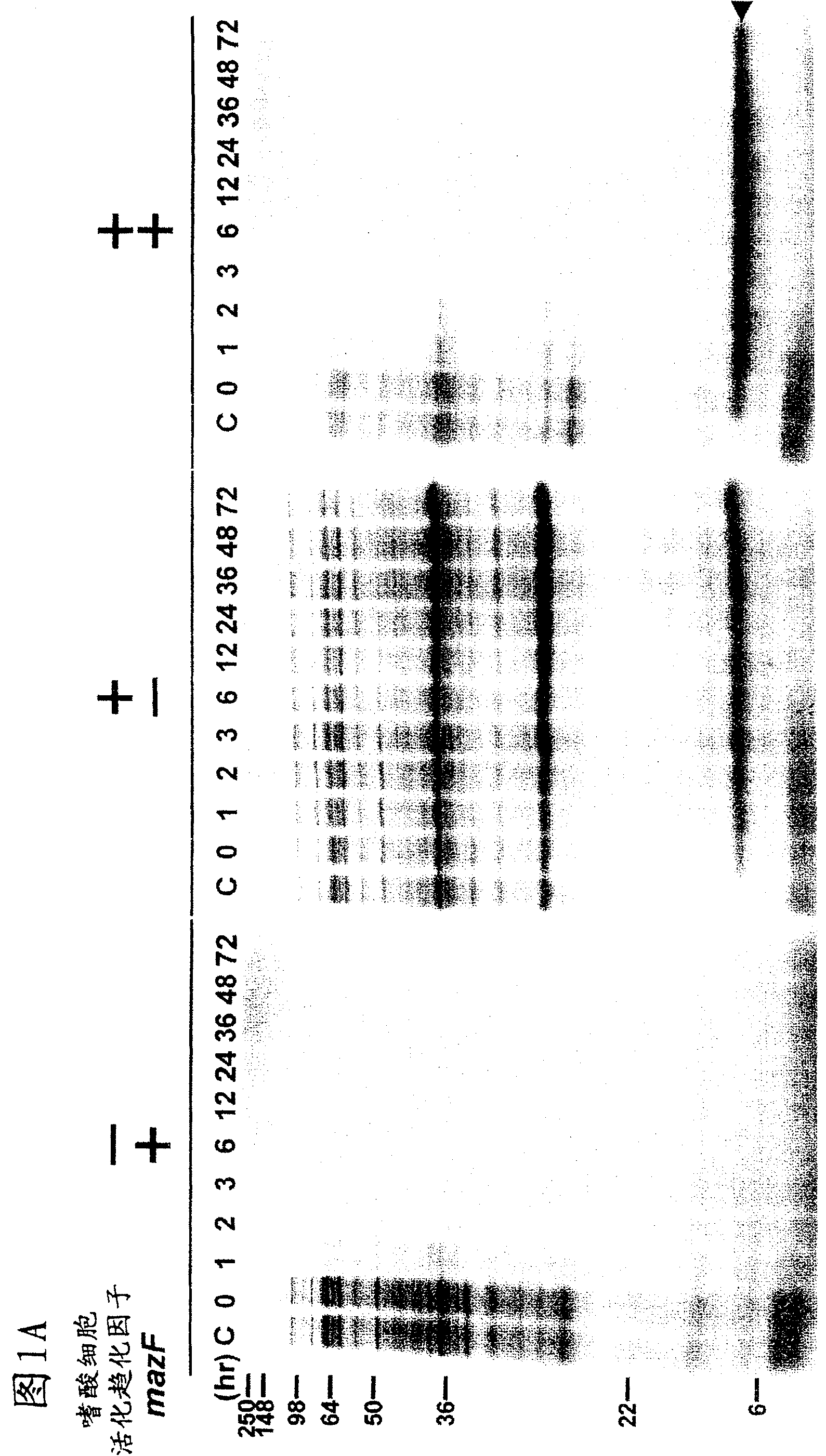
Single protein production in living cells facilitated by a messenger RNA interferase
InactiveUS20100035346A1Inhibit protein synthesisInhibit synthesisBacteriaHydrolasesEndoribonucleaseSingle-Stranded RNA
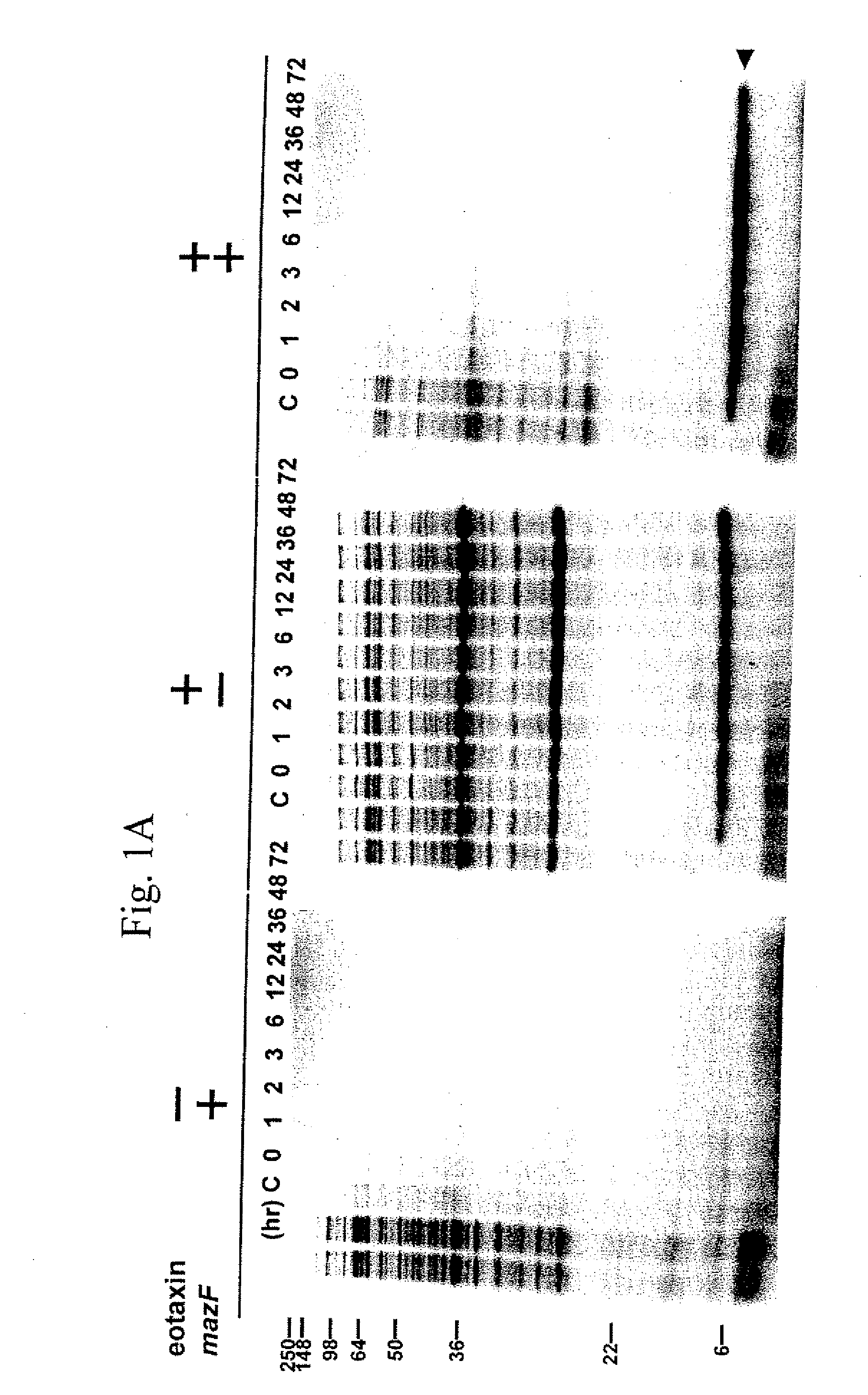
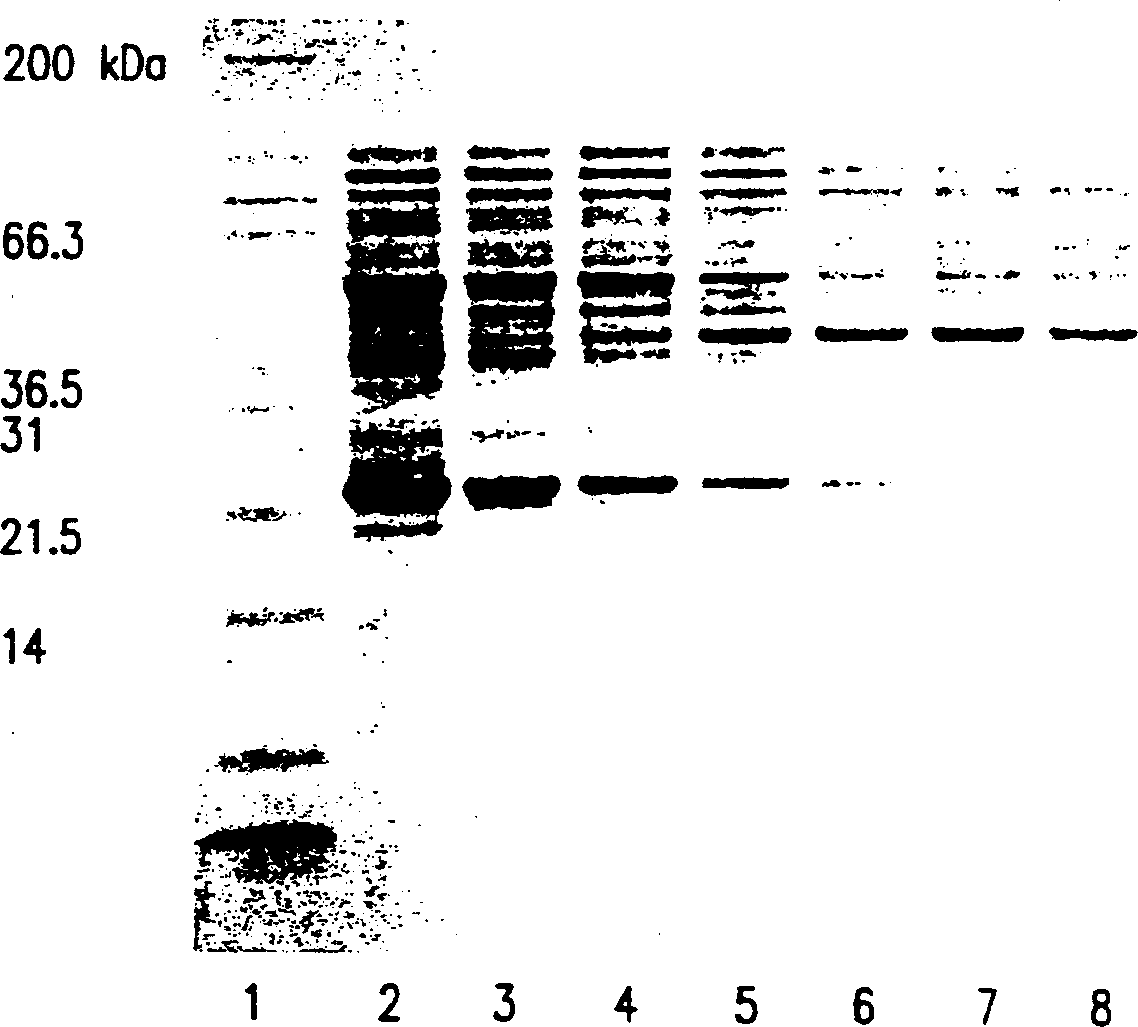
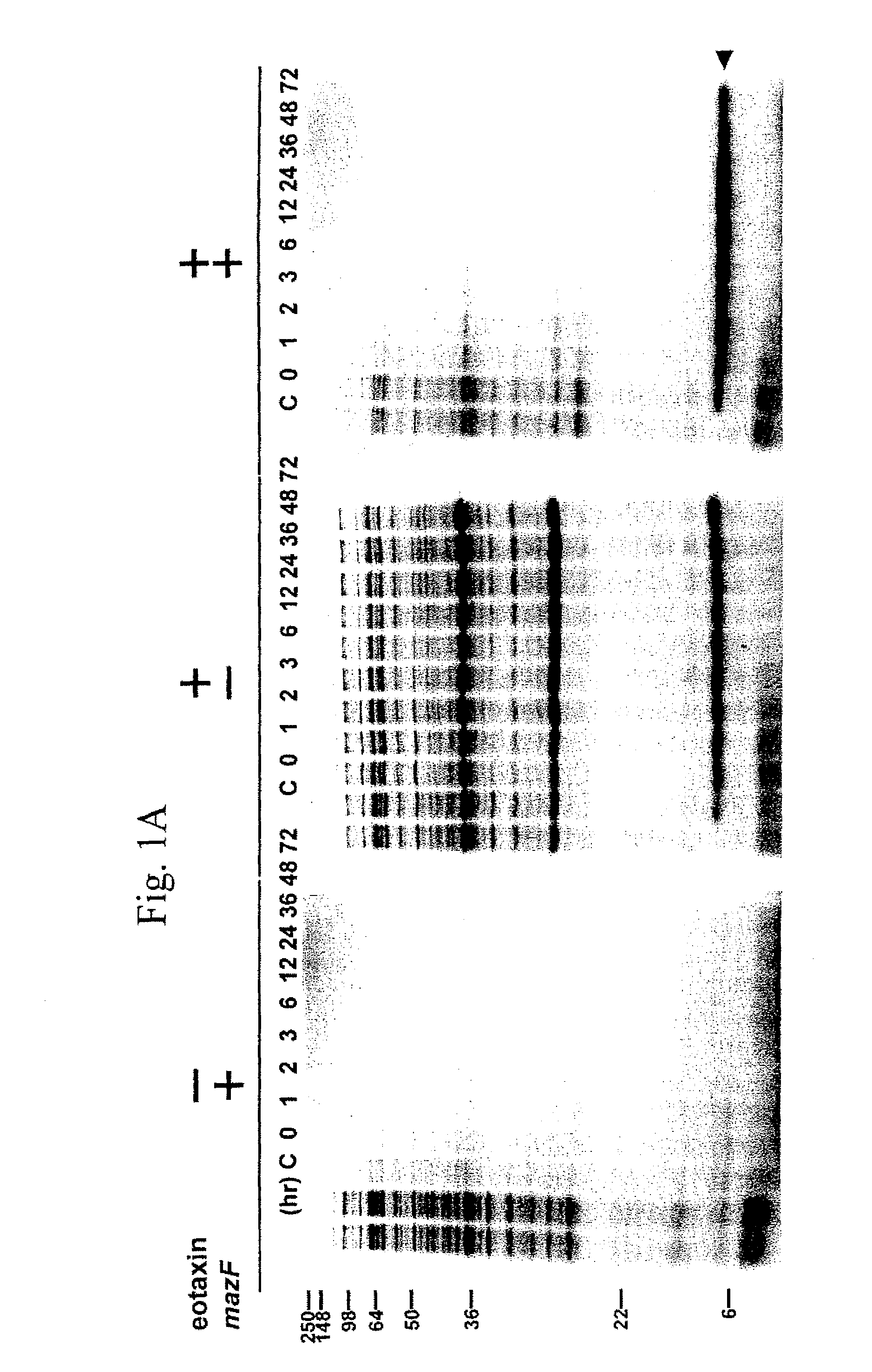
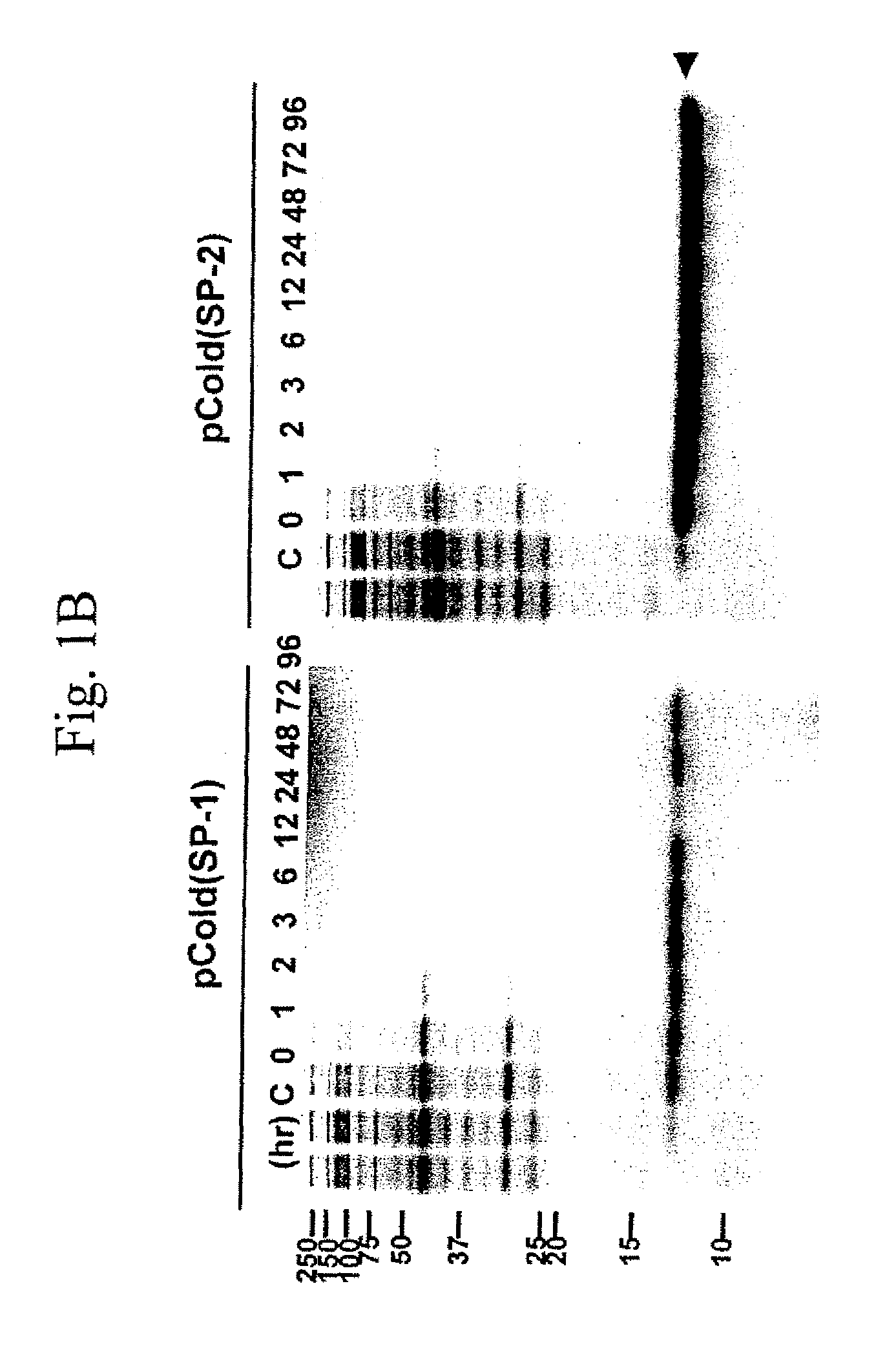
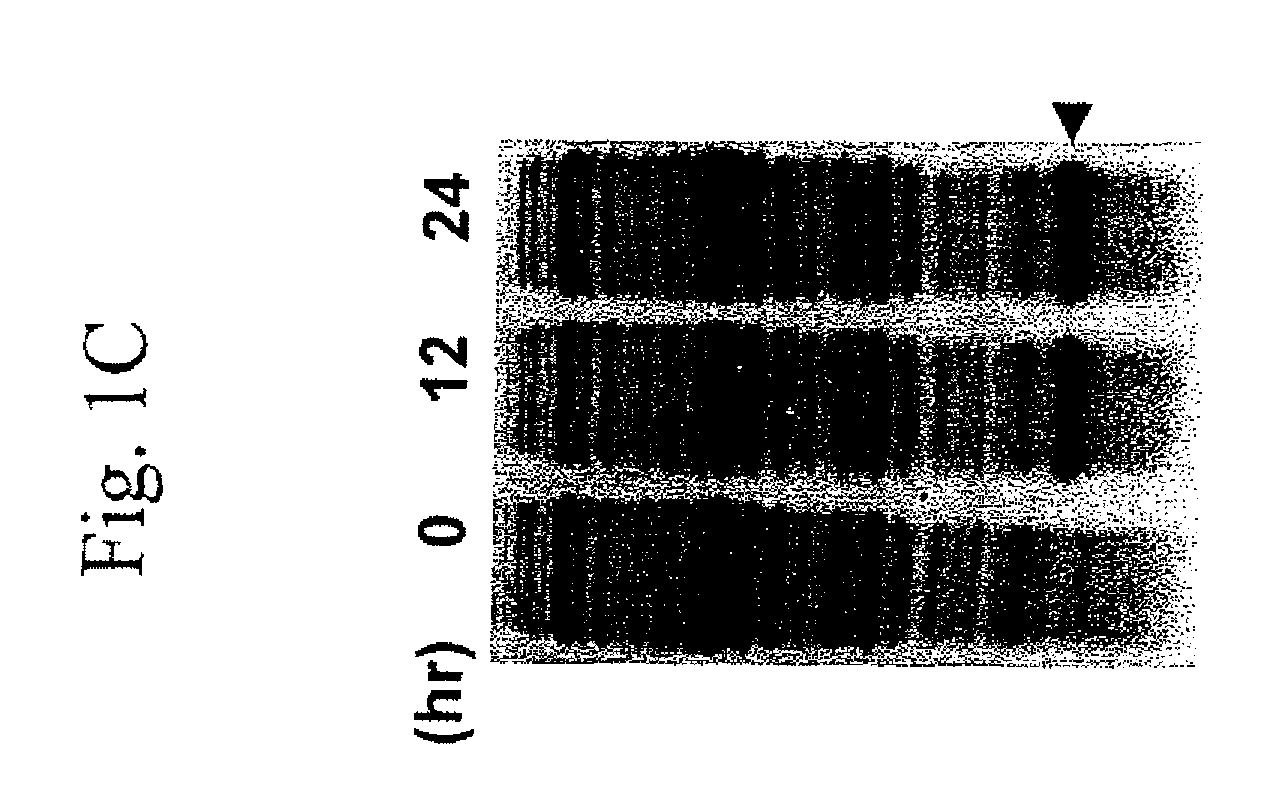
The present invention describes a single-protein production (SPP) system in living E. coli cells that exploits the unique properties of an mRNA interferase, for example, MazF, a bacterial toxin that is a single stranded RNA- and ACA-specific endoribonuclease, which efficiently and selectively degrades all cellular mRNAs in vivo, resulting in a precipitous drop in total protein synthesis. Concomitant expression of MazF and a target gene engineered to encode an ACA-less mRNA results in sustained and high-level (up to 90%) target expression in the virtual absence of background cellular protein synthesis. Remarkably, target synthesis continues for at least 4 days, indicating that cells retain transcriptional and translational competence despite their growth arrest. SPP technology works well for yeast and human proteins, even a bacterial integral membrane protein. This novel system enables unparalleled signal to noise ratios that should dramatically simplify structural and functional studies of previously intractable but biologically important proteins. The present invention also provides an optimized condensed single protein production system.
Owner:RUTGERS THE STATE UNIV
Differentially expressed tumour-specific polypeptides for use in the diagnosis and treatment of cancer
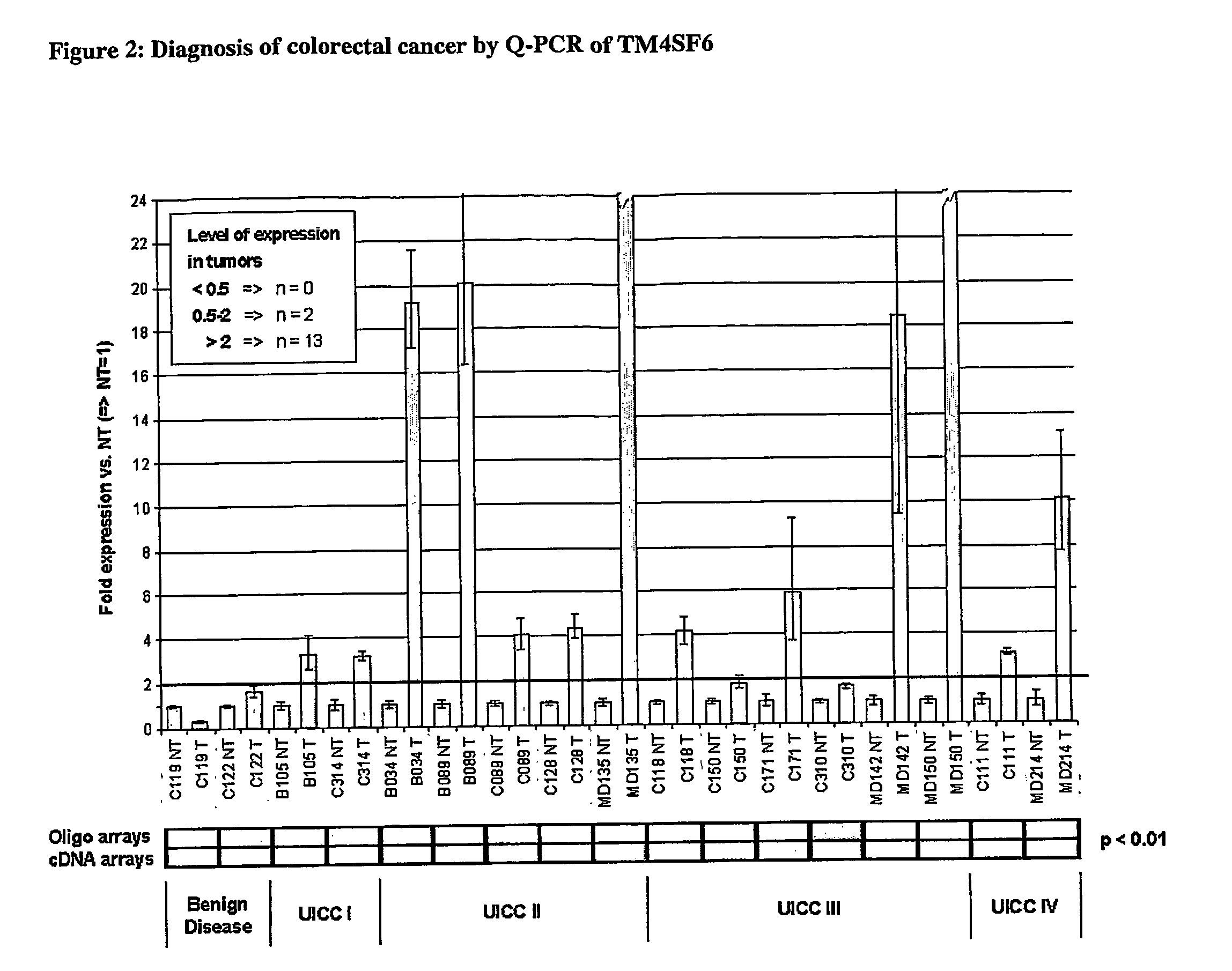
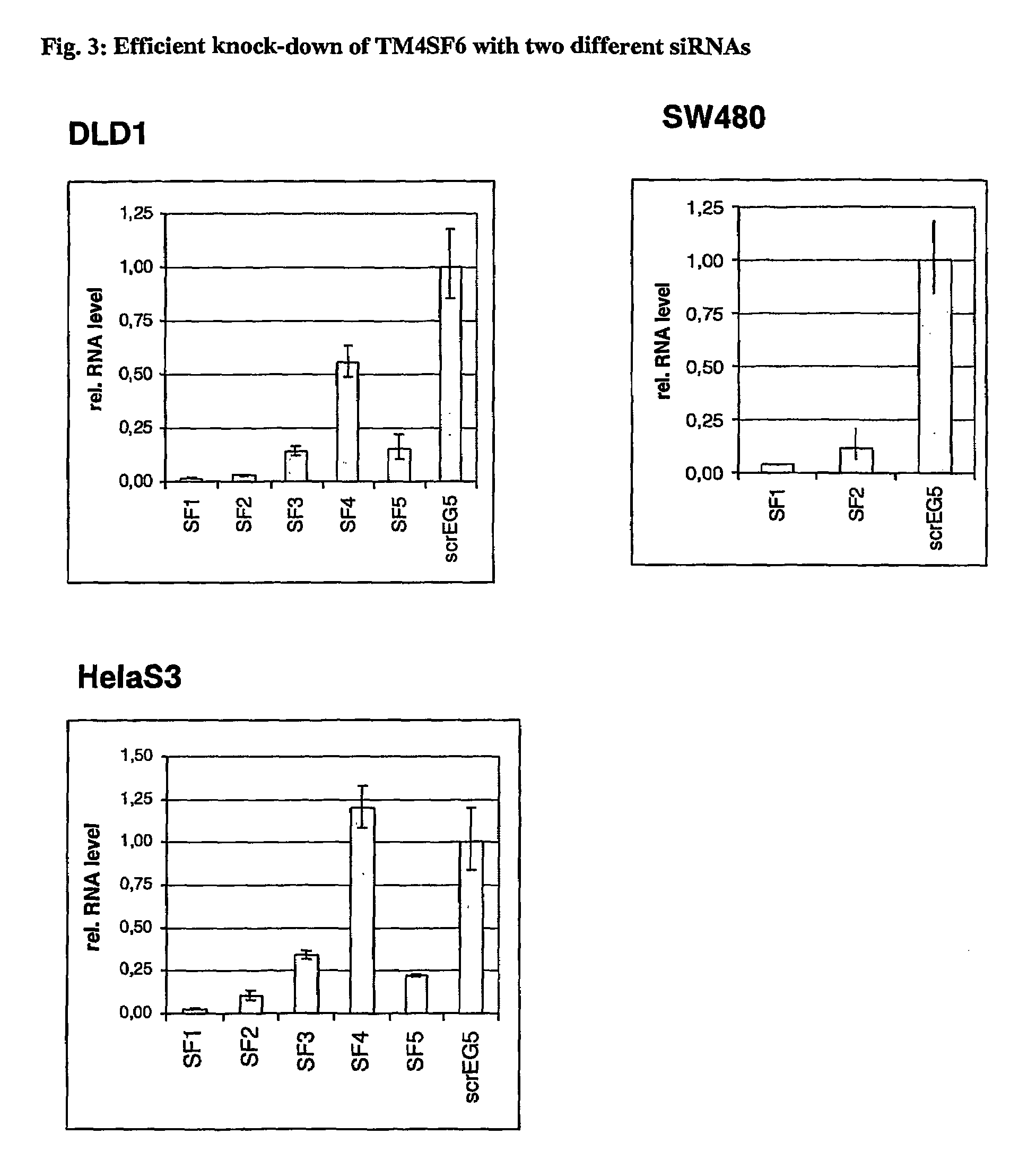
The invention relates to agents and methods for the diagnosis, prognosis and treatment of cancer. Specifically, the invention relates to the use of nucleic and amino acid sequences encoding transmembrane superfamily member 6 (TM4SF6), synaptophysin like protein (SYPL), stomatin like 2 (STOML2), Ras related GTP binding protein RAGA), nucleotide sensitive chloride channel 1A (CLNS1A), prion protein (p27-30) (PRNP), guanine nucleotide binding protein beta 2-like 1 (GNB2L1), guanine nucleotide binding protein 4 (GNG4), integral membrane protein 2B (ITM2B), integral membrane protein 1 (ITM1), transmembrane 9 superfamily member 2 (TM9SF2), opiate receptor-like 1 protein (OPRL1), low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 4 (LRP4), human glomerular epithelial protein 1 (GLEPP1), toll-like receptor 3 (TLR3), and / or zona pellucida glycoprotein 3A (ZP3) for the diagnosis of both early and late stage non-steroid specific cancers, cancer prognosis, as well as screening for therapeutic agents that regulate the gene expression and / or biological activity of said proteins. This invention further relates to the biological technologies designed to inhibit the gene expression and / or biological activity of said proteins including using agents identified in screening assays described herein, vector delivery of antisense polynucleotide sequences, and antibody targeting of said proteins. In specific embodiments, the proteins are of human origin.
Owner:GENMAB AS
Compositions of influenza viral proteins and methods of use thereof
InactiveCN101087808AStimulate immune responsePrevention and treatment of influenza infectionViral antigen ingredientsVirus peptidesIntegral membrane proteinPathogen-Associated Molecular Pattern Molecules
Compositions, fusion proteins and polypeptides comprise at least one pathogen-associated molecular pattern and at least a portion of at least one integral membrane protein of an influenza viral antigen. The compositions, fusion proteins and polypeptides are used to stimulate an immune response in a subject.
Owner:VAXINNATE
High throughput assay systems and methods for identifying agents that alter surface expression of integral membrane proteins
ActiveUS20050014202A1Effective treatmentPreventing and treating cardiac arthythmiaOrganic active ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementIntegral membrane proteinMammalian cell
Disclosed are high throughput assay systems and methods for identifying agents that alter the level of surface expression of integral membrane proteins, such as cardiac ion channels, in mammalian cells. Also disclosed are therapeutic methods of using agents identified using such methods.
Owner:THE METRO HEALTH SYST +2
Treatment method of sample for membrane protein analysis identification
InactiveCN102854272AHigh activityActivity will not decreaseComponent separationProteomic ProfileIntegral membrane protein
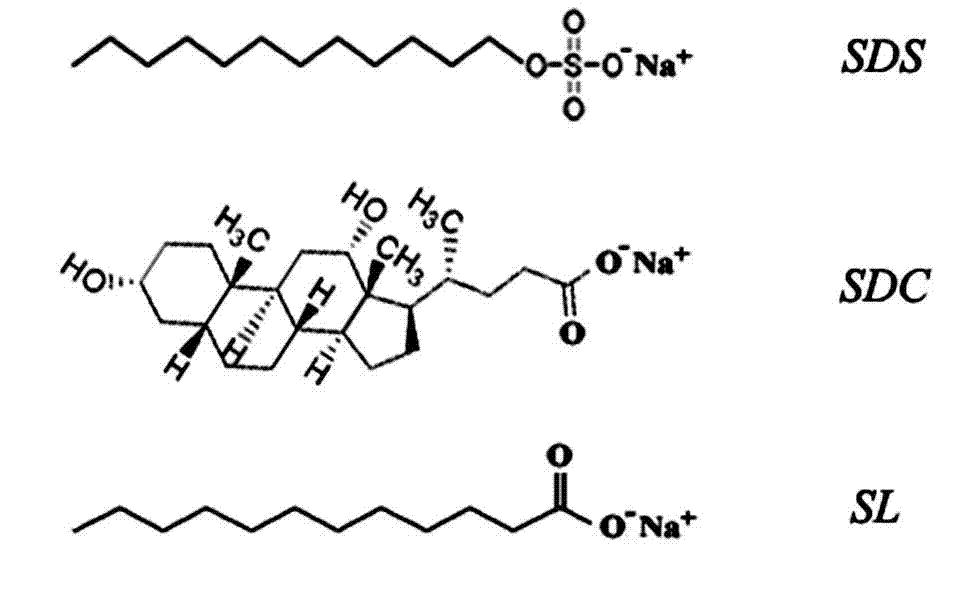
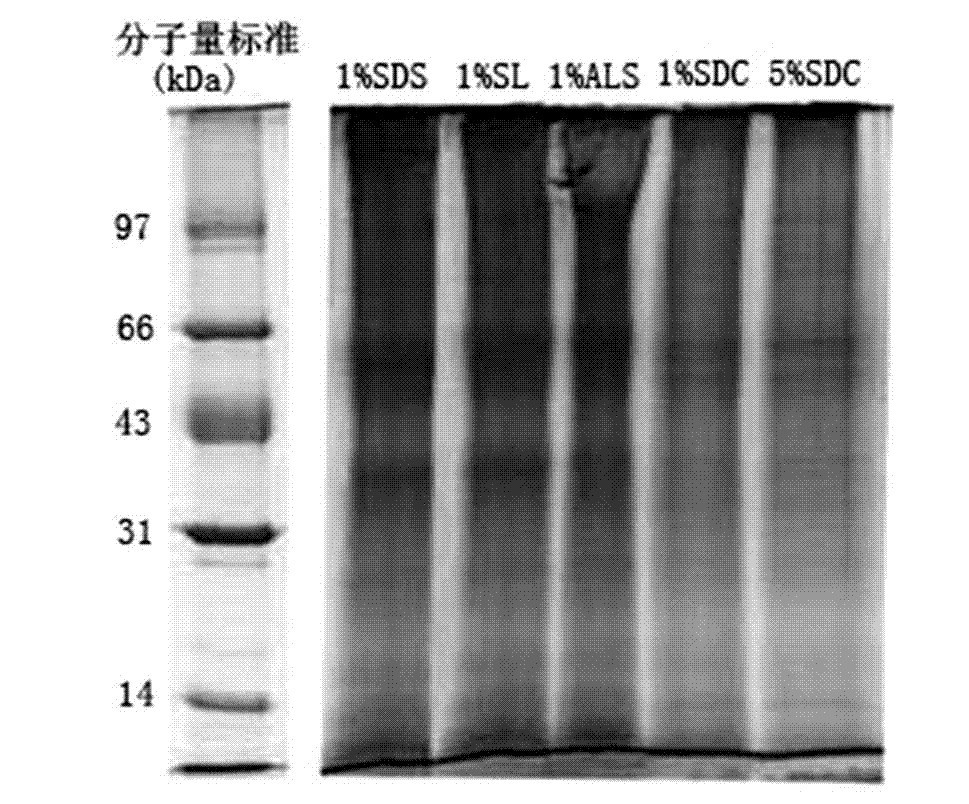
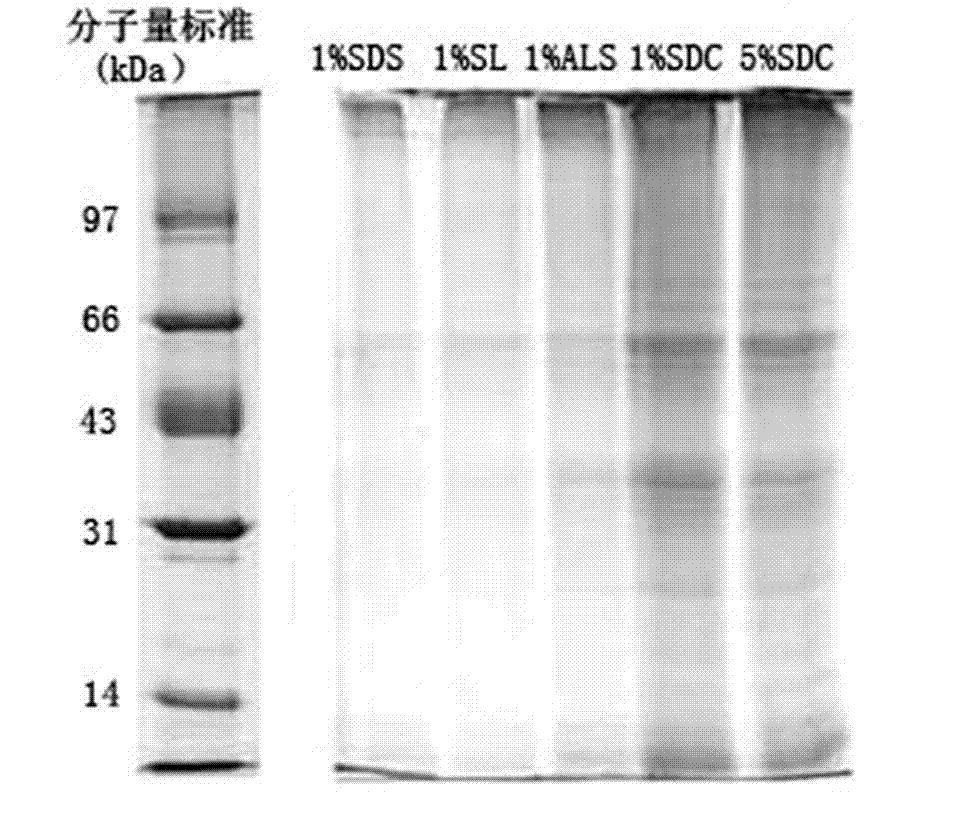
The present invention relates to the field of membrane proteomics research, specifically to a treatment method of a sample for membrane protein analysis identification. According to the treatment method of the present invention, SL is adopted as a detergent, and is provided for membrane protein analysis identification, wherein SL molecules have a linear hydrophobic hydrocarbon chain tail similar to SDS molecules, and a carboxyl head similar to SDC molecules, and experiment results show that SL provides significant advantages in identifications of membrane proteins, especially in identifications of integral membrane proteins having high hydrophobicity and / or multiple transmembrane regions compared with ALS and SDC.
Owner:HUNAN NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Extraction of integral membrane proteins
InactiveCN1358196AIncrease surface areaSimplify processing stepsMicroorganism based processesPeptide preparation methodsDownstream processingProtein insertion
A process is described for extracting gram-negative integral membrane proteins from bacteria or bacterial host cells containing a recombinant vector by differential detergent tangential flow diafiltration. This process has several advantages over alternate processes. First, it combines the clarification and extraction processes into one unit operation. The product is extracted from the cells and it is separated from cell debris with only one continuous diafiltration process. Second, the membrane proteins are extracted in a semi-purified state, which simplifies the downstream processing steps. Third, this process is very scalable because the only requirement is that the surface area of the membranes be increased proportionally with the amount of cells.
Owner:WYETH HOLDINGS CORP
Single protein production in living cells facilitated by a messenger RNA interferase
Owner:RUTGERS THE STATE UNIV
Self-assembling nanoparticles composed of transmembrane peptides and their application for specific intra-tumor delivery of Anti-cancer drugs
The invention provides a method of handling a hydrophobic agent, which method comprises (a) combining in an aqueous solution (i) a hydrophobic agent and (ii) an isolated peptide that is a structural analog of a transmembrane domain of an integral membrane protein, wherein one terminus of the peptide has one or more negatively charged residues, and (b) allowing the peptide to self-assemble into nanoparticles, wherein the nanoparticles comprise the hydrophobic agent.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
Biocompatible implants and methods of making and attaching the same
Owner:DOHENY EYE INST
Compositions and methods for making water-soluble integral membrane proteins
ActiveUS20170275343A1Functional and structural studyHigh expressionPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsIntegral membrane proteinMoiety
The present invention relates to a nucleic acid construct having a chimeric nucleic acid molecule comprising a first nucleic acid moiety encoding an amphipathic shield domain protein; a second nucleic acid moiety encoding an integral membrane protein; and a third nucleic acid moiety encoding a water soluble expression decoy protein, as well as a chimeric nucleic acid molecule having a first nucleic acid moiety encoding an amphipathic shield domain protein and a second nucleic acid moiety encoding an integral membrane protein. The present invention further relates to an expression vector, a host cell, and a protein encoded by the nucleic acid construct. Also disclosed is a method of recombinantly producing an integral membrane protein in soluble form.
Owner:CORNELL UNIVERSITY
Polymer-Encased Nanodiscs With Improved Buffer Compatibility
ActiveUS20190062469A1Avoid prolonged useHydrolasesEnzyme stabilisationNanodiscIntegral membrane protein
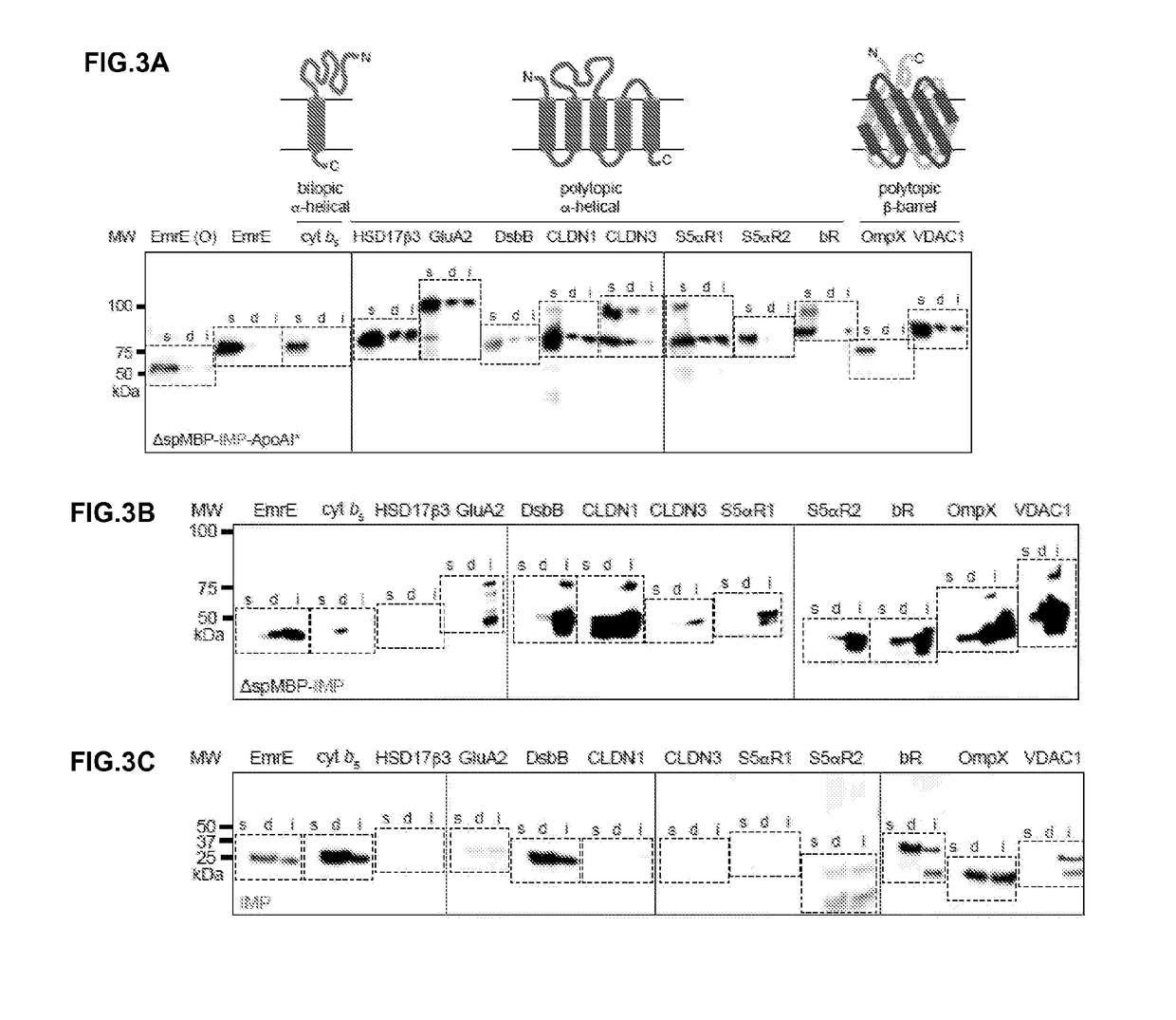
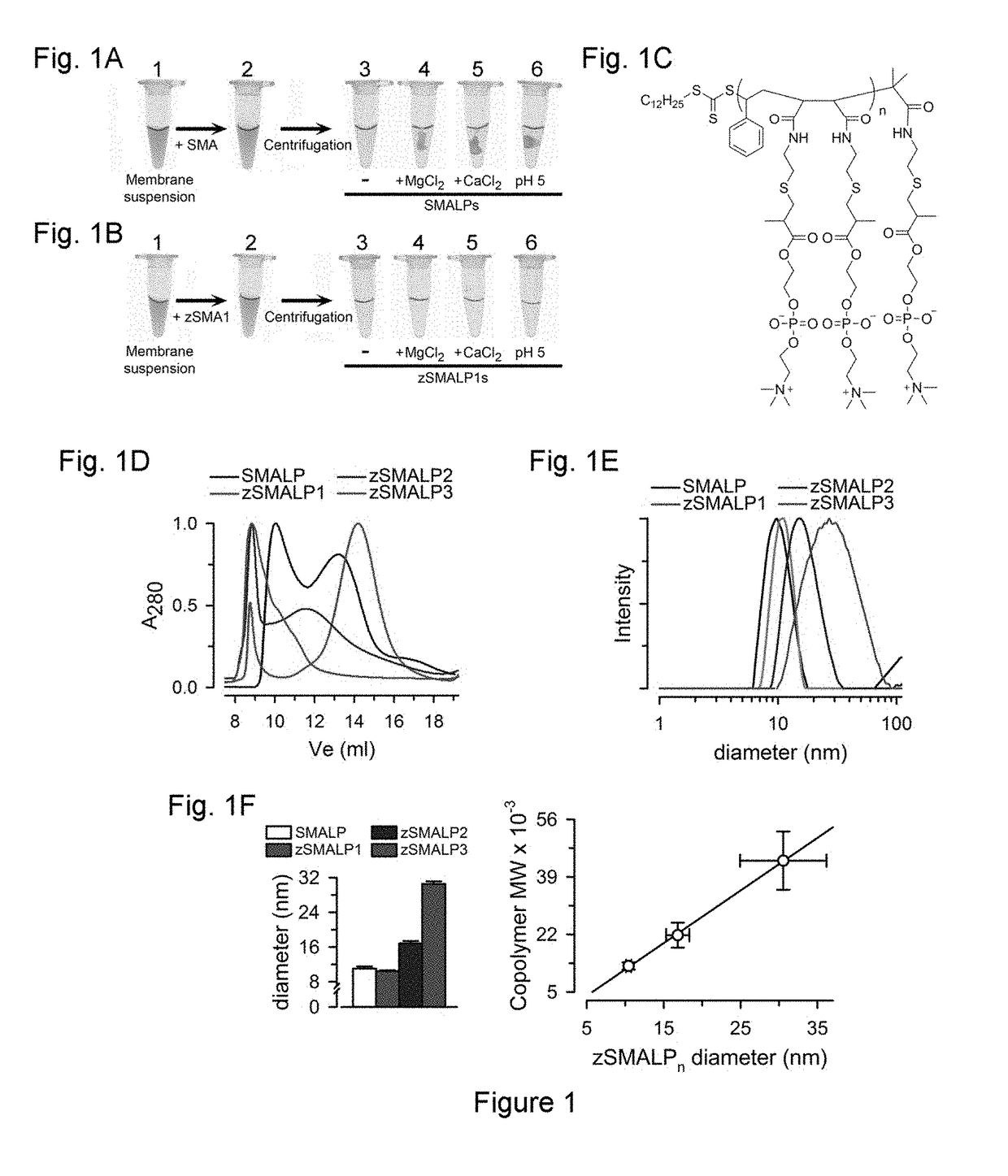
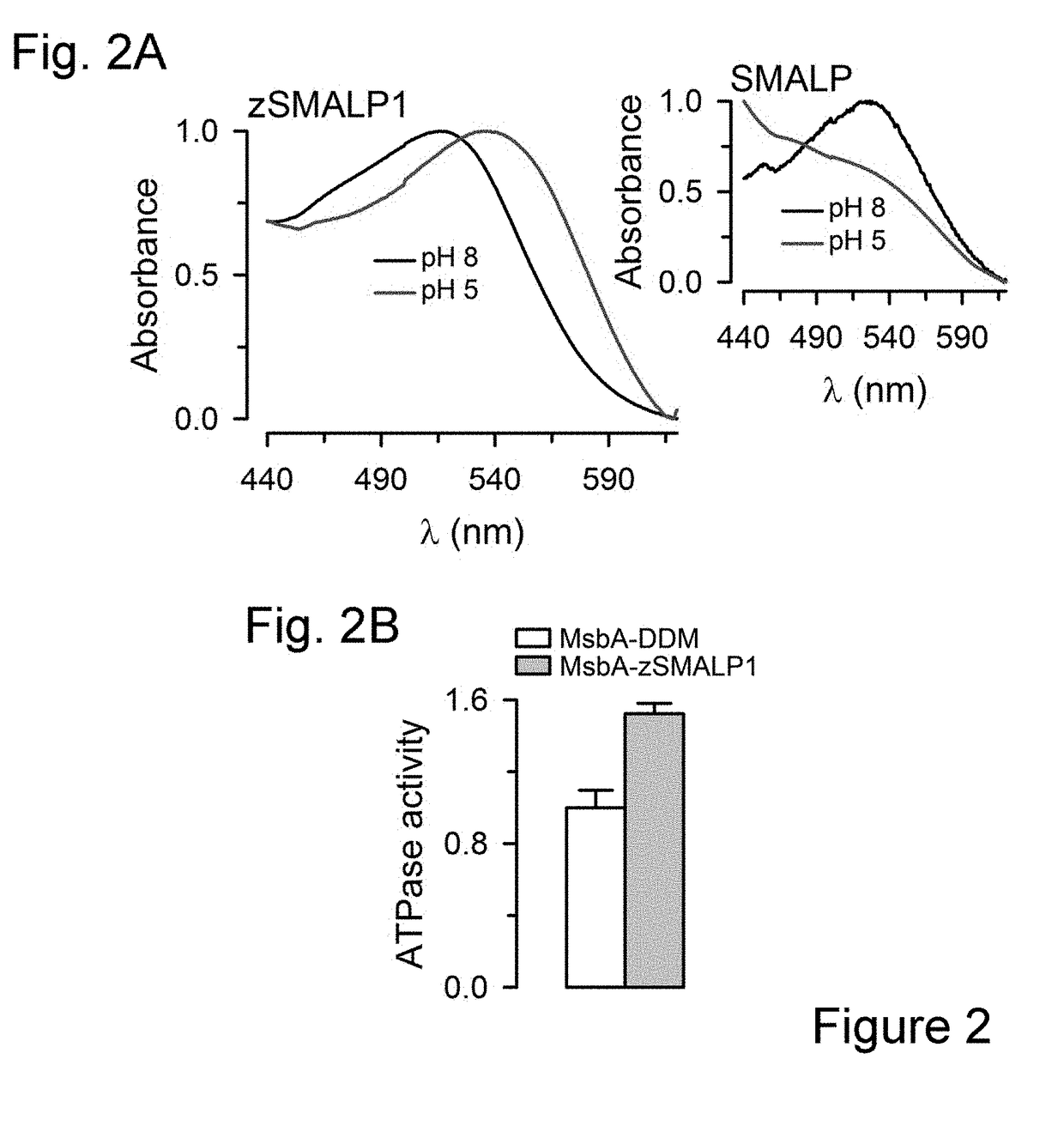
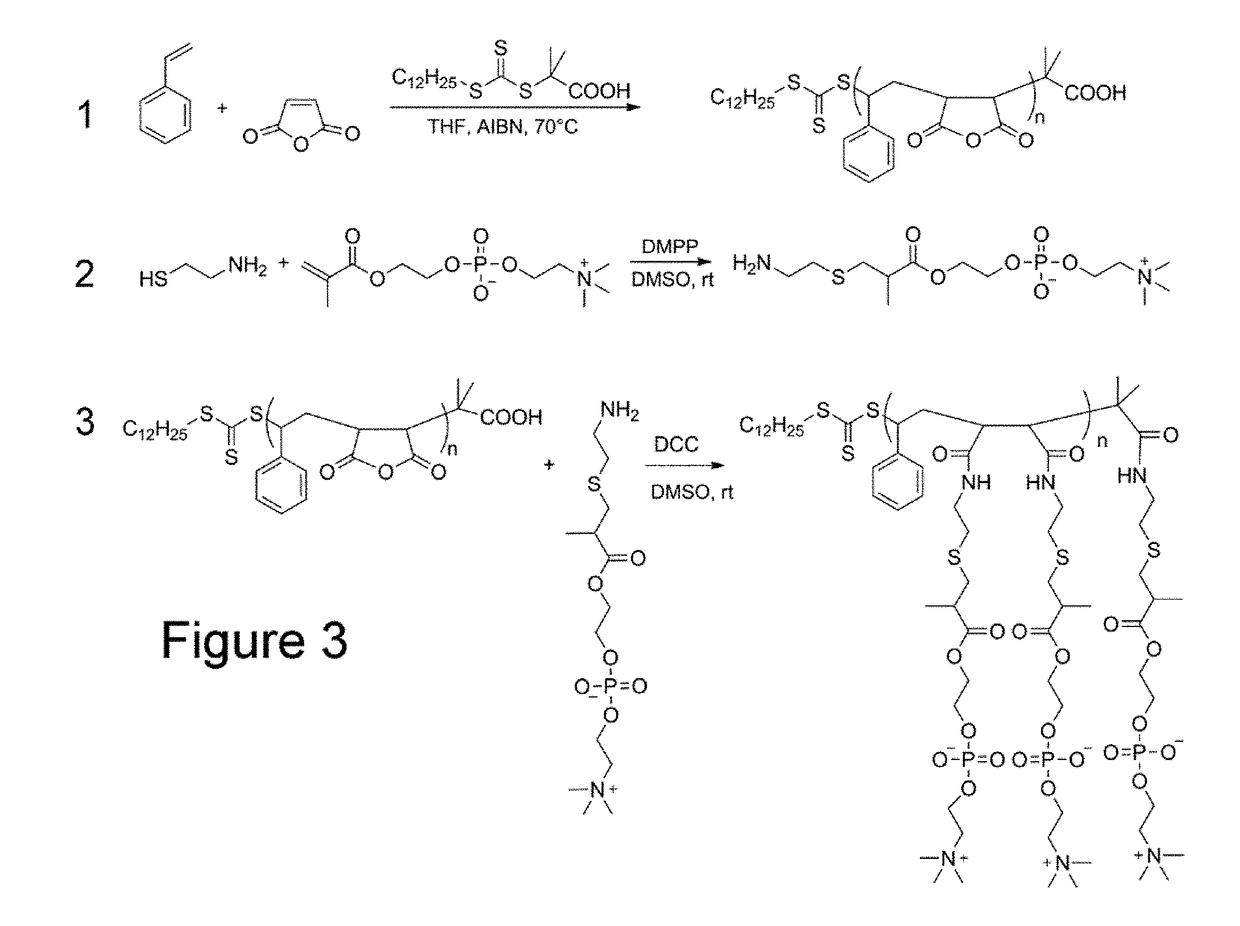
The present invention includes compositions, methods, and methods of making and using a polymer-encased nanodisc comprising: one or more integral membrane proteins in a lipid layer; and a polymer comprising zwitterionic styrene-maleic acid derivative repeating units that carry zero or nearly zero negative charge, and the polymer-encased nanodiscs.
Owner:TEXAS TECH UNIV SYST
High throughput assay systems and methods for identifying agents that alter surface expression of integral membrane proteins
ActiveUS7211407B2Organic active ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementIntegral membrane proteinBiology
Disclosed are high throughput assay systems and methods for identifying agents that alter the level of surface expression of integral membrane proteins, such as cardiac ion channels, in mammalian cells. Also disclosed are therapeutic methods of using agents identified using such methods.
Owner:THE METRO HEALTH SYST +2
Amphiphilic compounds
ActiveUS9206221B2Peptide/protein ingredientsOther chemical processesIntegral membrane proteinBiochemistry
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV +1
Single protein production in living cells facilitated by a messenger RNA interferase
The present invention describes a single-protein production (SPP) system in living E. coli cells that exploits the unique properties of an mRNA interferase, for example, MazF, a bacterial toxin that is a single stranded RNA- and ACA-specific endoribonuclease, which efficiently and selectively degrades all cellular mRNAs in vivo, resulting in a precipitous drop in total protein synthesis. Concomitant expression of MazF and a target gene engineered to encode an ACA-less mRNA results in sustained and high-level (up to 90%) target expression in the virtual absence of background cellular protein synthesis. Remarkably, target synthesis continues for at least 4 days, indicating that cells retain transcriptional and translational competence despite their growth arrest. SPP technology works well for yeast and human proteins, even a bacterial integral membrane protein. This novel system enables unparalleled signal to noise ratios that should dramatically simplify structural and functional studies of previously intractable but biologically important proteins.
Owner:UNIV OF MEDICINE & DENTISTRY OF NEW JERSEY
High throughput assay systems and methods for identifying agents that alter surface expression of integral membrane proteins
InactiveCN1878553AOrganic active ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementIntegral membrane proteinIntrinsic Membrane Protein
Owner:CHANXPRESS
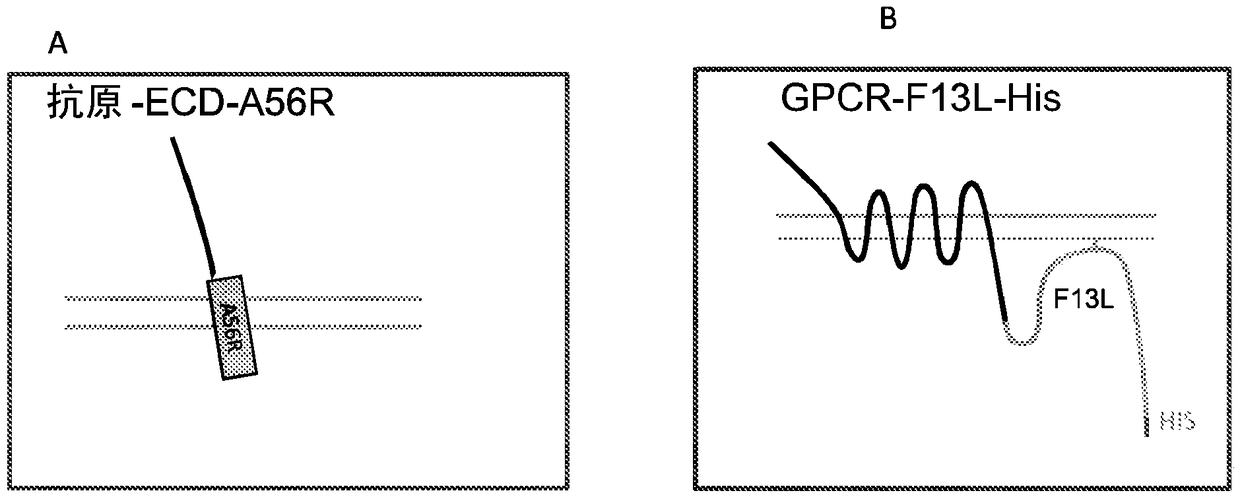
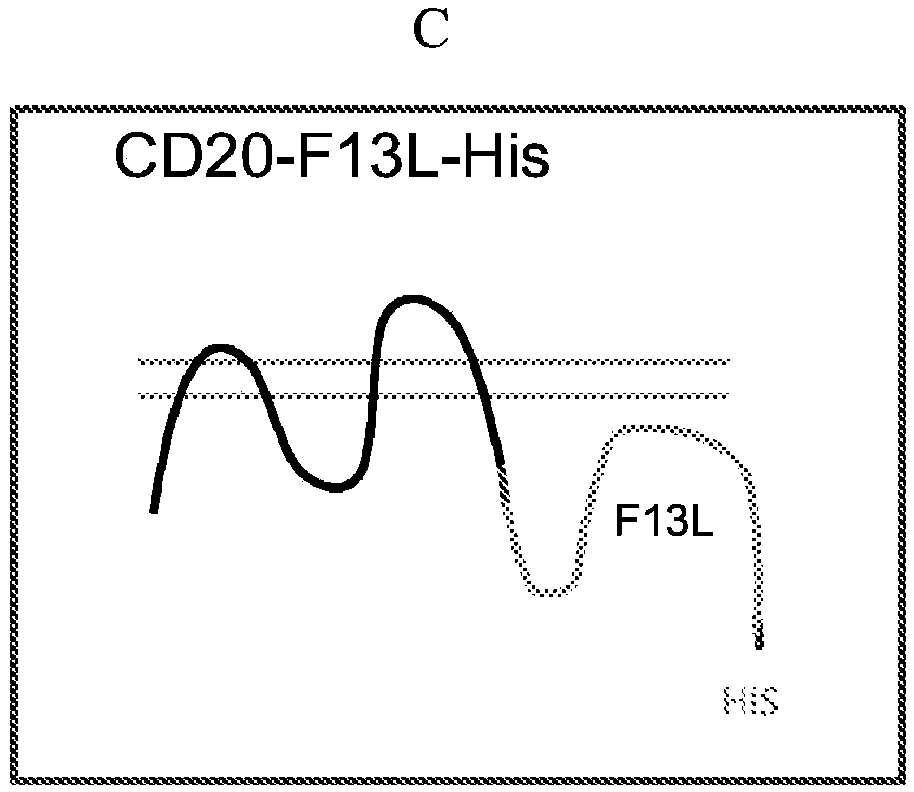
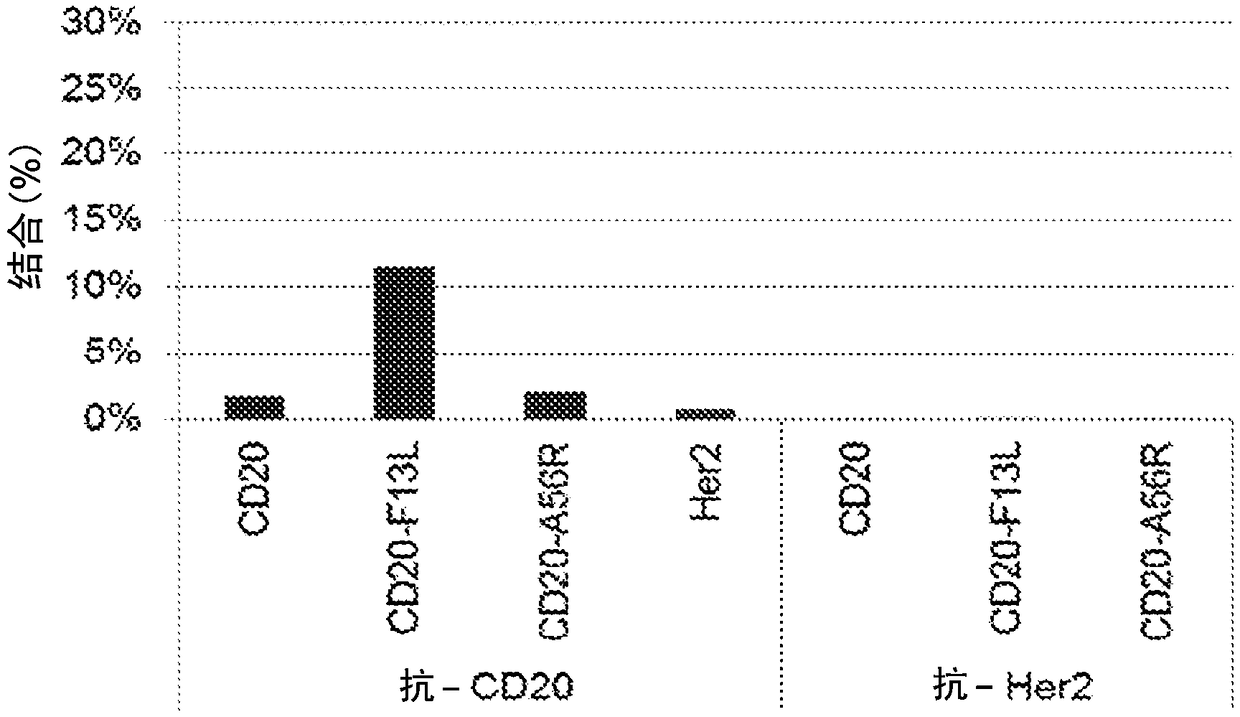
Integral membrane protein display on poxvirus extracellular enveloped virions
This disclosure provides compositions and methods for expressing and displaying isolated integral membrane proteins (IMPs) or fragments thereof in a native conformation for use in the screening, selecting, and identifying of antibodies or antibody-like molecules that bind to a target IMP of interest.
Owner:VACCINEX
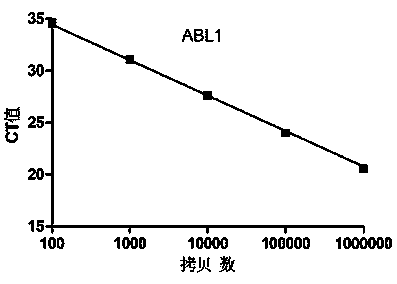
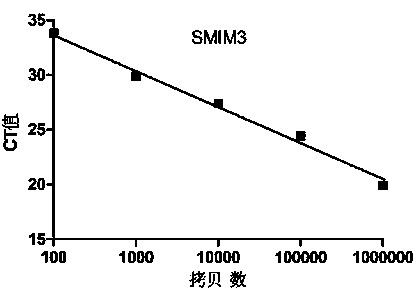
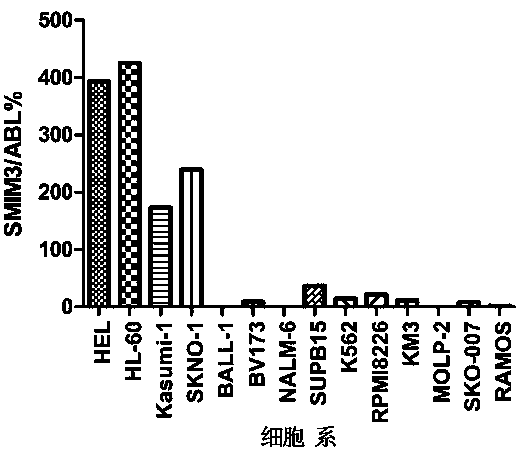
Primer probe set, kit and method for quantitative detection of expression level of small integral membrane protein 3 (SMIM3) gene
PendingCN111100931AHigh sensitivityImprove reliabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationForward primerIntegral membrane protein
The invention discloses a primer probe set, kit and method for quantitative detection of an expression level of a small integral membrane protein 3 (SMIM3) gene. The primer probe set comprises a component A and a component B; the component A includes a forward primer SMIM3-FP, a reverse primer SMIM3-RP and a probe SMIM3-probe; and the component B includes a forward primer ABL1-FP, a reverse primerABL1-RP and a probe ABL1-probe. The primer probe set, the kit and the method have the advantages that quantitative detection of the relative expression level of the SMIM3 gene in a cell is realized;moreover, the sensitivity of the SMIM3 gene and the sensitivity of an ABL1 gene both reach up to 100 copies; the sensitivity is high, results are accurate, and the reliability is high; a new auxiliarydiagnosis method or auxiliary identification method is provided for hematologic tumor cells (especially acute myelogenous leukemia and acute lymphoblastic leukemia); and the primer probe set, the kitand the method have broader application prospects.
Owner:THE FIRST AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF ZHENGZHOU UNIV
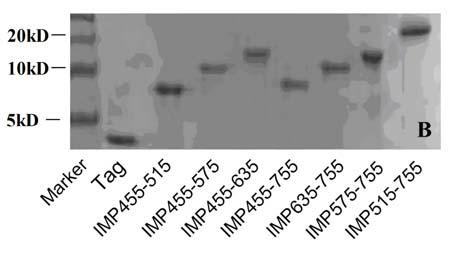
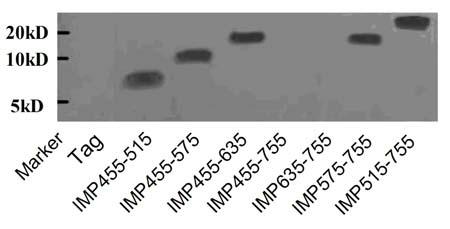
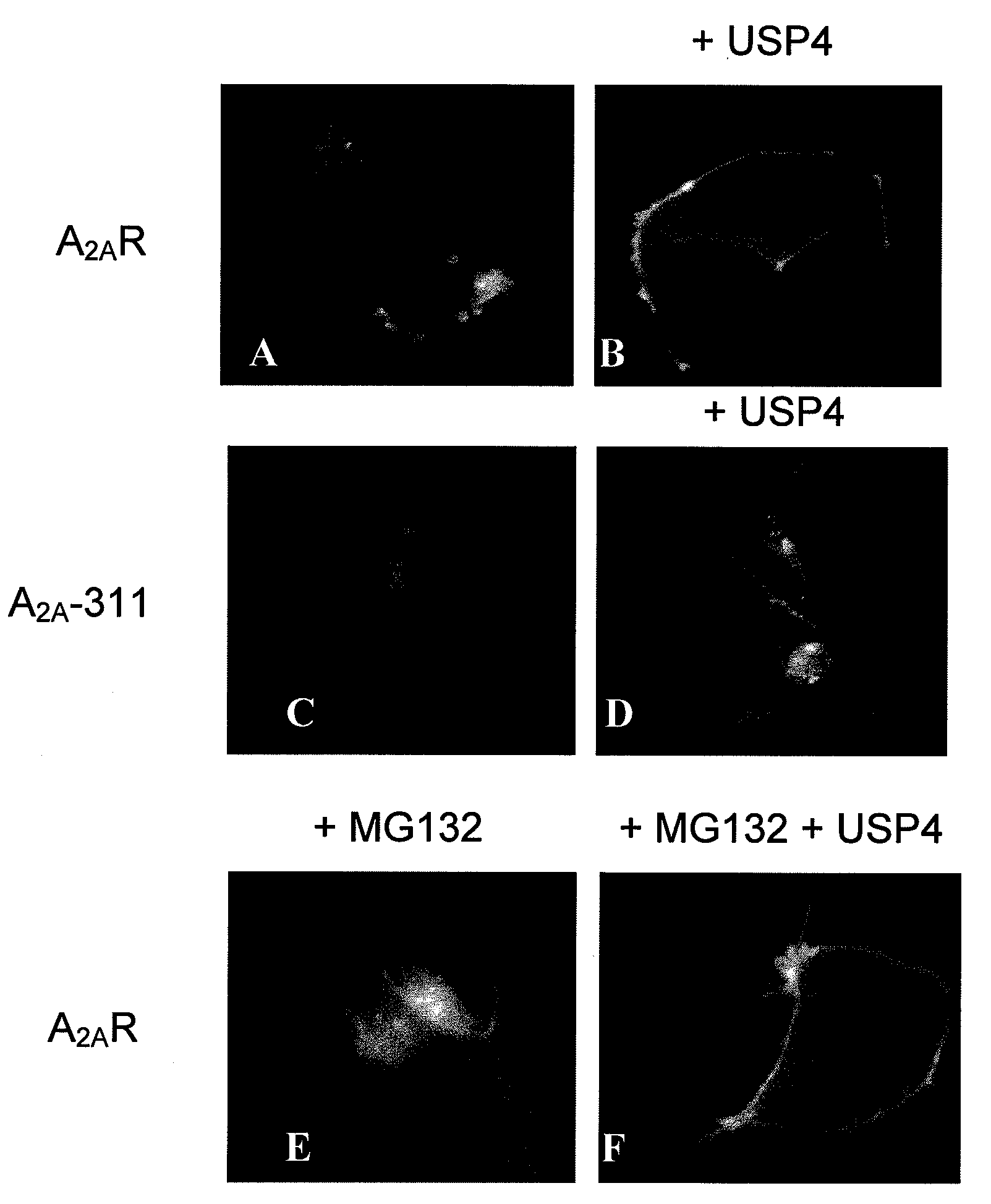
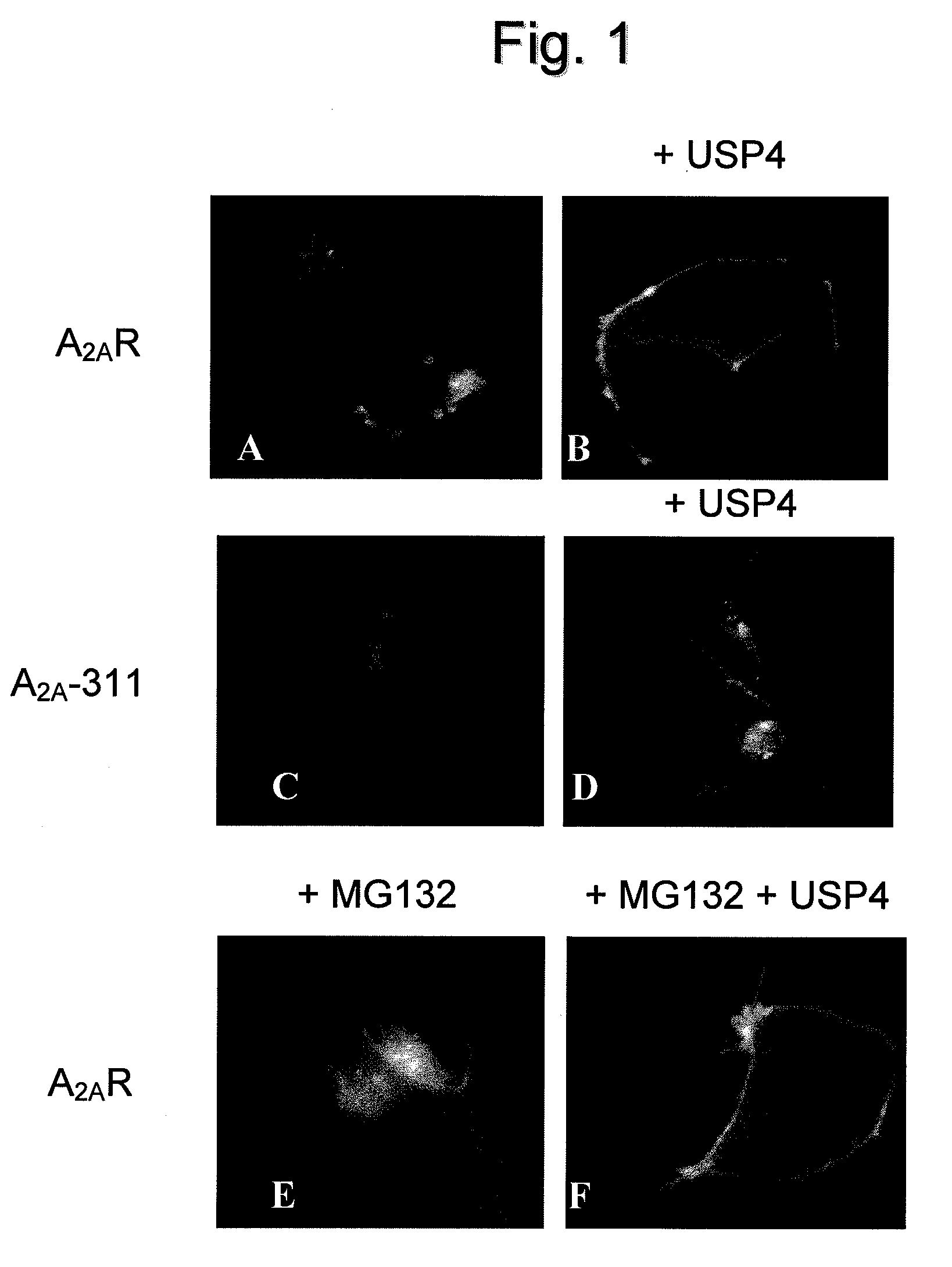
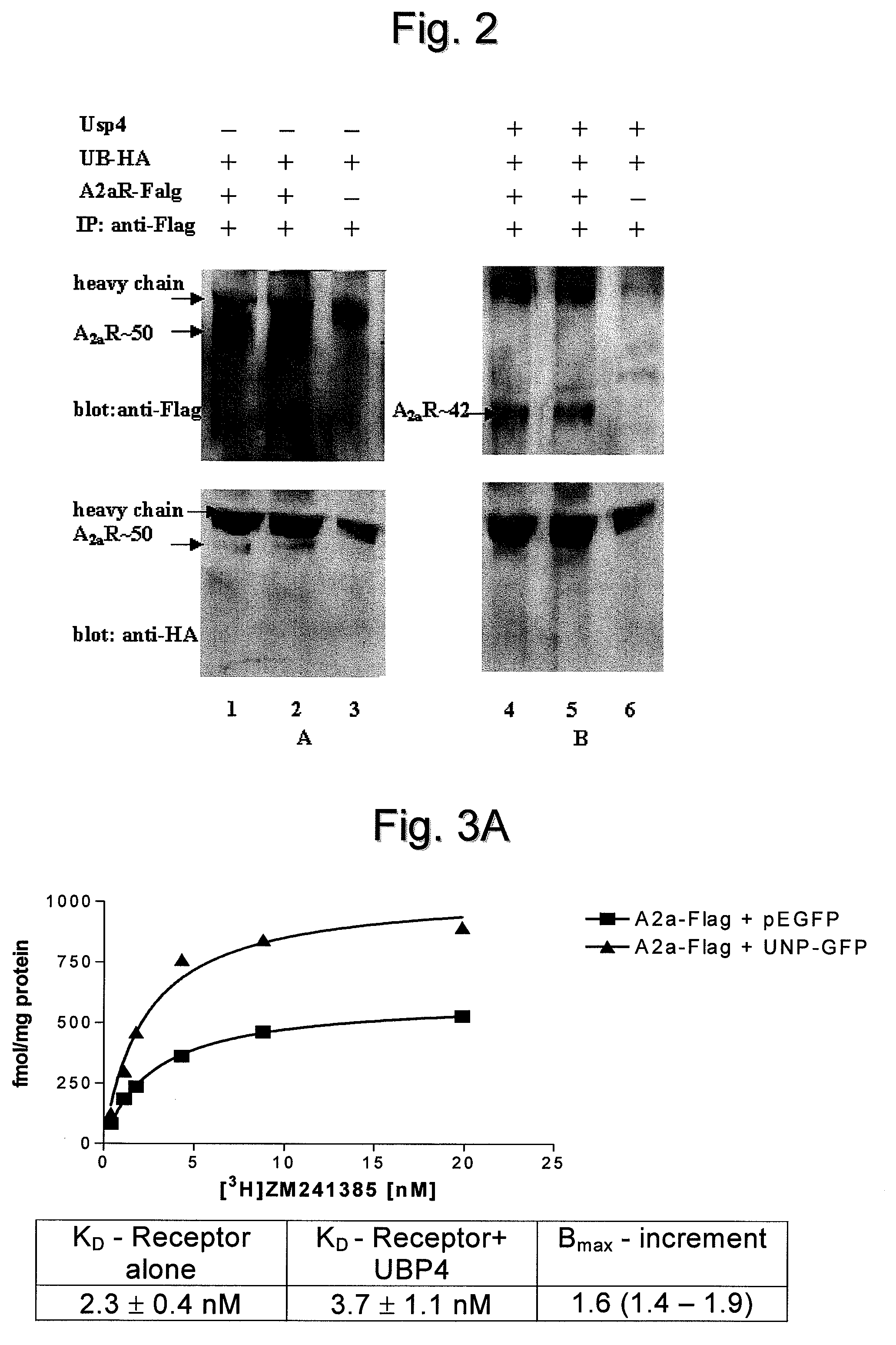
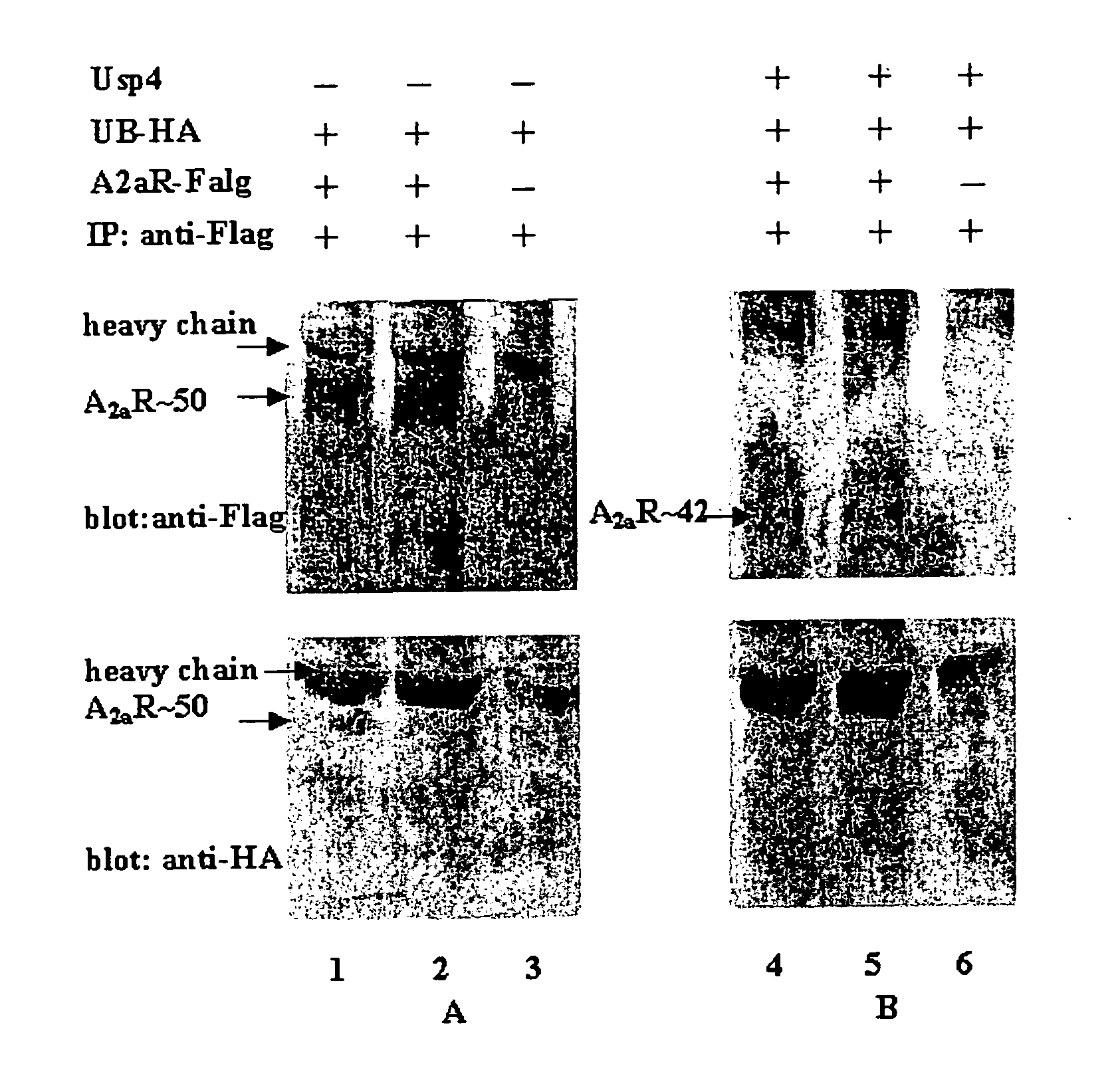
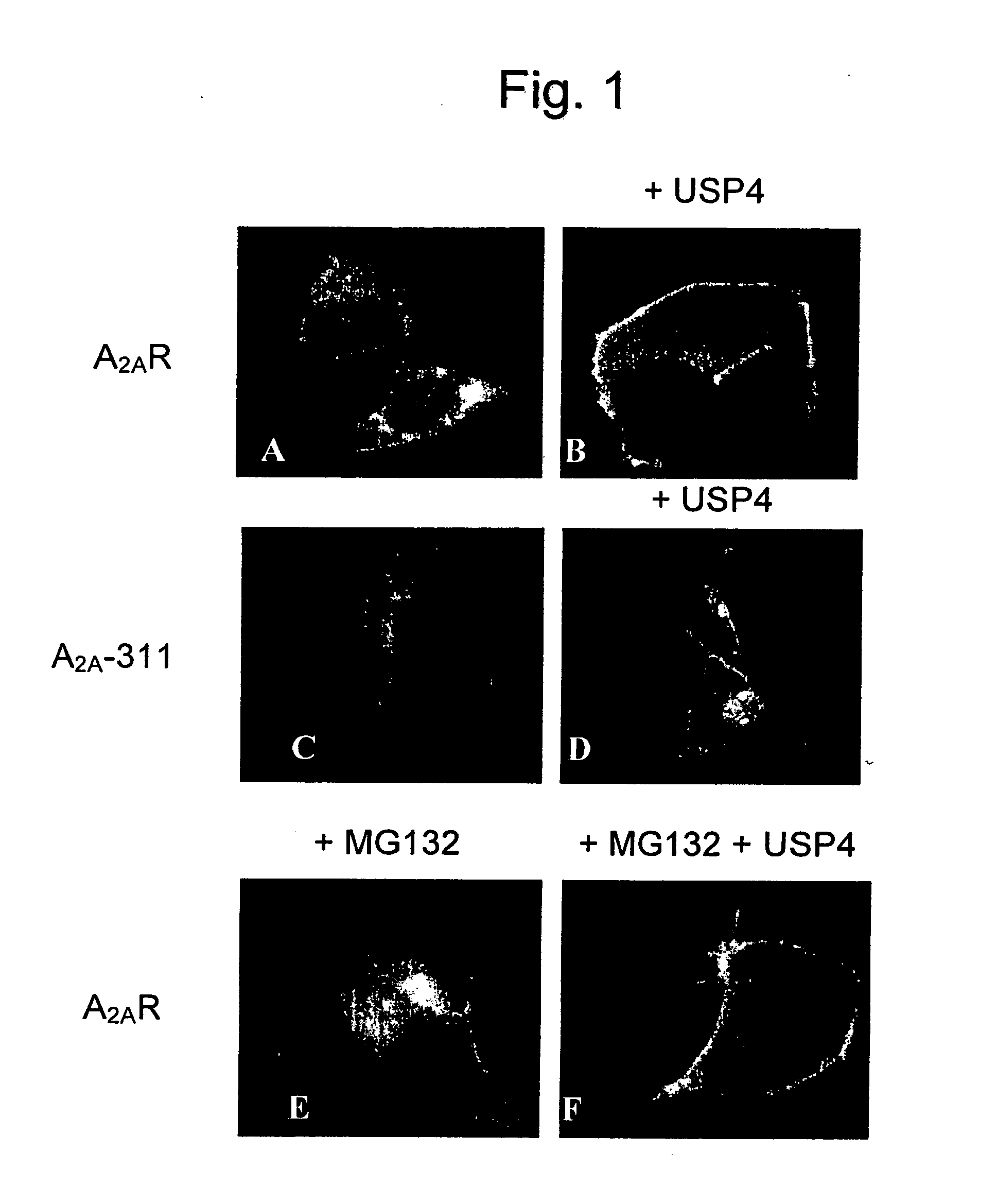
Use of a compound for enhancing the expression of membrane proteins on the cell surface
InactiveUS20070218043A1High expressionLower Level RequirementsSugar derivativesMetabolism disorderMedicineIntegral membrane protein
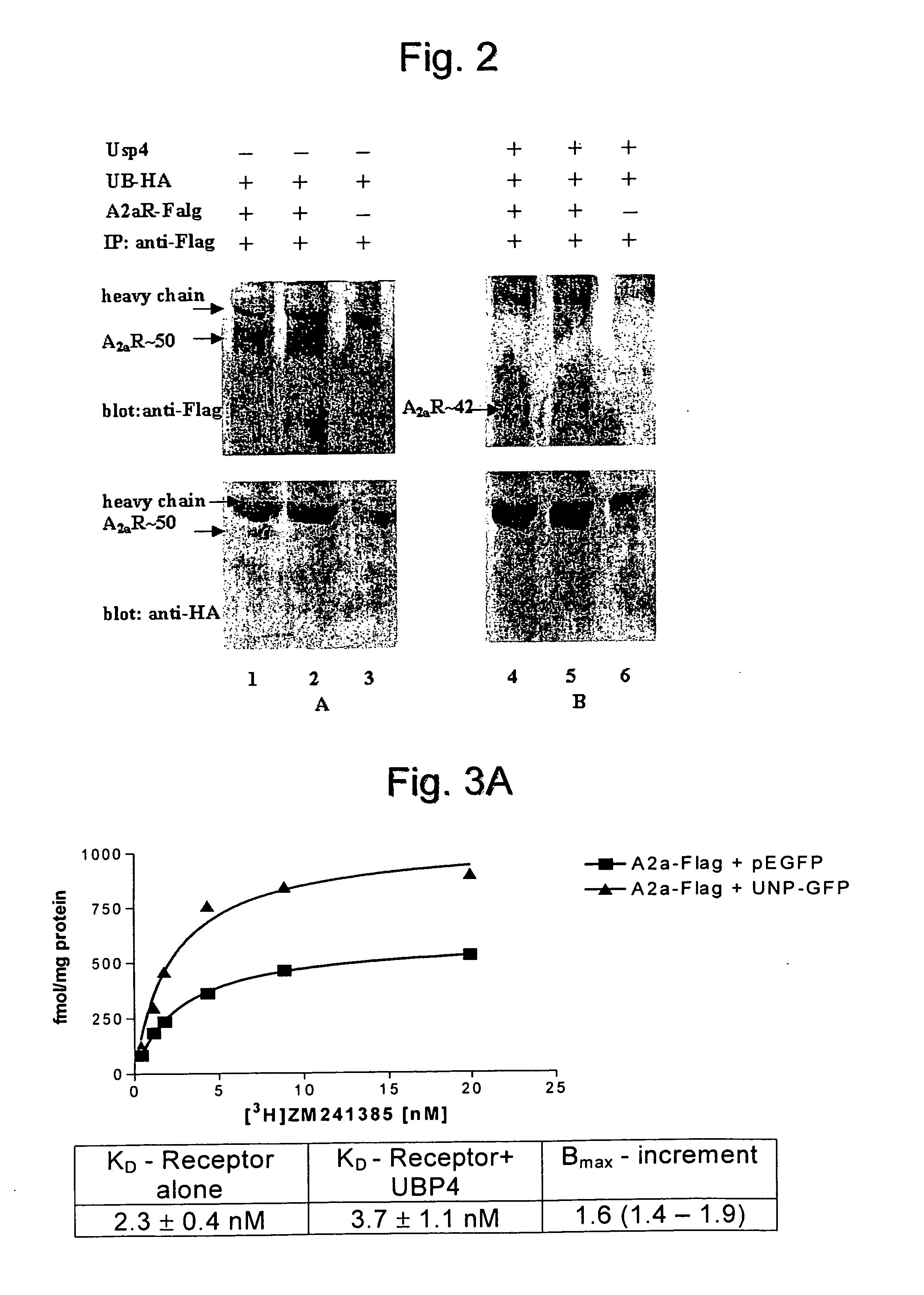
The present invention is directed to the use of a compound stimulating deubiquitinating activity in a cell for the manufacture of a medicament for enhancing the expression of integral membrane proteins on the cell surface. Especially, the invention is directed to the use of such compound for the manufacture of a medicament for the treatment of a disease of condition selected from the group consisting of cystic fibrosis, diabetes insipidus, hypercholesterinaemia and long QT-syndrome-2.
Owner:AXENTIS PHARMA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com