Extraction of integral membrane proteins
A protein and diafiltration technology, applied in the preparation methods of peptides, microorganism-based methods, peptides, etc., can solve the problems that centrifugation is not suitable for large-scale protein extraction and troublesome.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
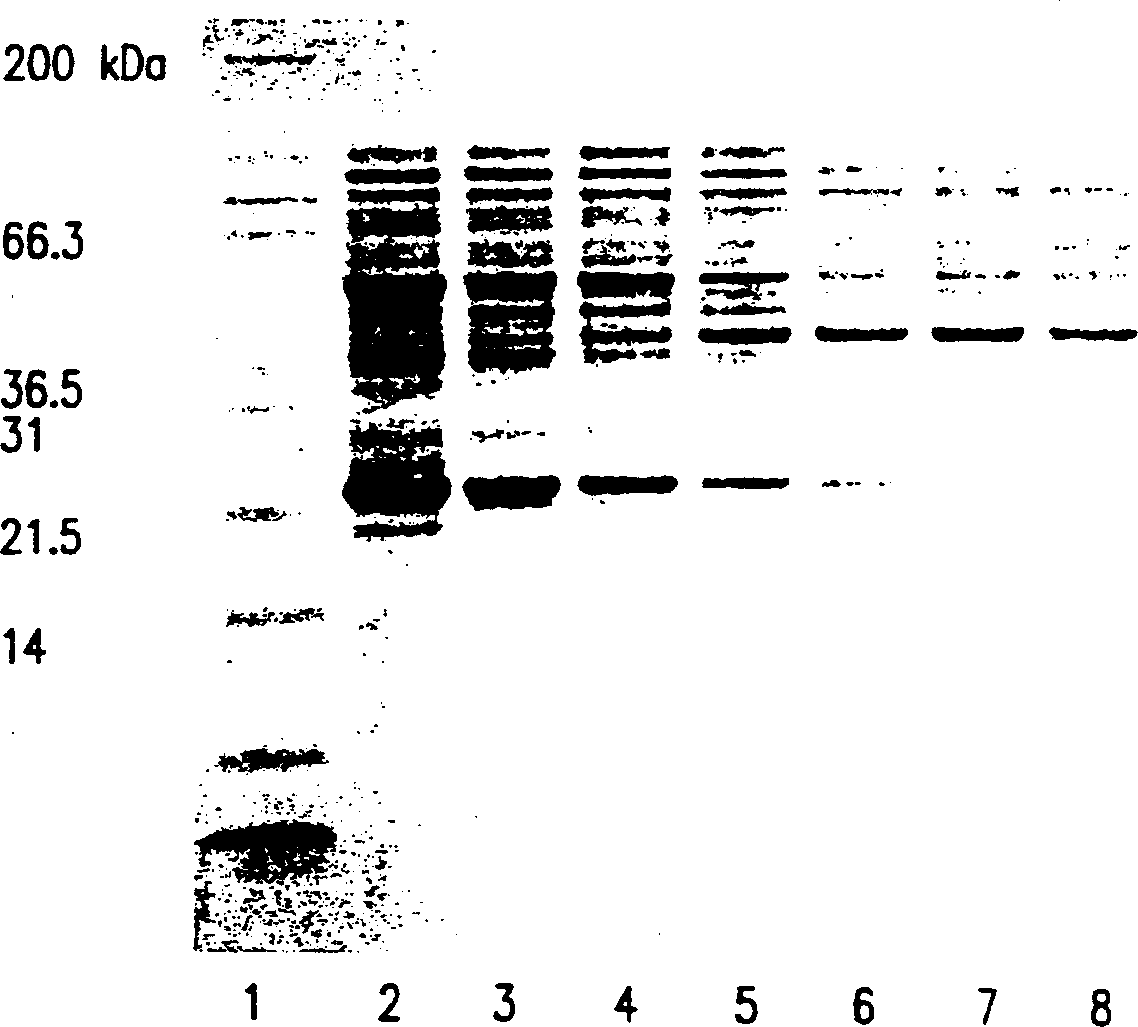
[0129] Membrane extraction of lipidated rP4 with different detergents
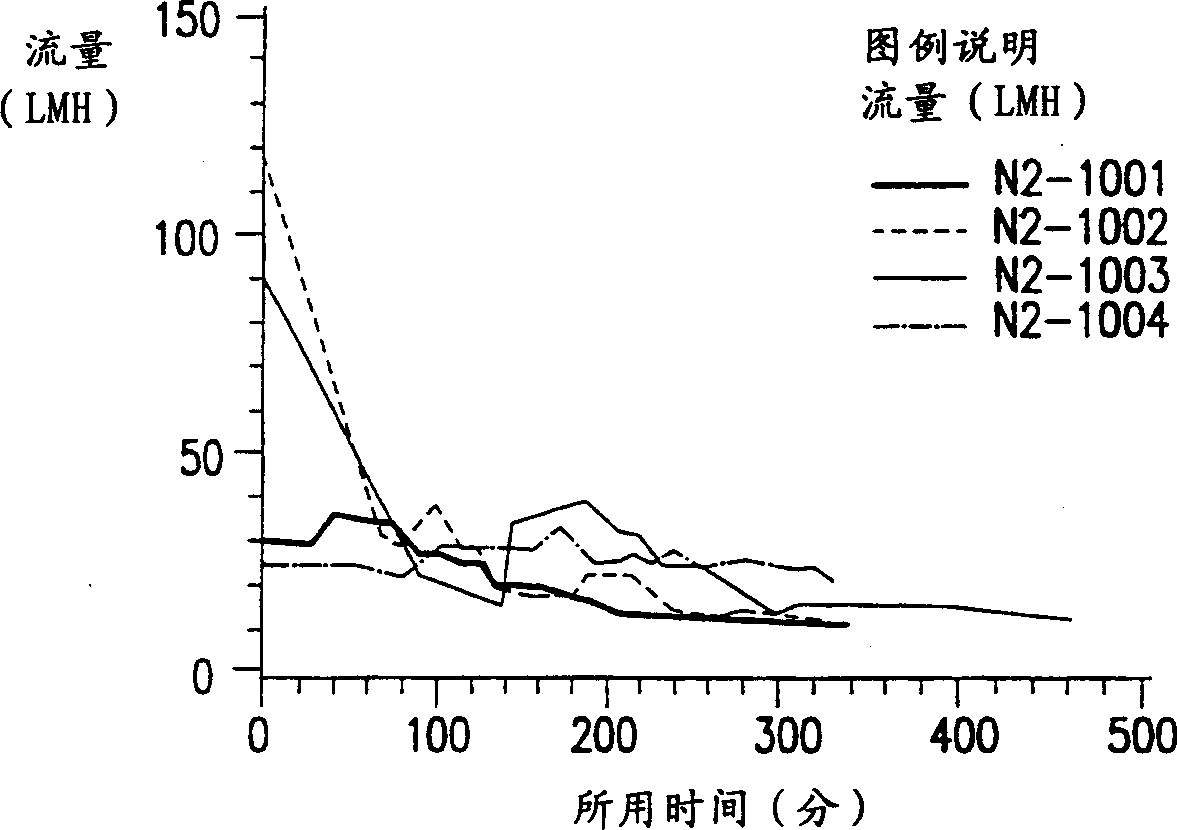
[0130] The overall process of extraction of lipidated rP4 from bacterial cells (such as E. coli cells) involves microfluidization or cell lysis and membrane extraction with different detergents. The fermentation broth was collected and 5mM EDTA was added to inhibit protein degradation caused by possible metalloproteases. The culture solution was then diluted to below 5% (w / v) cell wet weight concentration and lysed with a high-pressure microfluidizer (Microfluidics, Newton, MA). Use includes a surface area of 0.002m 2 1000KD regenerated cellulose Millipore membrane tangential flow system per g wet weight of cells, adding buffers in a specific order to diafilter lysed cells. The order of buffer addition was chosen to solubilize inner membrane proteins first, followed by outer membrane proteins including rP4. During diafiltration, appropriately sized soluble proteins that are smaller than th...
Embodiment 2
[0144] Another Extraction Method of Lipidated rP4
[0145] This example presents the data obtained by other four extraction methods of lipidated rP4. In each operation, 5 mM EDTA was first added to the recombinant E. coli fermentation broth to inhibit possible protein degradation by metalloproteases. Then the wet cell concentration of the fermentation medium was adjusted to 10%, and lysed by Microfluidics microfluidizer. This cell lysate was then divided into aliquots containing 500 g of cells and frozen at -70°C.
[0146] Remove a 500-gram aliquot of the lysed E. coli fermentation broth at -70°C and thaw it in a water bath whose temperature does not exceed 40°C. The cell lysate was then diluted to 5% wet weight of cells. The 5% cell lysate was then extracted with different detergents as described in Example 1 using tangential flow diafiltration. There is only a slight difference in step (4), where diafiltration was done 2 times instead of 3 times.
[01...
Embodiment 3
[0156] Membrane extraction of lipidated rP6 with different detergents
[0157] The method for extracting lipidated rP6 is similar to the method for extracting lipidated rP4. However, the diafiltration process requires more steps because lipidated rP6 is tightly bound to peptidoglycan. The fermentation broth of E. coli cells expressing lipidated rP6 was treated with 10 mM EDTA and then diluted to below 10% cell wet weight / volume before homogenization. Cells were then lysed using a high-pressure microfluidizer and sequentially diafiltered with buffers at room temperature using a flow-through membrane filtration device. It was determined that the minimum membrane area that allows the transport of effective mass of dissolved protein across the membrane is approximately 0.002m 2 / g cell wet weight. Soluble proteins with a size smaller than the 1000KD molecular weight cut-off of the membrane pass through the membrane with the permeate, while larger molecules and insolubl...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com