Treatment method of sample for membrane protein analysis identification
A processing method and membrane protein technology, applied in the field of membrane proteomics research, can solve the problems of troublesome operation, difficult to obtain good results, and the ability to extract membrane proteins is not as good as SDS.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
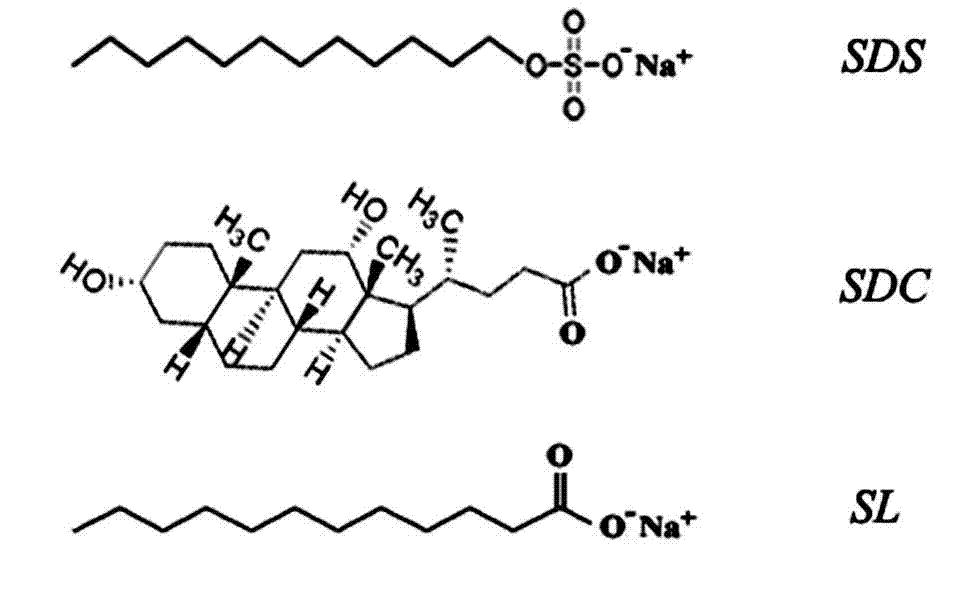
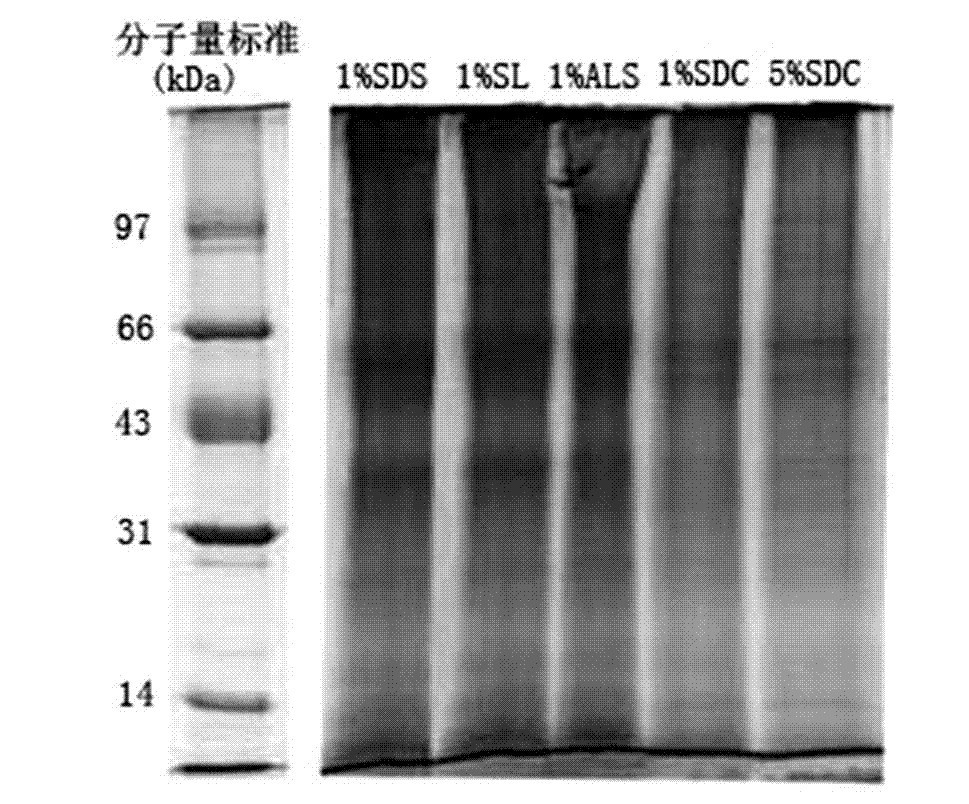
[0021]Example 1 A standard protein mixture consisting of 5 μg each of myoglobin, bacteriorhodopsin and bovine serum albumin. Among them, myoglobin, bacteriorhodopsin and bovine serum albumin are the representatives of refractory protein, hydrophobic multi-transmembrane protein and soluble protein respectively. Dissolve the above standard protein mixture in 50 mM NH containing 1.0% (mass percentage concentration, the same below) SL 4 HCO 3 Solution (diluted to 0.1% SL before enzymatic hydrolysis), then enzymatic hydrolysis, acidification, extraction and removal of lauric acid precipitated after acidification, and then freeze-drying in vacuum to obtain analytical samples, which are used for liquid chromatography-tandem Identification by mass spectrometry. In addition, the above standard protein mixture was dissolved in 50mM NH 4 HCO 3 (pH 7.8) solution, 50 mM NH containing 1.0% ALS 4 HCO 3 solution (diluted to 0.1% ALS before enzymatic digestion) and 50 mM NH with 1% SDC ...
Embodiment 2
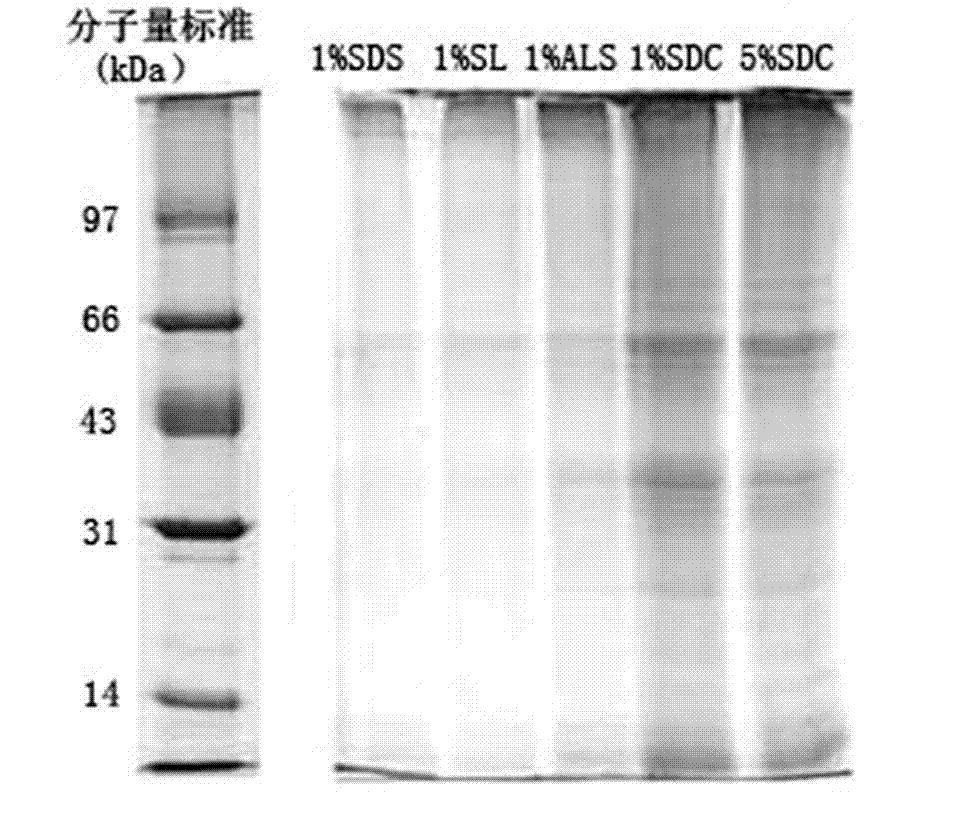
[0026] Example 2 The rat liver cell membrane sample (containing 20 μg membrane protein) enriched by differential centrifugation and sucrose density gradient centrifugation was dissolved in 50 mM NH containing 1.0% SL 4 HCO 3 Solution (dilute to SL concentration of 0.1% before enzymatic hydrolysis). Proteins were reduced in 5 mM dithiothreitol for 60 minutes and then reacted in 25 mM iodoacetamide for 45 minutes in the dark. After enzymatic hydrolysis and acidification, the lauric acid precipitated after acidification was extracted and removed, and then freeze-dried in a vacuum to obtain a sample for analysis. The samples for analysis were used for analysis and identification by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. In addition, the same rat liver cell membrane samples as above were dissolved in 50mM NH containing 1.0% ALS 4 HCO 3 solution (ALS concentration diluted to 0.1% before enzymatic digestion) and 50mM NH containing 1% SDC 4 HCO 3 Solution, enzymatic hy...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com