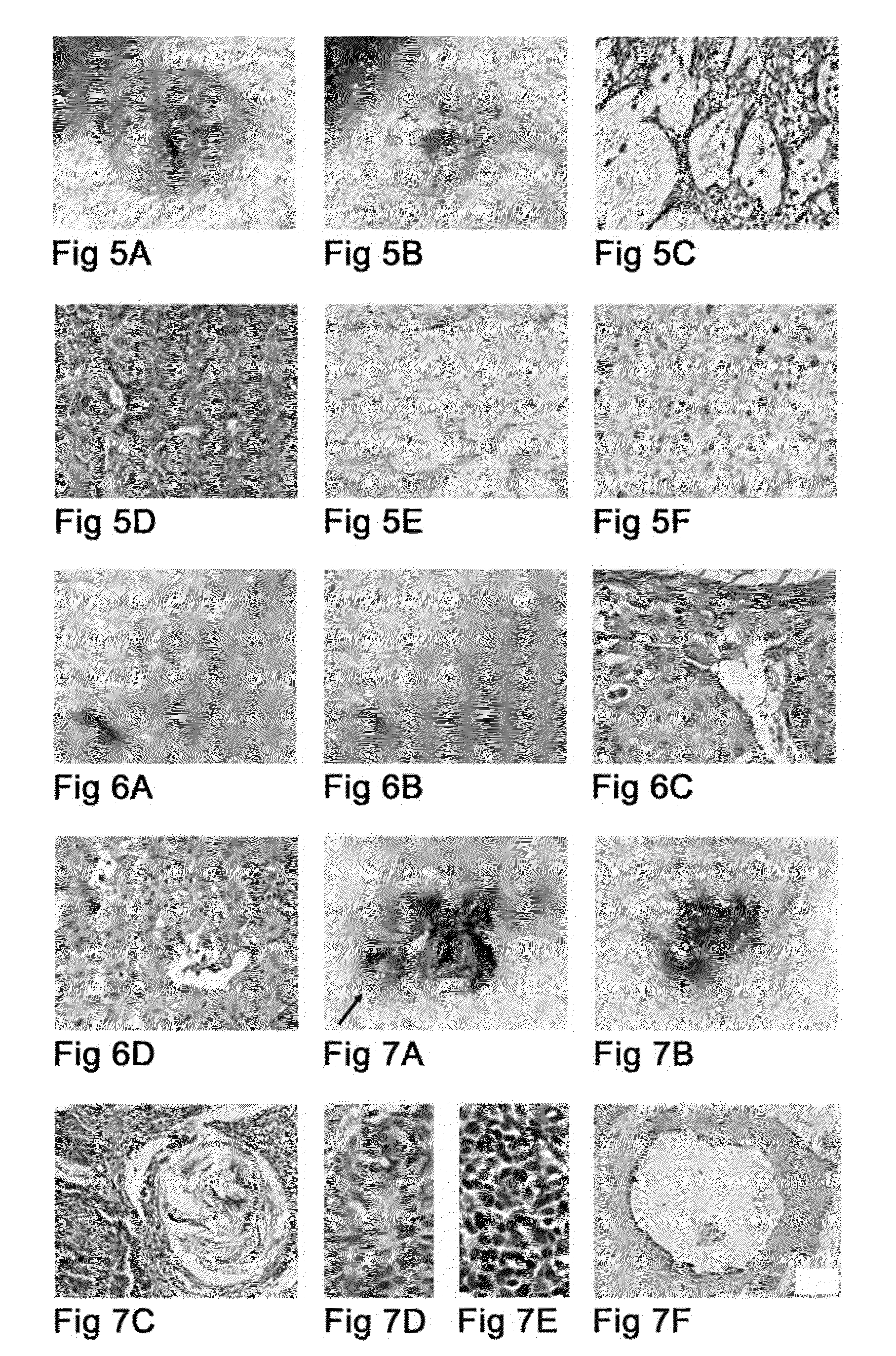
Patents
Literature
154 results about "Undifferentiated cell" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
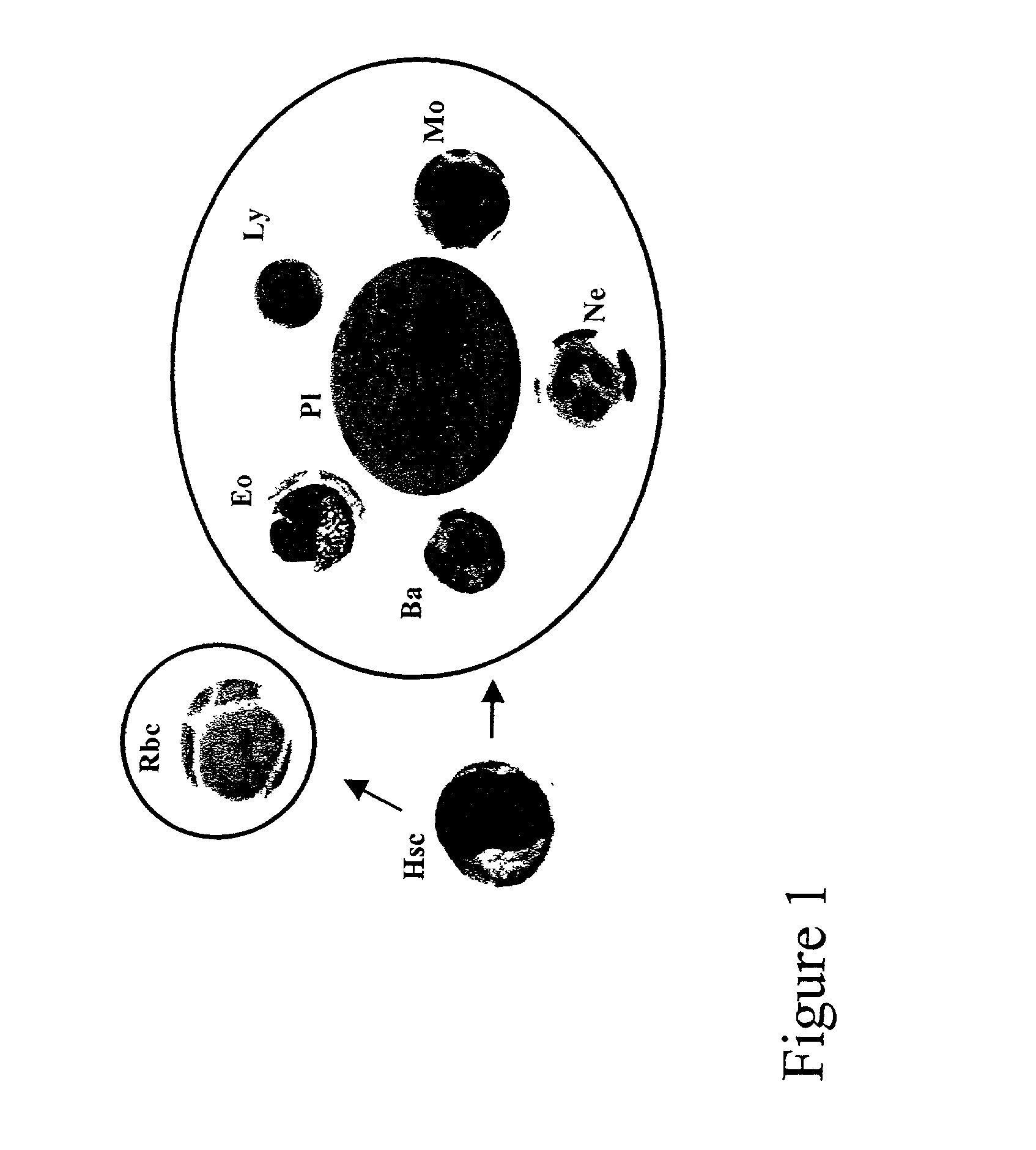
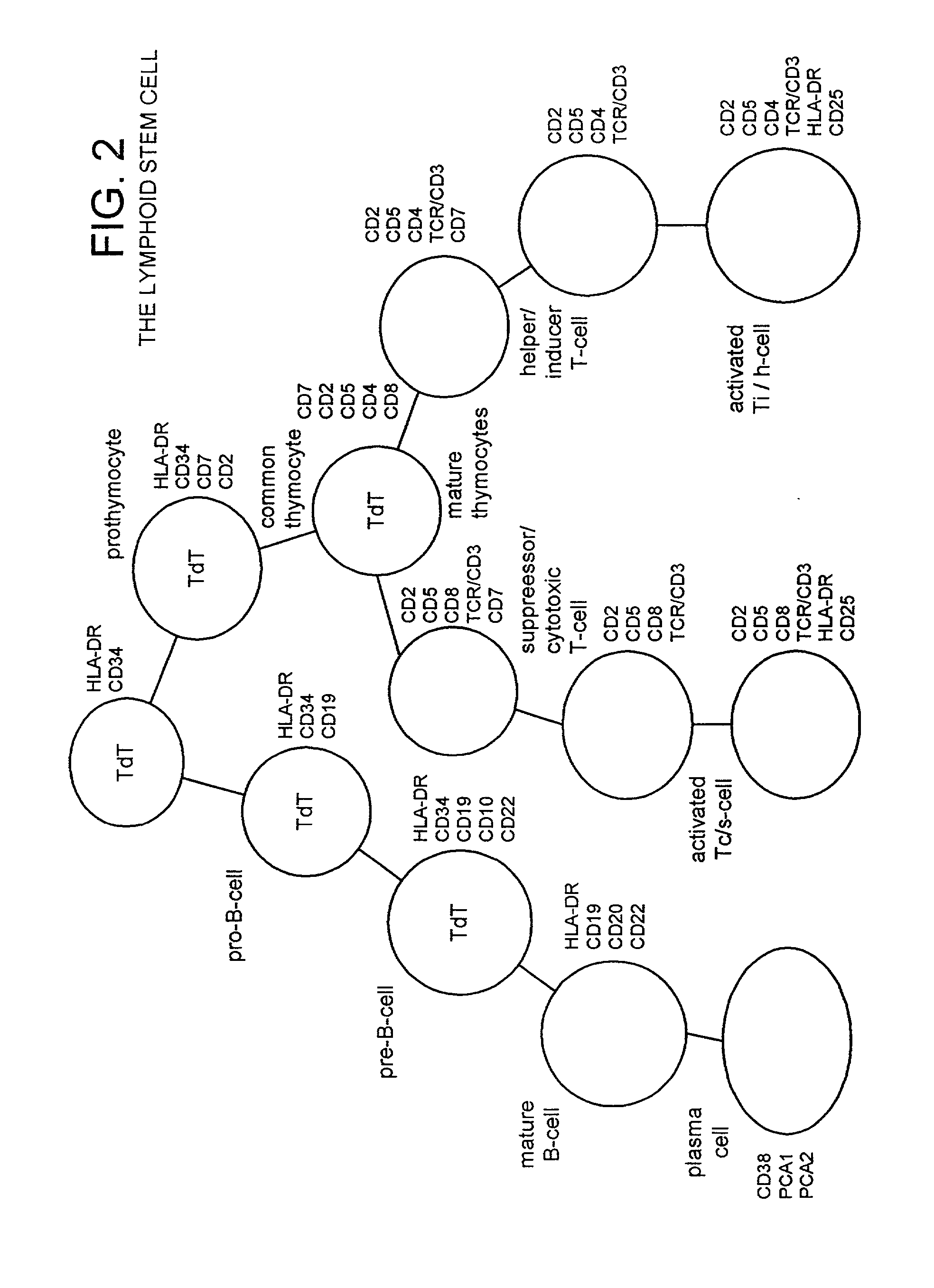
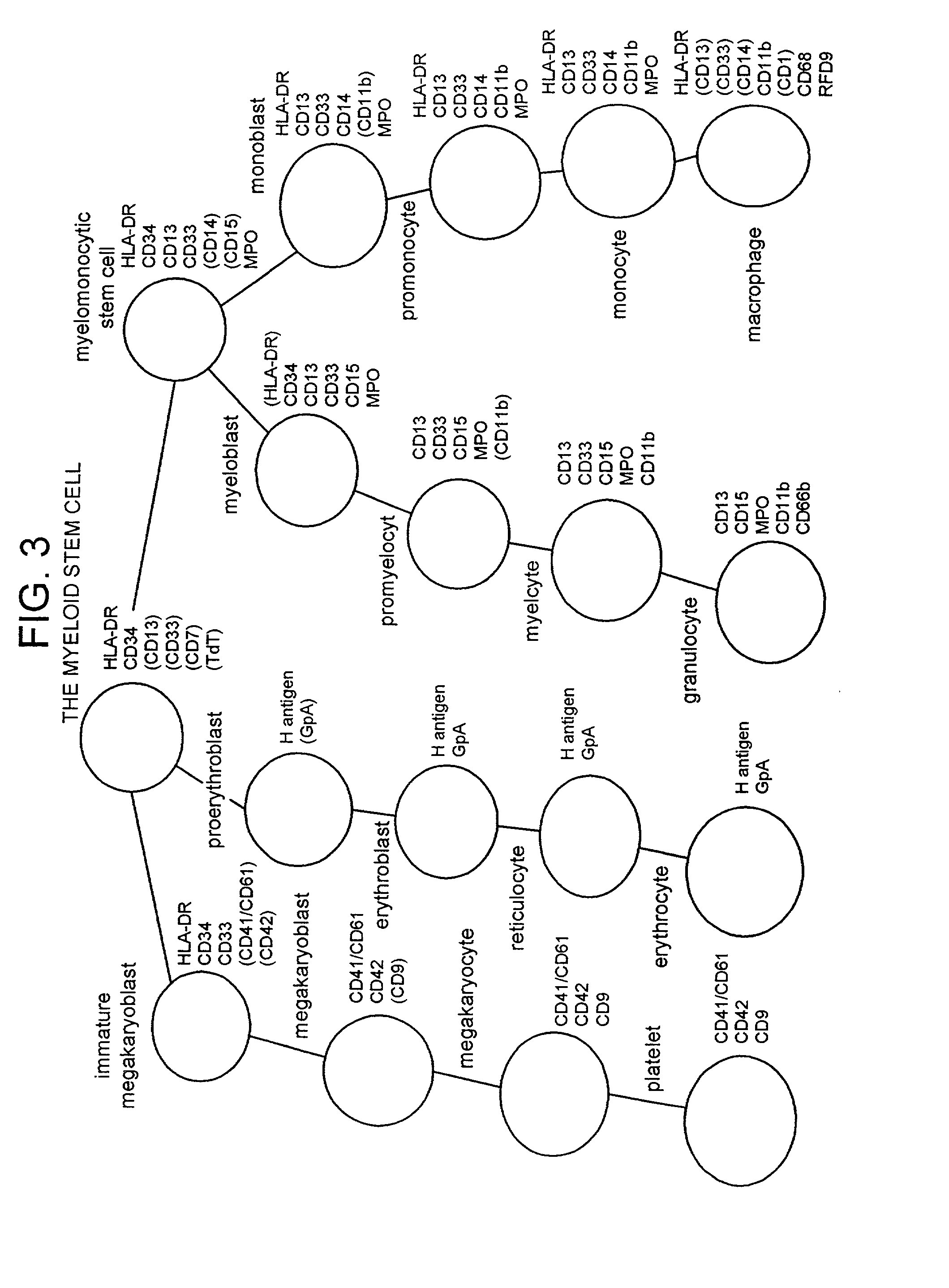
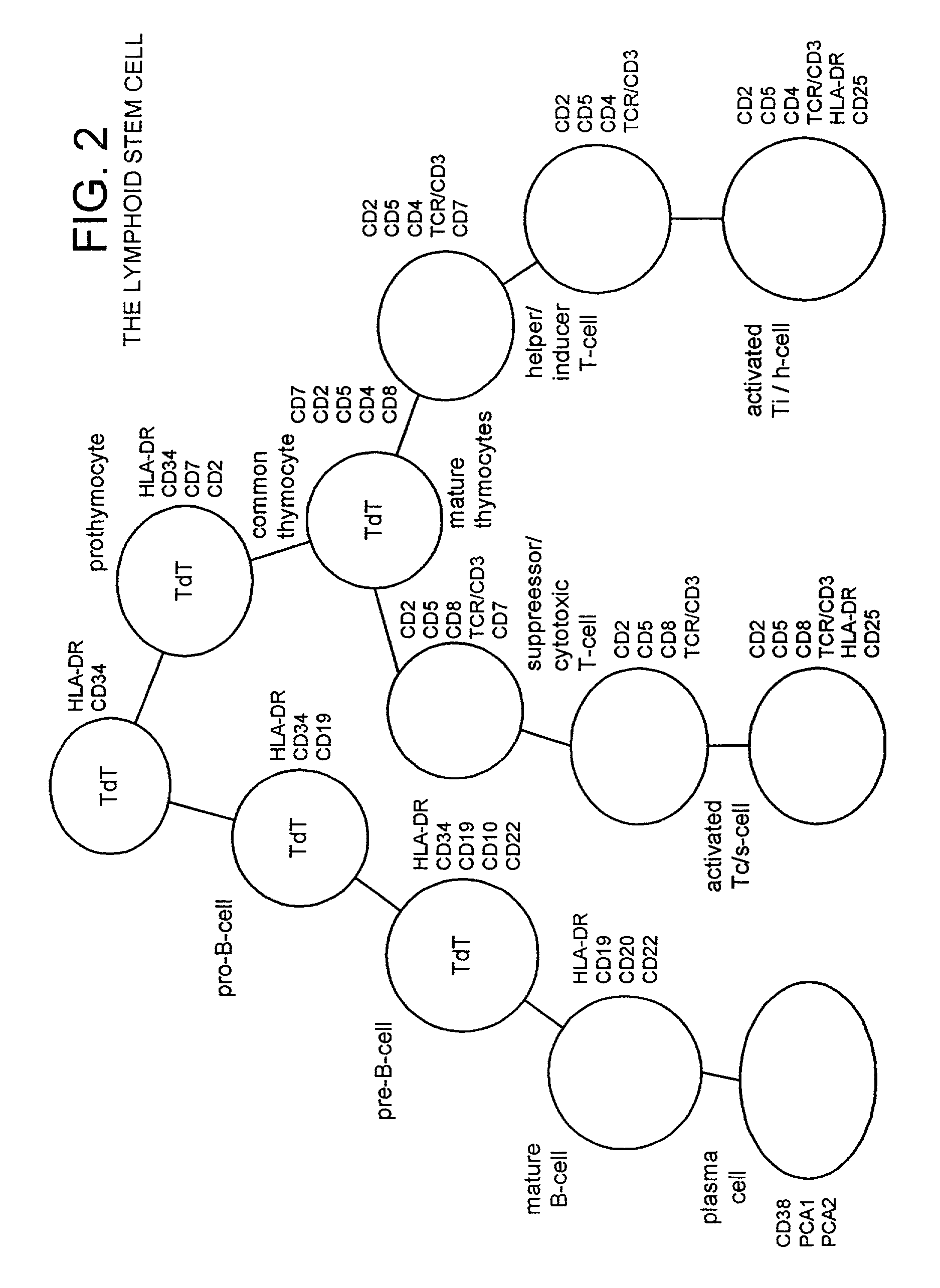
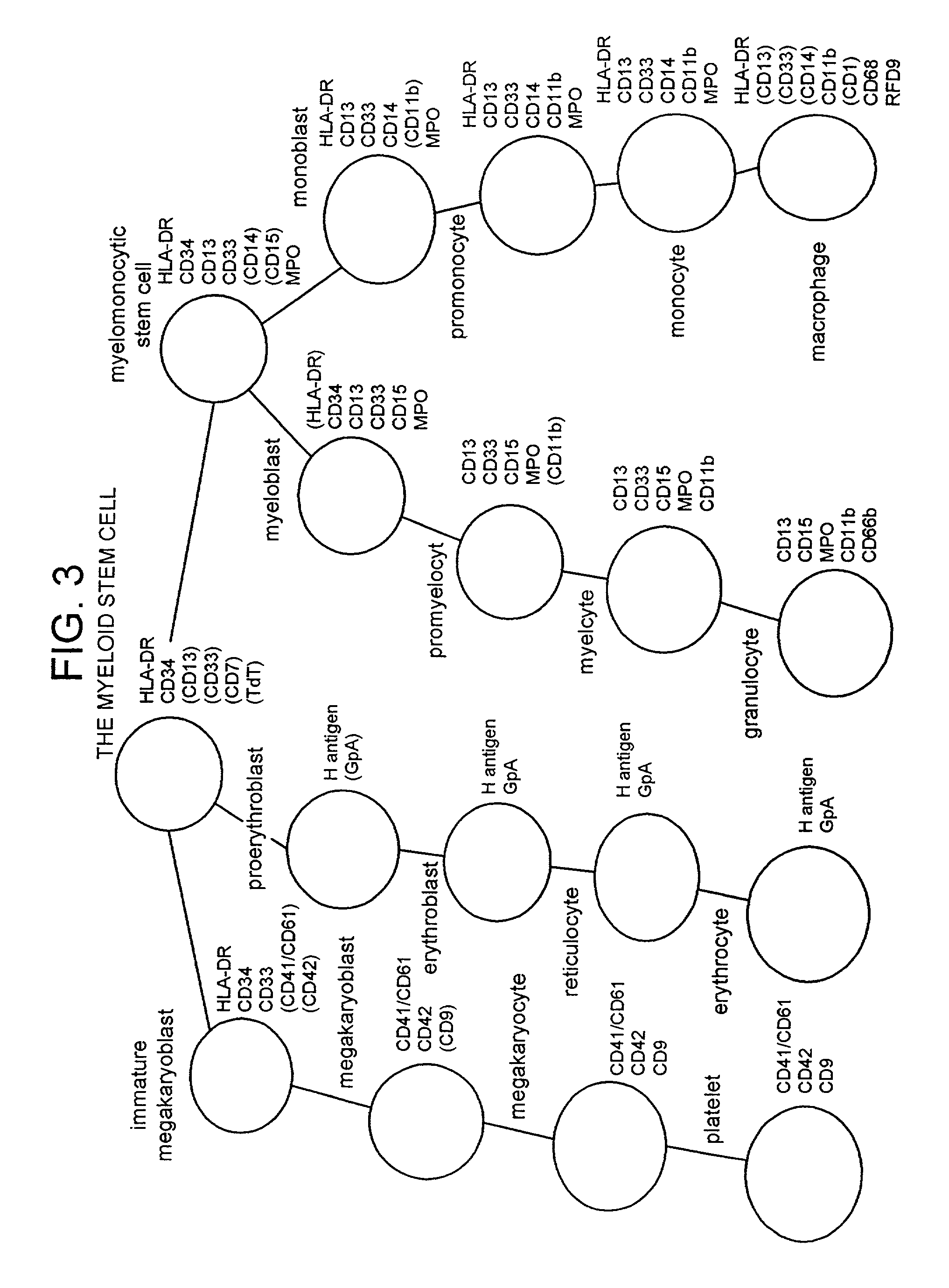
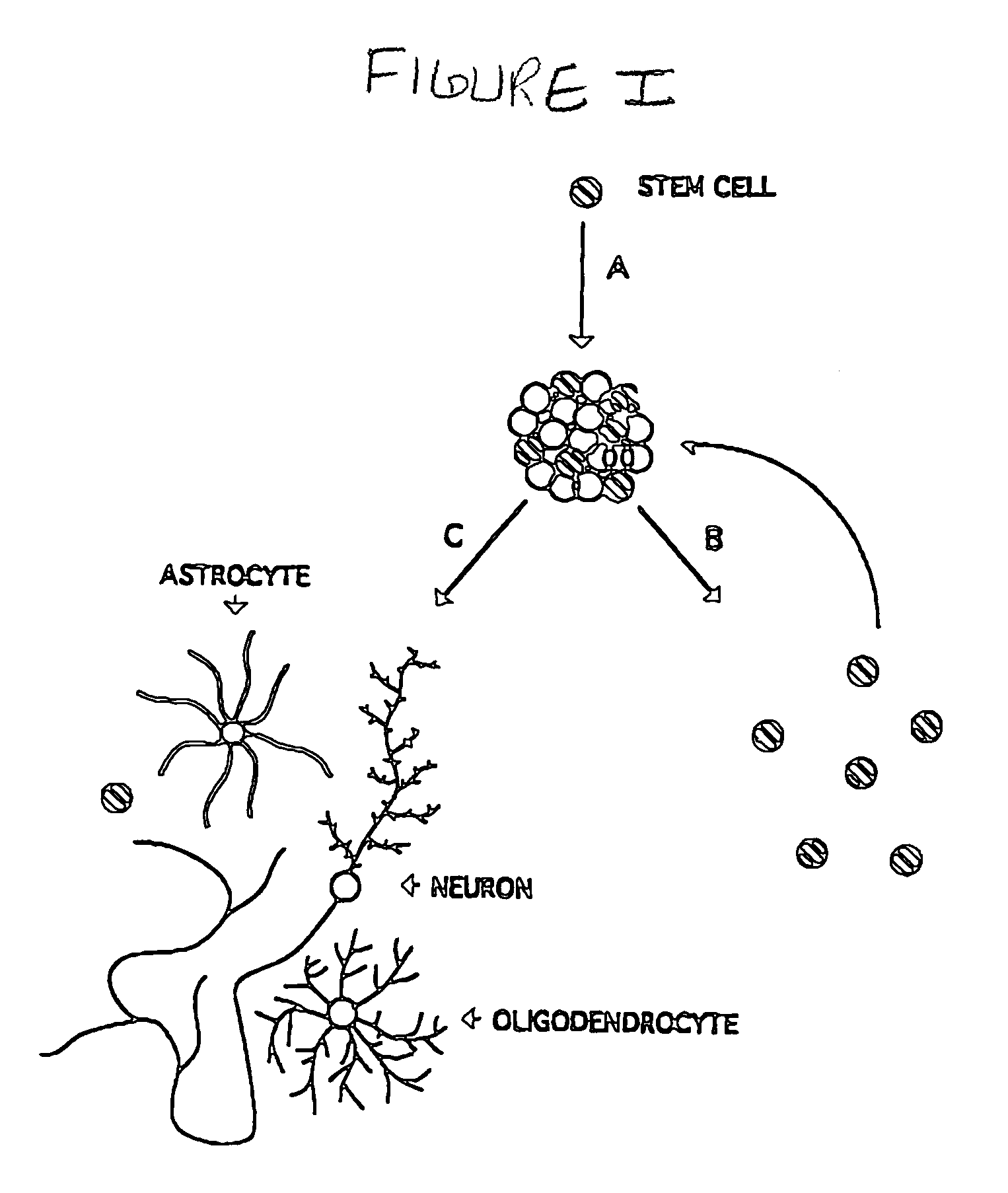
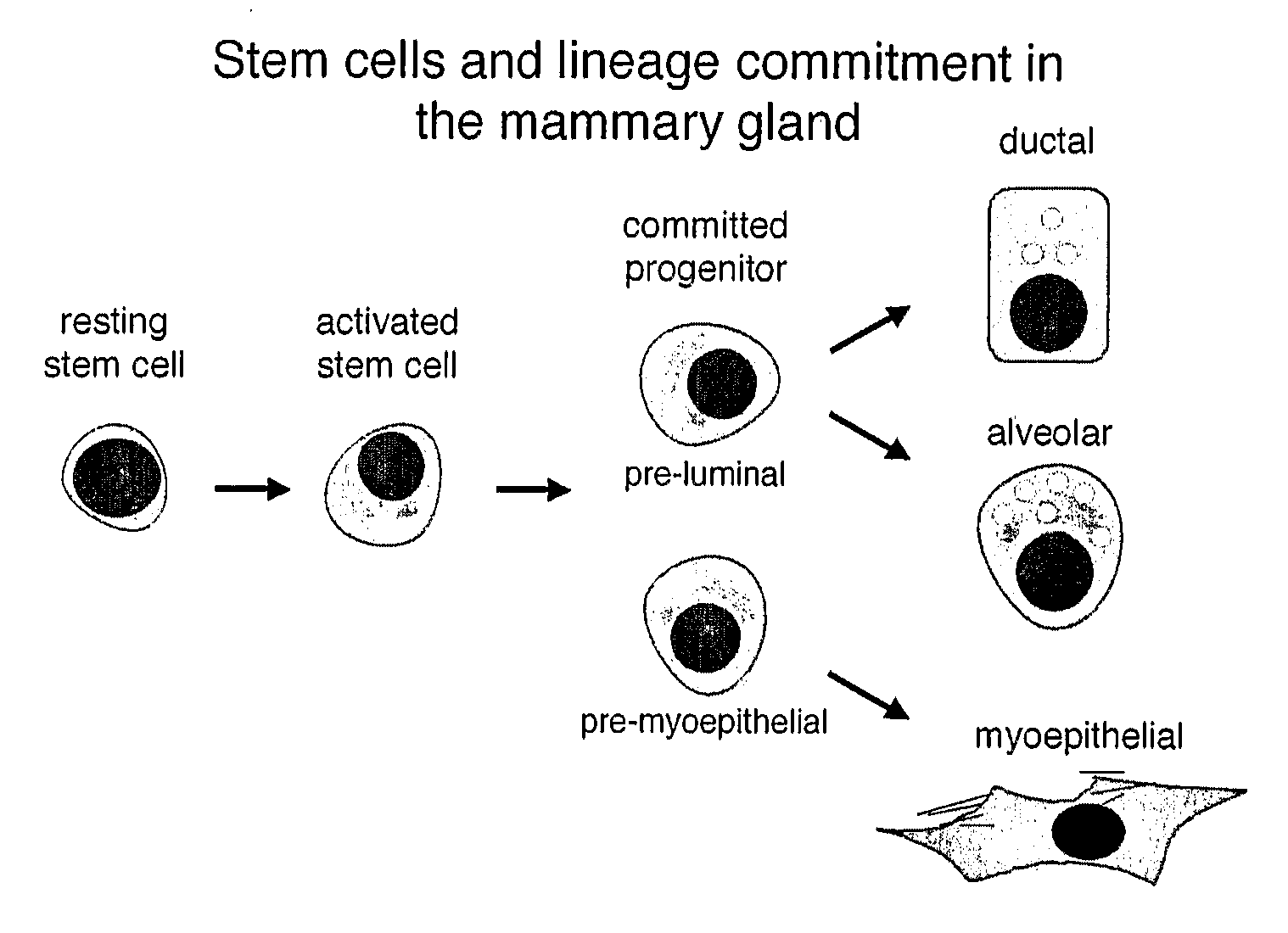
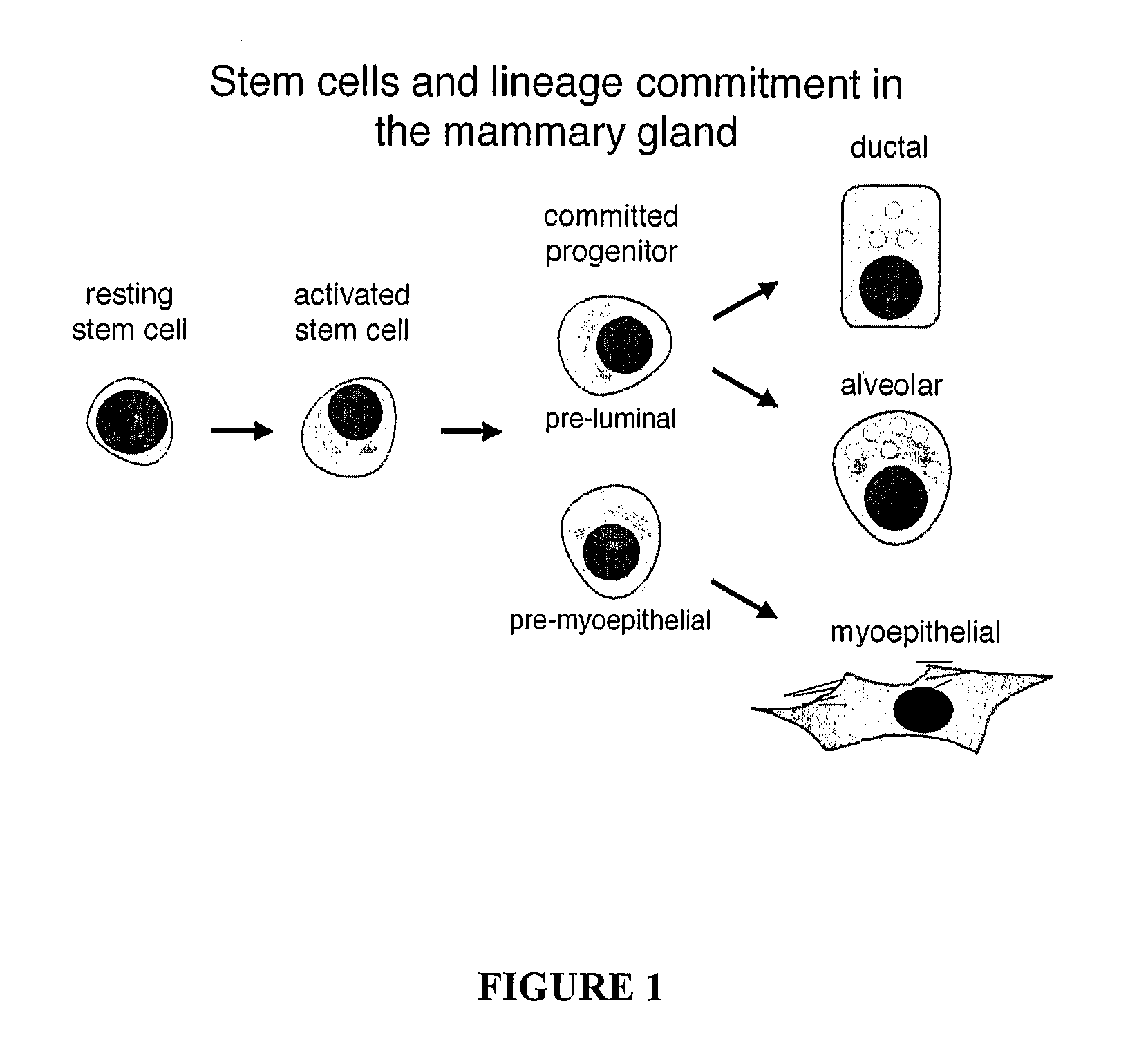
Undifferentiated cells are a type of immature cells found in the body of multicellular organisms. They are also known as stem cells. The two main characteristic features of undifferentiated cells are their ability to self-renew while differentiating into specialized cells.
Compositions and methods for augmentation or repair of intervertebral discs
InactiveUS20050118228A1Enhance the imageGood treatment effectBiocideBone implantStem Cell IsolationIntervertebral disc
A method of augmenting and / or repairing an intervertebral disc by administering stem cell material into the disc. The stem cells may be undifferentiated cells, or they may be cells that have differentiated and have subsequently been dedifferentiated. The stem cells may be induced to express at least one characteristic of human intervertebral disc cells, such as fibroblast cells, chondrocyte cells, or notochordal cells, by exposing them to agents and / or environments calculated to induce the desired differentiation. In some embodiments, the stem cell material may be provided in conjunction with a collagen-based material, which may be a collagen-rich lattice or particles of collagen material. The stem cell material may be provided as a stem cell isolate, which may be substantially free of non-stem cell material. Other therapeutic agents may be administered with the stem cell material.
Owner:SDGI HLDG
Methods for culturing human embryonic stem cells
InactiveUS20050158852A1Improve breeding conditionsImprove survival rateGenetically modified cellsArtificial cell constructsCell-Extracellular MatrixIn vitro growth
The present invention discloses a method for improving growth and survival of single human embryonic stem cells. The method includes the step of obtaining a single undifferentiated HES cell; mixing the single undifferentiated cell with an extracellular matrix (ECM) to encompass the cell; and inoculating the mixture onto feeder cells with a nutrient medium in a growth environment. Therefore the single cells can survive, proliferate and grow in vitro.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
Method of preparing an undifferentiated cell
InactiveUS20030166272A1Increase the number ofReduce needGenetically modified cellsGenetic material ingredientsCell biologyUndifferentiated cell
A method of increasing the relative number of cells expressing one or more stem cell markers in a cell population including committed cells is described. The method comprises: i. contacting the cell population with an agent that operably engages said committed cells; and ii. incubating committed cells that are engaged by said agent such that the relative number of cells expressing one or more stem cell markers increases as a result of said engaging.
Owner:GHAZI JASWINDER DHOOT
Method of preparing an undifferentiated cell
InactiveUS7410773B2Increase the number ofGenetically modified cellsGenetic material ingredientsUndifferentiated cellStem cell marker
A method of increasing the relative number of cells expressing one or more stem cell markers in a cell population including committed cells is described. The method comprises: i. contacting the cell population with an agent that operably engages said committed cells; and ii. incubating committed cells that are engaged by said agent such that the relative number of cells expressing one or more stem cell markers increases as a result of said engaging.
Owner:GHAZI JASWINDER DHOOT
Use of cyclopamine in the treatment of basal cell carcinoma and other tumors
InactiveUS7893078B2Avoid problemsUseful or even desirableCosmetic preparationsBiocideApoptosisRadical radiotherapy
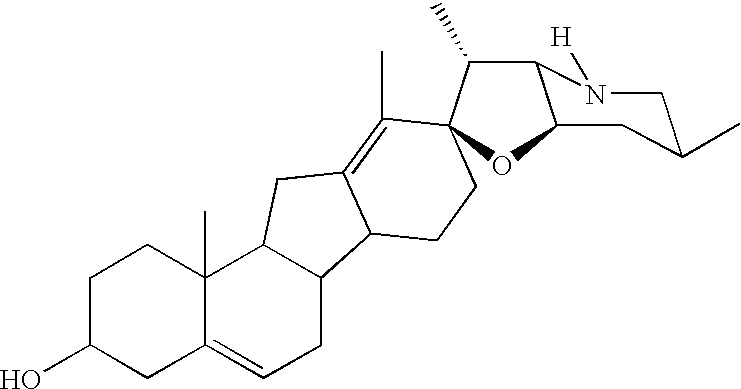
This invention concerns the use of cyclopamine in vivo on basal cell carcinomas (BCC's) to achieve therapeutic effect by causing differentiation of the tumor cells and, at the same time, apoptotic death and removal of these tumor cells while preserving the normal tissue cells, including the undifferentiated cells of the normal epidermal basal layer and hair follicles. Causation of apoptosis by cyclopamine is by a non-genotoxic mechanism and thus unlike the radiation therapy and most of the currently used cancer chemotherapeutics which act by causing DNA-damage. These novel effects, previously unachieved by a cancer chemotherapeutic, make the use of cyclopamine highly desirable in cancer therapy, in the treatment of BCC's and other tumors that use the hedgehog / smoothened signal transduction pathway for proliferation and prevention of apoptosis.
Owner:TAS SINAN
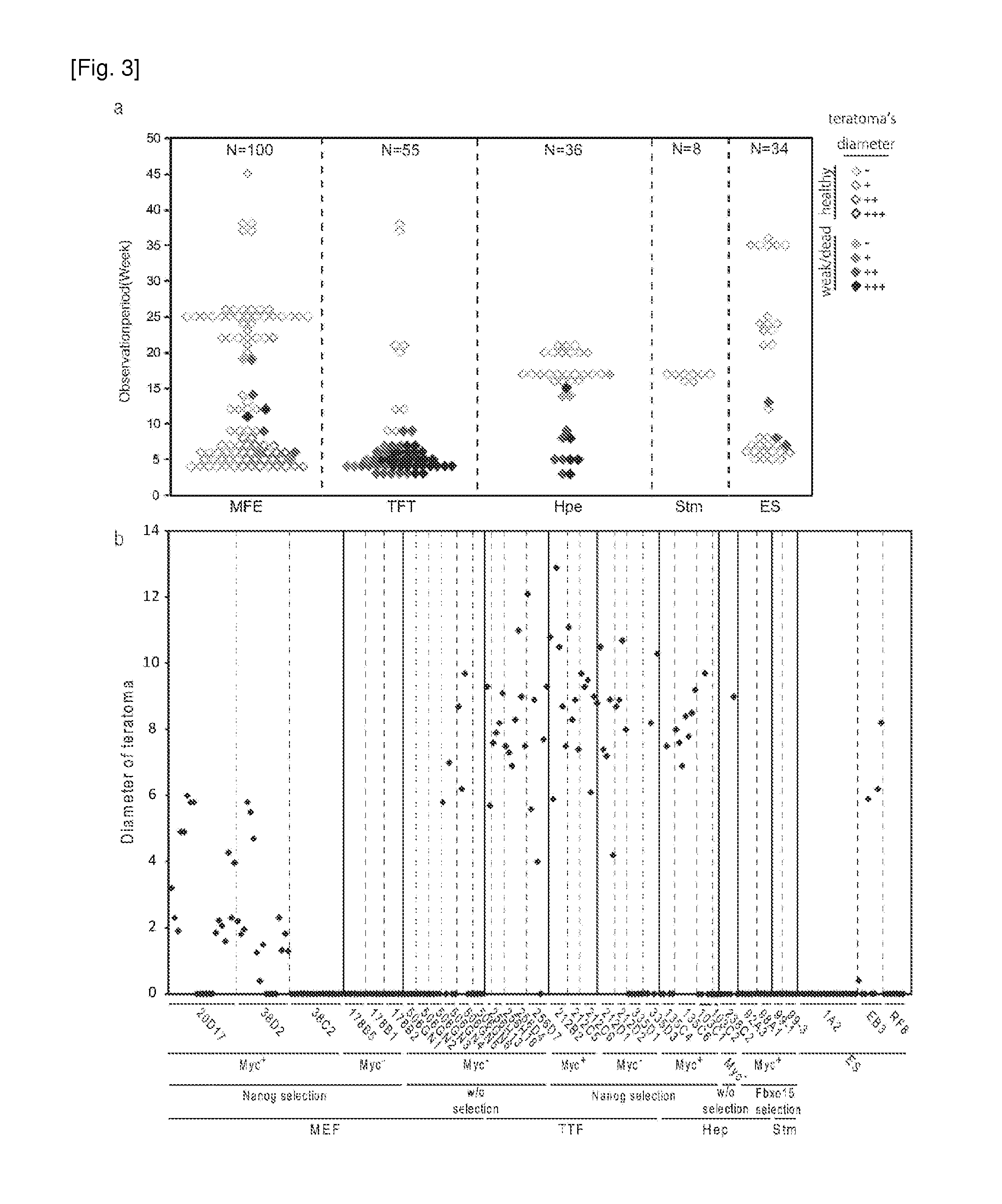
Method for selecting clone of induced pluripotent stem cells
InactiveUS20120129172A1Efficiently identifying and selectingImprove securityMicrobiological testing/measurementGenetically modified cellsIn vivoLiving body
To efficiently identify and select a clone from clones of induced pluripotent stem cells (iPS cell) having low tumor formation rate in vivo when allowed to differentiate and transplanted in a living body, iPS cells of the clones are induced to differentiate, undifferentiated cells among the cells after the induction of differentiation are detected, and a clone having the content of the undifferentiated cell below a control is selected.
Owner:KYOTO UNIV
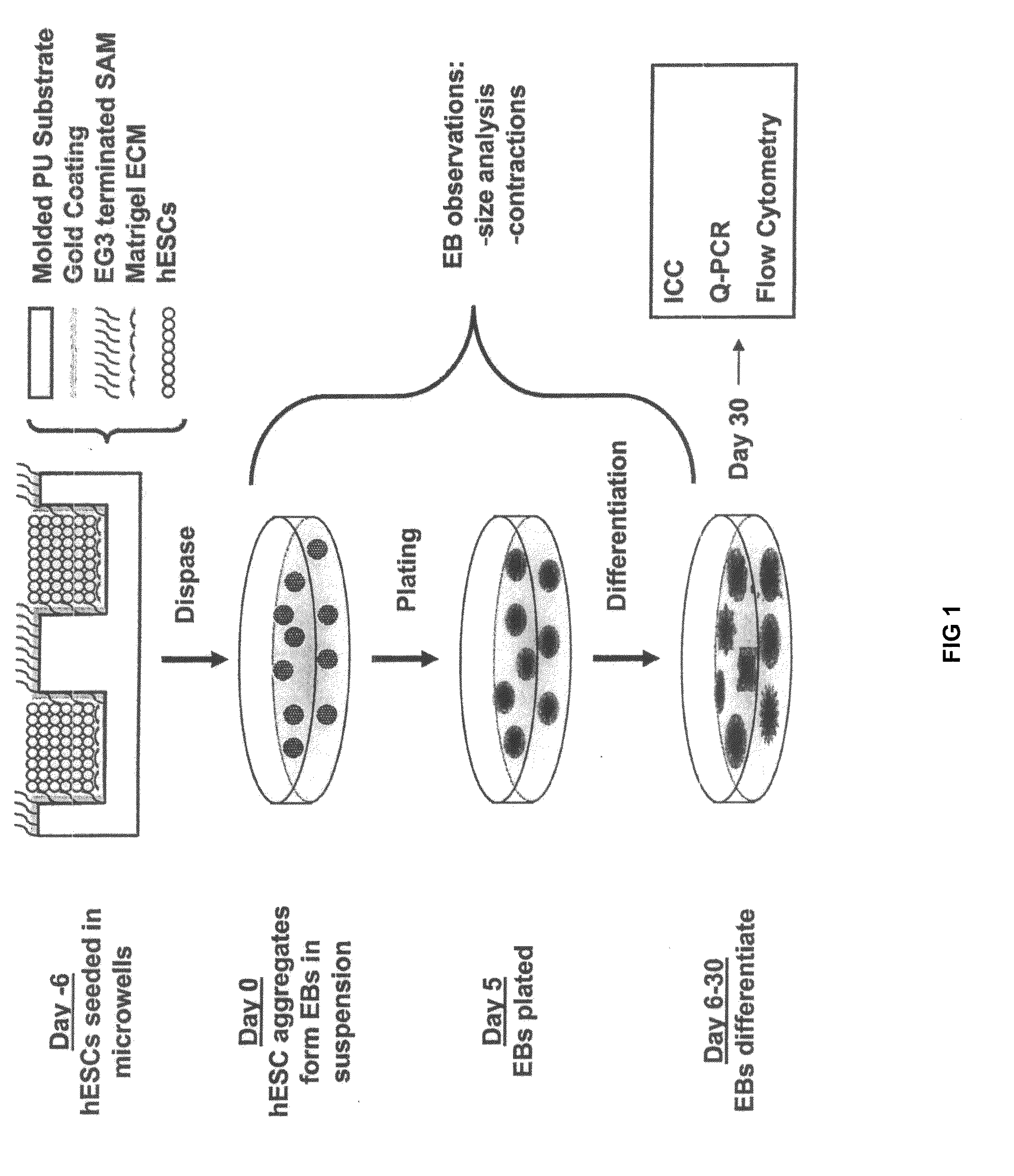
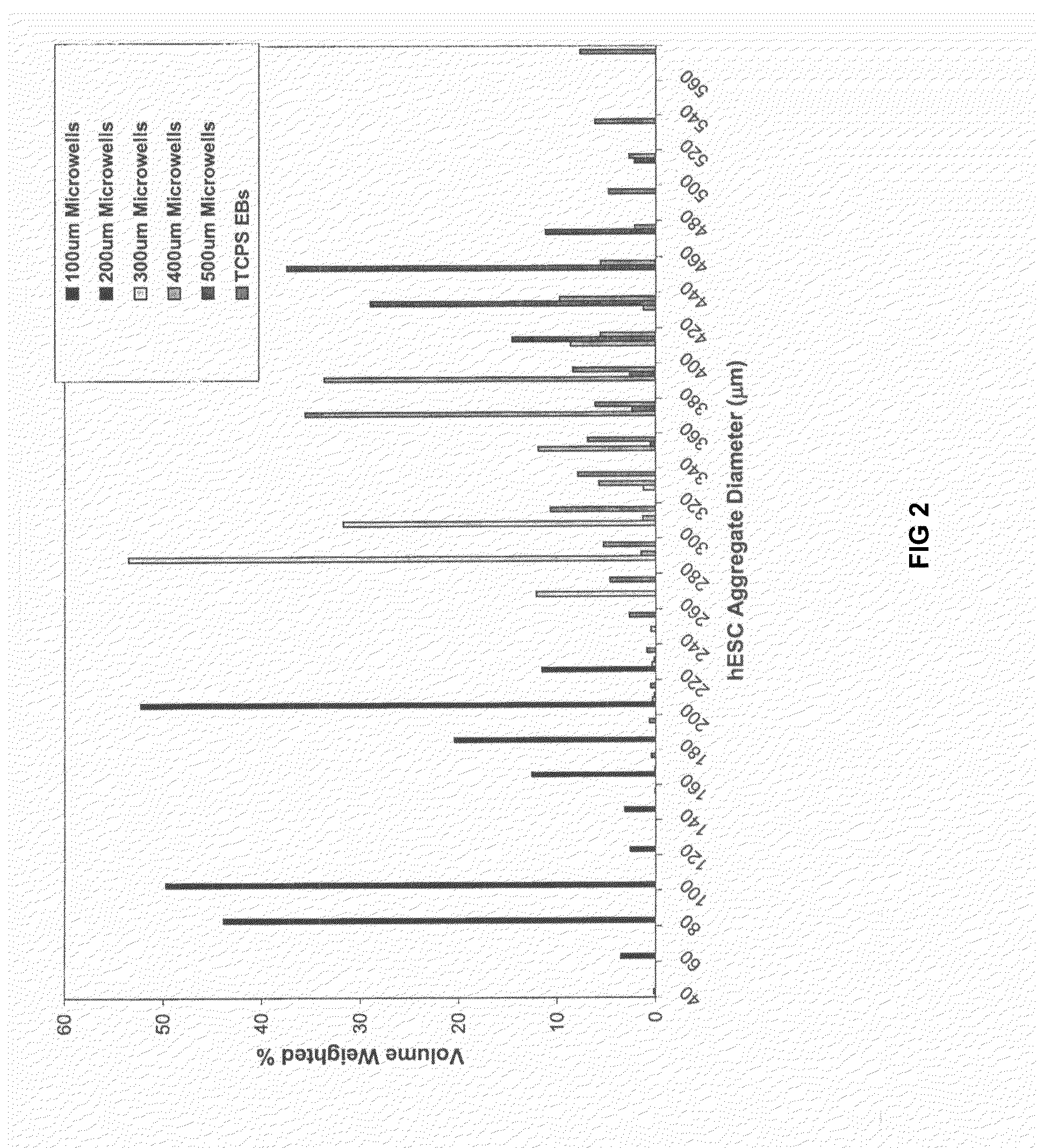
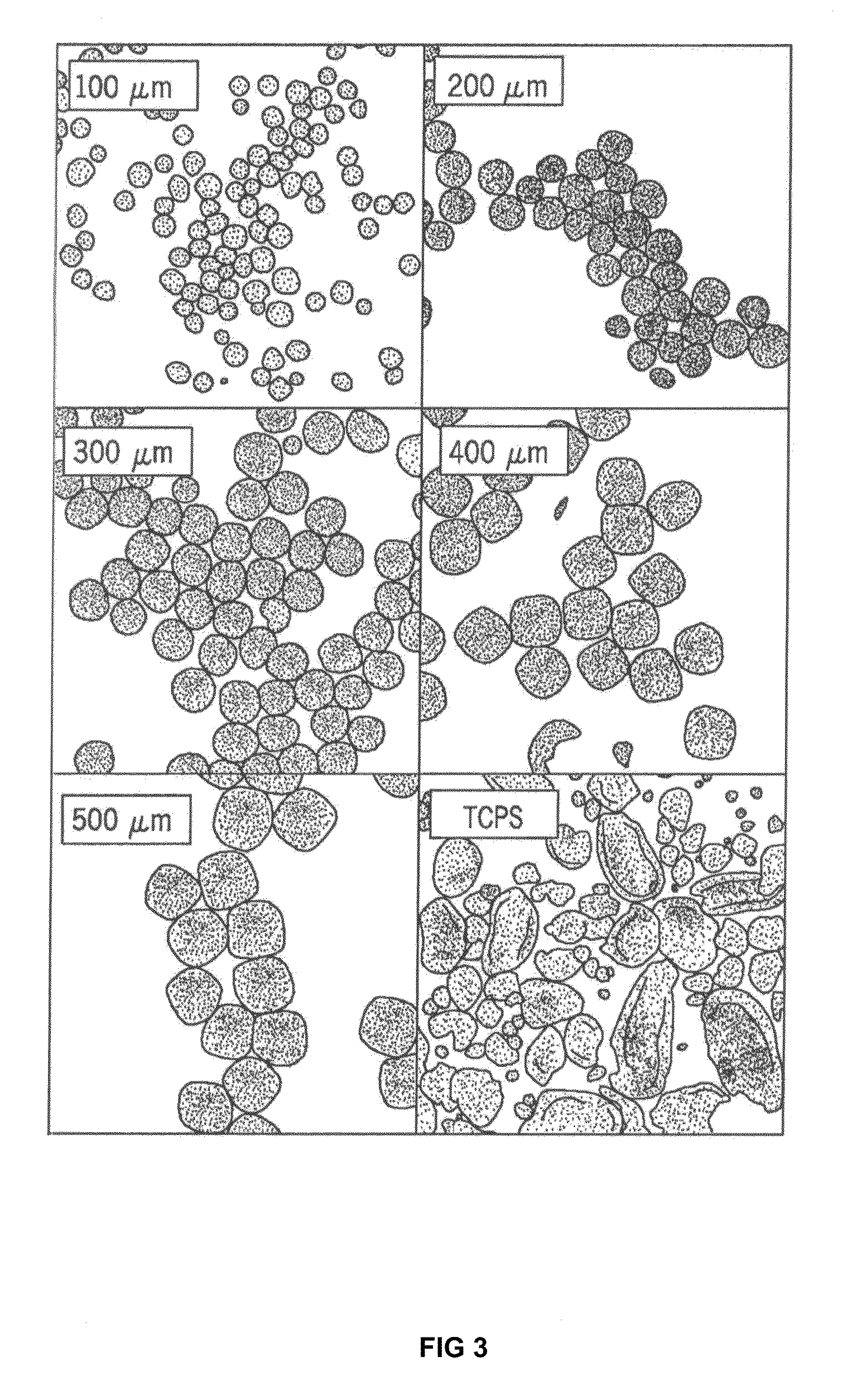
Method for culturing stem cells
ActiveUS20100197013A1Narrow size distributionUniform sizeMacromolecular librariesImmunoglobulins against animals/humansGerm layerMatrigel
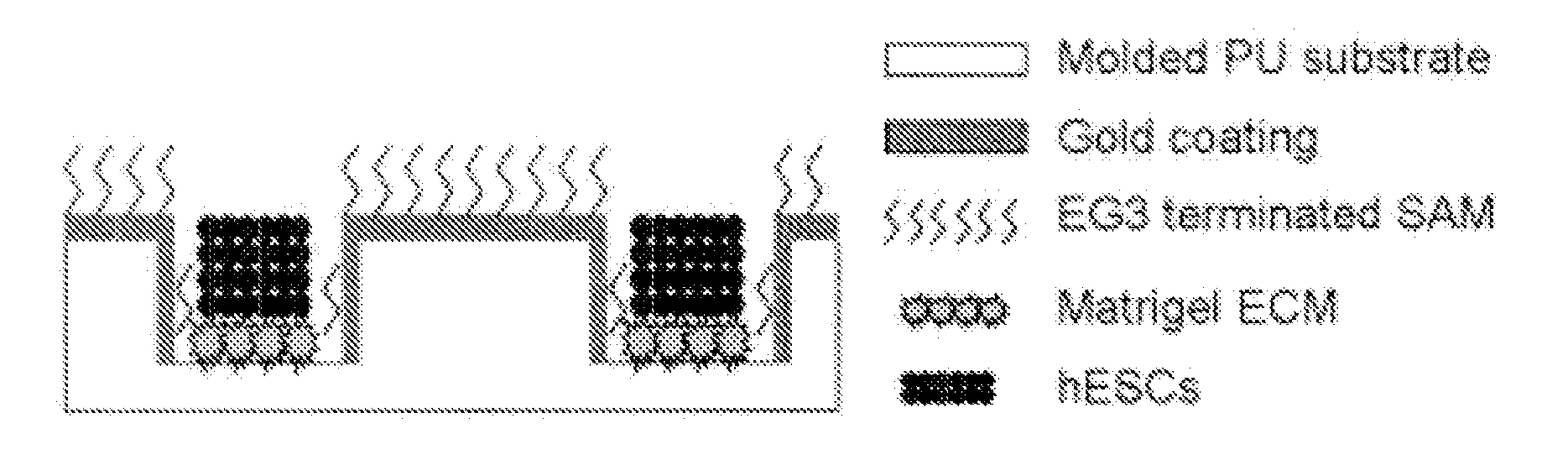
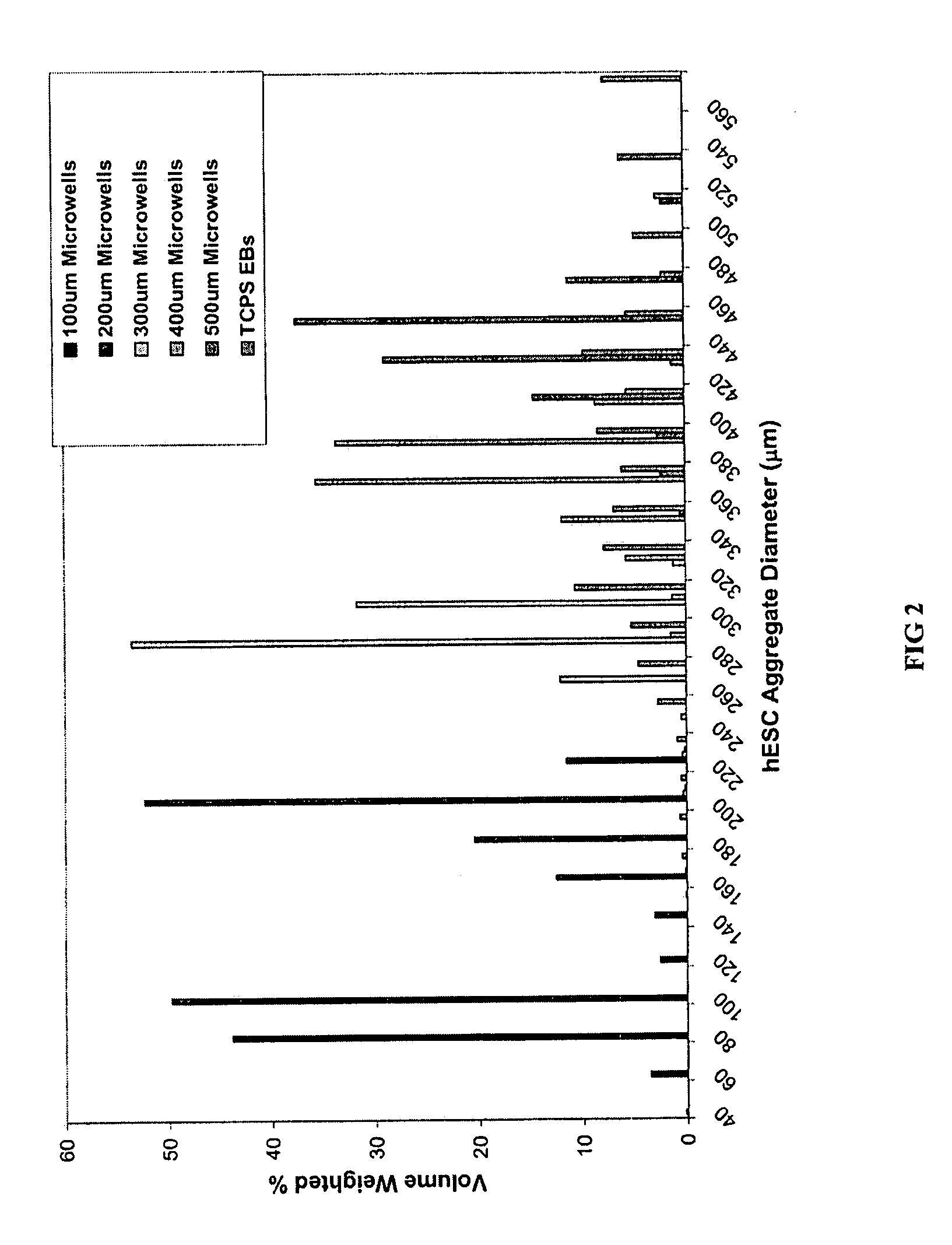
A three-dimensional microwell system that supports long term pluripotent cell culture and formation of homogeneous embryoid bodies (EBs) is described. Microwell-cultured pluripotent cells remain viable and undifferentiated for several weeks in culture and maintain undifferentiated replication when passaged to Matrigel®-coated, tissue culture-treated polystyrene dishes. Microwell-cultured pluripotent cells maintain pluripotency, differentiating to each of the three embryonic germ layers. Pluripotent cell aggregates released from microwells can be passaged for undifferentiated replication or differentiated to monodisperse EBs. The ability to constrain pluripotent cell growth in three dimensions advantageously provides for more efficient, reproducible culture of undifferentiated cells, high-throughput screening, and the ability to direct pluripotent cell differentiation by generating monodisperse EBs of a desired size and shape. Cardiomyocyte-rich EBs are obtained from pluripotent cells cultured in microwells of defined size and shape.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Multipotent neural stem cell compositions
ActiveUS7361505B1Peptide/protein ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsGlial fibrillary acidic proteinGlial Fibrillary Acid Protein
The invention provides in vitro cell culture compositions consisting of neurospheres and culture medium, wherein the neurospheres consist of undifferentiated cells that are nestin+, glial fibrillary acid protein (GFAP)−, neurofilament (NF)−, and myelin basic protein (MBP)− and are not nestin−.
Owner:BOCO SILICON VALLEY INC
Cell culture method and cell sheet
InactiveUS20060063252A1Facilitated releaseEasily have magnetic propertyBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsNeodymium magnetEngineering
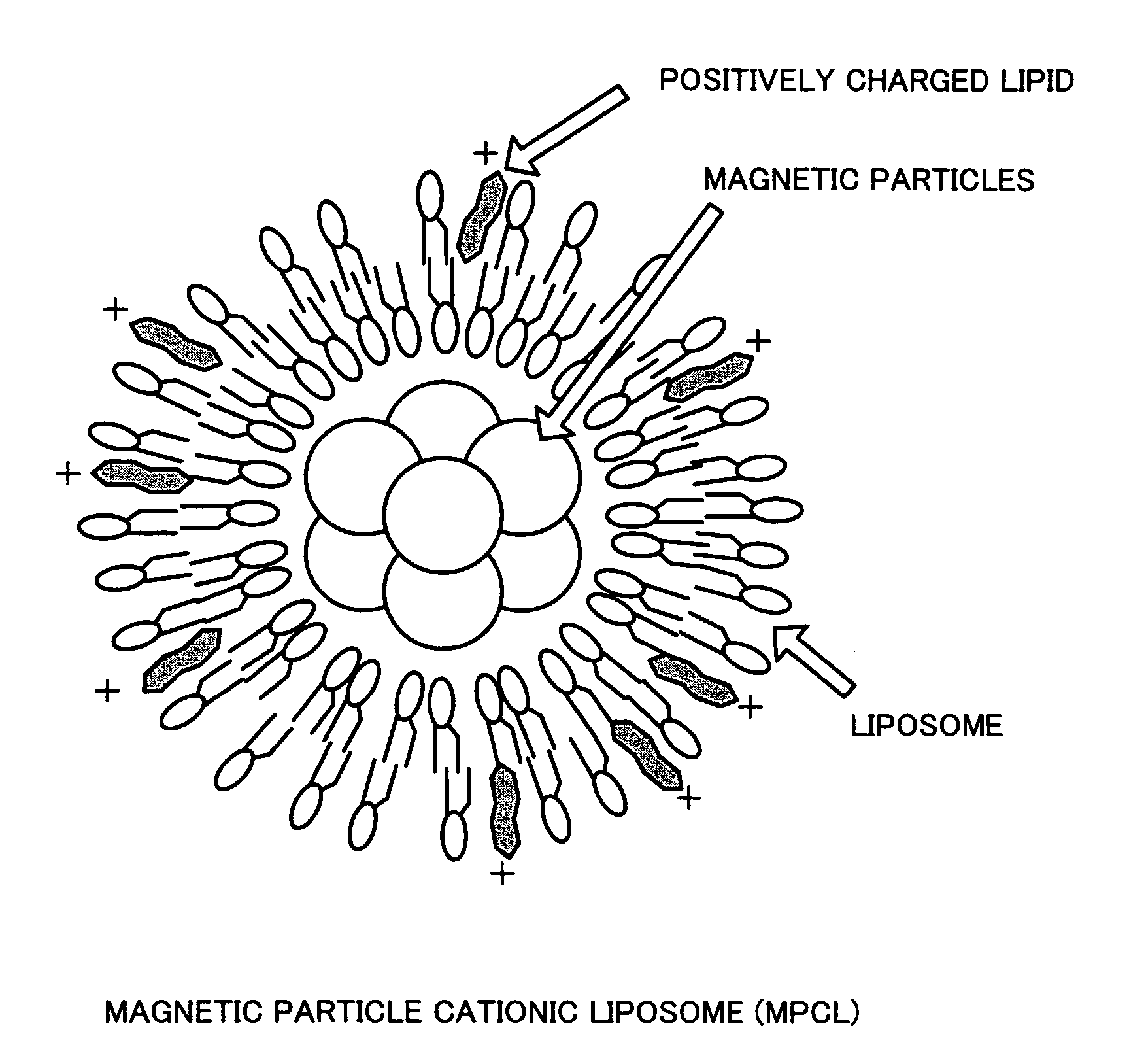
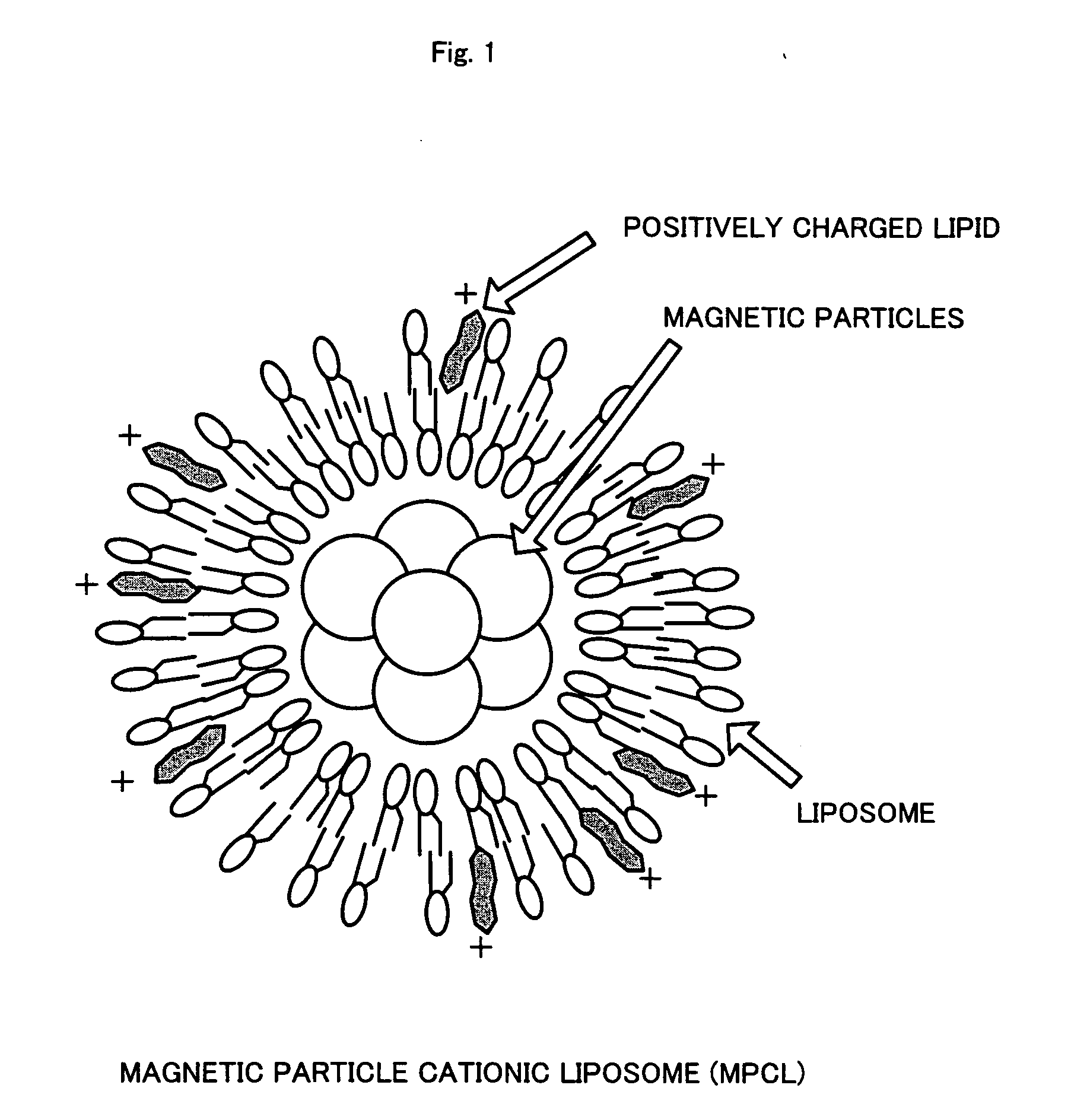
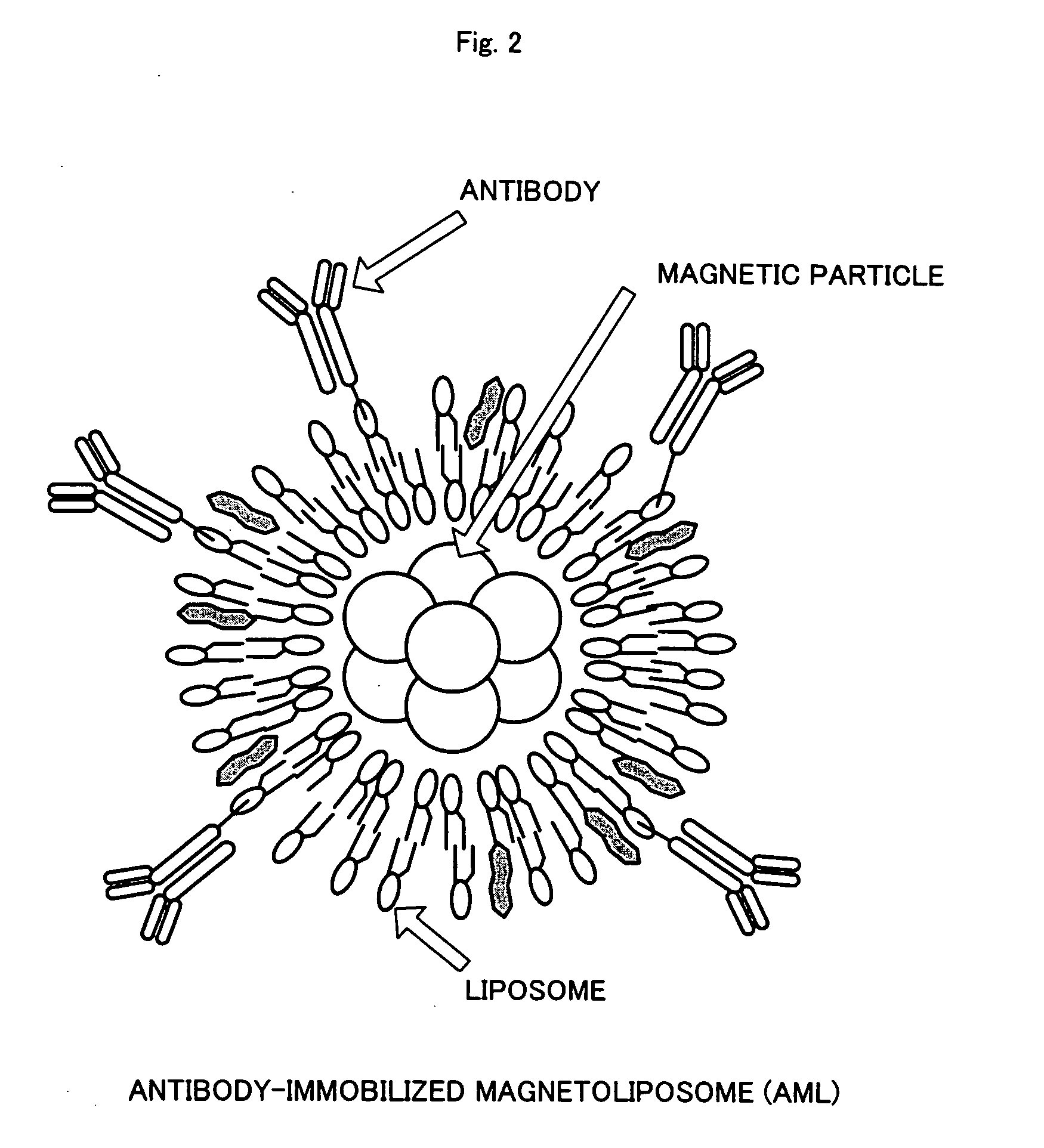
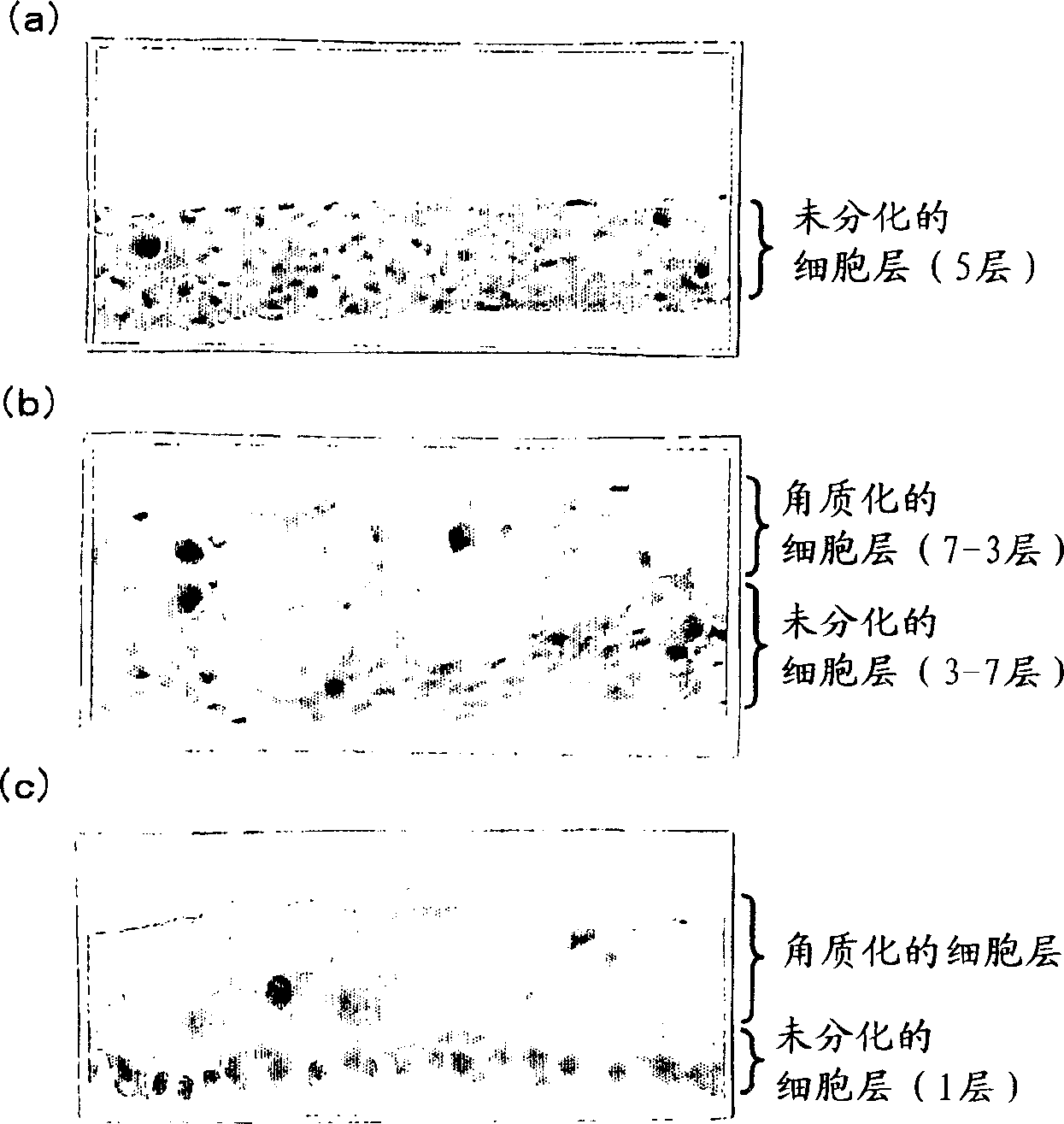
Epidermal keratinocytes not incorporating magnetic particles therein and epidermal keratinocytes incorporating magnetic particles therein were seeded in a 24-well ultra-low-attachment plate, and cultured for one day after a neodymium magnet was placed outside the bottom of the well. As a result, control epidermal keratinocytes not incorporating magnetic particles therein did not adhere to the bottom of the well and did not form an undifferentiated cell sheet. On the contrary, epidermal keratinocytes incorporating magnetic particles therein, while being attracted to the bottom of the well by magnetic force, formed a multilayered cell sheet. This cell sheet could be easily recovered by removing the neodymium magnet placed outside the bottom of the well, then bringing a magnet having a hydrophilic film attached thereto close to the cell sheet from upside and to attract it via this hydrophilic film, and lifting it.
Owner:HONDA HIROYUKI +1
Selective antibody targeting of undifferentiated stem cells
This invention provides a system for producing differentiated cells from a stem cell population for use wherever a relatively homogenous cell population is desirable. The cells contain an effector gene under control of a transcriptional control element (such as the TERT promoter) that causes the gene to be expressed in relatively undifferentiated cells in the population. Expression of the effector gene results in expression of a cell-surface antigen that can be used to deplete the undifferentiated cells. Model effector sequences encode glycosyl transferases that synthesize carbohydrate xenoantigen or alloantigen, which can be used for immunoseparation or as a target for complement-mediated lysis. The differentiated cell populations produced are suitable for use in tissue regeneration and non-therapeutic applications such as drug screening.
Owner:ASTERIAS BIOTHERAPEUTICS INC +1
Method for culturing stem cells
PendingUS20080026460A1AdvantageouslyCell differentiation profile of EBs can be controlledBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsGerm layerMatrigel
A three-dimensional microwell system that supports long term embryonic stem cell (ESCs) culture and formation of homogeneous embryoid bodies (EBs) is described. Microwell-cultured ESCs remain viable and undifferentiated for several weeks in culture and maintain undifferentiated replication when passaged to Matrigel®-coated, tissue culture-treated polystyrene dishes. Microwell-cultured ESCs maintain pluripotency, differentiating to each of the three embryonic germ layers. ESC aggregates released from microwells can be passaged for undifferentiated replication or differentiated to monodisperse EBs. The ability to constrain ESC growth in three dimensions advantageously provides for more efficient, reproducible culture of undifferentiated cells, high-throughput screening, and the ability to direct ESC differentiation by generating monodisperse EBs of a desired size and shape.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Use of RNA interference for the creation of lineage specific ES and other undifferentiated cells and production of differentiated cells in vitro by co-culture
InactiveUS20060240556A1Facilitate vivo enrichmentNew breed animal cellsMammal material medical ingredientsEmbryonic StageReprogramming
Methods for making human ES cells and human differentiated cells and tissues for transplantation are described, whereby the cells and tissues are created following somatic cell nuclear transfer. The nuclear transfer donor is genetically modified prior to nuclear transfer such that cells of at least one developmental lineage are de-differentiated, i.e., unable to develop, thereby resolving the ethical dilemmas involved in reprogramming somatic cells back to the embryonic stage. The method concomitantly directs differentiation such that the desired cells and tissues may be more readily isolated.
Owner:ADVANCED CELL TECH INC
Cartilidge and bone induction by artificially perforated organic bone matrix augmented by undifferentiated cells suspended in bone gel
InactiveUS20050074476A1Process can be usedBone implantJoint implantsBiomedical engineeringUndifferentiated cell
A novel method for cartilage and bone induction is introduced whereby an artificially perforated bone organic bone matrix augmented by live human undifferentiated cells suspended in a gel is used as a surgical implant.
Owner:GENDLER FAMILY PARTNERSHIP
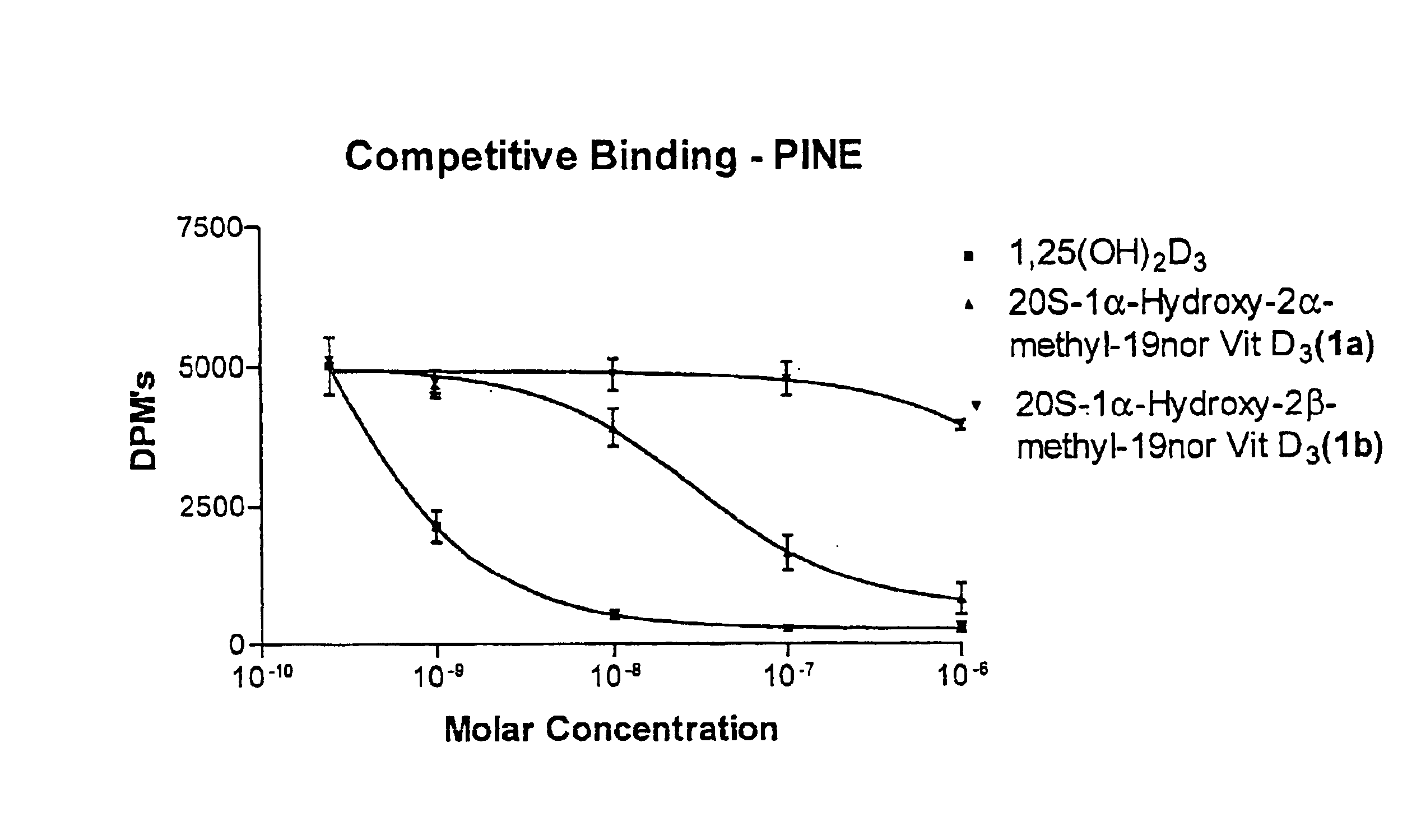
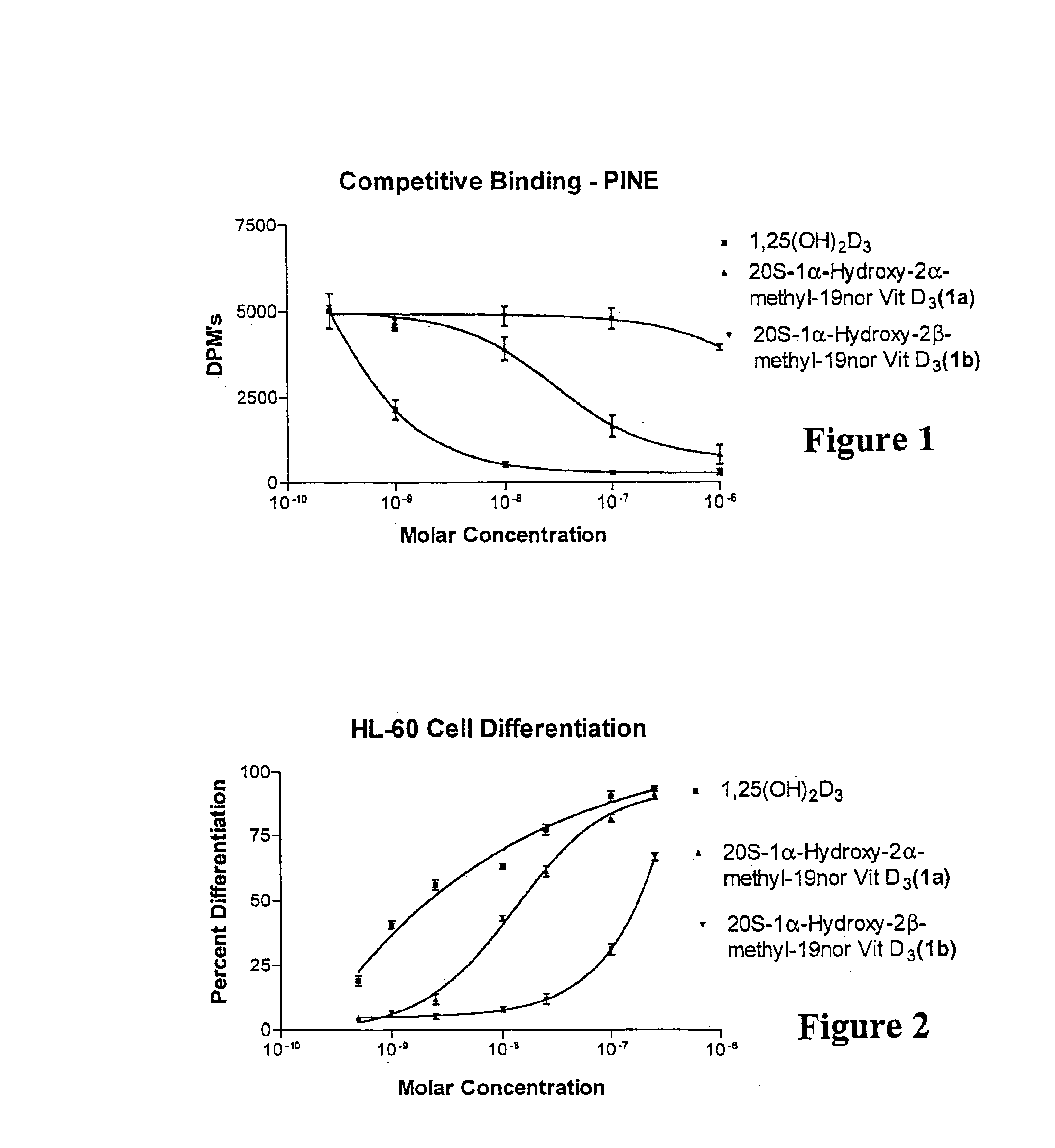
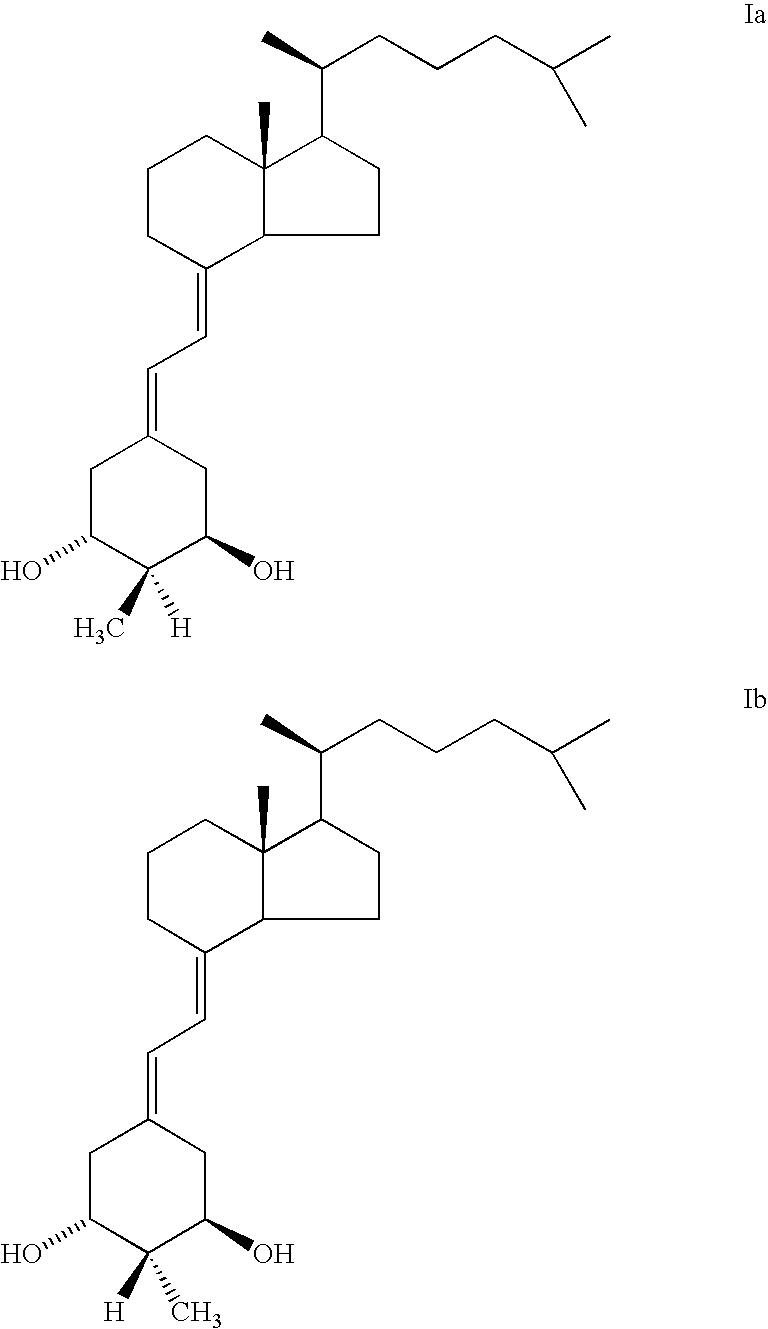
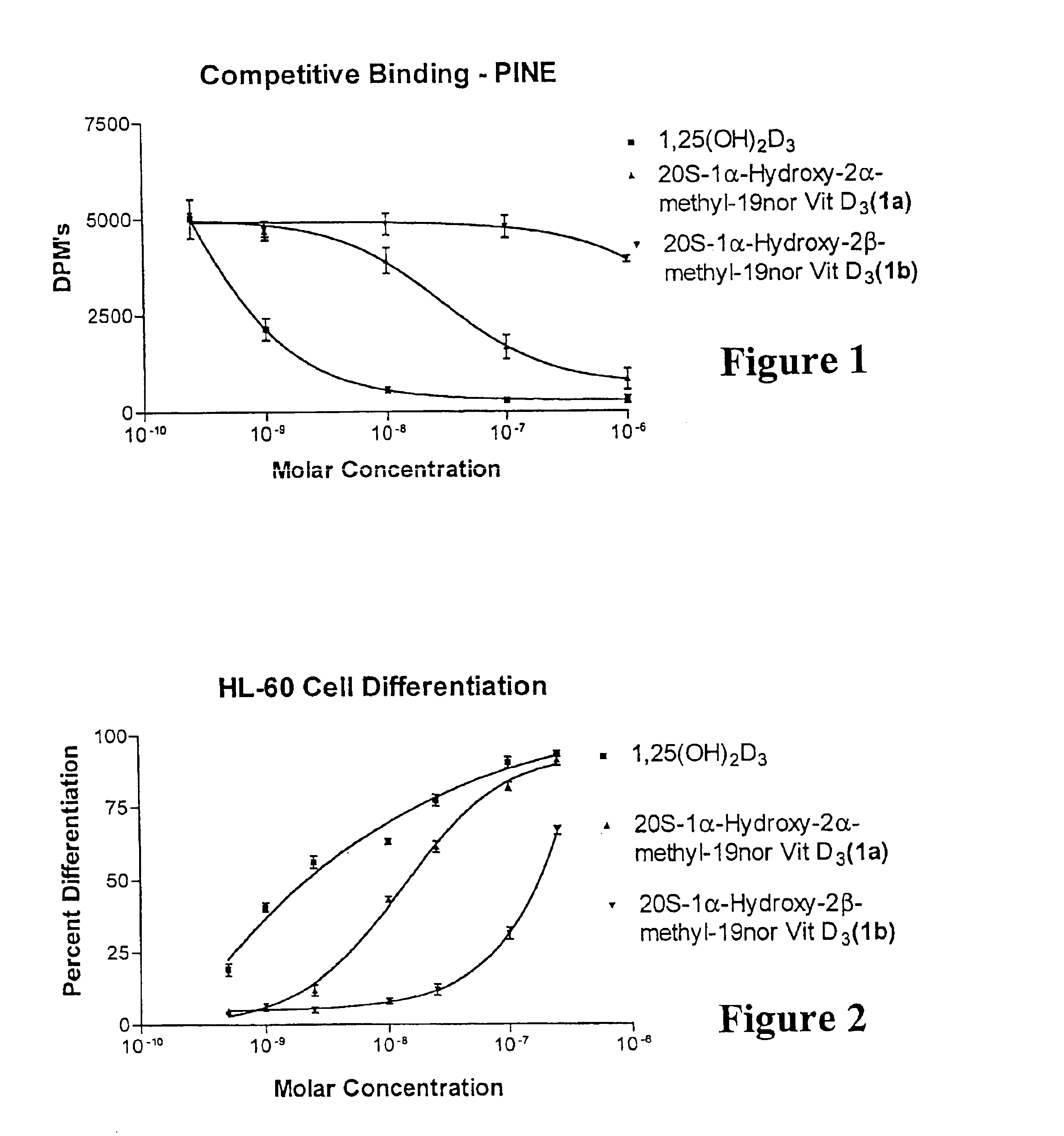
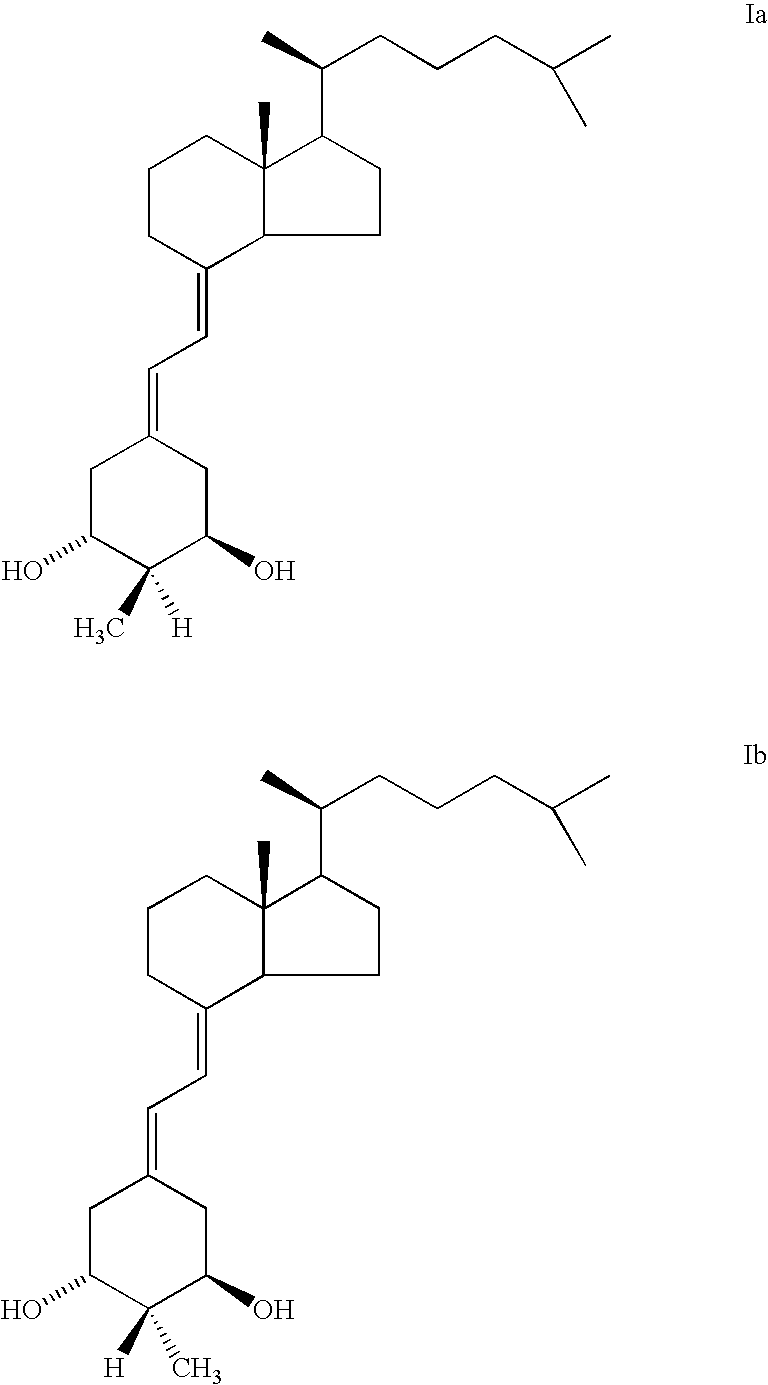
(20S)-1alpha-hydroxy-2alpha-methyl and 2beta-methyl-19-nor-vitamin D3 and their uses
InactiveUS6844332B2Potent calcemic activityHighly specificOrganic active ingredientsBiocideWrinkle skinAnticarcinogen
This invention discloses (20S)-1α-hydroxy-2α-methyl-19-nor-vitamin D3 and (20S)-1α-hydroxy-2β-methyl-19-nor-vitamin D3 and pharmaceutical uses therefor. These compounds exhibit pronounced activity in arresting the proliferation of undifferentiated cells and inducing their differentiation to the monocyte thus evidencing use as an anti-cancer agent and for the treatment of skin diseases such as psoriasis as well as skin conditions such as wrinkles, slack skin, dry skin and insufficient sebum secretion. These compounds also have very significant calcemic activity and therefore may be used to treat immune disorders in humans as well as metabolic bone diseases such as osteoporosis.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
(20S)-1alpha-hydroxy-2alpha-methyl and 2beta-methyl-19-nor-vitamin D3 and their uses
InactiveUS6844457B2High and significant cell differentiation activityEnhanced barrier functionOrganic active ingredientsBiocideWrinkle skinAnticarcinogen
This invention discloses (20S)-1α-hydroxy-2α-methyl-19-nor-vitamin D3 and (20S)-1α-hydroxy-2β-methyl-19-nor-vitamin D3 and pharmaceutical uses therefor. These compounds exhibit pronounced activity in arresting the proliferation of undifferentiated cells and inducing their differentiation to the monocyte thus evidencing use as an anti-cancer agent and for the treatment of skin diseases such as psoriasis as well as skin conditions such as wrinkles, slack skin, dry skin and insufficient sebum secretion. These compounds also have very significant calcemic activity and therefore may be used to treat immune disorders in humans as well as metabolic bone diseases such as osteoporosis.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Method of purification of cells
The present invention relates generally to a method for the generation of a substantially homogeneous population of undifferentiated cells. More particularly, the present invention relates to the purification of a substantially homogeneous population of stem cells and their progenitor or precursor cells. Even more particularly, the present invention provides a population of neural stem cells (NSCs). The subject invention is particularly directed to NSCs and precursor cells with the capacity to differentiate into cells and cell lineages required for the development, maintenance or repair of the central nervous system in an animal such as a mammal. The present invention is further directed to NSCs and progenitor and / or precursor cells which are capable of proliferation and differentiation into multiple cell lineages, such as but not limited to neurons, oligodendrocytes, glia and astrocytes. The subject invention further contemplates the use of NSCs and / or precursor cells for the repair or regeneration of tissue, such as tissue associated with the central nervous system, in an animal including a mammal. The NSCs of the present invention may be used to identify naturally occurring molecules such as cytokines as well as molecules obtained from natural product screening or screening of chemical libraries which induce proliferation of the NSCs. Such molecules are useful in the development of therapeutics.
Owner:THE UNIV OF QUEENSLAND
Laser isolation of viable cells
Methods for laser microdissection isolation of viable cells are provided. Cells of a desired type may be isolated from a diverse population, optionally with detection and exclusion of undesired cells. Desired cells may be isolated from a population that arose from differentiation of pluripotent cells, preferably embryonic stem cells or induced pluripotent stem cells, and undifferentiated stem cells may be detected and excluded from selection including the isolation of RPE cells sleeted based on morphology (e.g., characteristic mottled appearance) from a population of ES cells. The cells isolated by these methods, including RPE cells, may be essentially free of undifferentiated cells and thus suitable for use in cell-based therapies.
Owner:ADVANCED CELL TECH INC
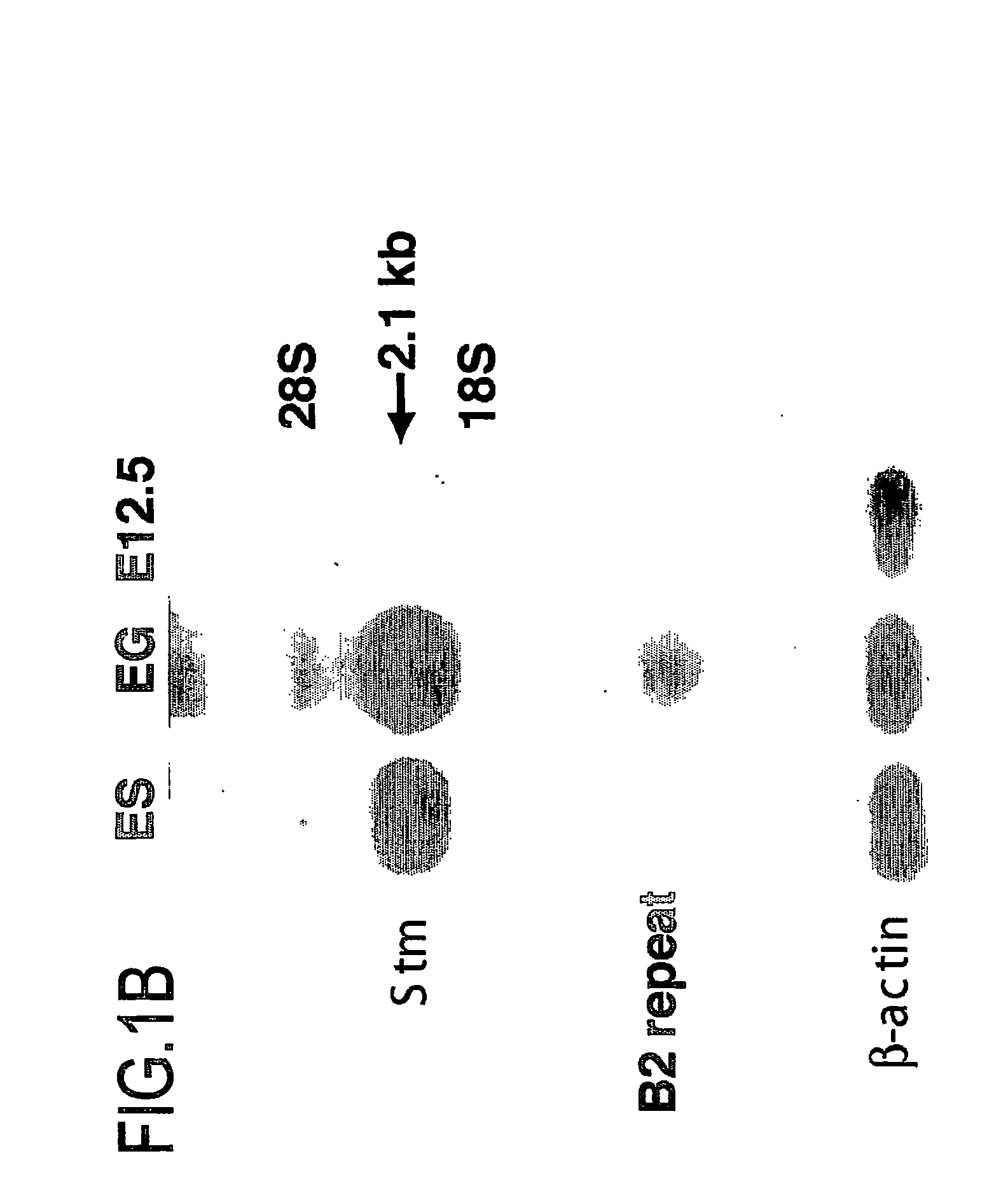
Marker for undifferentiated state of cell and composition and method for separation and preparation of stem cells
InactiveUS20060288431A1Efficient purificationAccurately determineImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsNon-embryonic pluripotent stem cellsGene productGene
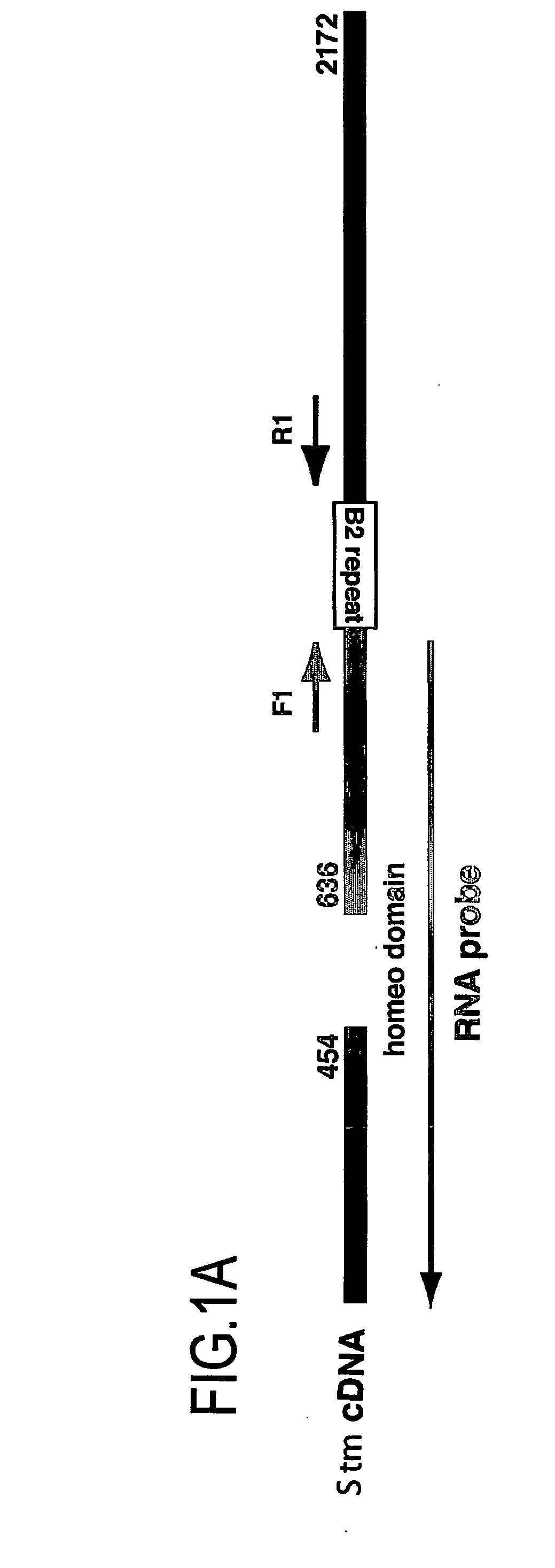
A gene is provided, which can be used as a marker for determining whether a certain cell, particularly an undifferentiated cell including a tissue stem cell, has pluripotency or an undifferentiated state. The gene is called Stm and includes a Stm1 gene, which is expressed specifically in a cell under an undifferentiated state if the cell has pluripotency. A kit for determining a differentiated state of a cell is also provided. The kit comprises (a) an agent capable of reacting specifically with a Stm gene or a Stm gene product; and (b) means for determining whether or not the Stm gene is expressed in the cell.
Owner:REPROCELL +4
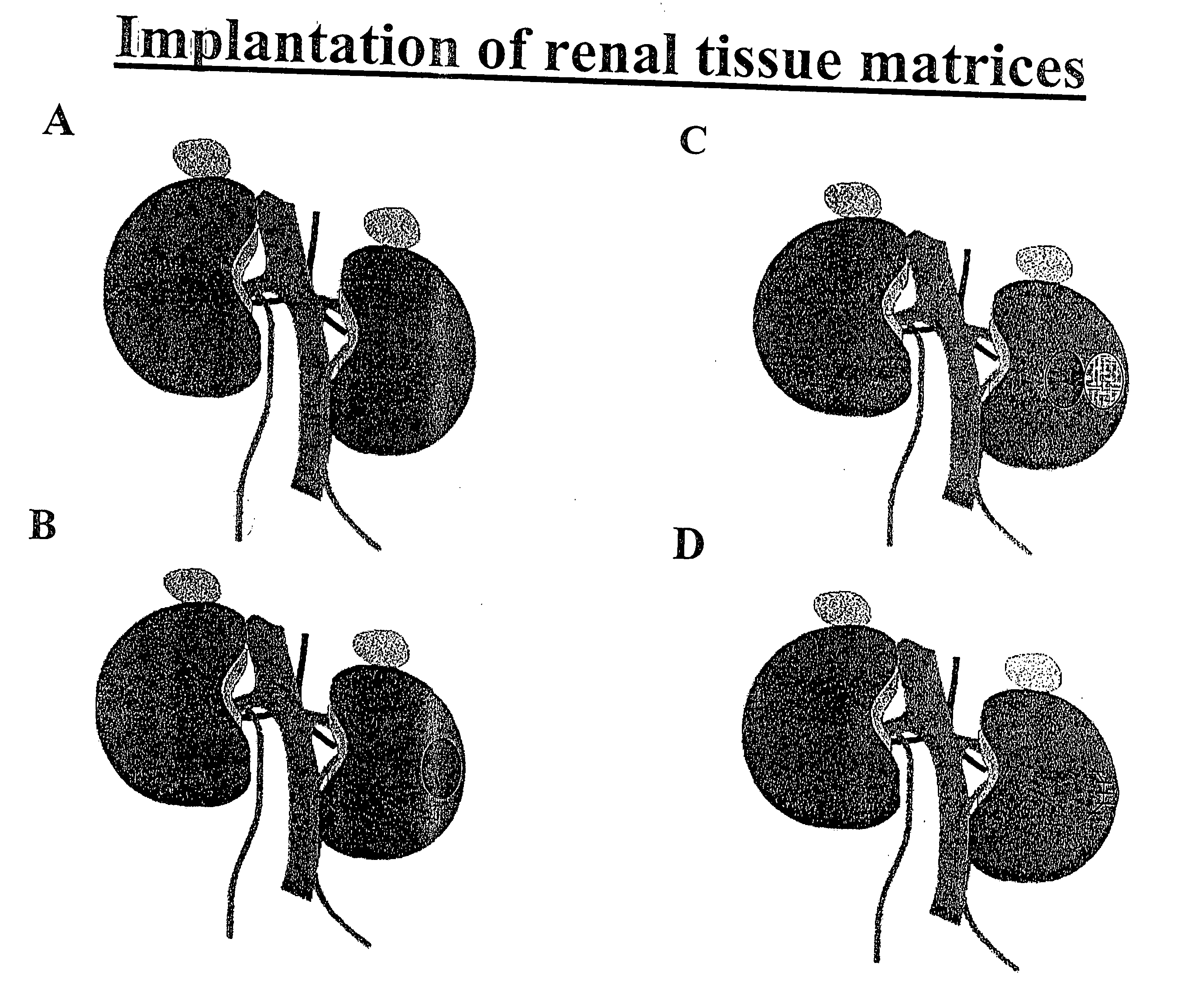
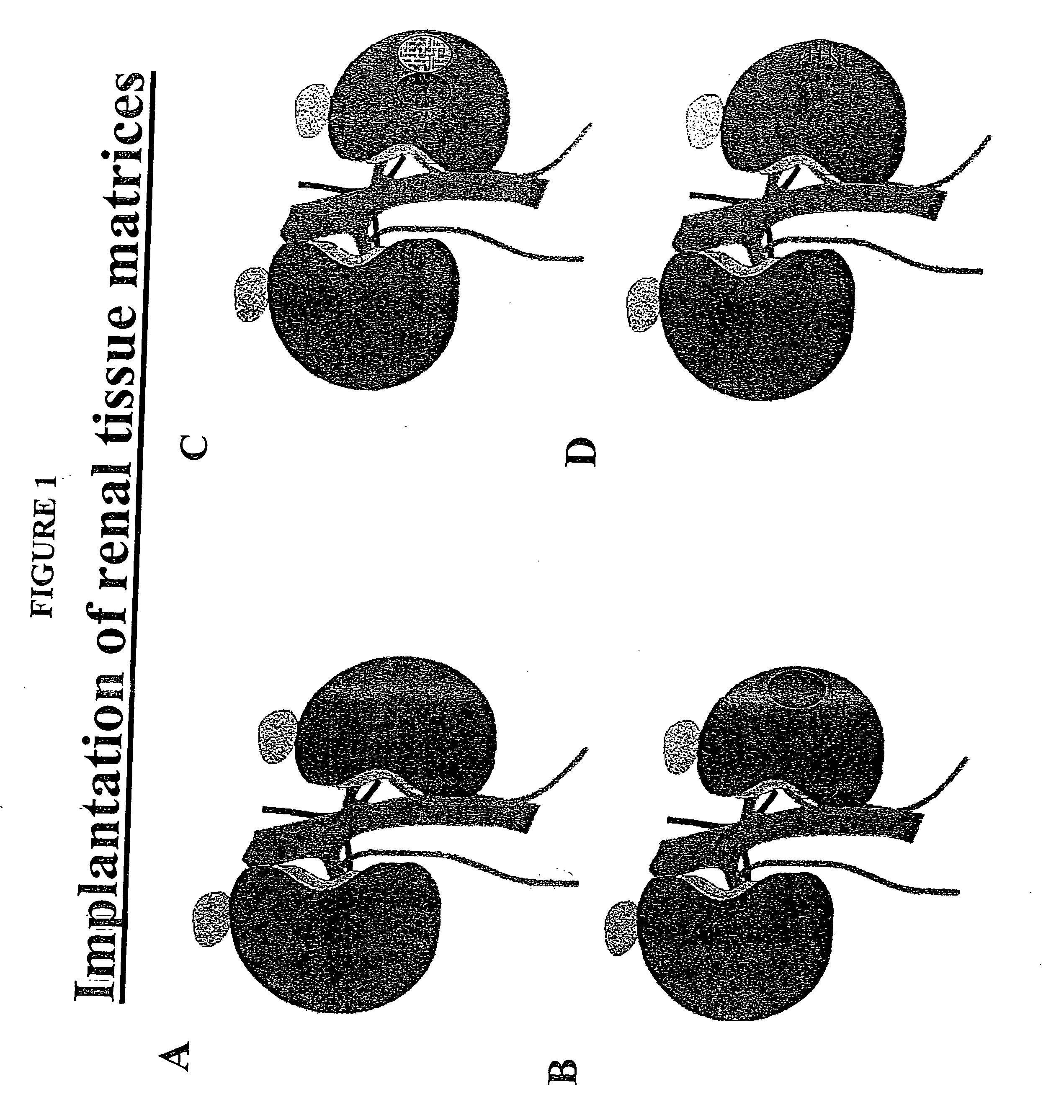
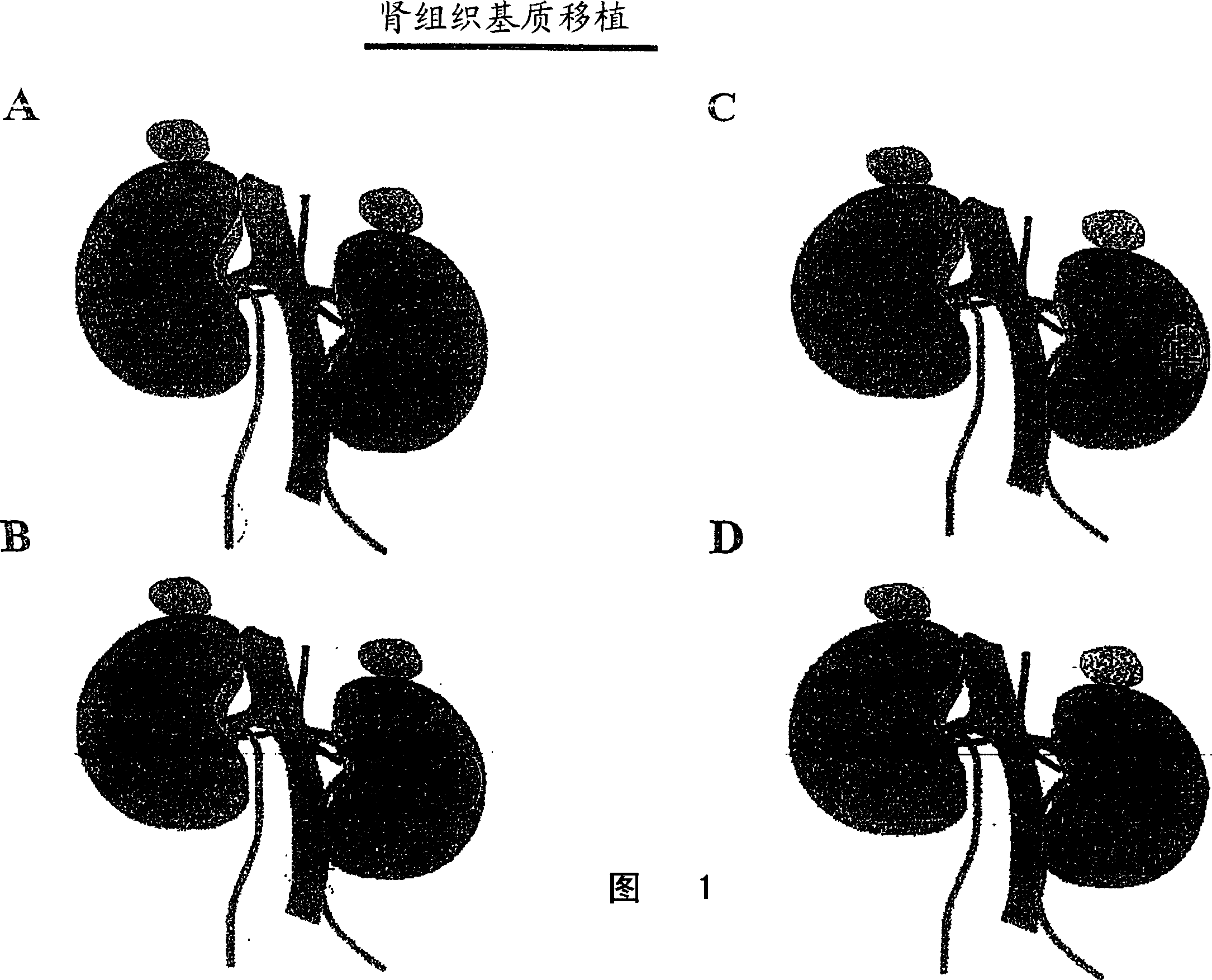
Augmentation of organ function
InactiveUS20070116679A1Support growthIncrease surface areaBiocideMammal material medical ingredientsOrgan functionIn vivo
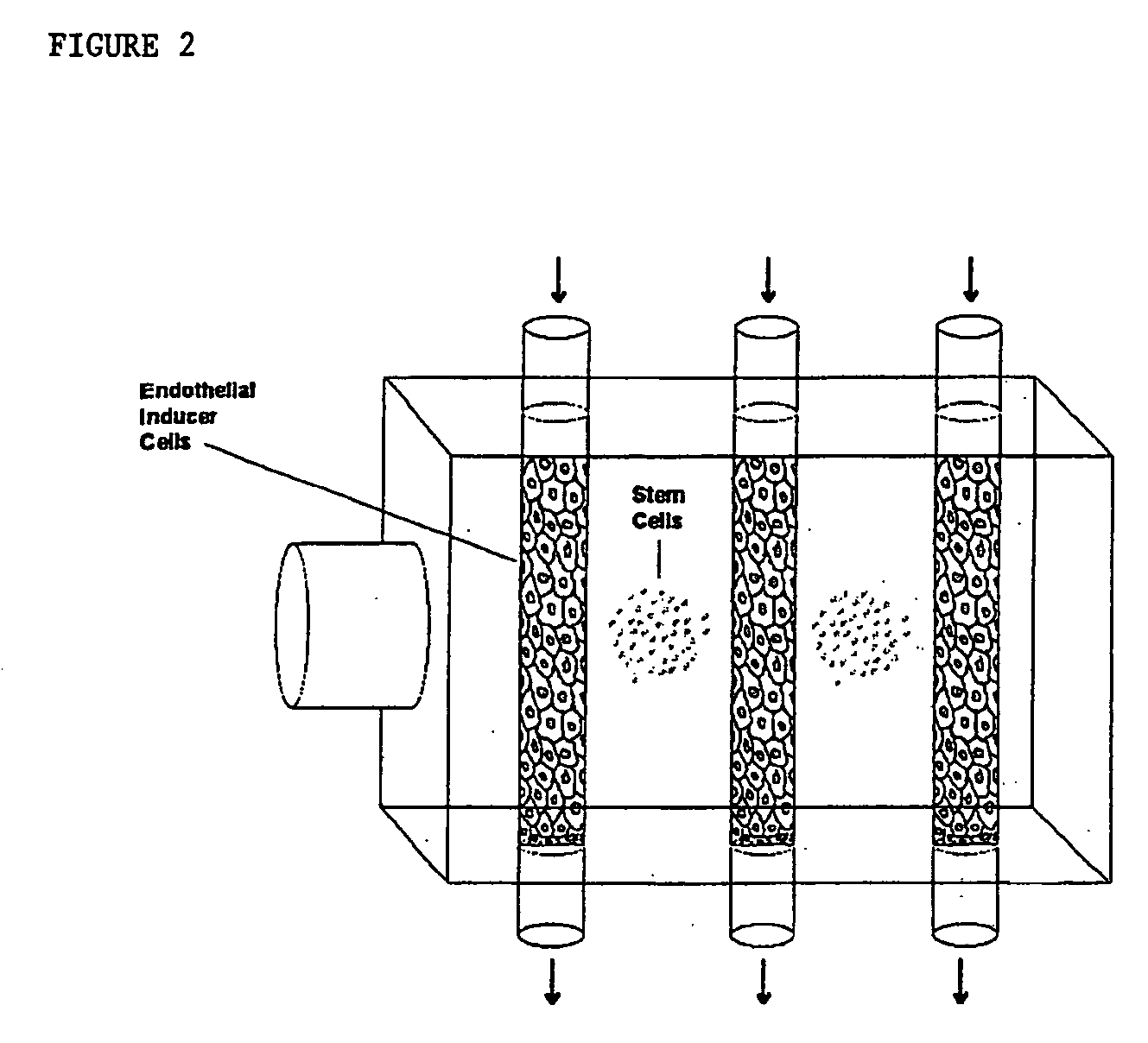
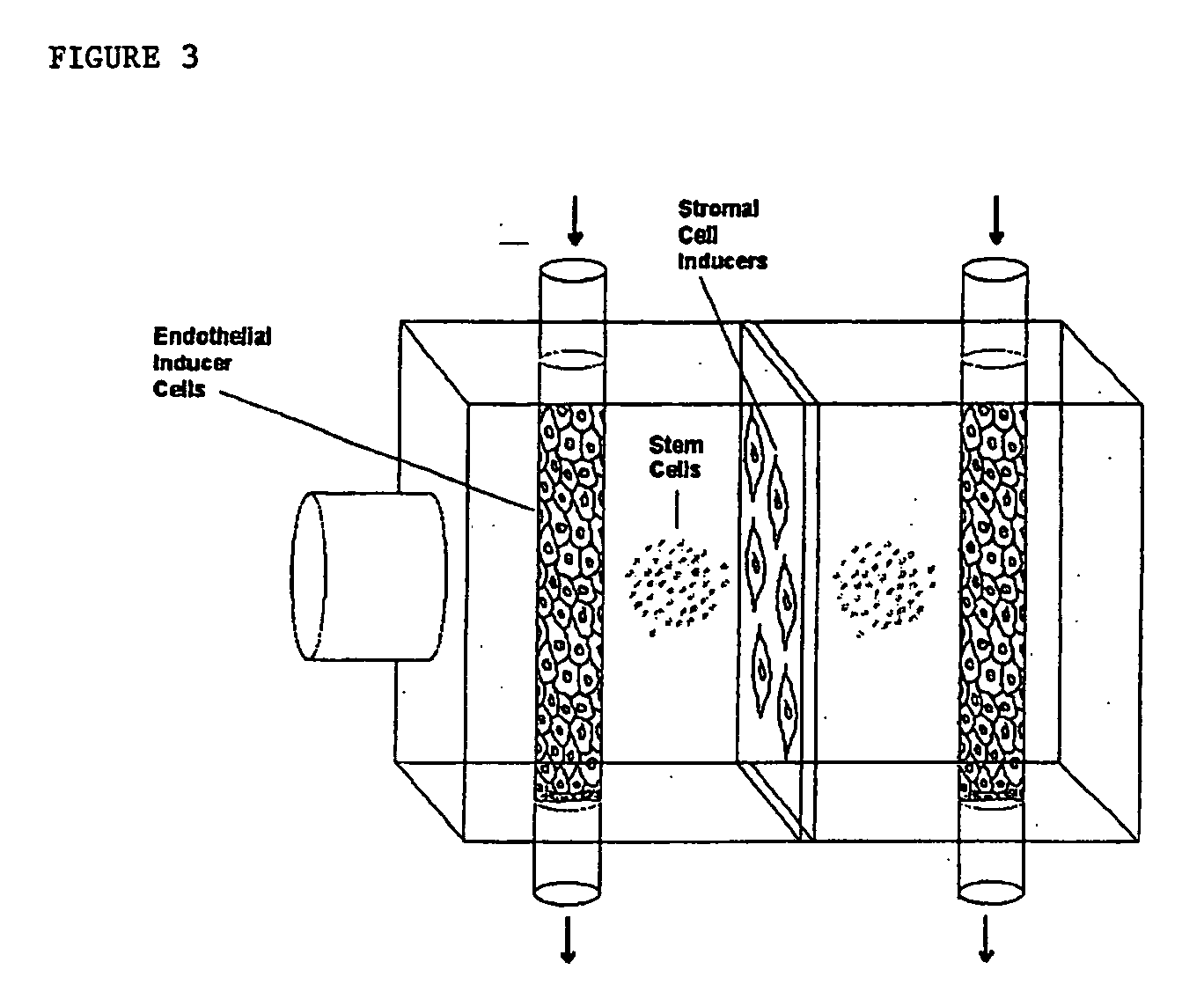
The present invention provides methods and compositions for augmenting organ functions using small-scale matrix implants generated by seeding tissue-specific or undifferentiated cells onto a matrix materials (e.g., a wafer, sponge, or hydrogel). The seeded matrix composition can then be implanted and will develop into an organ-supplementing structure in vivo. Continued growth and differentiation of the seeded cells on the implanted matrix results in the formation of a primitive vascular system in the tissue. The primitive vascular system can then develop into a mature vascular system, and can also support the growth and development of additional cultured cell populations. The seeded matrix system can be used to introduce a variety of different cells and tissues in vivo.
Owner:CHILDRENS MEDICAL CENT CORP
Augmentation of organ function
The present invention provides methods and compositions for augmenting organ functions using small-scale matrix implants generated by seeding tissue-specific or undifferentiated cells onto a matrix materials (e.g., a wafer, sponge, or hydrogel). The seeded matrix composition can then be implanted and will develop into an organ-supplementing structure in vivo. Continued growth and differentiation of the seeded cells on the implanted matrix results in the formation of a primitive vascular system in the tissue. The primitive vascular system can then develop into a mature vascular system, and can also support the growth and development of additional cultured cell populations. The seeded matrix system can be used to introduce a variety of different cells and tissues in vivo.
Owner:CHILDRENS MEDICAL CENT CORP
Novel population of multipotent cardiac precursor cells derived from human blastocysts derived stem cells
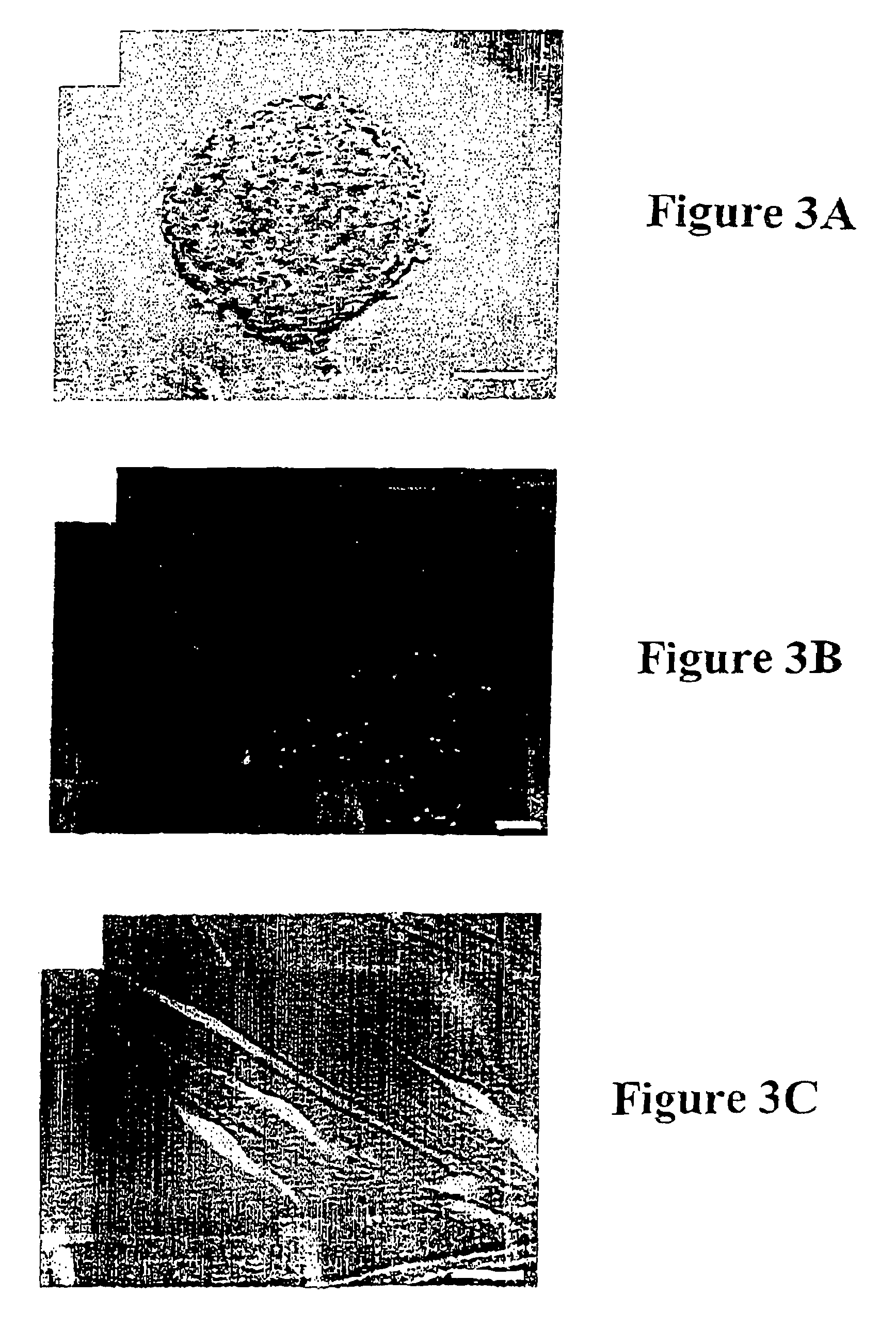
A novel population of multipotent cardiac precursor (MCP) cells derived from human blastocysts derived stem cells is disclosed, methods for the preparation thereof and use of the cells for in vitro testing. Basement cells derived from hBS cells are also disclosed and method for the preparation of MCP cells from basement cells. The MCP cells have the following characteristicsi) at least 1% of the cells exhibit no antigen expression of one or more markers for undifferentiated cell, the marker being selected from the group consisting of SSEA-3, SSEA-4, TRA-1-60, TRA-1-81 and Oct-4,ii) at least 1% of the cells exhibit no protein expression of one or more of a neural marker including nestin or GFAPiii) at least 1% of the cells exhibit protein and / or gene expression of one or more of a mesodermal marker including brachyury, vimentin or desminiv) at least 1% of the cells exhibit protein and / or gene expression of Flk-1 (KDR).Furthermore, the MCP cells have a characteristic morphology. They grow as clusters of small, round and phase-bright cells; individual cells are 5-20 μm in diameter and each cluster is composed of 2-500 cells. They form clusters of round or elongated shape, that appear as loosely adherent cell clumps that as illustrated in FIG. 2 panel a, b and c. Furthermore, they have a relatively high nucleus-to-cytoplasma ratio, e.g. 1:2-1:64 of the total volume of the cell and / or appear as balloons on a string, as illustrated in FIG. 18, schematic sketch. Moreover, the MCP cells are non-contracting.
Owner:CELLARTIS AB (SE)
Methods to enhance cell migration and engraftment
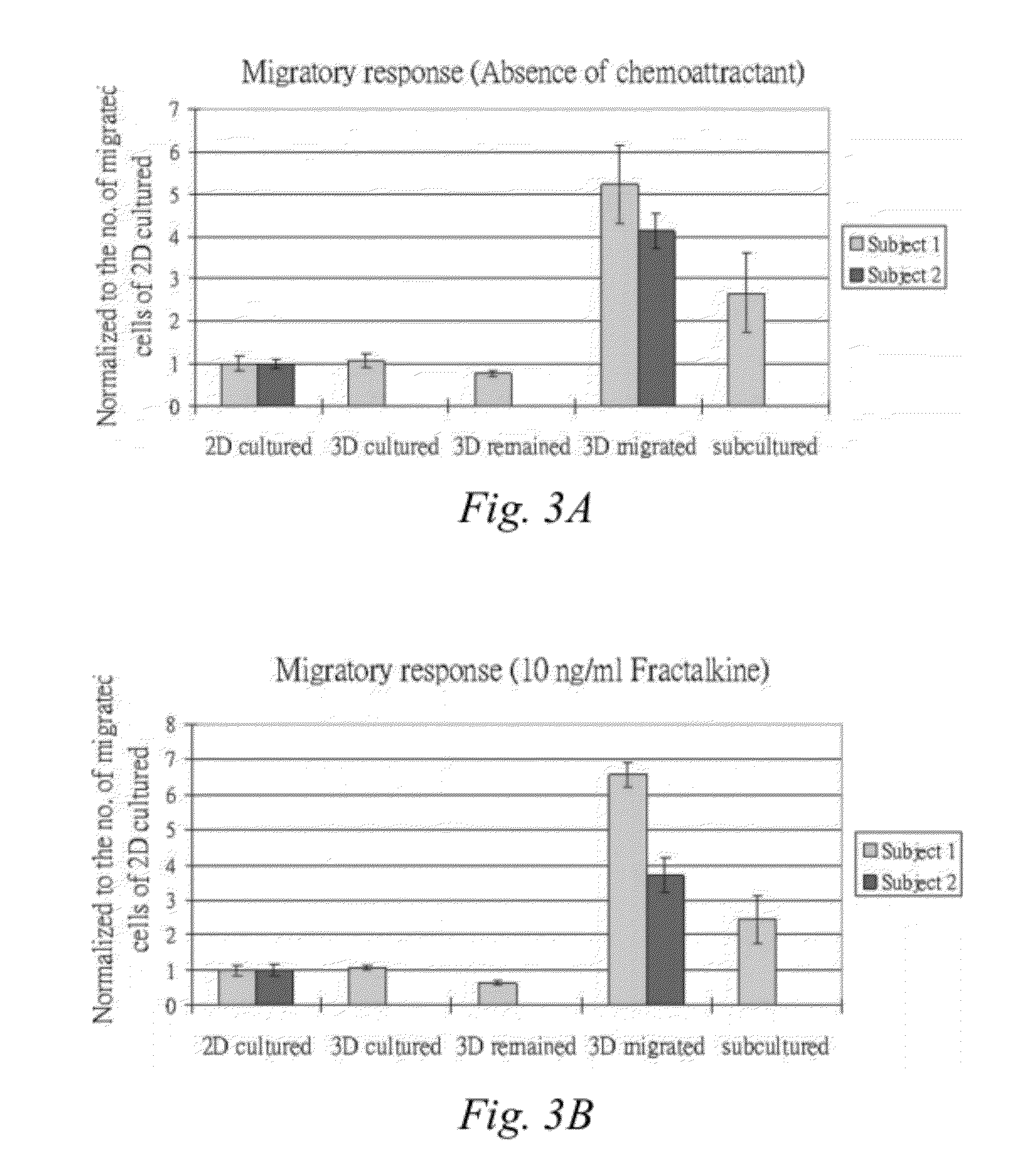
ActiveUS20120148537A1Migratory activityIncreasing cell migrationBiocideMammal material medical ingredientsWhole bodyMesenchymal stem cell
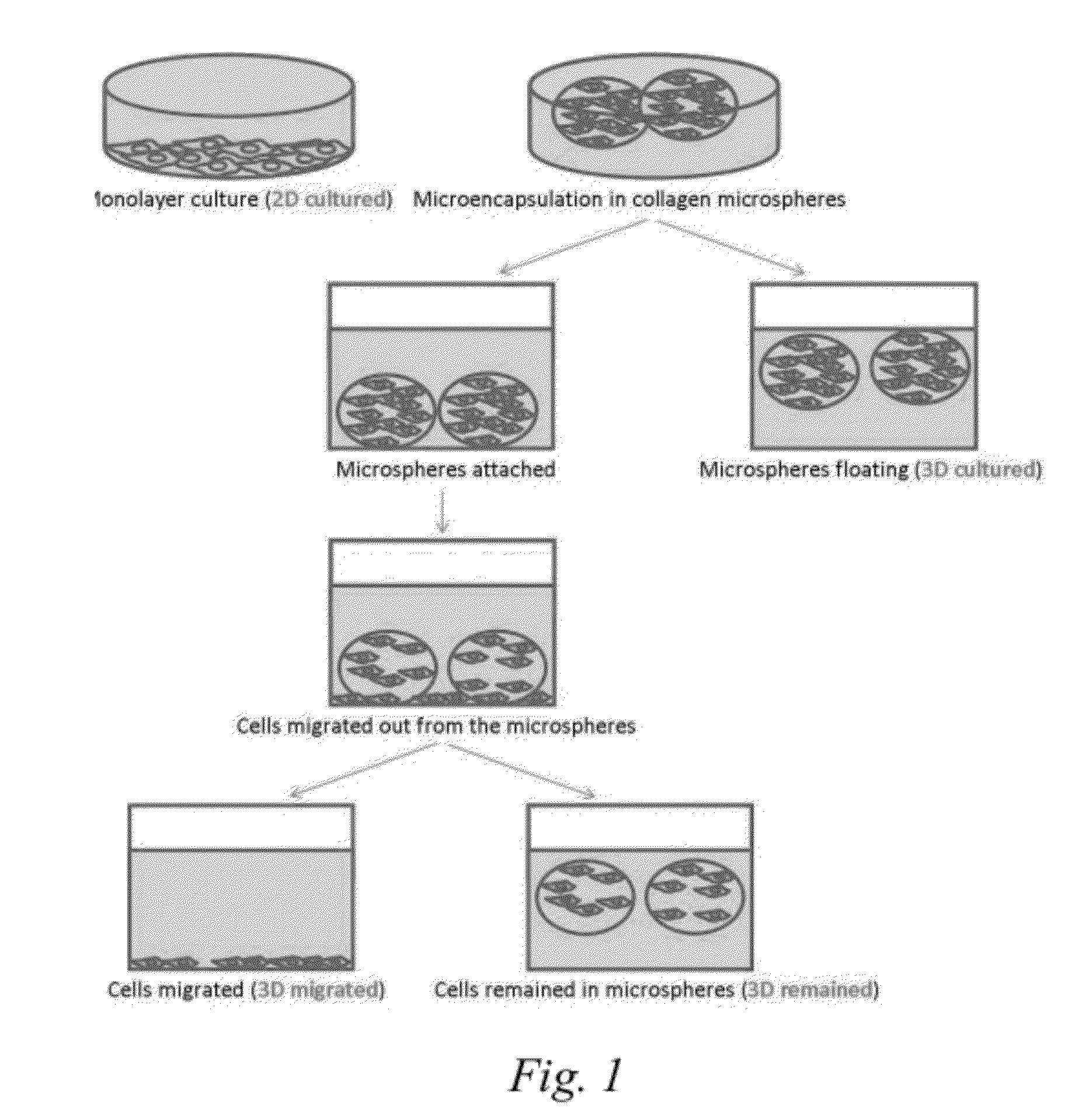
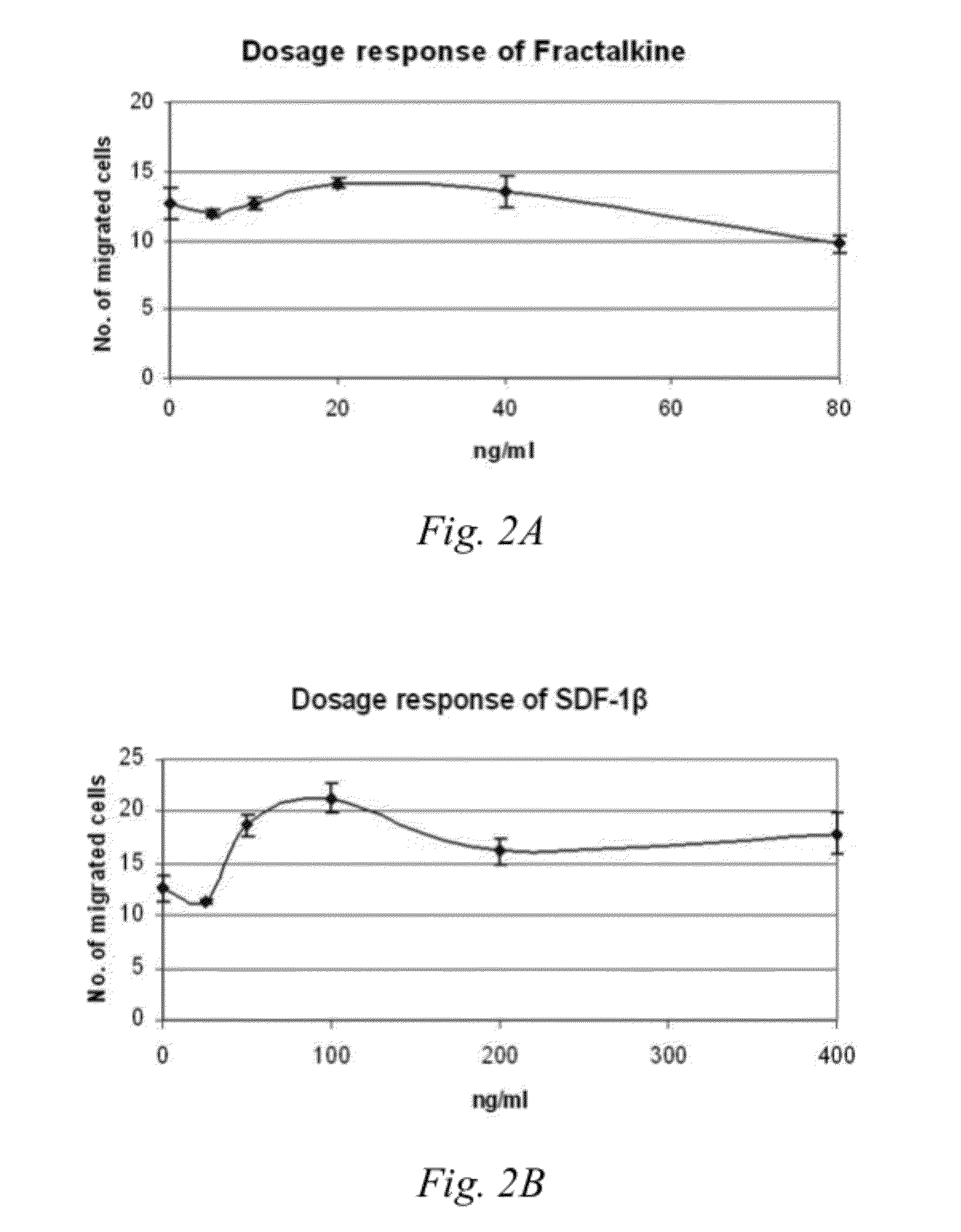
A method is provided to functionally select cells with enhanced characteristics relevant to cell engraftment, including both spontaneous migration and directional migration towards specific chemo-attractants. The cells are preferably undifferentiated cells, such as mesenchymal stem cells. The method involves entrapping or encapsulating the cells in a biomaterial barrier, optionally inducing cell migration, and selecting cells that migrated through the barrier. The cells selected by this method have better migratory activities and enhanced in vivo engraftment to injured tissues when they are supplemented systemically.
Owner:VERSITECH LTD
Method Of Cell Isolation
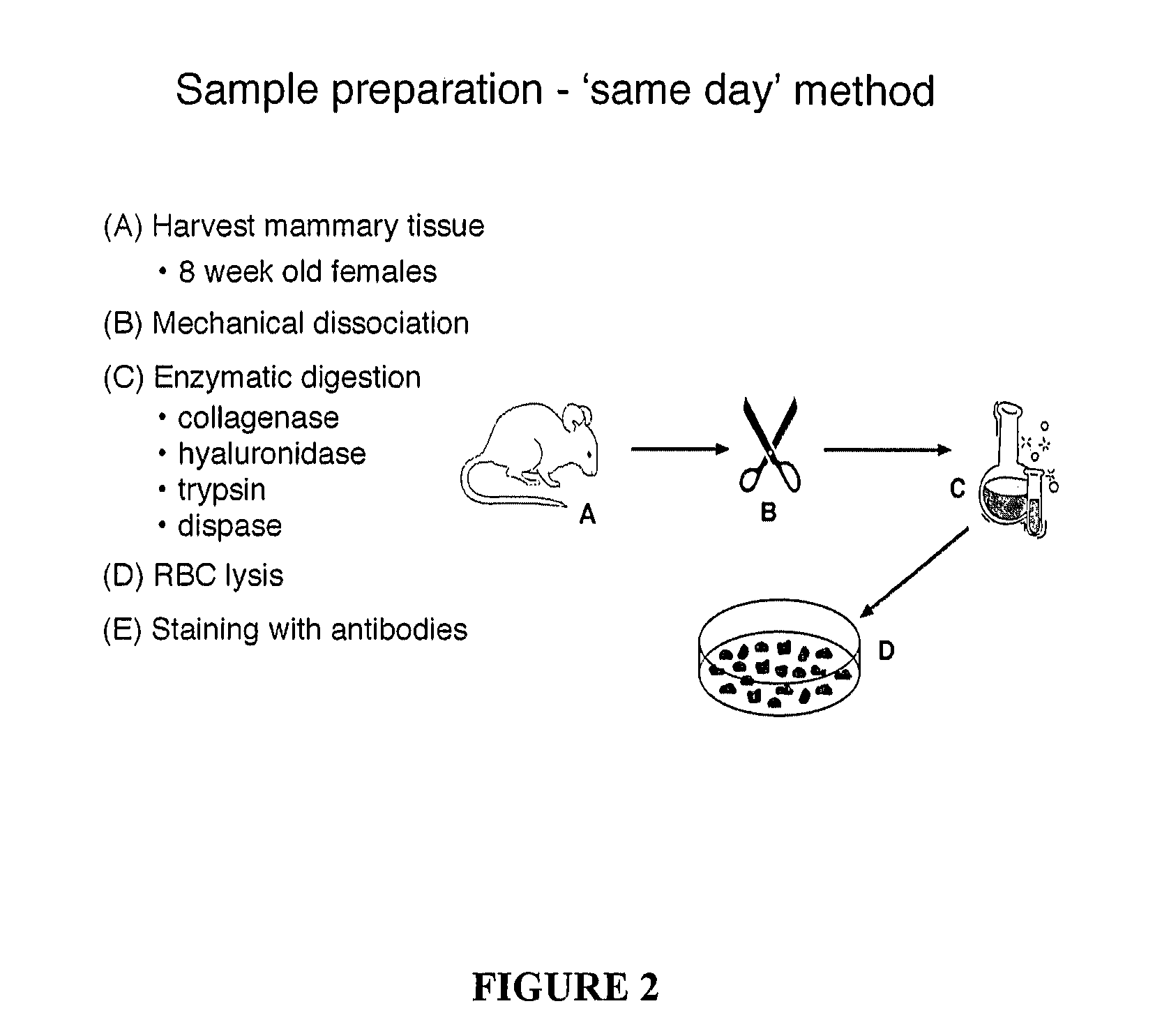
InactiveUS20080038230A1Provide goodFacilitate selection of cellBiocideEpidermal cells/skin cellsCell isolationTumor tissue
The present invention relates generally to a method for the generation of a substantially homogenous population of undifferentiated cells. More particularly, the present invention relates to a method for isolating a substantially homogenous population of stem cells, and in particular, mammary stem cells (MaSCs). The MaSCs of the present invention are isolated on the basis of differential levels of proteins present on their cell surface. The MaSCs of the present invention are particularly useful as targets for identifying agents which modulate MaSC survival, self-renewal, proliferation and / or differentiation in both normal and diseased tissue such as, but not limited to, tumor tissue, and, also as source of tissue for the regeneration, replacement and / or augmentation of tissue damaged and / or lost after disease or injury.
Owner:WALTER & ELIZA HALL INST OF MEDICAL RES
Method for obtaining differentiated cells and /or differentiated cell products from undifferentiated cell and a method of perfusion culture
ActiveUS20150275176A1Easy to getGastrointestinal cellsDead animal preservationPerfusion CultureOrgan of Corti
Disclosed is a method for obtaining differentiated cells and / or differentiated cell products, including the steps of: introducing undifferentiated cells into a perfused organ or living tissue; subjecting the undifferentiated cells introduced to perfusion culture together with the organ or living tissue so as to allow the undifferentiated cells to differentiate, thereby obtaining differentiated cells and / or differentiated cell products; collecting a perfusion culture solution that contains the resulting differentiated cells and / or differentiated cell products; and obtaining the differentiated cells and / or differentiated cell products contained in the collected perfusion culture solution.
Owner:SYSMEX CORP
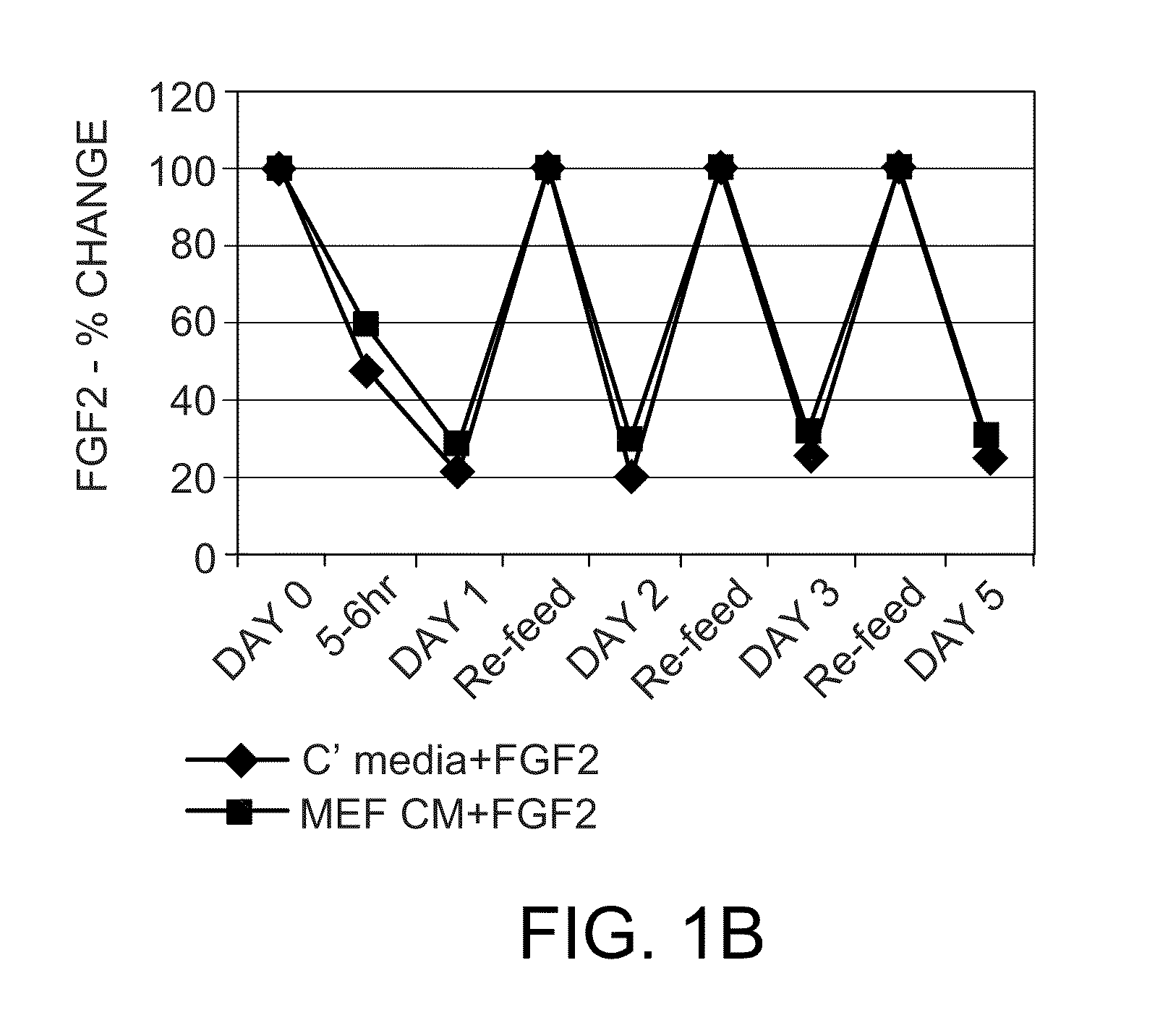
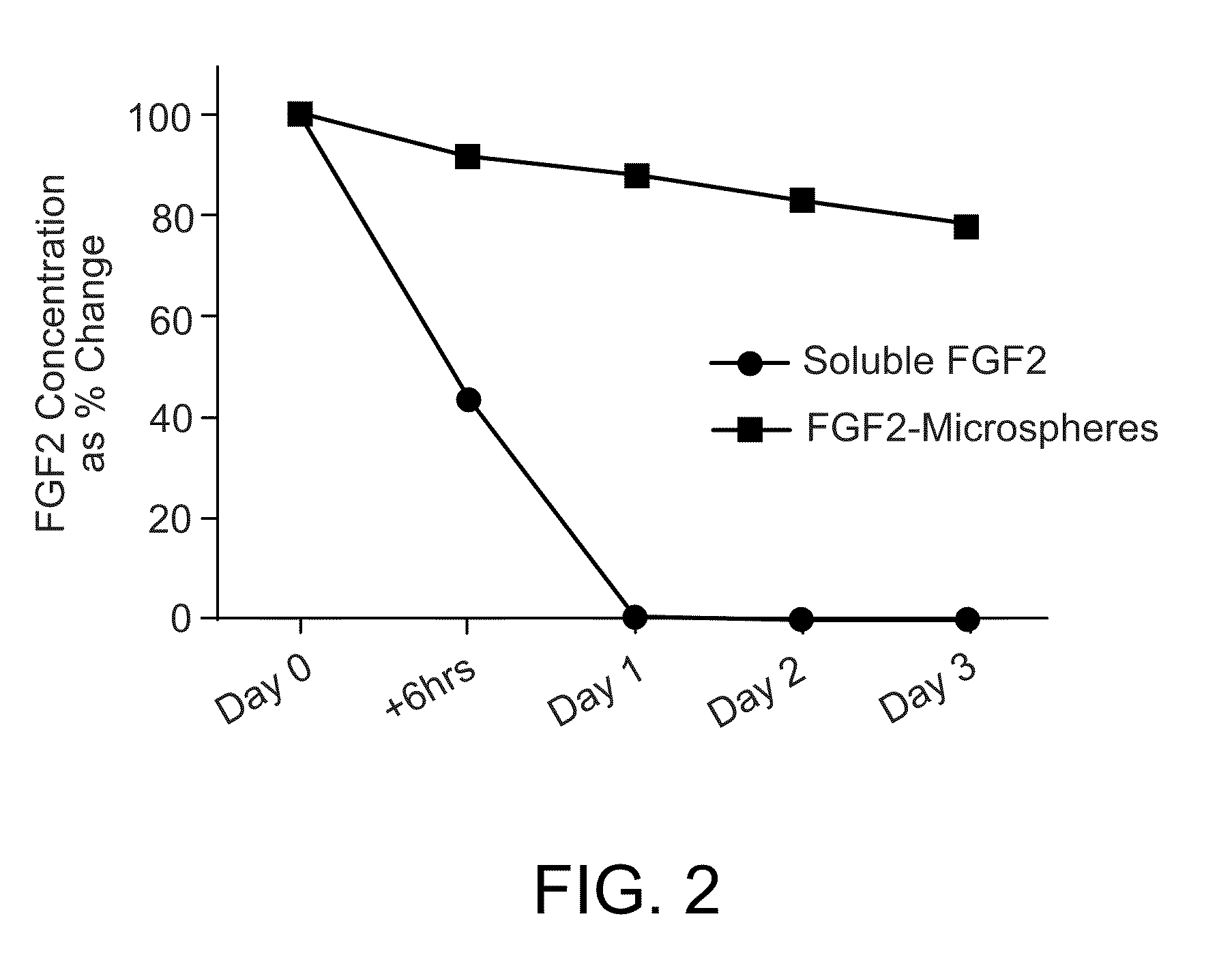
Methods for culturing undifferentiated cells using sustained release compositions
ActiveUS8481308B2Reduces and eliminates their spontaneous differentiationReduce expensesCulture processNervous system cellsProgenitorContinuous release
Methods for culturing undifferentiated mammalian cells, such as stem and progenitor cells, are provided. The methods involve incubating the cell in the presence of a sustained release composition containing at least one growth factor, wherein the sustained release composition continuously releases the growth factor(s), and wherein the presence of the sustained level of growth factor maintains the cell in an undifferentiated state.
Owner:REGENERATIVE RES FOUND
Cell culture method and cell sheet
InactiveCN1761743AGood healing effectBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsCuticleEngineering
Epidermal keratinocytes not having magnetic fine particles incorporated therein and epidermal keratinocytes having magnetic fine particles incorporated therein are seeded in a 24-well ultralow adhesion plate. A neodymium magnet is disposed outside the well bottoms, and the cells are cultured for one day. As a result, control epidermal keratinocytes not having magnetic fine particles incorporated therein do not adhere to the well bottoms, resulting in non-formation of undifferentiated cell sheet. By contrast, epidermal keratinocytes having magnetic fine particles incorporated therein, while being attracted to the well bottoms by magnetic force, form a multilayered cell sheet. This cell sheet can be easily recovered by removing the neodymium magnet disposed outside the well bottoms, causing a magnet having a hydrophilic film stuck thereto to come close to the cell sheet from upside and attract it through the hydrophilic film, and updrawing them.
Owner:本多 裕之 +1
Methods for complex tissue engineering
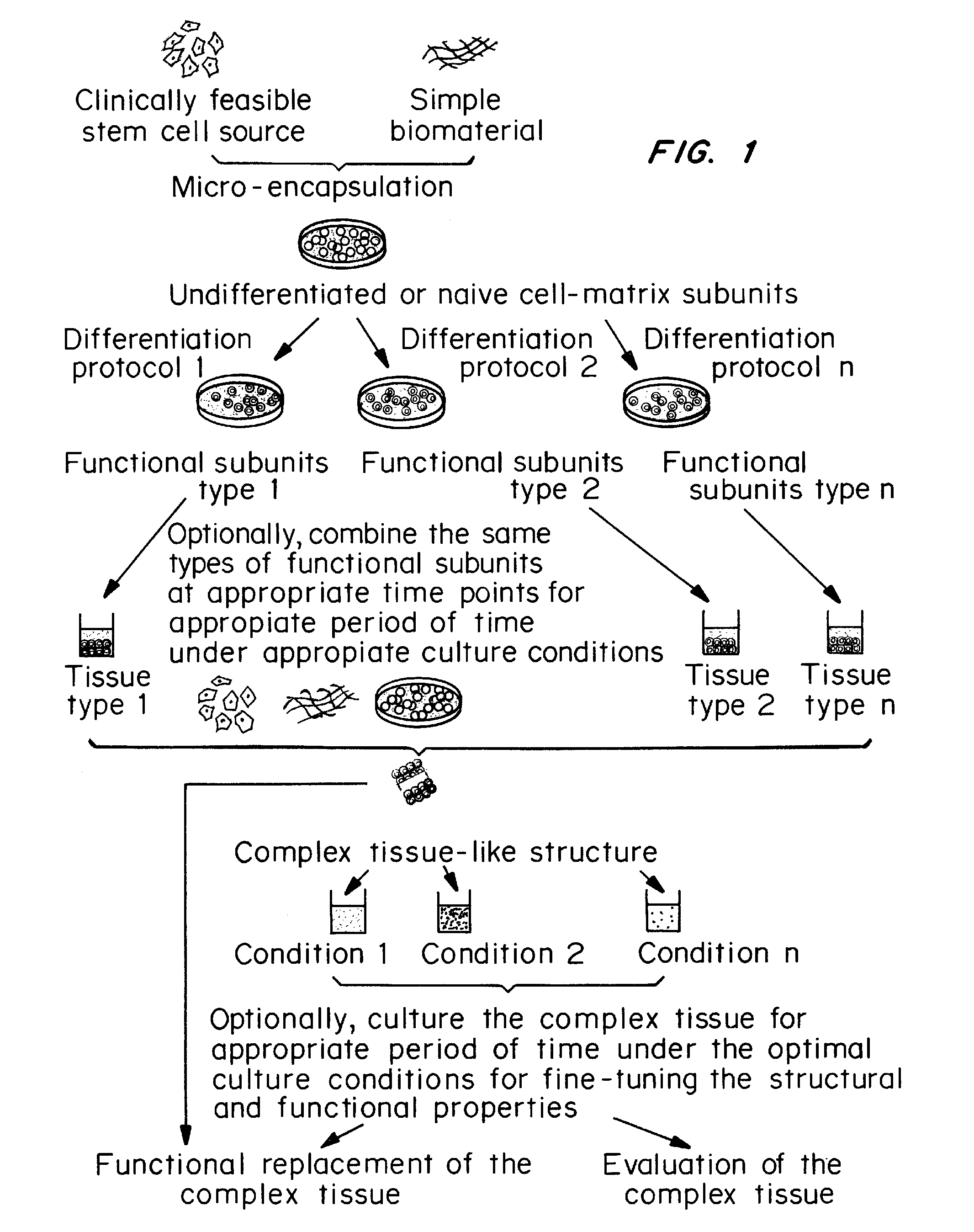
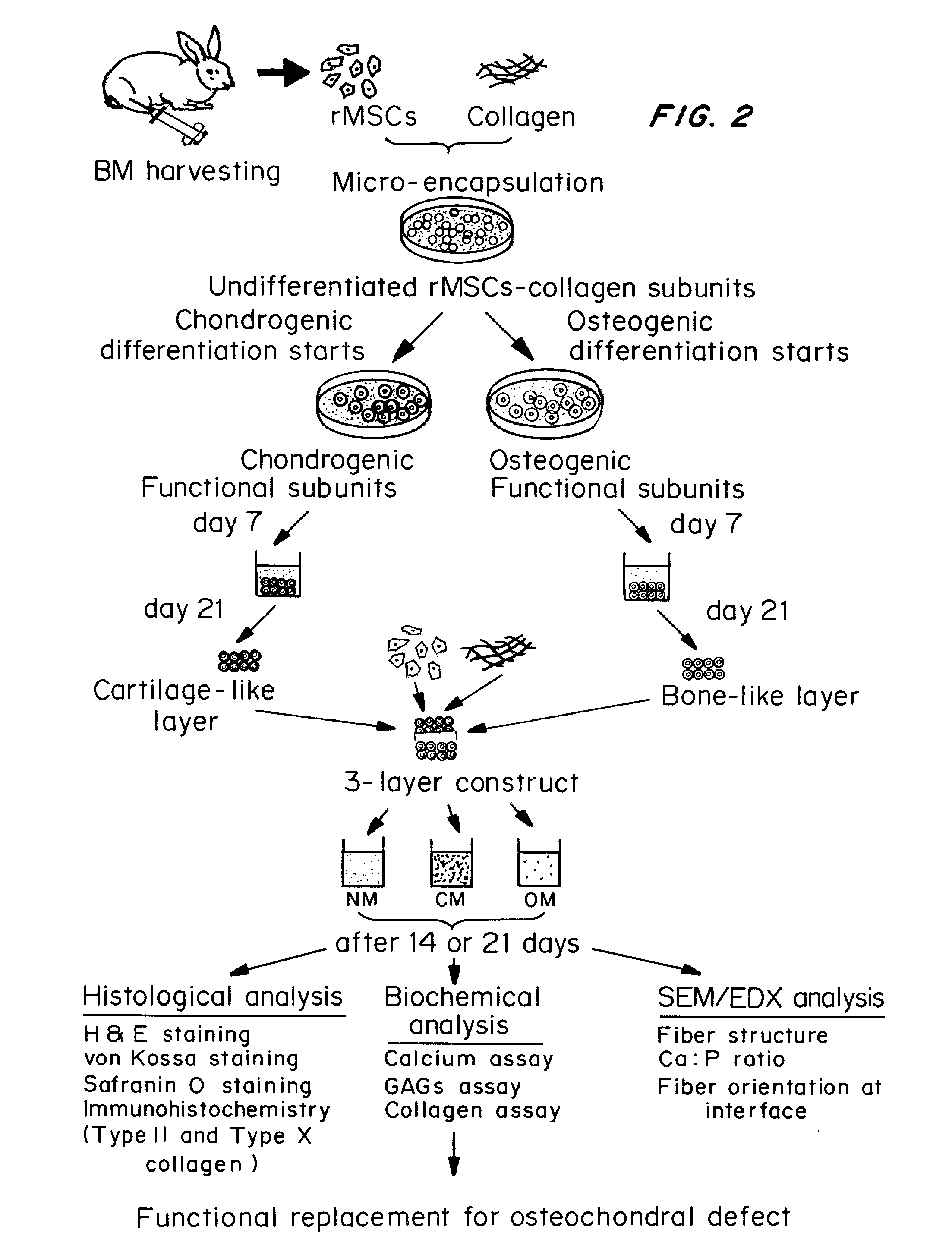
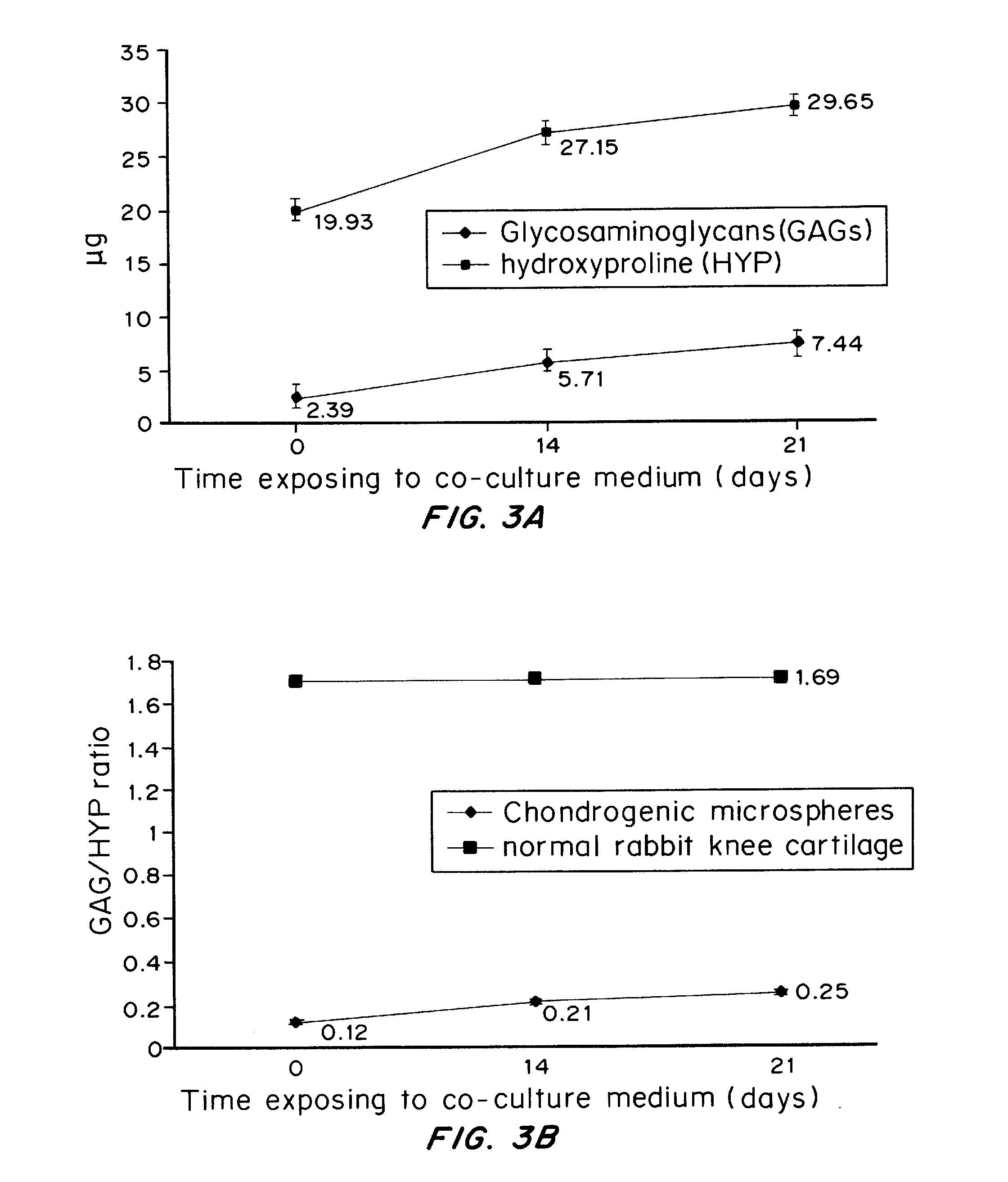
PendingUS20120148632A1Simple, highly flexible and scalableBiocidePharmaceutical delivery mechanismPhysical cultureTissue Graft
A simple, highly flexible and scalable platform for making functional complex tissues with heterogeneity and irregularity is provided. The method includes combining undifferentiated cells, such as pluripotent or multipotent stem cells, with a biomaterial to make multiple undifferentiated or naïve subunits, exposing the undifferentiated or naïve subunits to different cell culture environments for induction of differentiation towards different lineages as required by that complex tissue, and combining the then functional subunits with or without the undifferentiated subunits. The differentiated subunits thus combined can be cultured under biological, chemical, and / or physical culture conditions suitable to fine-tune the structural and functional properties of the bioengineered complex tissue to form a bioengineered tissue graft that mimics the structural and functional characteristics of native complex tissue. The bioengineered tissue graft can then used to replace dysfunctional tissue.
Owner:VERSITECH LTD
Method of effecting de-differentiation of a cell
InactiveUS20110165570A1Maintain pluripotencySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementDe differentiationCell biology
The invention provides a method of effecting de-differentiation of an at least partially differentiated cell or of maintaining pluripotency and / or self-renewing characteristics of an undifferentiated cell. The method comprises increasing the amount or the activity of an Err protein, or a functional fragment thereof, in the cell.
Owner:AGENCY FOR SCI TECH & RES
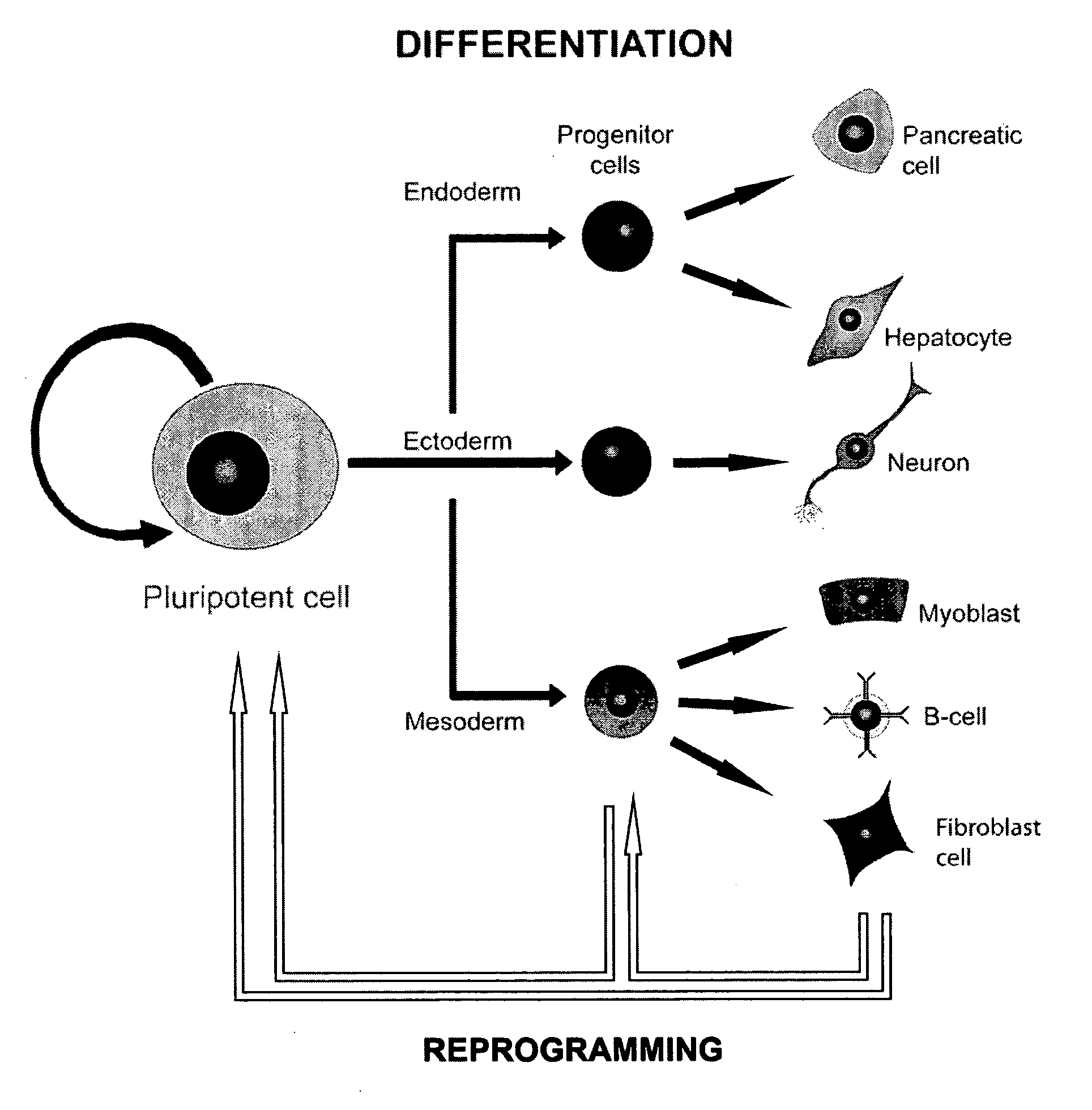
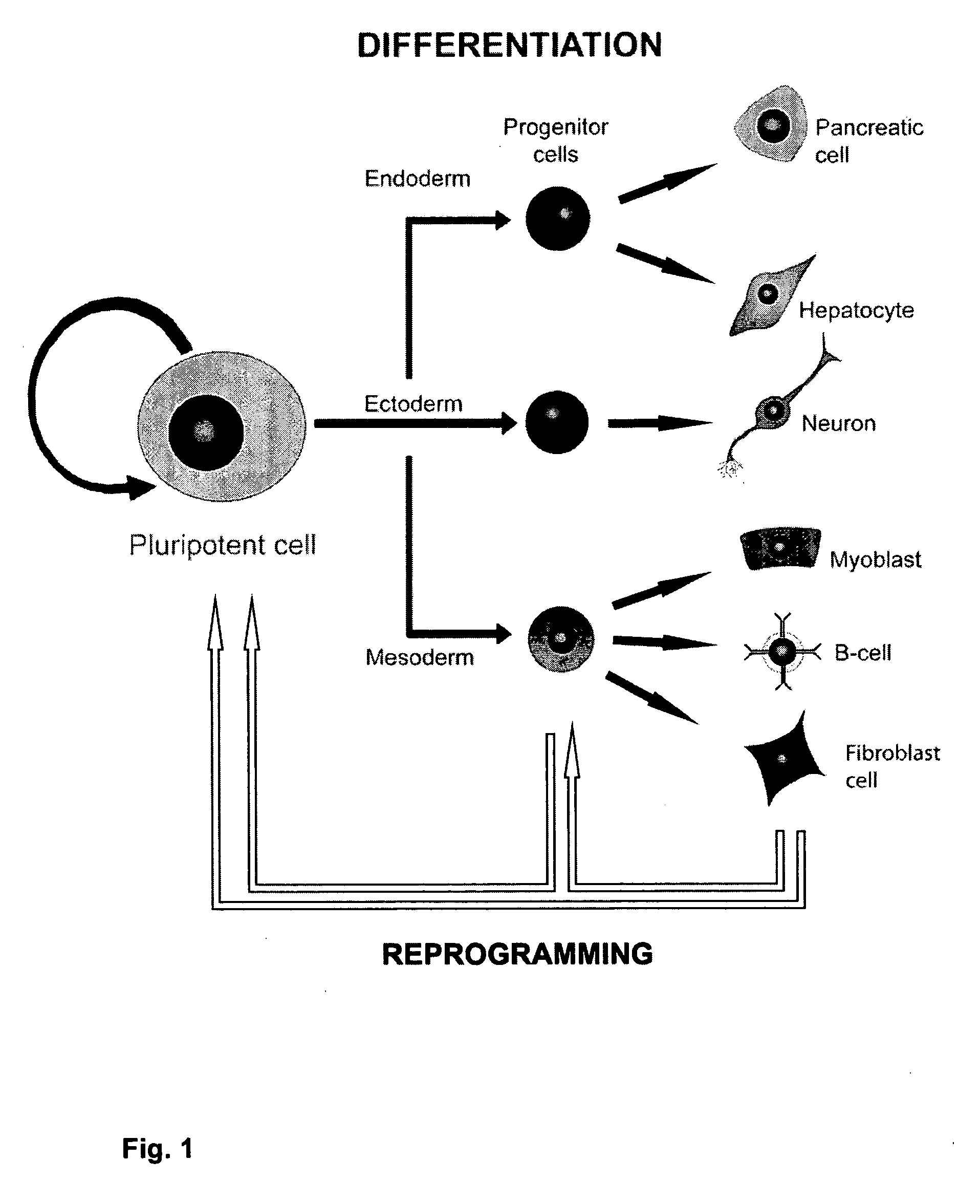
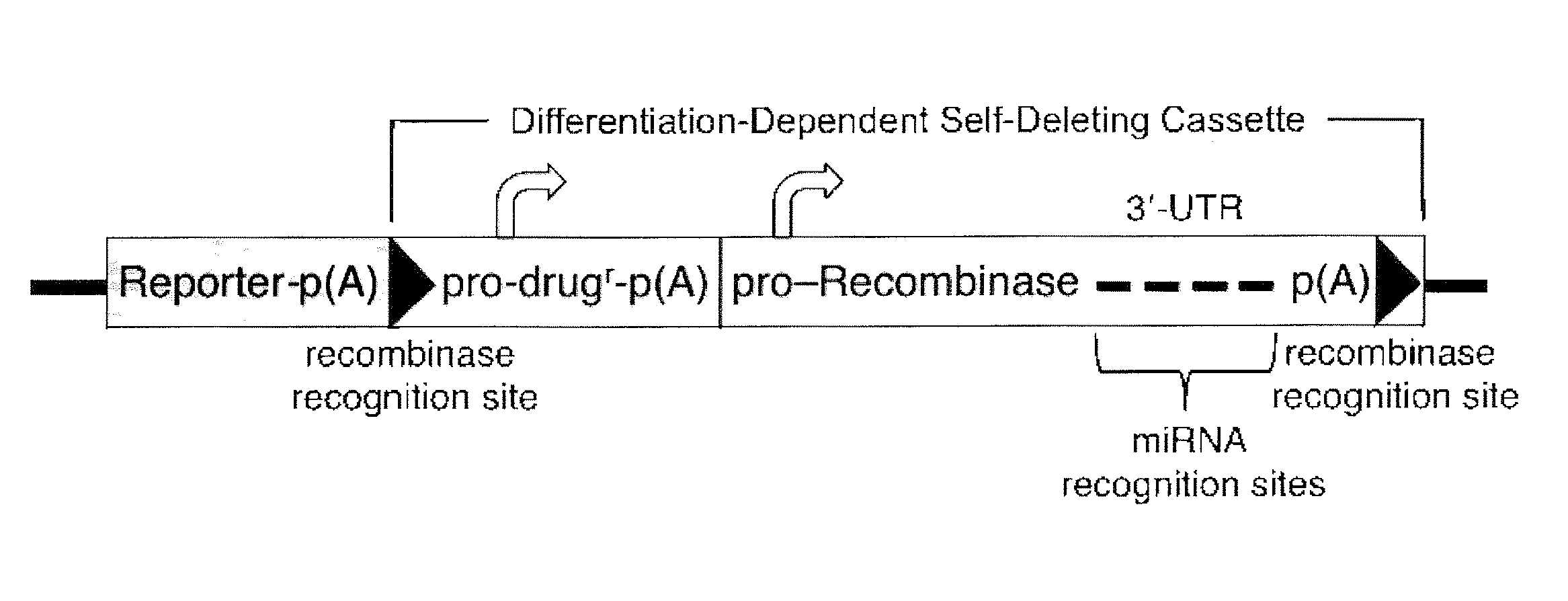
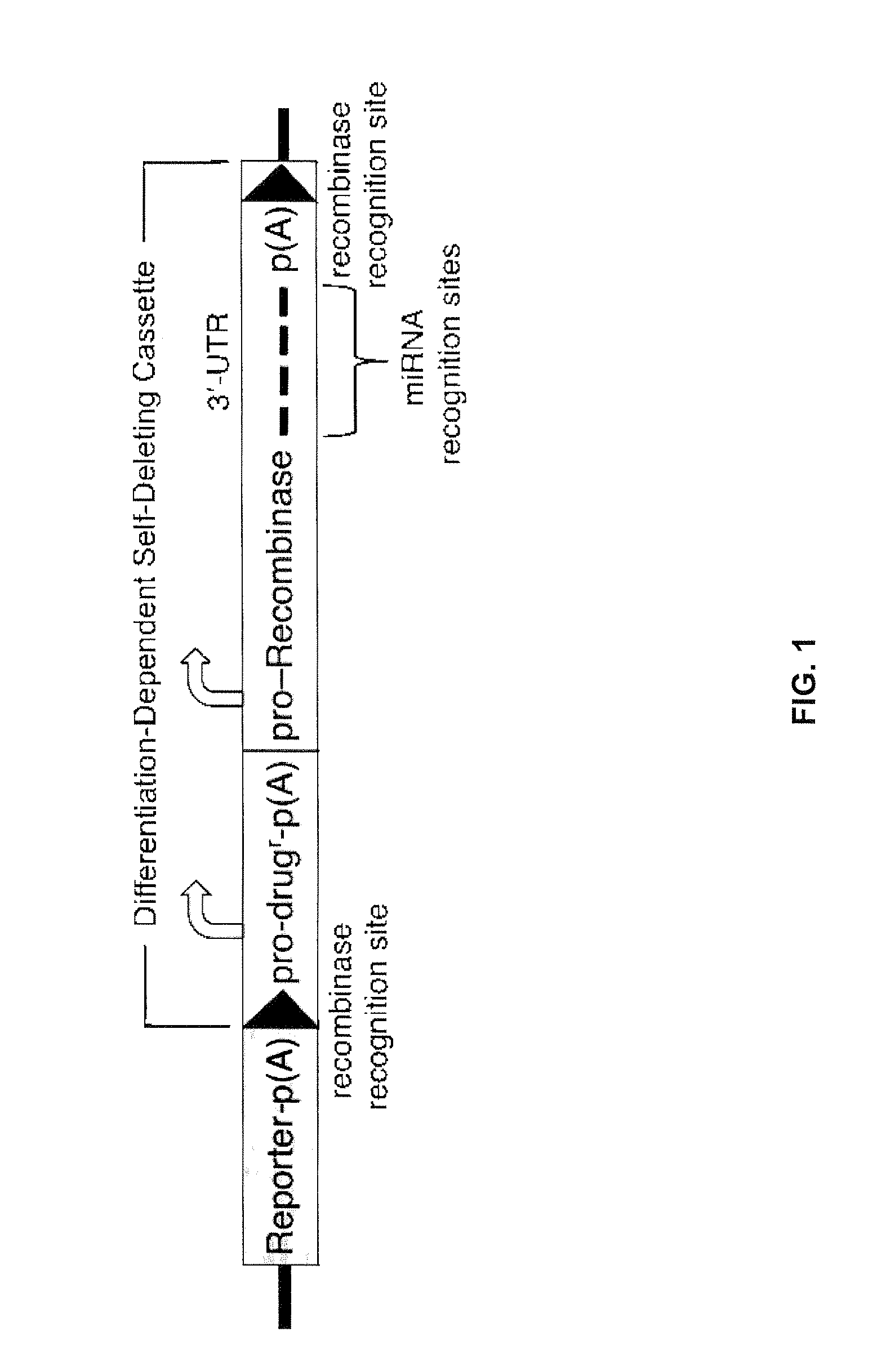
miRNA-Regulated Differentiation-Dependent Self-Deleting Cassette
Targeting constructs and methods of using them are provided for differentiation-dependent modification of nucleic acid sequences in cells and in non-human animals. Targeting constructs comprising a promoter operably linked to a recombinase are provided, wherein the promoter drives transcription of the recombinase in an differentiated cell but not an undifferentiated cell. Promoters include Blimp1, Prm1, Gata6, Gata4, Igf2, Lhx2, Lhx5, and Pax3. Targeting constructs with a cassette flanked on both sides by recombinase sites can be removed using a recombinase gene operably linked to a 3′-UTR that comprises a recognition site for an miRNA that is transcribed in undifferentiated cells but not in differentiated cells. The constructs may be included in targeting vectors, and can be used to automatically modify or excise a selection cassette from an ES cell, a non-human embryo, or a non-human animal.
Owner:REGENERON PHARM INC
Augmentation of organ function
InactiveUS20110059152A1Increase surface areaConducive maturationBiocideMammal material medical ingredientsOrgan functionTissue specific
The present invention provides methods and compositions for augmenting organ functions using small-scale matrix implants generated by seeding tissue-specific or undifferentiated cells onto a matrix materials (e.g., a wafer, sponge, or hydrogel). The seeded matrix composition can then be implanted and will develop into an organ-supplementing structure in vivo. Continued growth and differentiation of the seeded cells on the implanted matrix results in the formation of a primitive vascular system in the tissue. The primitive vascular system can then develop into a mature vascular system, and can also support the growth and development of additional cultured cell populations. The seeded matrix system can be used to introduce a variety of different cells and tissues in vivo.
Owner:CHILDRENS MEDICAL CENT CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com