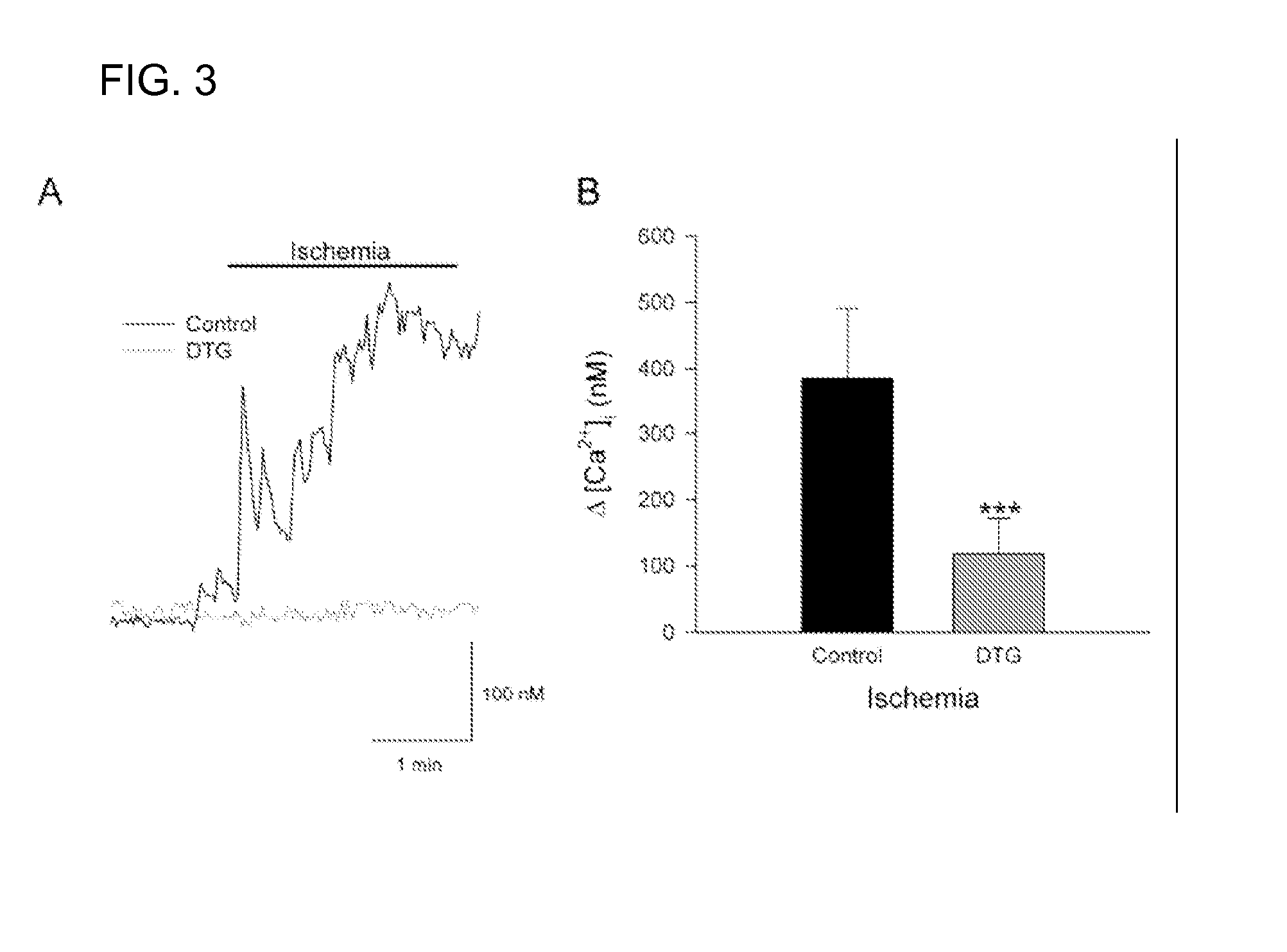Patents
Literature
59 results about "Glial fibrillary acidic protein" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) is a protein that is encoded by the GFAP gene in humans. Glial fibrillary acidic protein is an intermediate filament (IF) protein that is expressed by numerous cell types of the central nervous system (CNS) including astrocytes and ependymal cells during development. GFAP has also been found to be expressed in glomeruli and peritubular fibroblasts taken from rat kidneys Leydig cells of the testis in both hamsters and humans, human keratinocytes, human osteocytes and chondrocytes and stellate cells of the pancreas and liver in rats. First described in 1971, GFAP is a type III IF protein that maps, in humans, to 17q21. It is closely related to its non-epithelial family members, vimentin, desmin, and peripherin, which are all involved in the structure and function of the cell’s cytoskeleton. GFAP is thought to help to maintain astrocyte mechanical strength, as well as the shape of cells but its exact function remains poorly understood, despite the number of studies using it as a cell marker. Glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) was named and first isolated and characterized by Lawrence F. Eng in 1969.
Composition and methods for treatment of neurological disorders and neurodegenerative diseases
InactiveUS6187756B1Increased formationPromote activationBiocideElcosanoid active ingredientsDiseaseGlial fibrillary acidic protein
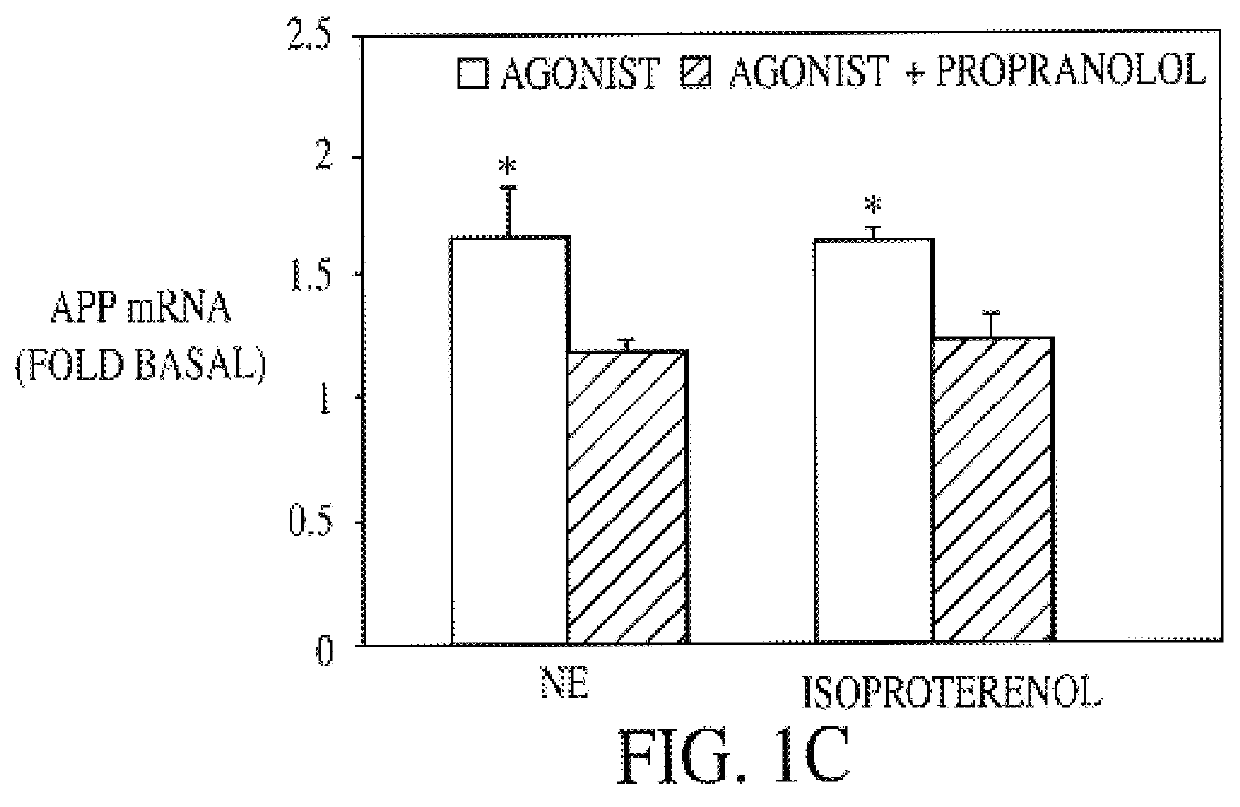
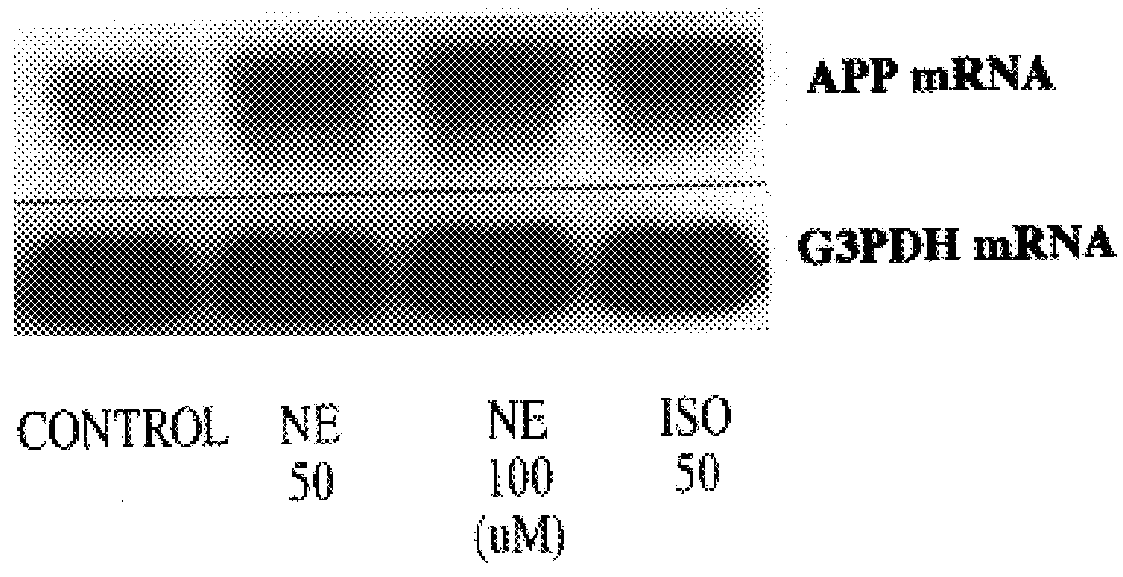
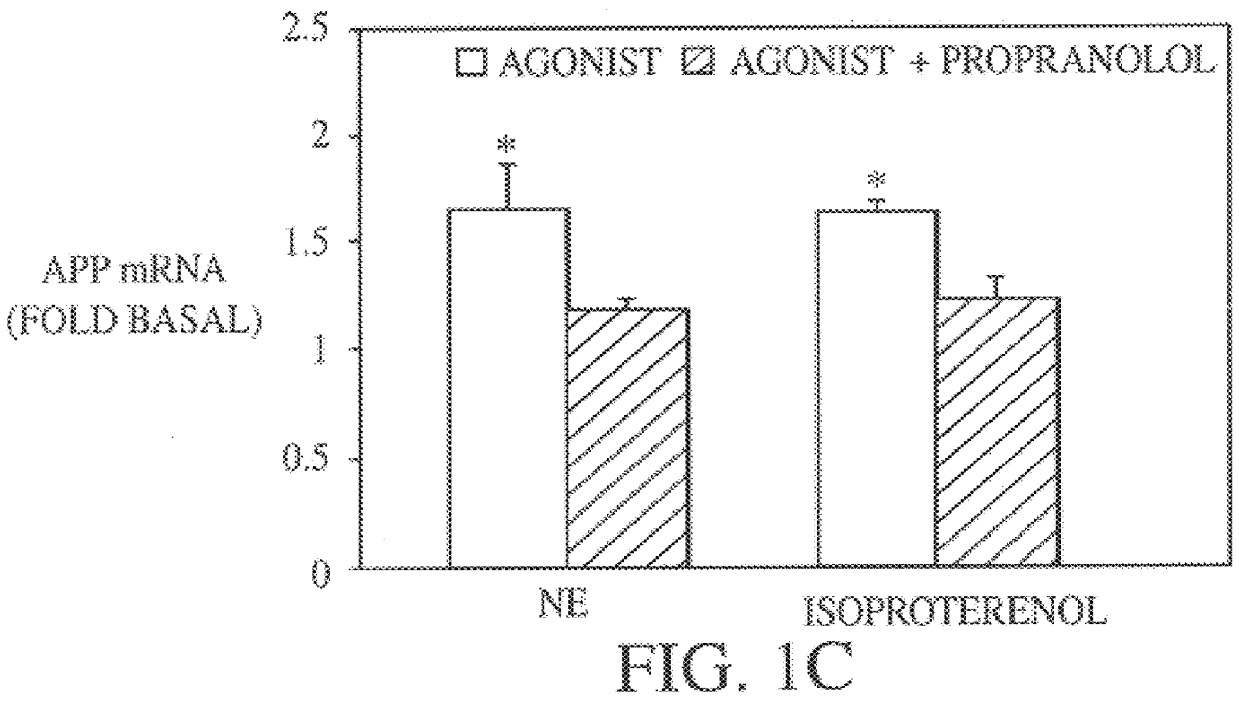
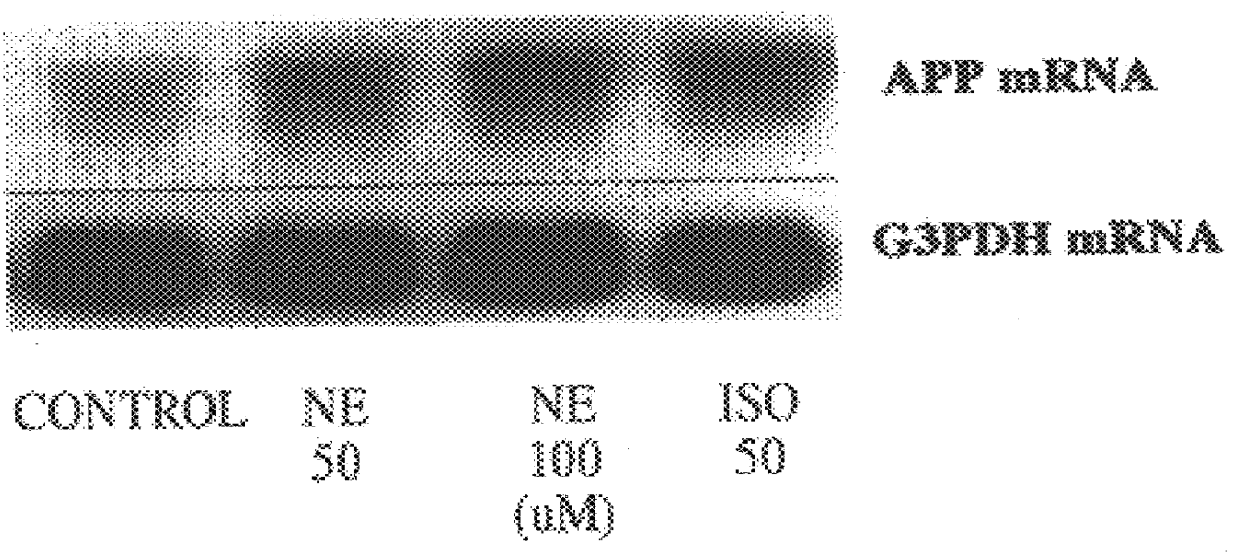
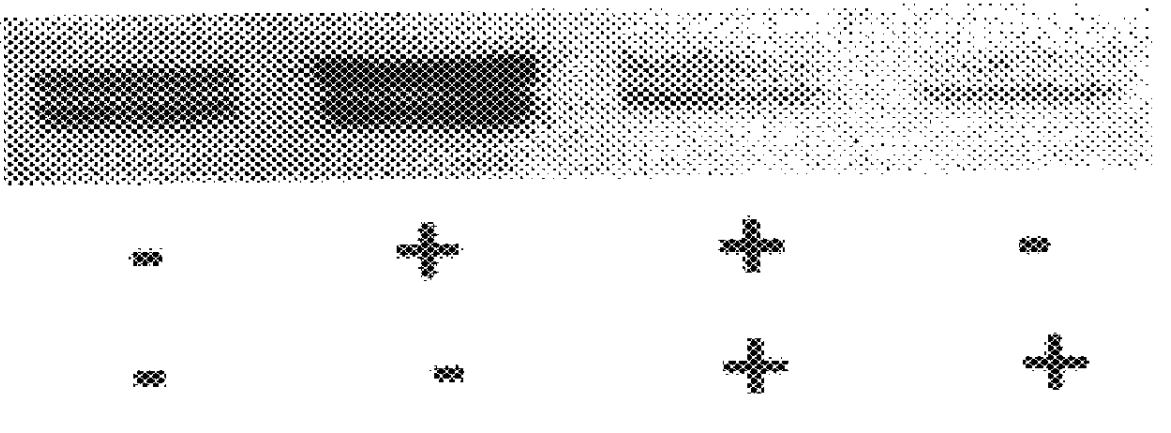
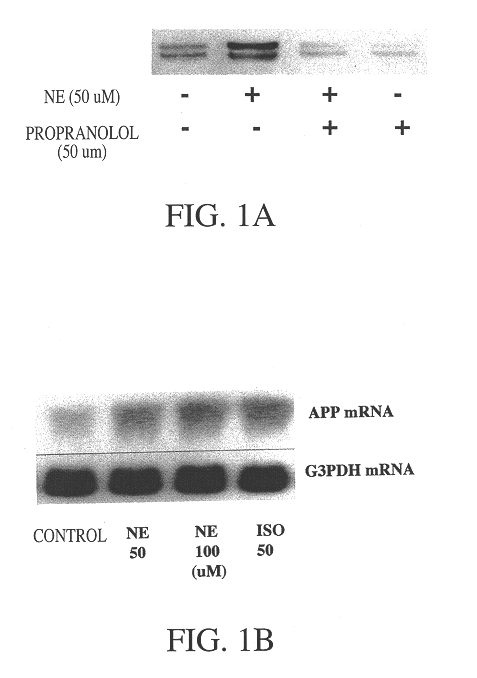
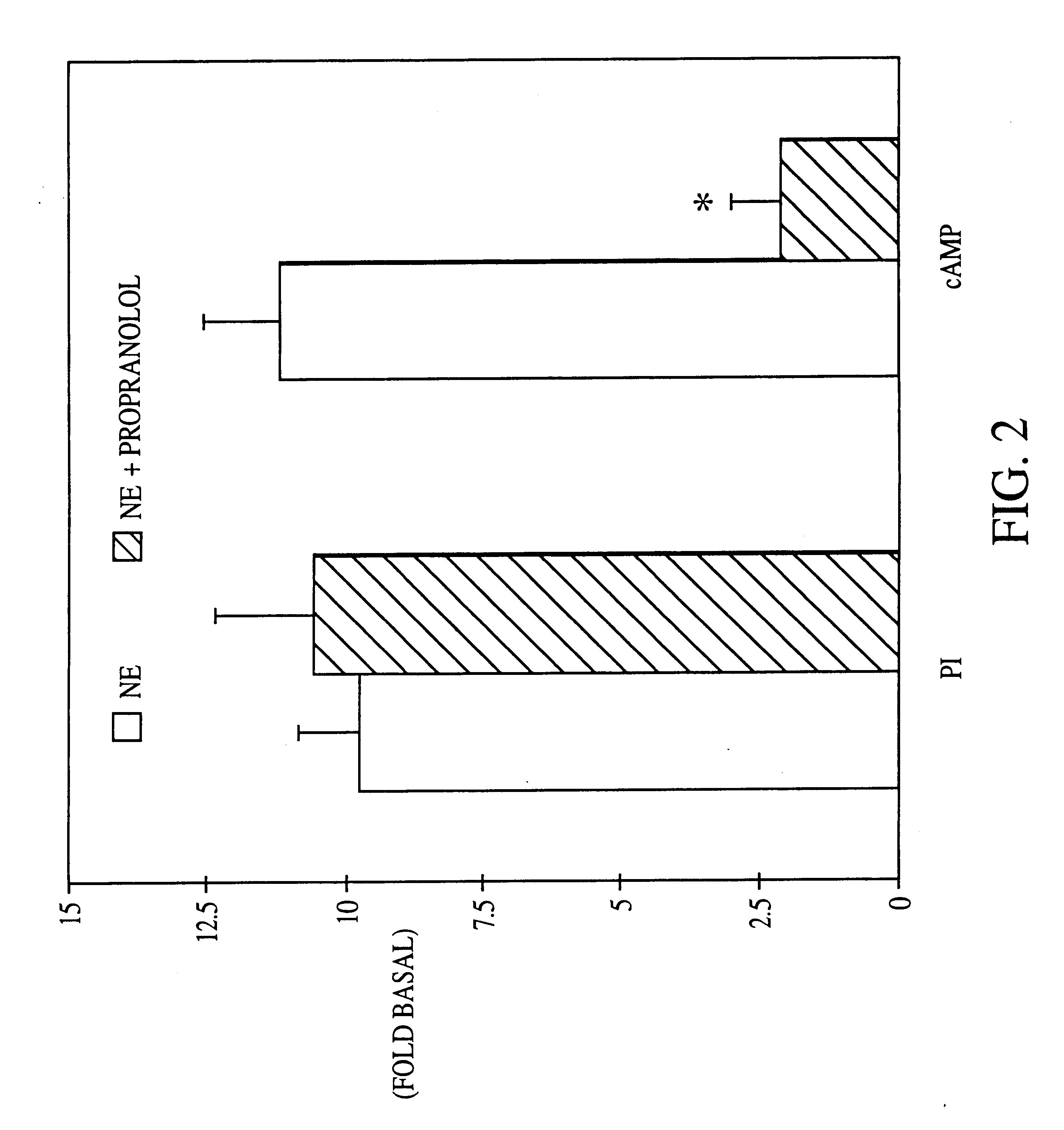
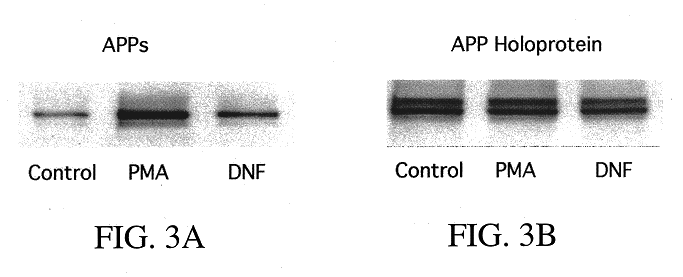
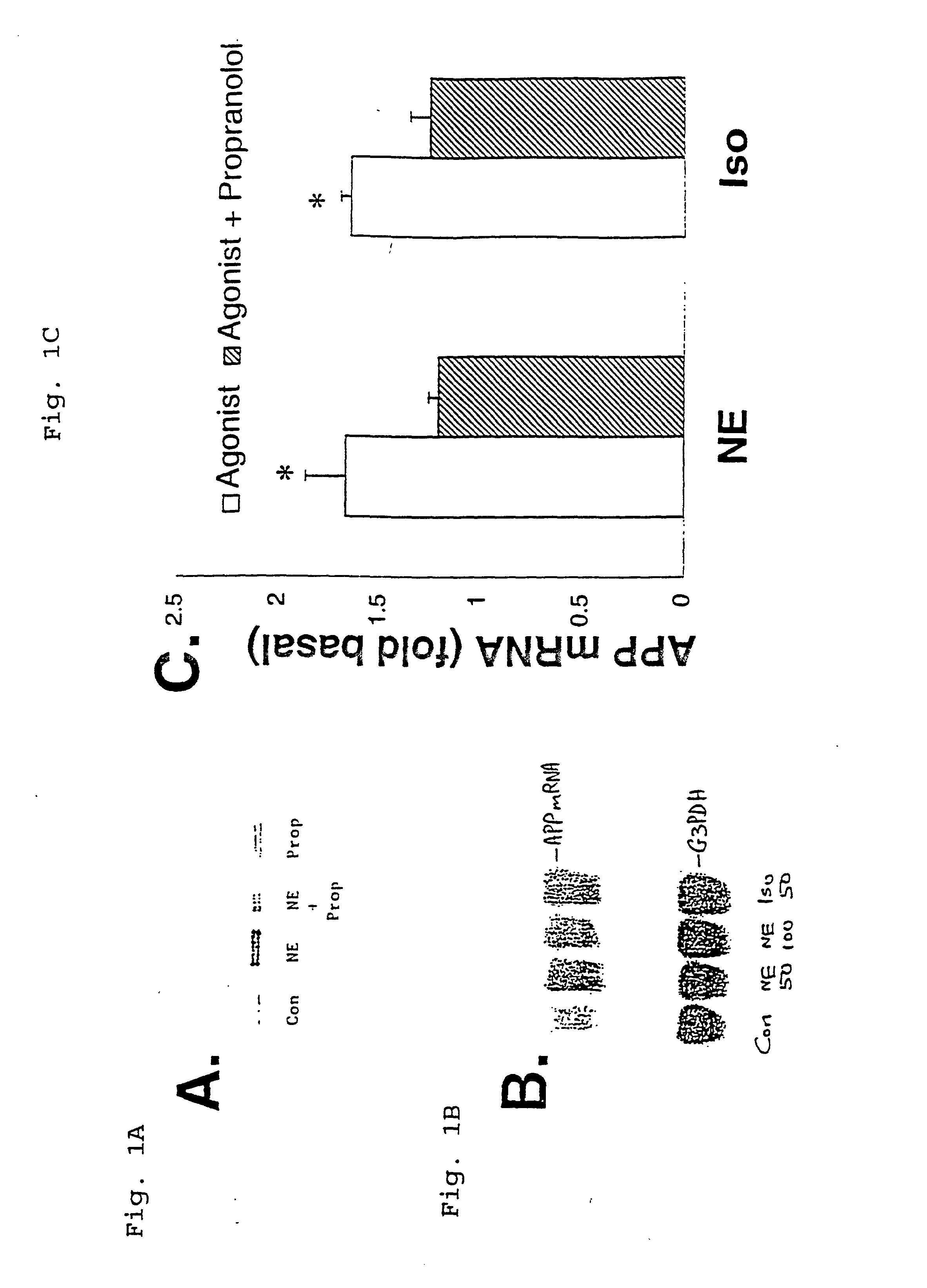
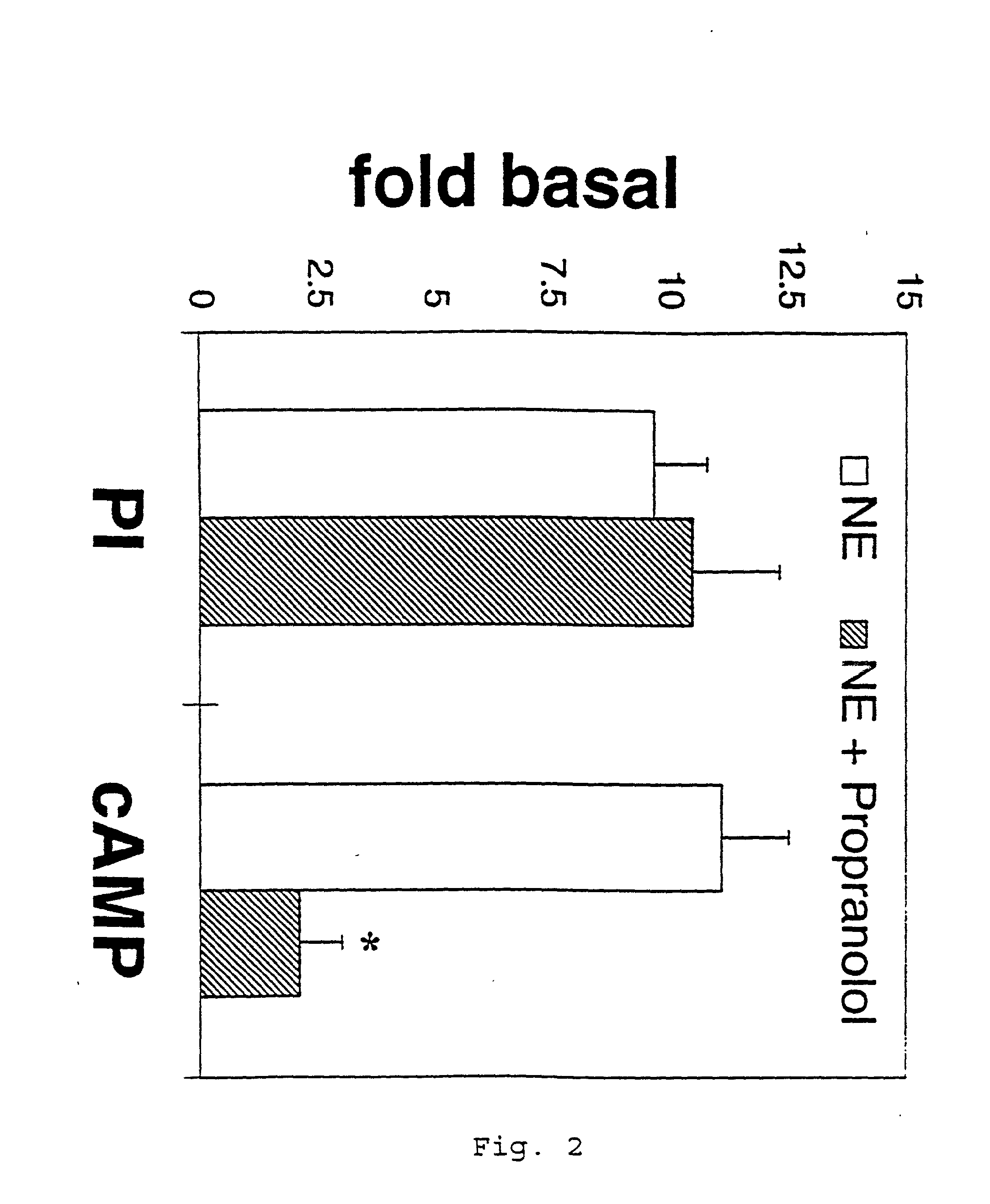
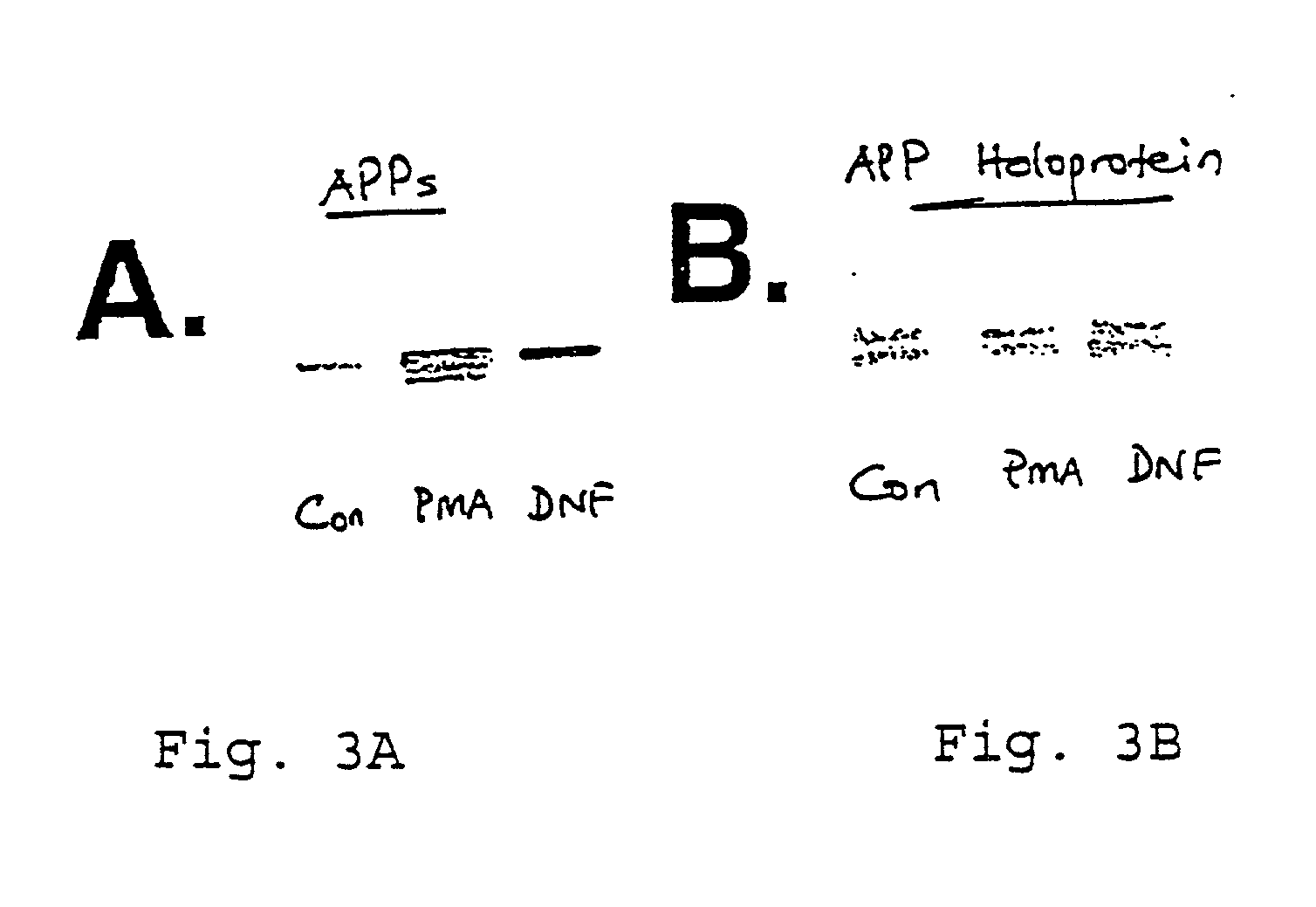
It has been discovered that the stimulation of beta-adrenergic receptors, which activate cAMP formation, give rise to increased APP and GFAP synthesis in astrocytes. Hence, the in vitro or in vivo exposure of neuronal cells to certain compositions comprising beta-adrenergic receptor ligands or agonists, including, e.g., norepinephrine, isoproterenol and the like, increases APP mRNA transcription and consequent APP overproduction. These increases are blocked by beta-adrenergic receptor antagonists, such as propranolol. The in vitro or in vivo treatment of these cells with 8Br-cAMP, prostaglandin E2 (PG E2), forskolin, and nicotine ditartrate also increased APP synthesis, including an increase in mRNA and holoprotein levels, as well as an increase in the expression of glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP). Compositions and methods are disclosed of regulating APP overexpression and mediating reactive astrogliosis through cAMP signaling or the activation of beta-adrenergic receptors. It has further been found that the increase in APP synthesis caused by 8Br-cAMP, PG E2, forskolin, or nicotine ditartrate is inhibited by immunosuppressants or anti-inflammatory agents, such as cyclosporin A, and FK-506 (tacrolimus), as well as ion-channel modulators, including ion chelating agents such as EGTA, or calcium / calmodulin kinase inhibitors, such as KN93. The present invention has broad implications in the alleviation, treatment, or prevention of neurological disorders and neurodegenerative diseases, including Alzheimer's Disease.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Compositions and methods for treatment of neurological disorders and neurodegenerative diseases
InactiveUS6043224AIncreased formationPromote activationBiocideElcosanoid active ingredientsGlial fibrillary acidic proteinDisease
It has been discovered that the stimulation of beta -adrenergic receptors, which activate cAMP formation, give rise to increased APP and GFAP synthesis in astrocytes. Hence, the in vitro or in vivo exposure of neuronal cells to certain compositions comprising beta -adrenergic receptor ligands or agonists, including, e.g., norepinephrine, isoproterenol and the like, increases APP mRNA transcription and consequent APP overproduction. These increases are blocked by beta -adrenergic receptor antagonists, such as propranolol. The in vitro or in vivo treatment of these cells with 8Br-cAMP, prostaglandin E2 (PG E2), forskolin, and nicotine ditartrate also increased APP synthesis, including an increase in mRNA and holoprotein levels, as well as an increase in the expression of glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP). Compositions and methods are disclosed of regulating APP overexpression and mediating reactive astrogliosis through cAMP signaling or the activation of beta -adrenergic receptors. It has further been found that the increase in APP synthesis caused by 8Br-cAMP, PG E2, forskolin, or nicotine ditartrate is inhibited by immunosuppressants or anti-inflammatory agents, such as cyclosporin A, and FK-506 (tacrolimus), as well as ion-channel modulators, including ion chelating agents such as EGTA, or calcium / calmodulin kinase inhibitors, such as KN93. The present invention has broad implications in the alleviation, treatment, or prevention of neurological disorders and neurodegenerative diseases, including Alzheimer's Disease.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Compositions and methods for treatment of neurological disorders and neurodegenerative diseases
InactiveUS6469055B2Increased formationPromote activationBiocideNervous disorderGlial fibrillary acidic proteinDisease
It has been discovered that the stimulation of beta-adrenergic receptors, which activate cAMP formation, give rise to increased APP and GFAP synthesis in astrocytes. Hence, the in vitro or in vivo exposure of neuronal cells to certain compositions comprising beta-adrenergic receptor ligands or agonists, including, e.g., norepinephrine, isoproterenol and the like, increases APP mRNA transcription and consequent APP overproduction. These increases are blocked by beta-adrenergic receptor antagonists, such as propranolol. The in vitro or in vivo treatment of these cells with 8Br-cAMP, prostaglandin E2 (PG E2), forskolin, and nicotine ditartrate also increased APP synthesis, including an increase in mRNA and holoprotein levels, as well as an increase in the expression of glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP). Compositions and methods are disclosed of regulating APP overexpression and mediating reactive astrogliosis through cAMP signaling or the activation of beta-adrenergic receptors. It has further been found that the increase in APP synthesis caused by 8Br-cAMP, PG E2, or forskolin is inhibited by immunosuppressants, immunophilin ligands, or anti-inflammatory agents, such as cyclosporin A, and FK-506 (tacrolimus), as well as ion-channel modulators, including ion chelating agents such as EGTA, or calcium / calmodulin kinase inhibitors, such as KN93. The present invention has broad implications in the alleviation, treatment, or prevention of neurological disorders and neurodegenerative diseases, including Alzheimer's Disease.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Compositions and methods for treatment of neurological disorders and neurodegenerative diseases
InactiveUS20020052407A1Prevent APP over-expressionInhibit overexpressionBiocideNervous disorderGlial fibrillary acidic proteinDisease
It has been discovered that the stimulation of beta-adrenergic receptors, which activate cAMP formation, give rise to increased APP and GFAP synthesis in astrocytes. Hence, the in vitro or in vivo exposure of neuronal cells to certain compositions comprising beta-adrenergic receptor ligands or agonists, including, e.g., norepinephrine, isoproterenol and the like, increases APP mRNA transcription and consequent APP overproduction. These increases are blocked by beta-adrenergic receptor antagonists, such as propranolol. The in vitro or in vivo treatment of these cells with 8Br-cAMP, prostaglandin E2 (PG E2), forskolin, and nicotine ditartrate also increased APP synthesis, including an increase in mRNA and holoprotein levels, as well as an increase in the expression of glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP). Compositions and methods are disclosed of regulating APP overexpression and mediating reactive astrogliosis through cAMP signaling or the activation of beta-adrenergic receptors. It has further been found that the increase in APP synthesis caused by 8Br-cAMP, PG E2, or forskolin is inhibited by immunosuppressants, immunophilin ligands, or anti-inflammatory agents, such as cyclosporin A, and FK-506 (tacrolimus), as well as ion-channel modulators, including ion chelating agents such as EGTA, or calcium / calmodulin kinase inhibitors, such as KN93. The present invention has broad implications in the alleviation, treatment, or prevention of neurological disorders and neurodegenerative diseases, including Alzheimer's Disease.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
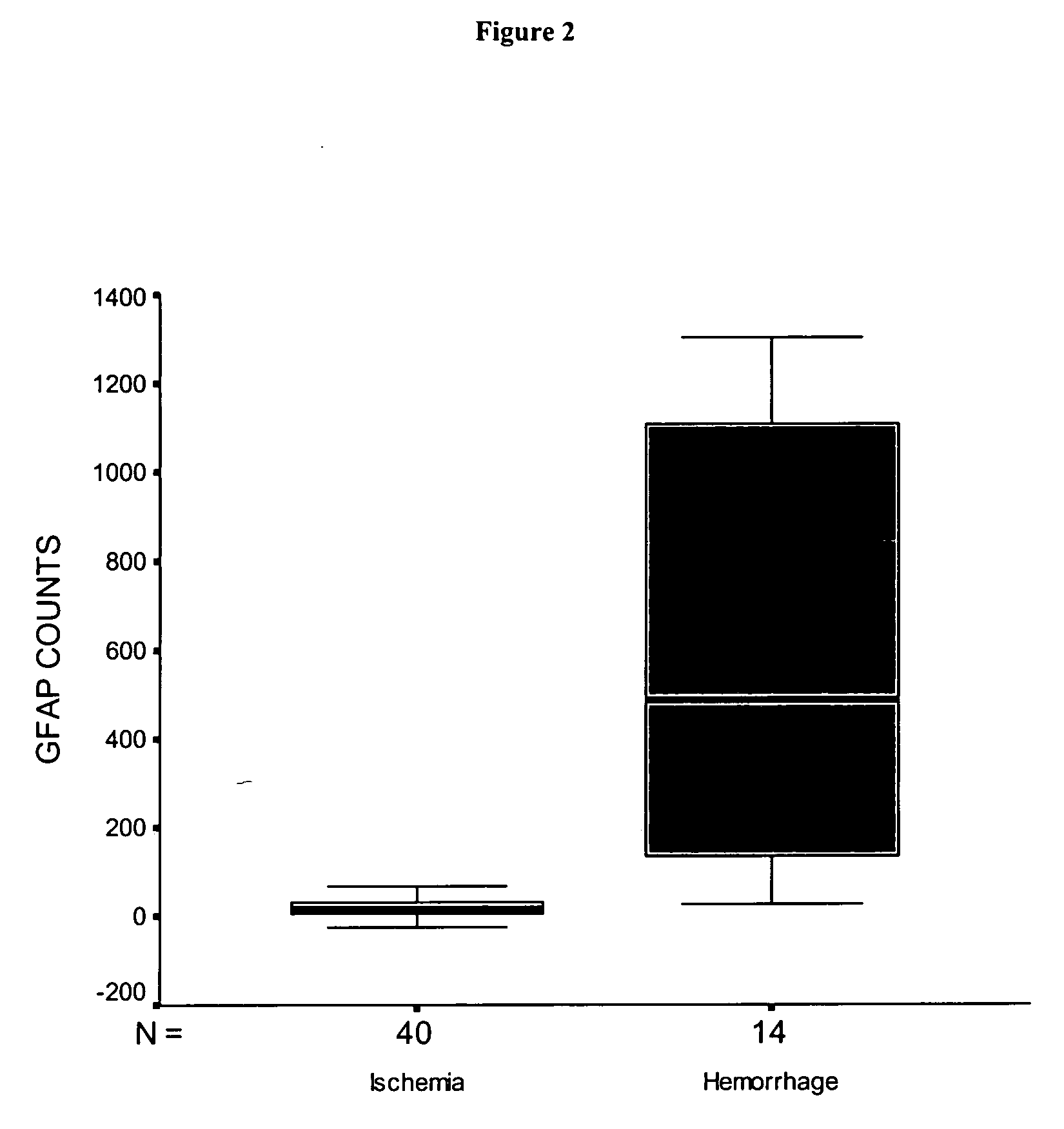
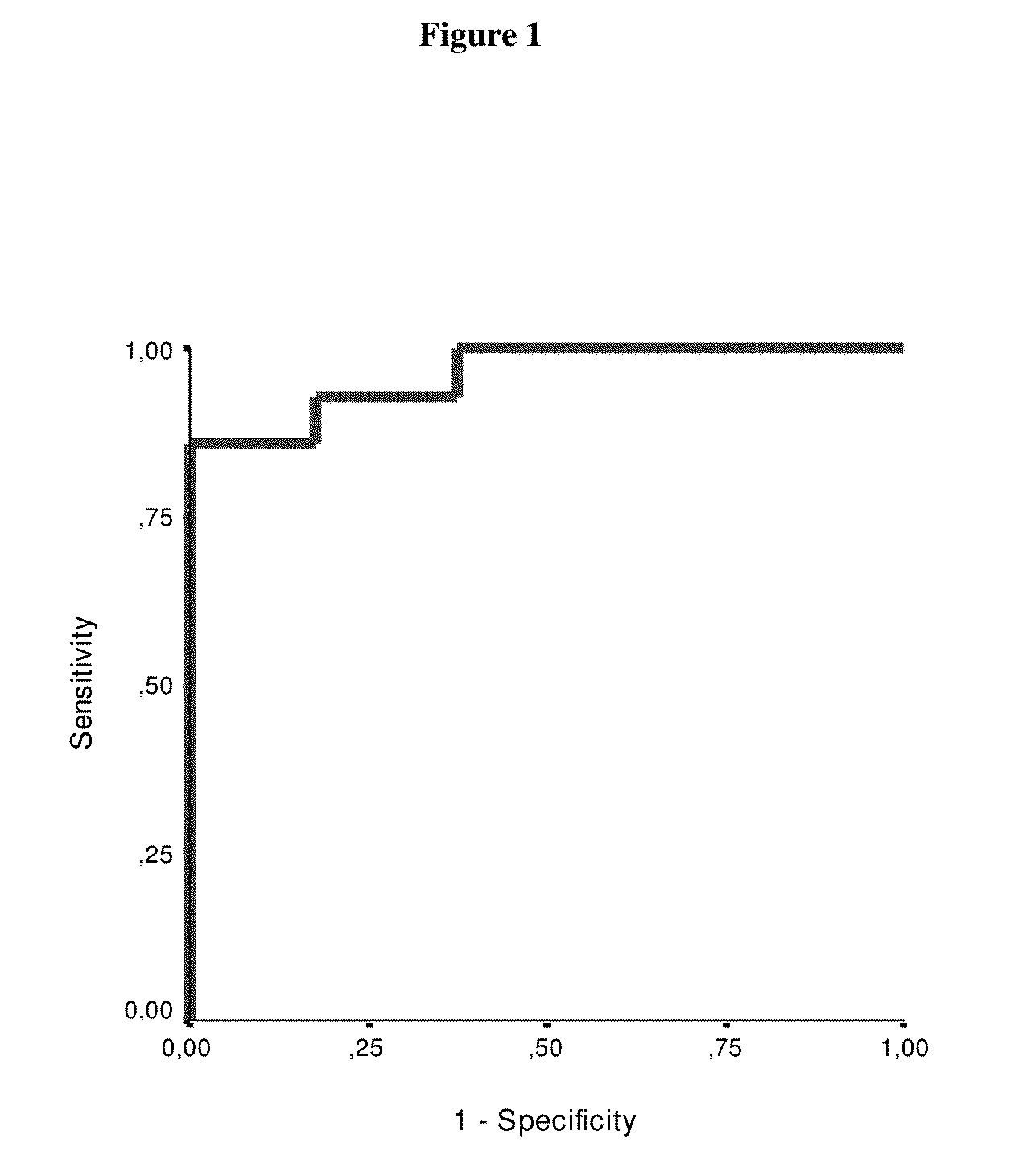
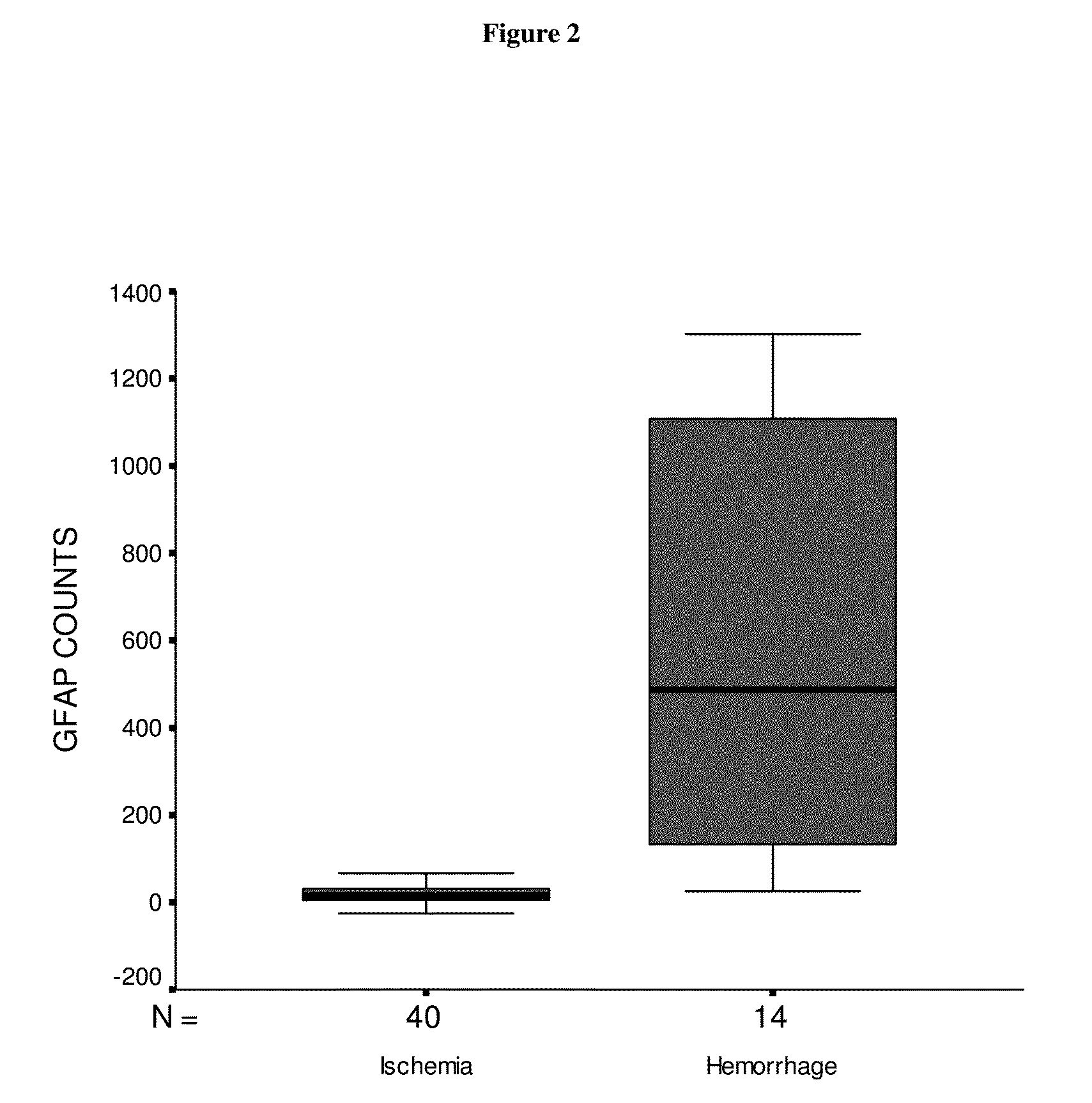
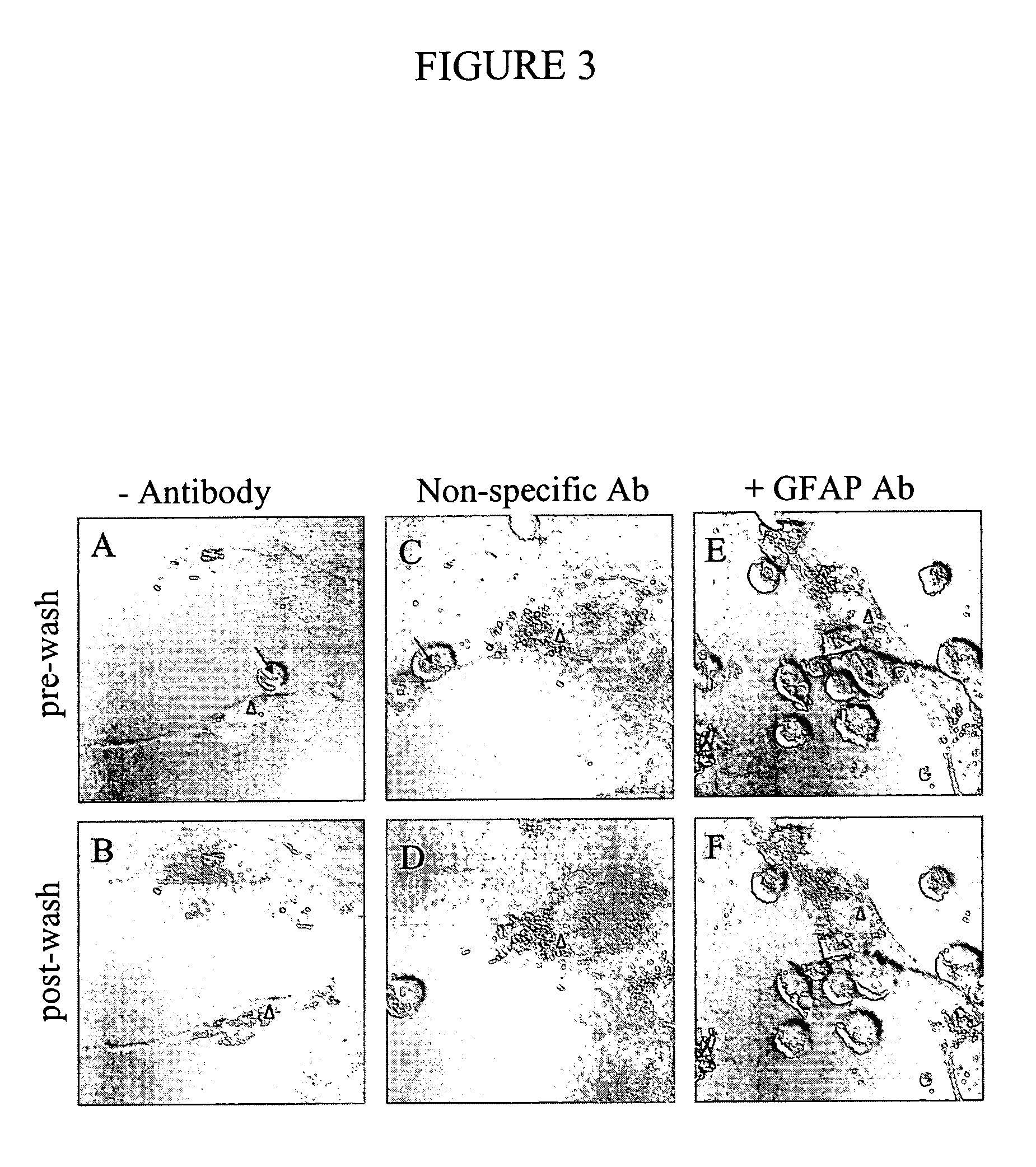
Use of GFAP for identification of intracerebral hemorrhage
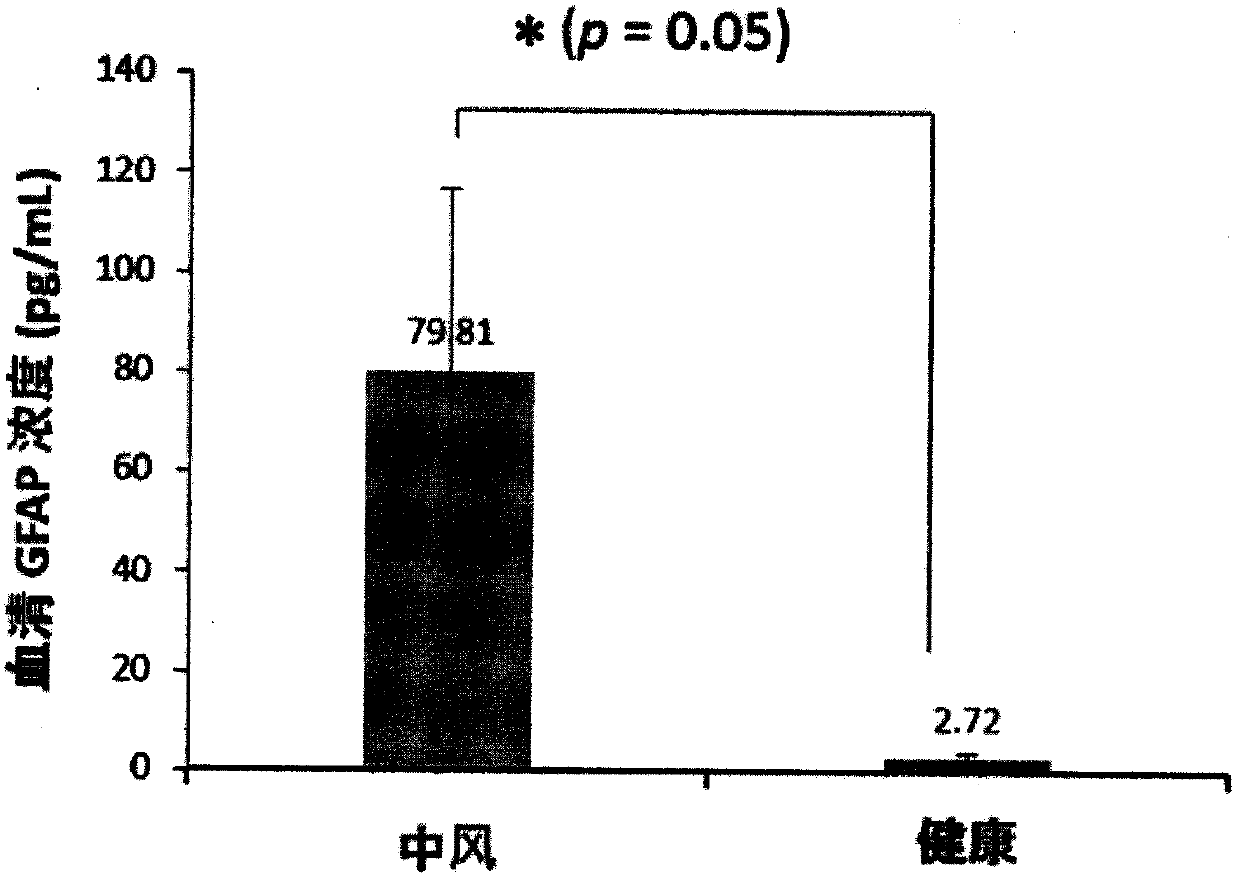
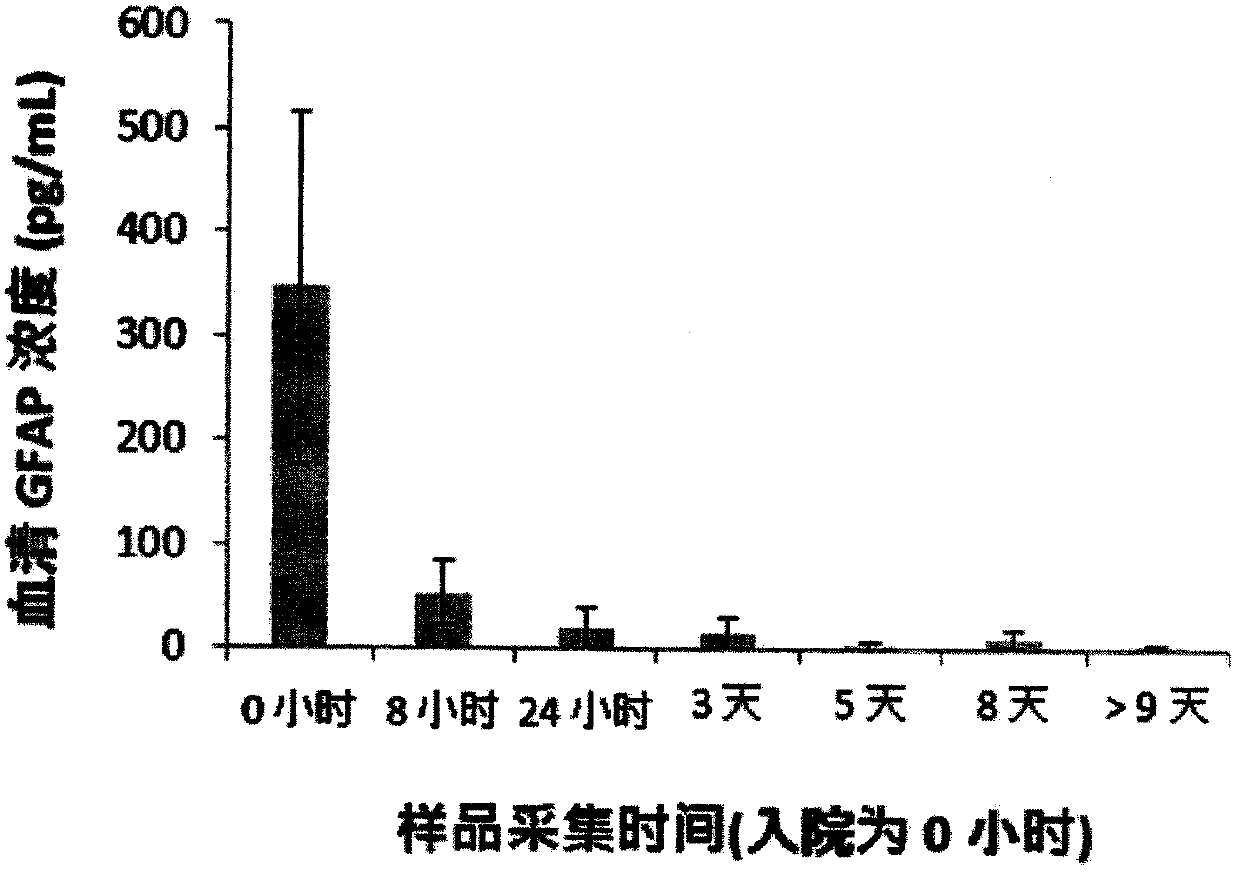
The present invention relates to the use of glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) as a diagnostic marker for intracerebral hemorrhage. The invention especially relates to methods for the early detection of intracerebral hemorrhage. Such early and rapid detection can be performed rapidly e.g. by a test strip format assay. GFAP can be used as a stand-alone marker or in combination with one or more other markers.
Owner:FOERCH CHRISTIAN +1
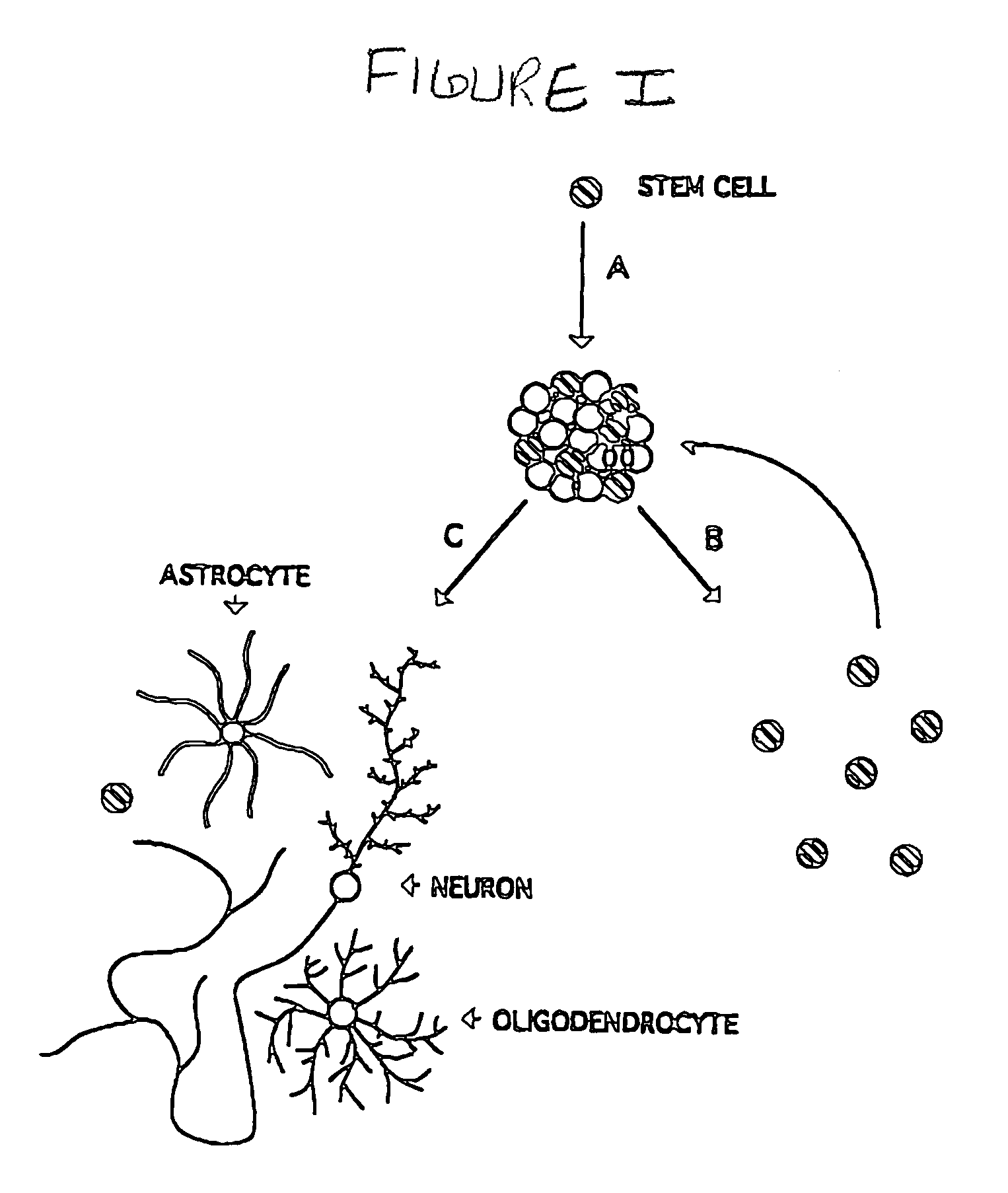
Multipotent neural stem cell compositions
ActiveUS7361505B1Peptide/protein ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsGlial fibrillary acidic proteinGlial Fibrillary Acid Protein
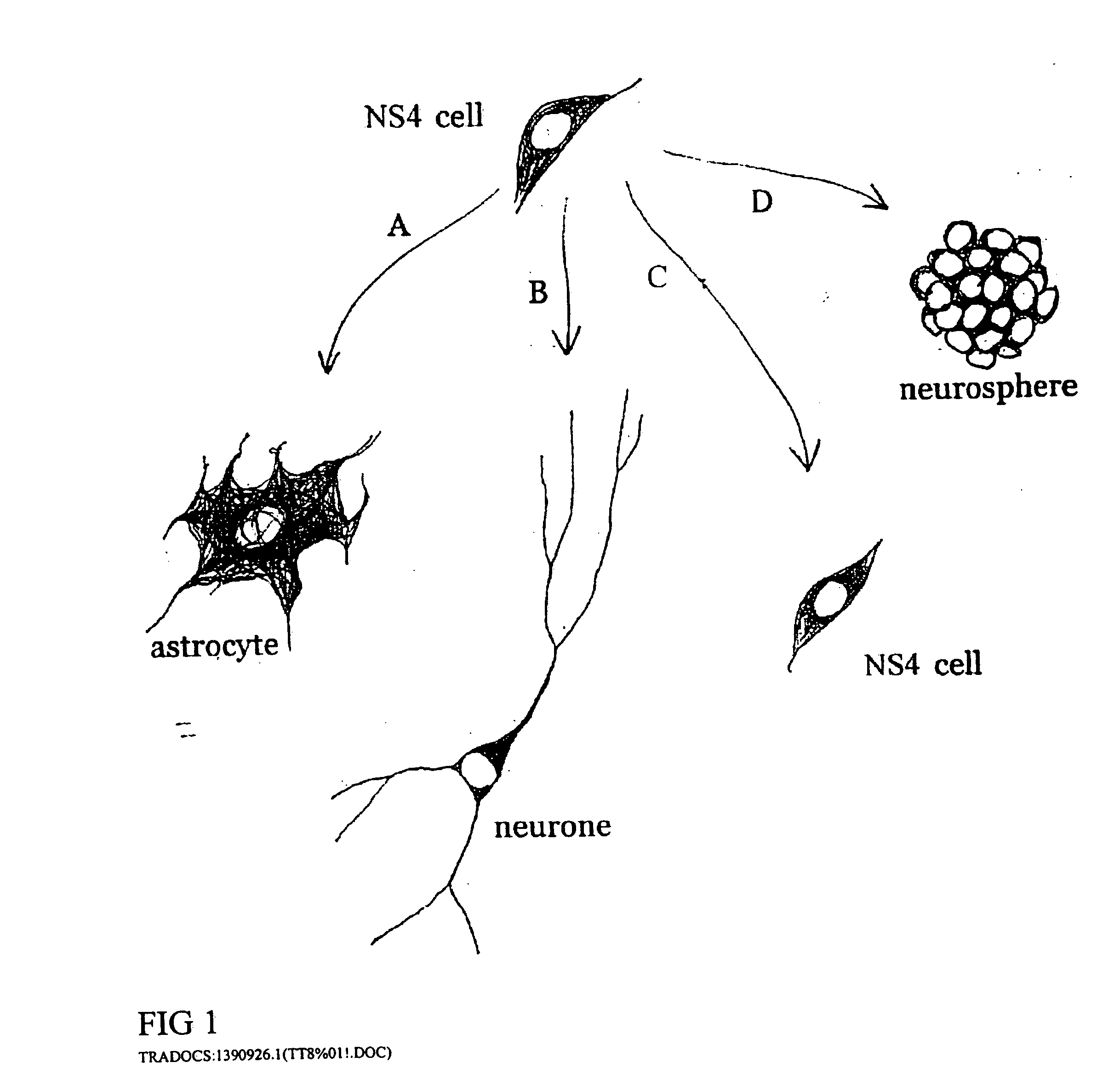
The invention provides in vitro cell culture compositions consisting of neurospheres and culture medium, wherein the neurospheres consist of undifferentiated cells that are nestin+, glial fibrillary acid protein (GFAP)−, neurofilament (NF)−, and myelin basic protein (MBP)− and are not nestin−.
Owner:BOCO SILICON VALLEY INC
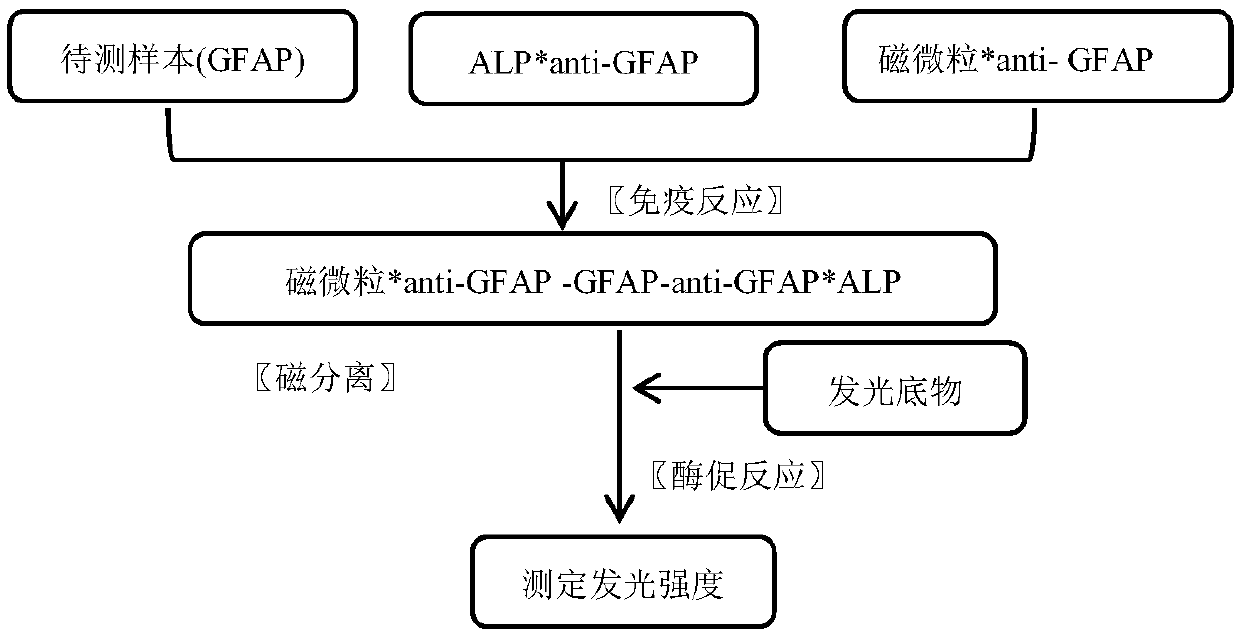
Magnetic-particle separation chemiluminescence immunoassay for detecting glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP)
InactiveCN109521004ALow pre-processing requirementsGuaranteed SensitivityChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceAntigenGlial fibrillary acidic protein
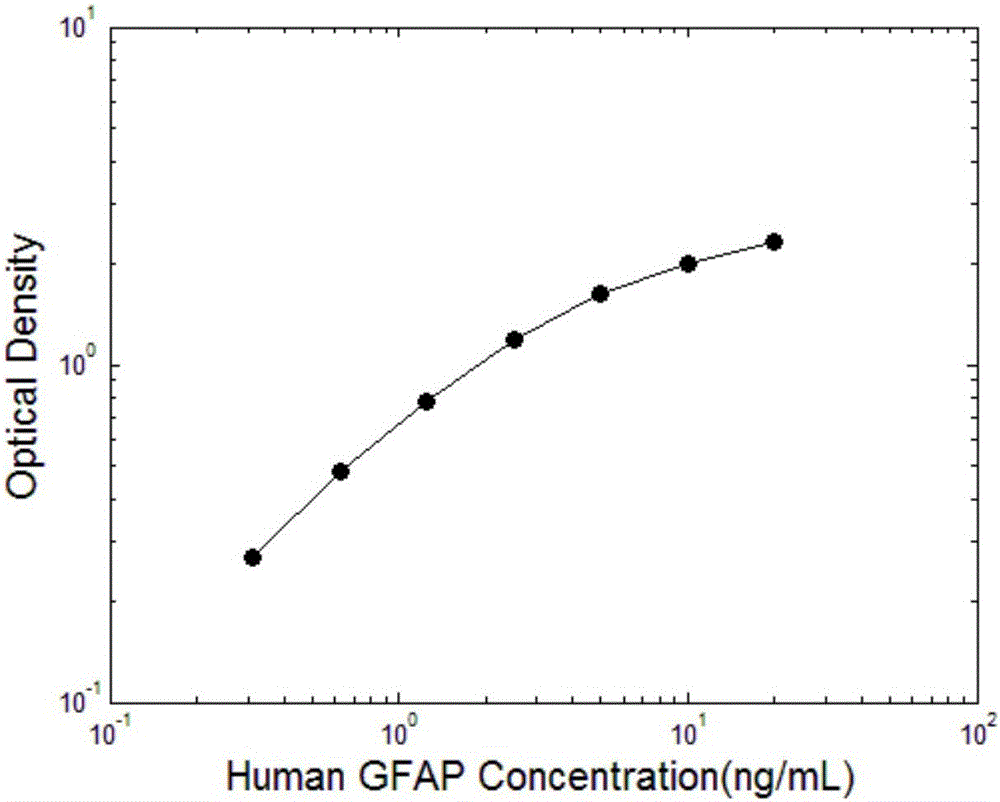
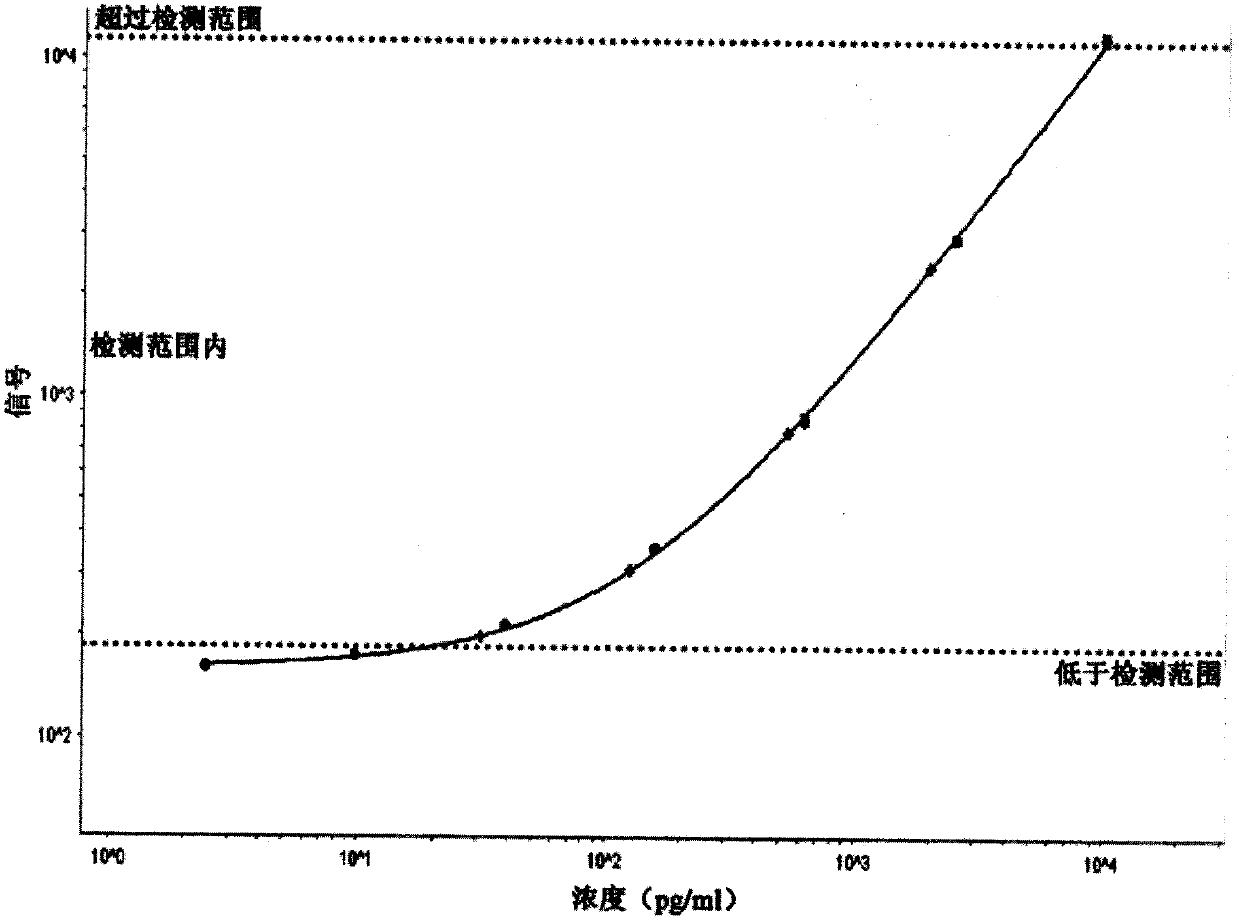
The invention discloses a magnetic-particle separation chemiluminescence immunodetection method for glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) of a human body. A kit comprises a calibration product, a quality control product reagent A, a reagent B, concentrated cleaning liquid and luminescent substrate liquid, wherein the calibration product is antigen containing a series concentrations of glial fibrillary acidic proteins and is used for establishing standard curves; the quality control product is prepared by buffering solution of antigens containing certain-concentration glial fibrillary acidic protein; the reagent A is antibody solution containing certain-concentration glial fibrillary acidic protein and labeled by magnetic particles; the reagent B is antibody solution containing certain-concentration glial fibrillary acidic protein and labeled by the alkaline phosphatase; the concentrated cleaning liquid is used for preparing cleaning liquid; the luminescent substrate liquid is luminescent substrate solution catalyzed by alkaline phosphatase (ALP). The magnetic-particle separation chemiluminescence immunodetection method disclosed by the invention has the beneficial effects that thesignal intensity and the sensitivity of immunoreaction are greatly improved, low-content substances also can generate strong chemiluminescence signals when in immunobinding, and a method with more accuracy, precision, convenience and simpleness is provided for detecting the glial fibrillary acidic protein of the human body.
Owner:BEIJING LEADMAN BIOCHEM
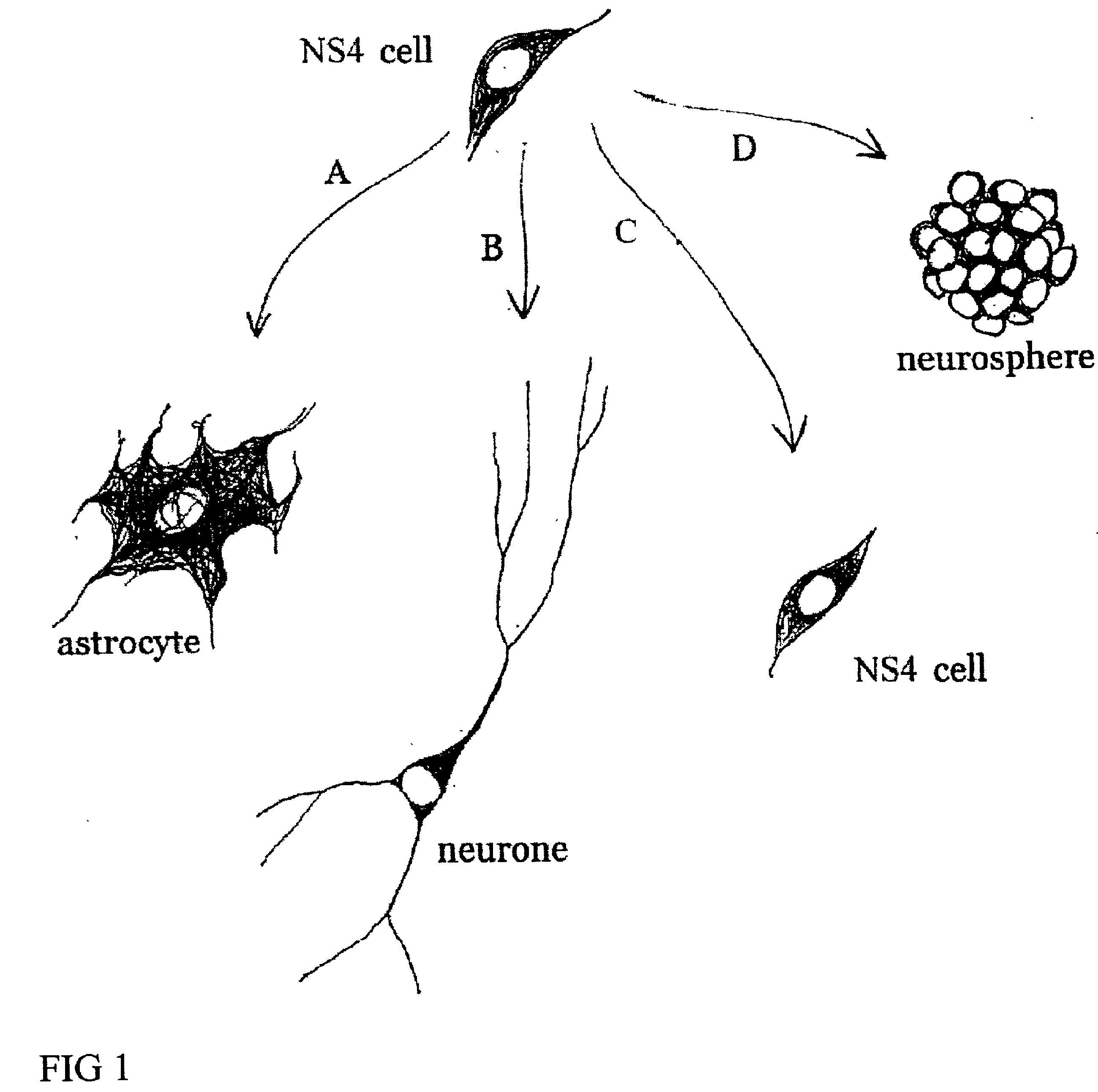
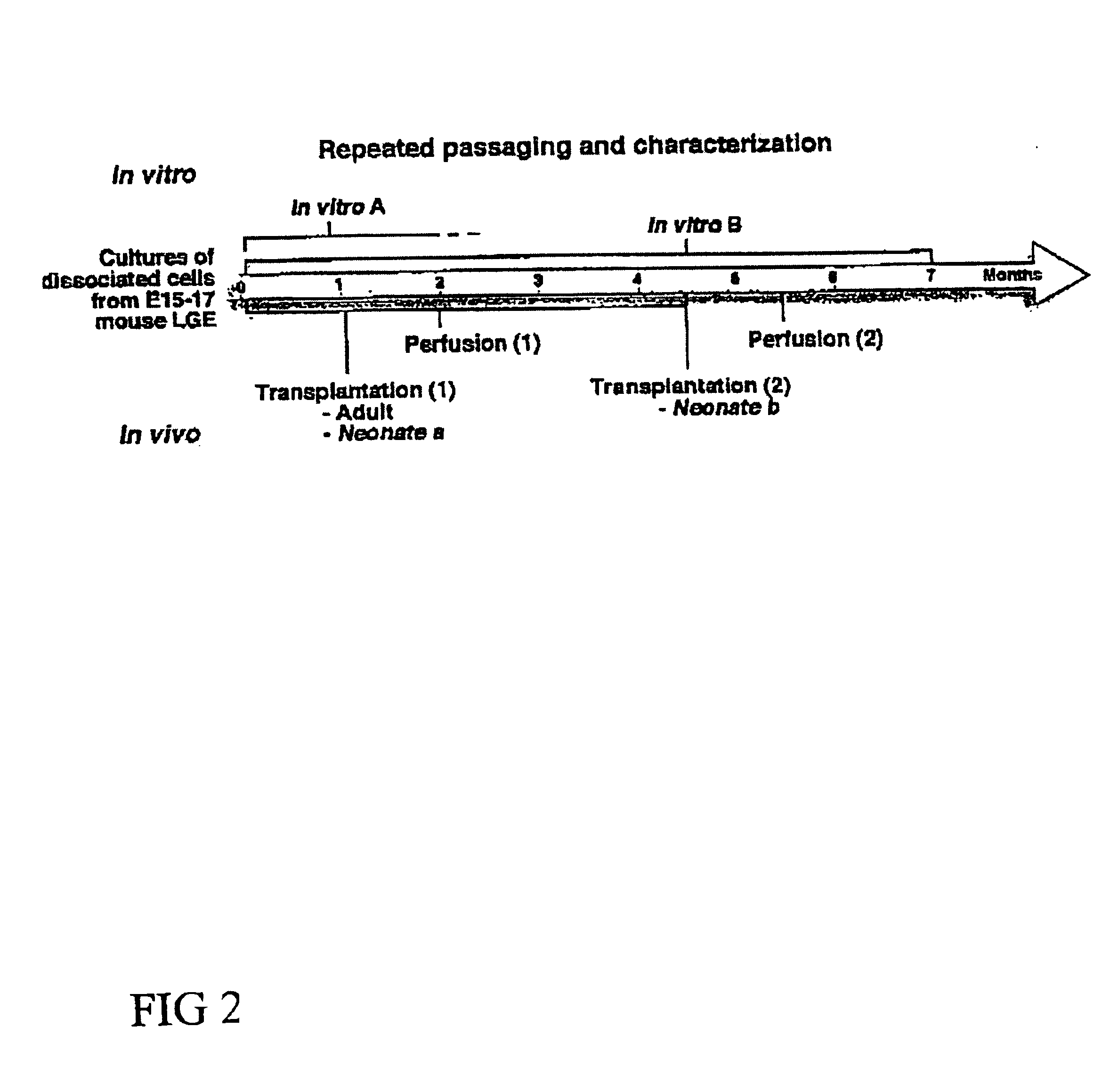
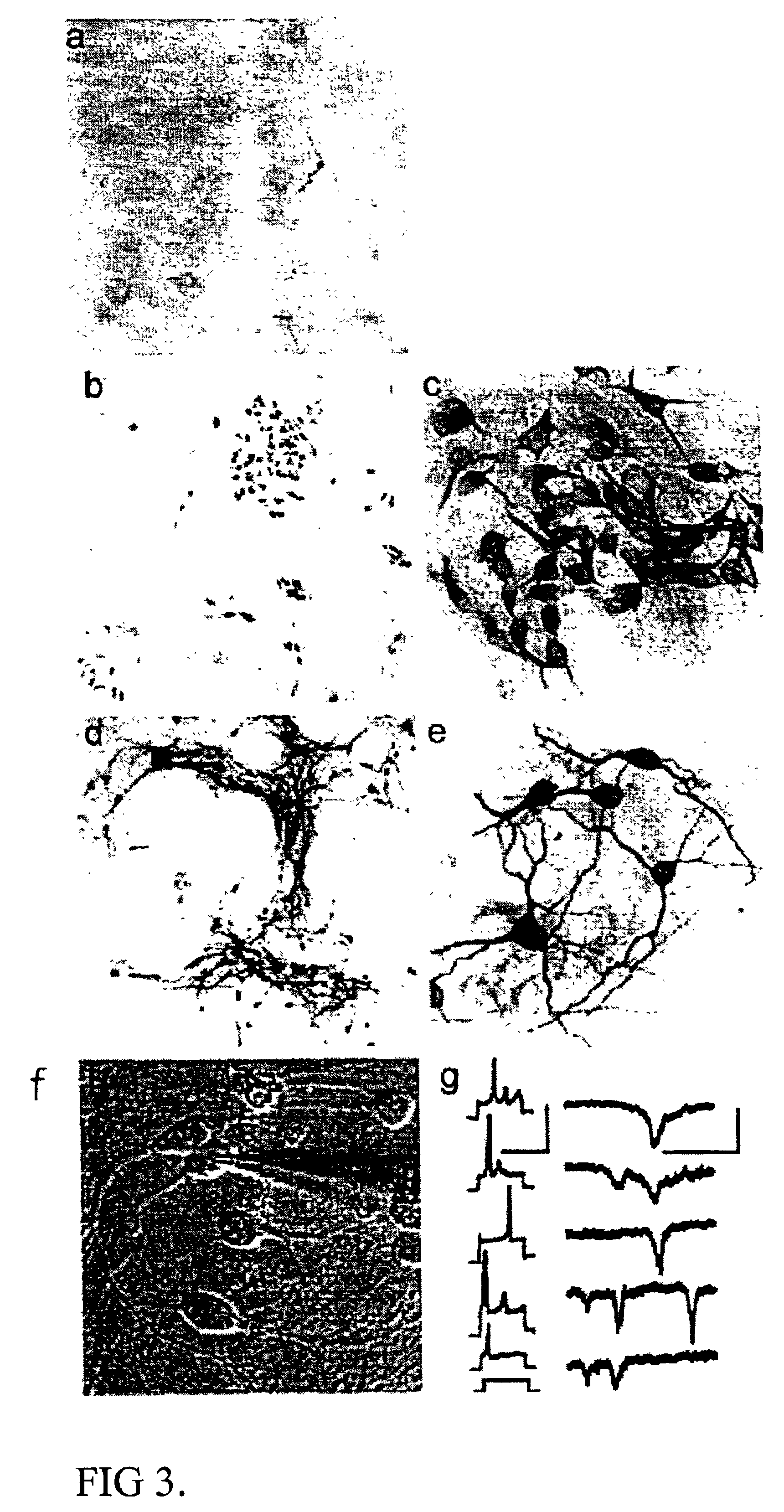
Cultures of GFAP+ nestin+ cells that differentiate to neurons
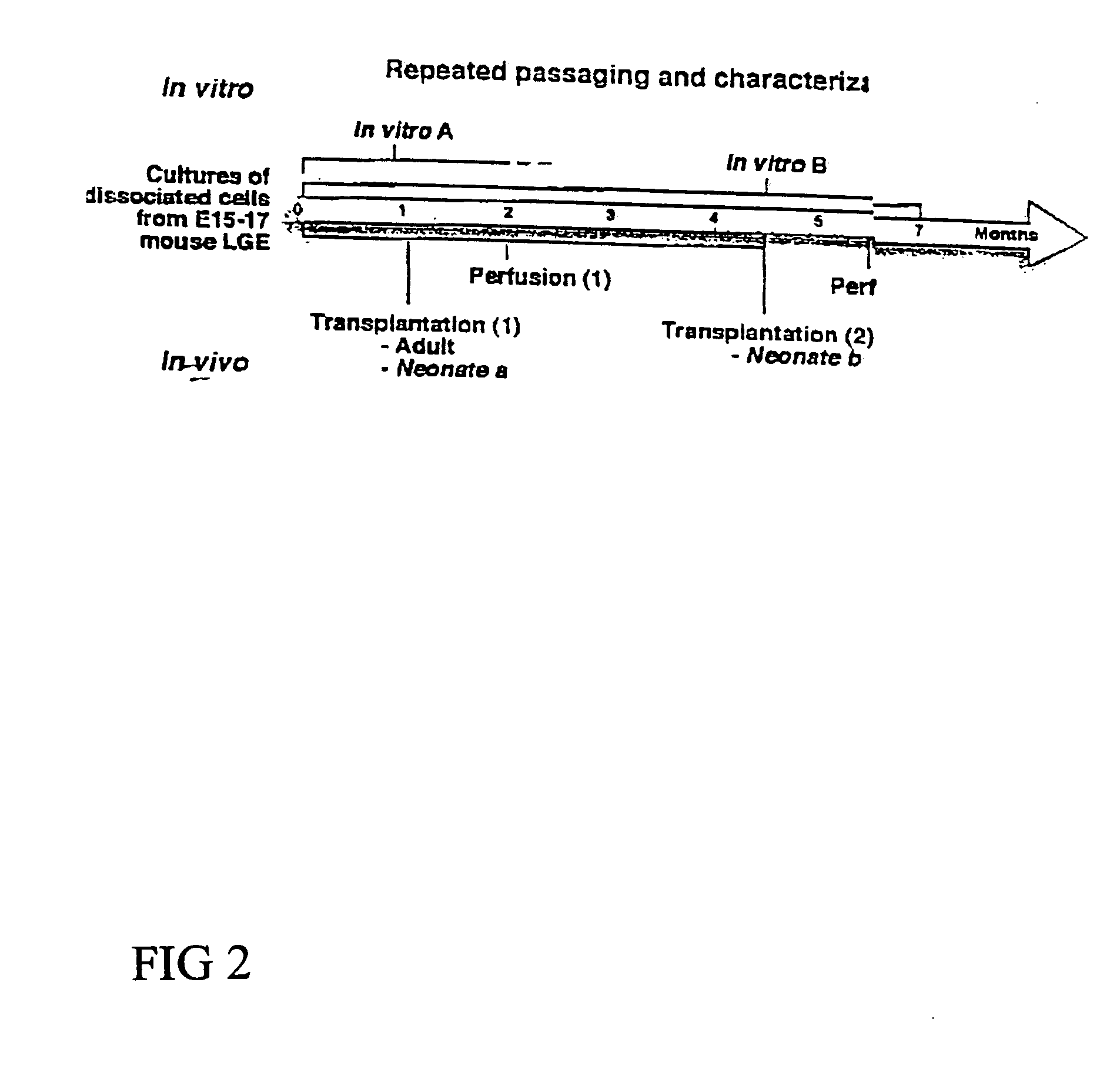
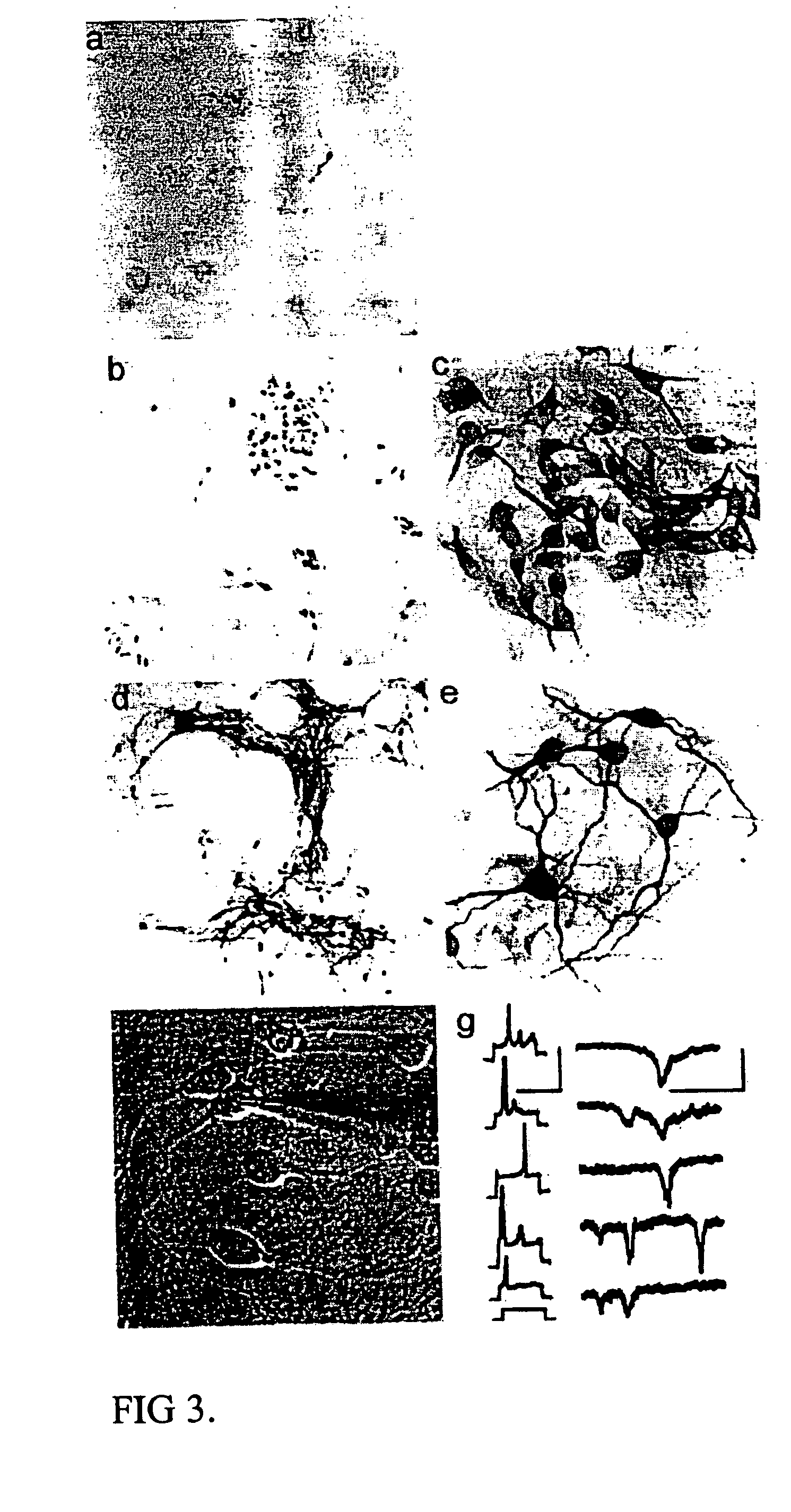
Cultures of cells immunoreactive for glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP), as well as for the intermediate filament marker nestin were grown in a medium including epidermal growth factor (EGF) and serum. The cultured cells had the morphology of astroglial cells. The cells can be proliferated in adherent or suspension cultures. Depending on the culture conditions, the cells can be induced to differentiate to neurons or glial cells. The cultures can be expanded over a large number of passages during several months, and survive, express an astroglial phenotype and integrate well after transplantation into both neonatal and adult rat forebrain.
Owner:BOCO SILICON VALLEY INC
Treatment with Sigma Receptor Agonists Post-Stroke
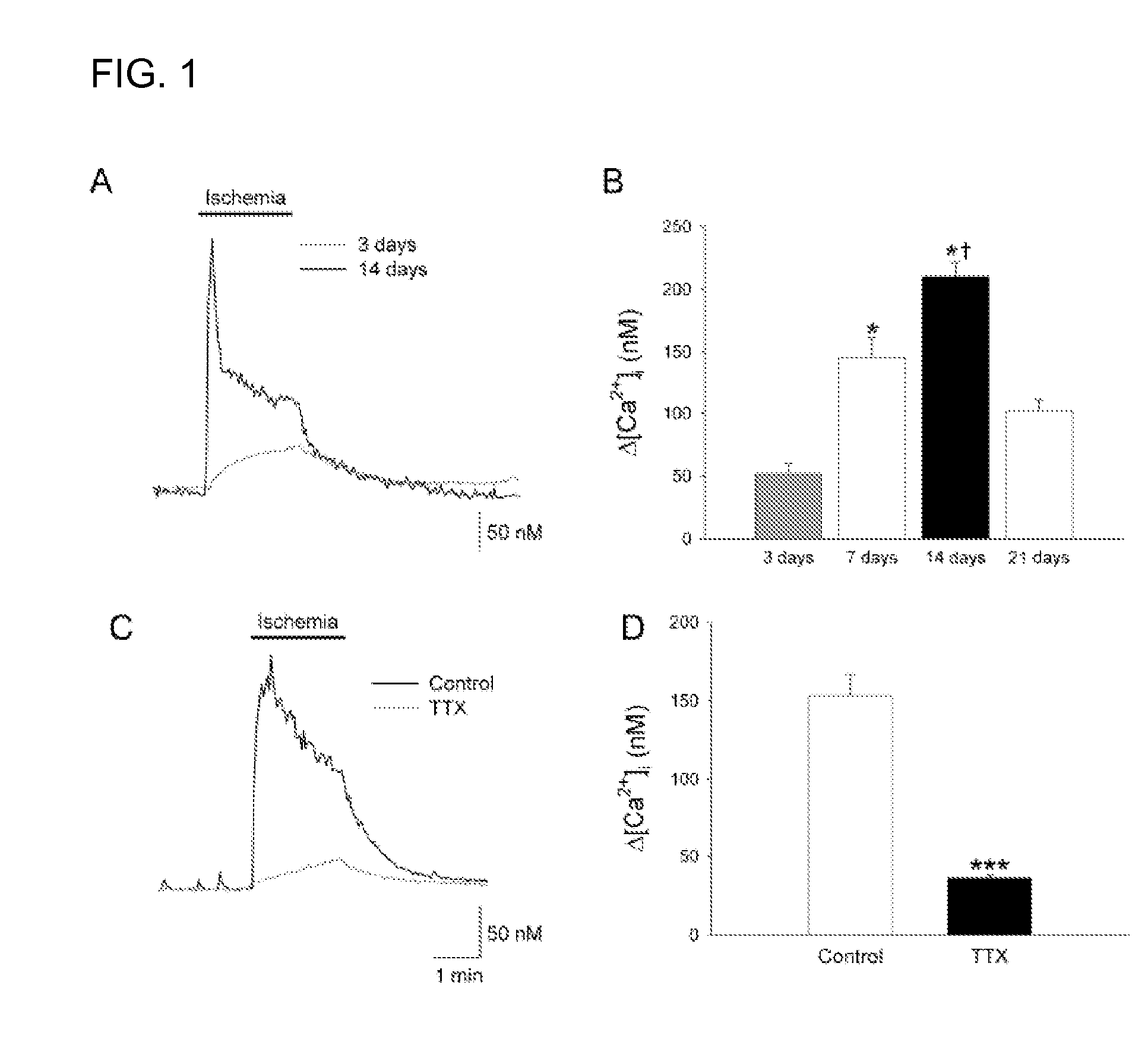
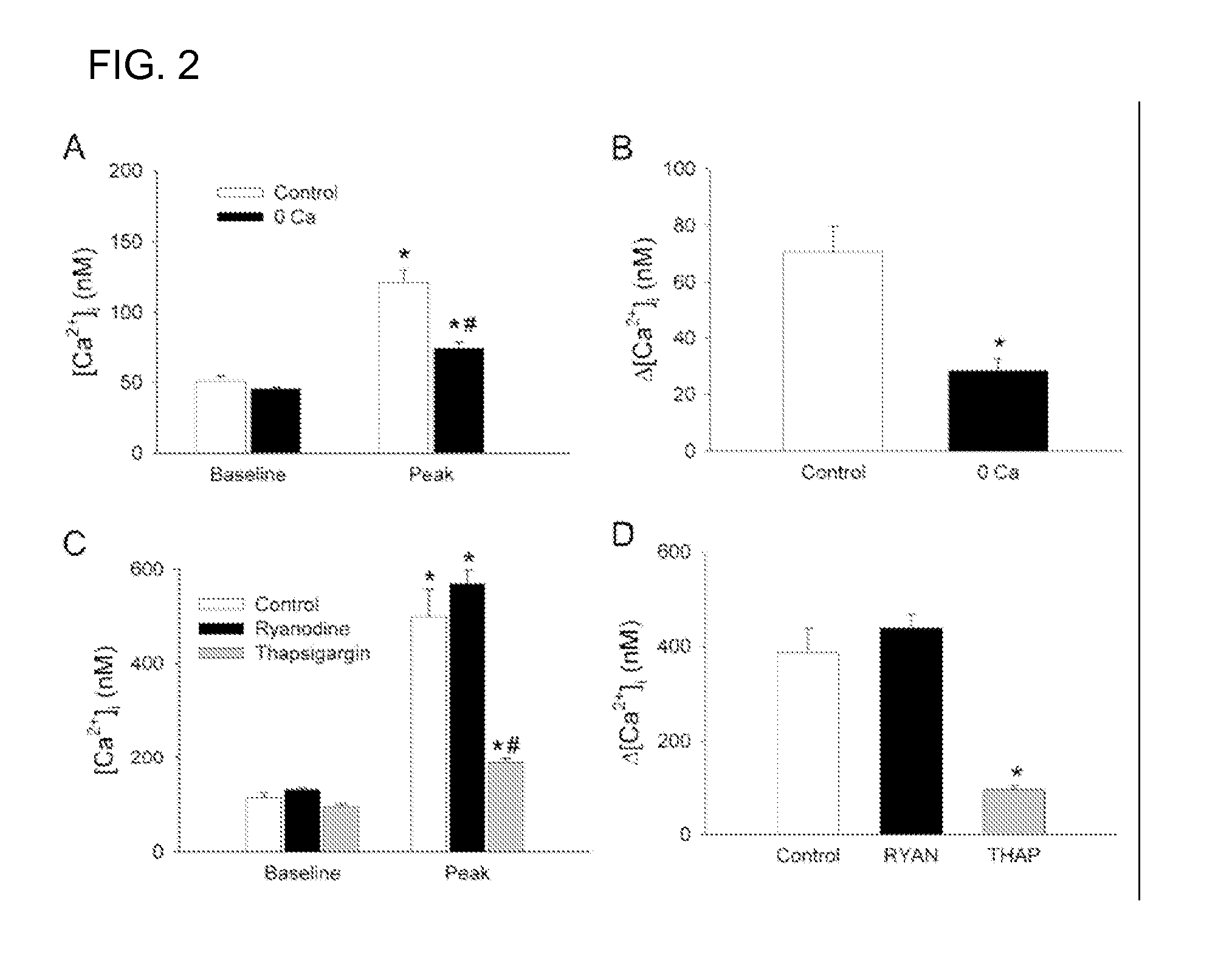
InactiveUS20070123556A1Decrease in infarction areaHigh affinityBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsHippocampal regionGlial fibrillary acidic protein
A method of post-stroke treatment at delayed timepoints with sigma receptor agonists. Sigma receptors are promising targets for neuroprotection following ischemia. One of the key components in the demise of neurons following ischemic injury is the disruption of intracellular calcium homeostasis. The sigma receptor agonist, DTG, was shown to depress [Ca2+]i elevations observed in response to ischemia induced by sodium azide and glucose deprivation. Two sigma receptor antagonists, metaphit and BD-1047, were shown to blunt the ability of DTG to inhibit ischemia-evoked increases in [Ca2+]i. DTG inhibition of ischemia-induced increases in [Ca2+]i was mimicked by the sigma-1 receptor-selective agonists, carbetapentane, (+)-pentazocine and PRE-084, but not by the sigma-2 selective agonist, ibogaine, showing that activation of sigma-1 receptors is responsible for the effects. Activation of sigma receptors can ameliorate [Ca2+]i dysregulation associated with ischemia in cortical neurons, providing neuroprotective properties. The effects of 1,3-di-o-tolyguanidine (DTG), a high affinity sigma receptor agonist, as a potential treatment for decreasing infarct area at delayed time points was further examined in rats. DTG treatment significantly reduced infarct area in both cortical / striatal and cortical / hippocampal regions by >80%, relative to control rats. These findings were confirmed by immunohistochemical experiments using the neuronal marker, mouse anti-neuronal nuclei monoclonal antibody (NeuN), which showed that application of DTG significantly increased the number of viable neurons in these regions. Furthermore, DTG blocked the inflammatory response evoked by MCAO, as indicated by decreases in the number of reactive astrocytes and activated microglia / macrophages detected by immunostaining for glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) and binding of isolectin IB4, respectively. Thus, the sigma receptor-selective agonist, DTG, can enhance neuronal survival when administered 24 hr after an ischemic stroke. In addition, the efficacy of sigma receptors for stroke treatment at delayed time points is likely the result of combined neuroprotective and anti-inflammatory properties of these receptors.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTH FLORIDA
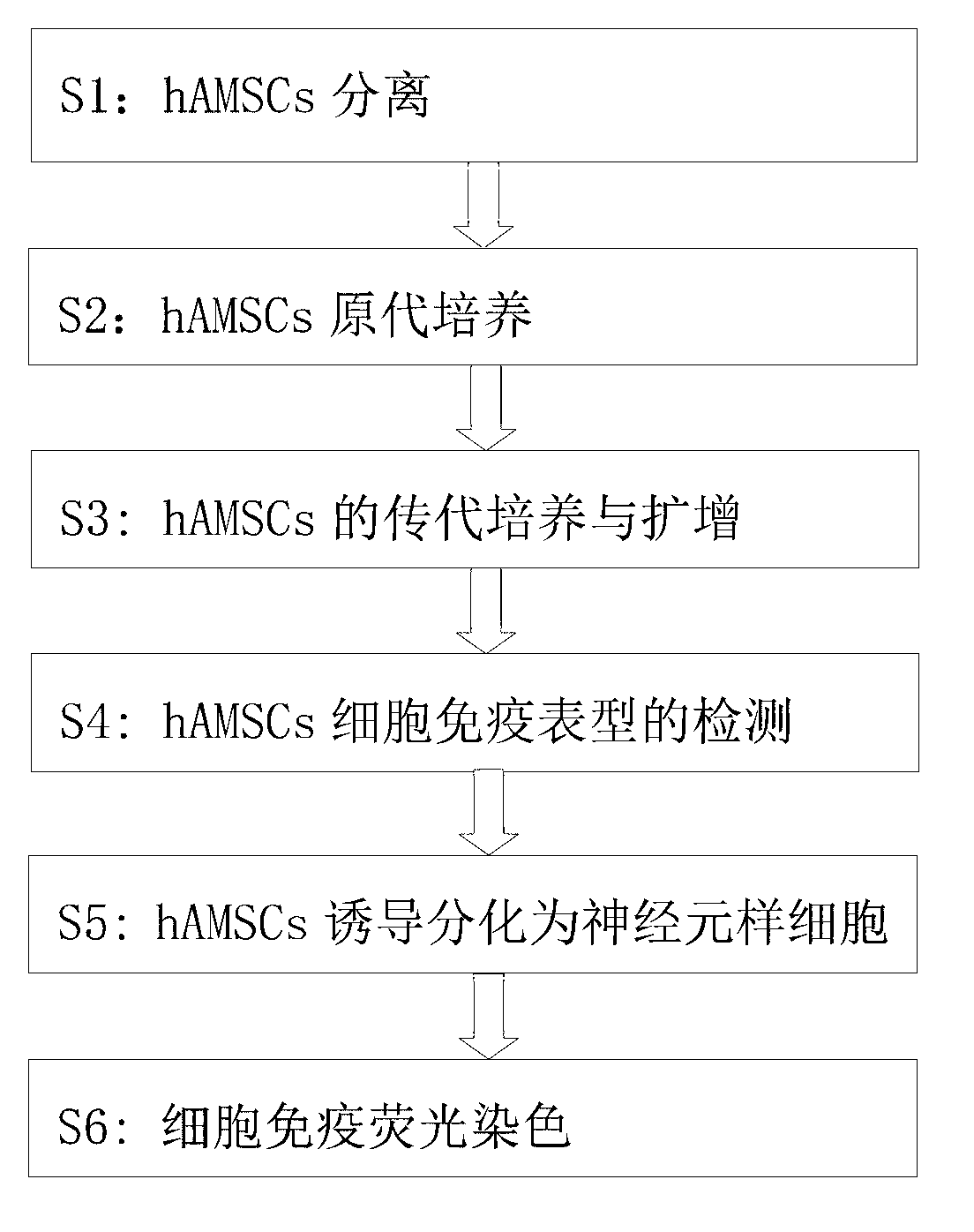
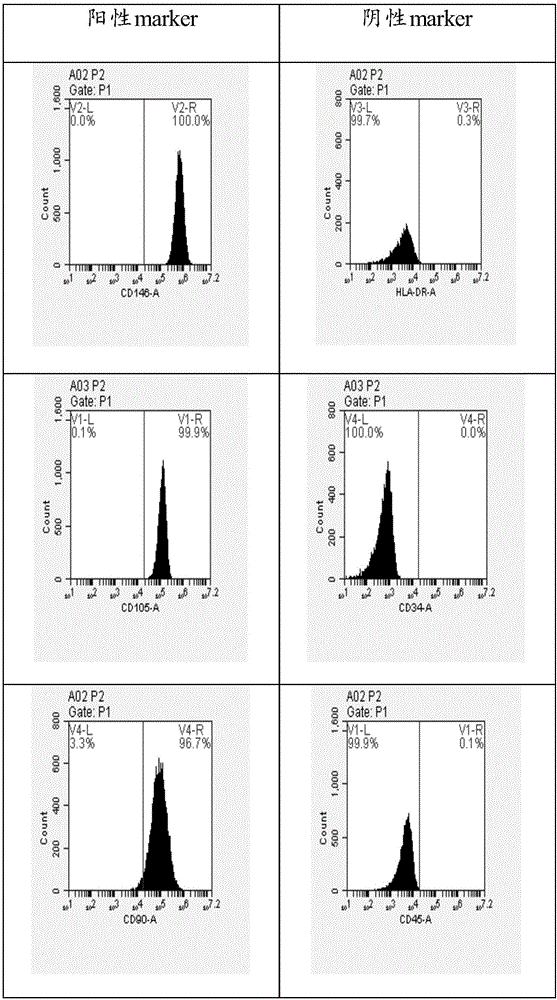
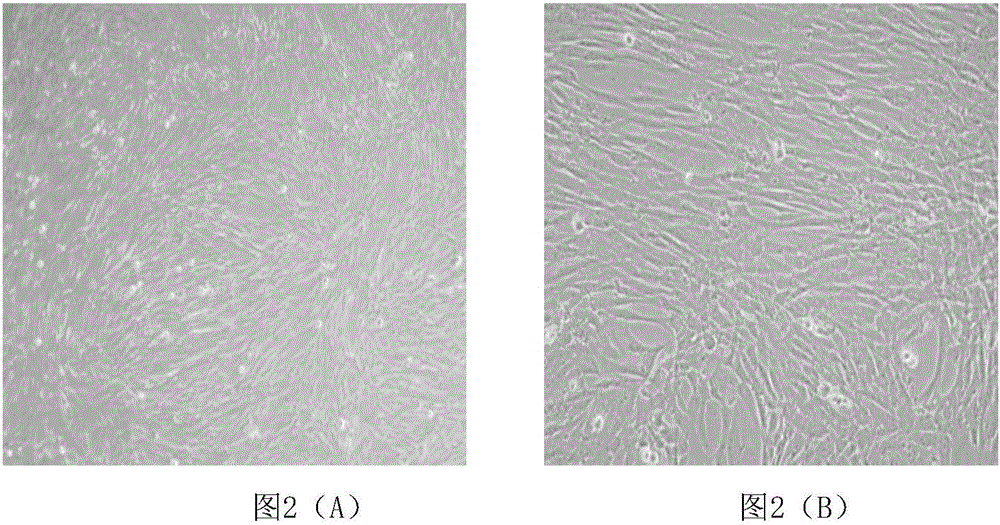
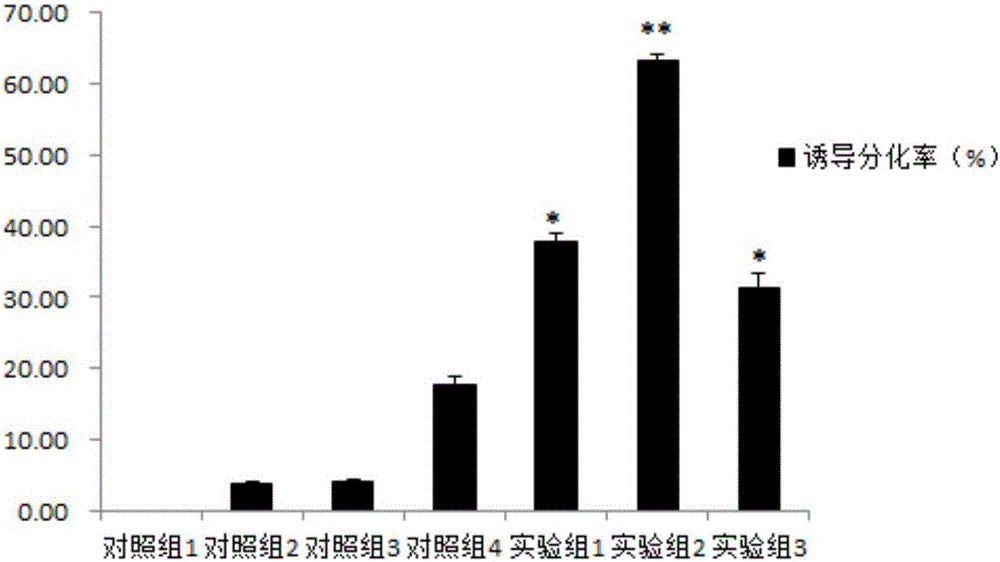
Method for inducing human amniotic mesenchymal stem cells to differentiate into neuron-like cells
InactiveCN103013917ANervous system cellsSkeletal/connective tissue cellsGerm layerGlial fibrillary acidic protein
The invention provides a method for inducing differentiating human amniotic mesenchymal stem cells (hAMSCs) to differentiate into neuron-like cells by adopting all-trans retinoic acids, a basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF) and an epidermal growth factor (EGF). The method comprises the following steps of: separating the hAMSCs, carrying out primary culture of the hAMSCs, subculturing and amplifying the hAMSCs, detecting hAMSCs immunophenotyping, inducing the hAMSCs to differentiate into the neuron-like cells and carrying out cellular immunity fluorescence staining. According to the inducing method provided by the invention, umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells are induced to differentiate into neutral stem cells by using the all-trans retinoic acids in combination of the bFGF and the EGF; the neural stem cells not only have the typical morphology of nerve cells, but also express neuron marker antigen neuron-specific emolase and astrocyte marker antigen glial fibrillary acidic proteins; and the capability of a mesenchymal cell trans-germinal layer differentiating into non mesenchymal cells is realized so that the mesenchymal cells are likely to turn into more ideal seed cells for clinical application in further.
Owner:陆华
Cultures of GFAP nestin cells that differentiate to neurons
Owner:BOCO SILICON VALLEY INC
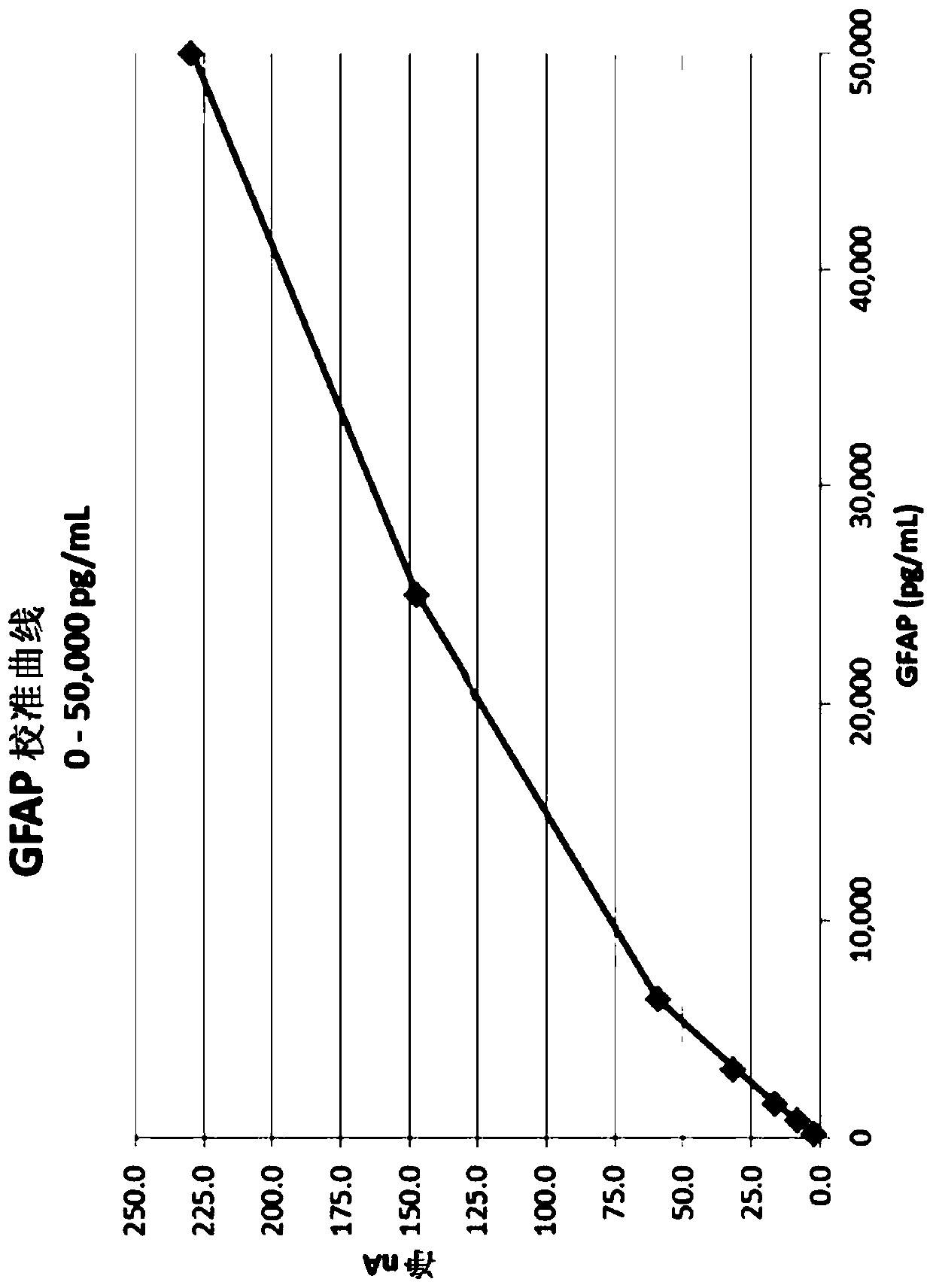
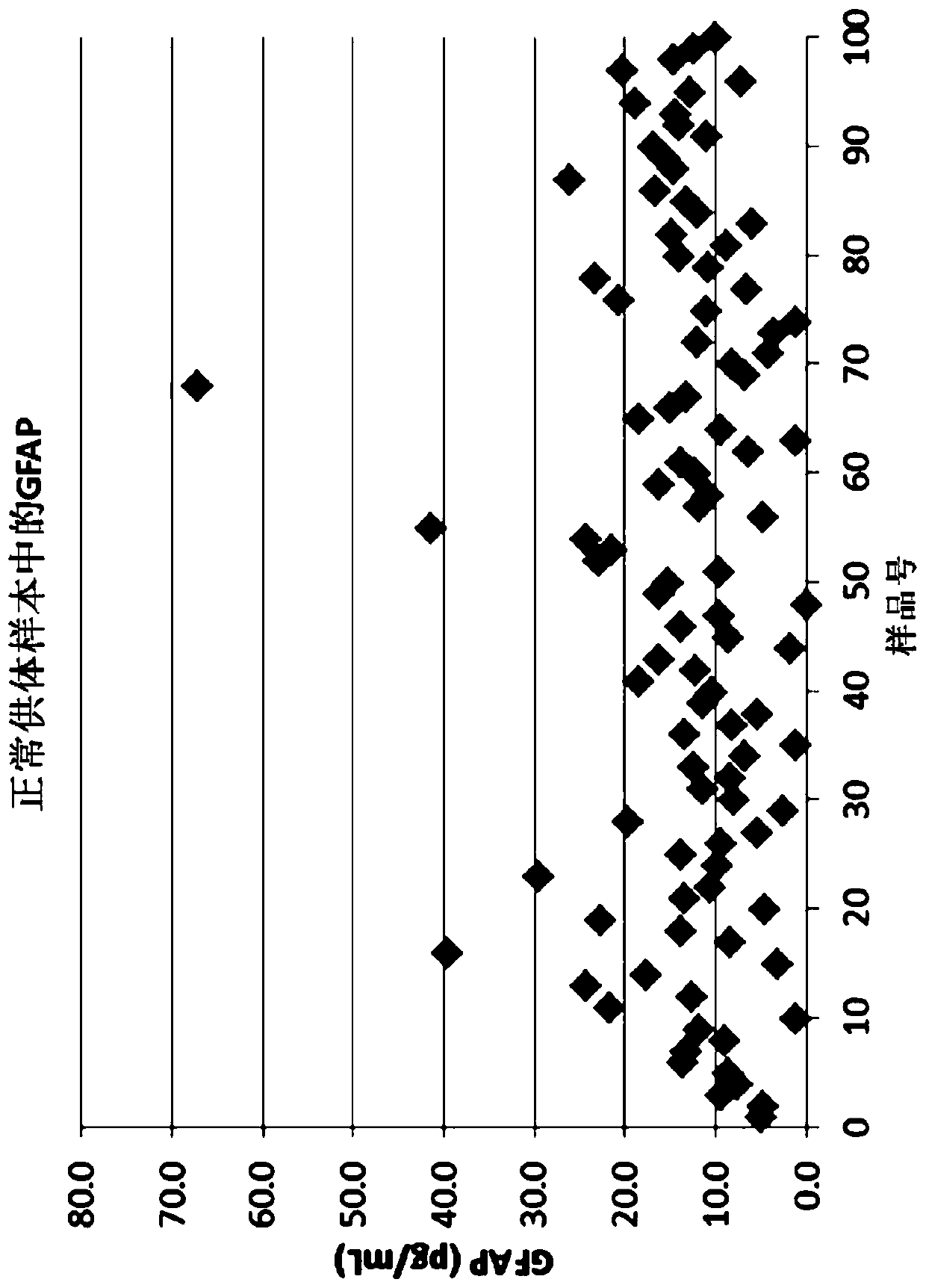
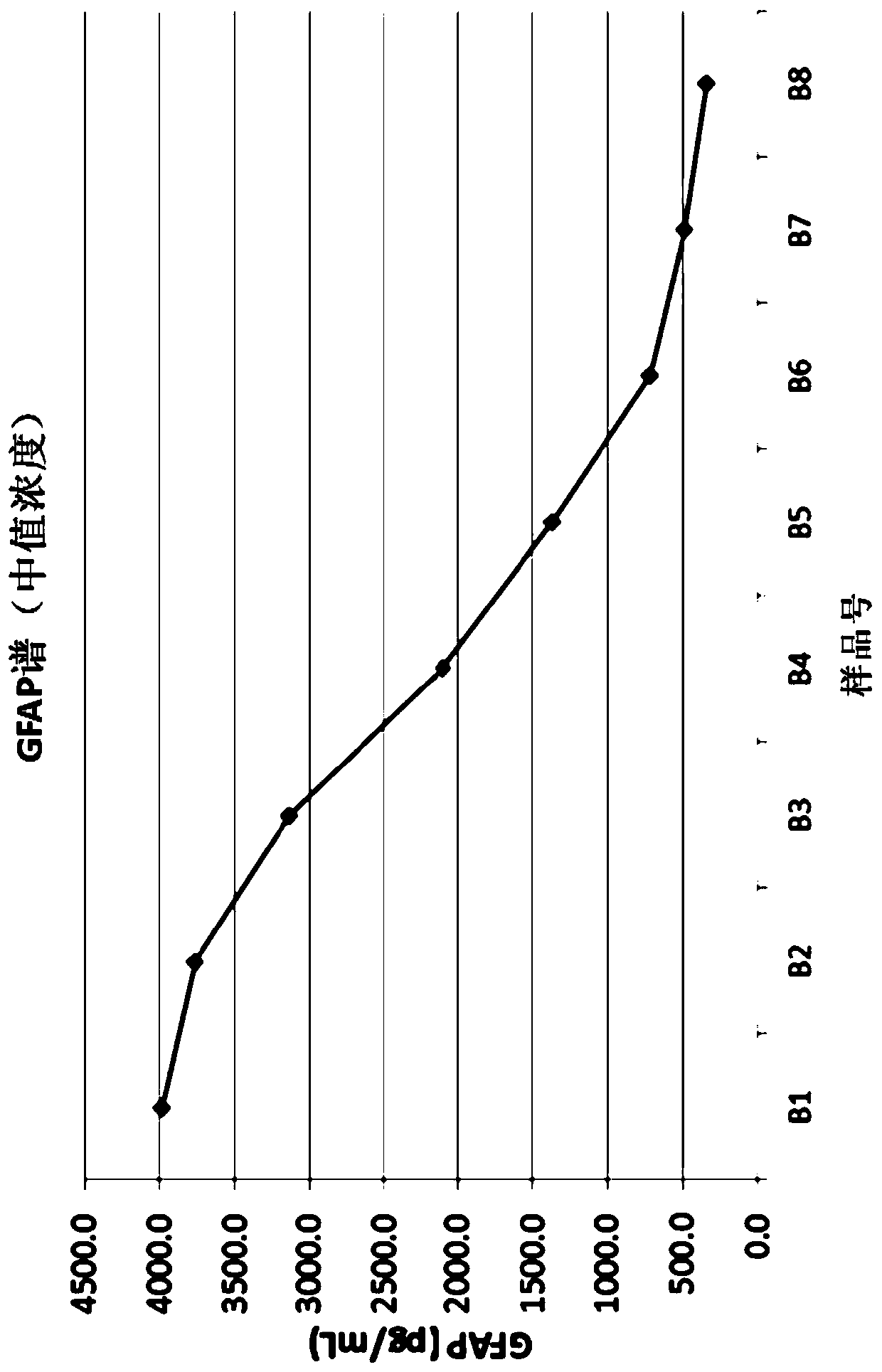
Kit for quantitatively detecting GFAP (glial fibrillary acidic protein) through magnetic microparticle chemiluminescence and preparation method of kit
InactiveCN108051586AMultiple surface areaEasy to detectChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceGlial fibrillary acidic proteinQuality control
The invention relates to the field of medical in vitro diagnosis, in particular to a kit for quantitatively detecting GFAP (glial fibrillary acidic protein) through magnetic microparticle chemiluminescence and a preparation method of the kit. The kit for quantitatively detecting the GFAP through the magnetic microparticle chemiluminescence comprises a magnetic separation reagent, an antibody reagent, an enzyme labeled reagent, a substrate, washing liquid, a calibration product, a quality control product, a magnetic sleeve and a sucker. The invention also discloses the preparation method of thekit. By adopting the kit provided by the invention, the detection upper limit and the reaction speed can be increased, and the sensitivity of a detection result is improved.
Owner:SOPHONIX CO LTD
Colloidal gold test paper strip for semiquantitatively detecting concentration of GFAP (Glial Fibrillary Acidic Protein) in human serum
ActiveCN102353787AAccurate and effective semi-quantitative detectionSimple and fast operationChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceGlial fibrillary acidic proteinSerum ige
The invention discloses a colloidal gold test paper strip for semiquantitatively detecting the concentration of a GFAP (Glial Fibrillary Acidic Protein) in a human serum. The colloidal gold test paper strip is produced by adhering a detection diaphragm, a colloidal gold combined diaphragm and a water-absorbing paper layer to a PVC (Poly Vinyl Chloride) board, wherein the colloidal gold combined diaphragm is coated by a colloidal gold-labeled antibody for resisting the GFAP; a detection line and a quality control line are arranged on the detection diaphragm; a capture antibody for resisting the GFAP is fixedly arranged on the detection line; a rabbit anti-mouse IgG (Immunoglobulin G) is fixedly arranged on the quality control line; and a sampling part, the colloidal gold combined diaphragm, the detection line, the quality control line and the water-absorbing paper are sequentially arranged on the test paper strip from the bottom up. The test paper strip disclosed by the invention can be used for semiquantitatively detecting the GFAP, has the advantages of high specificity, high sensitiveness, high accuracy, quickness, simpleness and convenience in operation, low expense, no need ofany apparatus, time-and-labor saving and the like as well as has favorable application prospect.
Owner:山东莱博生物科技有限公司
Use of gfap for identification of intracerebral hemorrhage
Owner:FOERCH CHRISTIAN +1
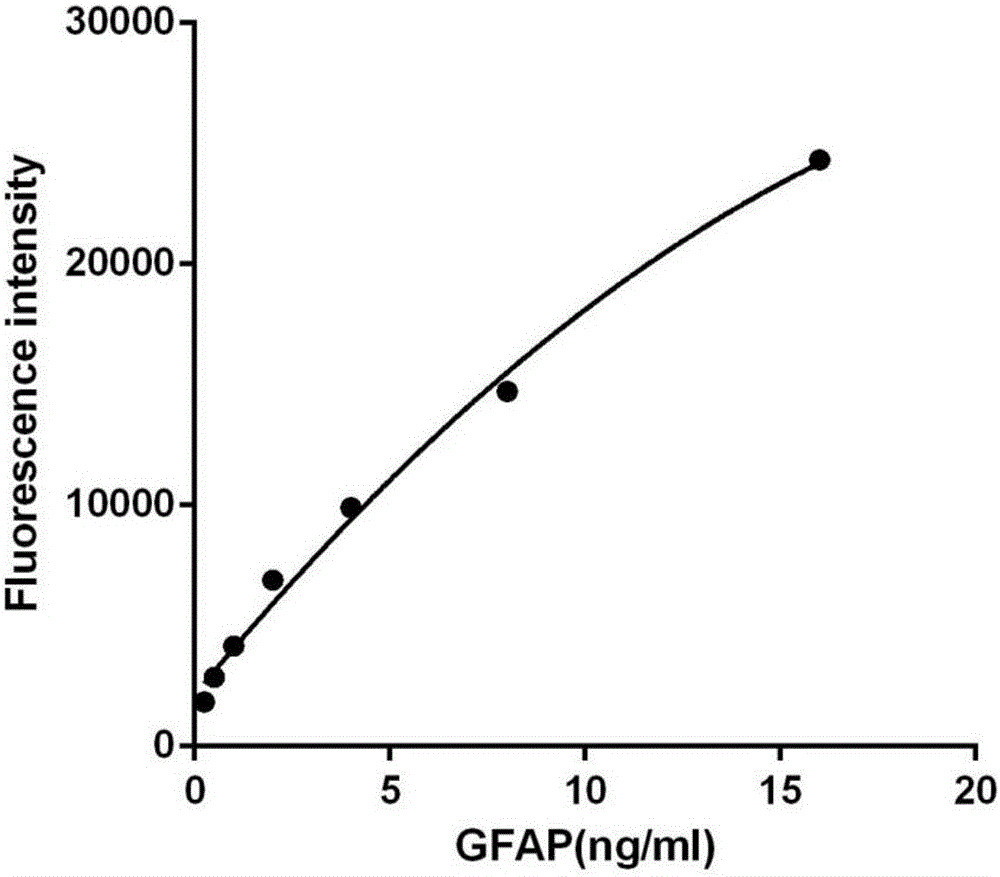
GFAP detection method based on fluorescence resonance energy transfer method
ActiveCN106568750AAids in diagnosisHelp with assessmentBiological testingFluorescence/phosphorescenceGlial fibrillary acidic proteinFluorescence
The present invention discloses a GFAP detection method based on a fluorescence resonance energy transfer method, wherein a micro-pore plate is coated with a purified glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) antibody to prepare a solid-phase antibody, glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) is sequentially added to the monoclonal antibody-coated micro-pores, combination with Alexa Fluor488 labeled and Alexa Fluor594 labeled GFAP antibody to form an antibody-antigen two-fluorescent-labeling-antibody complex, absorbance (OD value) is determined by using a fluorescent enzyme analyzer according to the FRET principle, and the human glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) content in the sample is calculated by using a standard curve. According to the present invention, with the use of the three kinds of the antibodies to simultaneously identify, such that the specificity is high, the accuracy is good, the detection time is substantially shortened compared to the existing method, the reference information is provided for the clinical diagnosis, the clinicians can be helped to diagnose and assess the progression of stroke, and the prognosis of patients can be improved.
Owner:SHAANXI MYBIOTECH CO LTD
Improved methods of assessing gfap status in patient samples
Disclosed herein are improved methods of assessing Glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) status in a subject (such as for examples, as a measure of traumatic brain injury or for other clinical reasons).
Owner:ABBOTT LAB INC
Improved immunohistochemical repairing solution
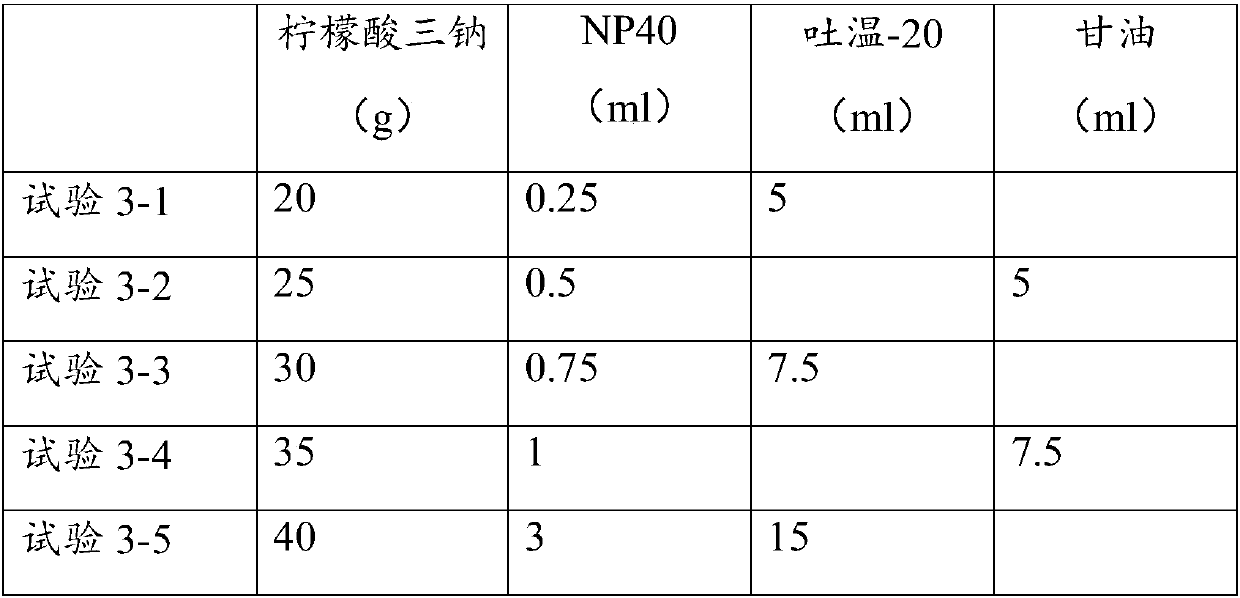
ActiveCN108051582AImprove repair effectEasy to dyePreparing sample for investigationGlial fibrillary acidic proteinAntigen
The invention relates to an improved immunohistochemical repairing solution. The improved immunohisochemical repairing solution is prepared from trisodium citrate, NP-40 (Nonidet P 40) and an emulsifying agent. According to the improved immunohistochemical repairing solution disclosed by the invention, a repairing effect is better, and tissue slices can be repaired under less dosage of the improved immunohisochemical repairing solution; the improved immunohisochemical repairing solution is suitable for antigens which are relatively difficult to be detected clinically, such as Fas (Fatty Acid Synthase), Bax (Bcl-2 associated X protein), FVIII (Factor VIII), Lamnin, CoIV, Keratin, CEA (Carcino Embryonie Antigen) and GFAP (Glial Fibrillary Acidic Protein); the tissue slices are easy to be dyed after being repaired by adopting the improved immunohistochemical repairing solution, and a dyeing effect is better.
Owner:珠海霍普金斯医药研究院股份有限公司 +1
Luminescent ELISA in vitro diagnosis reagent kit for cerebral apoplexy and in vitro test equipment
ActiveCN109696552AReduce distractionsImprove accuracyBiological testingGlial fibrillary acidic proteinIn vitro test
The invention provides a luminescent ELISA in vitro diagnosis reagent kit, which comprises an aqueous solution for stabilization of a body fluid sample. The body fluid sample comprises a nerve injurymarker protein component. In the aqueous solution for stabilization of the body fluid sample, solutes comprise human serum, animal serum albumin, inorganic base metal salt, Tris-methylamin, protein denaturant and nonionic surface active agent, and the pH value of the aqueous solution is 6.7-7.6. The in vitro diagnosis reagent kit optionally comprises an antibody against the nerve injury marker protein component (e.g. anti-GFAP (glial fibrillary acidic protein) antibody). The invention also provides in vitro test equipment. When a luminescent ELISA method is adopted to detect the nerve cell injury marker protein component GFAP from the body fluid sample (e.g. peripheral blood), the in vitro diagnosis reagent kit and the in vitro test equipment are very high in accuracy and repeatability, and can accurately and stably detect the pg-level GFAP in the body fluid.
Owner:成都蓝瑙生物技术有限公司
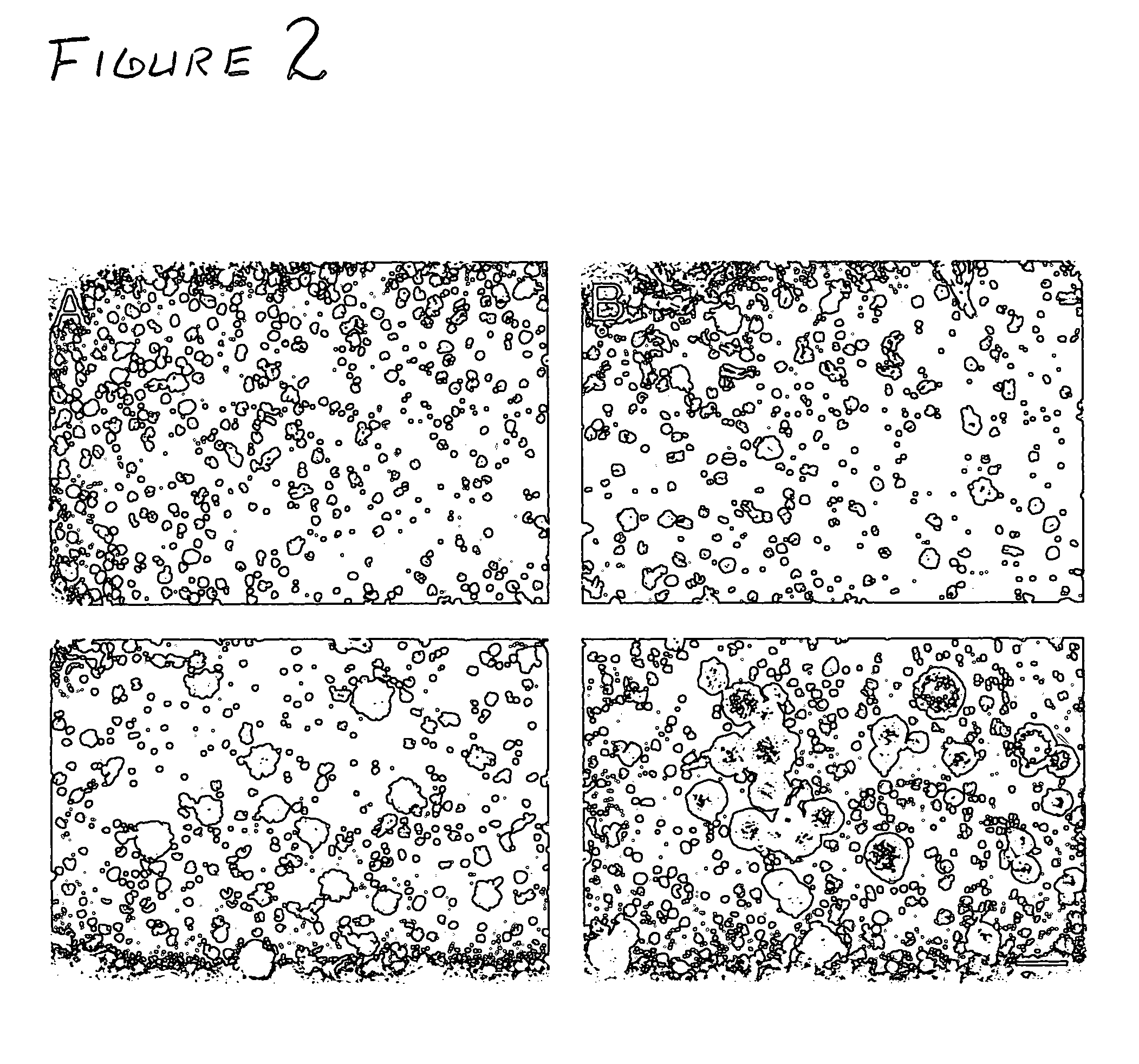
Application of E3 ubiquitin ligase CHIP in gliomatosis cerebri disease
InactiveCN101928747AOrganic active ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsGlial fibrillary acidic proteinMessenger RNA
The invention relates to application of E3 ubiquitin ligase CHIP in a gliomatosis cerebri disease. In glioma tissues, CHIP is mainly expressed in endochylema of a tumor cell and is localized with labeled protein GFAP (Glial Fibrillary Acidic Protein) of an astroglia, and the expression increases along with the increment of levels; after a CHIP expression amount rises, mRNA (Messenger RNA) and protein expression of a Survivin increase; and after the CHIP expression amount reduces, the mRNA (Messenger RNA) and the protein expression of the Survivin decrease and the protein expression of beta-catenin increases. Through immunohistochemistry, the invention compares the expression conditions of the CHIP in gliomas at different levels and normal gliomatosis cells, clarifies effects and pathological mechanisms of the CHIP in the processes of glioma occurrence, development, proliferation and invasiveness and provides powerful means for the biological target treatment of the glioma in future.
Owner:SECOND MILITARY MEDICAL UNIV OF THE PEOPLES LIBERATION ARMY
Glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) antibody detection test kit, and application thereof
PendingCN110806485AEasy to readHigh sensitivityDisease diagnosisBiological testingGlial fibrillary acidic proteinAntiendomysial antibodies
The invention provides a glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) antibody detection test kit, and an application thereof. The application comprises the following steps: S1, preparing a frozen animal brain slice; S2, respectively sucking a cerebrospinal fluid to be detected and a diluted rabbit anti-human GFAP antibody, and dripping the cerebrospinal fluid to be tested and the diluted rabbit anti-human GFAP antibody on a reaction plate at a ratio of 1 to 1; S3, covering the reaction plate with the frozen animal brain slice which is turned over, and carrying out incubation overnight at a temperature of 4 DEG C; S4, rinsing the brain slice with a PBS buffer solution twice; S5, respectively sucking goat anti-rabbit IgG, which is diluted and marked by the water-soluble fluorescent dye CY3, and agoat anti-human IgG mixed solution, which is diluted and FITC-marked, and dripping the goat anti-rabbit IgG and the goat anti-human IgG mixed solution on the reaction plate at a ratio of 1 to 1; S6,covering the reaction plate with the frozen animal brain slice which is turned over, and carrying out two-hour incubation at the room temperature; S7, rinsing the brain slice with the PBS buffer solution twice; S8, sealing the slice; and S9, placing the sealed slice under a fluorescent microscope for observation. The test kit and the application thereof provided by the invention have the advantages that the sensitivity is higher than that of cell method based detection, and a result can be conveniently interpreted.
Owner:THE SECOND AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF GUANGZHOU MEDICAL UNIV
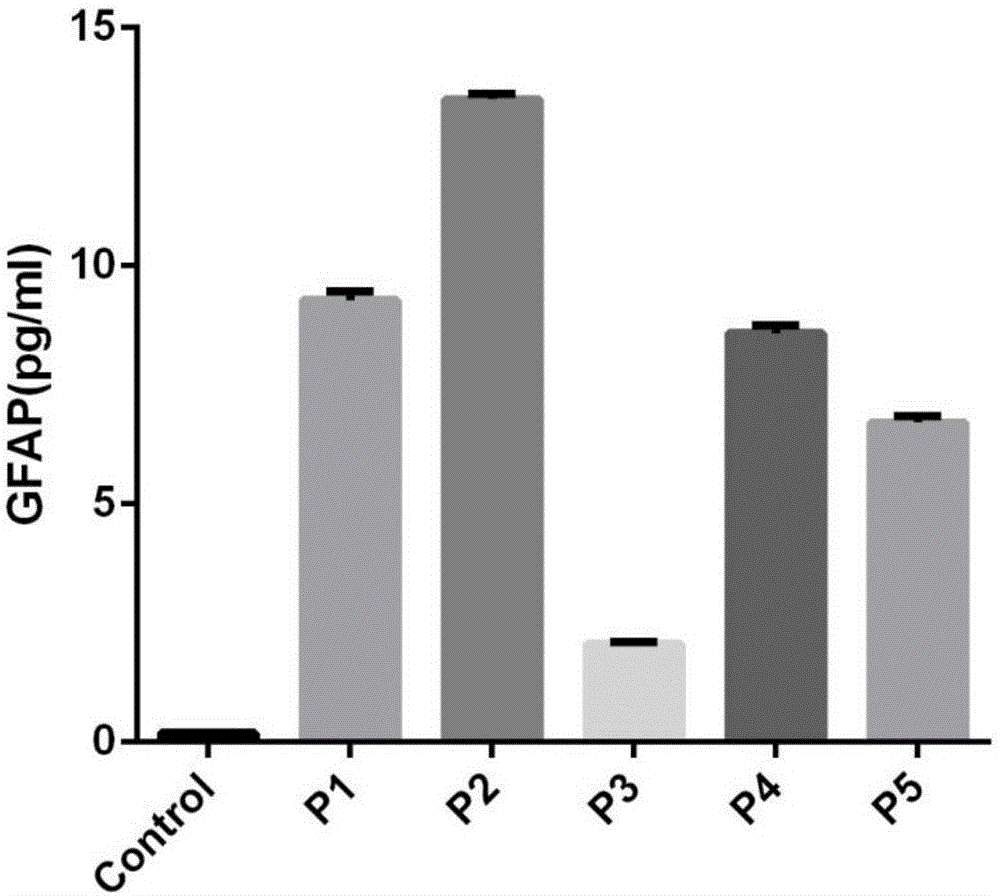
Method for quantitatively detecting glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) in blood serum
InactiveCN107102146AHigh single event brightness characteristicsGood water solubilityBiological testingGlial fibrillary acidic proteinDiethylenetriamine
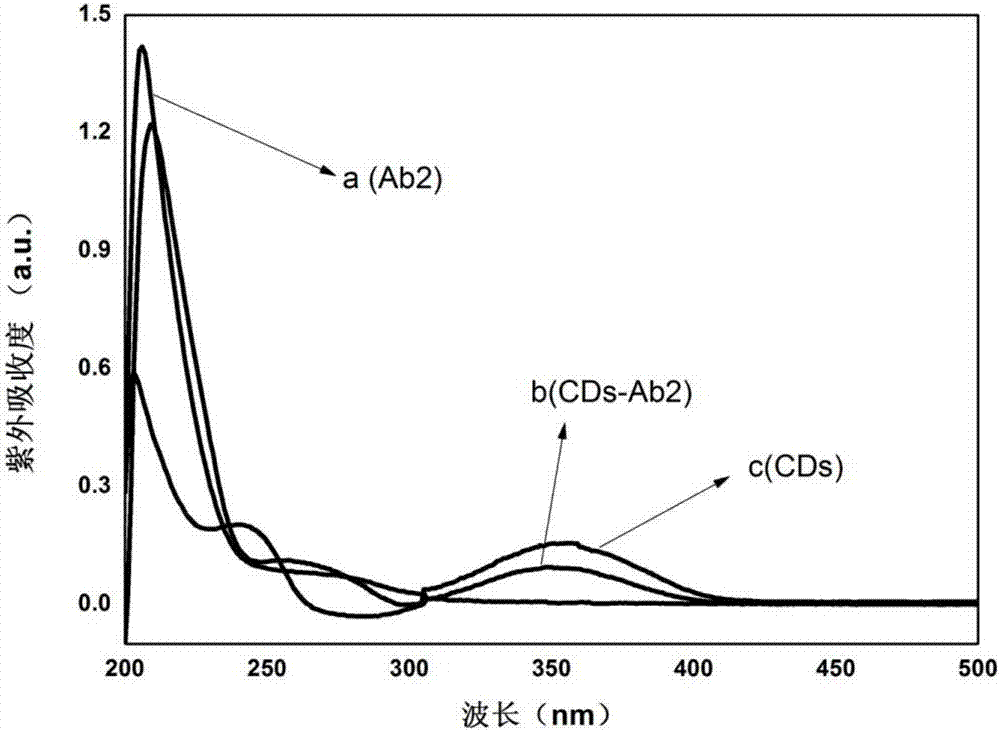
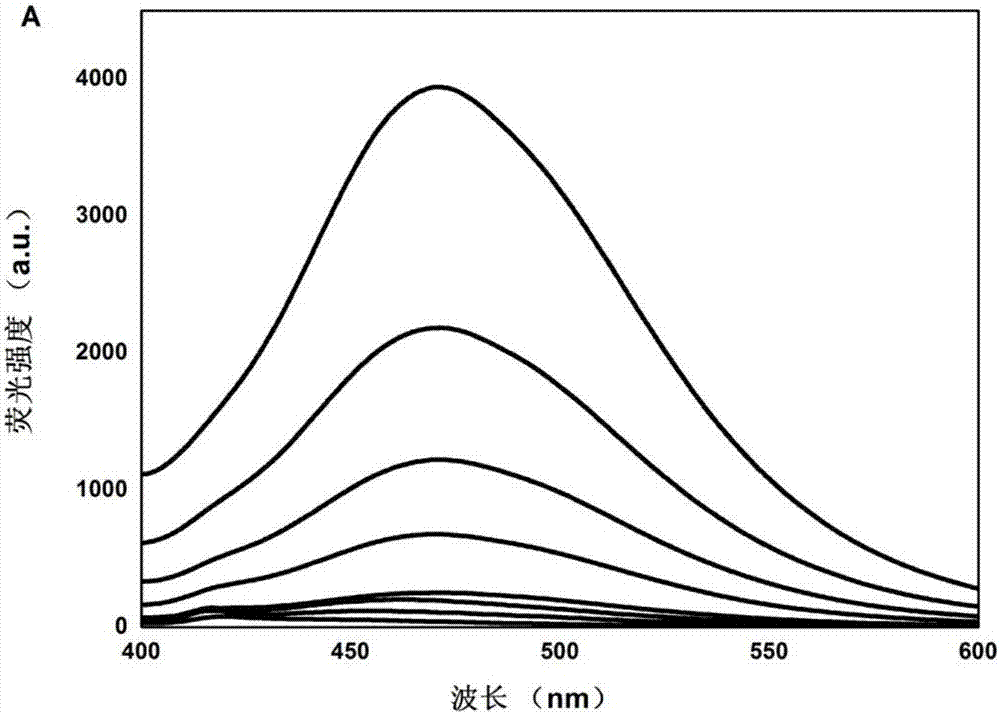
The invention discloses a method for quantitatively detecting glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) in a blood serum. The method comprises the steps of firstly, purifying a resin connecting antibody Ab1 through protein A / G agarose, capturing GFAP (Glial Fibrillary Acidic Protein) in the blood serum to form PA / G-Ab1-GFAP, and centrifugally cleaning to achieve the aims of separation and enrichment; secondly, adopting citric acid as a carbon source and diethylenetriamine as a passivator for synthesizing carbon dots (CDs), connecting with an antibody Ab2 through an amido bond, and forming a fluorescence labelled probe CDs-Ab2; then combining the PA / G-Ab1-GFAP and the CDs-Ab2 to form a sandwich structure PA / G-Ab1-GFAP-Ab2-CDs, detecting fluorescence intensity, and obtaining the content of the GFAP in the blood serum according to a standard curve. The method provided by the invention has the advantages of high sensitivity and simplicity and convenience in detection, and the characteristics of high selectivity and high affinity of immunoreaction, and can be directly applied in determining the GFAP in the blood serum.
Owner:NANJING MEDICAL UNIV
Method for retarding or precluding Alzheimer's dementia
InactiveUS20060134108A1Improve efficiencySlow downOther blood circulation devicesMicrobiological testing/measurementGlial fibrillary acidic proteinAutoantibody production
A method for treating a condition related to the development of Alzheimer's disease (AD) is disclosed. The method involves the removal of circulating autoantibodies of a biochemical marker or markers, specifically human glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) and glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate-dehydrogenase (GAPDH), from the sera of a patient in an amount effective to reduce or eliminate phagocytosis of astrocytic cells. The invention further includes a process of immune system modulation effective for autoantibody removal.
Owner:JACKOWSKI GEORGE +1
Composition, inducer containing composition and induction method
InactiveCN106566810ANervous system cellsSkeletal/connective tissue cellsGerm layerTransdifferentiation
Owner:GUANGZHOU SALIAI STEMCELL SCI & TECH CO LTD
Application of SAG in preparation of drug for treating diseases of hypoxic-ischemic brain damage during development
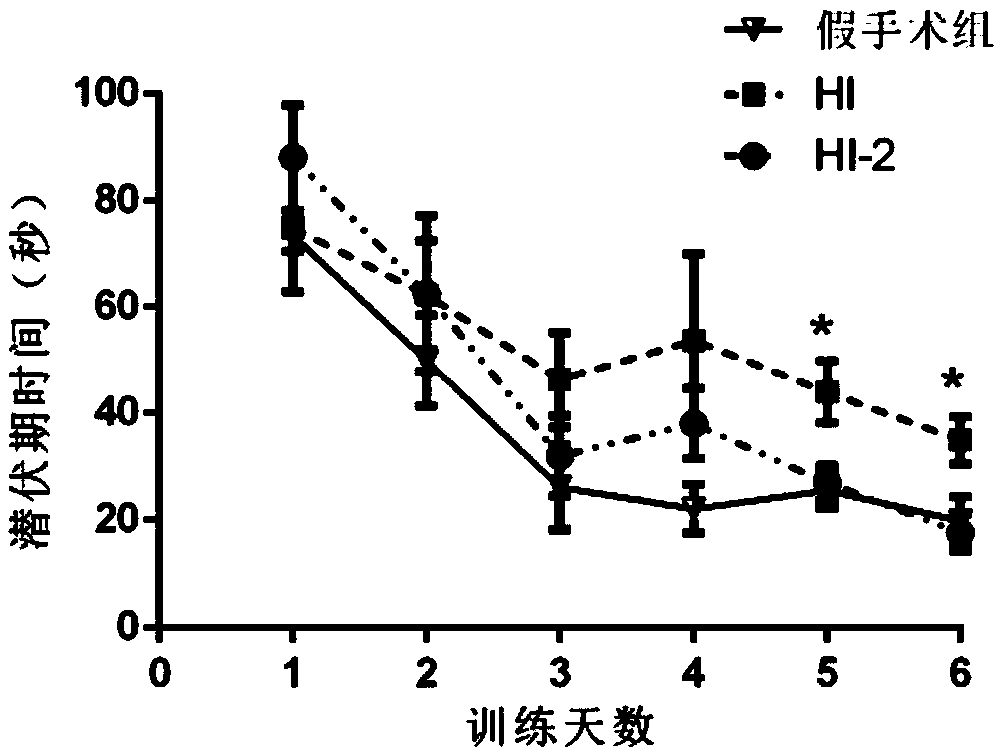
The invention discloses an application of SAG in preparation of a drug for treating diseases of hypoxic-ischemic brain damage during development. Experiments show that intraperitoneal injection of 5-25mg / kg of SAG after 2 hours after hypoxic-ischemia in neonatal rats can reduce cerebral infarction. Further study on the neonatal rats applied with 15mg / kg of SAG shows that SAG can significantly improve brain damage and reduce nerve cell disintegration and necrosis after anoxia and ischemia. The Morris water maze experiments prove that 15mg / kg of SAG can effectively improve the learning ability of hypoxic-ischemic rats. Further study shows that 2, 3, 5-cholo-triphenyltetrazolium-positive cells of the rats in the SAG medium-dose experimental group rat (15mg / kg SAG) are significantly reduced, the IL-1 beta and TNF-alpha mRNA in the cerebral cortex are decreased and the expression of a glial fibrillary acidic protein is reduced.
Owner:THE WEST CHINA SECOND UNIV HOSPITAL OF SICHUAN
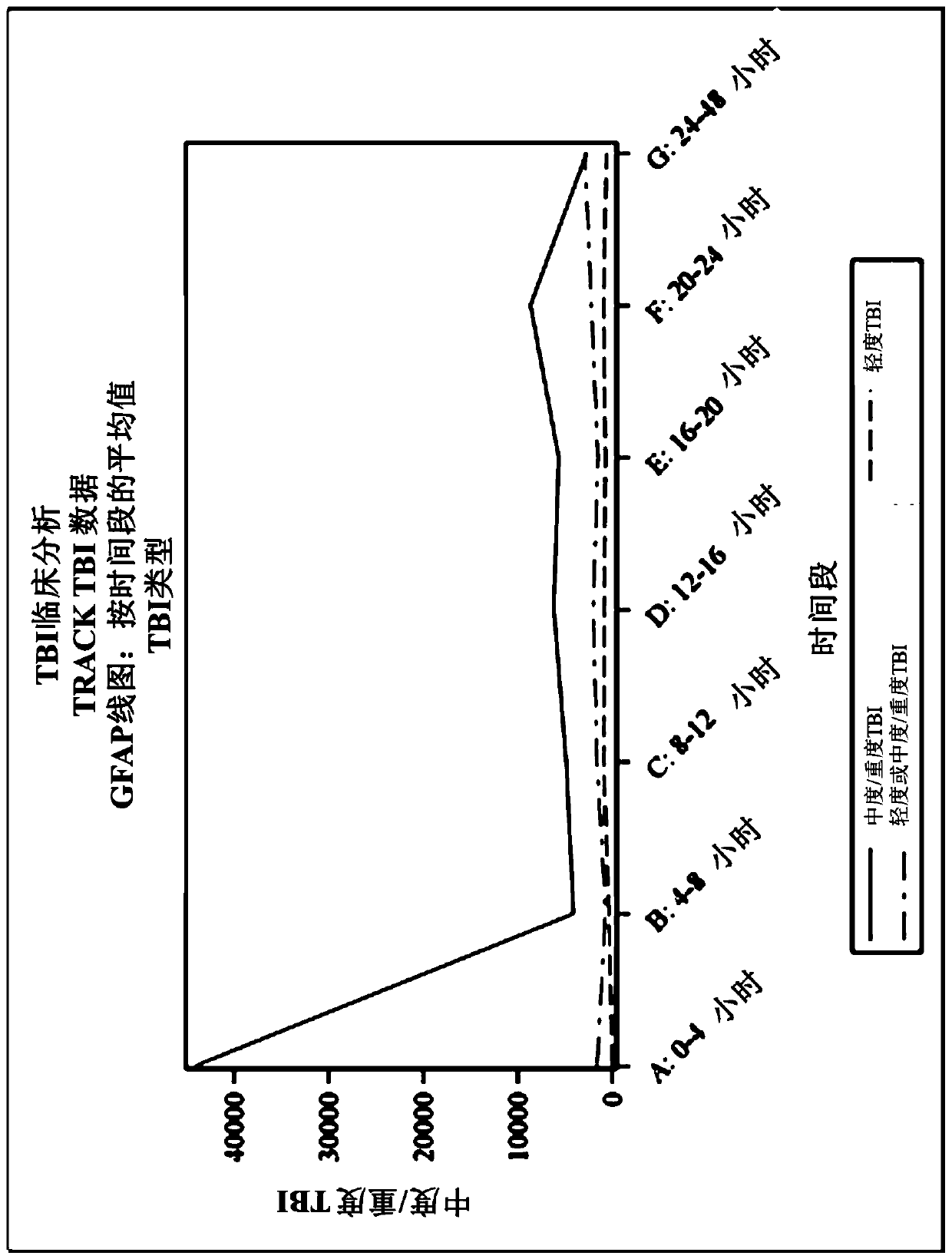
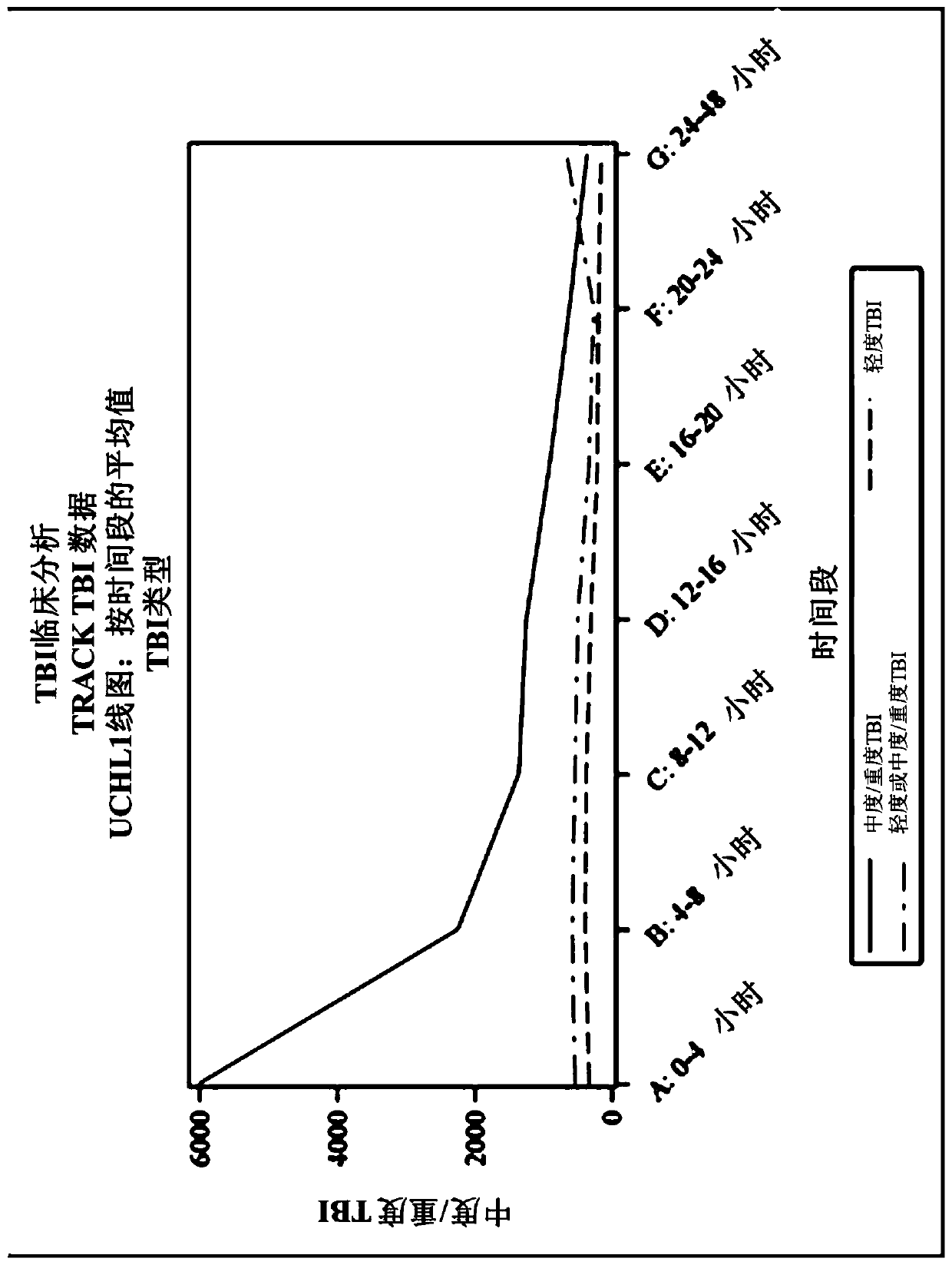
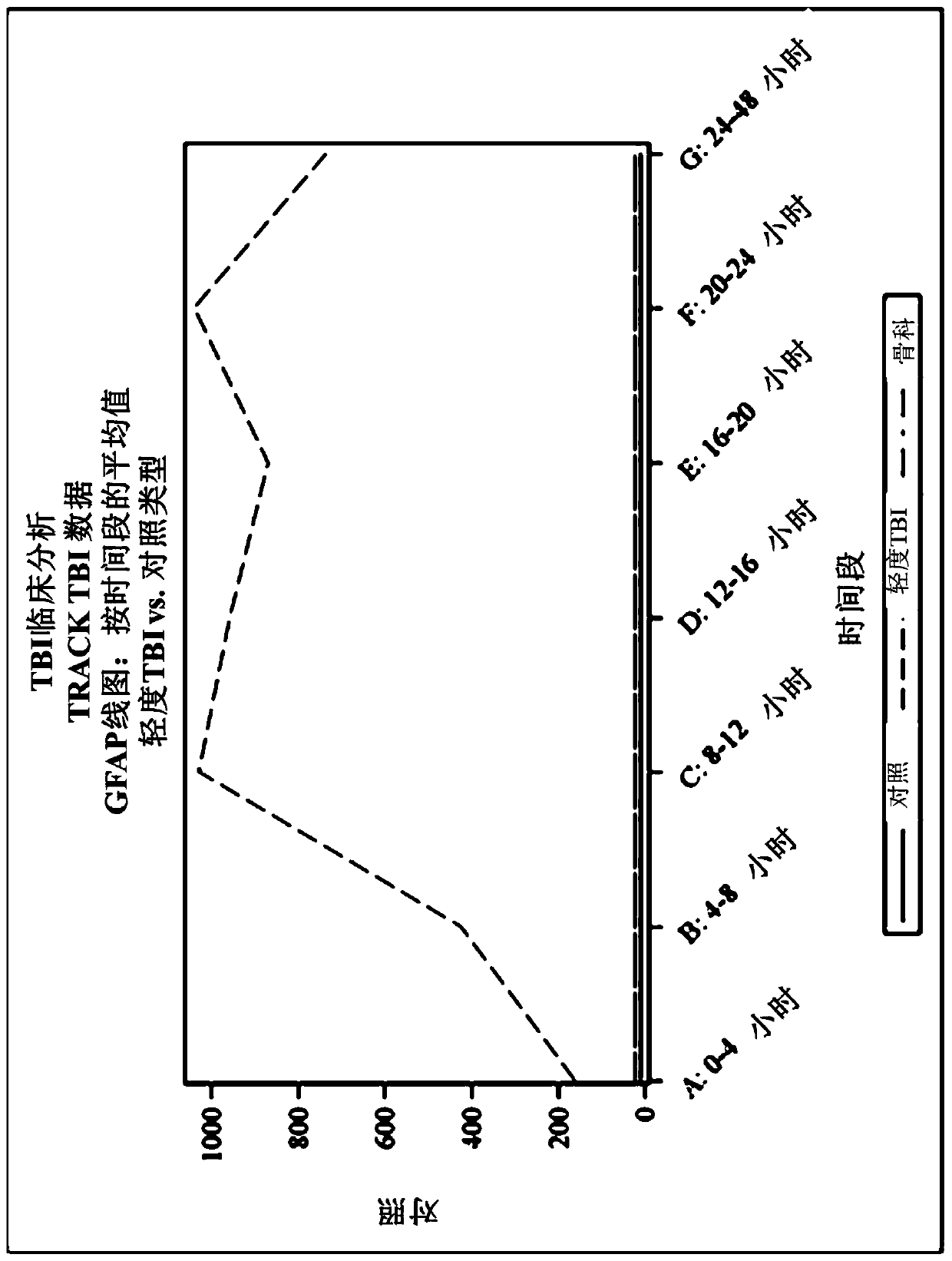
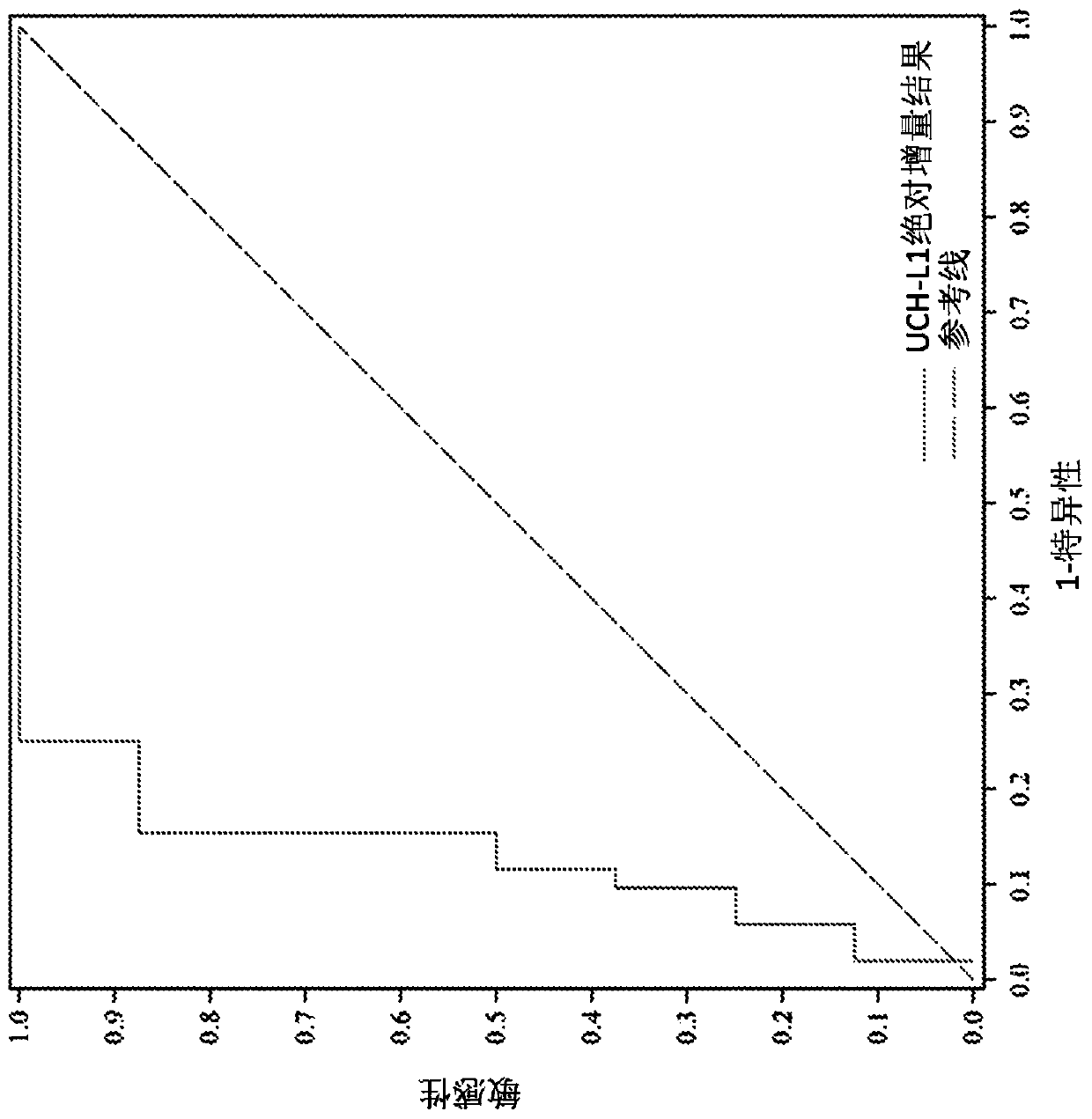
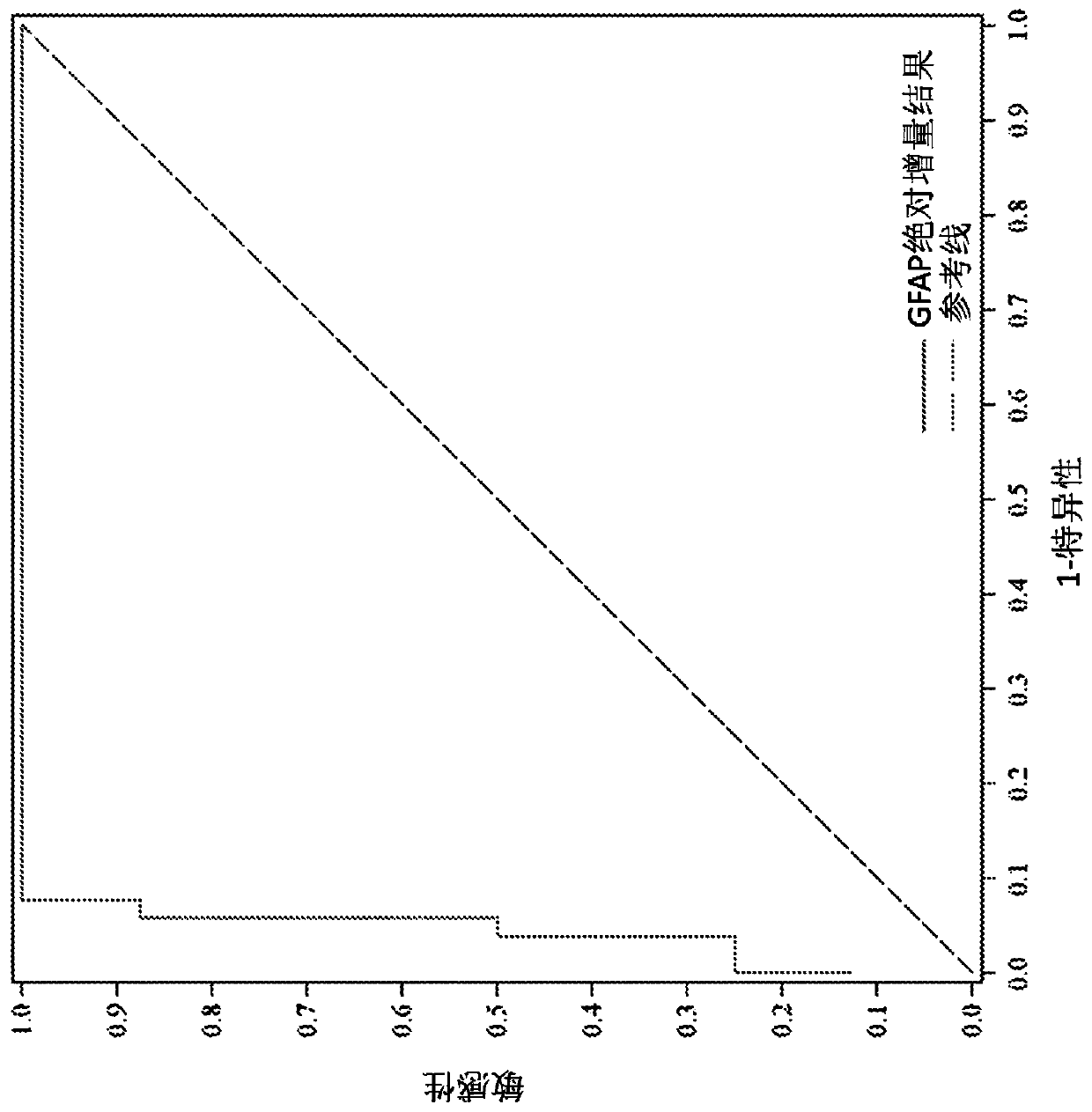
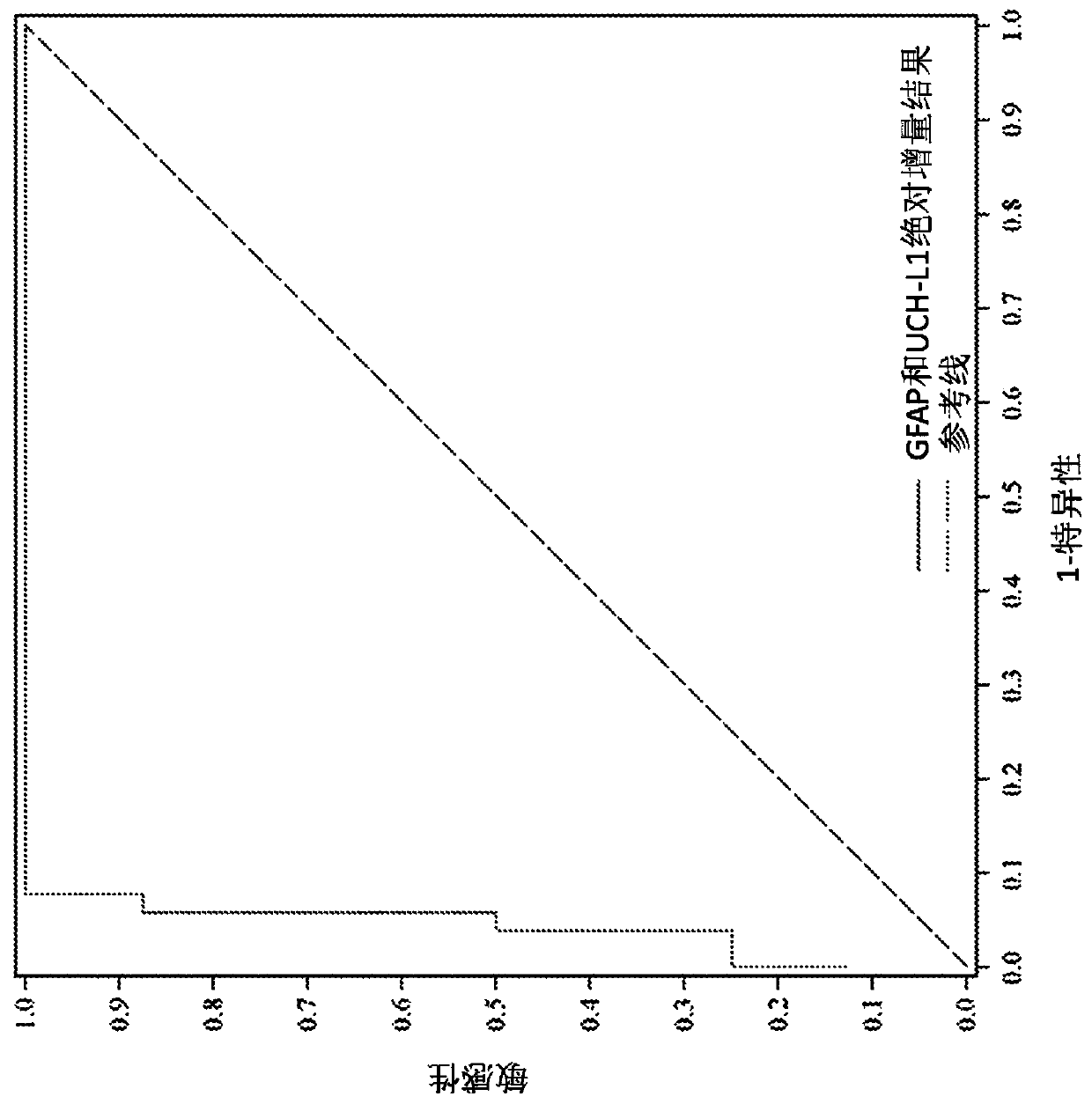
Methods for aiding in diagnosing and evaluating a traumatic brain injury in a human subject using a combination of gfap and uch-l1
PendingCN110892266ADisease diagnosisBiological testingGlial fibrillary acidic proteinCerebral damage
Disclosed herein are methods of aiding in the diagnosis and evaluation of a subject that has sustained or may have sustained an injury to the head. For example, the present disclosure provides methodsfor aiding in the diagnosis and evaluation of a subject to determine whether the subject has sustained a traumatic brain injury (TBI) by detecting or measuring a combination of the levels of ubiquitin carboxy-terminal hydrolase L1 (UCH-L1) and glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) in samples taken at various time points within 48 hours after the subject has sustained or may have sustained an injury to the head.
Owner:ABBOTT LAB INC
Sequences of variable regions of anti-GFAP (glial fibrillary acidic protein) monoclonal antibody and method for preparing same
InactiveCN103173458AImmunoglobulins against animals/humansFermentationGlial fibrillary acidic proteinNucleotide
The invention relates to sequences of variable regions of an anti-GFAP (glial fibrillary acidic protein) monoclonal antibody. The sequences comprise a nucleotide sequence CM10330-VH and a nucleotide sequence CM10330-VL. A method for preparing the sequences comprises the following steps of: immunizing a mouse by taking a GFAP protein as an antigen, detecting to obtain the mouse of which the corresponding antibody expression is positive, separating the spleen cell of the mouse, fusing the spleen cell with the myeloma cell, culturing the spleen cell and the myeloma cell in an HAT culture medium, detecting to obtain the positive antibody-expression cloning, extracting the total RNA (ribonucleic acid) of the positive hybridoma cell, carrying out inverse transcription by taking the mRNA (messenger ribonucleic acid) in the total RNA as a template to obtain the cDNA (complementary deoxyribonucleic acid) of the gene of the corresponding antibody, obtaining the heavy-chain variable region and the light-chain variable region of the corresponding antibody by using a specific primer through PCR (polymerase chain reaction), and cloning and testing the sequences.
Owner:百奇生物科技(苏州)有限公司
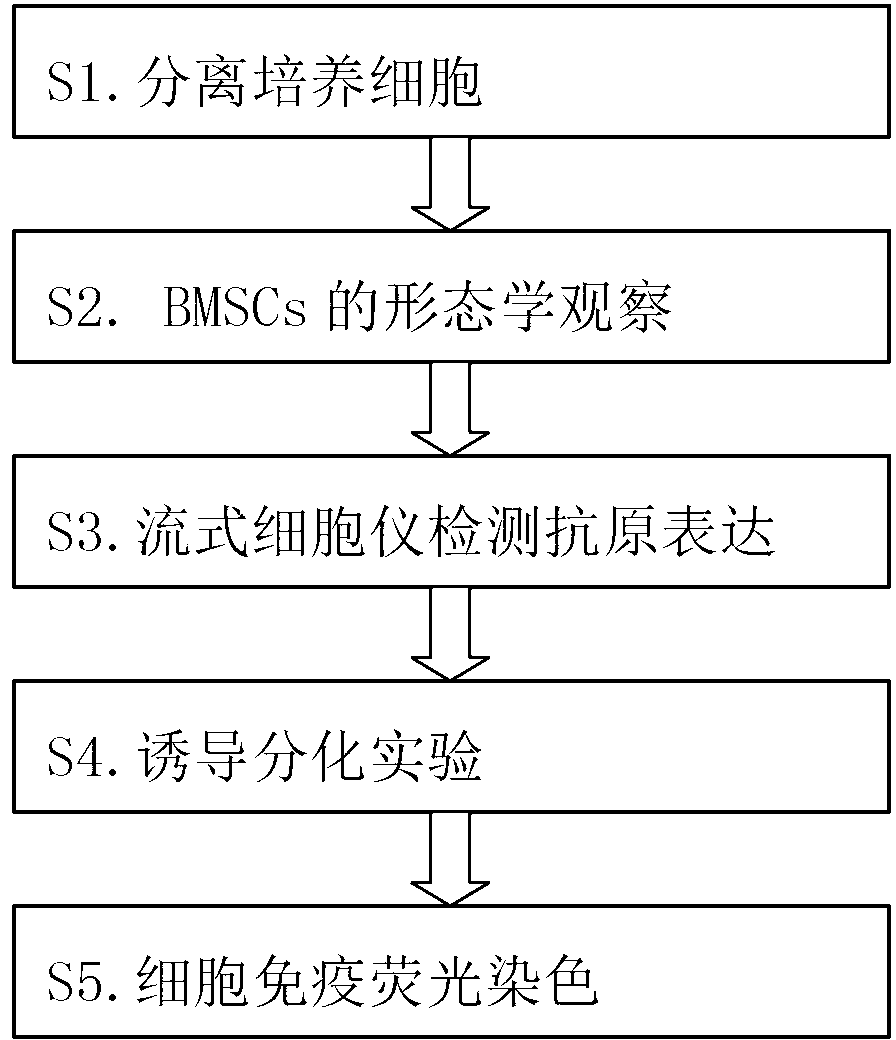
Method for inducing bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells to be differentiated into neuron-like cells
The invention provides a method for inducing bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells to be differentiated into neuron-like cells. The method comprises the steps of cultured cell separation, mesenchymal stem cell morphology observation, flow cytometry antigen presentation detection, differentiation experiment induction and cell immunofluorescence staining. According to the method, the bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells are induced to be differentiated into the neuron-like cells by using all-trans retinoic acids, basic fibroblast growth factors and epidermal growth factors, so that the neuron-like cells not only have the typical morphology of nerve cells, but also express the neuron-specific enolase of neuron marker antigens and the glial fibrillary acidic protein of astrocyte marker antigens; and the bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells maintain the capability that the bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells can be differentiated into non-mesenchymal cells in a germ-layer-crossing manner, and can be differentiated into the neuron-like cells in the germ-layer-crossing manner, so that the neuron-like cells are expected to become seed cells for nerve cell replacement therapy.
Owner:陆华
Methods for aiding in the hyperacute diagnosis and determination of traumatic brain injury using early biomarkers on at least two samples from the same human subject
The present invention discloses methods that aid in the hyperacute diagnosis and evaluation of a human subject that has sustained or may have sustained an injury to the head, such as mild, moderate, severe, or moderate to severe traumatic brain injury (TBI), using an early biomarker, such as ubiquitin carboxy-terminal hydrolase L1 (UCH-L1), glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP), or a combinationthereof. Also disclosed here are methods that aid in the hyperacute determination of whether a human subject that has sustained an injury or may have sustained to the head would benefit from and thusreceive a head computerized tomography (CT) scan based on the levels of UCH-L1. These methods involve detecting changes of levels of an early biomarker, such as ubiquitin carboxy-terminal hydrolase L1(UCH-L1), glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP), or a combination thereof, in samples taken from a human subject at a time point within about 2 hours, such as about 10, 12, or 20 minutes, after thesubject has sustained or may have sustained an injury to the head and a second time point about 3 hours to about 6 hours after the first sample is taken.
Owner:ABBOTT LAB INC
Immunochromatographic detection card for rapidly detecting glial fibrillary acidic protein and preparation method thereof
PendingCN110488007AImprove detection efficiencyHigh sensitivityMaterial analysisGlial fibrillary acidic proteinSerum ige
The invention relates to an immunochromatographic detection card for rapidly detecting glial fibrillary acidic protein. The immunochromatographic detection card comprises a test strip, wherein the test strip comprises a detection line and a quality control line, the detection line is coated with mouse-anti-human GFAP monoclonal antibodies, and the quality control line is coated with goat-anti-rabbit polyclonal antibodies. The immunochromatographic detection card for rapidly detecting glial fibrillary acidic protein provided by the invention can be used for detecting serum, plasma and whole blood, and has important clinical significance for early judgment of degrees of brain injuries and prognosis of patients.
Owner:TIANJIN SAVANT BIOTECH CO LTD
Multi-protein biomarker assay for brain injury detection and outcome
ActiveUS20200116739A1Reduce utilizationLow costMicrobiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisGlial fibrillary acidic proteinInjury brain
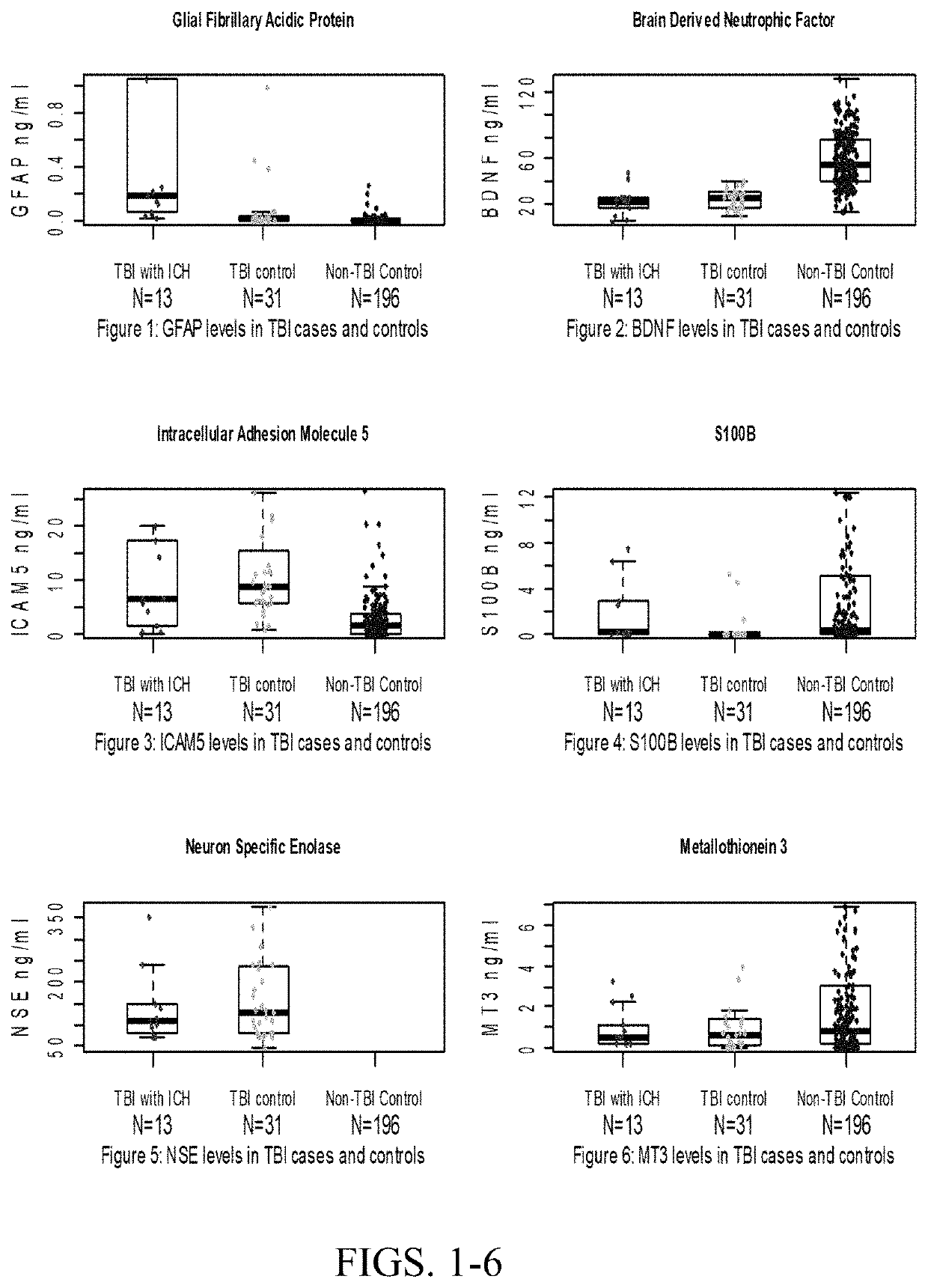
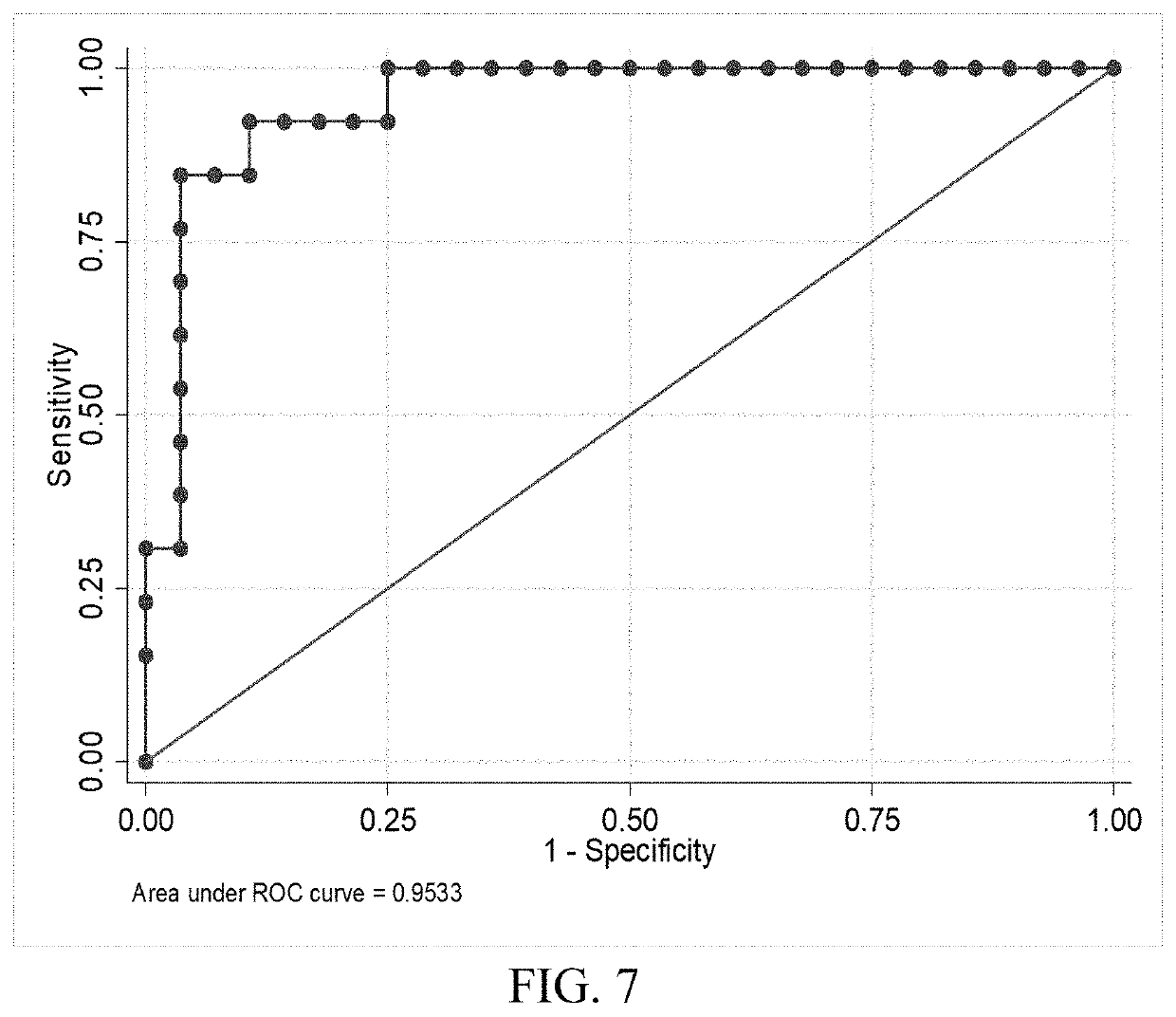
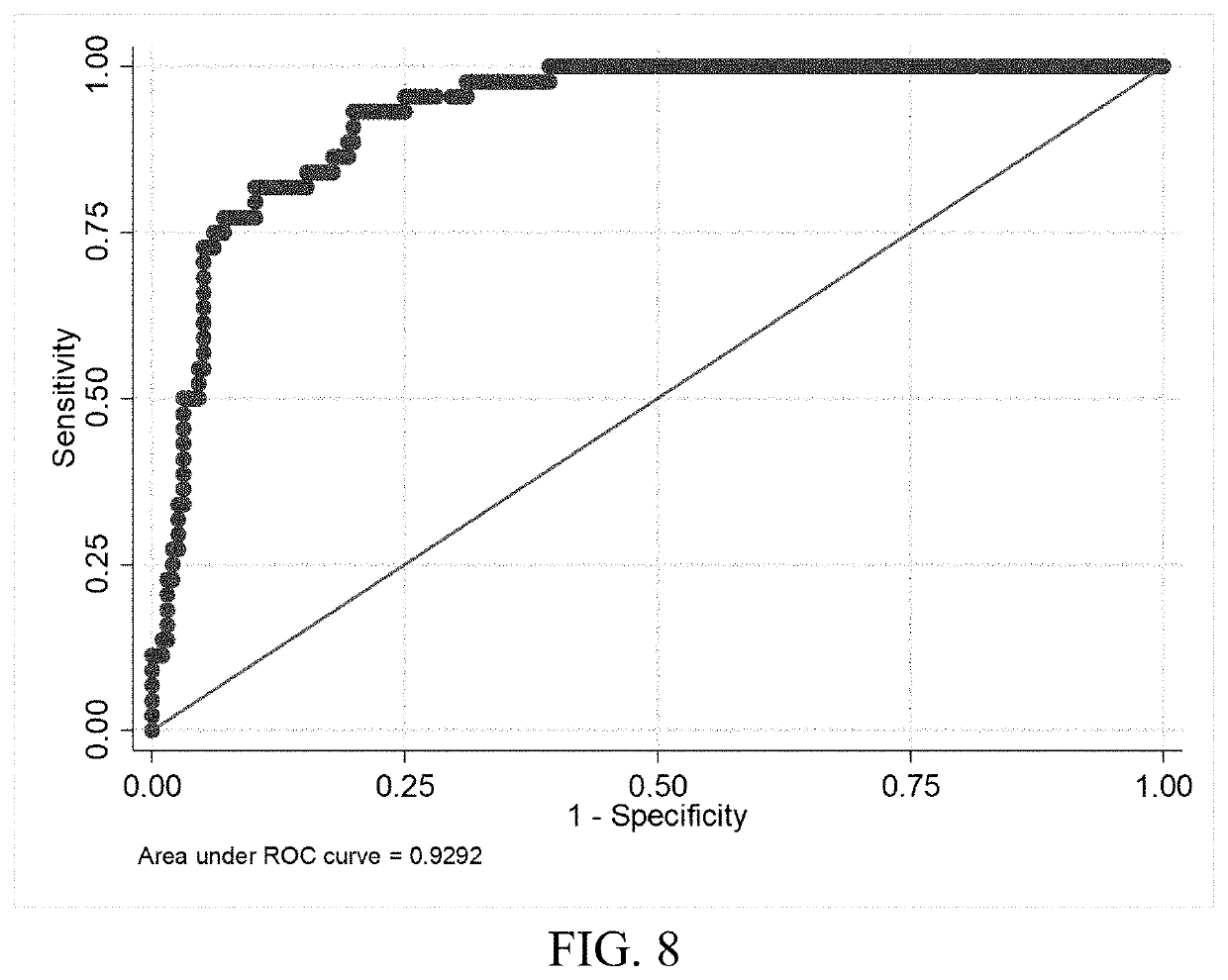
The present invention relates to the field of brain injuries. More specifically, the present invention provides methods and compositions useful in the diagnosis / prognosis / assessment of brain injuries. In a specific embodiment, a method for identifying which patients with traumatic brain injury (TBI) require a head computerized tomography (CT) scan for diagnosing acute intracranial pathology comprises the steps of (a) obtaining or collecting a sample from the patient; (b) measuring the levels of one or more biomarkers in the blood sample obtained from the patient, wherein the biomarkers comprise glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP), S100B, metallothionein 3 (MT3), neuron specific enolase (NSE) and intracellular adhesion molecule 5 (ICAM5); and (c) identifying the patient as requiring or not requiring a head CT scan based on the measured levels of one or more of biomarkers comprising GFAP, S100B, MT3, NSE and ICAM5.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com