Methods for aiding in the hyperacute diagnosis and determination of traumatic brain injury using early biomarkers on at least two samples from the same human subject
A biomarker, subject technology, used in radiological diagnostic instruments, diagnostics, biological testing, etc., to solve problems such as test failures and inability to assess subtle differences in results
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
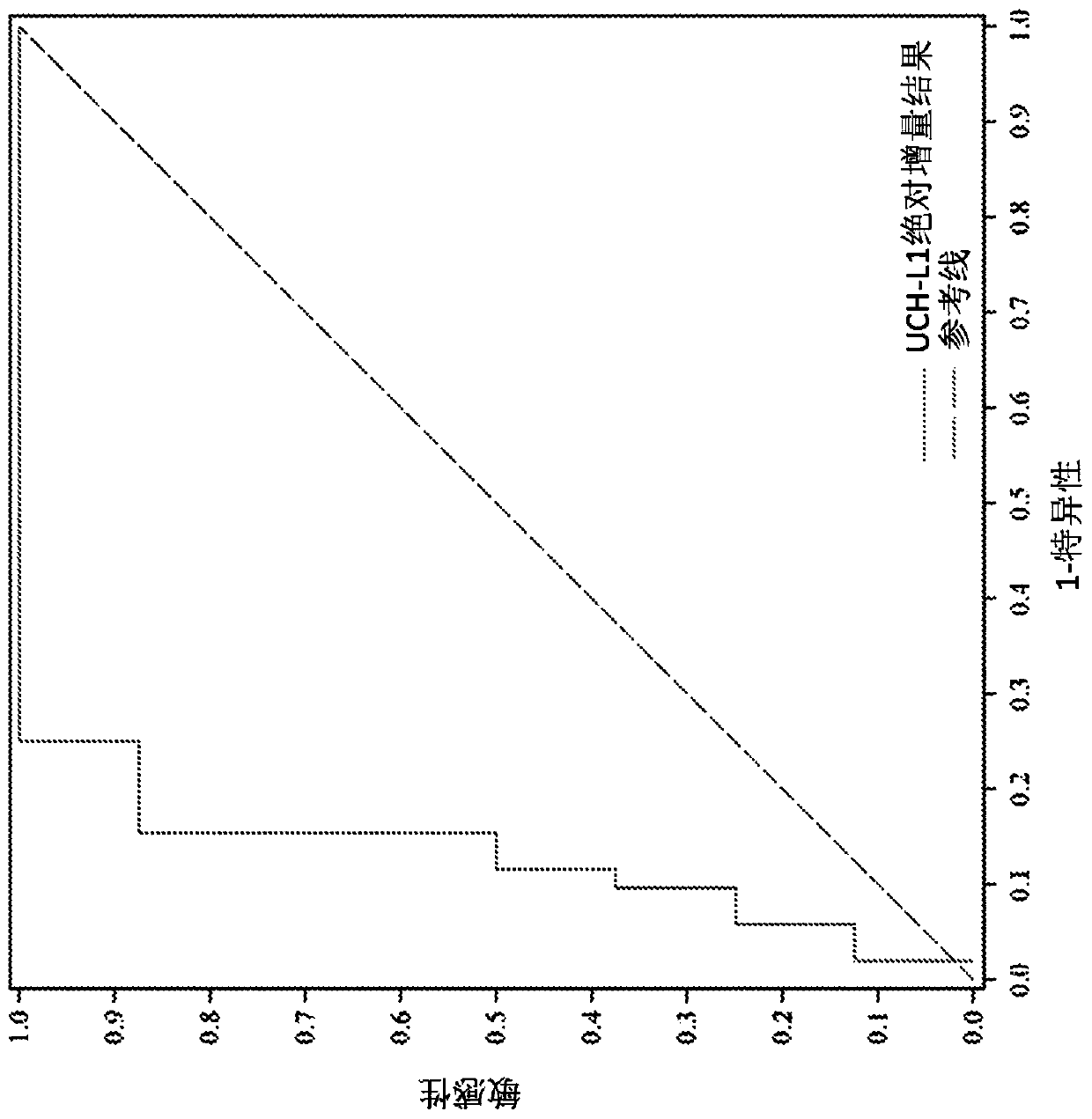
[0425] UCH-L1 assay
[0426] Will The UCH-L1 assay was used in a TBI patient cohort study. A pair of monoclonal antibodies, such as antibody A, is used as the capture monoclonal antibody, and antibodies B and C are used as the detection monoclonal antibodies. Antibody A is an exemplary anti-UCH-L1 antibody developed in-house at Abbott Laboratories (Abbott Park, IL). Antibodies B and C, which recognize different epitopes of UCH-L1 and enhance detection of antigen in samples, were developed by Banyan Biomarkers (Alachua, Florida). Other antibodies developed in-house at Abbott Laboratories (Abbott Park, IL) also showed or were expected to show similar signal enhancement when used together in various combinations as capture or detection antibodies. The UCH-L1 assay design was evaluated for key performance attributes. Cassette configuration is antibody configuration: Antibody A (capture antibody) / Antibody B+C (detection antibody); reagent conditions: 0.8% solids, 125 μg / mL F...
Embodiment 2
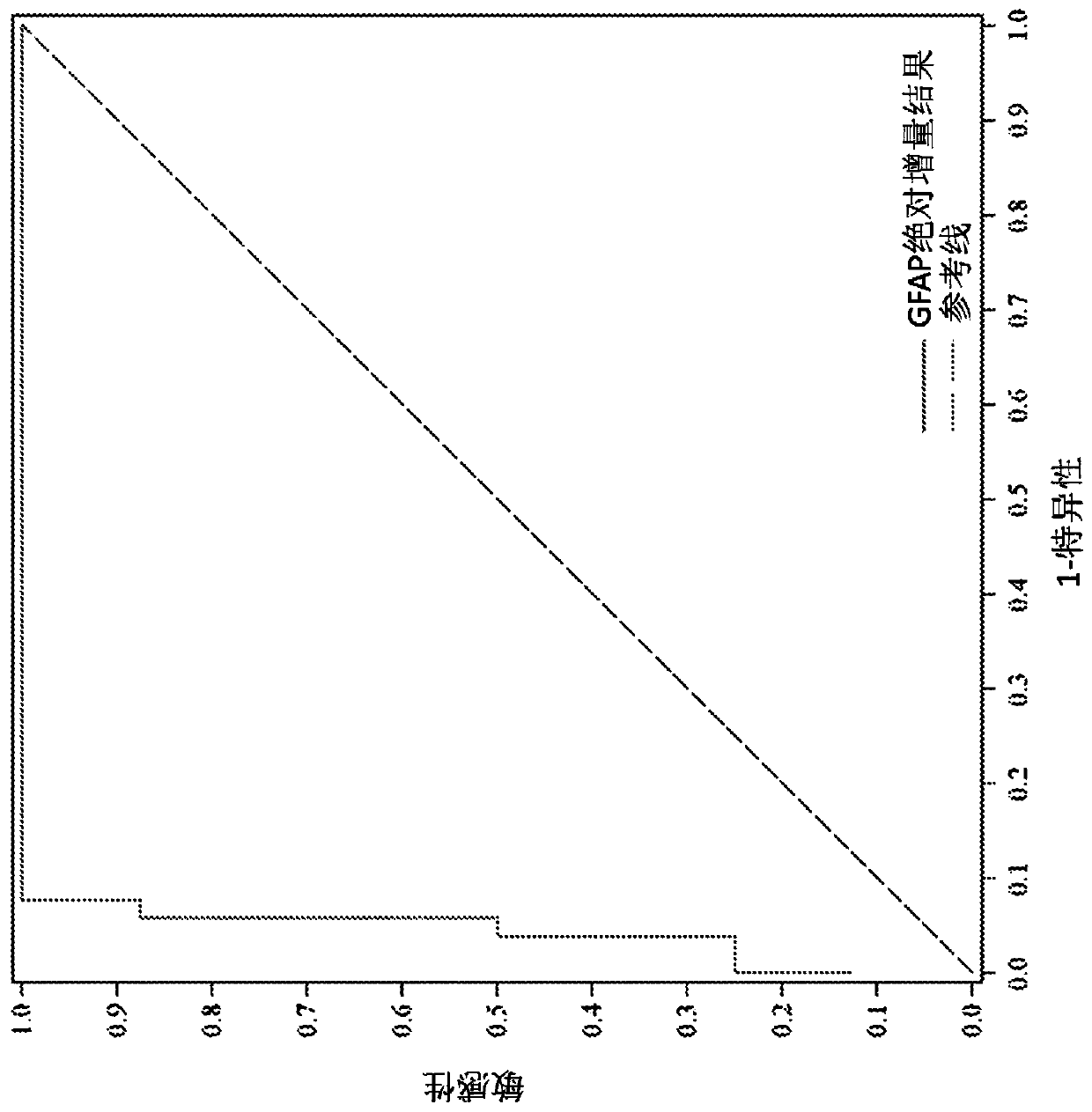
[0428] GFAP assay
[0429] Will The GFAP assay was used in a population study of TBI patients. Use a monoclonal antibody pair such as antibody A as the capture monoclonal antibody and use antibody B as the detection monoclonal antibody. Antibody A and Antibody B are exemplary anti-GFAP antibodies developed in-house at Abbott Laboratories (Abbott Park, IL). The GFAP assay design was evaluated for key performance attributes. The cartridge configuration was antibody configuration: Antibody A (capture antibody) / Antibody B (detection antibody); reagent conditions: 0.8% solids, 250 μg / mL Fab alkaline phosphatase cluster conjugate; and injection print: GFAP specific. The assay time was 10-15 min (with a sample capture time of 7-12 min).
Embodiment 3
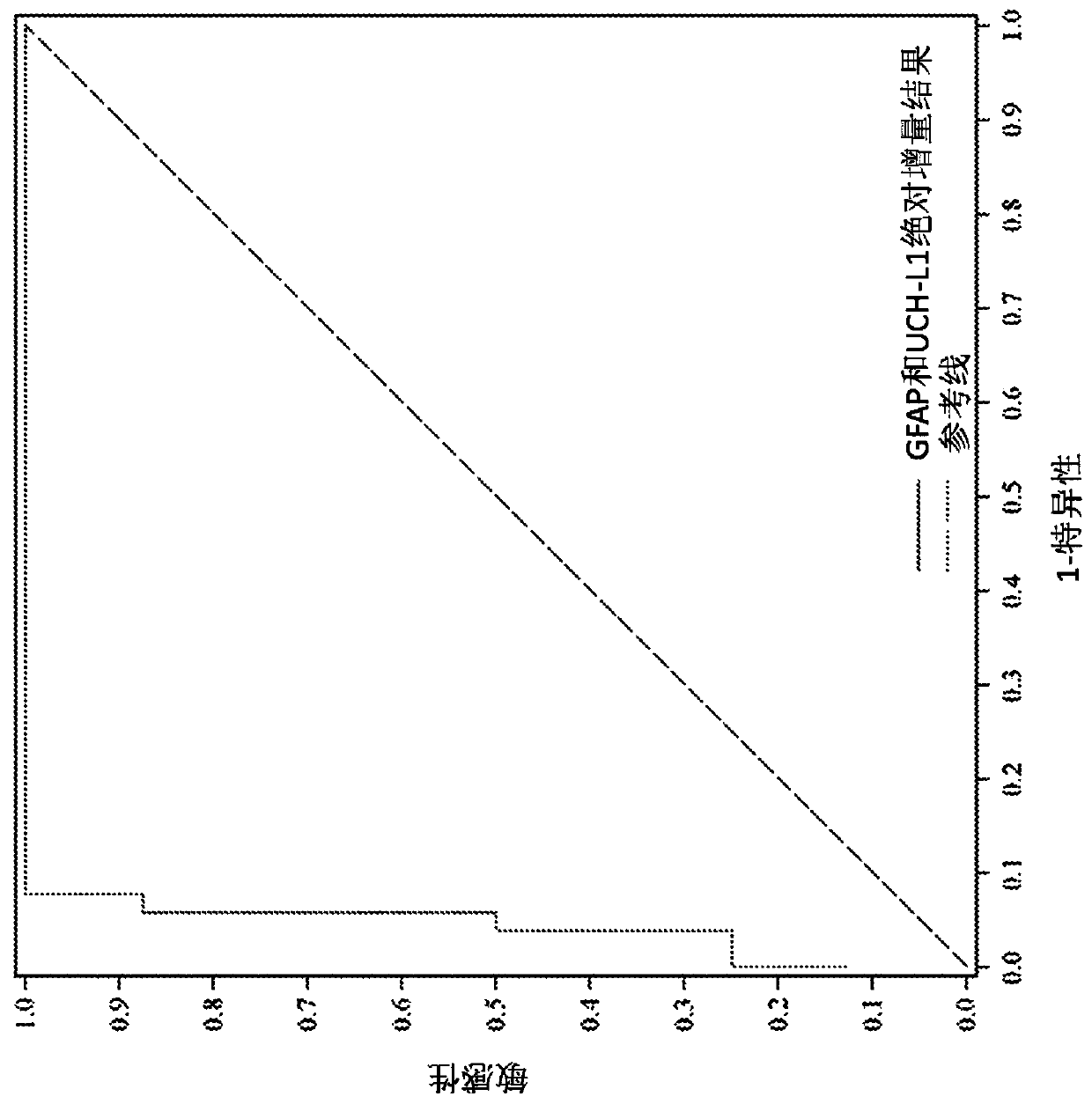
[0431] Development of a multimodal classification scheme for traumatic brain injury
[0432] The aim of this study was to develop a classification scheme for brain injuries that specifies the nature (type) and severity of the injury. For example, serum biomarkers reveal cell type. Trauma patients were divided into three groups for analysis: brain injury only, non-brain injury only, and combined injury. Brain-injured and non-brain-injured trauma groups were compared to each other and to the brain / non-brain-trauma combination. These trauma groups were compared to a non-trauma control group. The CSF of trauma patients was compared with that of non-trauma patients. A secondary objective was to determine whether any of the measures (alone or in combination) could be used as an indicator of clinical outcome after TBI.
[0433] An objective multimodal classification scheme and outcome measures for traumatic brain injury were developed based on several measures: 1) blood-based bio...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com