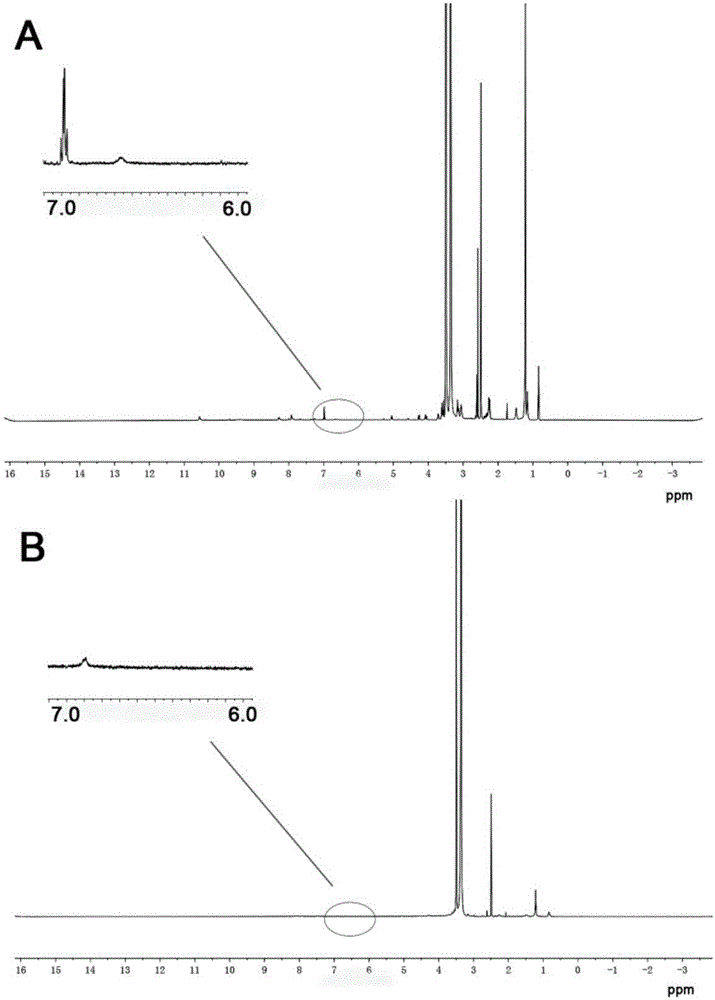
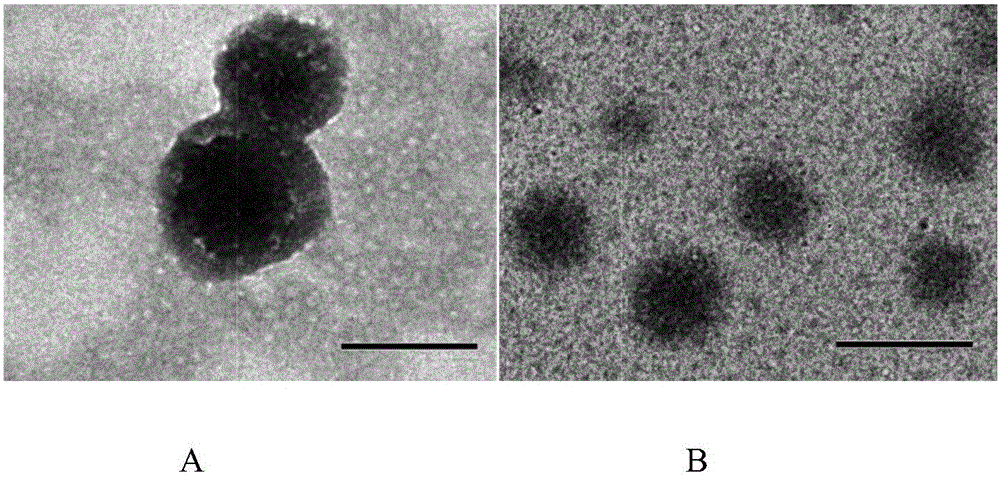
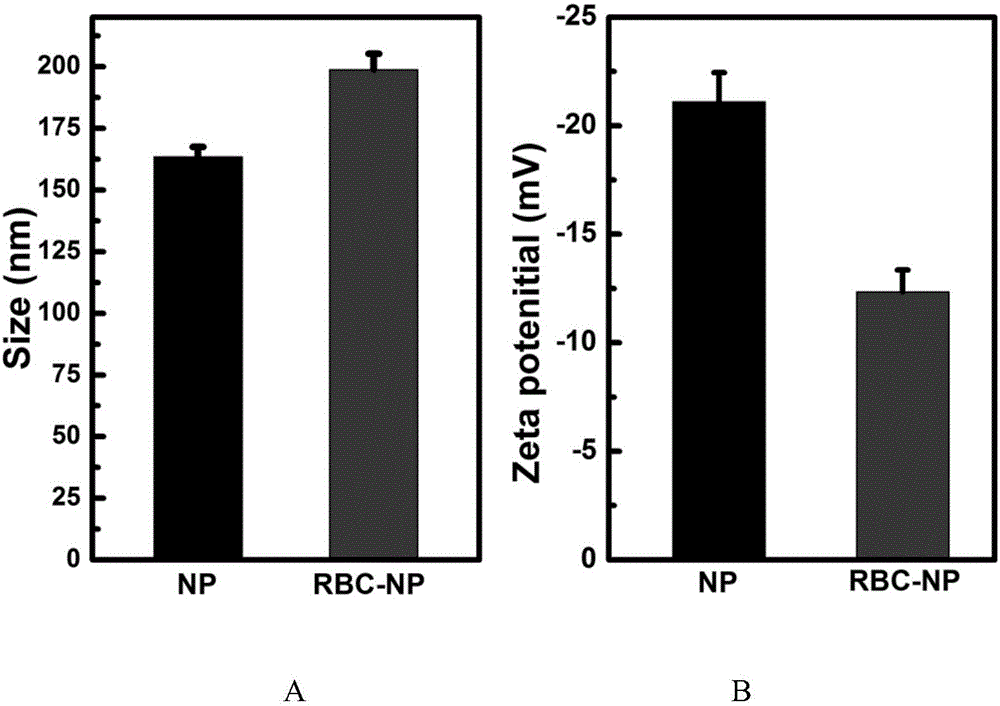
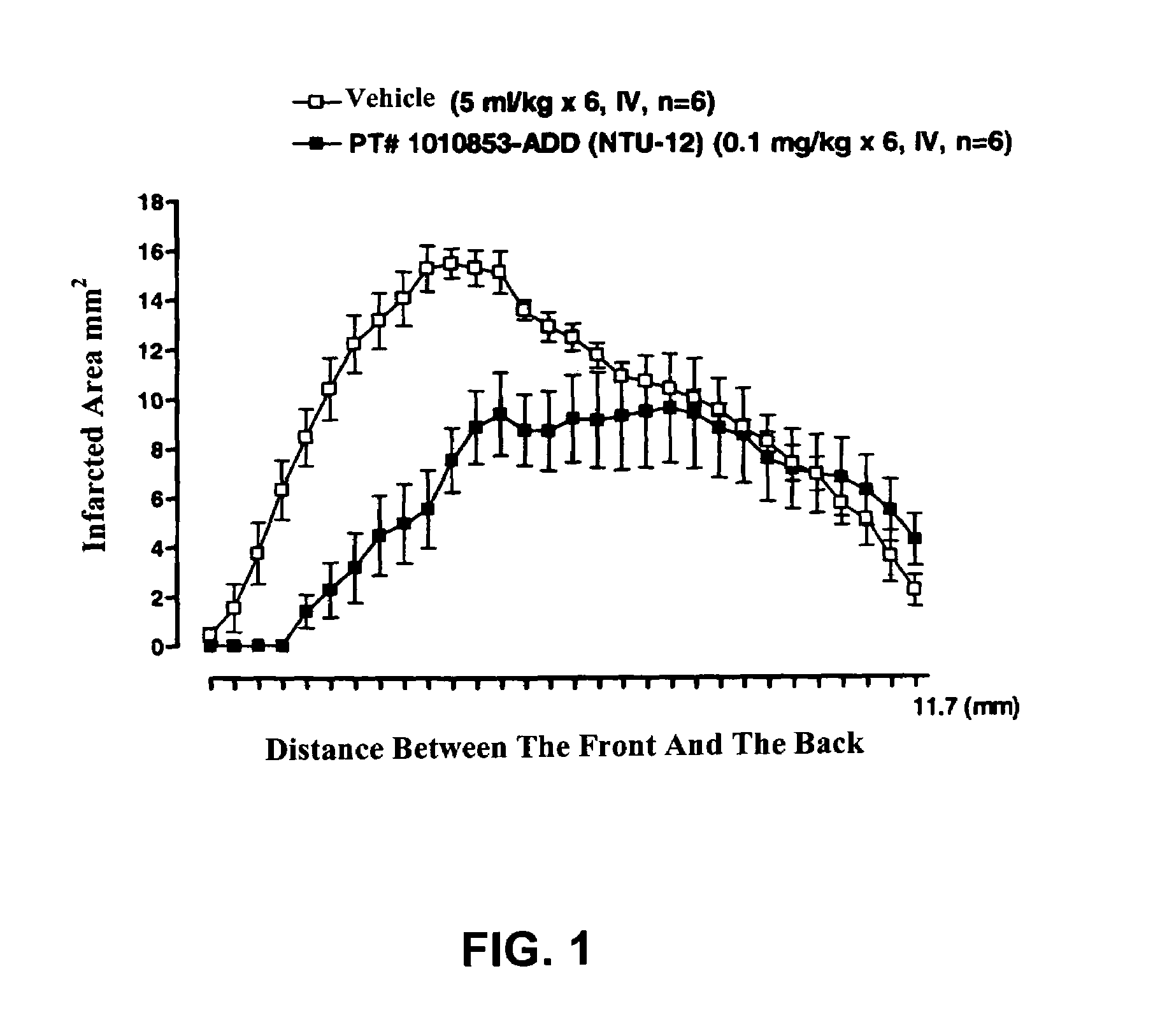
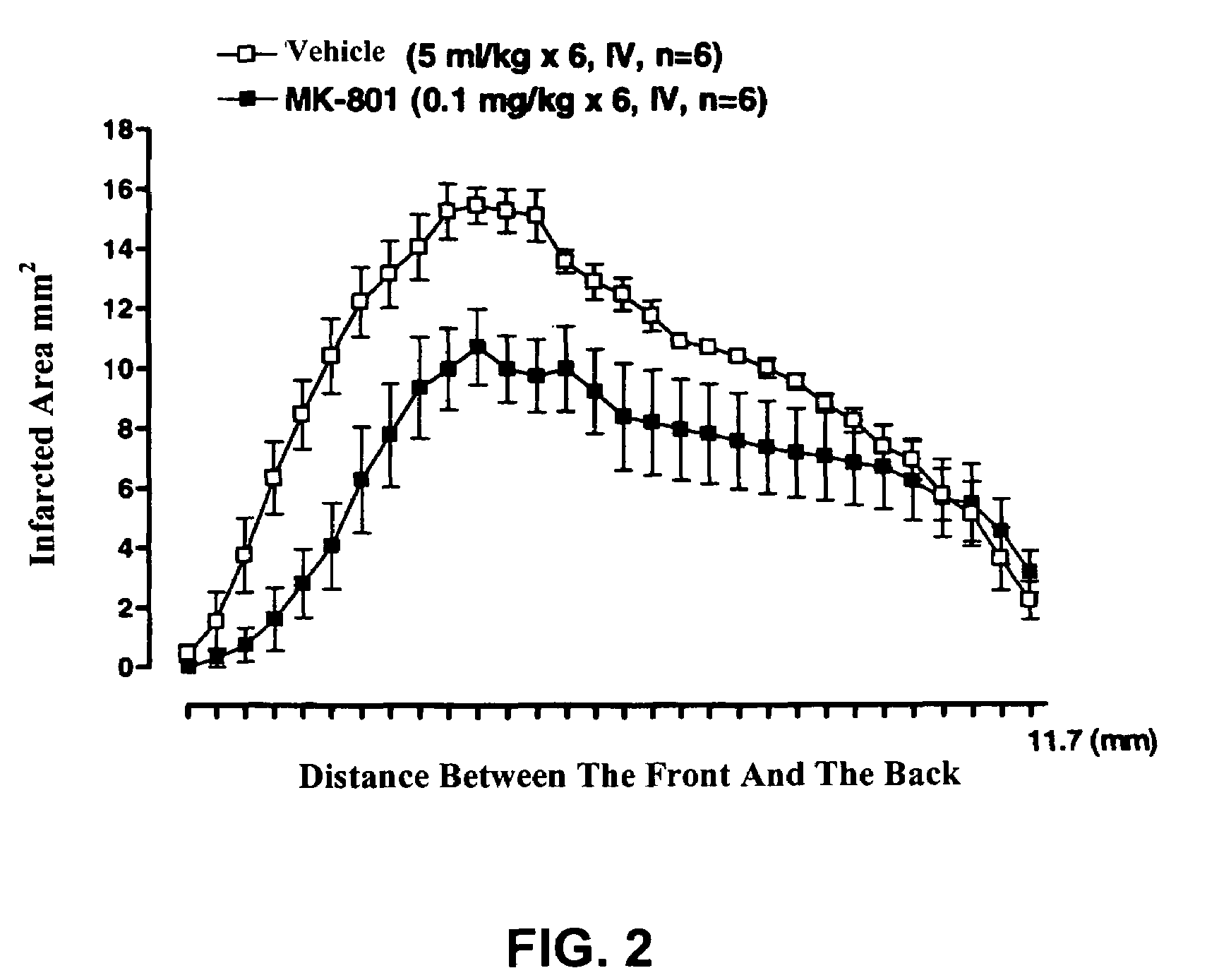
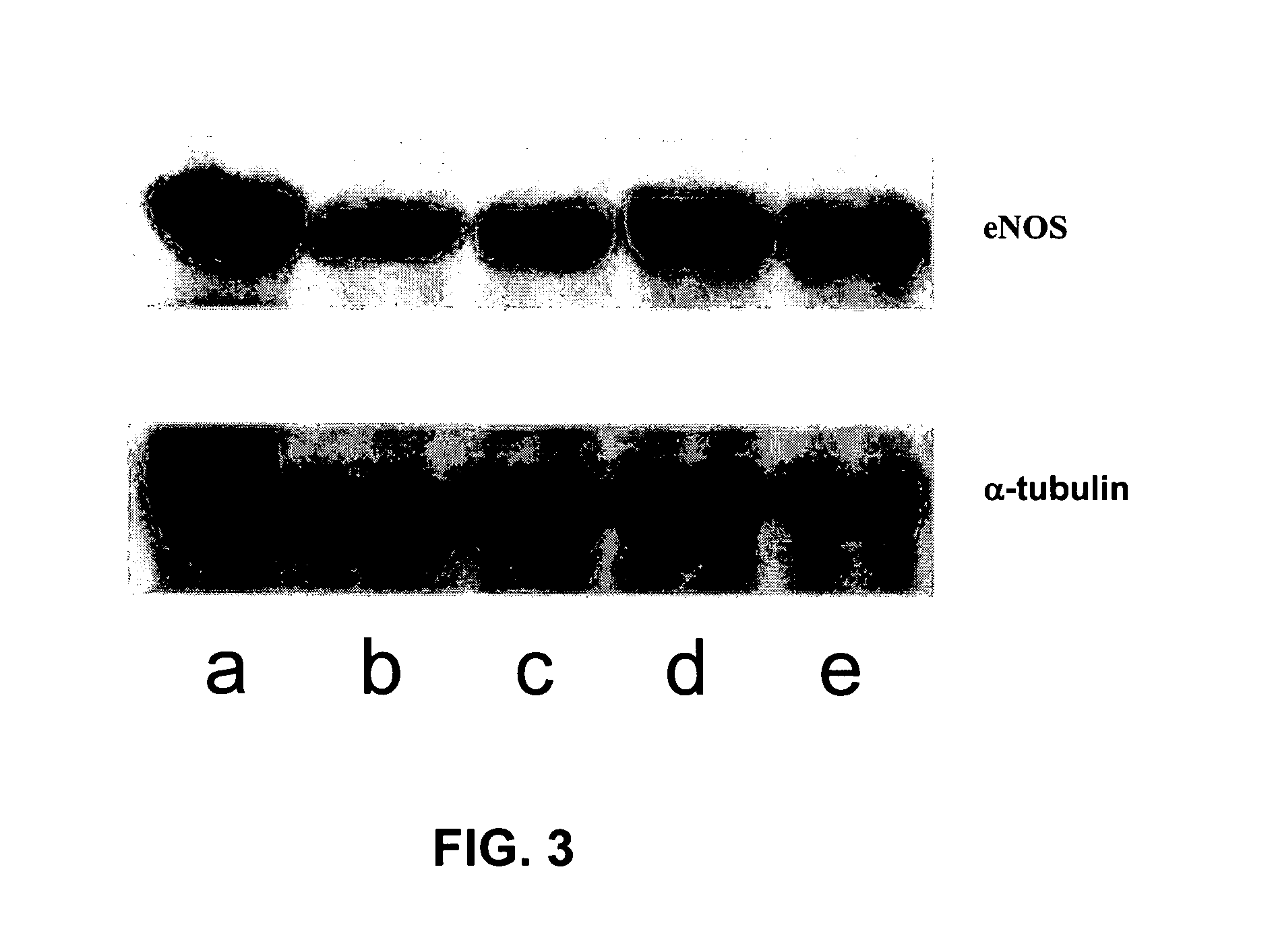
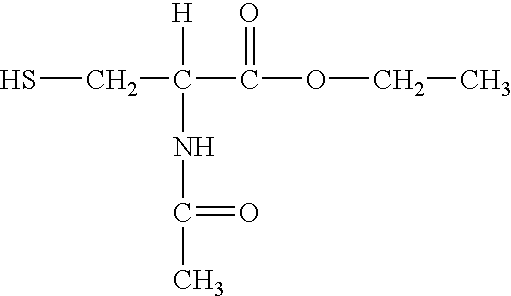
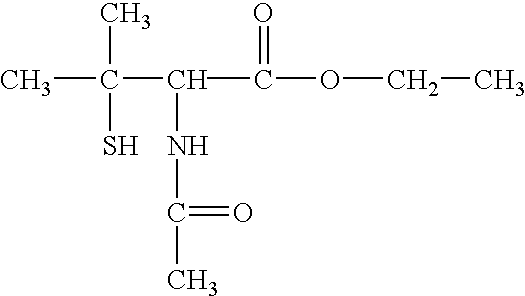
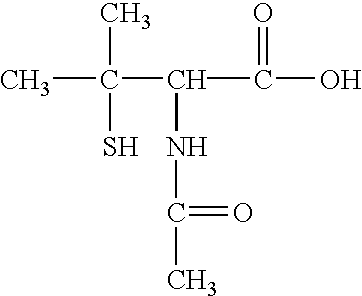
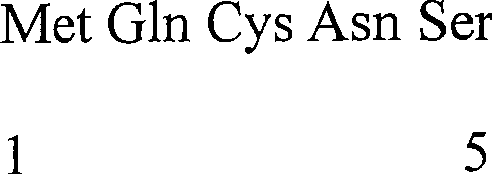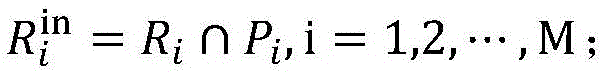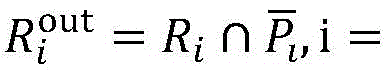Patents
Literature
382 results about "Ischemic brain" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Brain ischemia is a condition in which there is insufficient blood flow to the brain to meet metabolic demand. This leads to poor oxygen supply or cerebral hypoxia and thus to the death of brain tissue or cerebral infarction / ischemic stroke.
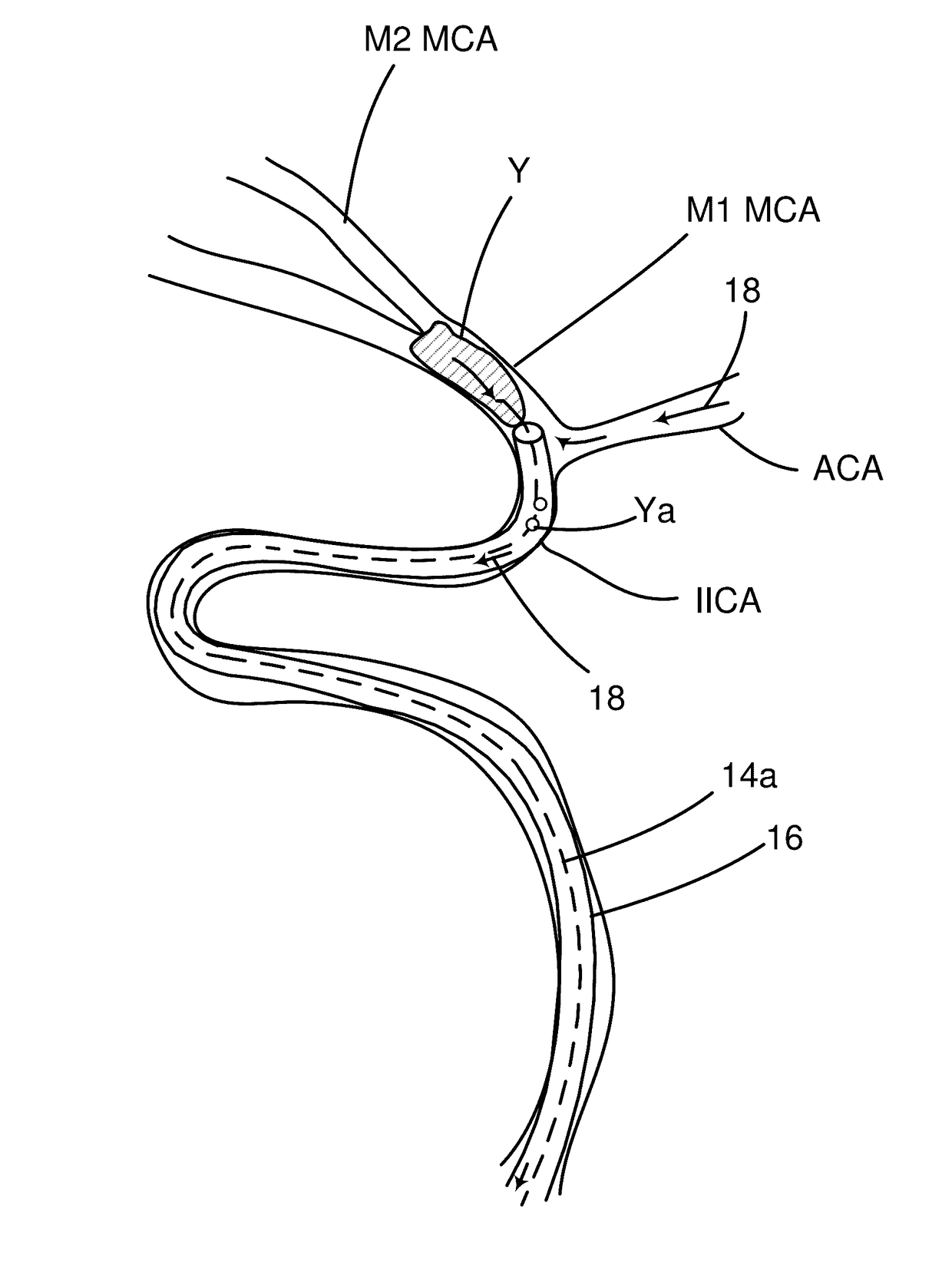
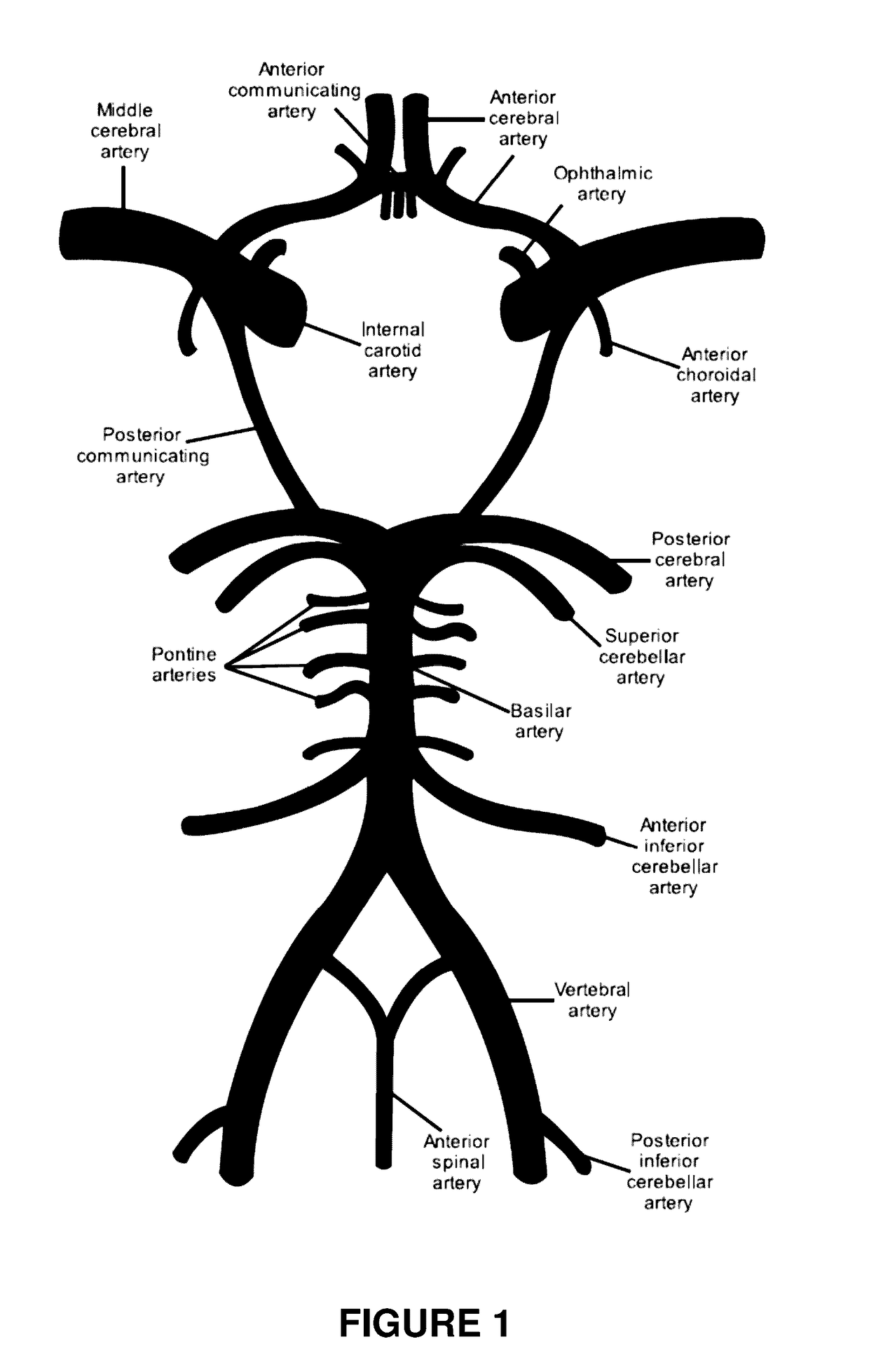
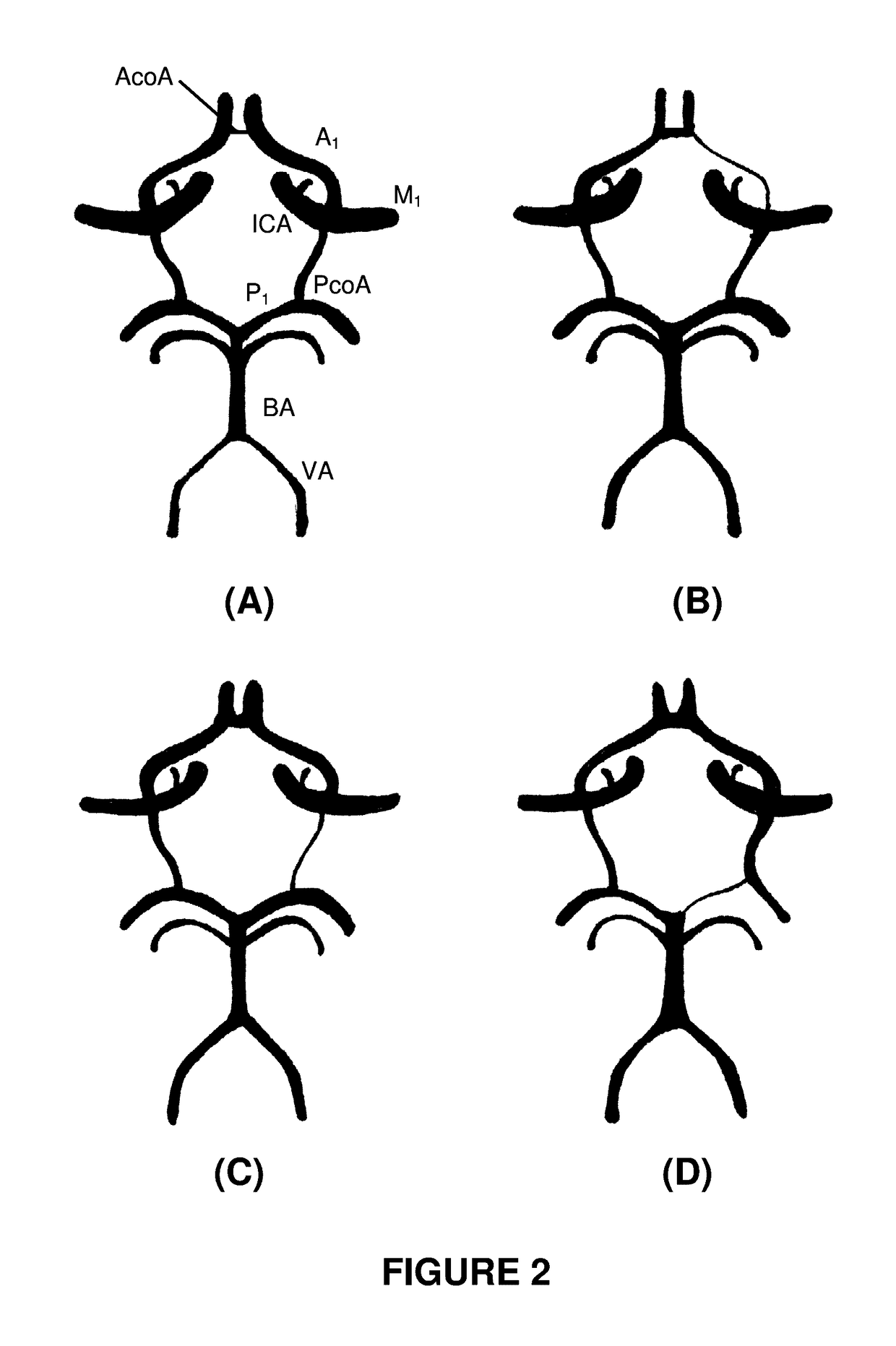
Systems and methods to improve perfusion pressure during endovascular intervention
The invention relates to systems and methods to improve perfusion flow and pressure during endovascular intervention. In particular, the invention relates to catheters that enable both antegrade and retrograde flow through the catheter during a recanalization procedure and specifically at the step in a procedure where a clot is being withdrawn. Additionally, the invention provides systems for supplying fluids and fluid compositions to improve nutrition to ischemic brain.
Owner:MG STROKE ANALYTICS INC
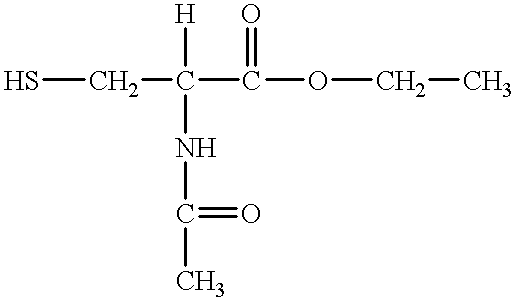
Treatment of ischemic brain injuries with brain targeted anti oxidant compounds
A method of reducing oxidative stress in the brain of an organism having a blood brain barrier and suffering an ischemic brain injury, the method comprising the step of administering a compound to the organism, the compound having (a) a combination of molecular weight and membrane miscibility properties for permitting the compound to cross the blood brain barrier of the organism; (b) a readily oxidizable chemical group for exerting antioxidation properties; and (c) a chemical make-up for permitting the compound or its intracellular derivative to accumulate within the cytoplasm of cells.
Owner:YISSUM RES DEV CO OF THE HEBREWUNIVERSITY OF JERUSALEM LTD +1
Genetic remedies for neurodegenerative diseases
ActiveUS20040265283A1Effective preventionEffective therapyBiocideNervous disorderCerebrovascular disorderPeripheral neuritis
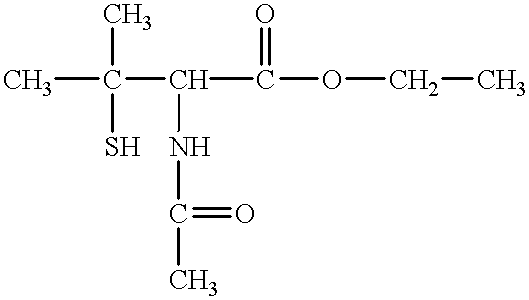
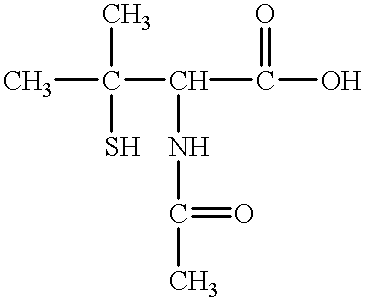
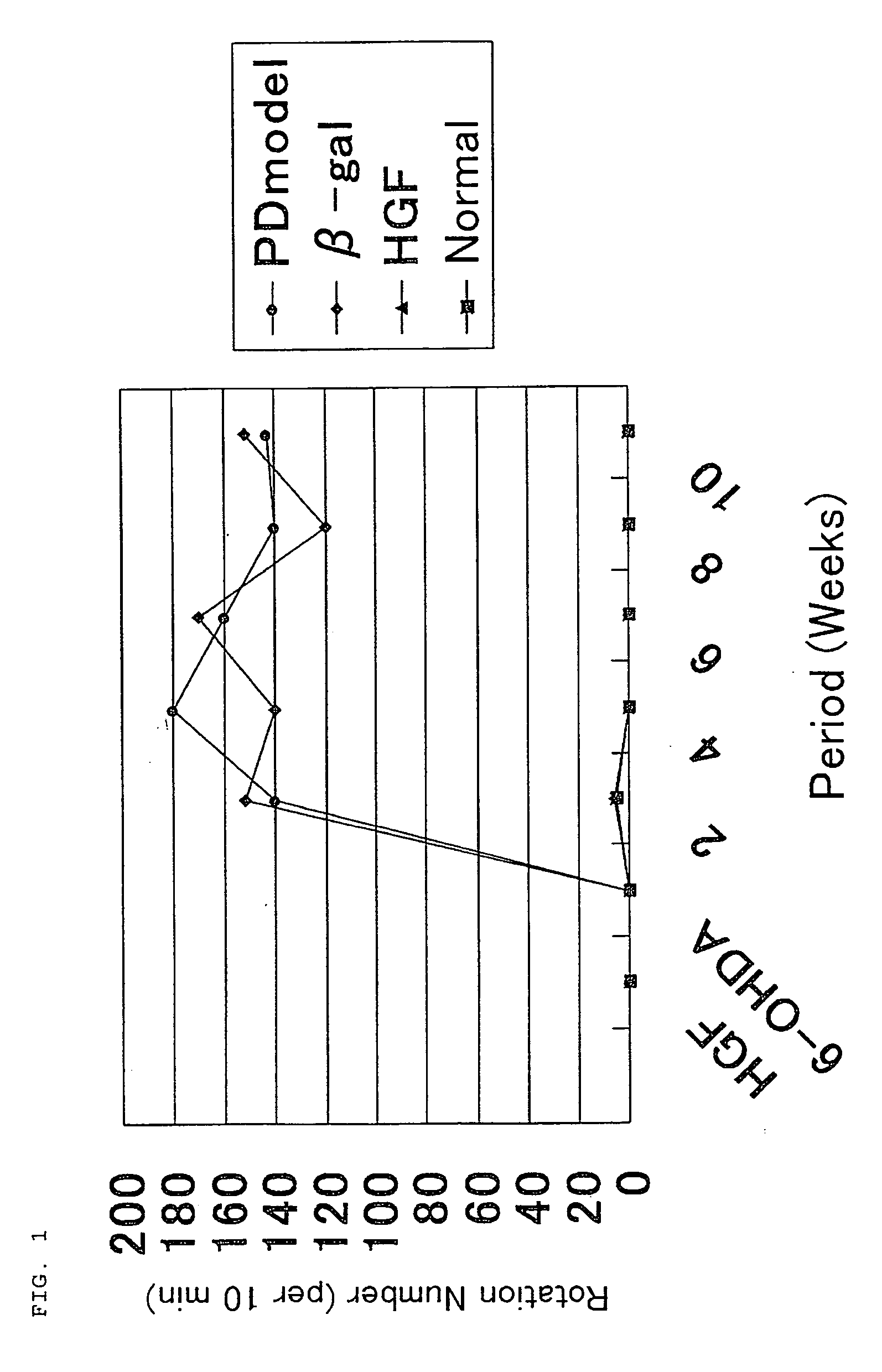
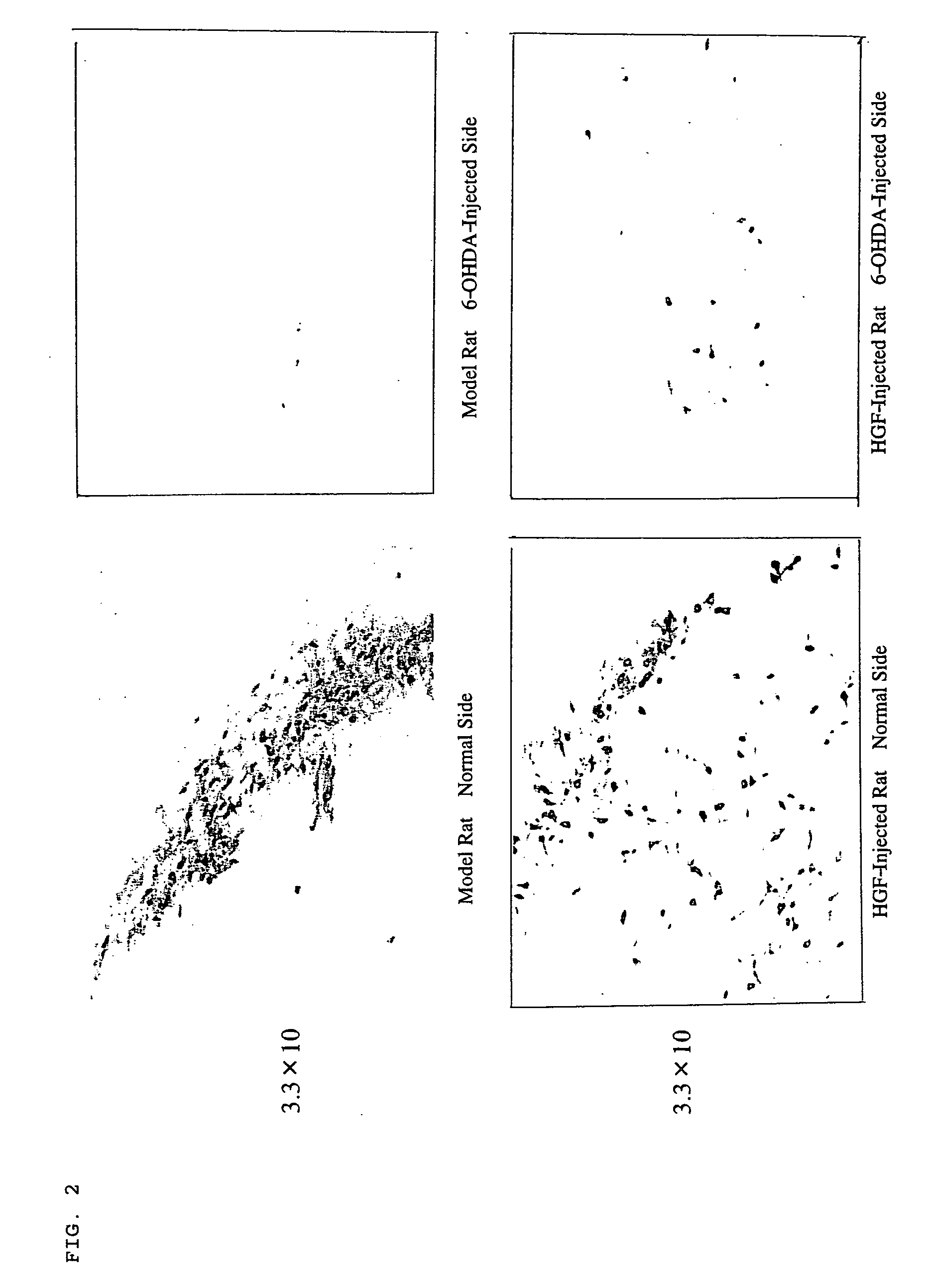
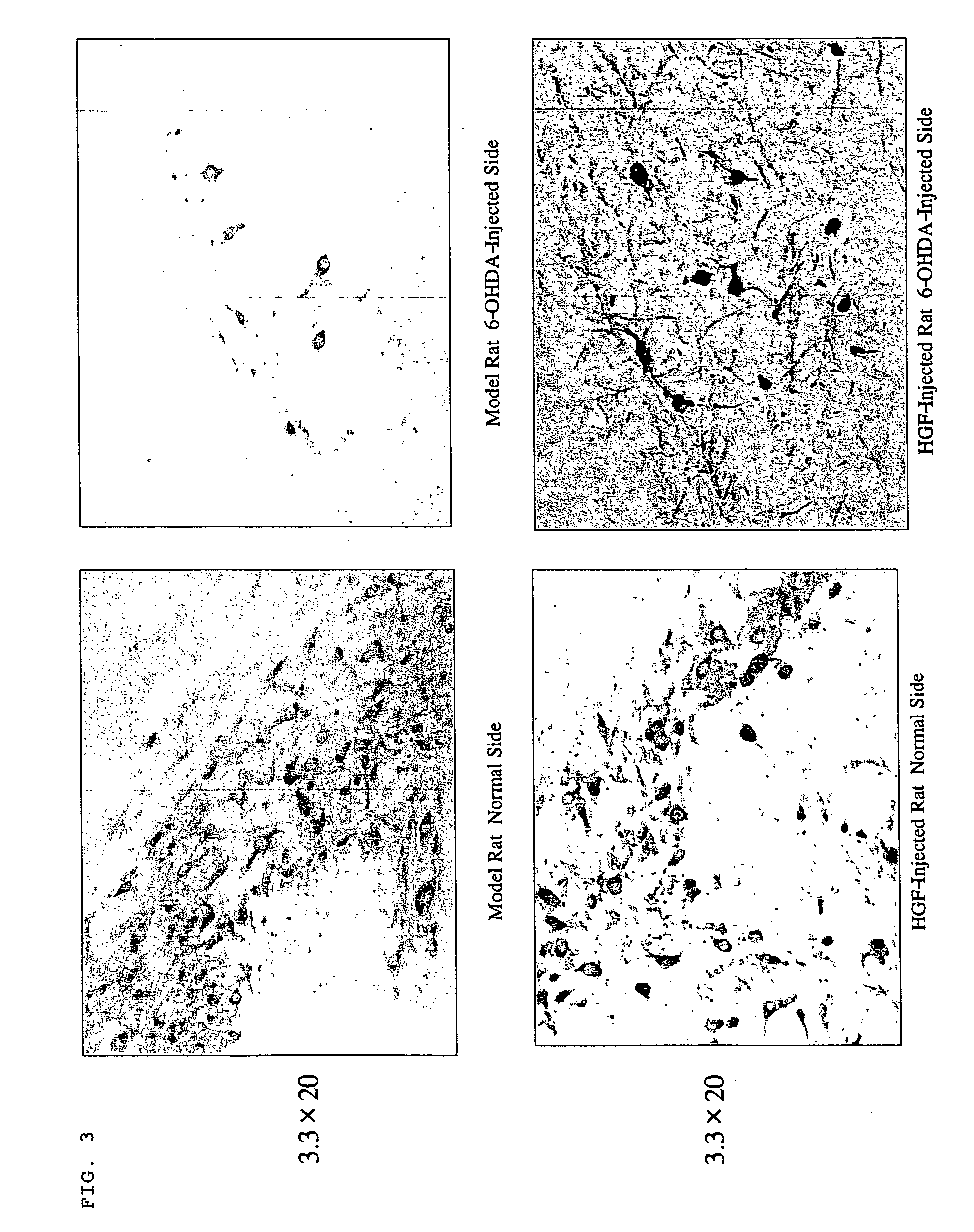
The present invention provides a therapeutic agent containing as an active ingredient an HGF gene used for therapy of neurodegenerative diseases such as Parkinson's disease, Alzheimer's disease, spinal cord injury, diabetic peripheral neuritis, and ischemic cerebrovascular disorders (cerebral infarction, cerebral haemorrhage, etc.) More specifically, the present invention provides a therapeutic agent for neurodegenerative diseases, containing a hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) gene as an active ingredient.
Owner:ANGES MG INC
Use of polypeptides micro-molecule in preparing medicine for preventing and treating ischemic cerebrovascular disease
ActiveCN101361961AImprove protectionHigh transparencyTripeptide ingredientsCardiovascular disorderDiseaseBrain protection
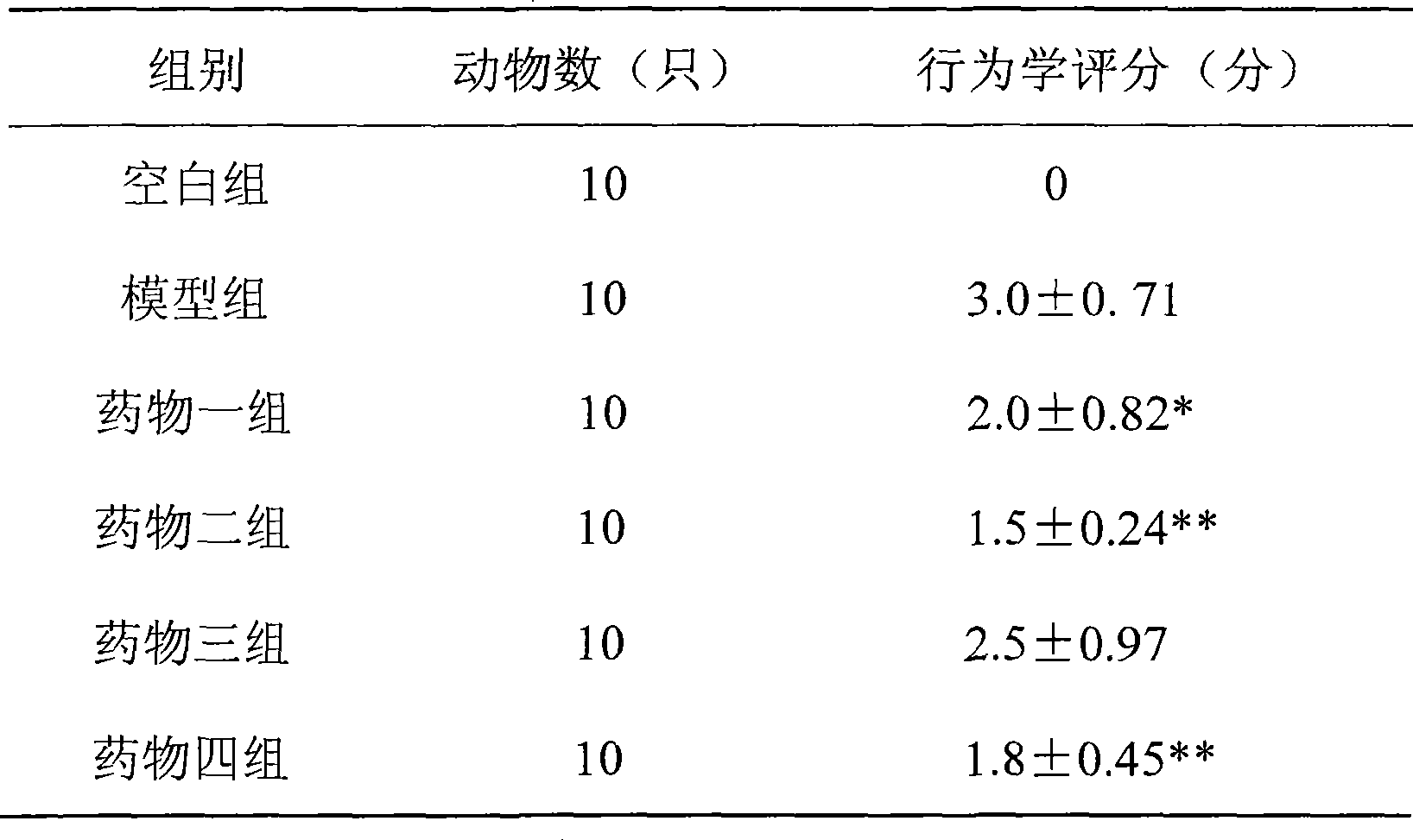
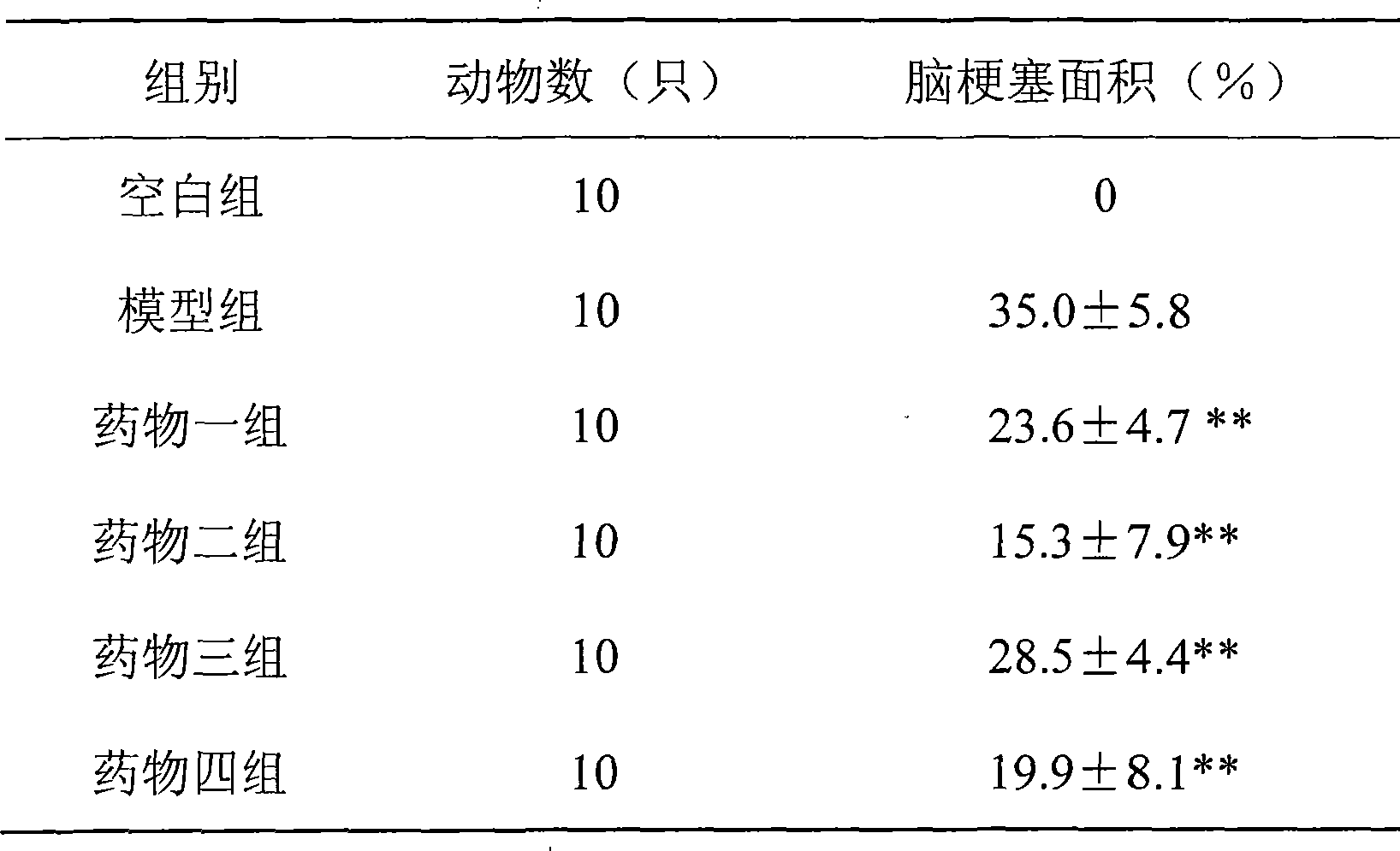
The invention relates to the technical field of biological medicines, which is an application of a small polypeptide molecule in preparing a drug for preventing ischemic cerebrovascular disease. The research of the invention finds out that polypeptide bioactive molecules and polypeptide spliceosomes extracted from the secretion of amoeba histolytica have the pharmacological action of preventing ischemic cerebrovascular disease. The pentapeptide and tripeptide are proved to be capable of remarkably reducing the brain damage to the mouse caused by ischemia-reperfusion and remarkably improving the neuro behavioral of the mouse after ischemia by the results of pharmacological experiment on mouse models with focal cerebral ischemia. Compared with the kindred protein drugs, the small polypeptide molecule has strong brain protection effects; in addition, molecular weight is small, thereby being easy to permeate blood-brain barrier and having remarkable advantage of brain permeability. Therefore, the small polypeptide molecule provided has good application prospect in preparing the drug for preventing the ischemic cerebrovascular disease.
Owner:GUILIN EIGHT PLUS ONE PHARMA CO LTD
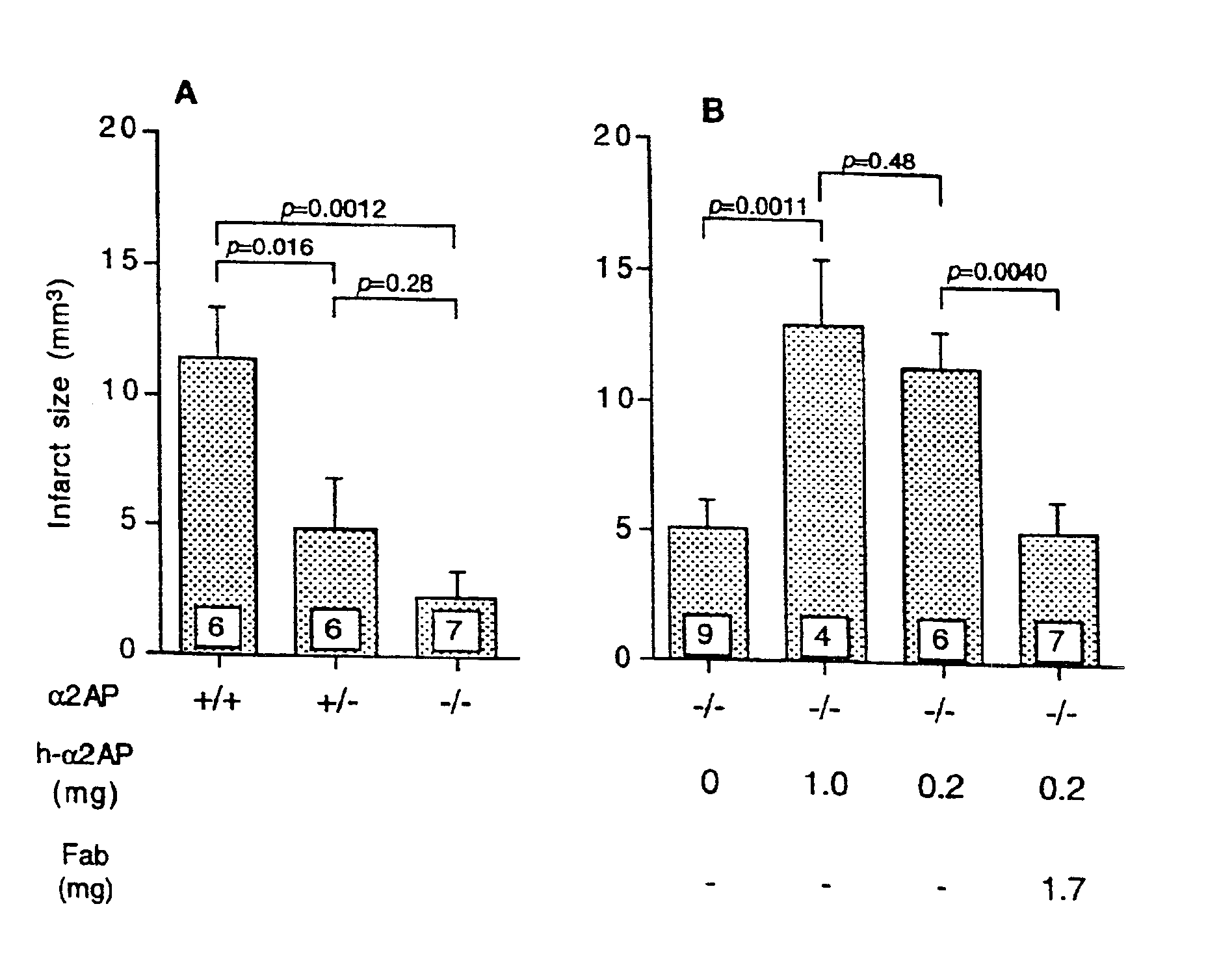
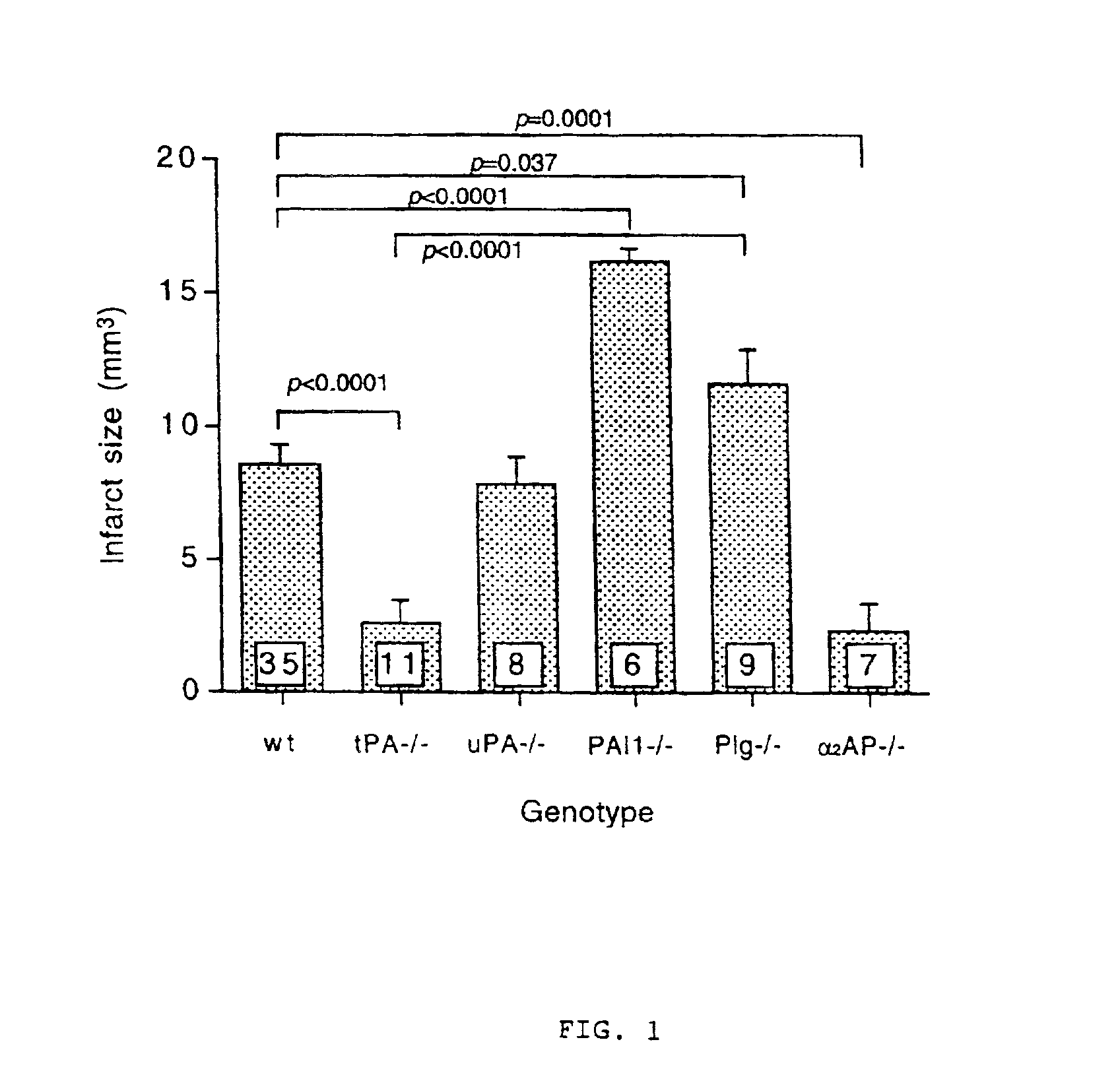
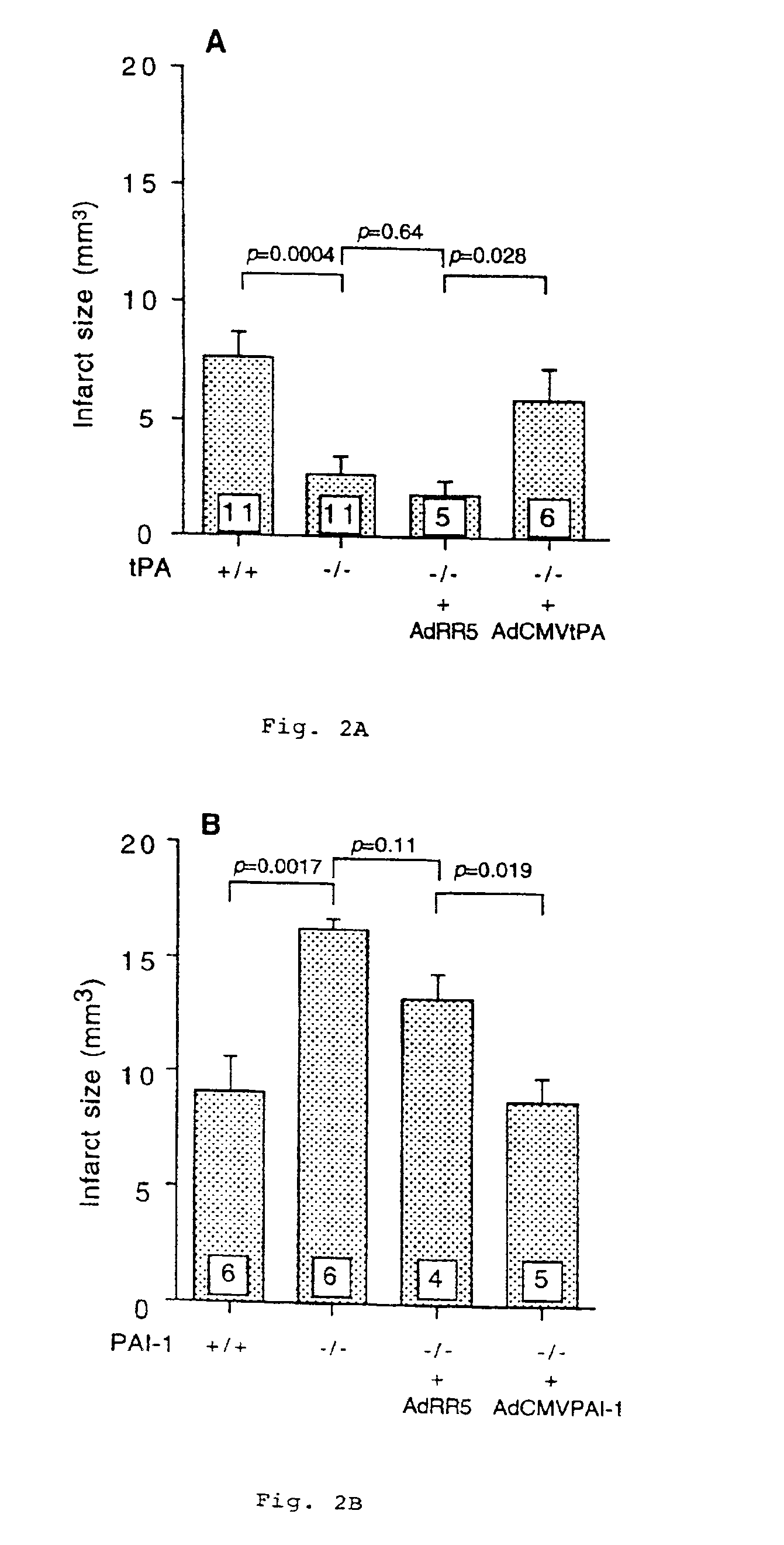
Use of compounds that reduce alpha2-antiplasmin in vivo for the preparation of a composition for the treatment of ischemic stroke
InactiveUS6946438B1Reduced activityReduce concentrationNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsAlpha 2-antiplasminIschemic cerebral infarction
The present invention relates to a new means for the treatment of focal ischemic cerebral infarction (ischemic stroke). It has been found that reduction of α2-antiplasmin leads to a significantly smaller focal cerebral infarct size. The invention therefore provides the use of compounds that reduce α2-antiplasmin concentration or activity in vivo, for the preparation of a therapeutical composition for the treatment of focal cerebral ischemic infarction (ischemic stroke).
Owner:COLLEN DESIRE JOSE +1
Functional platelet bionic intelligent carrier and application thereof in anti-ischemic cerebral apoplexy
ActiveCN109364263AGood biocompatibilityPromote degradationOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsSide effectBiocompatibility Testing
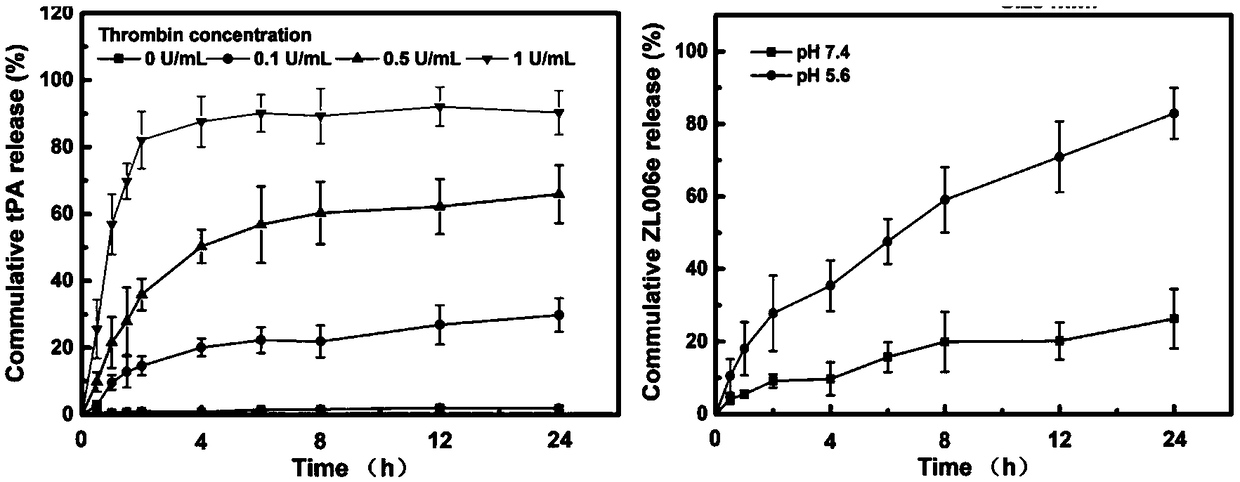
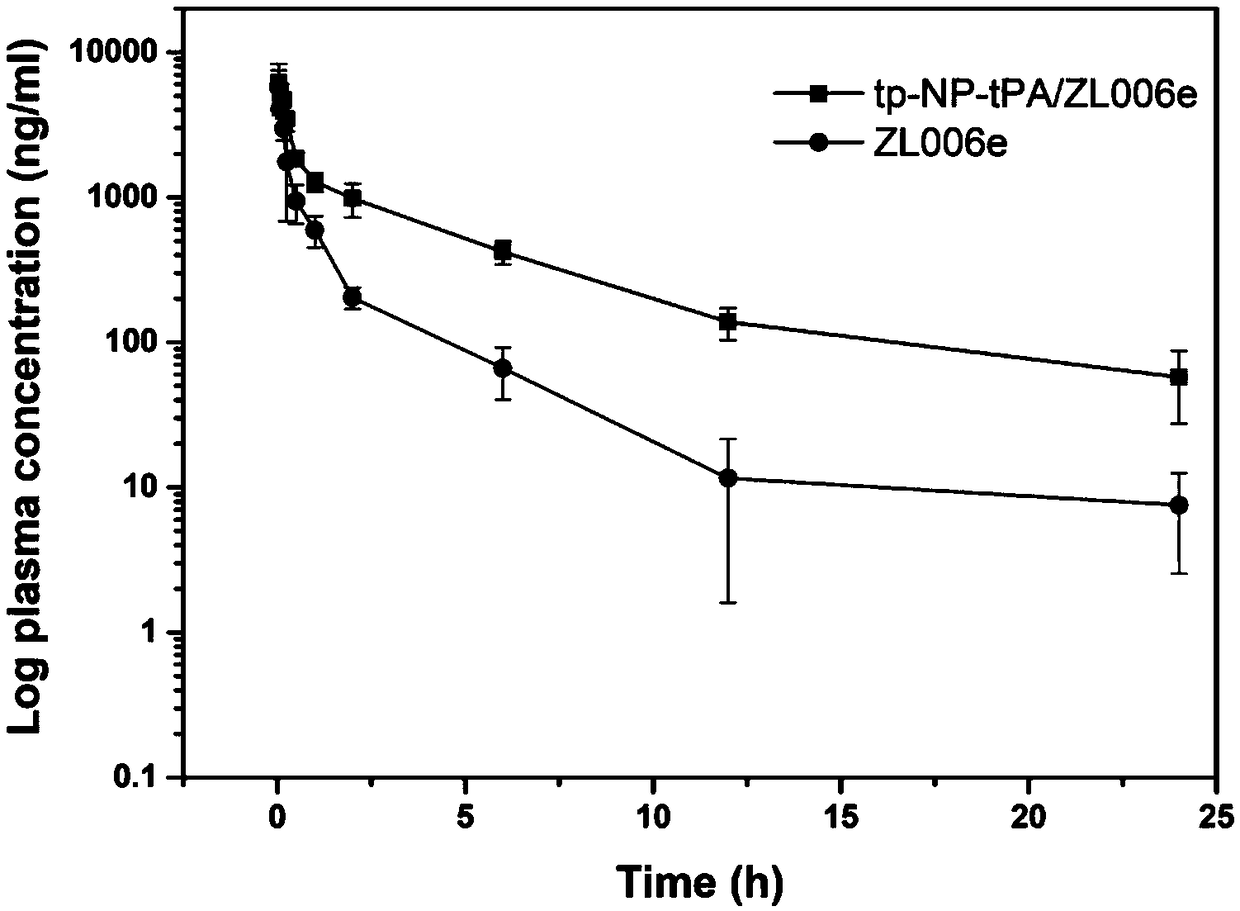
The invention discloses a functional platelet bionic intelligent carrier and application thereof in anti-ischemic cerebral apoplexy. The bionic carrier is composed of polymer nanoparticles of a platelet membrane coated neuroprotectant ZL006e, a Tat cell-penetrating peptide as well as substrate peptide fragments and fibrinolytic protein conjugates capable of being cut by thrombin. The carrier system has the characteristics of excellent biocompatibility, capacity of effectively prolonging in-vivo cycle time and the like, and is capable of targeting micro-thrombus in lesions of ischemic cerebralapoplexy and releasing thrombolytic drugs. Meanwhile, the exposed Tat cell-penetrating peptide mediated neuroprotectant is capable of increasing blood-brain barrier permeability, the pH serves as an intelligent drug release switch, and the pH-mediated degradation at the lesions is responded, so that the drug is quickly released at lesions of cerebral ischemia, the curative effects are improved tothe greatest degree, and toxic and side effects are reduced.
Owner:NANJING MEDICAL UNIV
Method of reducing injury to mammalian cells
InactiveUS7595297B2Prevent negative consequenceReduce signalingNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsNR1 NMDA receptorN methyl D aspartate receptors
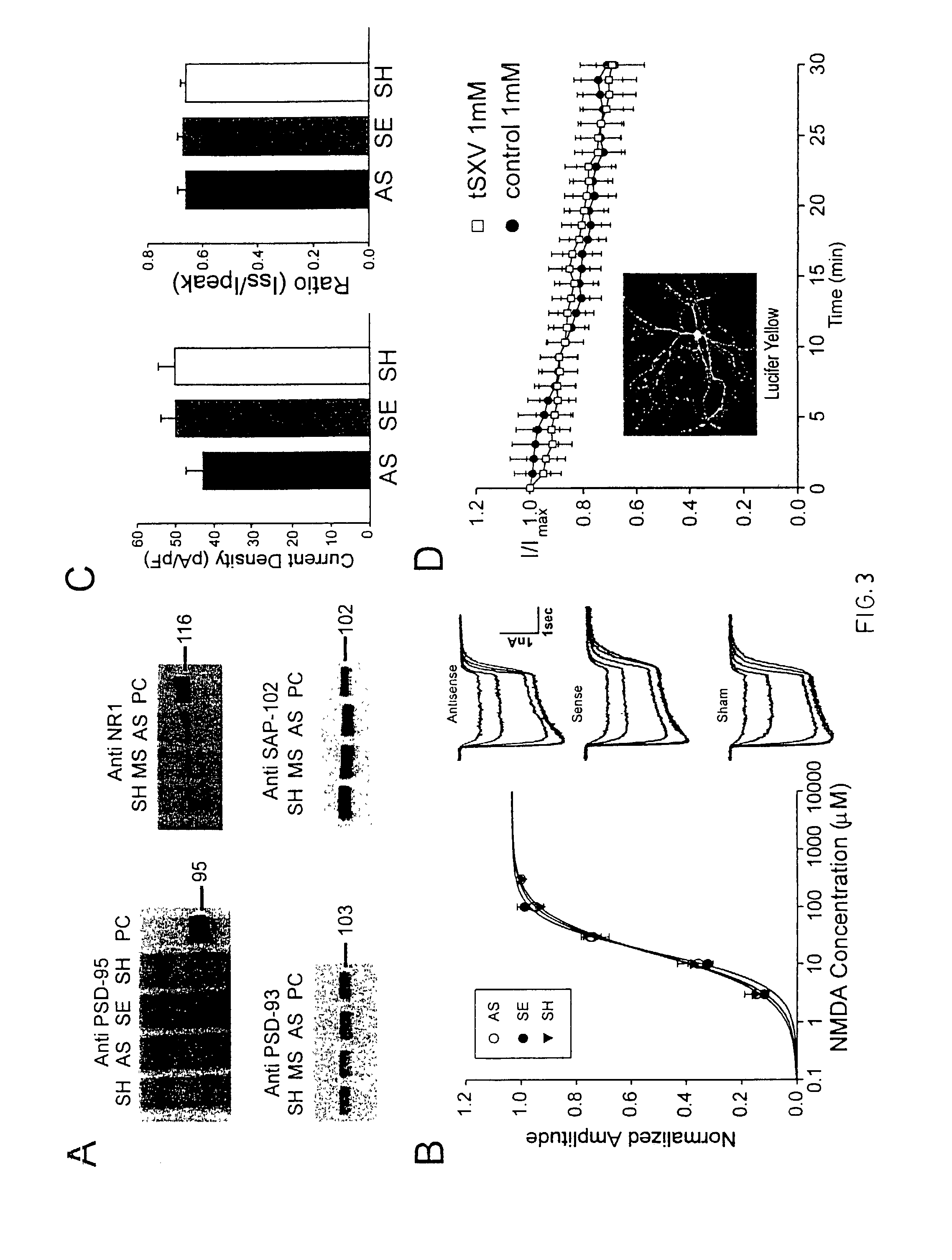
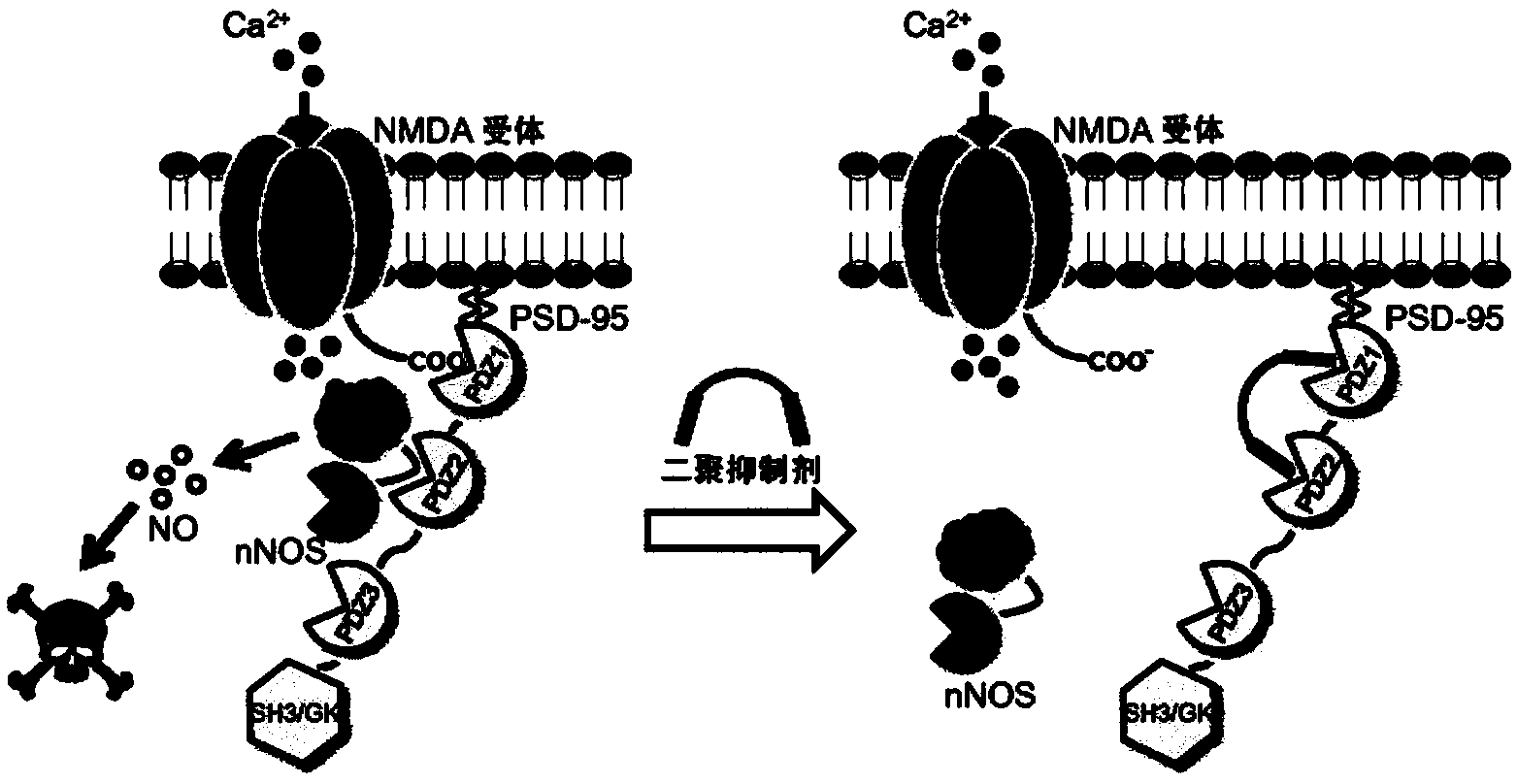
A method of inhibiting the binding between N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors and neuronal proteins in a neuron the method comprising administering to the neuron an effective inhibiting amount of a peptide replacement agent for the NMDA receptor or neuronal protein interaction domain that effect said inhibition of the NMDA receptor neuronal protein. The method is of value in reducing the damaging effect of injury to mammalian cells. Postsynaptic density-95 protein (PSD-95) couples neuronal N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors (NMDARs) to pathways mediating excitotoxicity and ischemic brain damage. This coupling was disrupted by transducing neurons with peptides that bind to modular domains on either side of the PSD-95 / NMDAR interaction complex. This treatment attenuated downstream NMDAR signaling without blocking NMDAR activity, protected cultured cortical neurons from excitotoxic insults and dramatically reduced cerebral infarction volume in rats subjected to transient focal cerebral ischemia. The treatment was effective when applied either before, or one hour after, the onset of excitotoxicity in vitro and cerebral ischemia in vivo. This approach prevents negative consequences associated with blocking NMDAR activity and constitutes practical therapy for stroke.
Owner:NONO INC
HGG (Human Gammaglobulin) polypeptide in combination with tissue specificity of cerebral arterial thrombosis and application thereof
ActiveCN104592352ASmall molecular weightHigh activityPeptidesMacromolecular non-active ingredientsTissue targetingNeuroprotective Drugs
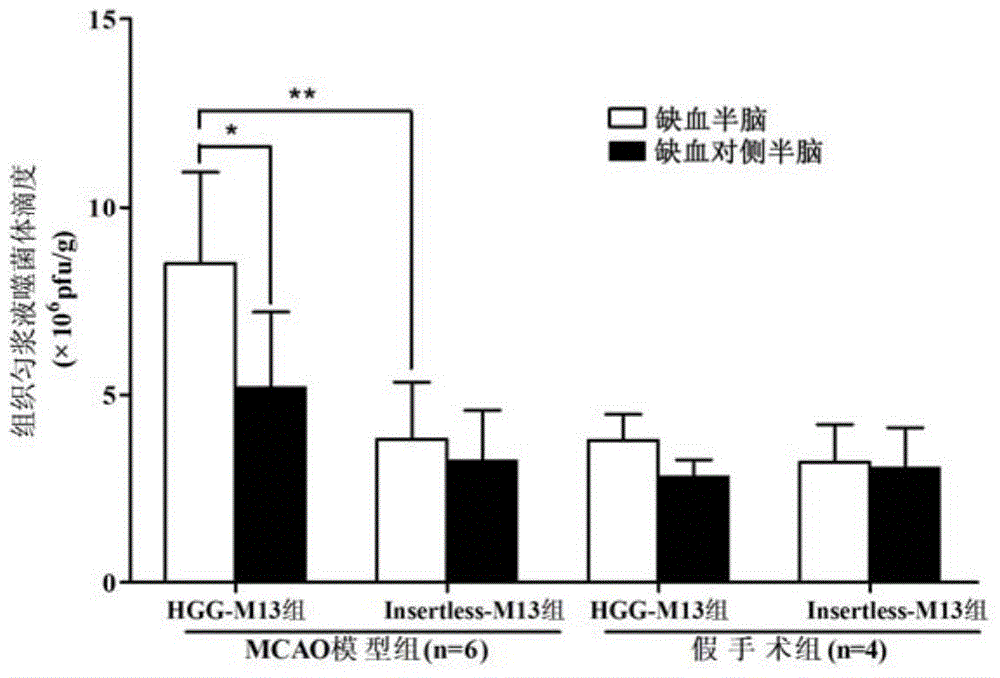
The invention discloses HGG (Human Gammaglobulin) polypeptide in combination with the tissue specificity of cerebral arterial thrombosis. The invention relates to a method for obtaining the polypeptide. The method comprises the following steps: carrying out in-vivo selection of a mouse MCAO (Middle Cerebral Artery Occlusion) cerebral arterial thrombosis model by adopting an in-vivo phage display peptide library screening technology so as to obtain phage clones in combination with cerebral arterial thrombosis tissue; and randomly selecting the plurality of phage clones to sequence, and authenticating the in-vivo combination specificity of HGG peptide and coded phage clones HGG-M13 thereof. The invention further relates to application of the polypeptide in preparation of a high-sensitivity imaging molecular probe and a targeting delivery neuroprotective drug for cerebral stroke. The polypeptide can be synthesized through an artificial method; the polypeptide is low in molecular weight, high in activity and penetrating power, good in specificity and low in toxicity, and has good tissue targeting of cerebral arterial thrombosis in vivo; and therefore, the polypeptide is applicable to serving as a carrier of the high-sensitivity imaging molecular probe and the targeting delivery neuroprotective drug.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
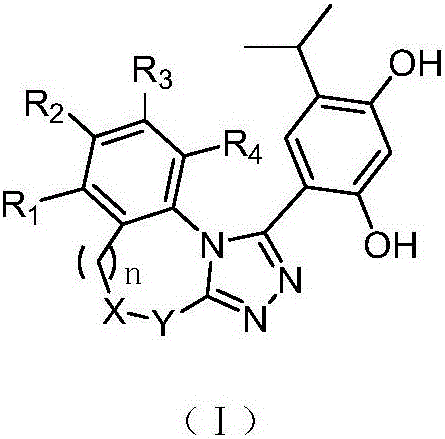
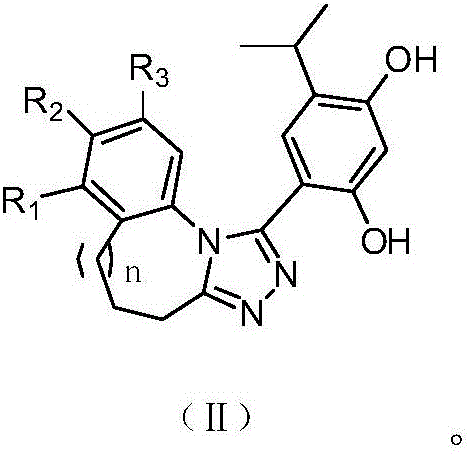
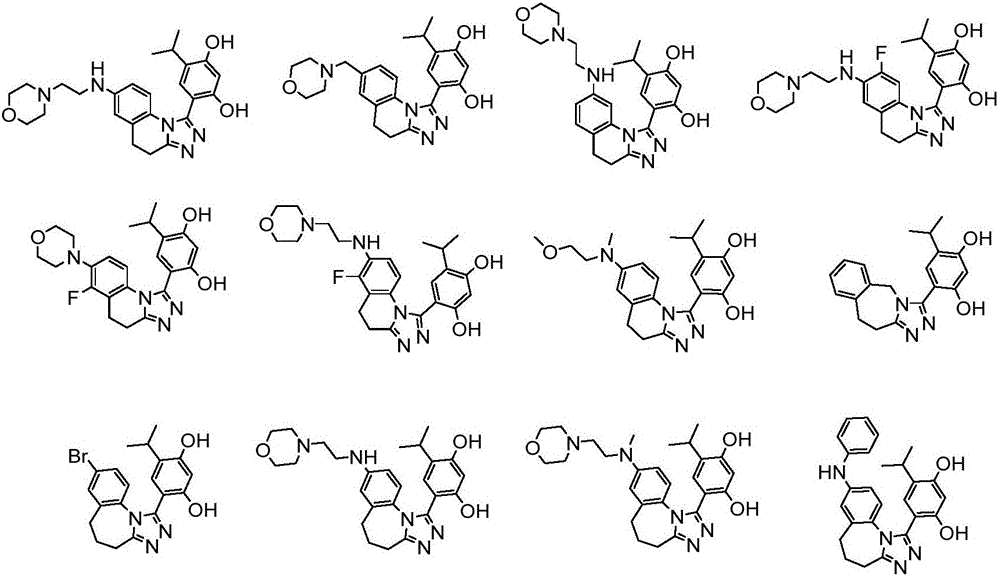
Triazole derivative having HSP90 (Heat Shock Protein) inhibiting activity, as well as preparation method and application of triazole derivative
The invention discloses a triazole derivative having an HSP90 (Heat Shock Protein) inhibiting activity, as well as a preparation method and an application of the triazole derivative. Specifically, the invention relates to the triazole derivative having a structure as shown in a formula (I), a stereisomer of the triazole derivative and a pharmaceutically acceptable salt, wherein the definition of each substituent group in the formula (I) and the definition in a description are the same. The compound with a novel structure has the HSP90 inhibiting activity, can be used to cure cancers, neurodegenerative disorders, inflammation diseases, autoimmune diseases, ischemic brain injuries and the like, and has a broad application prospect.
Owner:SHANGHAI HANSOH BIOMEDICAL +1
Fasudic hydrochloride oral formulation
ActiveCN1813762AEasy to useImprove bioavailabilityOrganic active ingredientsPill deliveryDiseaseOral drug preparation
The present invention relates to a fashudil hydrochloride oral preparation for curing ischemic cerebrovascular disease due to cerebrovascular spasm after subarachnoid hemorrhage. It can be made into tablet, capsule and granule preparation.
Owner:TIANJIN CHASE SUN PHARM CO LTD
Medicinal composition containing tanshinone and its preparation process and usage
InactiveCN1839819AReduce solubilityImprove solubilityOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderReperfusion injuryDiabetic complication
Owner:海口绿科南药研究开发有限公司
Gene Promoting Vascular Endothelial Cell Growth
ActiveUS20070281888A1Promoting transcriptionAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsVascular endotheliumAngina
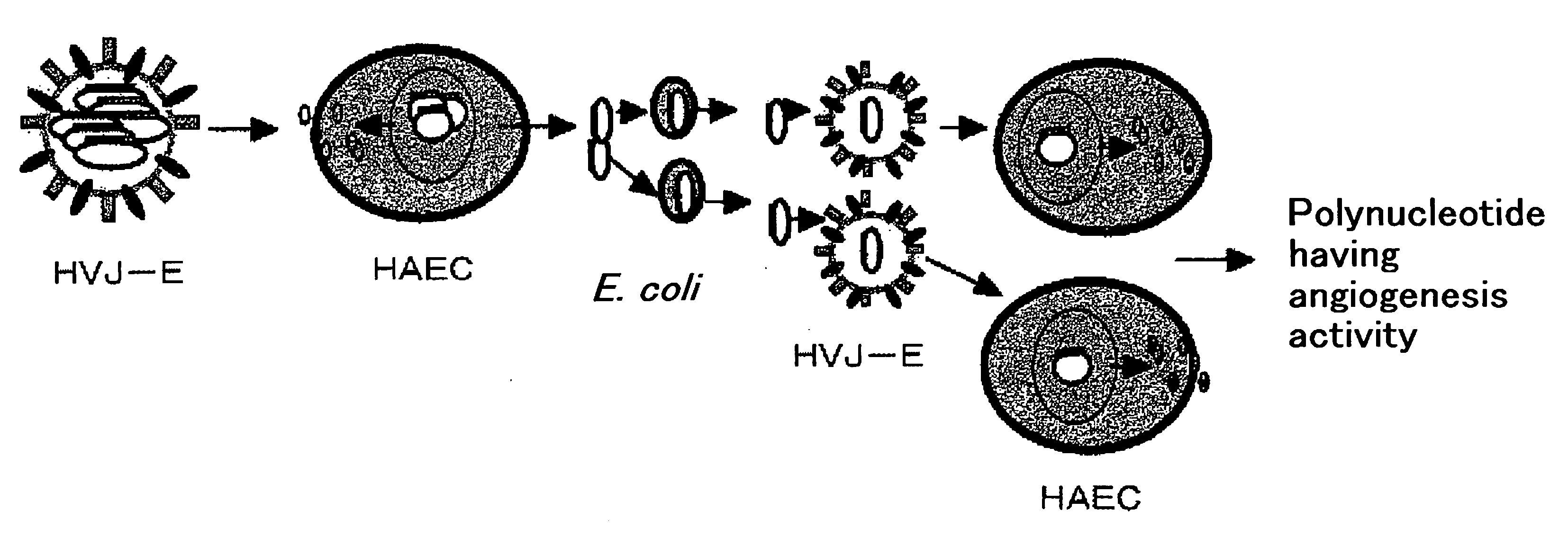
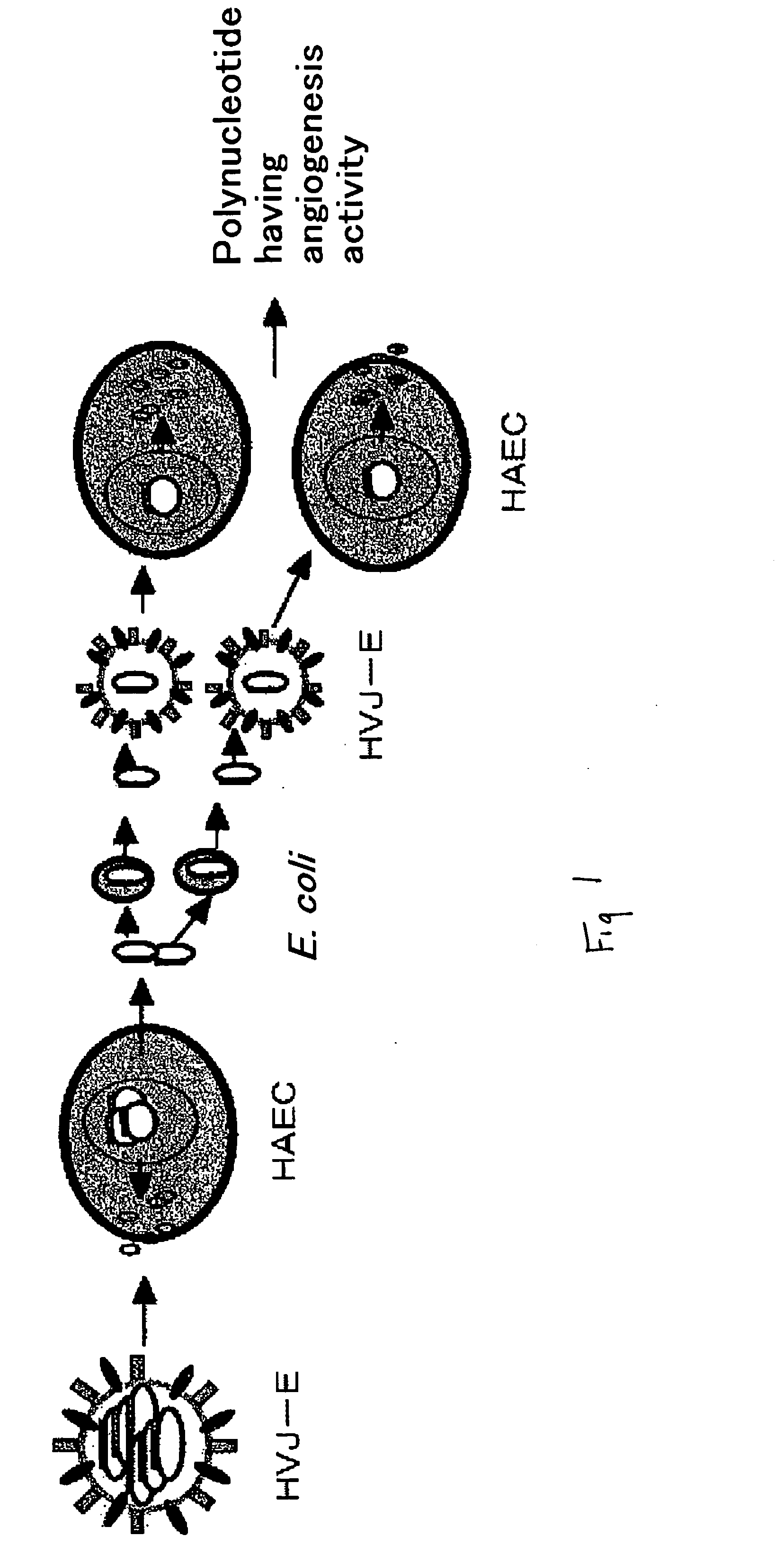
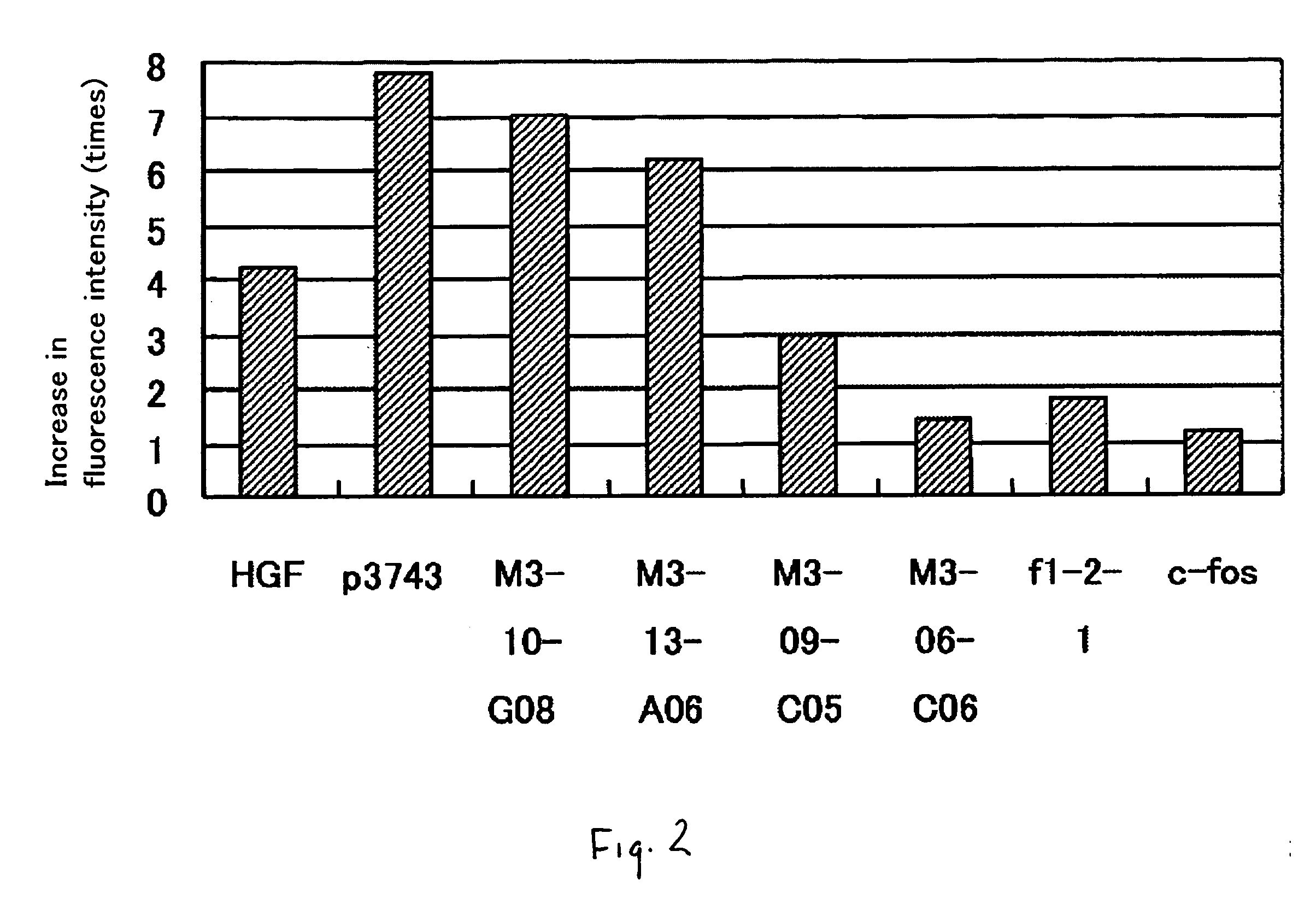
It is intended to provide a novel polypeptide having an activity of growing vascular endothelial cells, an activity of promoting transcription form c-fos promoter, an activity of promoting transciption from VEGF promoter and / or an angiogenic activity; a polynucleotide encoding this polypeptide; the above polypeptide and / or a pharmaceutical composition containing the polypeptide for treating a disease selected from the group consisting of obstructive arteriosclerosis, Buerger's disease, peripheral vascular disorder, angina, myocardial infraction, brain infarction, ischemic heart disease and ischemic brain disease; a method of treating these diseases; and an antibacterial composition. The above problems can be solved by isolating a novel peptide having the above-described activities and a nucleotide encoding this peptide.
Owner:FUNPEP CO LTD
Epimedium extract and preparation method, preparation and use thereof
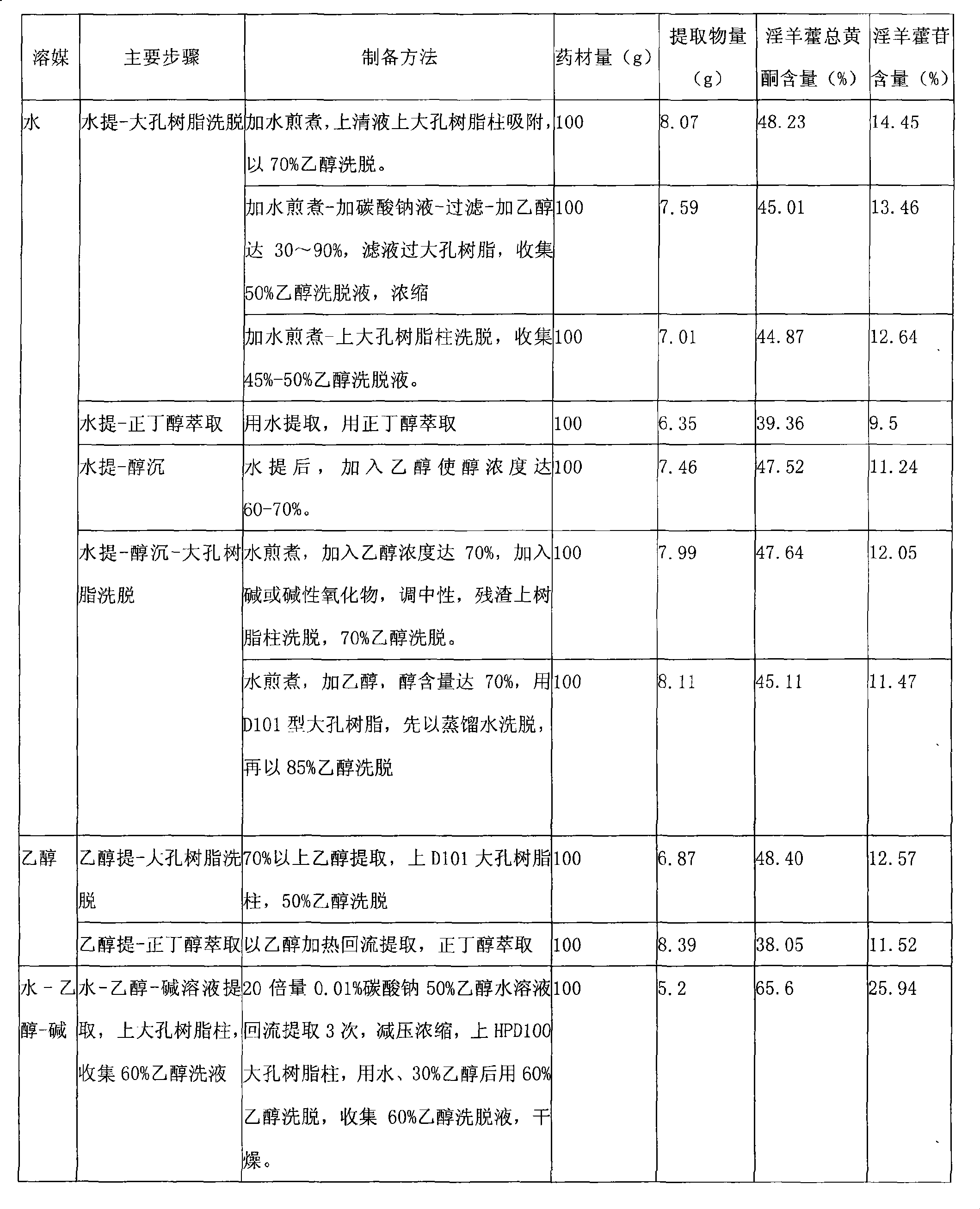
The invention provides a herba epimedii extract, in particular to a high-content herba epimedii total flavonoids extract, and the preparation method thereof mainly comprises the following steps: (1) alkali-ethanol-water is taken as a menstruum for refluxing extraction; (2) decompression and concentration are carried out; (3) pH value is adjusted; (4) macroporous resin column elution is carried out; and (5) an eluant is dried and the content of the obtained total flavonoids is over 65 percent and the content of icariin is over 20 percent. The extract can be prepared into various oral preparations according to the requirements in pharmacy, which can be hard capsules, soft capsules, conventional tablets, orally disintegrating tablets, buccal tablets, dispersible tablets, sustained-release preparations, controlled release preparations, granules, water-paste pills, dripping pills, honeyed pills, and the like. The extract and effective medicines containing the extract can be applied to preparing brain tissue protective agents, especially to preparing medicines that prevent and treat cerebral infarction, cerebral infarction sequela and other ischemic cerebrovascular diseases.
Owner:南京宇道科技开发有限公司
Cerebral arterial thrombosis targeted red cell membrane bionic intellectual drug carrier and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN106265594AGood encapsulation effectAvoid phagocytosisNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsRed blood cellBiocompatibility Testing
The invention discloses a cerebral arterial thrombosis targeted red cell membrane bionic intellectual drug carrier. The drug carrier is prepared from a nanometer vesica, a red cell membrane and cerebral ischemia homing peptide SHp, wherein the nanometer vesica serves as an inner core and is used for packing NR2B9C, the red cell membrane is arranged on the outer layer, the cerebral ischemia homing peptide SHp is modified on the surface of the cerebral ischemia, and the wrapping fusion between the nanometer vesica serving as the inner core and the red cell membrane on the outer layer is achieved through an ultrasonic fusion technique. The nanometer vesica is prepared from amphiphilic block copolymer (PHB-Dextran) serving as a carrier material, the amphiphilic block copolymer is prepared from hydrophobic borate which is grafted to a hydrophilic glucan framework, the nanometer vesica is used for wrapping a neuroprotective agent NR2B9C, and the amino acid sequence of the neuroprotective agent NR2B9C is KLSSIESDV. The carrier has the characteristics of having biocompatibility, prolonging circulation time in the body and initiatively targeting the focus position of the cerebral arterial thrombosis.
Owner:NANJING MEDICAL UNIV
Aporphine and oxoaporphine compounds and pharmaceutical use thereof
InactiveUS7057044B2Prevention and treatment of local ischemiaAvoid ischemic injuryBiocideOrganic chemistryMorphineApomorphine
The invention provides aporphine and oxoaporphine compounds that have endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS) maintaining or enhancing activities and may be used to manufacture a medicaments for preventing or treating ischemic diseases in human and mammal, and the ischemic diseases may include ischemic cerebral apoplexy, ischemic cerebral thrombosis, ischemic cerebral embolism, hypoxic ischemic encephlopathy, ischemic cardiac disease or ischemic enteropathy etc.
Owner:LOTUS PHARMA CO LTD
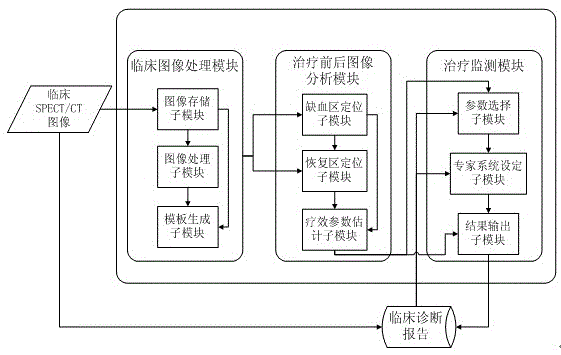
System for monitoring treatment of ischemic cerebrovascular disorder on the basis of image information
InactiveCN105678762AComparableEasy to upgradeImage enhancementImage analysisCerebrovascular disorderTherapeutic effect
The invention discloses a system for monitoring treatment of ischemic cerebrovascular disorder on the basis of image information. The system comprises: a clinical image processing module, a before-treatment and after-treatment image analysis module, and a treatment monitoring module. The clinical image processing module is used for performing importing, saving, format converting, grouping and image normalizing to clinic cerebral blood flow perfusion images, and generating cerebral blood flow perfusion templates; the before-treatment and after-treatment image analysis module is used for performing contrastive analysis to cerebral blood flow perfusion sequential images before clinical treatment and after clinical treatment, computing and obtaining quantitative parameters for therapeutic effect evaluation; the treatment monitoring module is used for selecting the quantitative parameters, establishing the relation between the quantitative parameters and traditional clinic assessment of recovery level, generating a specialist judging module of therapeutic effect evaluation, and monitoring the treatment process for ischemic cerebrovascular disorder on the basis of the specialist judging module.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Class of compounds for treating ischemic brain damage and purpose thereof
InactiveCN104628657AOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryPharmaceutical SubstancesMedicinal chemistry
The invention discloses a class of compounds and pharmaceutical compositions and novel purpose thereof in treating ischemic brain damage. The of above compounds have very significant effects on the treatment of ischemic brain damage.
Owner:韩冰
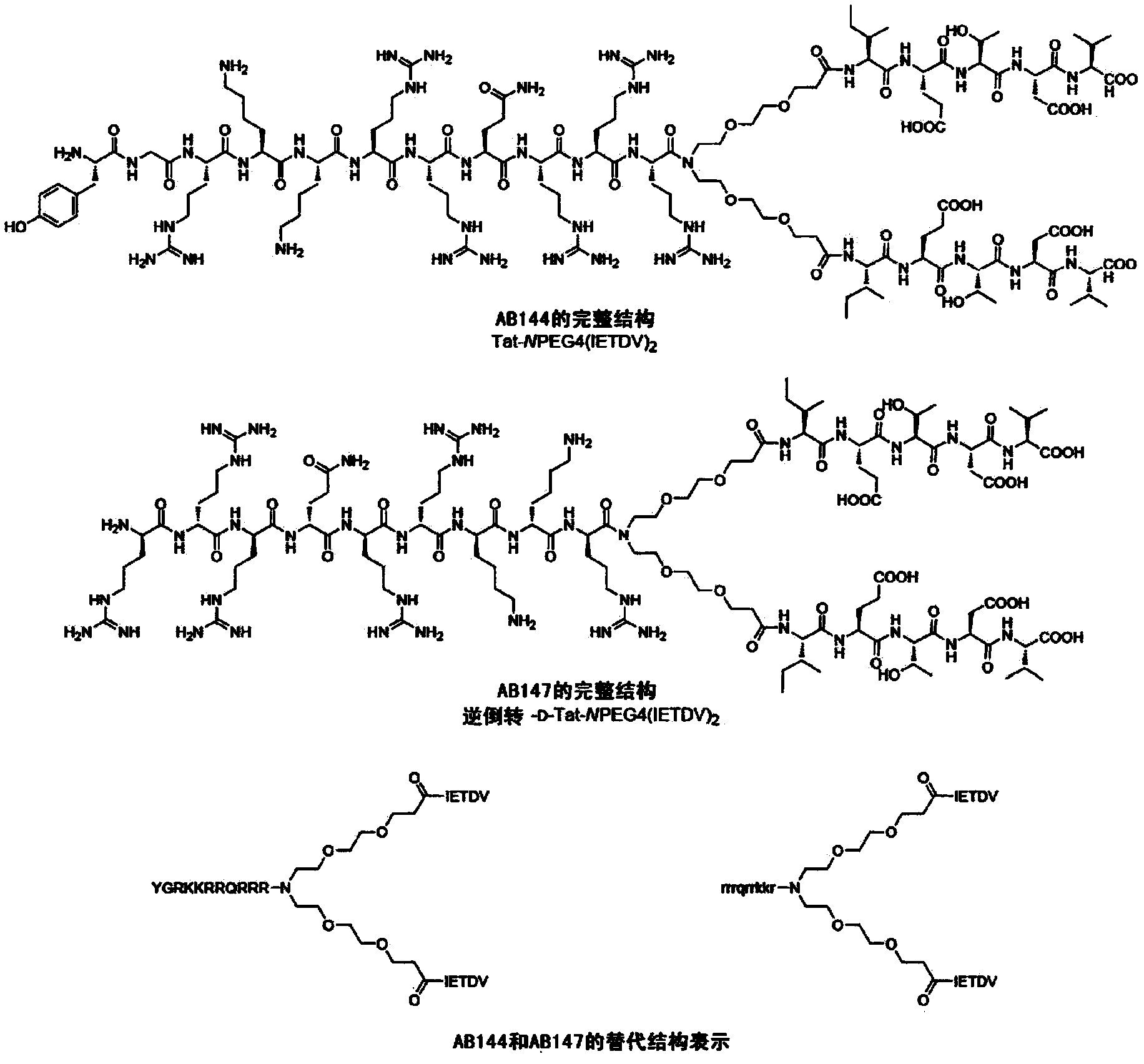
High-affinity, dimeric inhibitors of psd-95 as efficient neuroprotectants against ischemic brain damage and for treatment of pain
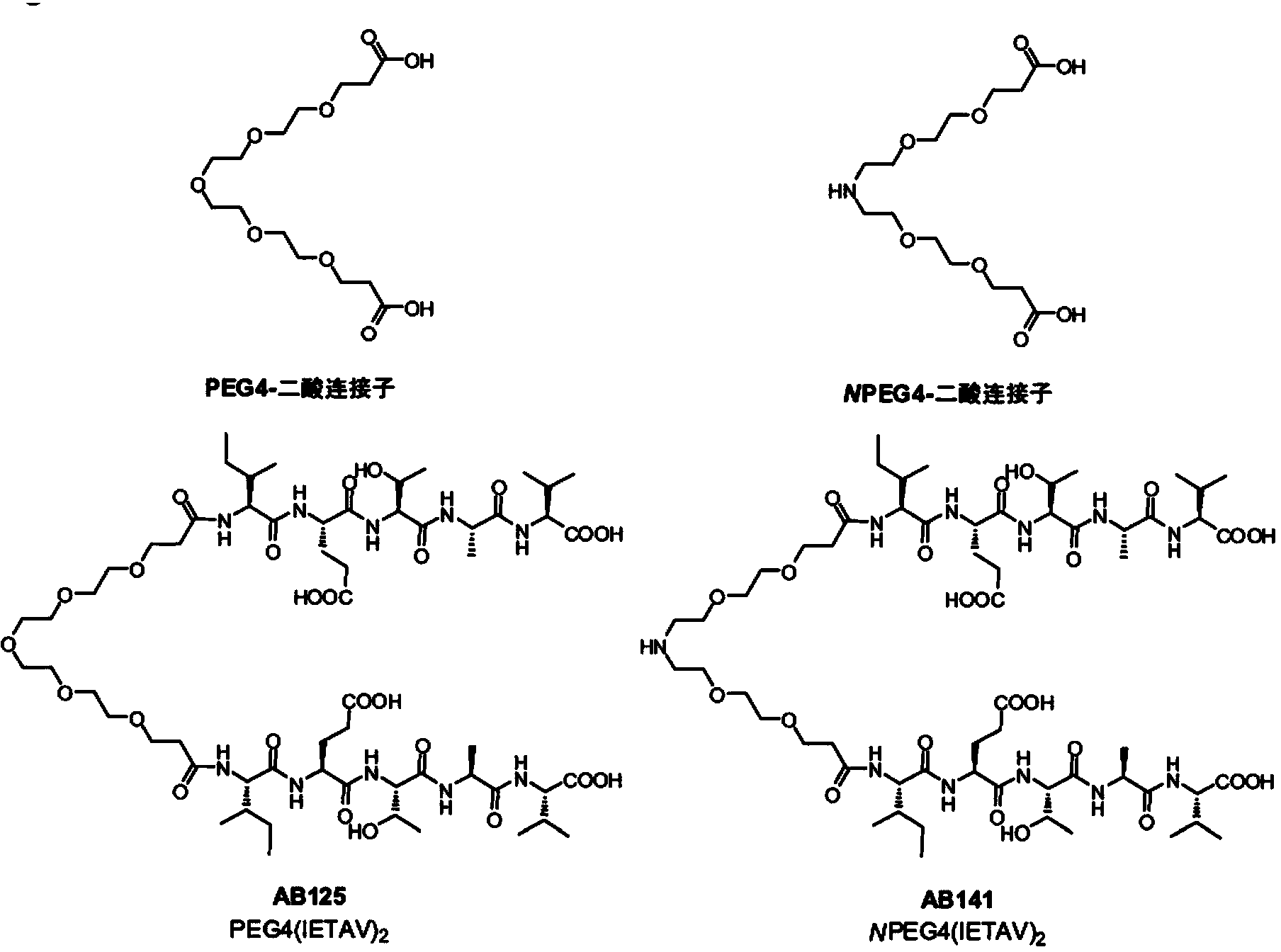
The invention provides novel potent inhibitors of the ternary protein complex of nNOS, PSD-95, and the NMDA receptor and pharmaceutical compositions comprising the inhibitors for prophylaxis and / or treatment of excitotoxic-related disease and chronic pain conditions in a subject. The inhibitors are dimeric PSD-95 inhibitors comprising a first peptide or peptide analogue linked to a second peptide or peptide analogue by a linker, wherein the first and the second peptide or peptide analogue comprise at least four amide-bonded residues having a sequence YTXV or YSXV, wherein a. Y is selected from among E, Q, and A, or an analogue thereof, and b. X is selected from among A, Q, D, N, N-Me-A, N-Me-Q, N-Me-D, and N-Me-N or an analogue thereof, and wherein a Cell Penetrating Peptide (CPP) is linked to the linker or to an amino acid side chain of the first and second peptide or peptide analogue. The linker can be a PEG or NPEG linker.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF COPENHAGEN
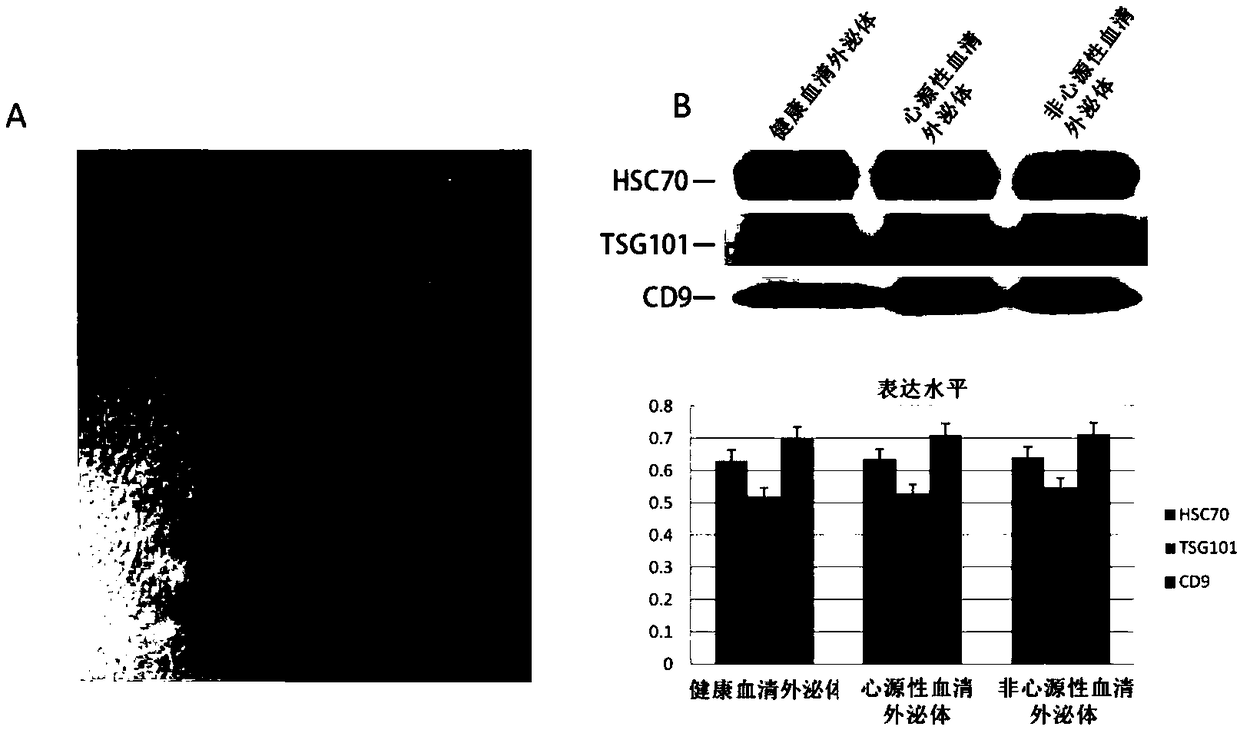
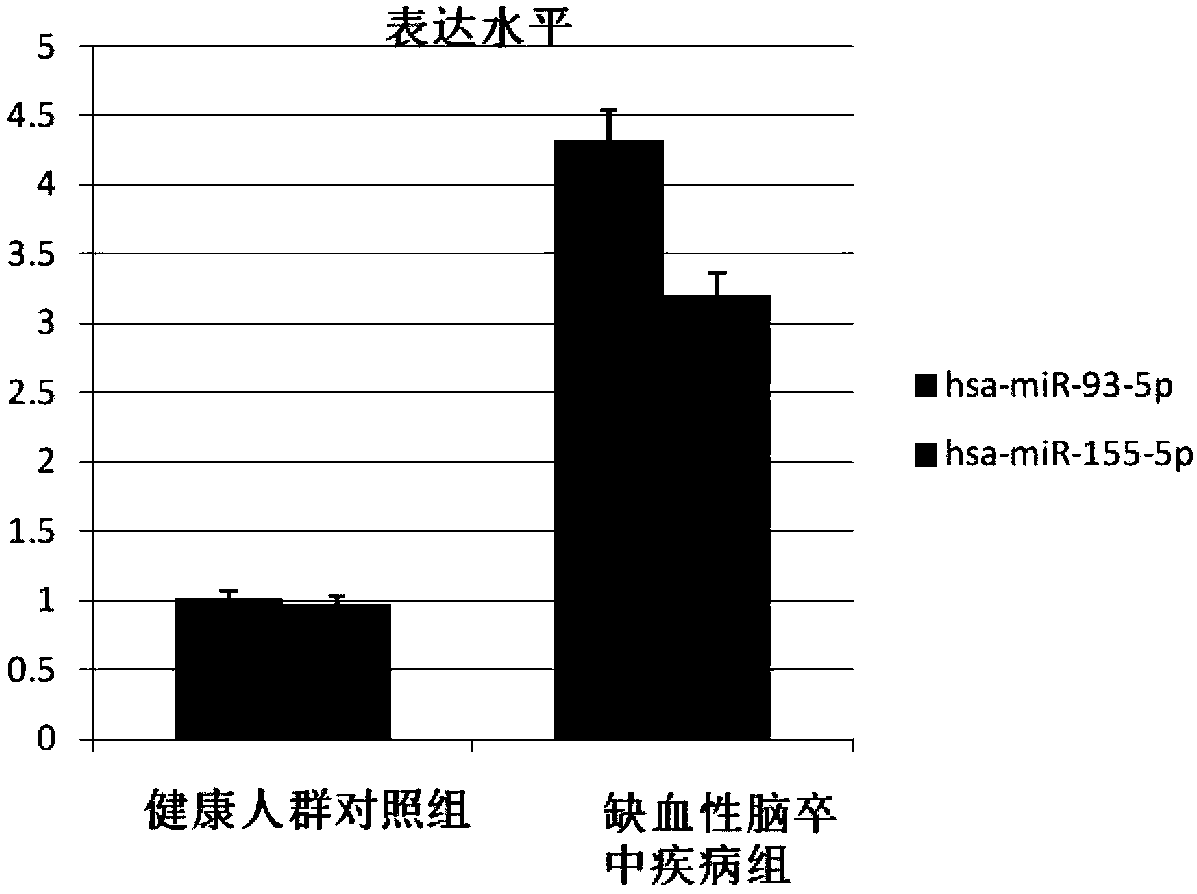
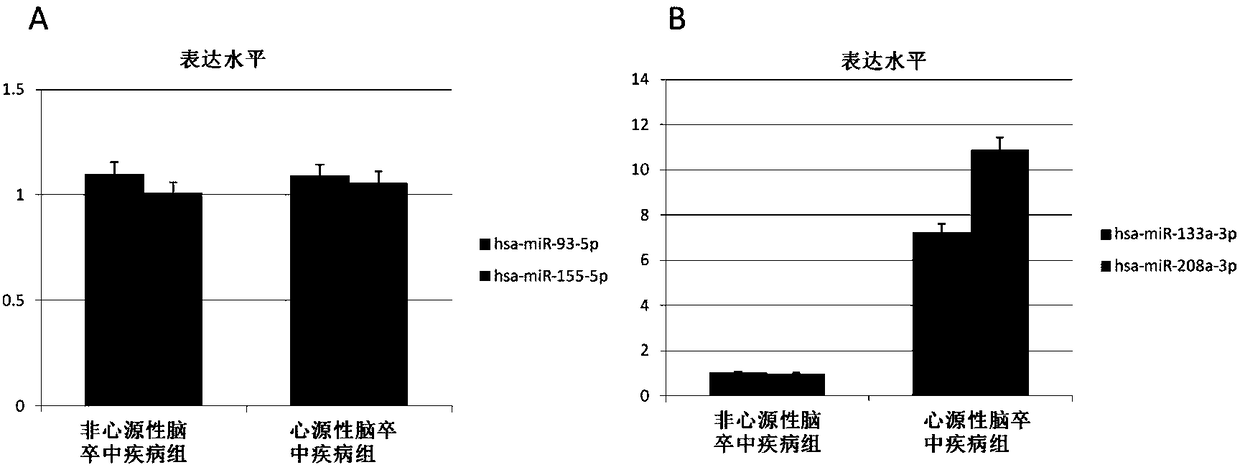
Use of microRNA in exosomes for diagnosis of cerebral arterial thrombosis
ActiveCN108070650AImprove the level ofAccurately reflectMicrobiological testing/measurementProtein markersIschemic injury
The invention discloses the use of an agent for detecting microRNA in exosomes in the preparation of a product for judging the presence and / or degree of cerebral ischemic injury, and relates to a method for early discrimination of a subject suffering from cardiogenic ischemic stroke and non-cardiogenic ischemic stroke. The method uses the exosomes in high-molecular polymer precipitate serum and areal-time fluorescence quantitative PCR technology, and experimental results show that the specificity and sensitivity of miR-155-5p and miR-93-5p are significantly higher than existing protein markers. Meanwhile, miR-133a-3p and miR-208a-3p expression of the exosomes of patients with cardiogenic ischemic stroke is significantly higher compared with patients with non-cardiogenic ischemic stroke under the condition of no significant changes in the serum miR-133a-3p and miR-208a-3p at the early stage so that the agent can be used as a marker to distinguish the cardiogenic ischemic stroke and thenon-cardiogenic ischemic stroke.
Owner:CHI BIOTECH CO LTD
Fucoidans as Ligands for the Diagnosis of Degenerative Pathologies
InactiveUS20120183475A1In-vivo radioactive preparationsSugar derivativesAbnormal tissue growthReperfusion injury
The present invention relates to the diagnosis of clinical conditions characterized by undesirable and / or abnormal selectin expression. In particular, the invention provides for the use of fucoidans for the detection of selectins using imaging techniques including ultrasonography, scintigraphy and MRI. Selectin-targeted imaging agents are provided that comprise at least one fucoidan moiety associated with at least one detectable moiety. Methods and kits are described for using these imaging agents in the diagnosis of clinical conditions such as thrombosis, myocardial ischemia / reperfusion injury, stroke and ischemic brain trauma, neurodegenerative disorders, tumor metastasis and tumor growth, and rheumatoid arthritis.
Owner:INST NAT DE LA SANTE & DE LA RECHERCHE MEDICALE (INSERM)
Treatment of ischemic brain injuries with brain targeted antioxidant compounds
A method of reducing oxidative stress in the brain of an organism having a blood brain barrier and suffering an ischemic brain injury, the method comprising the step of administering a compound to the organism, the compound having (a) a combination of molecular weight and membrane miscibility properties for permitting the compound to cross the blood brain barrier of the organism; (b) a readily oxidizable chemical group for exerting antioxidation properties; and (c) a chemical make-up for permitting the compound or its intracellular derivative to accumulate within the cytoplasm of cells.
Owner:YISSUM RES DEV CO OF THE HEBREWUNIVERSITY OF JERUSALEM LTD +2
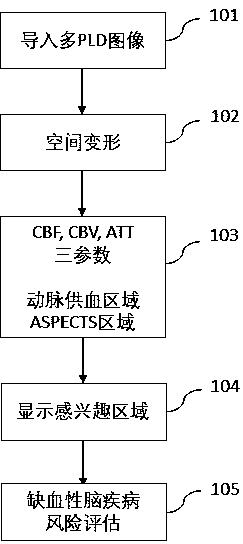
Method for auxiliary assessment of ischemic disease risk based on magnetic resonance cerebral perfusion image
InactiveCN110490871AEffective assessment methodImage enhancementImage analysisHead movementsDisease cause
The invention provides an automatic image processing and displaying method based on a magnetic resonance cerebral perfusion image, which is used for assisting in evaluating cerebral ischemia disease risks and is characterized by comprising spatial deformation, multi-parameterization, brain map coverage and a method for evaluating ischemic cerebral disease risks. The image space deformation methodcomprises the following steps: head movement correction, which is used for adjusting a space difference generated by head movement in a cerebral perfusion imaging process; and standard brain registration: taking the standard brain as a reference to realize standardization of the imported cerebral perfusion image. The multi-parameterization is used for converting the original nuclear magnetic datainto cerebral image perfusion parameters such as cerebral blood flow, cerebral blood volume and artery arrival time, wherein the coverage brain map is used for enabling the parameterized cerebral perfusion image data to cover standard brain maps of different templates to form different regions of interest, and calculating average parameter values of the different regions of interest.The standard cerebral map comprises a cerebral artery blood supply area and an early CT scoring area of an Albetan stroke project. The ischemic brain disease risk assessment method is used for comparing the averageparameter value of the region of interest with a reference range, displaying the differentiation degree and automatically displaying the region of interest beyond the reference range. According to the invention, multi-parameter automatic partitioning and quantitative processing from nuclear magnetic cerebral perfusion original number to ischemic cerebral disease early-stage risk assessment are realized, and an effective assessment method is provided for early-stage screening, early-stage diagnosis and early-stage treatment of cerebral ischemic diseases.
Owner:安影科技(北京)有限公司
Achyranthes bidentata polypeptide, preparing process and uses
InactiveCN101270147APromote growthInhibit apoptosisNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsDiseaseMedicinal herbs
The present invention discloses achyranthes bidentata polypeptide, a production method and applications, and the achyranthes bidentata polypeptide is produced with the steps including polypeptide extraction, polypeptide separation, etc. The achyranthes bidentata polypeptide is used to the preparation of drugs and health products for treating peripheral nerve injuries, cerebrovascular accidents, ischemic brain injuries, cerebral traumas, optic nerve injuries, spinal cord injuries and central nervous system injuries, antiaging and preventing neurodegenerative diseases. Experiments prove that the extracted achyranthes bidentata polypeptide (protein) of the present invention has the effects of promoting the growth of nerves, preventing the fading of nerve cells and promoting the regeneration of injured nerves, the source of medicinal materials is single, the preparation method is advanced, the technique is reasonable, the ingredients of preparations are definite, safety is high, and pharmacological action is obvious.
Owner:NANTONG UNIVERSITY
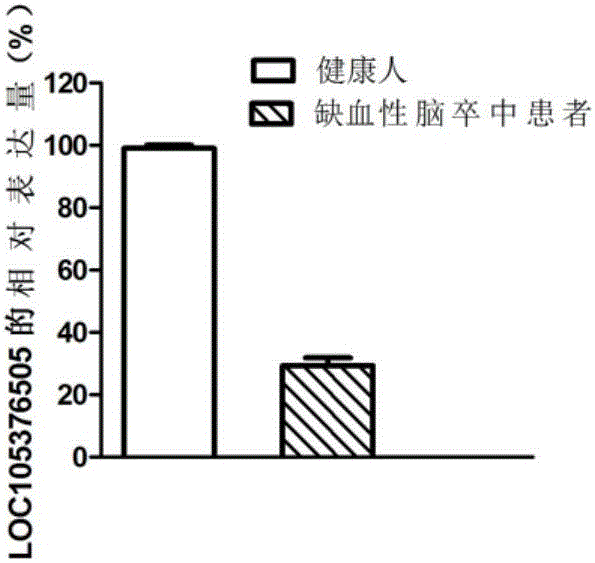
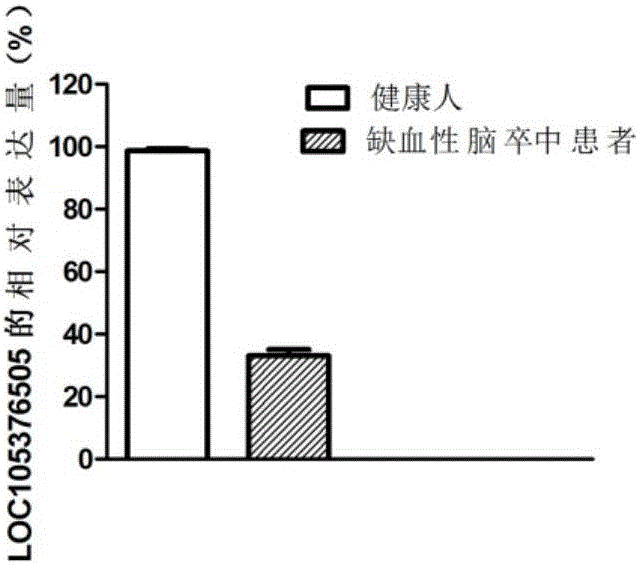
LncRNA for diagnosing cerebral arterial thrombosis
ActiveCN106337089AImprove survival rateMicrobiological testing/measurementCerebral arterial thrombosisPathogenesis
The invention discloses lncRNA for diagnosing cerebral arterial thrombosis. The lncRNA is LOC105376505. According to the lncRNA for diagnosing cerebral arterial thrombosis, the LOC105376505 gene is related to occurrence and development of cerebral arterial thrombosis, expression in cerebral arterial thrombosis patients is reduced, and researching of pathogenesis of cerebral arterial thrombosis is further enriched.
Owner:THE FIRST AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF SHANTOU UNIV MEDICAL COLLEGE
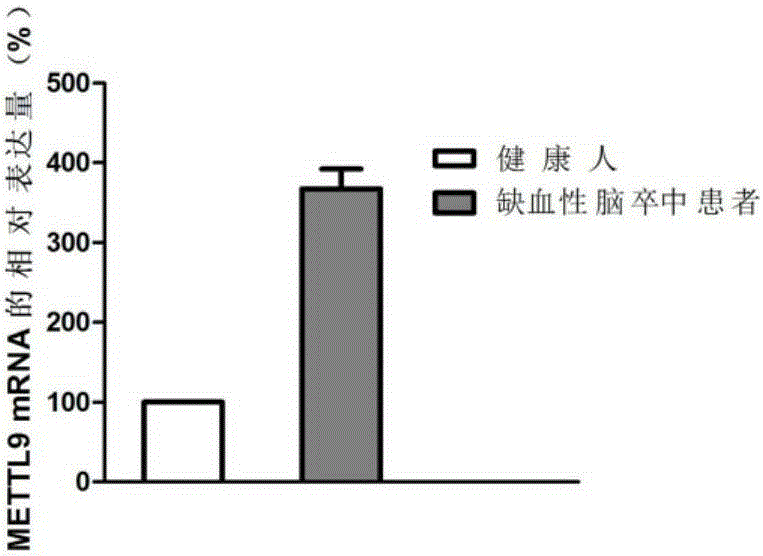
Gene marker related to ischemic stroke
ActiveCN105296659AAchieve early diagnosisReduce mortalityMicrobiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisMETTL9 geneMedicine
The invention discloses a gene marker related to ischemic stroke. The expression of an METTL9 gene in ischemic stroke is upregulated, and early diagnosis can be provided for ischemic stroke patients by detecting the expression level of the METTL9 gene, so that early detection and treatment can be realized to reduce mortality of the ischemic stroke patients.
Owner:QINGDAO MEDINTELL BIOMEDICAL CO LTD
Tetrafluorobenzyl derivatives and pharmaceutical composition for preventing and treating acute and chronic neurodegenerative diseases in central nervous system containing the same
InactiveUS20050239896A1Potent neuroprotective activityOrganic active ingredientsBiocideHuntingtons choreaNervous system
The present invention relates to a tetrafluorobenzyl derivative and a pharmaceutical composition for prevention and treatment of acute and chronic neurodegenerative disease in central nervous system and ophthalmic diseases containing the same. The tetrafluorobenzyl derivative of the present invention can effectively be used to prevent and treat chronic neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease and Huntington's disease, degenerative brain disease such as epilepsy and ischemic brain disease such as stroke.
Owner:NEUROTECH PHARMA
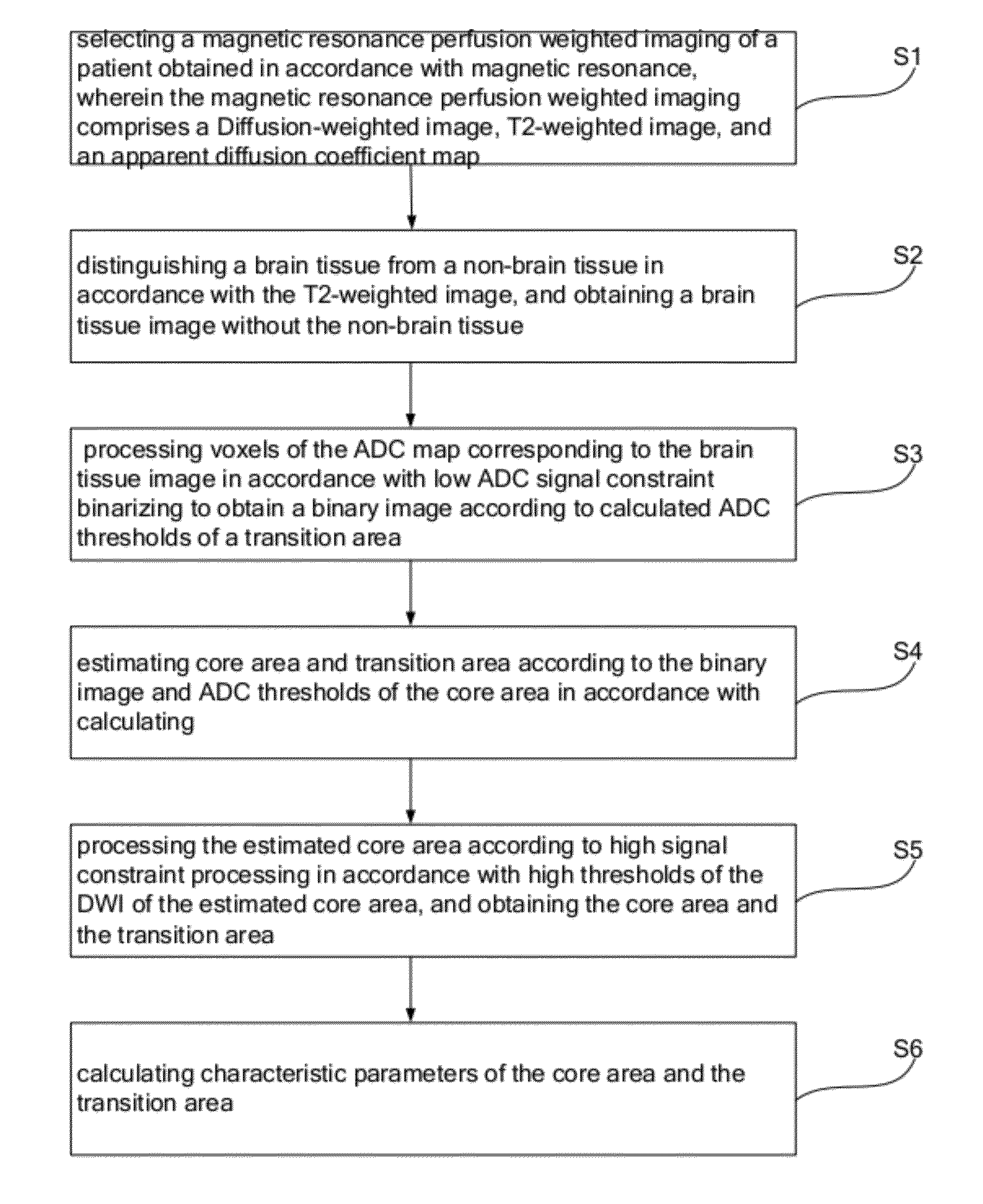
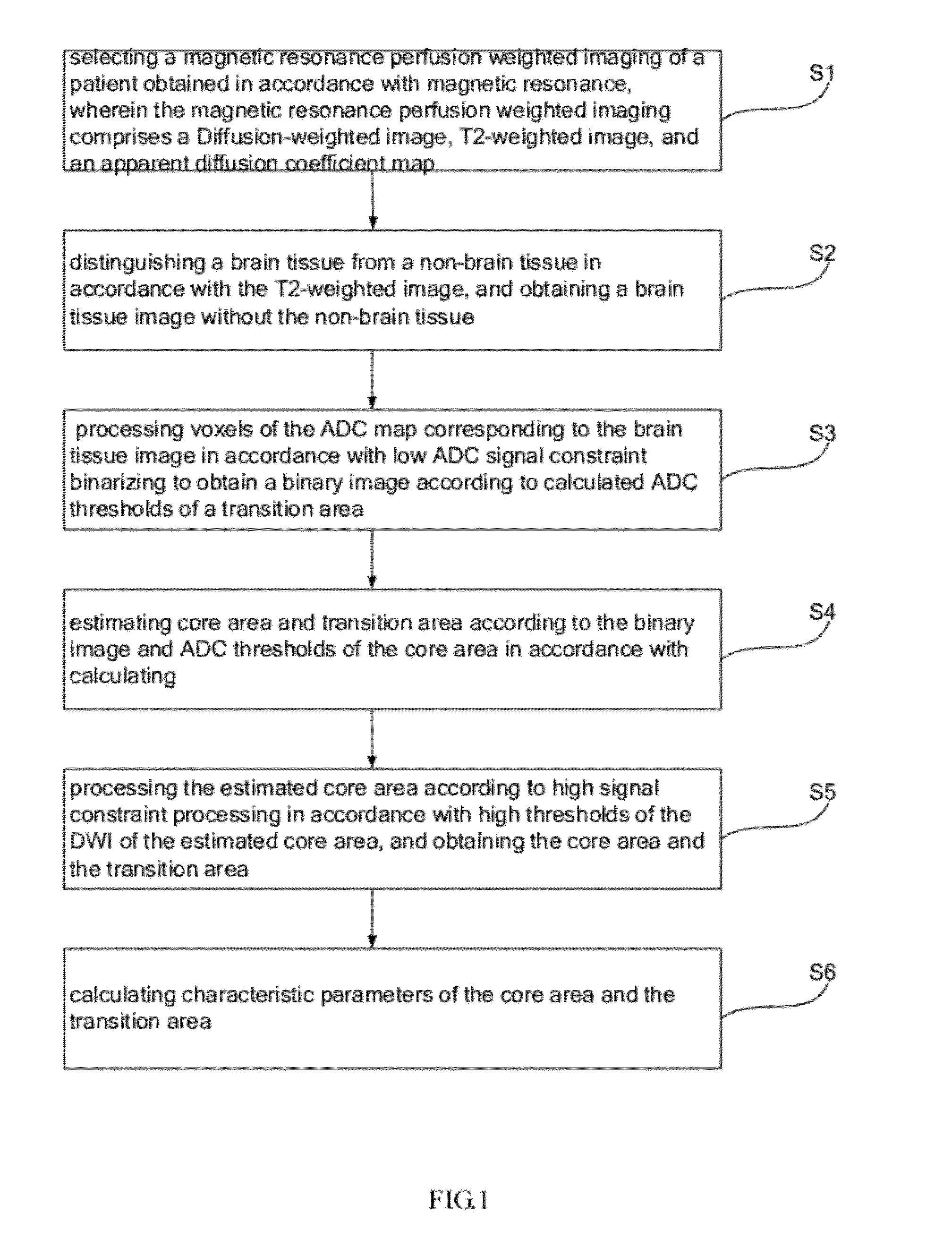
Method and system for obtaining brain characteristic parameters, thrombolysis decision guideline system and method thereof
ActiveUS20120076387A1Low costShorten the timeImage enhancementImage analysisGuidelinePerfusion Weighted MRI
Method and system for obtaining brain characteristic parameters, thrombolysis decision guideline system and method thereof, provide middle of reference data for early diagnosis and treatment of acute ischemic brain death, and provide effective reference data for thrombolytic therapy. The present invention uses diffusion-weighted imaging, comparing to the clinical programs of diffusion-weighted imaging and perfusion weighted imaging, perfusion weighted imaging can omitted and the degree of functional characterization of perfusion abnormalities is reflected without the perfusion weighted imaging, to provide middle data of brain tissue can be saved and the risk of thrombolytic therapy. The present invention based on ADC low signal constraint and DWI high signal constraint DWI binarization processing to obtain the core area and transition area, that is more accurate.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
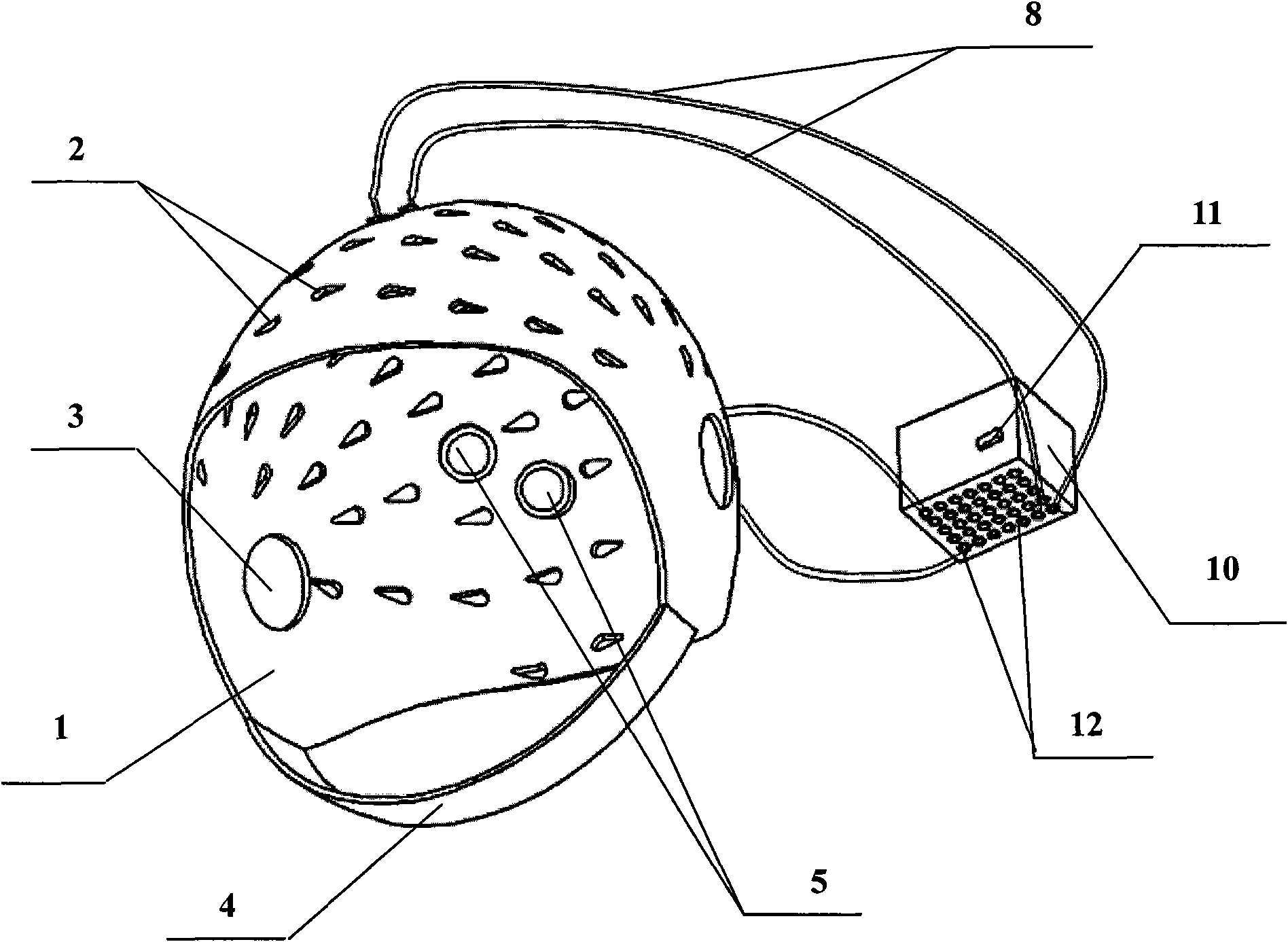
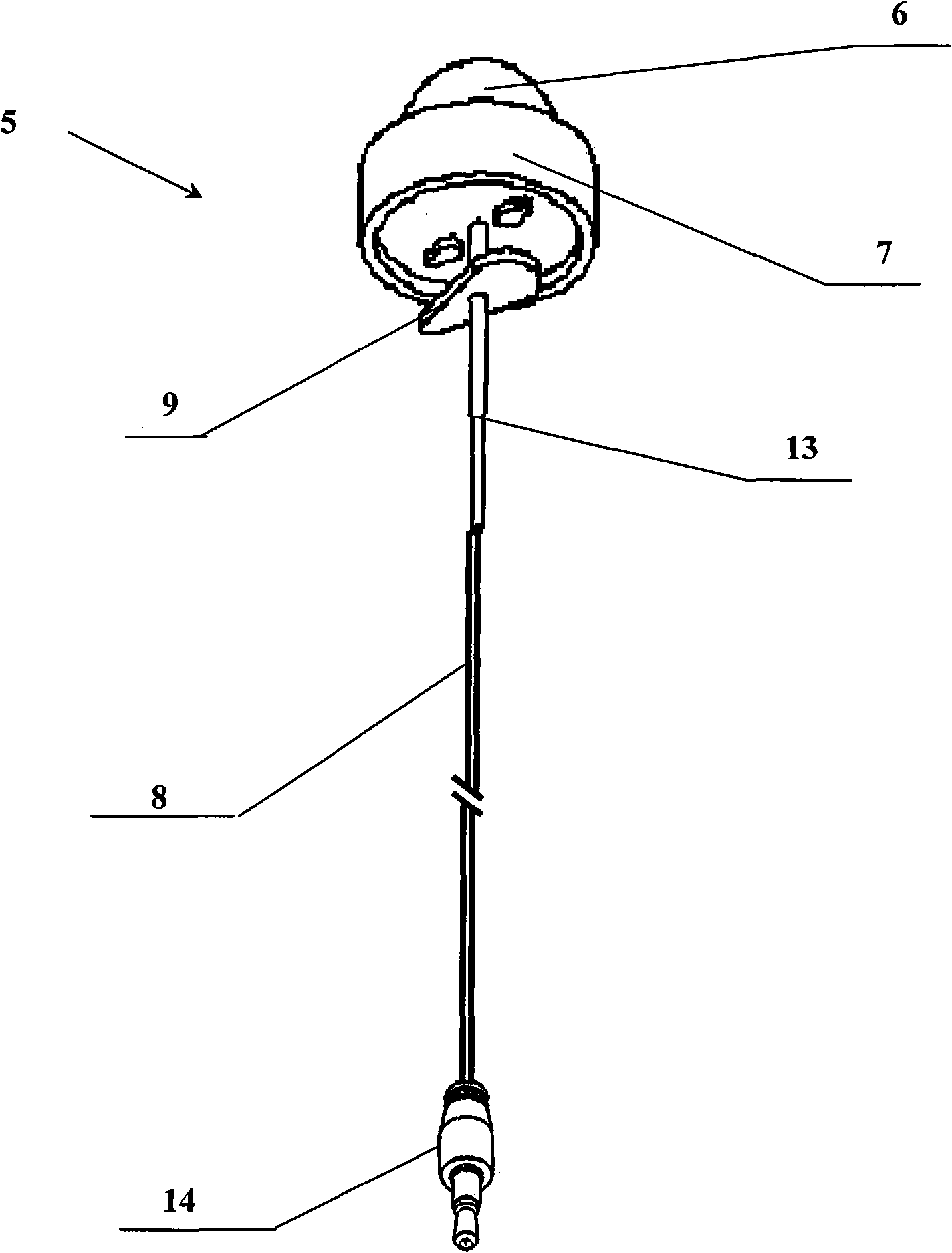
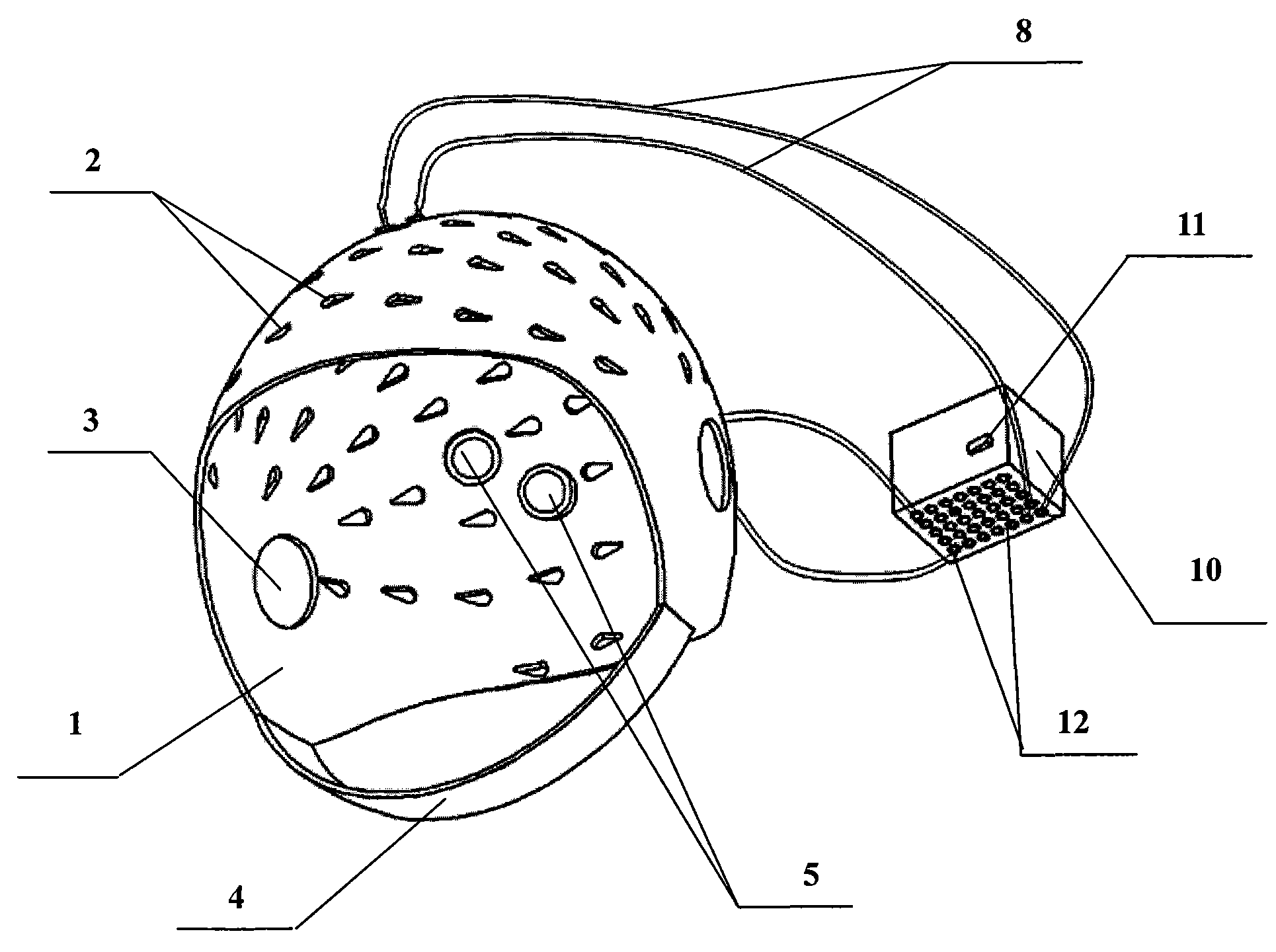
Hood device for treating brain central nervous system diseases
The invention relates to a hood device for treating brain central nervous system diseases. The hood device comprises a hood body, a plurality of light-emitting diode components and a control device; the hood body is provided with a plurality of mounting holes; the light-emitting diode components are arranged in the mounting holes; the installation number and positions of the light-emitting diode components are determined according to lesion sites of a patient; and the control device is electrically connected with the light-emitting diode components to control luminescence of the plurality of light-emitting diode components. The hood device realizes a novel light-emitting diode (LED) light radiation treatment method, can be worn on the head of the patient to make LED light penetrate scalp and skull to reach damaged brain cells so as to fulfill the aim of effectively treating the brain central nervous system diseases, has the advantages of simple operation, no toxic or side effects, obvious effect and low medical treatment cost and can be used for treatment and rehabilitation of the brain central nervous system diseases, such as ischemic cerebral apoplexy, senile dementia, Parkinsons disease and the like.
Owner:UNIV OF SHANGHAI FOR SCI & TECH
Methods and compositions for modulation of blood-neural barrier
ActiveUS20070265203A1Improve breathabilityStable physiologic environmentBiocideSenses disorderMedicineIschemic stroke
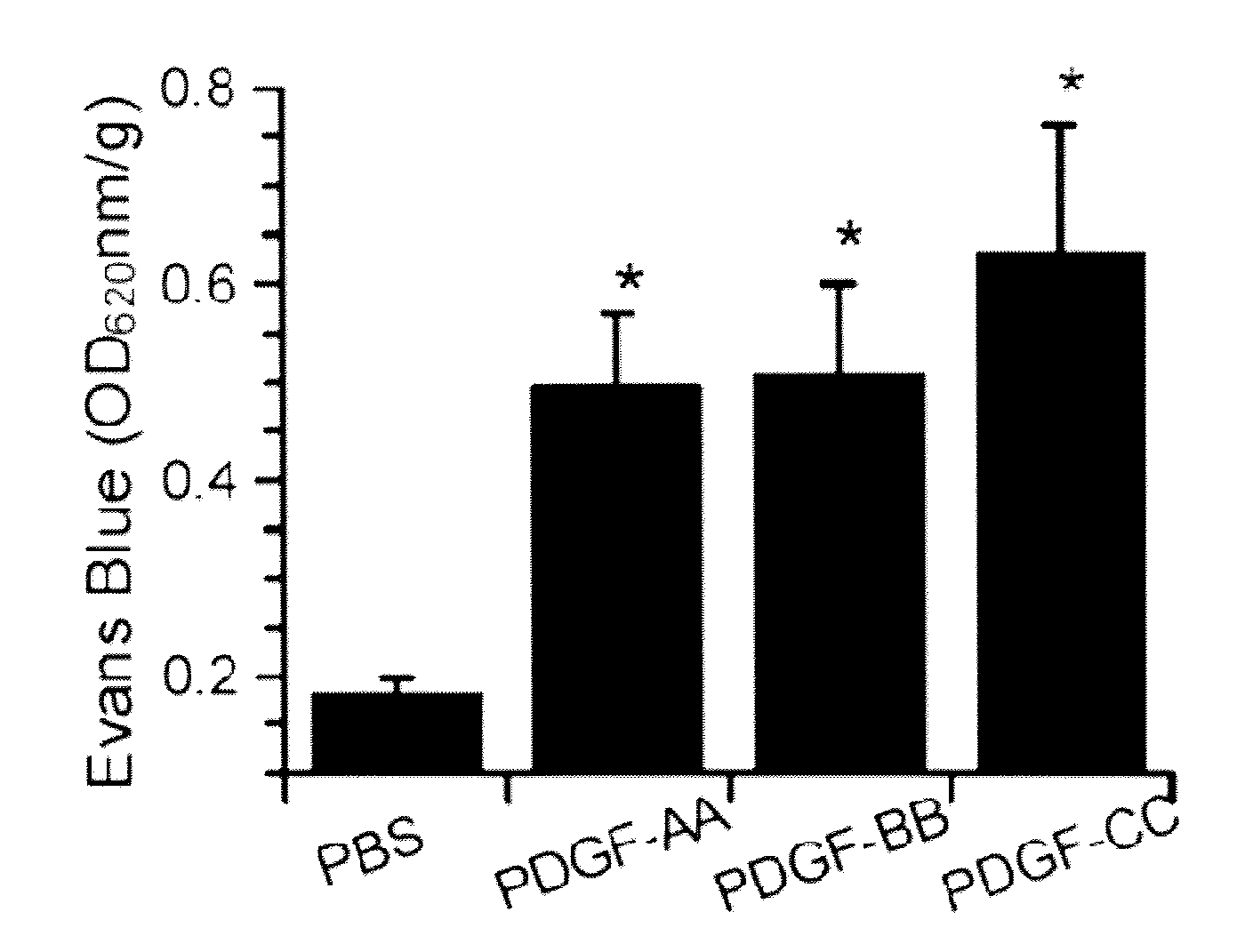
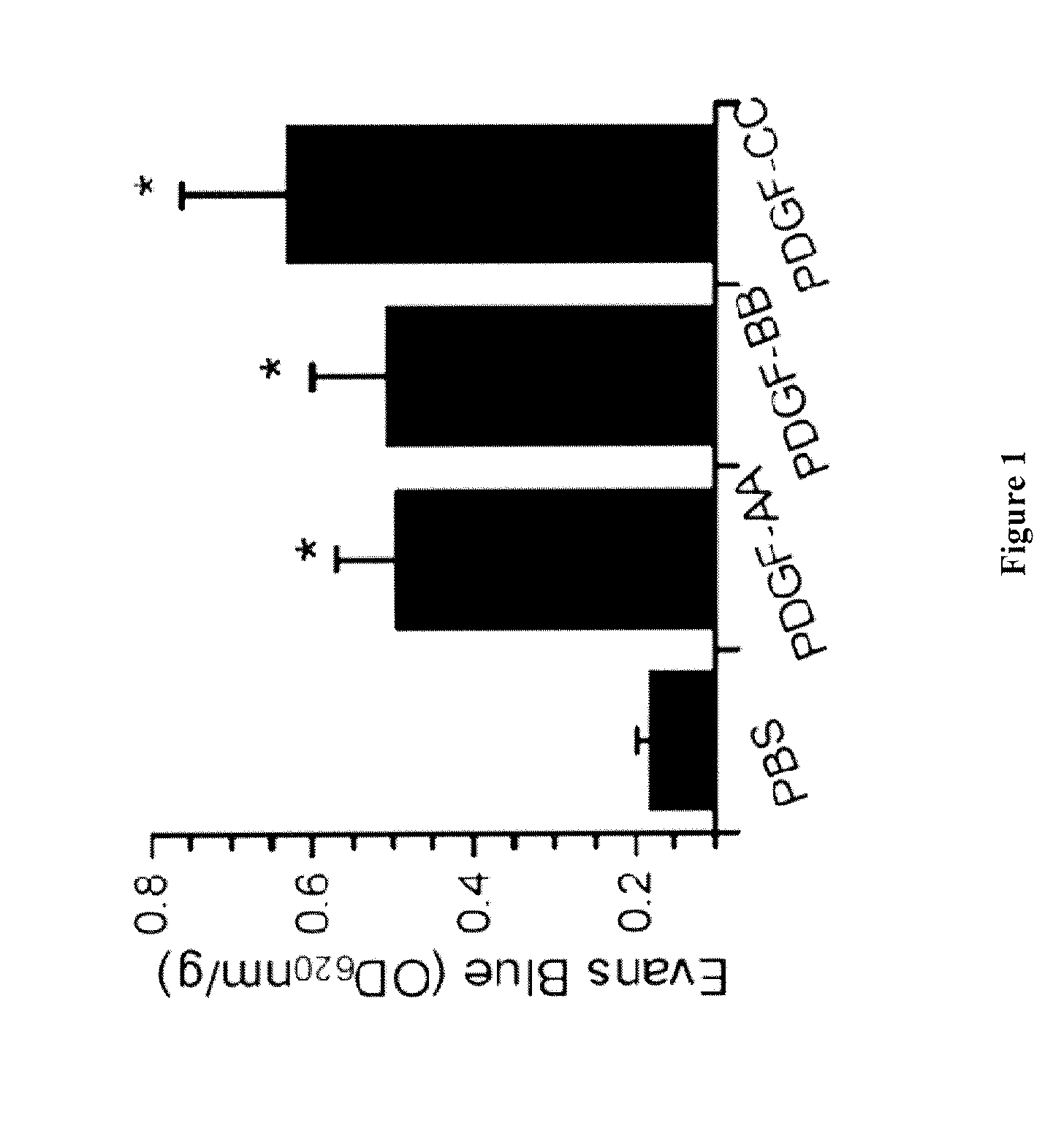
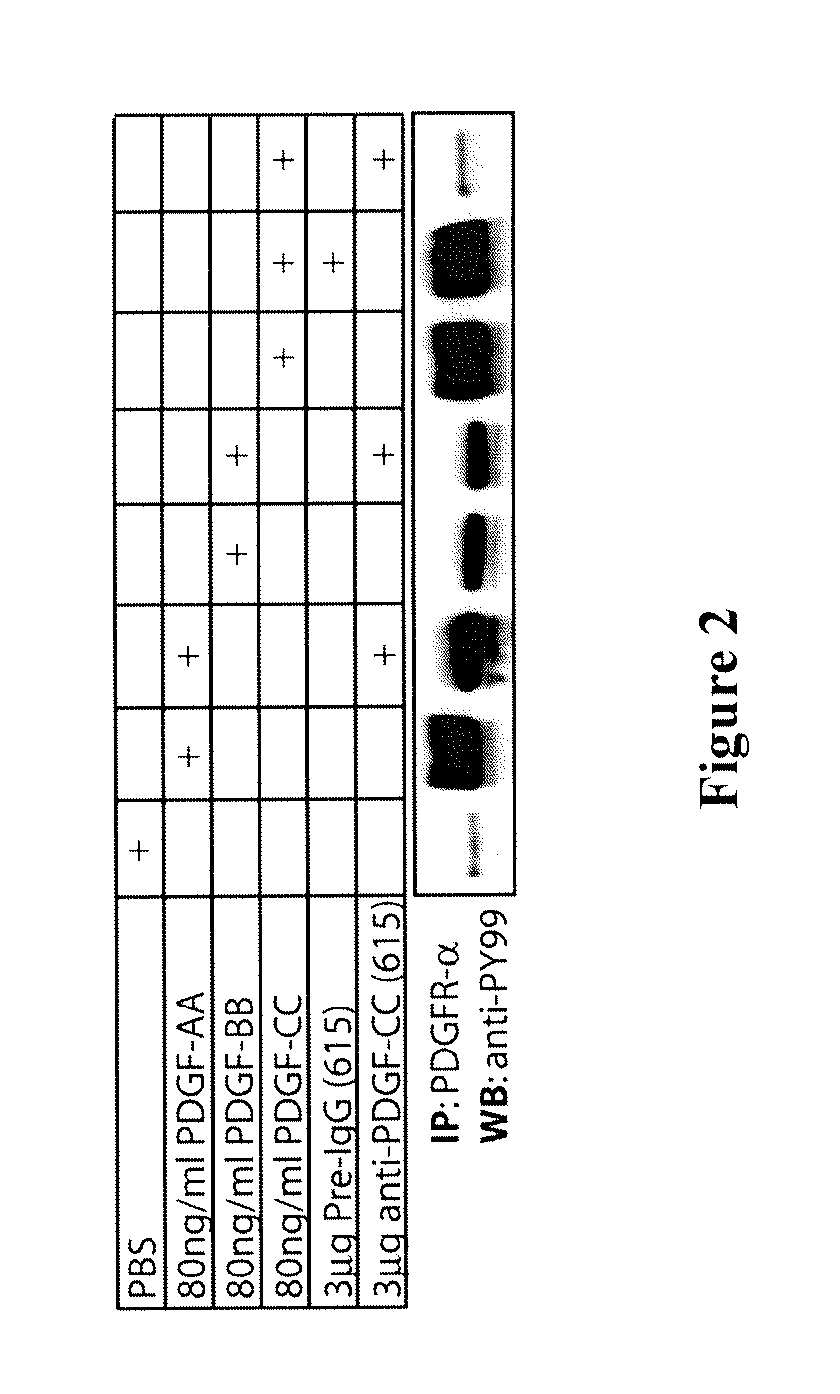
Methods and compositions for modulating blood-neural barrier (BNB) for the treatment of CNS conditions such as edema, and for increased drug delivery efficacy across the BNB. The present invention further relates to improved tPA treatment of ischemic cerebrovascular and related diseases in combination with antagonism of the PDGF signaling pathway. The inventive method and composition is particularly suitable for conjunctive therapy of ischemic stroke using tPA and an anti-PDGF-C antagonist or an anti-PDGFR-α antagonist.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN +2
Method for preparing Chinese medicine composition for treating ischemic brain apoplexy
ActiveCN1615994ATake a small doseKeep active ingredientsUnknown materialsPill deliveryAlcoholCentrifugation
The preparation process of Chinese medicine composition for treating ischemic brain apoplexy includes the following steps: supercritical CO2-water extracting angelica to obtain extractive, alcohol extract angelica dregs, astragalus root, figwort, honeysuckle, dendrobium stem and licorice to obtain alcohol extracted liquid; decompression recovering alcohol, concentration, centrifugation, water washing and precipitation to obtain supernatant, adsorption in macroporous resin column and alcohol elution to obtain elutent; decompressing the elutent, concentrating, drying and crushing to obtain extractum powder; and merging the extractive and the extractum powder to obtain the Chinese medicine composition. The present invention has the advantages of maintenance of volatile component in angelica, well enrichment of the effective components, high curative effect, etc.
Owner:NANJING UNIVERSITY OF TRADITIONAL CHINESE MEDICINE +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com