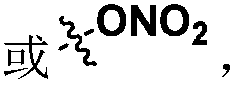
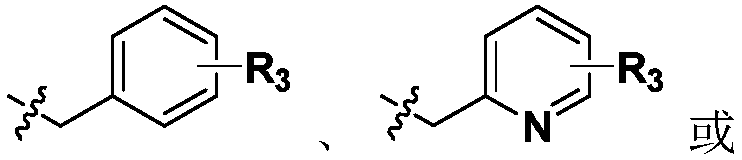
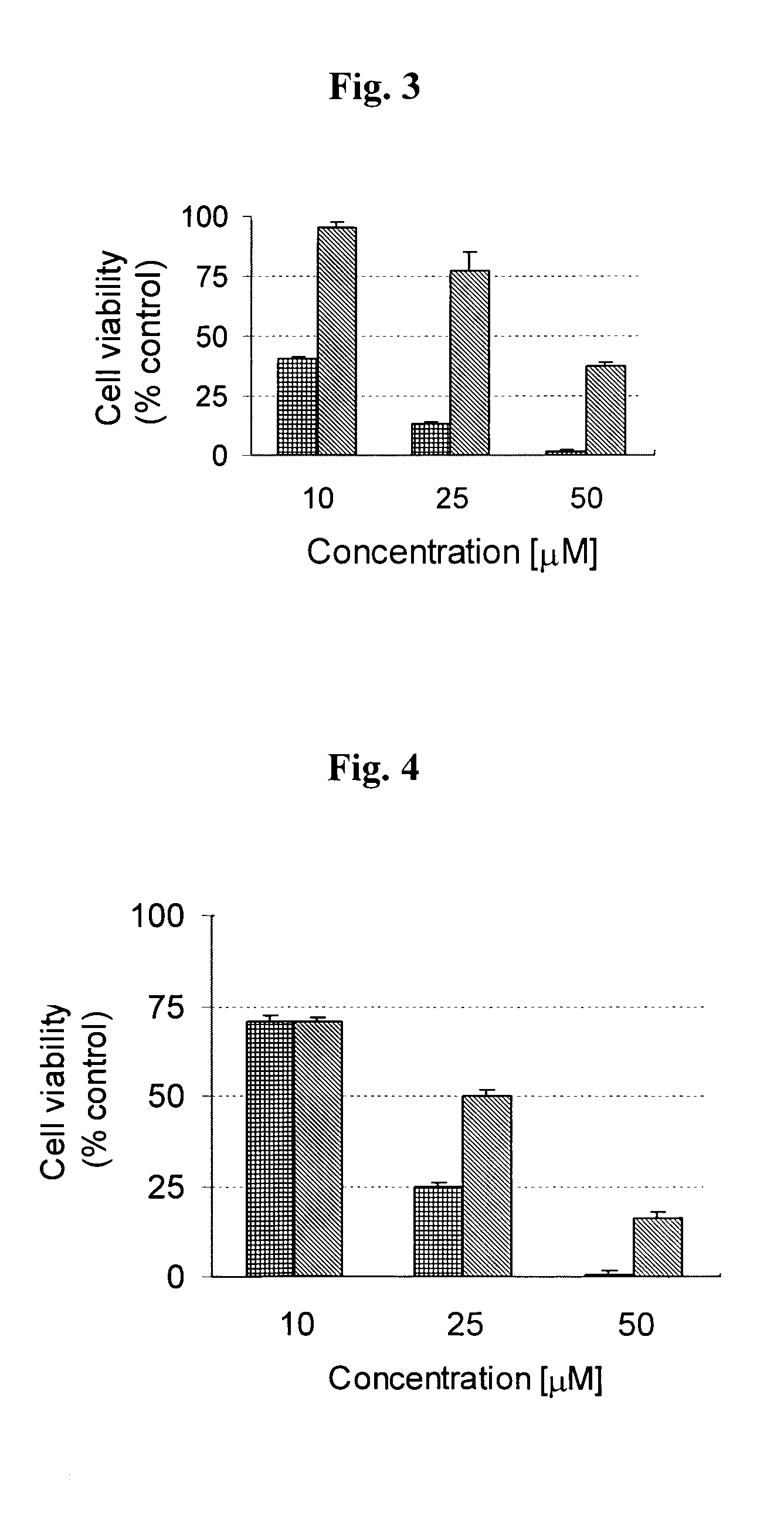
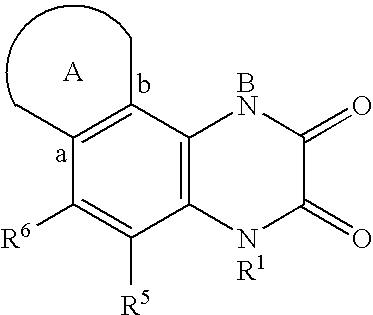
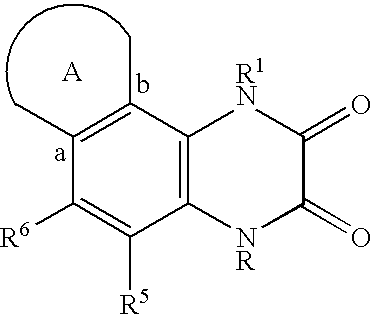
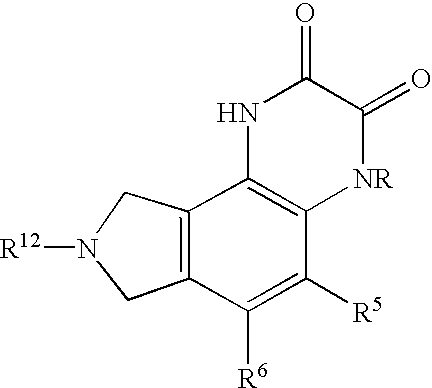
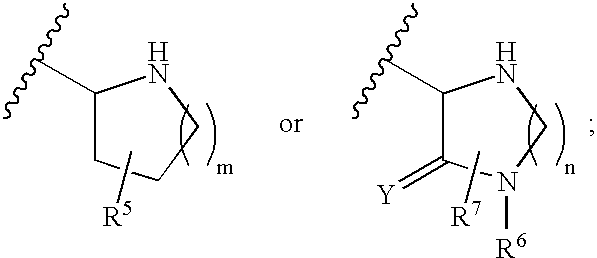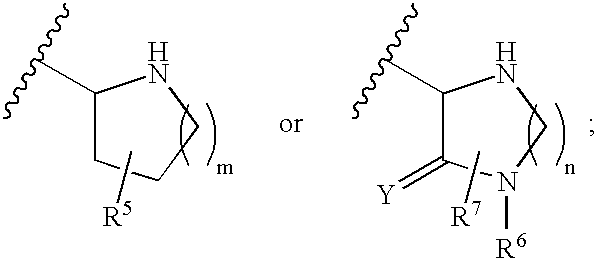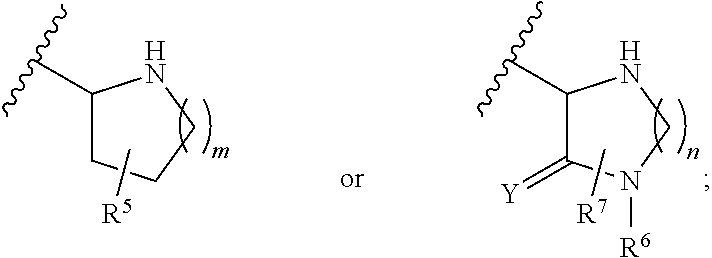Patents
Literature
40 results about "Aspartate receptors" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The aspartate receptor, Tar, is a member of a family of transmembrane receptors that mediate chemotactic response in certain enteric bacteria, such as Salmonella typhimurium and Escherichia coli.
Novel pharmaceutical compositions for treating chronic pain and pain associated with neuropathy
InactiveUS20080058362A1Reduced plasma concentrationEffective pain managementBiocideAmide active ingredientsDextrorphanSustained release drug
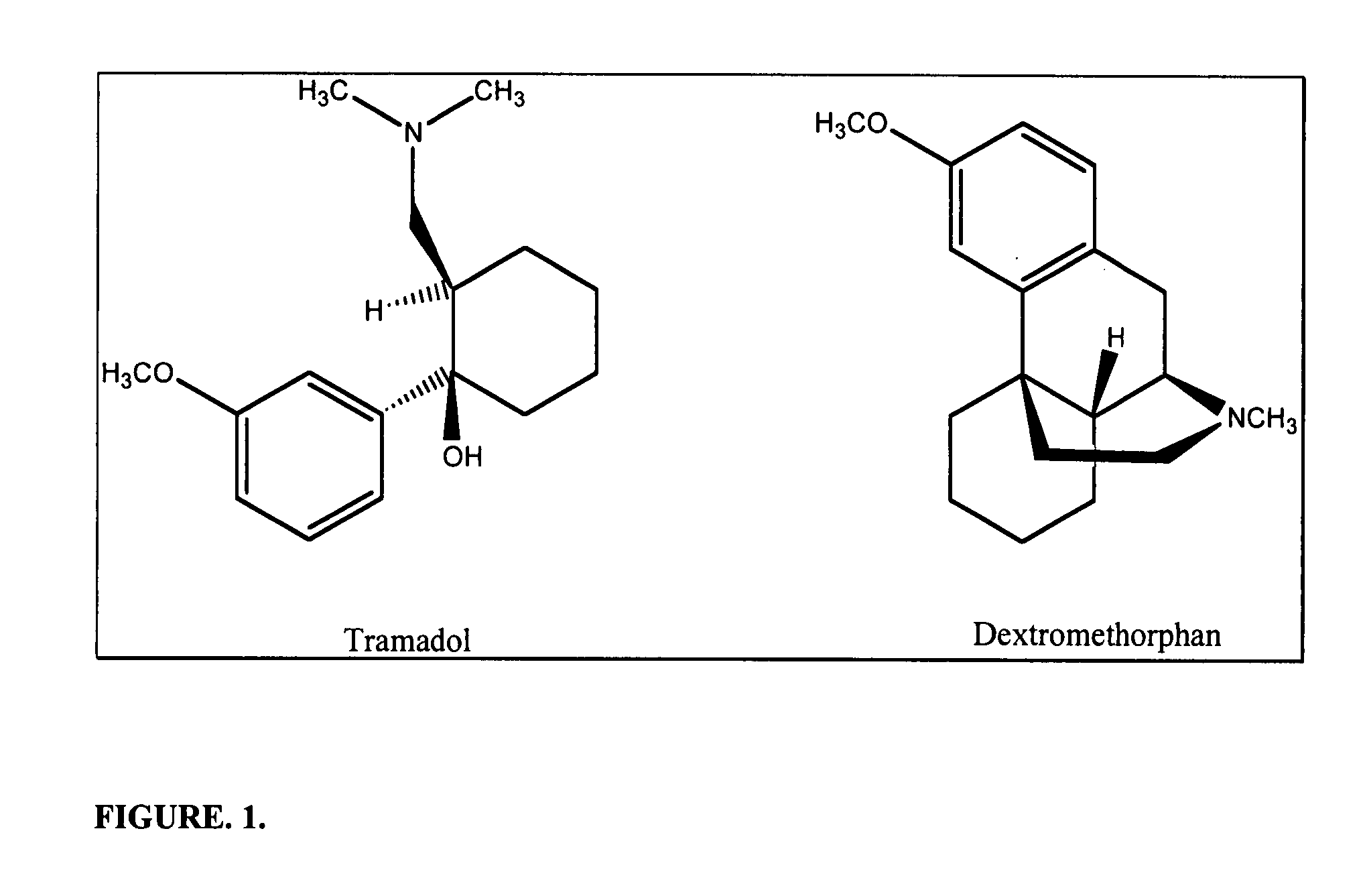
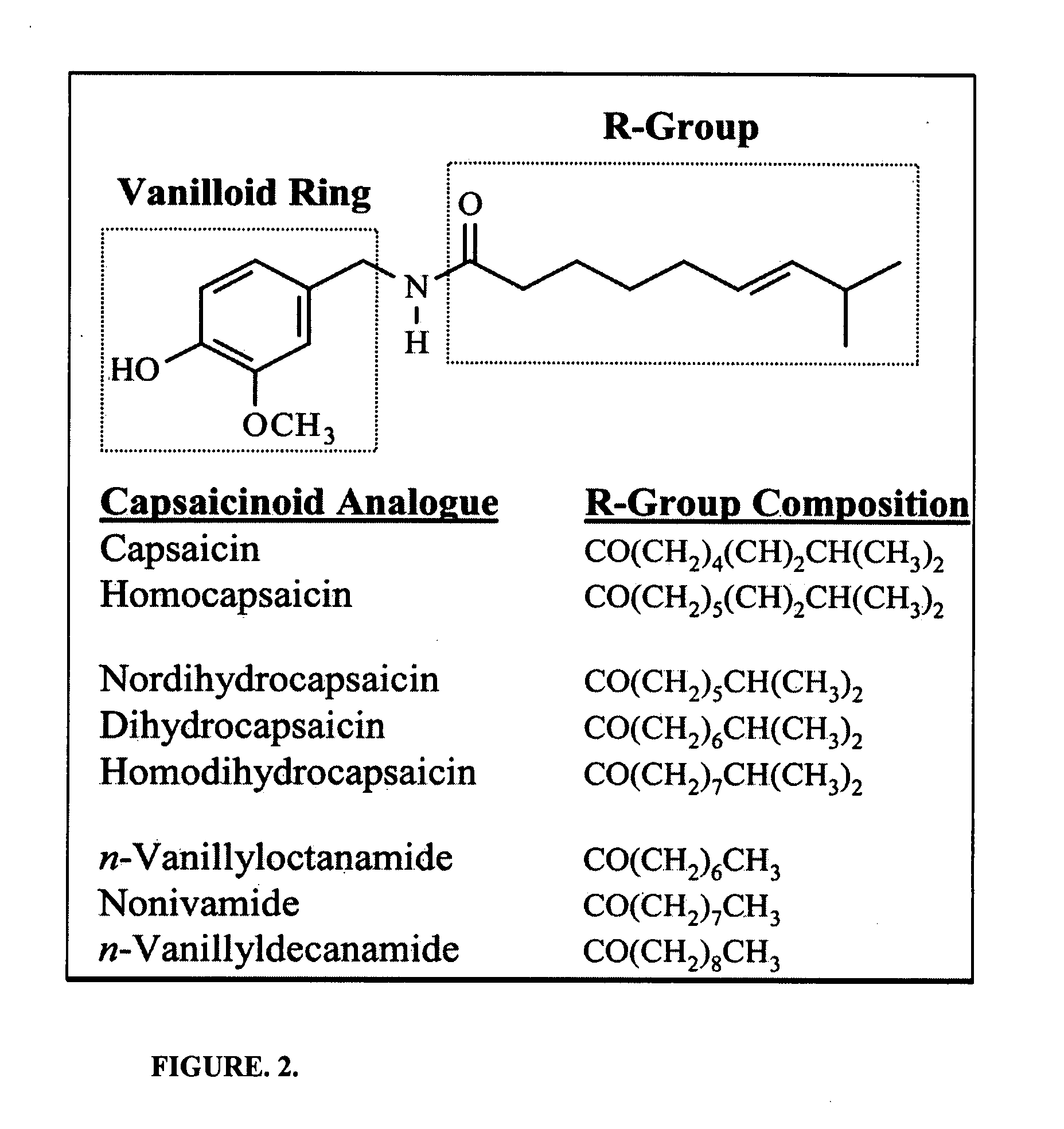
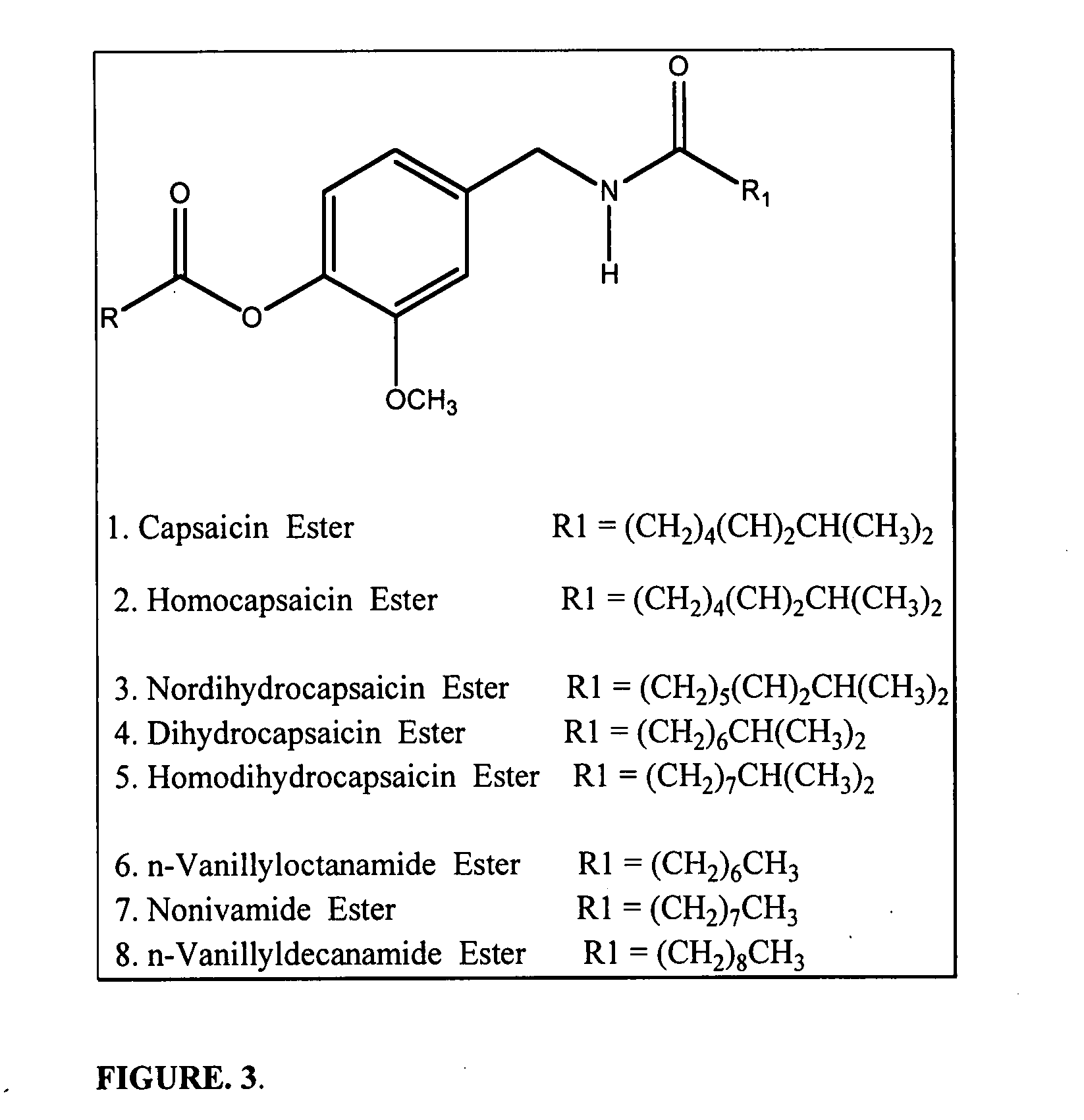
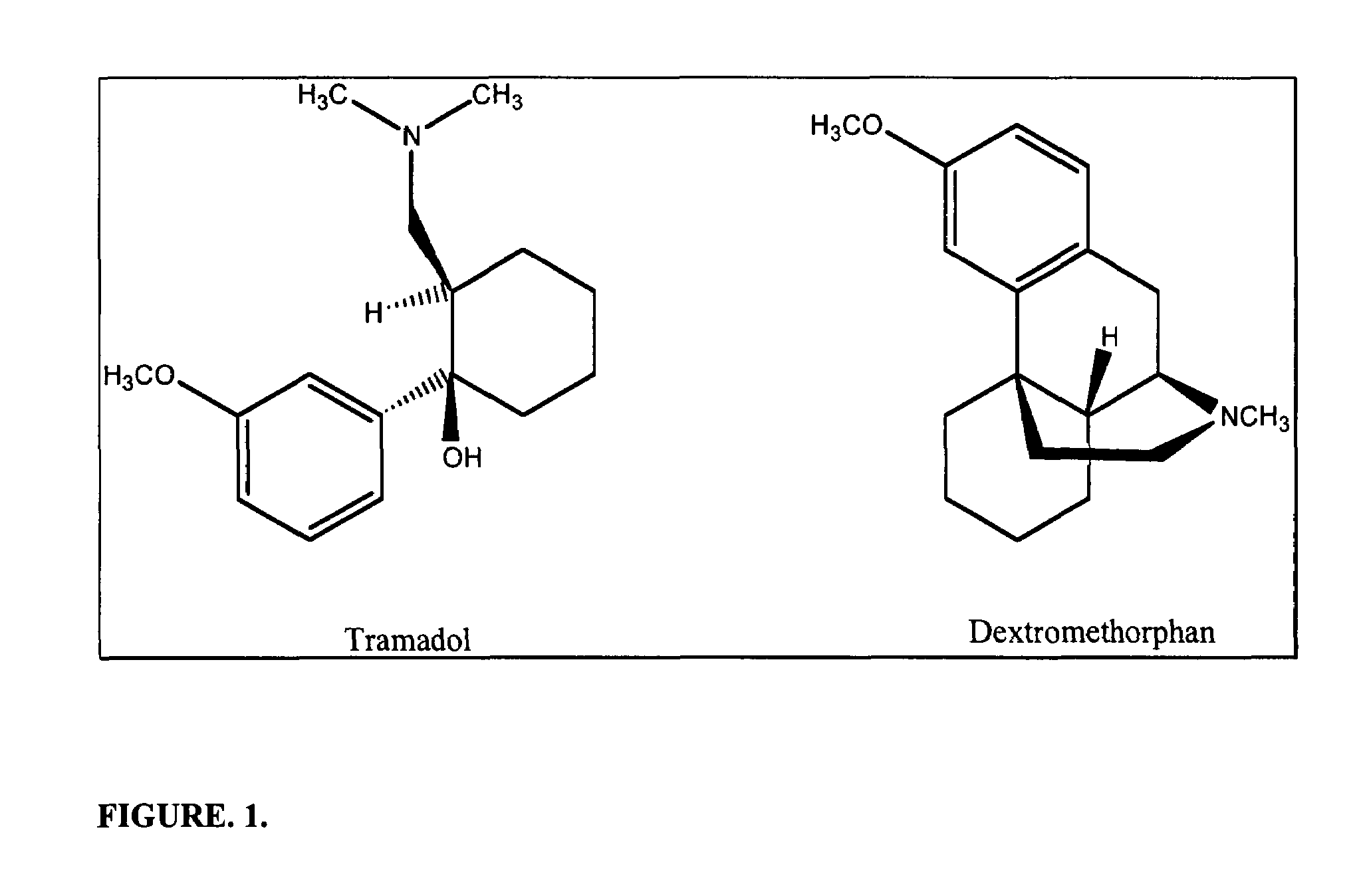
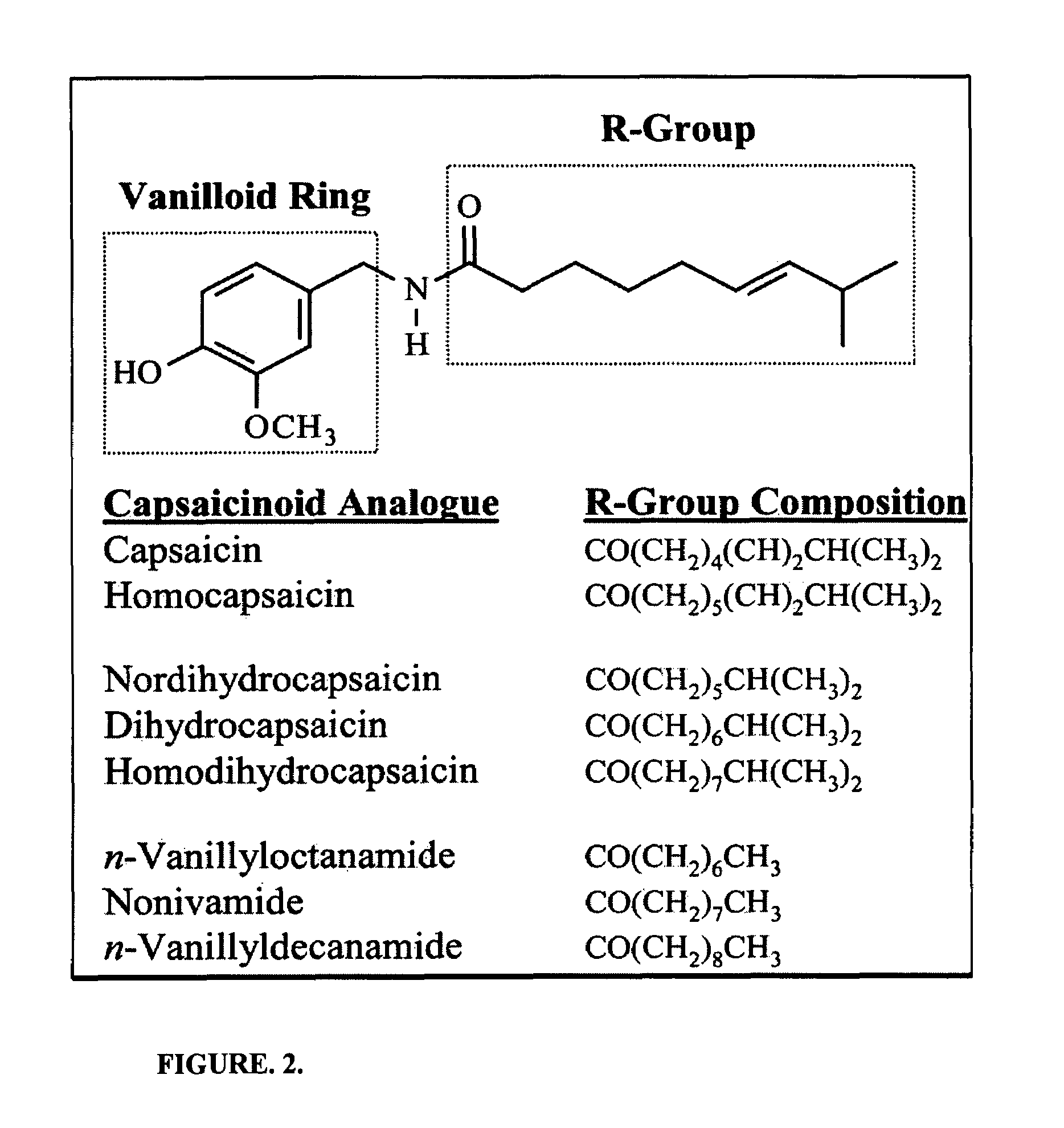
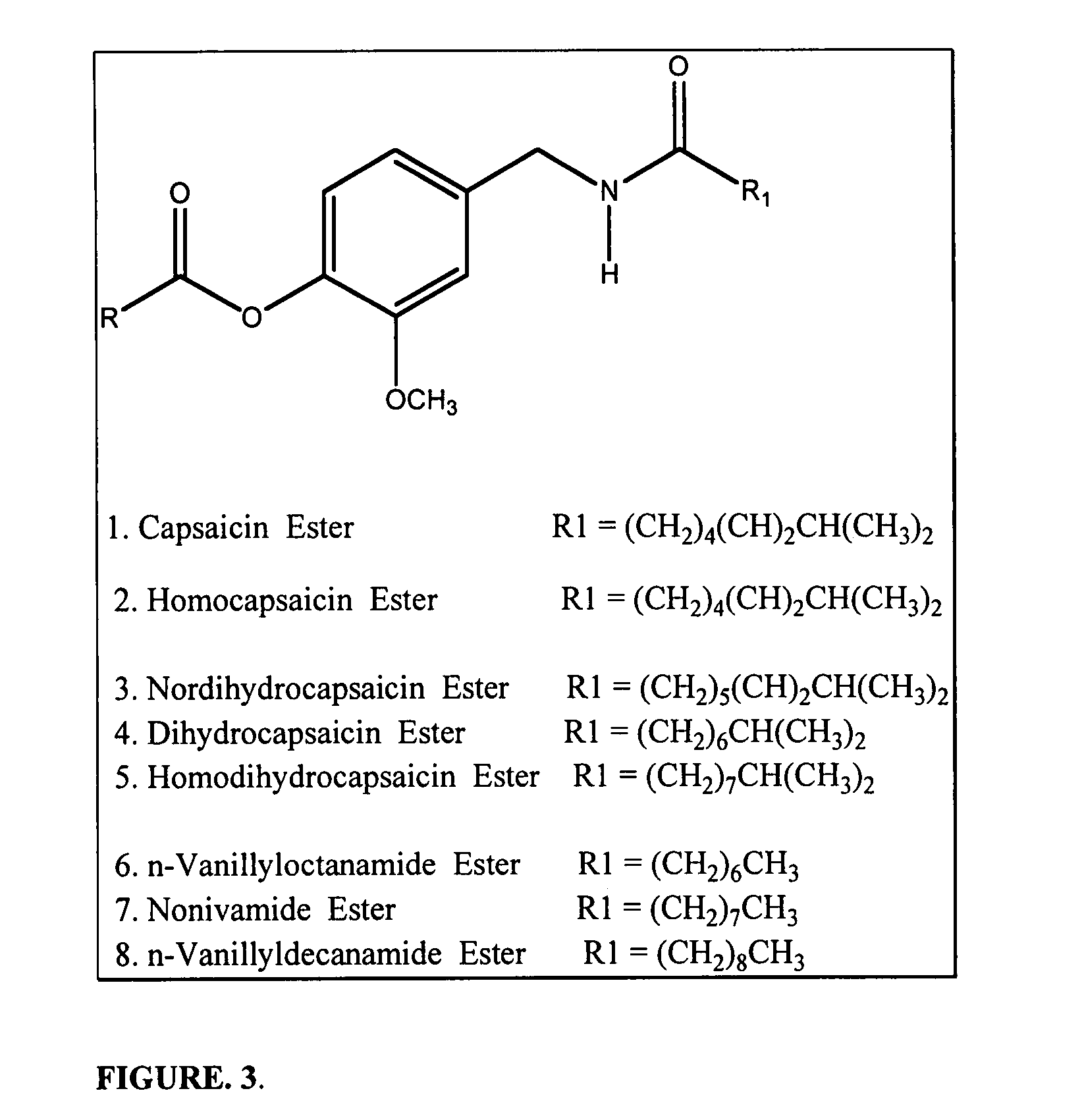
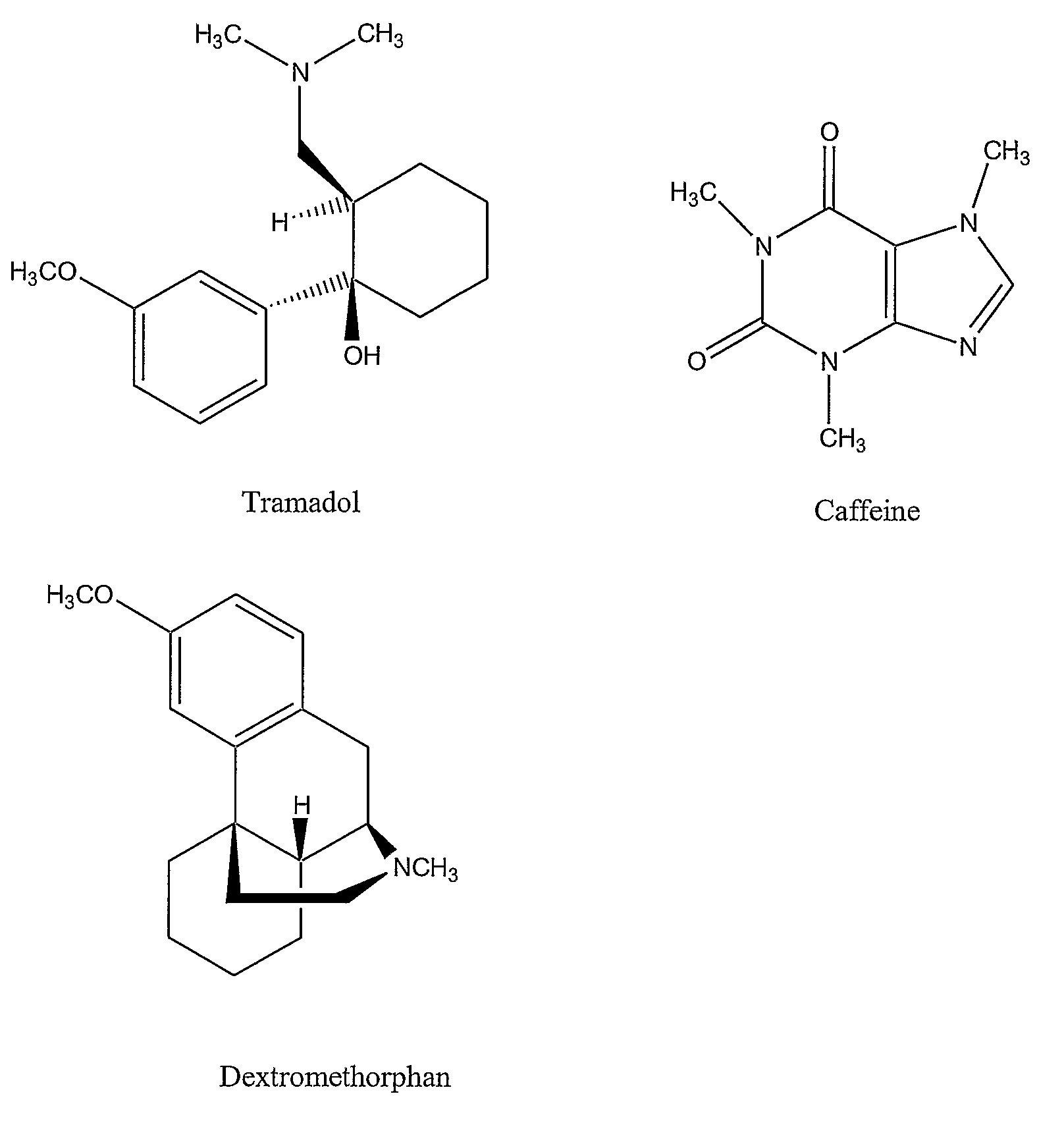
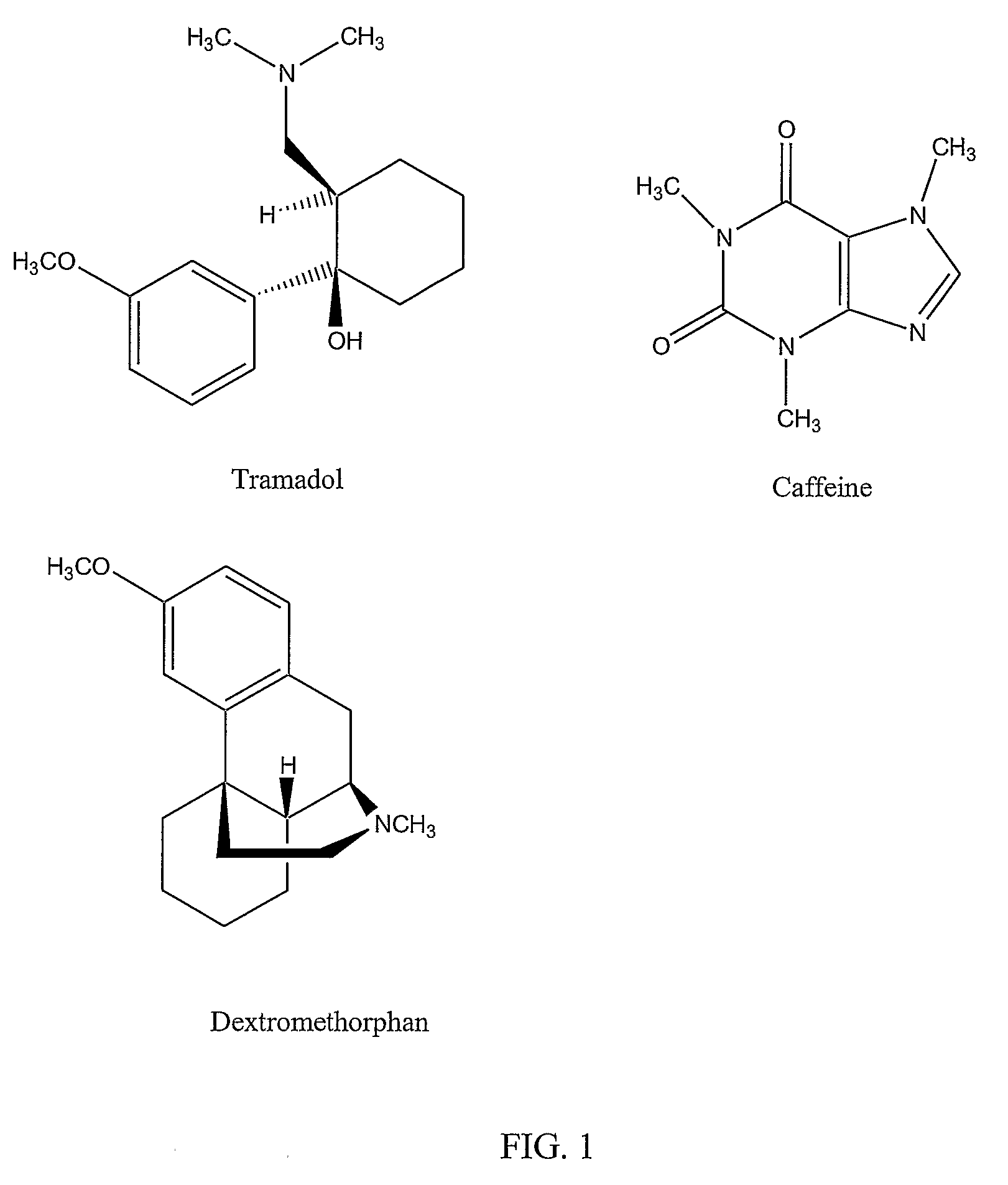
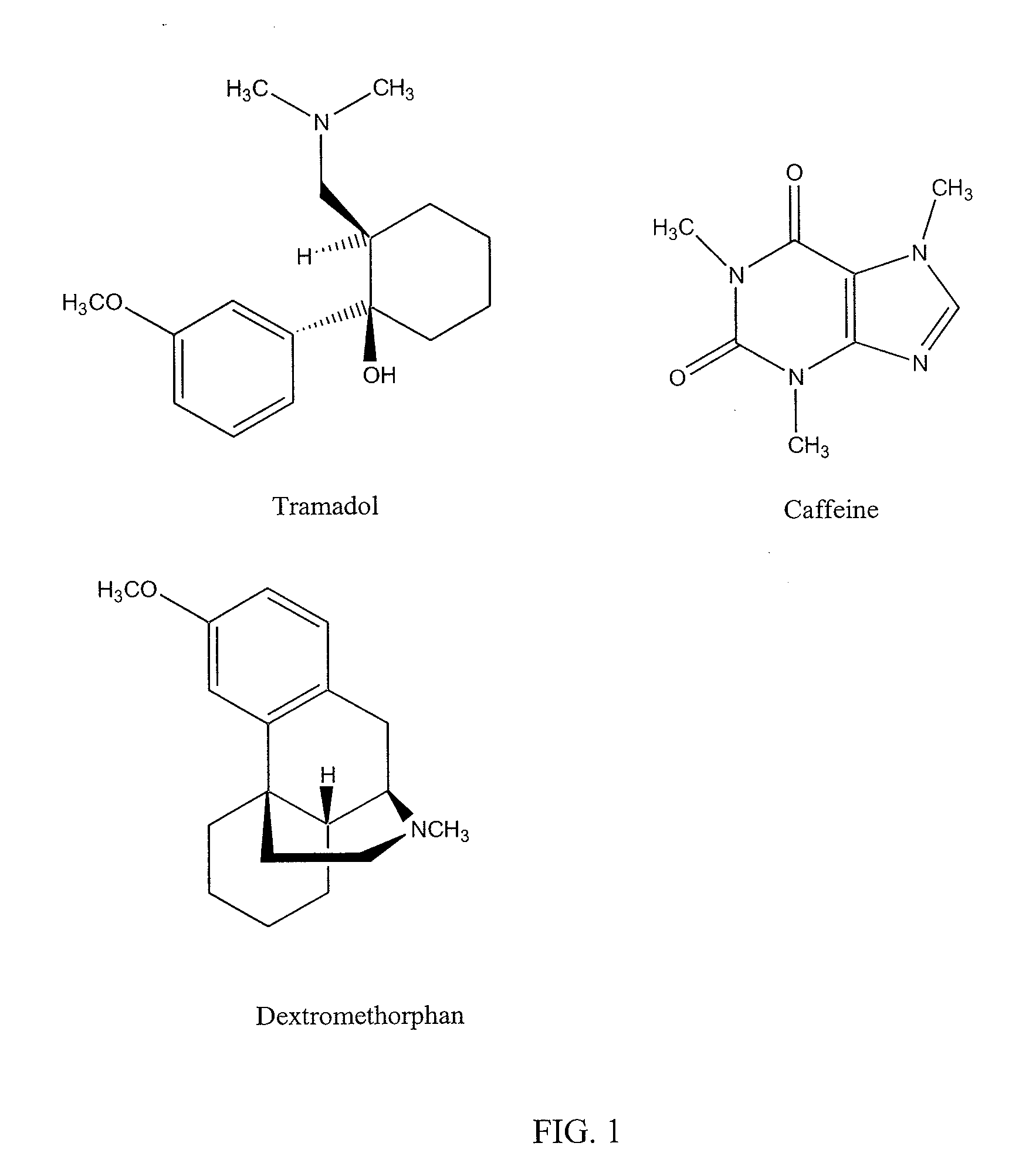
Chronic pain is alleviated in a mammal suffering there from by administering to the mammal a chronic pain alleviating amount of a nontoxic N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor antagonist such as dextromethorphan, dextrorphan, ketamine or pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, in combination with a μ-opiate analgesic such as tramadol or an analogously acting molecular entity, and a capsaicin or an ester of capsaicin, and optionally in sustained release dosage form.
Owner:TRINITY LAB INC
Pharmaceutical compositions for treating chronic pain and pain associated with neuropathy
InactiveUS7645767B2Reduce concentrationEfficient managementBiocideAmide active ingredientsOpiatePharmaceutical medicine
Chronic pain is alleviated in a mammal suffering there from by administering to the mammal a chronic pain alleviating amount of a nontoxic N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor antagonist such as dextromethorphan, dextrorphan, ketamine or pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, in combination with a μ-opiate analgesic such as tramadol or an analogously acting molecular entity, and a capsaicin or an ester of capsaicin, and optionally in sustained release dosage form.
Owner:TRINITY LAB INC
Abuse-resistant opioid solid dosage form
InactiveUS20060073102A1Prevent and discourage abuseGood curative effectOrganic active ingredientsPill deliveryN-methyl-D-aspartate Receptor AntagonistsOpioid abuse
The present invention pertains to a solid dosage form comprising an analgesically effective amount of opioid analgesic and an opioid abuse-deterring amount of a nontoxic N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor antagonist contained in a carrier which isolates, or separates, the antagonist from the opioid analgesic. The nontoxic N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor antagonist is released and made available only when the dosage form is misused, as would be the case when the dosage form is crushed or dissolved and thereafter administered in a manner other than that indicated, e.g., by injection or intranasally.
Owner:ENDO PHARMA INC
Substituted amide beta secretase inhibitors
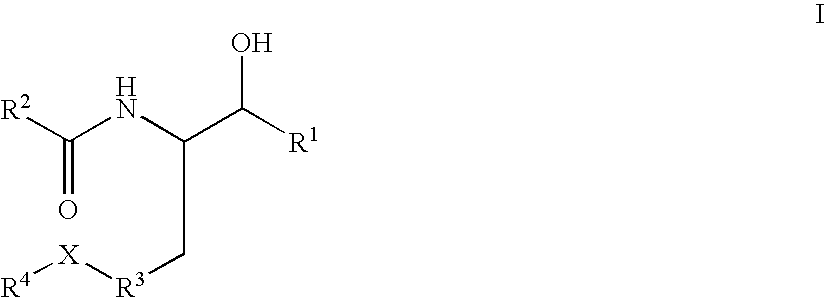
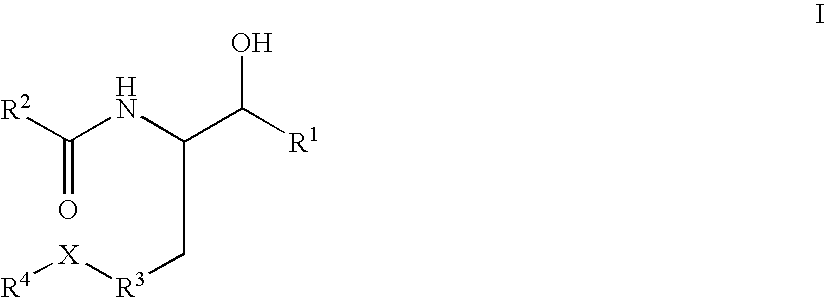
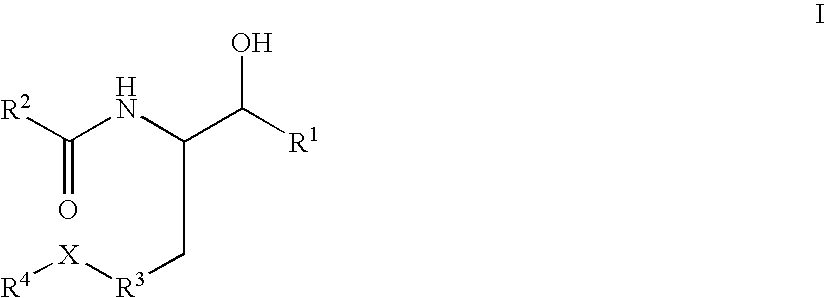
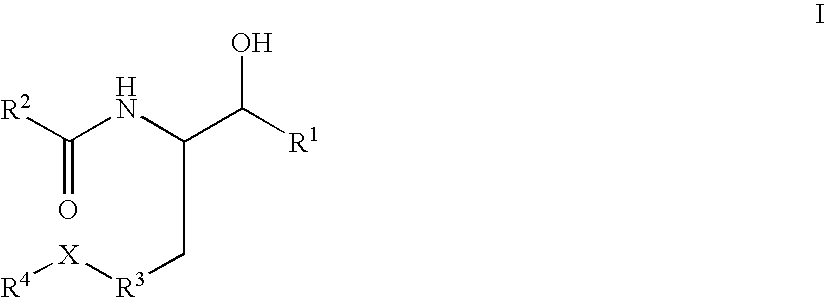
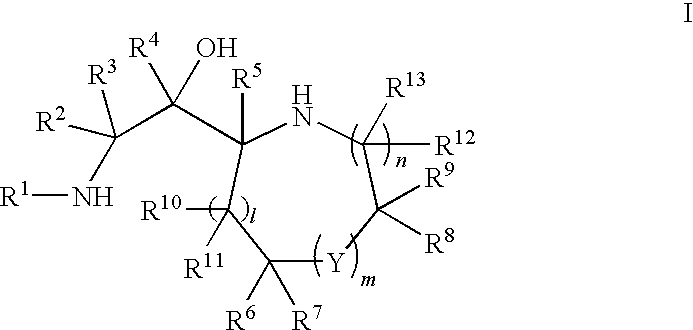
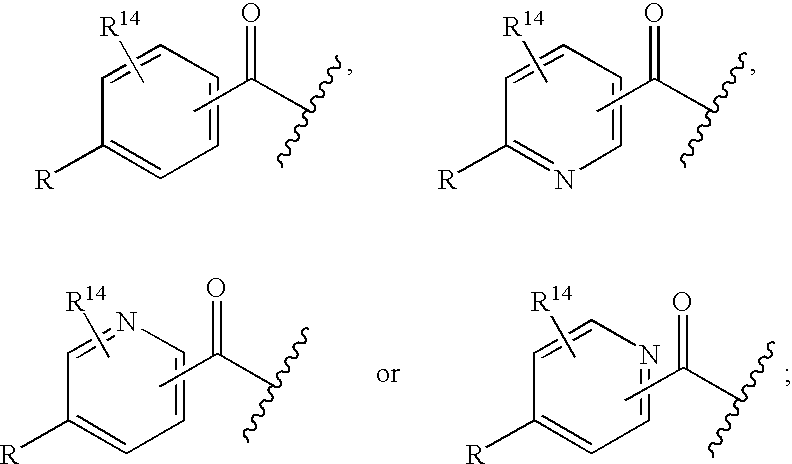
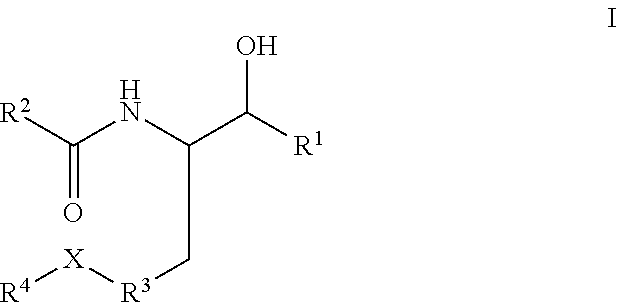
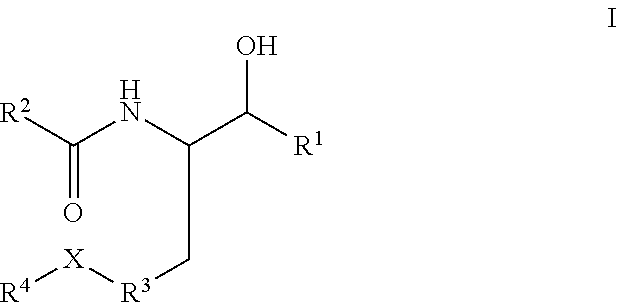
Disclosed are novel compounds of the formula or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt or solvate thereof, wherein R1, R2, R3, R4 and X are as defined in the specification. Also disclosed are pharmaceutical compositions comprising the compounds of formula I. Also disclosed are methods of treating cognitive or neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer's disease. Also disclosed are methods of treating a cognitive or neurodegenerative disease comprising administering to a patient I need of such treatment a combination of at least one compound of formula I and at least one compound selected from the group consisting of β-secretase inhibitors other than those of formula I, HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors, gamma-secretase inhibitors, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory agents, N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor antagonists, cholinesterase inhibitors and anti-amyloid antibodies.
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME LLC
Parenteral and topical compositions for pain
InactiveUS20180000804A1Inorganic non-active ingredientsAnaestheticsAdrenergic receptor agonistsN-methyl-D-aspartate Receptor Antagonists
This invention provides compositions, kits containing compositions, and methods for their use in treating subjects with pain. Instant compositions comprise two or more long acting aminoamide local anesthetics, at least one NSAID, at least one corticosteroid, at least one alpha-2 (α2) adrenergic receptor agonist, at least one N-methyl-D aspartate receptor antagonist, and optionally, epinephrine. Instant compositions are useful for infiltration anesthesia, field block anesthesia, regional anesthesia, peripheral nerve block, plexus anesthesia, epidural (or extradural) anesthesia, spinal anesthesia, local anesthesia, and transincision catheter anesthesia. The instant compositions have one or more superior properties of analgesia, duration of analgesia, safety, narcotic sparing, and motor sparing properties.
Owner:BERKHEIMER DAVID
Compounds, compositions and method suitable for amelioration of withdrawal syndromes and withdrawal-induced brain damage
InactiveUS6962930B1Lack of unwanted stimulatory effectReduce and prevent in vitro measureBiocideNervous disorderVoltage-sensitive sodium channelN-Methyl-D-aspartic acid
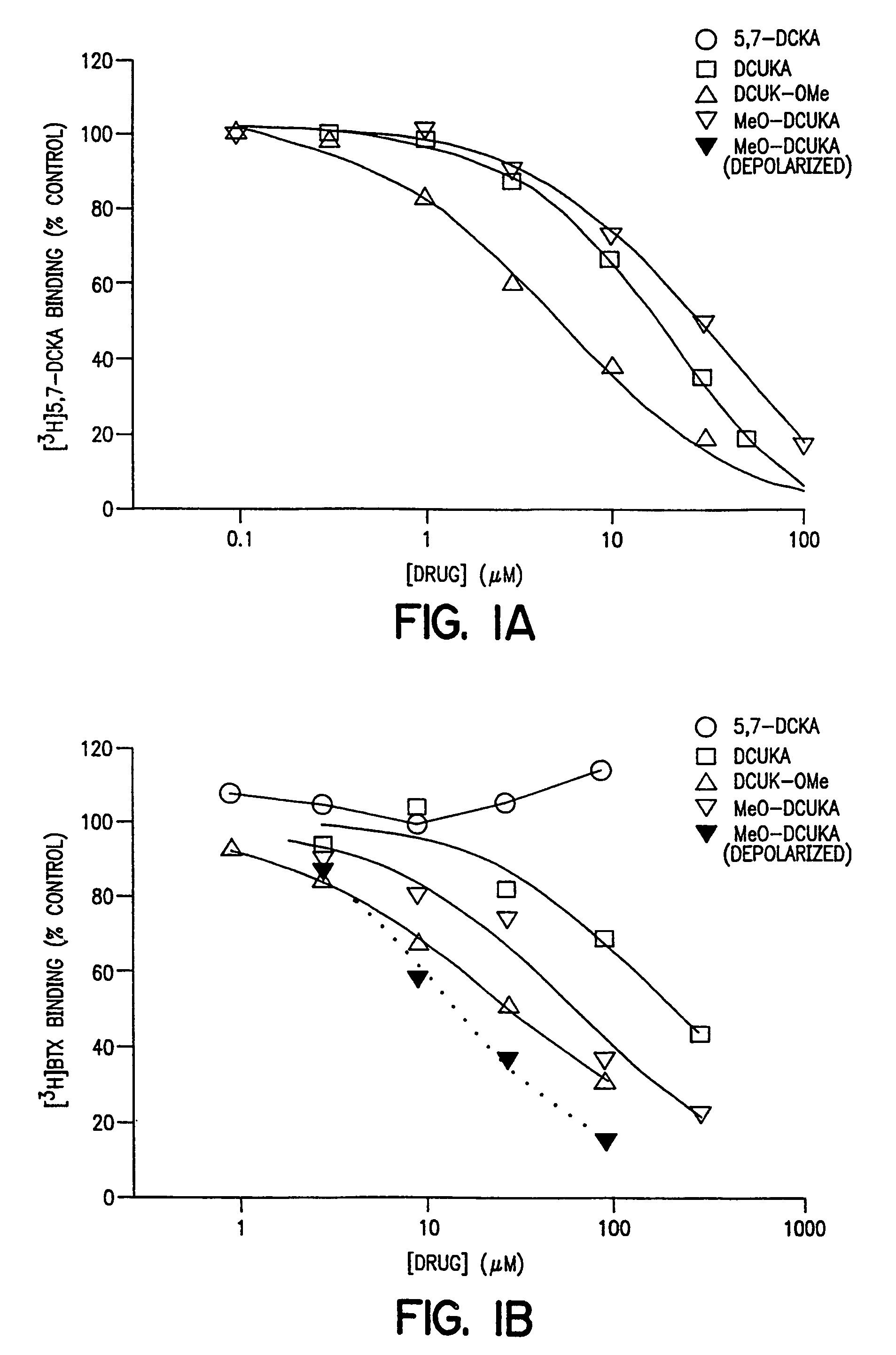
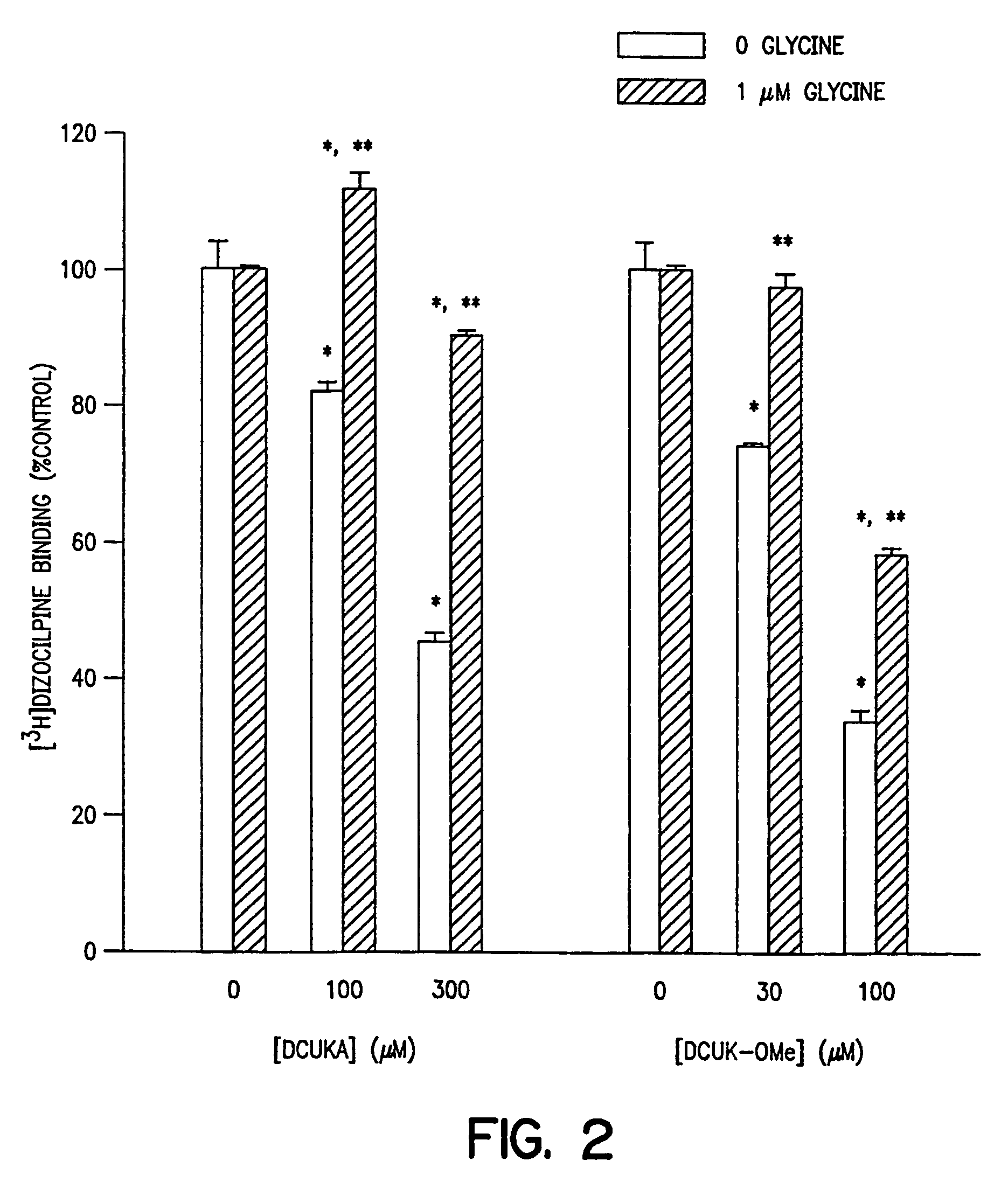
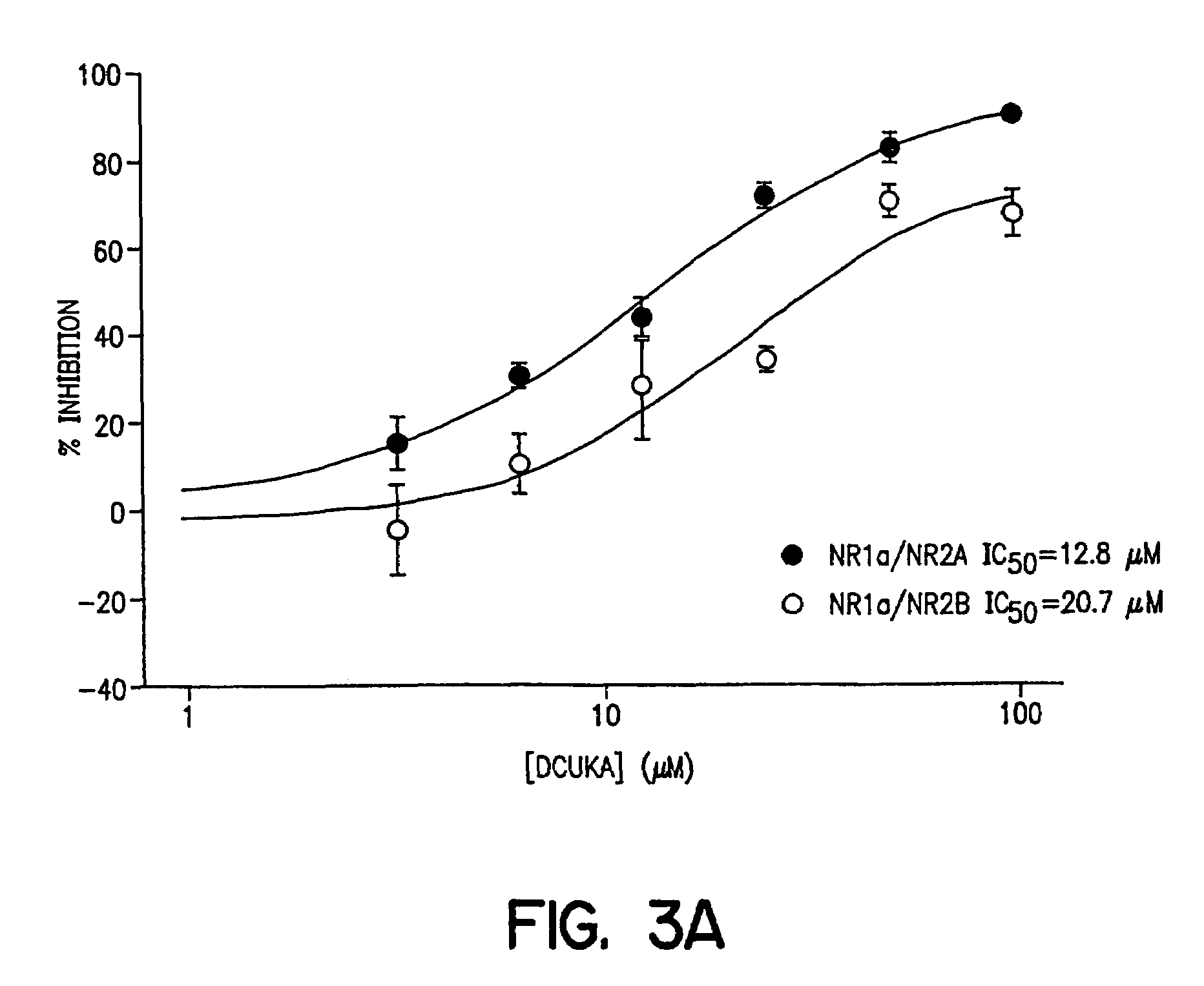
Compounds, composition and method for ameliorating alcohol or drug dependency withdrawal syndromes and withdrawal-induced brain damage are disclosed. In particular, a series of N-substituted-4-uredo-5,7-dihalo-2-carboxy quinoline compounds are disclosed having combined properties as antagonists of voltage-sensitive sodium channels (VSNaC) and as selective competitive antagonists at the strychnine-intensive glycine site of N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptors. The disclosed compounds prevent or reduce the signs and symptoms of neurohyperexcitability and particularly the neurohyperexcitability associated with withdrawal syndrome manifested by patients upon withdrawal from chronic use of dependence inducing agents (e.g. ethanol, barbiturates, opiates etc.). The combined actions of the disclosed compound on VSNaC and NMDA receptors also impart properties to these compounds that are important in preventing and reducing excitotoxic neurodegeneration and reducing anxiety without the undesirable CNS depressant side-effects of agents hitherto employed for these purposes.
Owner:LOHOCLA RES CORP
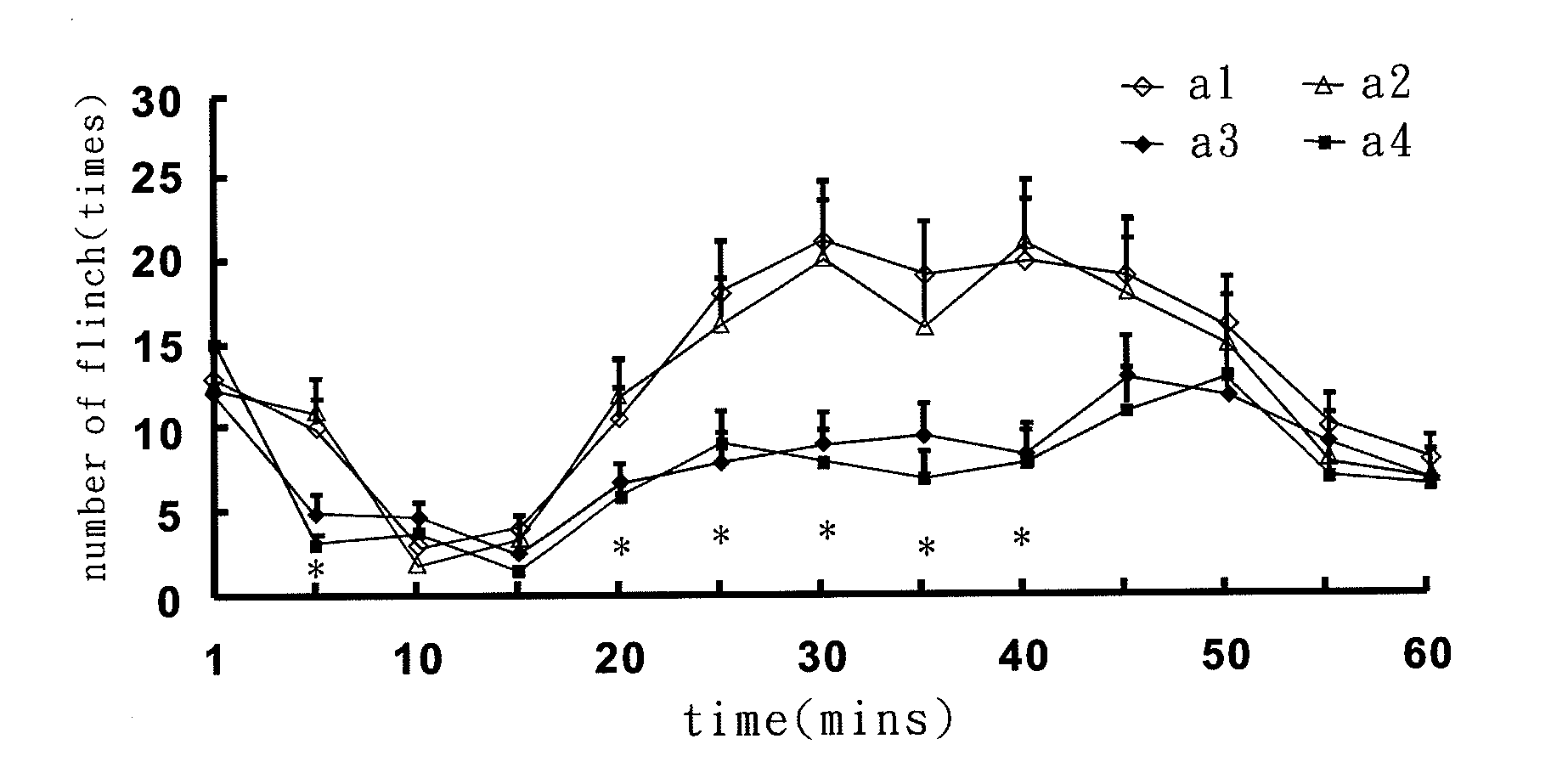
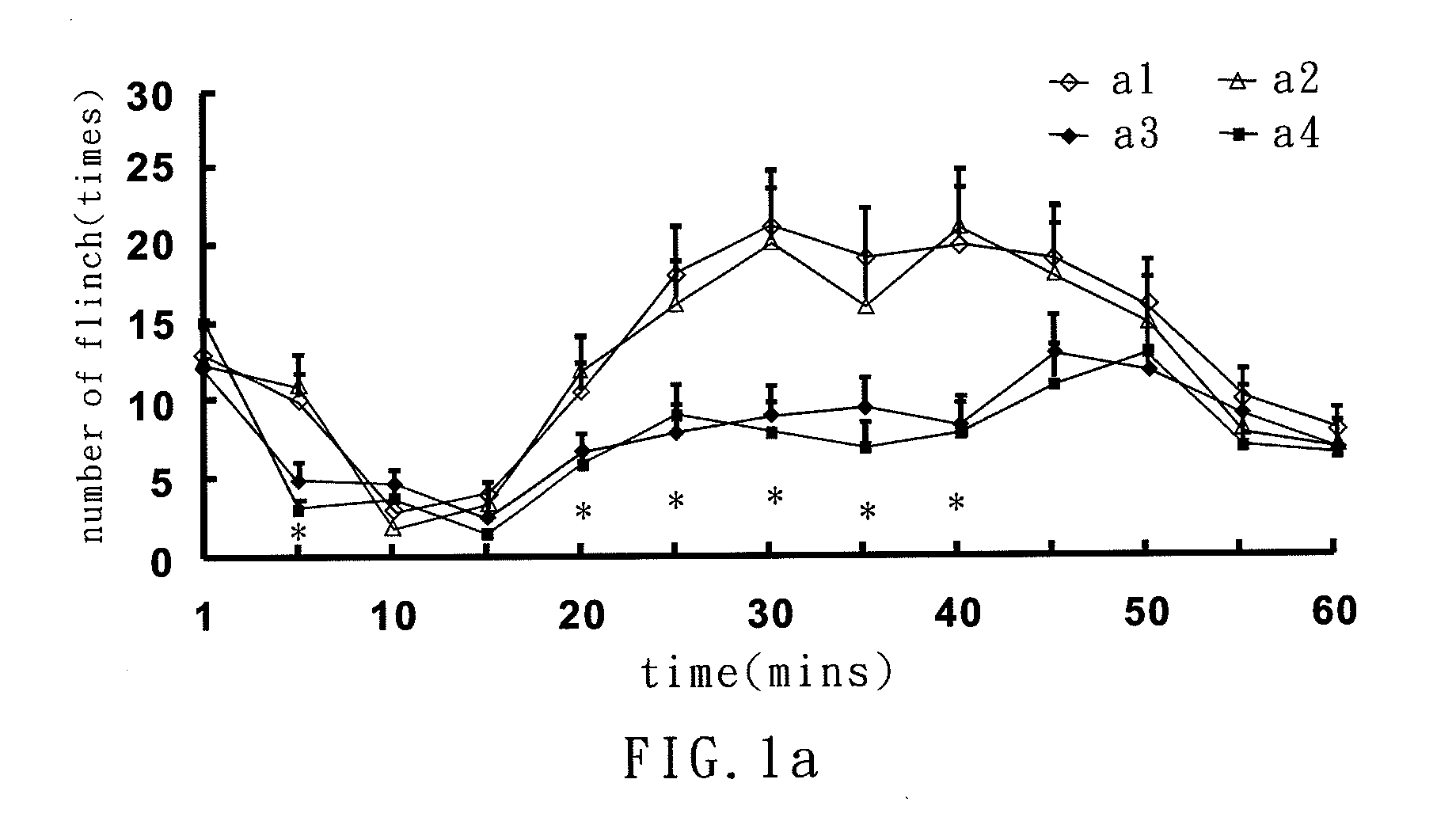
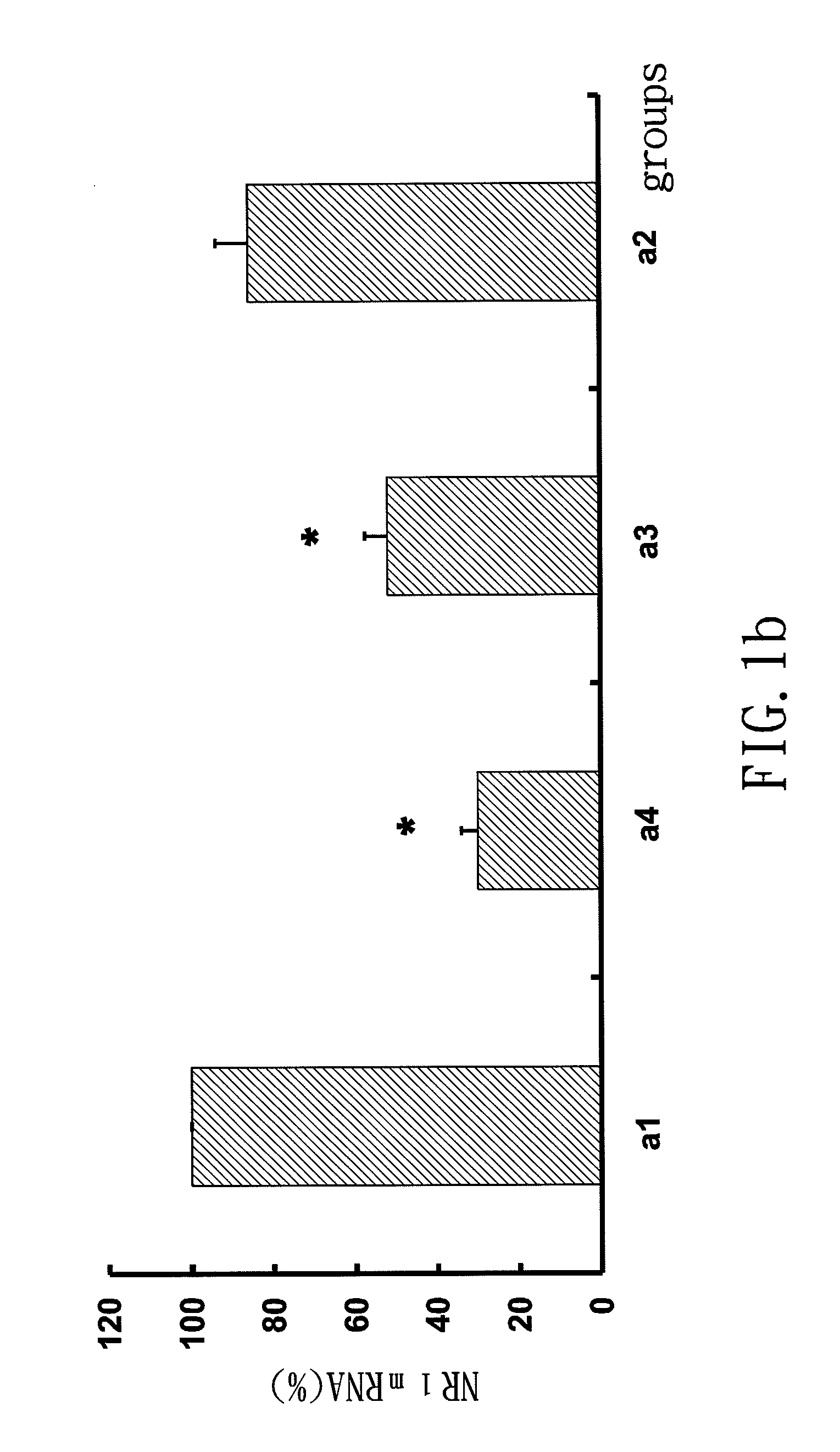
MicroRNA-based short hairpin RNA for gene knockdown of NR1 subunit of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor and its application on pharmaceutics
ActiveUS8575330B2Quick effectFrugal in costSugar derivativesAntipyreticSingle-Stranded RNAGene knockdown
The present invention relates to a microRNA-based short hairpin RNA for gene silencing the genetic expression of NR1 subunit of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor comprises a single strand RNA fragment comprising a first fragment, a second fragment and a connecting fragment, wherein the first fragment and the second fragment are complementary to each other, and are spaced and connected by the connecting fragment, with the connecting fragment being randomly arranged nucleotides, with the first fragment having a Drosha recognized cleavage site, a silencing site and a Dicer recognized cleavage site, with the Drosha recognized cleavage site and the Dicer recognized cleavage site being spaced and connected by the silencing site, with the silencing site encoding homologous nucleotides corresponding to NR1 subunit of subcutaneous N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor.
Owner:I-SHOU UNIVERSITY
Neuroprotective multifunctional compounds and pharmaceutical compositions comprising them
Multifunctional compounds are provided, comprising two or more functional moieties selected from: (i) a moiety that imparts an iron chelator function; (ii) a moiety that imparts a neuroprotective function; (iii) a moiety that imparts combined antiapoptotic, neuroprotective and / or neurorestorative functions; (iv) a moiety that imparts brain MAO inhibition, preferably with little or no MAO inhibition in liver and small intestine; (v) a moiety that imparts cholinesterase inhibitory function; and (vi) a moiety that imparts an N-methyl-D-aspartic acid receptor (NMDAR) inhibition, and pharmaceutically acceptable salts and optical isomers thereof. The multifunctional compounds are useful in the treatment or prevention of diseases, disorders or conditions that can be prevented and / or treated by iron chelation therapy, and / or neuroprotection and / or neurorestoration, and / or apoptosis inhibition and / or MAO inhibition and / or cholinesterase inhibition and / or NMADR inhibition. The present invention encompasses compounds of the formulas I to VI.
Owner:YEDA RES & DEV CO LTD +1
Substituted amide beta secretase inhibitors
Disclosed are novel compounds of the formulaor a pharmaceutically acceptable salt or solvate thereof, whereinR1, R2, R3, R4 and X are as defined in the specification.Also disclosed are pharmaceutical compositions comprising the compounds of formula I.Also disclosed are methods of treating cognitive or neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer's disease.Also disclosed are methods of treating a cognitive or neurodegenerative disease comprising administering to a patient I need of such treatment a combination of at least one compound of formula I and at least one compound selected from the group consisting of β-secretase inhibitors other than those of formula I, HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors, gamma-secretase inhibitors, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory agents, N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor antagonists, cholinesterase inhibitors and anti-amyloid antibodies.
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME LLC
Novel Pharmaceutical Compositions for Treating Acquired Chronic Pain and Associated Dysphoria
InactiveUS20080176873A1Good analgesic effectEffective pain managementBiocideNervous disorderDextrorphanSustained release drug
Chronic pain is alleviated in a mammal suffering there from by administering to the mammal a chronic pain alleviating amount of a nontoxic N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor antagonist such as dextromethorphan, dextrorphan, ketamine or pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, in combination with a μ-opiate analgesic such as tramadol or an analogously acting molecular entity, and a methylxanthine such as caffeine, and optionally in sustained release dosage form.
Owner:TRINITY LAB INC
Novel pharmaceutical compositions for treating acquired chronic pain and associated dysphoria
InactiveUS20090312361A1Reduce concentrationEfficient managementBiocideNervous disorderOpiateMethyl xanthine
Chronic pain is alleviated in a mammal suffering there from by administering to the mammal a chronic pain alleviating amount of a nontoxic N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor antagonist such as dextromethorphan, dextrorphan, ketamine or pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, in combination with a μ-opiate analgesic such as tramadol or an analogously acting molecular entity, and a methylxanthine such as caffeine, and optionally in sustained release dosage form.
Owner:STREEPER ROBERT T +1
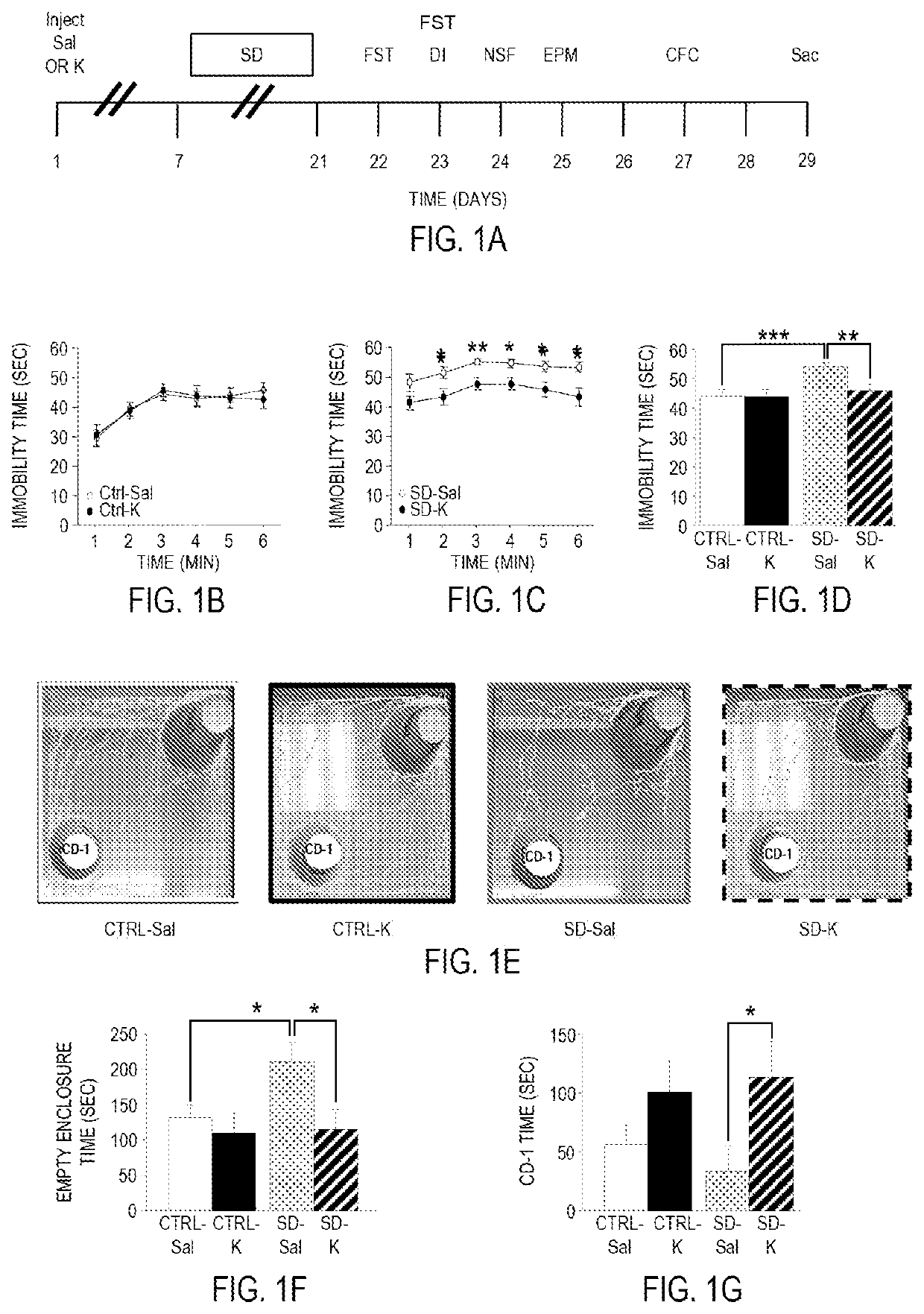
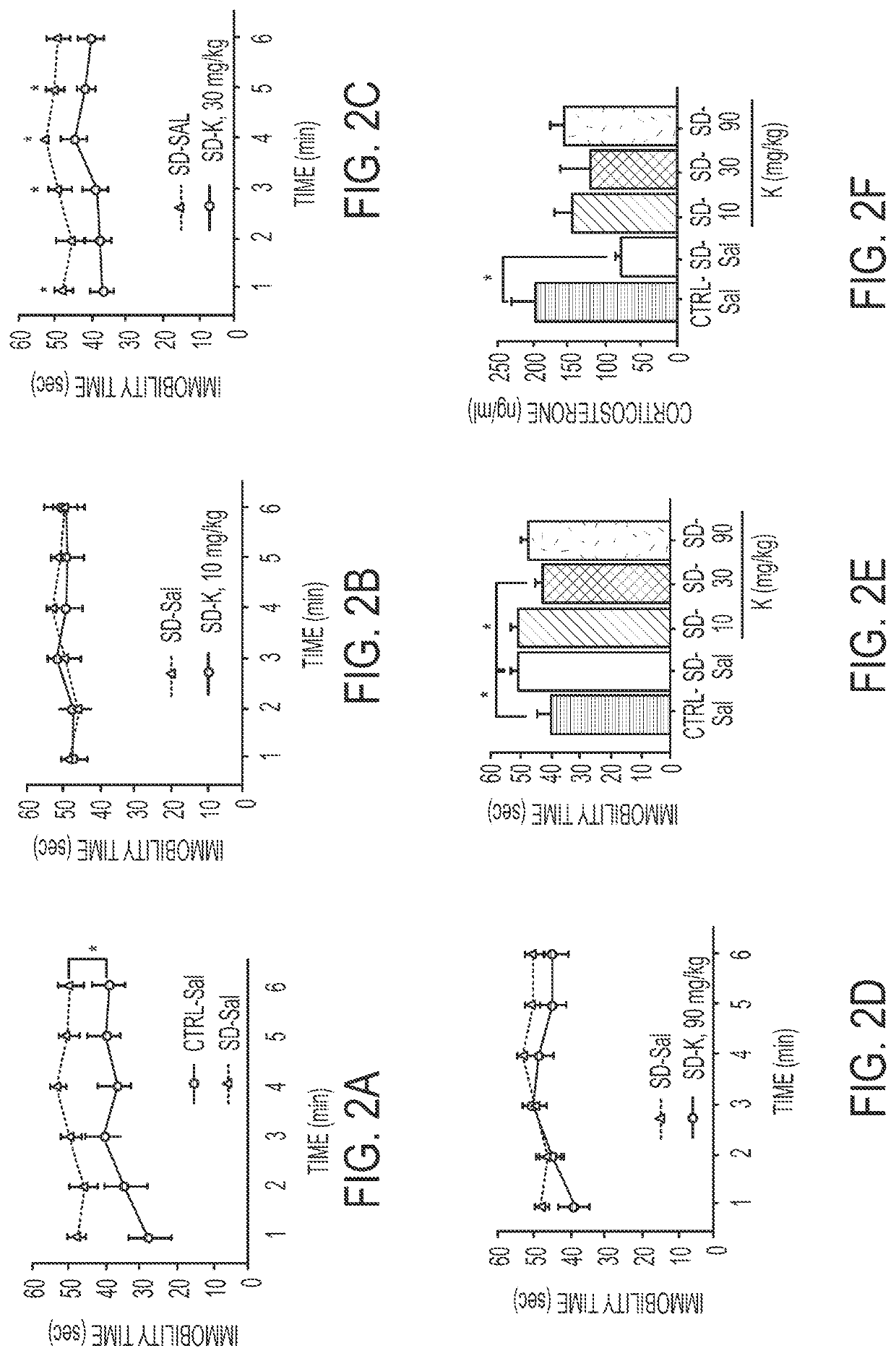
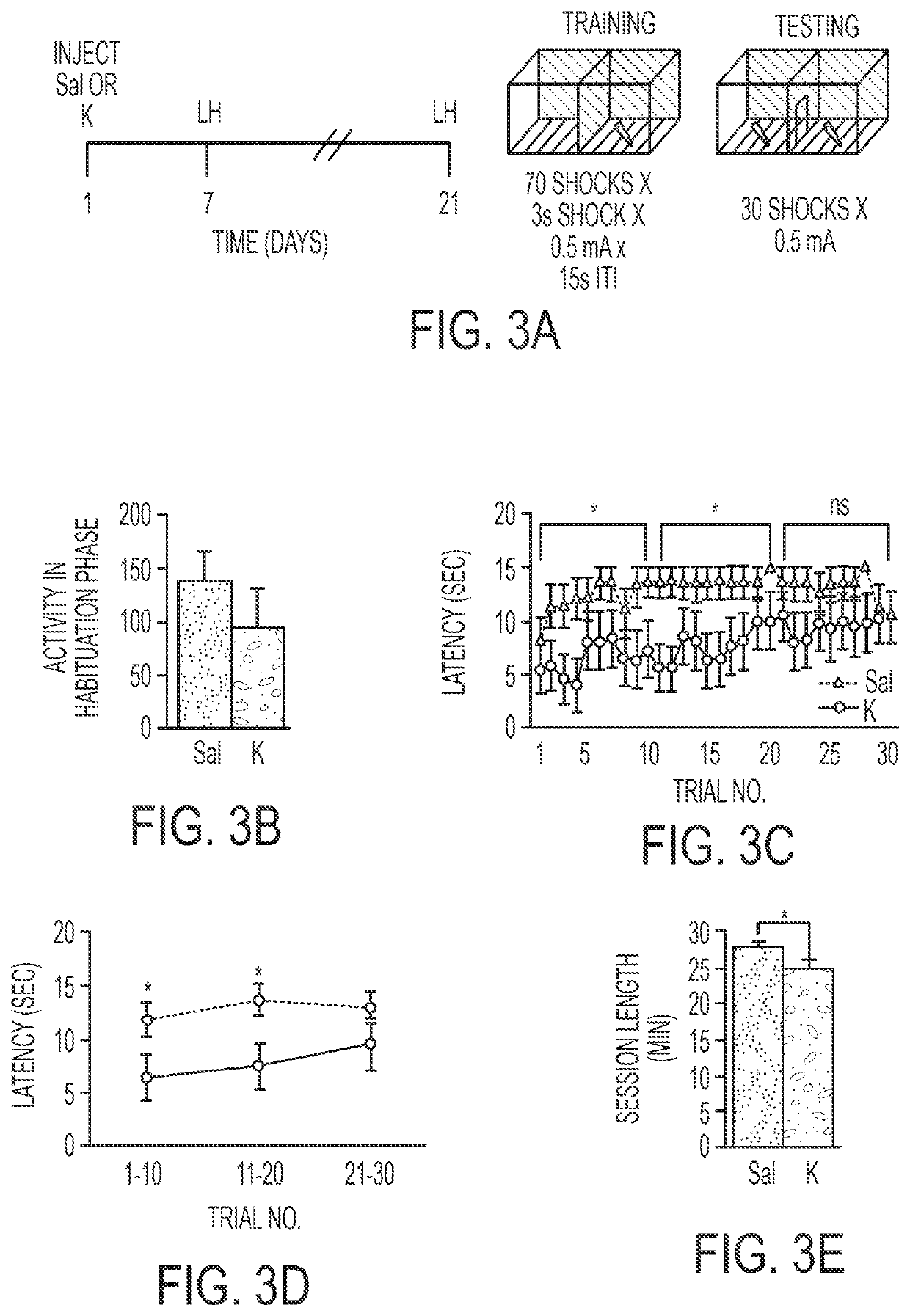
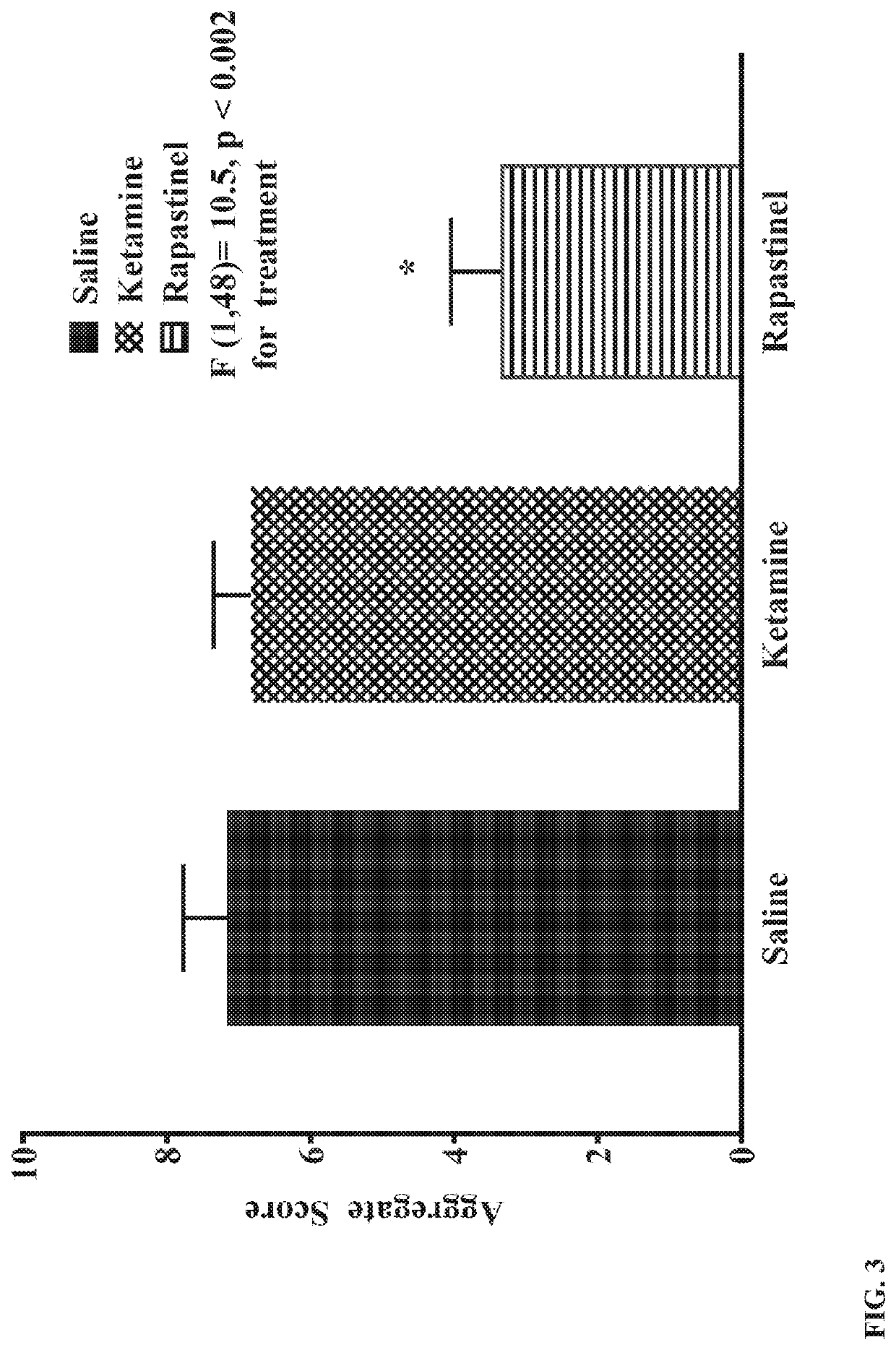
Pharmacological prophylactics against stress-induced affective disorders and their associated symptoms
Methods for prophylactically treating a stress-induced affective disorder or stress-induced psychopathology in a subject are provided. Also provided are methods for inducing and / or enhancing stress resilience in a subject. In certain embodiments, an effective amount, of an antagonist of the glutamate N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor, such as ketamine, or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt or derivative thereof, is administered to a subject prior to a stressor.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
Cyclic amine bace-1 inhibitors having a benzamide substituent
Disclosed are compounds of the formulaor a pharmaceutically acceptable salt or solvate thereof, whereinR1 isR is —C(O)—N(R27)(R28) orand the remaining variables are as defined in the specification.Also disclosed are pharmaceutical compositions comprising the compounds of formula I.Also disclosed are methods of treating cognitive or neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer's disease.Also disclosed are pharmaceutical compositions and methods of treating cognitive or neurodegenerative diseases comprising the compounds of formula I in combination with a β-secretase inhibitor other than those of formula I, an HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor, a gamma-secretase inhibitor, a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory agent, an N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor antagonist, a cholinesterase inhibitor or an anti-amyloid antibody.
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME CORP
Substituted amide beta secretase inhibitors
Disclosed are novel compounds of the formulaor a pharmaceutically acceptable salt or solvate thereof, whereinR1, R2, R3, R4 and X are as defined in the specification.Also disclosed are pharmaceutical compositions comprising the compounds of formula I.Also disclosed are methods of treating cognitive or neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer's disease.Also disclosed are methods of treating a cognitive or neurodegenerative disease comprising administering to a patient I need of such treatment a combination of at least one compound of formula I and at least one compound selected from the group consisting of β-secretase inhibitors other than those of formula I, HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors, gamma-secretase inhibitors, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory agents, N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor antagonists, cholinesterase inhibitors and anti-amyloid antibodies.
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME LLC
Small interfering RNA for gene knockdown of the subcutaneous n-methyl-d-aspartate receptor nr1 subunit, and it's application on pharmaceutics
ActiveUS20110263676A1Avoid effectHigh efficiencyOrganic active ingredientsSugar derivativesBurning PainN-Methyl-D-aspartic acid
A small interfering RNA for gene knockdown of the N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor NR1 subunit comprises 21 to 25 ribonucleic acids, which are homologous to the RNA sequence of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor NR1 subunit. A method of using the small interfering RNA, applying the small interfering RNA on subcutaneous tissues temporary interfere with the genetic expression of the NMDA receptor NR1 subunit in hypoderm. A use of the small interfering RNA on pharmaceutics, applying the small interfering RNA manufacture into new analgesic drugs for moderating the inflammatory pain or intolerable chronic pain, especially on clinical chronic pain and burn pain patients. An analgesic drug for skin inflammatory pain comprising: the small interfering RNA and a siRNA acceptable vehicle.
Owner:I-SHOU UNIVERSITY
Composition and method for neuroprotection against excitotoxic injury
InactiveUS20120115943A1Increased locomotor activityDecreased locomotor activityBiocideNervous disorderCombined treatmentN-methyl-D-aspartate Receptor Antagonists
The present invention discloses the combined treatment of memantine (N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor antagonist) and tea polyphenol (an antioxidant and anti-inflammatory agent) is more effective (synergistic) in neuroprotection than either memantine or tea polyphenol alone in mouse excitotoxic injury. These findings provide useful information about the potential application of memantine and tea polyphenols in preventing or treating clinical excitotoxic injury such as brain trauma, brain ischemia, epilepsy, and Alzheimer's disease.
Owner:NAT TAIWAN UNIV
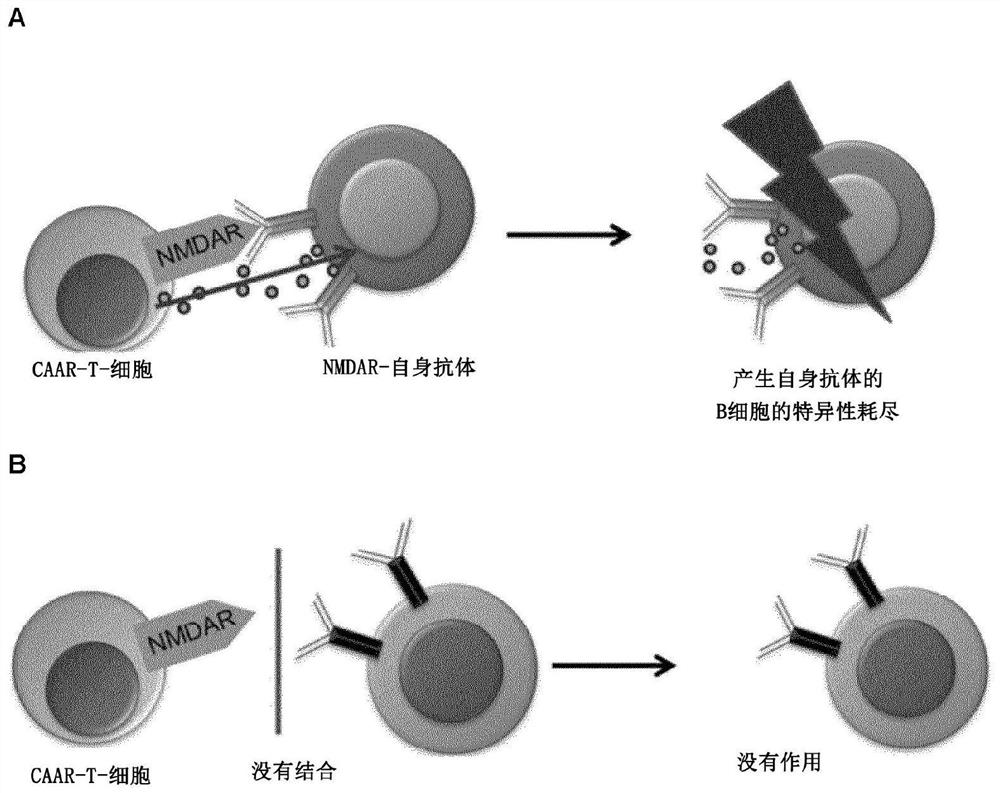
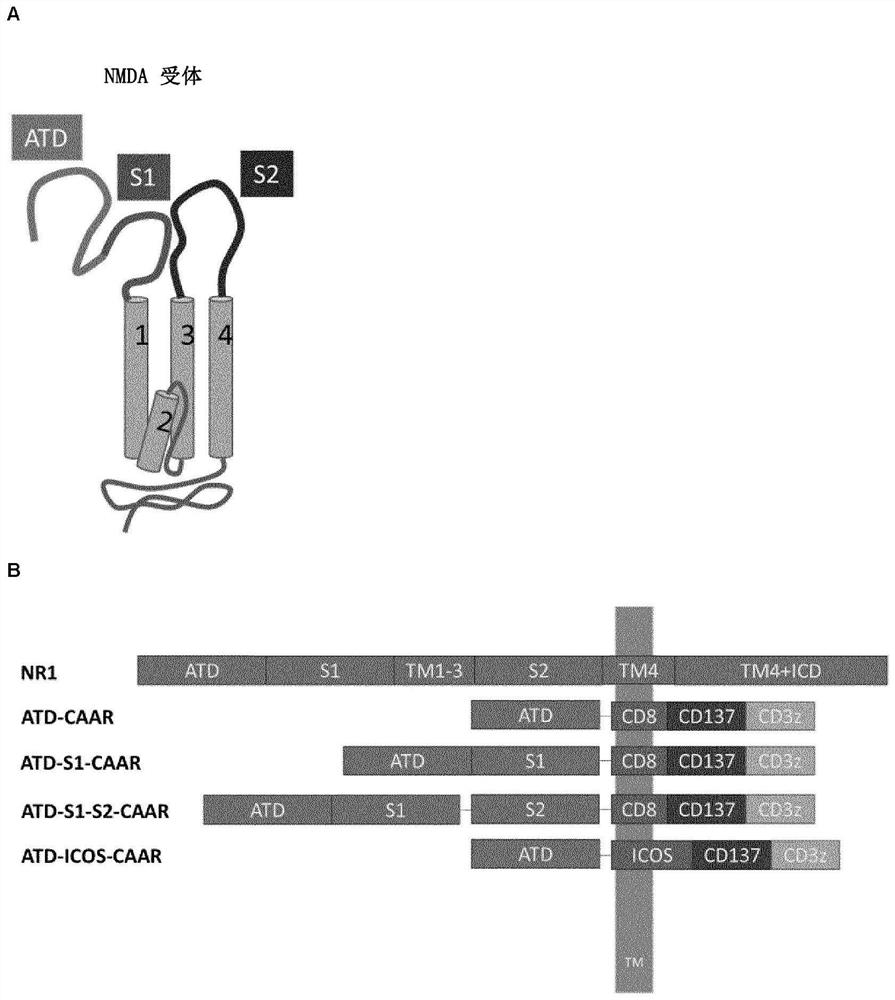
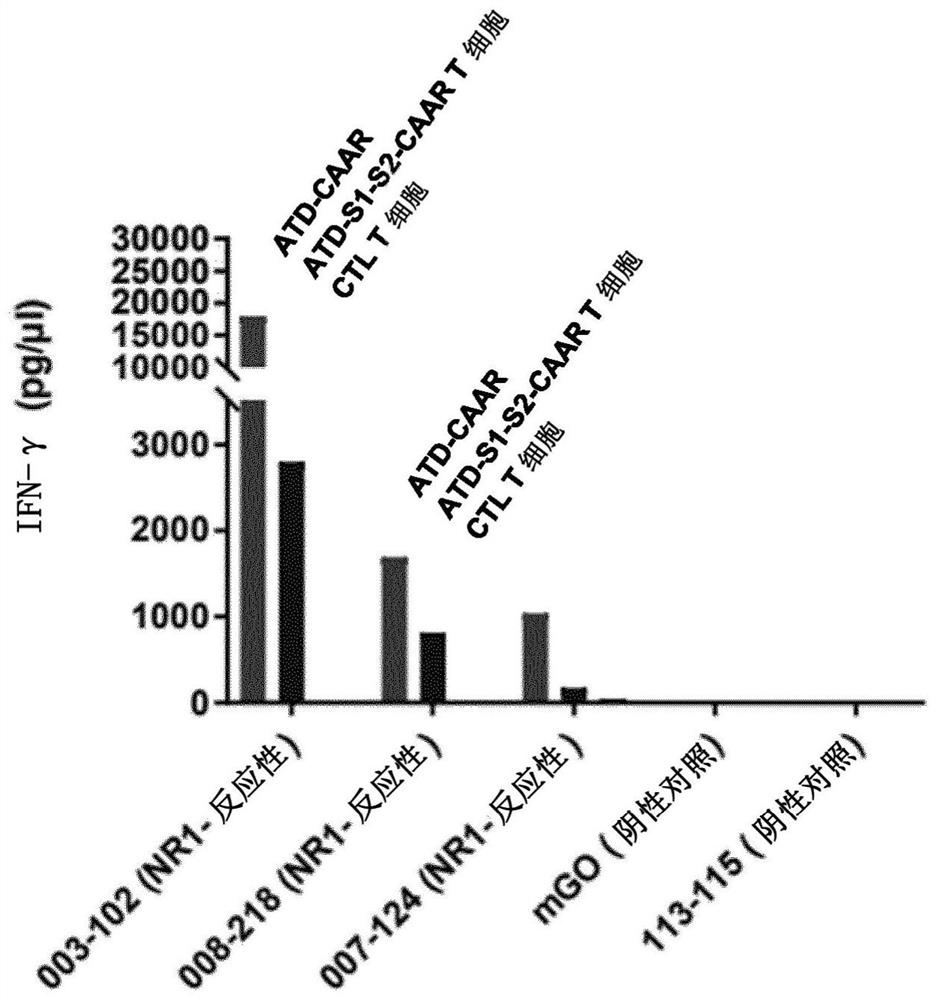
Chimeric autoantibody receptor (CAAR) that binds autoantibodies targeting the central nervous system in neurological autoimmune disease
PendingCN114008204APrevent or significantly reduce the risk of clinical relapseNo or reduced immunosuppressionOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderAutoimmune conditionNmdar encephalitis
The invention relates to a chimeric autoantibody receptor (CAAR) that enables targeting of an immune cell to autoantibody producing B cells. The CAAR comprises an autoantigen or fragment thereof that is bound by autoantibodies associated with a neurological autoimmune disease primarily targeting the central nervous system. The invention relates to a nucleic acid molecule encoding a chimeric autoantibody receptor (CAAR), the nucleic acid molecule comprising a sequence encoding an autoantigen or fragment thereof that is bound by autoantibodies associated with a neurological autoimmune disease primarily targeting the central nervous system, a sequence encoding a transmembrane domain, and a sequence encoding an intracellular signaling domain. In one embodiment, the autoantigen encoded by the nucleic acid sequence comprises or consists of an N- methyl-D-aspartate receptor (NMDAR), or one or more NMDAR fragments. The invention further relates to the chimeric autoantibody receptor (CAAR) protein of the invention, a vector comprising a nucleic acid molecule encoding a chimeric autoantibody receptor (CAAR) of the invention, a genetically modified immune cell comprising the nucleic acid molecule encoding the CAAR and the use of the immune cell in the treatment or prevention of a neurological autoimmune disease primarily targeting the central nervous system, such as an autoimmune encephalopathy or encephalomyelopathy, preferably anti-NMDAR encephalitis.
Owner:德国神经退行性疾病中心 +1
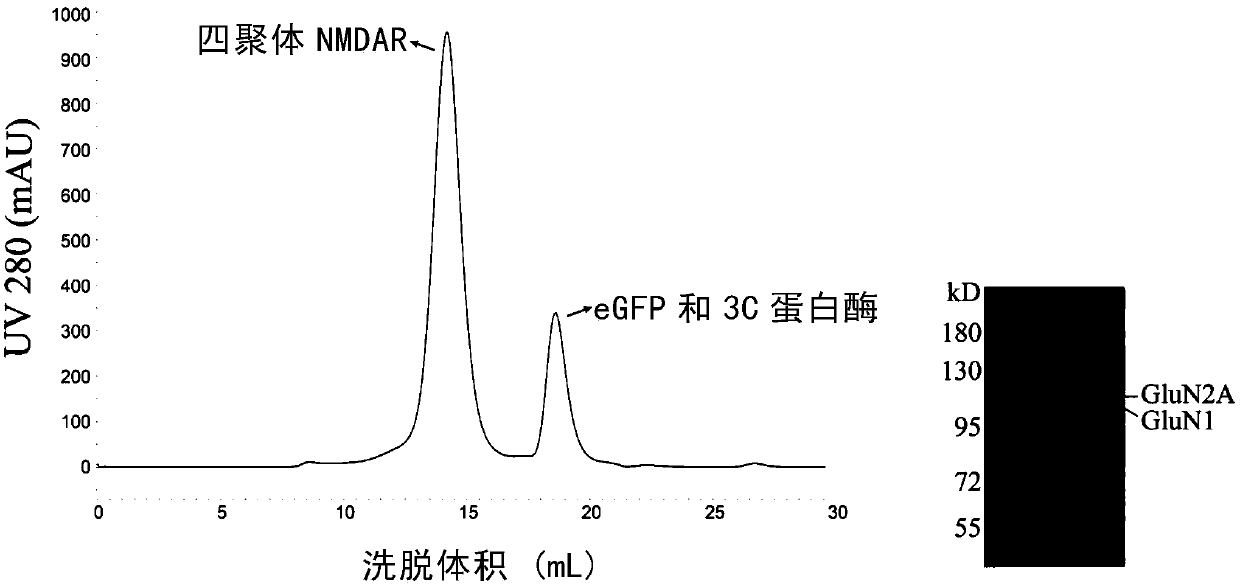
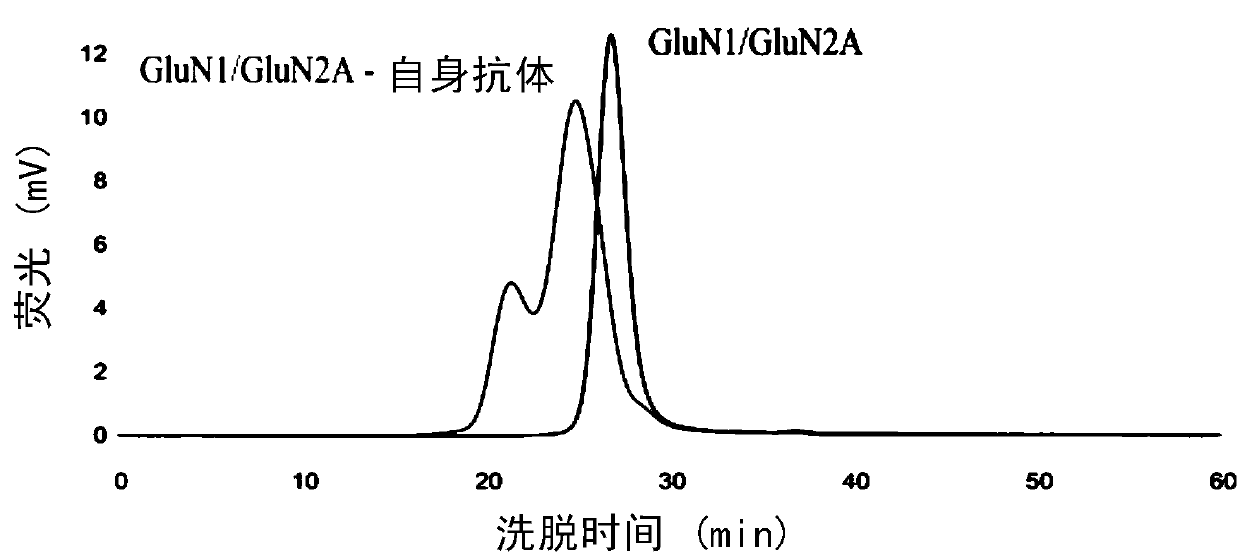
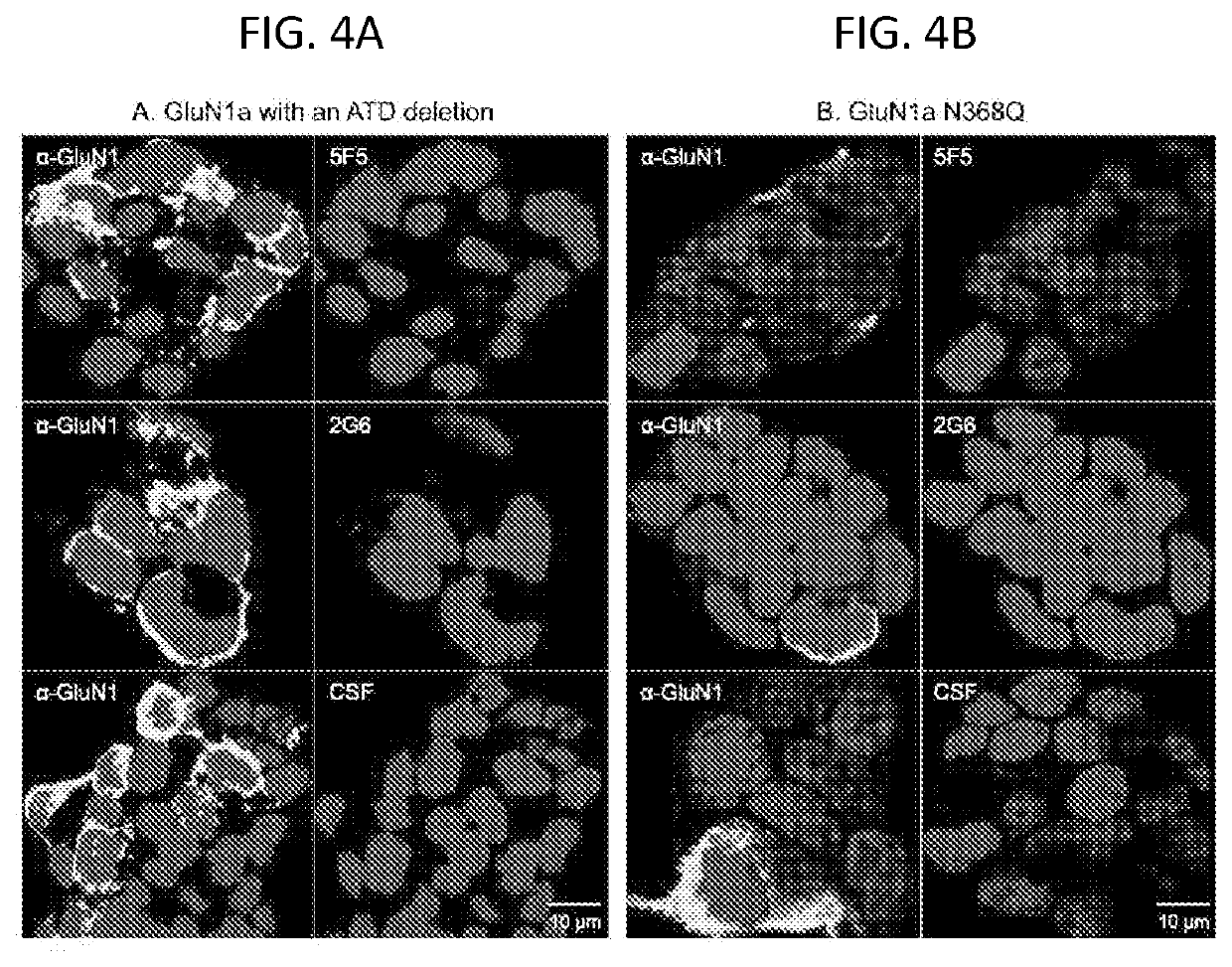
Expression and applications of GluN1/GluN2A tetramer of human N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor
ActiveCN111320684ACell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsBiological testingAntigenReceptor
The invention relates to expression and applications of GluN1 / GluN2A tetramer of a human N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor. It is revealed that some loci at the transmembrane and extracellular domains ofsubunits GluN1 and GluN2A of the N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor are closely related to the stability of recombinant expression of the receptor and the antigen-antibody binding activity. On the basis ofperforming mutation, recombinant expression can be performed by only obtaining the transmembrane and extracellular domains of a mutant, so that an N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor mutant with stable expression and a polymer form of an ideal spatial structure can be obtained. Therefore, the problems of instability of the type of protein and poor antibody binding capacity can be solved.
Owner:CENT FOR EXCELLENCE IN BRAIN SCI & INTELLIGENCE TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
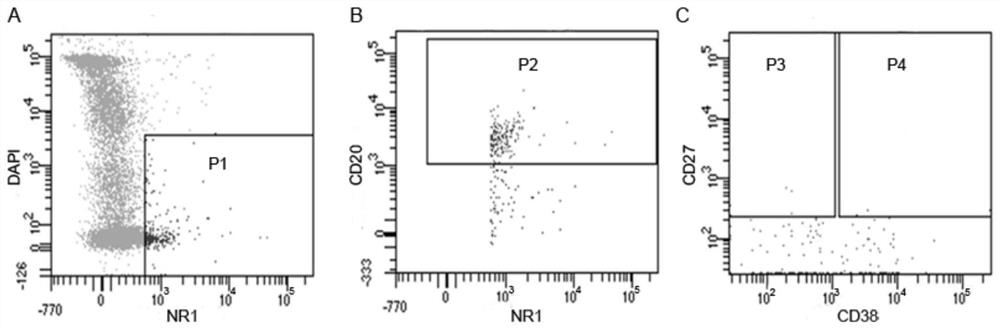
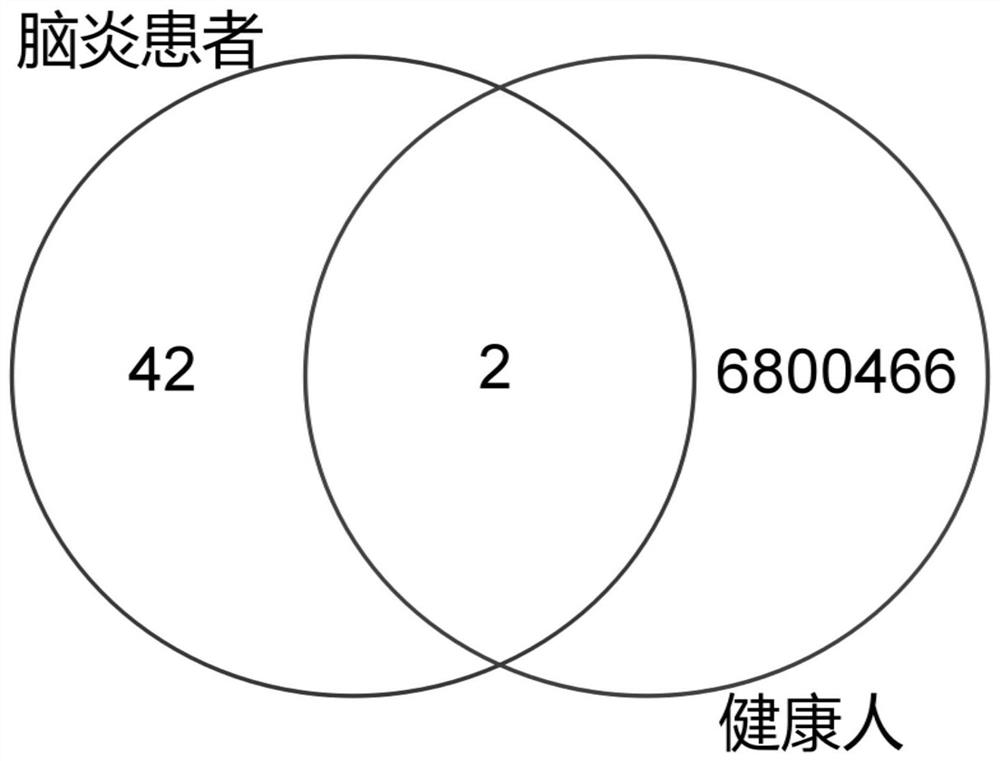
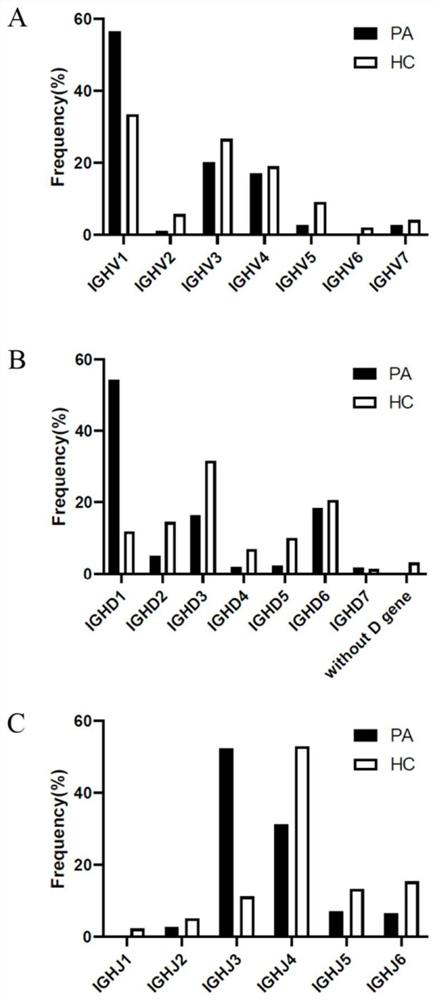
Method for acquiring B cell antibody gene for resisting N-methyl-D-aspartic acid receptor encephalitis and immune repertoire research of B cell antibody gene
PendingCN111808195AReduce distractionsImprove capture efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsAspartic acid receptorsDisease
The invention belongs to the technical field of gene engineering, and particularly relates to a method for acquiring single cell of B cell surface receptor (BCR) or an antibody gene of an anti-N-methyl-D-aspartic acid receptor encephalitis patient, and further discloses immune repertoire research of B cells of the anti-N-methyl-D-aspartic acid receptor encephalitis patient. According to a method for amplifying a variable region and a constant region of the single B cell humanized antibody gene and a method based on a single B cell reverse transcription and BCR amplification, the characteristicof antigen-antibody specific binding is used for the first time, a positive B cell combined with a pathogenic antigen NR1 protein subunit for resisting N-methyl-D-aspartic acid receptor encephalitisis screened out in advance by using a flow cytometry, the interference of other non-positive BCR / antibody information is reduced, the unnecessary workload is reduced, the correlation between the finally obtained antibody information and the disease is stronger, the efficiency of capturing the single-cell B cell antibody sequence is higher, the experiment steps are simpler and more convenient, andthe operability is stronger.
Owner:INST OF PSYCHOLOGY CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Dendrobium alkaloid derivatives as well as preparation method and medical application thereof
The invention relates to the field of medicinal chemistry, in particular to dendrobium alkaloid derivatives (I); pharmacodynamic experiments prove that the compounds provided by the invention has protection activity for neuron injury caused by N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor (NMDA), thus being used for preventing and treating neuron injury diseases. (The structural formula of the dendrobium alkaloidderivatives (I) is described in the description.).
Owner:ANHUI UNIVERSITY OF TRADITIONAL CHINESE MEDICINE +2
Neuroprotective multifunctional compounds and pharmaceutical compositions comprising them
Multifunctional compounds are provided, comprising two or more functional moieties selected from: (i) a moiety that imparts an iron chelator function; (ii) a moiety that imparts a neuroprotective function; (iii) a moiety that imparts combined antiapoptotic, neuroprotective and / or neurorestorative functions; (iv) a moiety that imparts brain MAO inhibition, preferably with little or no MAO inhibition in liver and small intestine; (v) a moiety that imparts cholinesterase inhibitory function; and (vi) a moiety that imparts an N-methyl-D-aspartic acid receptor (NMDAR) inhibition, and pharmaceutically acceptable salts and optical isomers thereof. The multifunctional compounds are useful in the treatment or prevention of diseases, disorders or conditions that can be prevented and / or treated by iron chelation therapy, and / or neuroprotection and / or neurorestoration, and / or apoptosis inhibition and / or MAO inhibition and / or cholinesterase inhibition and / or NMADR inhibition. The present invention encompasses compounds of the formulas I to VI.
Owner:YEDA RES & DEV CO LTD +1
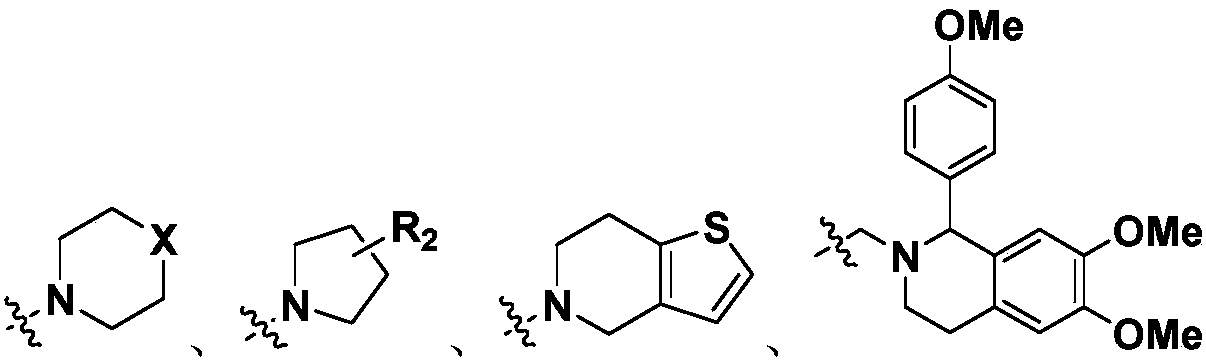
Quinoxalinedione derivatives, their preparation and use
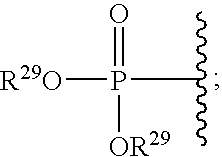
A compound having the formulaor a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof whereinR is hydrogen or hydroxy;R<1 >is hydrogen,alkyl,arylalkyl,(CH2)nOH, or(CH2)nNR<7>R<8>;R<5 >and R<6 >are each independentlyhydrogen,halogen,NO2,CN,CF3,SO2NR<7>R<8>,PO3R<9>R<10>,alkyl,alkenyl,alkynyl,(CH2)nCONR<7>R<8>,(CH2)nCO2R<10>,NHCOR<11>,A is a ring formed by the following:a-NR<12>-CHR<13>-CHR<14>-b,a-CHR<13>-CHR<14>-NR<12>-b,a-CHR<13>-NR<12>-CHR<14>-b,a-CHR<14>-CH2-NR<12>-CHR<13>-b,a-CHR<13>-NR<12>-CH2-CHR<14>-b,a-CH2-CH2-CHR<13>-NR<12>-b,a-NR<12>-CHR<13>-CHR<12>-CH2-CH2-b,a-CH2-CH2-NR<12>-CH2-CH2-b,a-CH2-CH2-CH2NR<12>-CH2-b,a-CH2-NR<12>-CH2-CH2-ba-CH2-CH2-CH2-CH2-NR<12>-b,a-NR<12>-CH2-CH2-CH2-CH2-b,The compounds are useful in the treatment of disorders responsive to the blockade of glutamic and aspartic acid receptors.
Owner:NEUROSEARCH AS
Analgesic formulations and methods for reduced postoperative nausea and vomiting and enhanced postoperative pain relief
A multimodal anti-emetic anesthetic / analgesic formulation for pain control not limited to postoperative pain control is described herein. The opioid-free / sparing anesthetic / analgesic formulation comprises a local anesthetic, an N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor antagonist, and a cyclooxygenase (COX) inhibitor such as Bupivacaine Hydrochloride, Ketamine Hydrochloride, and Ketorolac Tromethamine, which is effective to significantly reduce postoperative nausea and vomiting and enhance postoperative pain relief as compared to existing prior art anesthetics / analgesics. The formulation is administered to a mammal in need of anesthesia / analgesia and can be used as a preemptive and preventative multimodal analgesic. The formulation may have a buffer to enhance its shelf life and improve pharmacokinetics. The formulation may further comprise an alpha agonist, a steroid, a Transient Receptor Potential Channel agonist or antagonist, a beta-lactam antibiotic, a protein kinase inhibitor, a competitive or non-competitive glycine or glutamate antagonist, a glutamate or glycine inhibitor, a cyclooxygenase 3 inhibitor, or combinations thereof.
Owner:HUTCHISON HEALTH LLC
Assay for detection of transient intracellular CA2+
InactiveUS8304198B2Biological material analysisTransferasesNR1 NMDA receptorN methyl D aspartate receptors
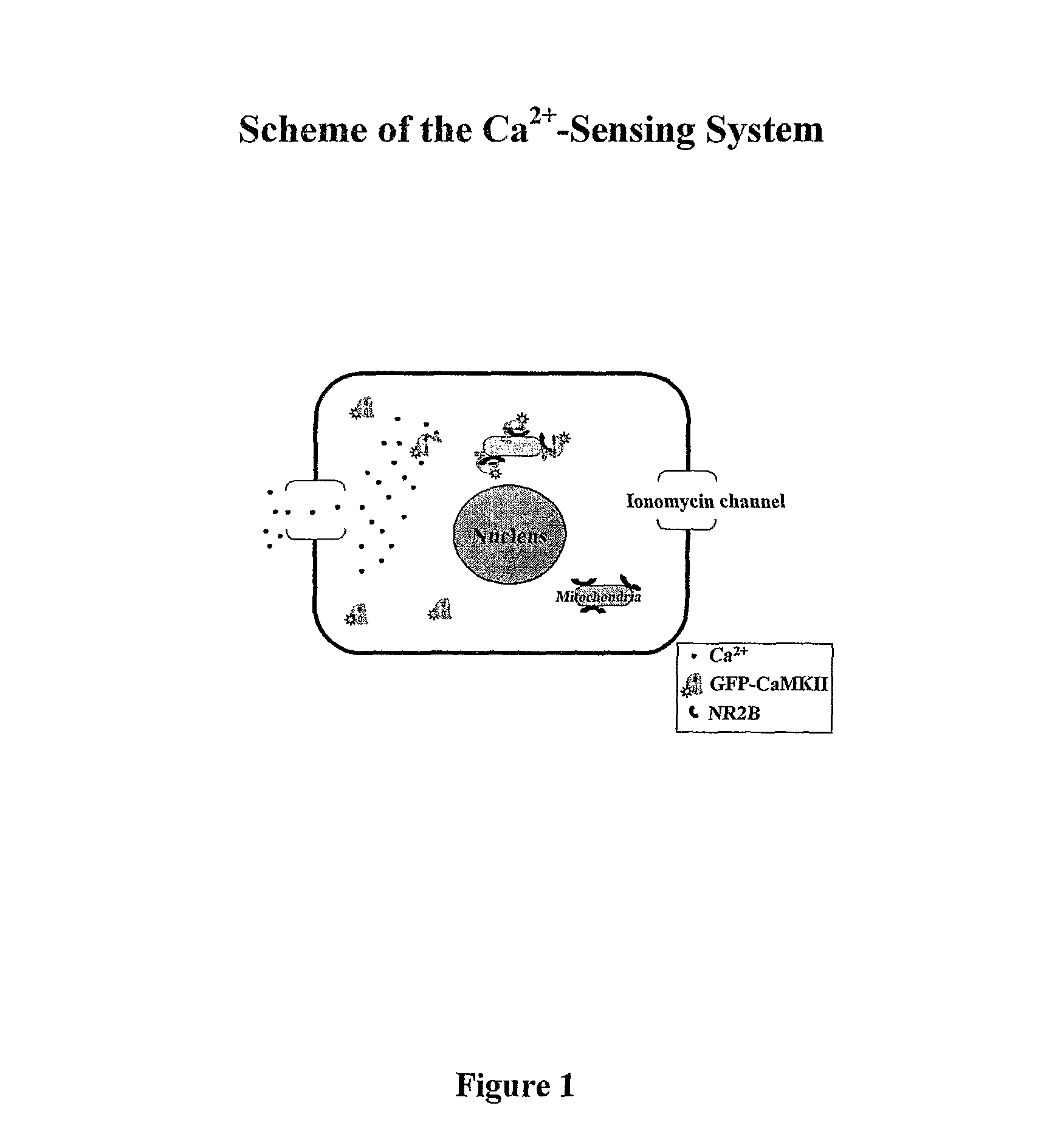
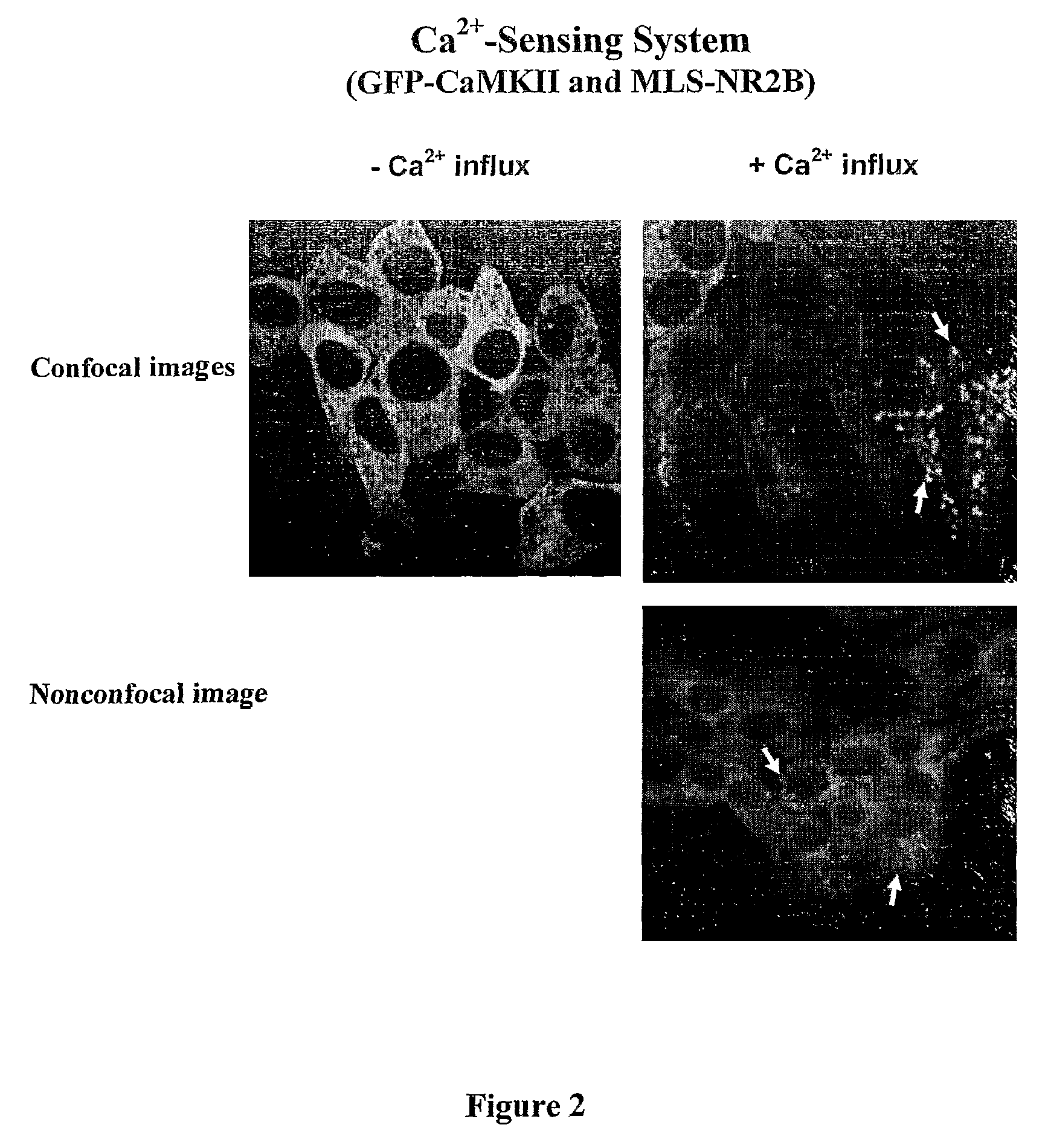
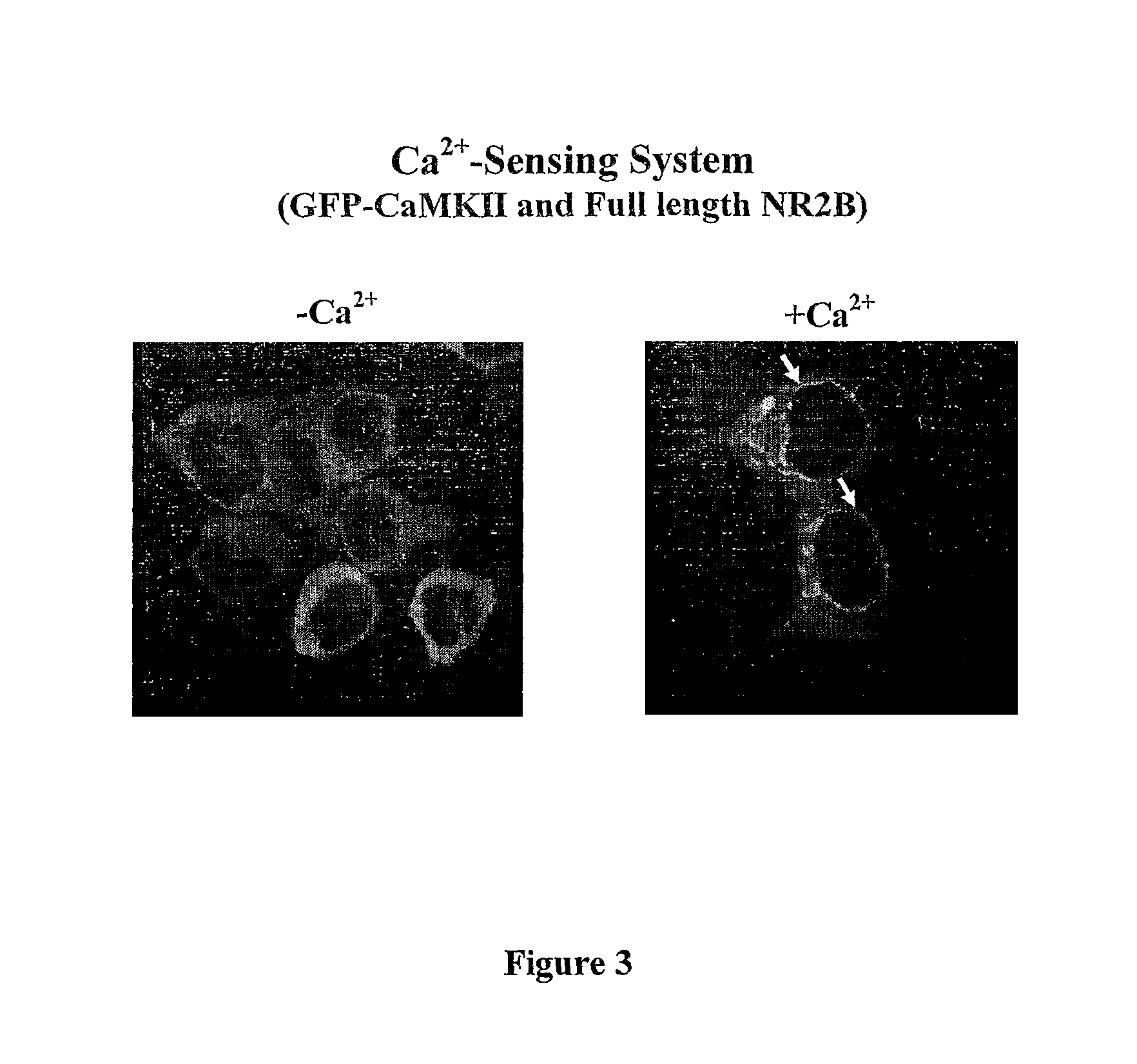
This invention relates to a simple end point assay for detection of transient intracellular Ca2+ with broad applicability to many Ca2+ channel proteins comprising, Generation of expression constructs for the fusion proteins having the Ca2+ / calmodulin dependent protein kinase II (CaMKII) phosphorylation sites of NR2A or NR2B subunits of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor (NMDAR) or the voltage gated potassium channel of Drosophila (Eag) or any protein sequence which binds to the T-site of CaMKII similar to NR2B, conjugated to mitochondrial localizing signal sequence, or mutants of these sequences as described herein. Generation of mammalian expression constructs of α-CaMKll as a chimera with green fluorescent protein (GFP-α-CaMKII) or its mutants as described herein. Site-Directed mutagenesis, Transfection, Ca2+ stimulation, imaging and quantification of the number of cells with Ca2+-dependent signal, wherein, NMDA receptor activity assay, TRPVI receptor activity assay, GluR4 receptor activity assay are performed to detect the activity Of Ca2+ channel proteins.
Owner:RAJIV GANDHI CENT FOR BIOTECH +1
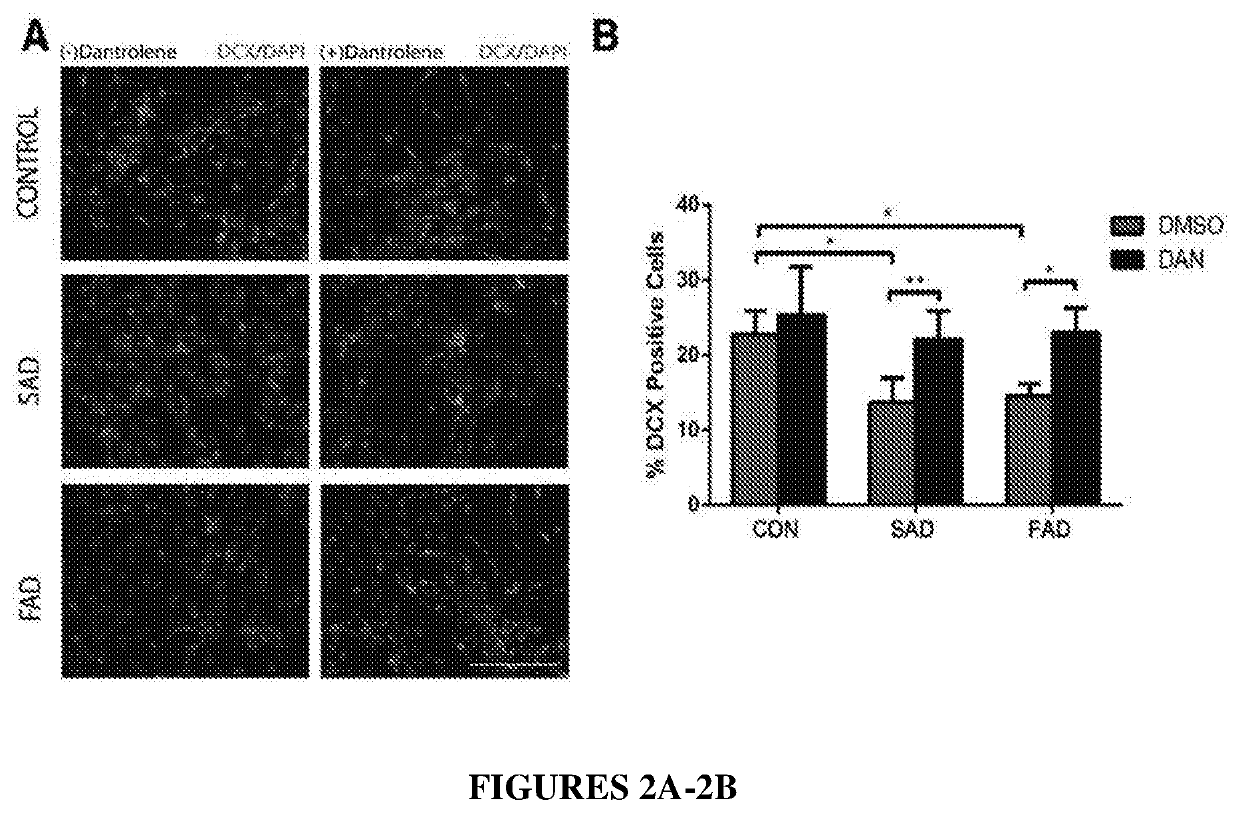
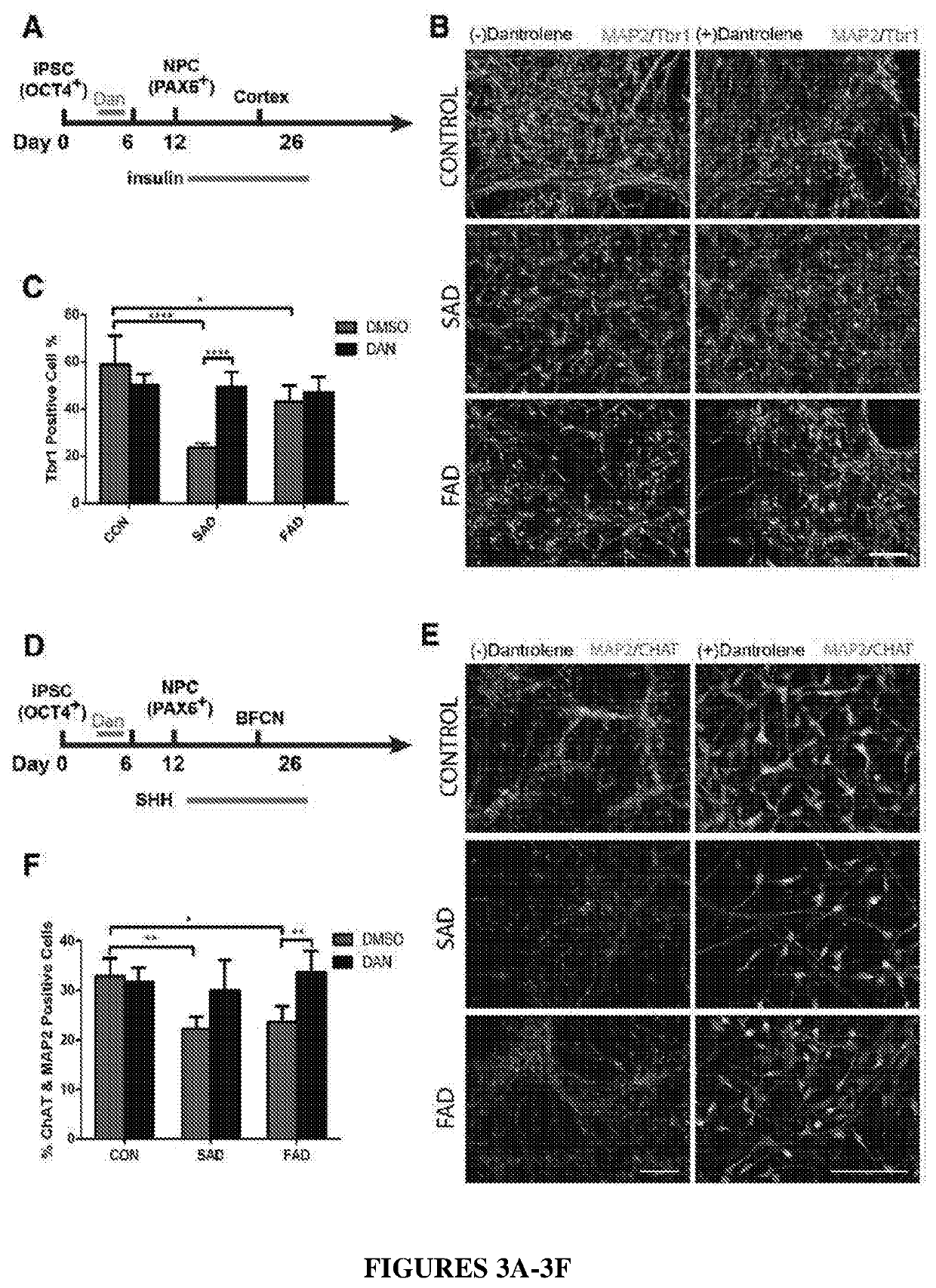
Ntranasal dantrolene administration for treatment of alzheimer's disease
PendingUS20220354827A1Reduce releaseImproving and slowing declineOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderRyanodine receptorSynaptogenesis
Methods for inhibiting impaired neurogenesis and / or synaptogenesis in neurons in a subject with or suspected of having Alzheimer's Disease (AD), methods for improving and / or slowing the decline of cognitive function after onset of neuropathology and cognitive dysfunction, which neuropathology and cognitive dysfunction are caused by AD, methods for improving and / or slowing the decline of memory before onset of symptoms of AD, methods for increasing concentration and duration of dantrolene in the brain, and methods for improving and / or slowing the decline of memory after onset of symptoms of AD, the methods comprising intranasally administering to a subject in need thereof an amount of a pharmaceutical composition comprising dantrolene effective to inhibit over-activation of N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMVDA) receptor and / or ryanodine receptor (RyR). Methods further comprise administering a therapeutically effective amount of a glutamate receptor antagonist to the subject.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
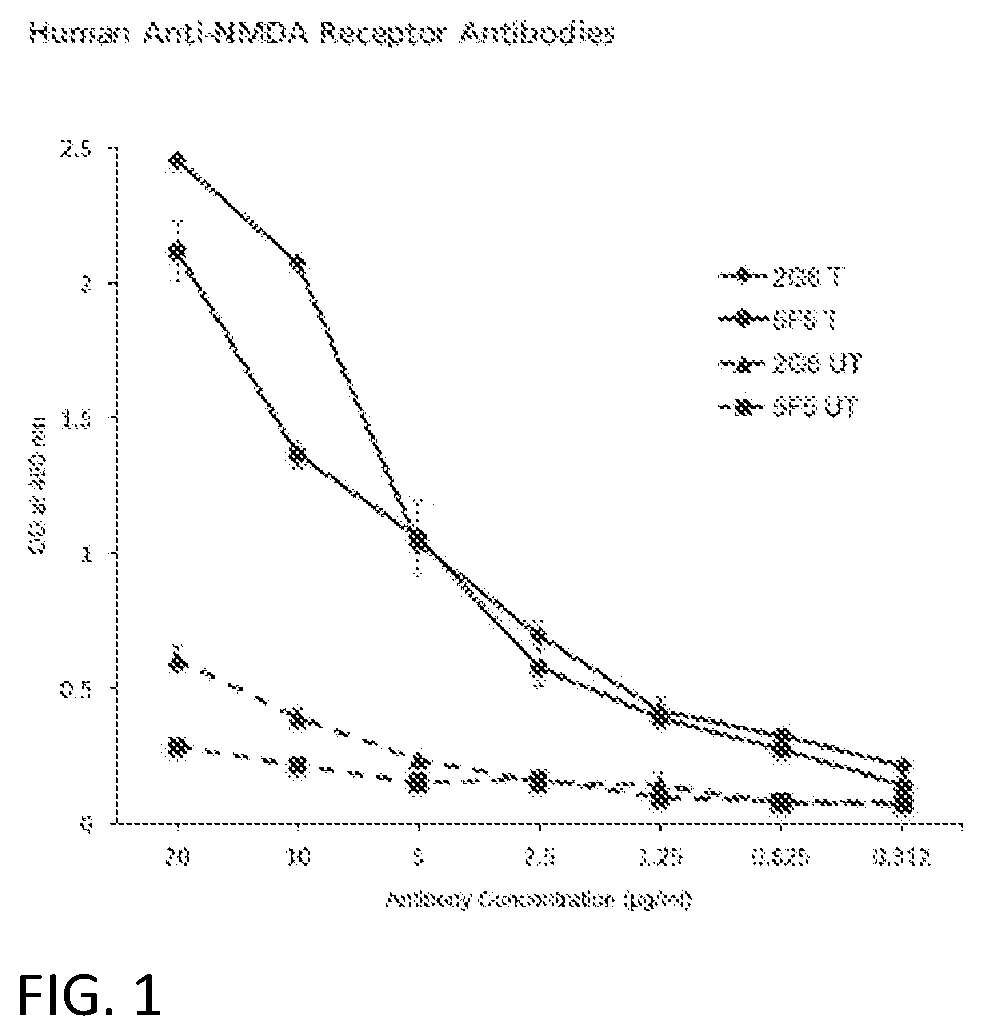
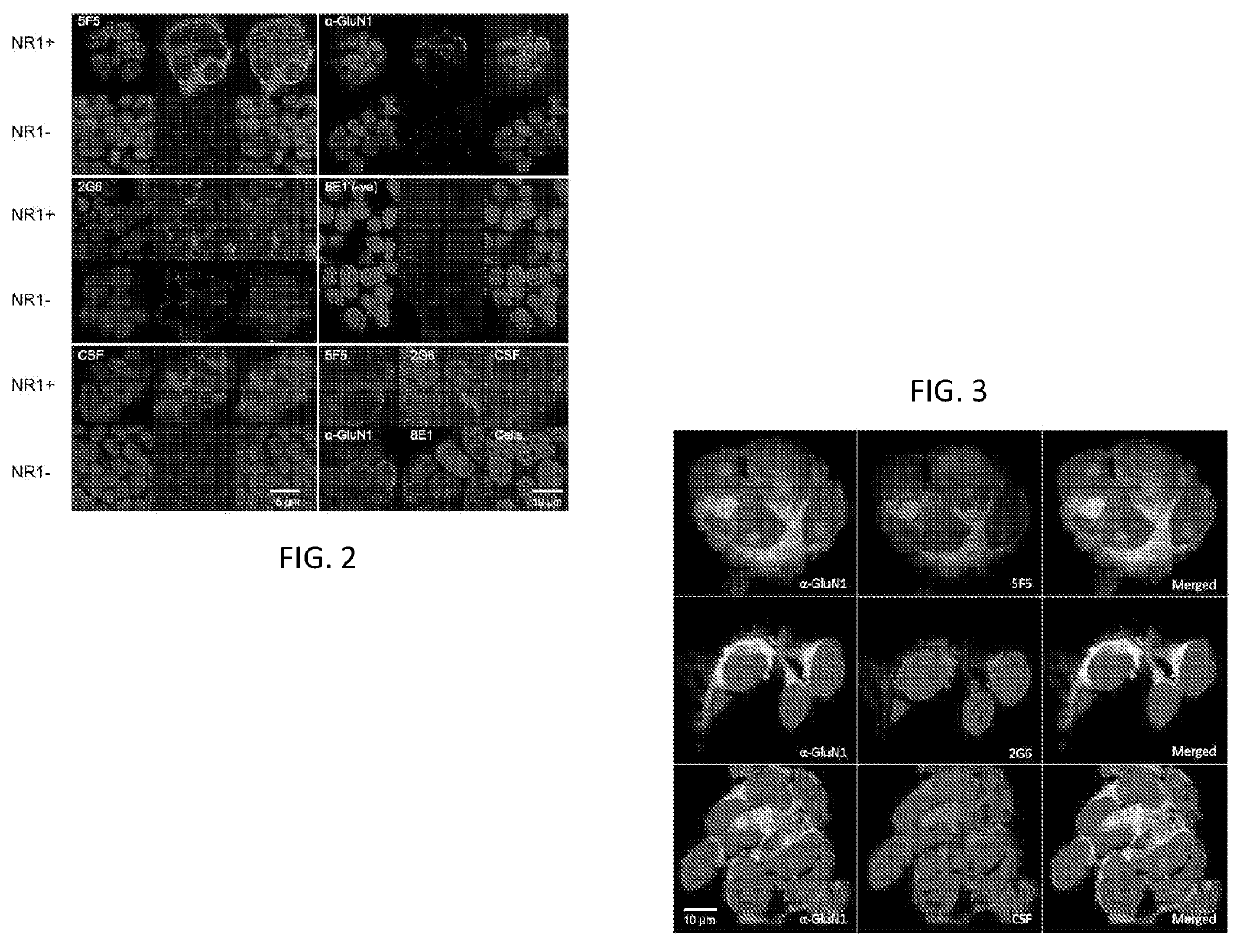
Anti-nmda receptor antibodies and methods of use
PendingUS20220073611A1Nervous disorderImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsNR1 NMDA receptorAntiendomysial antibodies
A recombinant, synthetic or monoclonal human antibody or fragment thereof that binds to an N-methyl-D-aspartate Receptor (NMDAR) epitope, which antibody or fragment comprises at least one a heavy chain variable domain sequence encoded by a nucleic acid sequence that is at least 80% identical to SEQ ID NOs. 1, 3, or 5; or at least one a light chain variable domain sequence encoded by a nucleic acid sequence that is at least 80% identical to SEQ ID NOs: 2, 4, or 6. Assays for diagnosis of ANRE employ these NMDAR-binding antibodies, constructs, or epitope binding fragments. In one embodiment, multiple of the NMDAR-binding antibodies or fragments are used as controls because they bind non-overlapping target sequences on the NMDAR ATD.
Owner:LANKENAU INST FOR MEDICAL RES
Methods for treating symptomatic orthostatic hypotension
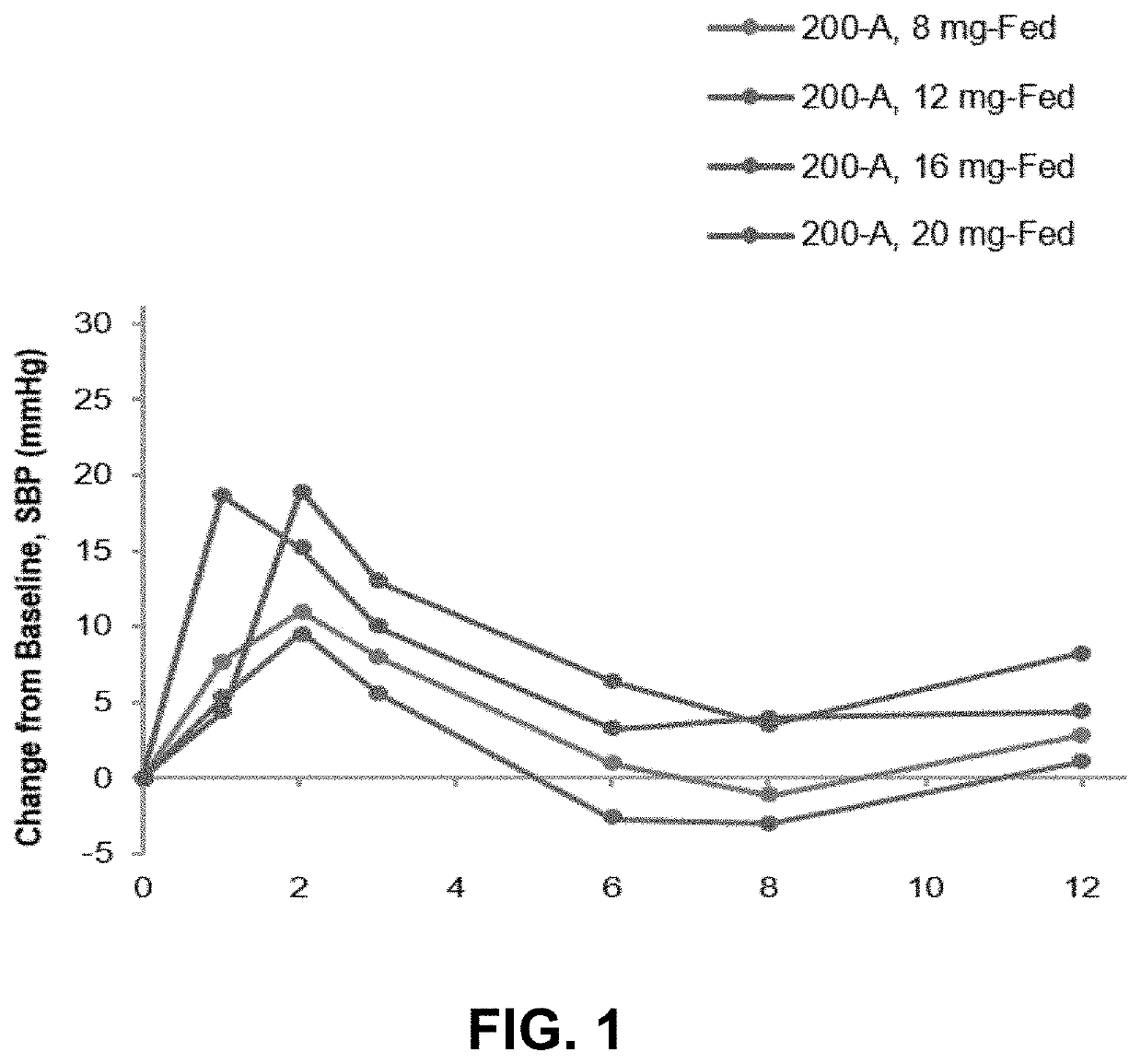
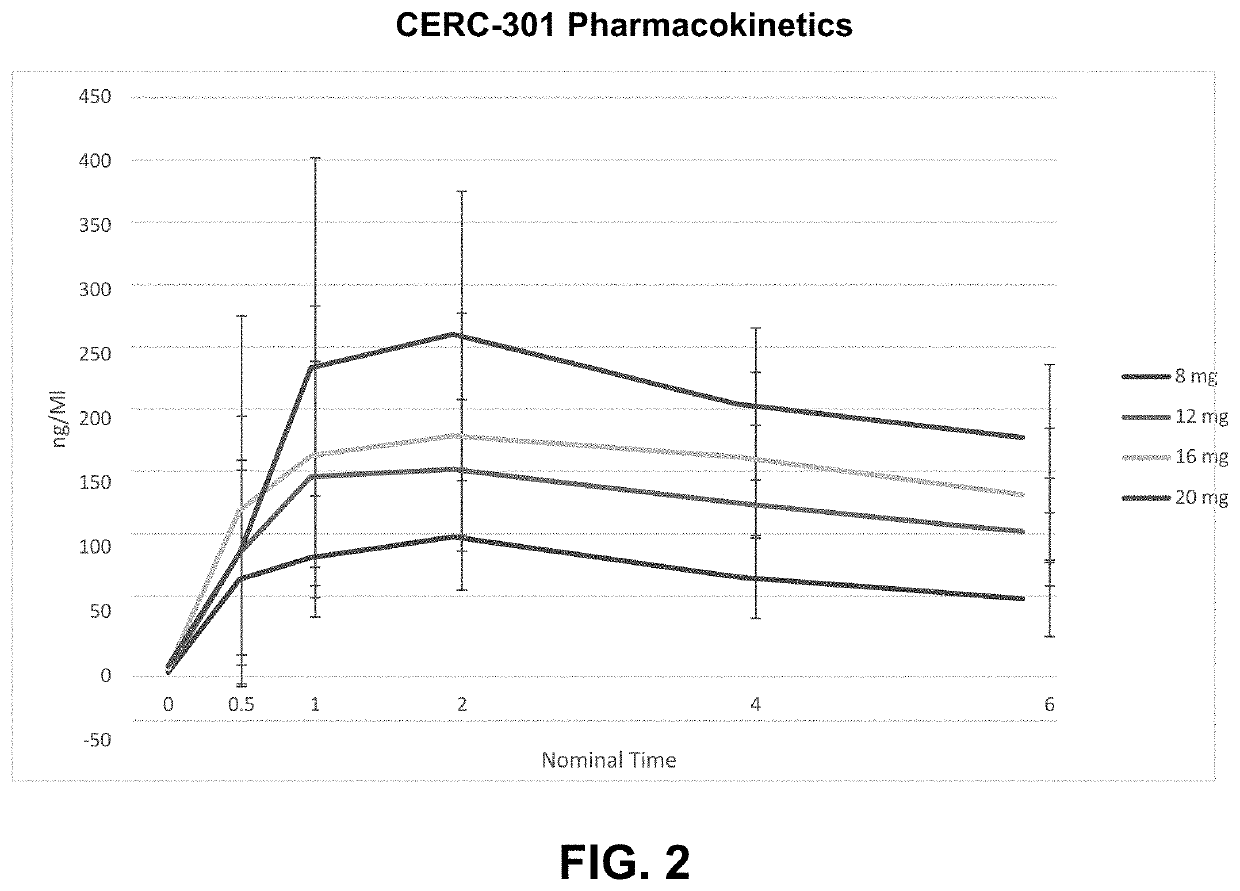
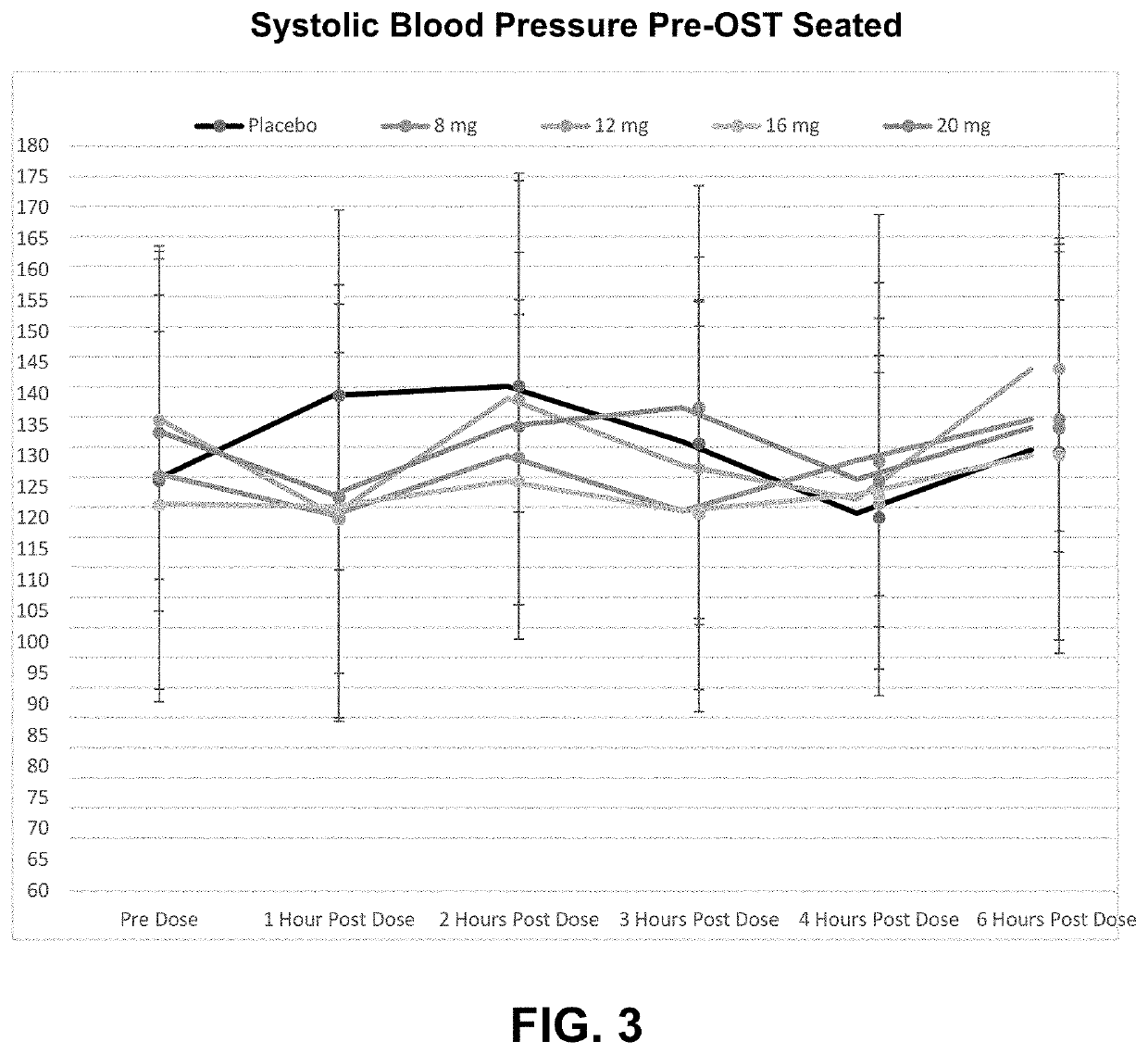
PendingUS20220168301A1Long-term effective therapeutic treatmentImprove toleranceOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryReceptor subunitAspartic acid
The present disclosure provides a method for treating symptomatic orthostatic hypotension using a potent selective antagonist of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor subunit 2B (NMDA-GluN2B or NR2B).
Owner:CERECOR INC
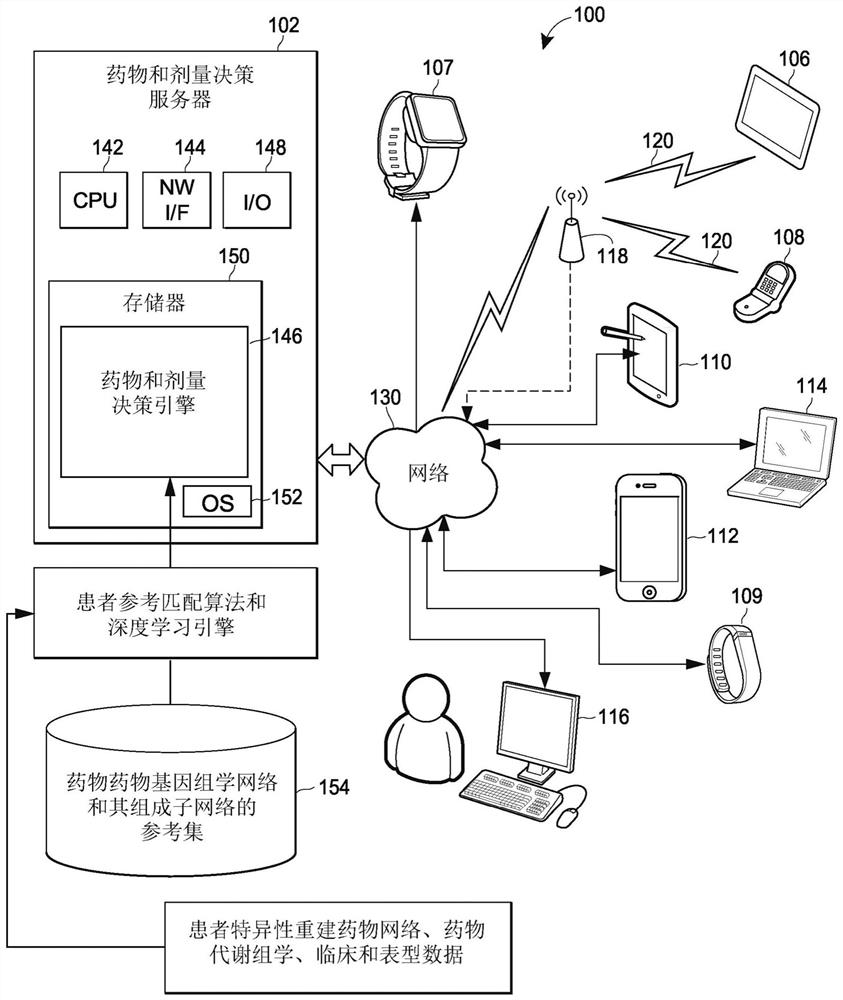
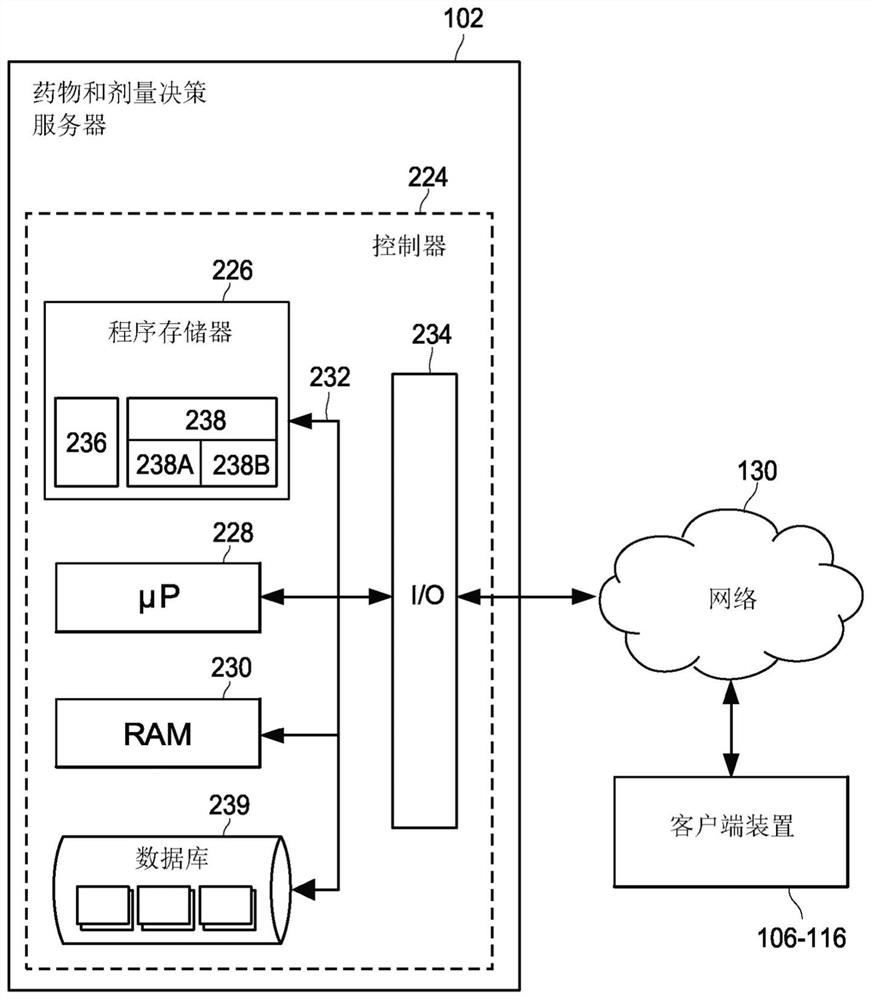
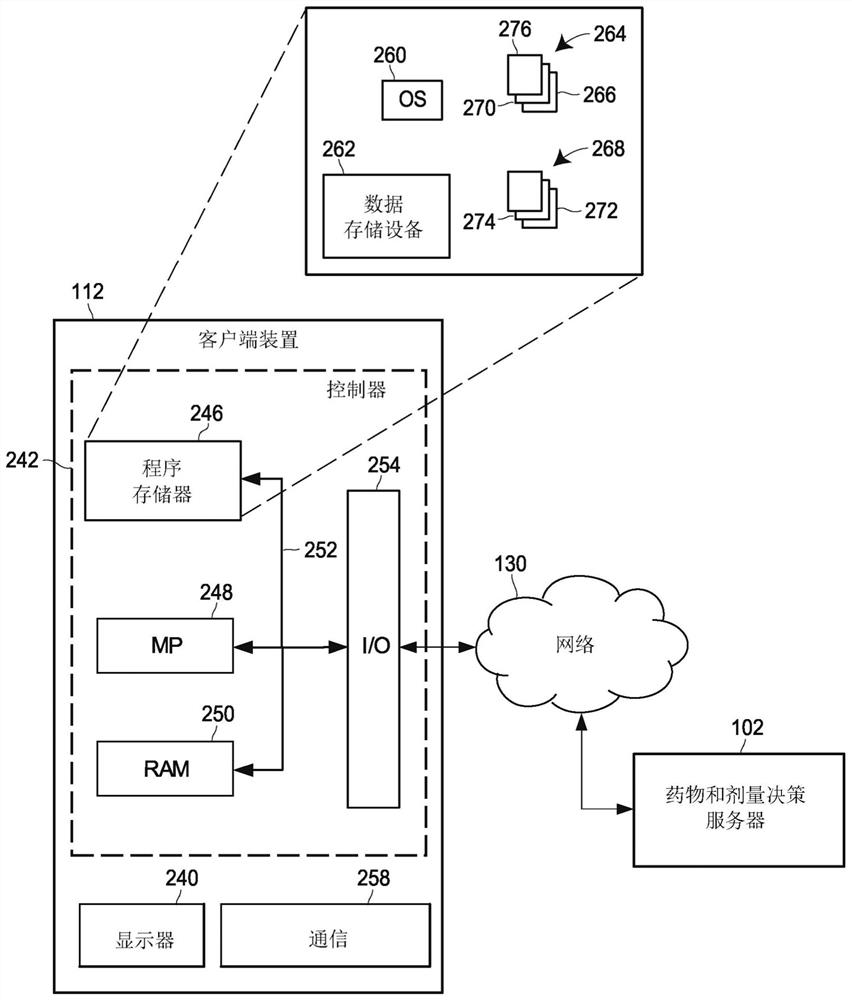
Pharmacogenomic decision support for modulators of the nmda, glycine, and ampa receptors
PendingCN113632174AExtensive computingExtensive Computing SolutionsMedical simulationDrug and medicationsNucleotideEfficacy
Methods for identifying patients diagnosed with treatment resistant or refractory depression, pain or other clinical indications who are eligible to receive N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor antagonist, glycine receptor beta (GLRB) modulator, or alpha-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic acid receptor (AMPAR)-based therapies to include determining the appropriate medication, an optimal dose for each patient, and determining which patients are not eligible to receive the therapy. The pharmacogenomic clinical decision support assays include targeted single nucleotide polymorphisms and clinical values or a combination of targeted single nucleotide polymorphisms, targeted ketamine- specific expansion and contraction of topologically associated domains, and clinical values. The methods described herein allow for a more effective determination of which patients will experience drug efficacy and which patients will experience adverse drug events. The methods provide personalized patient recommendations for dose, the frequency of medication administration, and recommendations on drug choice.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
Methods and compositions for the treatment of opioid dependence and for the treatment of pain
PendingUS20220031798A1Prevent relapseReduce the possibilityNervous disorderOrganic chemistrySubstance dependencePharmaceutical drug
The present invention relates to methods of treating opioid dependence, enhancing the treatment of opioid dependence, treating opioid withdrawal, or alleviating one or more opioid withdrawal symptoms in a subject, preventing or reducing the likelihood of opioid dependence relapse in a subject treated for opioid dependence, reducing the vulnerability of a subject to develop opioid dependence in adulthood following opioid exposure during adolescence, or treating pain in a subject, comprising administering a therapeutically effective amount of a N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor (NMDA) partial agonist to the subject. The present invention further relates to compositions comprising an NMDA partial agonist for use with the aforementioned methods.
Owner:DUKE UNIV
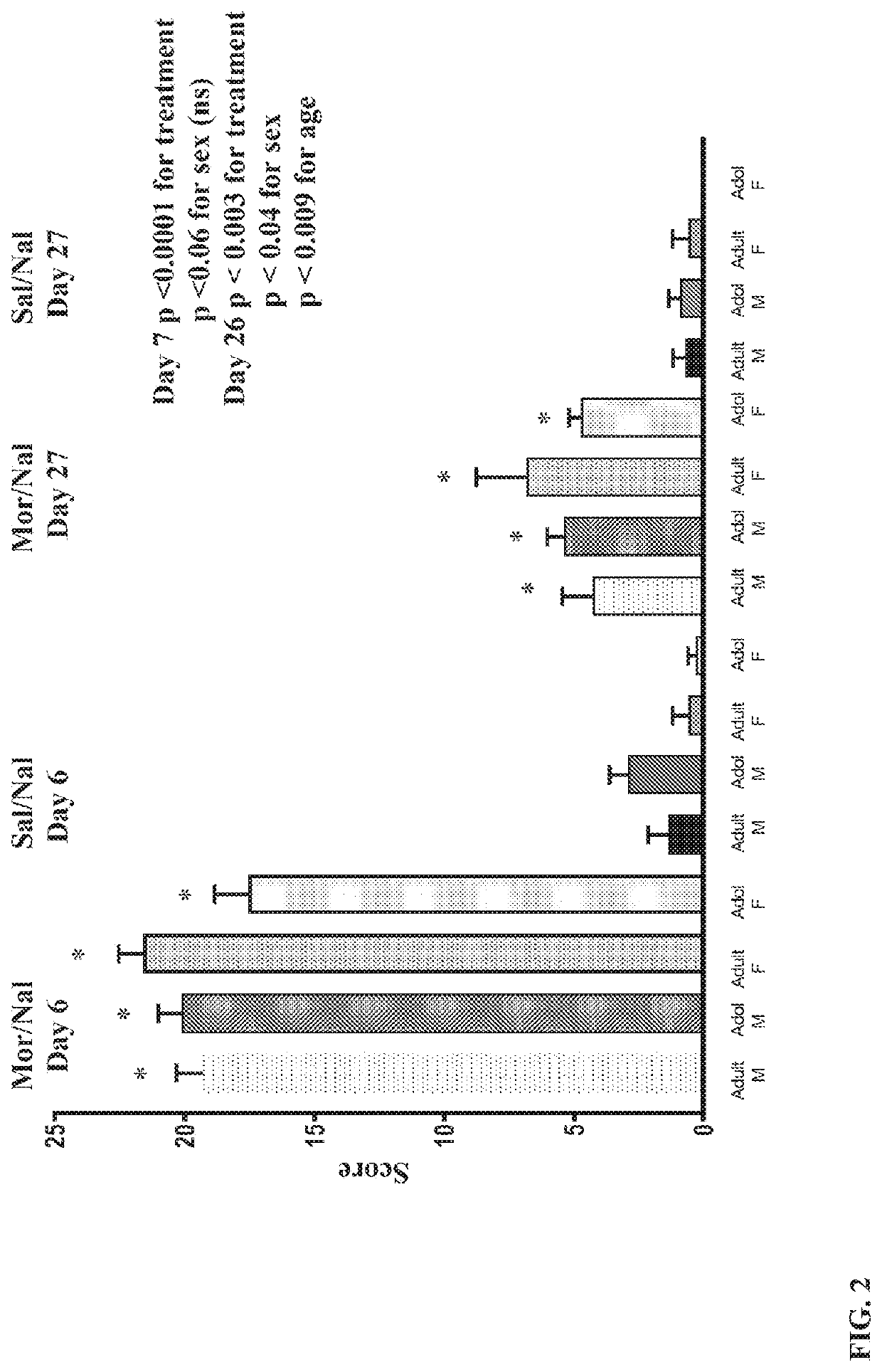
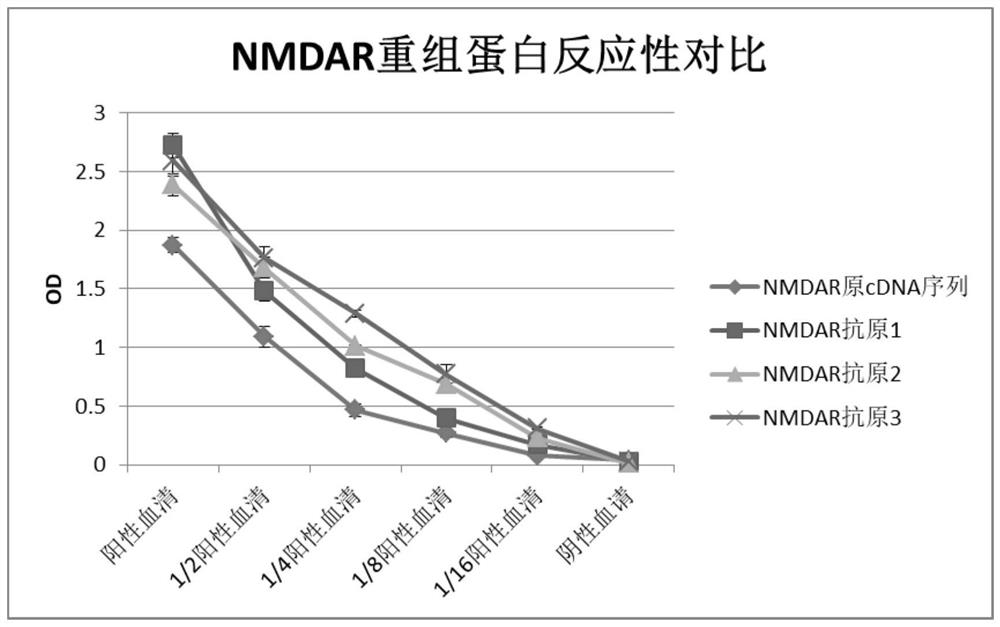
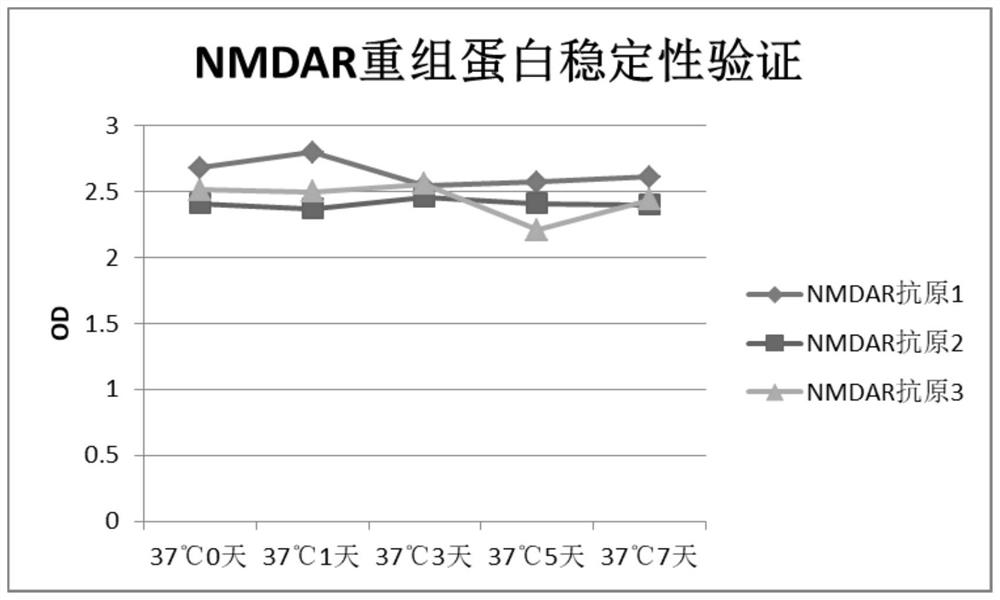
N-methyl-D-aspartic acid receptor recombinant antigen, preparation method thereof and kit containing recombinant antigen
PendingCN114369154AHigh expressionHigh protein activityCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsInvertebrate cellsAspartic acid receptorsAntigen
The invention provides an N-methyl-D-aspartic acid receptor recombinant antigen, a preparation method thereof and a kit containing the recombinant antigen. The recombinant antigen comprises subunit GluN1a recombinant protein, and the amino acid sequence of the subunit GluN1a recombinant protein is as follows: Asn61, Asn350, Asn471 and Asn771 in the sequence shown in SEQ ID NO: 1 are mutated into Gln, Cys22 is mutated into Ser, Glu595 and Glu597 are mutated into Ser, and Glu598 is mutated into Thr. The N-methyl-D-aspartic acid receptor recombinant antigen further comprises a natural subunit GluN2A recombinant protein and / or a subunit GluN2B recombinant protein, and the amino acid sequence of the N-methyl-D-aspartic acid receptor recombinant antigen is characterized in that Asn348 in the sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO: 3 is mutated into Asp, and Cys838 and Cys849 in the sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO: 3 are mutated into Ser.
Owner:迪亚莱博(张家港)生物科技有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com