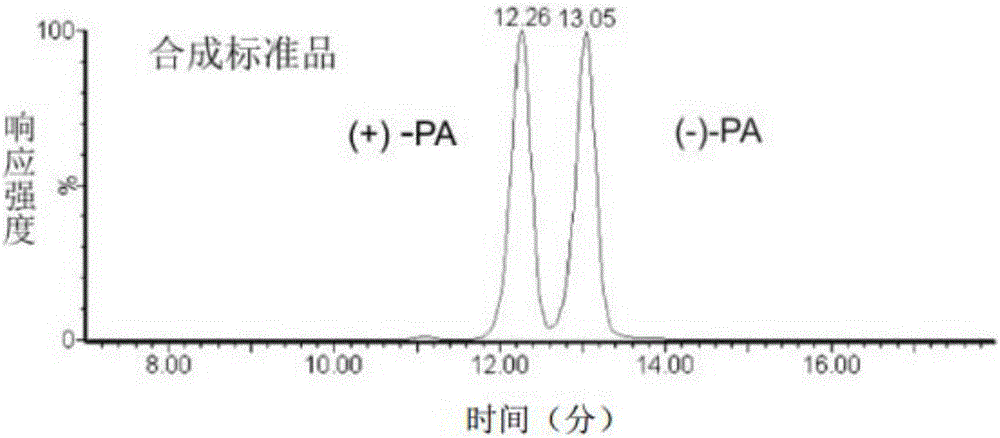
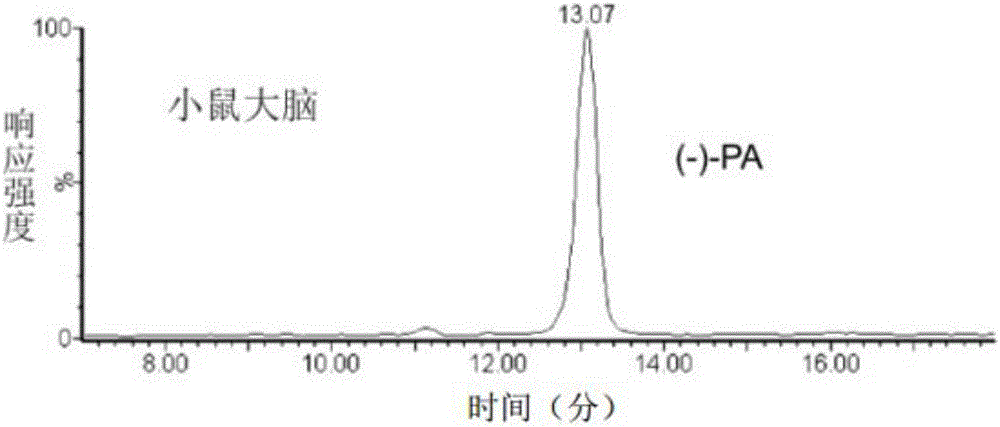
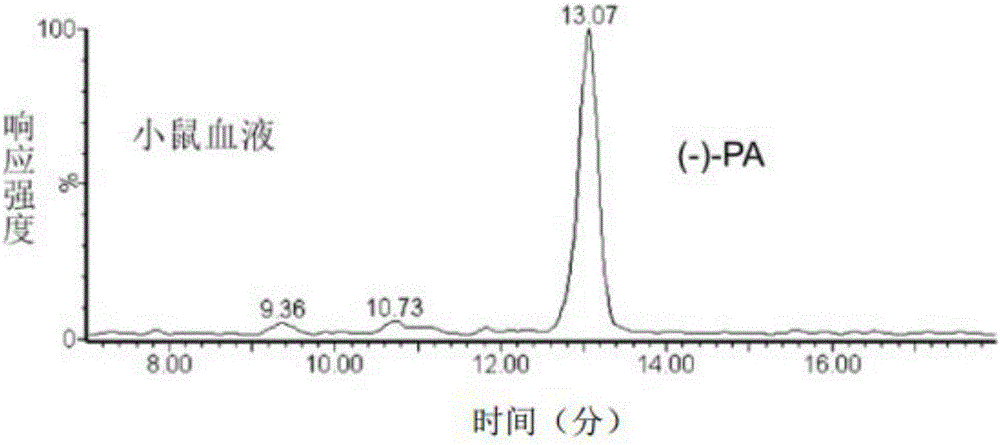
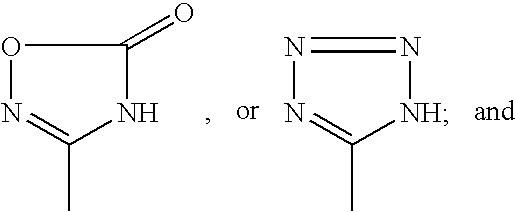Patents
Literature
63 results about "Glutamate receptor" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
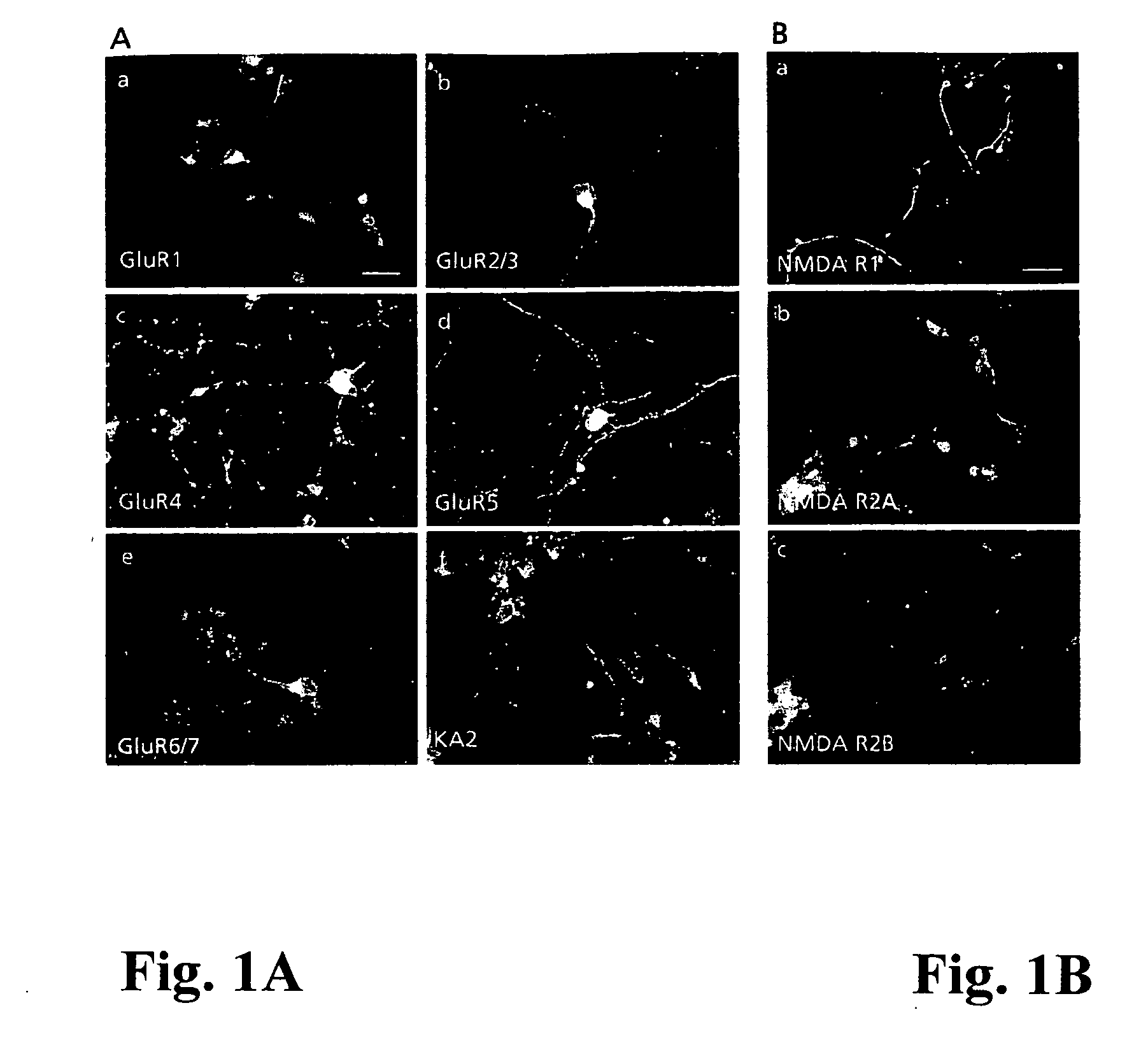
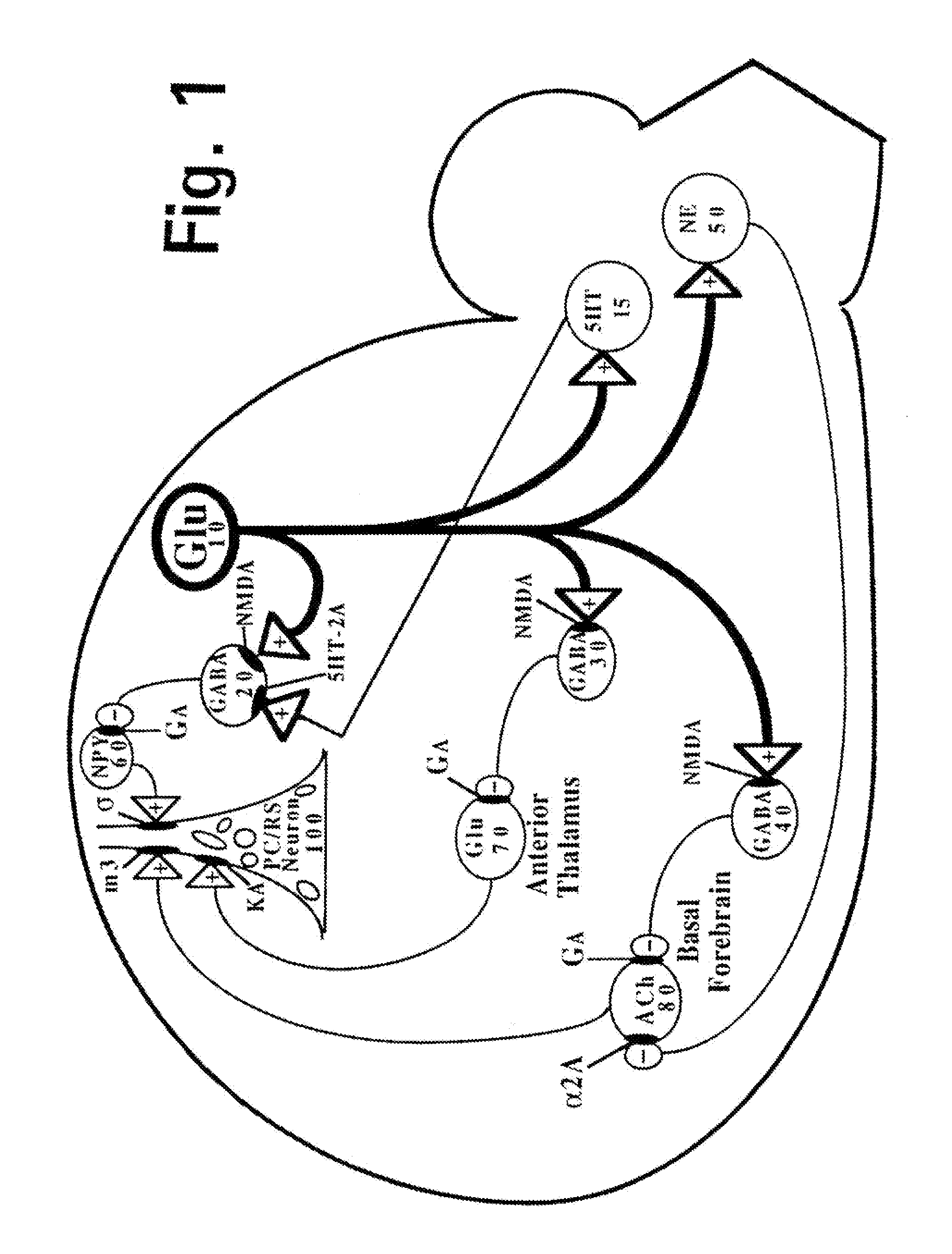
Glutamate receptors are synaptic and non synaptic receptors located primarily on the membranes of neuronal and glial cells. Glutamate (the conjugate base of glutamic acid) is abundant in the human body, but particularly in the nervous system and especially prominent in the human brain where it is the body's most prominent neurotransmitter, the brain's main excitatory neurotransmitter, and also the precursor for GABA, the brain's main inhibitory neurotransmitter. Glutamate receptors are responsible for the glutamate-mediated postsynaptic excitation of neural cells, and are important for neural communication, memory formation, learning, and regulation.
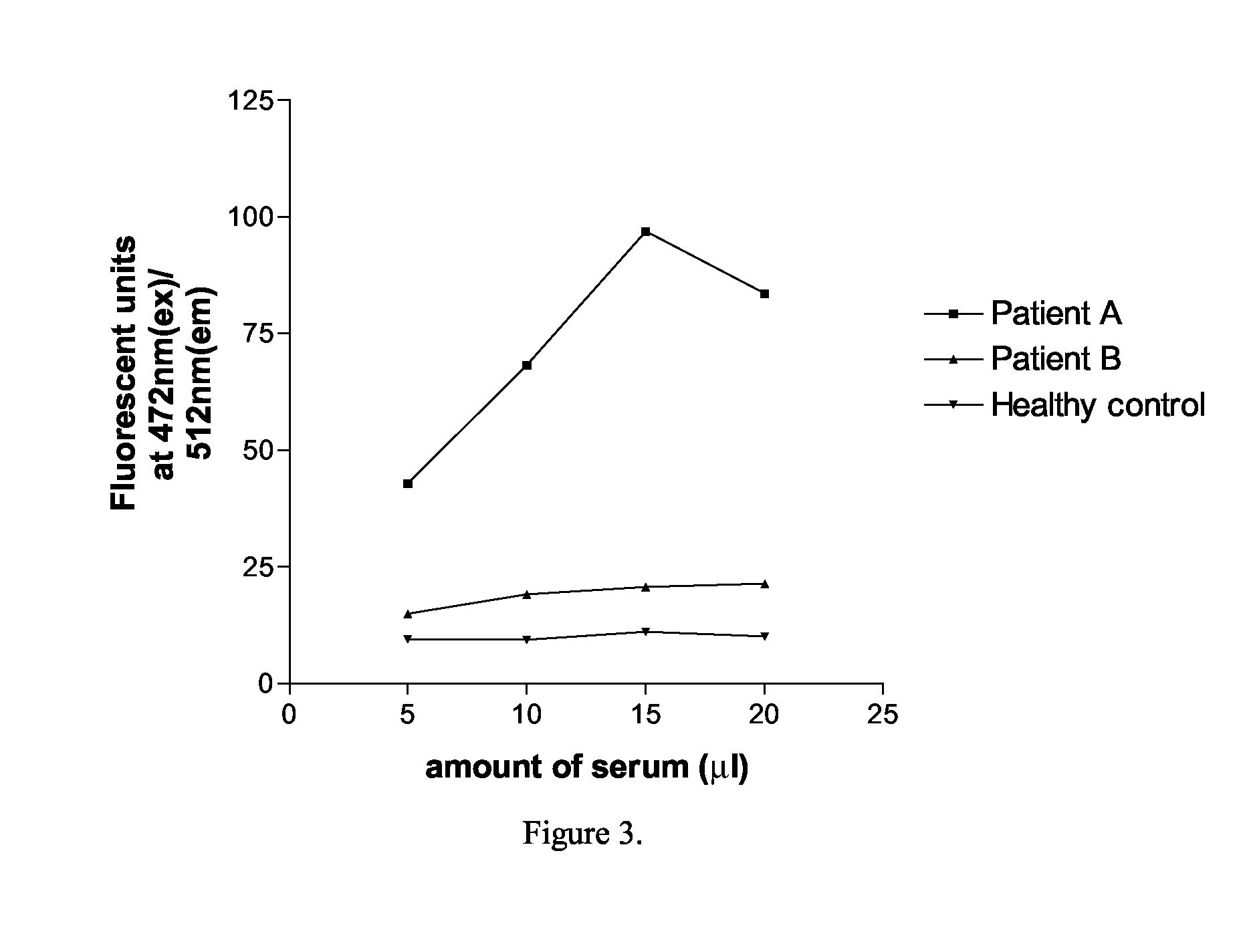
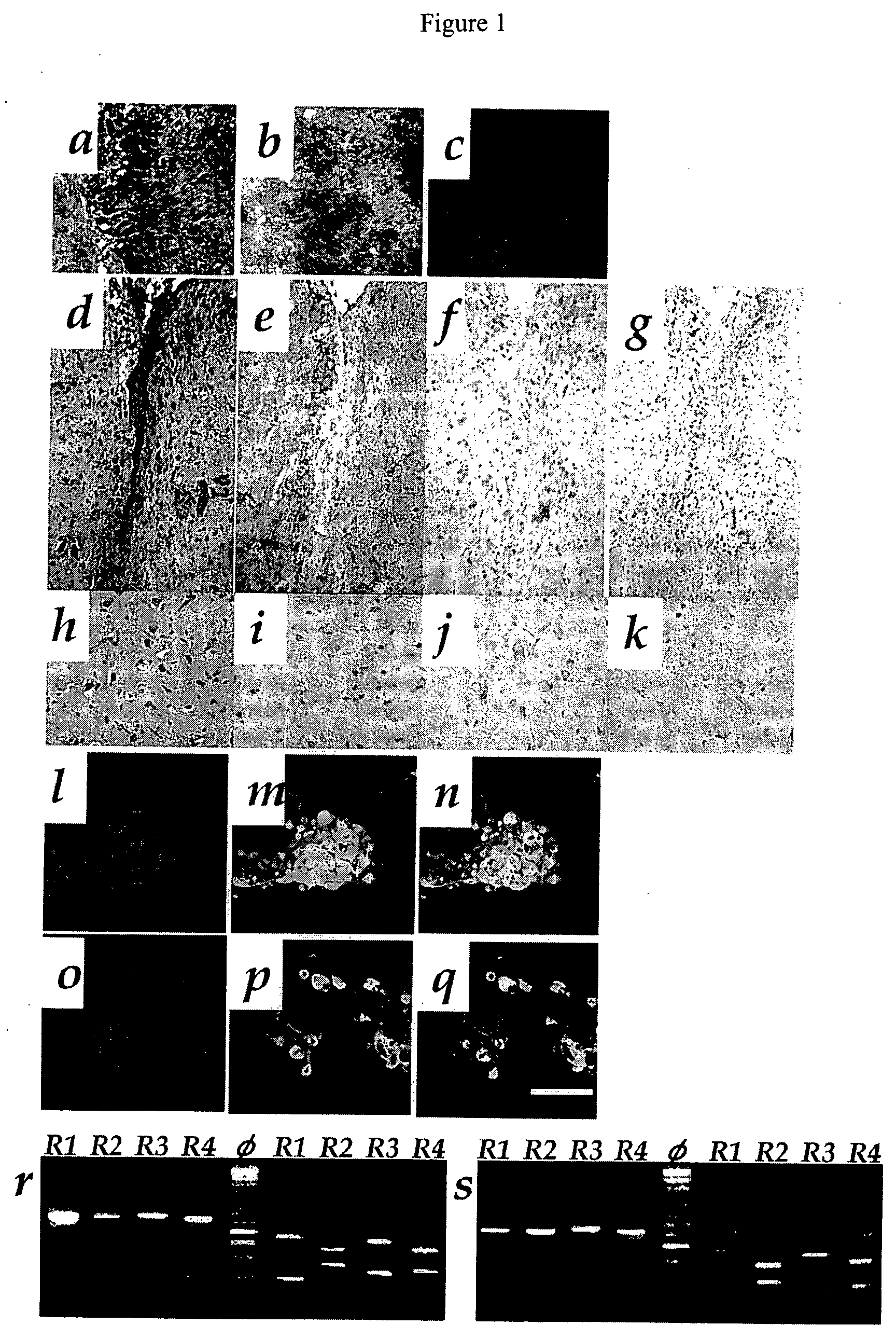
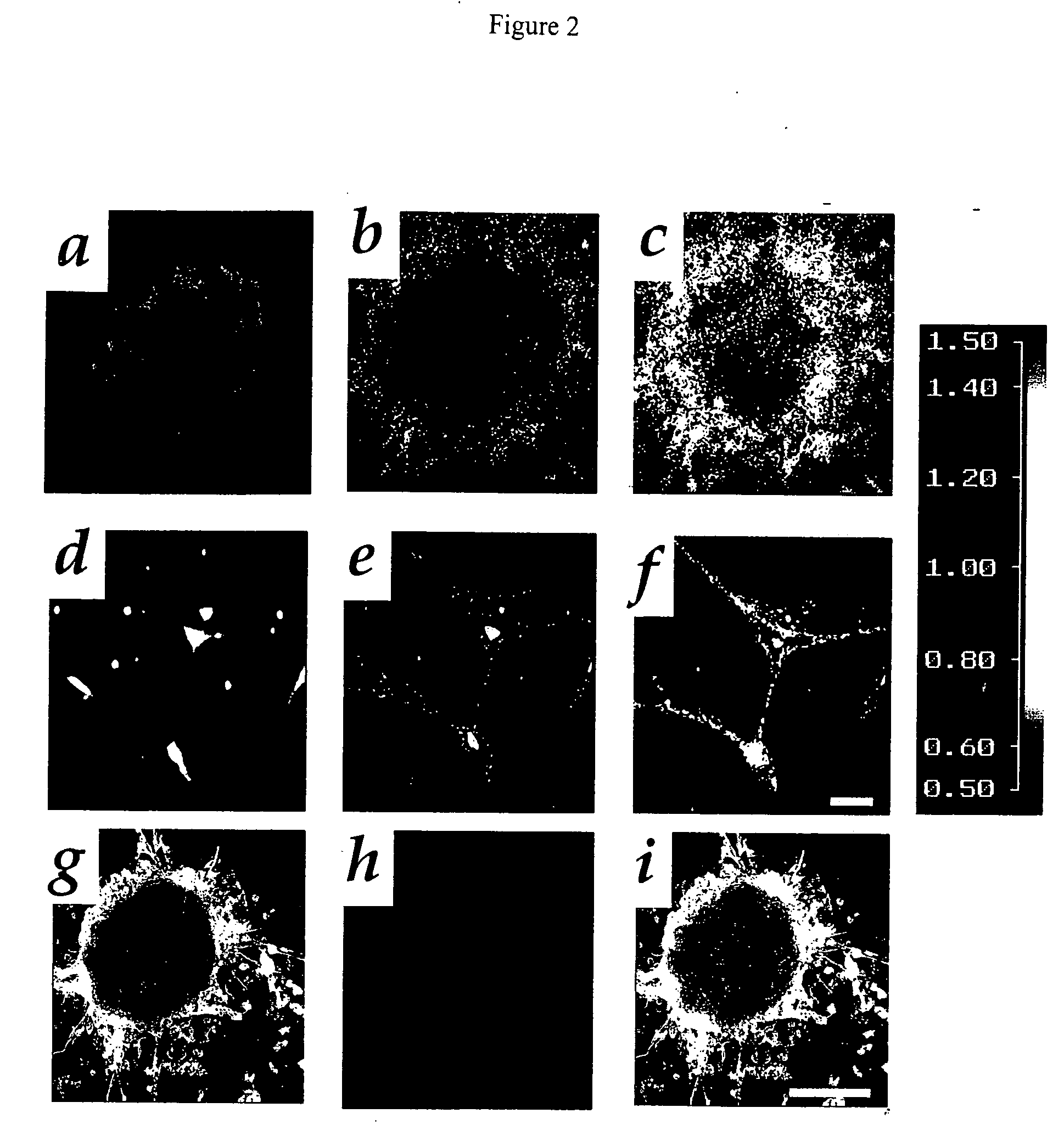
Autoantibodies to neurotransmitter receptors
InactiveUS6010854AReduce in quantityGood effectPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsAmyotrophic lateral sclerosisMedicine
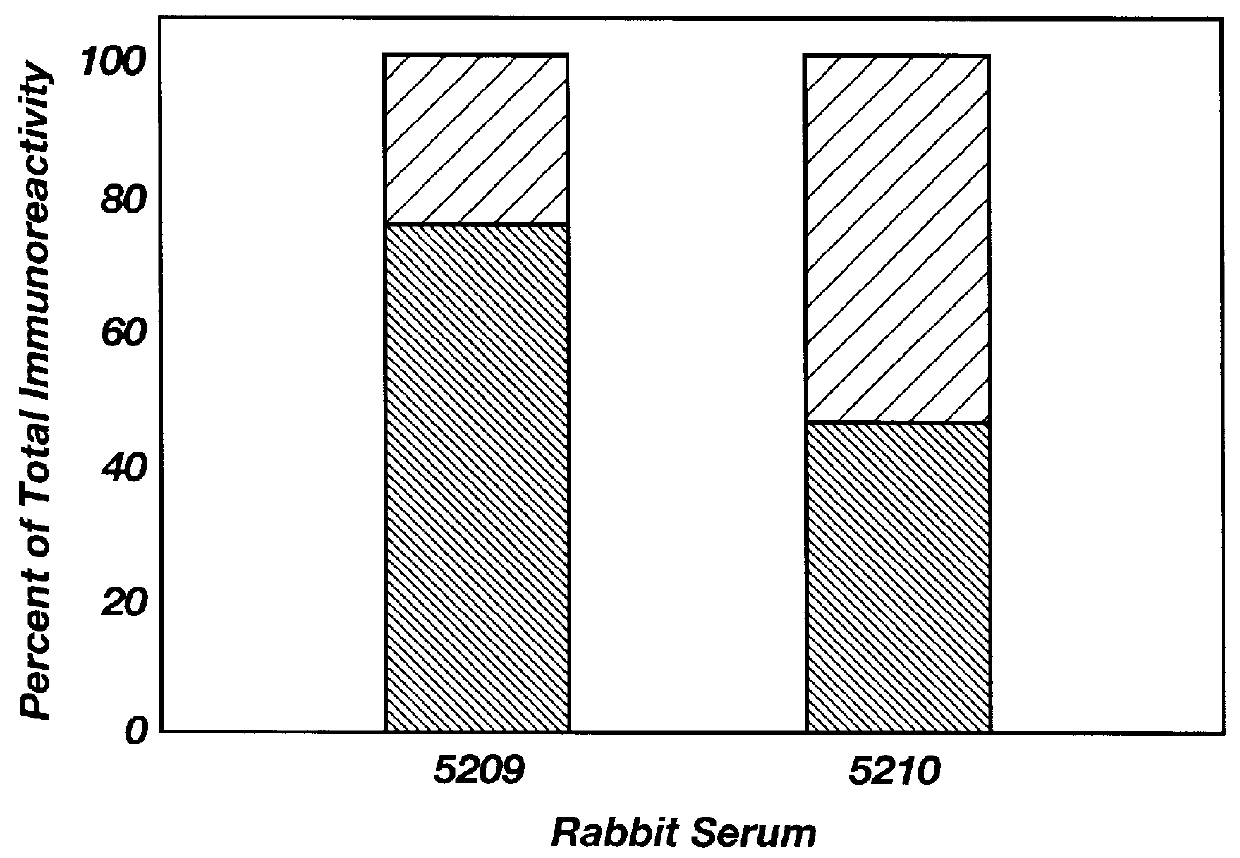
A peptide containing 24 amino acid residues that binds to anti-neuronal-glutamate-receptor autoantibodies associated with Rasmussen's encephalitis and that blocks activation of the GluR3 subunit is described. Methods of making the peptide and treating Rasmussen's encephalitis are also disclosed. Autoantibodies to other glutamate receptor subunits are associated with paraneoplastic neurodegenerative disease, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, and neurodegenerative disease of unknown diagnosis. Methods of screening patients and of monitoring patients being treated for these disorders and syndromes are further described.
Owner:UNIV OF UTAH RES FOUND
Biologically active peptides as glutamate receptor inhibitors
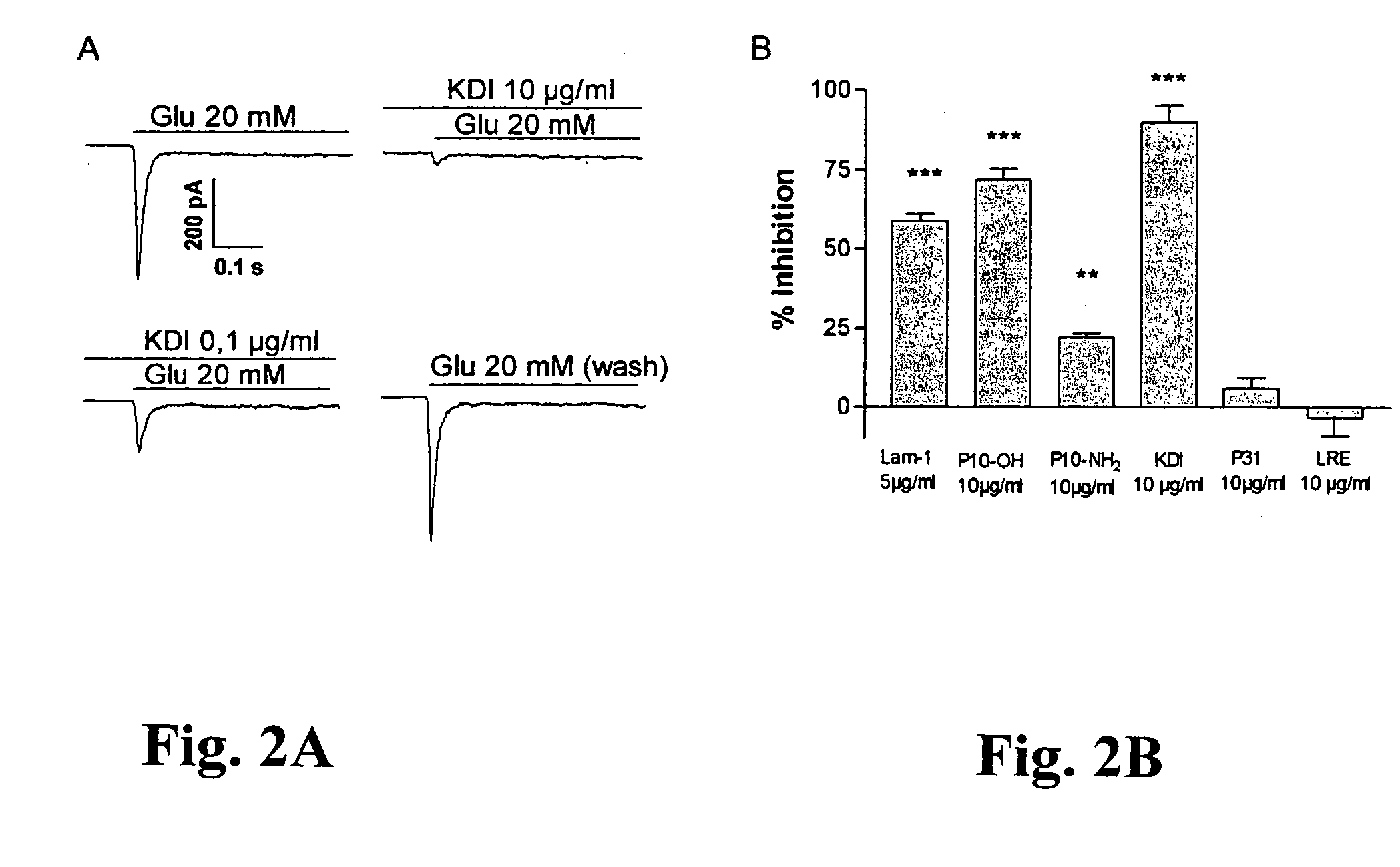
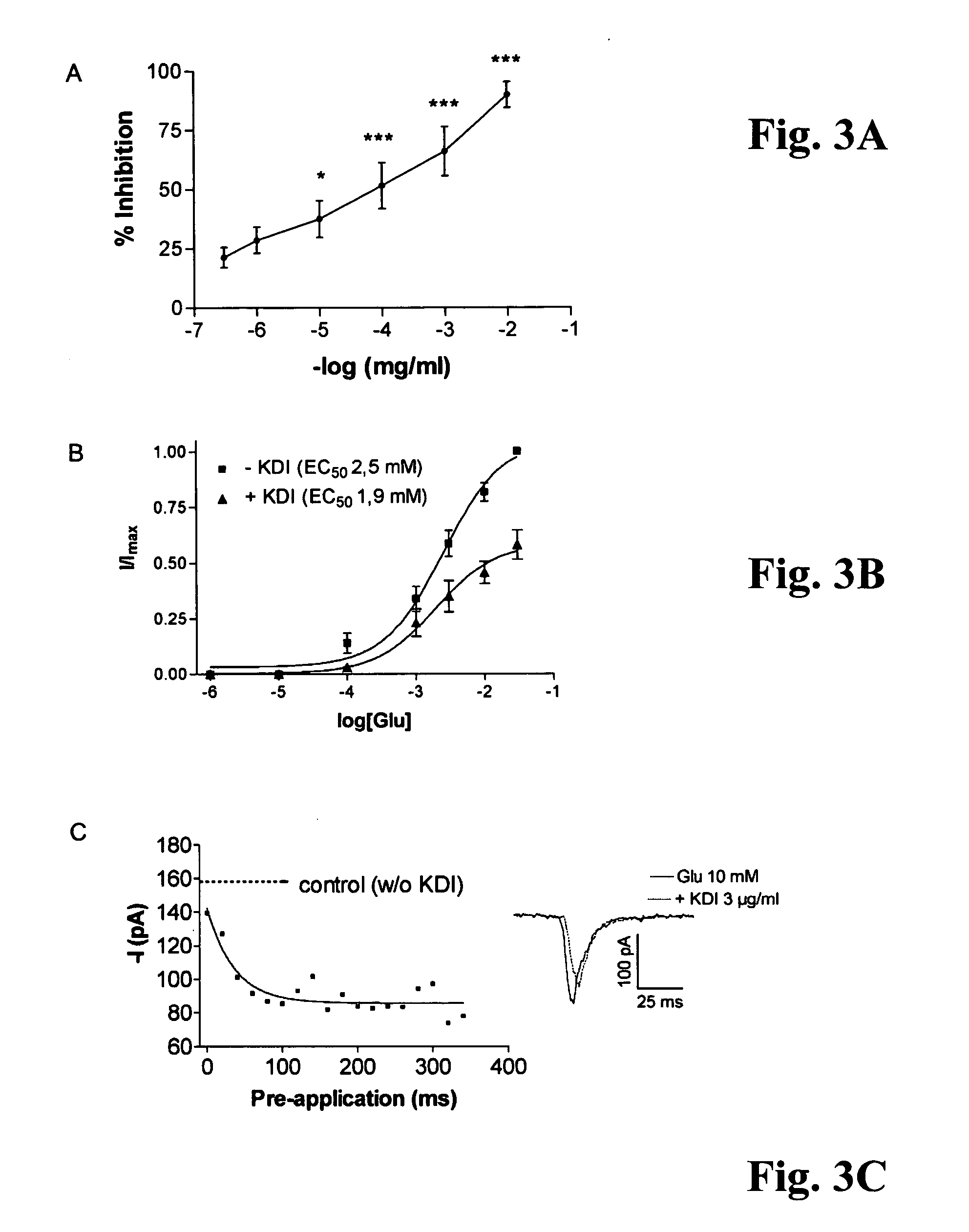
The present invention relates to biologically active peptides derived from the neurite outgrowth-promoting domain of luminin-1, i.e. the γ1-chain of laminin-1. These peptides include the decapeptide RDIAEIIKDI (SEQ ID NO: 1) and the truncated peptides derived therefrom comprising the biologically active domain thereof, the tripeptide KDI. The invention is directed to the biologically active tripeptide motifKDI, and to its use in promoting regeneration of neuronal or non-neuronal tissues and, in specific, to its use in the treatment of spinal cord injuries.
Owner:LIESI PAIVI
Detection of Antibodies
InactiveUS20090029388A1Efficient methodImprove the signal-to-background ratioBiological testingAutoimmune diseaseWater Channel Proteins
The present invention relates to a method for detecting antibodies against a target antigen in a sample which comprises contacting the sample with labelled target antigen, subjecting the sample to immunoprecipitation to precipitate antibodies in the sample and detecting the presence of antibodies against the target antigen in the sample by means of the presence of labelled target antigen in the immunoprecipitate, wherein the labelled target antigen is a fusion protein comprising the target antigen and a fluorescent protein label and the presence of labelled target antigen in the immunoprecipitate is detected by means of the fluorescence of the fluorescent label. The method is particularly suitable for use where the target antigen is an autoantigen and can also be used to identify autoantigens implicated in a particular autoimmune disorder by screening serum samples from patients with a clinical phenotype indicative or suggestive of an autoimmune disorder and suitable controls. The target protein may be from the cys-loop acetyl choline receptor ion channel gene superfamily, the voltage-gated calcium, sodium or potassium ion channel gene superfamily, the glutamate receptor gene family, a receptor tyrosine kinase, or other membrane associated channels such as aquaporin gene family.
Owner:BEESON DAVID
Inhibition of proliferation and infiltration of brain tumor cells caused by expression of ampa-type glutamate receptor subunit
InactiveUS20060128645A1Prevent proliferationVirusesMicrobiological testing/measurementGlioblastomaBrain tumor
The present invention is to provide a method of treatment which inhibits proliferation and invasion of brain tumor cells in developing animal brain tumor cells, and a method for measuring proliferation / invasion activity of brain tumor cells, in the brain tumor cells, preferably, in glioblastoma. Proliferation and invasion of brain tumor cells are inhibited by regulating Ca2+ permeability by glutamate receptor subunits in developing animal brain tumor cells. Regulation of Ca2+ permeability by glutamate receptor subunits can be conducted by introducing the GluR2 gene into AMPA-type glutamate receptors in brain tumor cells. Further, the present invention provides a method for measuring proliferation / invasion activity of brain tumor cells by detecting / measuring the expression of glutamate receptor subunits in developing animal brain tumor cells.
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP
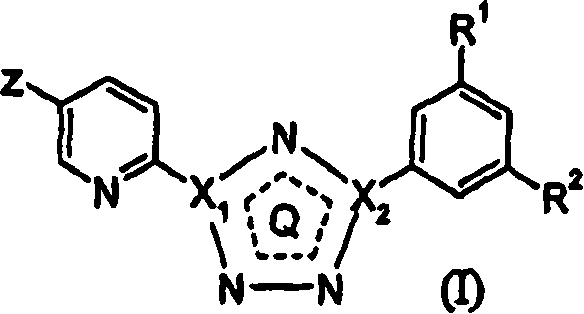
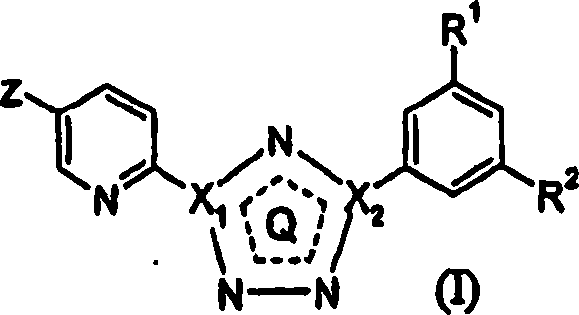
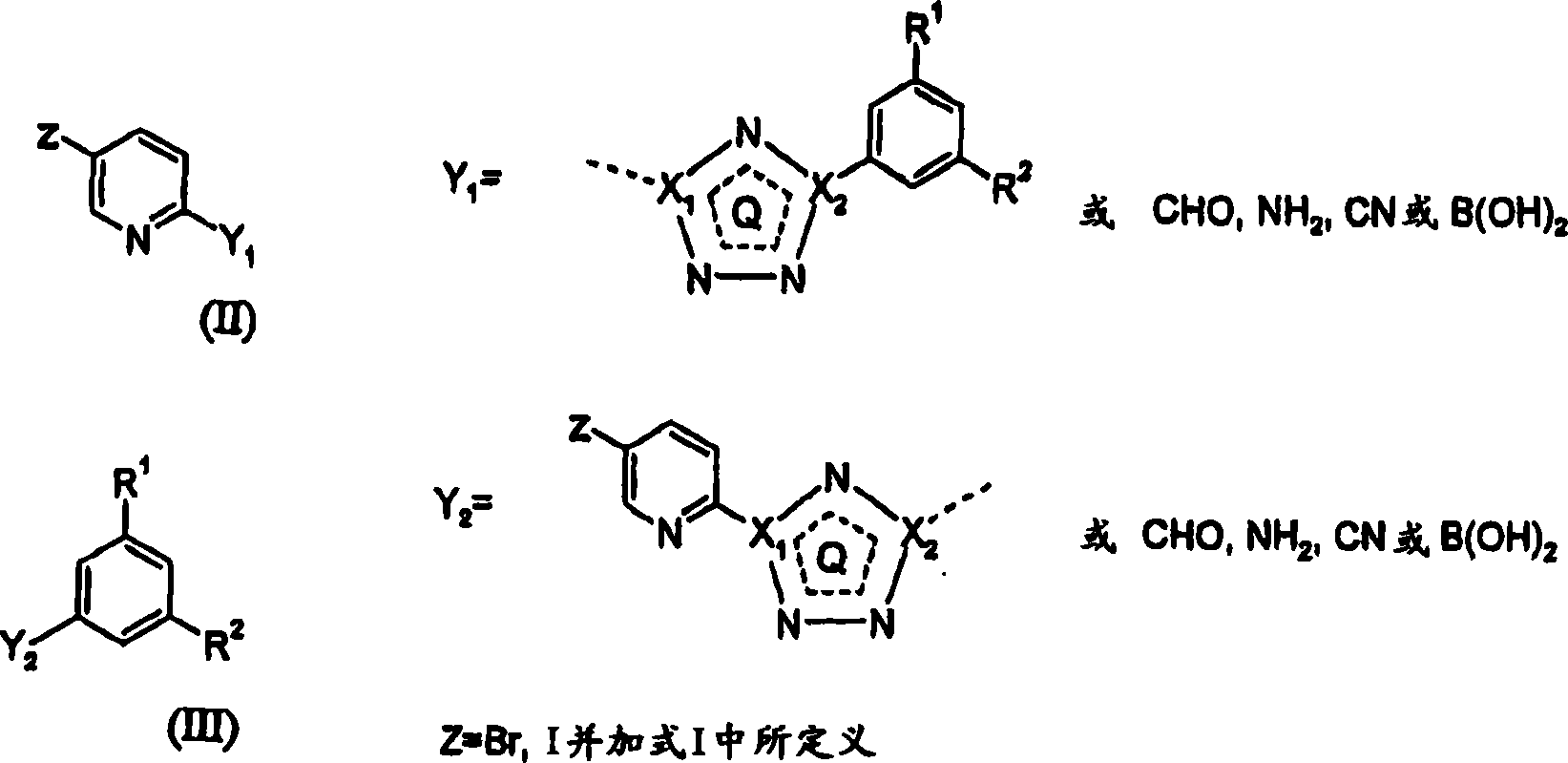
5-fluoro-, chloro- and cyano-pyridin-2-yl-tetrazoles as ligands of the metabotropic glutamate receptor-5
InactiveCN1906187AOrganic active ingredientsSenses disorderMetabotropic glutamate receptor 5Pharmaceutical formulation
Owner:ASTRAZENECA AB
Use of compositions that increase glutamate receptor activity in treatment of brain injury
InactiveUS20060167099A1Increase glutamate receptor activityFacilitated releaseOrganic active ingredientsBiocideInitial treatmentNR1 NMDA receptor
The present invention provides a method for treating a brain injury. This method comprises administering to a mammal afflicted with a brain injury a pharmaceutical composition therapeutically effective to increase glutamate receptor activity in the brain of said mammal. The pharmaceutical composition is to be administered after an acute postinjury phase of said affliction, a time when the level of NMDA receptor activity in the brain is below normal. The pharmaceutical composition may be administered subsequent to an initial treatment with an NMDA antagonist, the NMDA antagonist being administered during the acute postinjury phase of said affliction, a time when the level of NMDA receptor activity is above normal.
Owner:BIEGON ANAT +1
Combination of adrenergic agonist and tricyclo-alkylamine for relieving chronic pain without adverse side effects
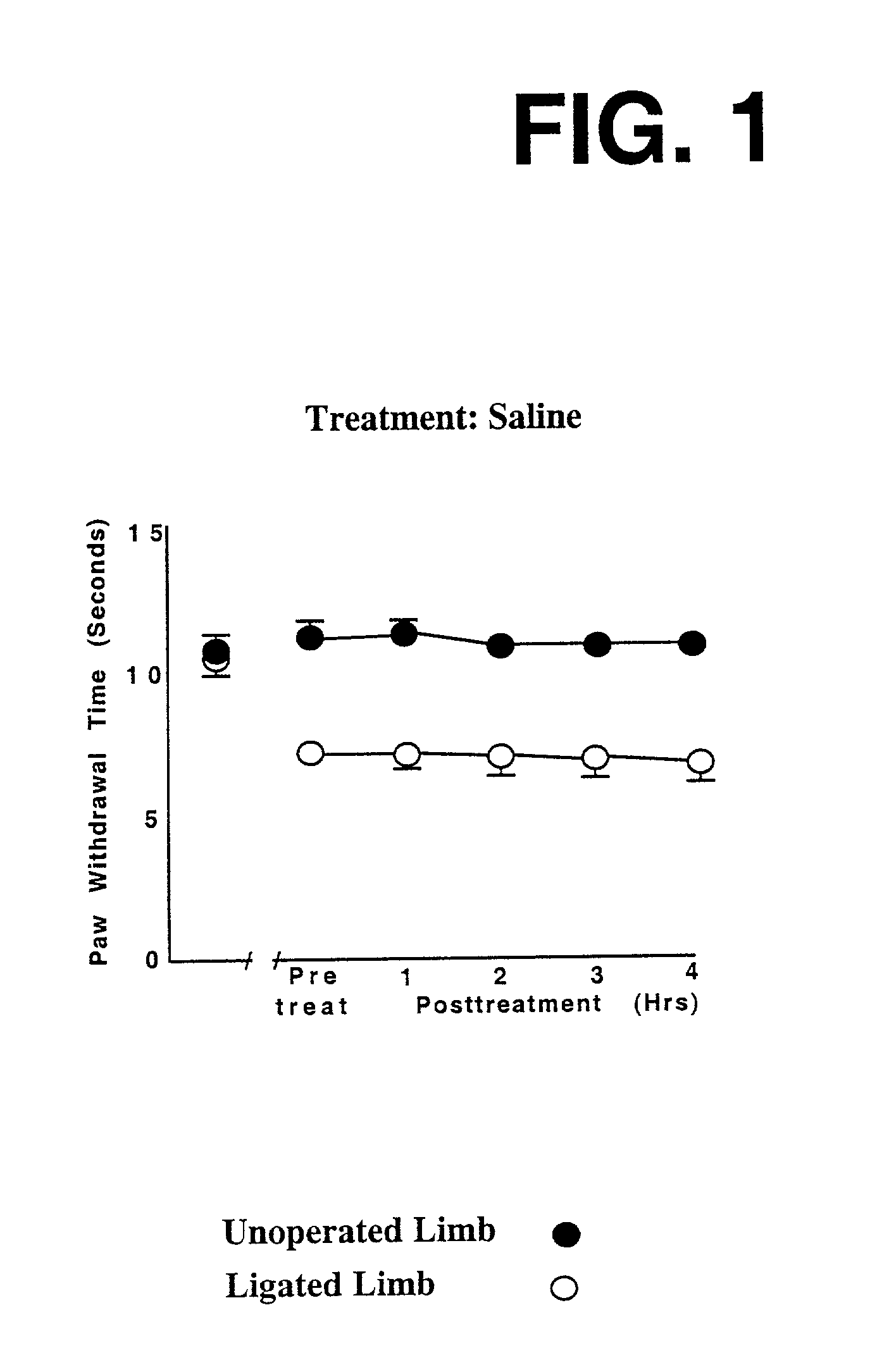
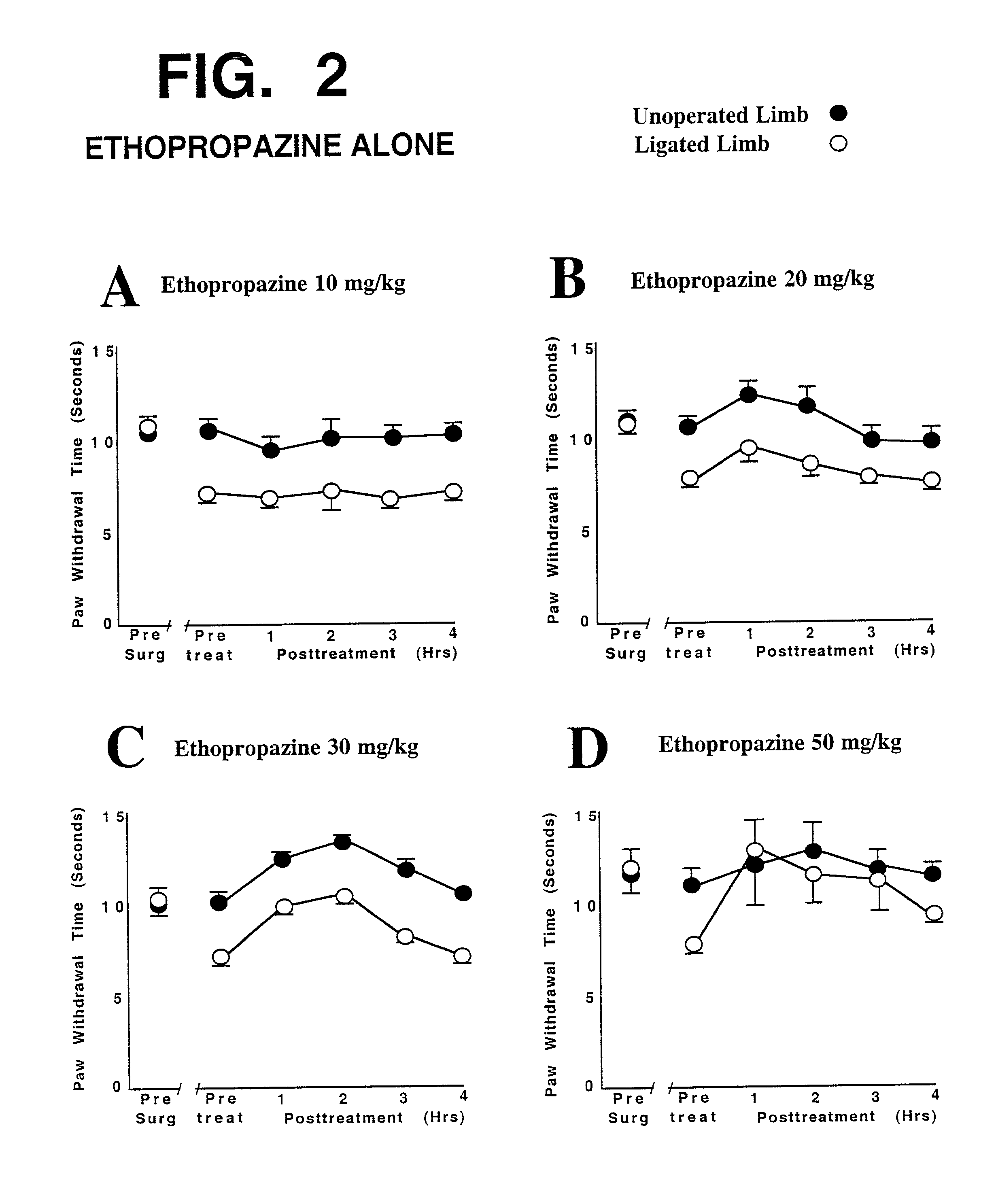
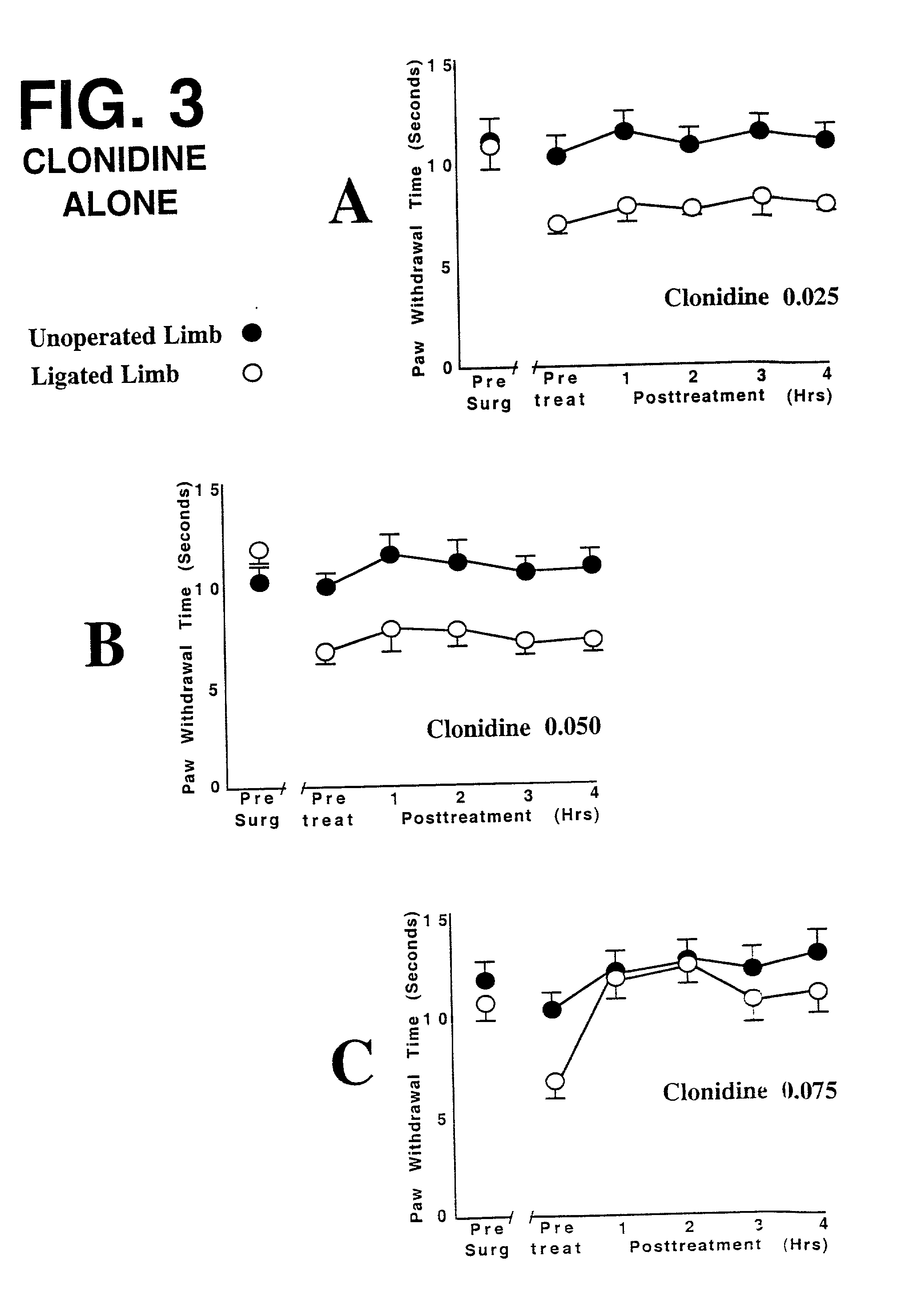
This invention discloses that a combination of two drugs, from two different and previously unrelated categories, provides effective and long-lasting relief from neuropathic pain. Both drugs can be taken orally, in a convenient, painless, non-invasive manner that does not require injections. One drug in this combination is an alpha2 adrenergic agonist, exemplified by clonidine. The other drug in the pain-relieving combination has a tri-cyclo-alkyl-amine (TCAA) structure. At least some TCAA drugs have antagonist (receptor-blocking) activity at two entirely different classes of neuronal receptors: the muscarinic subclass of acetylcholine (ACh) receptors, and the NMDA subclass of glutamate receptors. Such drugs include ethopropazine, normally used as an anti-cholinergic drug, and desipramine, normally used as an anti-depressant. Tests by the Applicants have shown that at least some TCAA drugs can relieve neuropathic pain to a limited extent, but at the doses required to relieve pain, they cause adverse side effects, and any pain relief is relatively brief and short-lived. However, when a TCAA drug such as ethopropazine is administered together with an alpha2 adrenergic agonist such as clonidine, these drugs mutually potentiate one another's neuropathic pain-relieving action, and provide potent and sustained neuropathic pain relief, even when each agent is administered at a low dosage that is below its threshold for causing adverse side effects. Accordingly, this drug combination can provide safe and effective relief of neuropathic pain and possibly other types of chronic and / or intractable pain, at dosages which are so low that they do not pose serious risks of adverse side effects.
Owner:OLNEY JOHN W +2
Methods for diagnosing and treating neuroendocrine cancer
ActiveUS7842468B2Reduce spreadInhibits and decreases activity and expressionMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisAspartic acidNeuroendocrine Cancer
Owner:TRUSTEES OF DARTMOUTH COLLEGE THE
Methods to identify patients at risk of developing adverse events during treatment with antidepressant medication
InactiveUS20080102467A1Increased riskSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementGRIK2Medicine
The invention provides a method of screening patients to identify those patients more likely to exhibit an increased risk of treatment-emergent suicidal ideation comprising: (a) obtaining a sample of genetic material from the patients, and (b) assaying the sample for the presence of a genotype in the patients which is associated with an increased risk of treatment-emergent suicidal ideation, wherein the genotype is characterized by a polymorphism in a gene selected from the group consisting of glutamine receptor, ionotropic, kainate 2 (GRIK2); glutamate receptor ionotropic AMPA 3 (GRIA3); and combinations thereof.
Owner:GOVERNMENT OF THE US REPRESENTED BY THE SEC +1
Biosensor having nano wire for detecting food additive mono sodium glutamate and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveUS7927651B2Prevent degradationUseful in detectionBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsFood additiveNanowire
Owner:SEOUL NAT UNIV R&DB FOUND +1
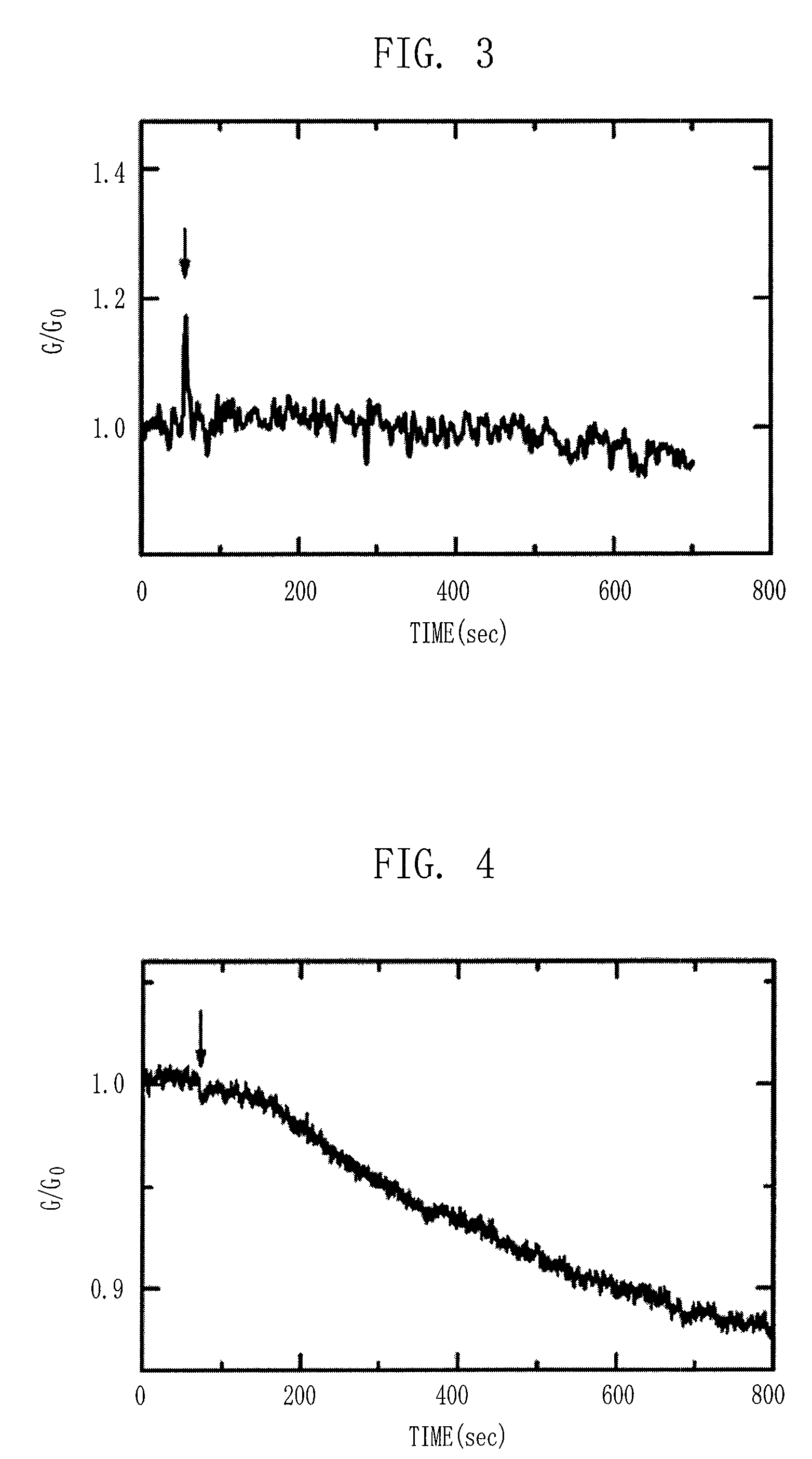
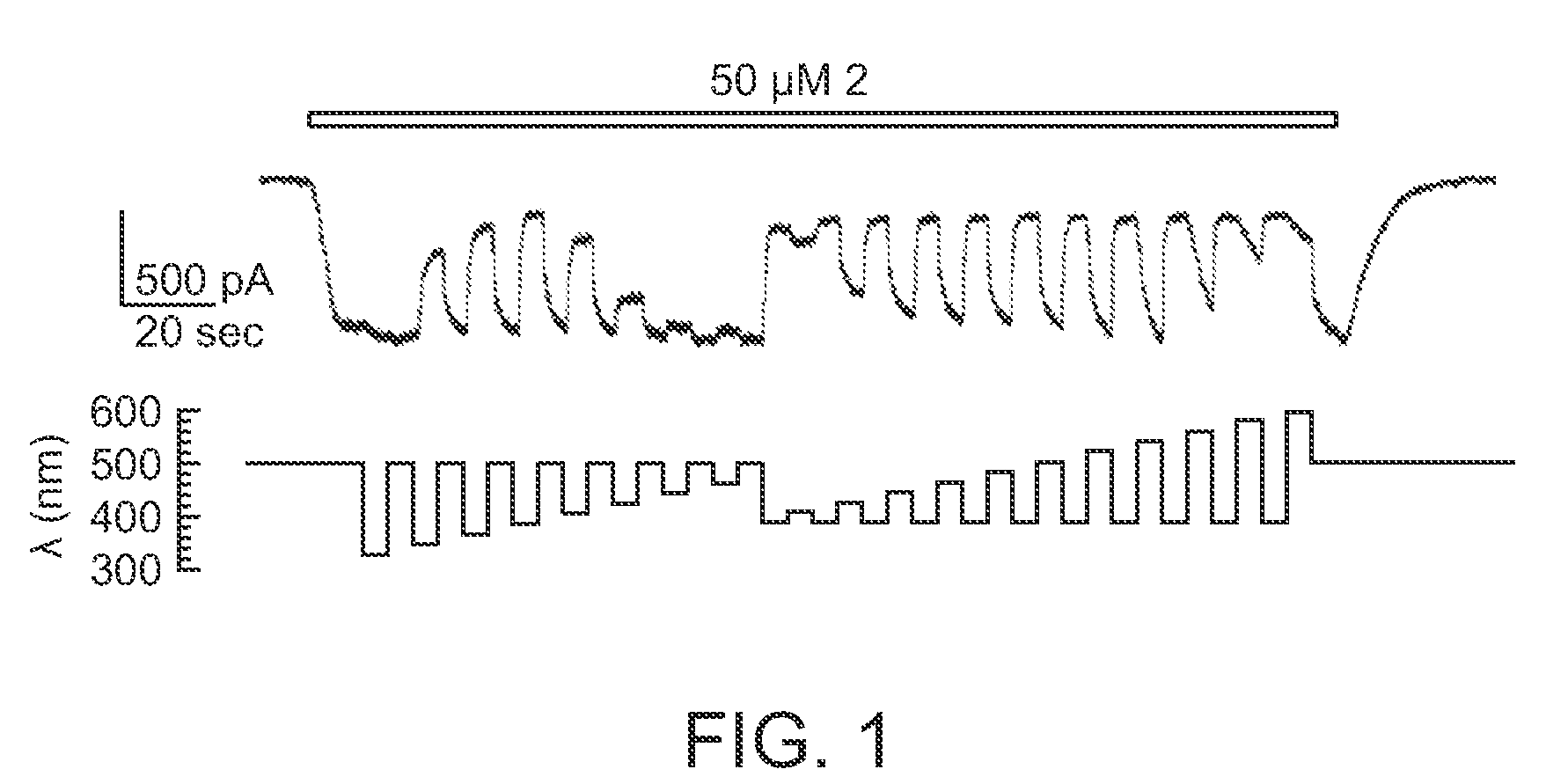
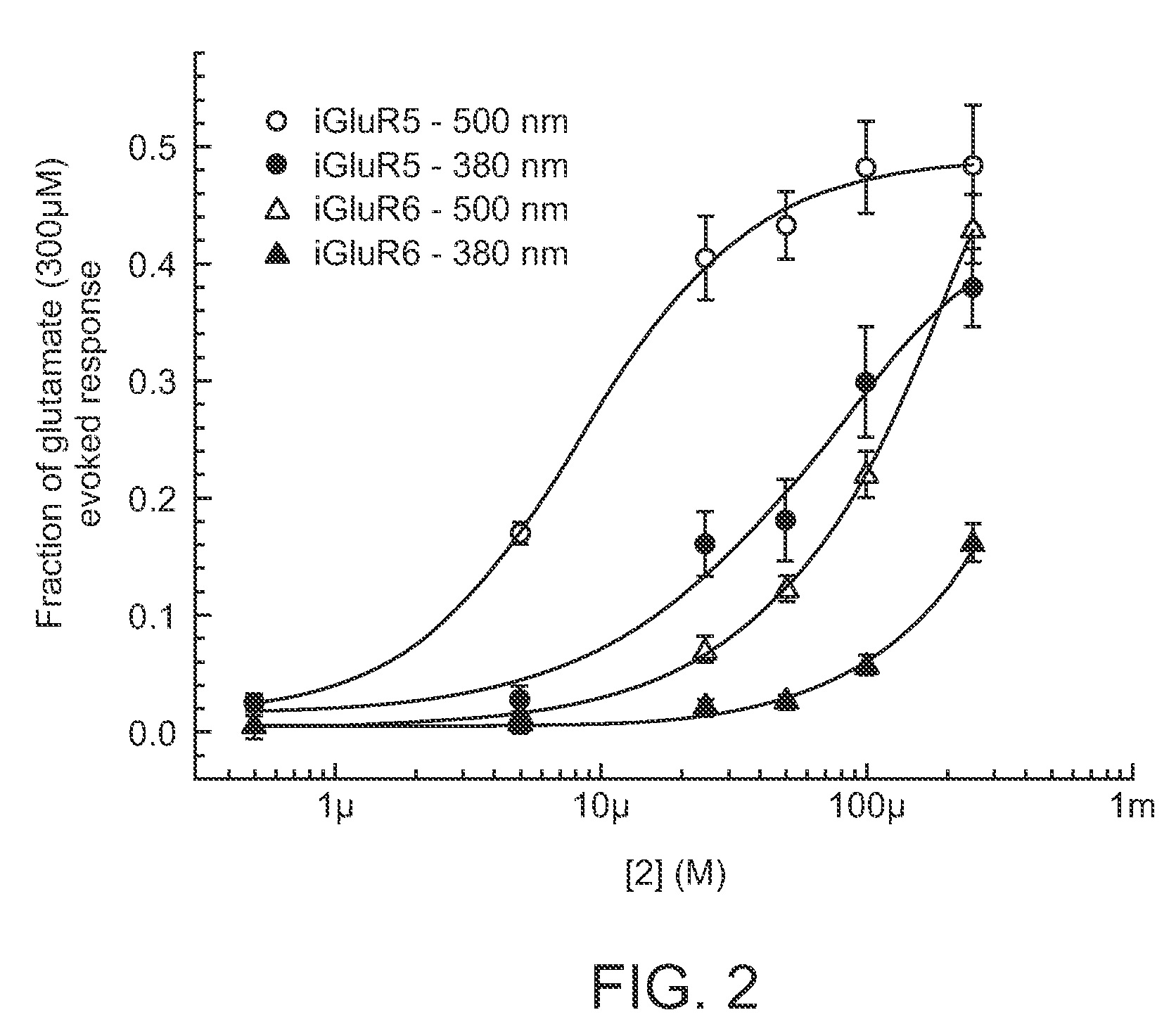
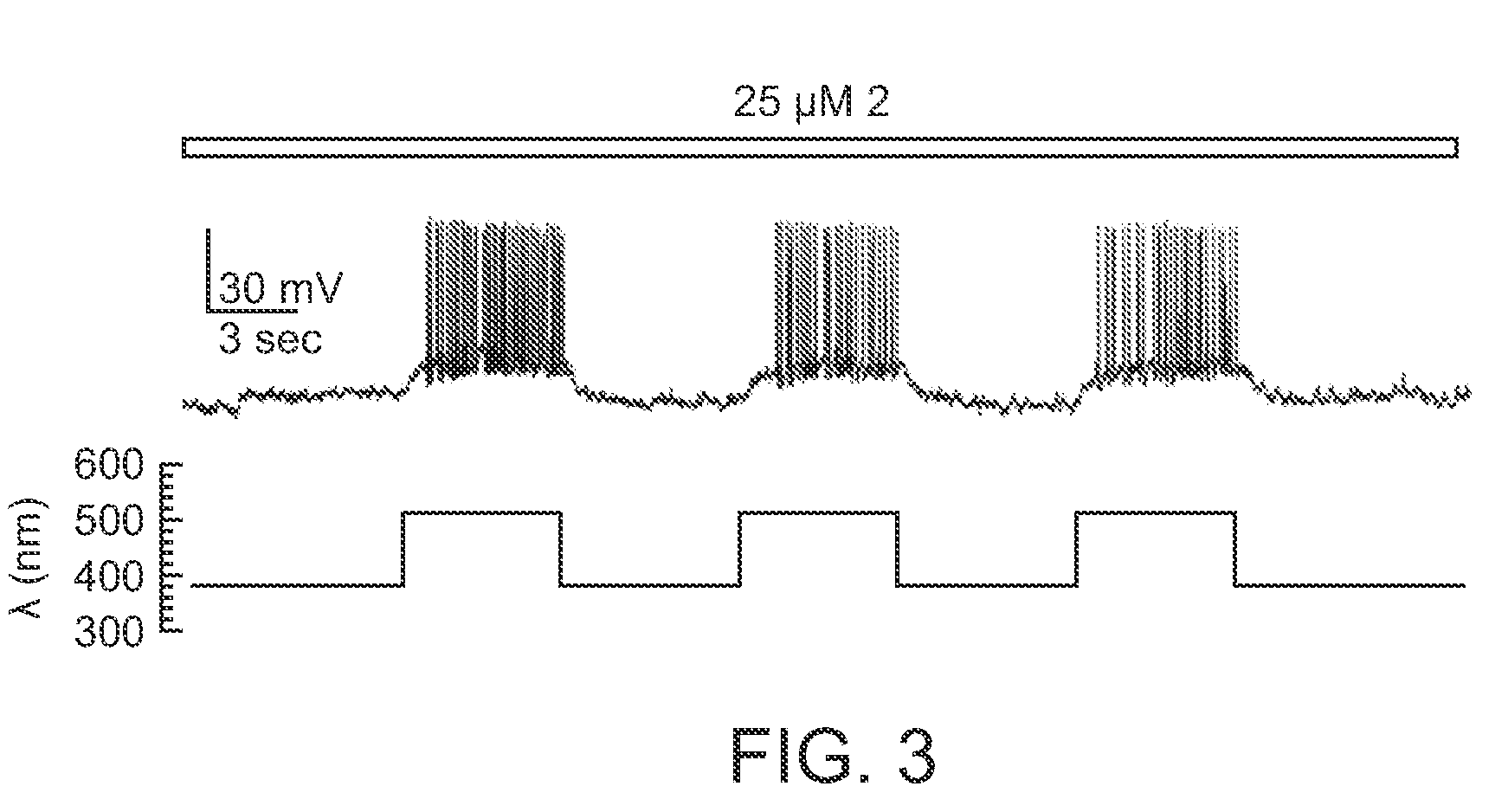
Photoreactive regulator of glutamate receptor function and methods of use thereof
The present invention provides a synthetic regulator of glutamate receptor function, which regulator is a light-sensitive (photoreactive) regulator. The present invention further provides a light-regulated glutamate receptor that includes a subject synthetic regulator non-covalently associated with the glutamate receptor. Also provided are cells and membranes comprising a subject light-regulated glutamate receptor. The present invention further provides methods of modulating glutamate receptor function, involving use of light. The present invention further provides methods of identifying agents that modulate glutamate receptor function.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
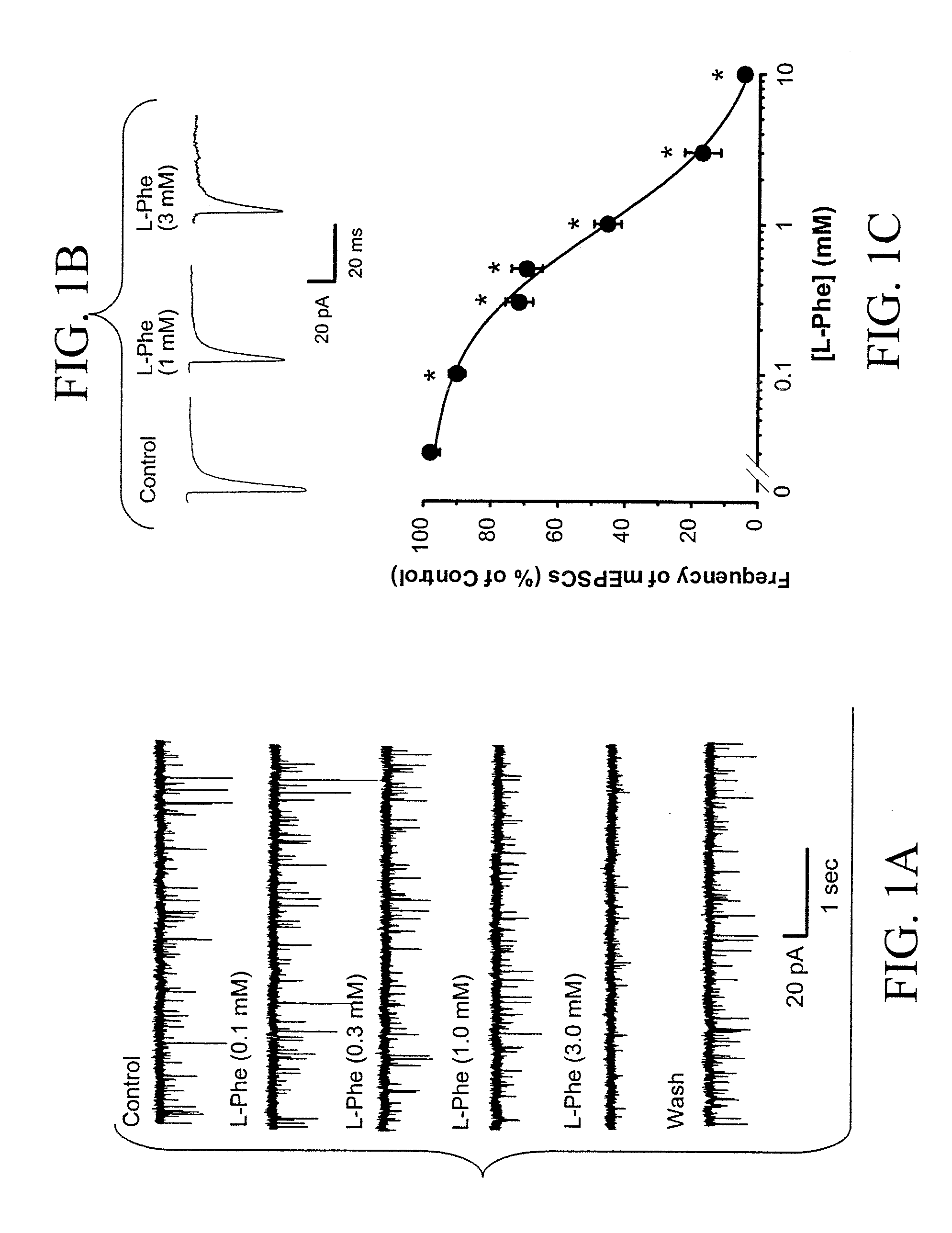
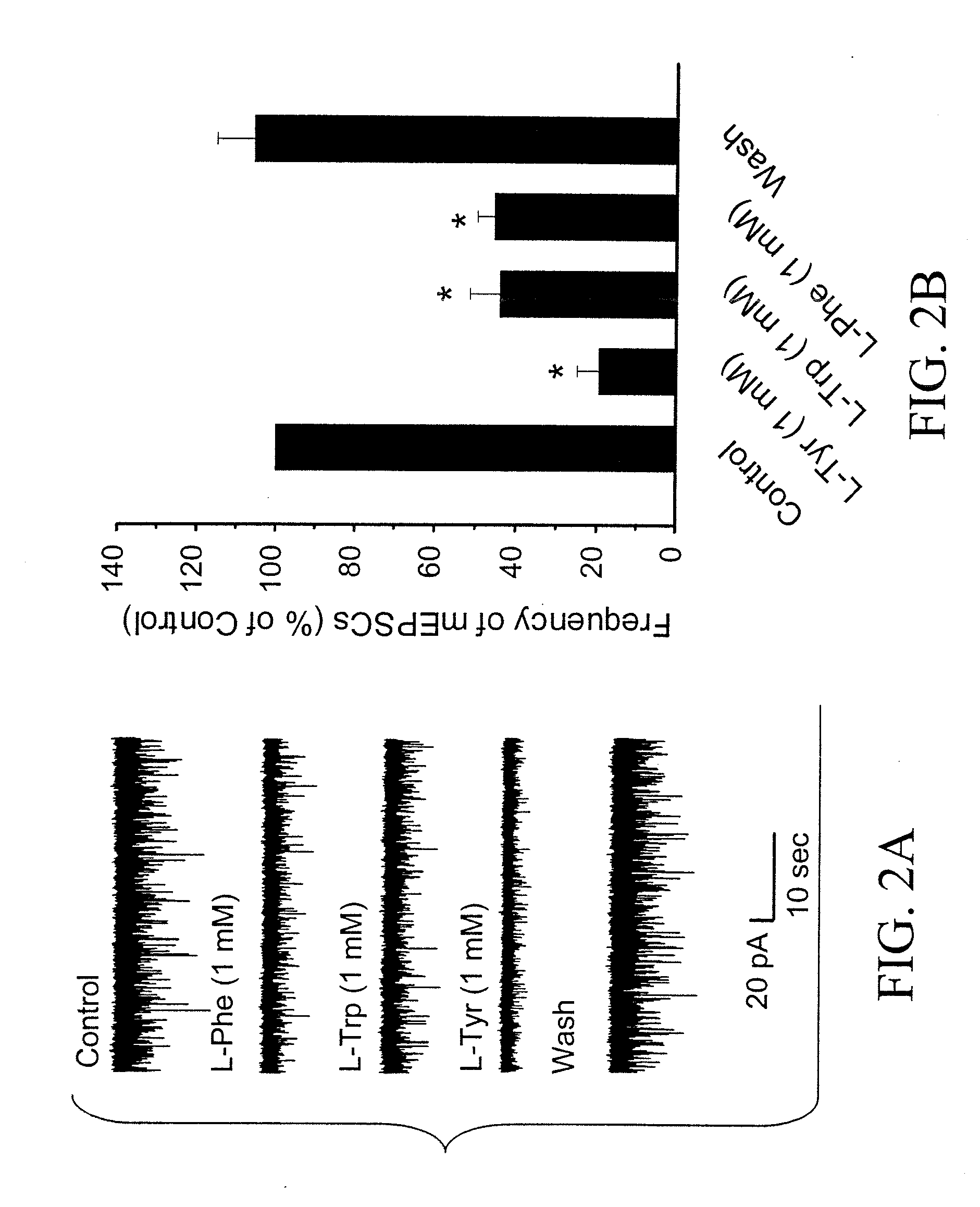
Article of manufacture comprising aromatic amino acids isomers, analogs, or derivatives thereof to treat neurological disorders involving dysfunction of glutamatergic synaptic transmission
InactiveUS20070088074A1Lowering Glu concentrationModulate activityBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsGlutamate receptor activityNeurological disorder
Disclosed herein are articles of manufacture that comprise compositions comprising one or more aromatic amino acids, analogs or isomers thereof, and / or combinations thereof. The articles of manufacture are useful for treatment of neurological conditions related to or which can be affected by, modulation of glutamate receptor (GluR) activity.
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
Methods for diagnosing and treating neuroendocrine cancer
ActiveUS20090074764A1Reduce spreadInhibits and decreases activityMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisAspartic acidCancer research
Owner:TRUSTEES OF DARTMOUTH COLLEGE THE
Biosensor having NANO wire for detecting food additive mono sodium glutamate and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveUS20090155816A1Prevent degradationUseful in detectionImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsFood additiveElectricity
There is provided a biosensor capable of increasing a detecting sensitivity of a target substance of glutamate, by using a nano wire having excellent electrical characteristics and by immobilizing a receptor of glutamate to be detected on a substrate which is disposed between a nano wire and another nano wire and a method for manufacturing the same. The biosensor for detecting glutamate according to the present invention can be manufactured with an arrangement in which the nano wire is selectively arranged on a solid substrate in a matrix. Since this biosensor can prevent the degradation of the nano wire in the electrical characteristic, it can sensitively detect glutamate even through a small amount thereof is contained in a food so that it can be effectively used in detecting the food additive existing in the processed foodstuffs.
Owner:SEOUL NAT UNIV R&DB FOUND +1
Methods for the treatment of substance abuse
The present invention relates to methods of therapy for substance addiction comprising the administration to a subject in need thereof a combination of: (i) a mu-opioid receptor antagonist; (ii) a calcium channel blocker which is long-acting or in sustained-release form or which is nimodipine in rapid release form; and (iii) an NMDA glutamate receptor modulator; as well as combinations, kits and composition useful therefor.
Owner:艾伯特·舒尔曼
Safener drug combinations for use with NMDA antagonist drugs
InactiveUS20120232025A1Reduce or prevent the neurotoxic and psychotomimetic side effectsBlock and prevent potentially toxic side effectBiocideNervous disorderNR1 NMDA receptorSide effect
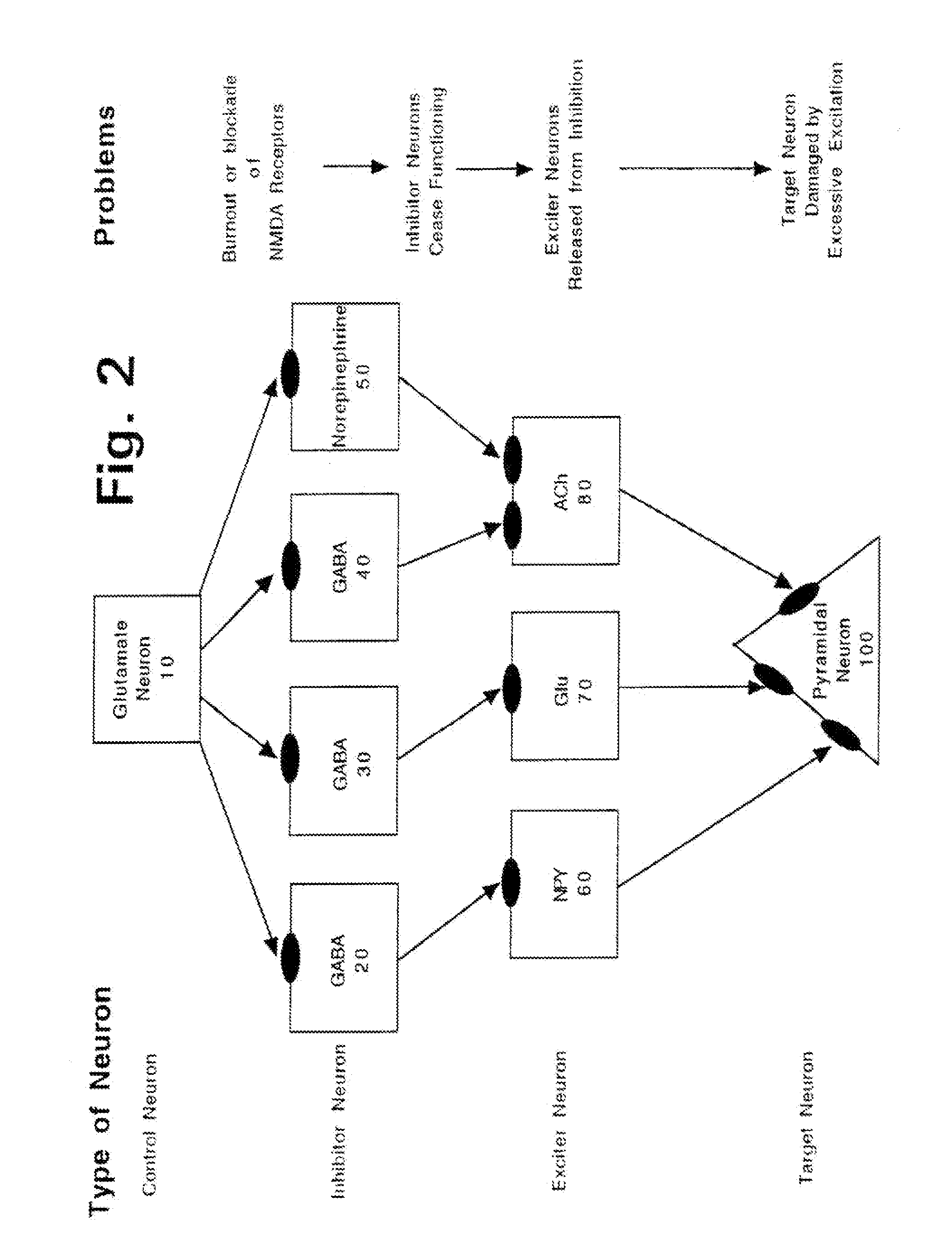
Prolonged administration of subanesthetic dosages of ketamine, which suppresses activity at NMDA receptors, can provide a damaged central nervous system with an opportunity to use its innate healing processes to “reset” NMDA receptors which were pushed into an unwanted hyper-sensitized state by unusually high activity. However, such treatments can cause permanent brain damage, if the ketamine dosage is too heavy or prolonged. Certain types of “safener” drugs have previously been identified, which can block or at least reduce those unwanted side effects. It is disclosed that if two classes of safener drugs are combined, which will simultaneously suppress activity at both (i) muscarinic acetylcholine receptors, and (ii) the kainate and AMPA classes of glutamate receptors, those safener drug combinations can provide exceptionally potent and reliable safening activity, which can enable the safe use of potent NMDA antagonist drugs for a number of highly beneficial purposes.
Owner:OLNEY JOHN W
AMPA-binding human GluR2 receptors
Described herein are isolated polynucleotides which code for an AMPA-type human CNS glutamate receptor, designated the human GluR2B receptor. The receptor is characterized structurally and the construction and use of cell lines expressing these receptor is disclosed.
Owner:NPS PHARM INC
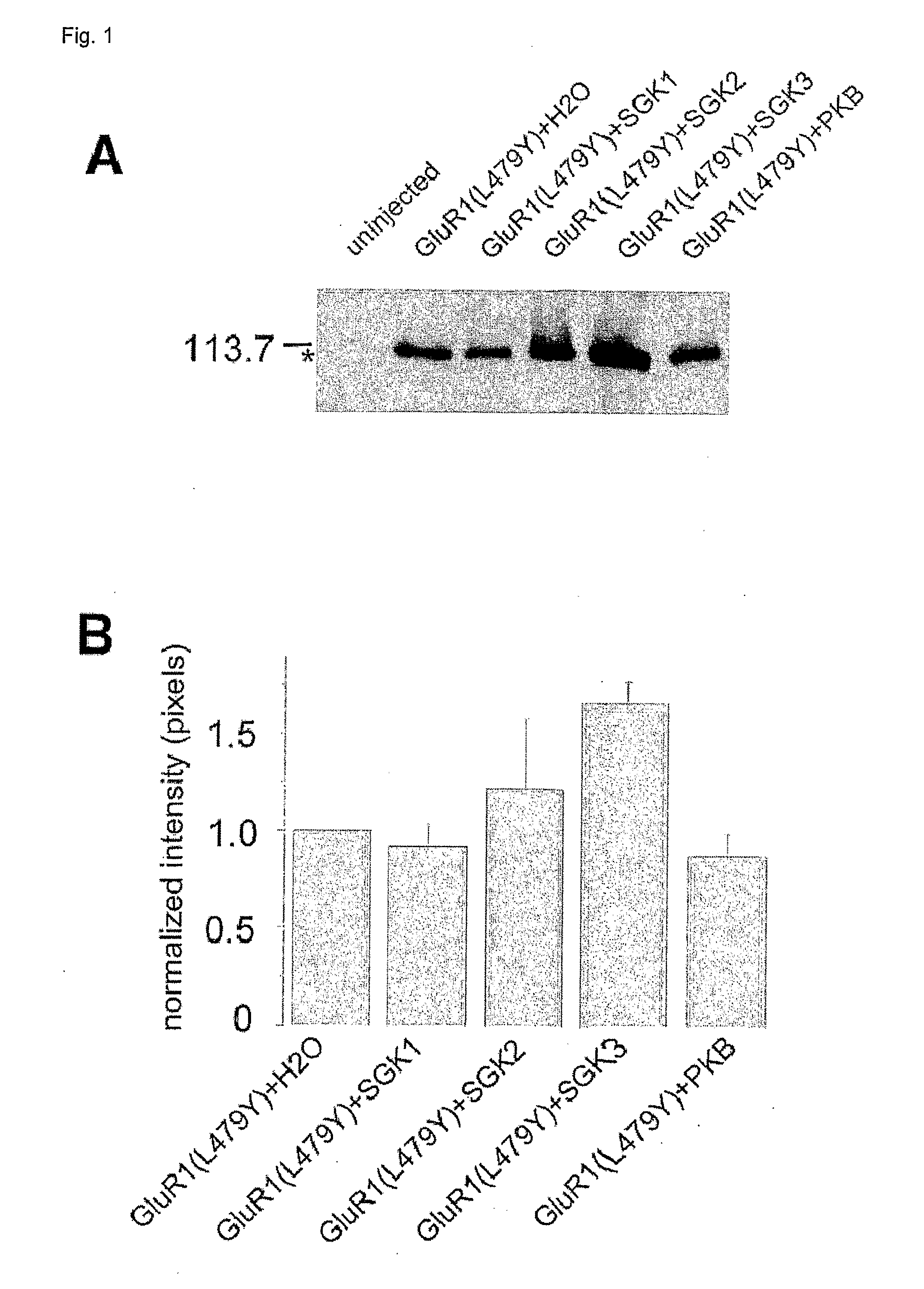
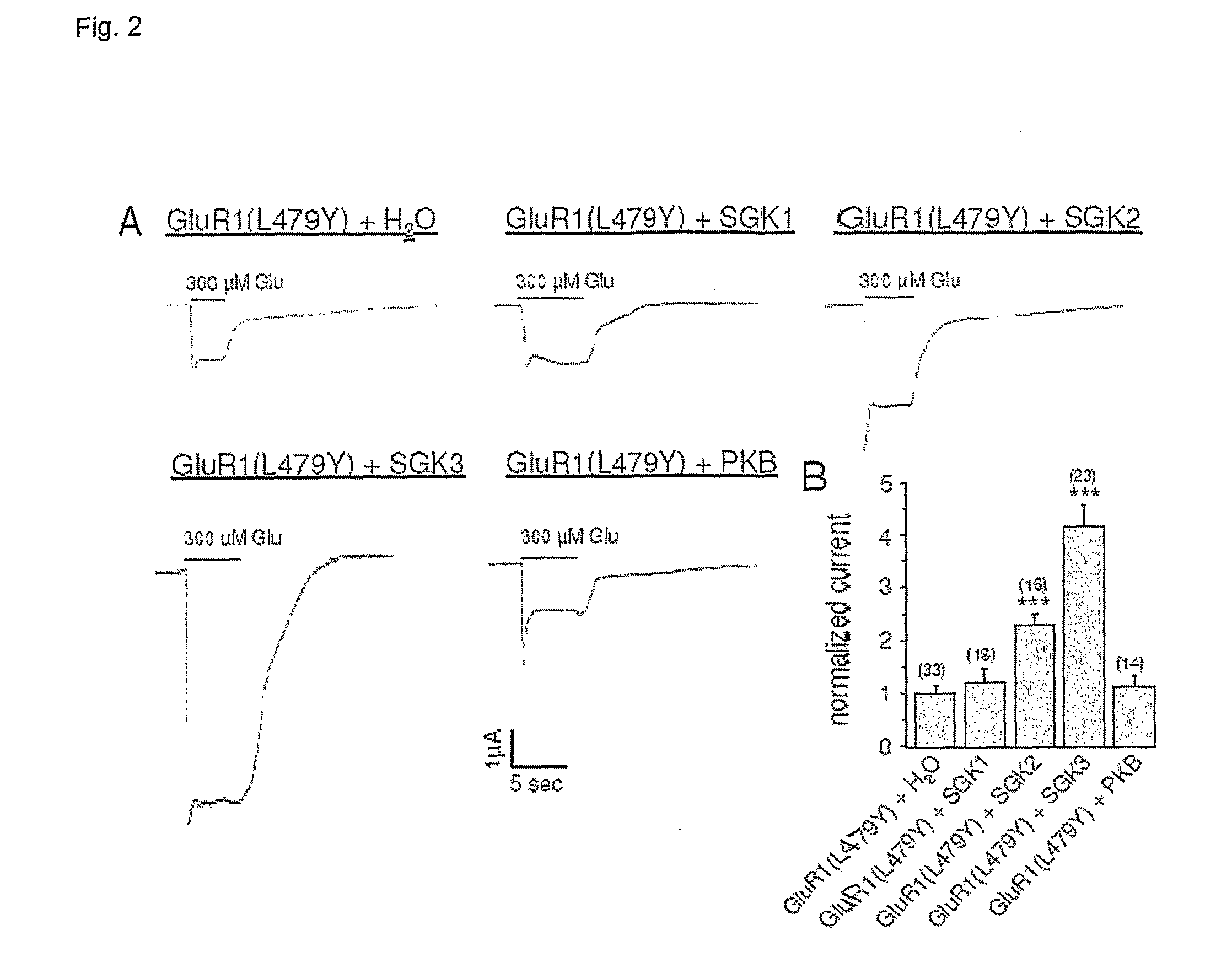
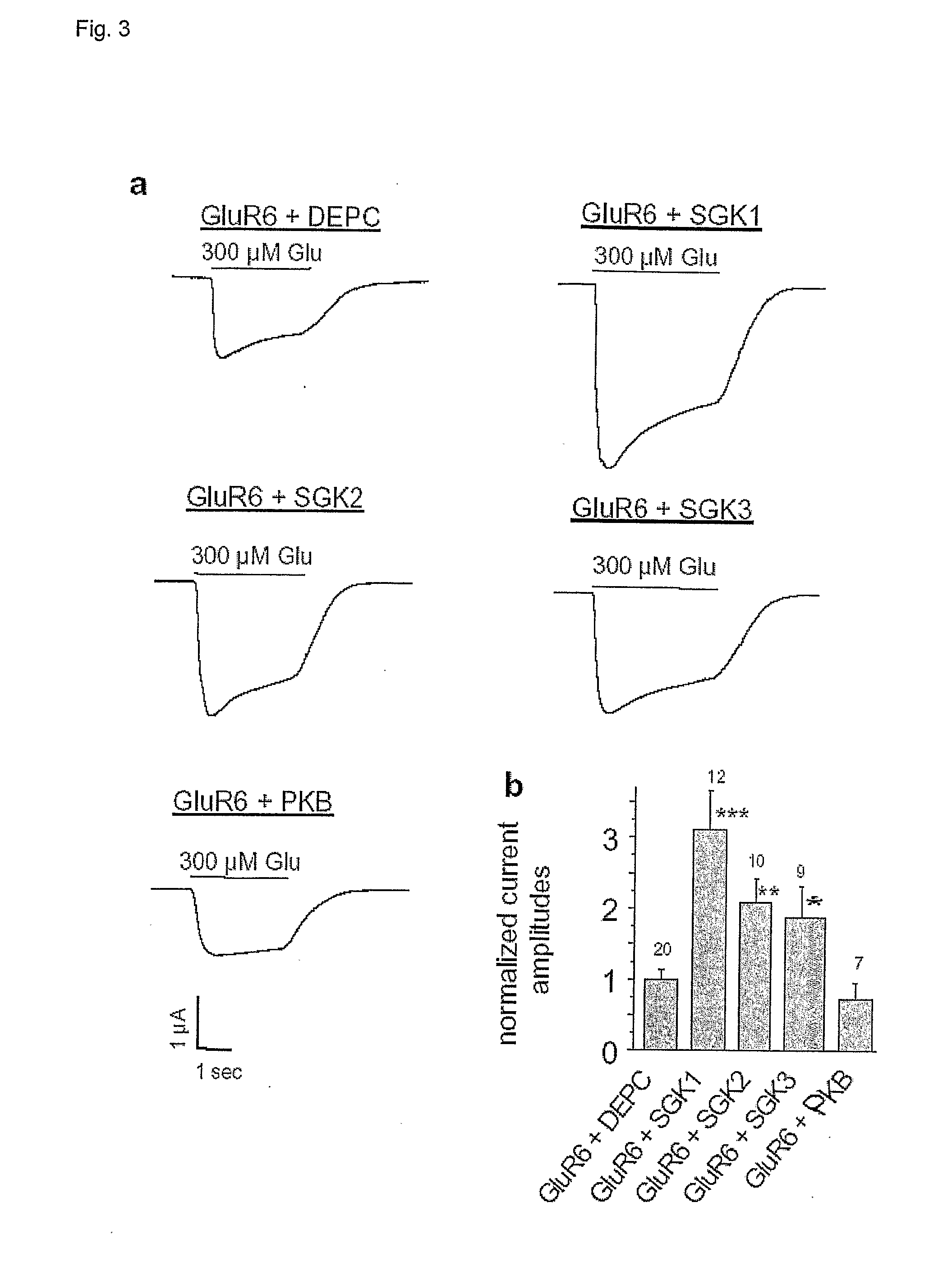
Methods for modulating glutamate receptors for treating neuropsychiatric disorders comprising the use of modulators of serum and glucocorticoid inducible kinases
InactiveUS20070191326A1Increase abundanceIncrease currentOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderDiseaseCompound (substance)
Modulation of the activity of serum and glucocorticoid inducible kinases to restore glutamate receptor activity. Also disclosed are methods and compounds useful for the detection and treatment of neuropsychiatric disorders.
Owner:MERCK PATENT GMBH
Nucleic acid suppression molecule for suppressing expression of brain eIF6 gene and screening method and application thereof
InactiveCN103525900APrecise positioningEnhance learning and memoryOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderExercise-induced fatigueScreening method
The invention provides a method for screening a nucleic acid suppression molecule for effectively suppressing the expression of a brain eIF6 gene from in-vitro cultured cells on the basis of the effect of eIF6 on negative regulation of memory and enhancement on glutamate receptor expression, the nucleic acid inhibition molecule screened by the method, and an application of the nucleic acid inhibition molecule in preventing and / or treating exercise-induced fatigue and / or forgetfulness and related diseases.
Owner:THE FIRST AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF THIRD MILITARY MEDICAL UNIVERSITY OF PLA
Methods for diagnosing and treating neuroendocrine cancer
InactiveUS20080145849A1Reduce spreadInhibits and decreases activityBiocideMicrobiological testing/measurementAspartic acidCancer research
Owner:TRUSTEES OF DARTMOUTH COLLEGE THE
A neuroprotective agent
ActiveCN106377520AReduce calcium influxProtection from glutamate toxicityOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderChemical compoundCortical neurons
The invention relates to a neuroprotective agent. The neuroprotective agent comprises a chemical compound having a structure formula shown as follows. The chemical compound having the structure formula can reduce cell calcium influx through a glutamate receptor invertibility inhibiting function, thus protecting cortical neurons from excitatory toxicity initiated by glutamic acid. The neuroprotective agent is extremely effective.
Owner:SOUTH UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY OF CHINA
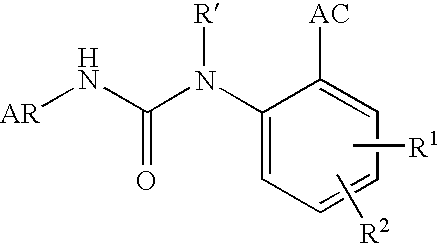
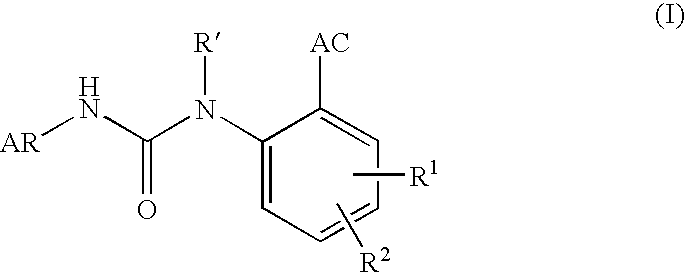
Aryl ureido benzoic acid derivatives and their use
This invention relates to novel aryl ureido benzoic acid derivatives useful as selective and non-competitive antagonists of the ionotropic GluR5 receptor. Due to their biological activity, the aryl ureido derivatives of the invention are considered useful for treating diseases that are responsive to modulation of an aspartate or a glutamate receptor. Moreover the invention provides chemical compounds for use according to the invention, as well as pharmaceutical compositions comprising the chemical compounds, and methods of treating diseases or disorders or conditions responsive to modulation of an aspartate or a glutamate receptor.
Owner:NEUROSEARCH AS
Mechanism of astricyte-neuron signaling
InactiveUS20080299109A1Nervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsG protein-coupled receptorNeurotransmission
The present invention relates to a novel communication mechanism between astrocytes and neurons at a synapse. More specifically, the present invention relates to a signaling mechanism between astrocytes and neurons, by activating astrocytic G-protein coupled receptors, thereby activating glutamate receptors on a membrane of neighboring postsynaptic neurons, resulting in increasing the level of intracellular Ca2+ and inducing a depolarization inward current to control neurotransmission in neurons.
Owner:KOREA INST OF SCI & TECH
Treatment of Parkinson's disease with oligonucleotides
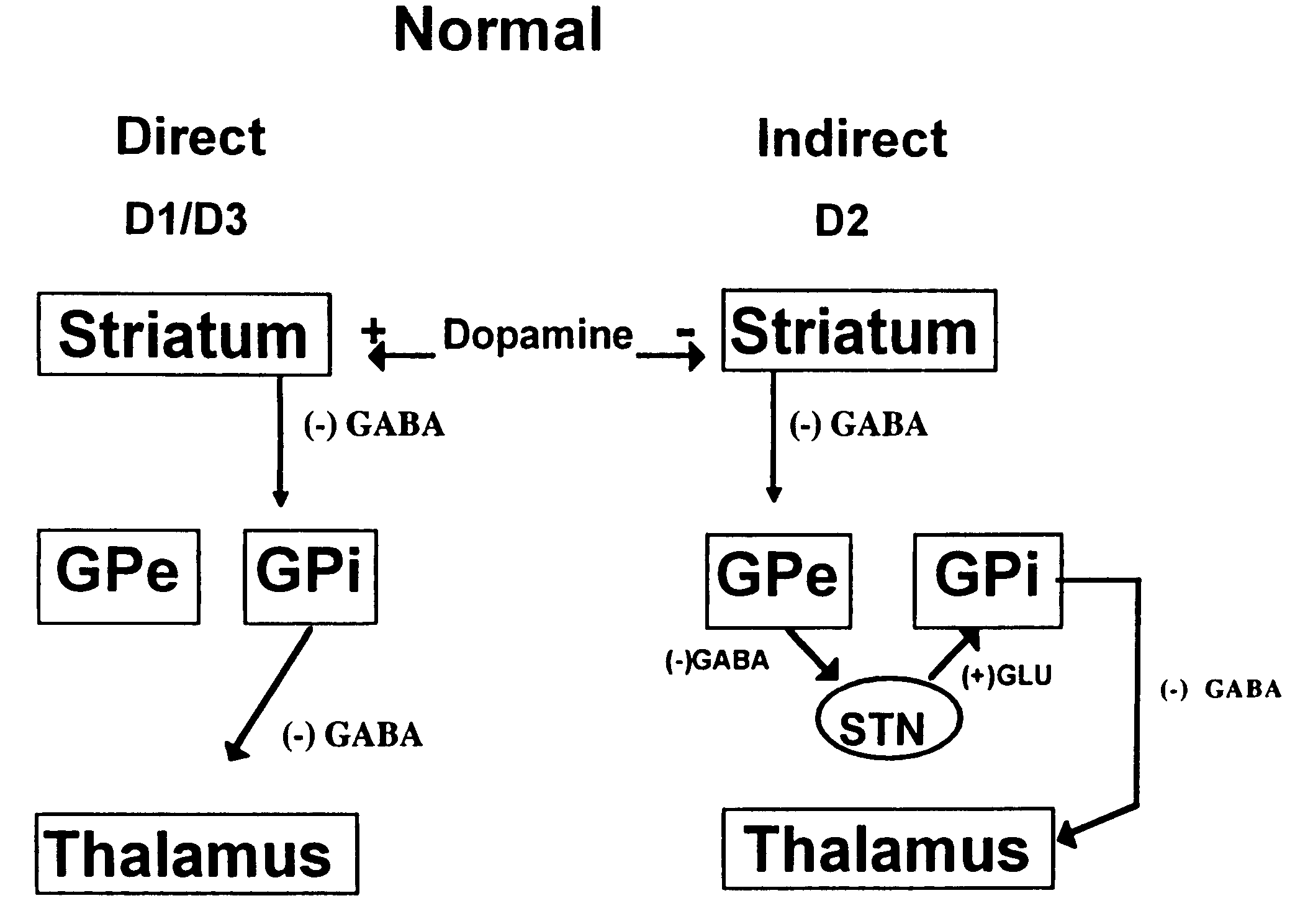
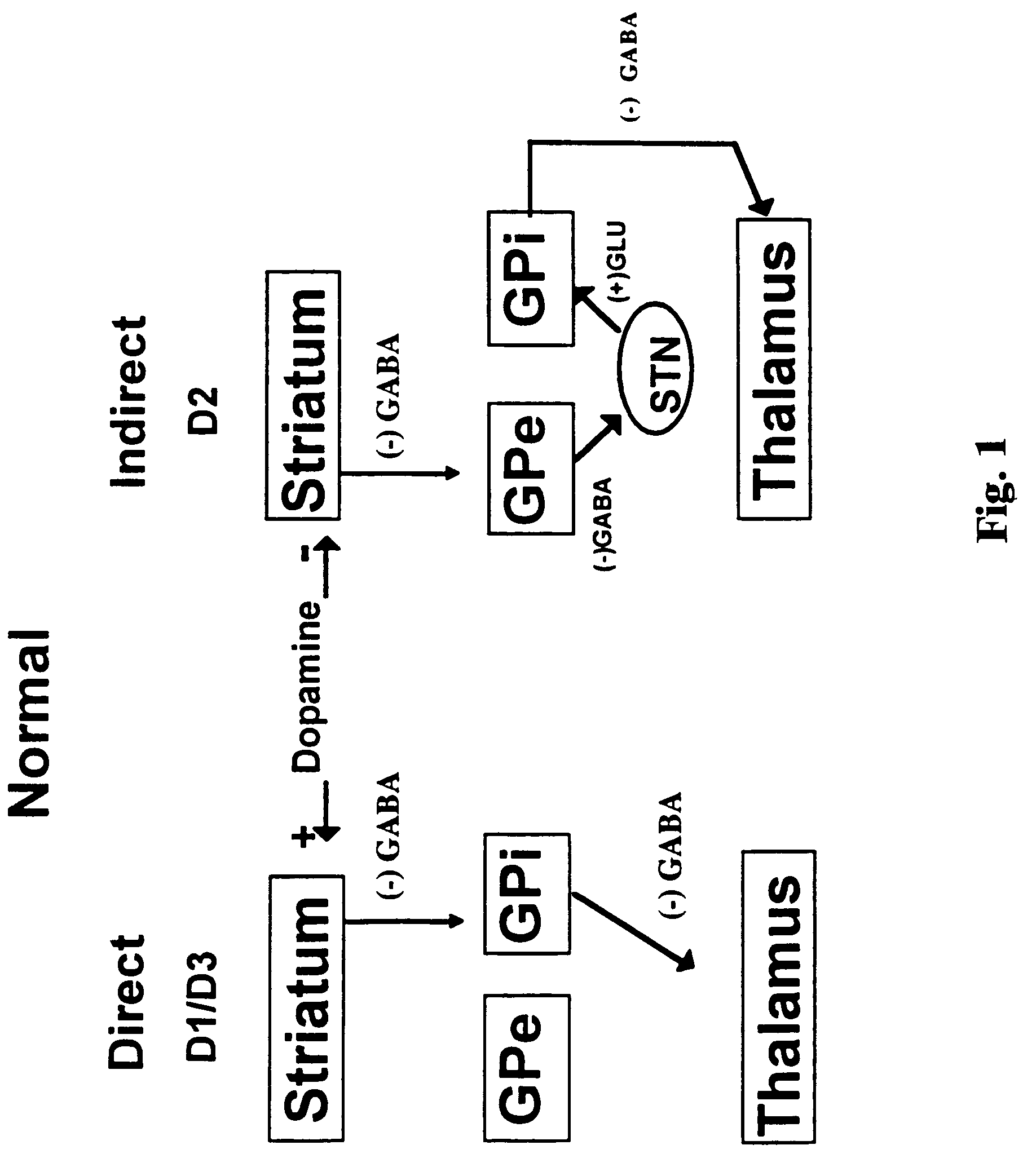
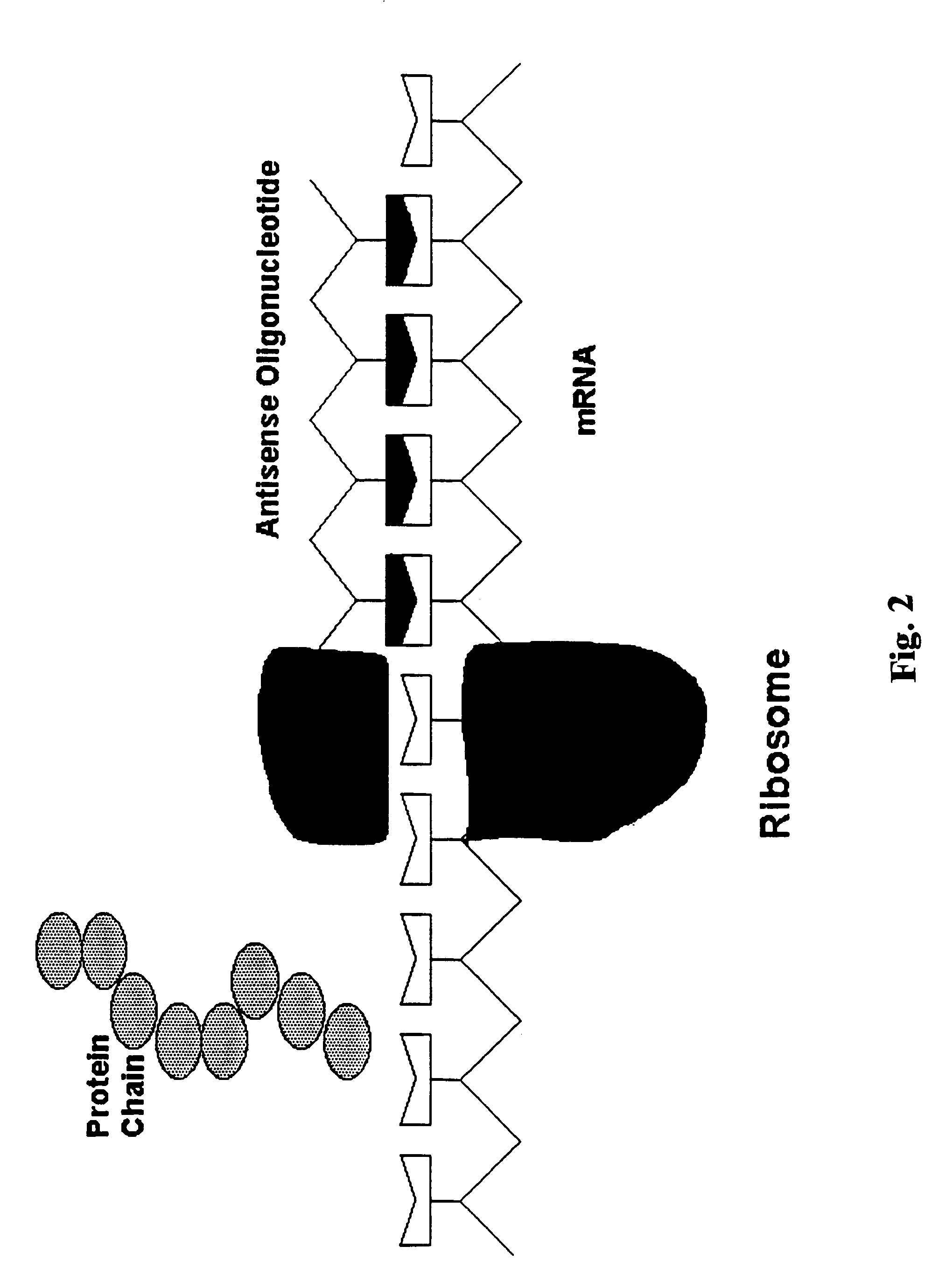
The present invention relates to a method of treatment of Parkinson's disease, and to the use of antisense oligonucleotides or triplex oligonucleotides introduced into targeted brain structures to decrease the function of brain circuits known to be overactive in the Parkinsonian brain. Antisense or triplex oligonucleotides are targeted to the internal globus pallidus and / or substantia nigra pars reticulata (SNr) where the expression of glutamic acid decarboxylase (GAD67, GAD65, or a combination of the two isoforms) is downregulated. The present invention also relates to a method of treatment of Parkinson's disease where antisense or triplex oligonucleotides are targeted to the internal globus pallidus and / or substantia nigra pars reticulata for the downregulation of glutamate receptors. The present invention further relates to a method of treatment of Parkinson's disease where antisense or triplex oligonucleotides are targeted to the thalamic motor nuclei for the downregulation of GABA receptors.
Owner:THOMAS JEFFERSON UNIV
Methods for Diagnosing and Treating Neuroendocrine Cancer
InactiveUS20110014202A1Reduce spreadInhibits and decreases activity and expressionBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsAspartic acidNeuroendocrine Cancer
Owner:TRUSTEES OF DARTMOUTH COLLEGE THE
Methods to identify patients at risk of developing adverse events during treatment with antidepressant medication
The invention provides a method of screening patients to identify those patients more likely to exhibit an increased risk of treatment-emergent suicidal ideation comprising: (a) obtaining a sample of genetic material from the patients, and (b) assaying the sample for the presence of a genotype in the patients which is associated with an increased risk of treatment-emergent suicidal ideation, wherein the genotype is characterized by a polymorphism in a gene selected from the group consisting of glutamine receptor, ionotropic, kainate 2 (GRIK2); glutamate receptor ionotropic AMPA 3 (GRIA3); and combinations thereof.
Owner:GOVERNMENT OF THE US REPRESENTED BY THE SEC +1
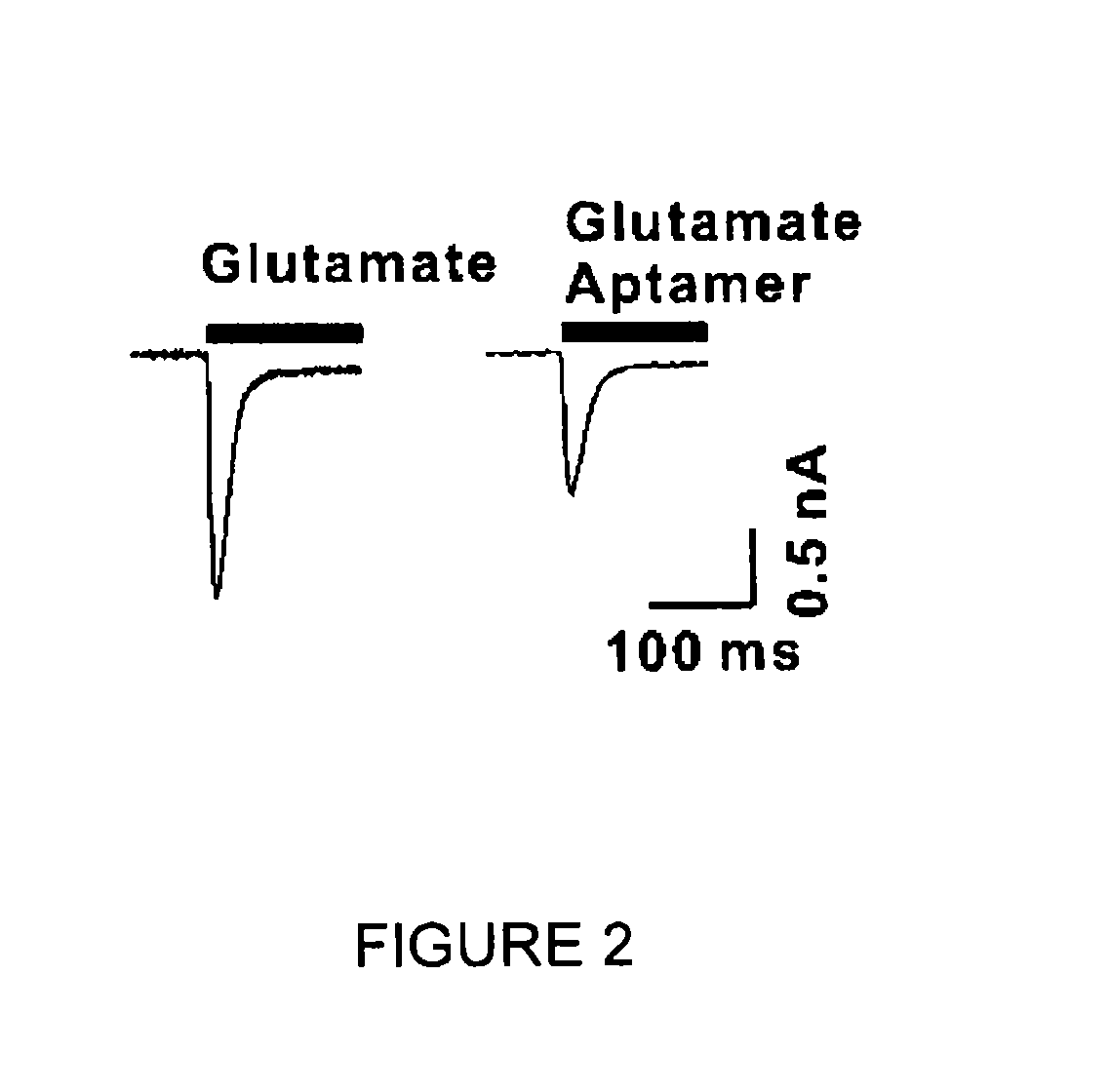
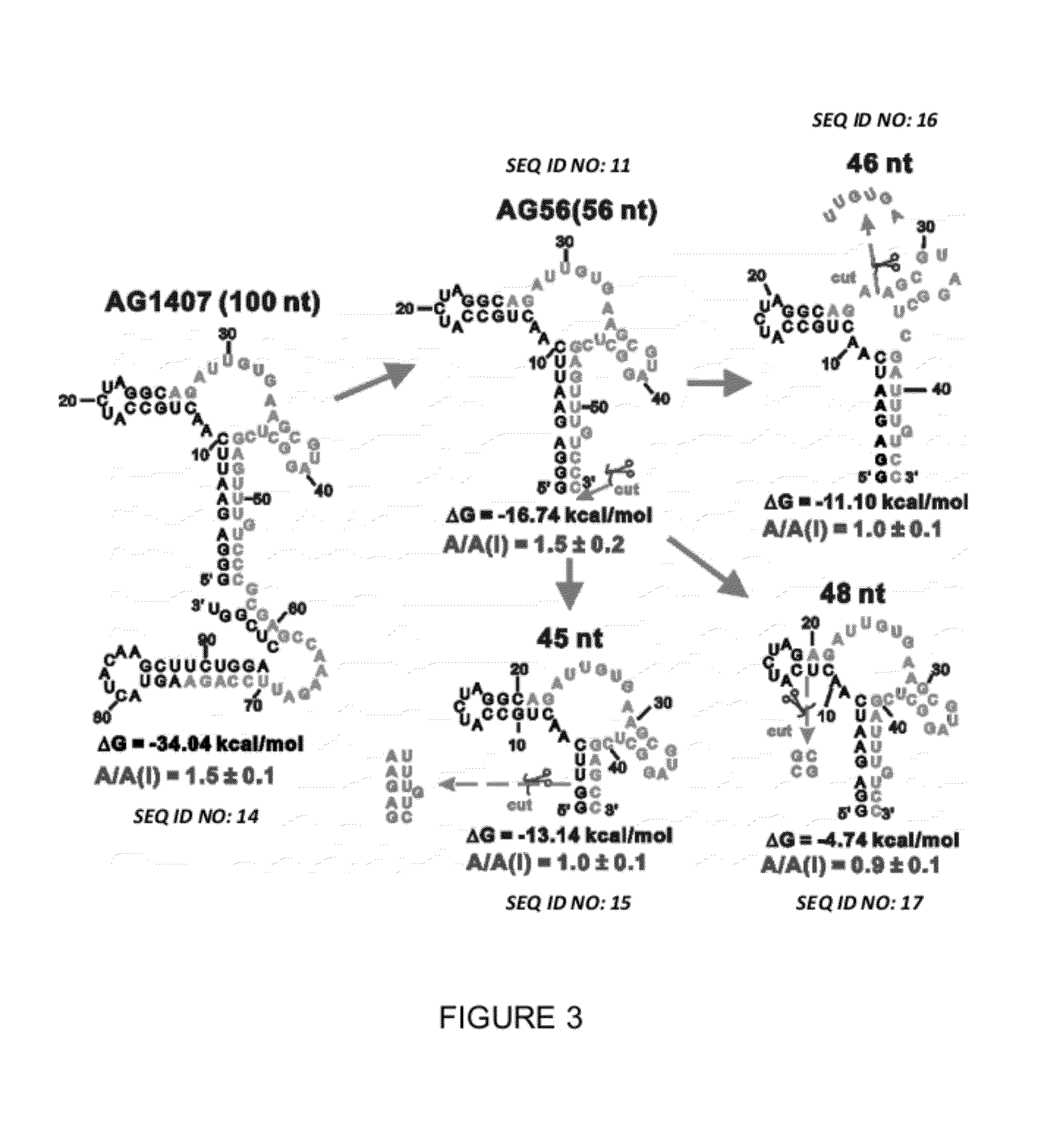
Conformation-selective nucleic acid inhibitors of AMPA glutamate receptors
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK
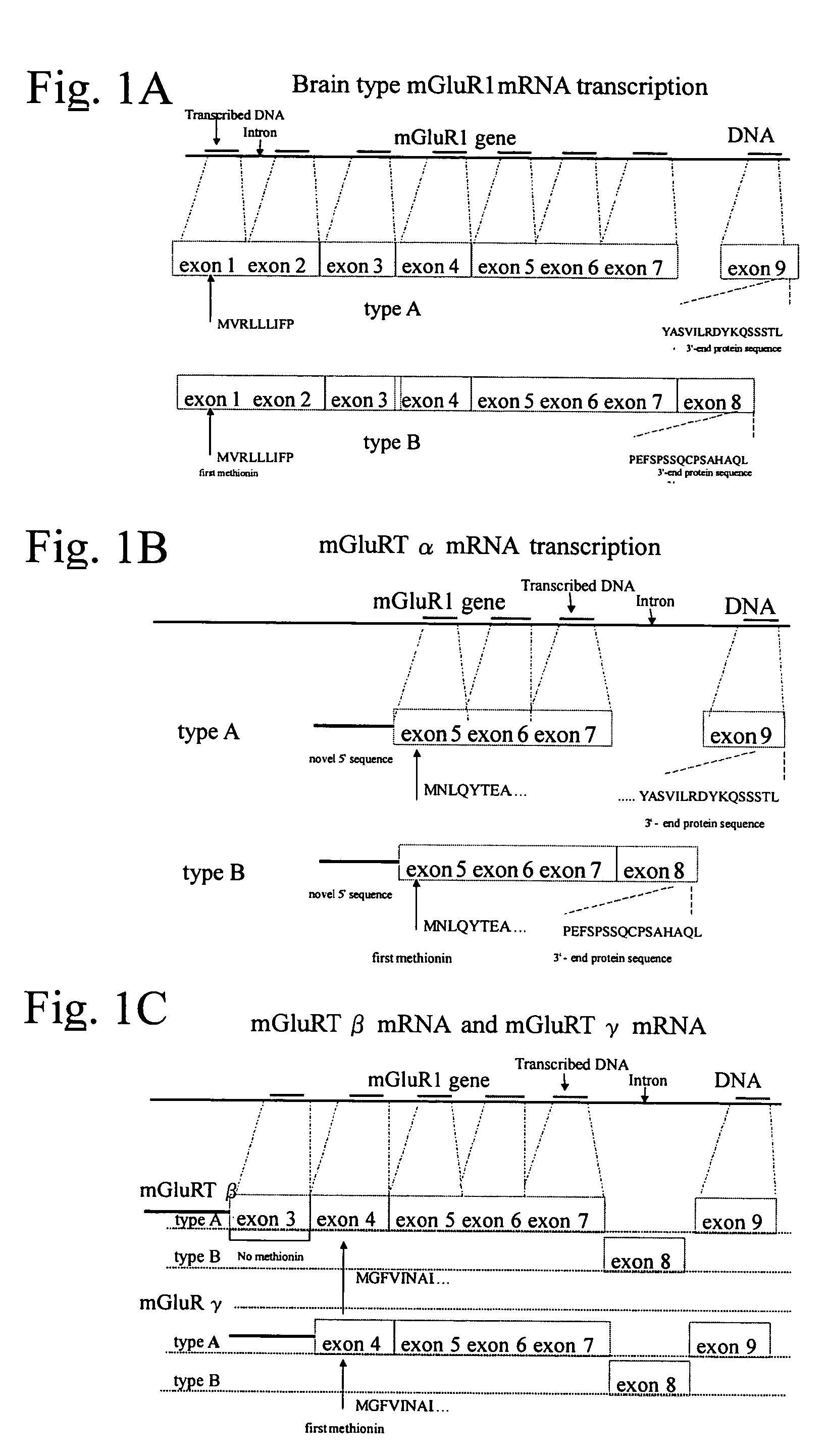
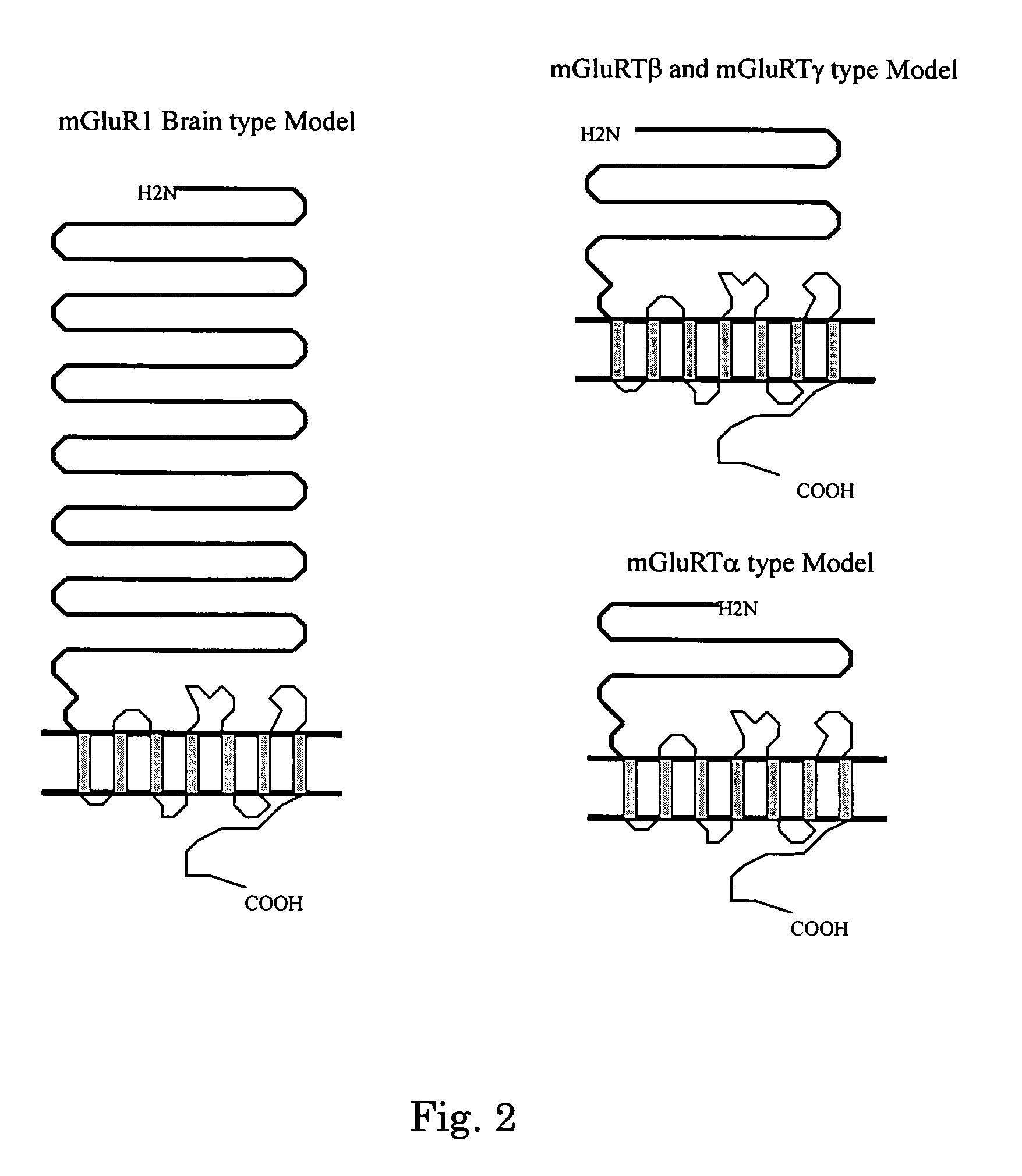
Glutamate receptor and utilization thereof
InactiveUS7186819B2Prevent and improve symptomNervous disorderBacteriaAllosteric modulatorSubject matter
The inventive subject matter relates to a glutamate receptor, DNA which encodes the receptor, a transformed cell expressing the receptor, a method for producing the receptor, a method for identifying an agonist, antagonist, or allosteric modulator for glutamic acid, a method for identifying an agonist for glutamic acid, an antibody to the receptor, and processes for making glutamate receptor modulators and pharmaceutical compositions comprising said modulator.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
Fertilized egg isolate and use thereof
Fertilized egg isolate, methods for preparing the fertilized egg isolate and uses thereof for treating mental health disorders and disease or conditions mediated by or associated with one or more glutamate receptors or by the neurokinin 2 (NK2) receptor.
Owner:UNITED PARAGON ASSOCS
Methods for diagnosing and treating neuroendocrine cancer
InactiveUS8592168B2Reduce spreadInhibits and decreases activity and expressionBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsAspartic acidNeuroendocrine Cancer
Owner:TRUSTEES OF DARTMOUTH COLLEGE THE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com