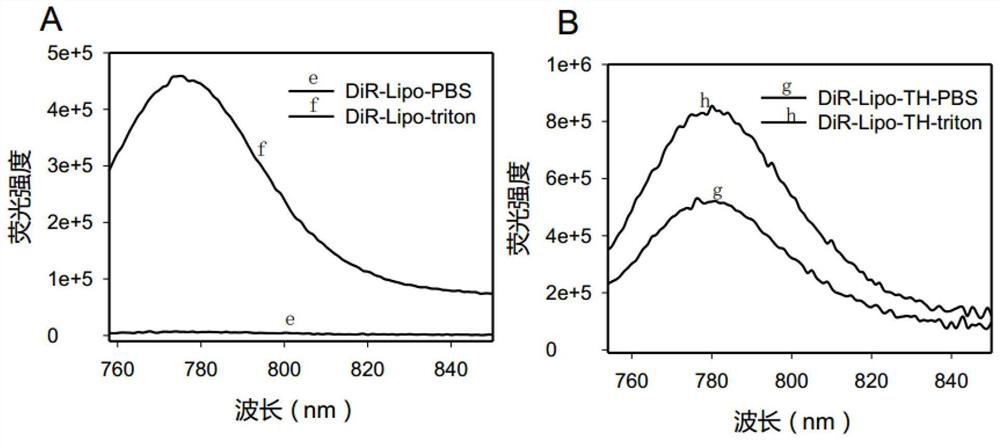
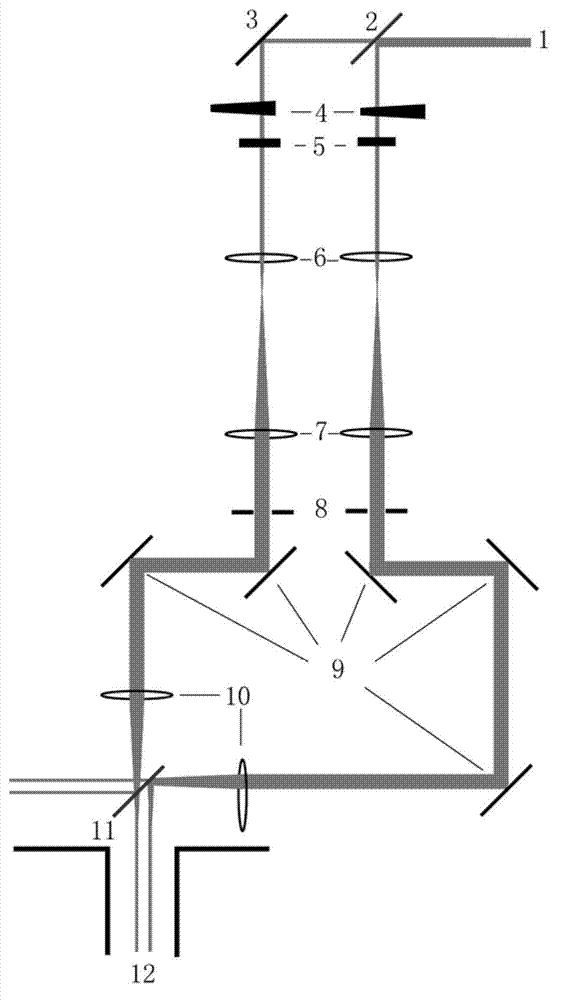
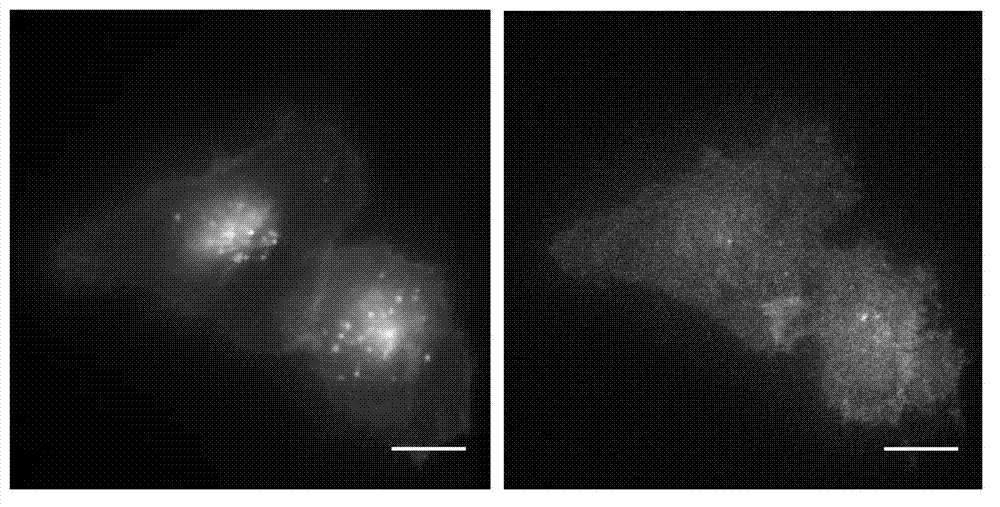
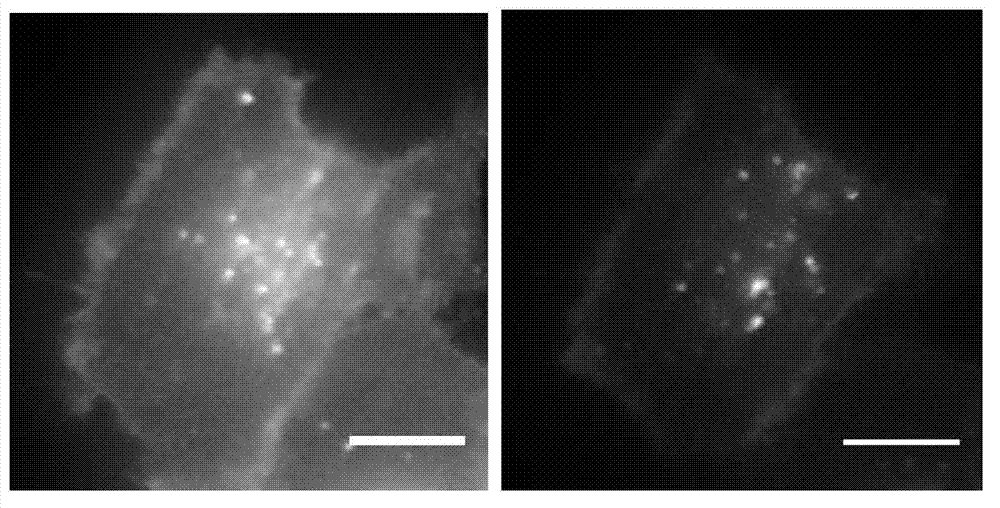
Patents
Literature
33results about How to "Improve the signal-to-background ratio" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
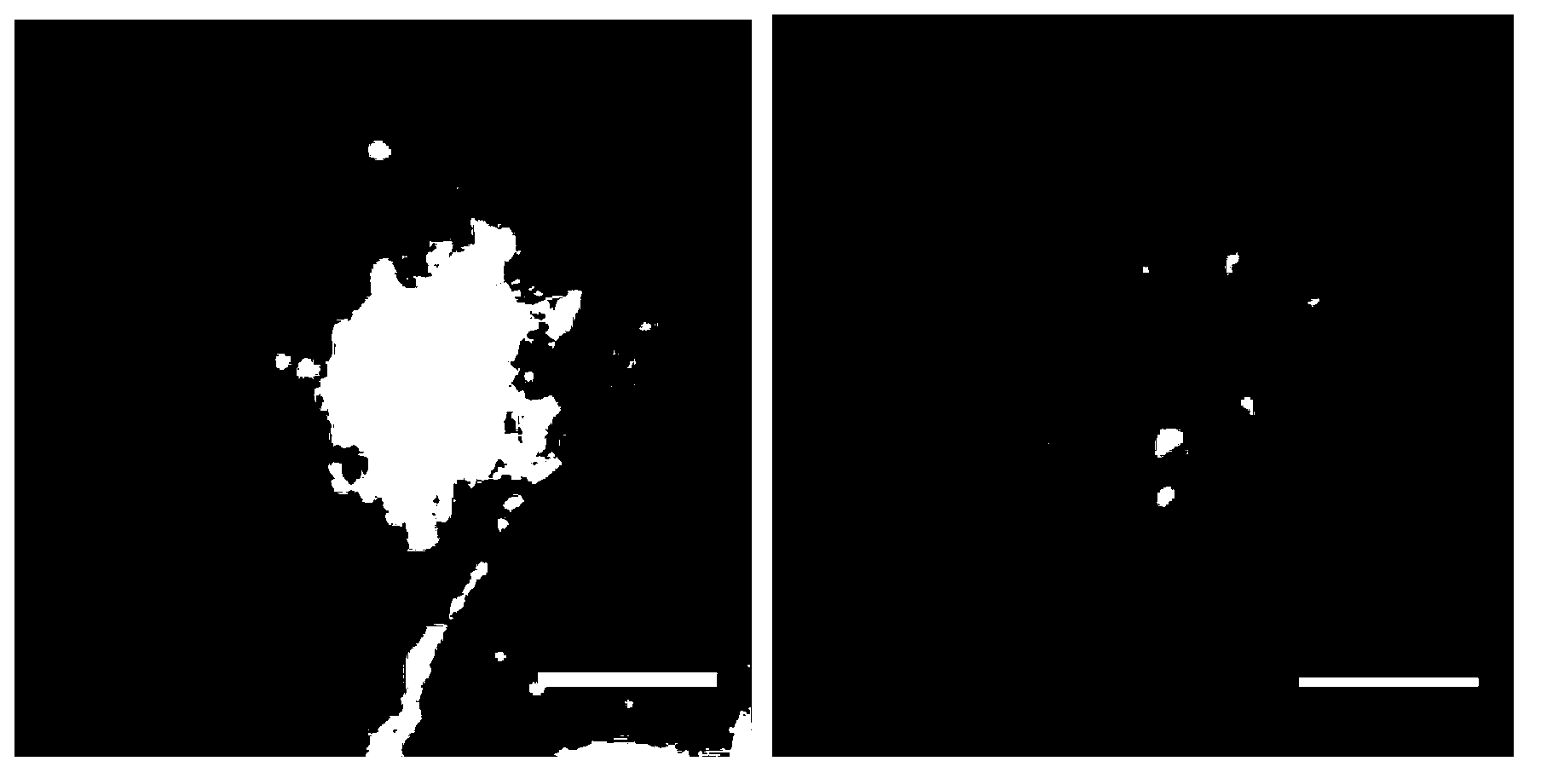
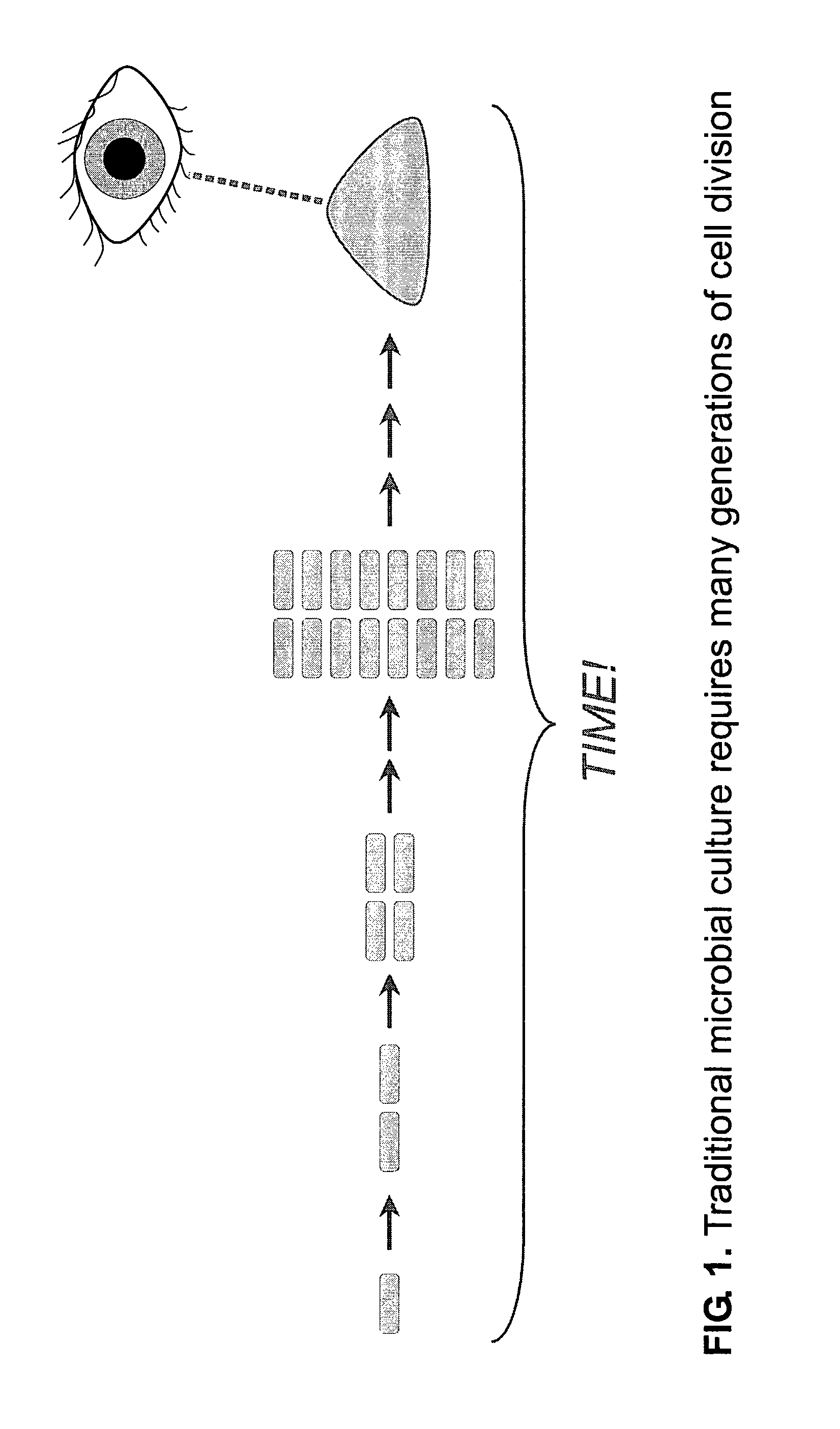
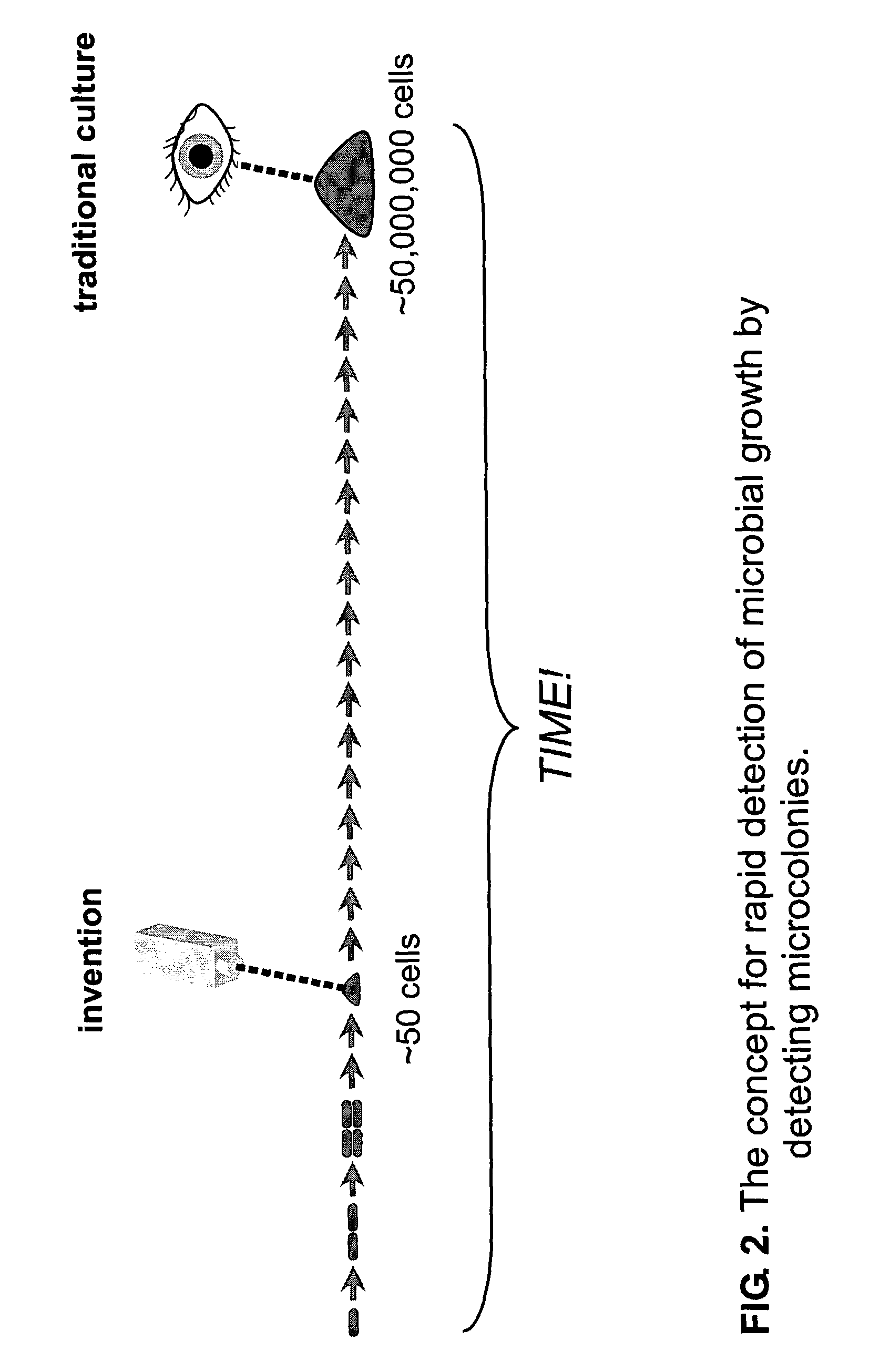
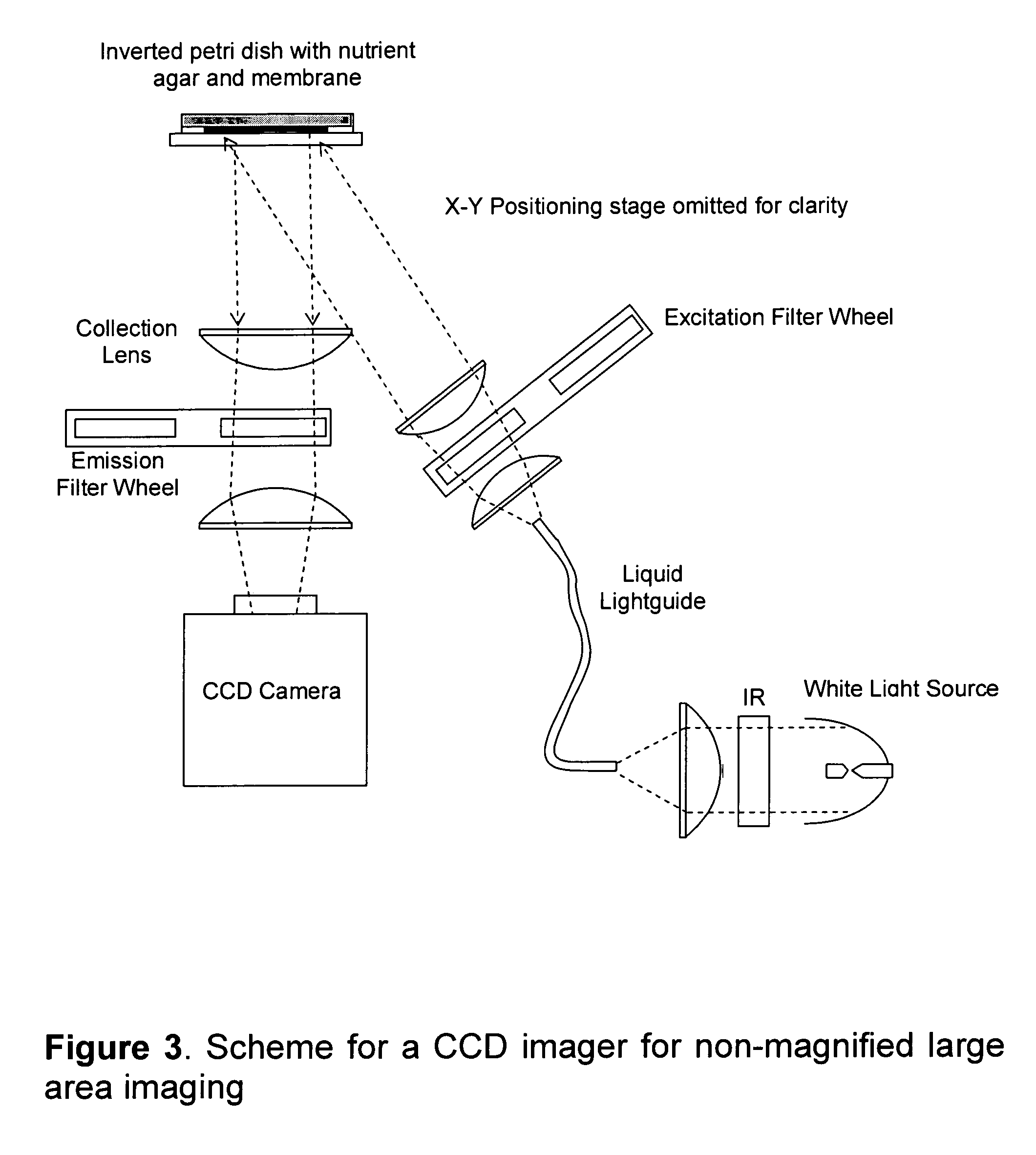
Rapid detection of replicating cells
ActiveUS7582415B2Reduce riskFast resultsBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsNon destructiveMicroorganism
The invention enables efficient, rapid, and sensitive enumeration of living cells by detecting microscopic colonies derived from in situ cell division using large area imaging. Microbial enumeration tests based on the invention address an important problem in clinical and industrial microbiology—the long time needed for detection in traditional tests—while retaining key advantages of the traditional methods based on microbial culture. Embodiments of the invention include non-destructive aseptic methods for detecting cellular microcolonies without labeling reagents. These methods allow for the generation of pure cultures which can be used for microbial identification and determination of antimicrobial resistance.
Owner:RAPID MICRO BIOSYSTEMS INC
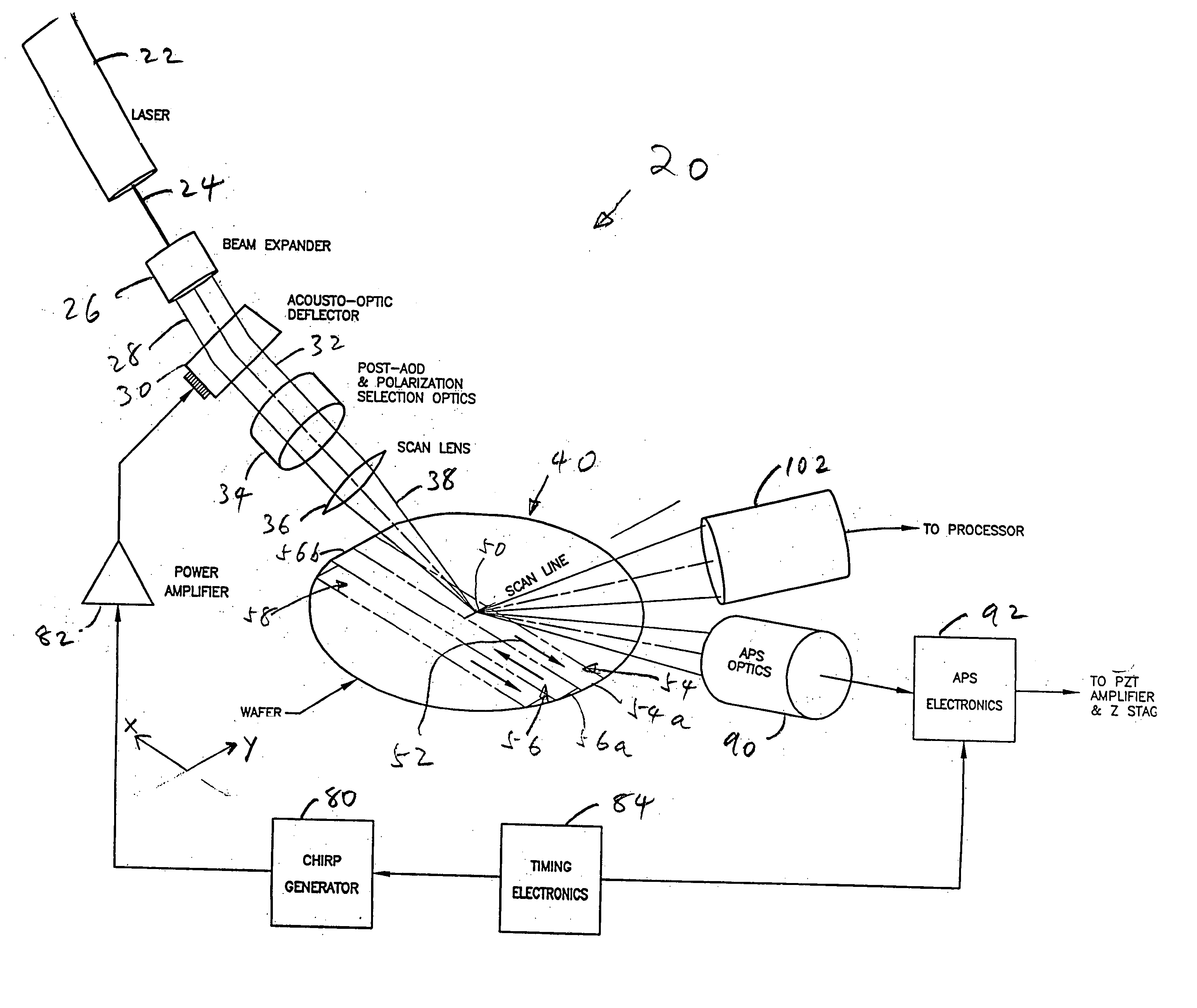
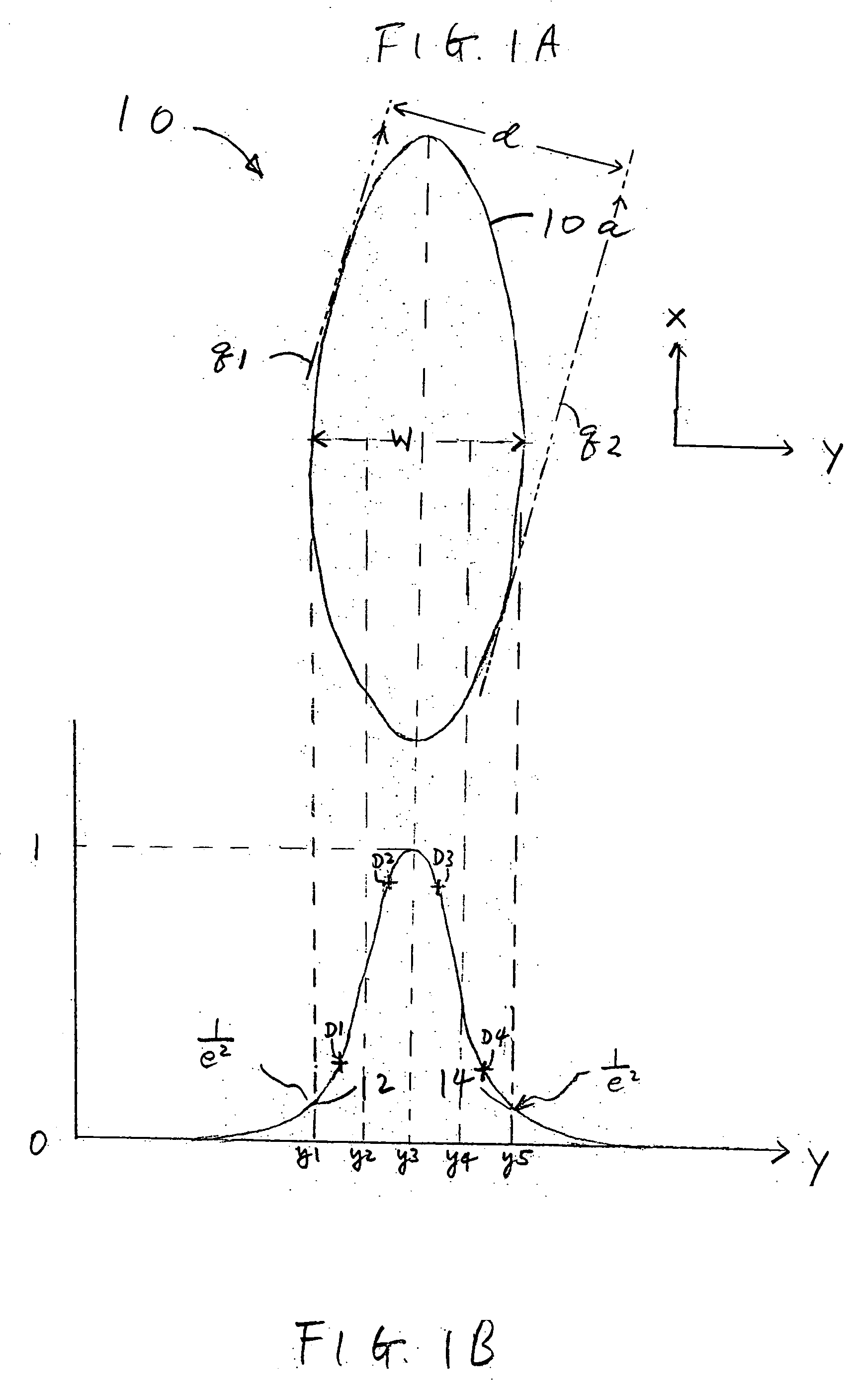
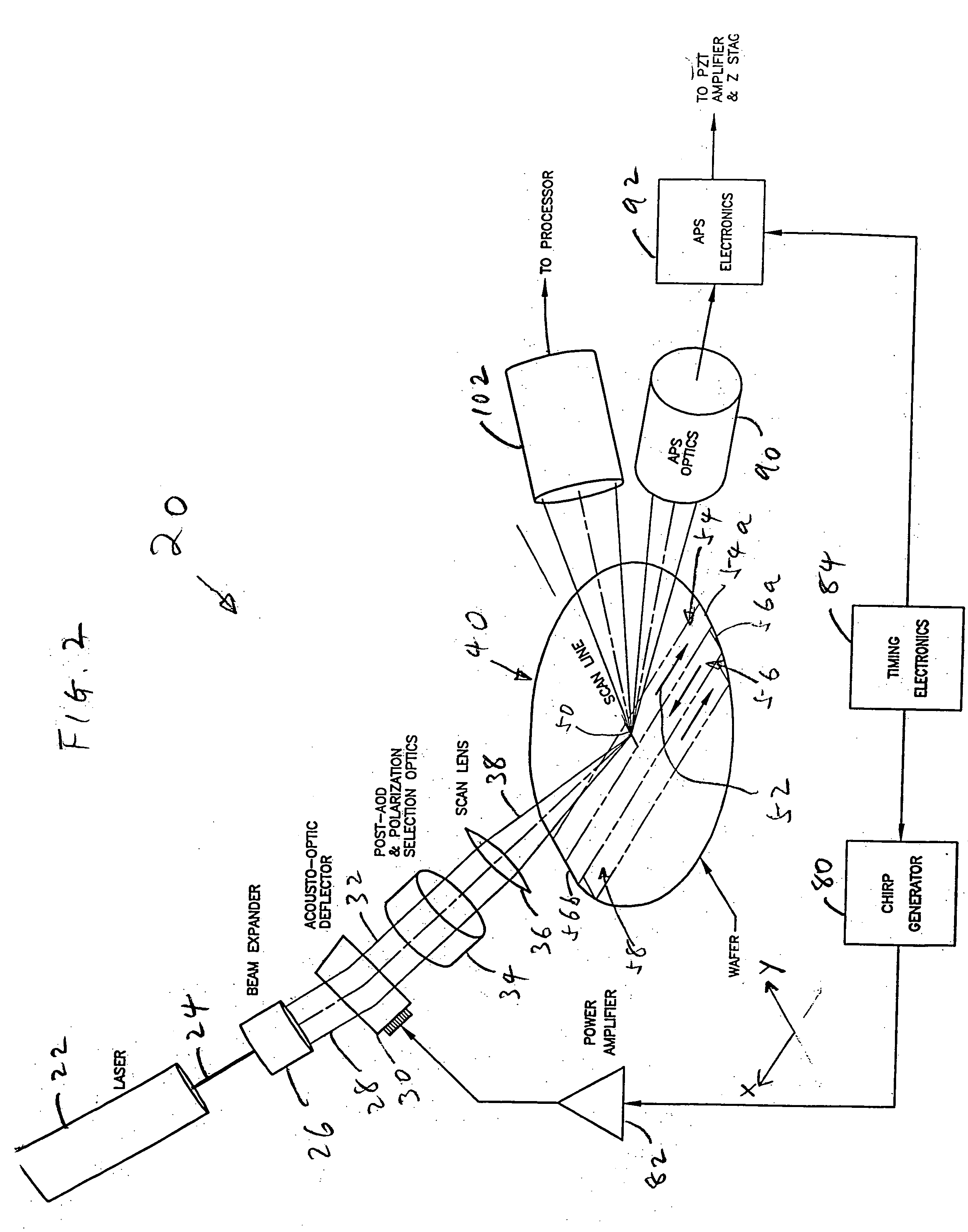
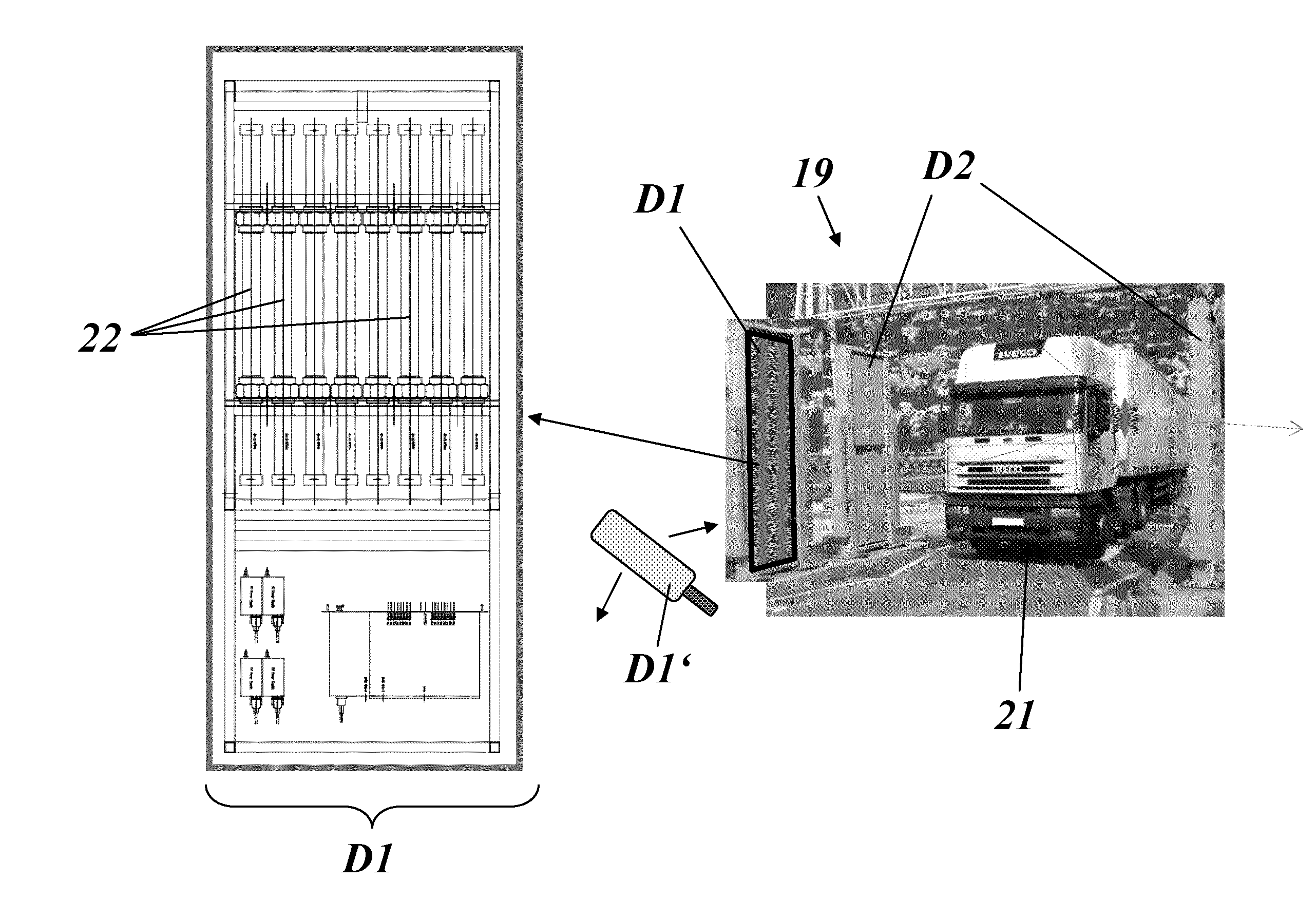
Scanning system for inspecting anamolies on surfaces
InactiveUS20050110986A1Maintain consistencyReduce areaOptically investigating flaws/contaminationParticulatesOptical scanning
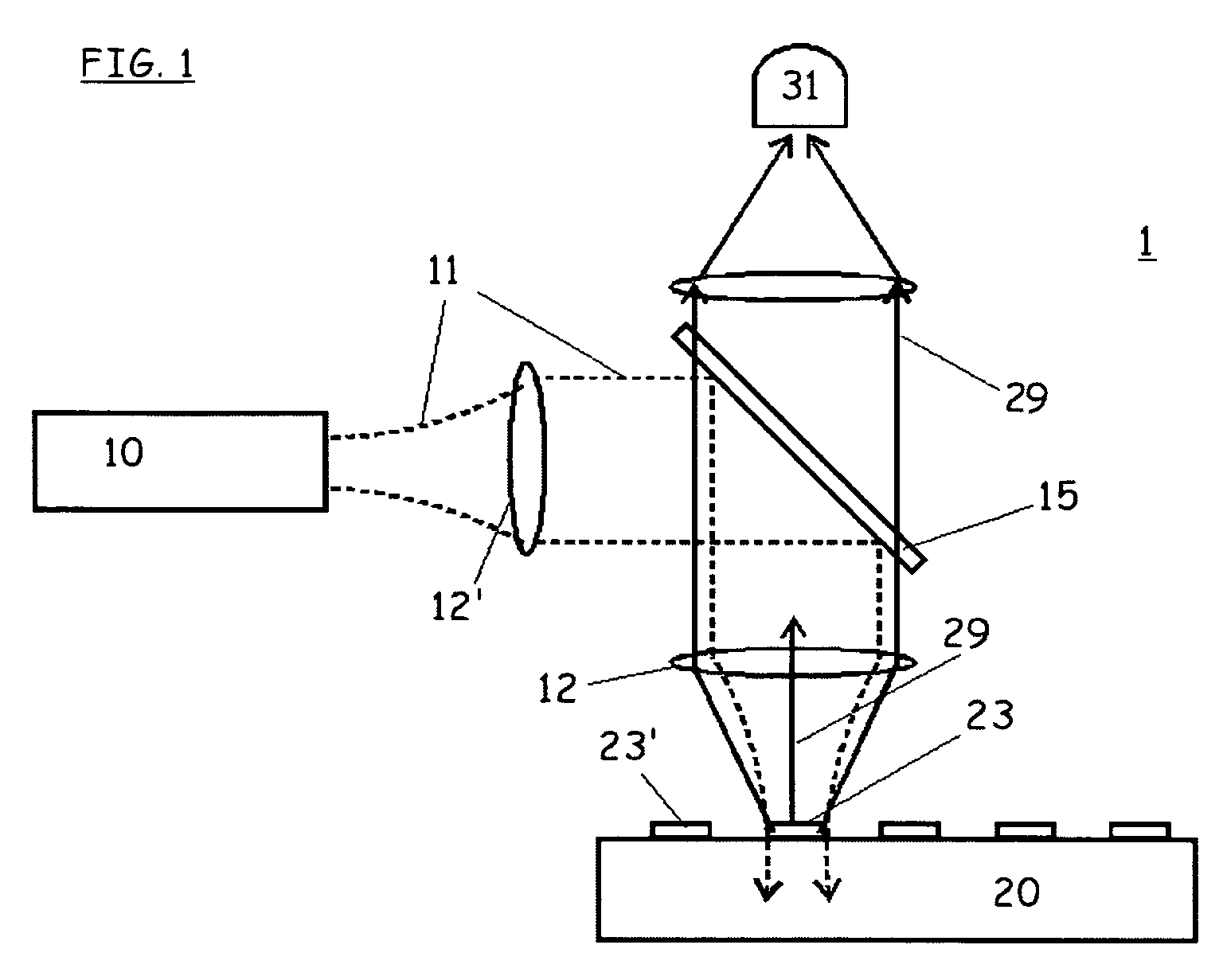
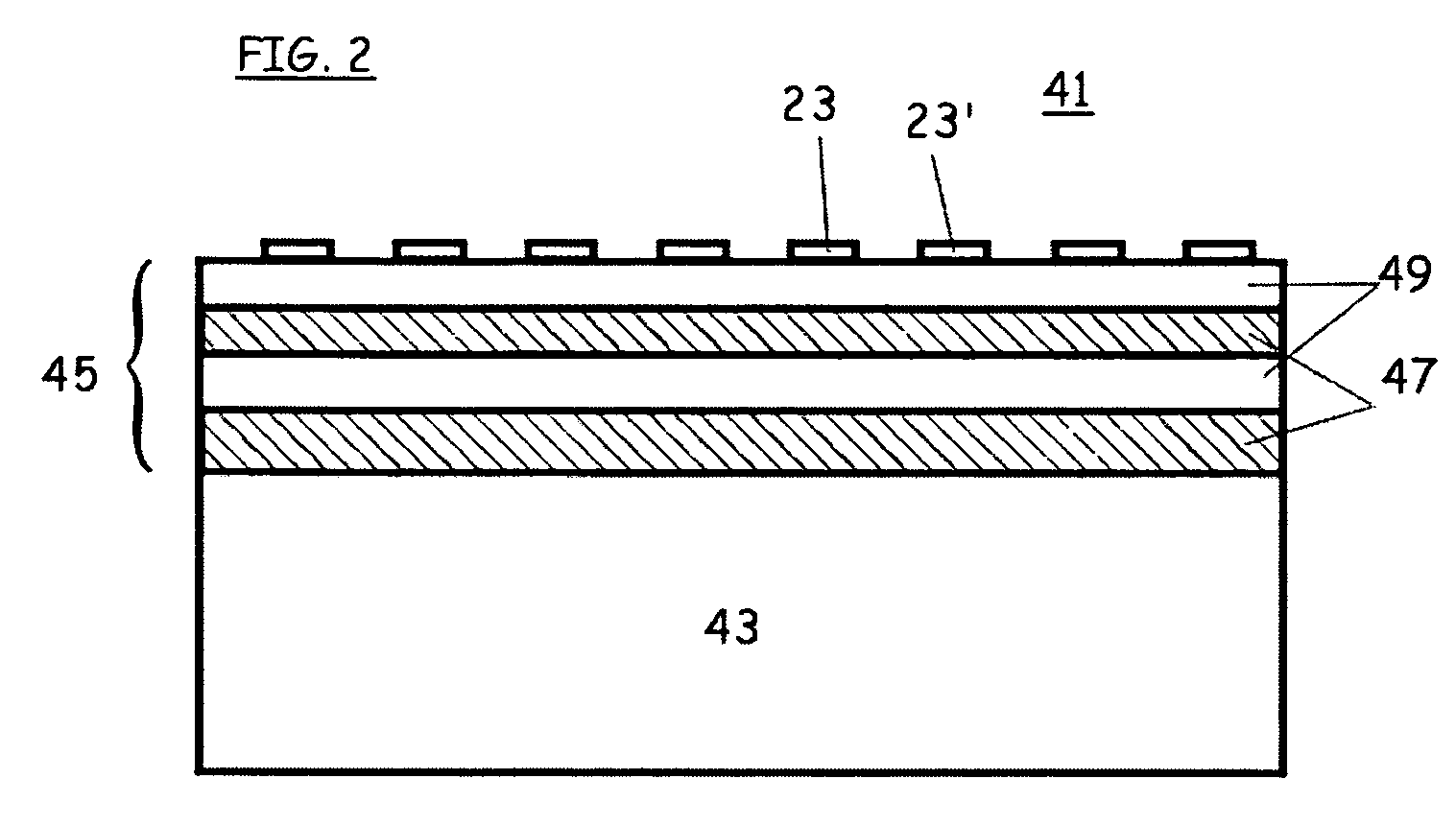
An optical scanning system and method for detecting anomalies, including pattern defects and particulate contaminants, on both patterned and unpatterned surfaces, using a light beam, scanning at a grazing angle with respect to the surfaces, a plurality of detectors and an interchannel communication scheme to compare data from each detector, which facilitates characterizing anomalies. The light beam illuminates a spot on the surface which is scanned over a short scan-line. The surface is moved in a manner so that the spot is scanned over its entire area in a serpentine fashion along adjacent striped regions. The plurality of detectors include groups of collector channels disposed circumferentially around the surface, a bright field reflectivity / autoposition channel, an alignment / registration channel and an imaging channel. The collector channels in each group are symmetrically disposed, in the azimuth, on opposite sides of the center of the scan line. The position of the collector channels, as well as the polarization of the beam, facilitates distinguishing pattern defects from particulate contaminants. The bright field reflectivity / autoposition channel is positioned to receive specularly reflected light that carries information concerning local variation in reflectivity, which is used to classify detected anomalies, as well as determine variations in the height of the surface. The alignment / registration channel is positioned to detect a maximum of the light scattered from the pattern on the surface to ensure that the streets of die present on the surface are oriented so as not to be oblique with respect to the scan line. The imaging channel combines the advantages of a scanning system and an imaging system while improving signal / background ratio of the present system.
Owner:NIKOONAHAD MEHRDAD +3
Compositions and methods to co-localize luminophores with luminescent proteins
InactiveUS20030153090A1Increase accuracyImprove stabilityAnalysis using chemical indicatorsOrganic chemistryLuminophoreCoelenterazine
A method of measuring the enzymatic activity of a luciferase includes contacting a luminogenic protein, such as a luciferase, with a protected luminophore to form a composition; and detecting light produced from the composition. The protected luminophore provides increased stability and improved signal-to-background ratios relative to the corresponding unmodified coelenterazine.
Owner:PROMEGA
Method and device for thermal treatment of substrates
InactiveUS7056389B2Careful yet rapid heating-upSignificant rateAfter-treatment detailsDiffusion/dopingLength waveThermal treatment
The object of the invention is to measure temperature using pyrometers, in a simple and economic way, enabling precise temperature measurement, even for low temperatures. The invention presents a device and method for thermally treating substrates, wherein the substrate is exposed to at least a first and at least a second radiation; the predetermined wavelengths of the first radiation are absorbed between the first radiation source and the substrate; a radiation from the substrate is measured in the predetermined wavelength using a radiation detector arranged on the same side as a second radiation source; the second radiation from the second radiation source is modulated and determined.
Owner:BEIJING E TOWN SEMICON TECH CO LTD +1
Method and apparatus for thermally treating substrates
InactiveUS20060291834A1Reduced wavelength rangeImprove the signal-to-background ratioAfter-treatment detailsDiffusion/dopingLength waveHot Temperature
The object of the disclosure is to measure temperature using pyrometers, in a simple and economic way, enabling precise temperature measurement, even for low temperatures. The disclosure presents an apparatus and method for thermally treating substrates, wherein the substrate is exposed to at least a first and at least a second radiation; the predetermined wavelengths of the first radiation are absorbed between the first radiation source and the substrate; a radiation from the substrate is measured in the predetermined wavelength using a radiation detector arranged on the same side as a second radiation source; the second radiation from the second radiation source is modulated and determined.
Owner:BEIJING E TOWN SEMICON TECH CO LTD
Device and method for eliminating back light signal by utilizing dual-optical switch
InactiveCN101969177AAchieve recoverySuppression of background optical noiseLaser detailsInformation processingLight signal
The invention relates to an optical signal detection technology, in particular to a device and a method for eliminating a back light signal by utilizing a dual-optical switch. The invention solves the problem that the existing back light restraining technology can not eliminate the back light signal which is synchronous with a pulse laser signal and has the same frequency with the pulse laser signal. The device for eliminating the back light signal by utilizing the dual-optical switch comprises a pulse laser, a practice target, the dual-optical switch, a single photon detector and a computer, wherein the dual-optical switch comprises a first acoustic optical modulator and a second acoustic optical modulator; the external trigger input end of the pulse laser is connected with a pulse signal generator; and the external trigger input end of the pulse signal generator is connected with a function signal generator, and the output end of the pulse signal generator is connected with a time-to-amplitude converter. The invention solves the problem that the existing back light restraining technology can not eliminate the back light which is synchronous with the pulse laser signal and has the same frequency with the pulse laser signal, and is suitable for weak pulse laser signal detection in the fields of precision measurement, communication, information processing, military and the like.
Owner:SHANXI UNIV
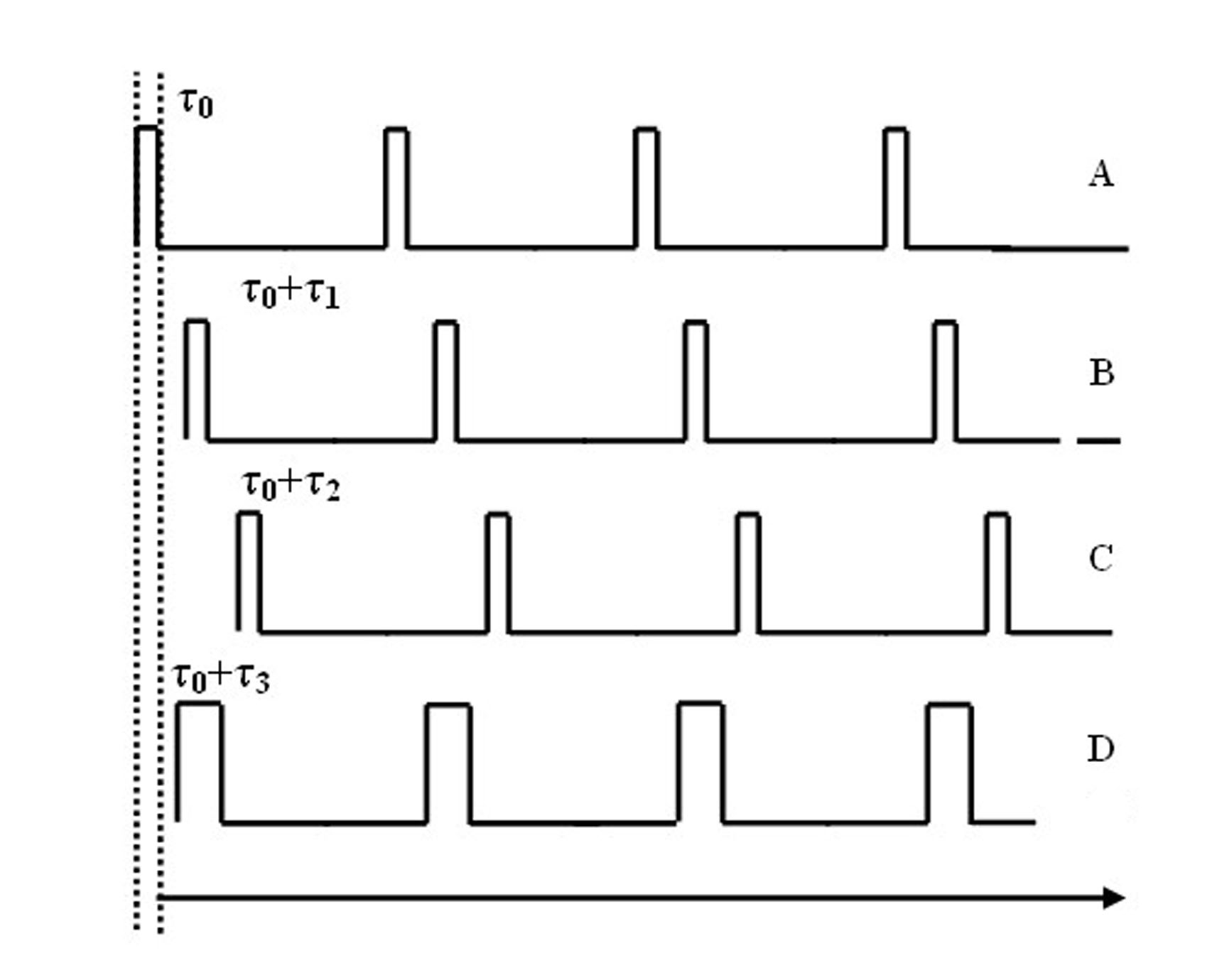
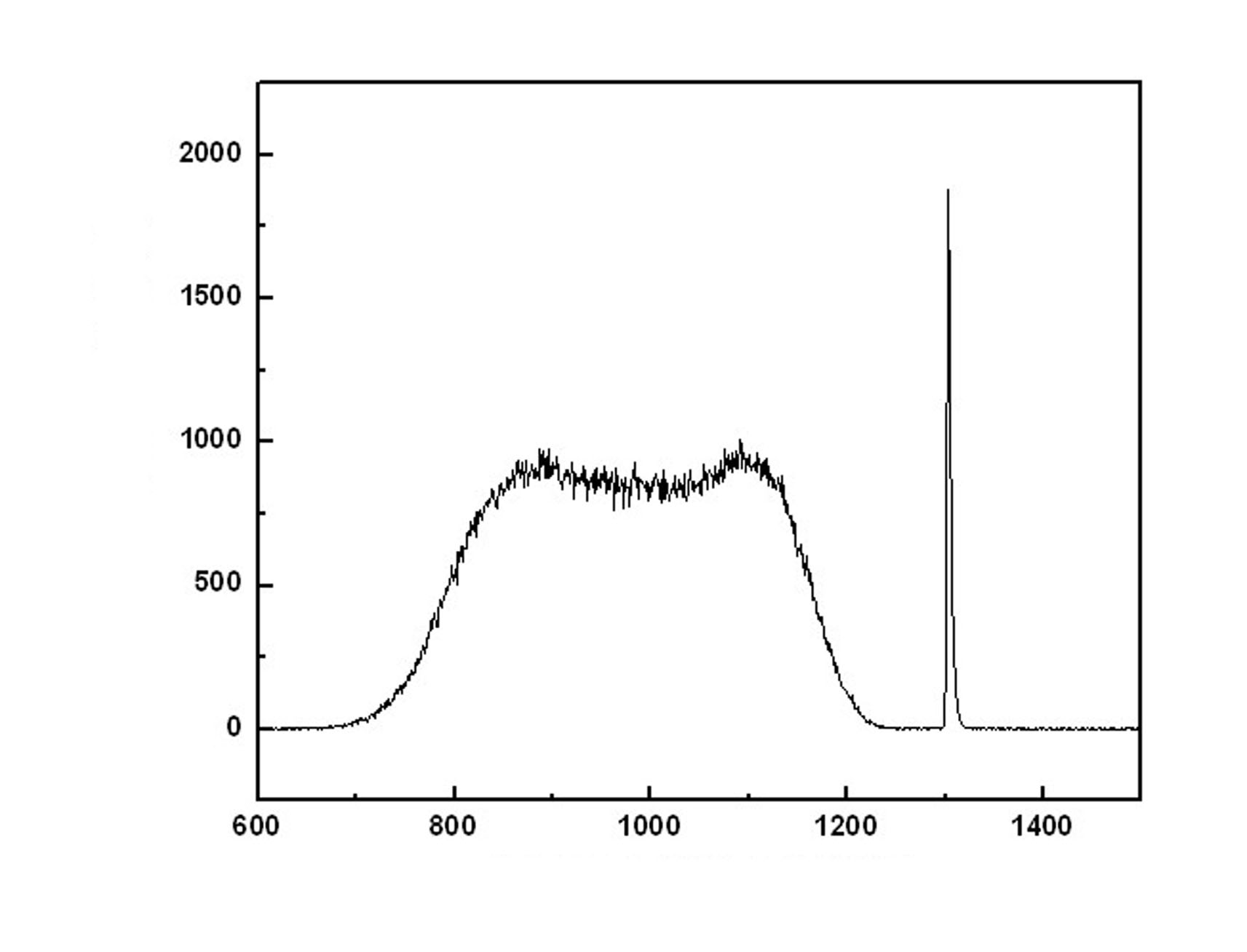
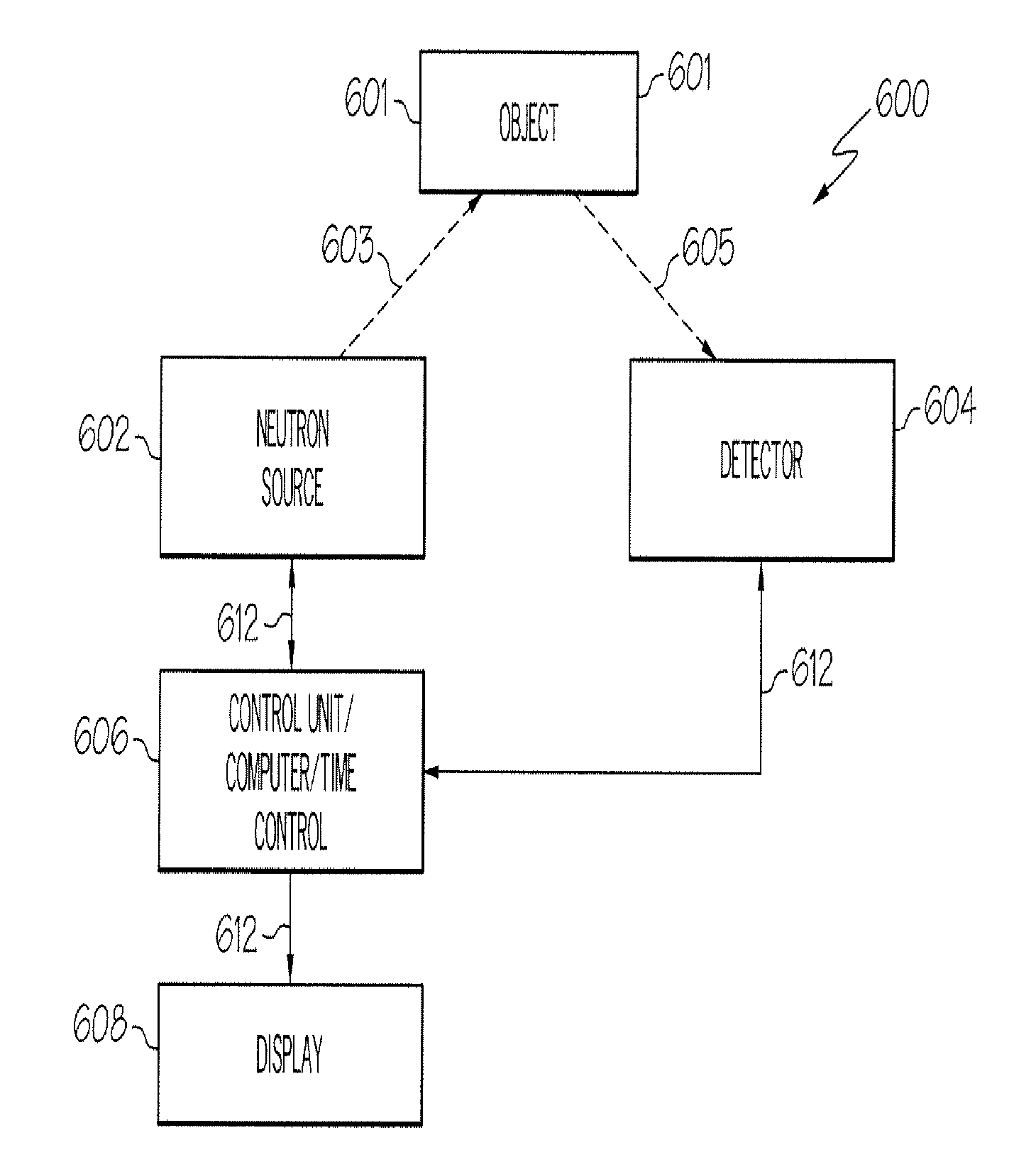
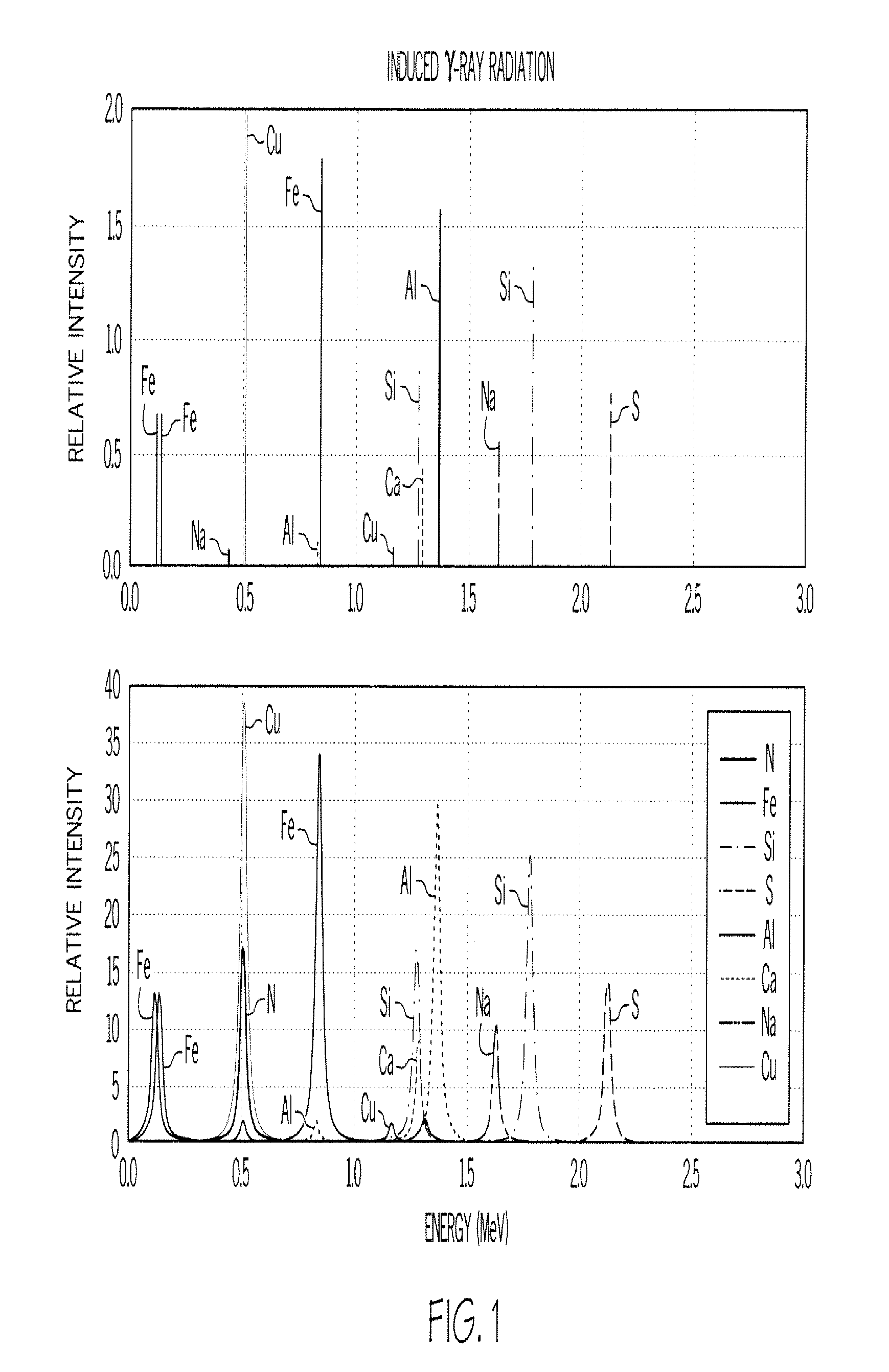
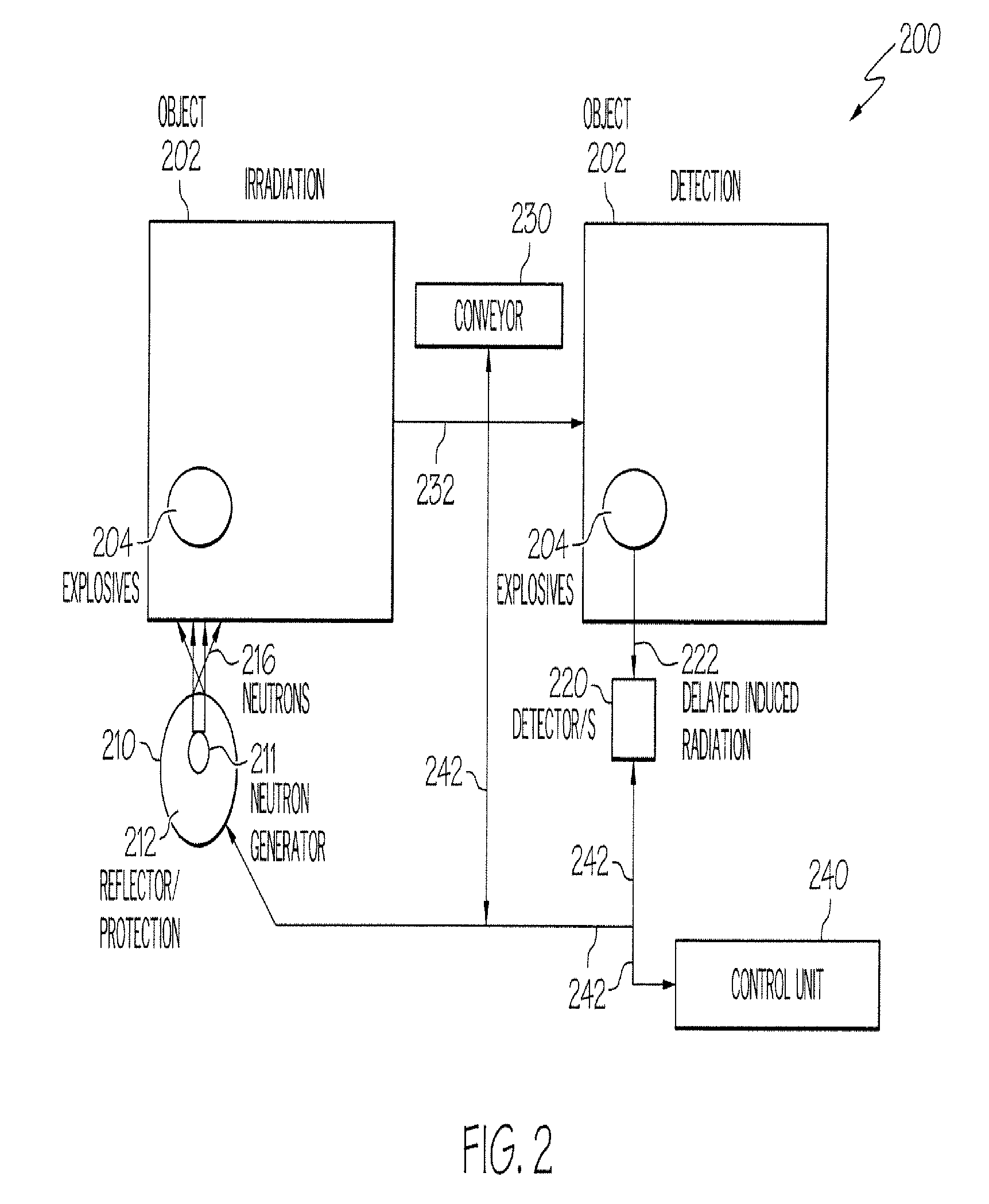
Explosives detector
ActiveUS20090114834A1Low signal to background ratioImprove the signal-to-background ratioMaterial analysis by optical meansMaterial analysis by transmitting radiationNeutron captureNeutron source
Apparatus and methods for determining the absence or presence of contraband in an object with a fast neutron source for irradiating the object; a detector for measuring γ-rays emitted by the irradiated object from energy state relaxation as a result of neutron capture, typically after the object has been irradiated.
Owner:BATTELLE MEMORIAL INST
Detection of Antibodies
InactiveUS20090029388A1Efficient methodImprove the signal-to-background ratioBiological testingAutoimmune diseaseWater Channel Proteins
The present invention relates to a method for detecting antibodies against a target antigen in a sample which comprises contacting the sample with labelled target antigen, subjecting the sample to immunoprecipitation to precipitate antibodies in the sample and detecting the presence of antibodies against the target antigen in the sample by means of the presence of labelled target antigen in the immunoprecipitate, wherein the labelled target antigen is a fusion protein comprising the target antigen and a fluorescent protein label and the presence of labelled target antigen in the immunoprecipitate is detected by means of the fluorescence of the fluorescent label. The method is particularly suitable for use where the target antigen is an autoantigen and can also be used to identify autoantigens implicated in a particular autoimmune disorder by screening serum samples from patients with a clinical phenotype indicative or suggestive of an autoimmune disorder and suitable controls. The target protein may be from the cys-loop acetyl choline receptor ion channel gene superfamily, the voltage-gated calcium, sodium or potassium ion channel gene superfamily, the glutamate receptor gene family, a receptor tyrosine kinase, or other membrane associated channels such as aquaporin gene family.
Owner:BEESON DAVID
Method of enhancing fluorescence
InactiveUS20060094042A1Fluorescence enhancementImprove stabilitySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementElectrophoresisOrganic chemistry
A method of enhancing the fluorescence of and / or producing an increased Stokes' shift in a fluorescent dye comprising combining the dye with a base and / or a detergent is described. The method is suitable in chemical or biochemical techniques using fluorescent dyes, particularly techniques requiring staining or labeling of organic molecules, such as electrophoresis.
Owner:FLUOROTECHNICS PTY LTD
Total internal reflection illumination and semi-total internal reflection illumination dual optical path fluorescence microscope system
InactiveCN103235406AAvoid background fluorescence interferenceImprove the signal-to-background ratioMicroscopesFluorescence/phosphorescenceTotal internal reflectionBeam splitter
The invention discloses a total internal reflection illumination and semi-total internal reflection illumination dual optical path fluorescence microscope system. A beam-splitter plate I is arranged on the light path of exciting light and the angle between the beam-splitter plate I and the light path is 135 degrees so that the exciting light is divided into a vertical transmission light and a vertical reflected light; the transmission light is reflected through a reflector so as to be parallel to the reflected light; the light paths of the reflected light and the transmission light are respectively and sequentially provided with a graded-density neutral filter, a convex lens I, a convex lens II and a light spot aperture regulator; the reflected light and the transmission light then form two vertical light paths by adjusting transmission directions through the reflector; convex lens III are respectively arranged on the mutually vertical light paths of the reflected light and the transmission light; the reflected light and the transmission light pass through the convex lens III so as to be incident to a beam-splitter plate II having an angle of 135 degrees with a light path of the reflected light; and two parallel lights divided through the beam-splitter plate II are incident to an exciting light inlet of a microscope. The total internal reflection illumination and semi-total internal reflection illumination dual optical path fluorescence microscope system can be used for bleaching fluorescence molecule of a cell membrane area, background fluorescence interference caused when the fluorescence molecule of the cell membrane area images a focal plane in a cell is avoided, and a signal background ratio of semi-total internal reflection fluorescence imaging in the cell is further improved.
Owner:INST OF CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
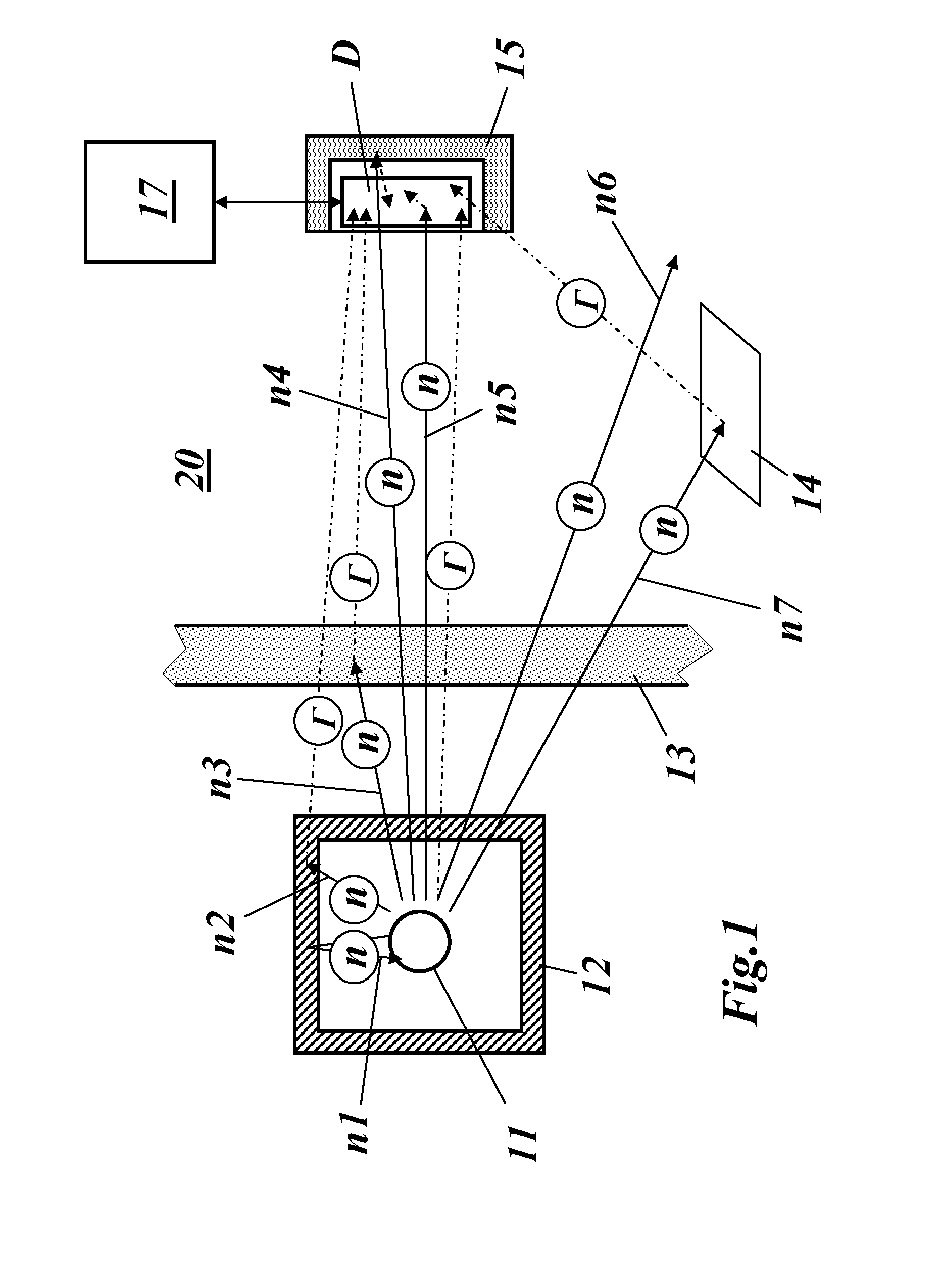
Method for Obtaining Information Signatures from Nuclear Material or About the Presence, the Nature and/or the Shielding of a Nuclear Material and Measurement Setup for Performing Such Method
ActiveUS20140264058A1Increase probabilityReduce sensitivityMeasurement with scintillation detectorsMaterial analysis by optical meansNuclear radiationHomeland security
The invention relates to a method for obtaining information or signatures about the presence or the nature of a nuclear radiation source, especially in a homeland security application, said nuclear radiation source emitting in a time or angle correlated manner at least a first radiation and a second radiation. The method includes the steps of detecting said first radiation with at least one first radiation detector and detecting said second radiation with at least one second radiation detector. The detection of said second radiation is triggered by said detection of said first radiation in a manner that is adapted to the radiation's correlation structure, thereby increasing the signal-to-background ratio for the detection of said second radiation.
Owner:ARKTIS RADIATION DETECTORS
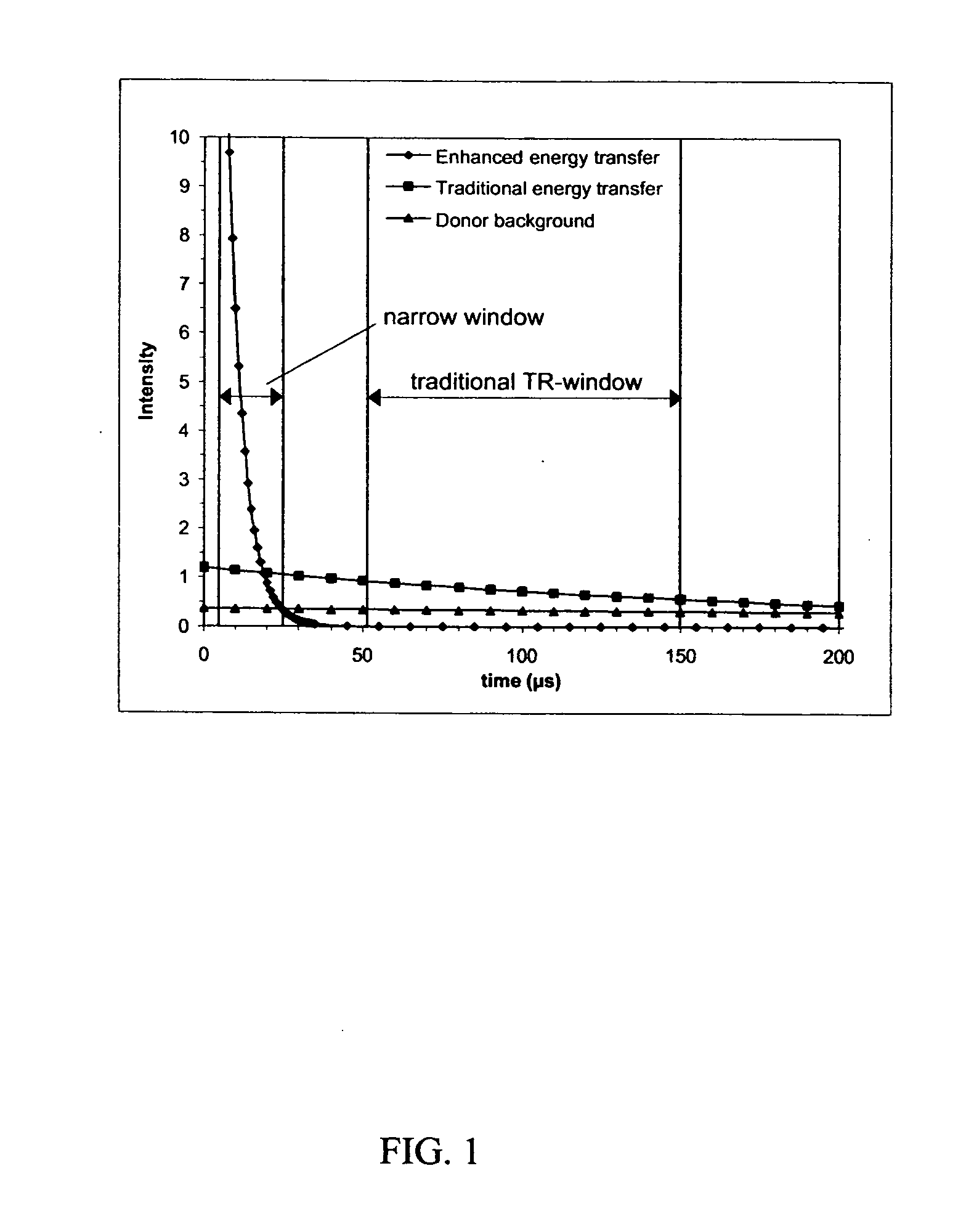
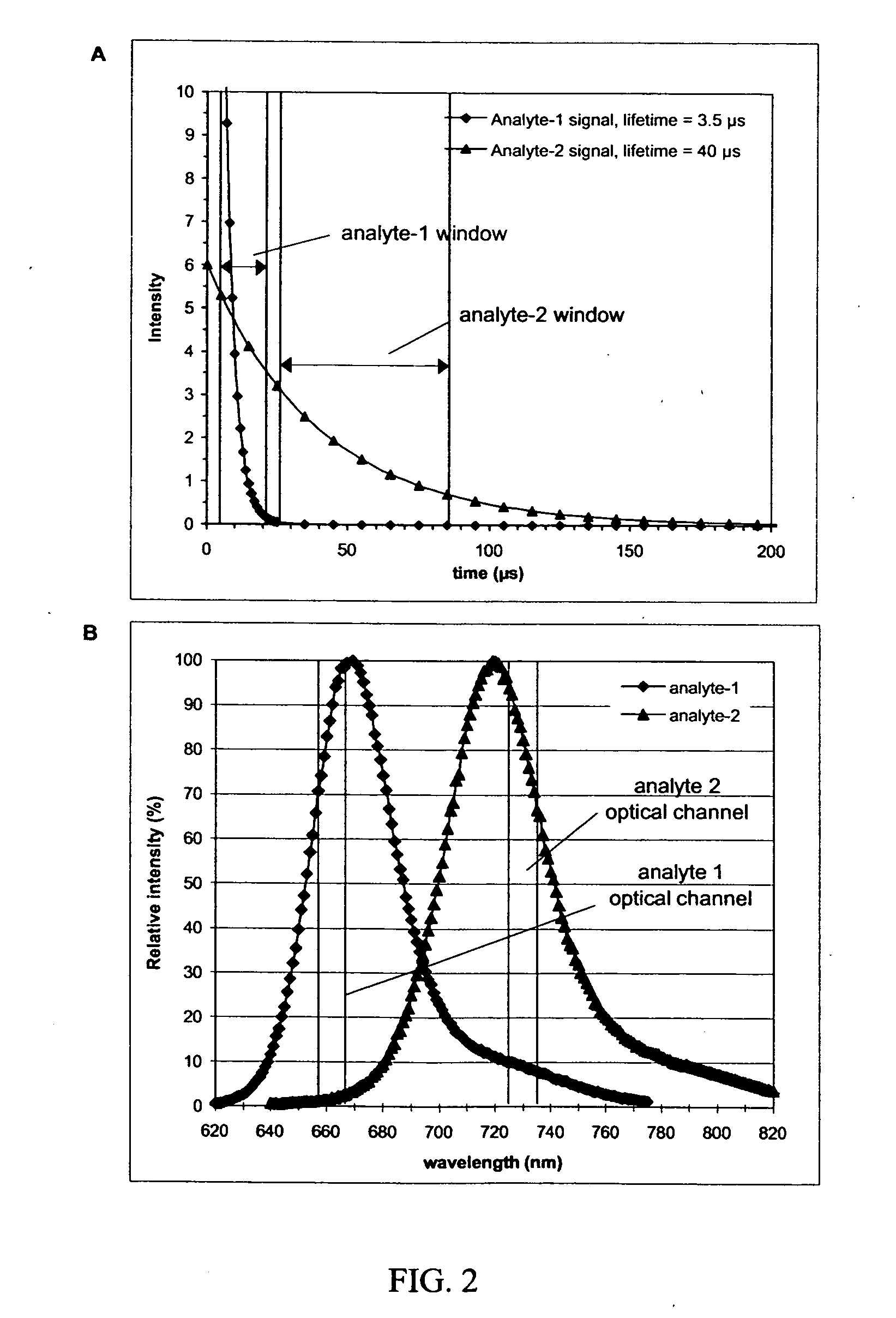
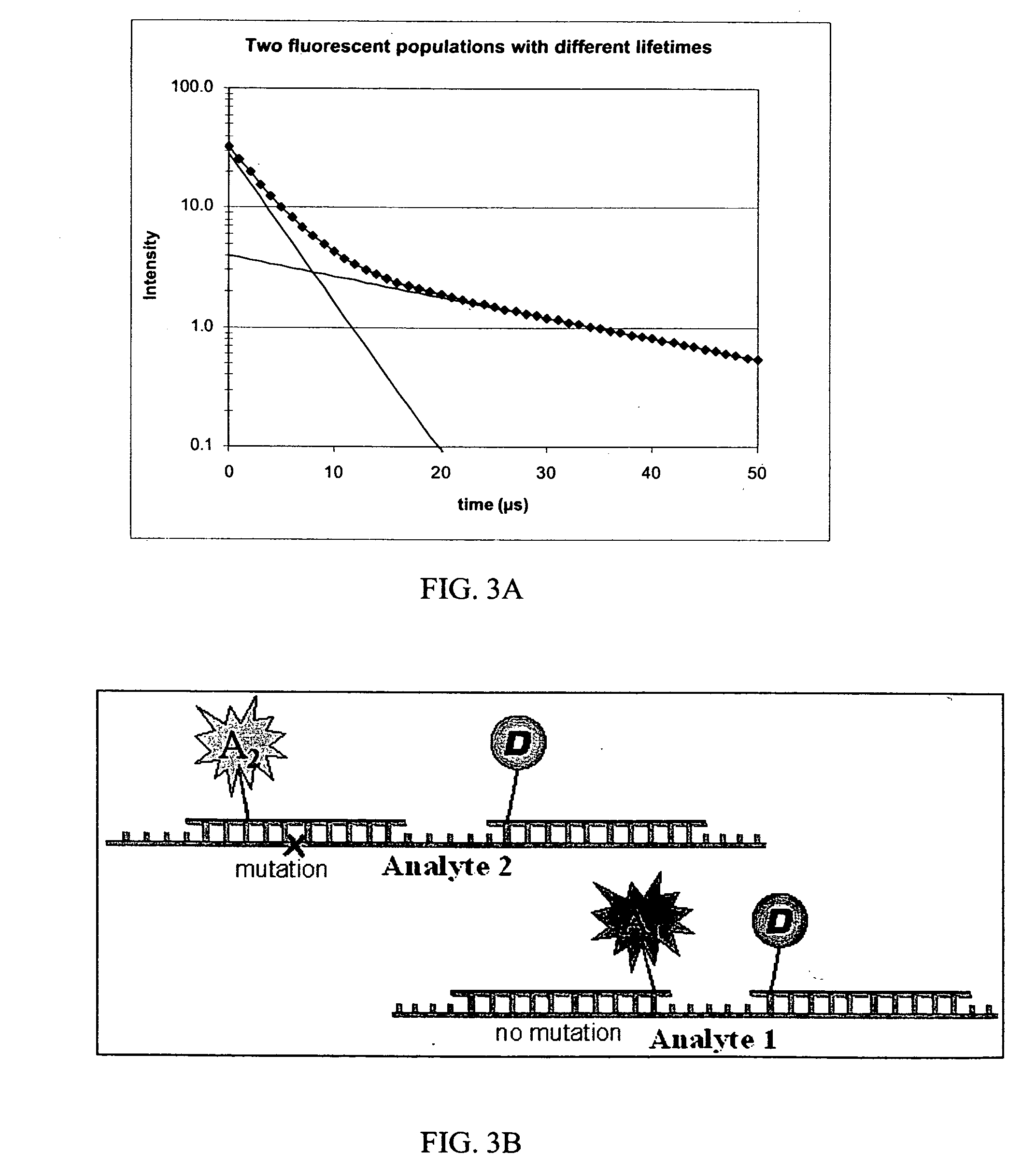
Homogeneous time-resolved energy transfer assay
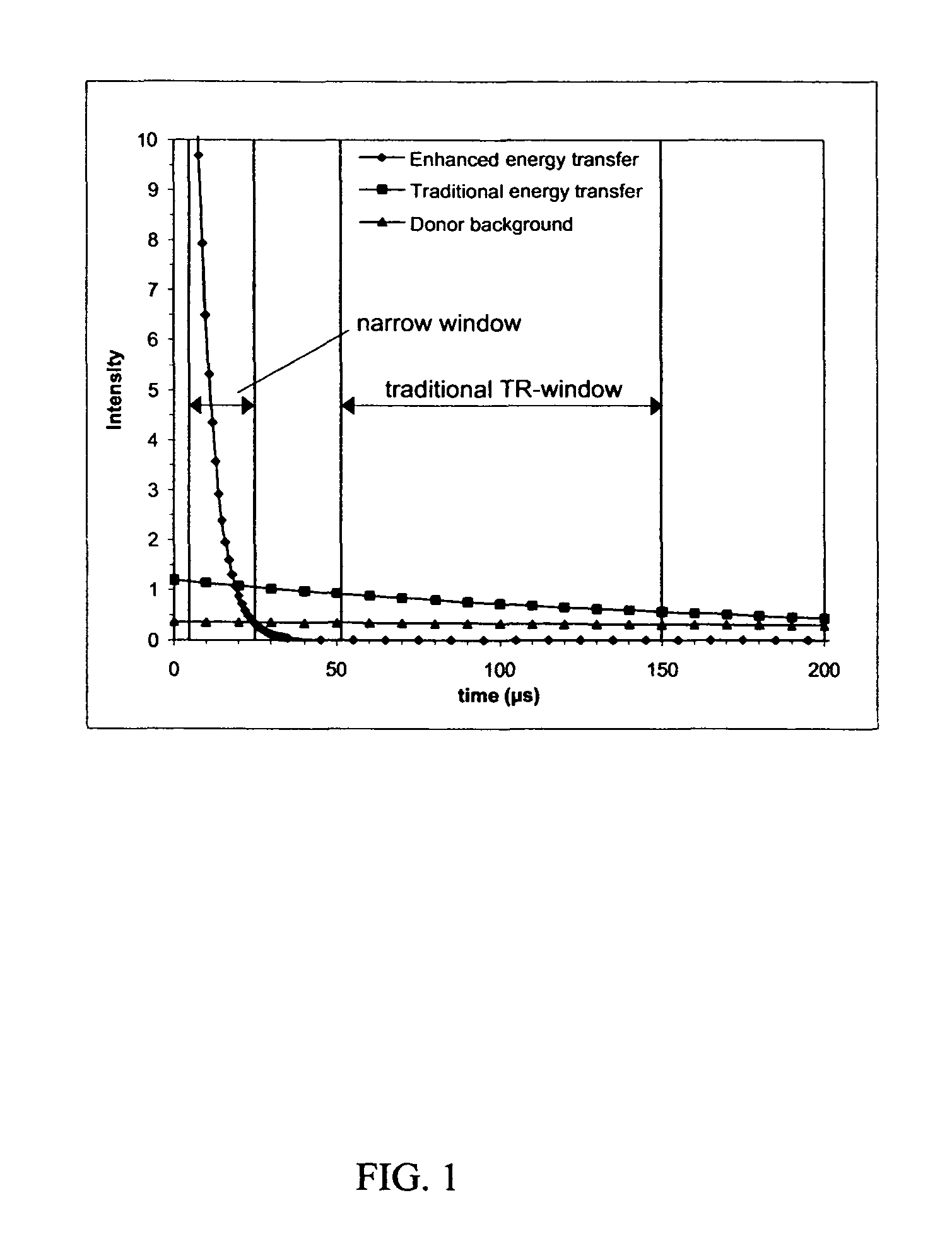
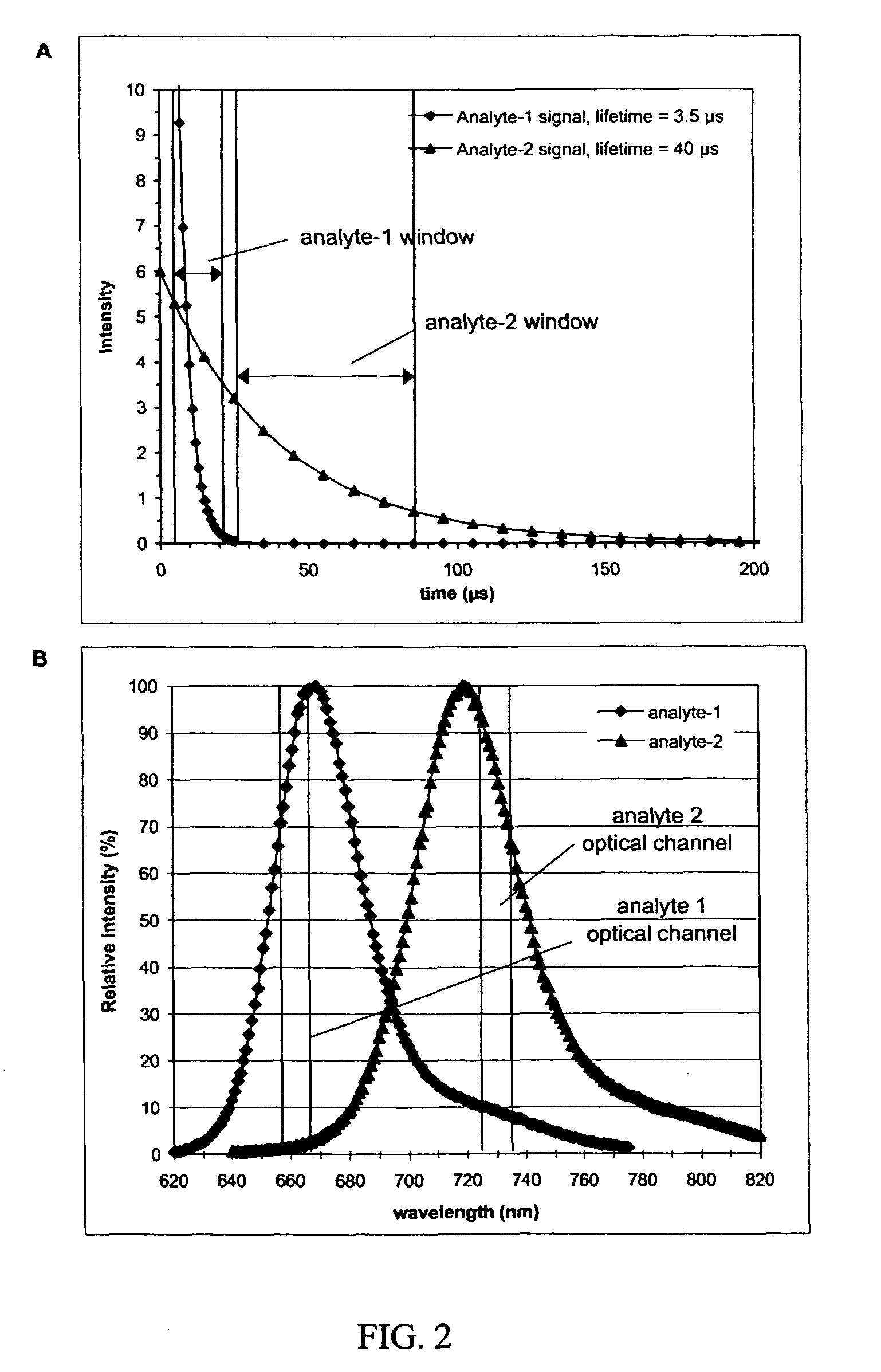
InactiveUS20050123957A1Improve the signal-to-background ratioHigh sensitivityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsEnergy transferHigh energy
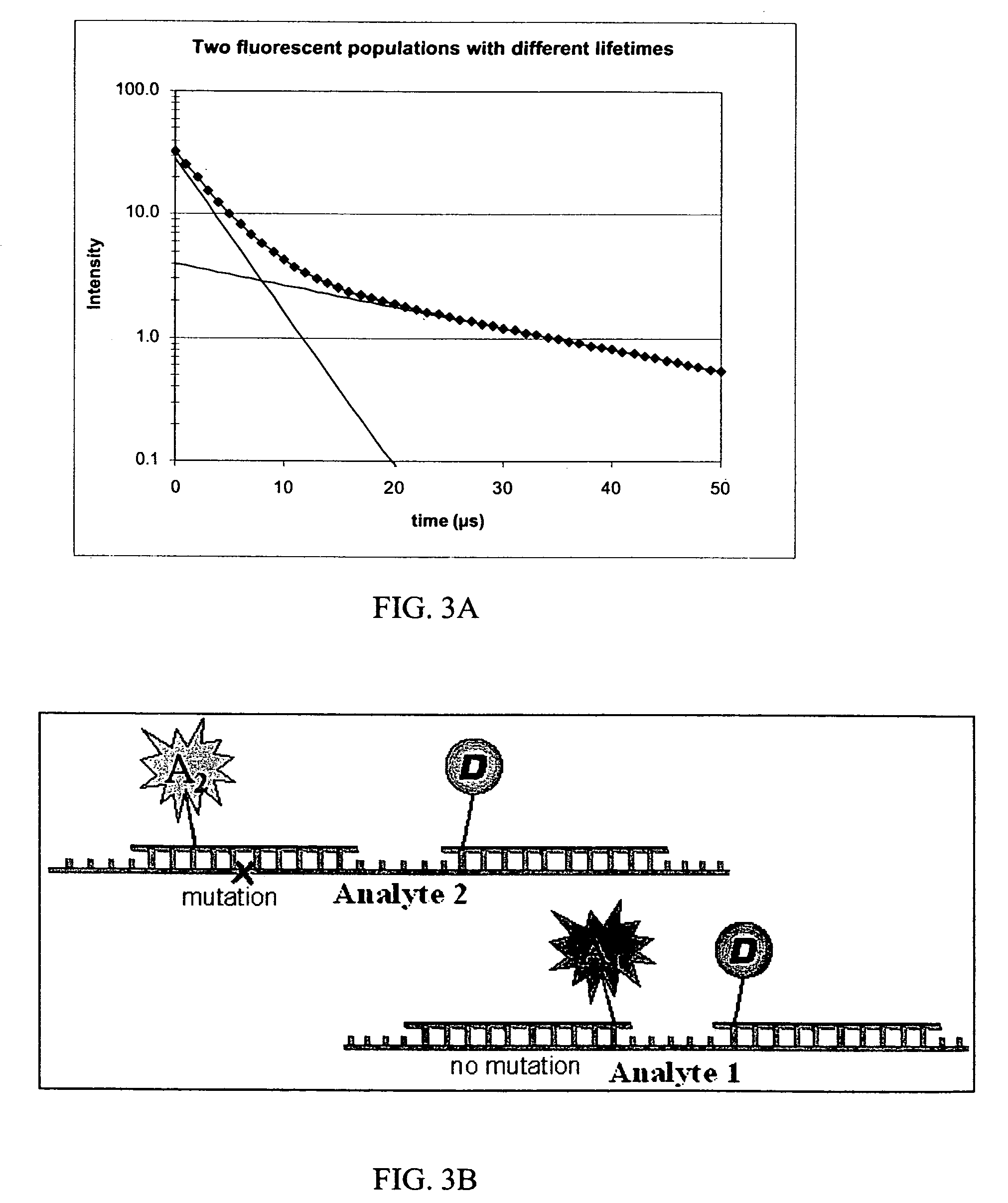
The invention relates to a method for improving the detection sensitivity in homogenous TR-FRET based bioaffinity assays. The sensitivity is improved by the use of long lifetime donors together with a high energy transfer efficiency and by carrying out the detection of the energy transfer based emission of the acceptor in a time window which is opened after a delay of 1 microsecond or more, but less than 50 microseconds, calculated from the donor excitation, and which time window has a width of 1 microsecond or more, but less than 100 microseconds. The invention concerns also the use of the improved method in multianalyte assays. Furthermore, the invention concerns a device suitable for carrying out the improved method.
Owner:WALLAC
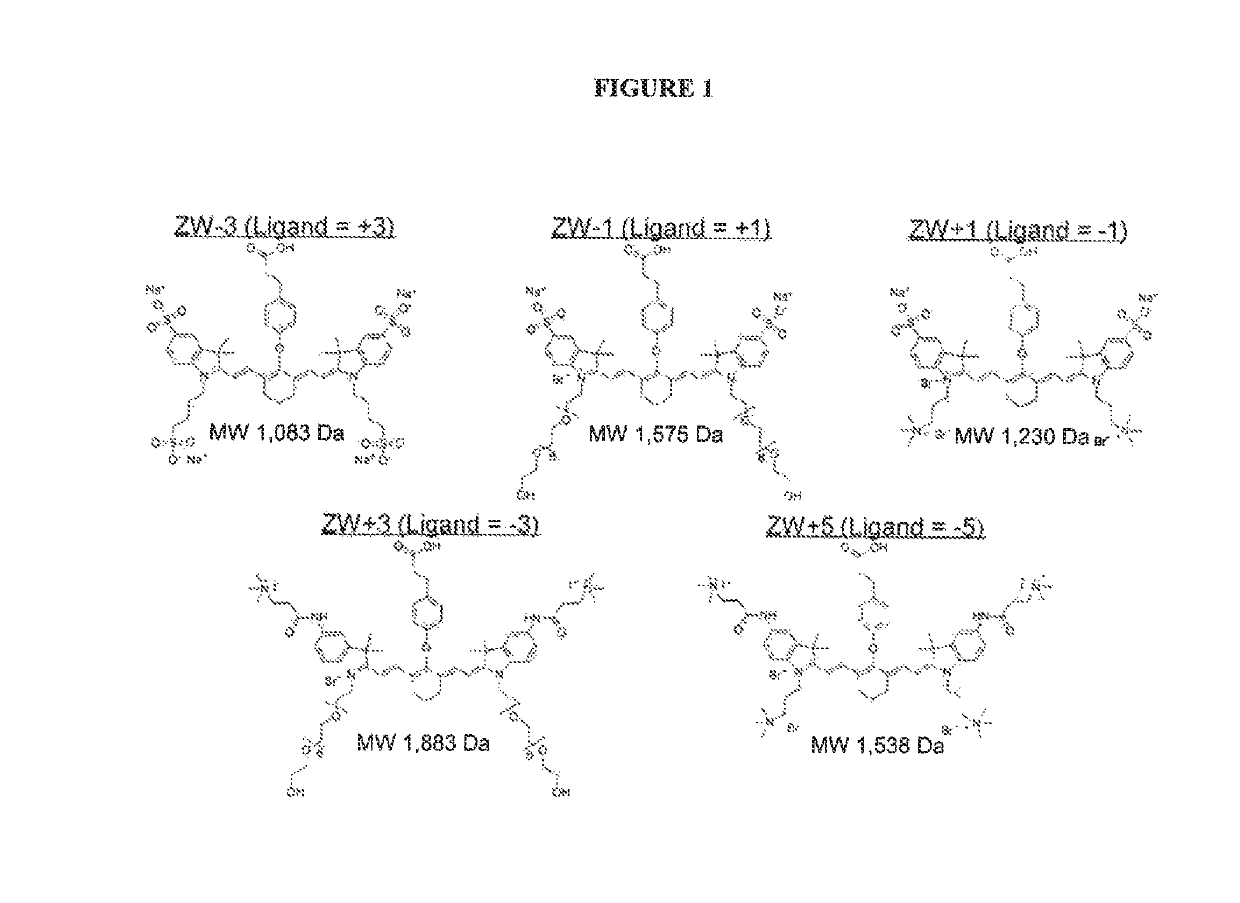
Charged-balanced imaging agents
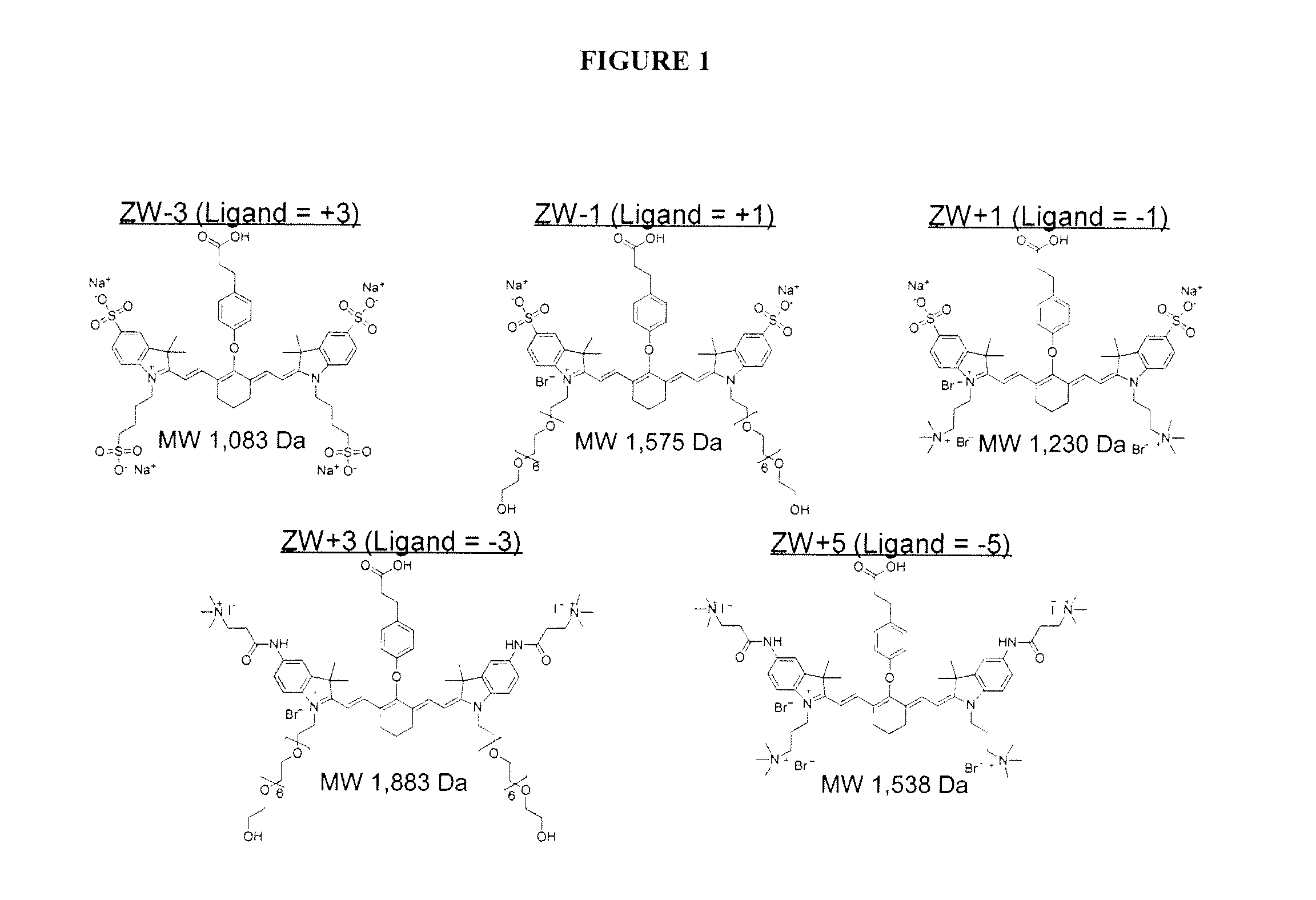
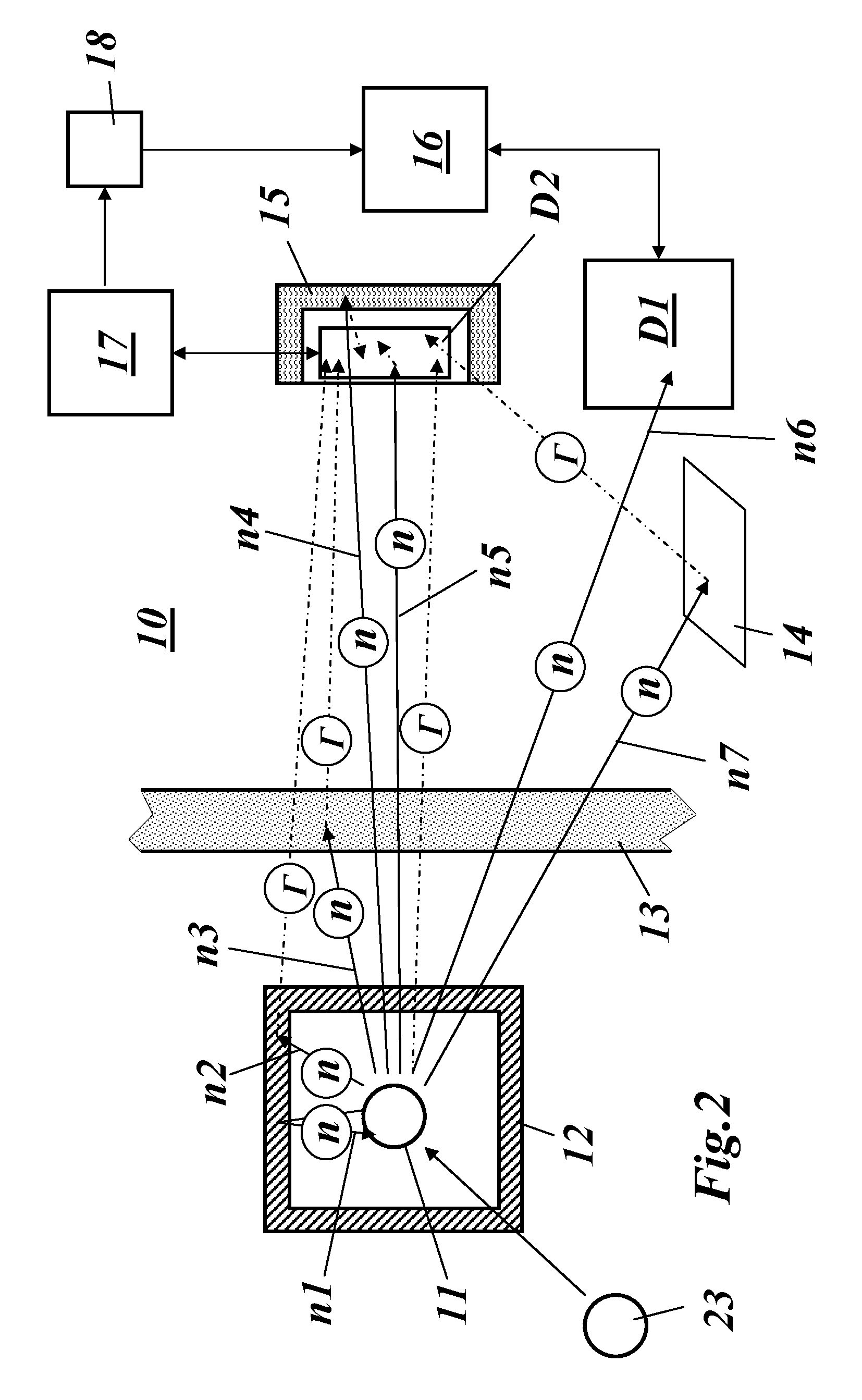
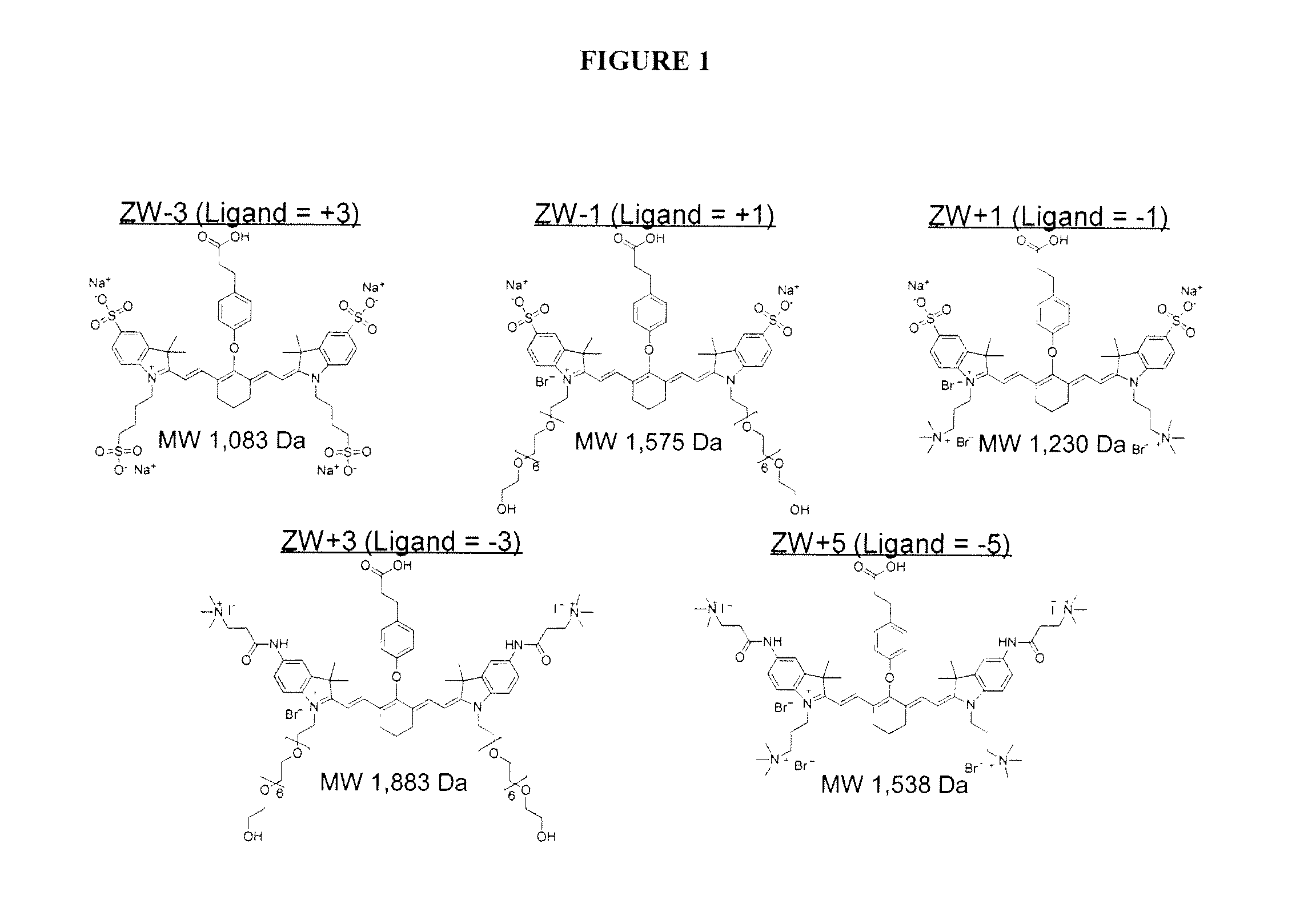
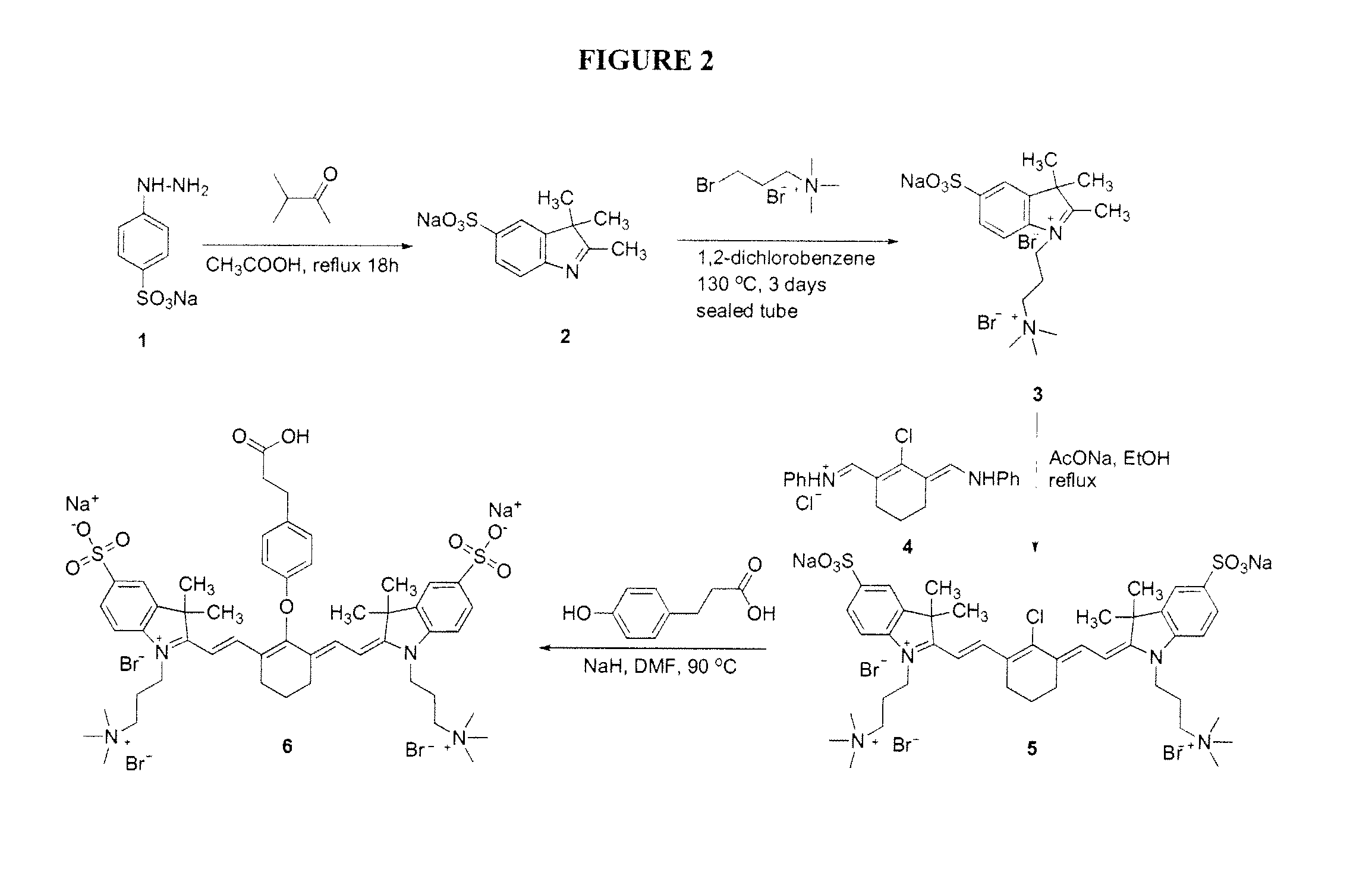
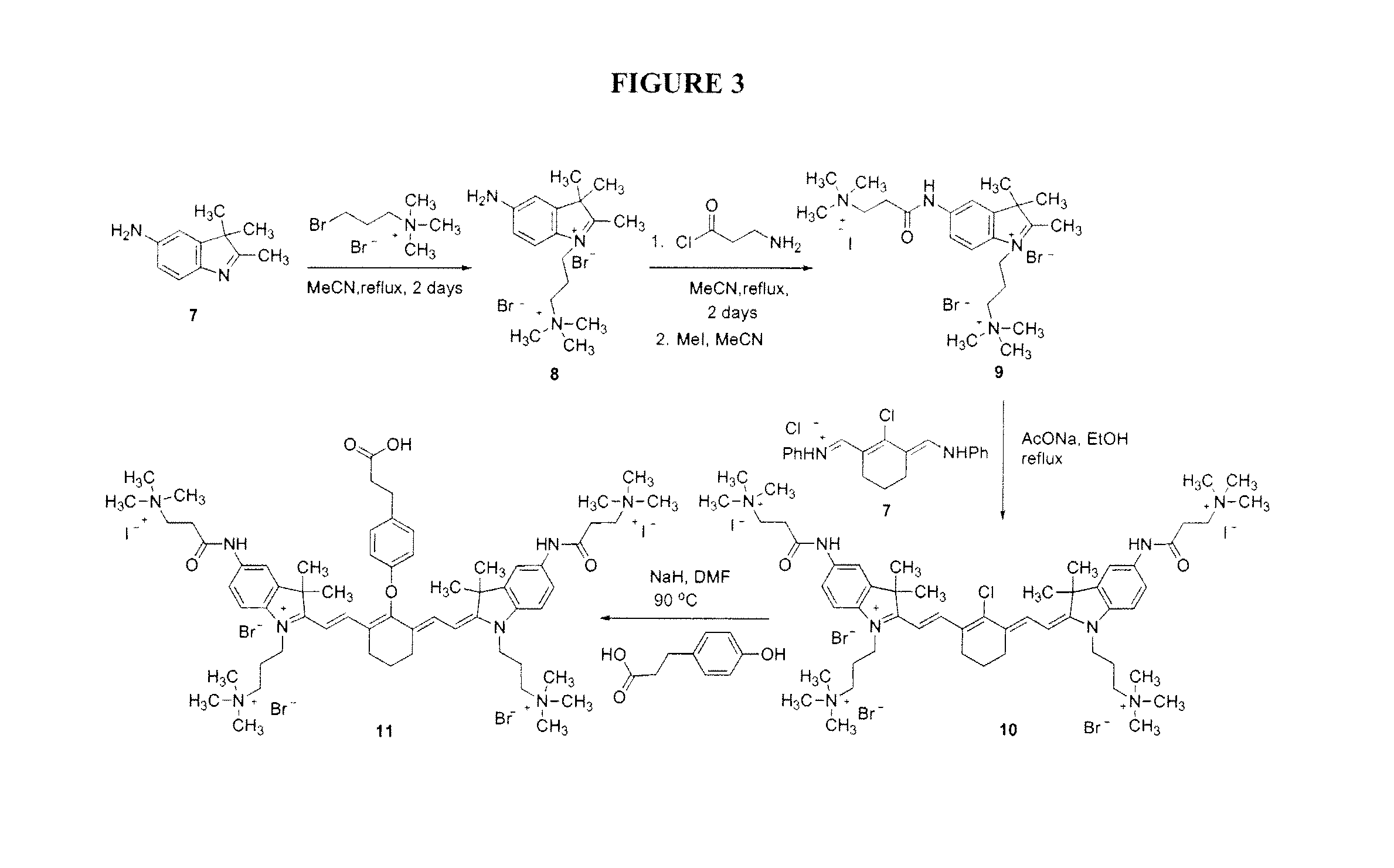
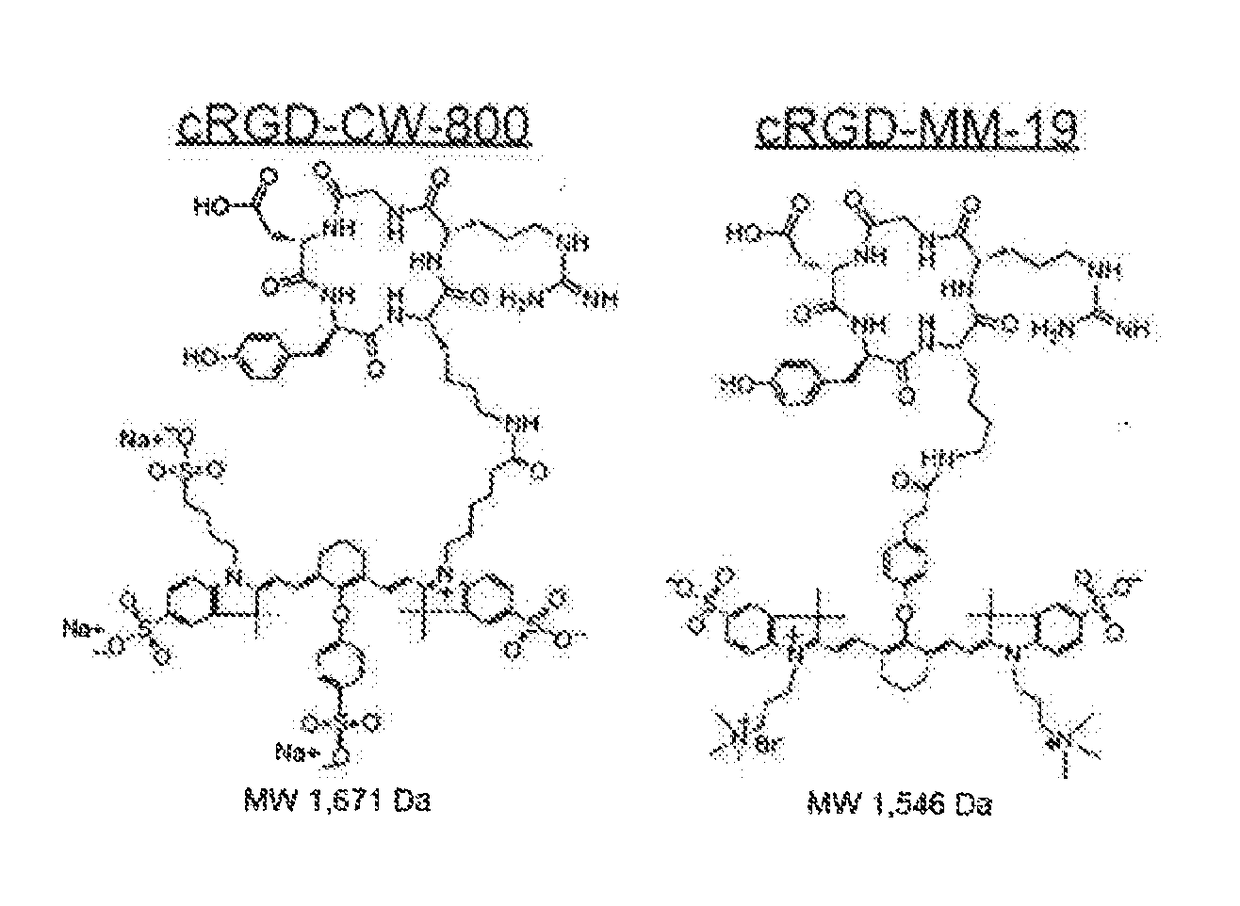
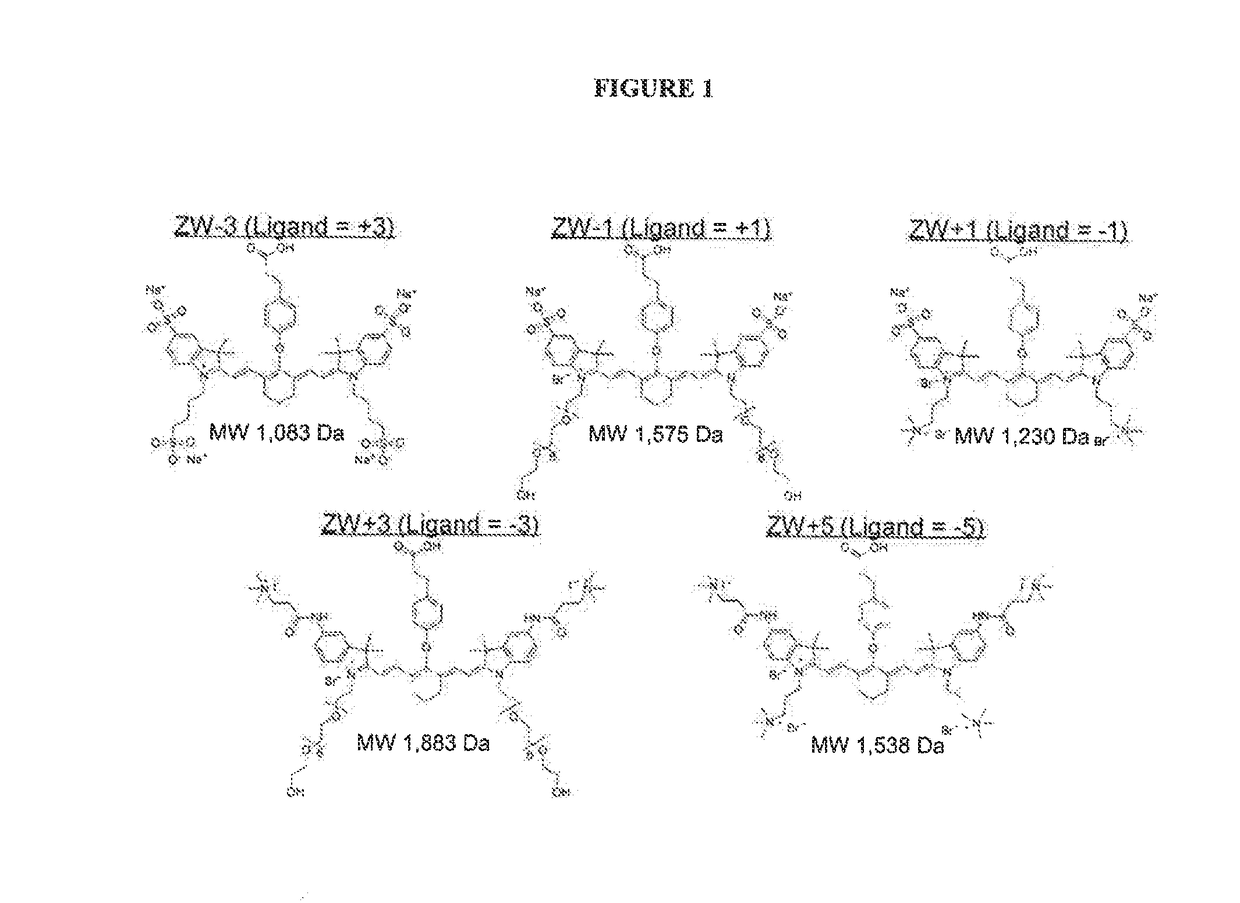
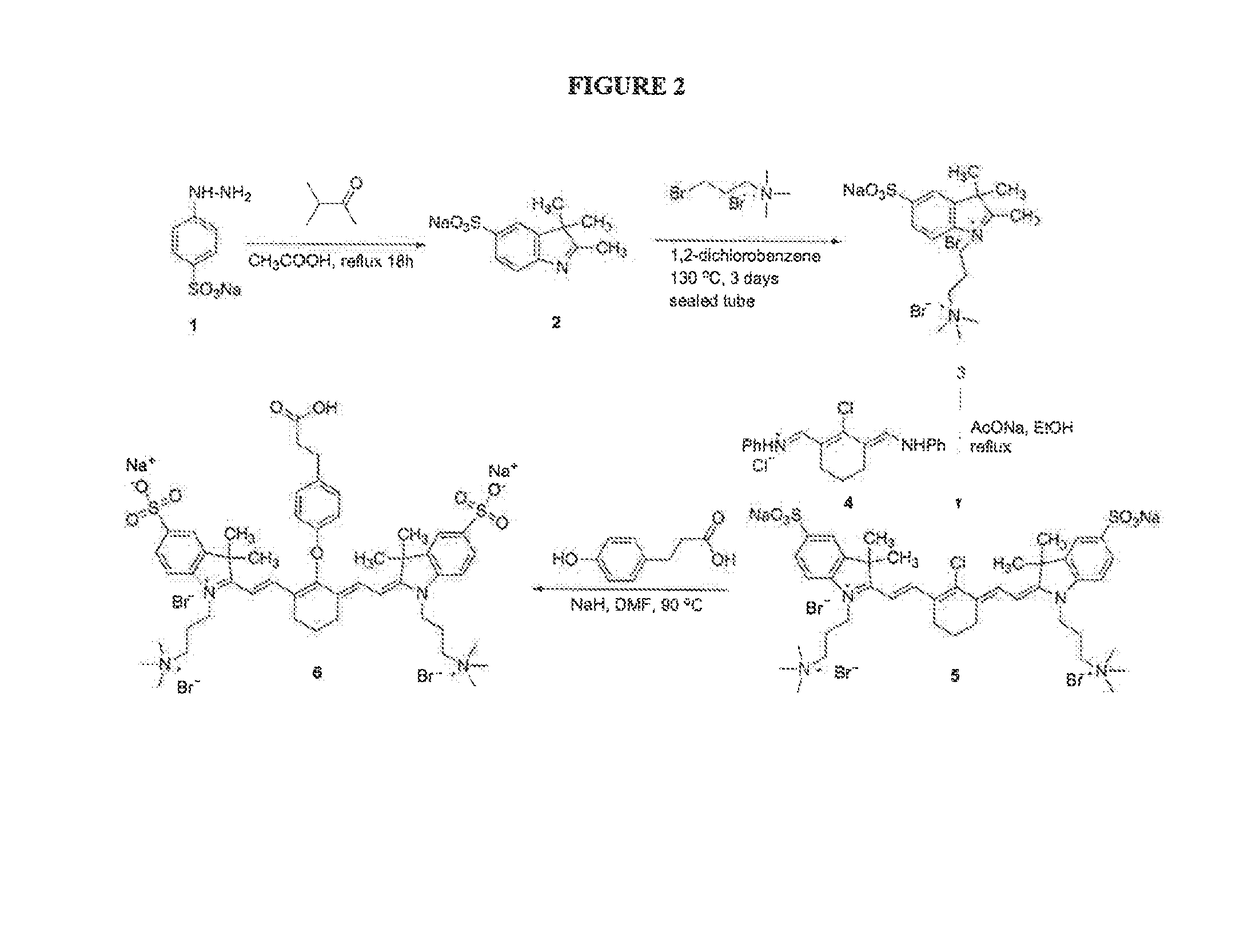
ActiveUS20120028291A1Improved in vivo propertySuperior clinical imaging characteristicMethine/polymethine dyesOrganic chemistryImaging agentMedical physics
Owner:GEORGIA STATE UNIV RES FOUND INC +1
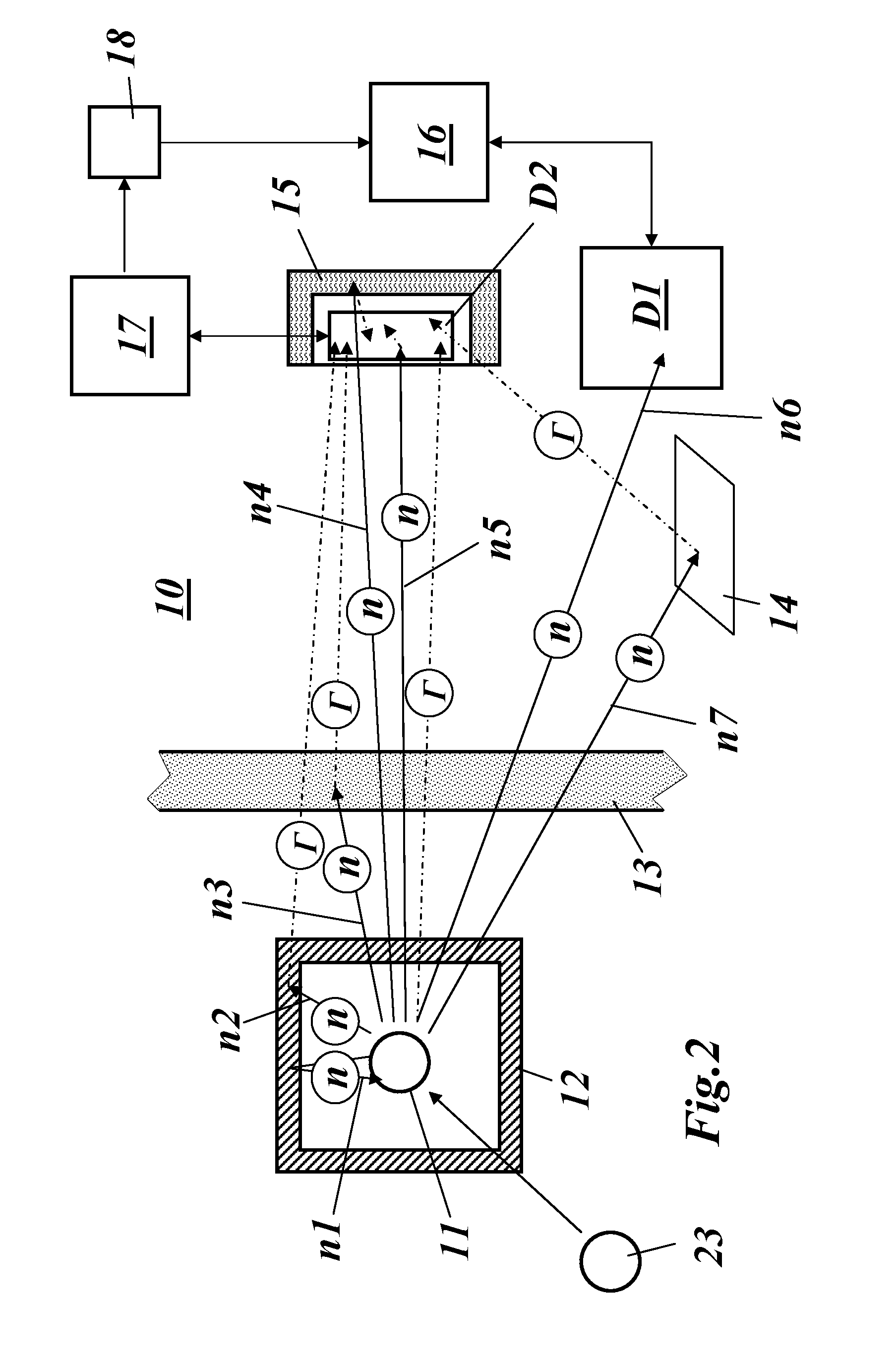
Method for obtaining information signatures from nuclear material or about the presence, the nature and/or the shielding of a nuclear material and measurement setup for performing such method
ActiveUS9477005B2Increase probabilityReduce sensitivityMeasurement with scintillation detectorsX/gamma/cosmic radiation measurmentNuclear radiationHomeland security
The invention relates to a method for obtaining information or signatures about the presence or the nature of a nuclear radiation source, especially in a homeland security application, said nuclear radiation source emitting in a time or angle correlated manner at least a first radiation and a second radiation. The method includes the steps of detecting said first radiation with at least one first radiation detector and detecting said second radiation with at least one second radiation detector. The detection of said second radiation is triggered by said detection of said first radiation in a manner that is adapted to the radiation's correlation structure, thereby increasing the signal-to-background ratio for the detection of said second radiation.
Owner:ARKTIS RADIATION DETECTORS
Charged-balanced imaging agents
ActiveUS9023611B2Improved in vivo propertyGood imaging propertiesMethine/polymethine dyesOrganic chemistryImaging agentNuclear medicine
Owner:GEORGIA STATE UNIV RES FOUND INC +1
X-ray detector module with a collimator
InactiveUS7812316B2Dead space is minimizedCompact structureSolid-state devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansX ray photonsRidge
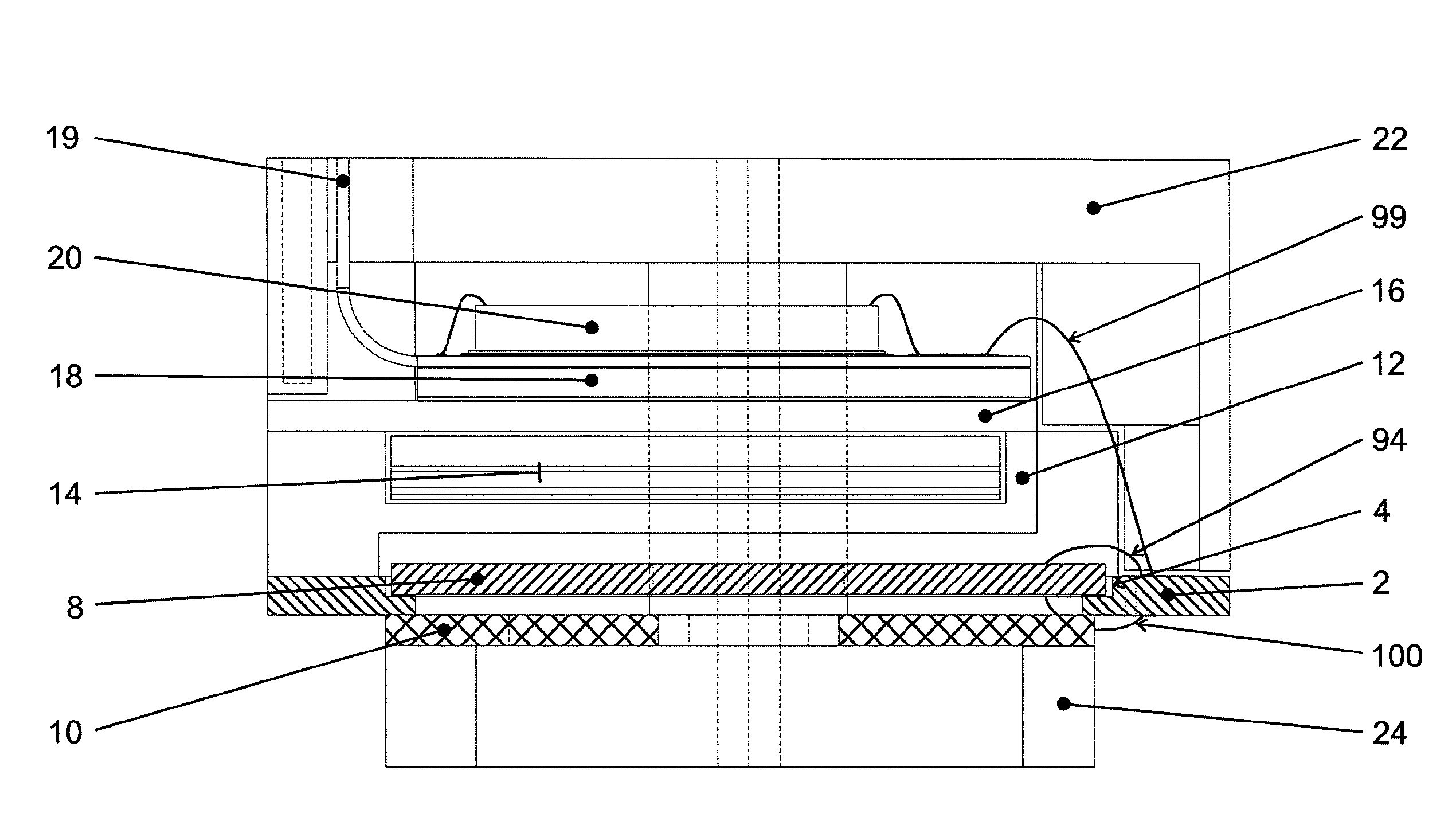
An x-ray detector module comprises a plurality of silicon drift detector cells arranged next to each other on a sensor chip. The sensor chip is arranged in a recess of a frame-shaped base support, such that the sensitive chip surface lies in the opening of the frame-shaped base support. A mask (10) is fixed to the side of the base support (2) opposite to the recess and covers the outer edge areas of external detector cells and ridges above the sensor chip (8) protrude into the opening of the base support (2). The ridges are arranged in such a manner that they cover the defining strips which are adjacent to the detector cells, in order to protect the external edge areas and the defining strips which are covered by the mask (10) counter to the incident x-ray photons.
Owner:DEUTES ELEKTRONEN SYNCHROTRON DESY
Fluorescent molecule and method for detecting target nucleic acid
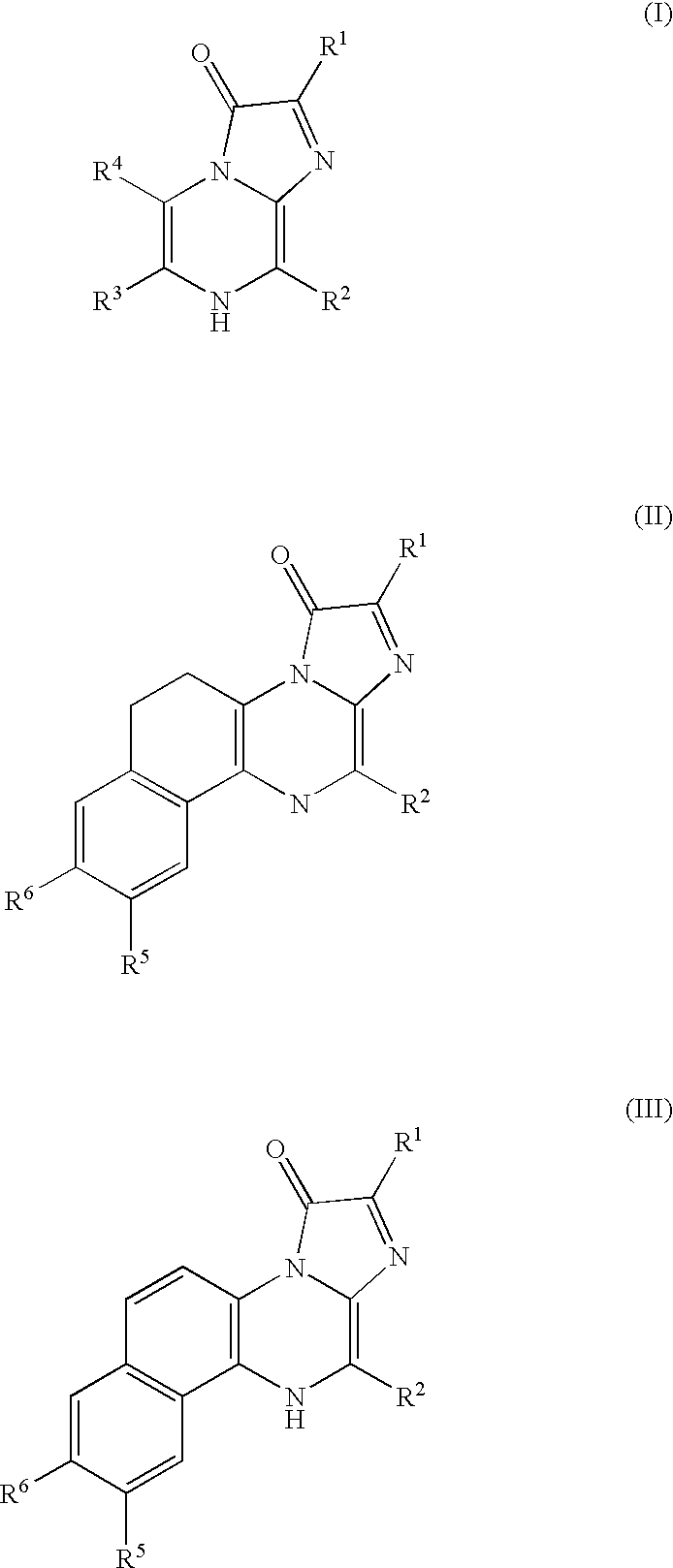
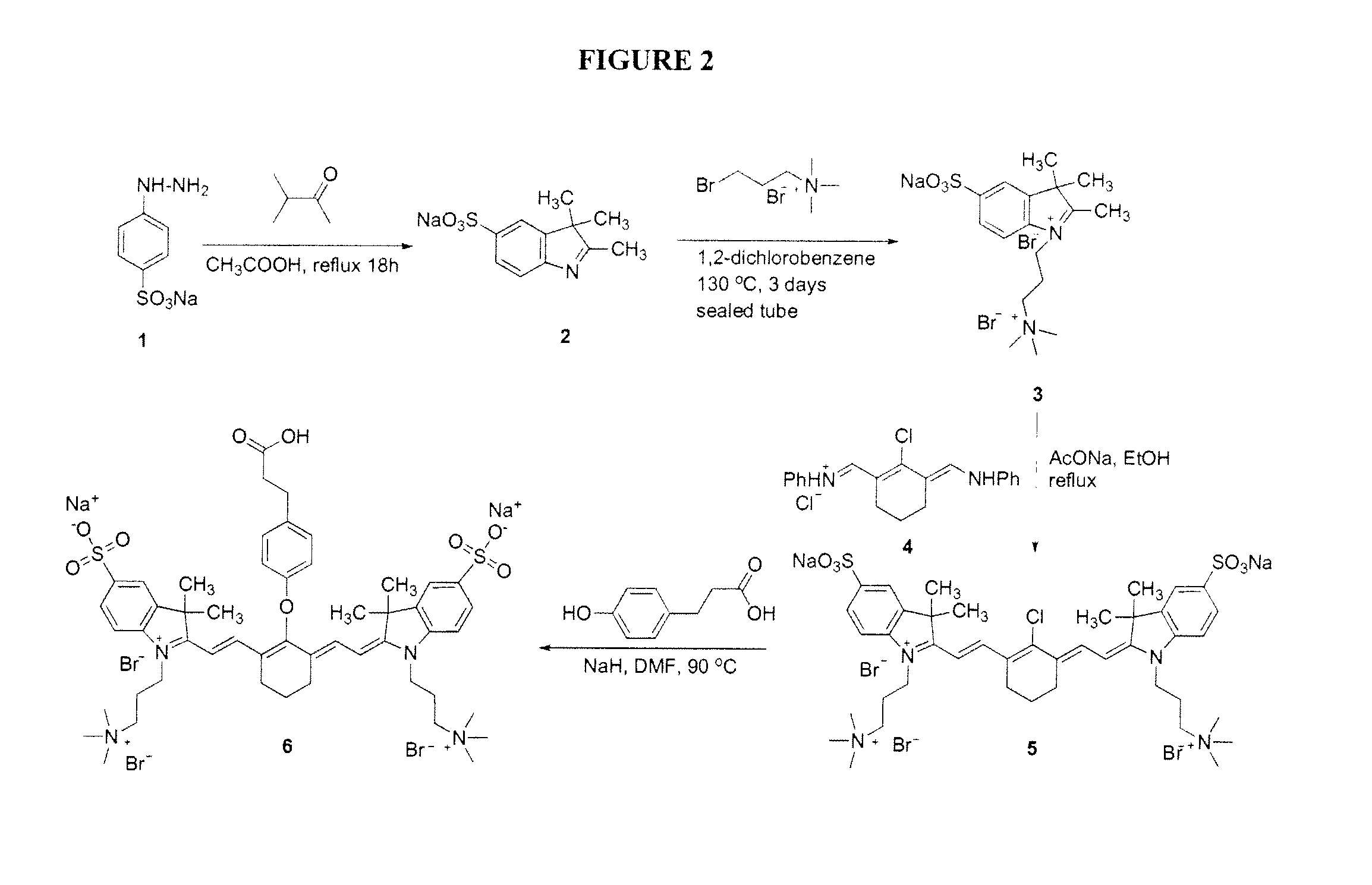
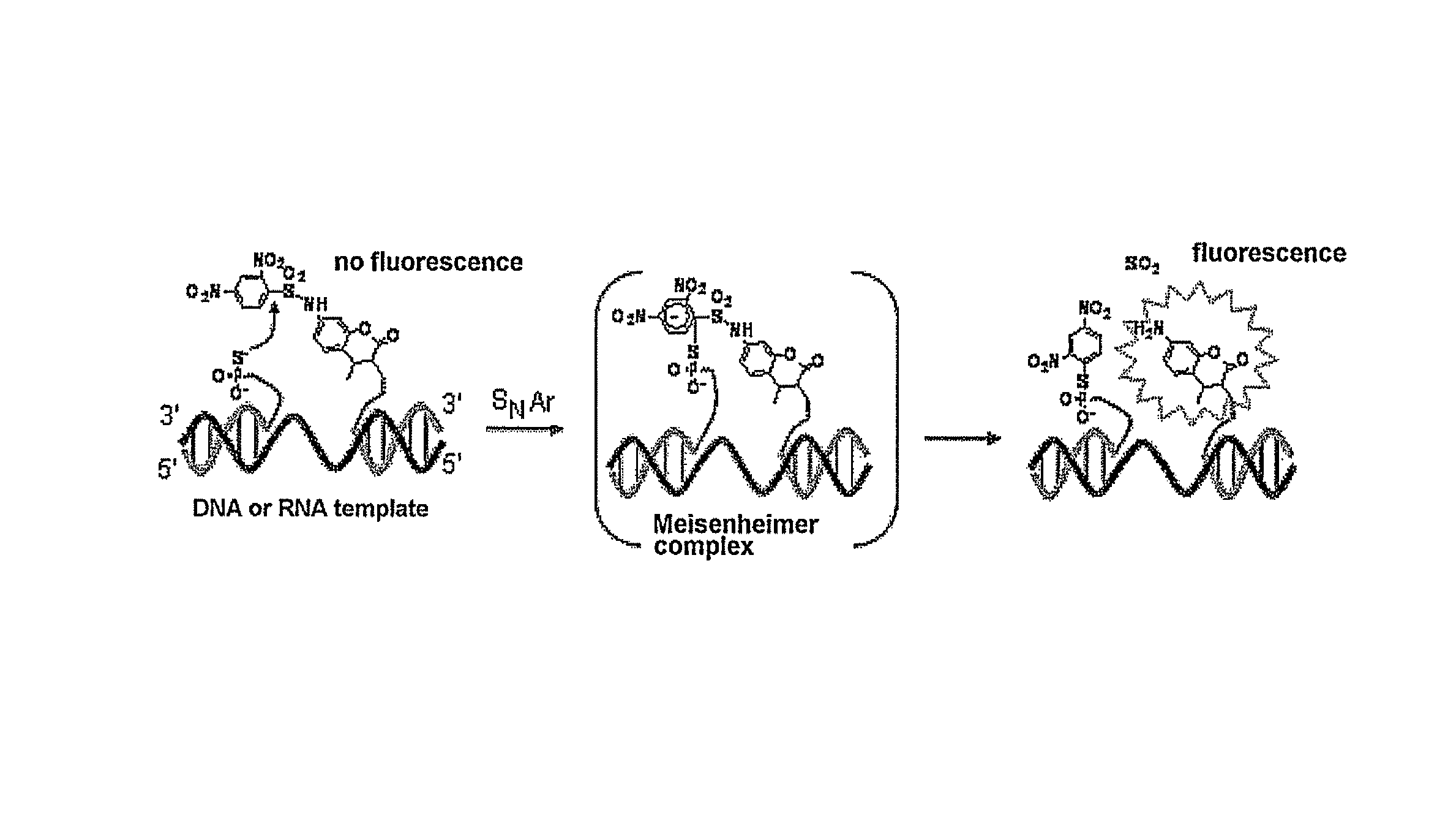
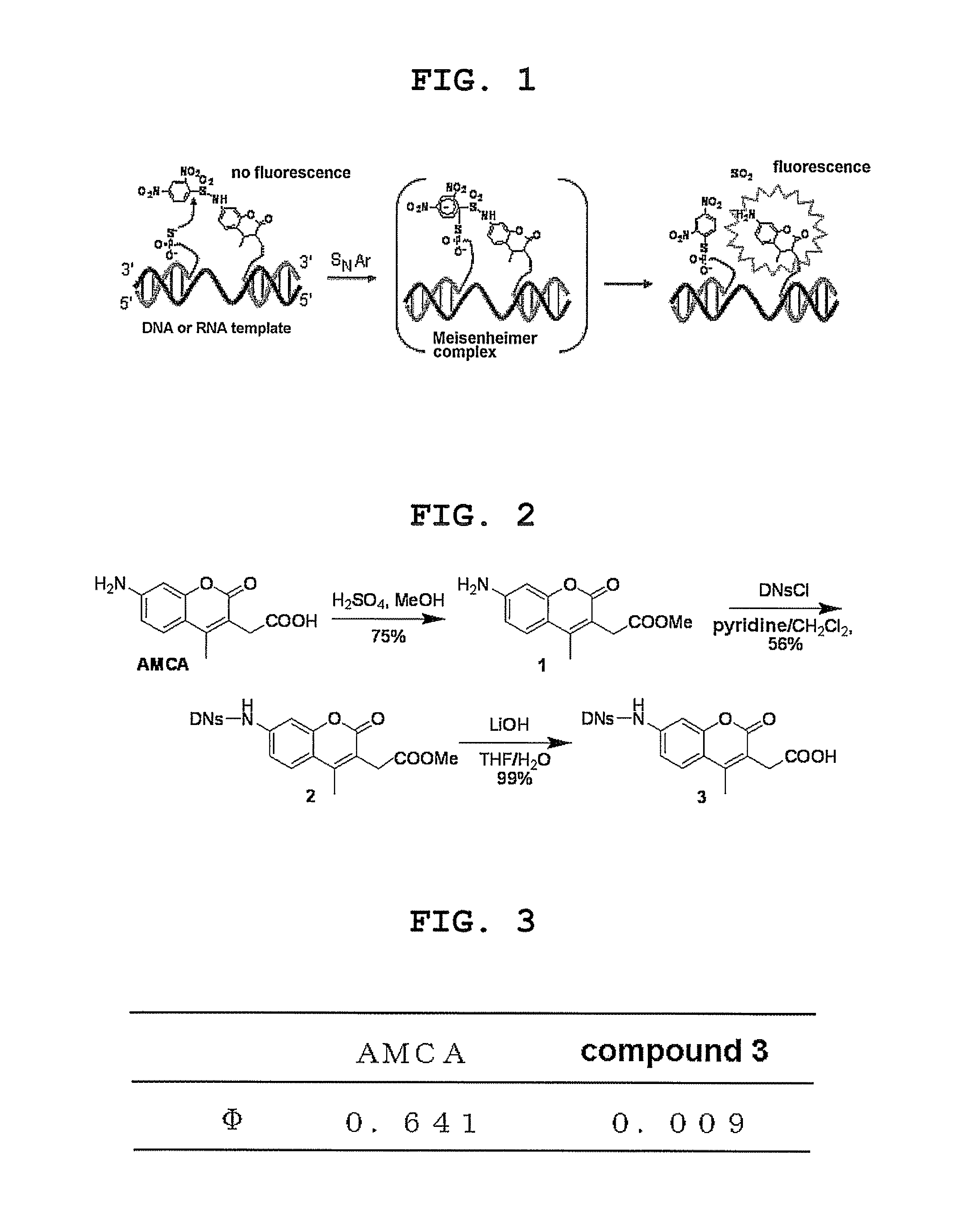
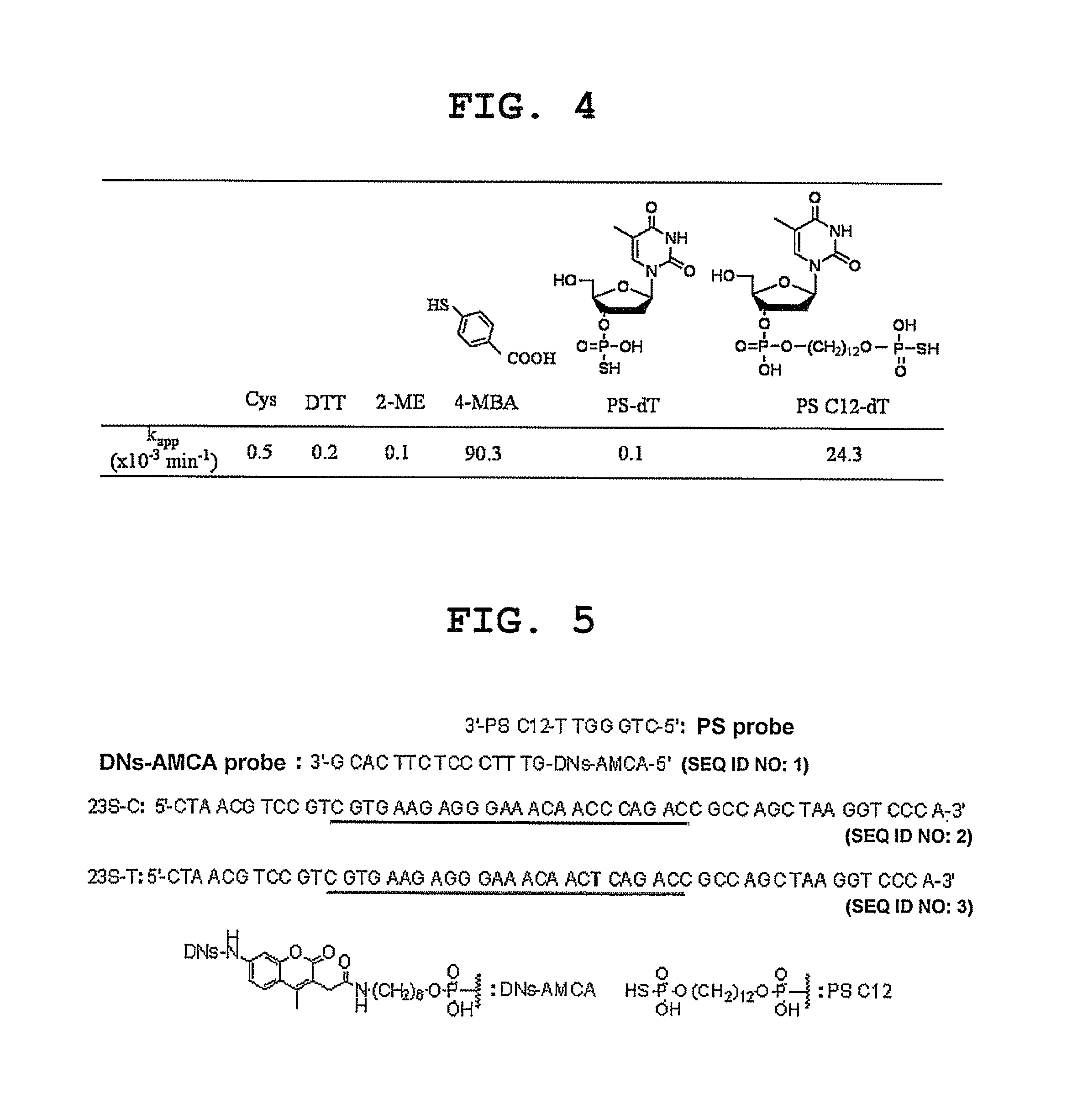
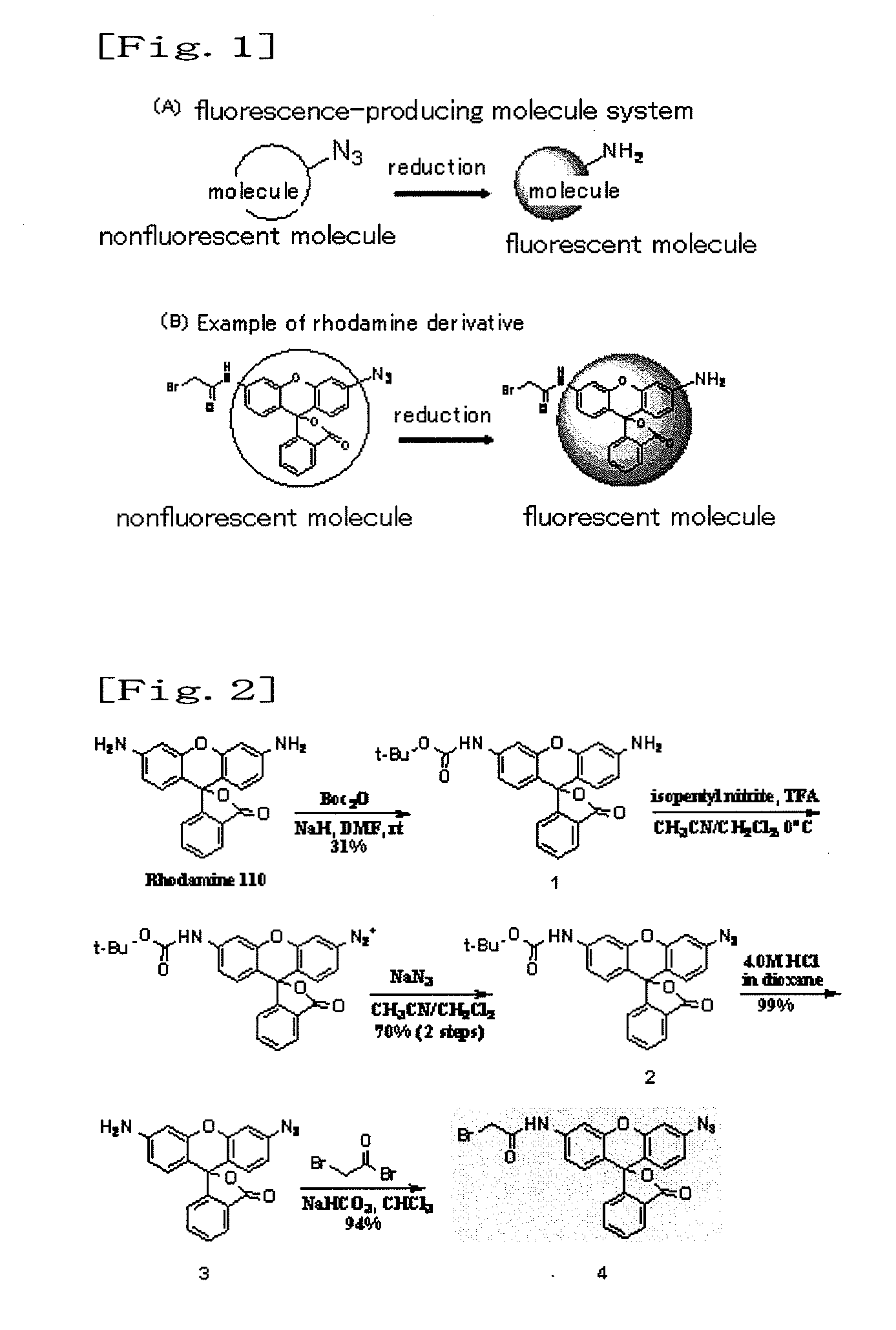
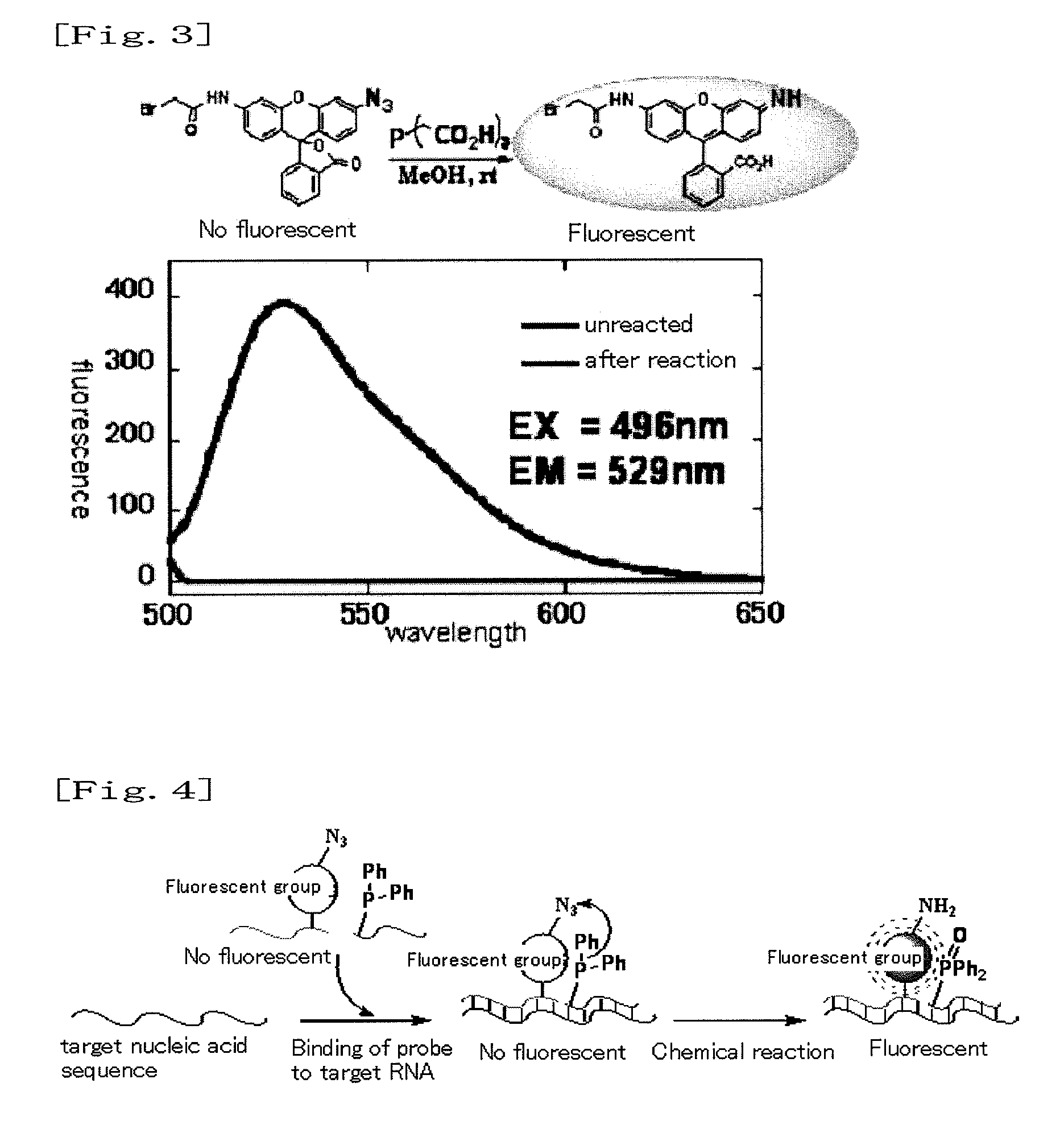
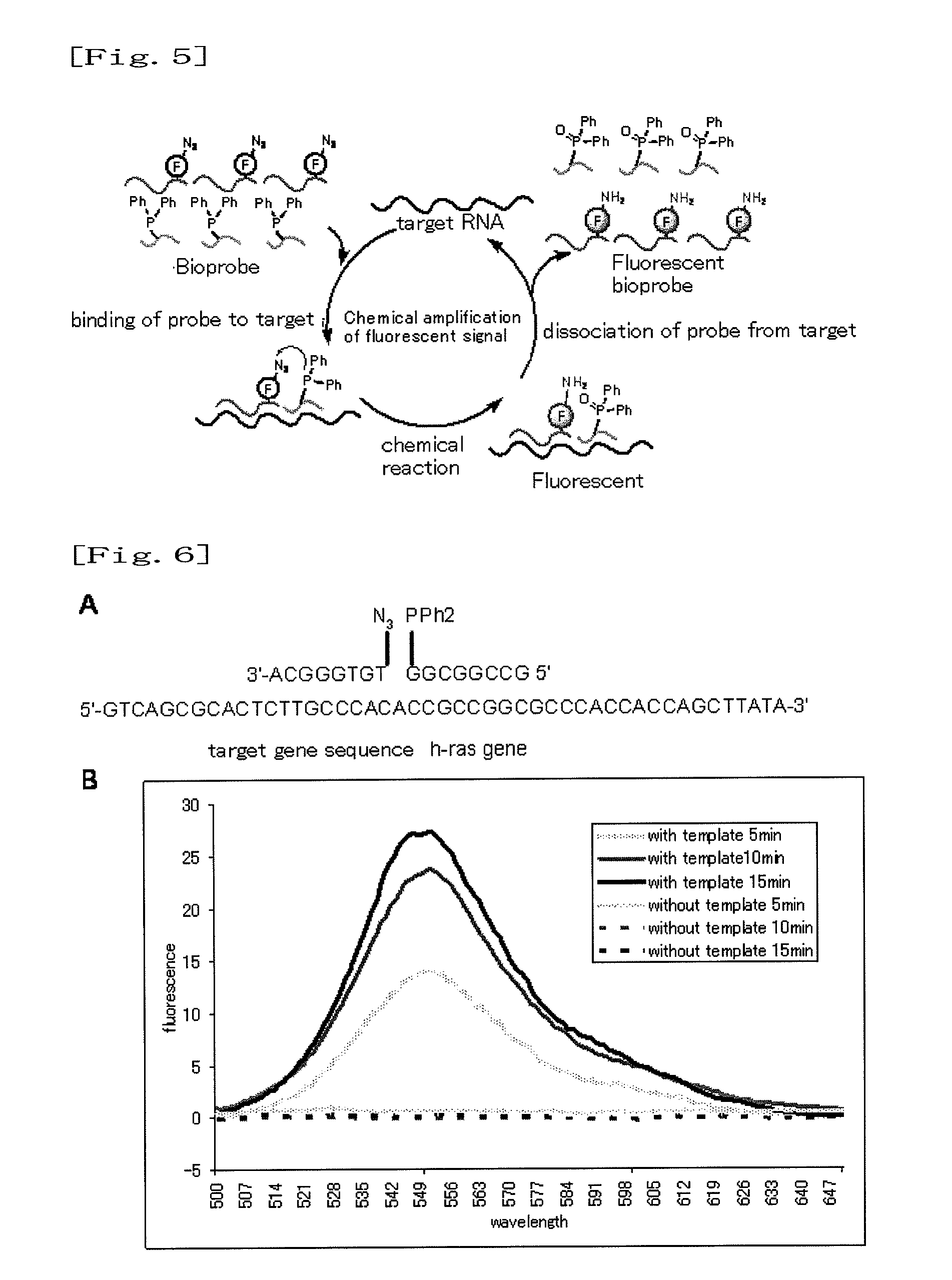
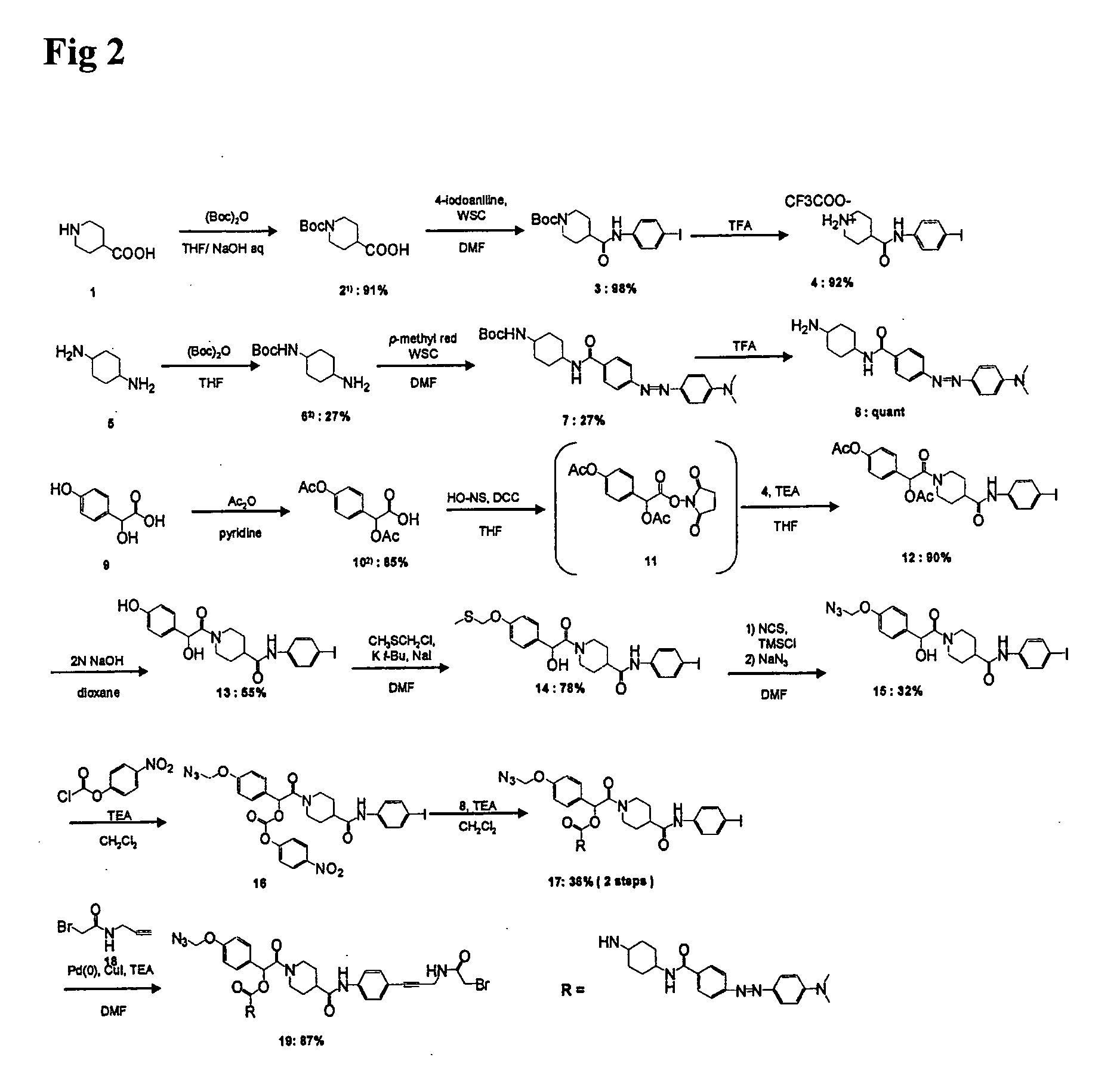
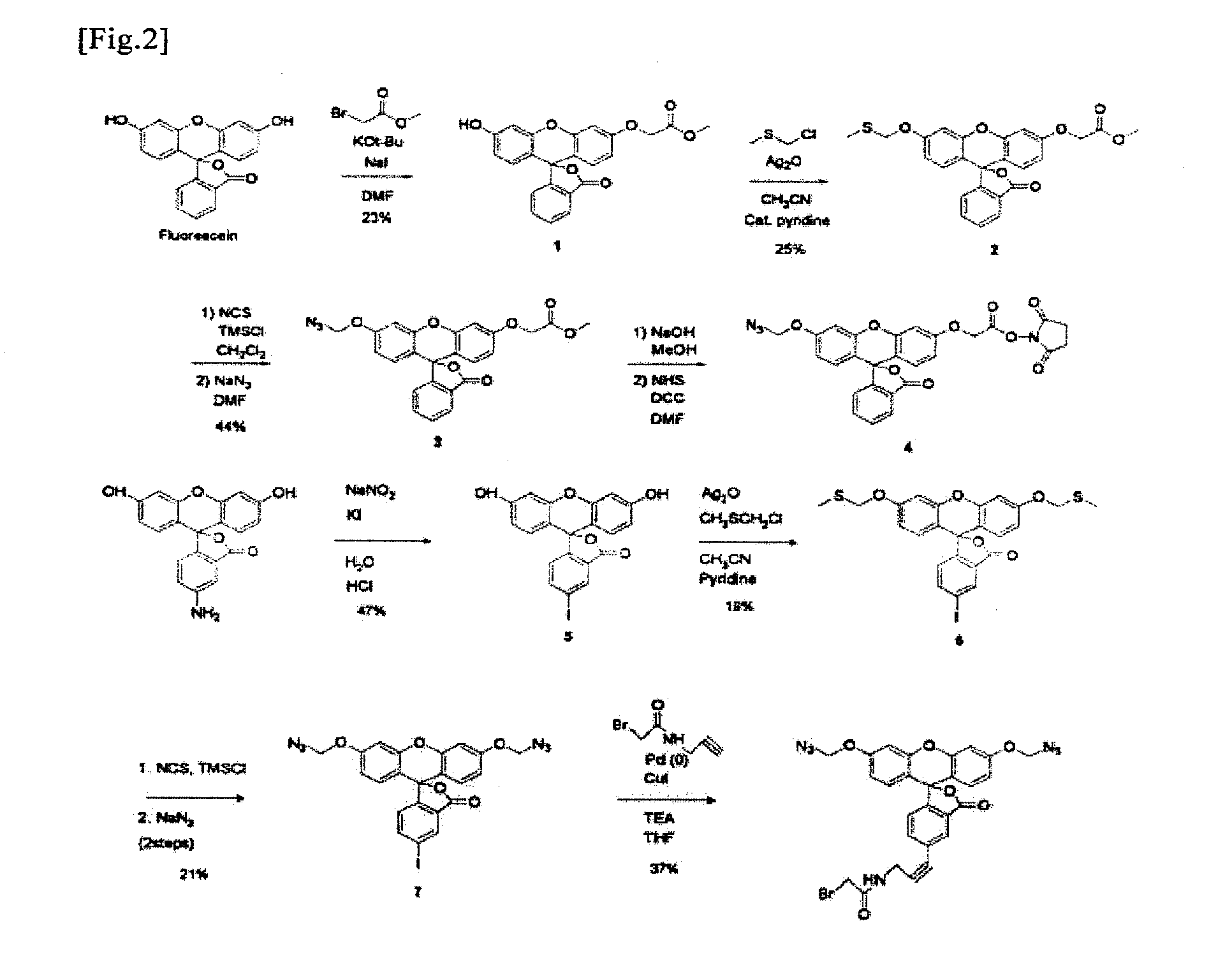
InactiveUS8709721B2Improve the signal-to-background ratioEnables amplificationSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementCarbon numberFluorescence
Provided are a fluorescent on / off switchable compound for a gene analysis, which is highly stable and highly sensitive, and enables amplification and observation of a trace gene signal, and a labeling reagent for detection of a bio-related material, which uses the fluorescent on / off switchable compound. A compound represented by the following formula (I′):wherein X is a hydrogen atom or a carboxylic acid-protecting group, Y is a 2,4-dinitrobenzenesulfonyl group, a 2-cyano-4-nitrobenzenesulfonyl group or a 5-nitropyridin-2-ylsulfonyl group, R1, R2, R3 and R4 are each independently a hydrogen atom, a halogen atom, a hydroxyl group, an alkyl group having a carbon number of 1 to 6, an alkoxy group having a carbon number of 1 to 6, an aryl group having a carbon number of 6 to 10, or a cyano group.
Owner:RIKEN
Homogeneous time-resolved energy transfer assay
InactiveUS7846658B2Improve energy transferHigh sensitivityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsEnergy transferHigh energy
The invention relates to a method for improving the detection sensitivity in homogenous TR-FRET based bioaffinity assays. The sensitivity is improved by the use of long lifetime donors together with a high energy transfer efficiency and by carrying out the detection of the energy transfer based emission of the acceptor in a time window which is opened after a delay of 1 microsecond or more, but less than 50 microseconds, calculated from the donor excitation, and which time window has a width of 1 microsecond or more, but less than 100 microseconds. The invention concerns also the use of the improved method in multianalyte assays. Furthermore, the invention concerns a device suitable for carrying out the improved method.
Owner:WALLAC
Method of enhancing fluorescence
InactiveUS7713694B2Fluorescence enhancementImprove stabilitySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementElectrophoresisOrganic chemistry
A method of enhancing the fluorescence of and / or producing an increased Stokes' shift in a fluorescent dye comprising combining the dye with a base and / or a detergent is described. The method is suitable in chemical or biochemical techniques using fluorescent dyes, particularly techniques requiring staining or labeling of organic molecules, such as electrophoresis.
Owner:FLUOROTECHNICS PTY LTD
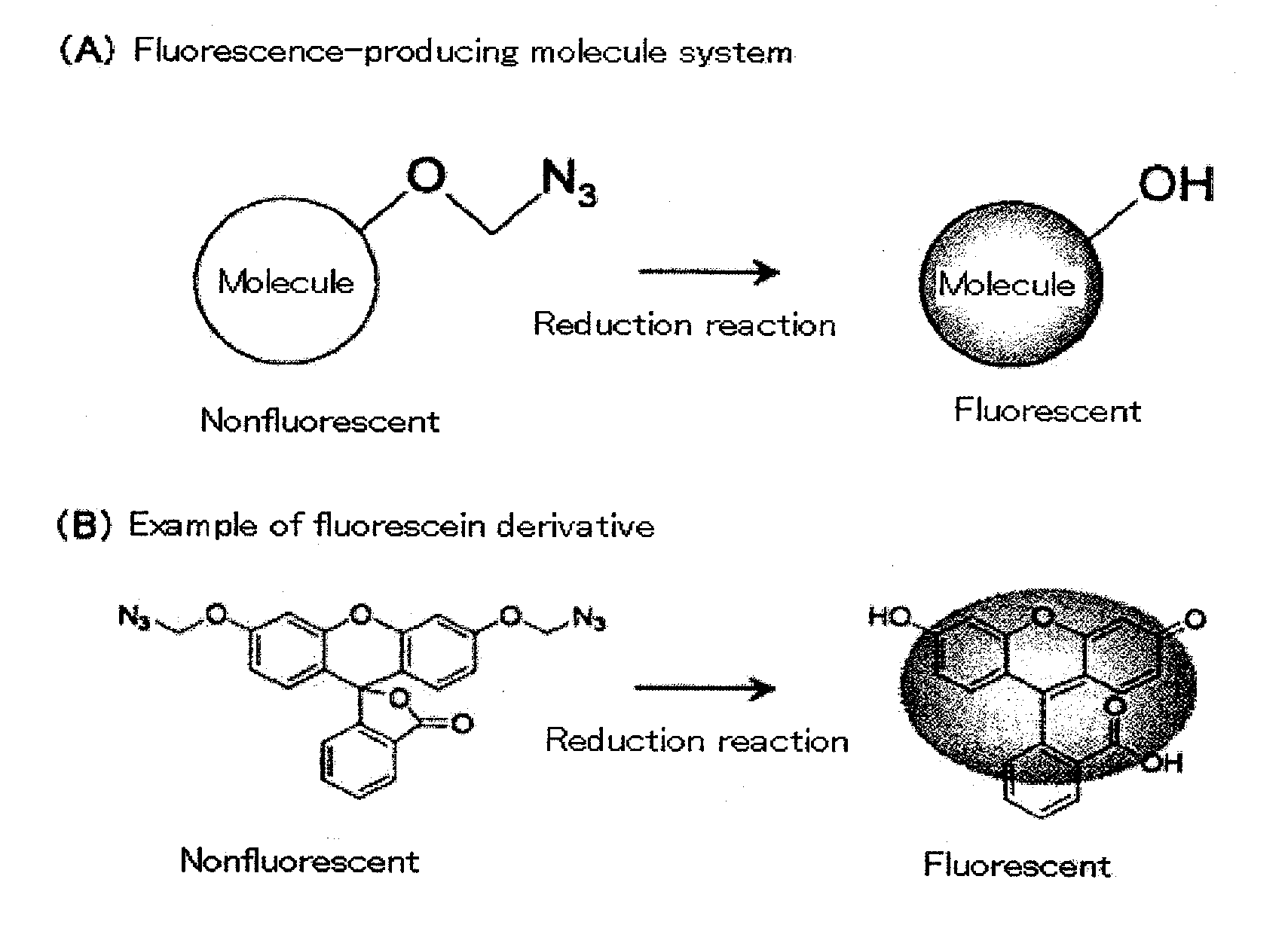
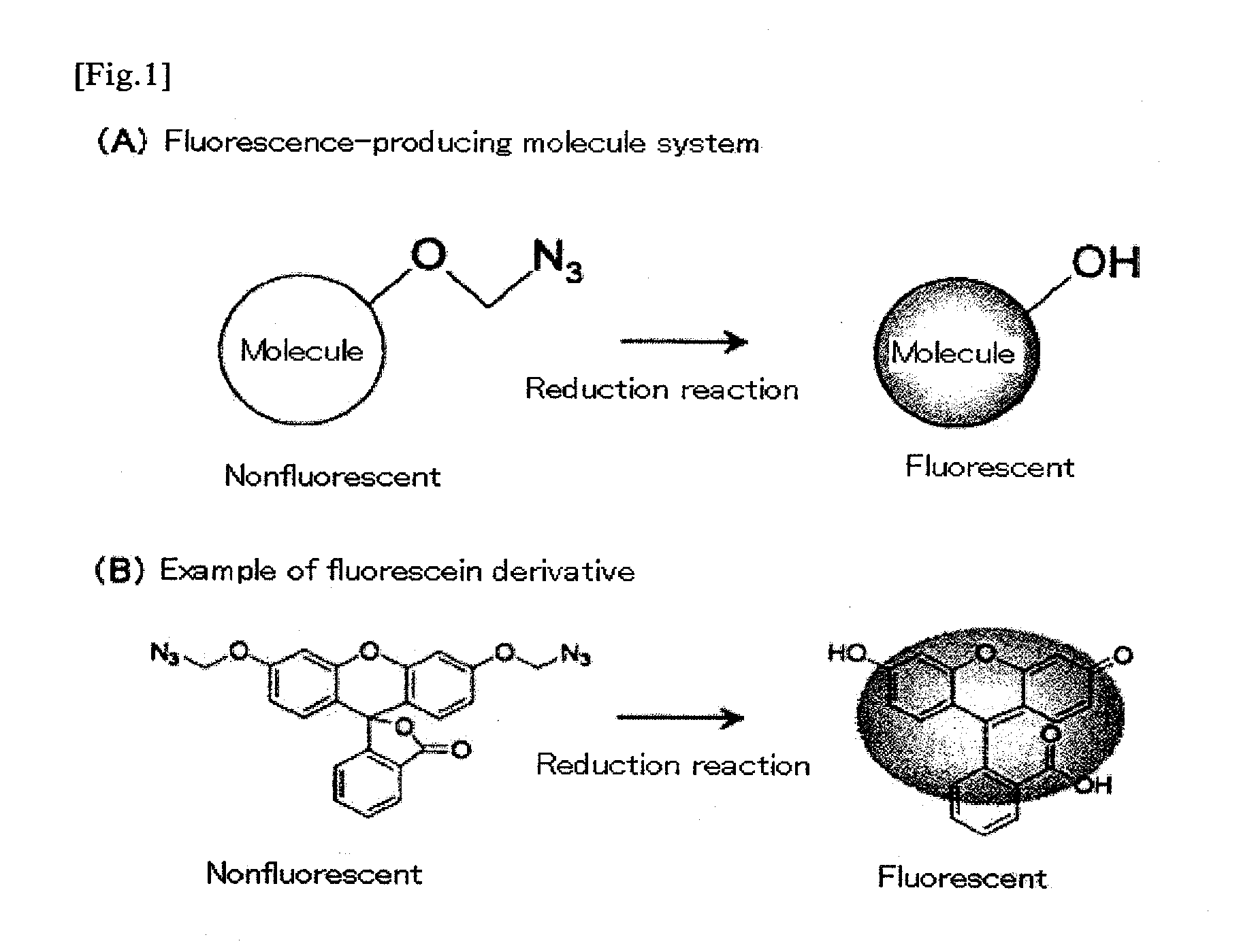
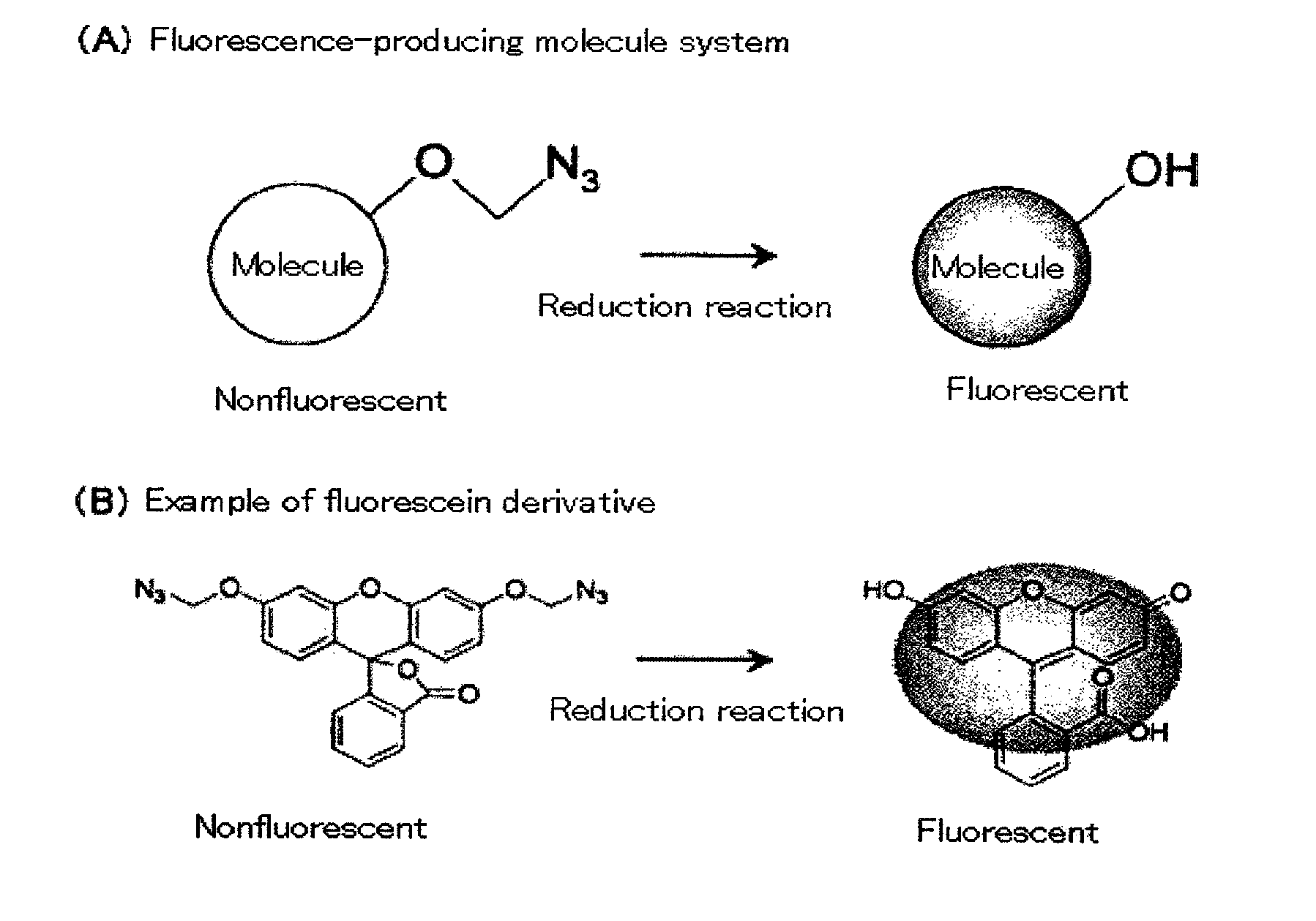
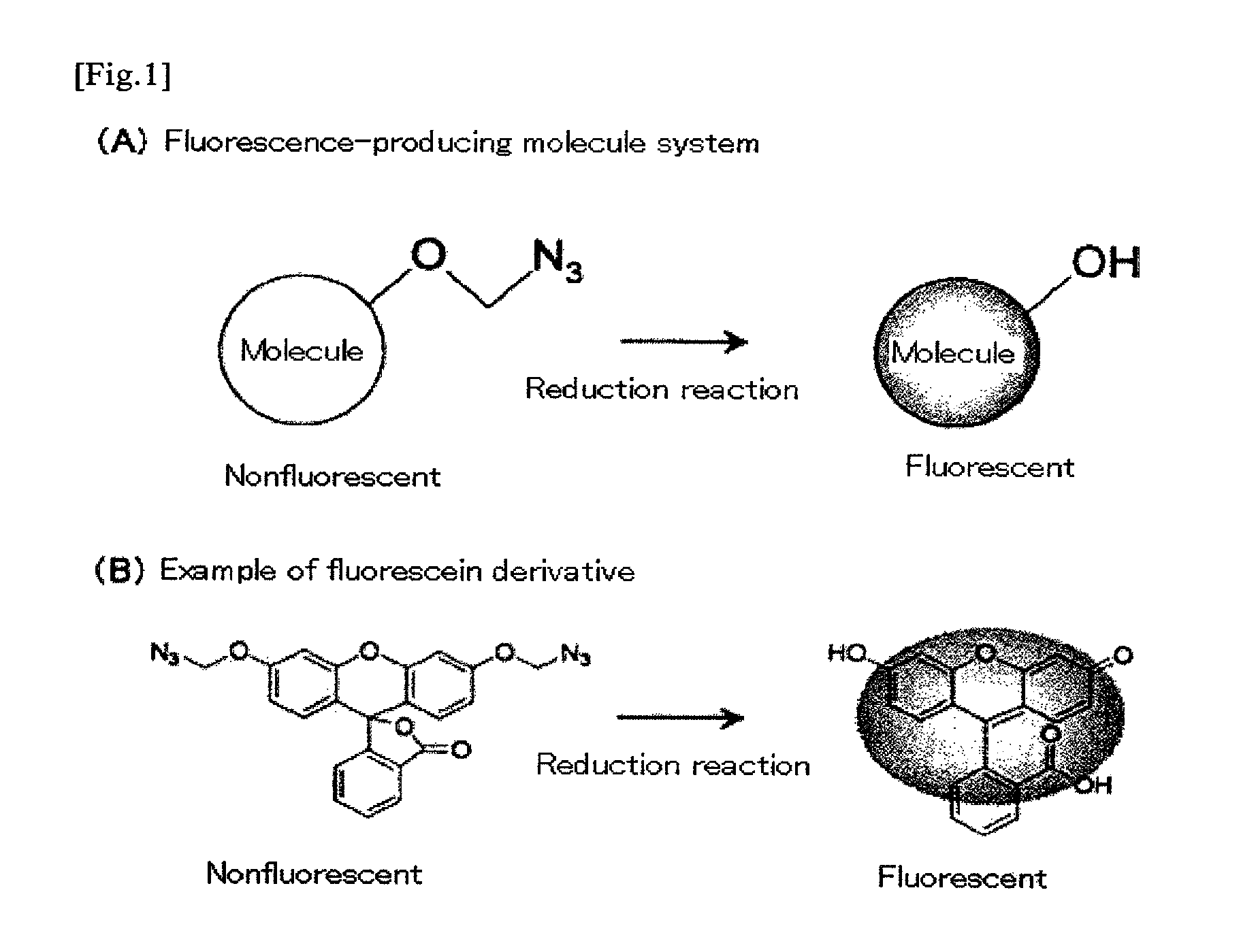
Fluorescence-producing molecule
InactiveUS20100190159A1Improve the signal-to-background ratioLow costOrganic chemistryMicrobiological testing/measurementArylHydrogen atom
It is an object of the present invention to provide an on-off type fluorescent compound used in gene analyses, which is highly stable and highly sensitive, and which enables amplification of a trace amount of gene signal and observation thereof. The present invention provides a compound represented by the following formula (1) or (2):wherein R1 represents an alkyl group containing 1 to 6 carbon atoms, an amino group, an amide group optionally having a protecting group or a substituent, a halogen atom, or a hydrogen atom; R2 independently represents an alkyl group containing 1 to 6 carbon atoms, a halogen atom, or a hydrogen atom; R3 represents an alkyl group containing 1 to 6 carbon atoms, an aryl group, or a hydrogen atom; R4 represents a group containing an oxygen atom, or a hydrogen atom, wherein R3 may bind to R4 to form a ring.
Owner:RIKEN
Optical device for surface-generated fluorescence
ActiveUS7285789B2Efficient separationImprove the signal-to-background ratioPhotometryLuminescent dosimetersFluorescenceMolecular physics
A sample substrate adapted for use with electromagnetic excitation light includes a base and a layer system. The layer system includes a multilayer interference coating with at least two layers wherein the thicknesses of the layers ensure that light emitted by a fluorescent sample material disposed on top of said multilayer interference coating is reflected. Light directed to a fluorescent sample material disposed on the substrate causes light to be emitted from the sample. The layer system includes a multilayer interference coating with at least two layers wherein thicknesses of the layers cause separation of the excitation light from the emitted light.
Owner:OERLIKON SURFACE SOLUTIONS AG PFAFFIKON
Beam generation unit and X-ray small-angle scattering apparatus
ActiveUS10145808B2Improve the signal-to-background ratioMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationHandling using diffraction/refraction/reflectionTwo dimensional detectorX-ray
Owner:RIGAKU CORP
Use of charge-balanced imaging agents for determining renal function
ActiveUS20170290928A1Improved in vivo propertyGood imaging propertiesOrganic chemistryMethine/polymethine dyesImaging agentTreatment use
Owner:BETH ISRAEL DEACONESS MEDICAL CENT INC +1
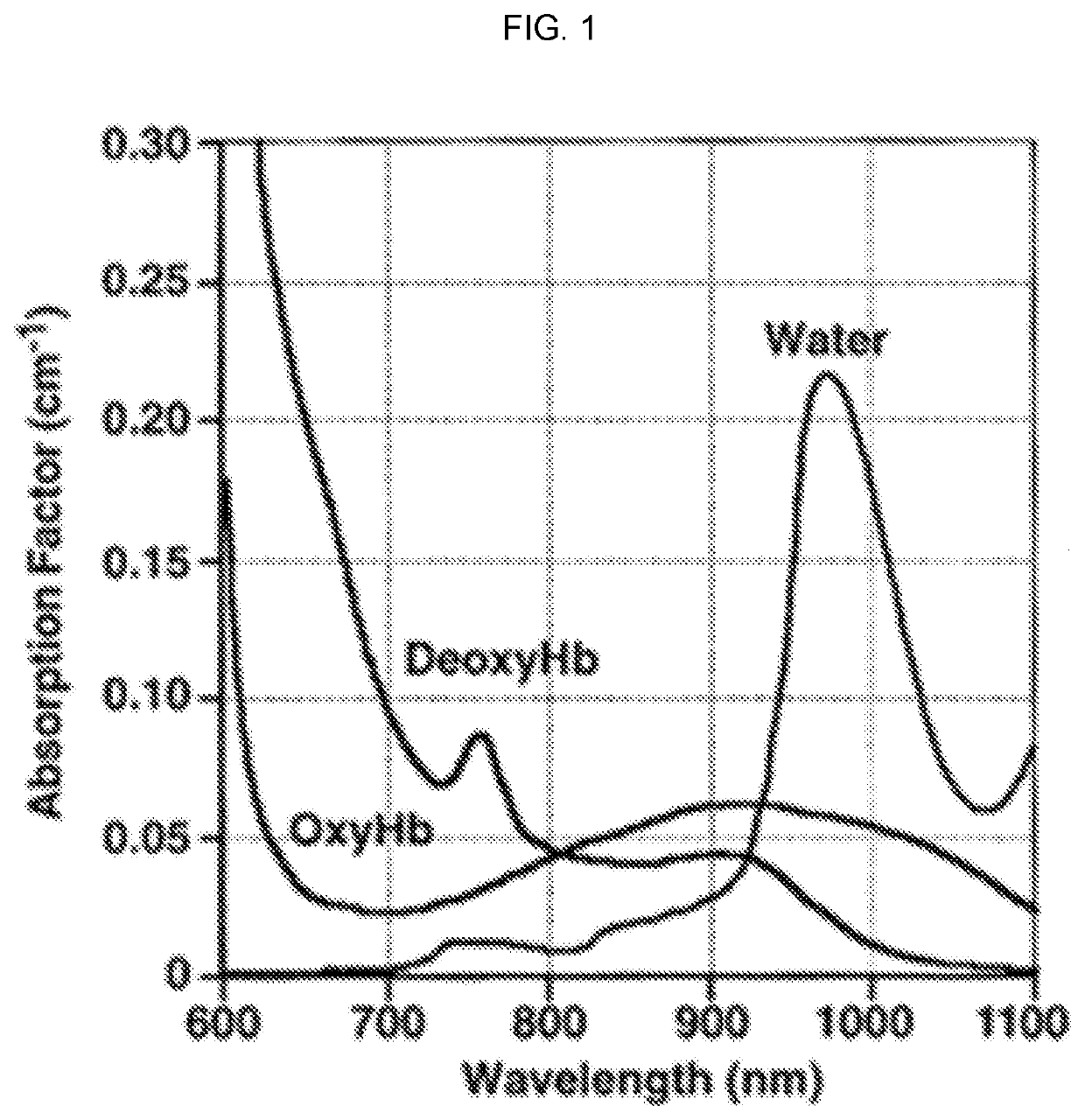
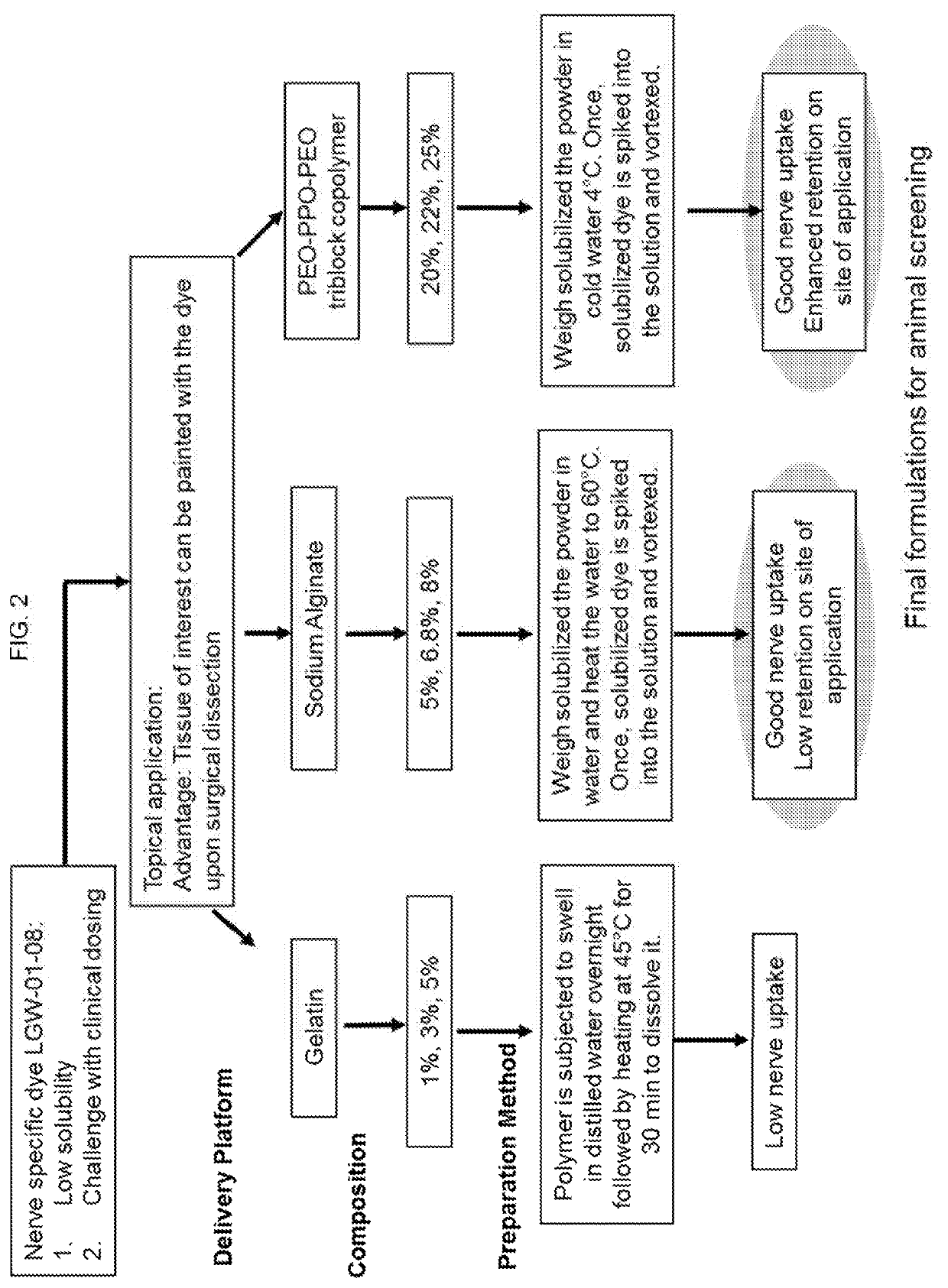
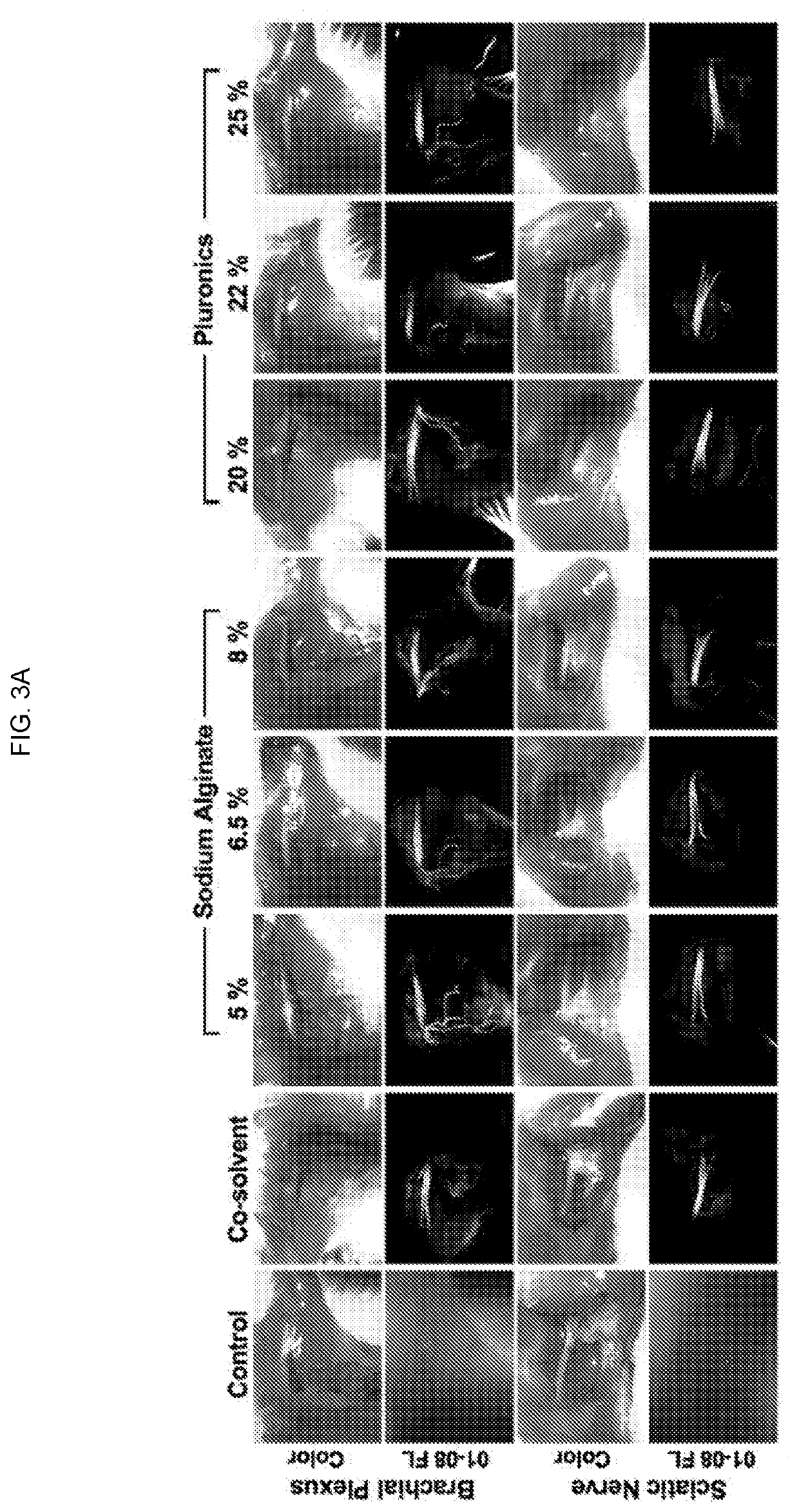
Nerve-specific fluorophore formulations for direct and systemic administration
PendingUS20210236657A1Improve the signal-to-background ratioReduce transmissionAerosol deliveryPreparing sample for investigationFluorophoreReoperative surgery
Nerve-specific fluorophore formulations for direct or systemic administration are described. The formulations can be used in fluorescence-guided surgery (FGS) to aid in nerve preservation during surgical interventions.
Owner:THE STATE OF OREGON ACTING BY & THROUGH THE OREGON STATE BOARD OF HIGHER EDUCATION ON BEHALF OF OREGON STATE UNIV +1
Use of charge-balanced imaging agents for determining renal function
ActiveUS10493169B2Improved in vivo propertyGood imaging propertiesOrganic chemistryMethine/polymethine dyesImaging agentTreatment use
Owner:BETH ISRAEL DEACONESS MEDICAL CENT INC +1
A switch-type liposome nano fluorescent probe and its preparation method and application
ActiveCN112168981BHigh encapsulation efficiencyHigh blood stabilityEmulsion deliveryIn-vivo testing preparationsFluoProbesCholesterol
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Total internal reflection illumination and semi-total internal reflection illumination dual optical path fluorescence microscope system
InactiveCN103235406BAvoid background fluorescence interferenceImprove the signal-to-background ratioMicroscopesFluorescence/phosphorescenceBeam splitterTotal internal reflection
The invention discloses a total internal reflection illumination and semi-total internal reflection illumination dual optical path fluorescence microscope system. A beam-splitter plate I is arranged on the light path of exciting light and the angle between the beam-splitter plate I and the light path is 135 degrees so that the exciting light is divided into a vertical transmission light and a vertical reflected light; the transmission light is reflected through a reflector so as to be parallel to the reflected light; the light paths of the reflected light and the transmission light are respectively and sequentially provided with a graded-density neutral filter, a convex lens I, a convex lens II and a light spot aperture regulator; the reflected light and the transmission light then form two vertical light paths by adjusting transmission directions through the reflector; convex lens III are respectively arranged on the mutually vertical light paths of the reflected light and the transmission light; the reflected light and the transmission light pass through the convex lens III so as to be incident to a beam-splitter plate II having an angle of 135 degrees with a light path of the reflected light; and two parallel lights divided through the beam-splitter plate II are incident to an exciting light inlet of a microscope. The total internal reflection illumination and semi-total internal reflection illumination dual optical path fluorescence microscope system can be used for bleaching fluorescence molecule of a cell membrane area, background fluorescence interference caused when the fluorescence molecule of the cell membrane area images a focal plane in a cell is avoided, and a signal background ratio of semi-total internal reflection fluorescence imaging in the cell is further improved.
Owner:INST OF CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for releasing molecule of interest based on target nucleic acid sequence
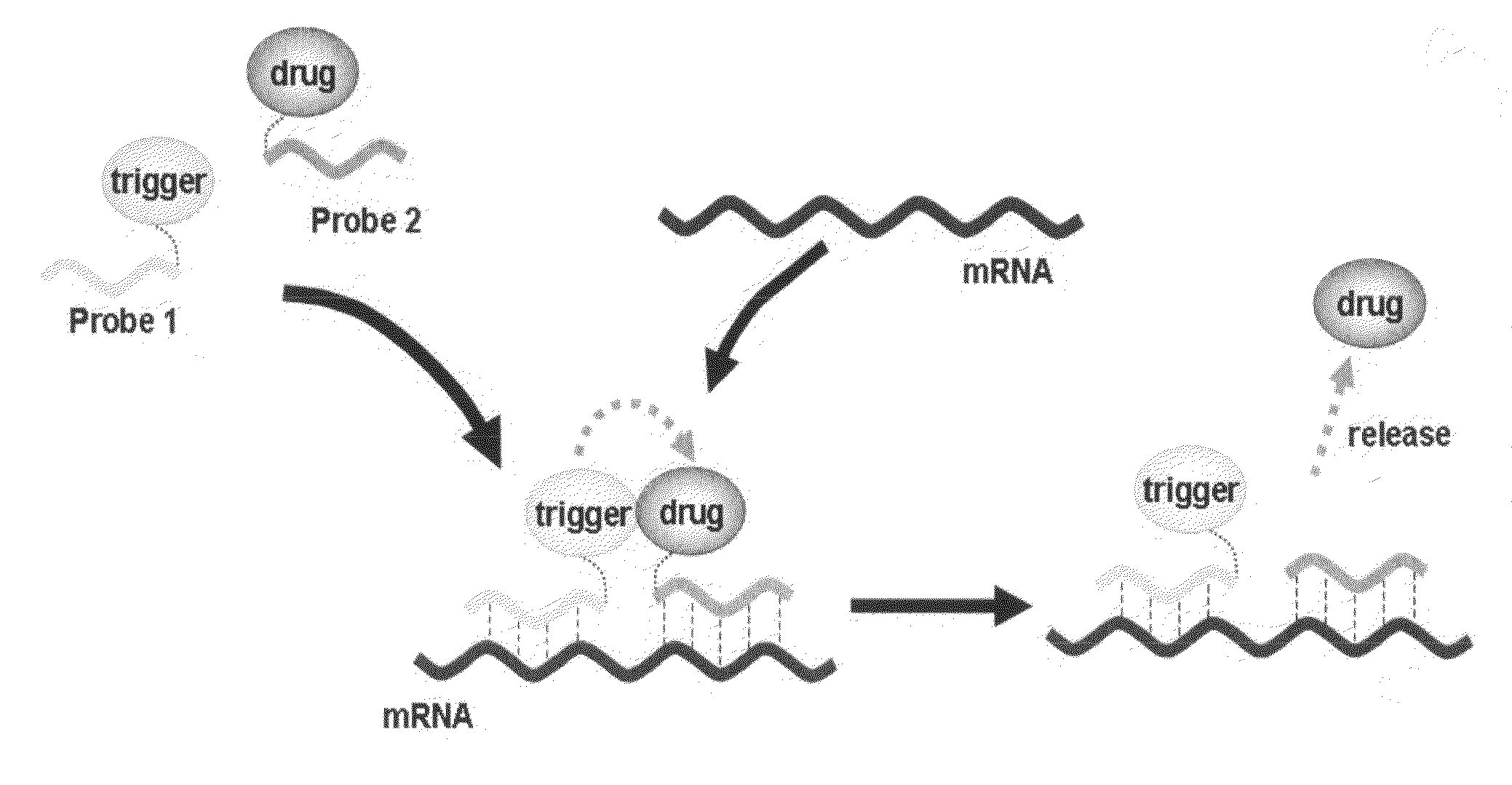
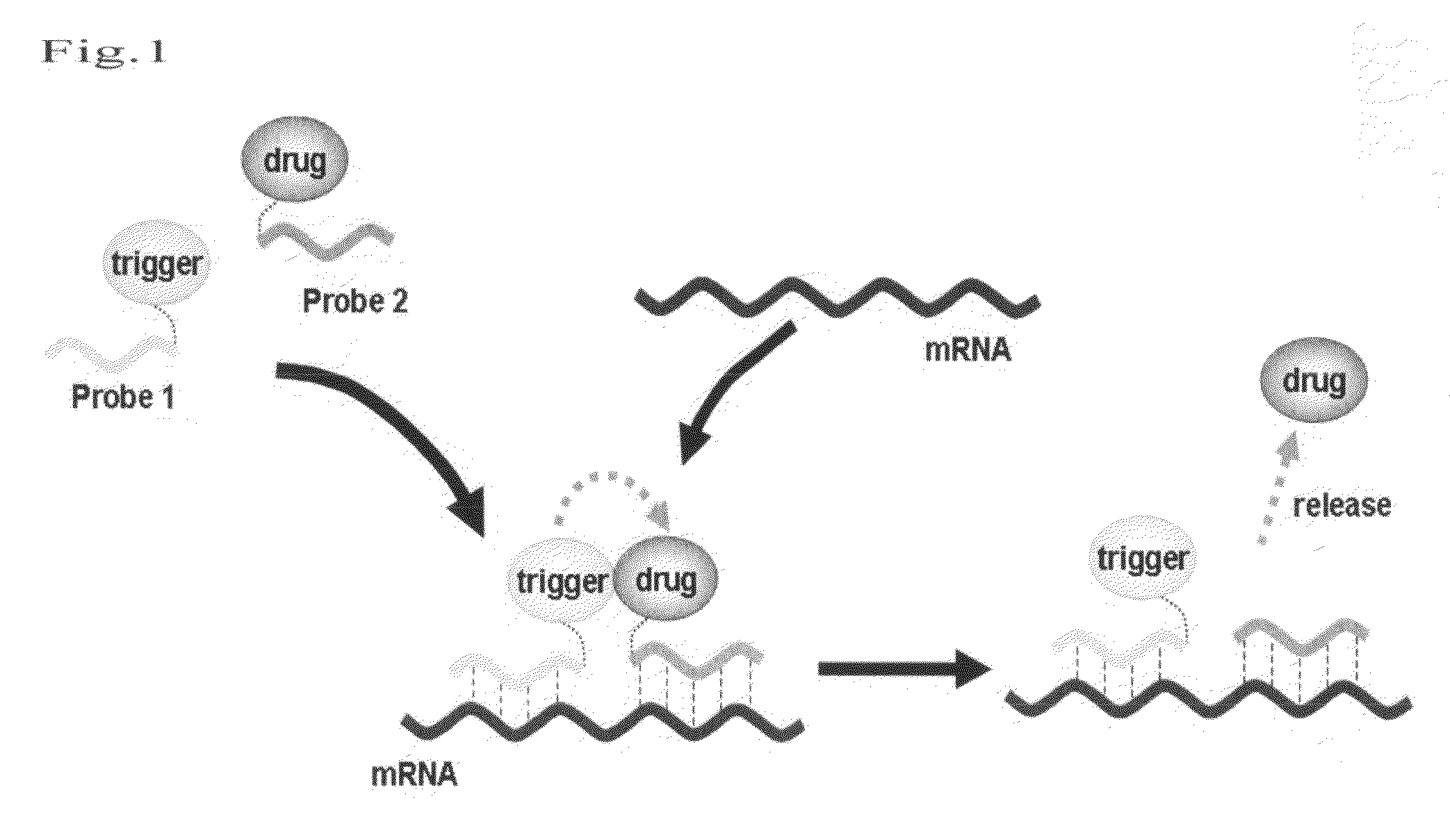
InactiveUS20090227691A1Suppressing influenceInhibition effectBiocideMonoazo dyesAzideNucleic Acid Probes
It is an object of the present invention to provide a method for highly selectively releasing a molecule of interest such as an agent at a desired site while suppressing the influence of catabolic enzymes existing in vivo. The present invention provides a method for releasing a molecule of interest, which comprises steps of: hybridizing each of an “electron donor-first nucleic acid probe” molecule formed by binding an electron donor structure to a first nucleic acid probe having a nucleotide sequence complementary to a portion of a target nucleic acid sequence and a “molecule of interest-electron acceptor-second nucleic acid probe” molecule formed by binding an electron acceptor structure having a molecule of interest and an azide group to a second nucleic acid probe that has a nucleotide sequence complementary to said target nucleic acid sequence and differing from that of said first nucleic acid probe, to said target nucleic acid sequence; and allowing said “electron donor-first nucleic acid probe” molecule to act on said “molecule of interest-electron acceptor-second nucleic acid probe” molecule, so as to release said molecule of interest.
Owner:RIKEN
Fluorescent molecule
InactiveUS20110076680A1High signal/background ratioSensitive detectionSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementFluoresceinCarbon atom
It is an object of the present invention to provide an on-off type fluorescent compound (a fluorescence-producing molecule system) used in gene analyses, which is highly stable (namely, being active for a long period of time) and highly sensitive, and which enables amplification of a trace amount of gene signal and observation thereof. The present invention provides a nonfluorescent molecule having a fluorescent substance skeleton such as fluorescein skeleton and having a group represented by —O—C(Y1)(Y2)-N3 wherein each of Y1 and Y2 represents a hydrogen atom, an alkyl group containing 1 to 6 carbon atoms, an alkoxy group containing 1 to 6 carbon atoms, an aryl group containing 6 to 10 carbon atoms, or a cyano group, in the molecule.
Owner:RIKEN
Fluorescent molecule
InactiveUS8084201B2Improve the signal-to-background ratioSensitive detectionSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementArylFluorescein
It is an object of the present invention to provide an on-off type fluorescent compound (a fluorescence-producing molecule system) used in gene analyses, which is highly stable (namely, being active for a long period of time) and highly sensitive, and which enables amplification of a trace amount of gene signal and observation thereof. The present invention provides a nonfluorescent molecule having a fluorescent substance skeleton such as fluorescein skeleton and having a group represented by —O—C(Y1)(Y2)-N3 wherein each of Y1 and Y2 represents a hydrogen atom, an alkyl group containing 1 to 6 carbon atoms, an alkoxy group containing 1 to 6 carbon atoms, an aryl group containing 6 to 10 carbon atoms, or a cyano group, in the molecule.
Owner:RIKEN
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com