Patents
Literature
48 results about "Active domain" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
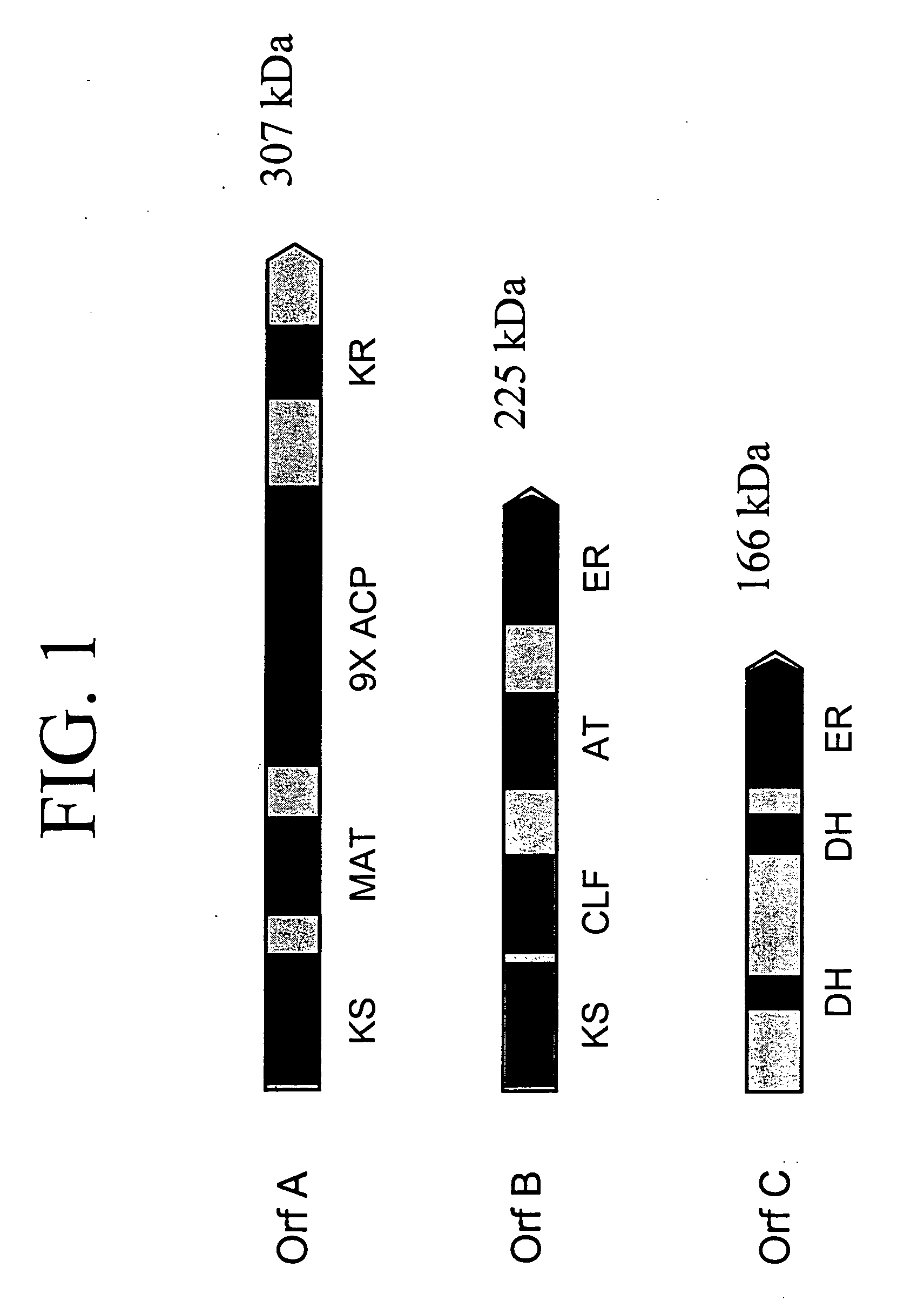
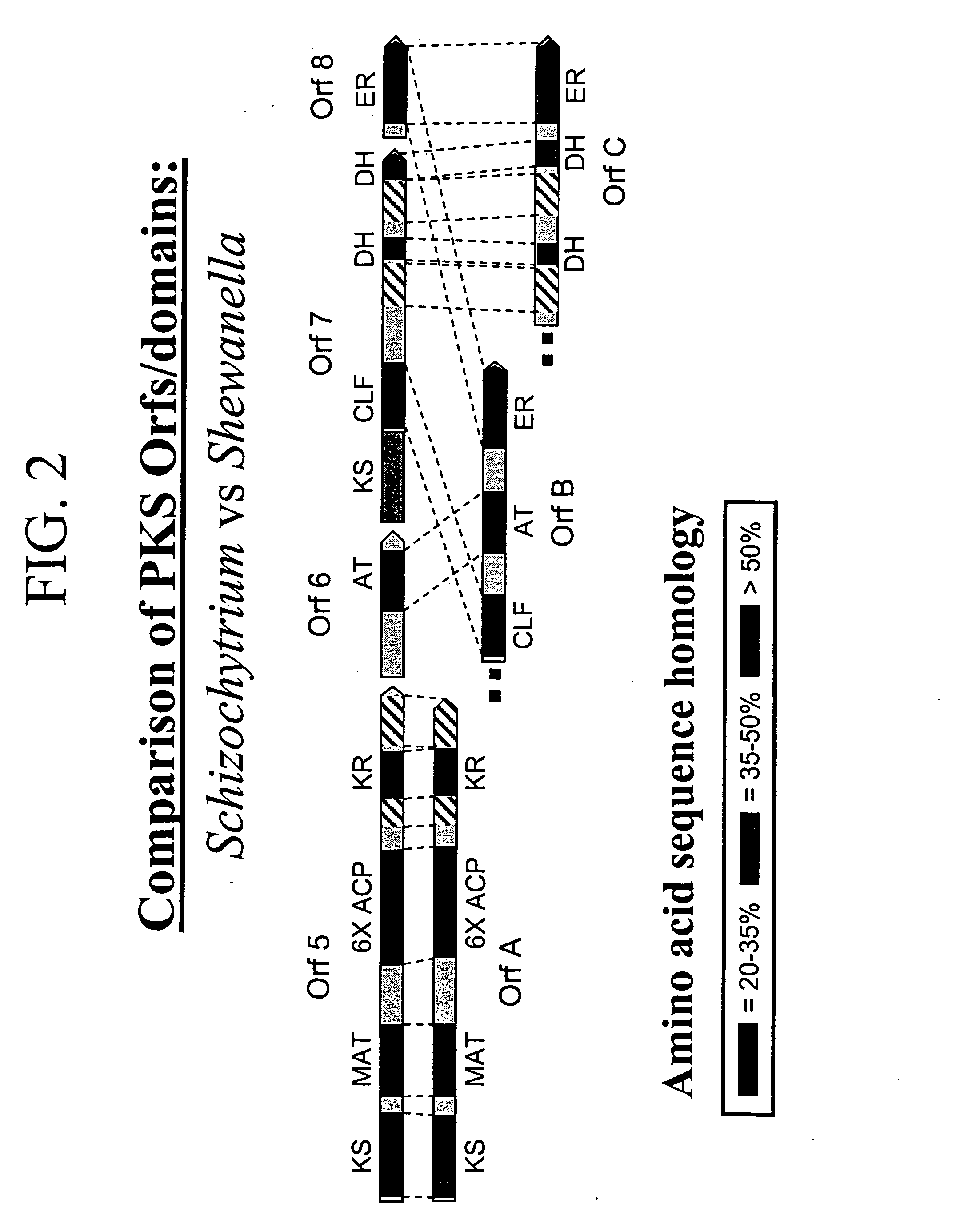
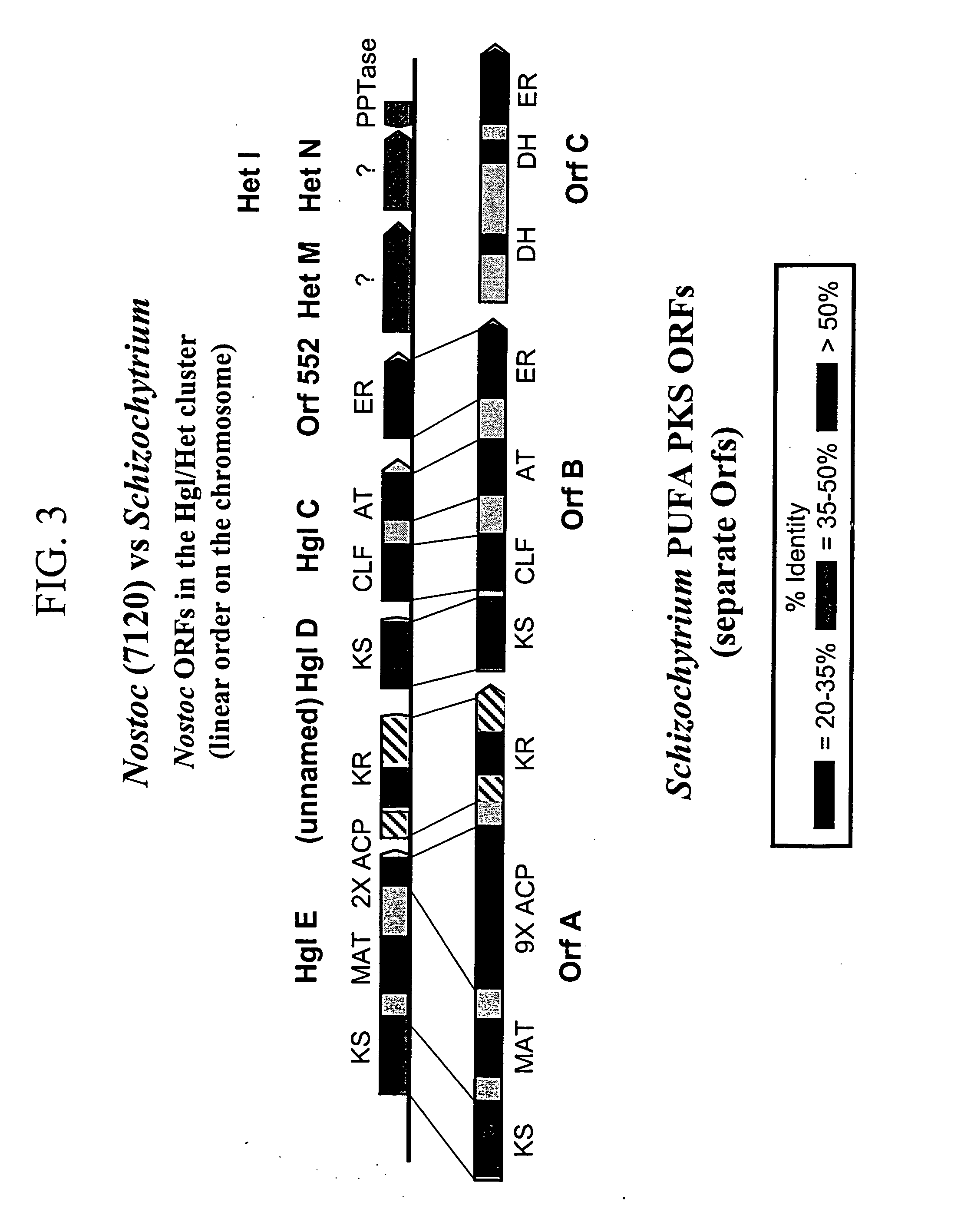
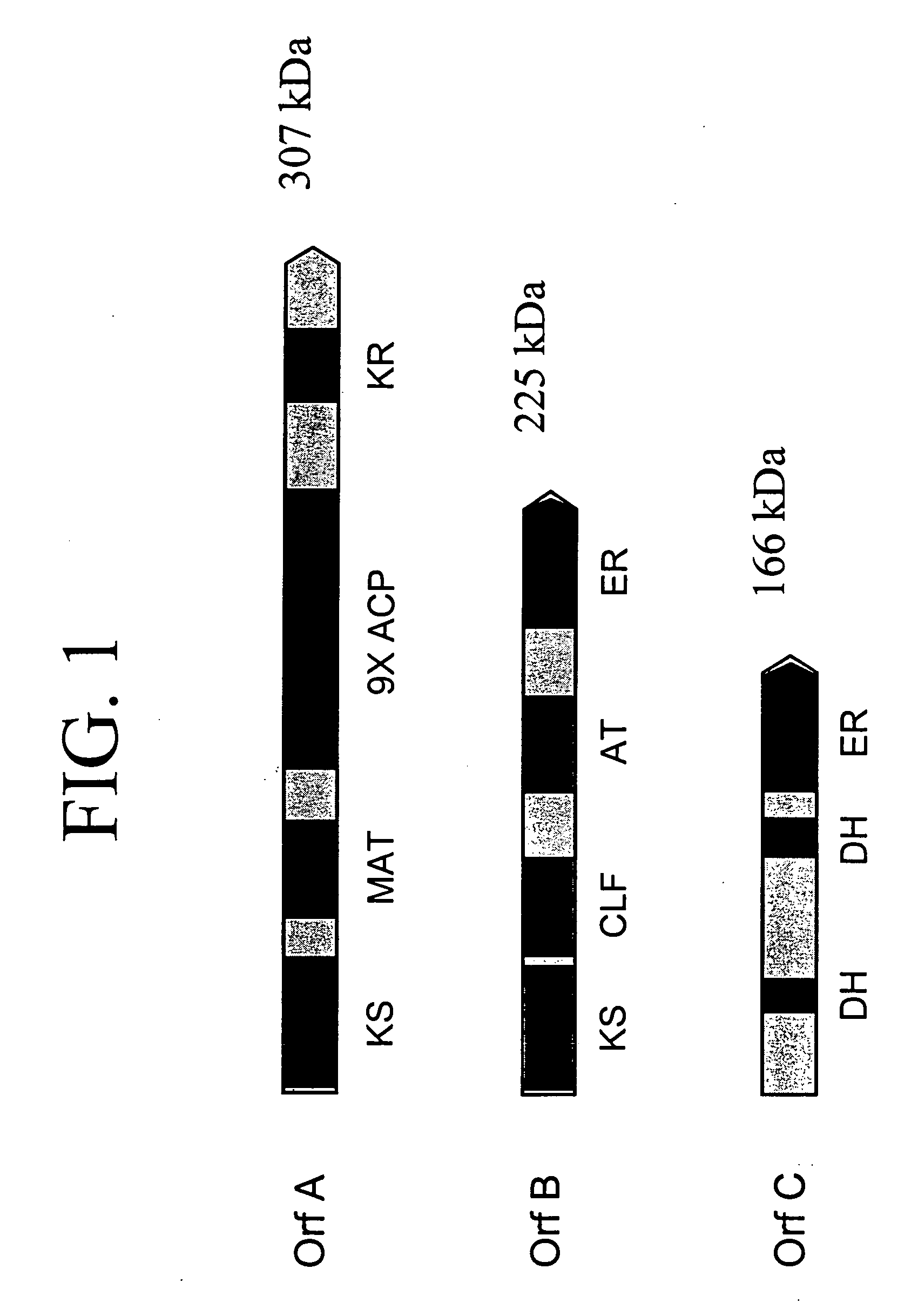
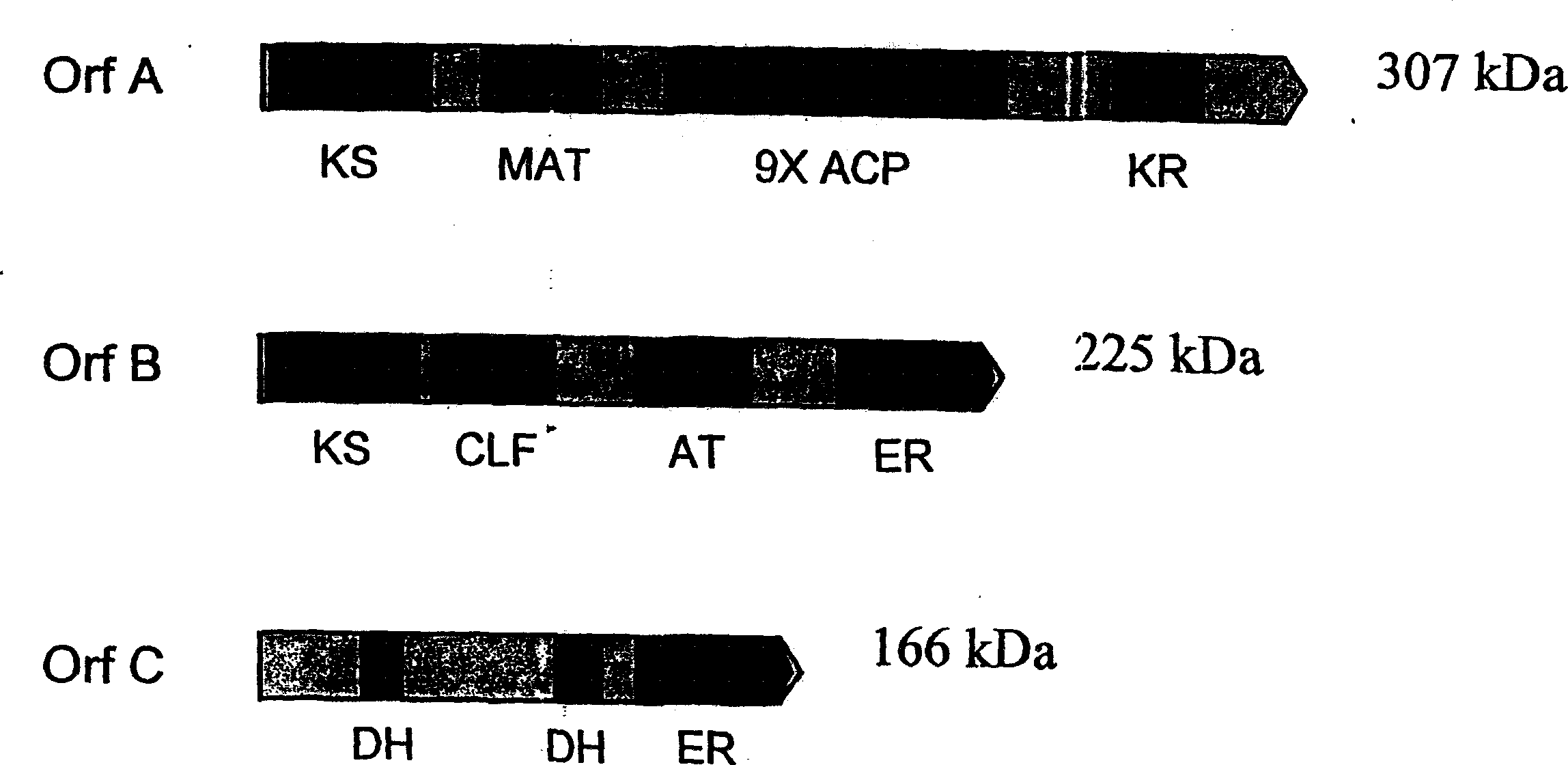
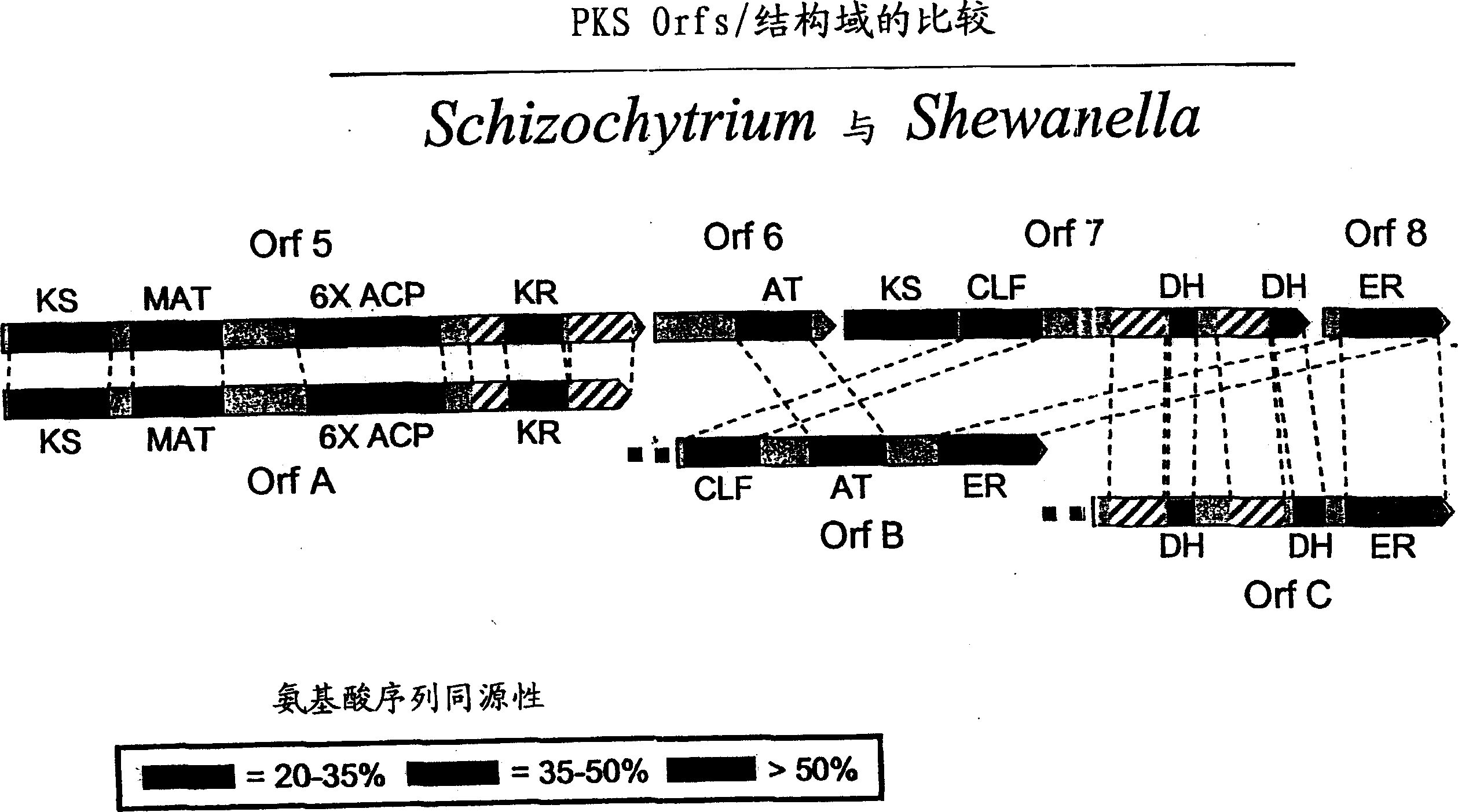
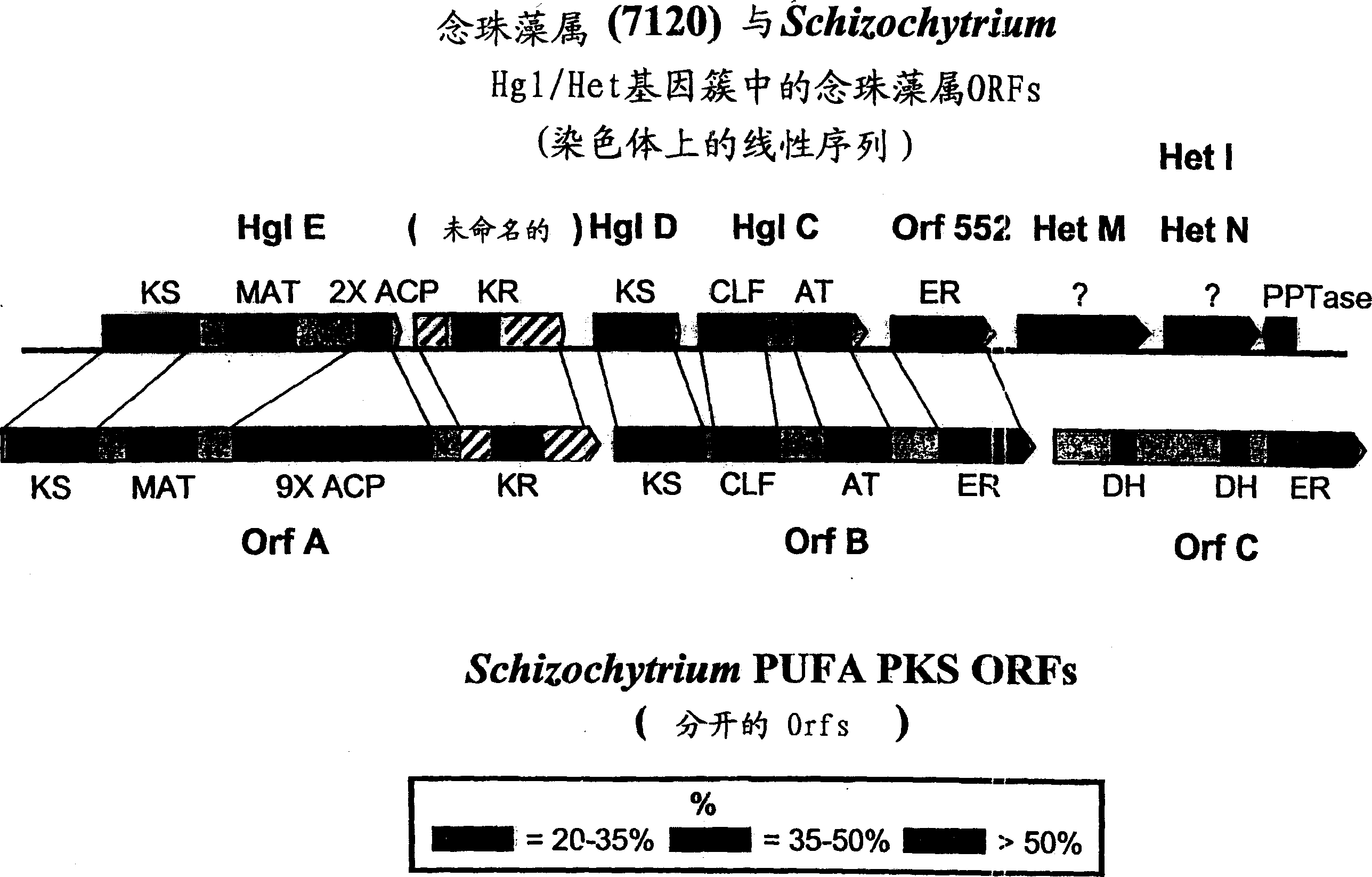
PUFA polyketide synthase systems and uses thereof
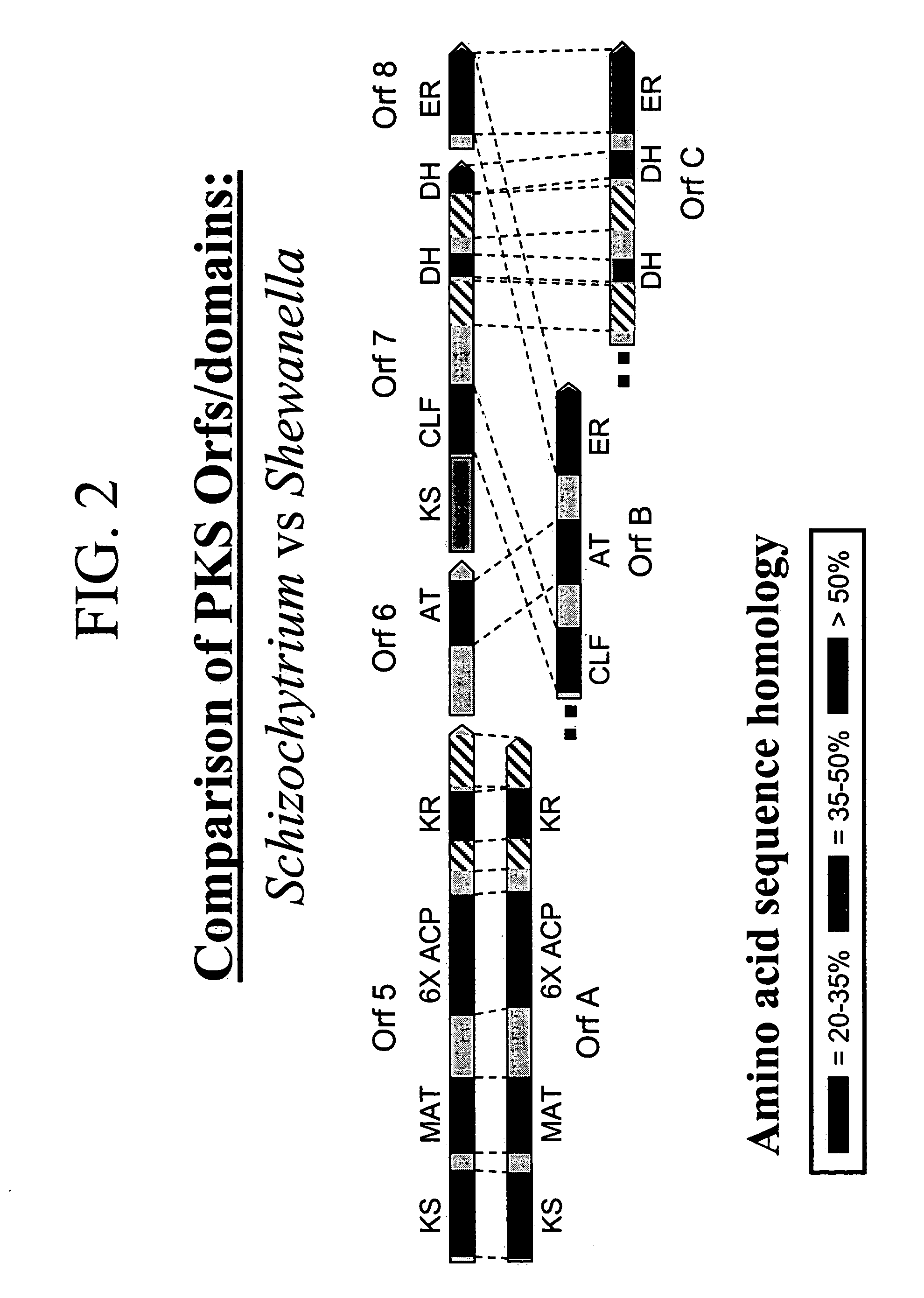
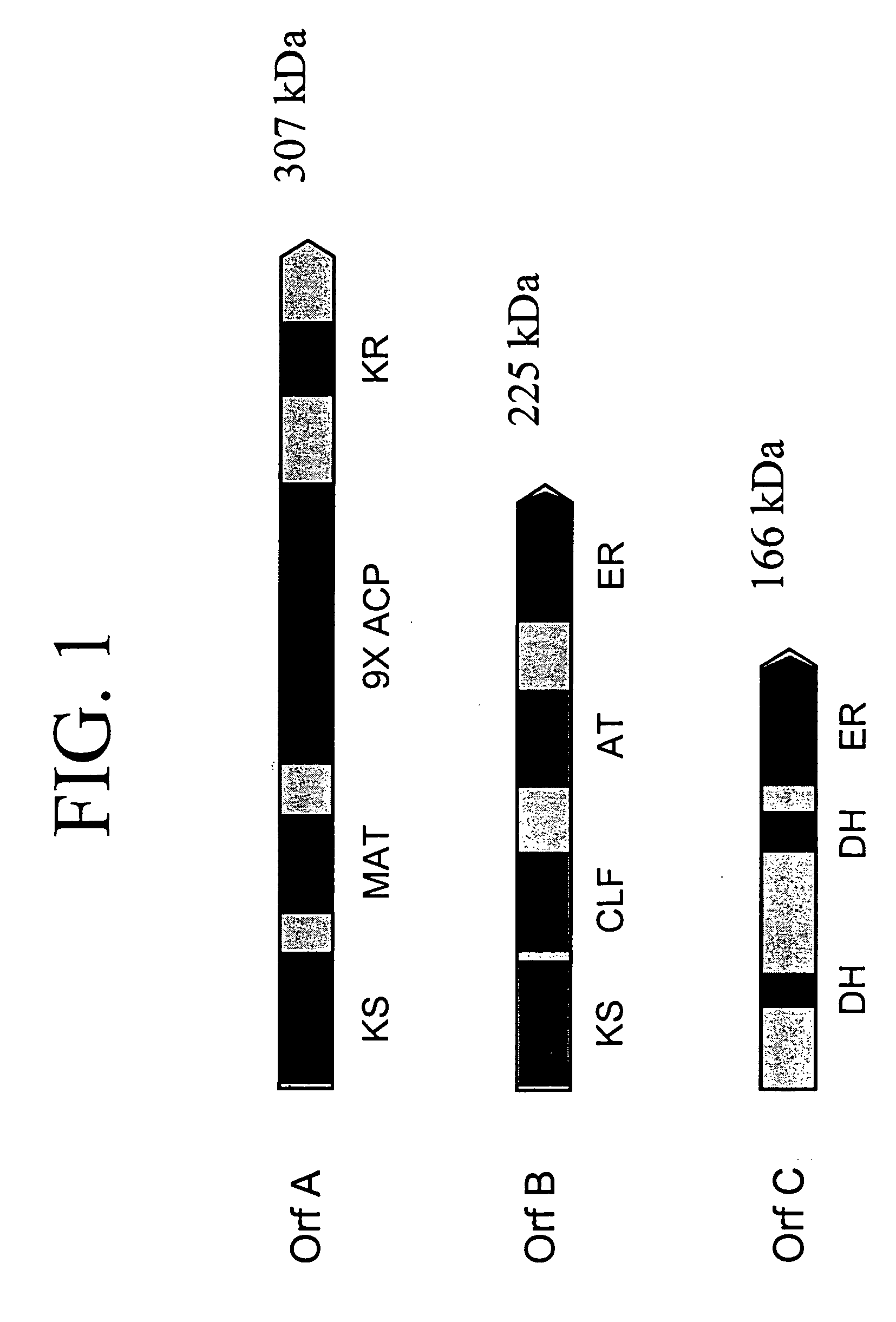
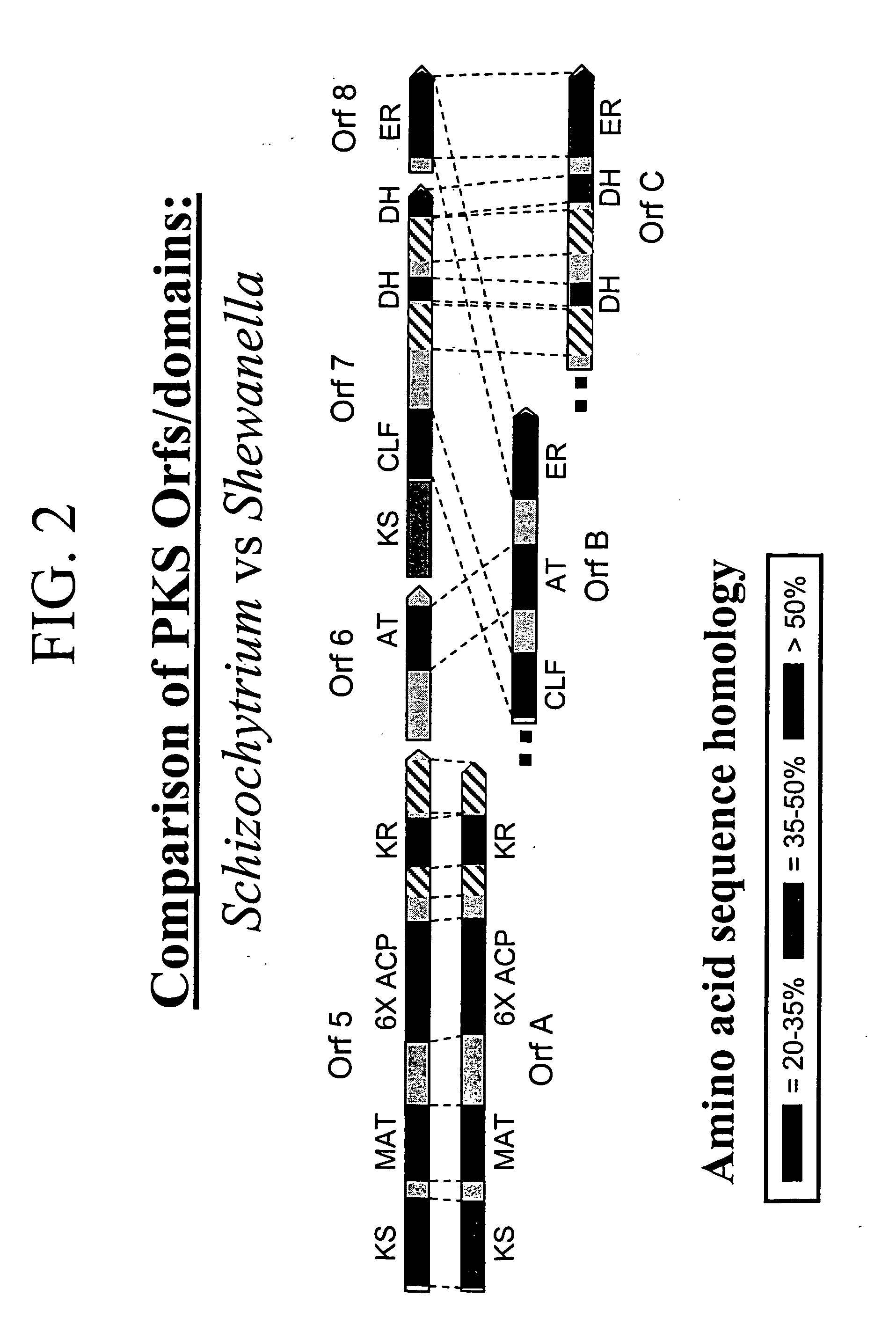
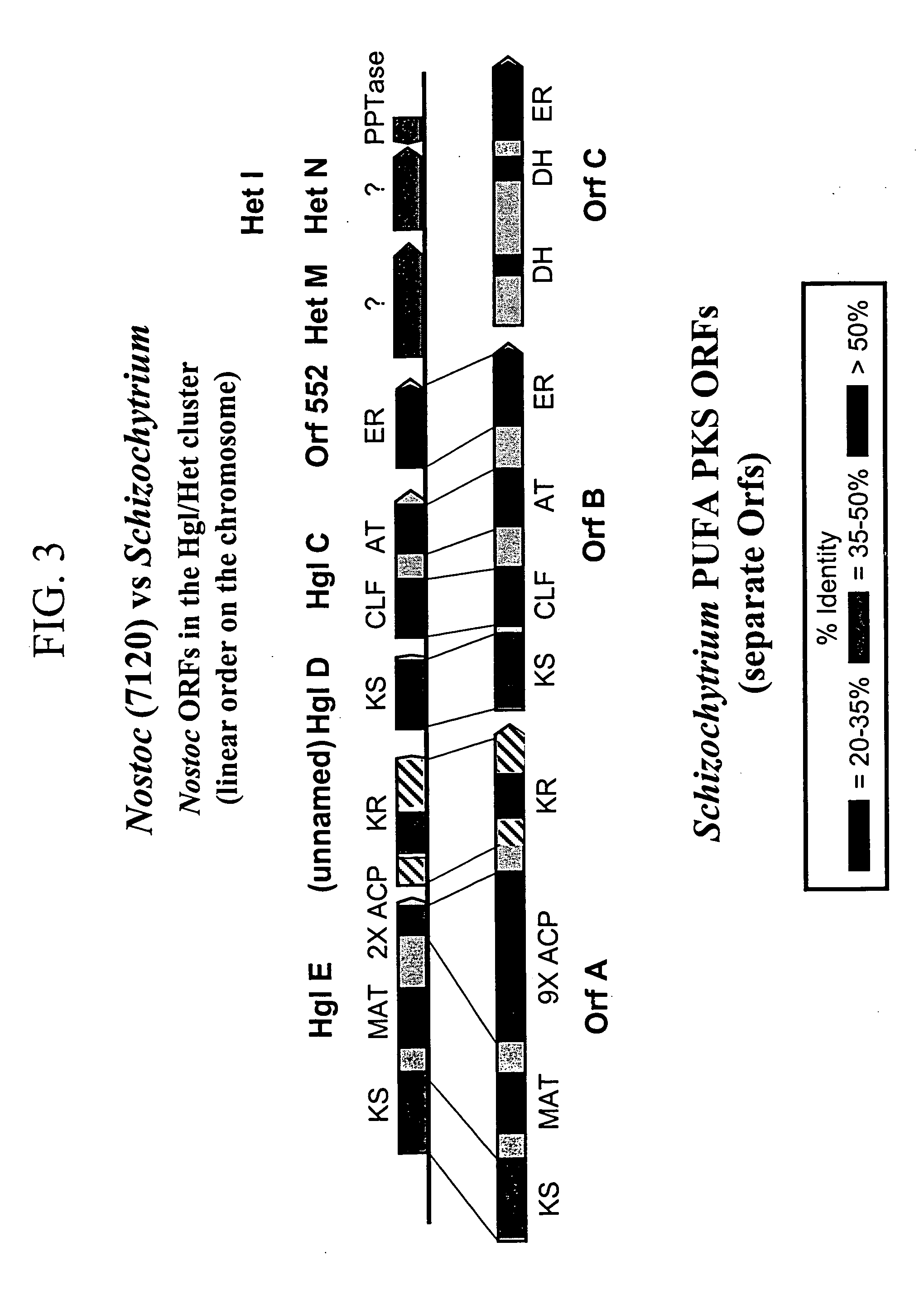
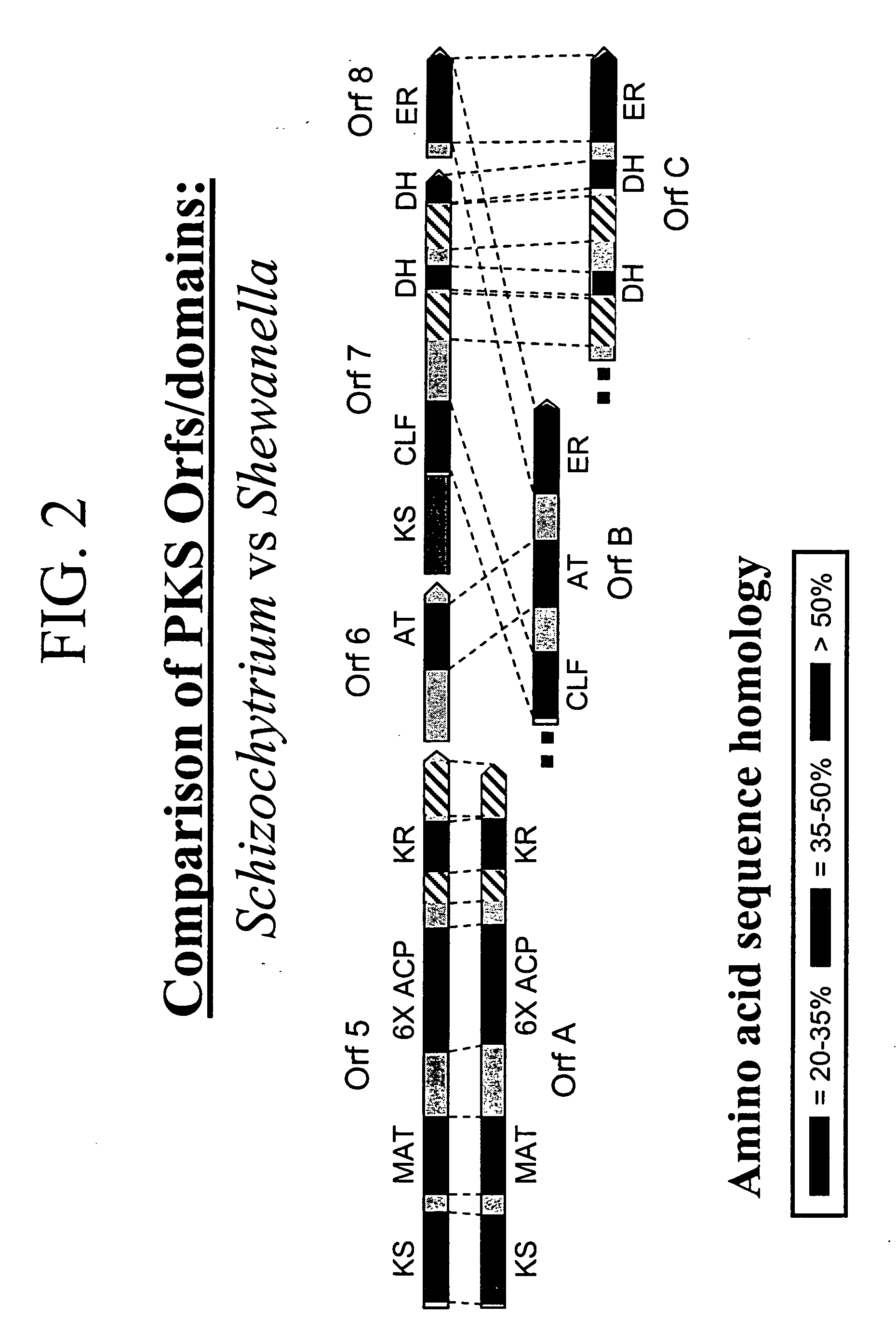
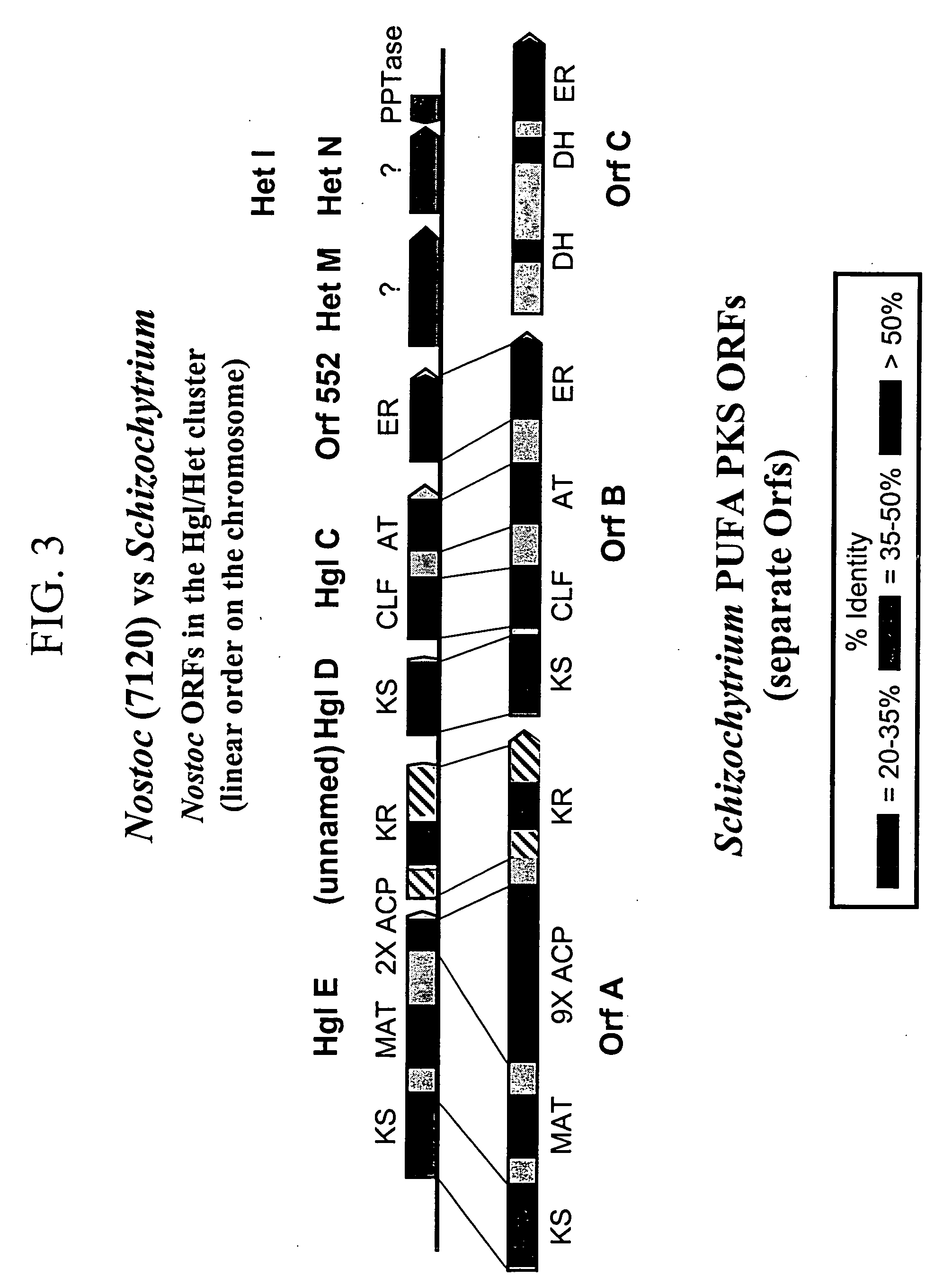
The invention generally relates to polyunsaturated fatty acid (PUFA) polyketide synthase (PKS) systems, to homologues thereof, to isolated nucleic acid molecules and recombinant nucleic acid molecules encoding biologically active domains of such a PUFA PKS system, to genetically modified organisms comprising PUFA PKS systems, to methods of making and using such systems for the production of bioactive molecules of interest, and to novel methods for identifying new bacterial and non-bacterial microorganisms having such a PUFA PKS system.
Owner:DSM IP ASSETS BV
PUFA polyketide synthase systems and uses thereof
Owner:DSM IP ASSETS BV
Pufa polyketide synthase systems and uses thereof
The invention generally relates to polyunsaturated fatty acid (PUFA) polyketide synthase (PKS) systems isolated from or derived from non-bacterial organisms, to homologues thereof, to isolated nucleic acid molecules and recombinant nucleic acid molecules encoding biologically active domains of such a PUFA PKS system, to genetically modified organisms comprising PUFA PKS systems, to methods of making and using such systems for the production of bioactive molecules of interest, and to novel methods for identifying new bacterial and non-bacterial microorganisms having such a PUFA PKS system.
Owner:DSM IP ASSETS BV
PUFA polyketide synthase systems and uses thereof
The invention generally relates to polyunsaturated fatty acid (PUFA) polyketide synthase (PKS) systems isolated from or derived from non-bacterial organisms, to homologues thereof, to isolated nucleic acid molecules and recombinant nucleic acid molecules encoding biologically active domains of such a PUFA PKS system, to genetically modified organisms comprising PUFA PKS systems, to methods of making and using such systems for the production of bioactive molecules of interest, and to novel methods for identifying new bacterial and non-bacterial microorganisms having such a PUFA PKS system.
Owner:DSM IP ASSETS BV
Synthetic peptide, inhibitor to DNA viruses
The present invention relates to the identification of the active domain of Herpoxin, a DNA virus-inhibiting-protein which was isolated from cobra venom in U.S. Pat. No. 5,648,339 and has a molecular weight of 13.5 kDa We have isolated a fragment of Herpoxin which contains the active domain and which we have named Herp. Herp mimics the activity of Herpoxin in inhibiting the replication of DNA viruses. A synthetic version of the active fragment was produced having the amino acid sequence Asn-Leu-Tyr-Gln-Phe-Lys-Asn-Met-Ile-Gln. The synthetic version of Herp consisting of ten amino acids inhibits the replication of DNA viruses such as herpes viruses types 1 and 2, cytomegalovirus and varicella zoster virus as well as Tubercle bacilli.
Owner:LIPPS BINIE V +1
Method and apparatus for detecting data collection omission in traffic collection device
ActiveCN107579874AImprove regulatory capacityReduce performance requirementsData switching networksDomain nameComputer network
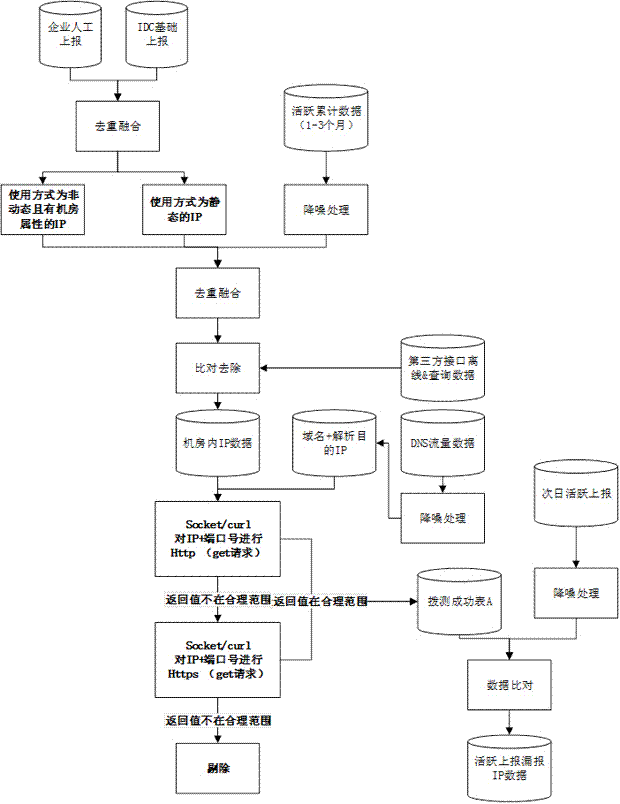
The invention discloses a method for detecting data collection omission in a traffic collection device and relates to an information security technology in the technical field of information. The method comprises the following steps: step 1 is discovery of omission of active IP data, and step 2 is discovery of omission of active domain name data. According to the invention, a DNS data source is used to supplement original data, and data which has the attribute of a computer room is extracted, and then a simulation request is performed, such that the performance demand for the simulation request is reduced, a more comprehensive simulation request is also provided, and discovered omission is more comprehensive and accurate. When the simulation request is performed, an http (get / post) requestis firstly performed, and then afterwards, data whose simulation request result return values are not within a reasonable scope is subjected to an https (get / post) request. Such a mode, compared to amode of performing http&https simulation requests on all data, can reduce the performance demand for the simulation request, and compared to a mode of only performing the http simulation request, canalso enhance comprehensiveness of the simulation request. According to the invention, the network supervision level can be effectively improved, and data missed by an information security managementsystem is discovered for analysis of omission reasons of the information security management system.
Owner:BEIJING ACT TECH DEV CO LTD
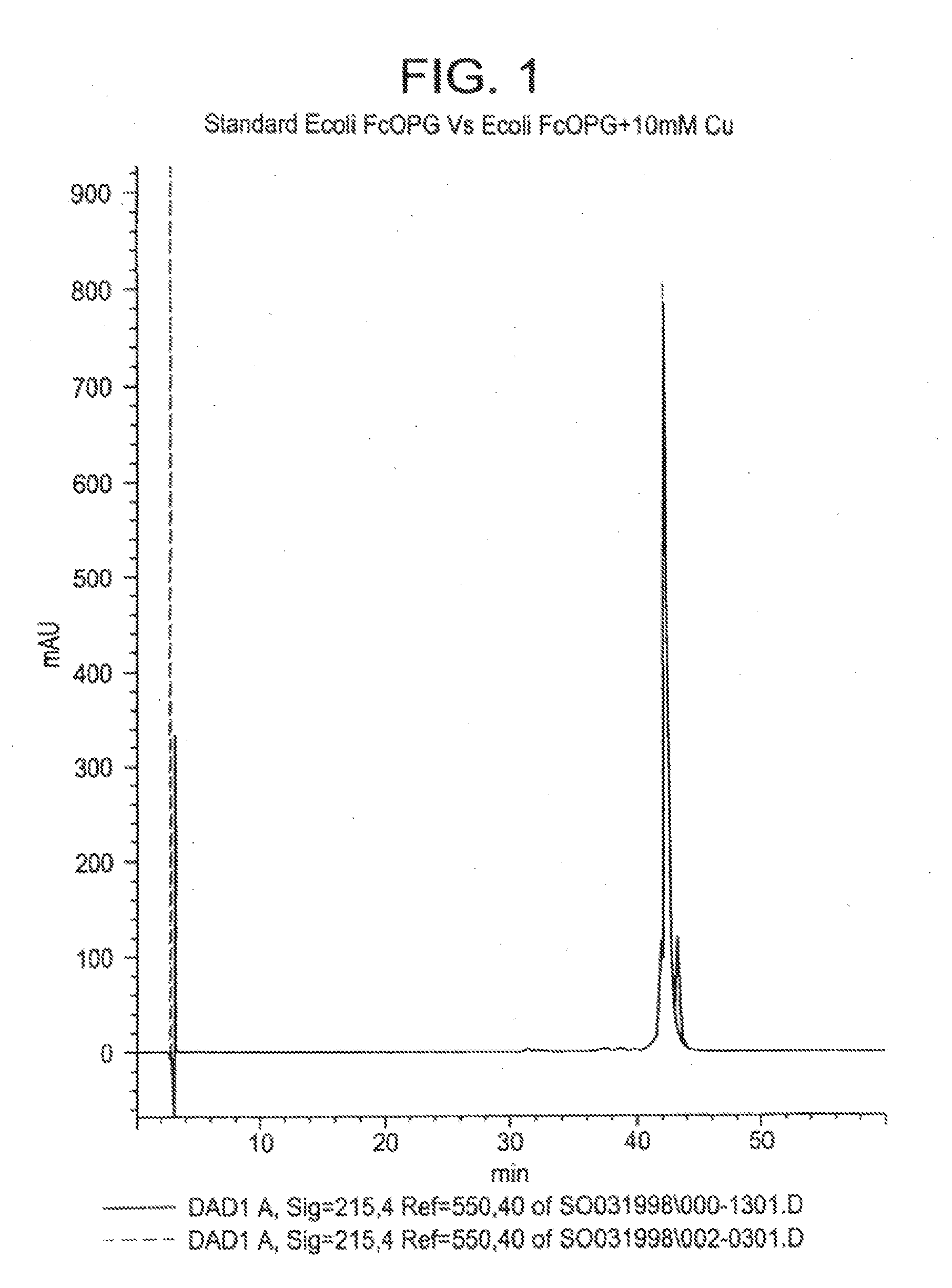
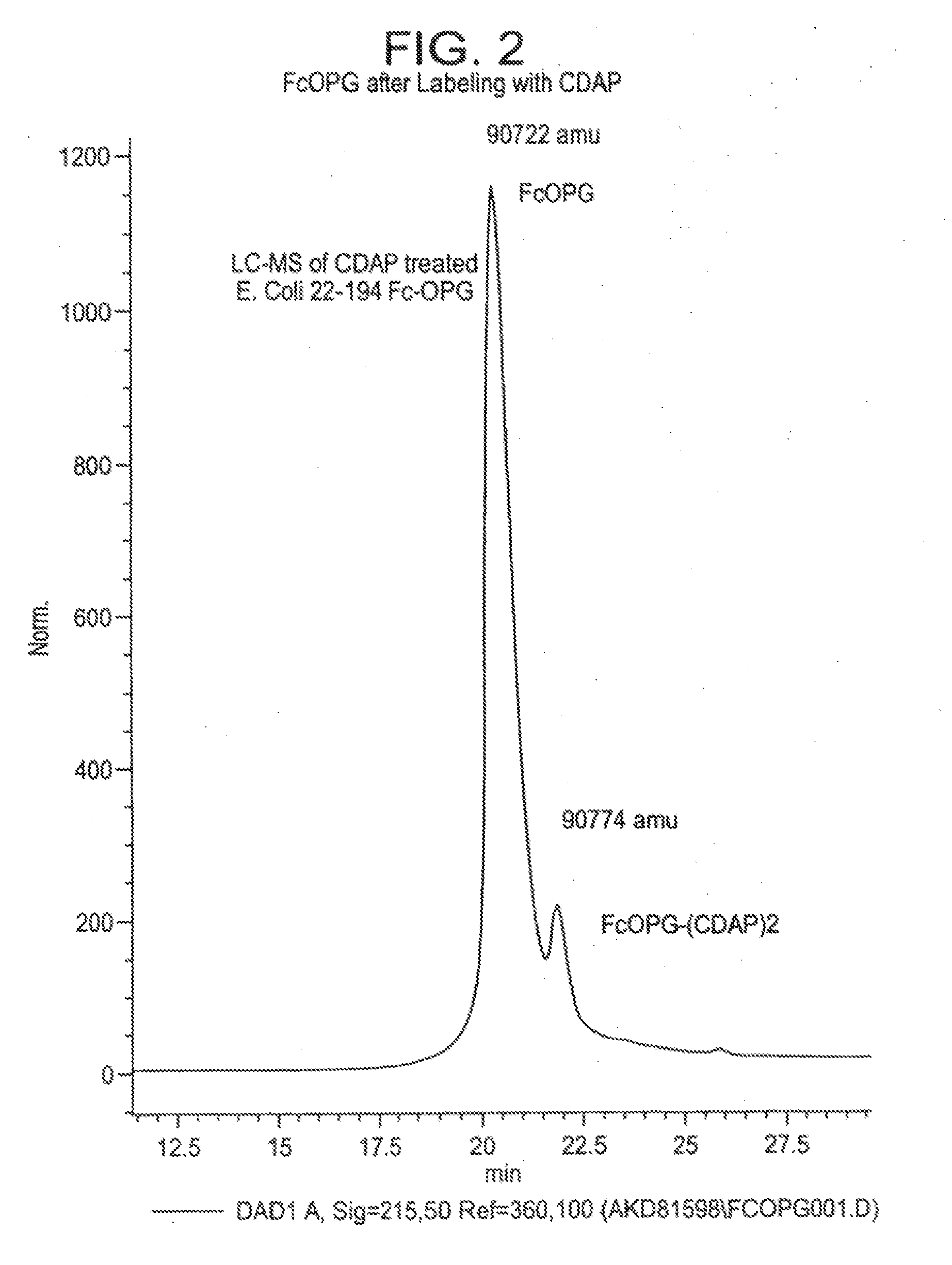
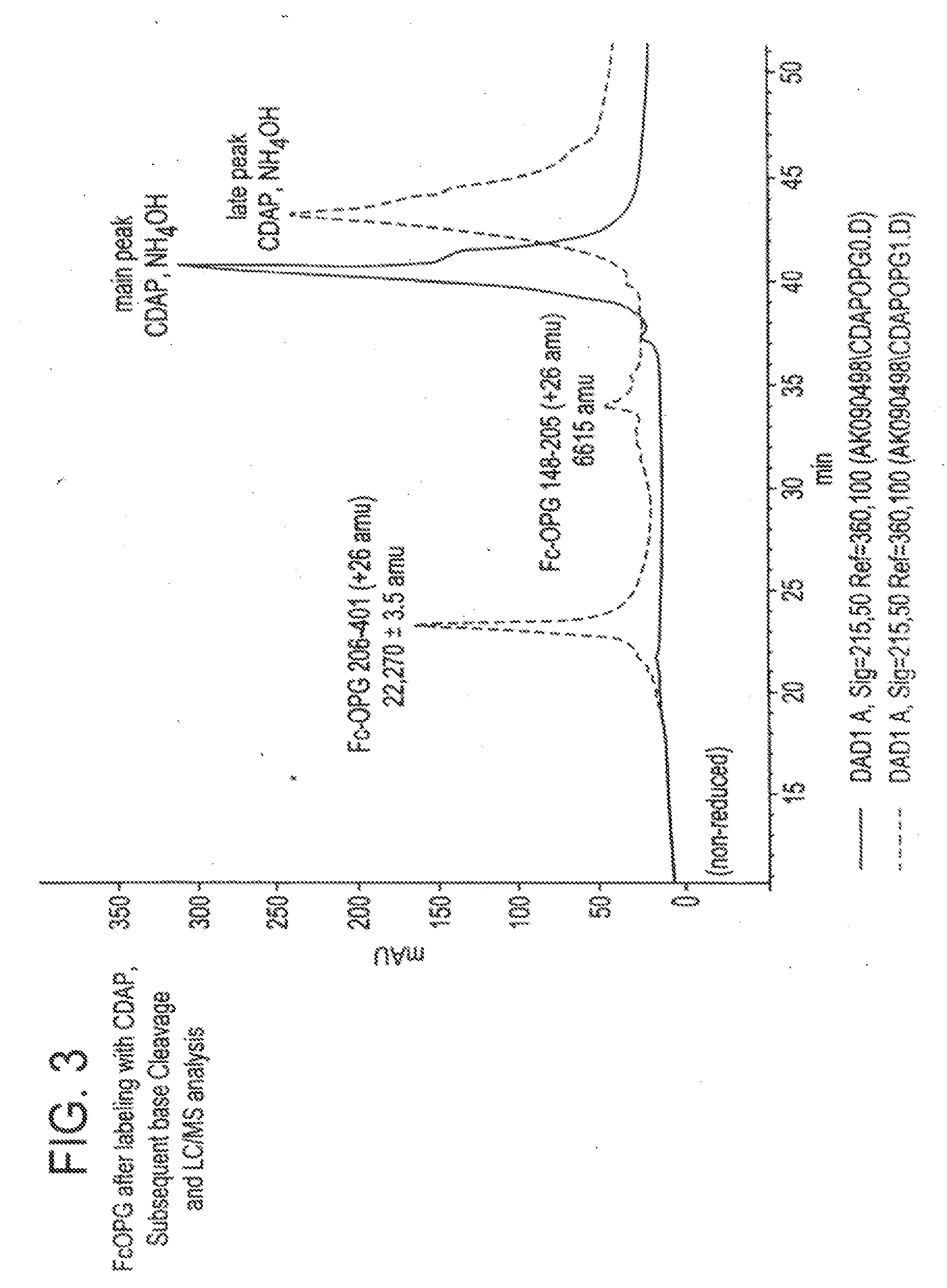
Process for correction of a disulfide misfold in Fc molecules
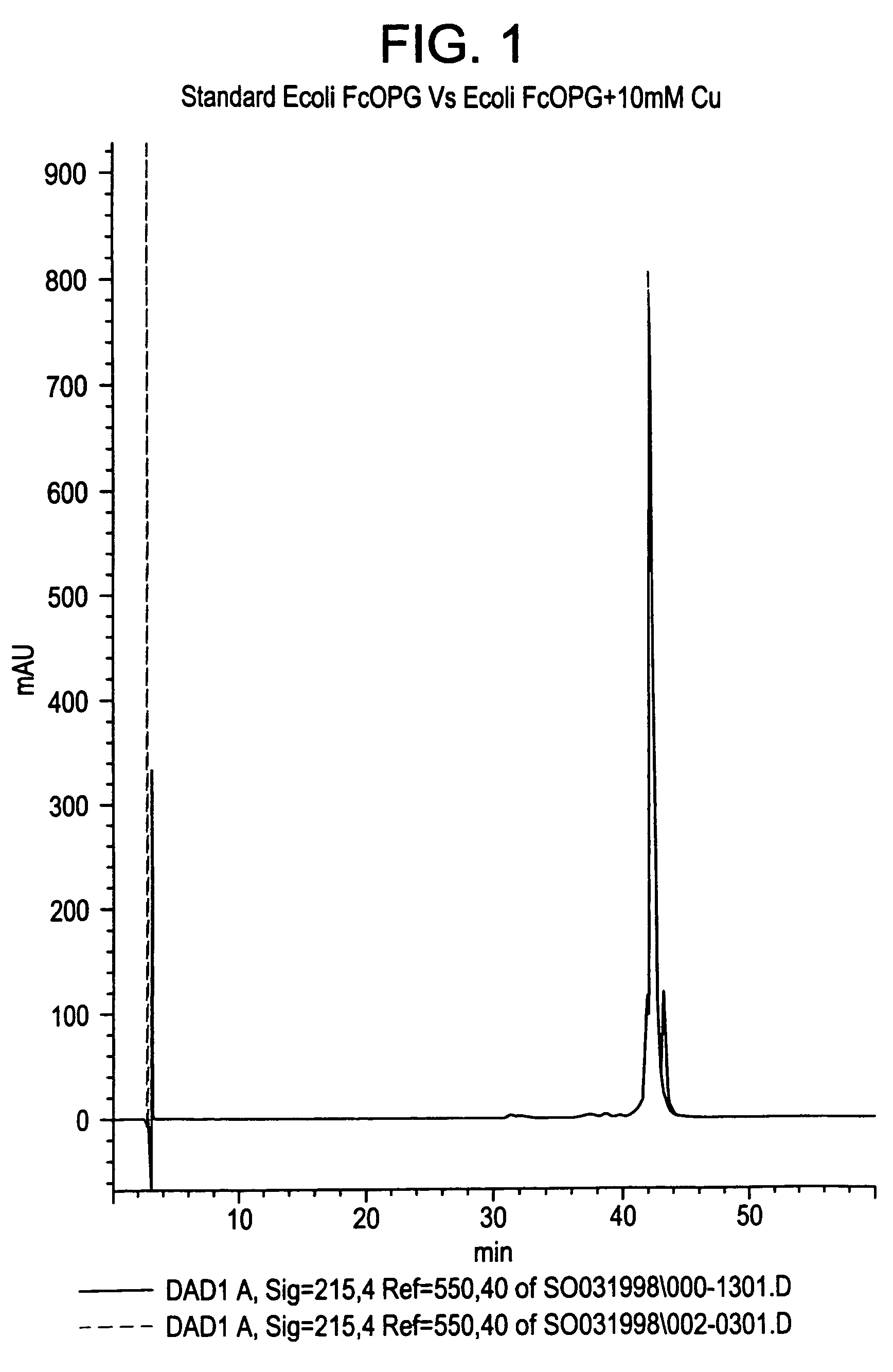
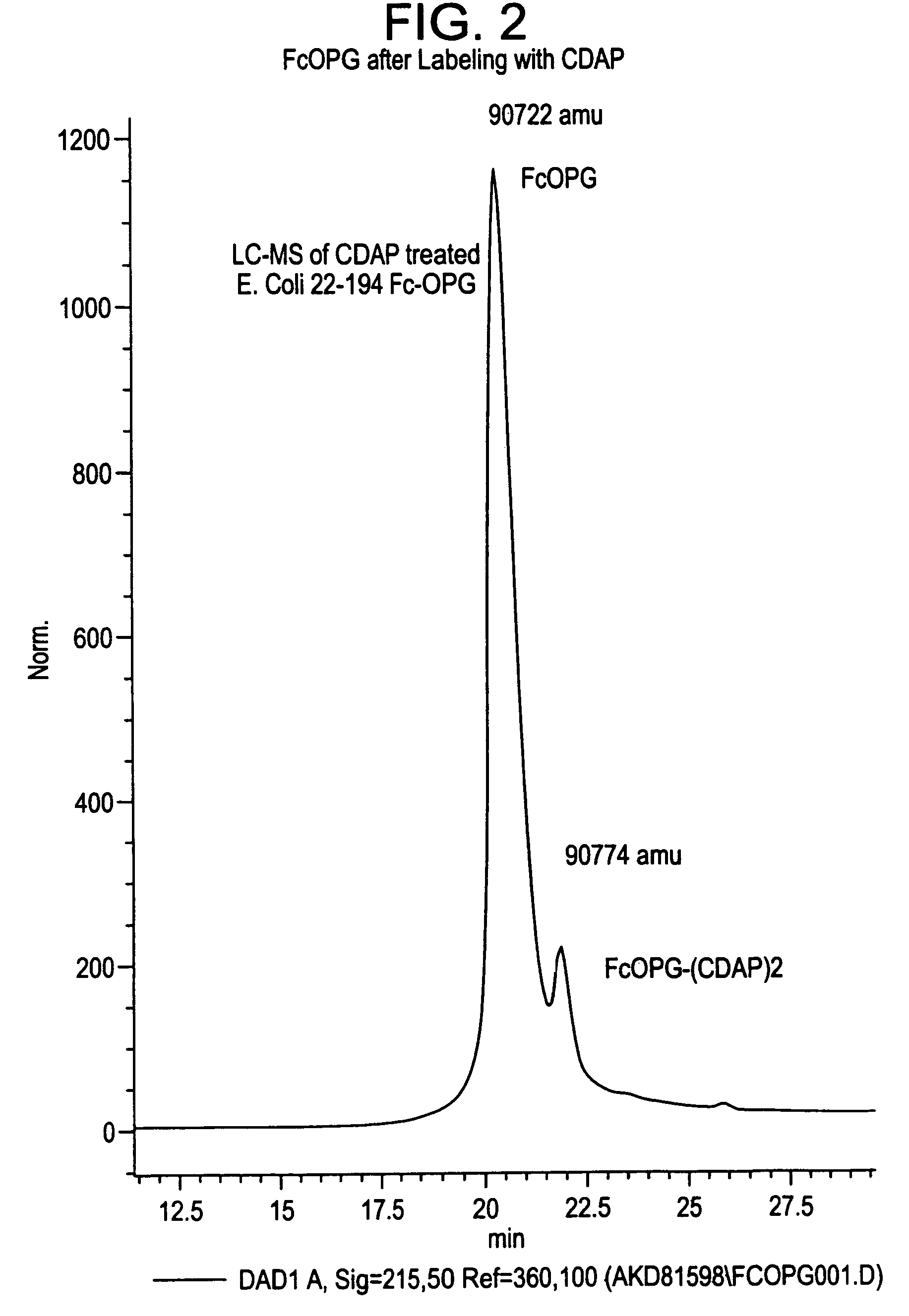
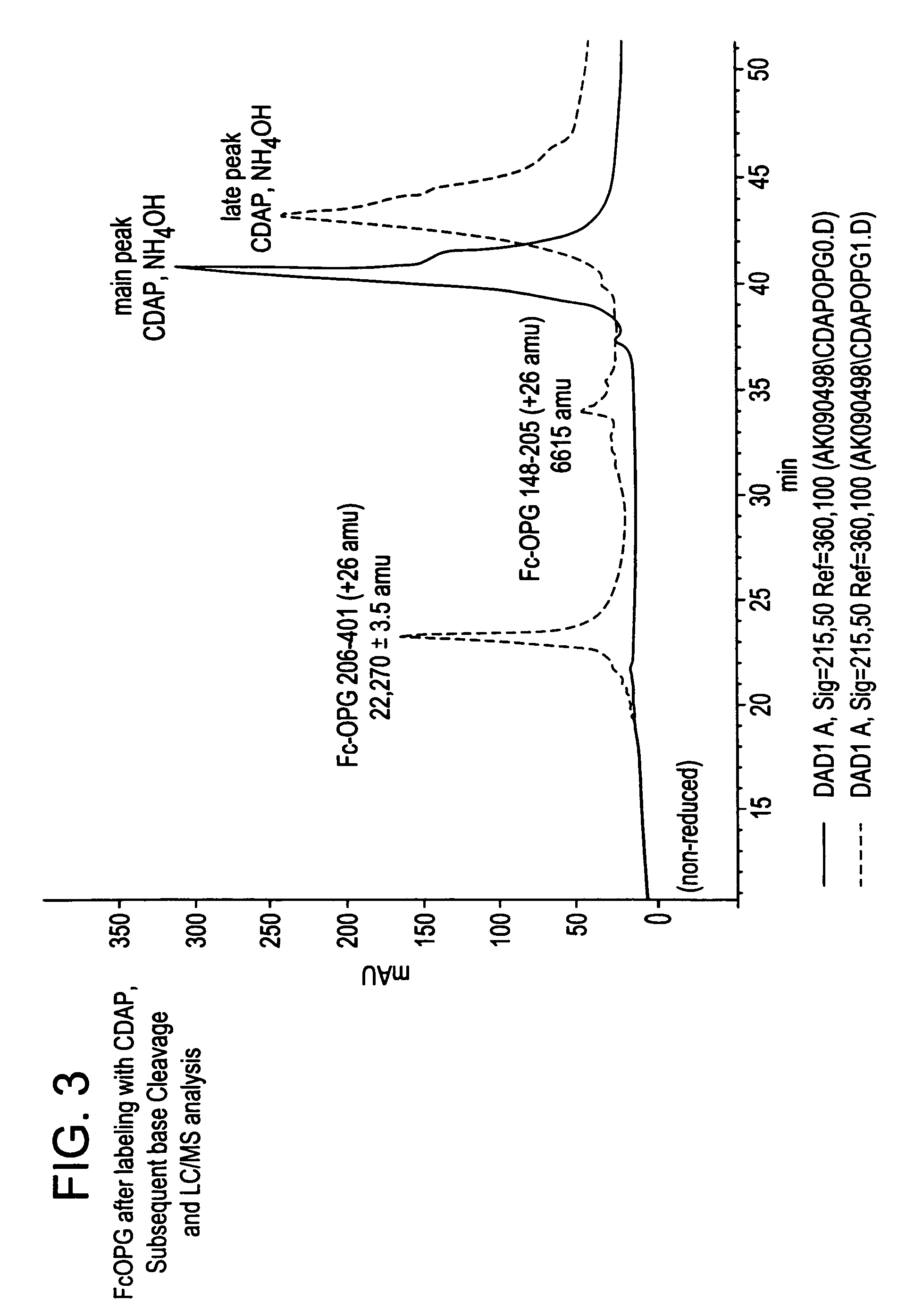
The present invention concerns a process by which a misfold in an Fc fusion molecule can be prevented or corrected. In one embodiment, the process comprises (a) preparing a pharmacologically active compound comprising an Fc domain; (b) treating the fusion molecule with a copper (II) halide; and (c) isolating the treated fusion molecule. The pharmacologically active compound can be an antibody or a fusion molecule comprising a pharmacologically active domain and an Fc domain. The preferred copper (II) halide is CuCl2. The preferred concentration thereof is at least about 10 mM for fusion molecules prepared in E. coli; at least about 30 mM for fusion molecules prepared in CHO cells. The process can be employed with any number of pharmacologically active domains. Preferred pharmacologically active domains include OPG proteins, leptin proteins, soluble portions of TNF receptors (e.g., wherein the fusion molecule is etanercept), IL-1ra proteins, and TPO-mimetic peptides. The Fc domain preferably has a human sequence, with an Fc sequence derived from IgG1 most preferred. An exemplary Fc sequence is shown in FIG. 5 hereinafter.
Owner:AMGEN INC
Method of treating cancer by inhibition of protein kinase-like endoplasmic reticulum protein kinase
The present invention relates to a method of identifying compounds useful in inhibiting protein kinase-like endoplasmic reticulum protein kinase (PERK). The method comprises providing a first model comprising PERK active domains, where the said active domains are selected from the group consisting of the peptide spanning from amino acid residue Asp144 to amino acid residue Ser191 of SEQ ID NO: 1 and a peptide comprising the amino acid residue at position 7 of SEQ ID NO: 1, providing one or more candidate compounds, evaluating contact between the candidate compounds and the first model to determine which of the one or more candidate compounds have an ability to bind to and / or fit in the first model, and identifying the compounds which, based on said evaluating, have the ability to bind to and / or fit in the first model as compounds potentially useful for inhibiting PERK. The present invention further relates to compounds that can be used for inhibition of PERK, for example human PERK, and methods related to treatment of PERK-mediated diseases.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
Biologically active peptides as glutamate receptor inhibitors
The present invention relates to biologically active peptides derived from the neurite outgrowth-promoting domain of luminin-1, i.e. the γ1-chain of laminin-1. These peptides include the decapeptide RDIAEIIKDI (SEQ ID NO: 1) and the truncated peptides derived therefrom comprising the biologically active domain thereof, the tripeptide KDI. The invention is directed to the biologically active tripeptide motifKDI, and to its use in promoting regeneration of neuronal or non-neuronal tissues and, in specific, to its use in the treatment of spinal cord injuries.
Owner:LIESI PAIVI
Chimeric Polypeptides and Their Use in Bacterial Decolonization
ActiveUS20130004476A1Overcome increasing numberRapid onsetAntibacterial agentsSugar derivativesBacterial diseaseStaphylococcus aureus
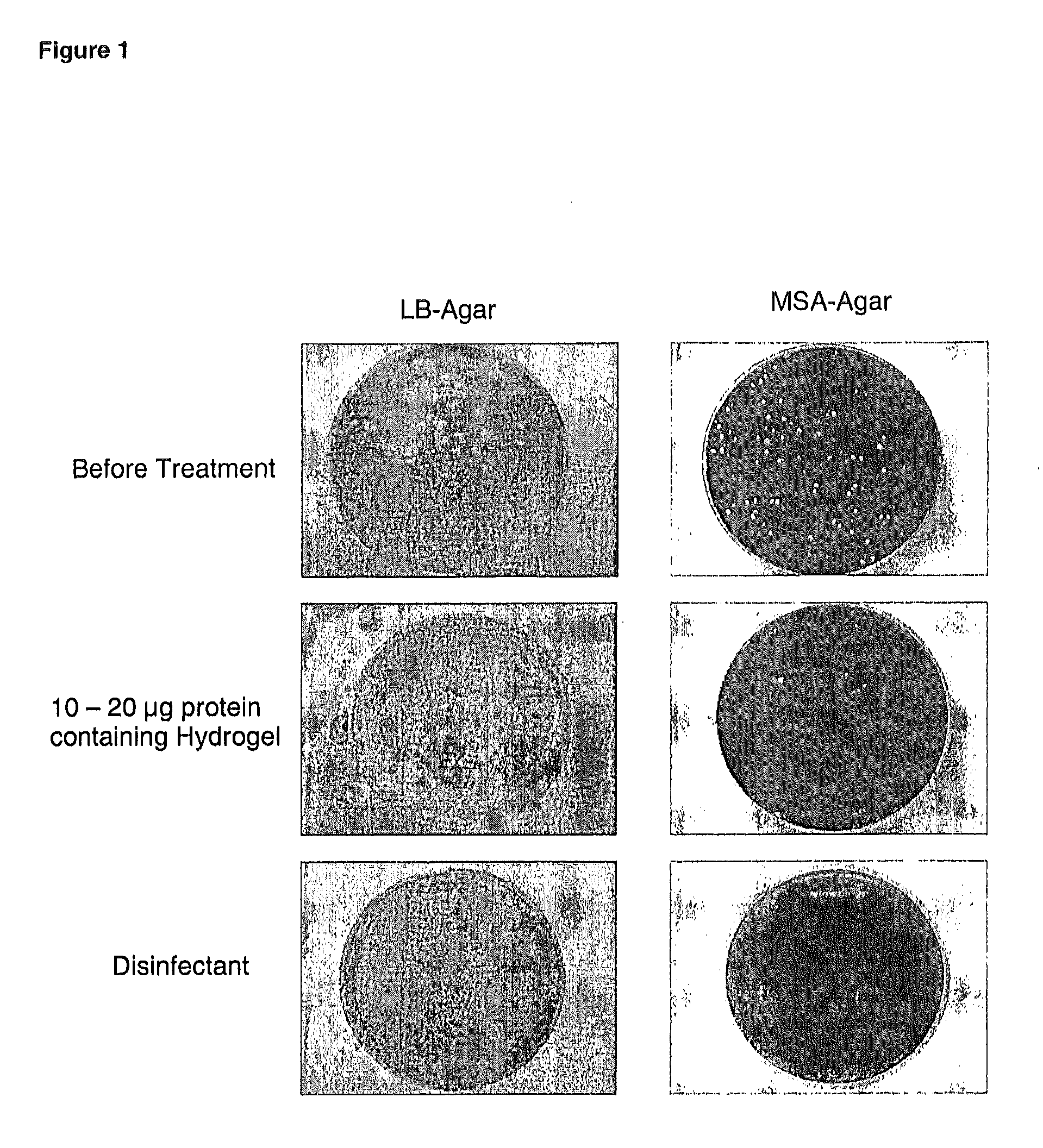
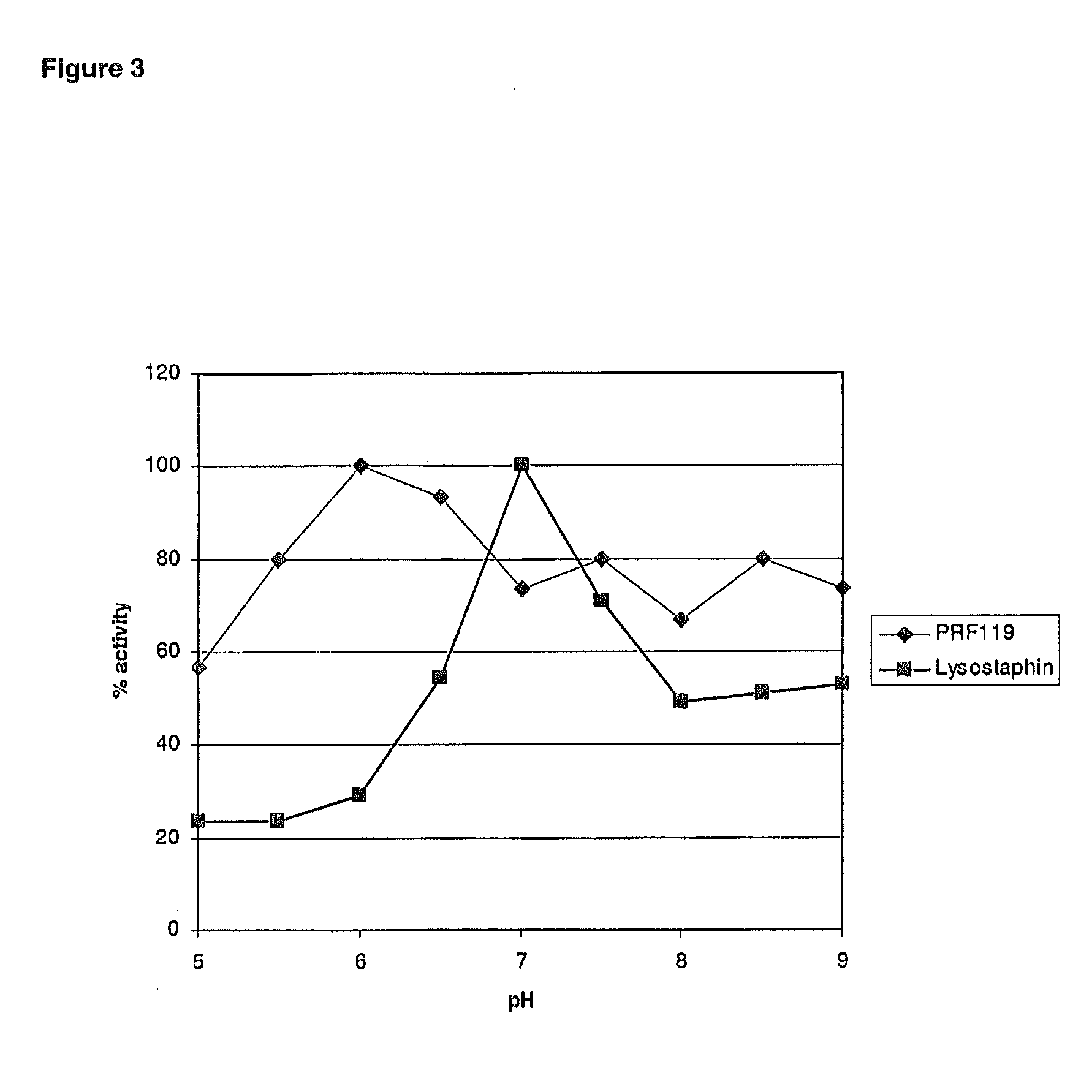
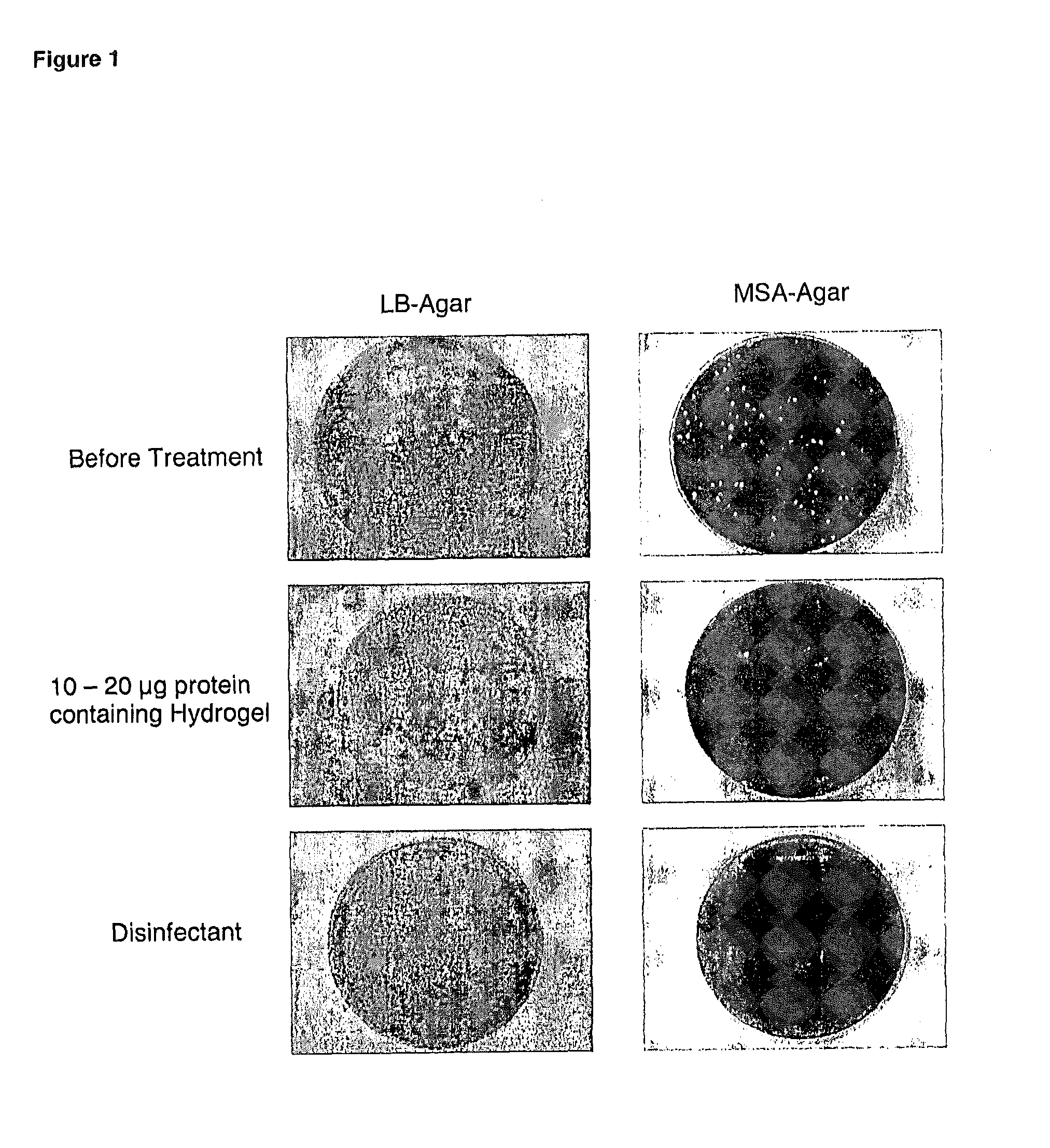
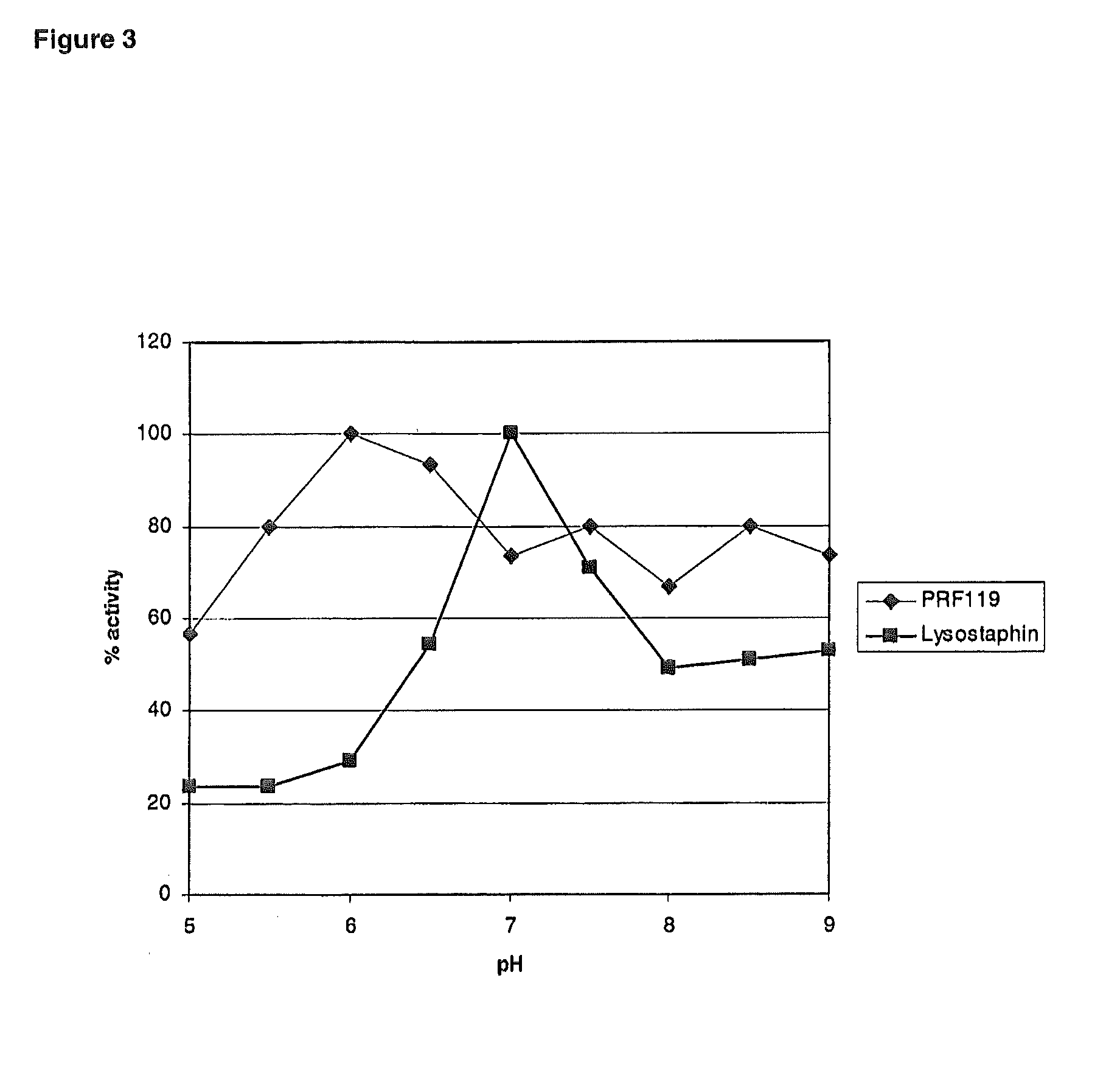
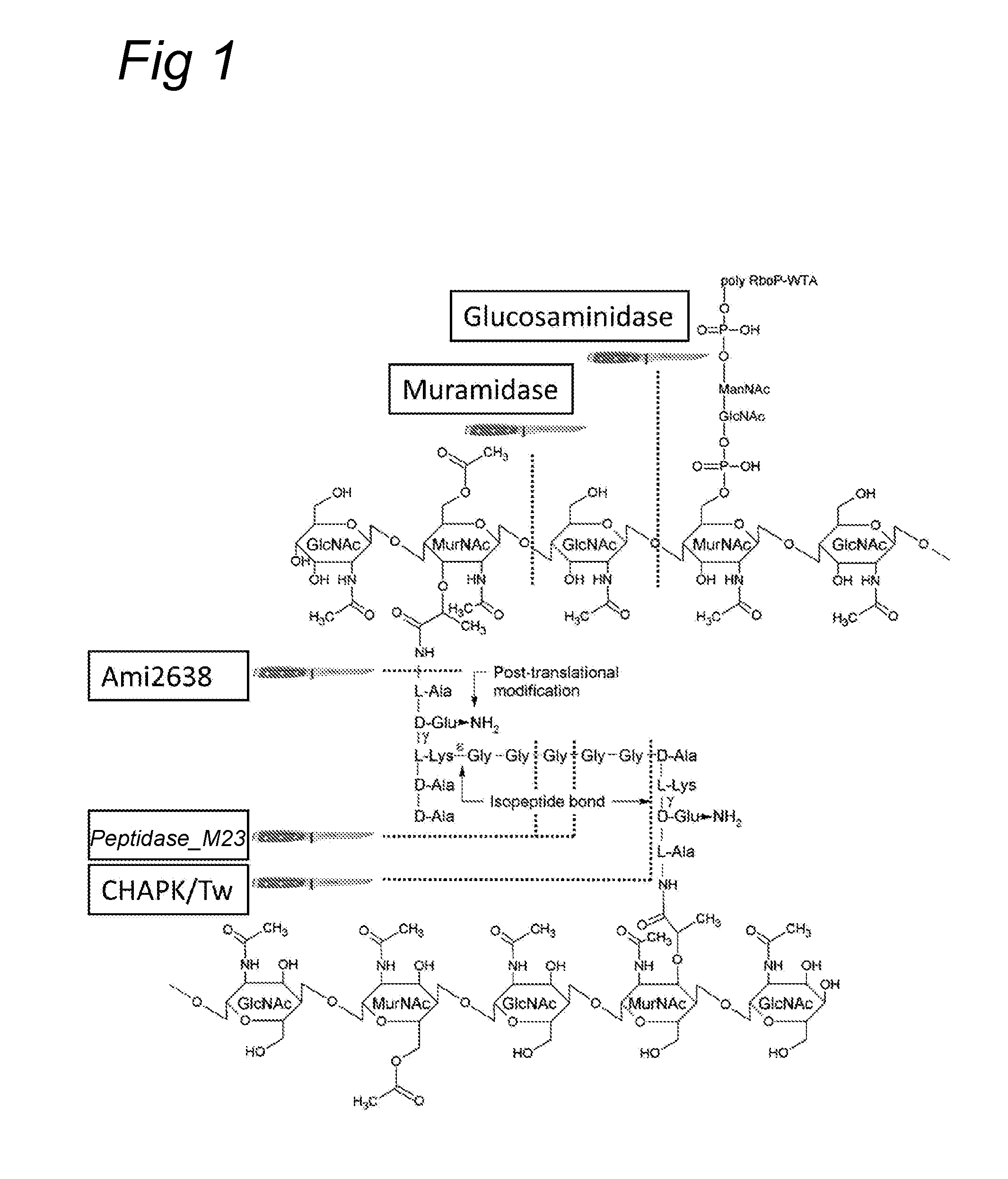
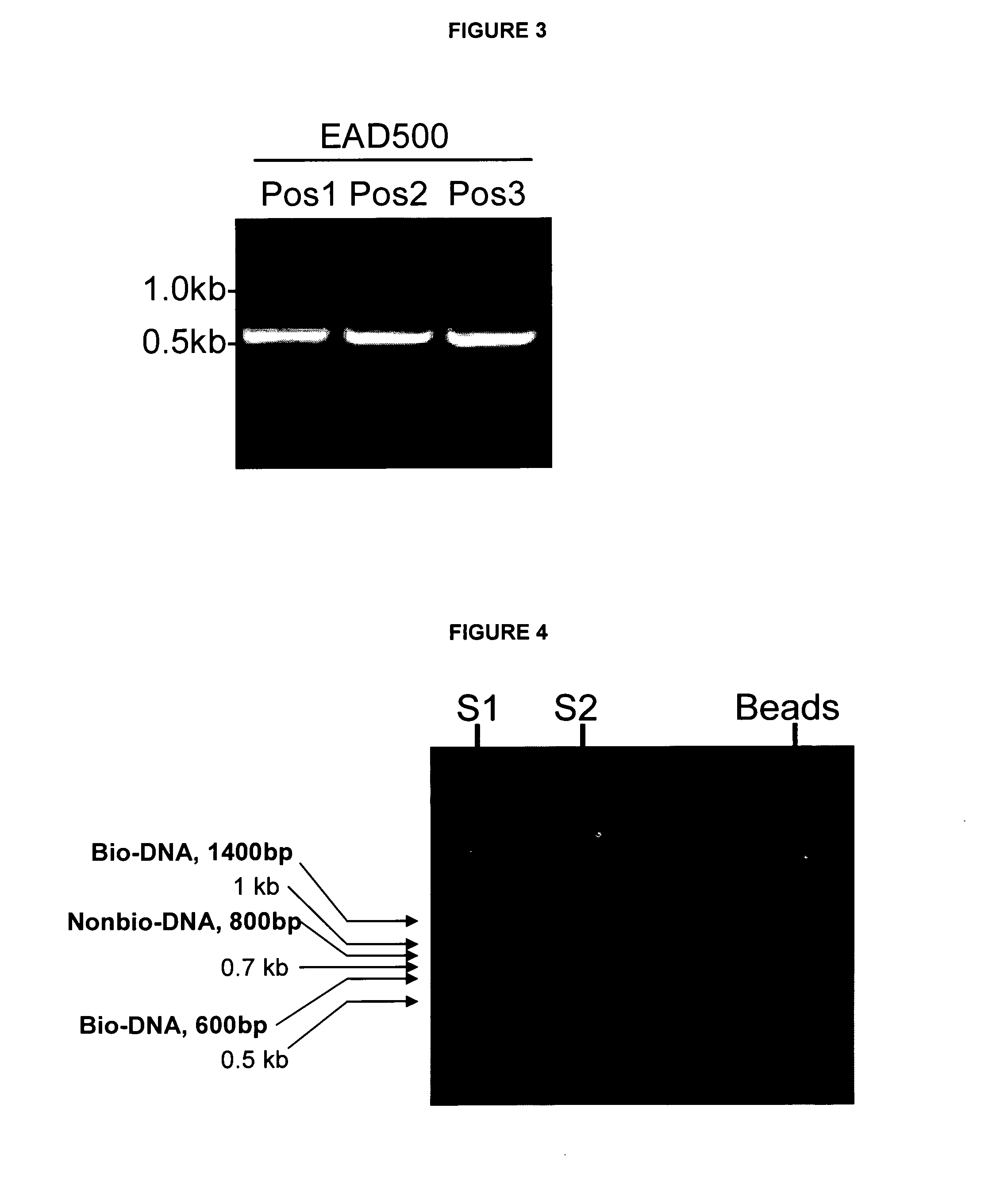
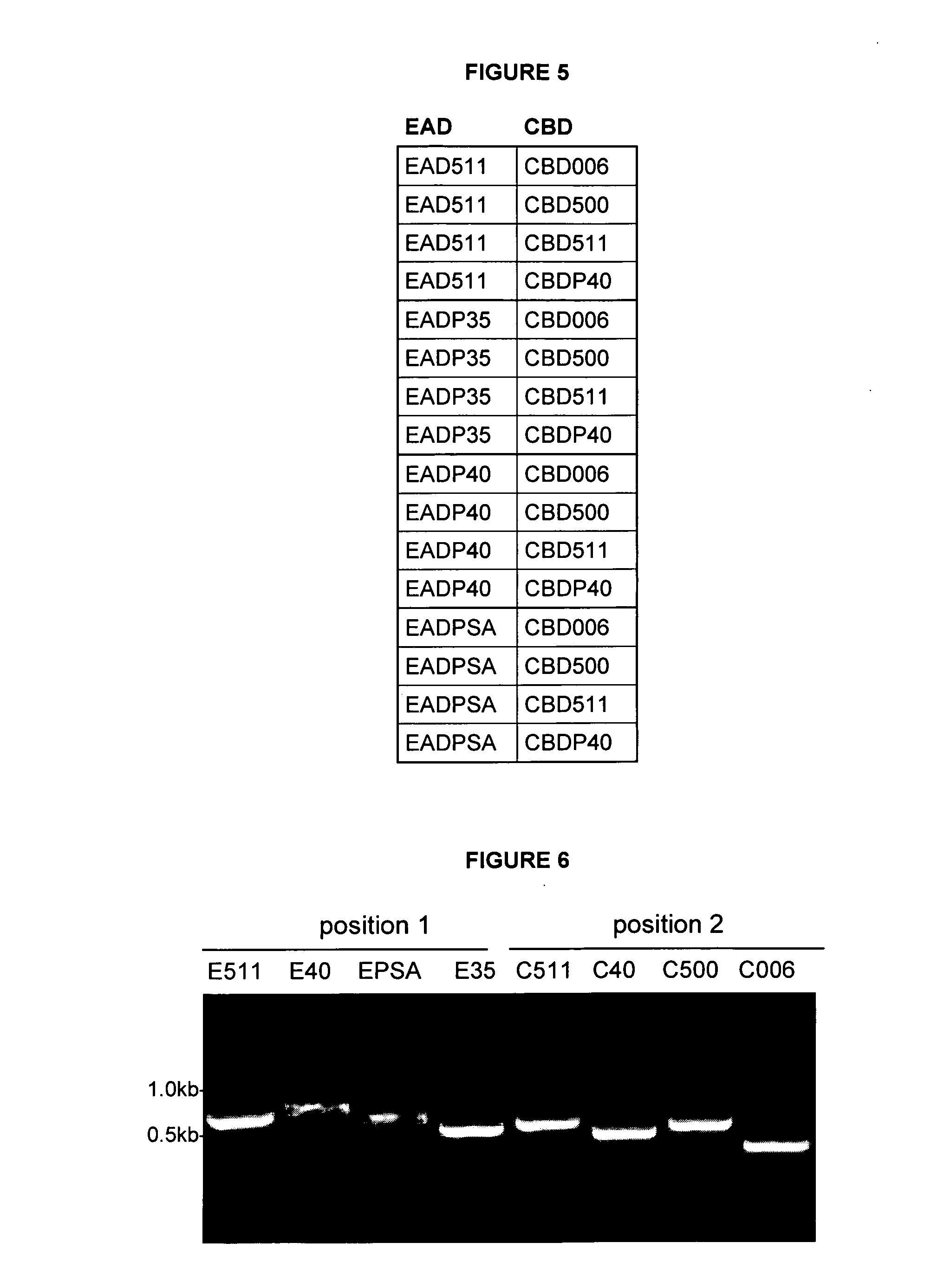
The present invention relates to chimeric polypeptides comprising a first portion, which comprises a bacteriocin cell wall-binding domain (CBD) and a second portion, which comprises an enzymatic active domain (EAD) selected from the lytic domain of a bacteriophage lysin, a bacteriocin and a bacterial autolysin. Provided are such chimeric polypeptides and variants and fragments thereof, nucleic acids encoding the same, vectors carrying such nucleic acids and host cells transformed or transfected with such vectors. The chimeric polypeptides of the present invention are useful for the reduction of certain bacterial populations, including methods and compositions for the treatment of various bacterial infections. For example, chimeric polypeptides of the present invention have been shown to effectively kill various bacteria, including methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA), as well as other human pathogens. Thus, provided are compositions comprising chimeric polypeptides according to the present invention, variants or fragments thereof, and the use of such compositions in prophylaxis or therapy of bacterial diseases, bacterial infections or bacterial colonisations.
Owner:HYPHARM GMBH
Family 9 endo-beta-1,4-glucanases
An enzyme exhibiting endo-β-1,4-glucanase activity which belongs to family 9 of glycosyl hydrolases is obtainable from or endogeneous to a strain belonging to the genus Bacillus such as Bacillus licheniformis, ATCC 14580; an isolated polynucleotide (DNA) molecule encoding an enzyme or enzyme core (the catalytically active domain of the enzyme) exhibiting endo-β-1,4-glucanase activity selected from (a) polynucleotide molecules comprising a nucleotide sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO:1 from nucleotide 76 to nucleotide 1455 or from nucleotide 76 to nucleotide 1941, (b) polynucleotide molecules that encode a polypeptide being at least 75% identical to the amino acid sequence of SEQ ID NO:2 from amino acid residue 26 to amino acid 485 or from amino acid residue 26 to amino acid residue 646, and (c) degenerate nucleotide sequences of (a) or (b), the expressed endoglucanase enzyme being useful in various industrial applications.
Owner:NOVOZYMES AS
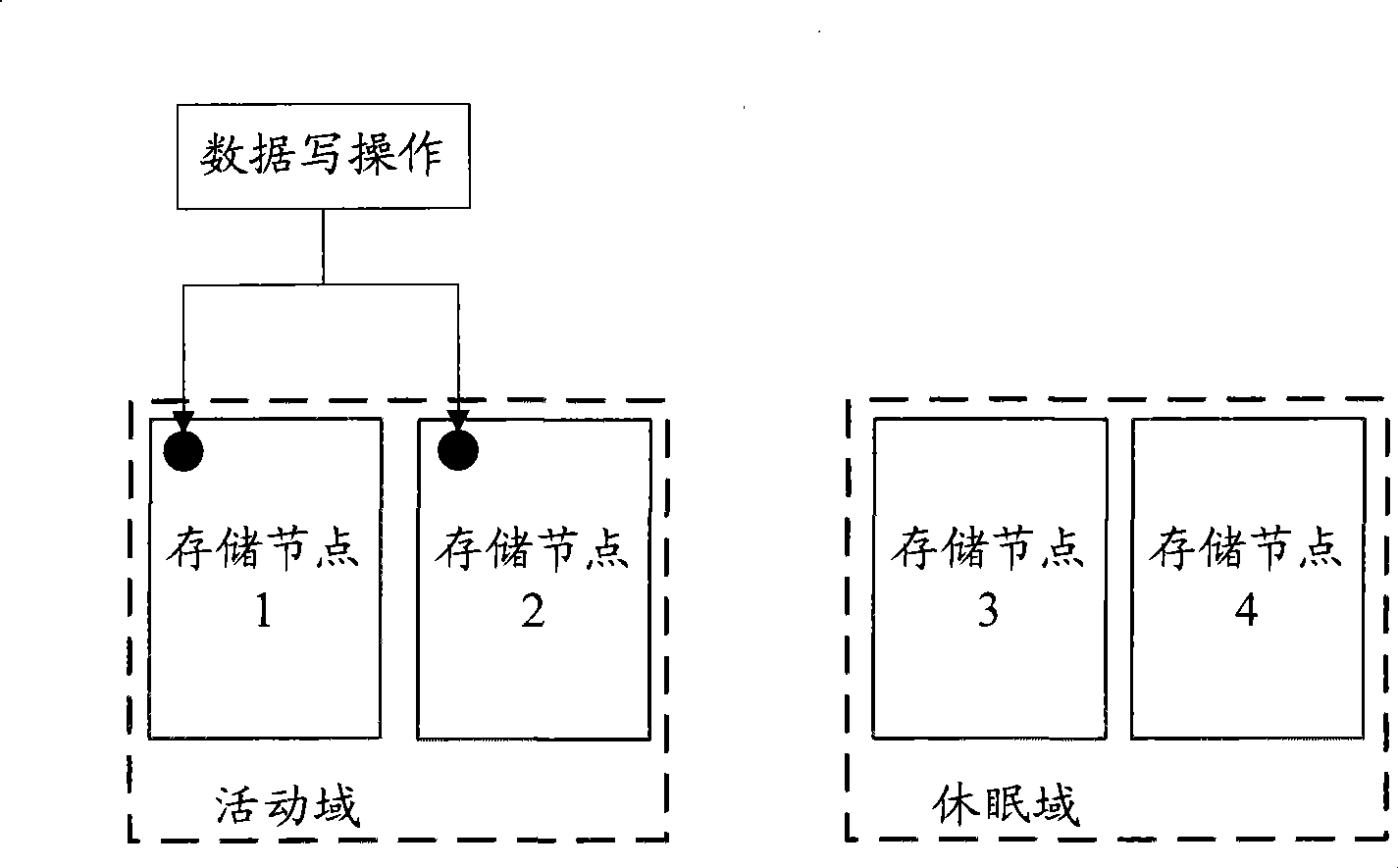
Method, device and system for storing data
ActiveCN101520688AReduce power consumptionInput/output to record carriersPower supply for data processingIdle timeData access
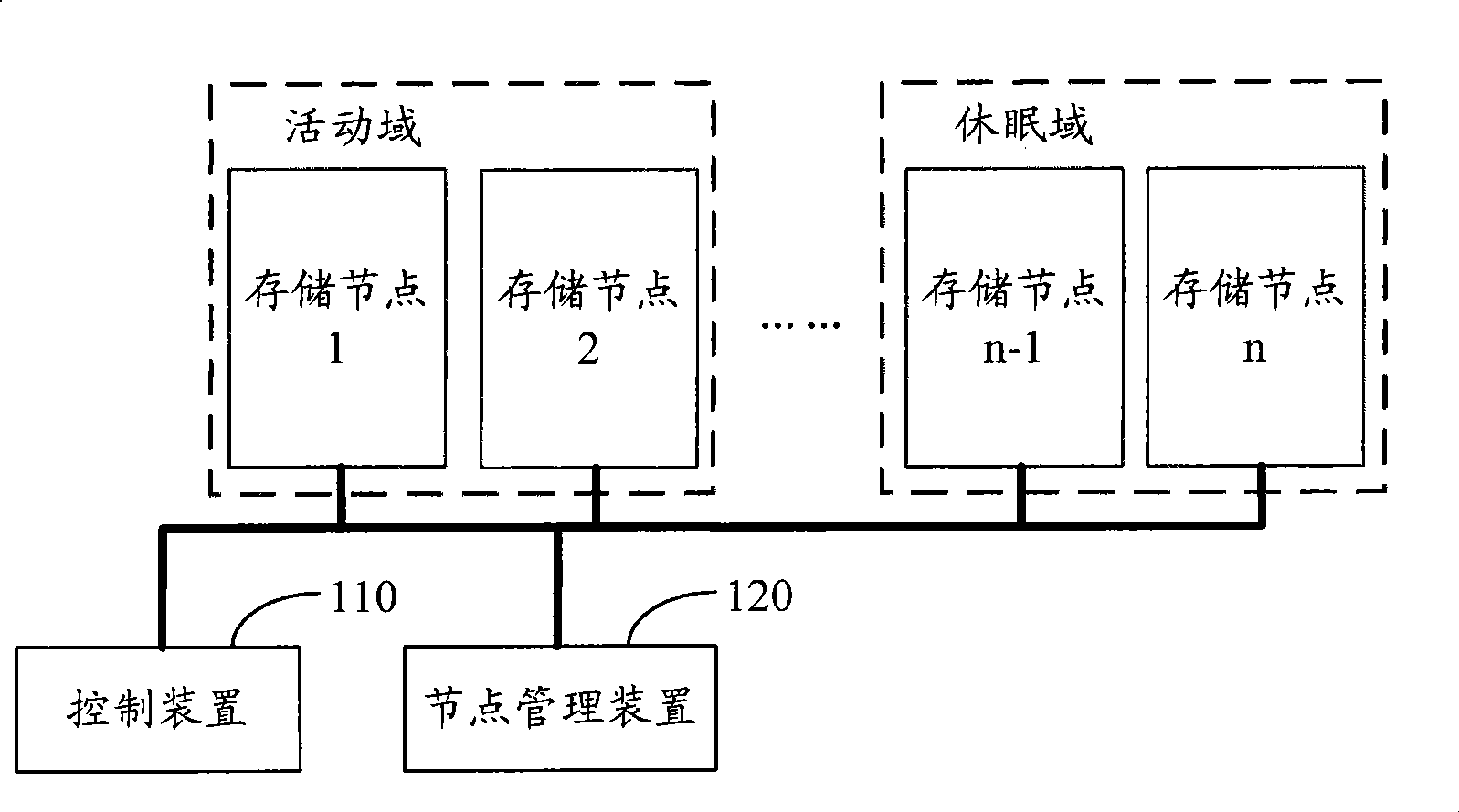
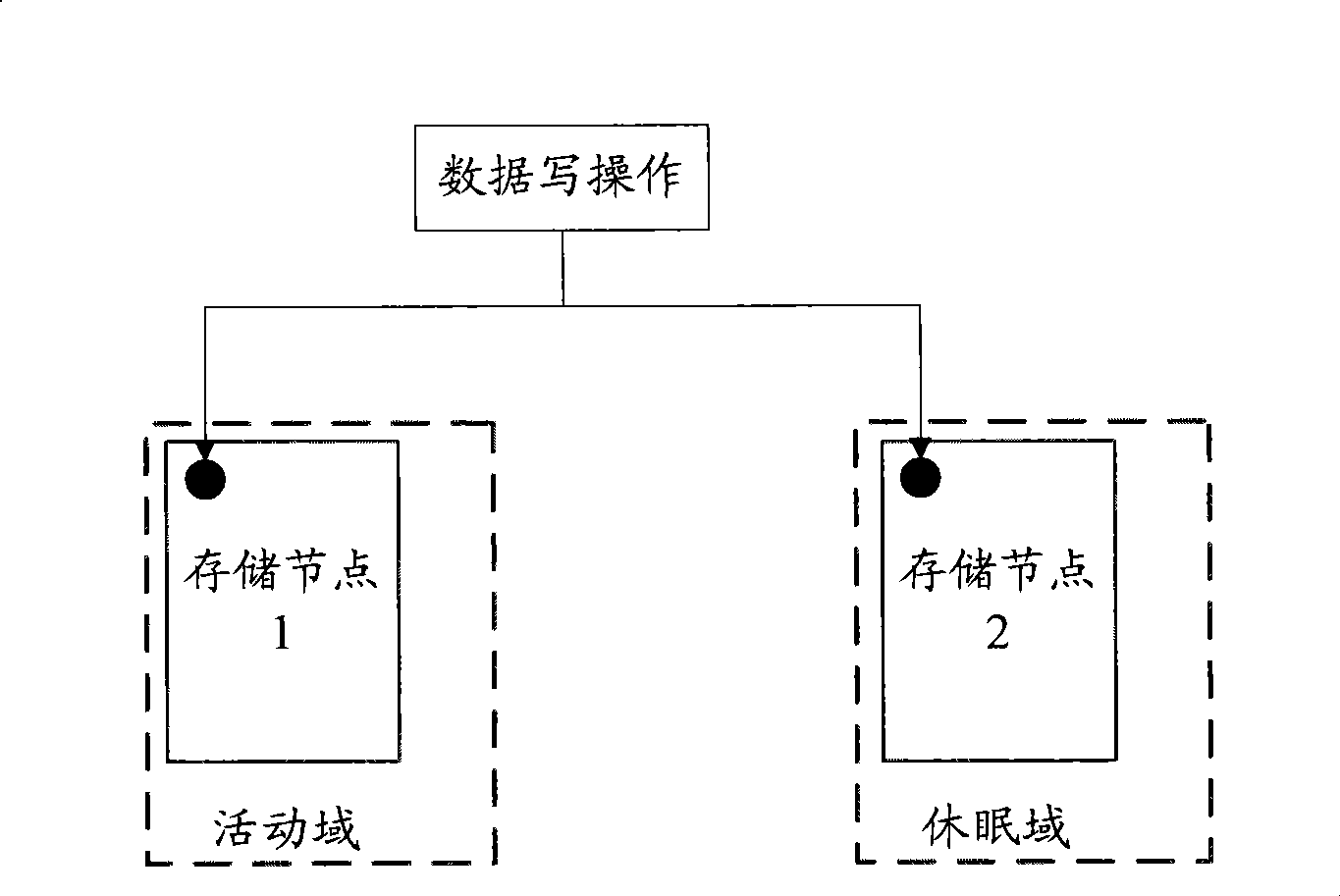
The embodiment of the invention discloses a method, a device and a system for storing data. The method for storing data comprises the following steps: data reading and wiring operation is performed on nodes in an active domain and a dormant domain which are divided in advance during the non-idle time period of a system, and data reading and wiring operation is performed on nodes in the active domain which is divided in advance during the idle time period of the system. The nodes in the dormant domain are in a standard working state during the non-idle time period of the system and in a low-power consumption state during the idle time of the system. During the idle time period of the system, data reading and wiring operation is only performed on the nodes in the active domain, while the nodes in the dormant domain are in the low-power consumption state. The invention can effectively reduce the power consumption of the whole system on condition that the data access requirement is met.
Owner:CHENGDU HUAWEI TECH
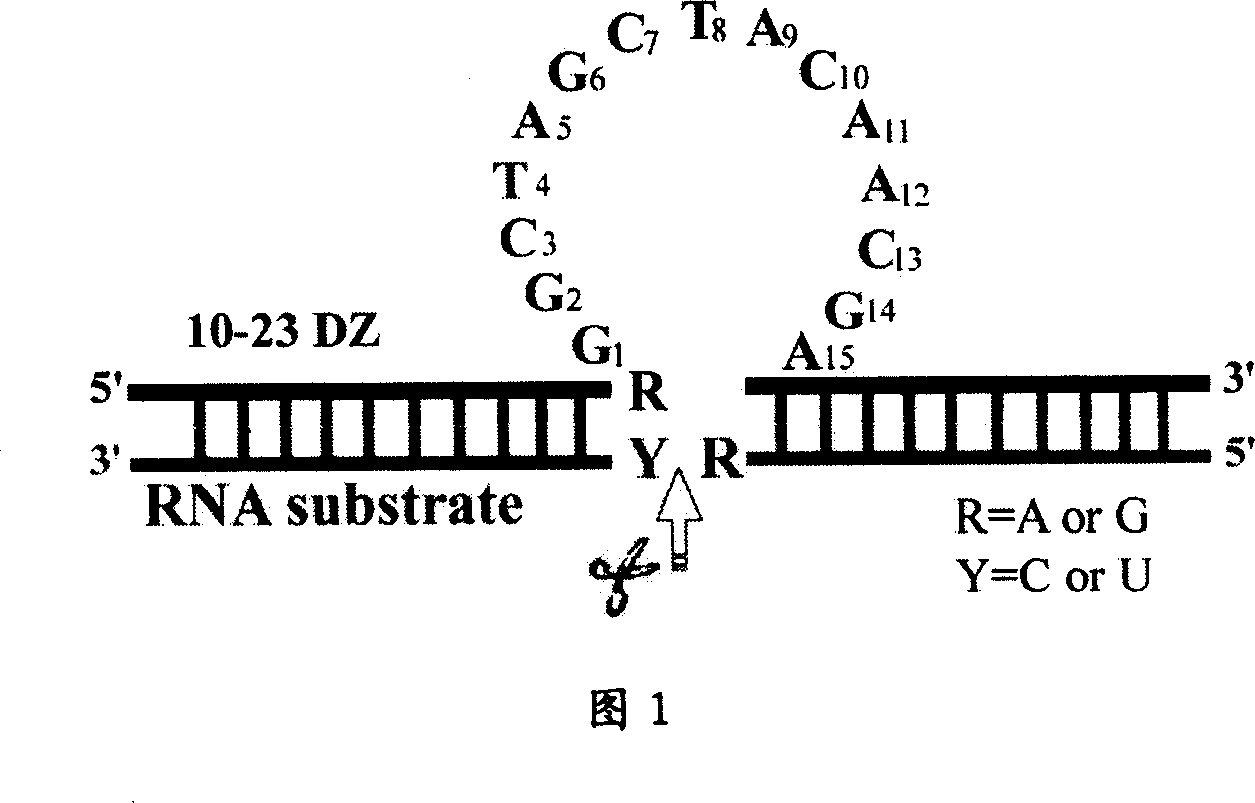
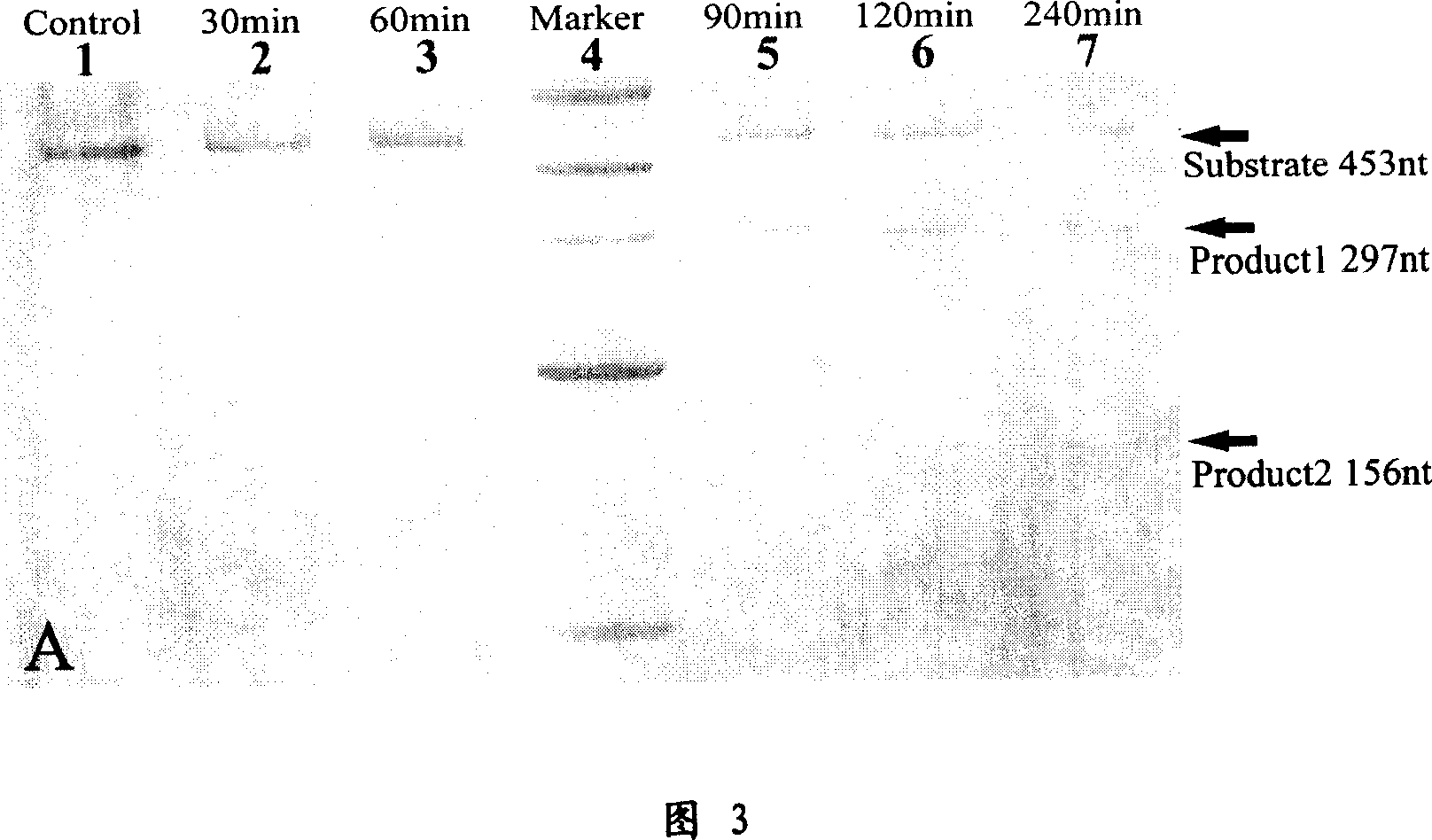
Deoxyzyme of anti-respiratory syncytial viruses and its medicinal use
InactiveCN101029313AInhibition of replicationIncreased sensitivityHydrolasesGenetic engineeringIncision SiteRespiratory syncytial virus (RSV)
A deoxyribonse of anti-respiratory tract syncytium virus and its medicinal use are disclosed. The deoxyribonse has purine in RSV RNA nucleotide sequence; pyramine site cracks RNA catalytic active domain specially, the No.1 combined domain adjacent to catalytic domain 5' end is supplemented combined with base sequence specificity at one side of RSV RNA incision site; the No.2 combined domain adjacent to catalytic domain 3' end is supplemented combined with base sequence specificity at one side of RSV RNA incision site. It contains 0.01mg-20mg / 50 mu l anti-respiratory tract syncytium virus deoxyribonse solution. It is non-toxic, has better medicine sensitivity and can inhibit respiratory tract syncytium virus duplication specially.
Owner:CHILDRENS HOSPITAL OF CHONGQING MEDICAL UNIV
PROCESS FOR CORRECTION OF A DISULFIDE MISFOLD IN Fc MOLECULES
InactiveUS20100267936A1Peptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsEscherichia coliImpurity
Owner:AMGEN INC
PUFA polyketide synthase systems and uses thereof
The invention generally relates to polyunsaturated fatty acid (PUFA) polyketide synthase (PKS) systems isolated from or derived from non-bacterial organisms, to homologues thereof, to isolated nucleic acid molecules and recombinant nucleic acid molecules encoding biologically active domains of such a PUFA PKS system, to methods of making and using such system for the production of bioactive molecules of interest, and to novel methods for identifying new bacterial and non-bacterial microorganisms having such a PUFA PKS system.
Owner:MARTEK BIOSCIENCES CORP (N D GES D STAATES DELAWARE) COLUMBIA
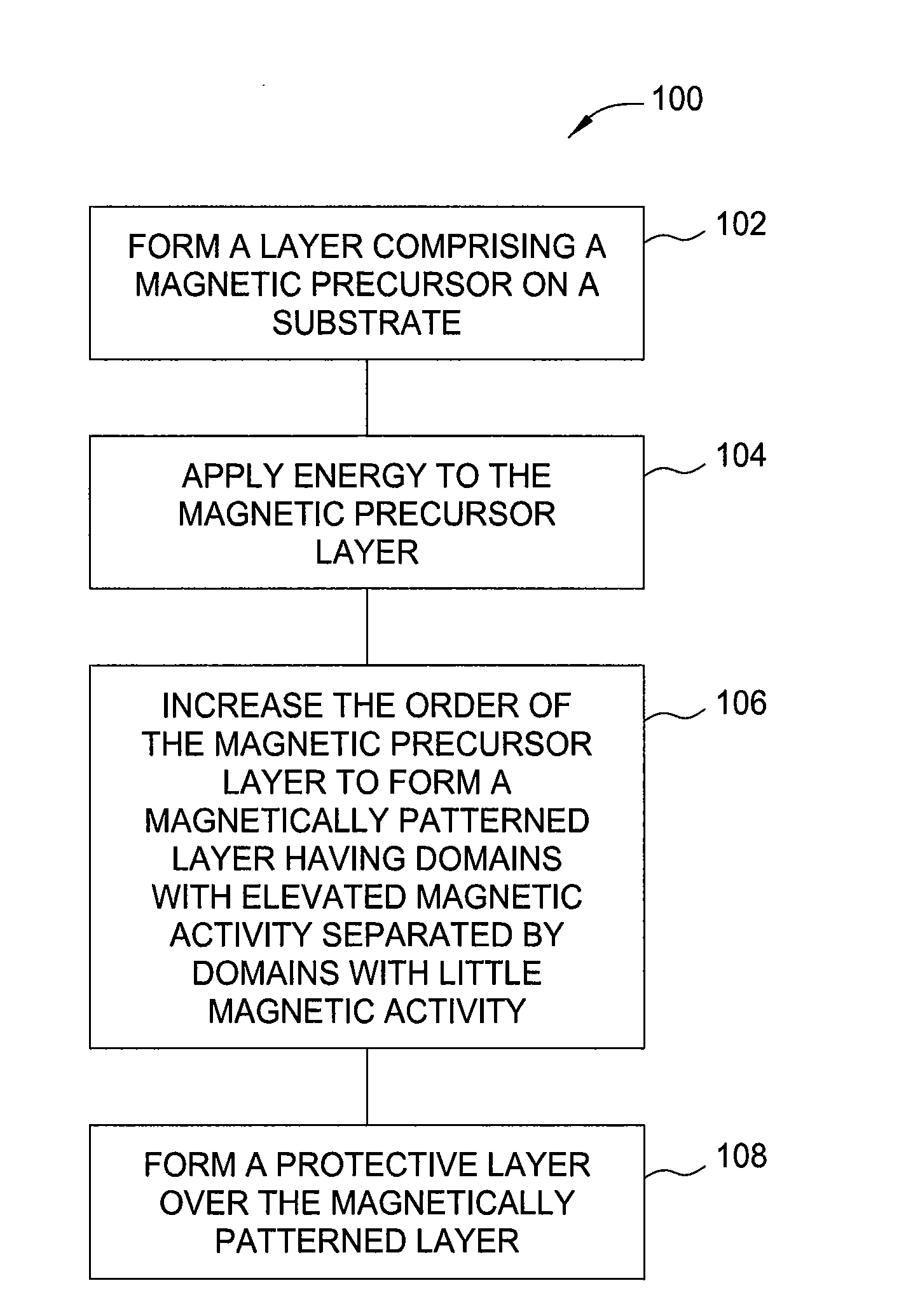
Apparatus and methods to manufacture high density magnetic media
InactiveUS20130062320A1Easy alignmentRadiation applicationsDecorative surface effectsThermal energyHigh density
A substrate having a pattern of magnetic properties may be formed by forming a magnetically inactive layer on the substrate, forming a magnetic precursor on the magnetically inactive layer, and forming magnetically active domains separated by magnetically inactive domains in the magnetic precursor by applying thermal energy to the magnetic precursor. The thermal energy may be applied using a laser, which may be pulsed. Forming the magnetically active domains may include crystallizing portions of the magnetic precursor.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Chimeric polypeptides and their use in bacterial decolonization
ActiveUS9057059B2Overcome increasing numberRapid onsetAntibacterial agentsSugar derivativesBacteroidesBacterial disease
The present invention relates to chimeric polypeptides comprising a first portion, which comprises a bacteriocin cell wall-binding domain (CBD) and a second portion, which comprises an enzymatic active domain (EAD) selected from the lytic domain of a bacteriophage lysin, a bacteriocin and a bacterial autolysin. Provided are such chimeric polypeptides and variants and fragments thereof, nucleic acids encoding the same, vectors carrying such nucleic acids and host cells transformed or transfected with such vectors. The chimeric polypeptides of the present invention are useful for the reduction of certain bacterial populations, including methods and compositions for the treatment of various bacterial infections. For example, chimeric polypeptides of the present invention have been shown to effectively kill various bacteria, including methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA), as well as other human pathogens. Thus, provided are compositions comprising chimeric polypeptides according to the present invention, variants or fragments thereof, and the use of such compositions in prophylaxis or therapy of bacterial diseases, bacterial infections or bacterial colonizations.
Owner:HYPHARM GMBH
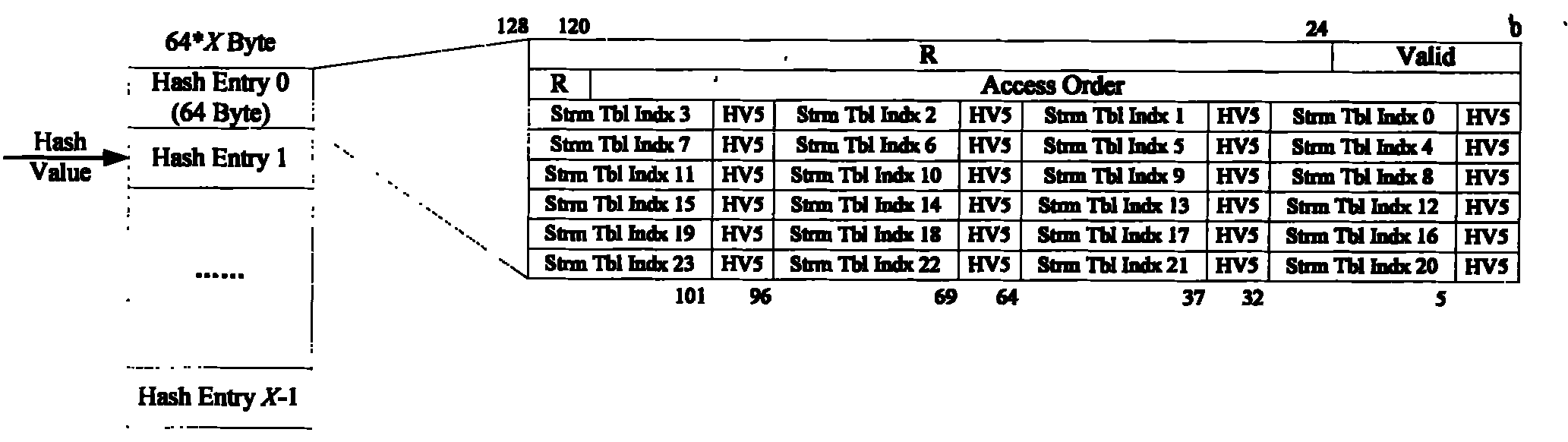
Elimination and replacement method of transmission control protocol (TCP) streams
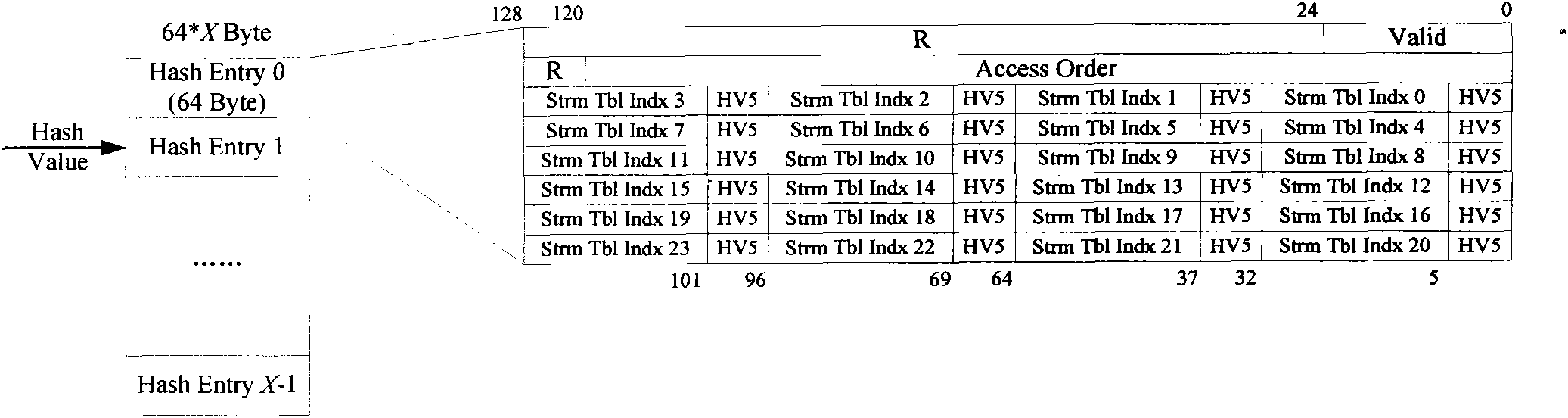
InactiveCN102098290AIncrease the lengthIncrease the number of handle connectionsTransmissionHash tableReplacement method
The invention provides an elimination and replacement method of transmission control protocol (TCP) streams, which is characterized in that a hash table chain is built in accordance with hash values; the lengths of hash collision chains permitted by each table entry are 24; active domains are determined in accordance with a Valid domain; and if 24 entries are used out, the connection which is built for the longest time is selected to replace in accordance with an Access Order domain. In the method, the size of the hash table and the barrel depth are selected reasonably, thus maximally reducing collision replacement and improving hardware performances.
Owner:SUGON INFORMATION IND
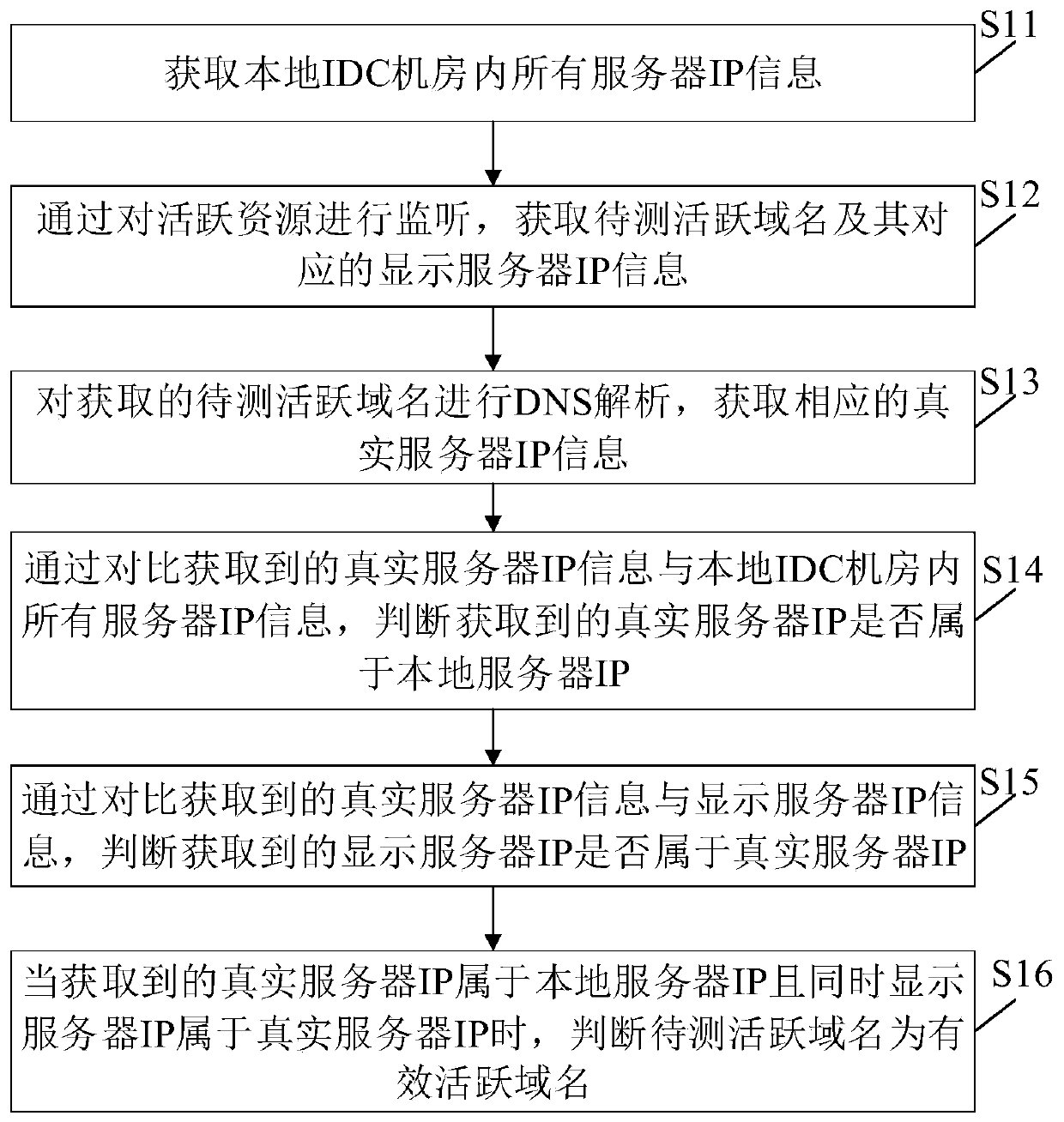
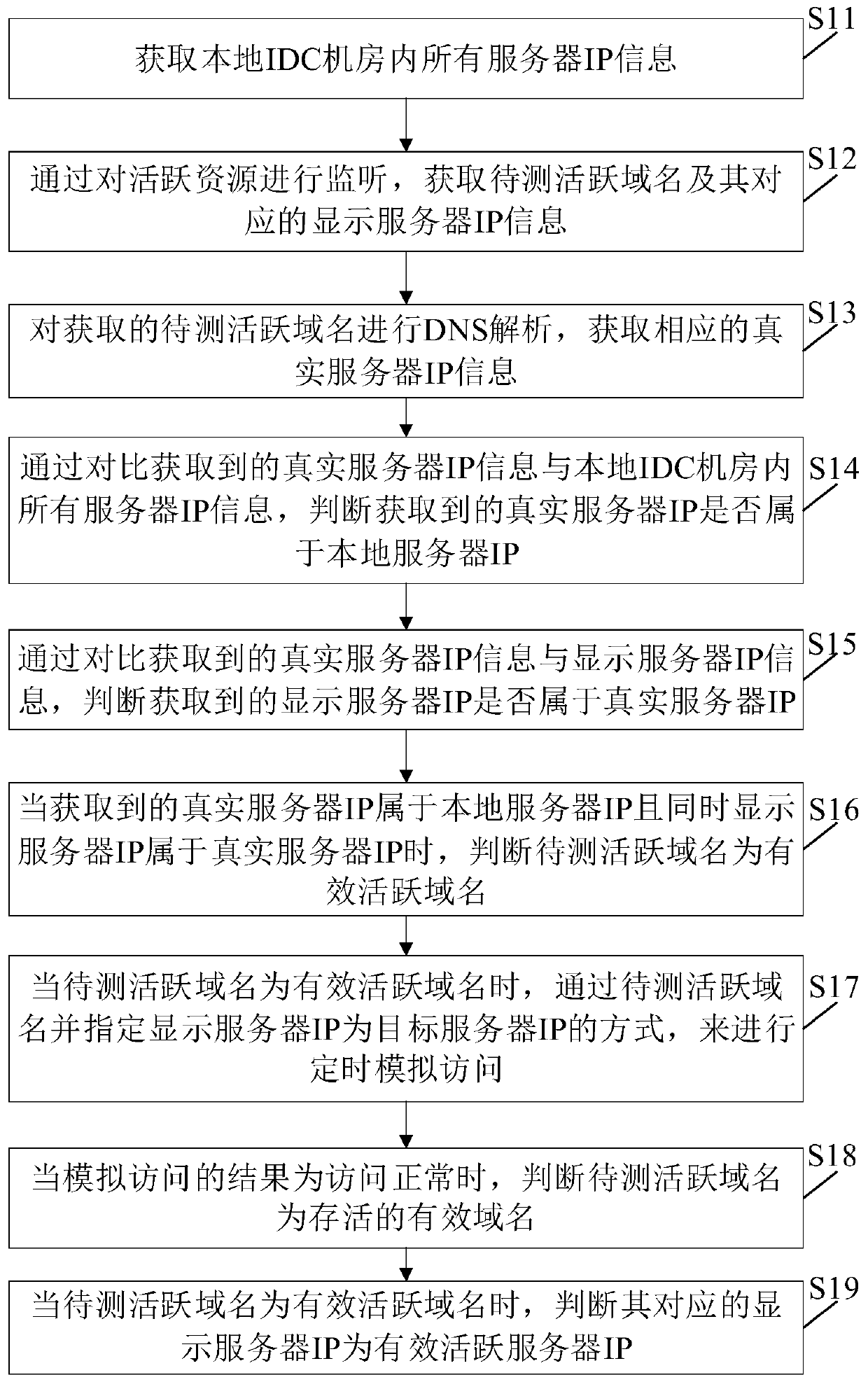
Method and device for validity diagnosing of active domain names in IDC computer room
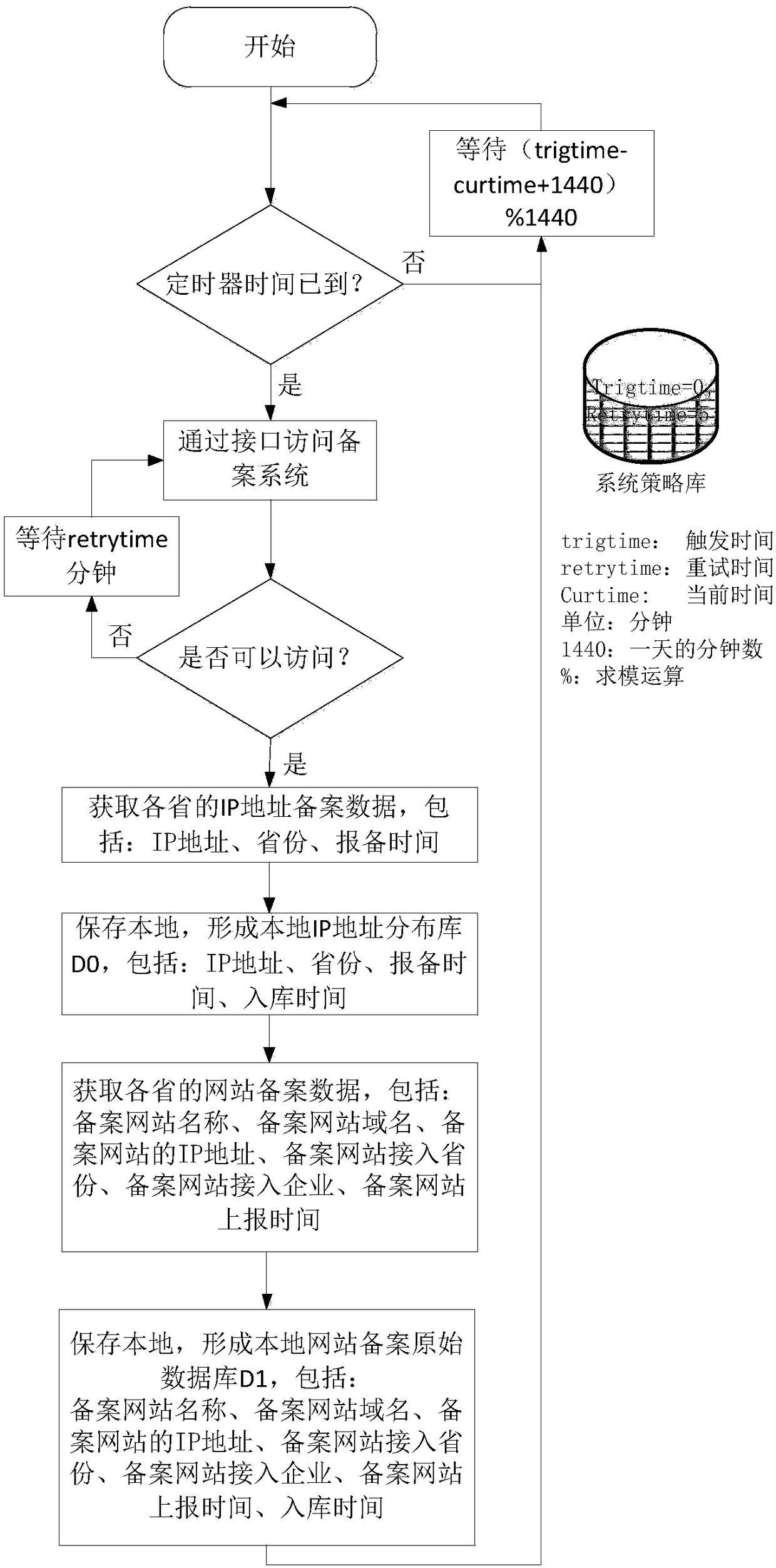
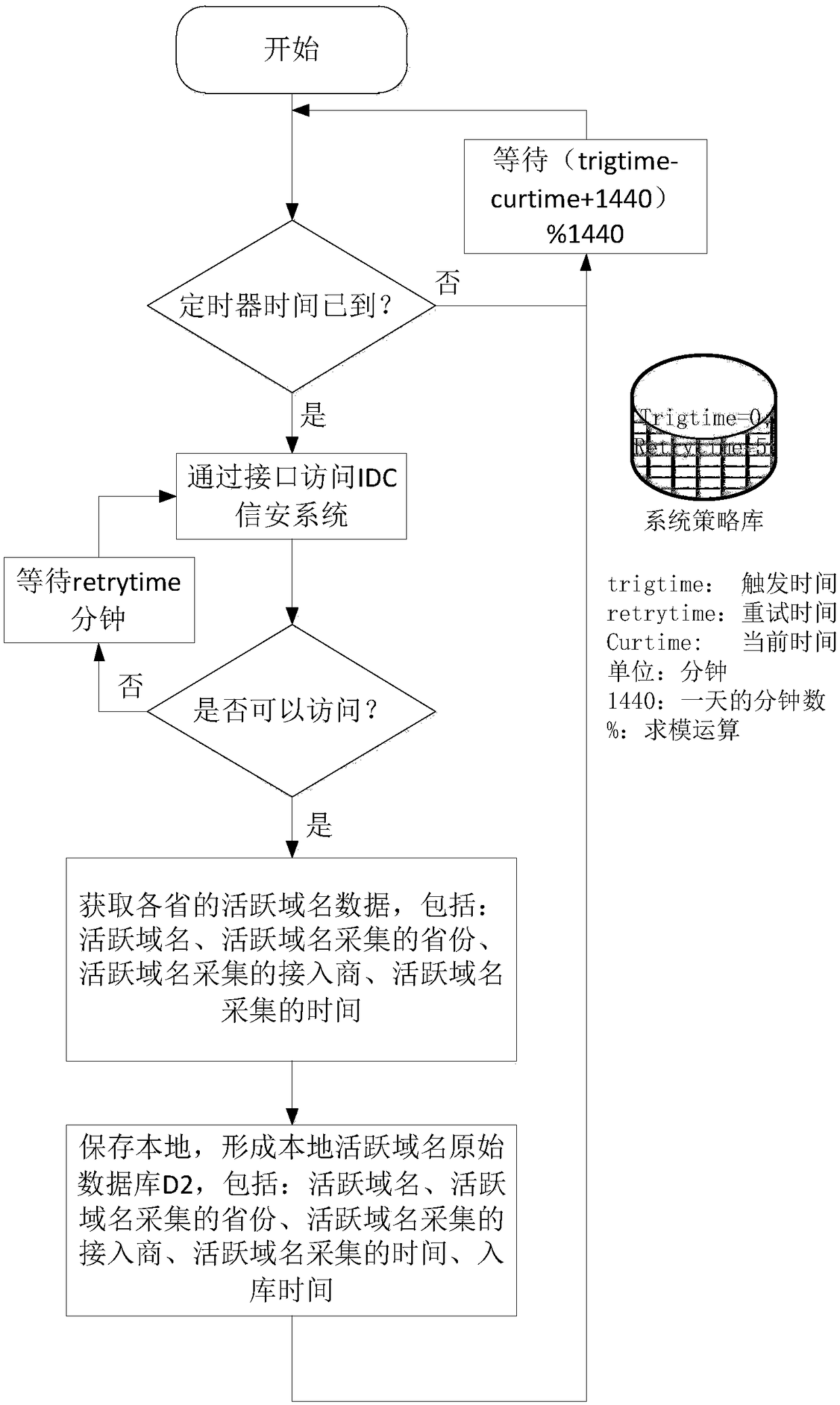
The invention discloses a method and device for validity diagnosing of active domain names in an IDC computer room. The method for validity diagnosing of the active domain names in the IDC computer room comprises the following steps: judging whether an obtained real server IP belongs to a local server IP or not by comparing the obtained real server IP information with all server IP information of the local IDC computer room; judging whether an obtained displaying server IP belongs to the real server IP or not by comparing the obtained real server IP information with the displaying server IP information; and determining an active domain name to be tested as a valid active domain name if the obtained real server IP belongs to the local server IP and the displaying server IP belongs to the real server IP. By means of the method provided by the invention, the validity of the active domain names is judged, and invalid domain names, domain names which do not correspond to the displaying server IP address but can be accessed and domain names which do not belong to the local IDC computer room can be effectively filtered out, therefore, the authenticity and accuracy of the active domain names can be furthest insured.
Owner:BEIJING ACT TECH DEV CO LTD +1
Polypeptide mixes with antibacterial activity
ActiveUS20150118189A1Easy to produceImprove diffusivityAntibacterial agentsBiocideAntibacterial activityEnzyme
The invention relates to the field of microbiology, specifically to a combination of a source of a first enzymatic active domain and a source of a second enzymatic active domain and to a composition comprising said combination. The invention further relates to a composition comprising said combination for use as a medicament, to the use of said composition as an antimicrobial agent and to a method for controlling microbial contamination in a food- or feed product, on and / or in food- or feed processing equipment, on and / or in food- or feed containers.
Owner:MICREOS HUMAN HEALTH
Method of treating cancer by inhibition of protein kinase-like endoplasmic reticulum protein kinase
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
Methods of generating and screening for lytic chimeric polypeptides
ActiveUS20130288926A1Overcome increasing numberRapid onsetAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsMicrobiological testing/measurementBinding domainContamination
The present invention relates to novel methods of generating and screening for chimeric polypeptides, which can be used in the treatment and prophylaxis of pathogenic bacterial contamination, colonisation and infection. The novel methods are based on random recombination of protein domains, and the chimeric polypeptides obtainable by the methods according to the invention are characterized in that they comprise at least one enzymatic active domain (EAD) and at least one cell binding domain (CBD). The present invention also relates to a library of chimeric polypeptides obtainable by the methods of the present invention.
Owner:HYPHARM GMBH
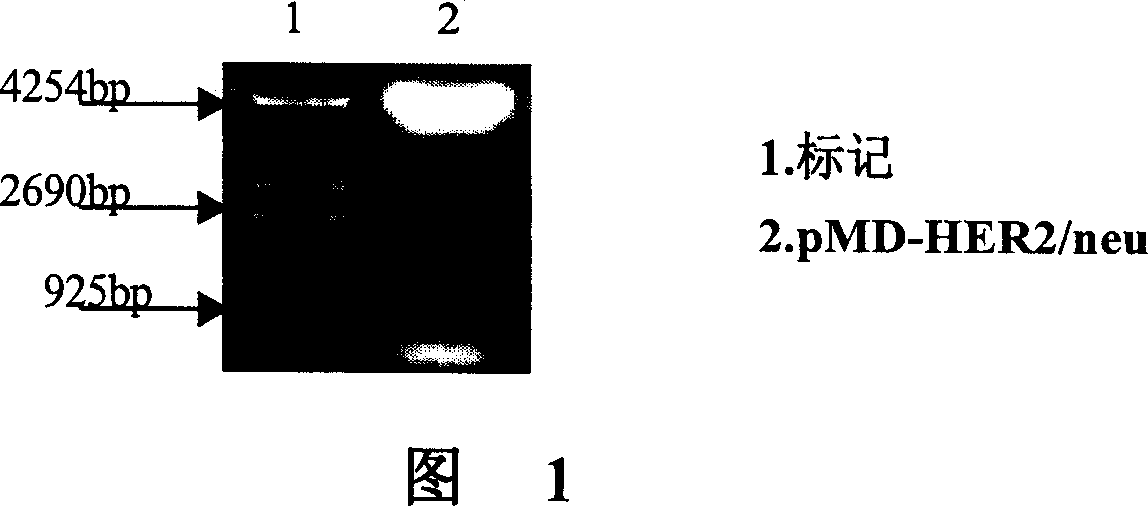
Construction of HER2/neu mRNA in vitro transcription vector and use thereof
ActiveCN1966684ALong half lifeBroad anti-tumor spectrumGenetic material ingredientsMammal material medical ingredientsCtl epitopeDendritic cell
The invention provides an HER2 / neu nucleic acid molecular for producing remedial vaccine for HER2 positive tumor and its applications. It includes the following elements: (a) a 7-methyl guanine cap sequence at 5'end, (b) a 110-200bp polyA tail at 3'end, (c) the coding sequences of HER2 / neu between elements (a) and (b). The said coding sequences includes multiple CTL epitopes that have been proved, do not include its PTK active domain eliminating its PTK activity, can be used for modifying dendritic cells, induce to produce specific immune response aiming at HER2 positive tumor, and can be used for preventing and treating HER2 positive tumor such as breast carcinoma. The invention also provides the said the method for constructing HER2 / neu mRNA in vitro transcription vector.
Owner:上海海欣生物技术有限公司
Homochiral metal-organic framework with enantiopure pillar[5]arene active domains
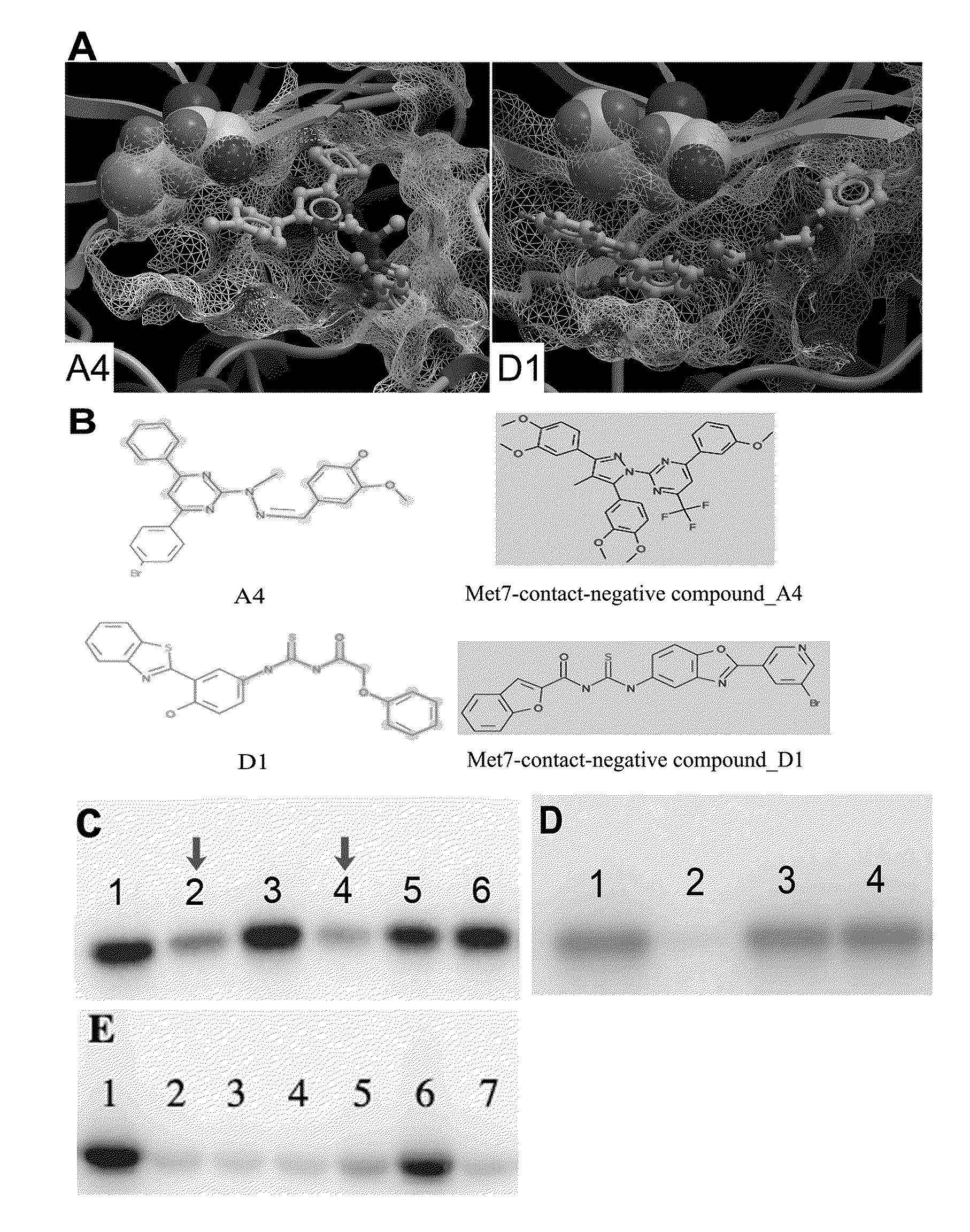
Homochiral metal organic framework (MOF) selected from a group consisting of (Sp)-P5A-MOF-1 and (Rp)-P5A-MOF-1 is provided. The homochiral MOFs are prepared from pure enantiomer struts of formula (I):The homochiral MOFs are suitable for separation of enantiomers from racemic mixtures.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN UNIV +1
Method for calculating the number of Internet access websites based on active and passive data
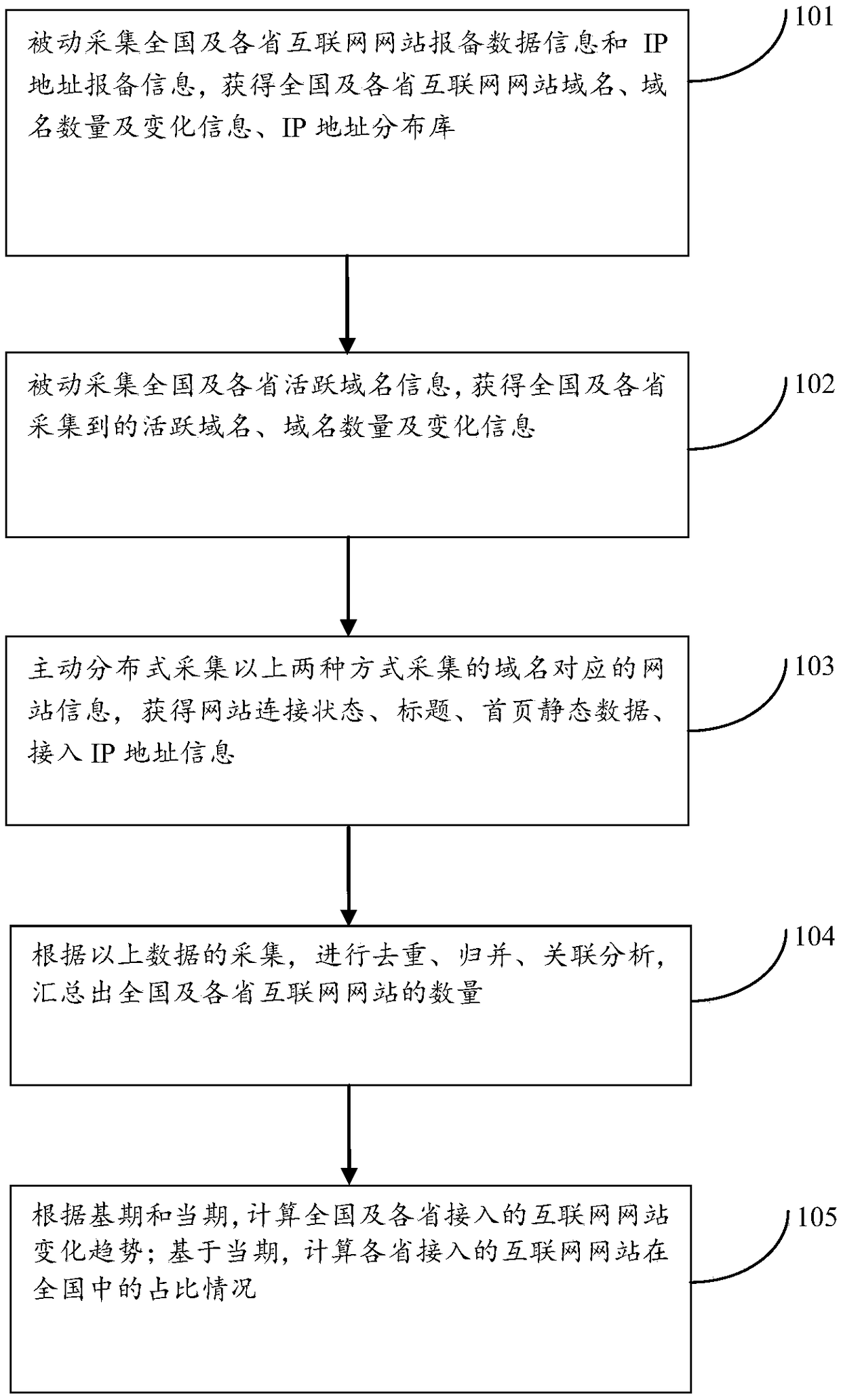
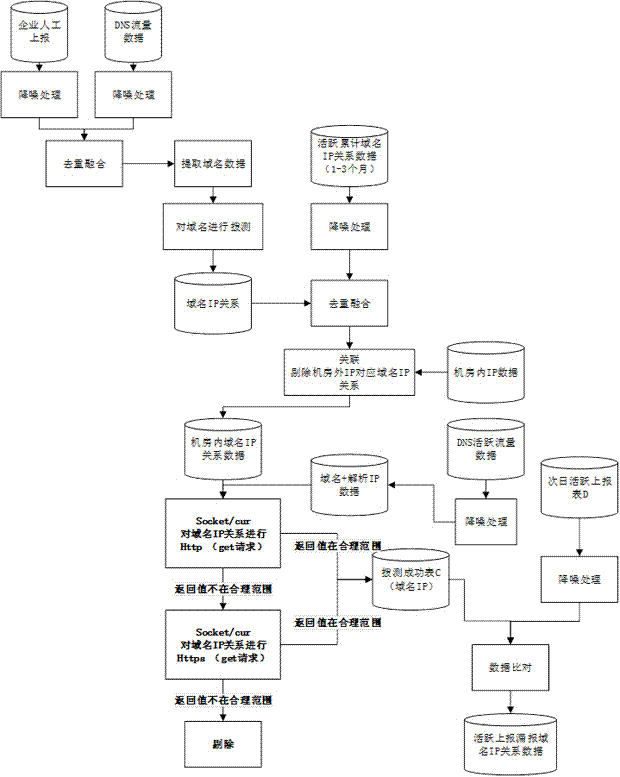
ActiveCN108880883AEffective monitoringEfficient StatisticsData switching networksSpecial data processing applicationsDomain nameWeb site
The invention discloses a method for calculating the number of Internet access websites based on active and passive data. The method comprises the following steps: passively collecting report data information and IP address report information of national and provincial Internet websites, and obtaining domain name information and IP address distribution databases recorded by the national and provincial Internet websites; passively collecting active domain name information of the nation and provinces, and obtaining the active domain name information collected in the nation and the provinces; actively collecting website information corresponding to the domain names collected in the above two manners in a distributed manner, and obtaining a website connection state, a title, homepage static data and access IP address information; and based on the above three types of data, analyzing the number of national and provincial Internet websites through mathematical modeling. By adoption of the statistical method disclosed by the invention, the overall number of national Internet websites, the overall number of provincial Internet websites, the proportions and the overall change situations canbe reflected to a greater extent, so that the application prospect is better.
Owner:EVERSEC BEIJING TECH
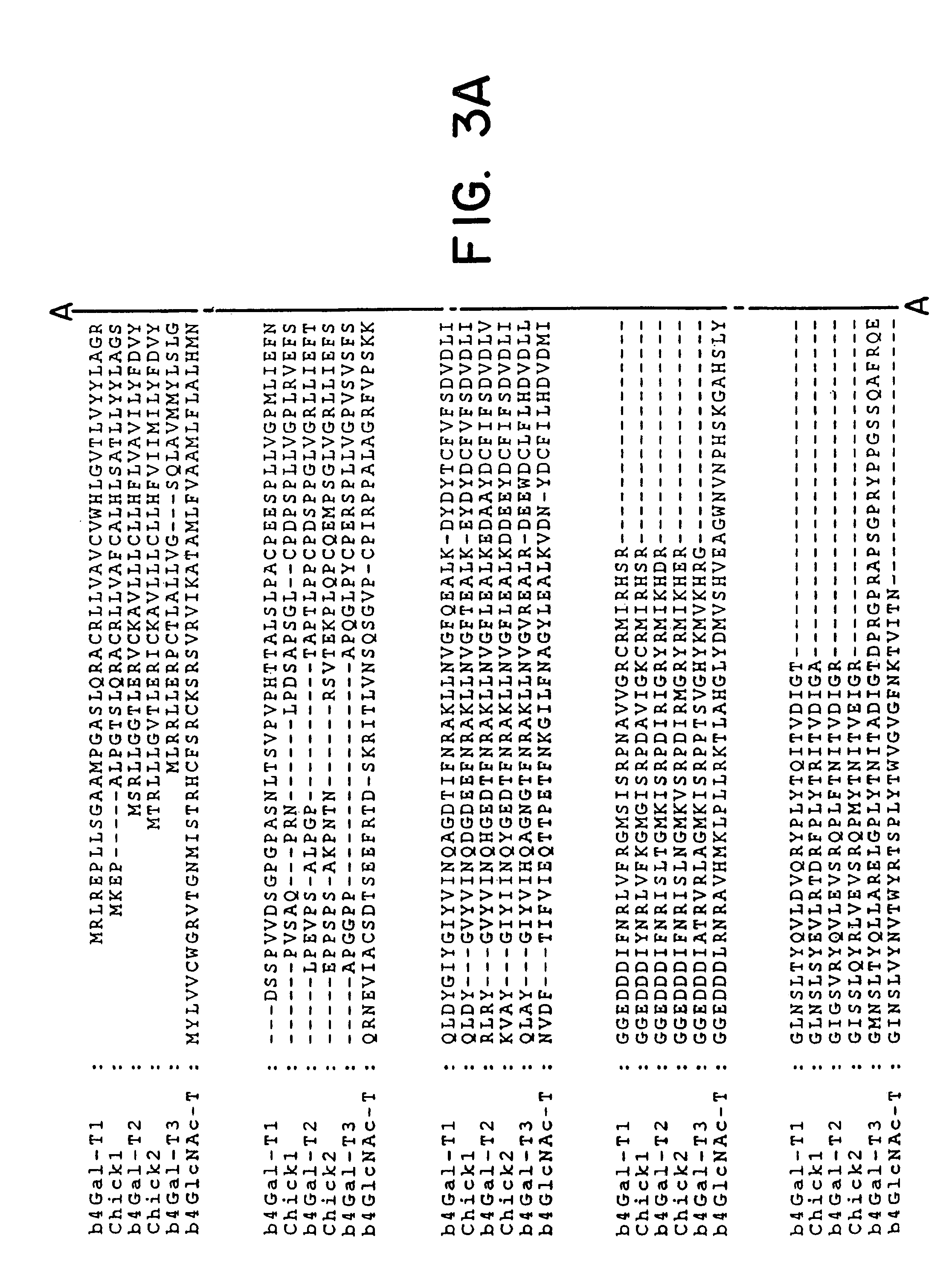
UDP-galactose: beta-N-acetyl-glucosamine beta-1,4-galactosyltransferase, beta4Gal-T2
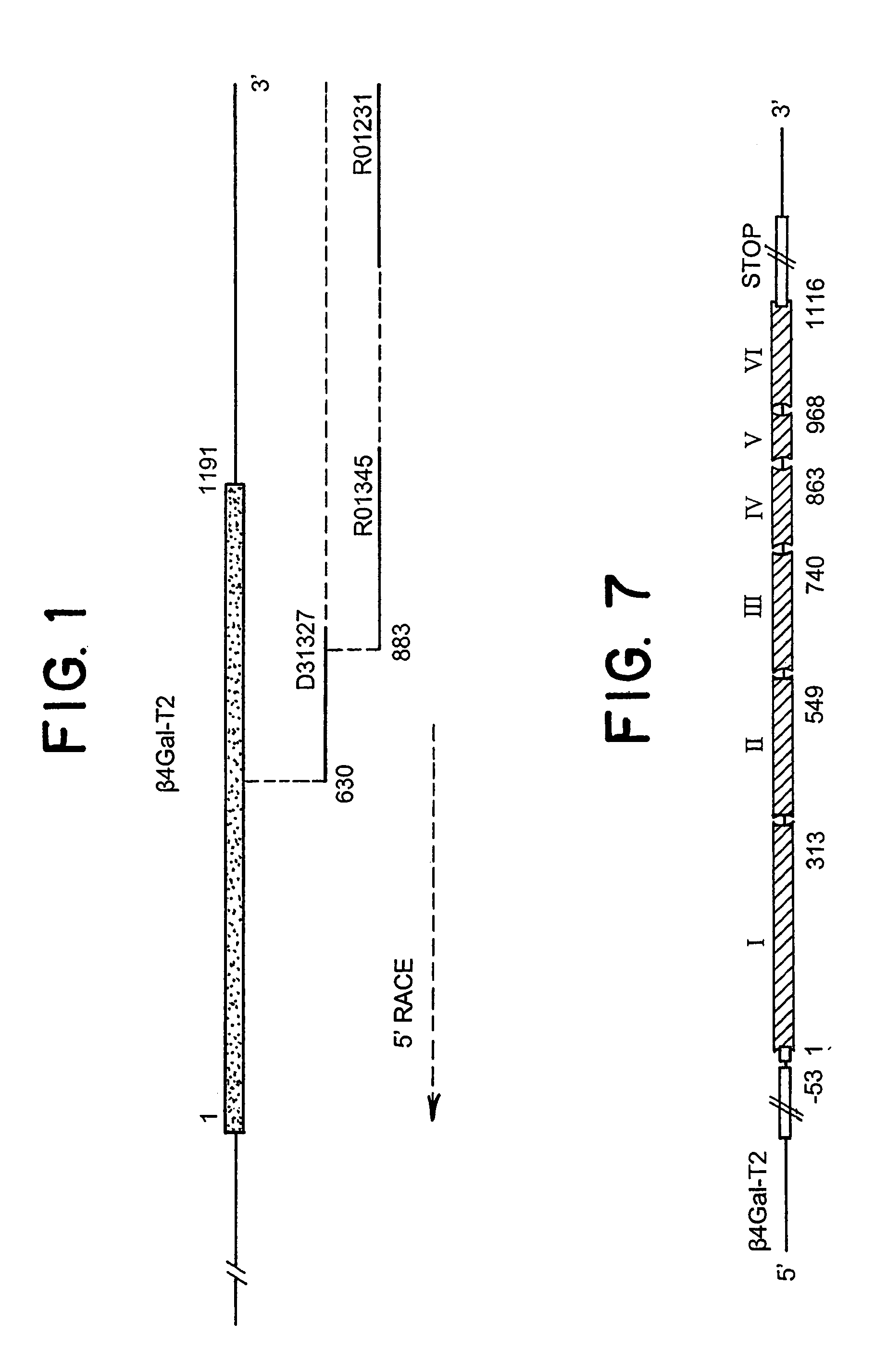
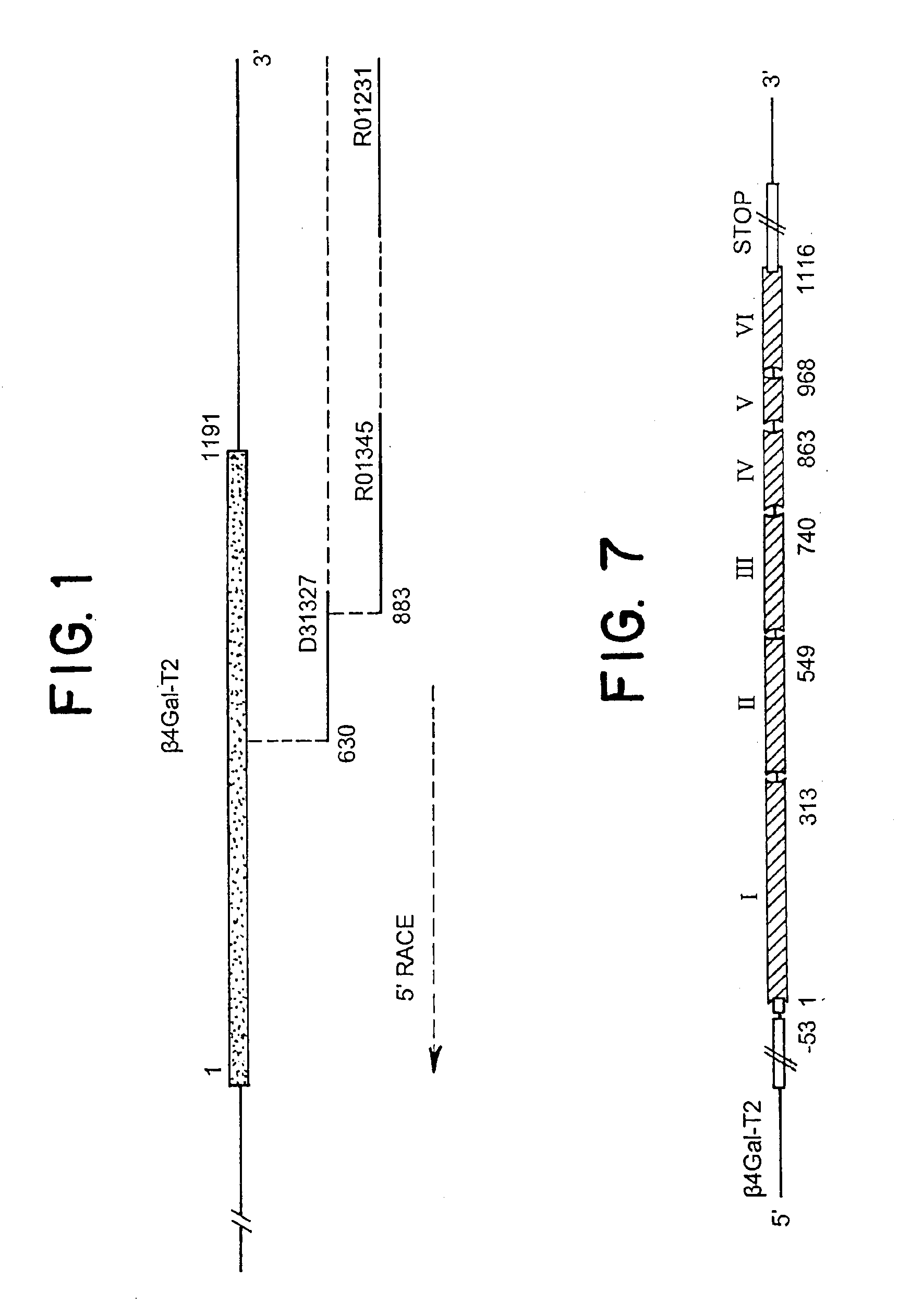
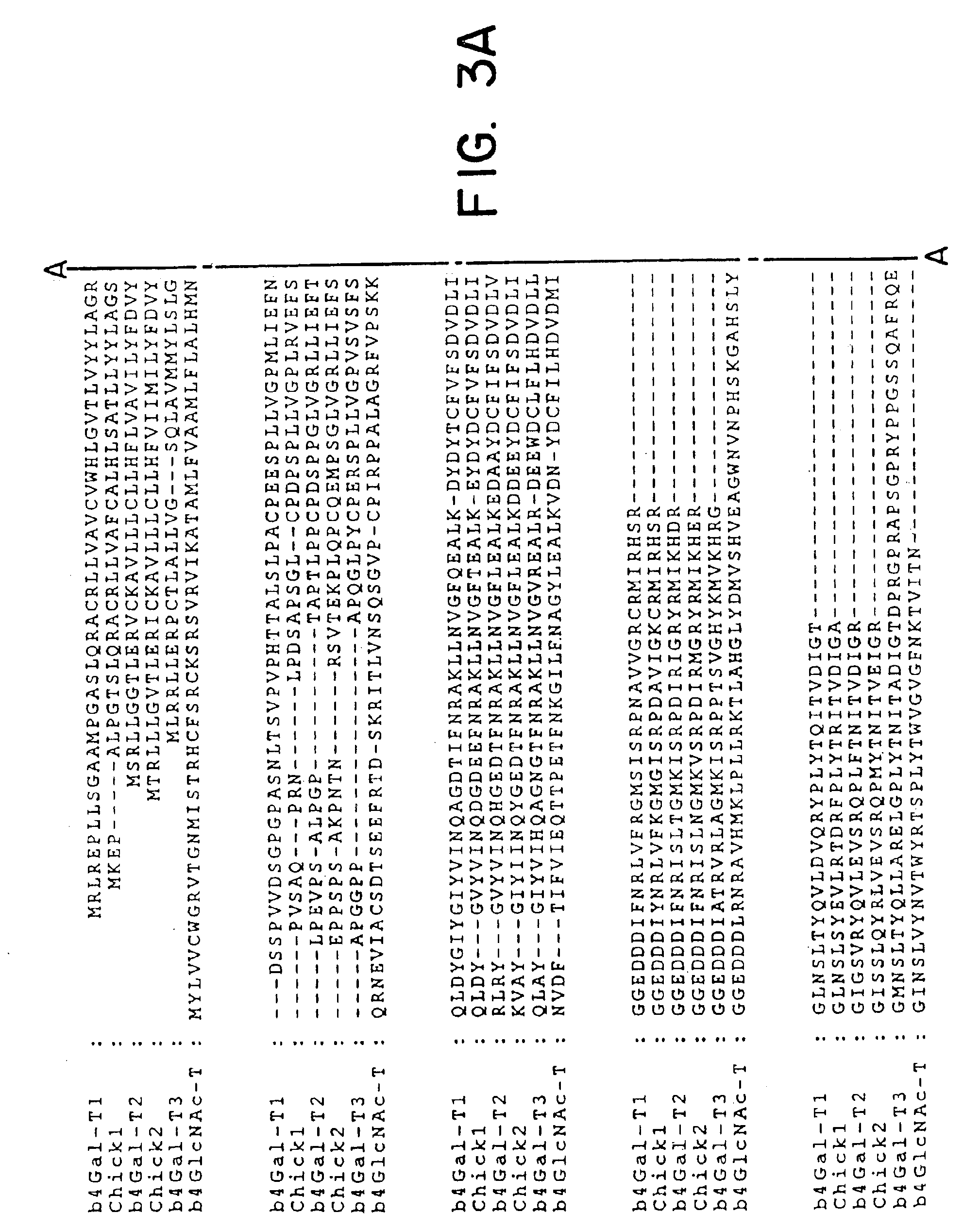
A novel gene defining a novel enzyme in the UDP-D-galactose: b-N-acetyl-glucosamine β-1,4-galactosyltransferase family, termed β4Gal-T2, with unique enzymatic properties is disclosed. The enzymatic activity of β4Gal-T2 is shown to be distinct from that of previously identified enzymes of this gene family. The invention discloses isolated DNA molecules and DNA constructs encoding β4Gal-T2 and derivatives thereof by way of amino acid deletion, substitution or insertion exhibiting β4Gal-T2 activity, as well as cloning and expression vectors including such DNA, cells transfected with the vectors, and recombinant methods for providing β4Gal-T2. The enzyme β4Gal-T2 and β4Gal-T2-active derivatives thereof are disclosed, in particular soluble derivatives comprising the catalytically active domain of β4Gal-T2. Further, the invention discloses methods of obtaining β-1,4-galactosyl glycosylated saccharides, glycopeptides or glycoproteins by use of an enzymically active β4Gal-T2 protein or fusion protein thereof or by using cells stably transfected with a vector including DNA encoding an enzymatically active β4Gal-T2 protein as an expression system for recombinant production of such glycopeptides or glycoproteins. Also a method for the identification of DNA sequence variations in the β4Gal-T2 gene by isolating DNA from a patient, amplifying β4Gal-T2-coding exons by PCR, and detecting the presence of DNA sequence variation, are disclosed.
Owner:GLYCOZYM
Development of viruses resistant to inactivation by the human complement system
InactiveUS6475756B1Antibody mimetics/scaffoldsGenetic material ingredientsVirus-RetrovirusTransfer system
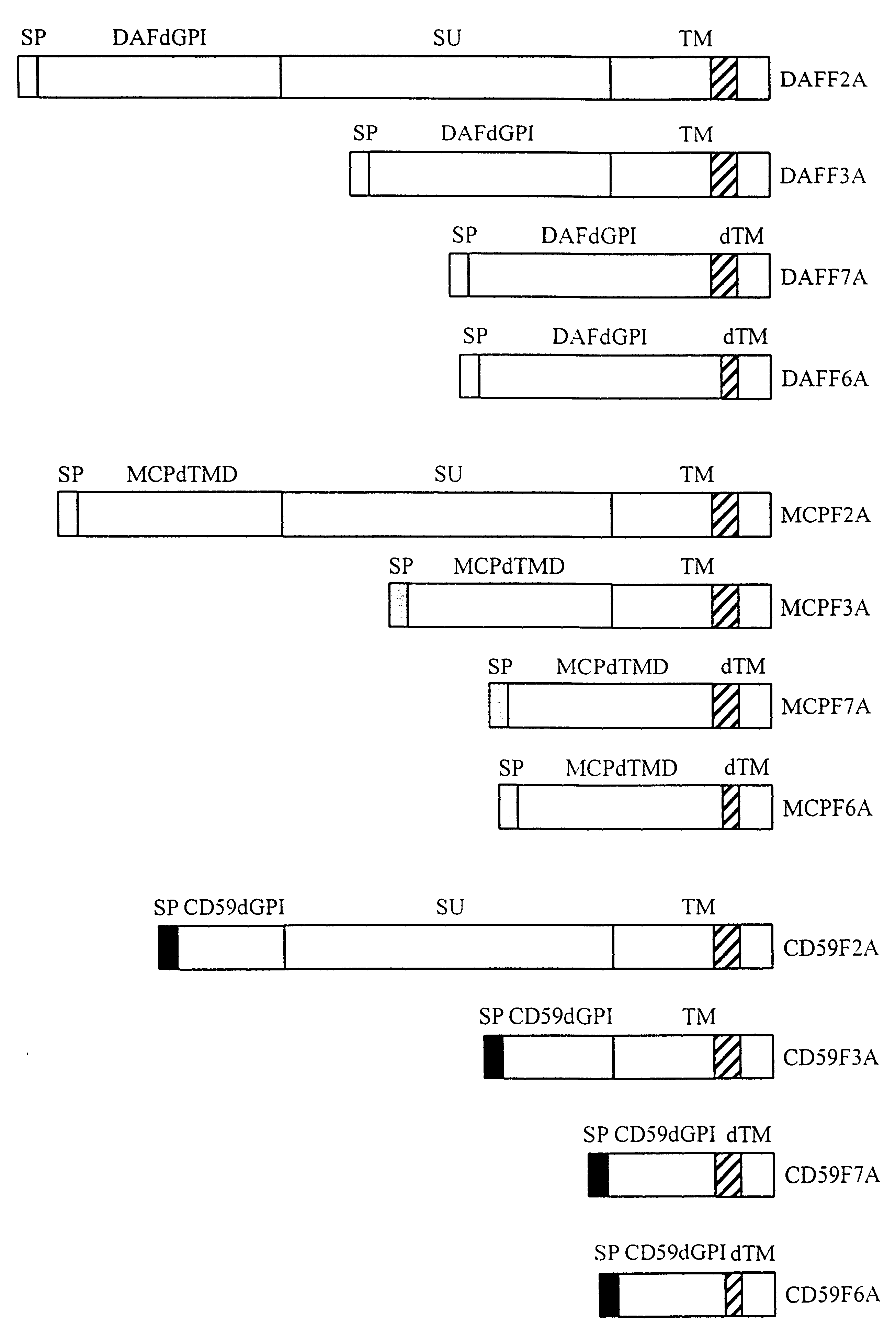
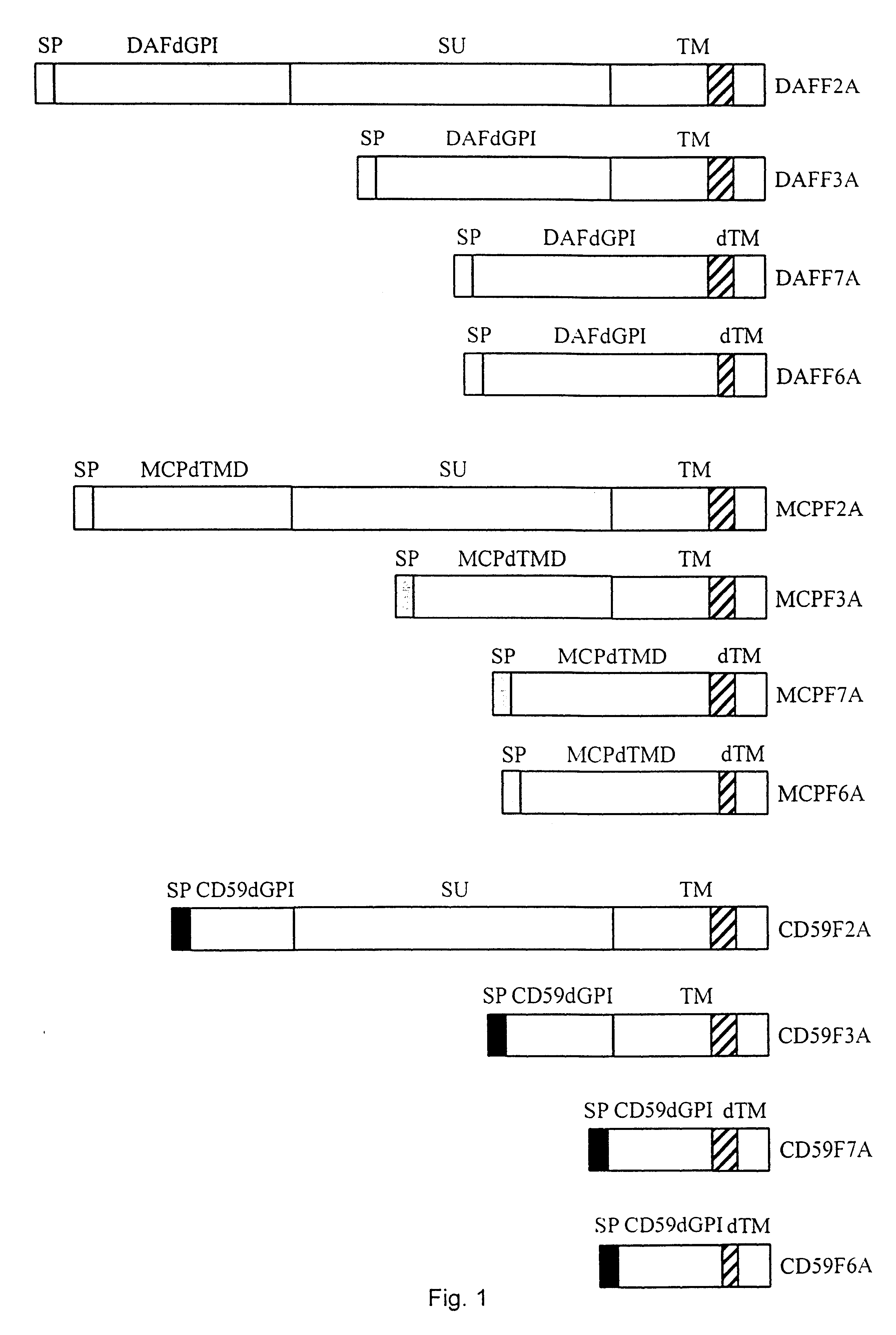
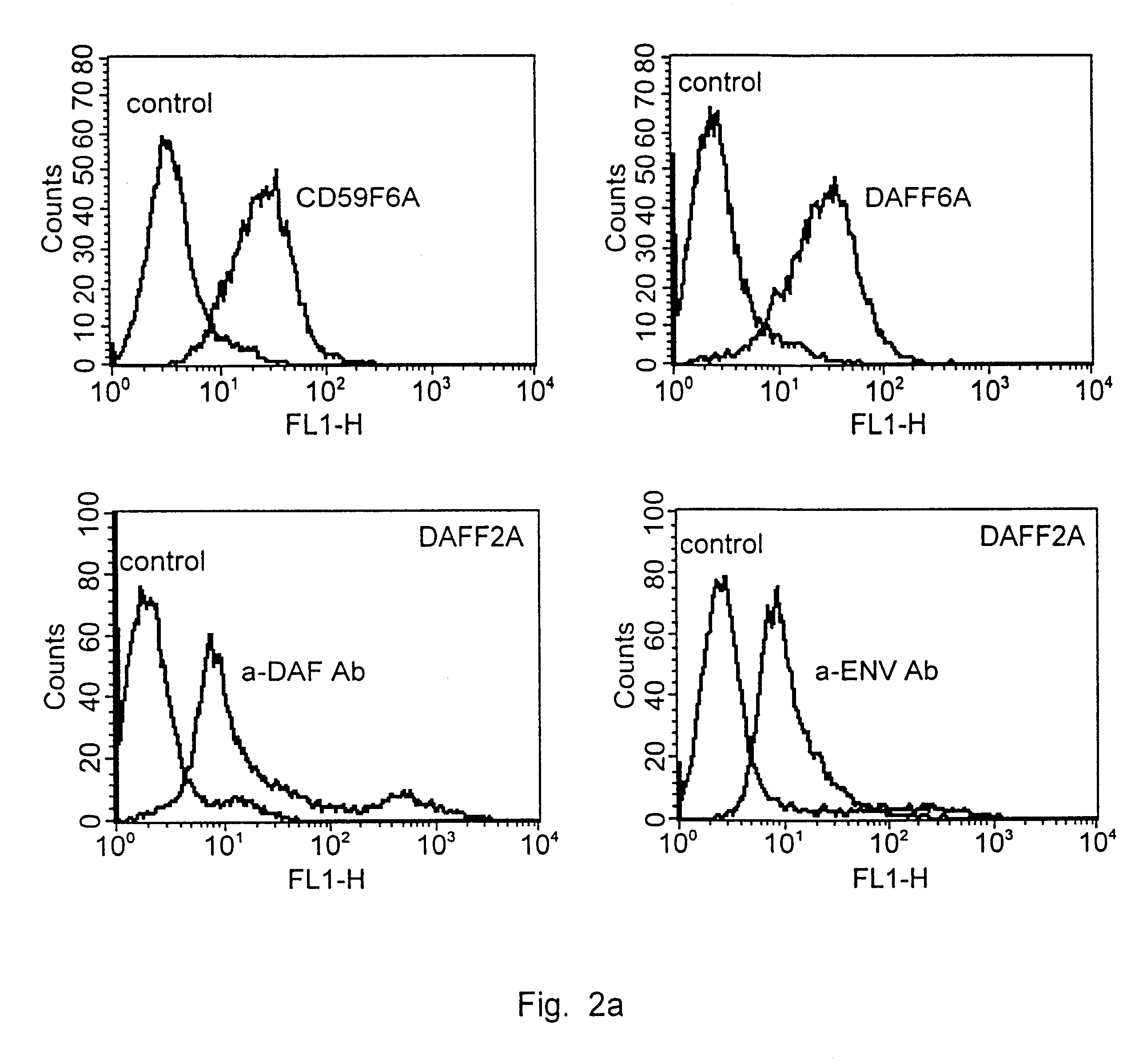
Murine retroviruses are the most important transfer systems for human gene therapy. However, their application is currently limited. One of the major restrictions both for an application in vivo resides in the problem that this virus type is sensitive to inactivation by human complement factors. Our invention overcomes this limitation. We have modified murine recombinant retroviruses in a way that they are resistant to human complement factors. This was achieved by genetic modification of the retroviral surface protein env which is responsible for receptor interaction: the receptor interacting domain of env was fused to catalytically active domains of human complement inactivation factors. These modified env were expressed in complement-sensitive cells and specifically integrated into virus particles. By this strategy cells and viruses are generated that are fully resistant to complement attack. Thus, this strategy provides a tool for establishment of complement resistant cells and generation of viruses for in vivo gene therapy.
Owner:GESELLSCHAFT FUR BIOTECHNOLOGISCHE FORSCHUNG MBH GBF
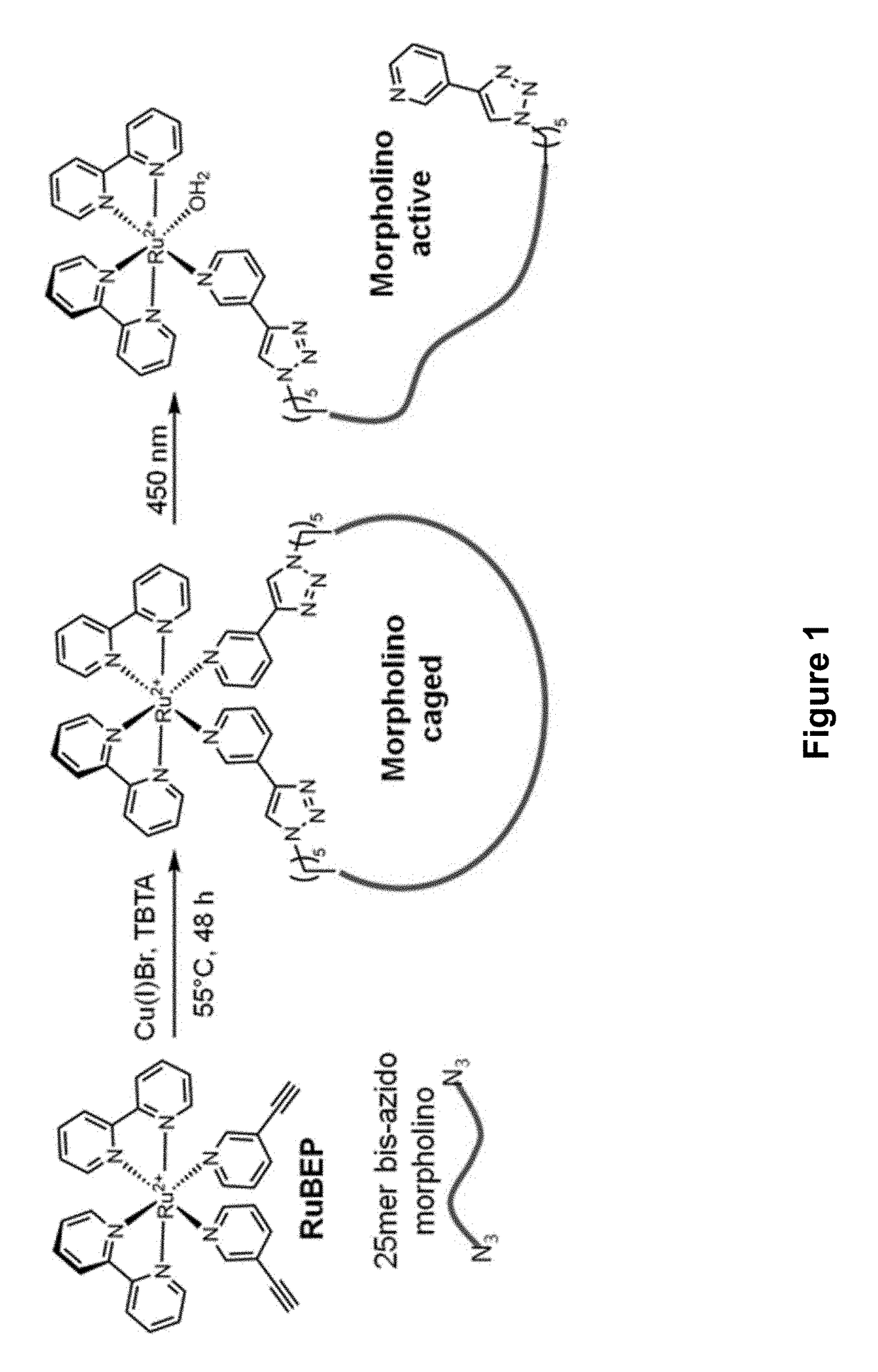
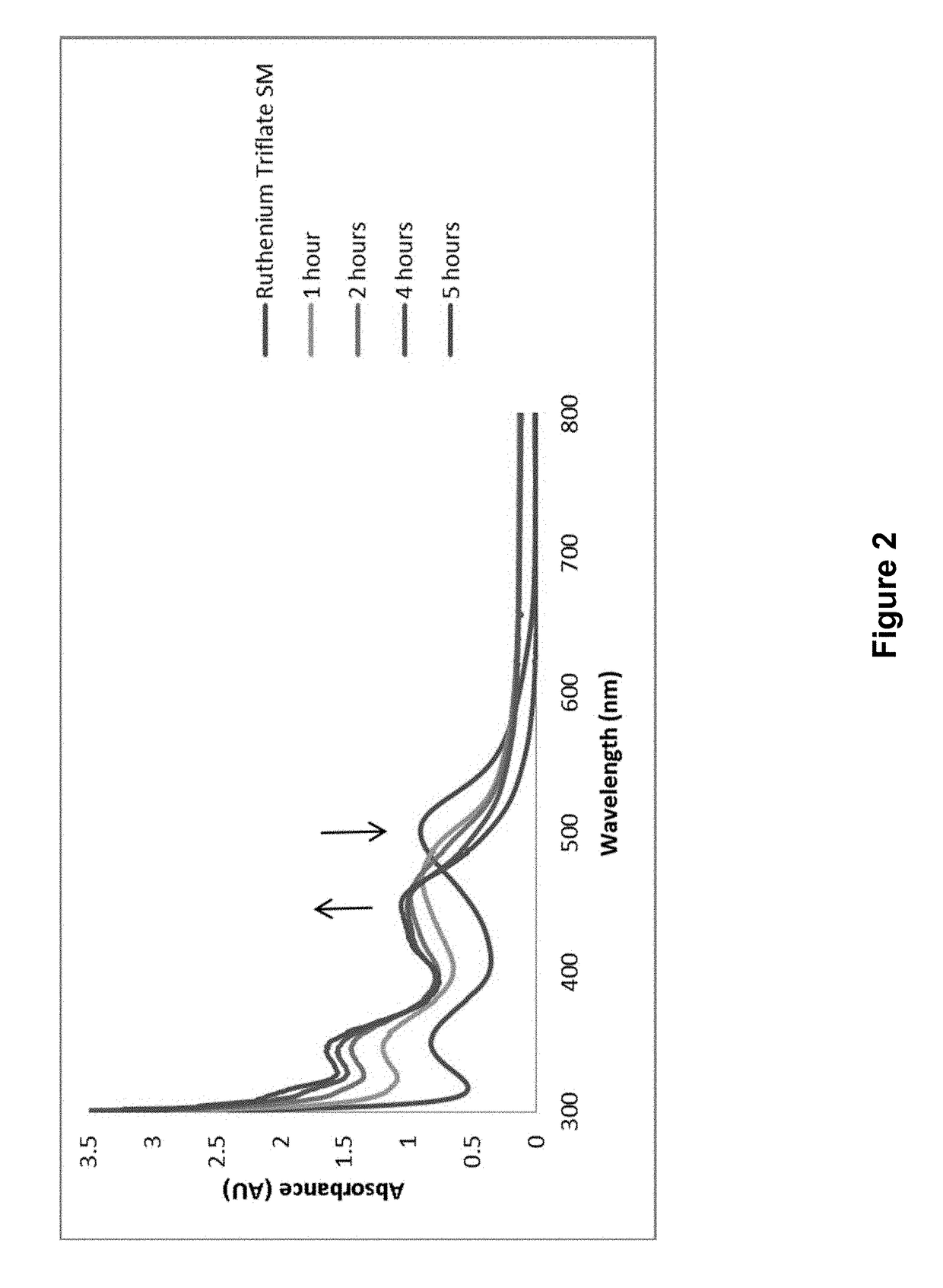
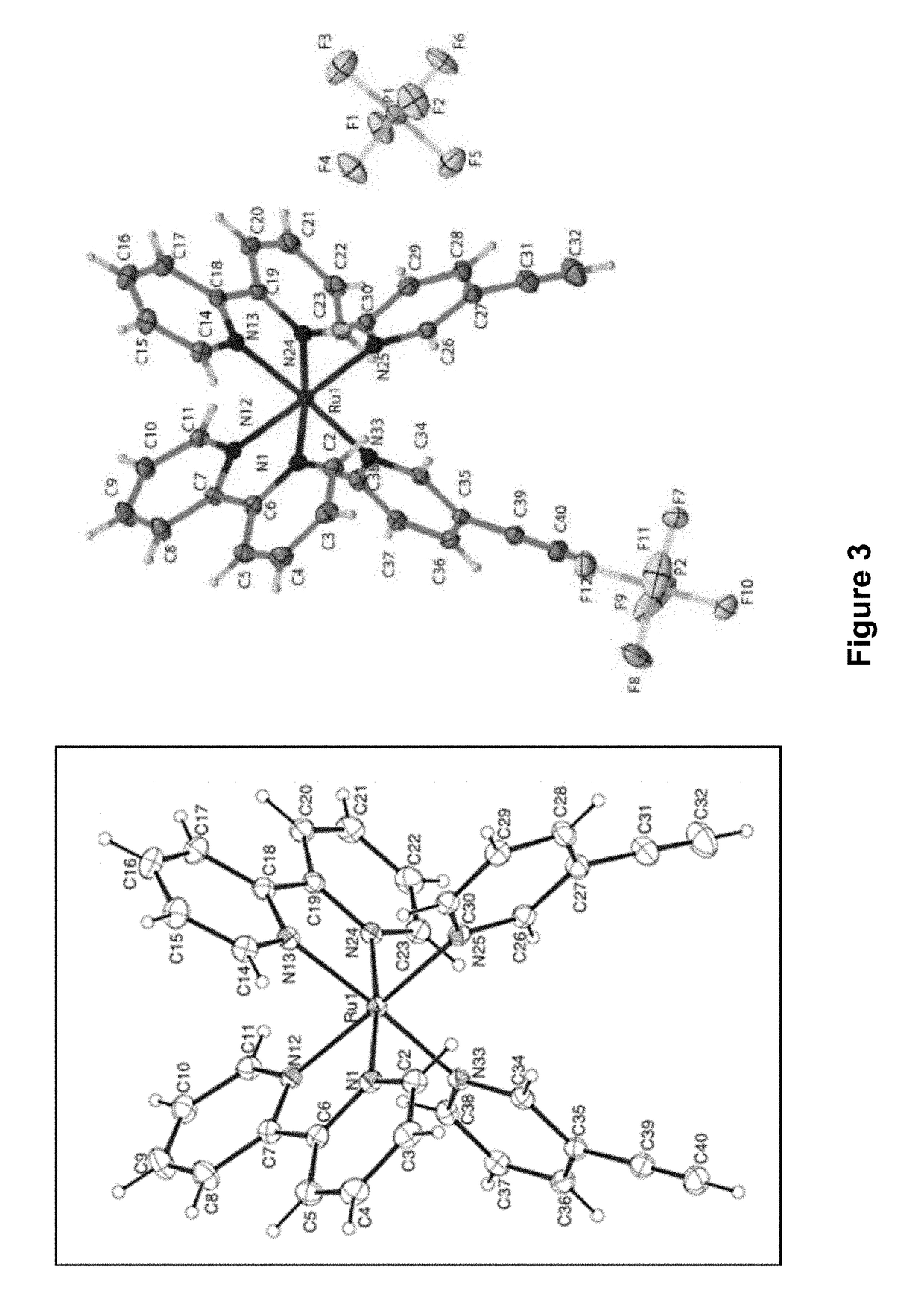
Ruthenium-Based Photolinkers and Methods of Use
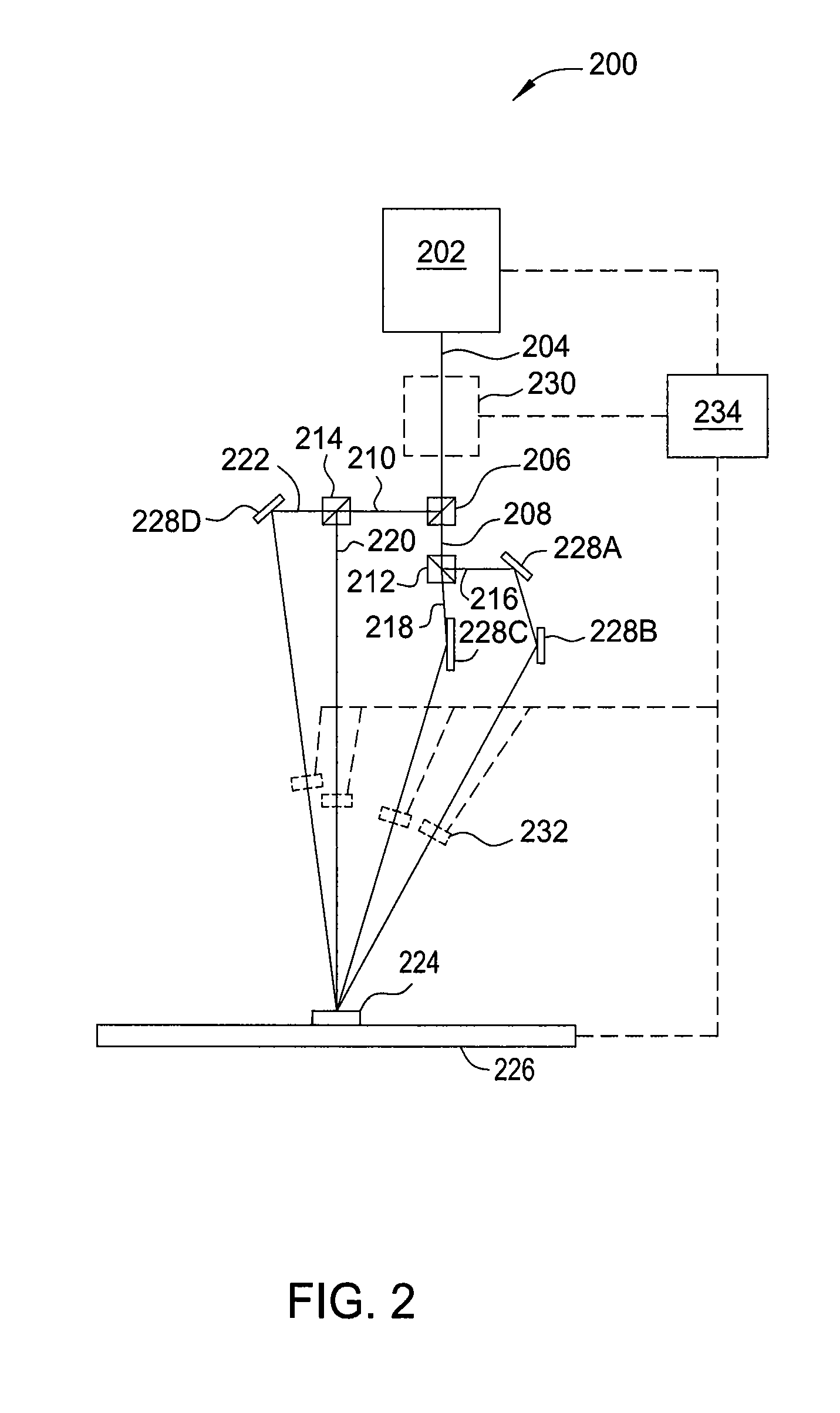
The present invention provides ruthenium-based photolinker compounds, caged molecules comprising the ruthenium-based photolinker compounds, and methods of use. In certain aspects, the compositions disclosed herein comprise an active domain conjugated to a ruthenium-based photolinker, such that irradiation of the photolinker exposes the active domain.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
Method and device for diagnosing validity of active domain names in IDC computer room
The invention discloses a method and a device for diagnosing the validity of active domain names in an IDC computer room. The method comprises: by comparing the acquired real server IP information with all server IP information in the local IDC computer room, judging whether the acquired real server IP belongs to the local server IP; by comparing the acquired real server IP information with the display server IP Information, to determine whether the obtained display server IP belongs to the real server IP; when the obtained real server IP belongs to the local server IP and the display server IP belongs to the real server IP at the same time, it is judged that the active domain name to be tested is a valid active domain name. The method provided by the present invention judges the validity of the active domain name, can effectively filter out invalid domain names, domain names that can be accessed but do not correspond to the IP address of the display server, and domain names in non-local IDC computer rooms, so as to ensure the authenticity of the active domain name to the greatest extent. sex and accuracy.
Owner:BEIJING ACT TECH DEV CO LTD +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com







![Homochiral metal-organic framework with enantiopure pillar[5]arene active domains Homochiral metal-organic framework with enantiopure pillar[5]arene active domains](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/e0942ae3-8526-48aa-803c-f9f555d3af98/US09815764-20171114-D00001.png)
![Homochiral metal-organic framework with enantiopure pillar[5]arene active domains Homochiral metal-organic framework with enantiopure pillar[5]arene active domains](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/e0942ae3-8526-48aa-803c-f9f555d3af98/US09815764-20171114-D00002.png)
![Homochiral metal-organic framework with enantiopure pillar[5]arene active domains Homochiral metal-organic framework with enantiopure pillar[5]arene active domains](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/e0942ae3-8526-48aa-803c-f9f555d3af98/US09815764-20171114-D00003.png)