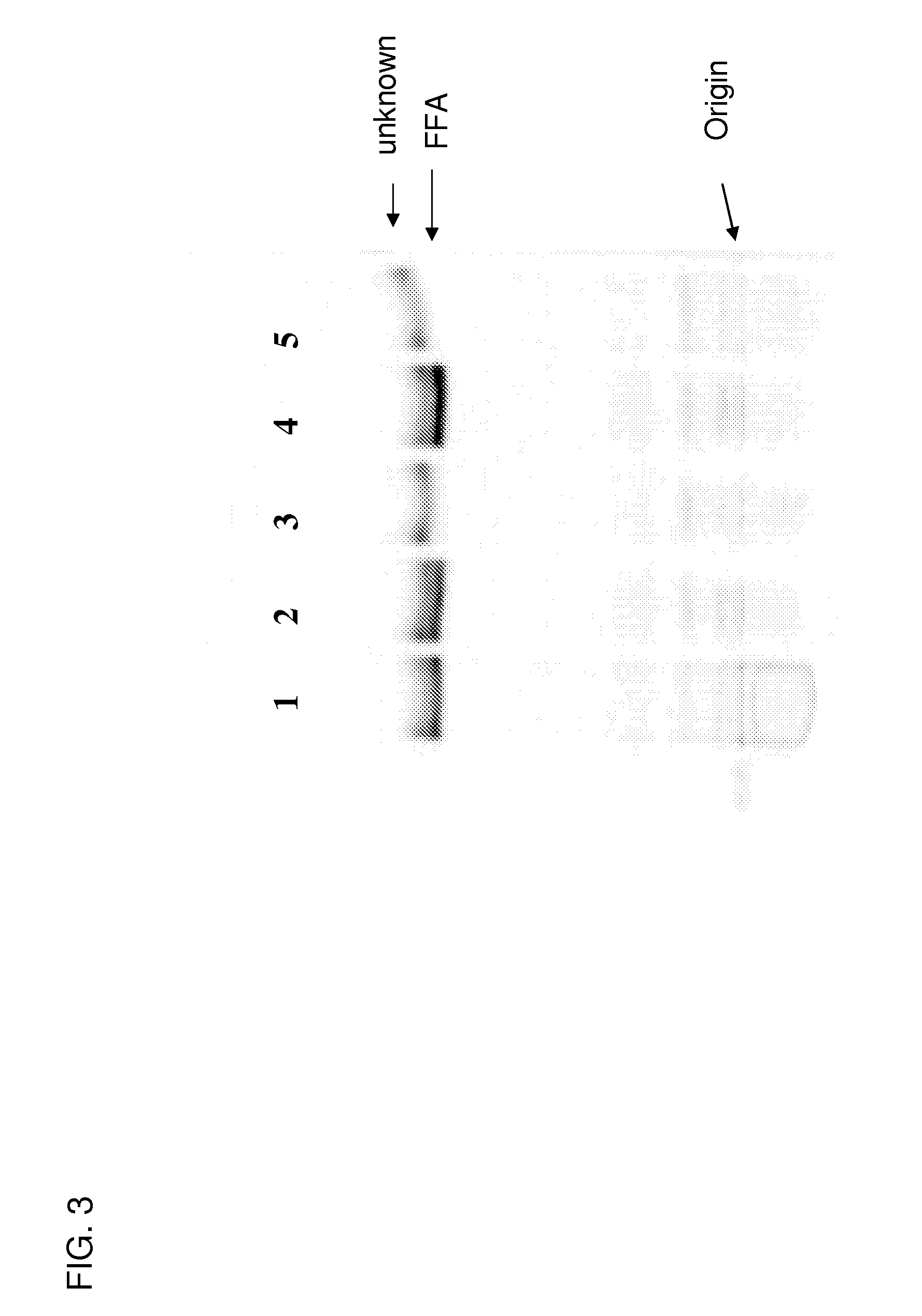
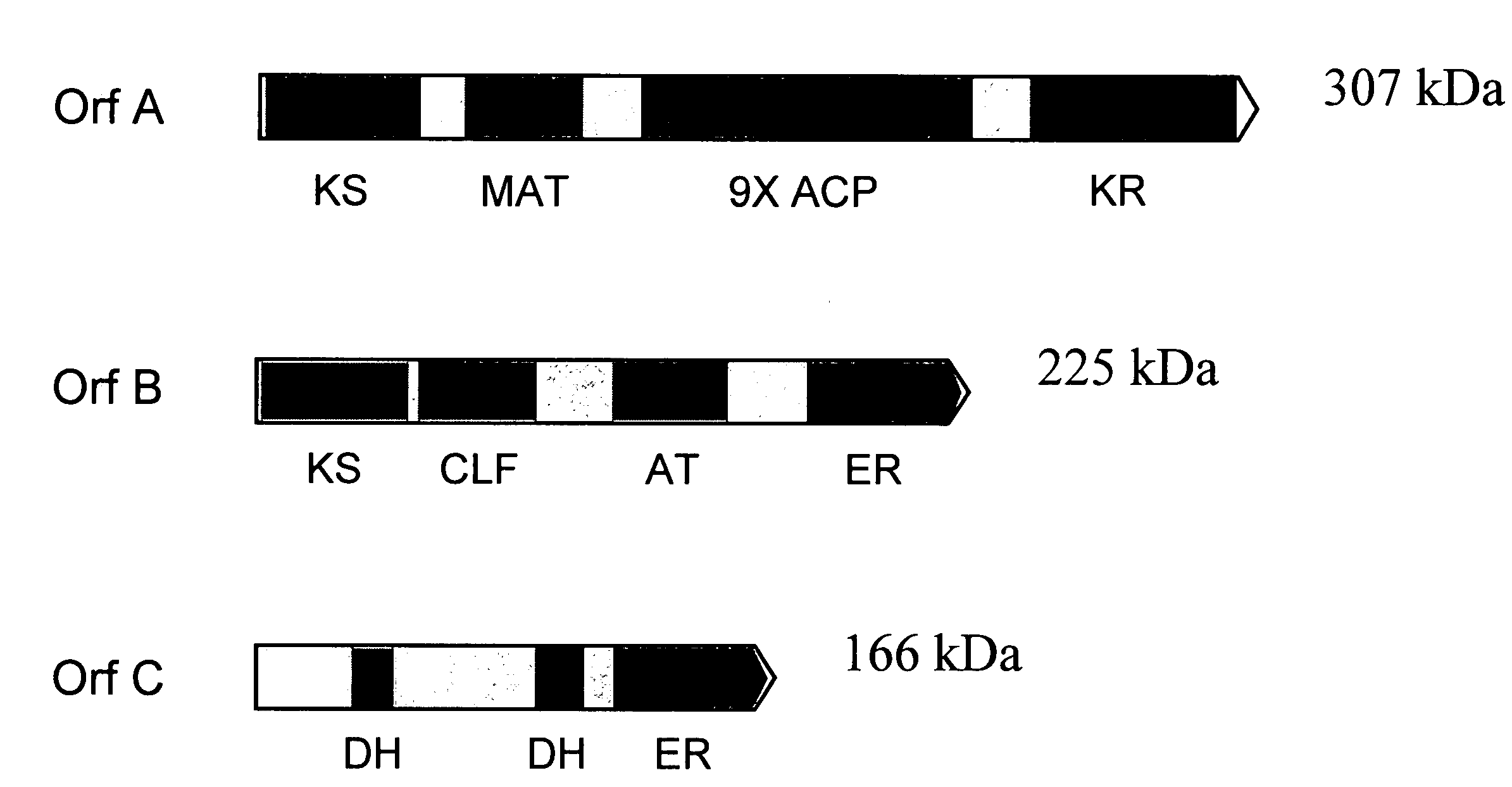
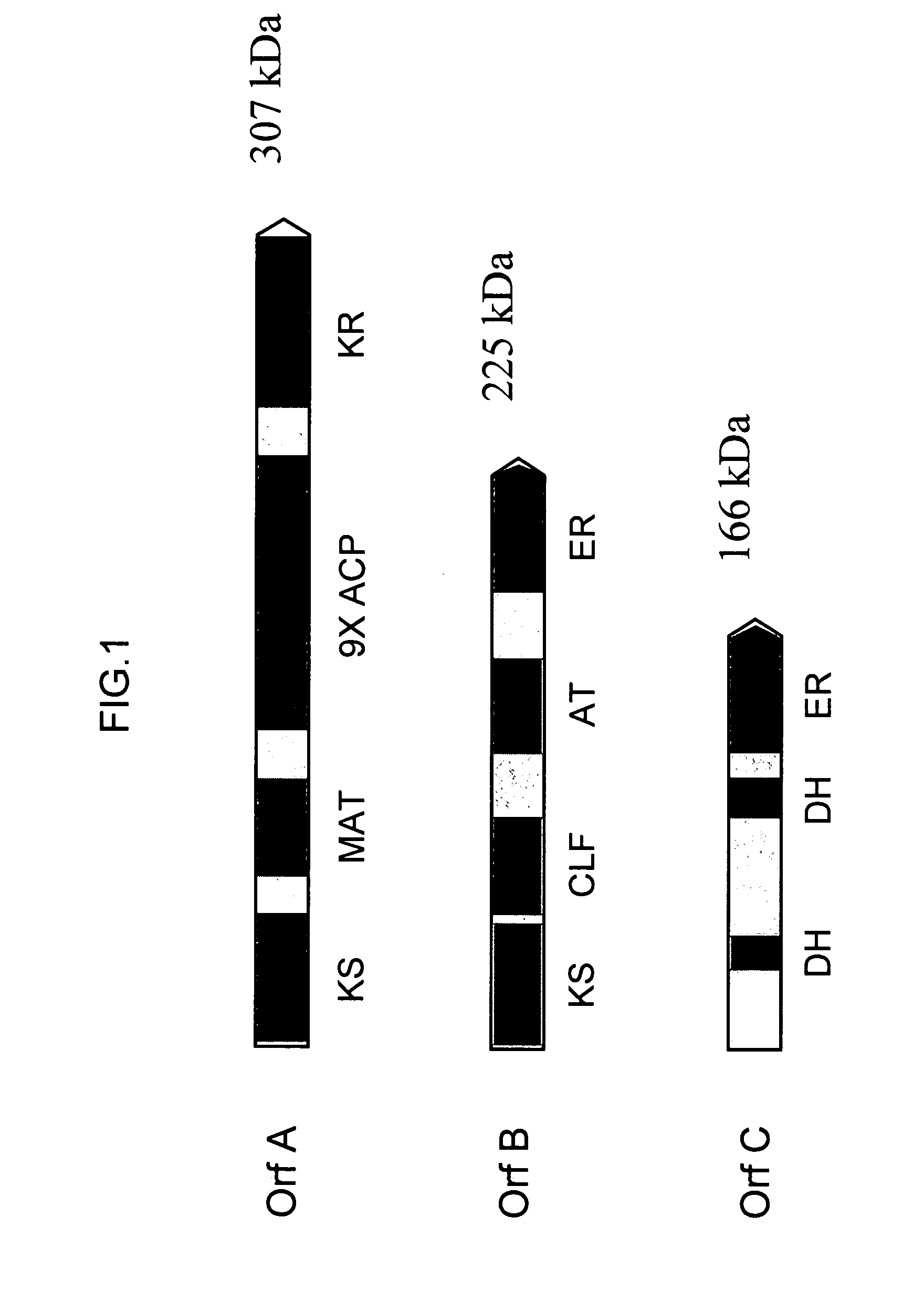
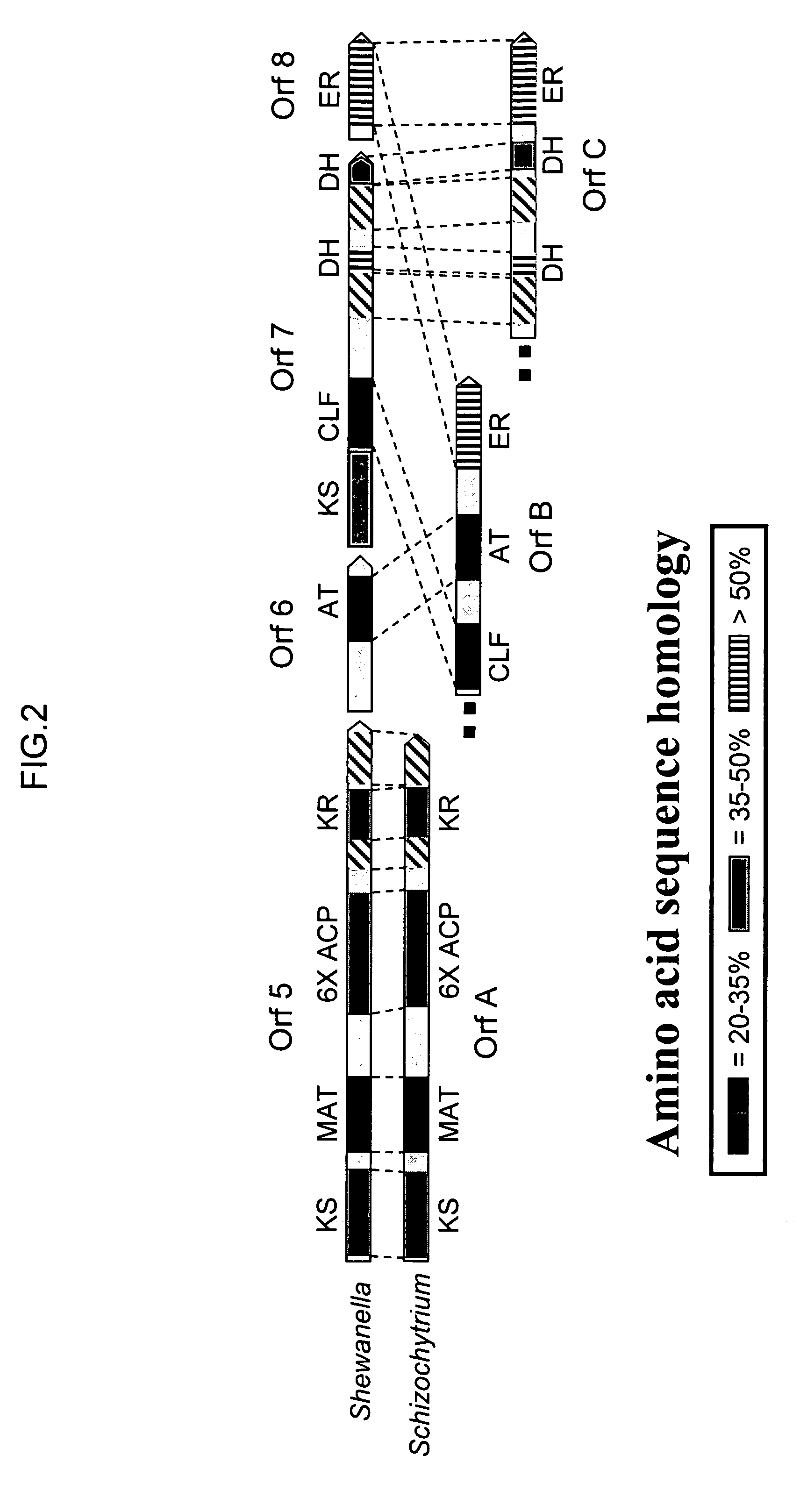
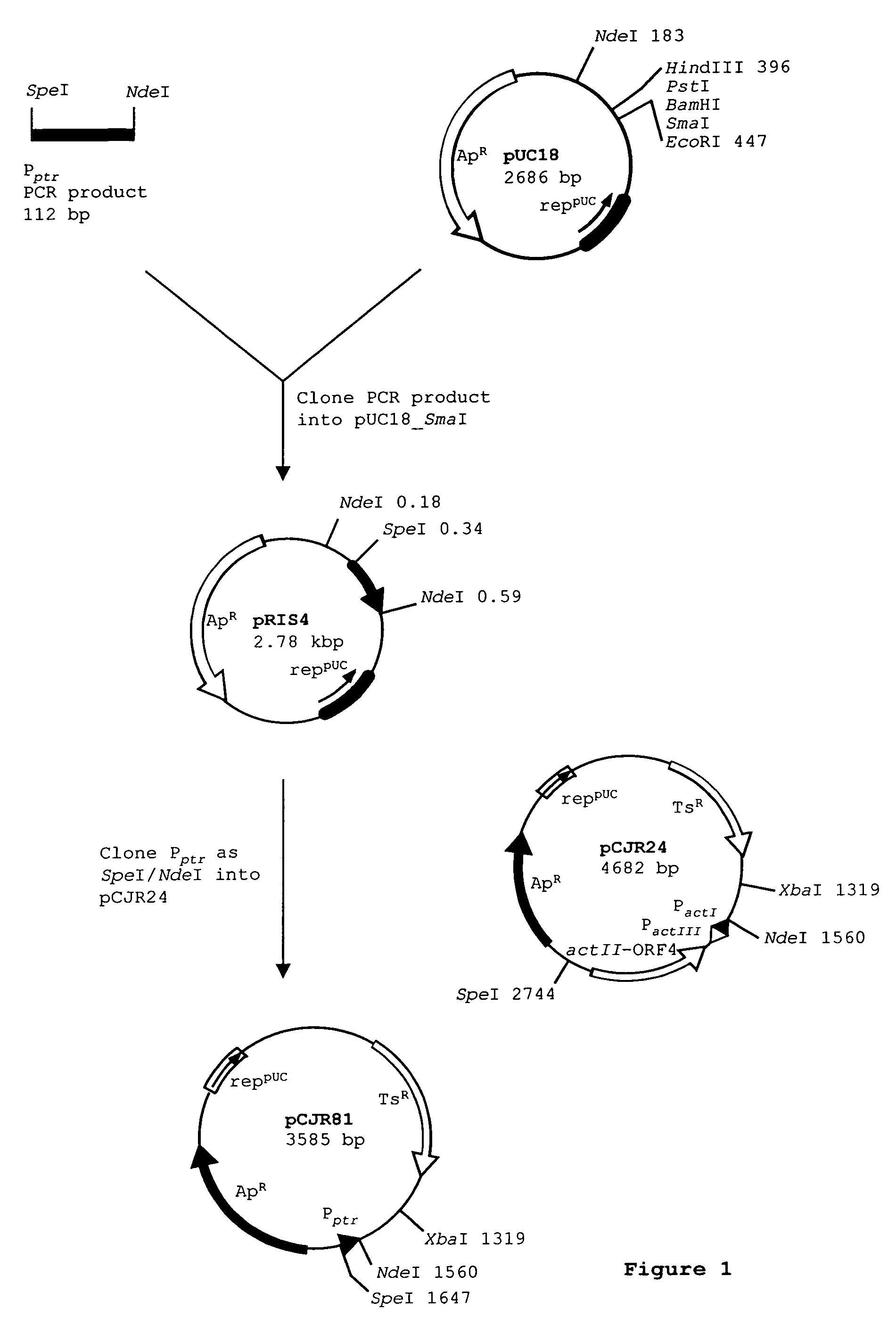
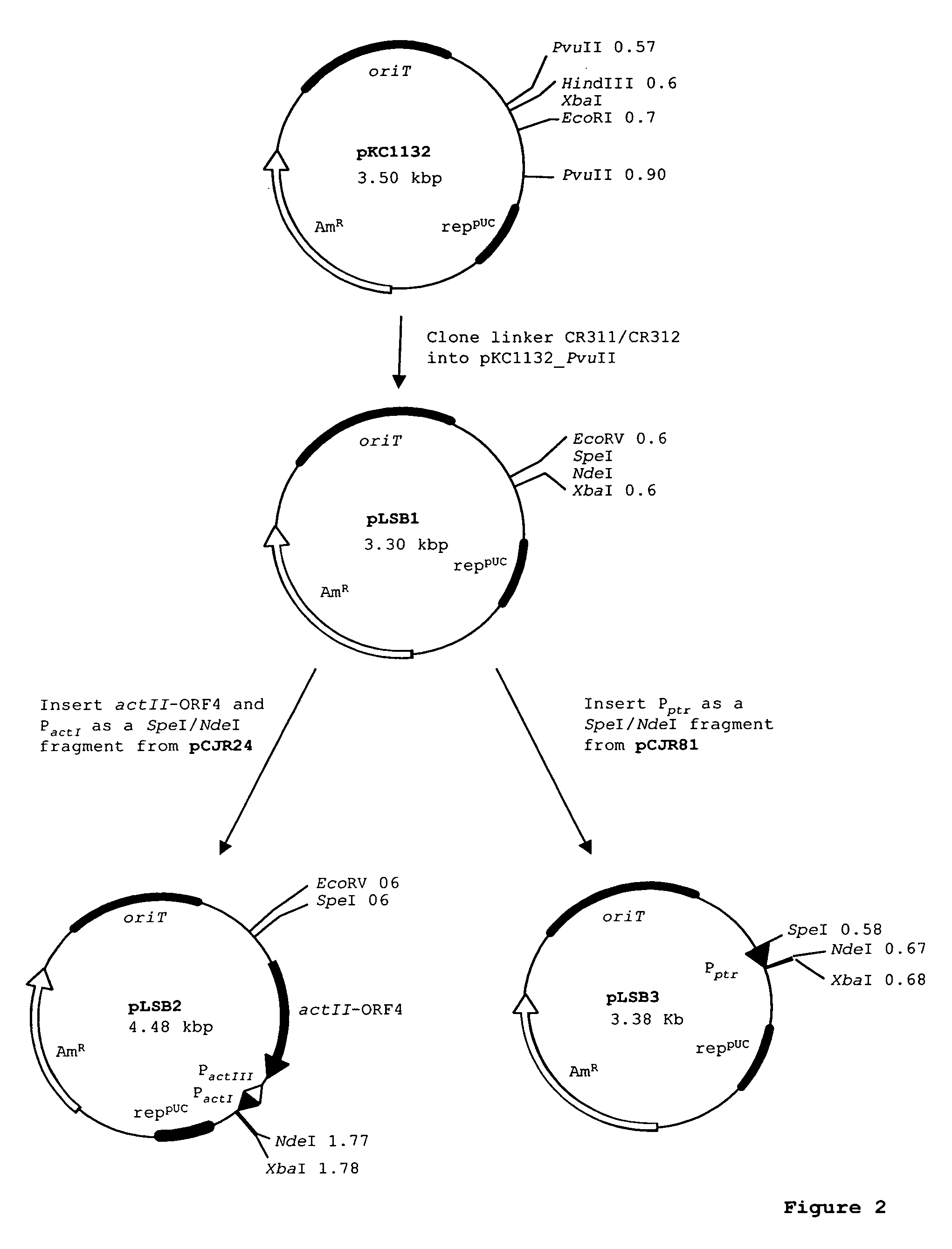
Patents
Literature
162 results about "Polyketide synthase" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
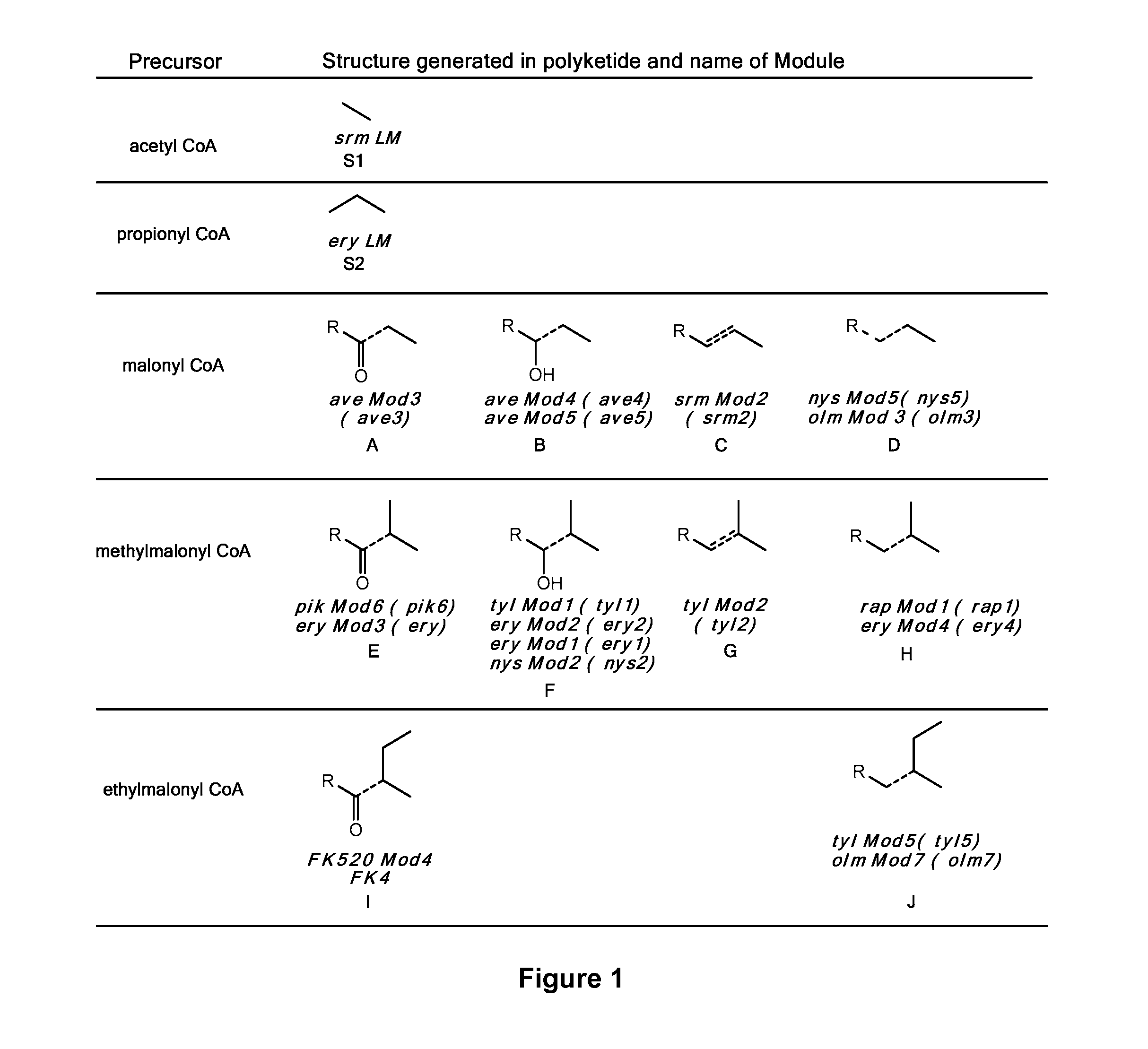
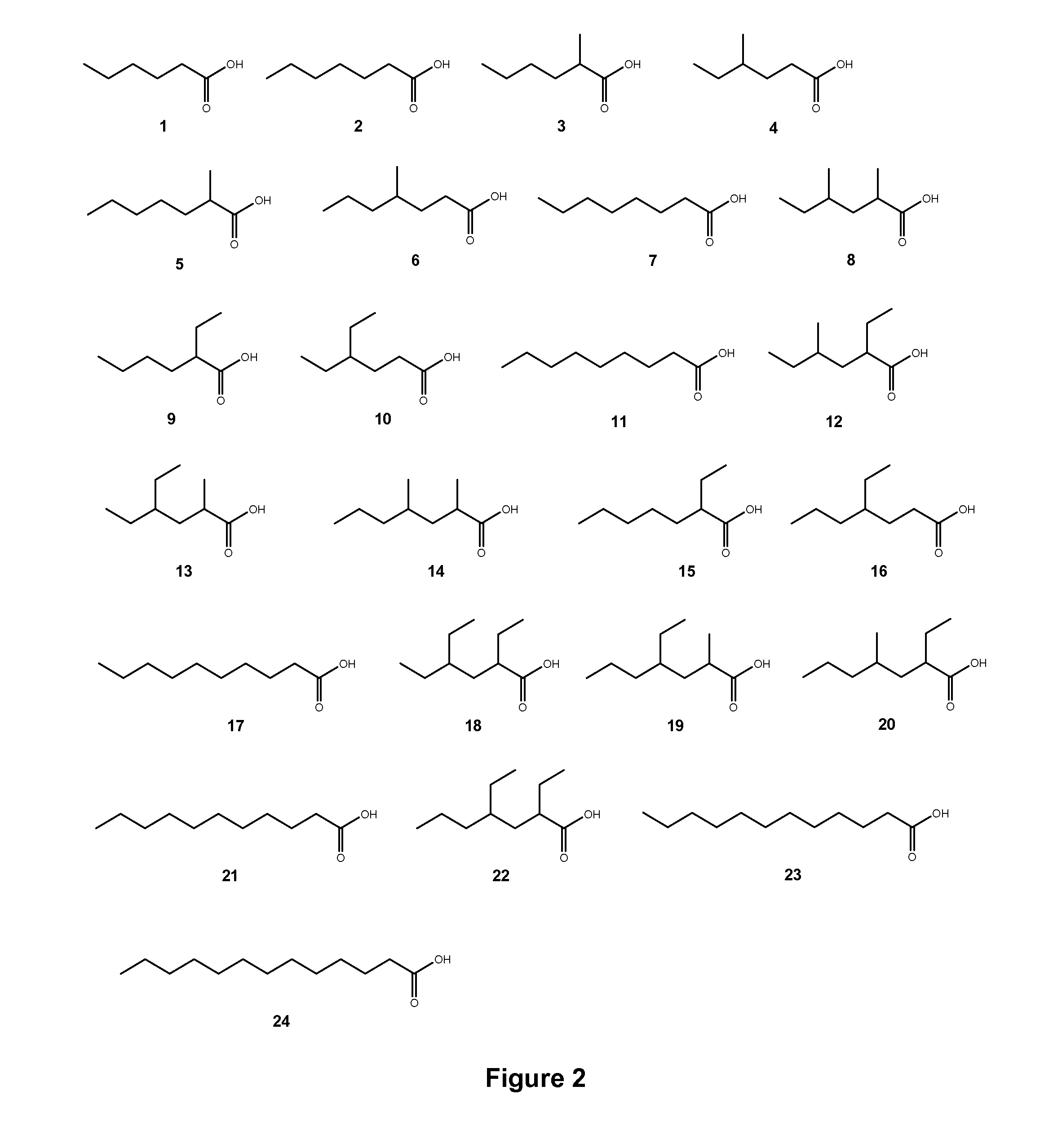
Polyketide synthases (PKSs) are a family of multi-domain enzymes or enzyme complexes that produce polyketides, a large class of secondary metabolites, in bacteria, fungi, plants, and a few animal lineages. The biosyntheses of polyketides share striking similarities with fatty acid biosynthesis.
Product and process for transformation of Thraustochytriales microorganisms
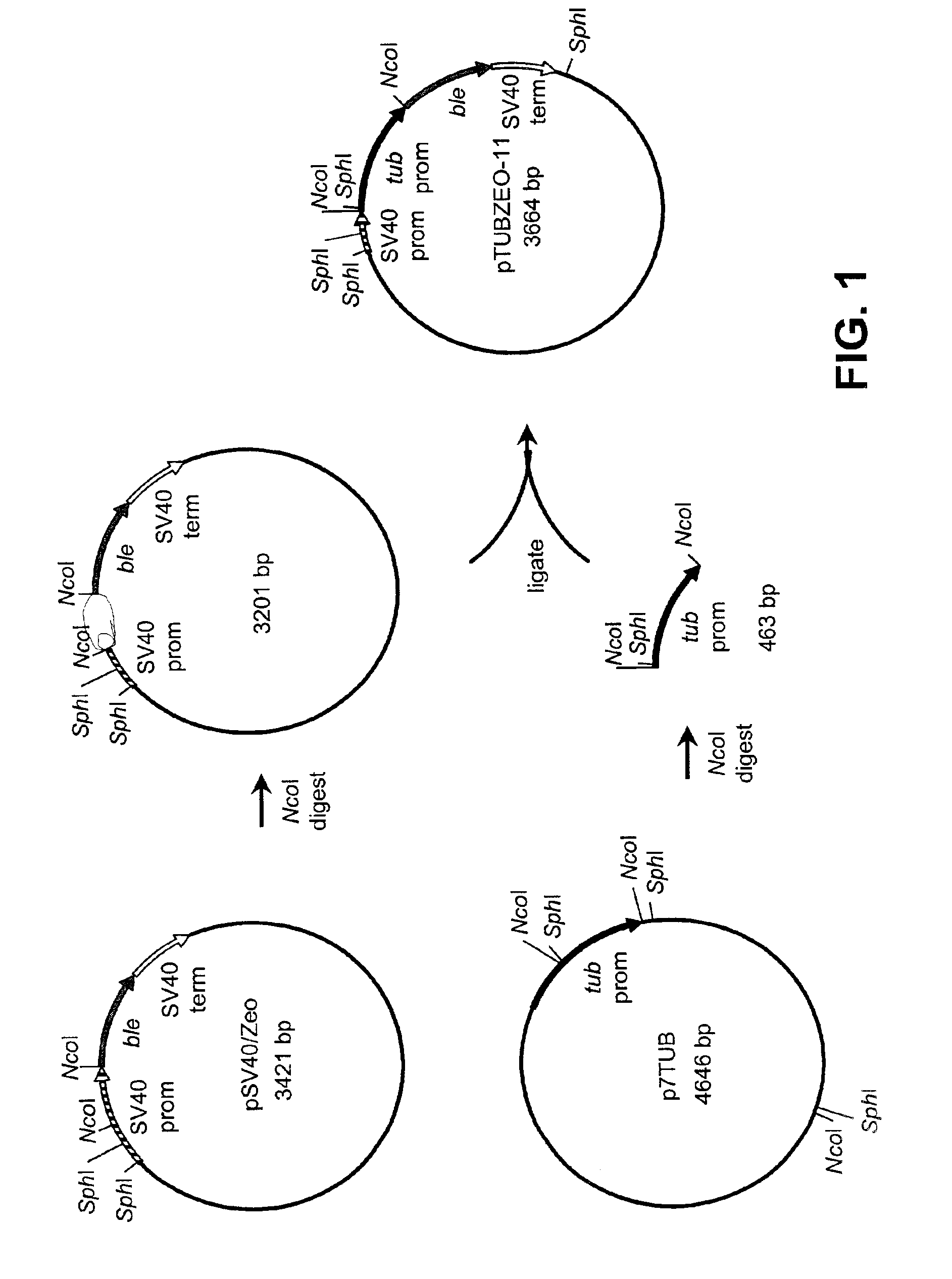
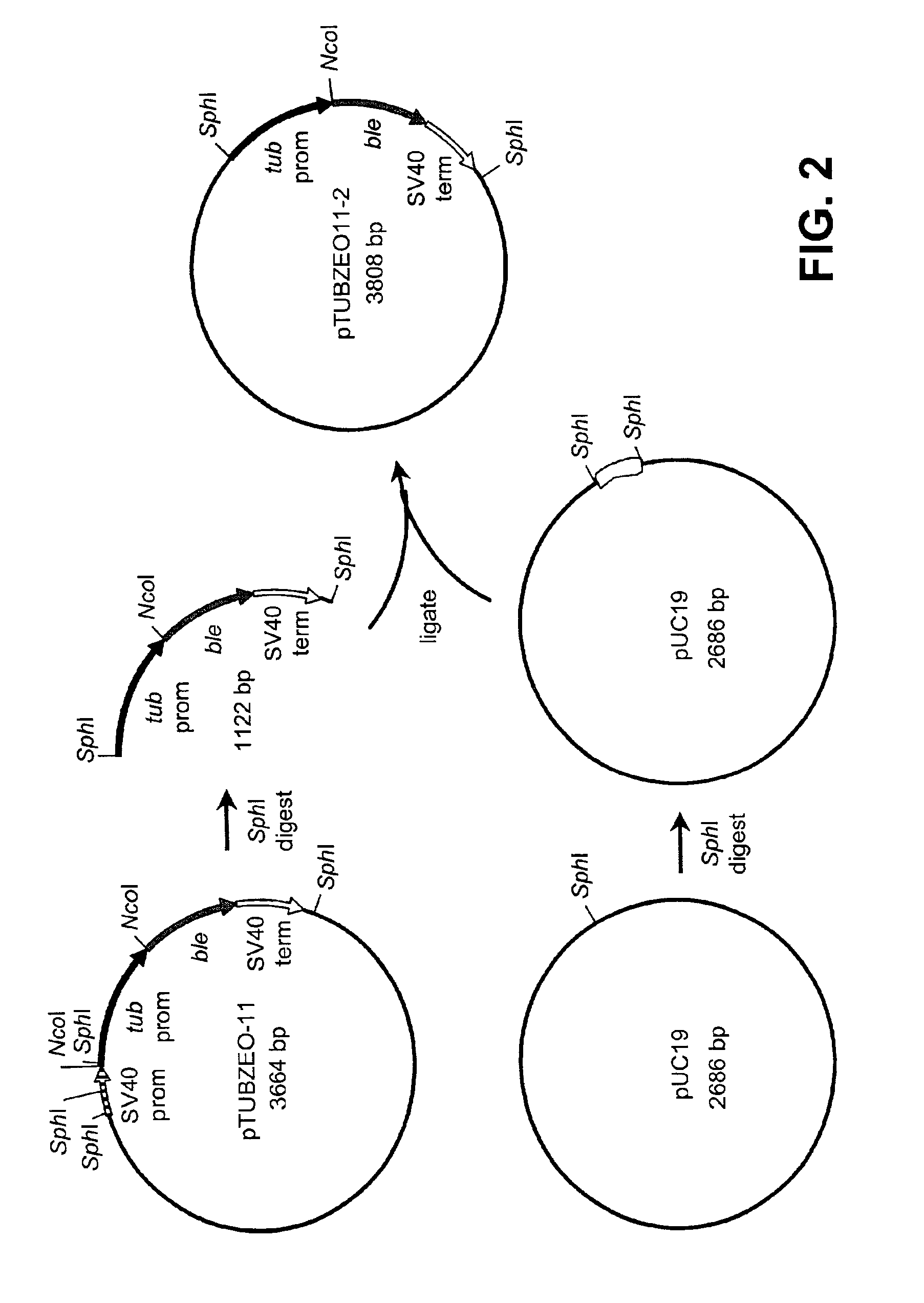
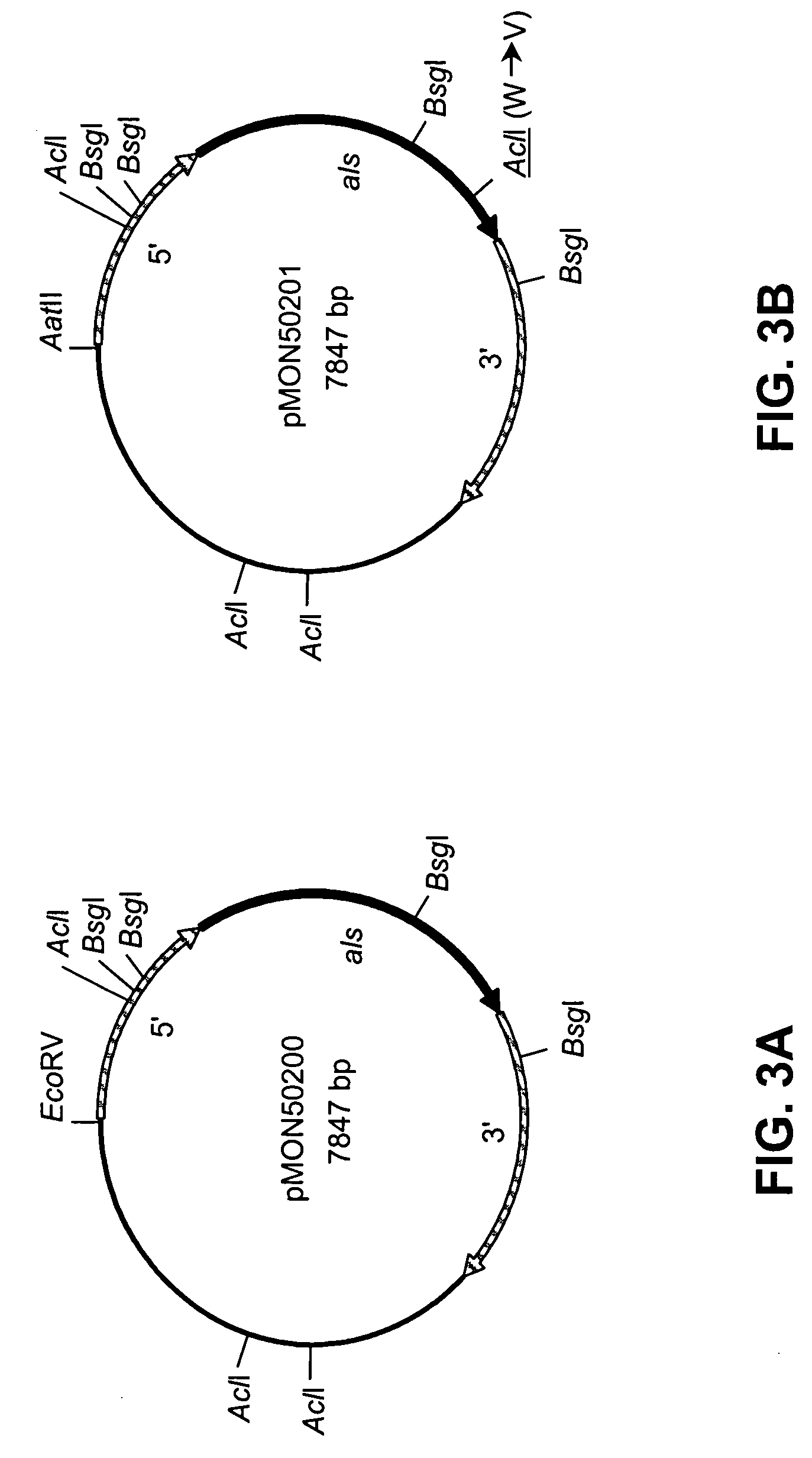
Disclosed are nucleic acid and amino acid sequences for acetolactate synthase, acetolactate synthase regulatory regions, α-tubulin promoter, a promoter from a Thraustochytriales polyketide synthase (PKS) system, and fatty acid desaturase promoter, each from a Thraustochytriales microorganism. Also disclosed are recombinant vectors useful for transformation of Thraustochytriales microorganisms, as well as a method of transformation of Thraustochytriales microorganisms. The recombinant nucleic acid molecules of the present invention can be used for the expression of foreign nucleic acids in a Thraustochytriales microorganism as well as for the deletion, mutation, or inactivation of genes in Thraustochytriales microorganisms.
Owner:DSM IP ASSETS BV
PUFA polyketide synthase systems and uses thereof
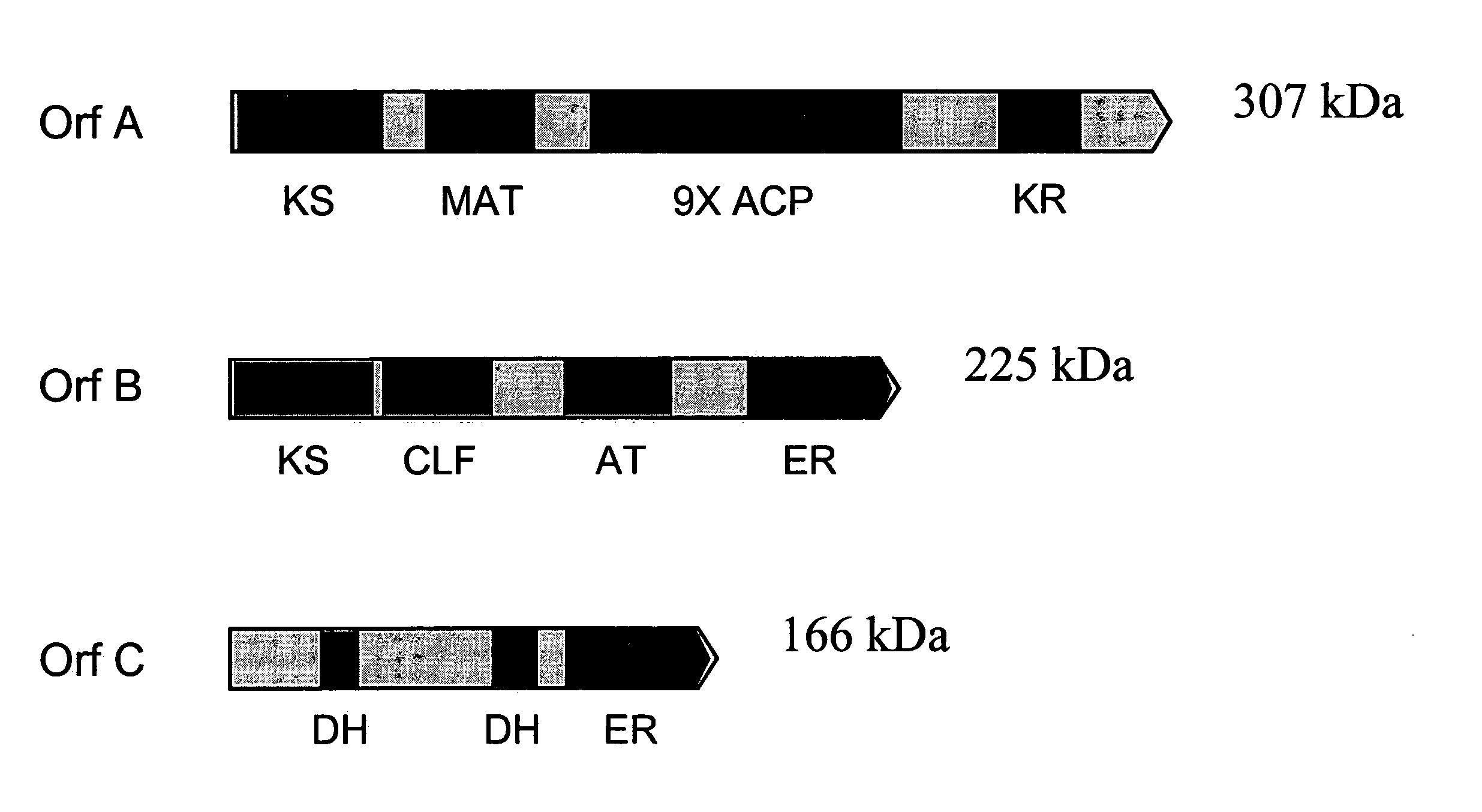
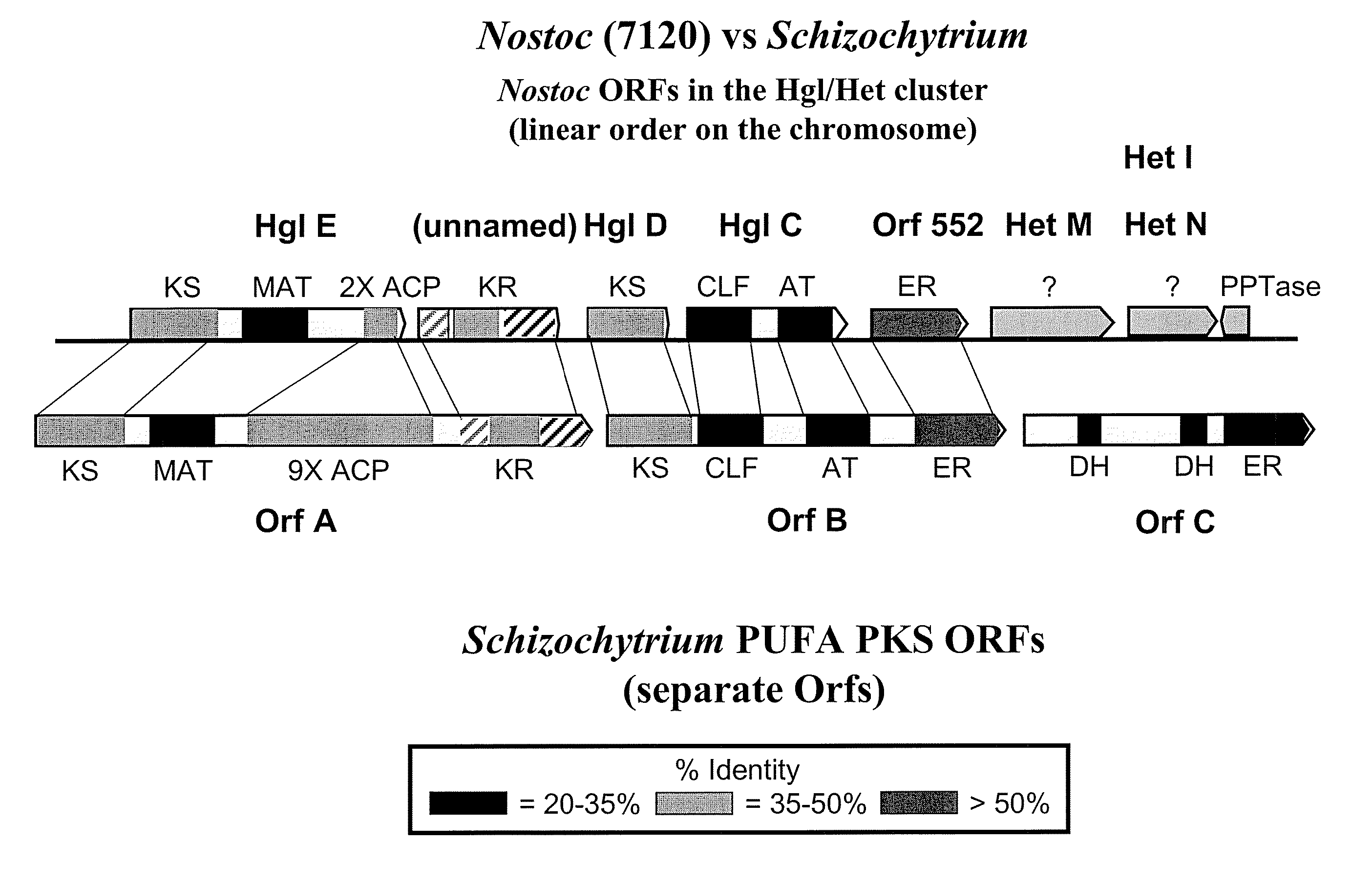
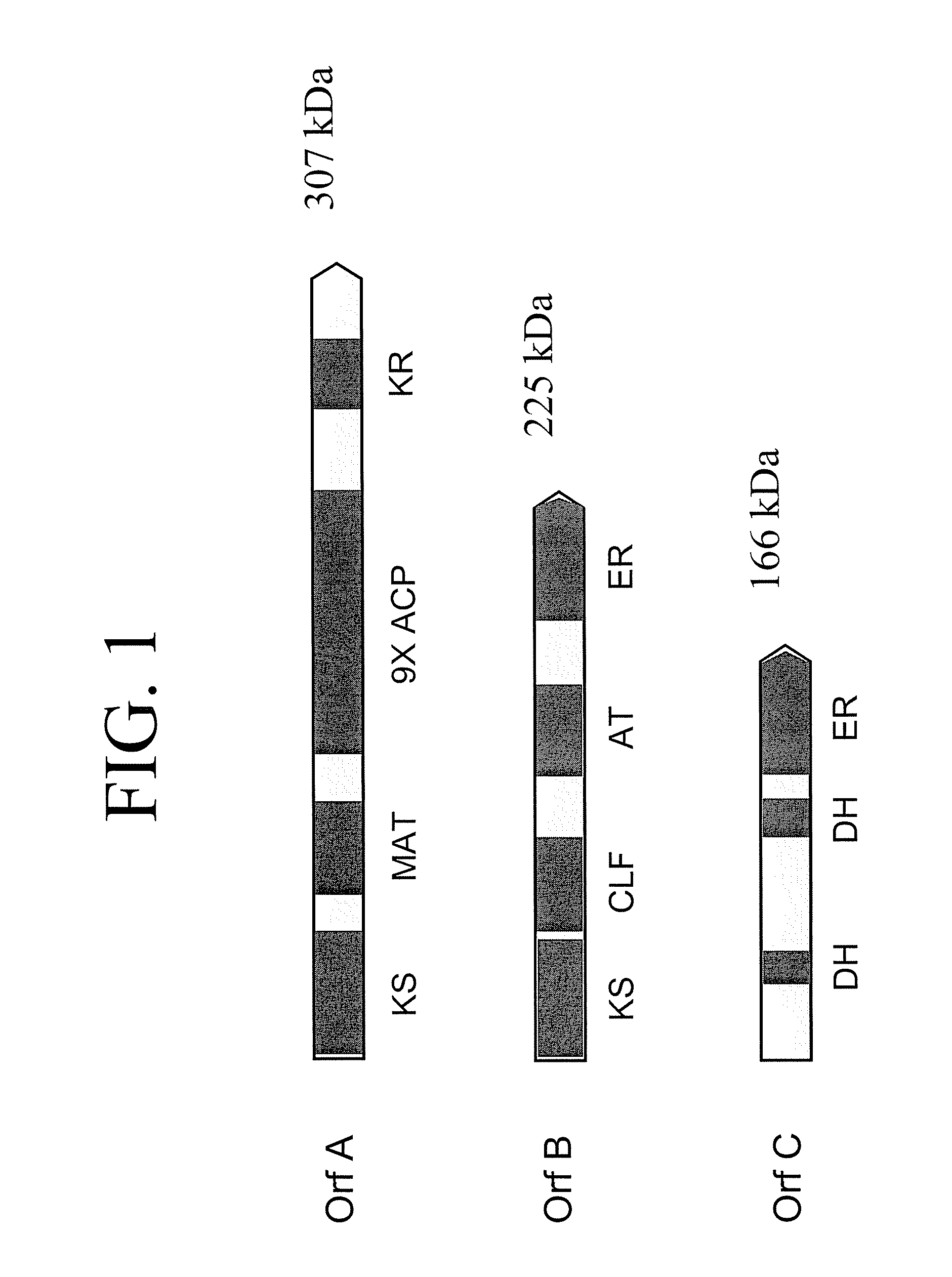
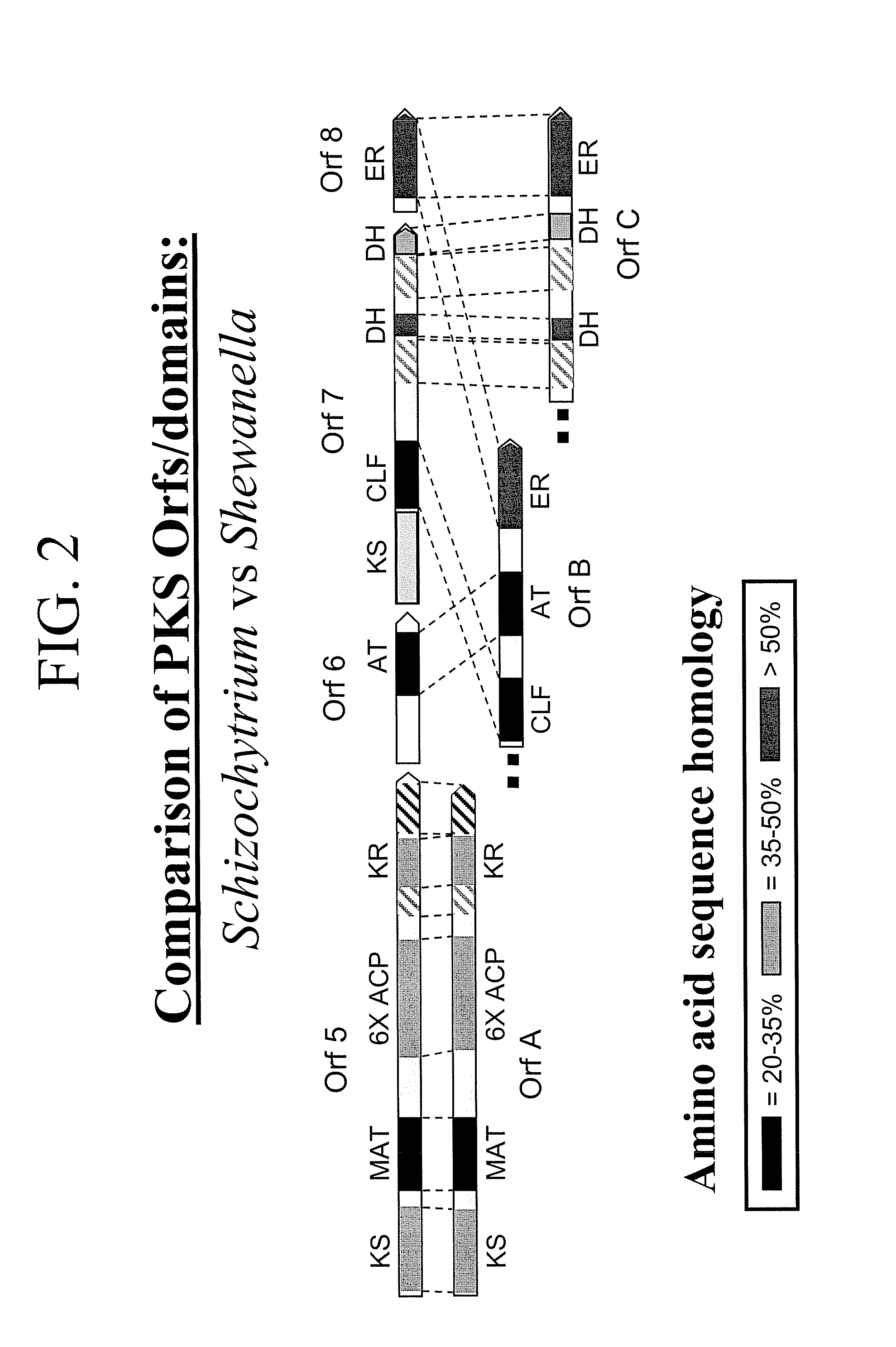
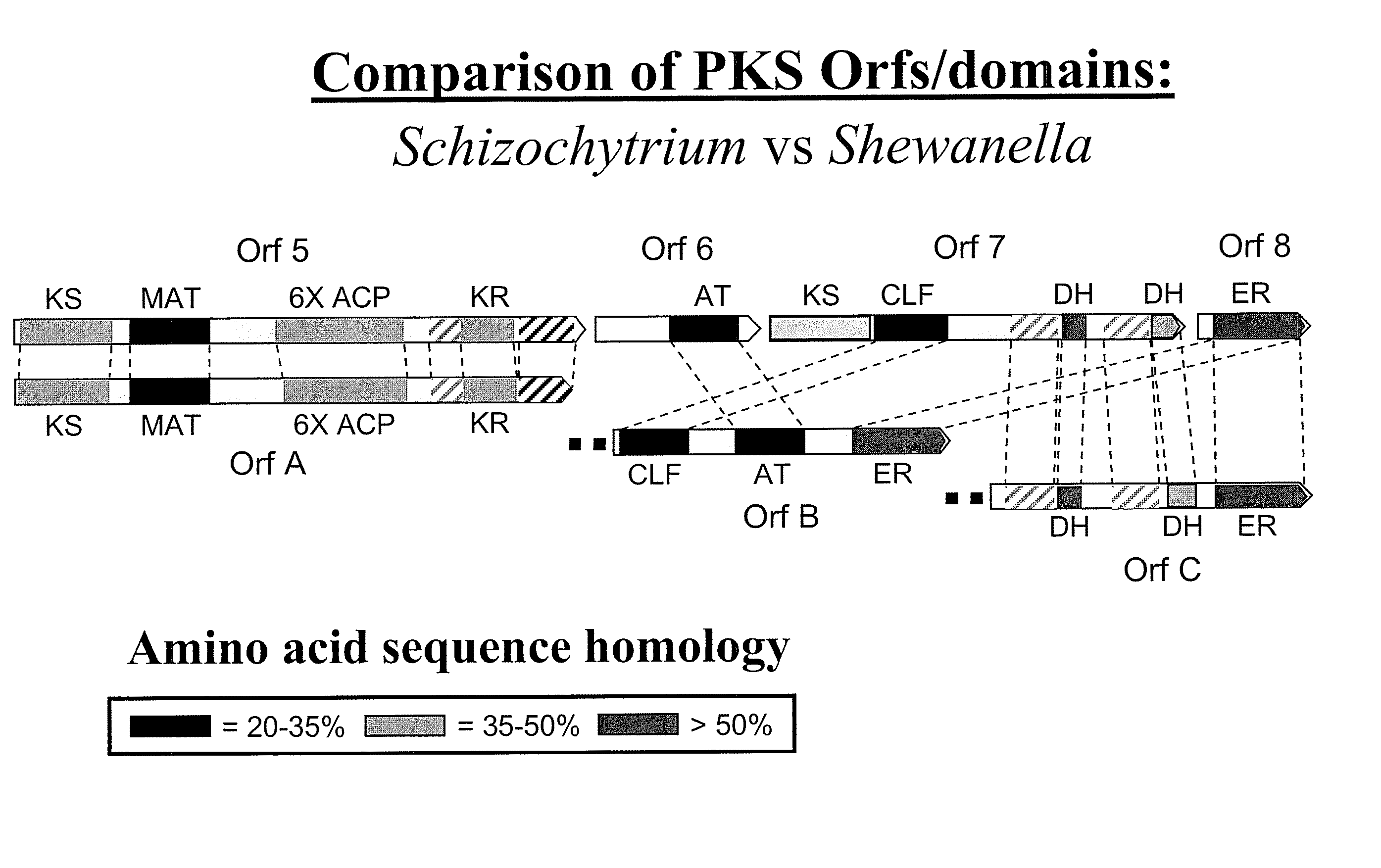
The invention generally relates to polyunsaturated fatty acid (PUFA) polyketide synthase (PKS) systems, to homologues thereof, to isolated nucleic acid molecules and recombinant nucleic acid molecules encoding biologically active domains of such a PUFA PKS system, to genetically modified organisms comprising PUFA PKS systems, to methods of making and using such systems for the production of bioactive molecules of interest, and to novel methods for identifying new bacterial and non-bacterial microorganisms having such a PUFA PKS system.
Owner:DSM IP ASSETS BV
Polyunsaturated fatty acid production in heterologous organisms using PUFA polyketide synthase systems
InactiveUS20070245431A1Improve the level ofReduce competitionOther foreign material introduction processesOxidoreductasesBiotechnologyHeterologous
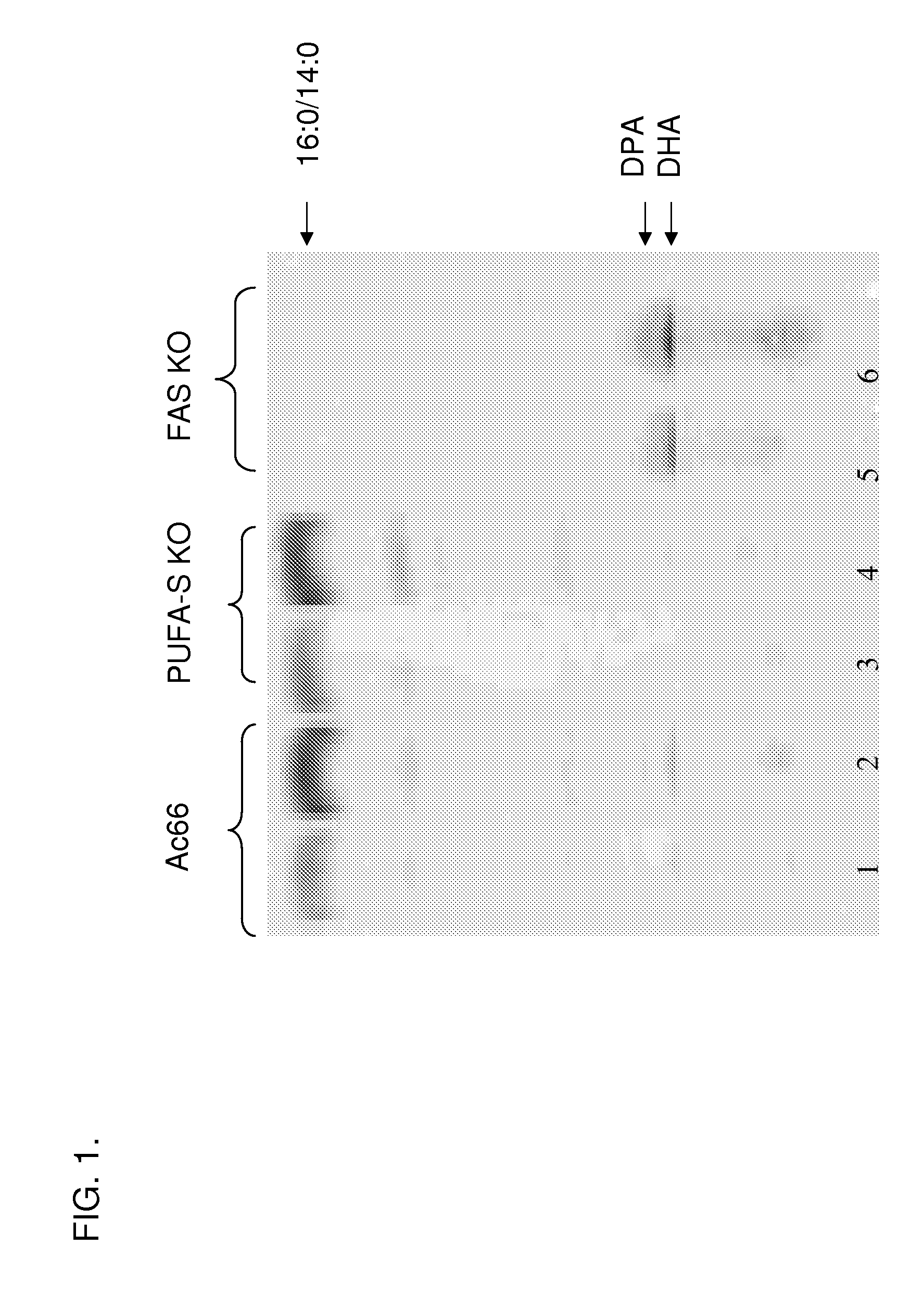
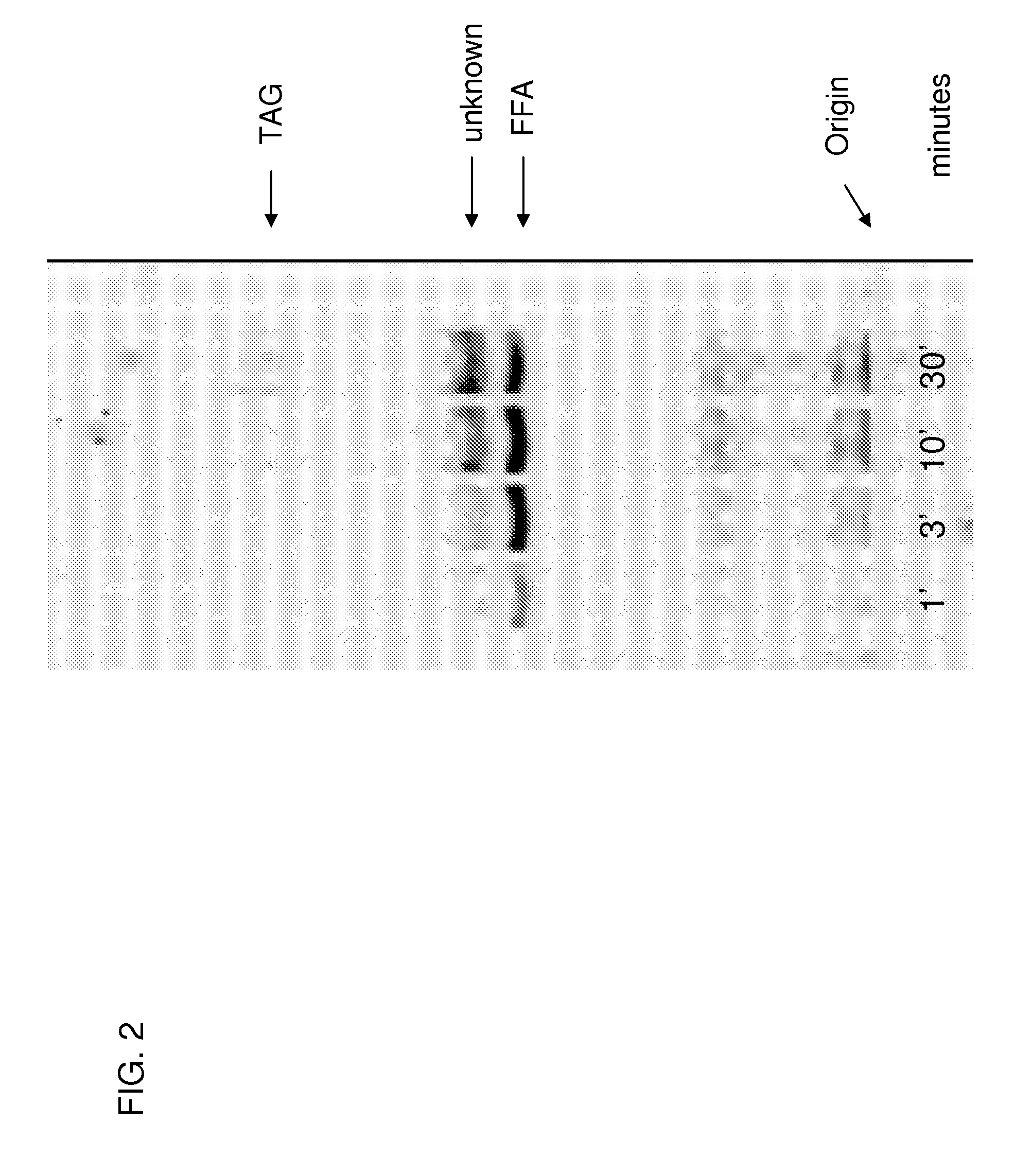
Disclosed are novel acyl-CoA synthetases and novel acyltransferases, nucleic acid molecules encoding the same, recombinant nucleic acid molecules and recombinant host cells comprising such nucleic acid molecules, genetically modified organisms (microorganisms and plants) comprising the same, and methods of making and using the same. Also disclosed are genetically modified organisms (e.g., plants, microorganisms) that have been genetically modified to express a PKS-like system for the production of PUFAs (a PUFA PKS system or PUFA synthase), wherein the organisms have been modified to express an acyl-CoA synthetase, to express an acyl transferase, to delete or inactivate a fatty acid synthase (FAS) expressed by the organism, to reduce competition for malonyl CoA with the PUFA synthase or to increase the level of malonyl CoA in the plant or plant cell, and in one aspect, to inhibit KASII or KASIII. Additional modifications, and methods to make and use such organisms, in addition to PUFAs and oils obtained from such organisms, are disclosed, alone with various products including such PUFAs and oils.
Owner:SEMBIOSYS GENETICS INC +1
PUFA polyketide synthase systems and uses thereof
InactiveUS7271315B2BryophytesOther foreign material introduction processesLipid formationBiotechnology
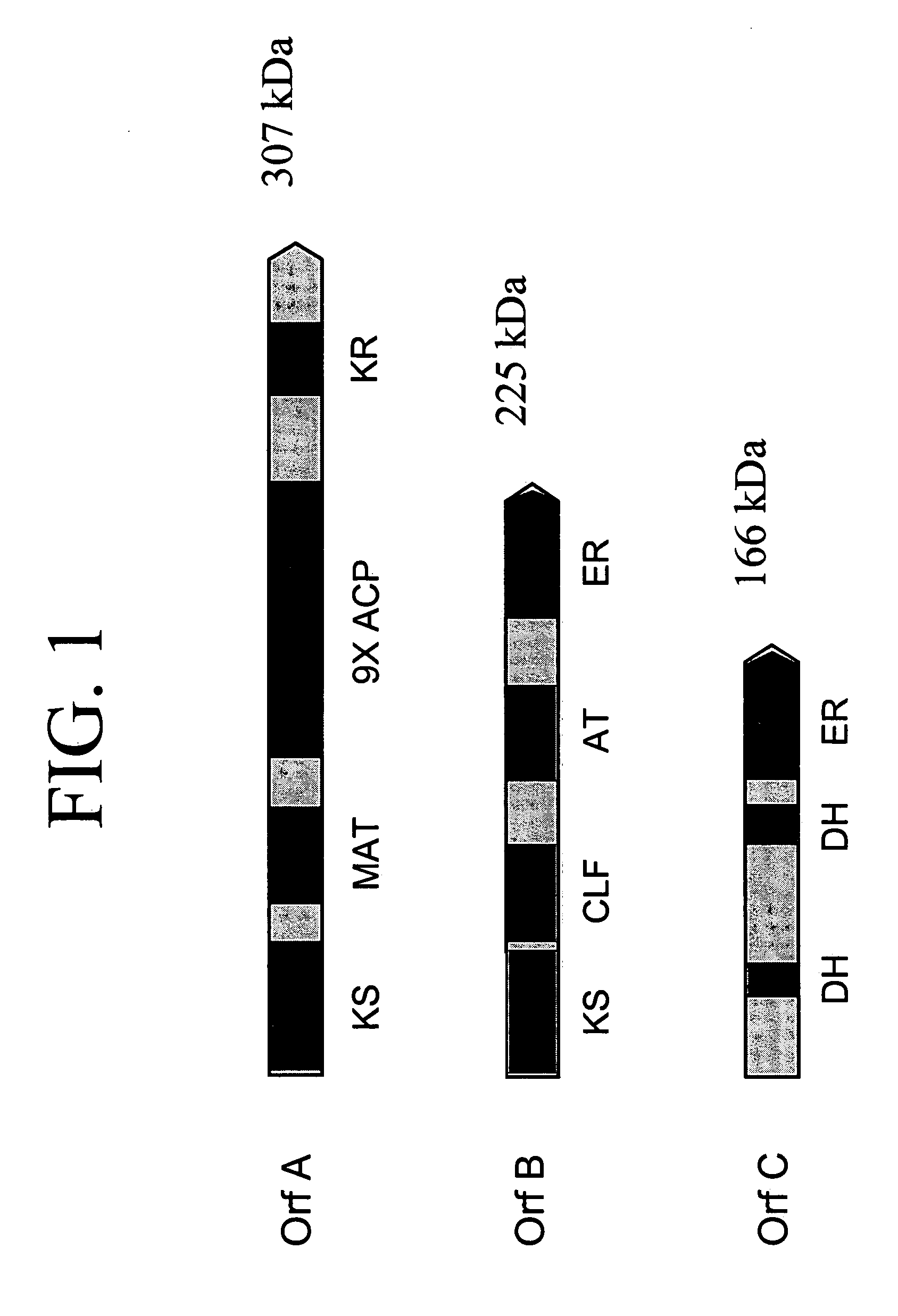
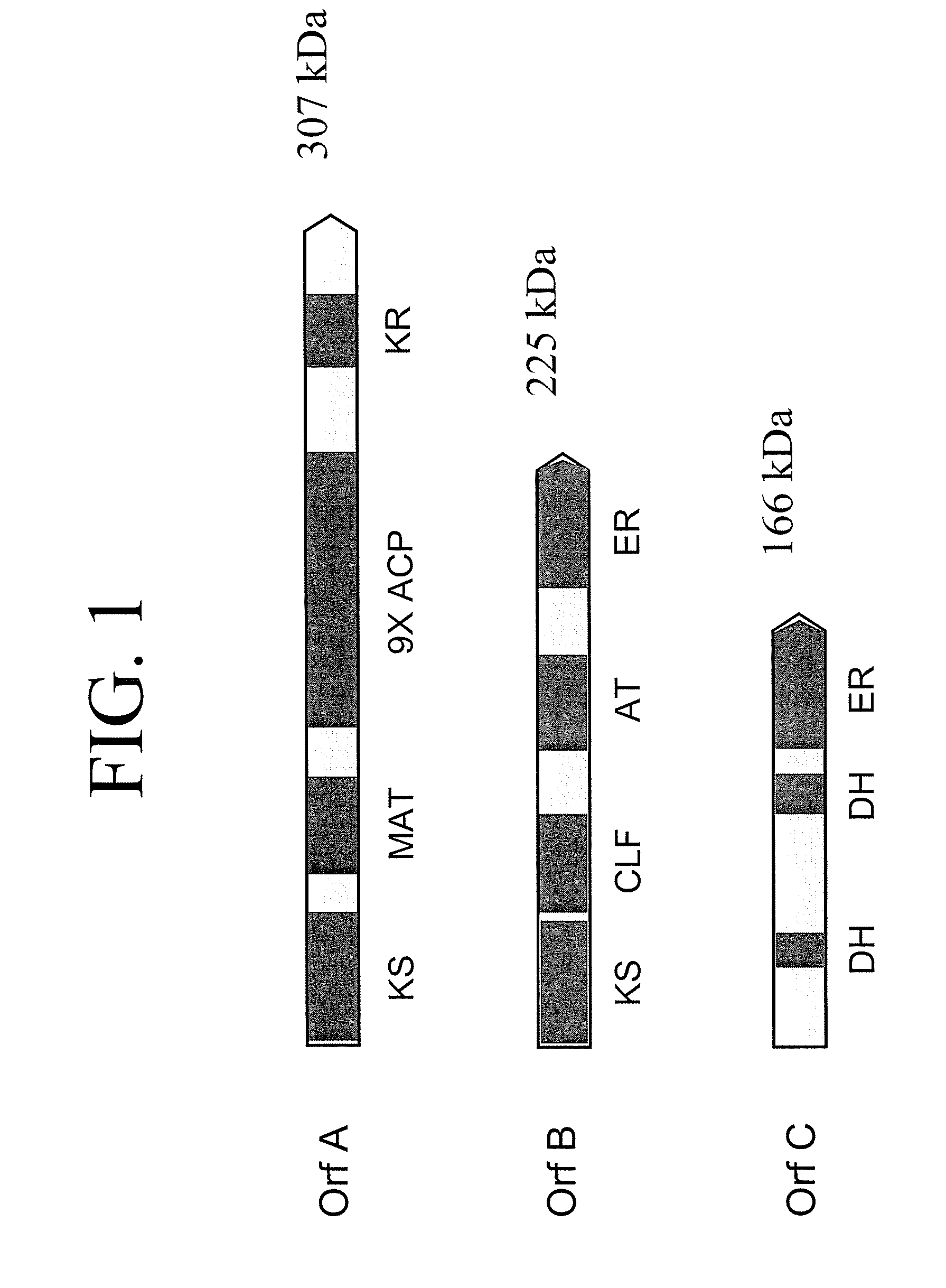
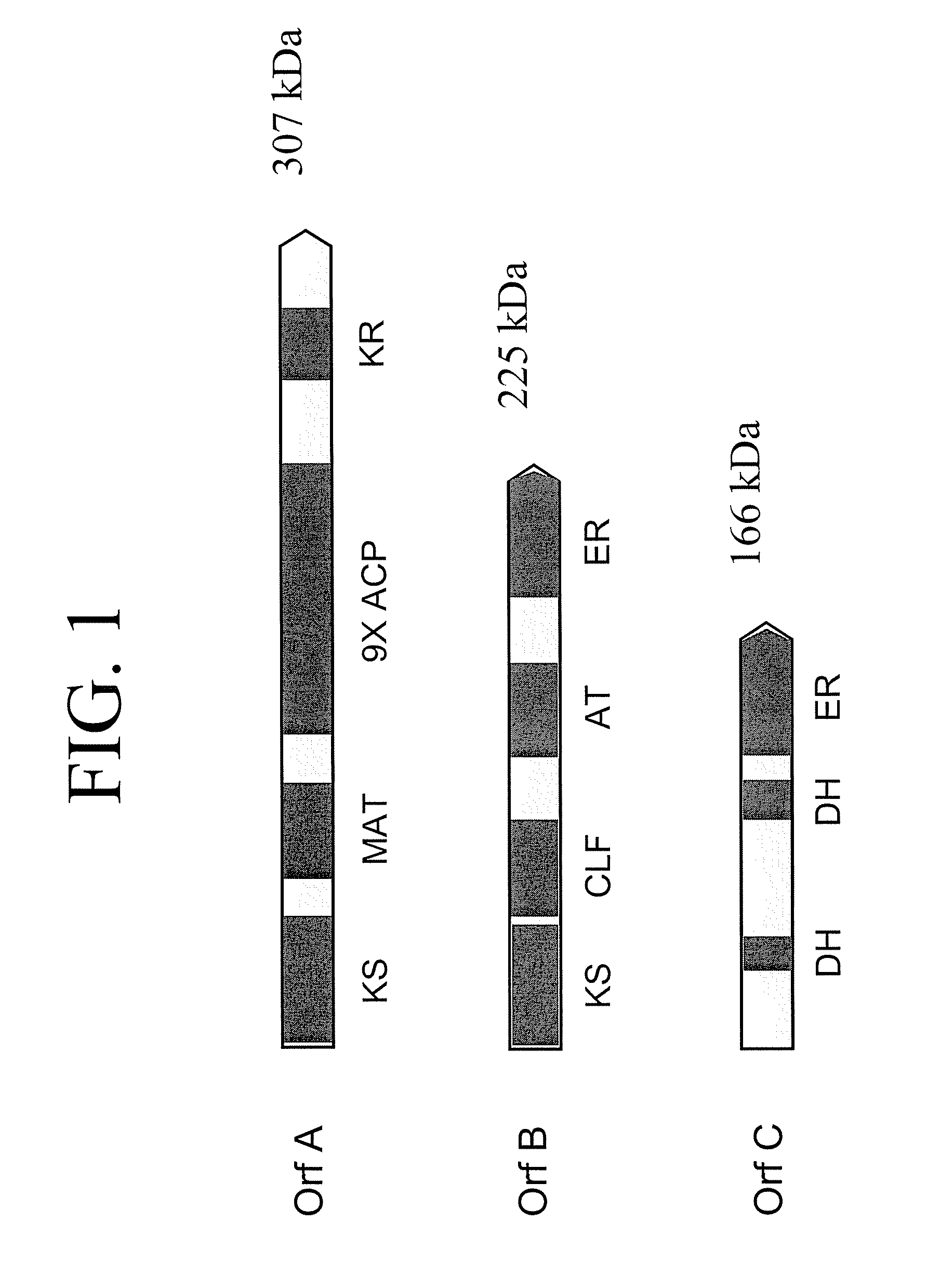
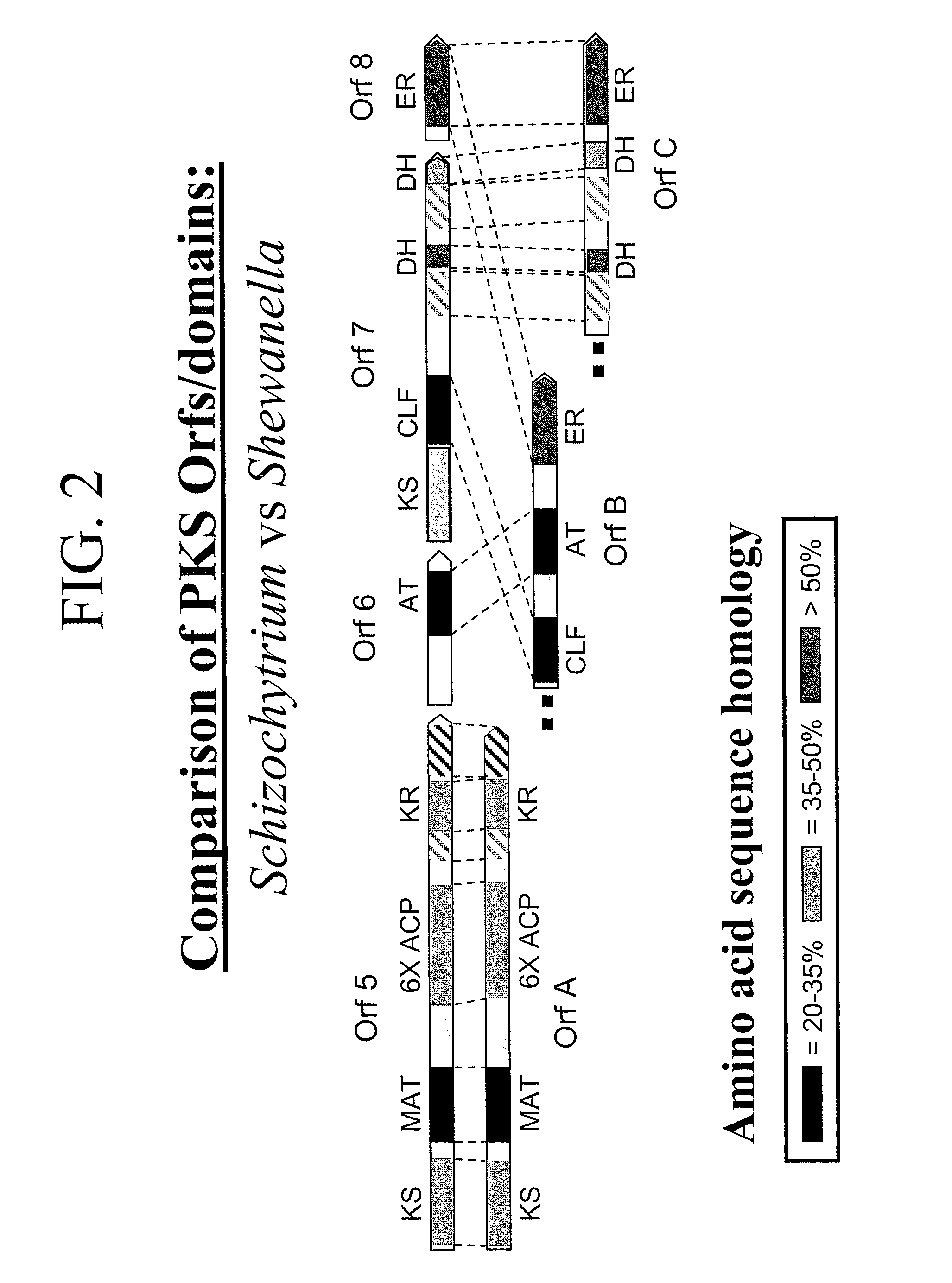
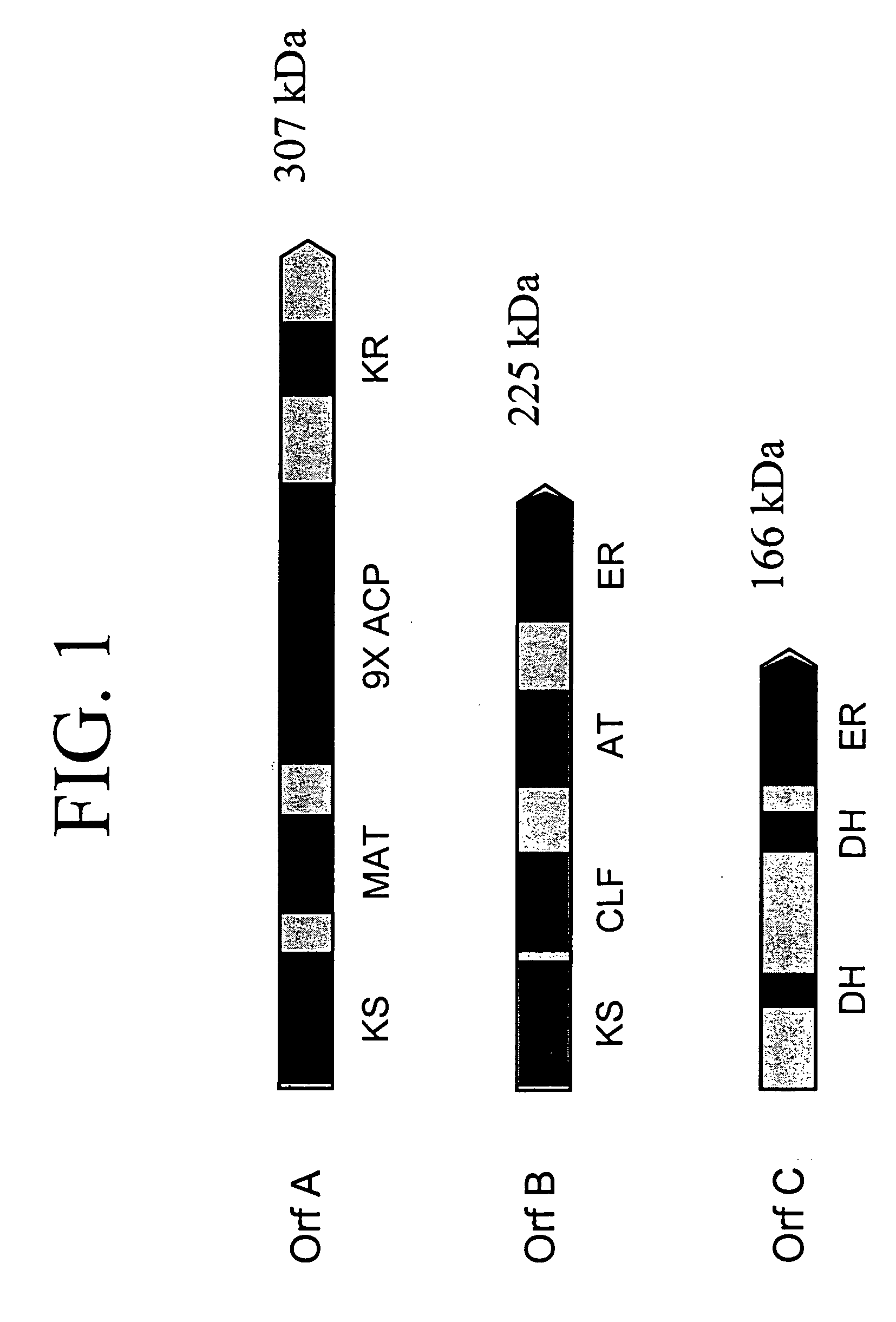
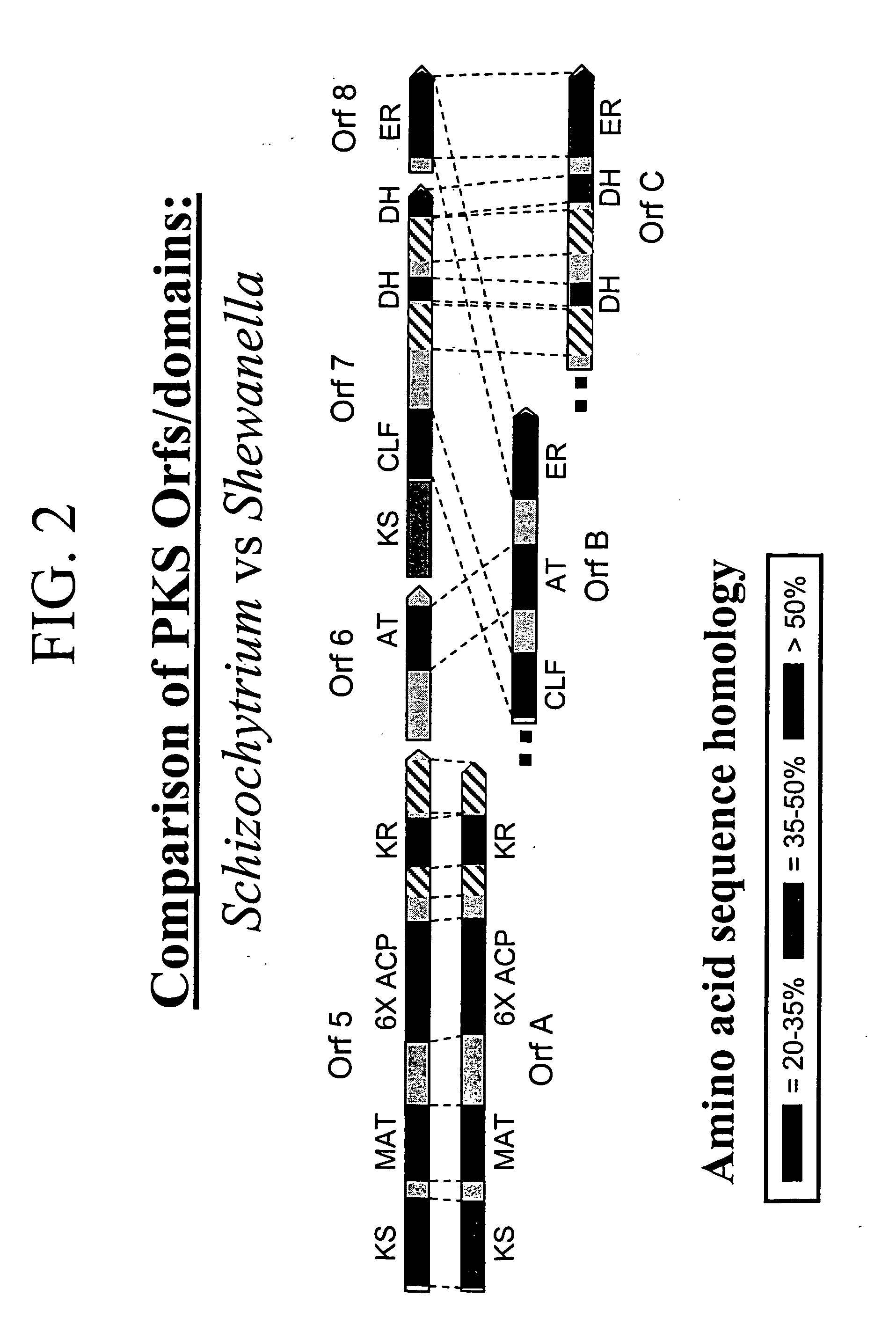
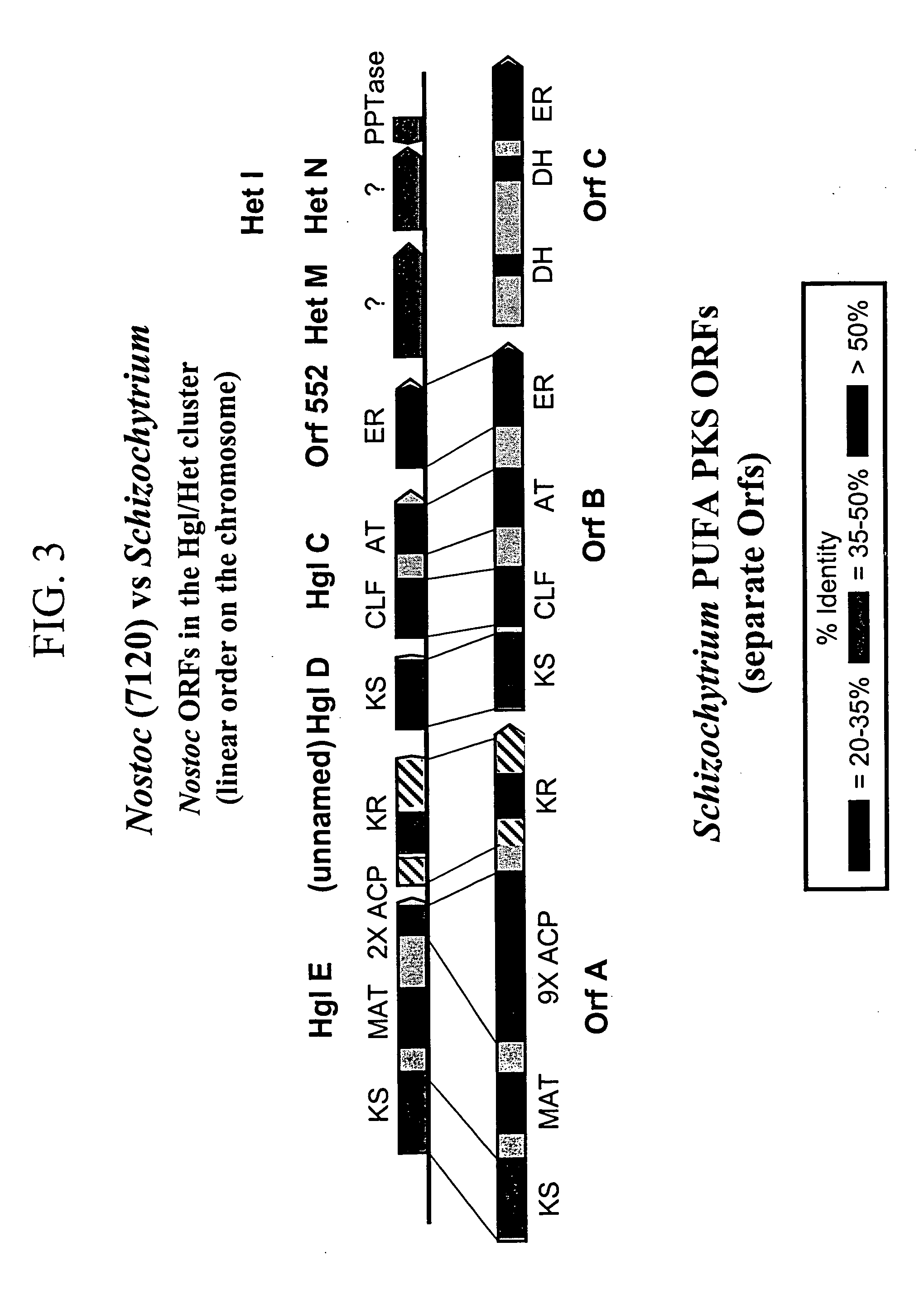
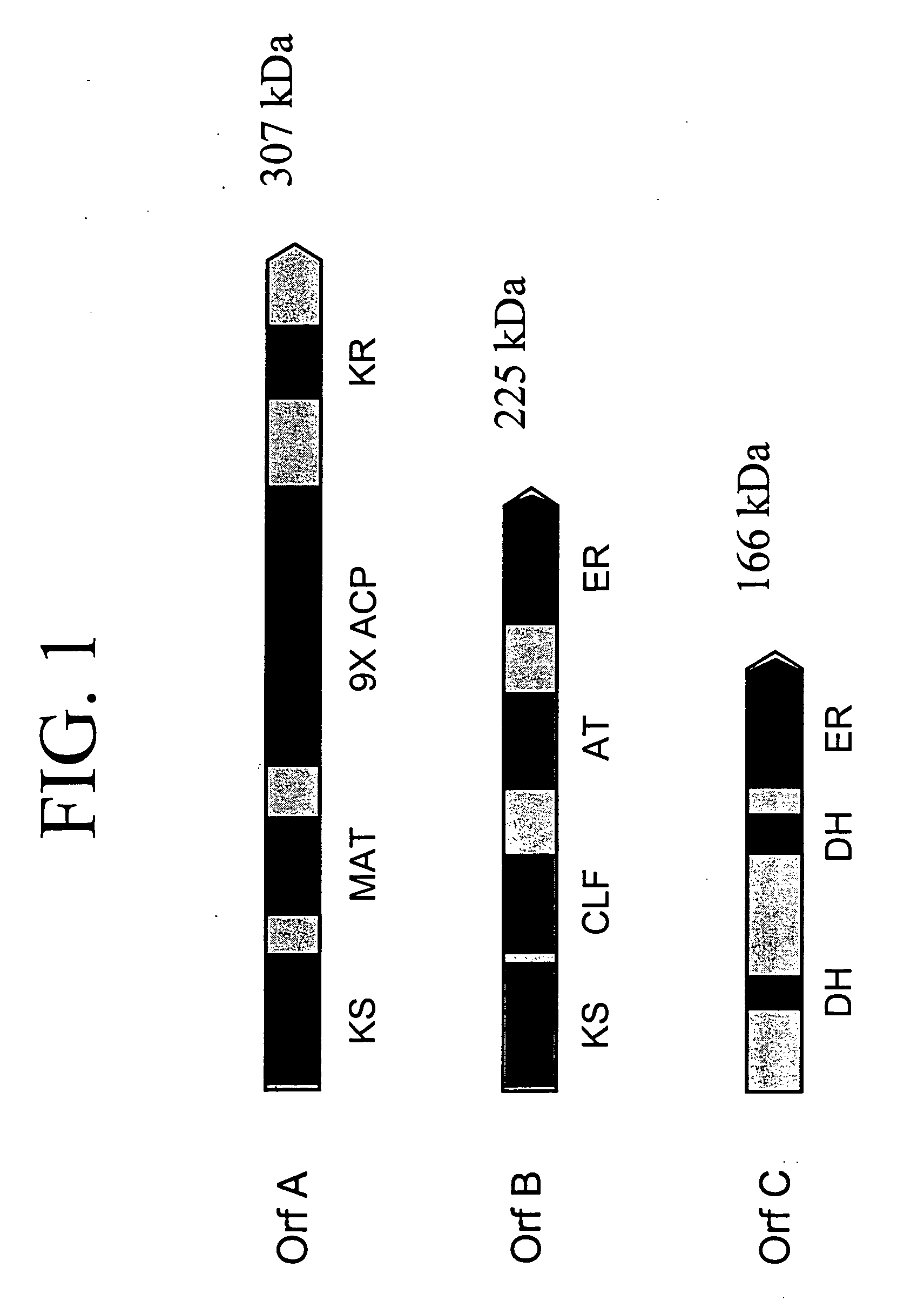
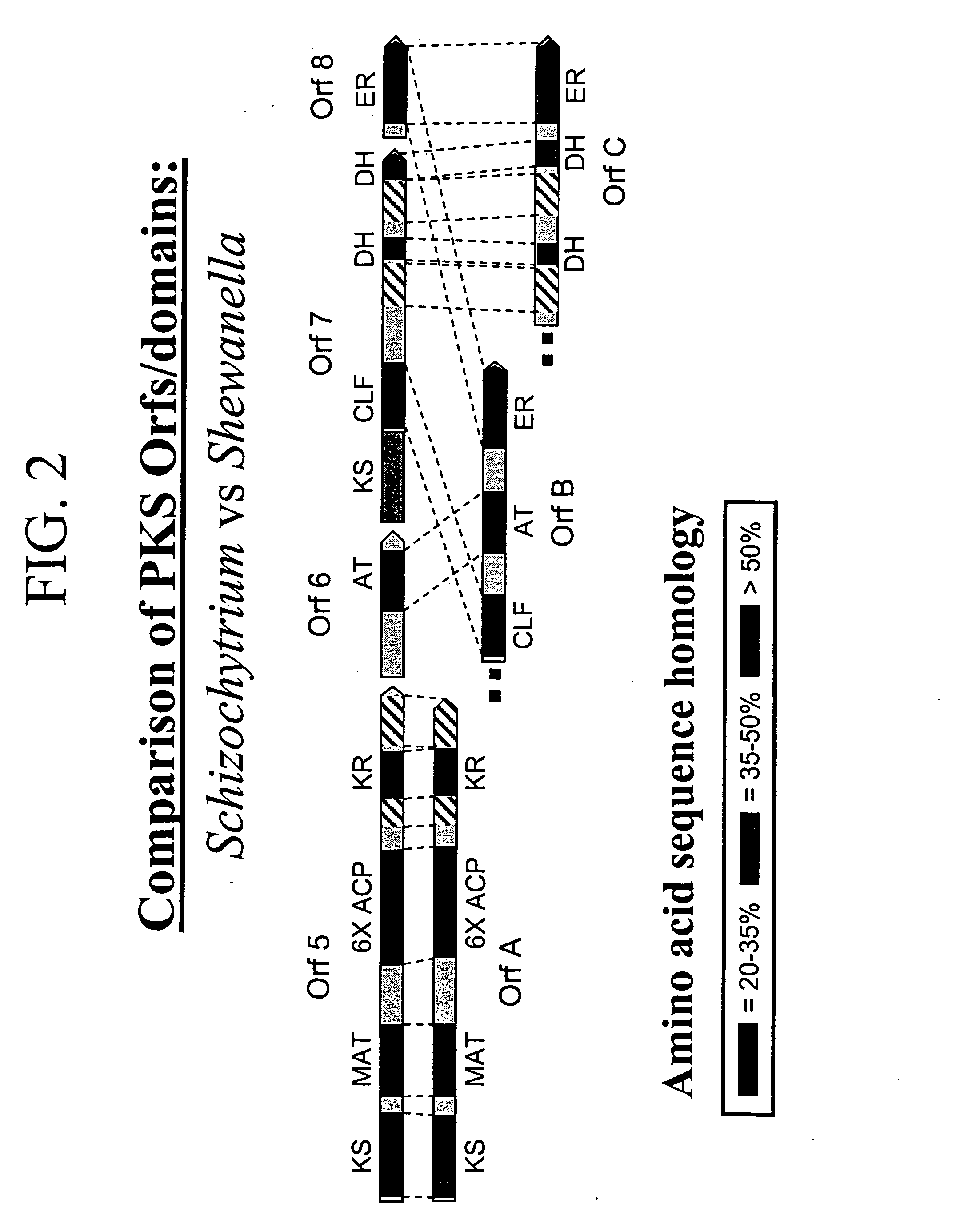
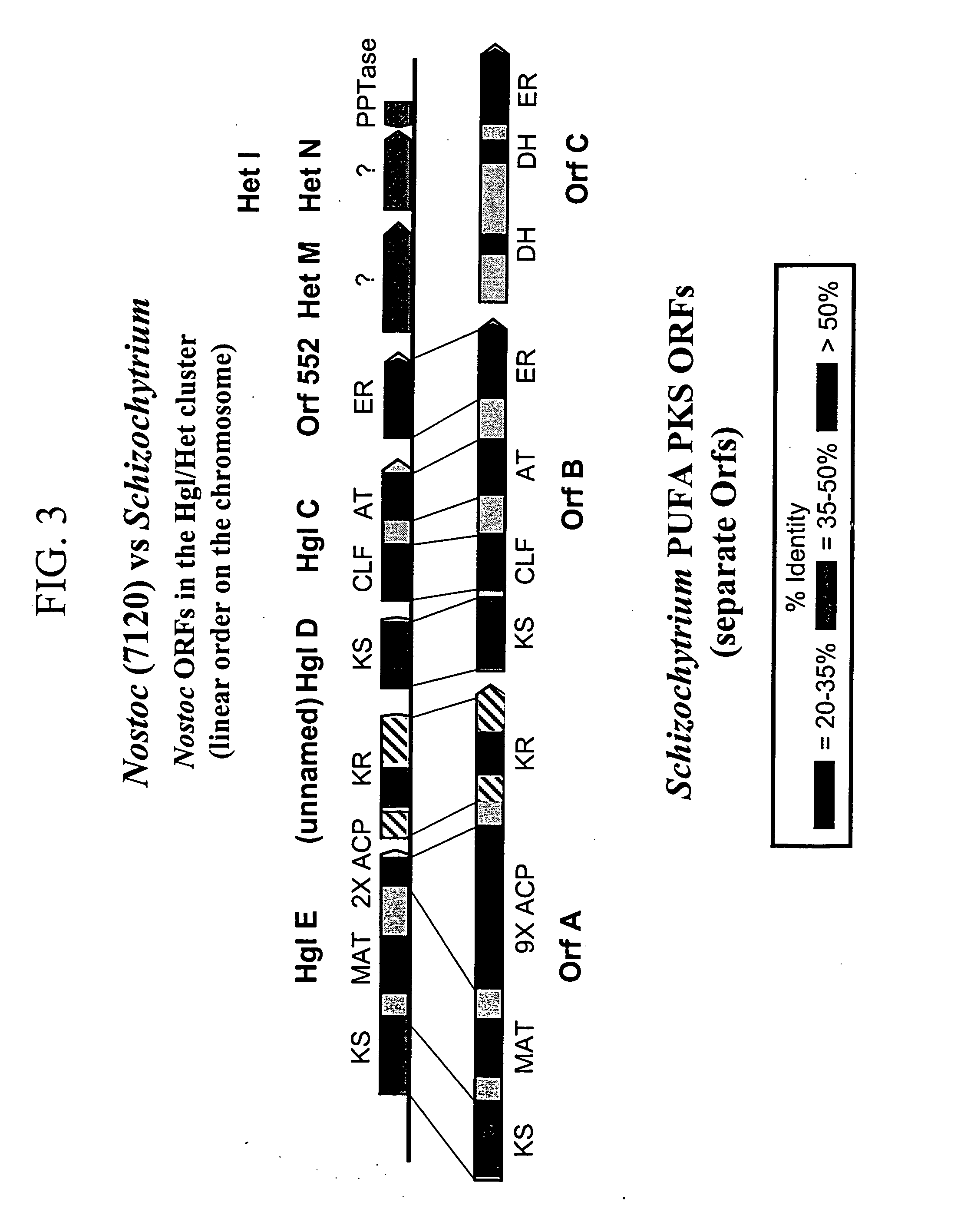
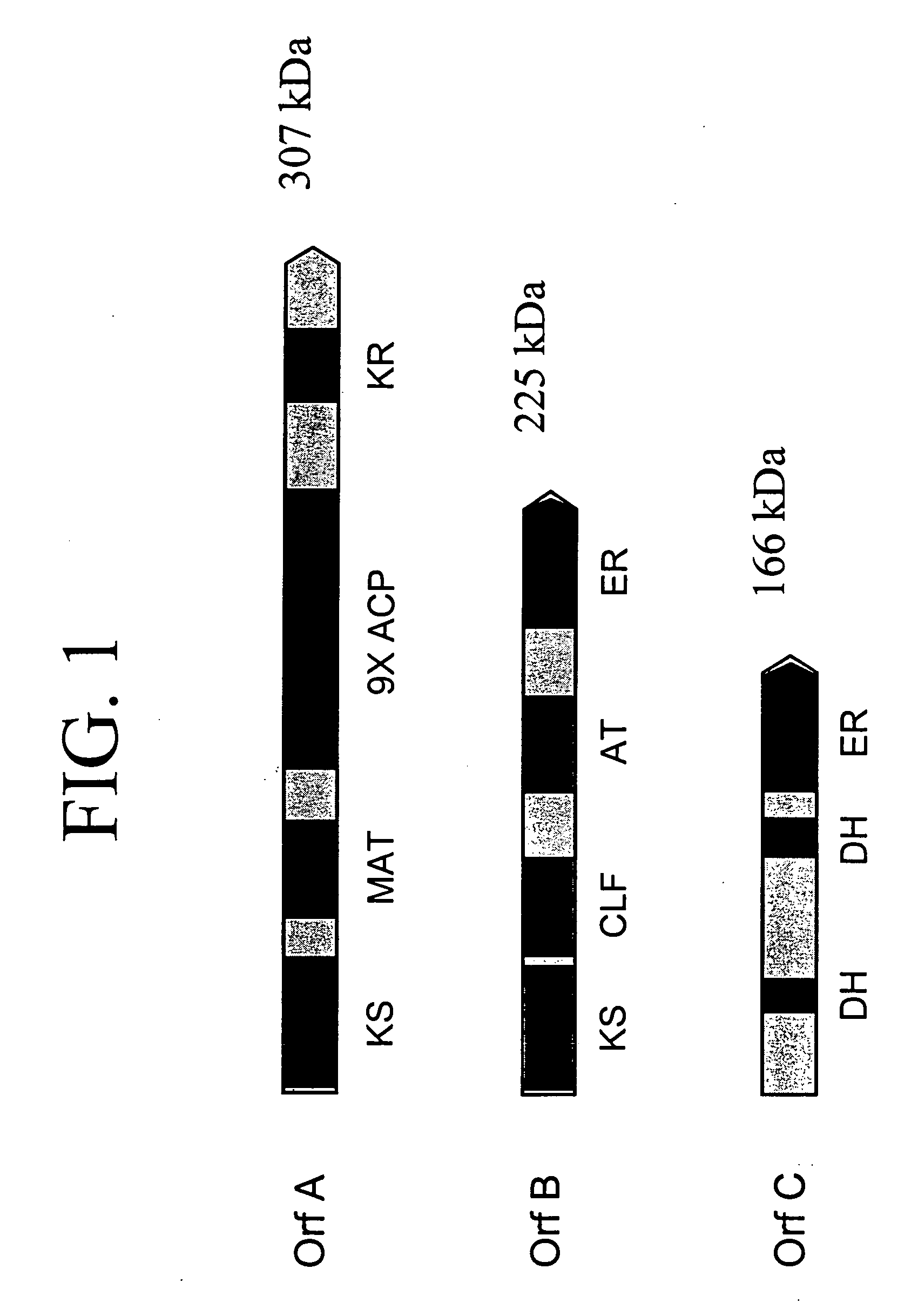
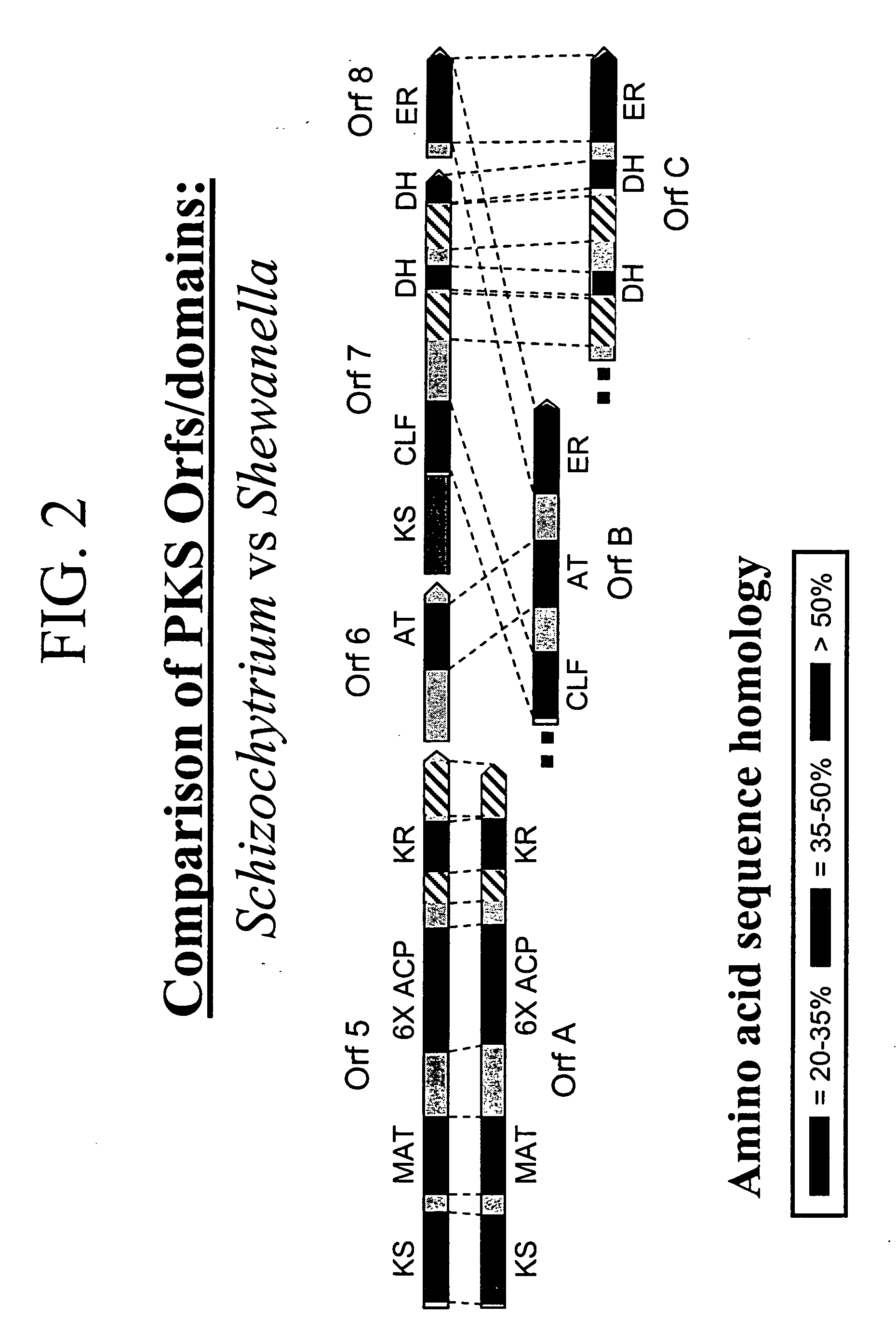
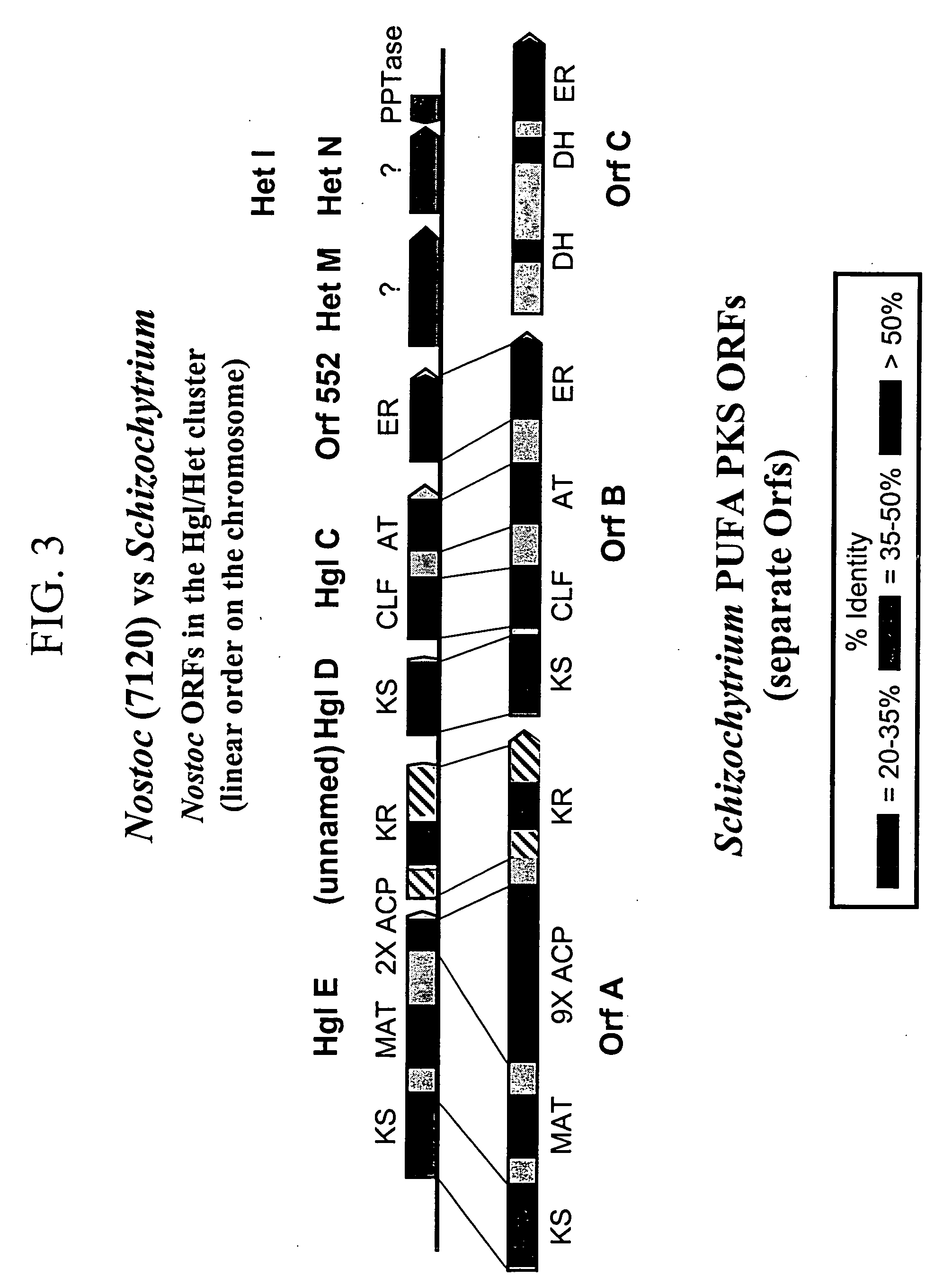
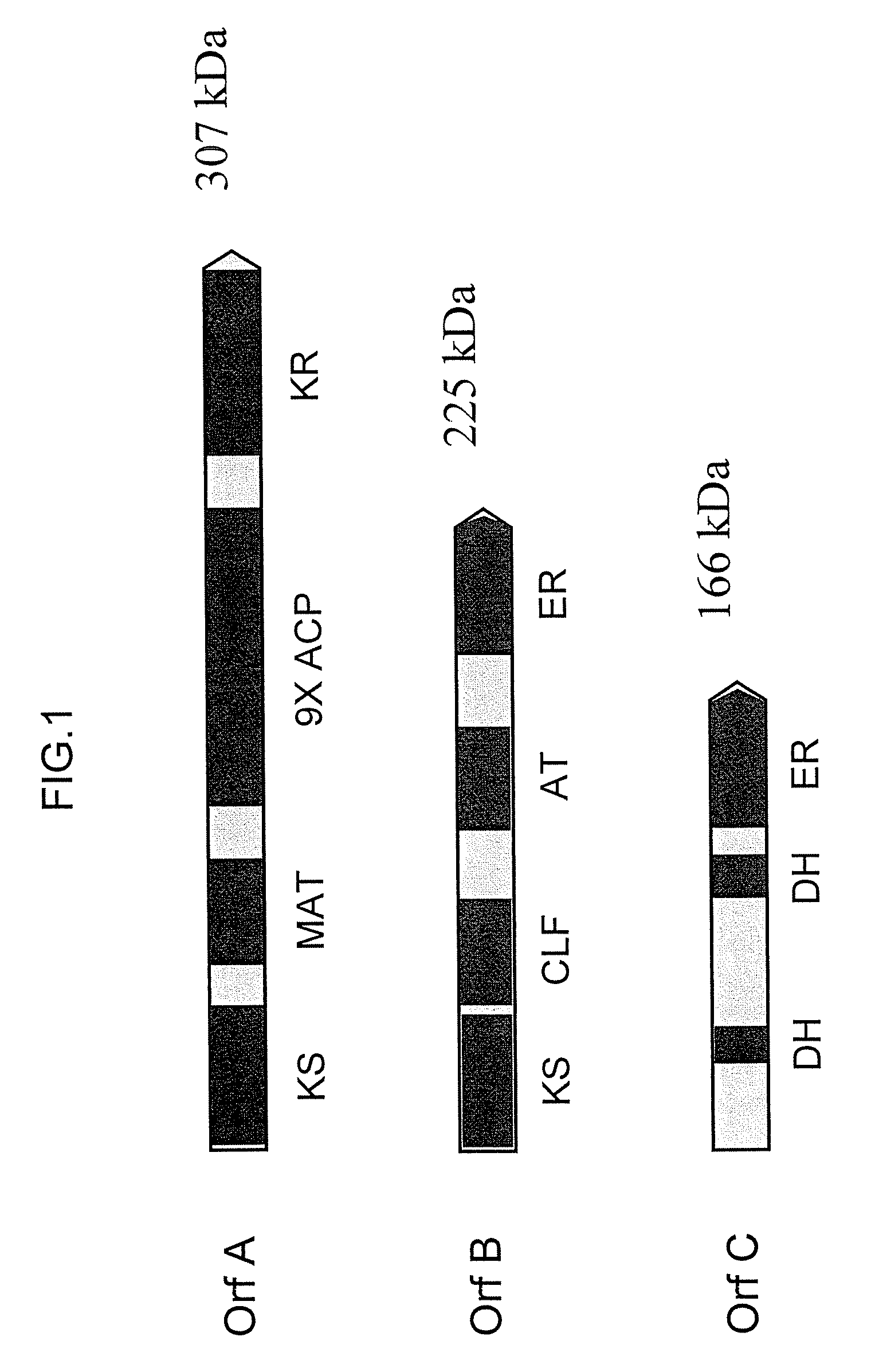
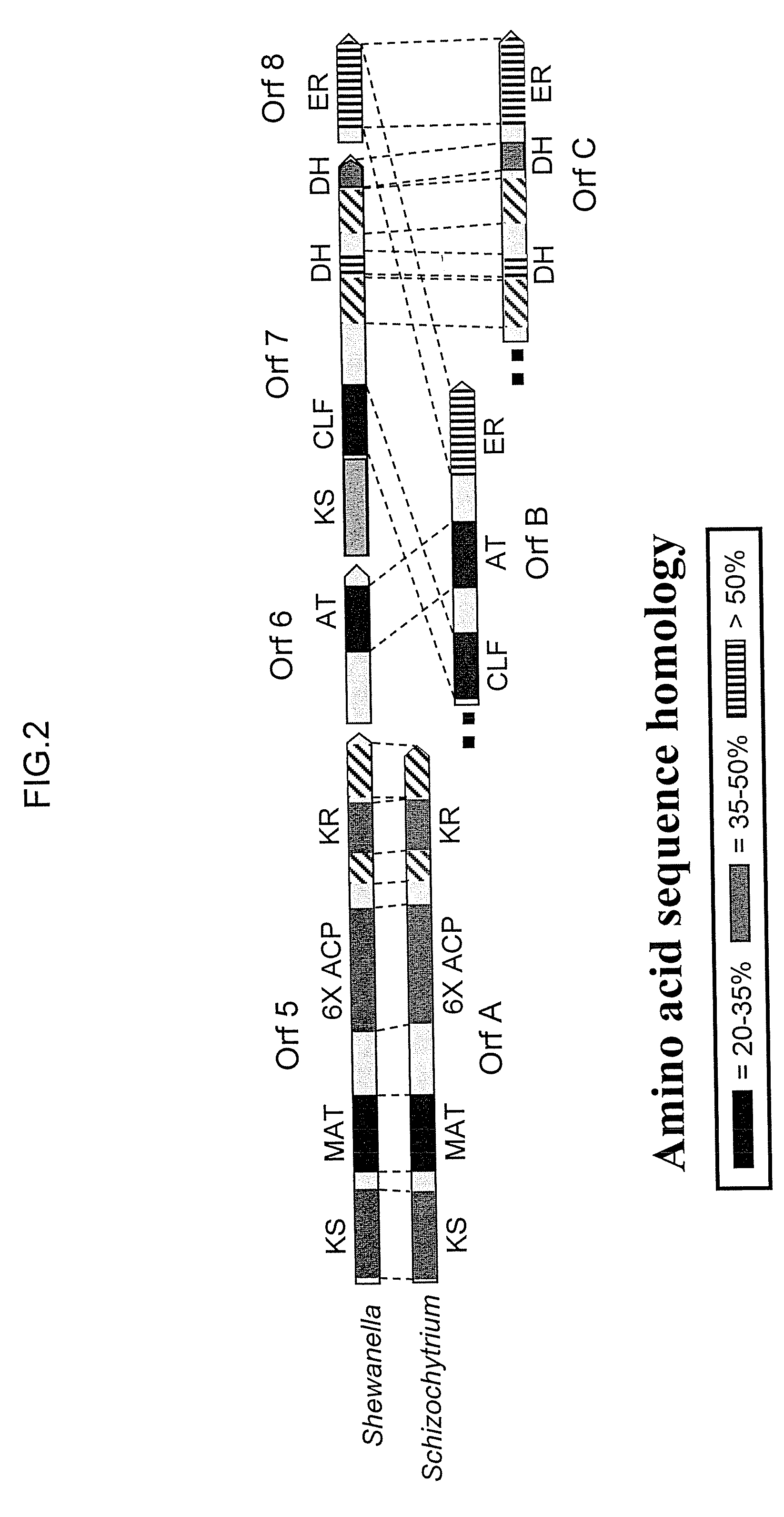
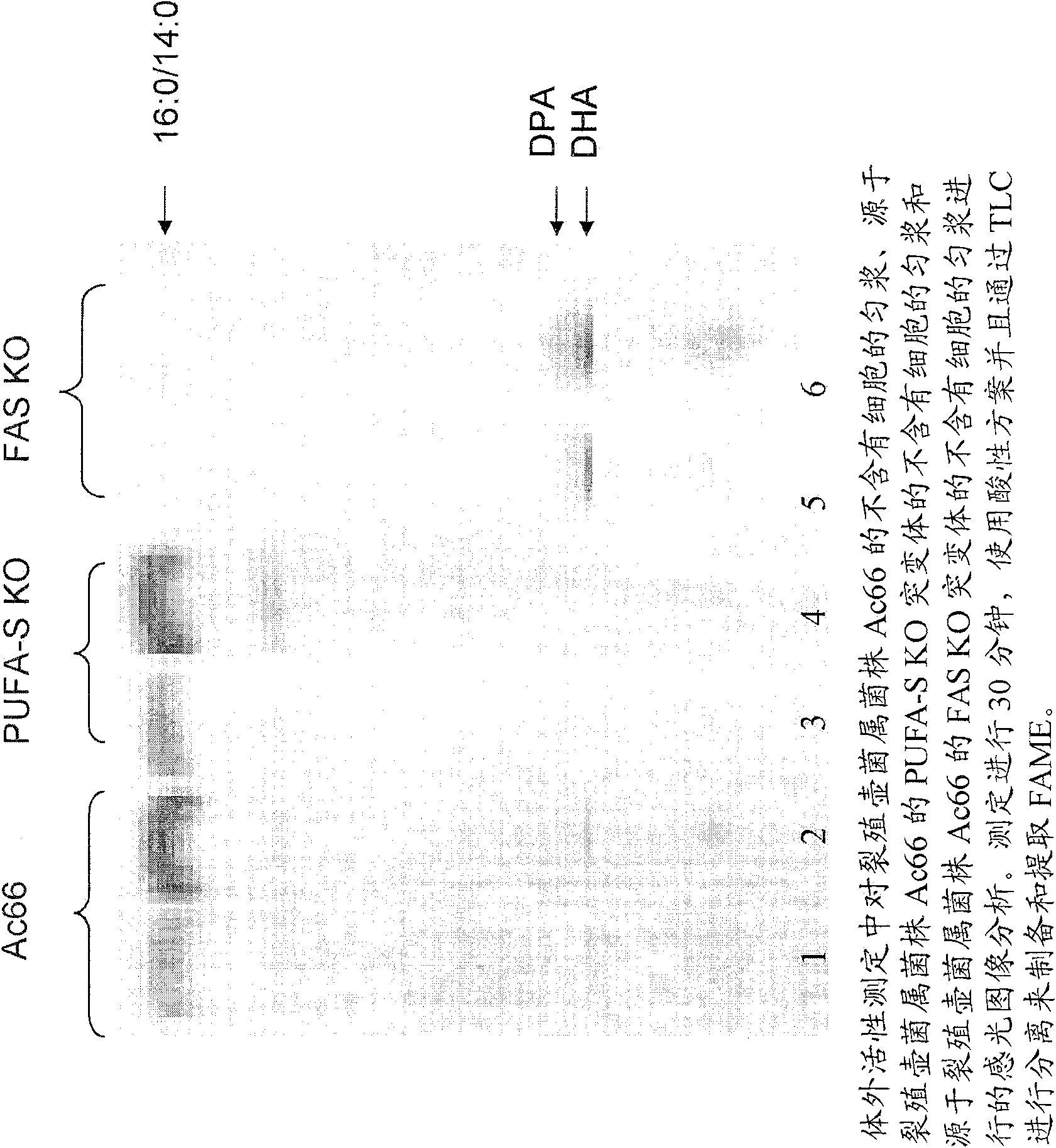
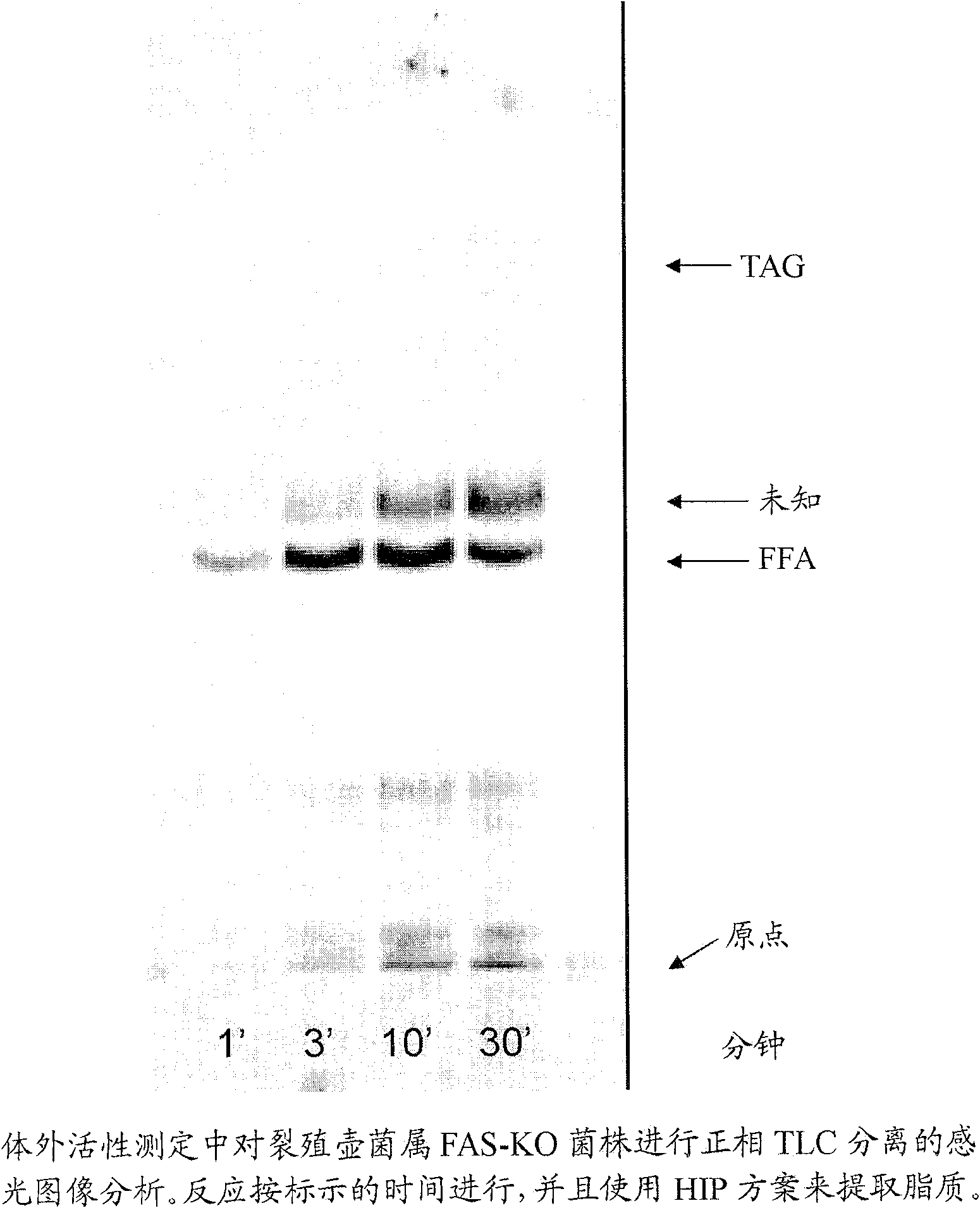
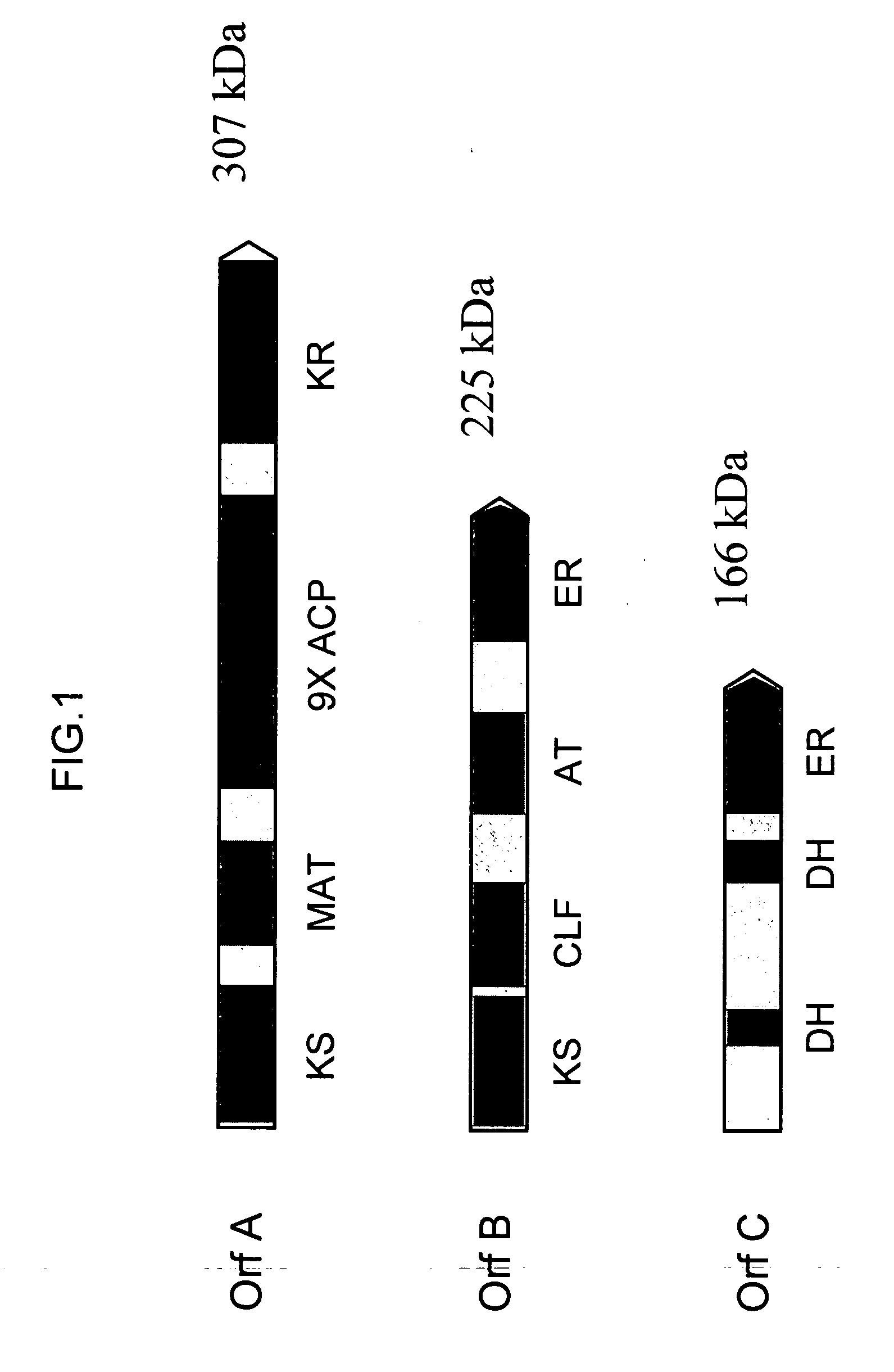
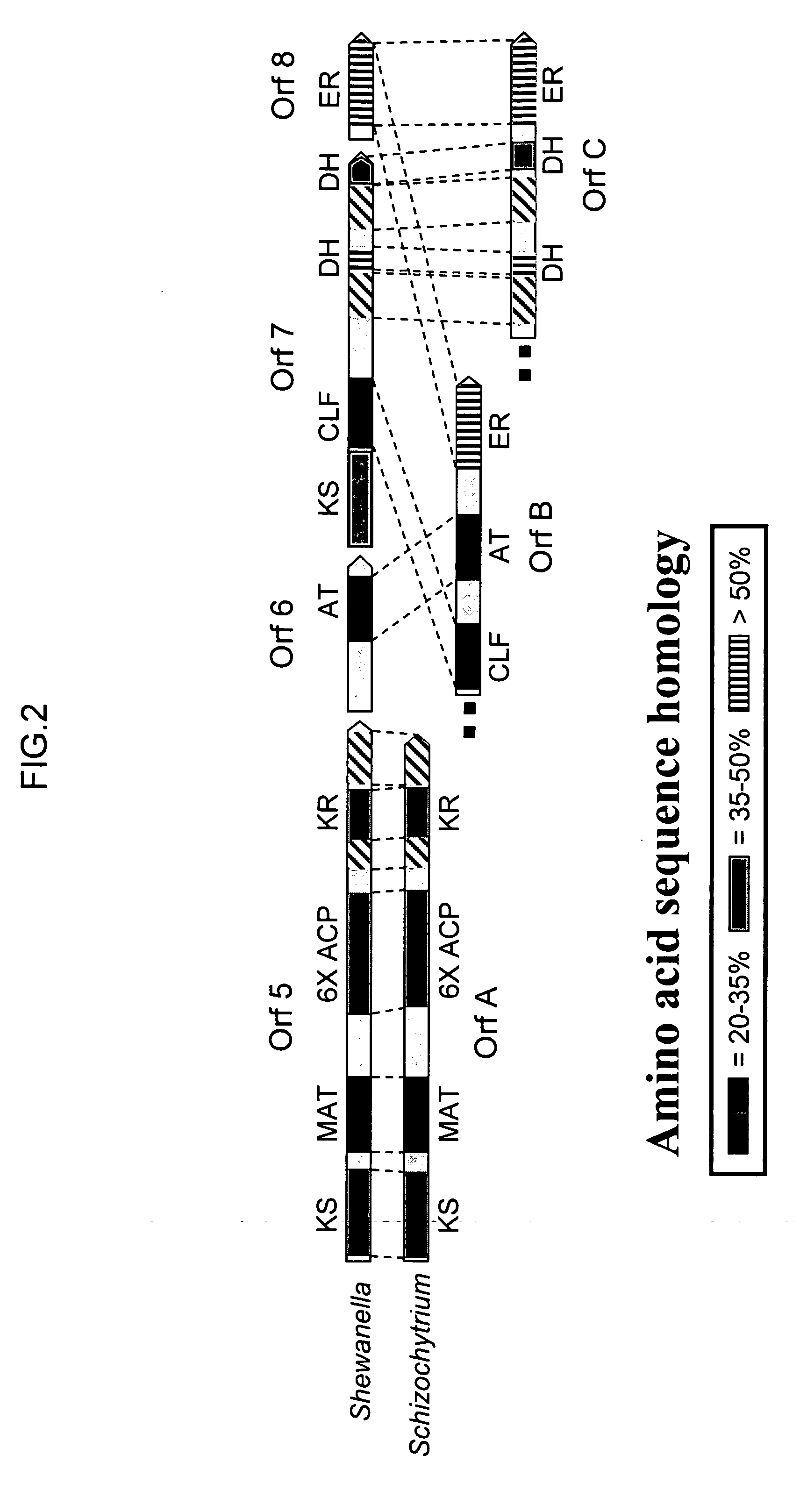
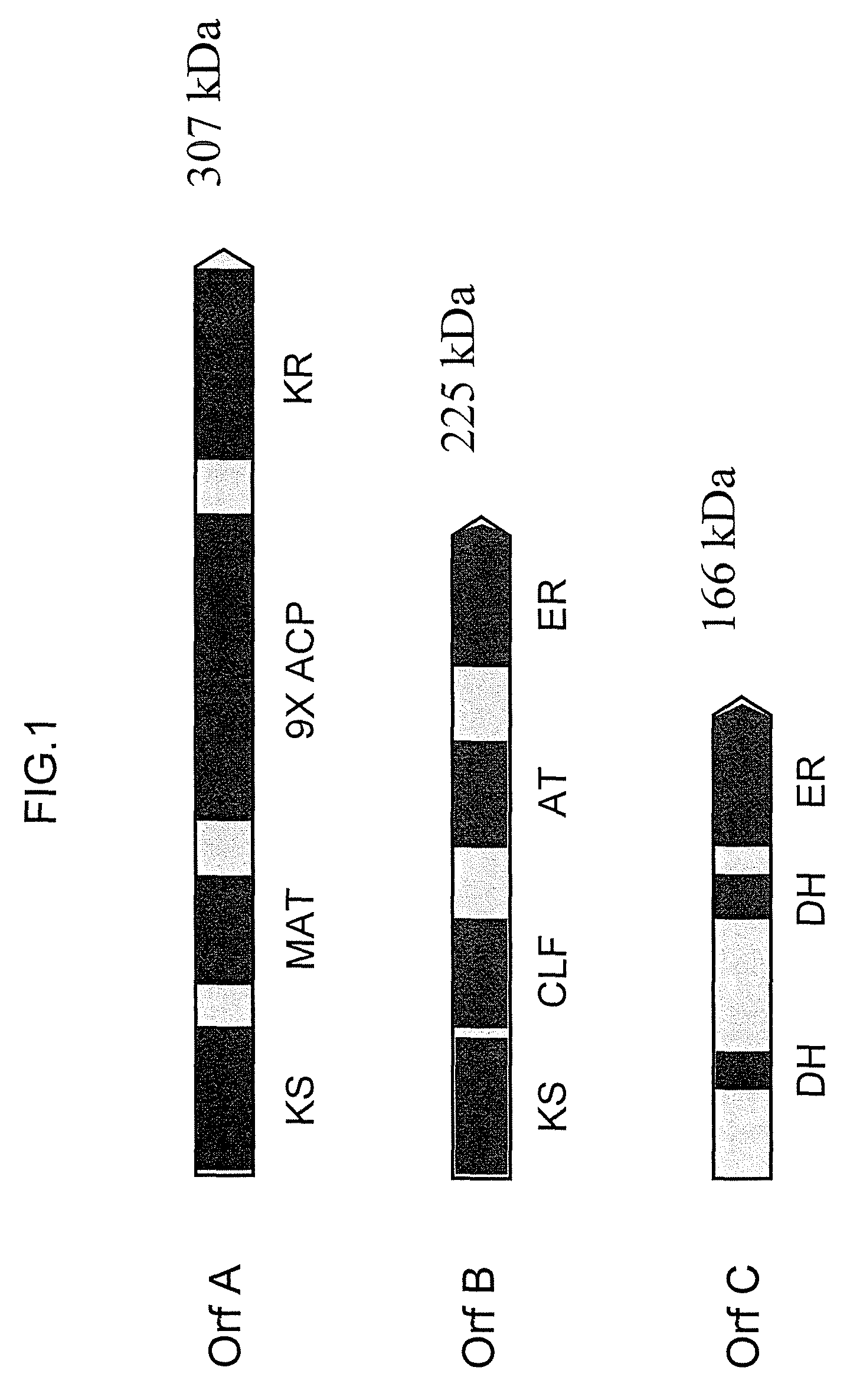
Disclosed are the complete polyunsaturated fatty acid (PUFA) polyketide synthase (PKS) systems from Schizochytrium, and biologically active fragments and homologues thereof. More particularly, this invention relates to nucleic acids encoding such PUFA PKS systems, to proteins and domains thereof that comprise such PUFA PKS systems, to genetically modified organisms (plants and microorganisms) comprising such PUFA PKS systems, and to methods of making and using the PUFA PKS systems disclosed herein. This invention also relates to genetically modified plants and microorganisms and methods to efficiently produce lipids enriched in various polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) as well as other bioactive molecules by manipulation of a PUFA polyketide synthase (PKS) system.
Owner:DSM IP ASSETS BV
PUFA polyketide synthase systems and uses thereof
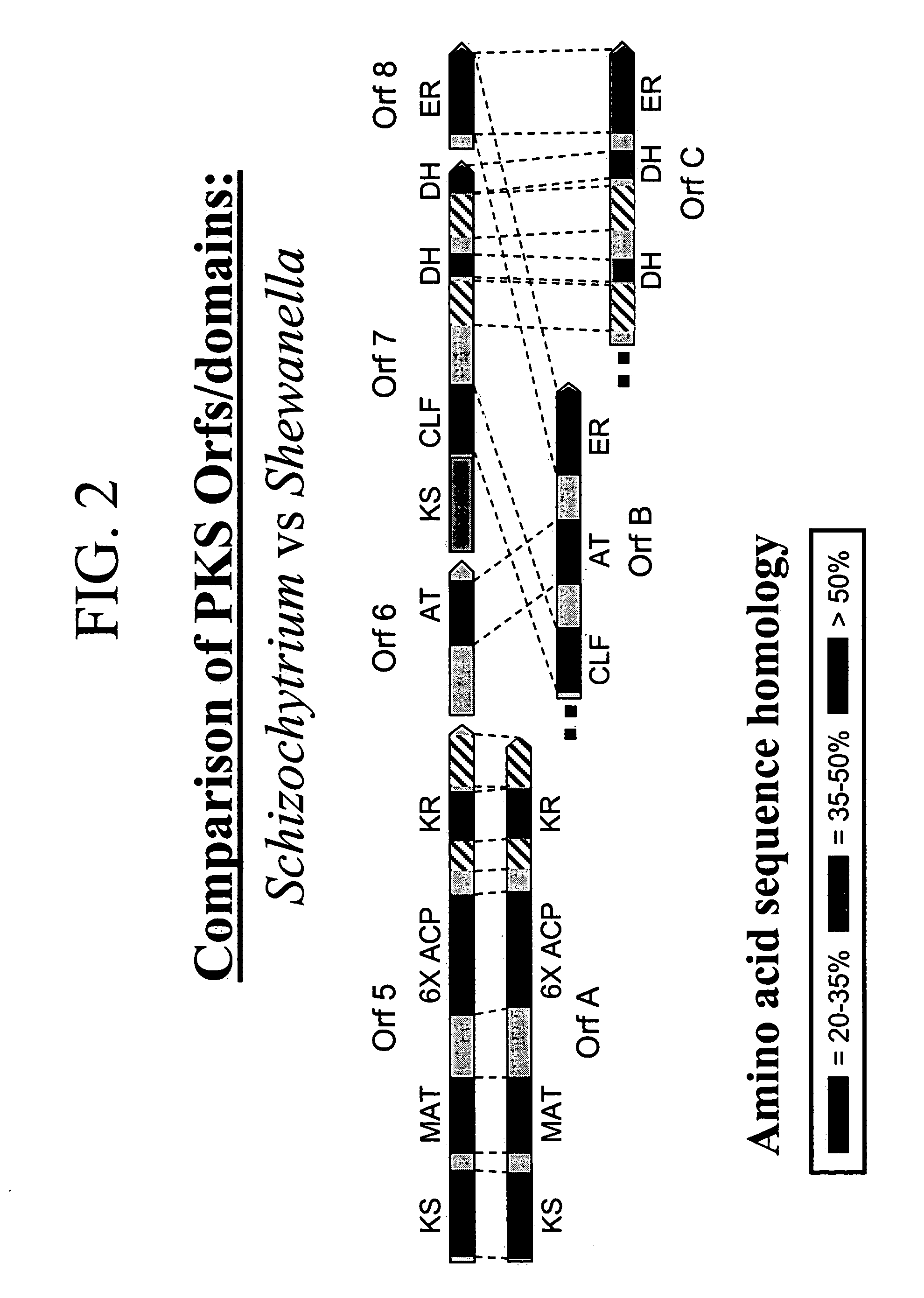
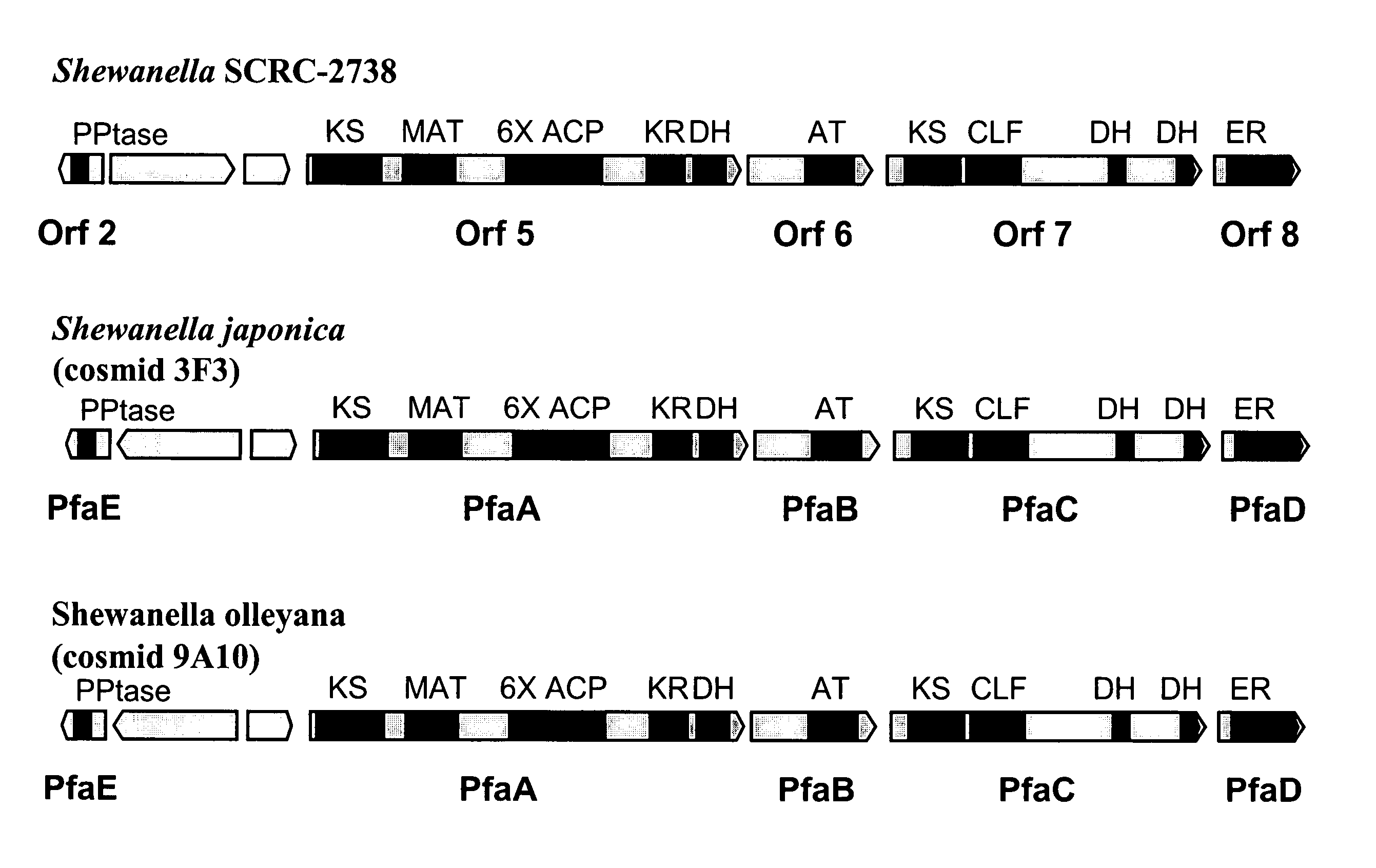
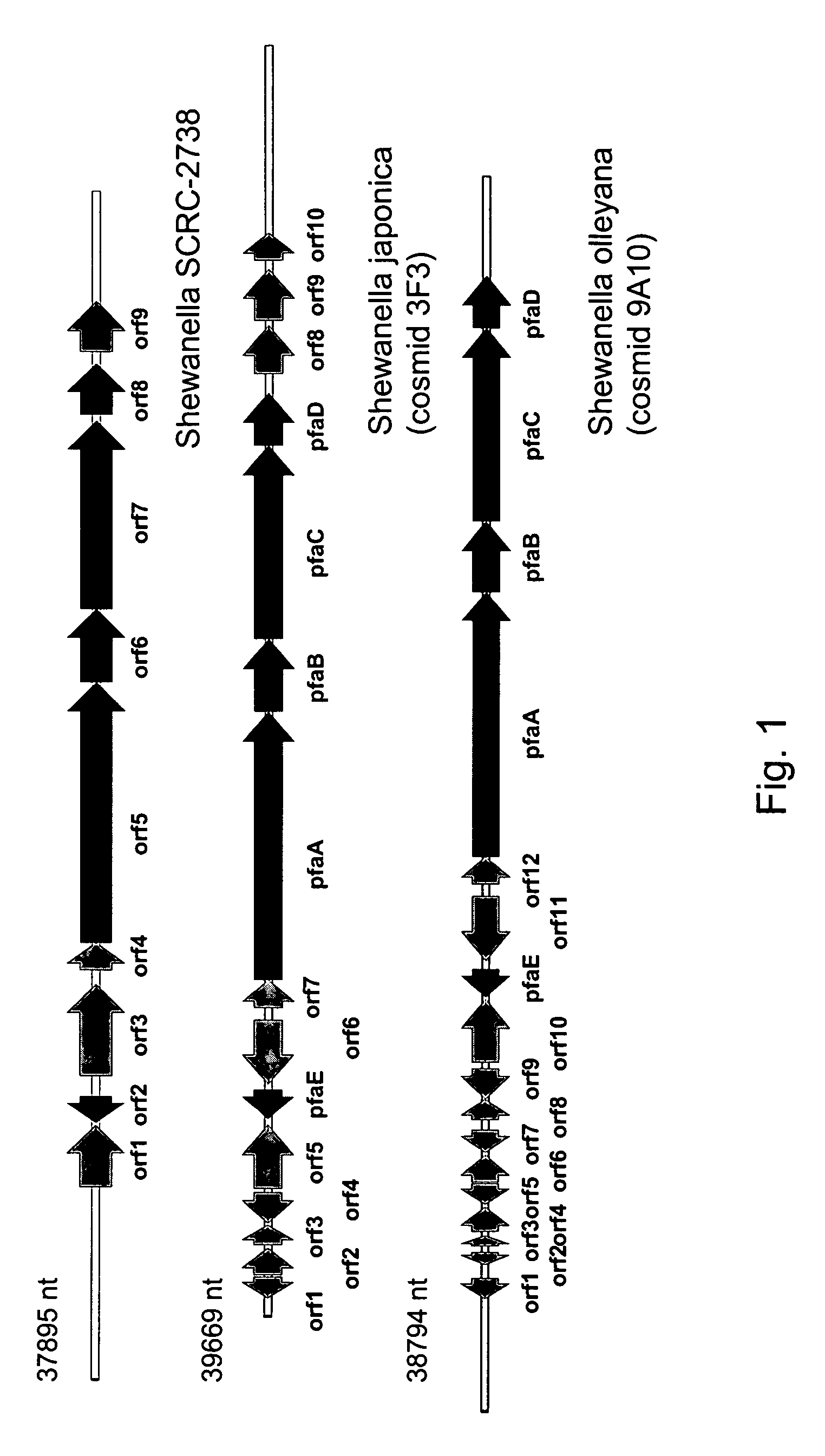
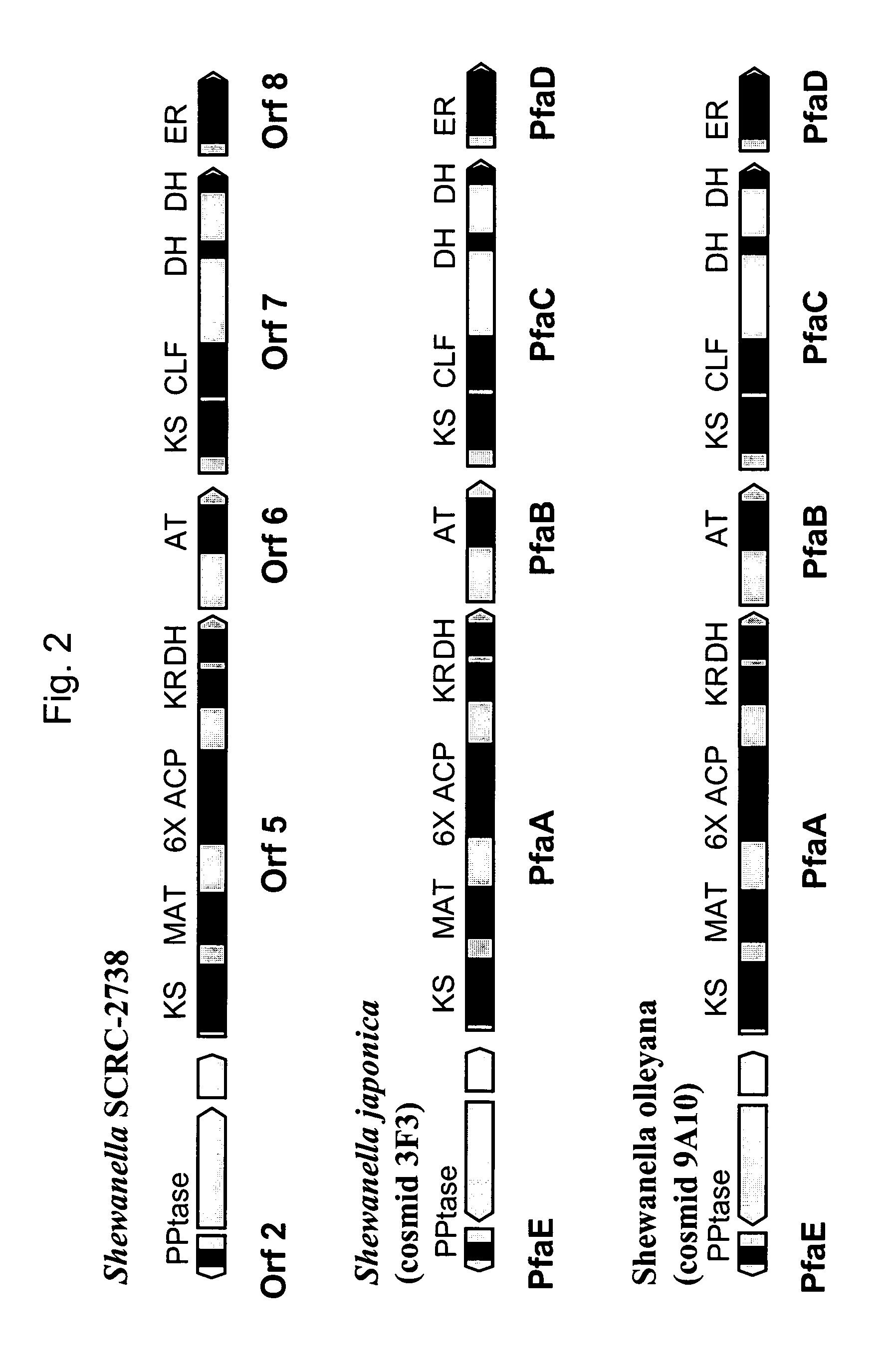
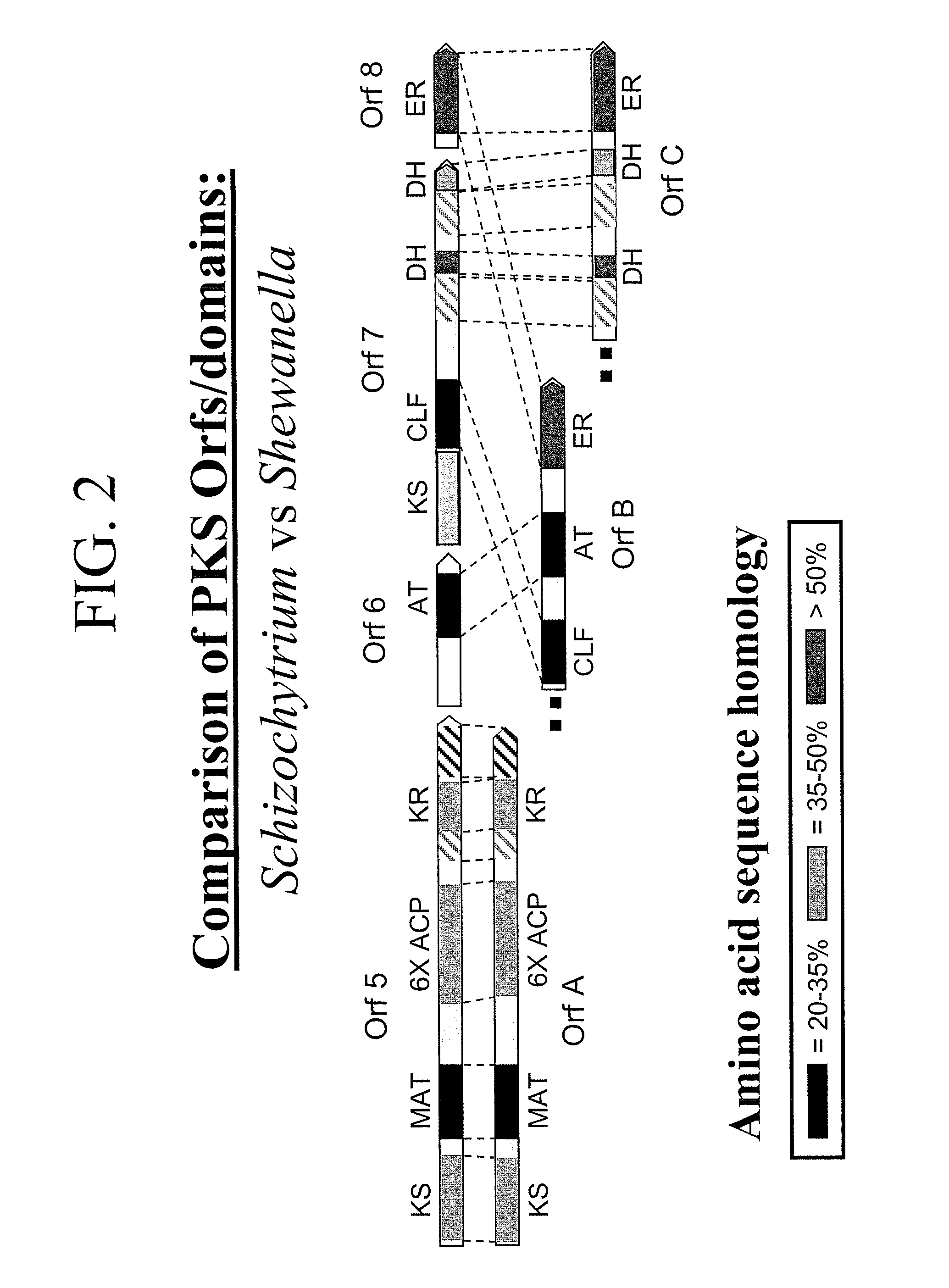
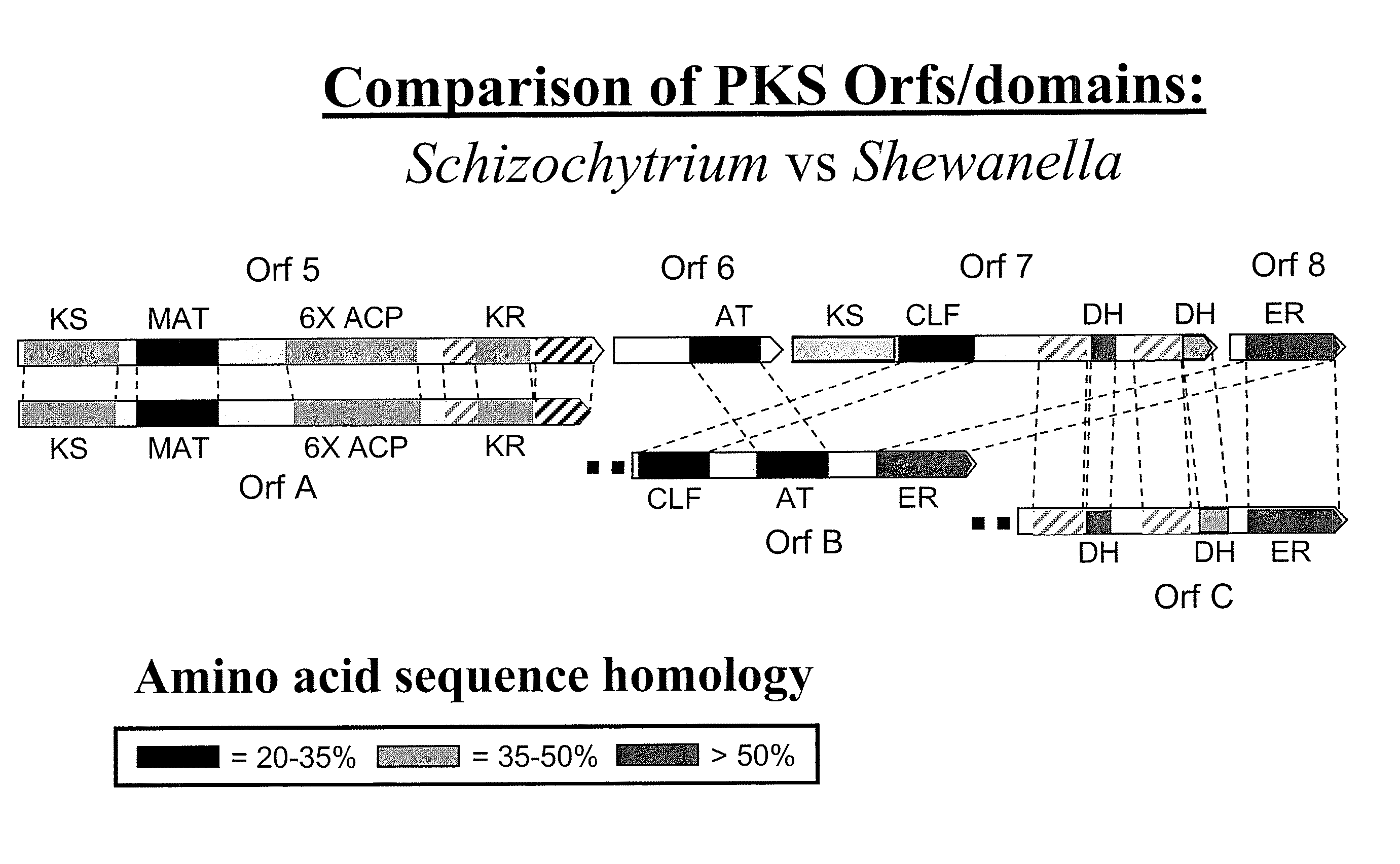
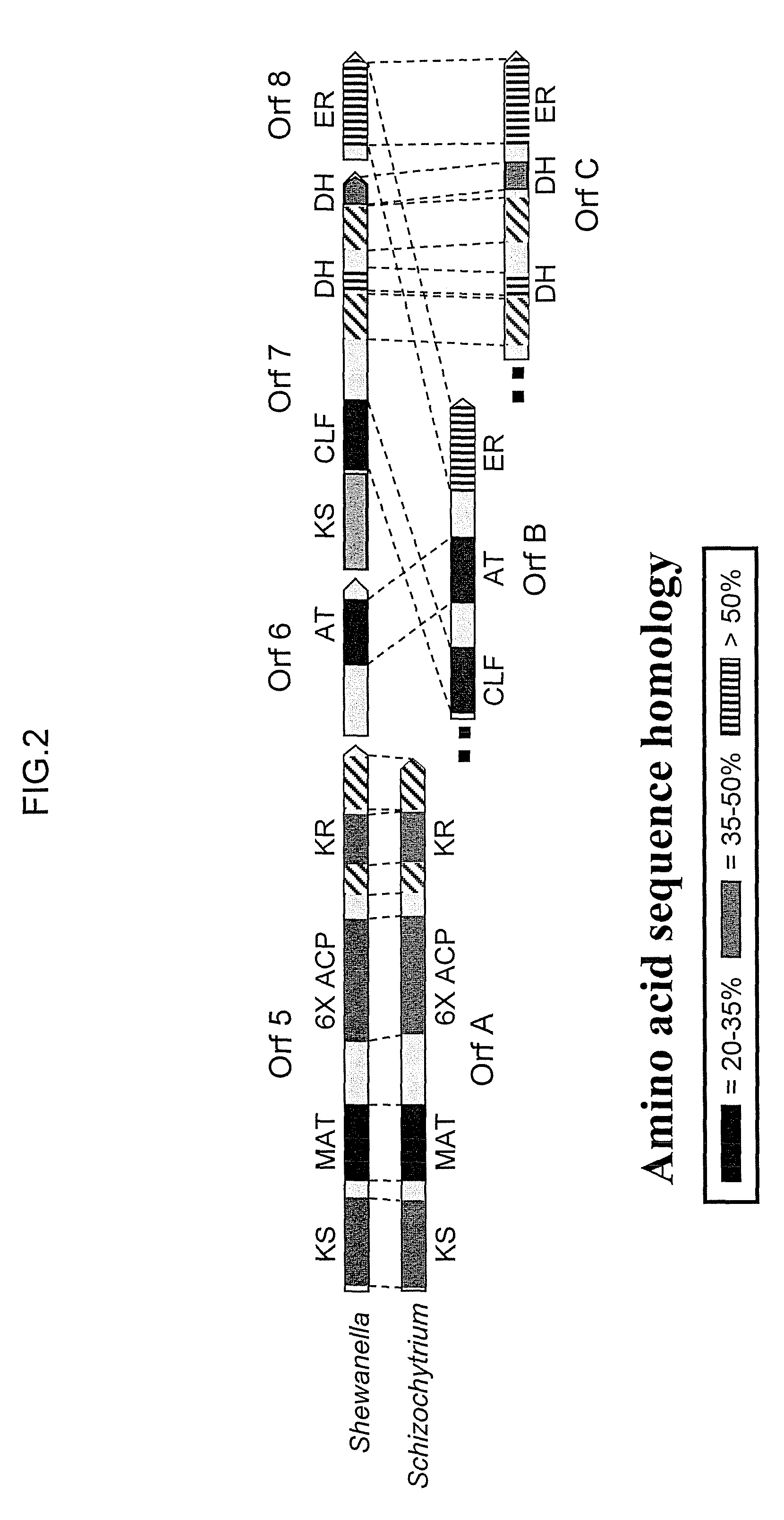
Disclosed are the complete polyunsaturated fatty acid (PUFA) polyketide synthase (PKS) systems from the bacterial microorganisms Shewanella japonica and Shewanella olleyana, and biologically active fragments and homologues thereof. More particularly, this invention relates to nucleic acids encoding such PUFA PKS systems, to proteins and domains thereof that comprise such PUFA PKS systems, to genetically modified organisms (plants and microorganisms) comprising such PUFA PKS systems, and to methods of making and using the PUFA PKS systems disclosed herein. This invention also relates to genetically modified plants and microorganisms and methods to efficiently produce lipids enriched in various polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) as well as other bioactive molecules by manipulation of a PUFA polyketide synthase (PKS) system.
Owner:DSM IP ASSETS BV
Polyunsaturated fatty acid production in heterologous organisms using pufa polyketide synthase systems
ActiveUS20070270494A1Improve the level ofReduce competitionAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsHeterologousAcyl-CoA synthetase
Disclosed are novel acyl-CoA synthetases and novel acyltransferases, nucleic acid molecules encoding the same, recombinant nucleic acid molecules and recombinant host cells comprising such nucleic acid molecules, genetically modified organisms (microorganisms and plants) comprising the same, and methods of making and using the same. Also disclosed are genetically modified organisms (e.g., plants, microorganisms) that have been genetically modified to express a PKS-like system for the production of PUFAs (a PUFA PKS system or PUFA synthase), wherein the organisms have been modified to express an acyl-CoA synthetase, to express an acyl transferase, to delete or inactivate a fatty acid synthase (FAS) expressed by the organism, to reduce competition for malonyl CoA with the PUFA synthase or to increase the level of malonyl CoA in the organism, and in one aspect, to inhibit KASII or KASIII. Additional modifications, and methods to make and use such organisms, in addition to PUFAs and oils obtained from such organisms, are disclosed, alone with various products including such PUFAs and oils.
Owner:DSM IP ASSETS BV
Pufa polyketide synthase systems and uses thereof
Disclosed are the complete polyunsaturated fatty acid (PUFA) polyketide synthase (PKS) systems from Schizochytrium, and biologically active fragments and homologues thereof. More particularly, this invention relates to nucleic acids encoding such PUFA PKS systems, to proteins and domains thereof that comprise such PUFA PKS systems, to genetically modified organisms (plants and microorganisms) comprising such PUFA PKS systems, and to methods of making and using the PUFA PKS systems disclosed herein. This invention also relates to genetically modified plants and microorganisms and methods to efficiently produce lipids enriched in various polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) as well as other bioactive molecules by manipulation of a PUFA polyketide synthase (PKS) system.
Owner:DSM IP ASSETS BV
Pufa polyketide synthase systems and uses thereof
The invention generally relates to polyunsaturated fatty acid (PUFA) polyketide synthase (PKS) systems, to homologues thereof, to isolated nucleic acid molecules and recombinant nucleic acid molecules encoding biologically active domains of such a PUFA PKS system, to genetically modified organisms comprising PUFA PKS systems, to methods of making and using such systems for the production of bioactive molecules of interest, and to novel methods for identifying new bacterial and non-bacterial microorganisms having such a PUFA PKS system.
Owner:DSM IP ASSETS BV
Pufa polyketide synthase systems and uses thereof
The invention generally relates to polyunsaturated fatty acid (PUFA) polyketide synthase (PKS) systems, to homologues thereof, to isolated nucleic acid molecules and recombinant nucleic acid molecules encoding biologically active domains of such a PUFA PKS system, to genetically modified organisms comprising PUFA PKS systems, to methods of making and using such systems for the production of bioactive molecules of interest, and to novel methods for identifying new bacterial and non-bacterial microorganisms having such a PUFA PKS system.
Owner:DSM IP ASSETS BV
Pufa polyketide synthase systems and uses thereof
The invention generally relates to polyunsaturated fatty acid (PUFA) polyketide synthase (PKS) systems, to homologues thereof, to isolated nucleic acid molecules and recombinant nucleic acid molecules encoding biologically active domains of such a PUFA PKS system, to genetically modified organisms comprising PUFA PKS systems, to methods of making and using such systems for the production of bioactive molecules of interest, and to novel methods for identifying new bacterial and non-bacterial microorganisms having such a PUFA PKS system.
Owner:DSM IP ASSETS BV
Genes involved in polyketide synthase pathways and uses thereof
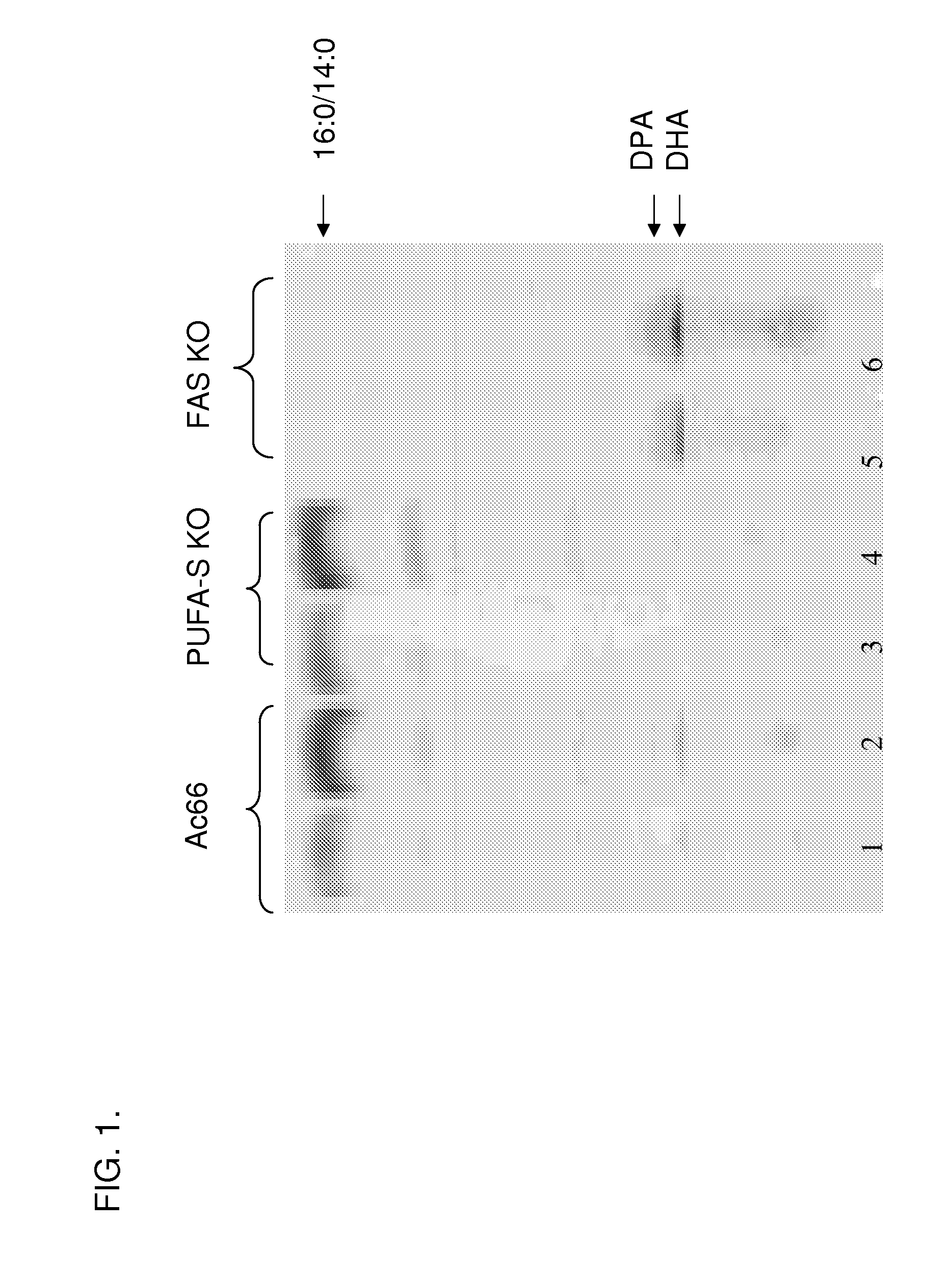
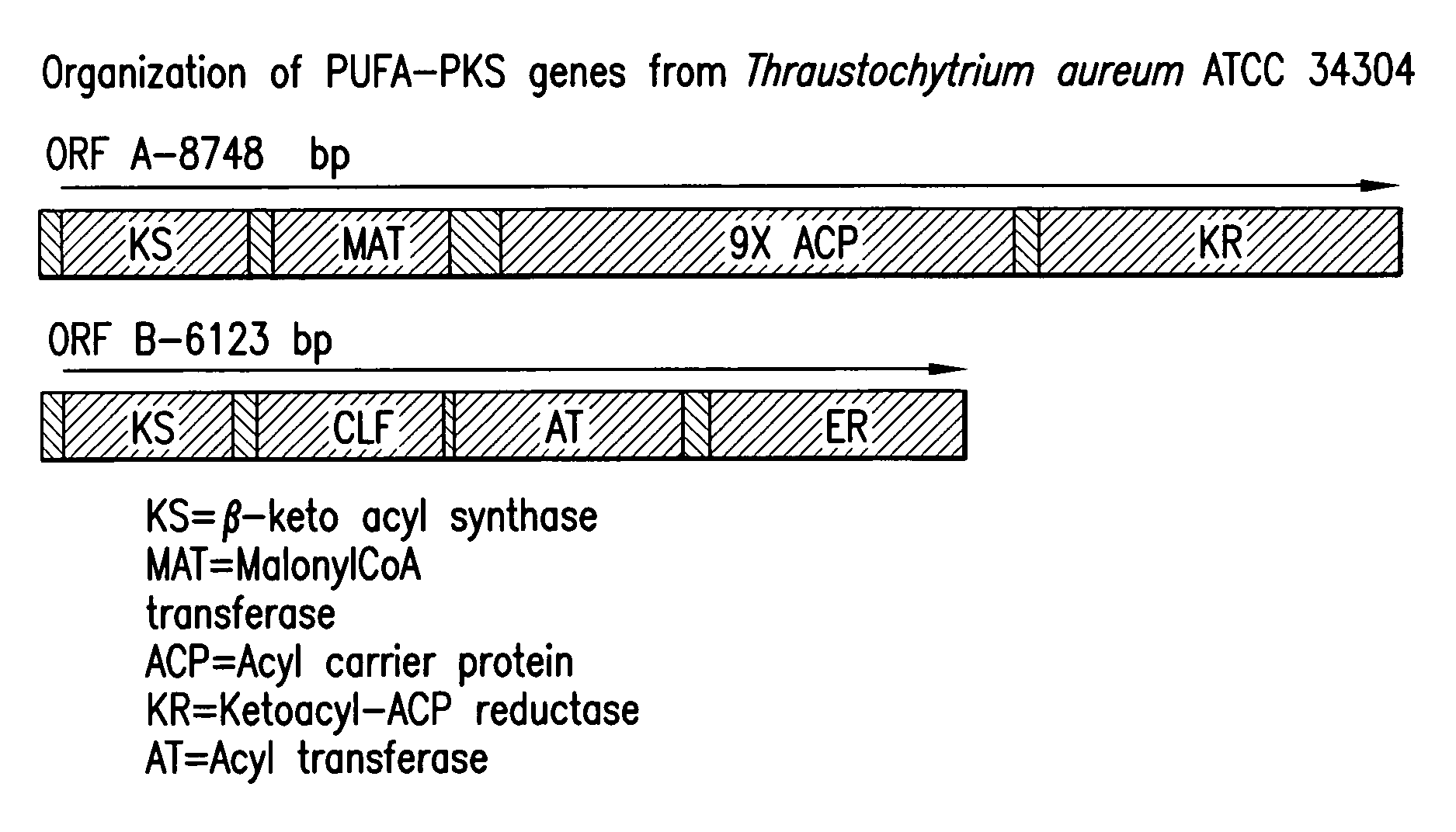
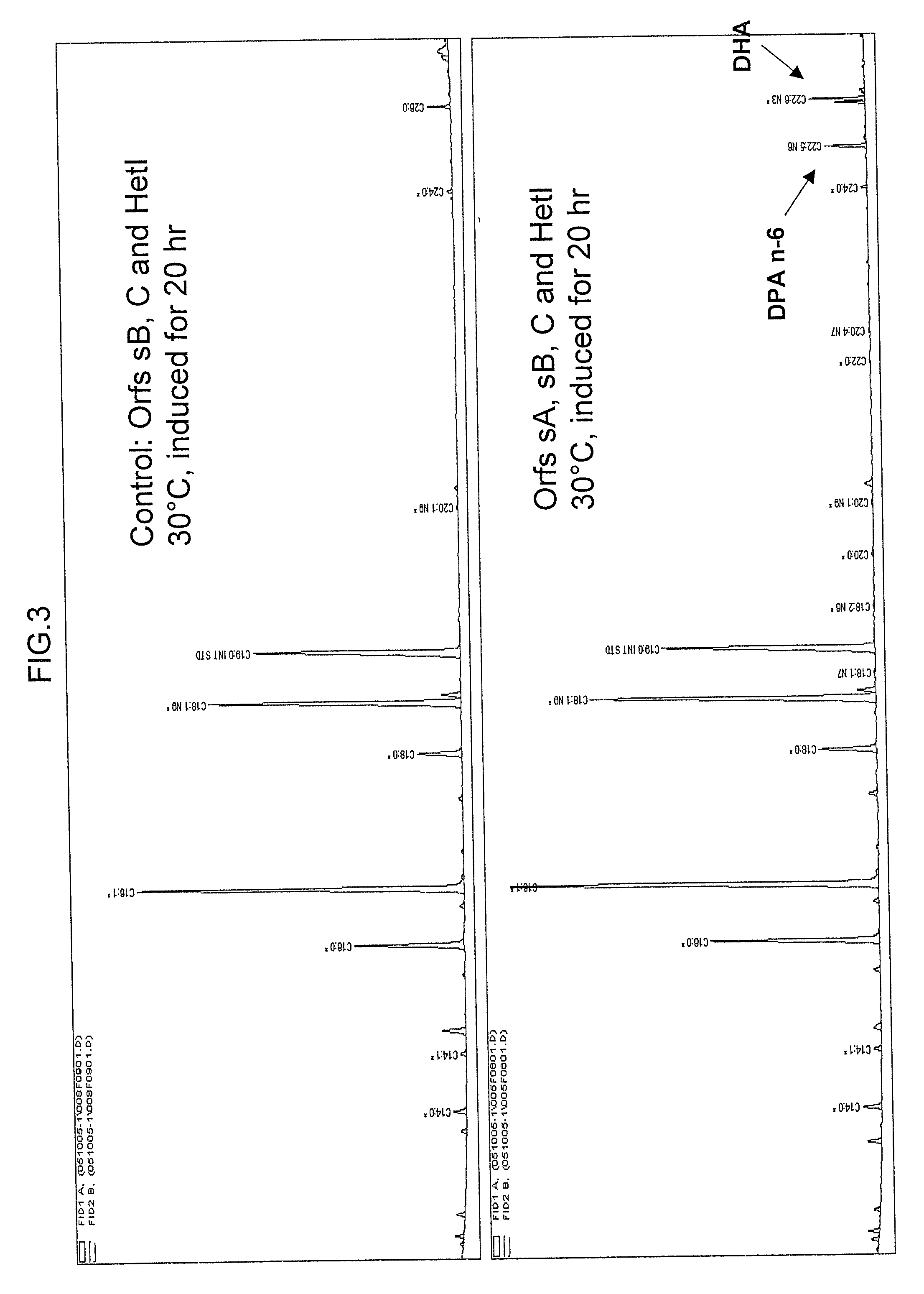
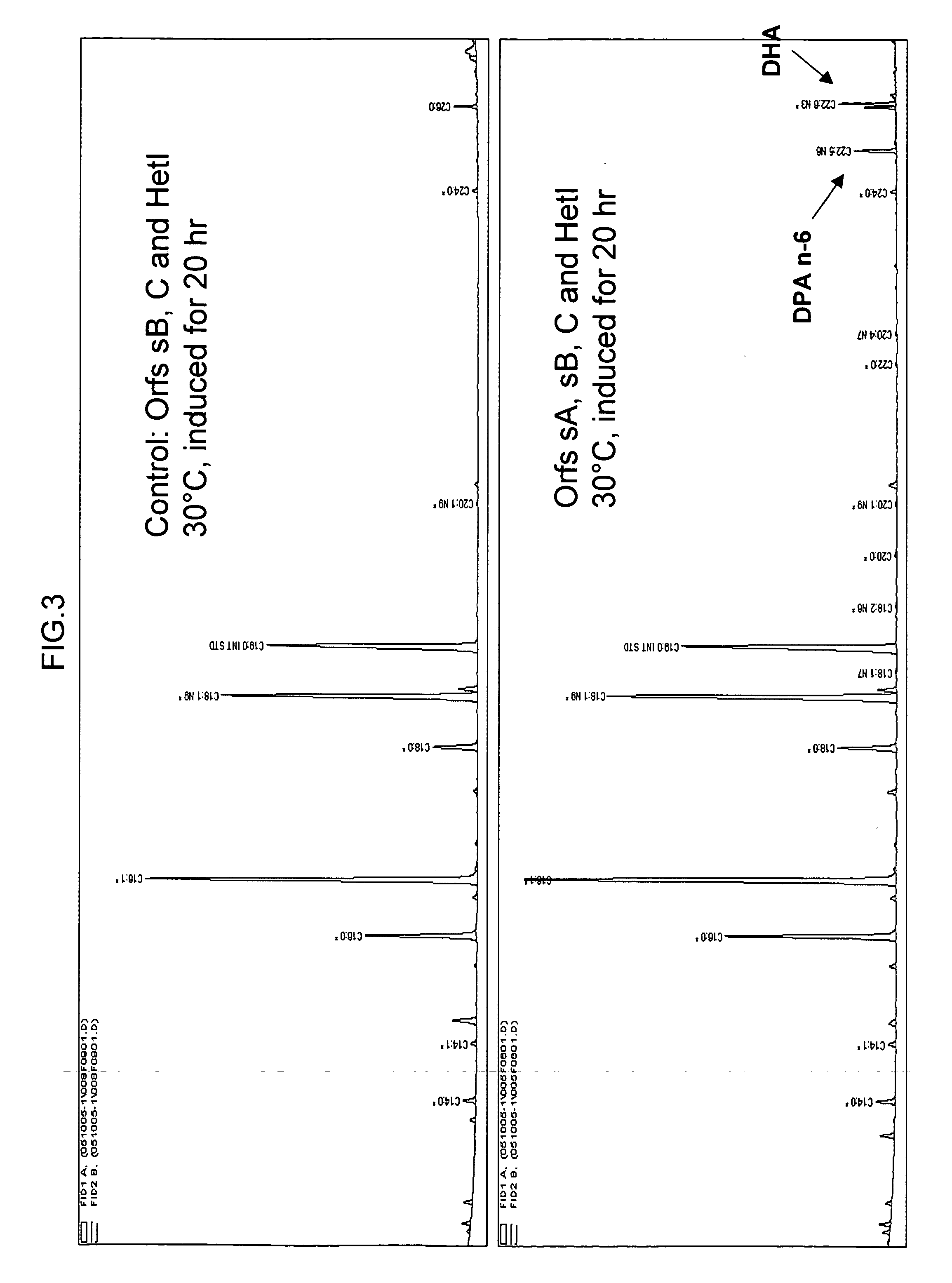
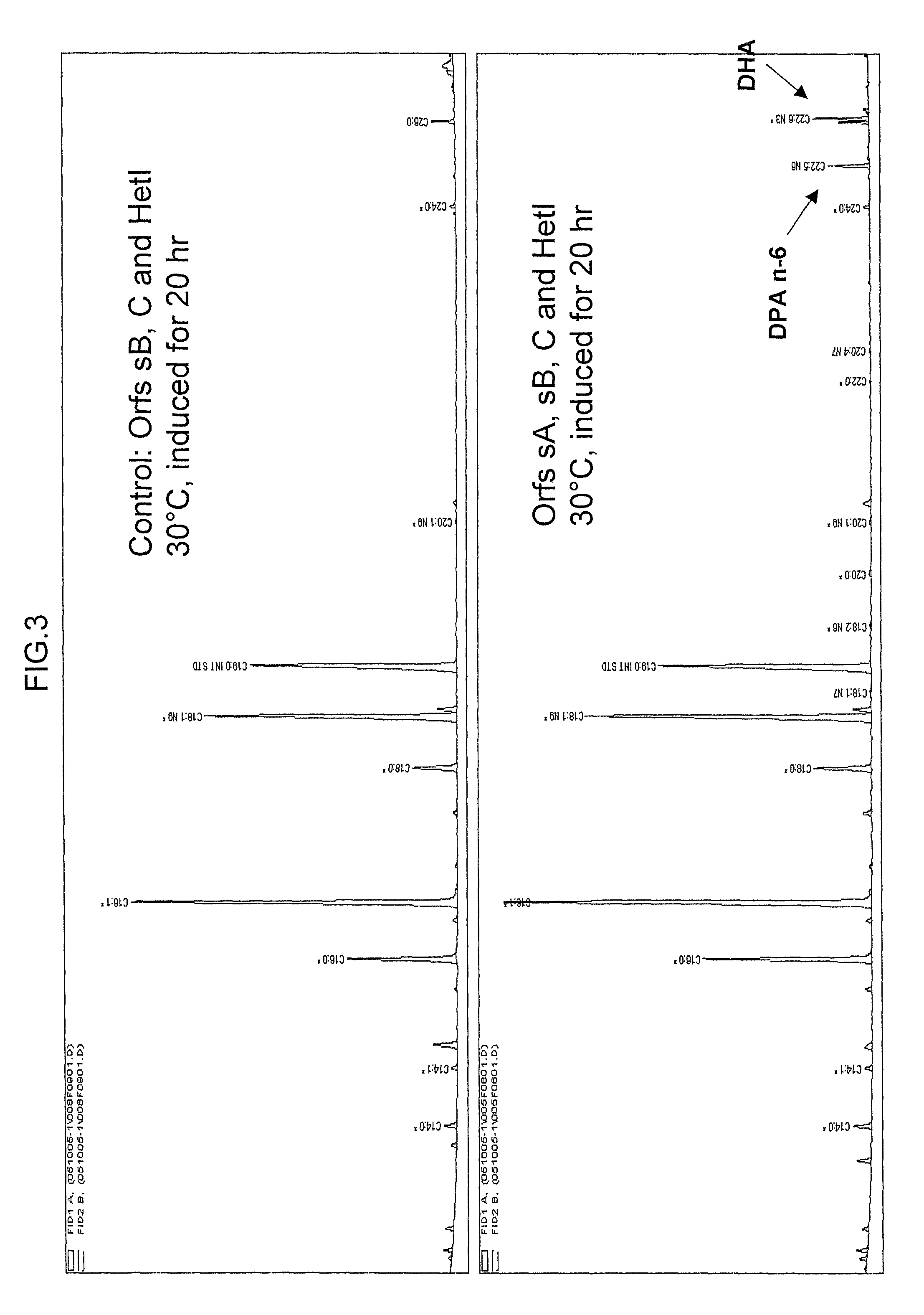
The subject invention relates to isolated nucleic acid sequences or genes involved in polyketide synthase (PKS) biosynthetic pathways. In particular, such pathways are involved in the production of polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) such as, for example, Eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and Docosahexaenoic acid (DHA). Specifically, the invention relates to isolating nucleic acid sequences encoding proteins involved in eukaryotic PUFA-PKS systems and to uses of these genes and encoded proteins in PUFA-PKS systems, in heterologous hosts, for the production of PUFAs such as EPA and DHA.
Owner:ABBOTT LAB INC
Product and process for transformation of thraustochytriales microorganisms
InactiveUS20050112719A1Reduce sensitivityReduce compoundingAlgae productsSugar derivativesAcetolactate synthaseΑ tubulin
Disclosed are nucleic acid and amino acid sequences for acetolactate synthase, acetolactate synthase regulatory regions, α-tubulin promoter, a promoter from a Thraustochytriales polyketide synthase (PKS) system, and fatty acid desaturase promoter, each from a Thraustochytriales microorganism. Also disclosed are recombinant vectors useful for transformation of Thraustochytriales microorganisms, as well as a method of transformation of Thraustochytriales microorganisms. The recombinant nucleic acid molecules of the present invention can be used for the expression of foreign nucleic acids in a Thraustochytriales microorganism as well as for the deletion, mutation, or inactivation of genes in Thraustochytriales microorganisms.
Owner:DSM IP ASSETS BV
PUFA polyketide synthase systems and uses thereof
Owner:DSM IP ASSETS BV
Pufa polyketide synthase systems and uses thereof
The invention generally relates to polyunsaturated fatty acid (PUFA) polyketide synthase (PKS) systems isolated from or derived from non-bacterial organisms, to homologues thereof, to isolated nucleic acid molecules and recombinant nucleic acid molecules encoding biologically active domains of such a PUFA PKS system, to genetically modified organisms comprising PUFA PKS systems, to methods of making and using such systems for the production of bioactive molecules of interest, and to novel methods for identifying new bacterial and non-bacterial microorganisms having such a PUFA PKS system.
Owner:DSM IP ASSETS BV
PUFA polyketide synthase systems and uses thereof
The invention generally relates to polyunsaturated fatty acid (PUFA) polyketide synthase (PKS) systems isolated from or derived from non-bacterial organisms, to homologues thereof, to isolated nucleic acid molecules and recombinant nucleic acid molecules encoding biologically active domains of such a PUFA PKS system, to genetically modified organisms comprising PUFA PKS systems, to methods of making and using such systems for the production of bioactive molecules of interest, and to novel methods for identifying new bacterial and non-bacterial microorganisms having such a PUFA PKS system.
Owner:DSM IP ASSETS BV
PUFA polyketide synthase systems and uses thereof
Disclosed are the complete polyunsaturated fatty acid (PUFA) polyketide synthase (PKS) systems from Schizochytrium, and biologically active fragments and homologues thereof. More particularly, this invention relates to nucleic acids encoding such PUFA PKS systems, to proteins and domains thereof that comprise such PUFA PKS systems, to genetically modified organisms (plants and microorganisms) comprising such PUFA PKS systems, and to methods of making and using the PUFA PKS systems disclosed herein. This invention also relates to genetically modified plants and microorganisms and methods to efficiently produce lipids enriched in various polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) as well as other bioactive molecules by manipulation of a PUFA polyketide synthase (PKS) system.
Owner:MARTEK BIOSCIENCES CORP
Polyunsaturated fatty acid production in heterologous organisms using pufa polyketide synthase systems
InactiveCN101573451AImprove the level ofReduce competitionMicrobiological testing/measurementAcyl Coenzyme A SynthetasesBiotechnology
Disclosed are novel acyl-CoA synthetases and novel acyltransferases, nucleic acid molecules encoding the same, recombinant nucleic acid molecules and recombinant host cells comprising such nucleic acid molecules, genetically modified organisms (microorganisms and plants) comprising the same, and methods of making and using the same. Also disclosed are genetically modified organisms (e.g., plants, microorganisms) that have been genetically modified to express a PKS-like system for the production of PUFAs (a PUFA PKS system or PUFA synthase), wherein the organisms have been modified to express an acyl-CoA synthetase, to express an acyl transferase, to delete or inactivate a fatty acid synthase (FAS) expressed by the organism, to reduce competition for malonyl CoA with the PUFA synthase or toincrease the level of malonyl CoA in the organism, and in one aspect, to inhibit KASII or KASIII. Additional modifications, and methods to make and use such organisms, in addition to PUFAs and oils o btained from such organisms, are disclosed, alone with various products including such PUFAs and oils.
Owner:DSM IP ASSETS BV
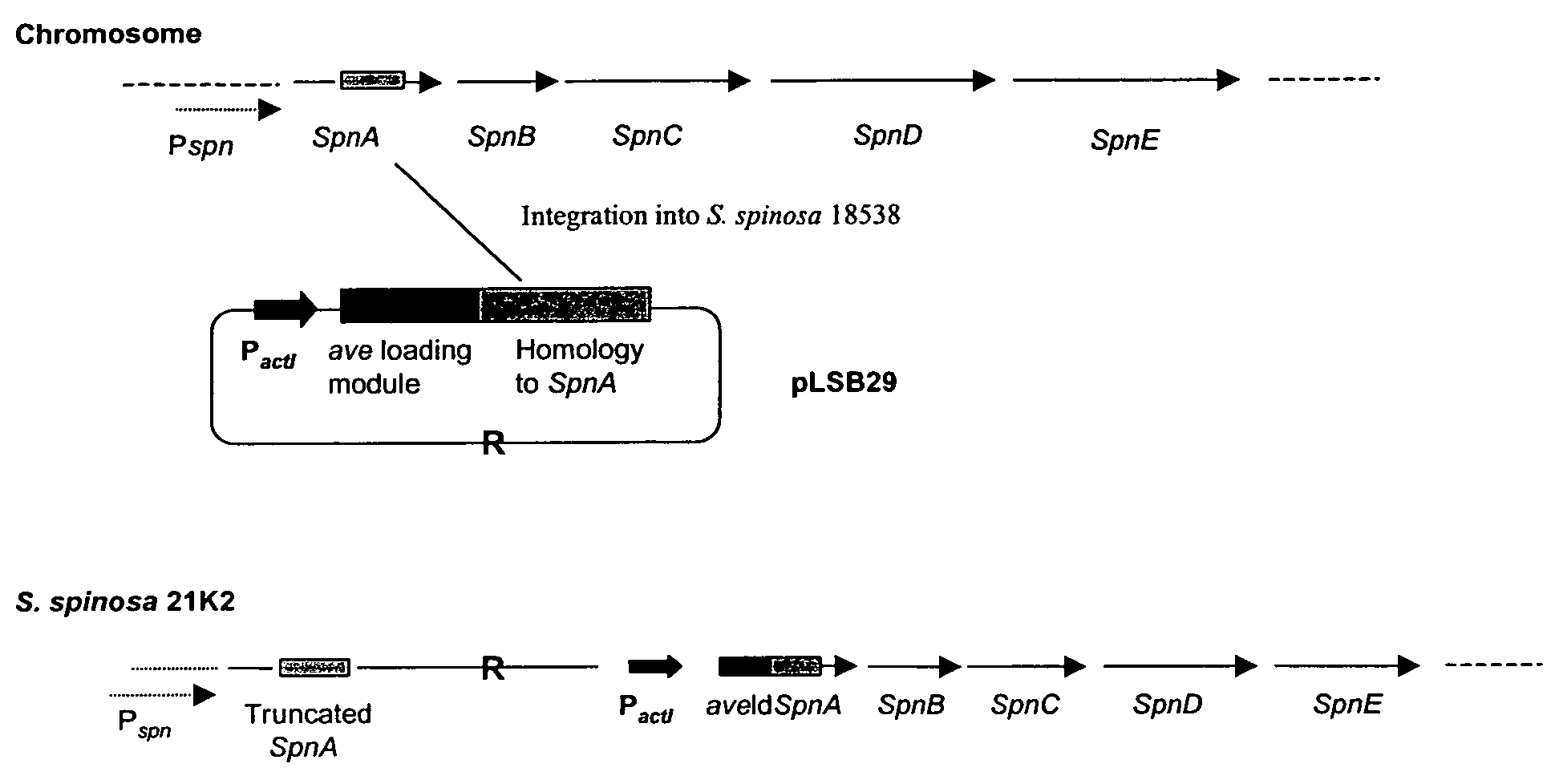
Spinosyn-producing polyketide synthases
The invention provides, biologically active spinosyns, hybrid spinosyn polyketide synthases capable of functioning in Saccharopolyspora spinosa to produce the spinosyns, and methods of controlling insects using the spinosyns.
Owner:CORTEVA AGRISCIENCE LLC
Marine streptomyces S187 having wide-spectrum antibacterial activity
InactiveCN101302482AHas broad-spectrum antimicrobial activityHigh antibacterial activityBiocideBacteriaEscherichia coliStaphylococcus aureus
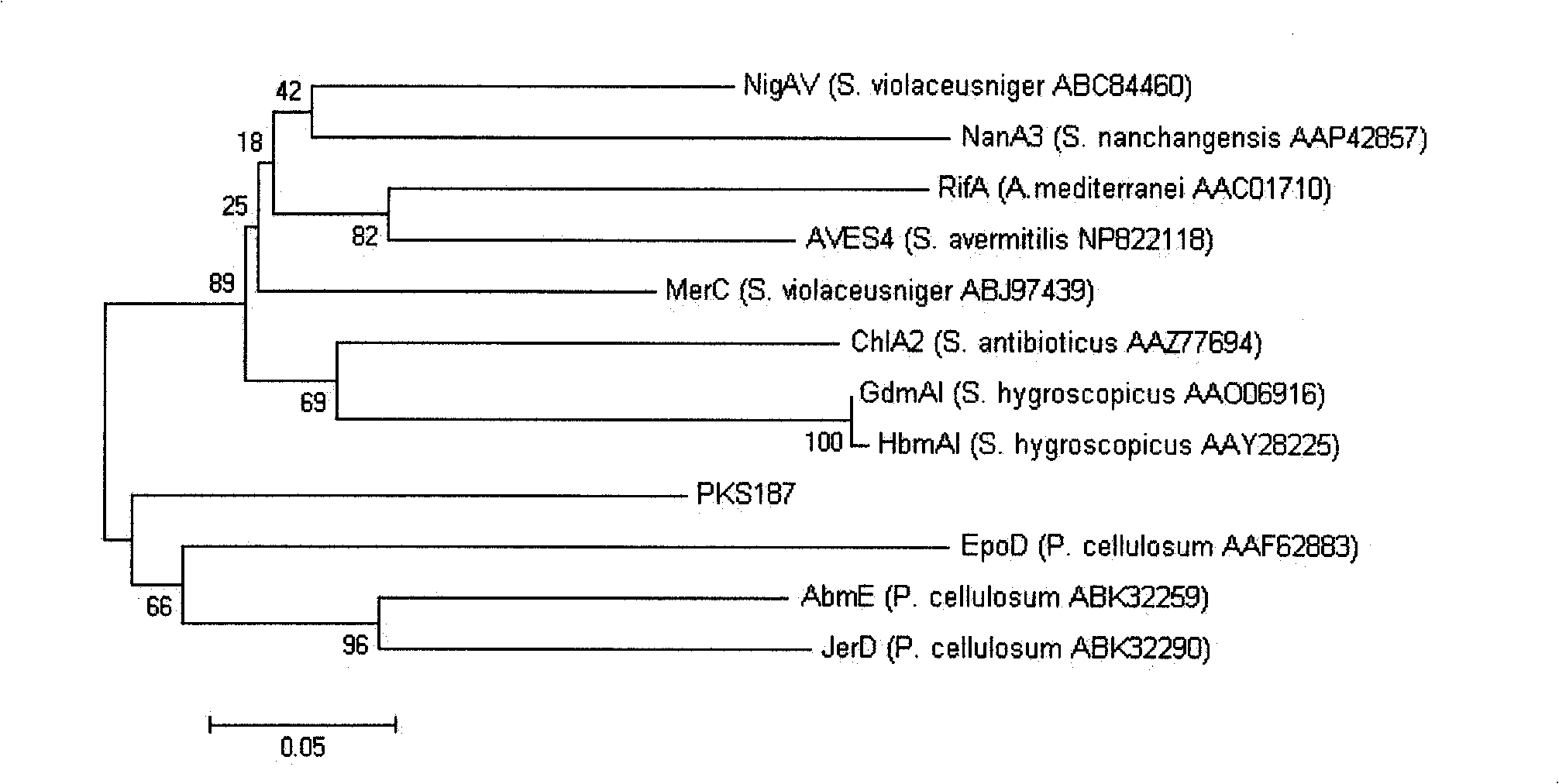
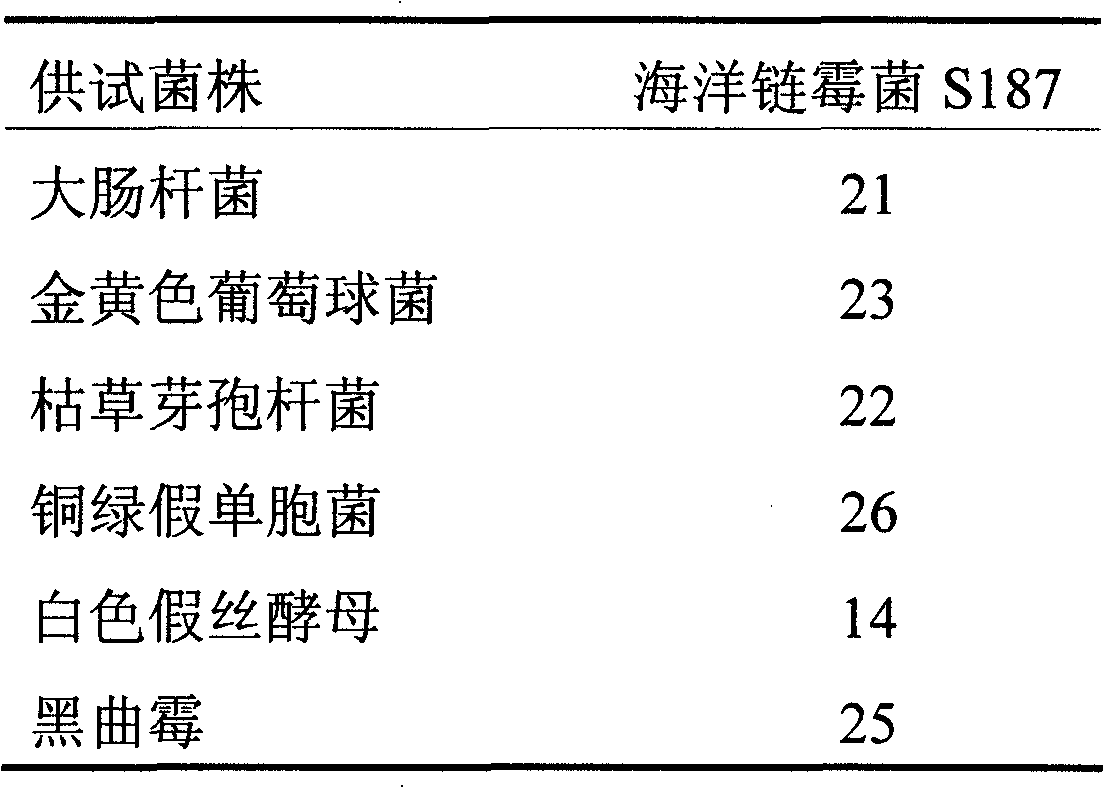
The invention relates to marine streptomyces S187 having broad-spectrum antibacterial activity, belonging to the microbiological actinomycetes field. The marine streptomyces S187 is separated from a sea mud sample at a depth of 20 meters underwater in coastal waters. Primary screening through an agar block method proves that the bacterial strain has very strong antibacterial activity to Escherichia coli, Staphylococcus aureus, Bacillus subtilis, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Candida albicans and Aspergillus niger; the result of fermentation liquid secondary screening confirms good activity for antagonizing the Escherichia coli, the Staphylococcus aureus and the Bacillus subtilis. The analysis for 16S rDNA shows that the only actinomycetes having the homology as high as 99 percent with the marine streptomyces S187 is the salt lake bacterial strain Streptomyces chungwhensis (DSM41483) separated by Korean scholars, but the bacterial strain is separated from the sea mud sample for the first time. I type polyketide synthase (PKSI) is successfully amplified out from the streptomyces S187, which indicates that the streptomyces S187 has the potential ability of generating polyketide.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Biological synthesis gene cluster for Azintamide
InactiveCN101275141AUnderstanding Biosynthetic MechanismsFermentationPlant genotype modificationHeterologousEnzyme Gene
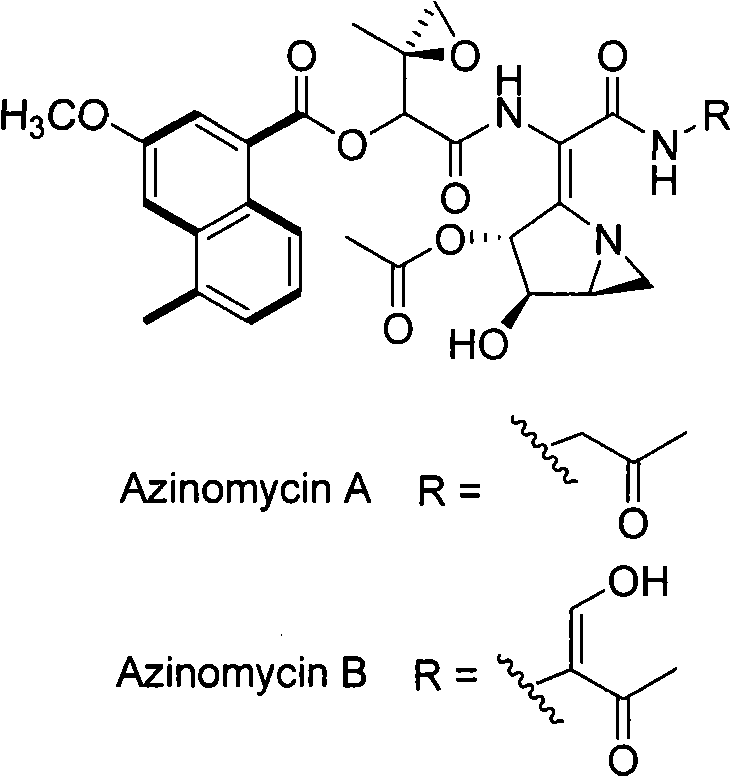
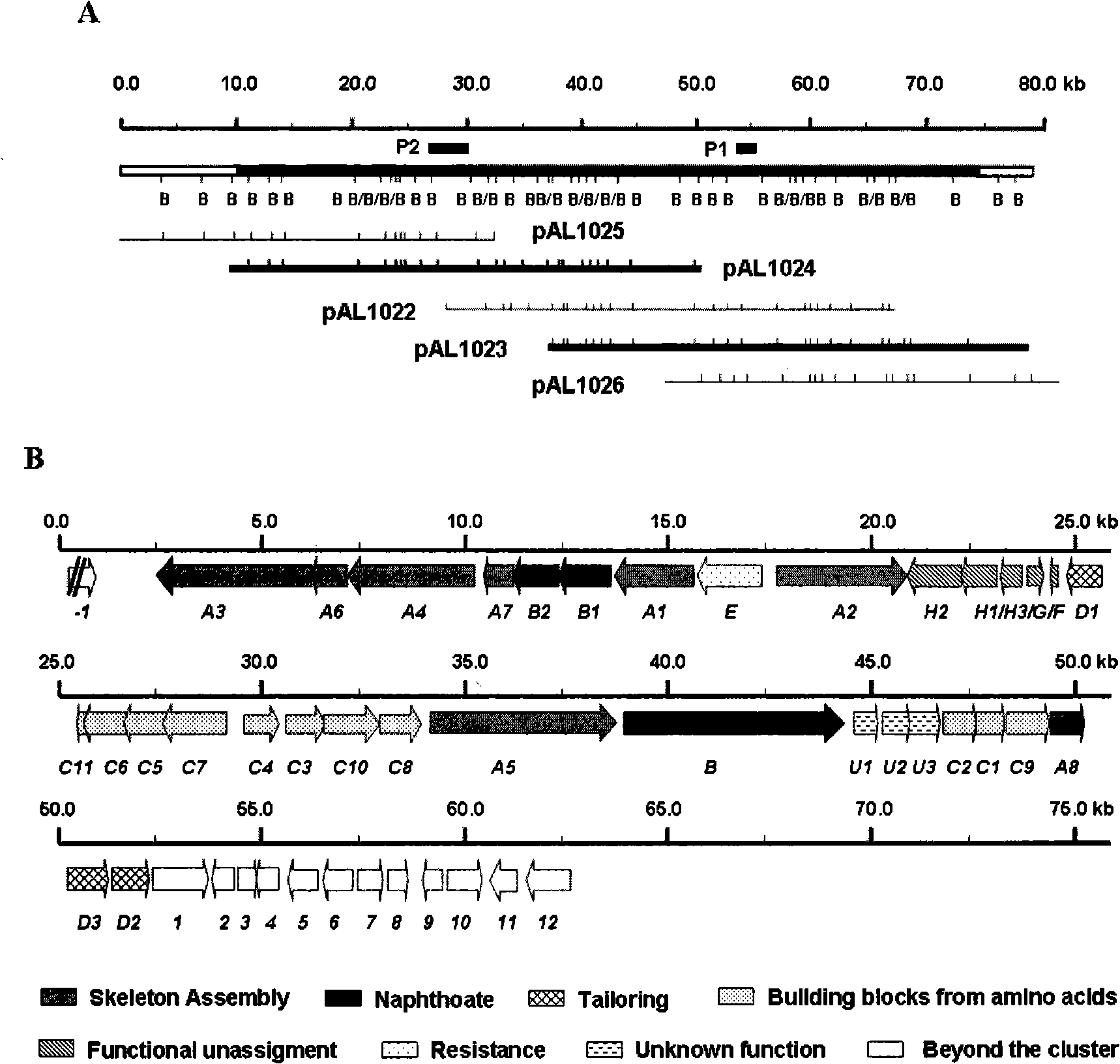
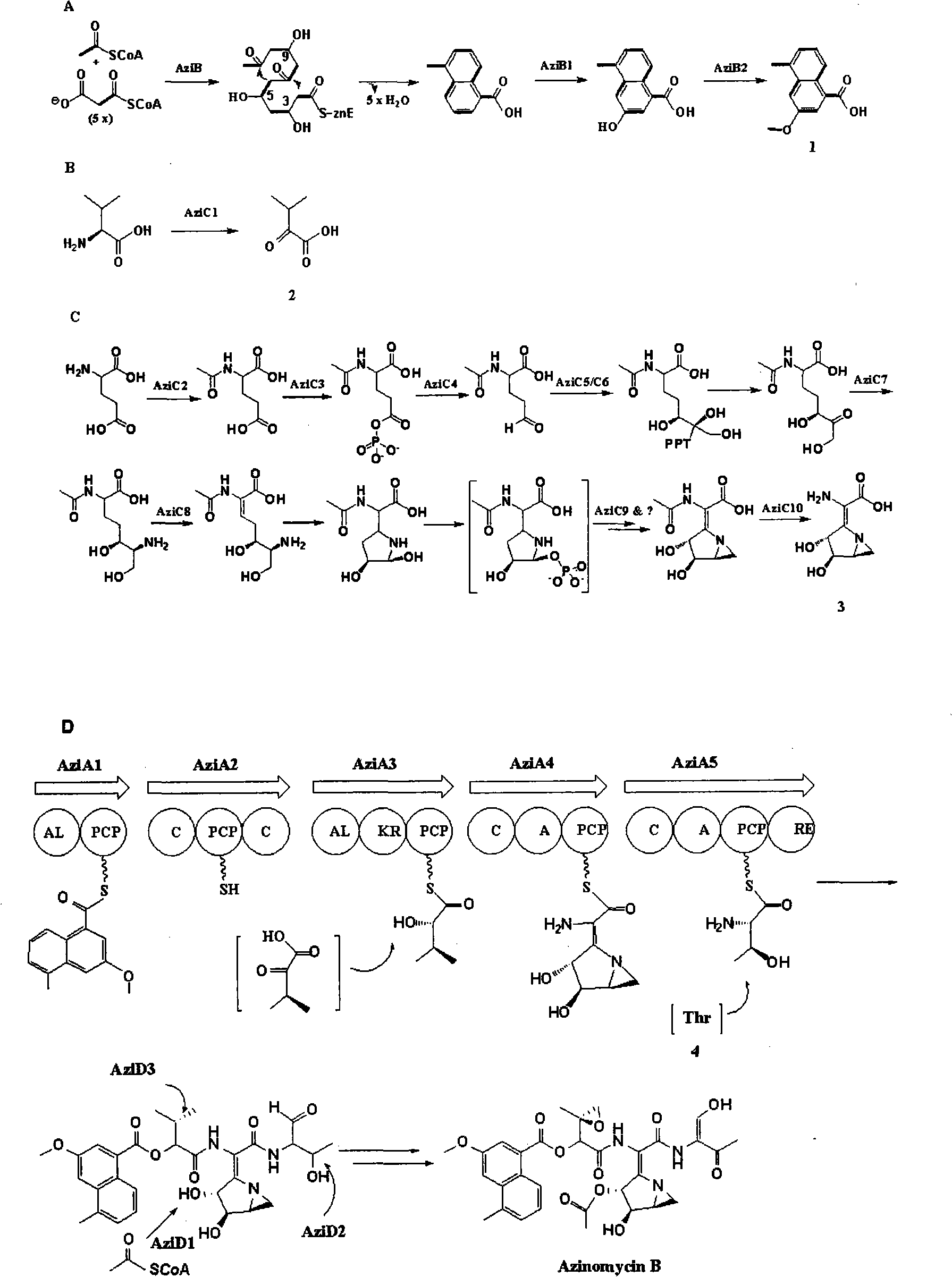
The present invention provides cloning sequencing, analyzing, function research of a biosynthesis gene cluster of an antibiotic-Azinomycin B having antitumor activity produced by streptomyces, and its application. The whole gene cluster includes 34 genes: one repeatedly using I type polyketide synthase gene; two naphthalene ring modification enzyme genes; 8 non-ribosomal polypeptide skeleton synthesis and modification enzyme genes; 11 non-natural amino acid structure unit synthase genes; 1 resistance gene; 3 post modification enzyme genes and 8 genes which functions are not determined. The genetic operation of the biosynthesis gene breaks the synthesis of Azinomycin B; the precursor compound is produced by the heterologous expression of synthesis gene and modification gene of naphthalene ring. The gene of the invention and the protein can be used for searching and finding compound or gene, protein applied in medical, industry or agriculture.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF ORGANIC CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Genetic engineering bacterium for high-yield phloroglucinol as well as construction method and application of genetic engineering bacterium
ActiveCN104388371AIncrease productionImprove synthesis abilityBacteriaPeptidesCarbon metabolismCarbon storage
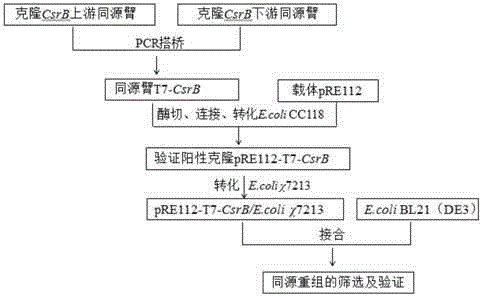
The invention discloses a genetic engineering bacterium for high-yield phloroglucinol as well as a construction method and an application of the genetic engineering bacterium and belongs to the technical field of genetic engineering. The genetic engineering bacterium over-expresses carbon storage and regulation factor gene CsrB shown by SEQ ID NO.1 and co-expresses a polyketide synthase gene phlD, a multiple resistance activating factor gene marA and acetyl CoA carboxylase gene ACCase. The invention also provides the construction method and the application of the genetic engineering bacterium for the high-yield phloroglucinol. With the adoption of the genetic engineering bacterium, the yield of the phloroglucinol is firstly increased by 115.6 percent by adopting a mode of globally regulating carbon metabolism after post-transcriptional level of the genetic engineering bacterium, and the genetic engineering bacterium has a high industrial application value.
Owner:QINGDAO INST OF BIOENERGY & BIOPROCESS TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Novel spinosyn-producing polyketide synthases
The invention provides, biologically active spinosyns, hybrid spinosyn polyketide synthases capable of functioning in Saccharopolyspora spinosa to produce the spinosyns, and methods of controlling insects using the spinosyns.
Owner:CORTEVA AGRISCIENCE LLC
Method for synthesizing phloroglucinol by microbial catalysis
A method for synthesizing phloroglucinol by microbial catalysis relates to a method for synthesizing phloroglucinol by catalysis of engineering escherichia coli cells. The method for synthesizing phloroglucinol by catalysis of engineering escherichia coli cells comprises the following steps of: compounding, inducing, selecting and optimizing anti-phloroglucinol mutant strains by employing HNO2 and LiCl; carrying out PCR amplification by taking the genome DNA of bacterium Pseudomonas fluorescens Pf-5 as a template to obtain a polyketide synthase gene (phlD); connecting with a pET carrier after cleavage, transferring to the anti-phloroglucinol mutant strains, and inudcing and expressing a target protein by using IPTG to obtain the engineering escherichia coli for catalyzing and synthesizing the phloroglucinol. The phloroglucinol can be obtained in the fermentation liquor after the engineering escherichia coli are fermented, and the phloroglucinol is extracted and concentrated to get the finished phloroglucinol. The invention first provides the method for synthesizing phloroglucinol by catalysis of the engineering escherichia coli, and lays a solid foundation for catalyzing and synthesizing phloroglucinol by an environment-friendly synthetic process in future.
Owner:青岛生物能源与过程研究所
Pufa polyketide synthase systems and uses thereof
Disclosed are the complete polyunsaturated fatty acid (PUFA) polyketide synthase (PKS) systems from Schizochytrium, and biologically active fragments and homologues thereof. More particularly, this invention relates to nucleic acids encoding such PUFA PKS systems, to proteins and domains thereof that comprise such PUFA PKS systems, to genetically modified organisms (plants and microorganisms) comprising such PUFA PKS systems, and to methods of making and using the PUFA PKS systems disclosed herein. This invention also relates to genetically modified plants and microorganisms and methods to efficiently produce lipids enriched in various polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) as well as other bioactive molecules by manipulation of a PUFA polyketide synthase (PKS) system.
Owner:DSM IP ASSETS BV
Preparing and detecting method for bacterium phosphopantetheinyl transferase antibody
The invention relates to a phosphopantetheinyl transferase. The phosphopantetheinyl transferase has a base sequence of a sequence table SEQ ID No.1, or has an amino acid sequence of a sequence table SEQ ID No.2. The invention further relates to a prokaryotic expression method for the phosphopantetheinyl transferase, a method for obtaining purified protein and a preparing method for a polyclonal antibody. According to the phosphopantetheinyl transferase antibody, an external-source phosphopantetheinyl transferase is obtained, and the polyclonal antibody of the protein and a Western blotting detecting method of the protein are obtained, the foundation is laid for further developing functional analysis of phosphoric-acid pantetheine in a bacterium, and the important basis is provided for a polyketide synthase system in the bacterium body in bioengineering.
Owner:HUBEI UNIV OF TECH
Gene modification method for increasing yield of phloroglucinol and application of same
InactiveCN104388457AIncrease productionHigh industrial application valueBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyCarbon metabolism
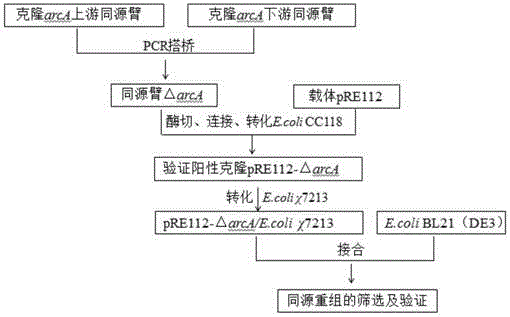
The invention discloses a gene modification method for increasing the yield of phloroglucinol and application of the same, and belongs to the technical field of genetic engineering. The gene modification method comprises the following steps: obtaining a mutant strain by virtue of a mode of knocking out or inserting a global regulating factor arcA gene of an original strain, converting the state of the mutant strain to a competent state, introducing recombinant plasmids containing a polyketide synthase gene phlD, a multiple resistance activating factor marA and acetyl CoA carboxylase gene ACCase, and obtaining a recombinant cell. The invention also provides a method of producing the phloroglucinol by utilizing the recombinant cell. According to the gene modification method and application disclosed by the invention, the yield of the phloroglucinol after fermentation is firstly increased by 2.06 times by adopting a mode of globally regulating carbon metabolism after post-transcriptional level, and the gene modification method and application have high industrial application value.
Owner:QINGDAO INST OF BIOENERGY & BIOPROCESS TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Producing biofuels using polyketide synthases
The present invention provides for a non-naturally occurring polyketide synthase (PKS) capable of synthesizing a carboxylic acid or a lactone, and a composition such that a carboxylic acid or lactone is included. The carboxylic acid or lactone, or derivative thereof, is useful as a biofuel. The present invention also provides for a recombinant nucleic acid or vector that encodes such a PKS, and host cells which also have such a recombinant nucleic acid or vector. The present invention also provides for a method of producing such carboxylic acids or lactones using such a PKS.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
PUFA polyketide synthase systems and uses thereof
Disclosed are the complete polyunsaturated fatty acid (PUFA) polyketide synthase (PKS) systems from Schizochytrium, and biologically active fragments and homologues thereof. More particularly, this invention relates to nucleic acids encoding such PUFA PKS systems, to proteins and domains thereof that comprise such PUFA PKS systems, to genetically modified organisms (plants and microorganisms) comprising such PUFA PKS systems, and to methods of making and using the PUFA PKS systems disclosed herein. This invention also relates to genetically modified plants and microorganisms and methods to efficiently produce lipids enriched in various polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) as well as other bioactive molecules by manipulation of a PUFA polyketide synthase (PKS) system.
Owner:DSM IP ASSETS BV
Bitespiramycin biosynthetic gene cluster
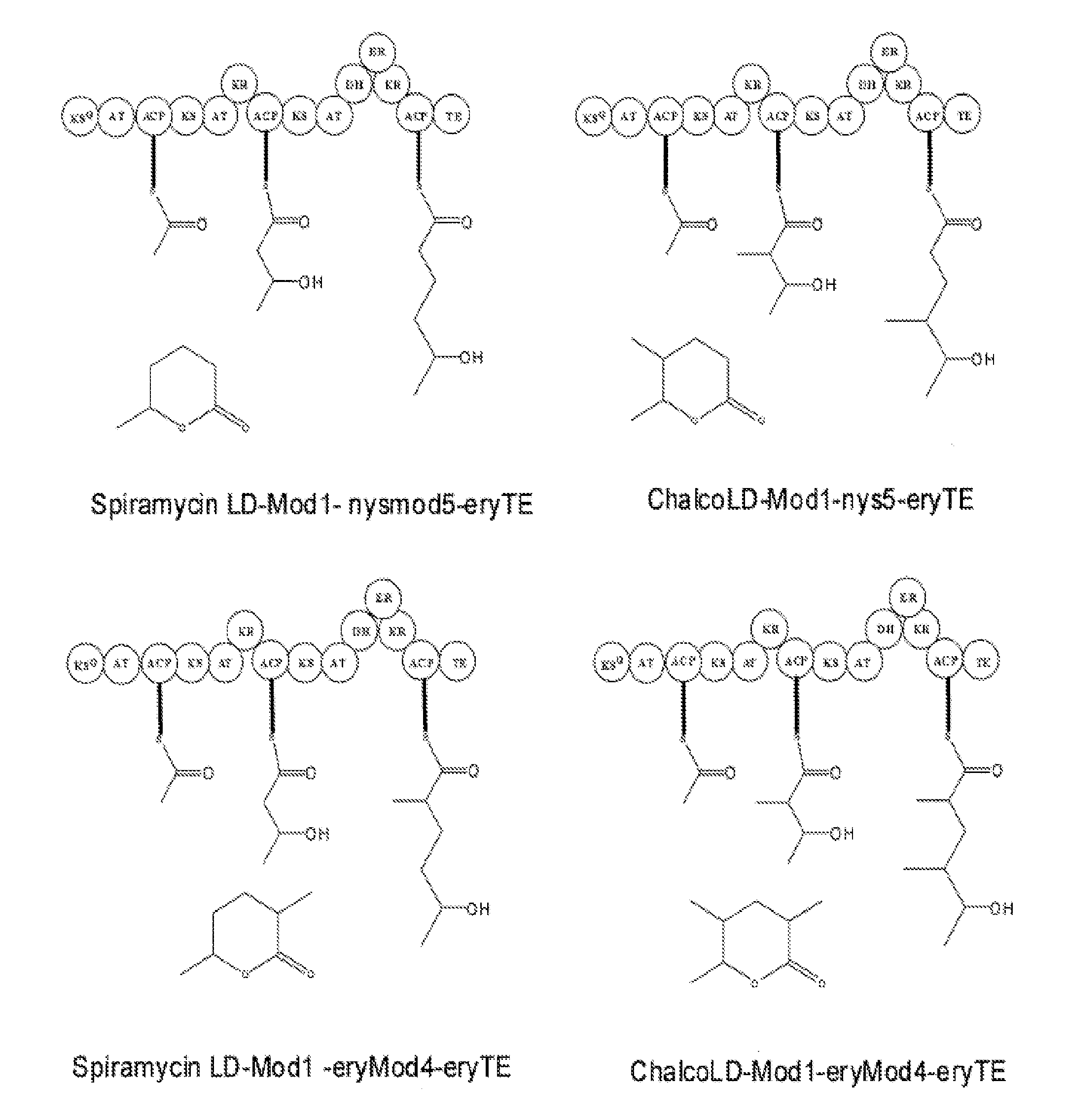
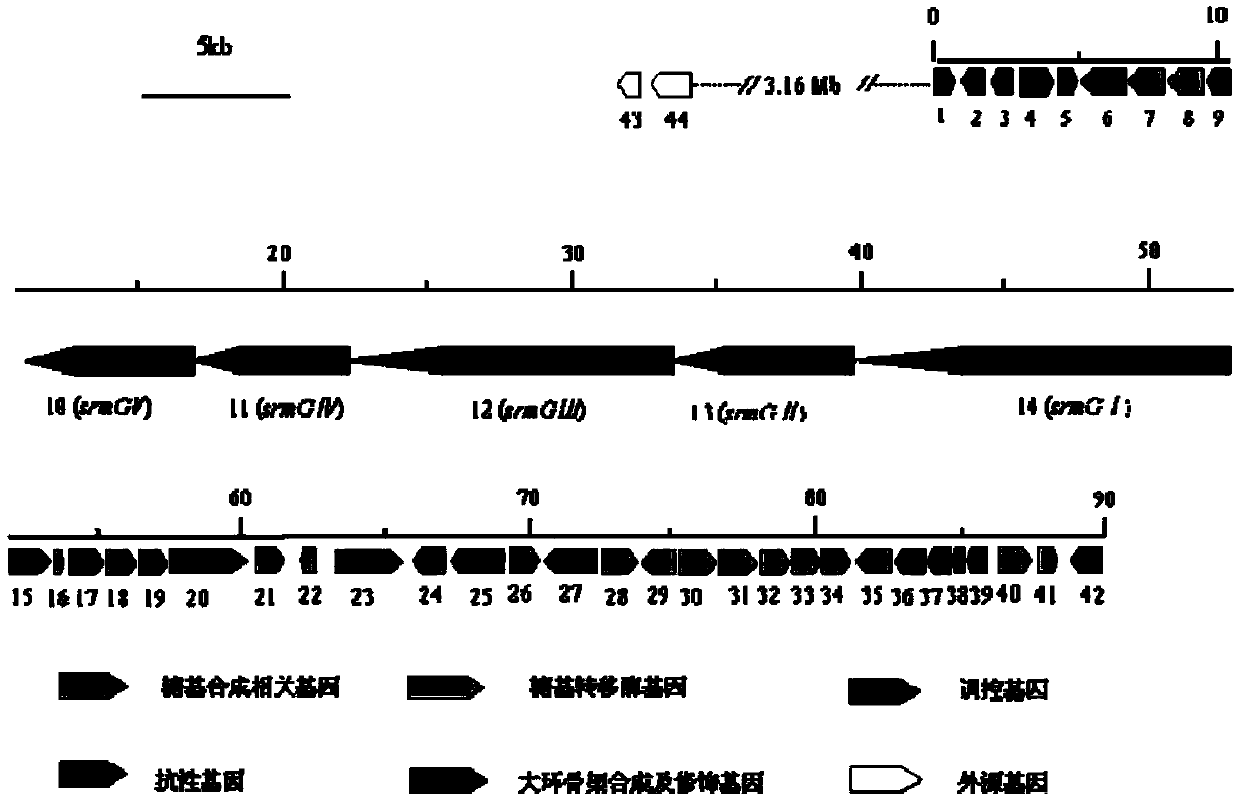
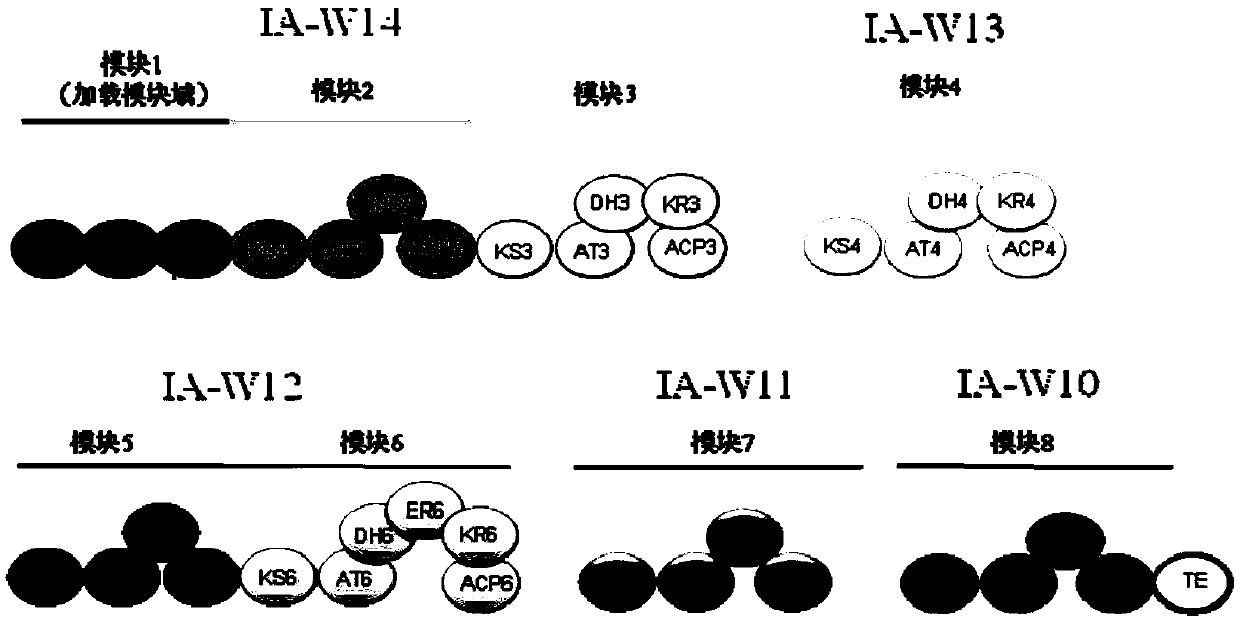
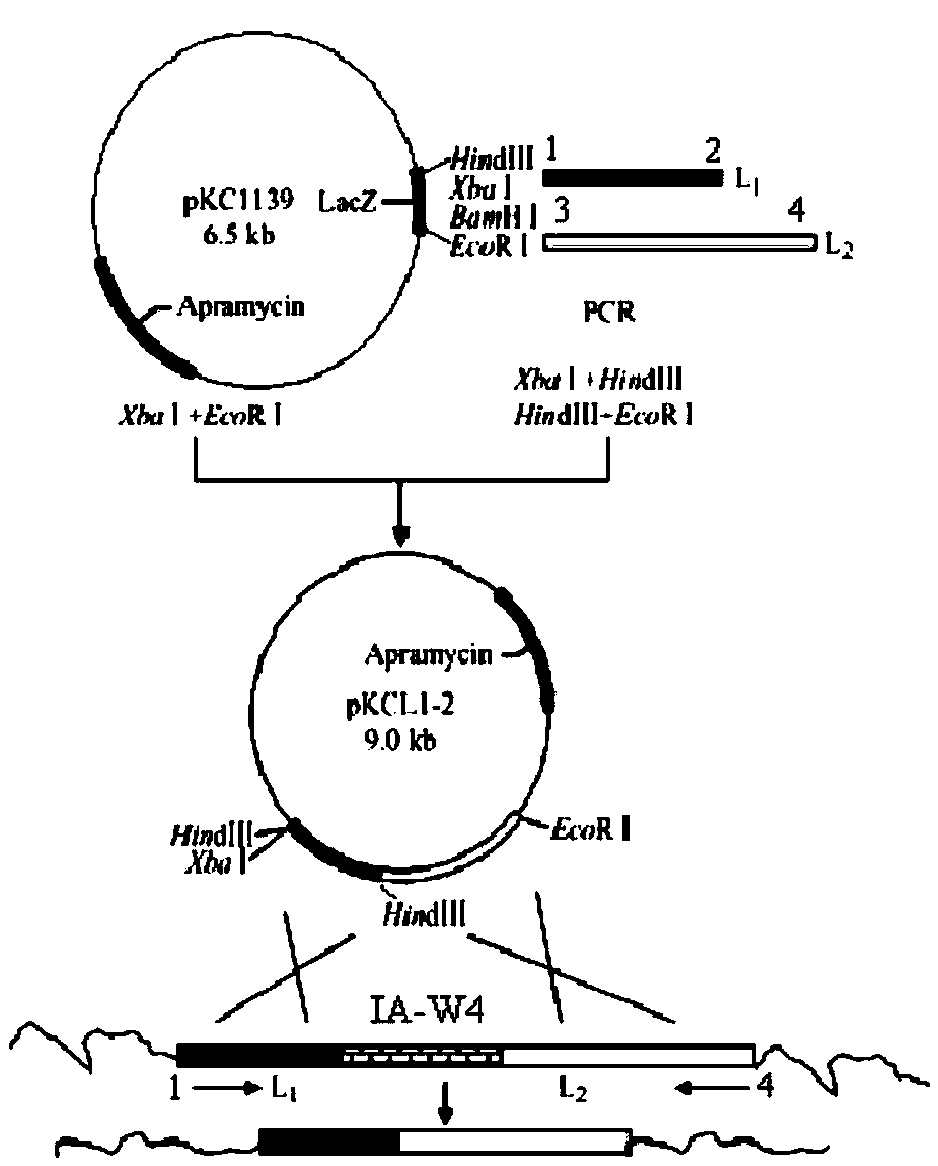
The invention provides a bitespiramycin biosynthetic gene cluster. The bitespiramycin biosynthetic gene cluster totally has 44 gene open reading frames, a total length of a nucleotide sequence is 89315 bp, and the bitespiramycin biosynthetic gene cluster contains 5 encoded polyketide synthases and comprises 8 modules, 37 structural domains, 9 orf related to the polyketone synthesis extension unit and modification, 16 orf related to glycosyl synthesis and 6 orf related to glycosyl transfer. By virtue of the analysis on the sequence information and structure of the gene cluster, the genetic manipulation can be further performed on a producing strain to obtain a novel and more effective antibiotic, for example, a novel macrolides antibiotic can be created by adopting the genetic manipulation to change the PKS synthetic modular structure, performing the alteration of lactonic ring post-translational modification and replacing or modifying the glycosyl, and the yield of the antibiotic can be increased by virtue of the genetic manipulation on a resistance gene or a regulation gene. The amino acid sequence provided by the invention can be used for separating needed proteins and can be used for preparing an antibody.
Owner:SHANGHAI TONGLIAN PHARMA CO LTD
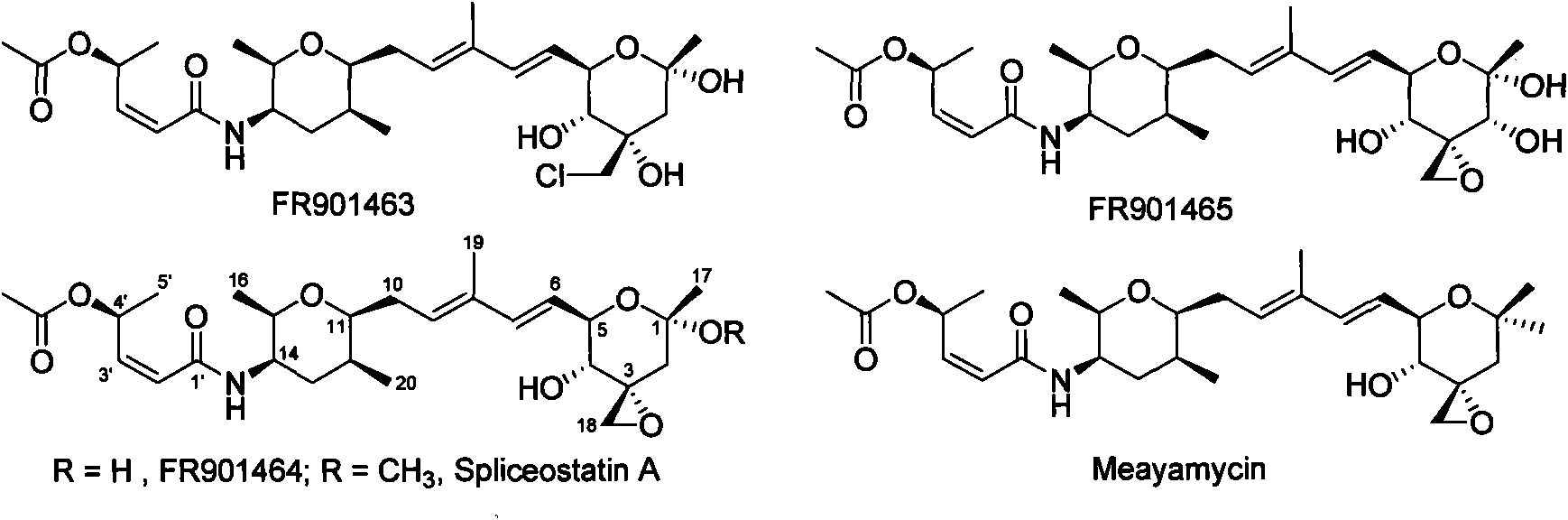
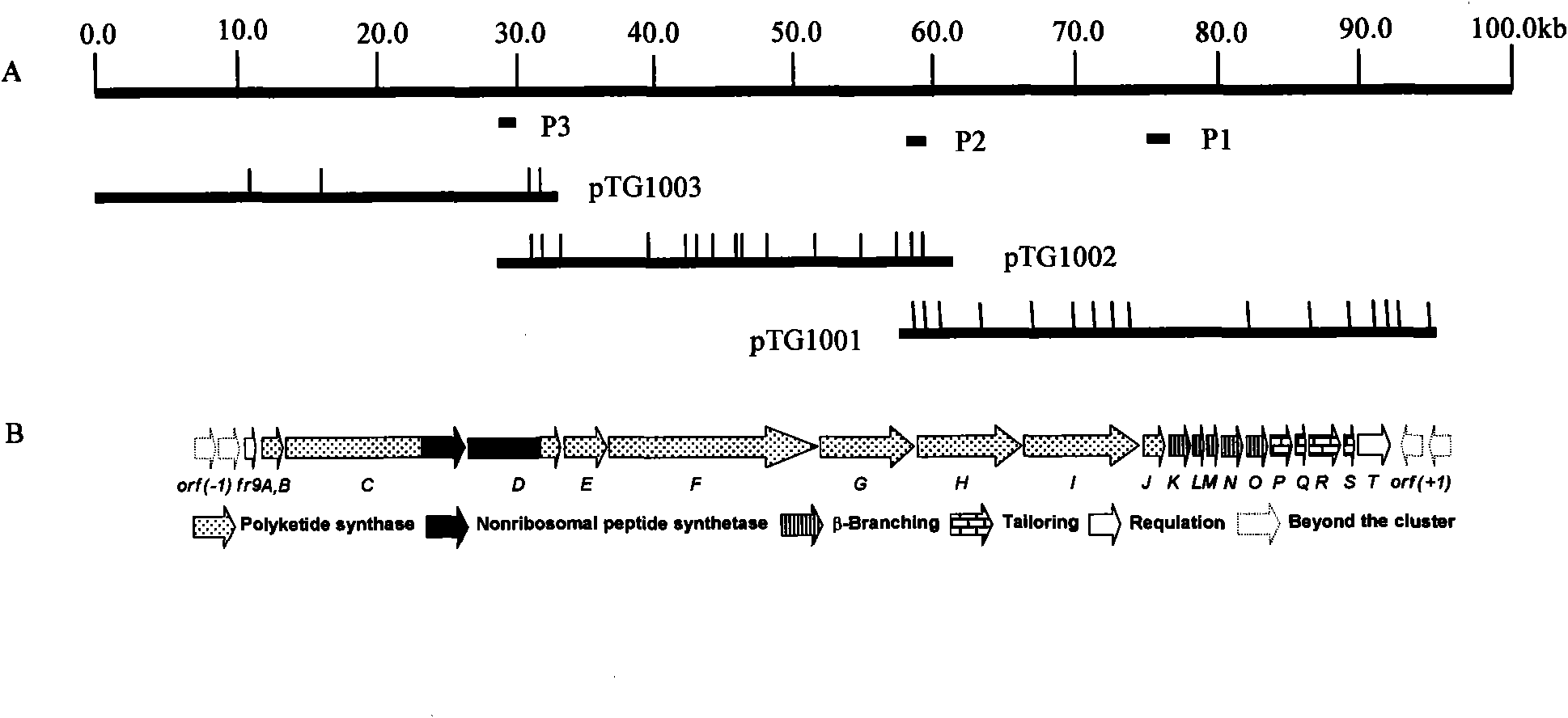
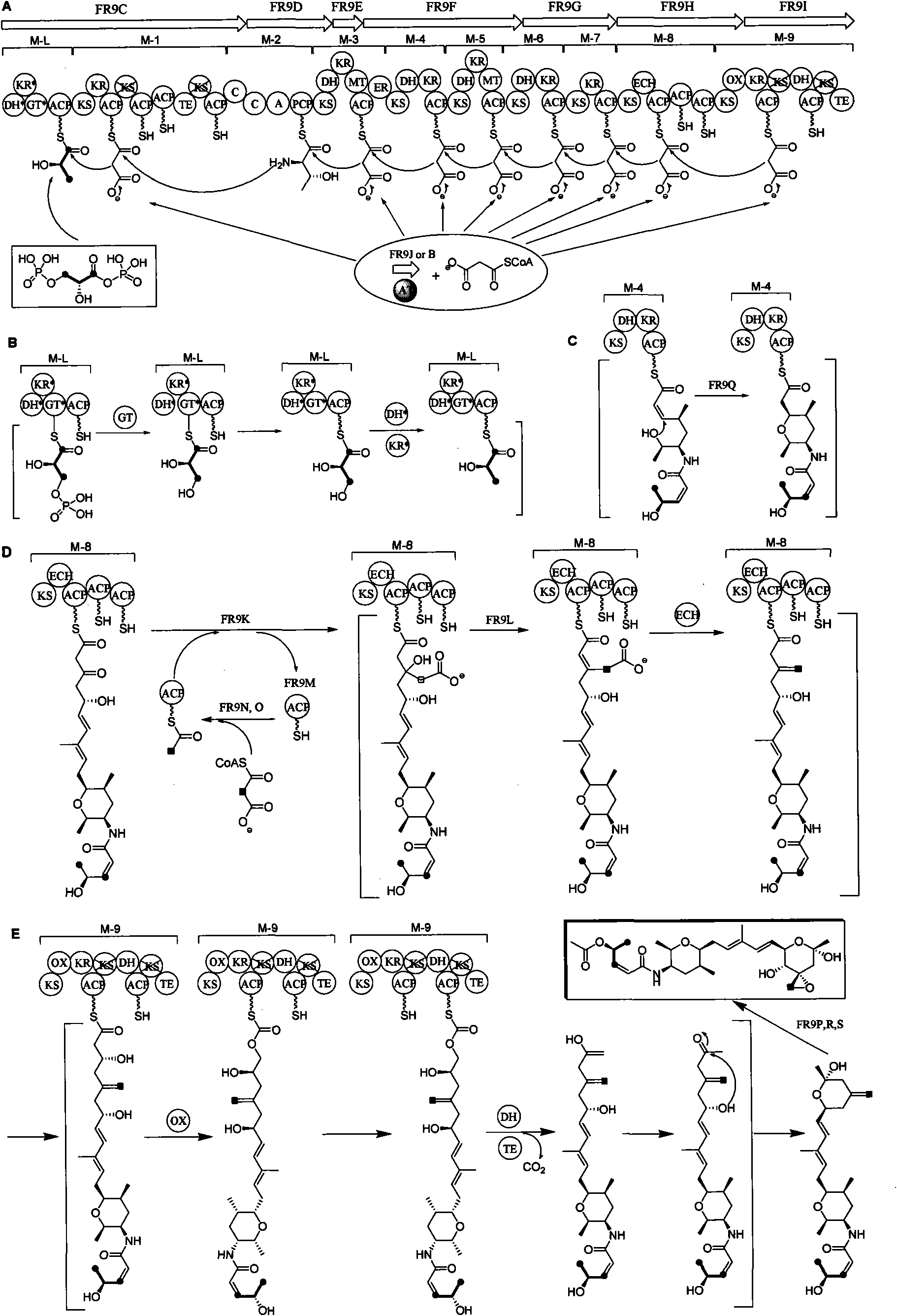
Biosynthetic gene cluster of FR901464
ActiveCN101818158AUnderstanding Biosynthetic MechanismsDepsipeptidesFermentationBiosynthetic genesGenetic engineering
The invention relates to cloning, sequencing, analysis and functional study of a biosynthetic gene cluster of a natural product FR901464 which has anti-tumor activity and is generated from pseudomonas as well as the application thereof. The whole gene cluster contains 20 genes: five polyketide synthase genes, one hybrid polyketide / non-ribosomal polypeptide synthase gene, one non-ribosomal polypeptide synthase gene, three independent acyltransferase genes, four genes related to polyketide backbone alkylation, four post-modification genes and two control-related genes. The genetic operation of the biosynthetic gene can block the biosynthesis of FR901464. The provided gene and protein thereof can be used for genetic engineering, protein expression, enzyme catalysis reaction, and the like of the compound and can also be used for searching and discovering compounds that can be used in medicines, industry or agriculture or genes and proteins thereof.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF ORGANIC CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com