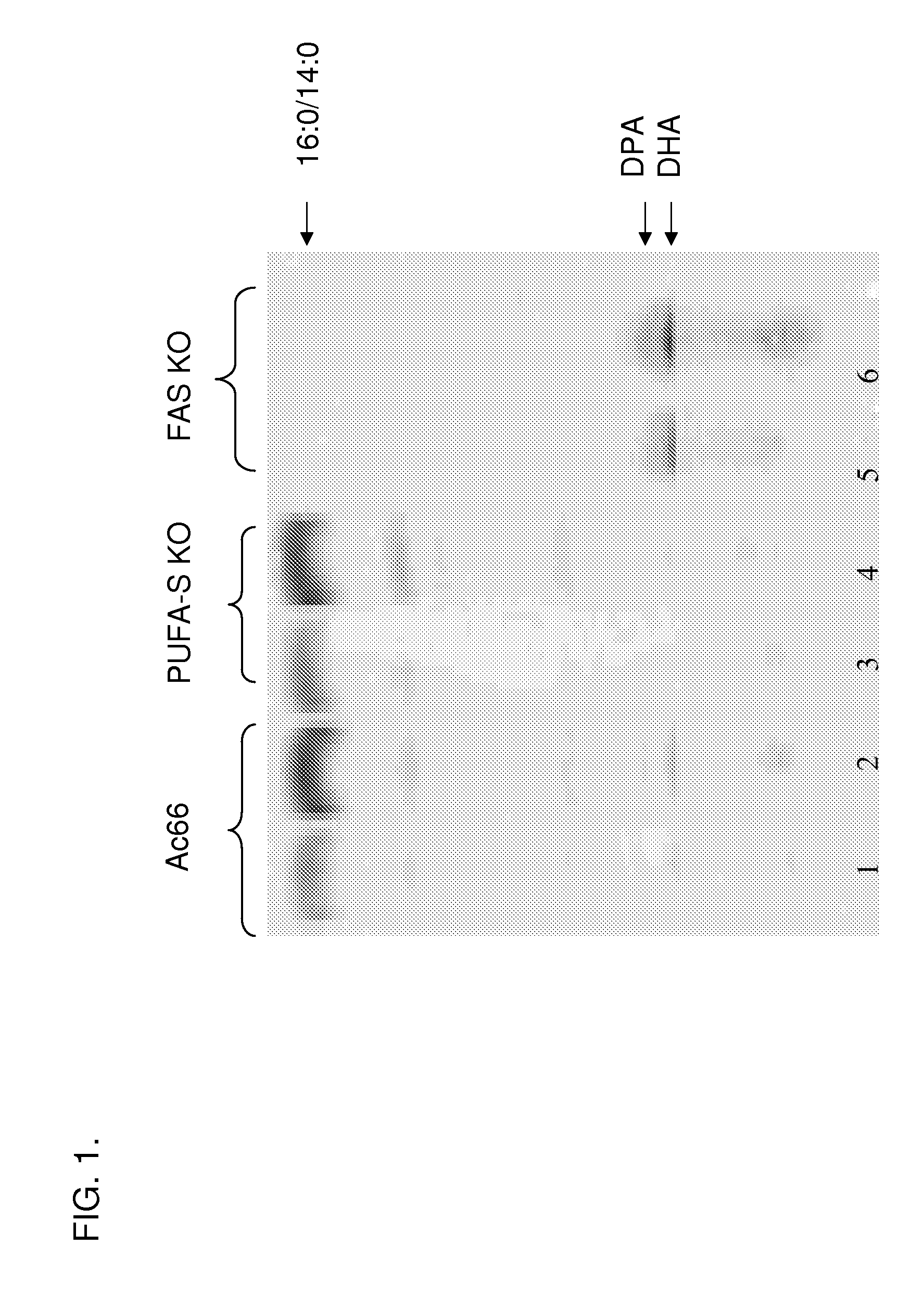
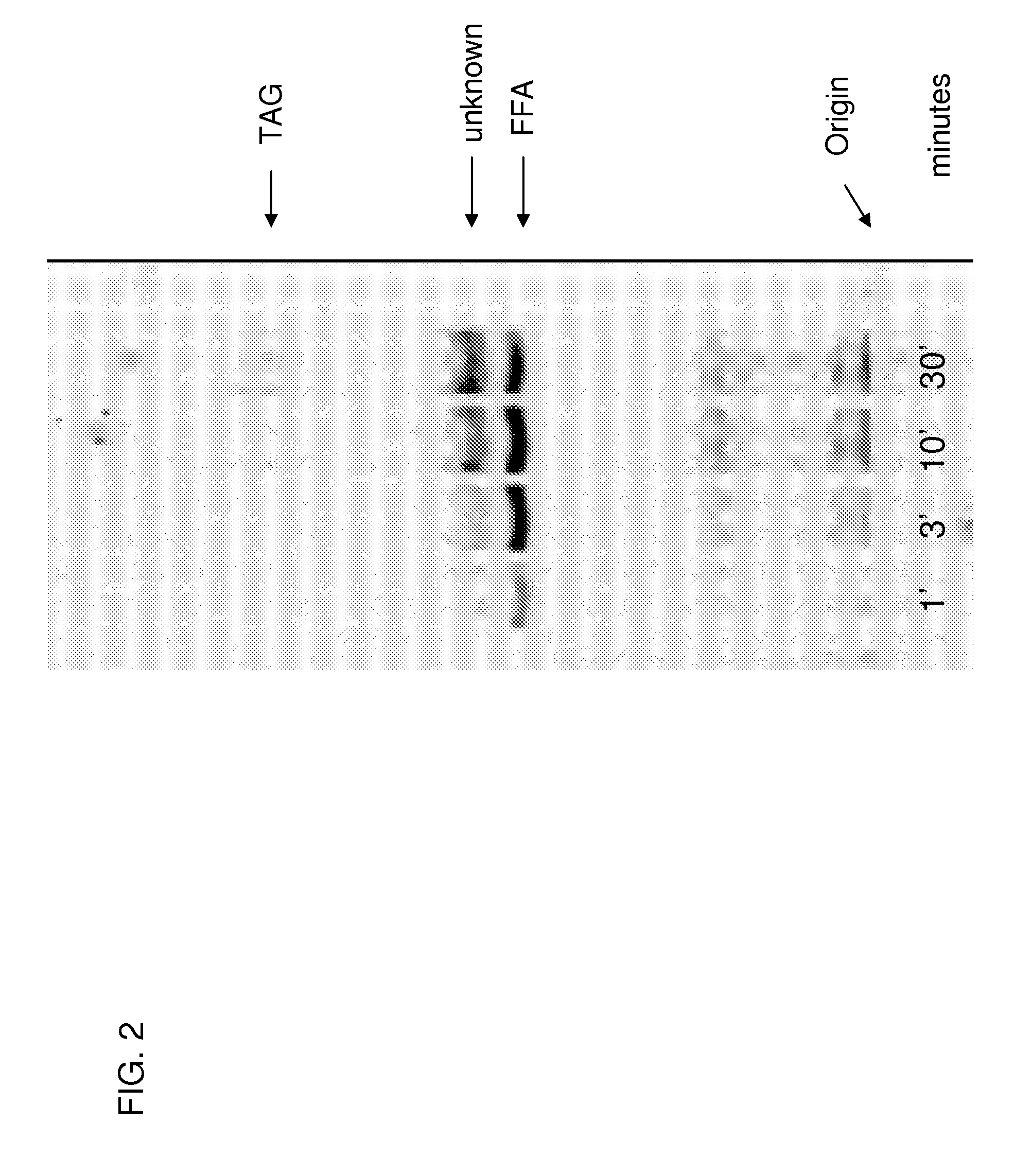
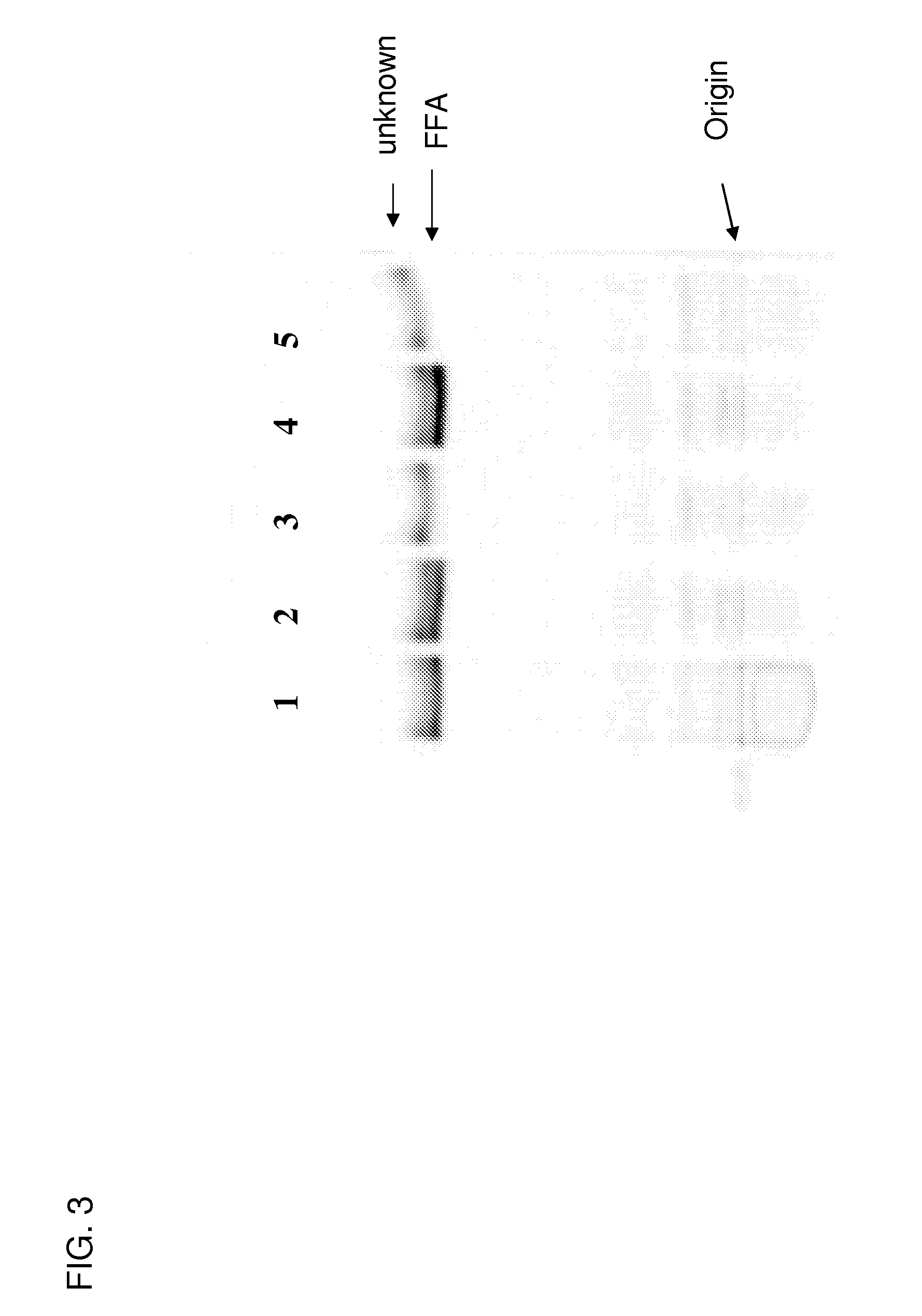
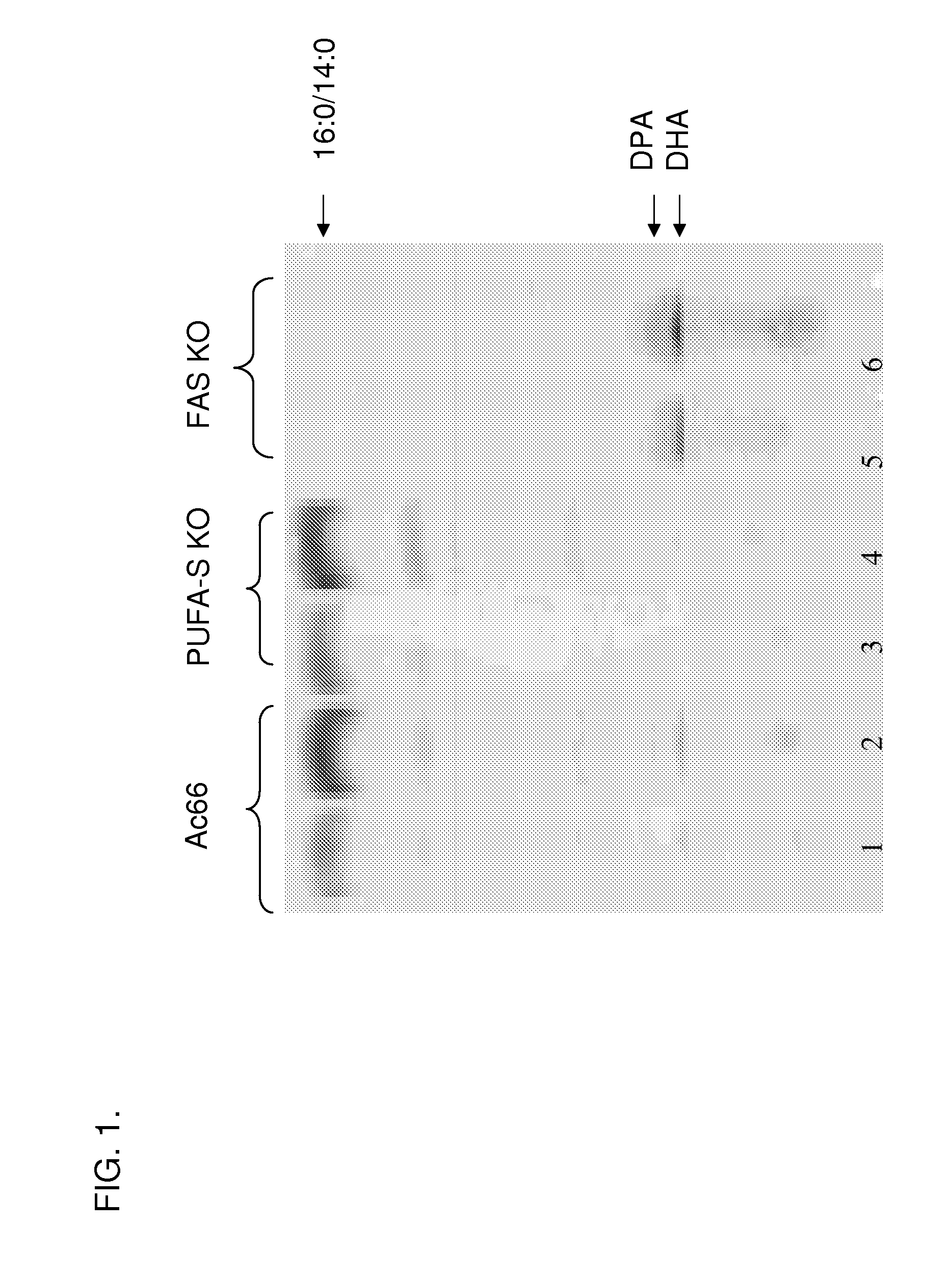
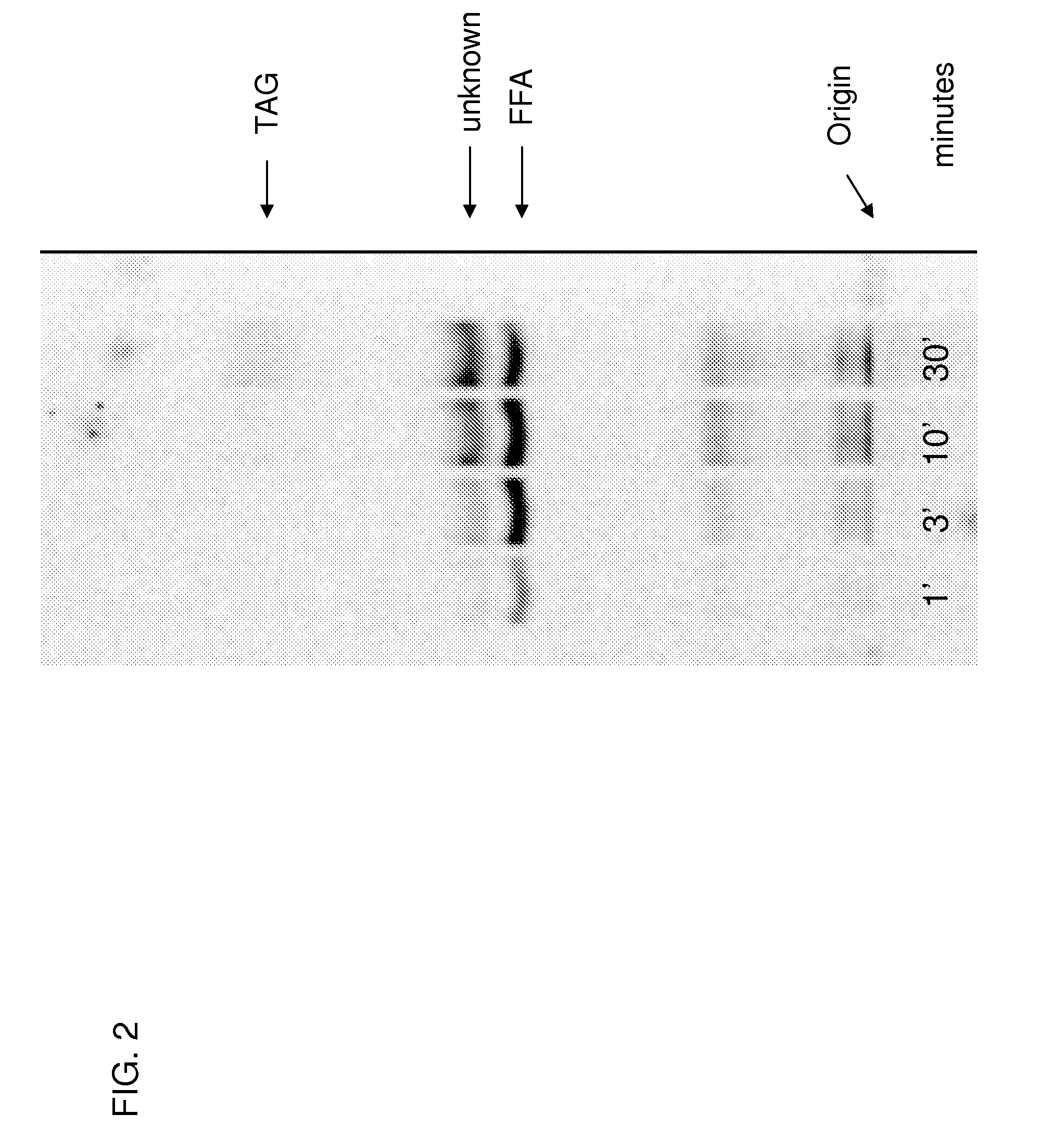
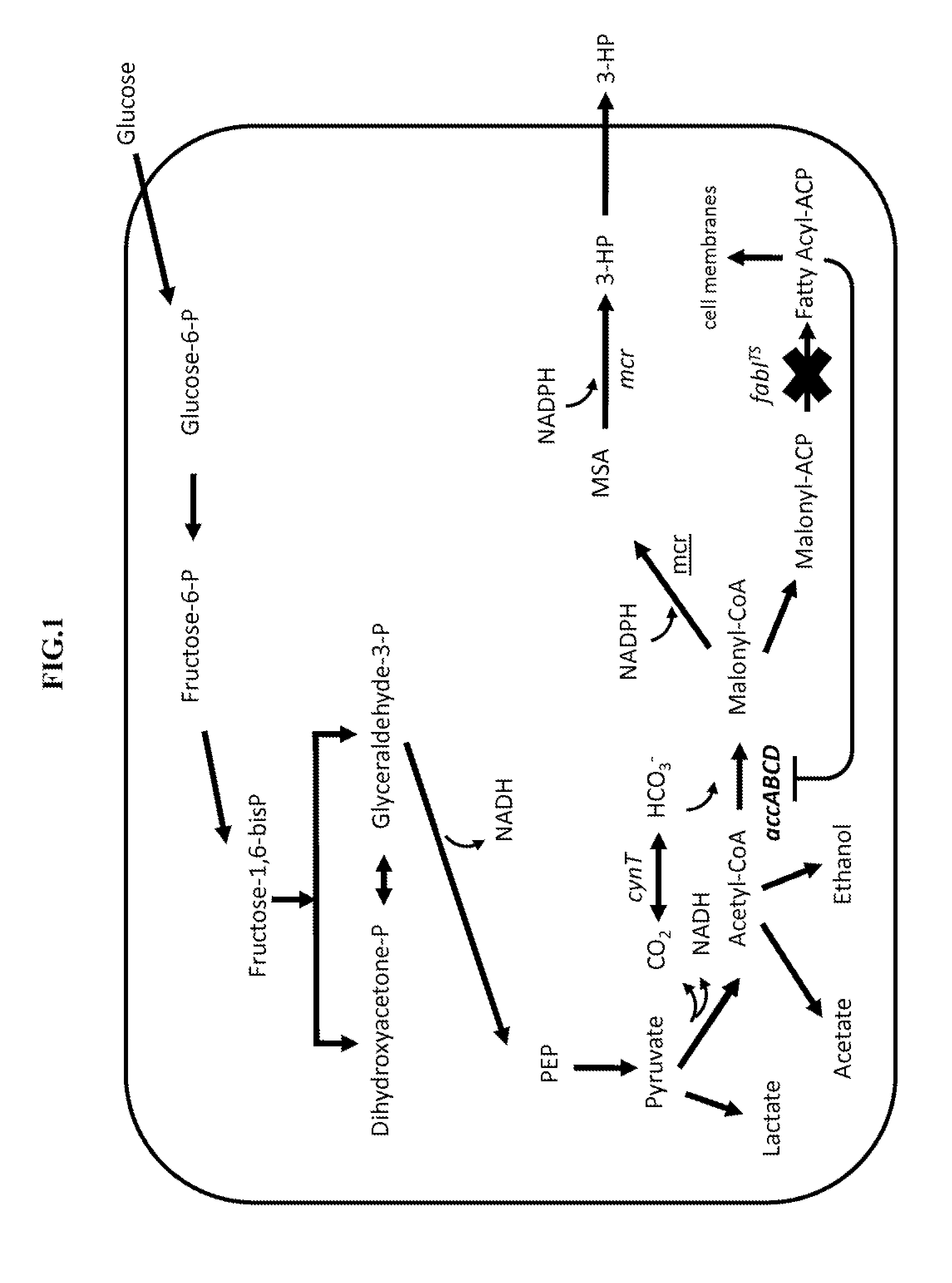
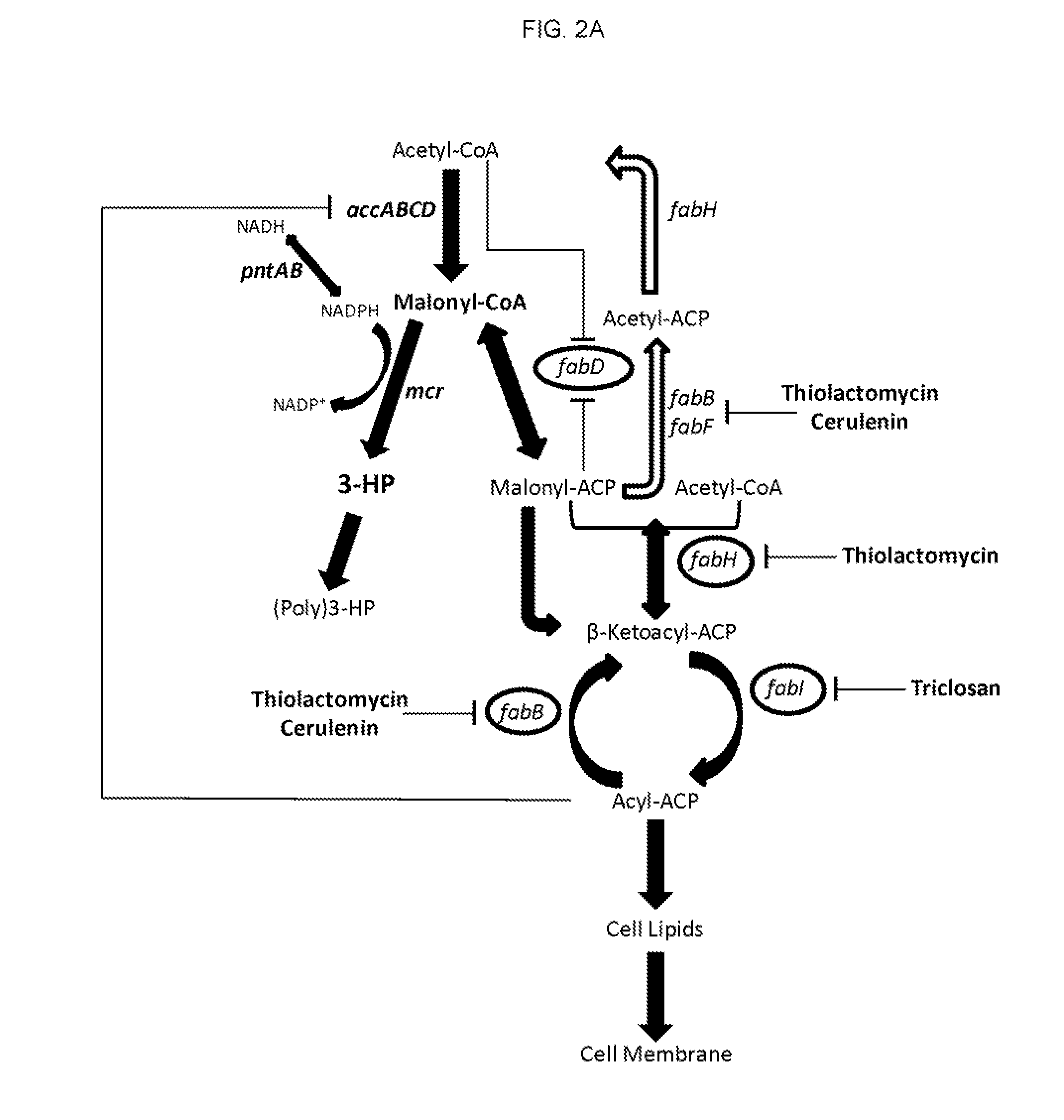
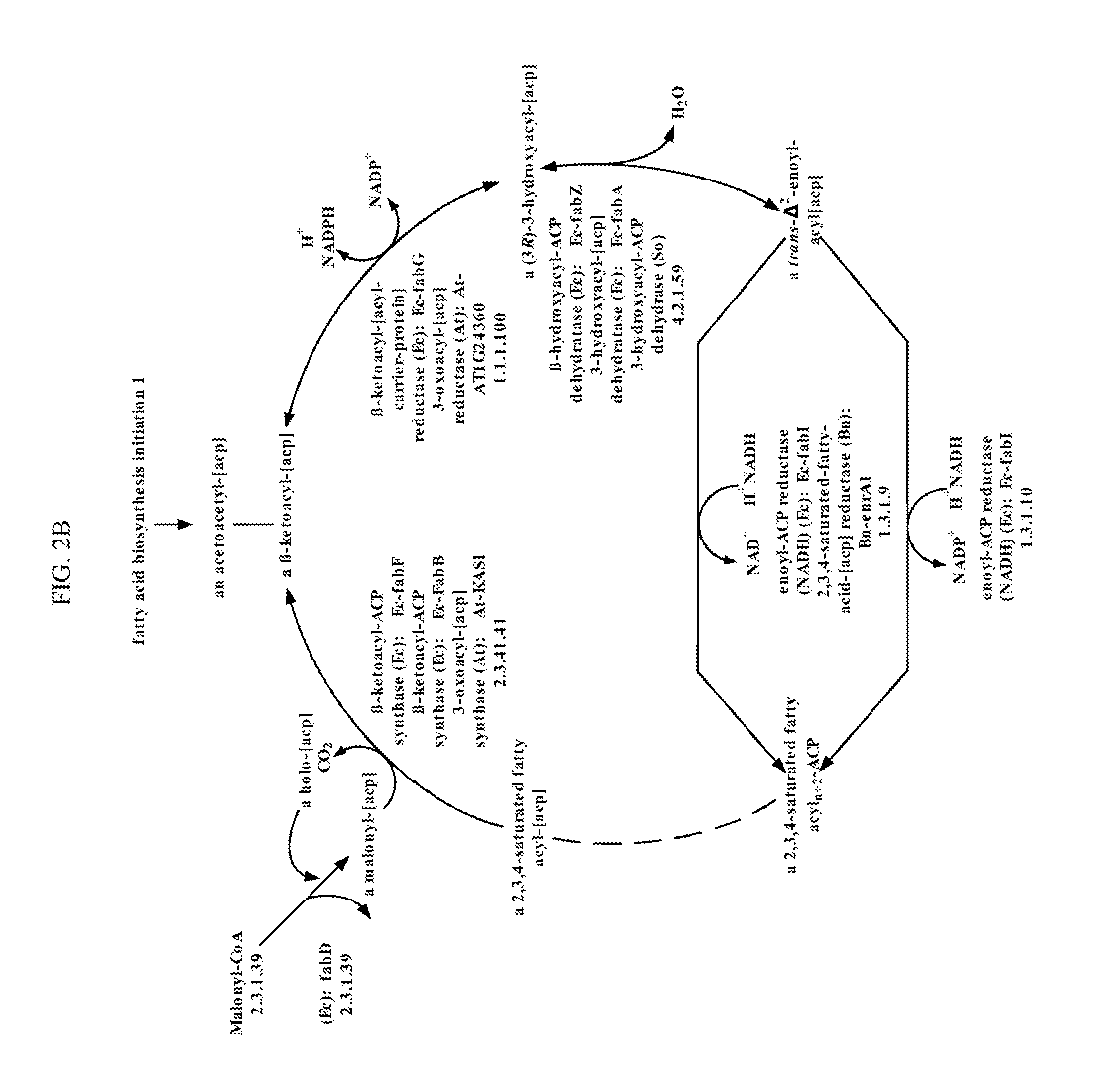
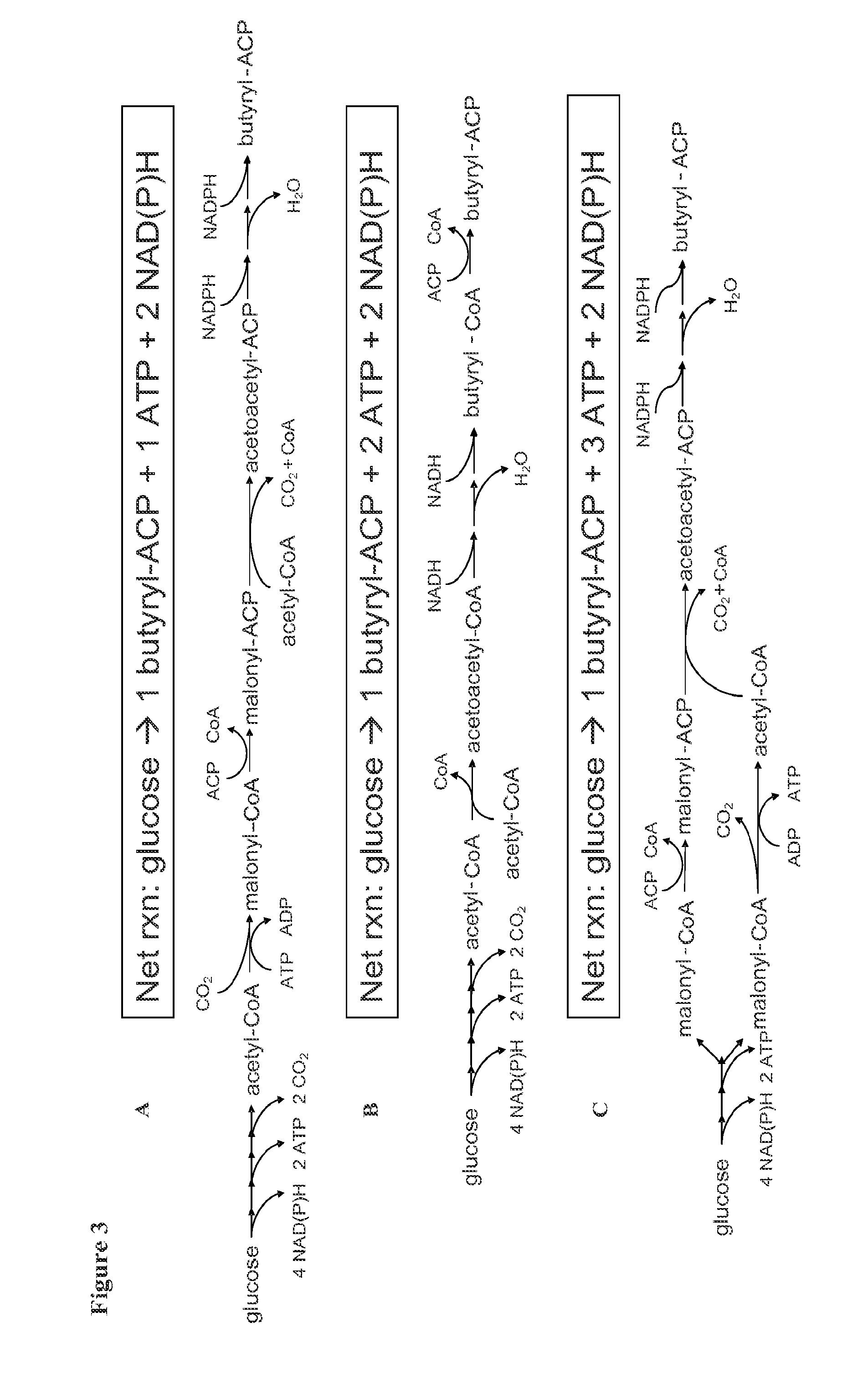
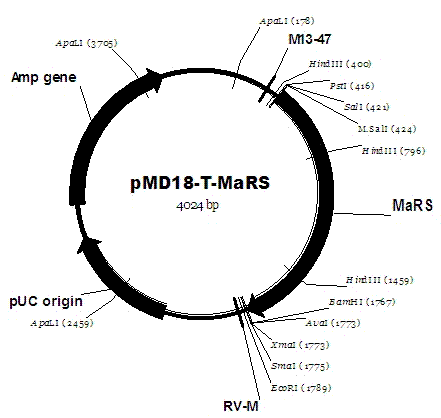
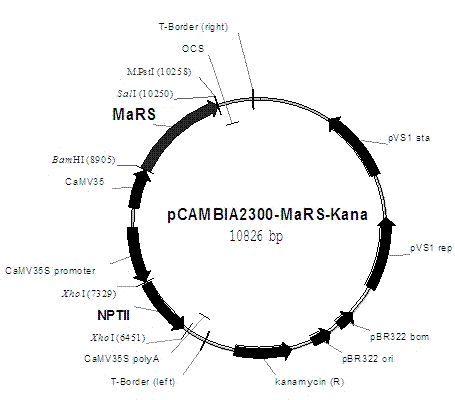
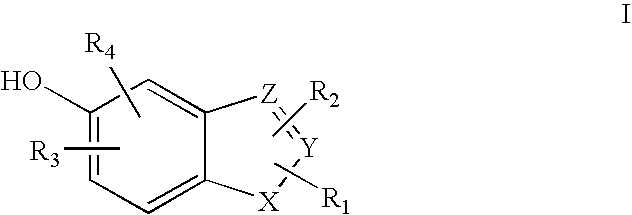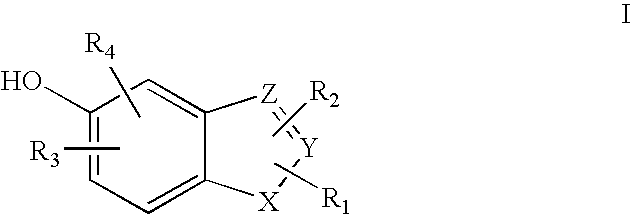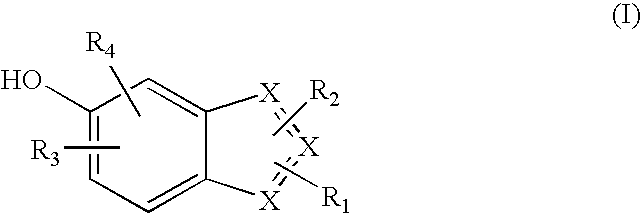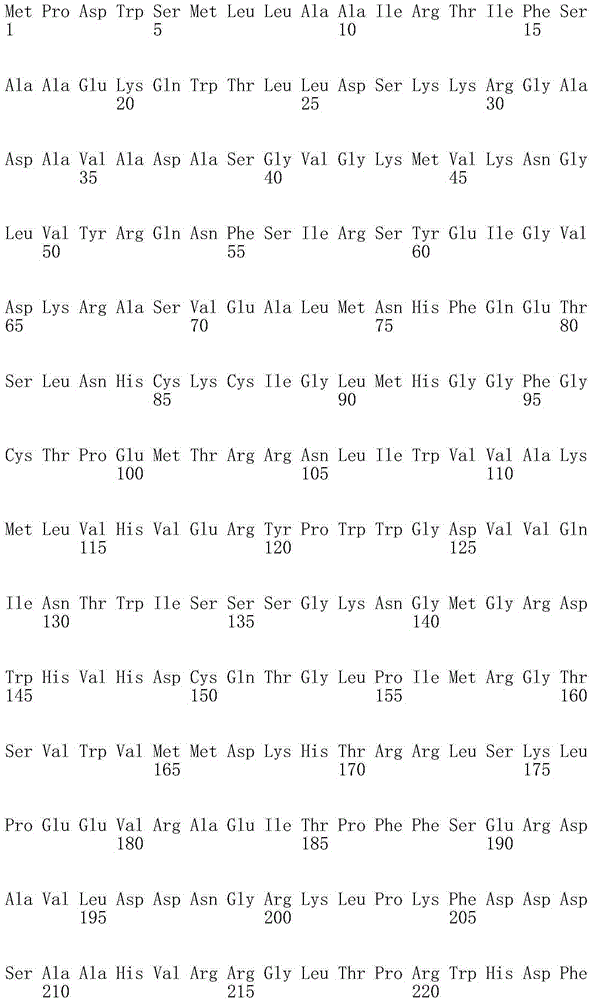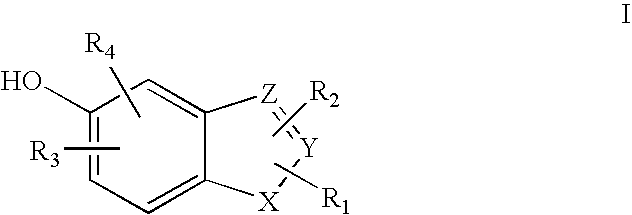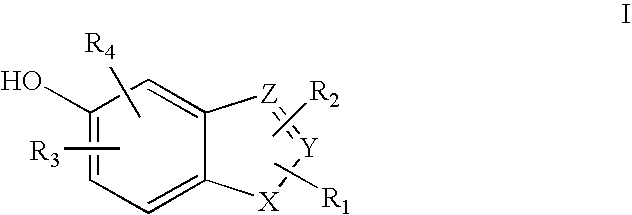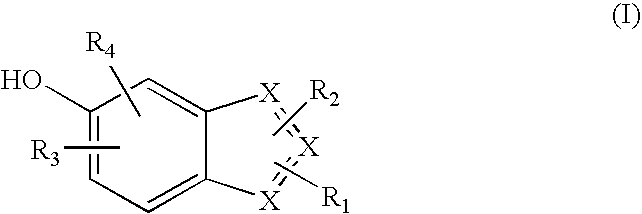Patents
Literature
49 results about "Malonyl-CoA" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
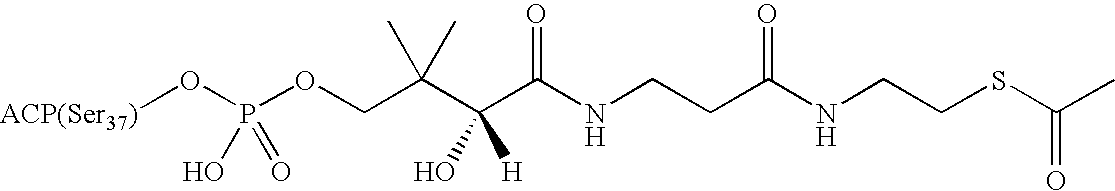
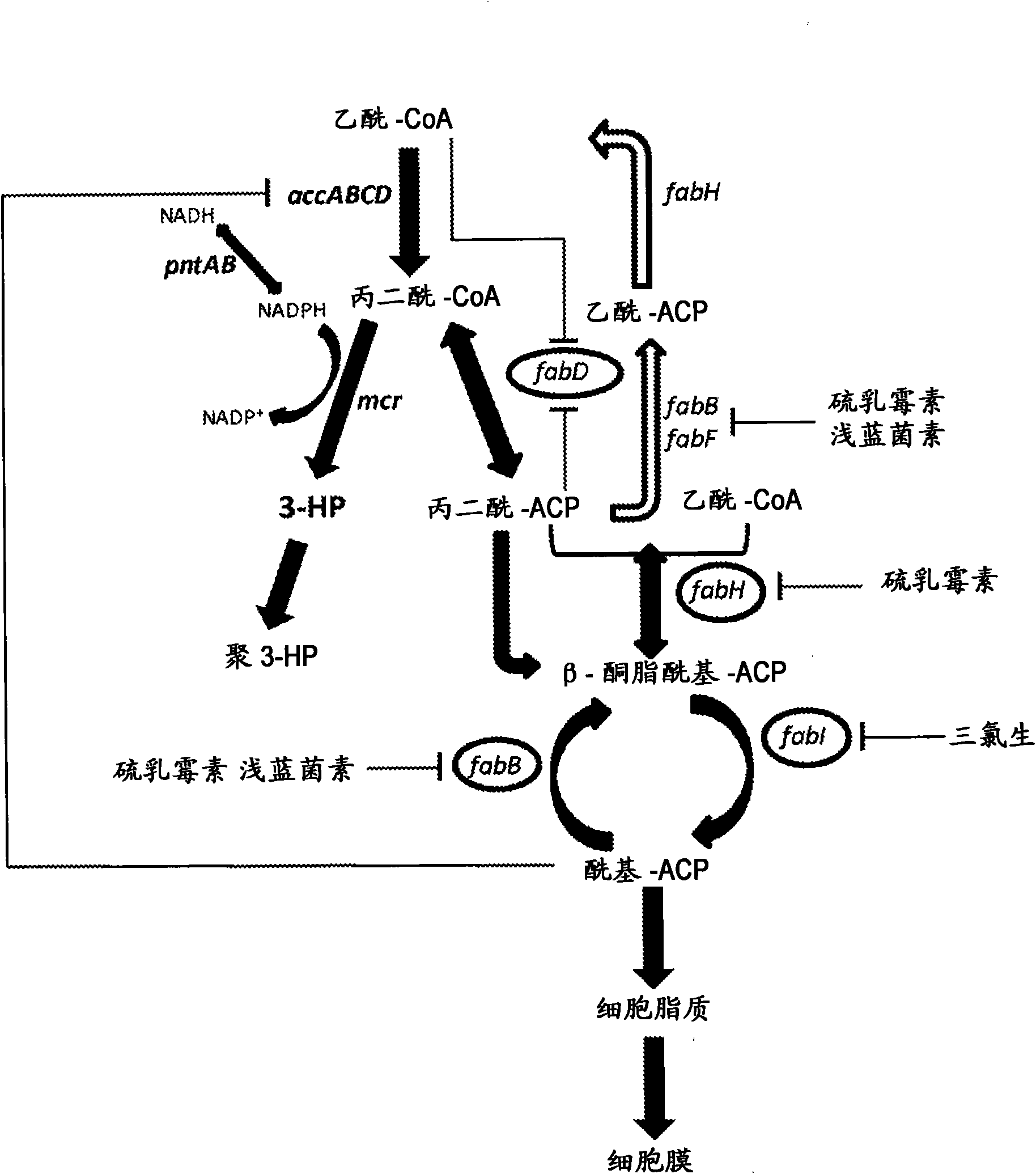
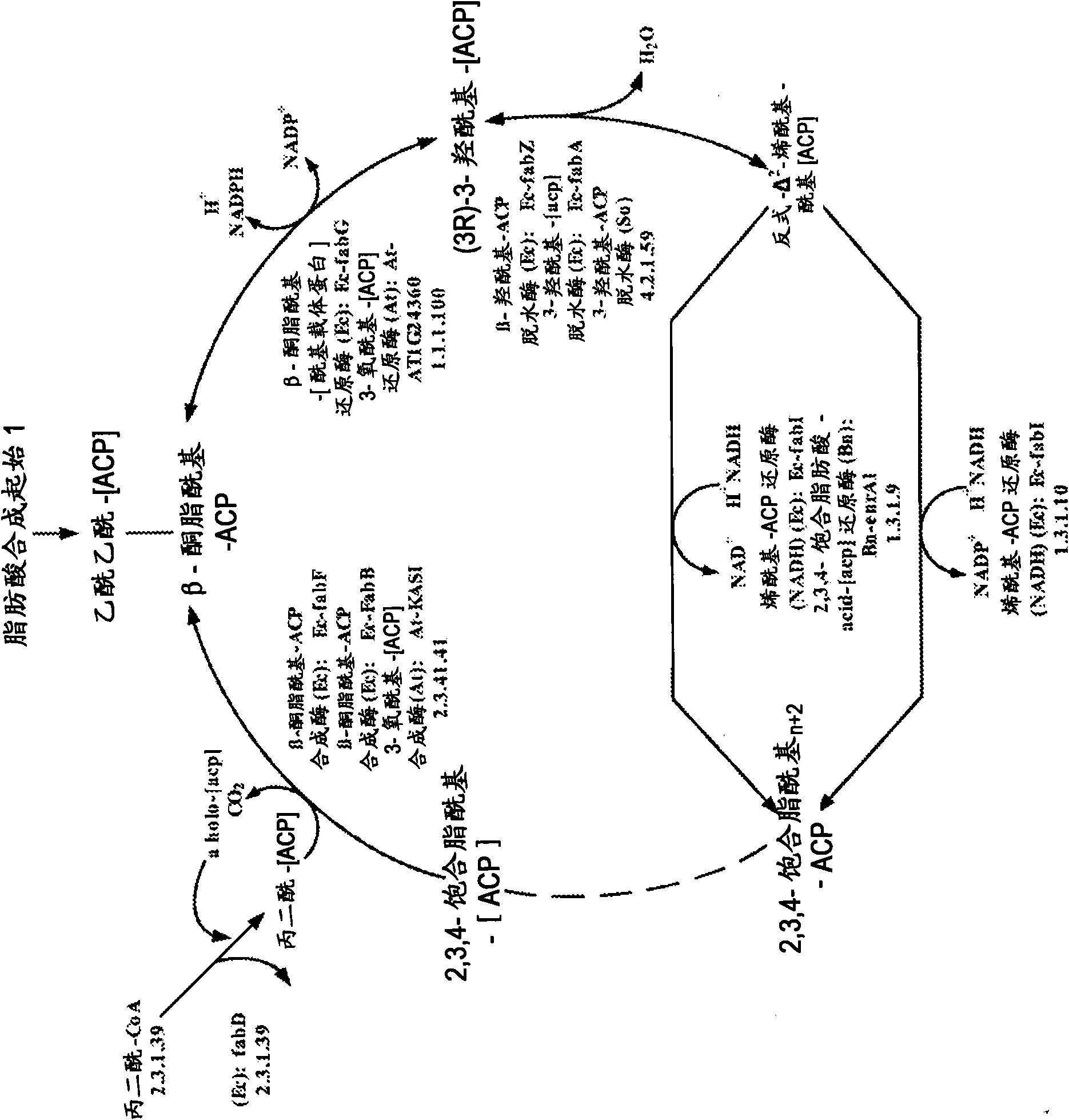
Malonyl-CoA is a coenzyme A derivative of malonic acid.
Polyunsaturated fatty acid production in heterologous organisms using PUFA polyketide synthase systems
InactiveUS20070245431A1Improve the level ofReduce competitionOther foreign material introduction processesOxidoreductasesBiotechnologyHeterologous
Disclosed are novel acyl-CoA synthetases and novel acyltransferases, nucleic acid molecules encoding the same, recombinant nucleic acid molecules and recombinant host cells comprising such nucleic acid molecules, genetically modified organisms (microorganisms and plants) comprising the same, and methods of making and using the same. Also disclosed are genetically modified organisms (e.g., plants, microorganisms) that have been genetically modified to express a PKS-like system for the production of PUFAs (a PUFA PKS system or PUFA synthase), wherein the organisms have been modified to express an acyl-CoA synthetase, to express an acyl transferase, to delete or inactivate a fatty acid synthase (FAS) expressed by the organism, to reduce competition for malonyl CoA with the PUFA synthase or to increase the level of malonyl CoA in the plant or plant cell, and in one aspect, to inhibit KASII or KASIII. Additional modifications, and methods to make and use such organisms, in addition to PUFAs and oils obtained from such organisms, are disclosed, alone with various products including such PUFAs and oils.
Owner:SEMBIOSYS GENETICS INC +1
Polyunsaturated fatty acid production in heterologous organisms using pufa polyketide synthase systems
ActiveUS20070270494A1Improve the level ofReduce competitionAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsHeterologousAcyl-CoA synthetase
Disclosed are novel acyl-CoA synthetases and novel acyltransferases, nucleic acid molecules encoding the same, recombinant nucleic acid molecules and recombinant host cells comprising such nucleic acid molecules, genetically modified organisms (microorganisms and plants) comprising the same, and methods of making and using the same. Also disclosed are genetically modified organisms (e.g., plants, microorganisms) that have been genetically modified to express a PKS-like system for the production of PUFAs (a PUFA PKS system or PUFA synthase), wherein the organisms have been modified to express an acyl-CoA synthetase, to express an acyl transferase, to delete or inactivate a fatty acid synthase (FAS) expressed by the organism, to reduce competition for malonyl CoA with the PUFA synthase or to increase the level of malonyl CoA in the organism, and in one aspect, to inhibit KASII or KASIII. Additional modifications, and methods to make and use such organisms, in addition to PUFAs and oils obtained from such organisms, are disclosed, alone with various products including such PUFAs and oils.
Owner:DSM IP ASSETS BV
Recombinant microorganism having butanol production capacity and butanol production method
This invention relates to a recombinant microorganism having improved butanol production capacity and butanol production with the use of such recombinant microorganism with good efficiency. In this invention, the acetoacetyl-CoA synthase gene encoding an enzyme capable of synthesizing acetoacetyl-CoA from malonyl-CoA and acetyl-CoA and a group of genes involved in butanol biosynthesis that enables synthesis of butanol from acetoacetyl-CoA are introduced into a host microorganism.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
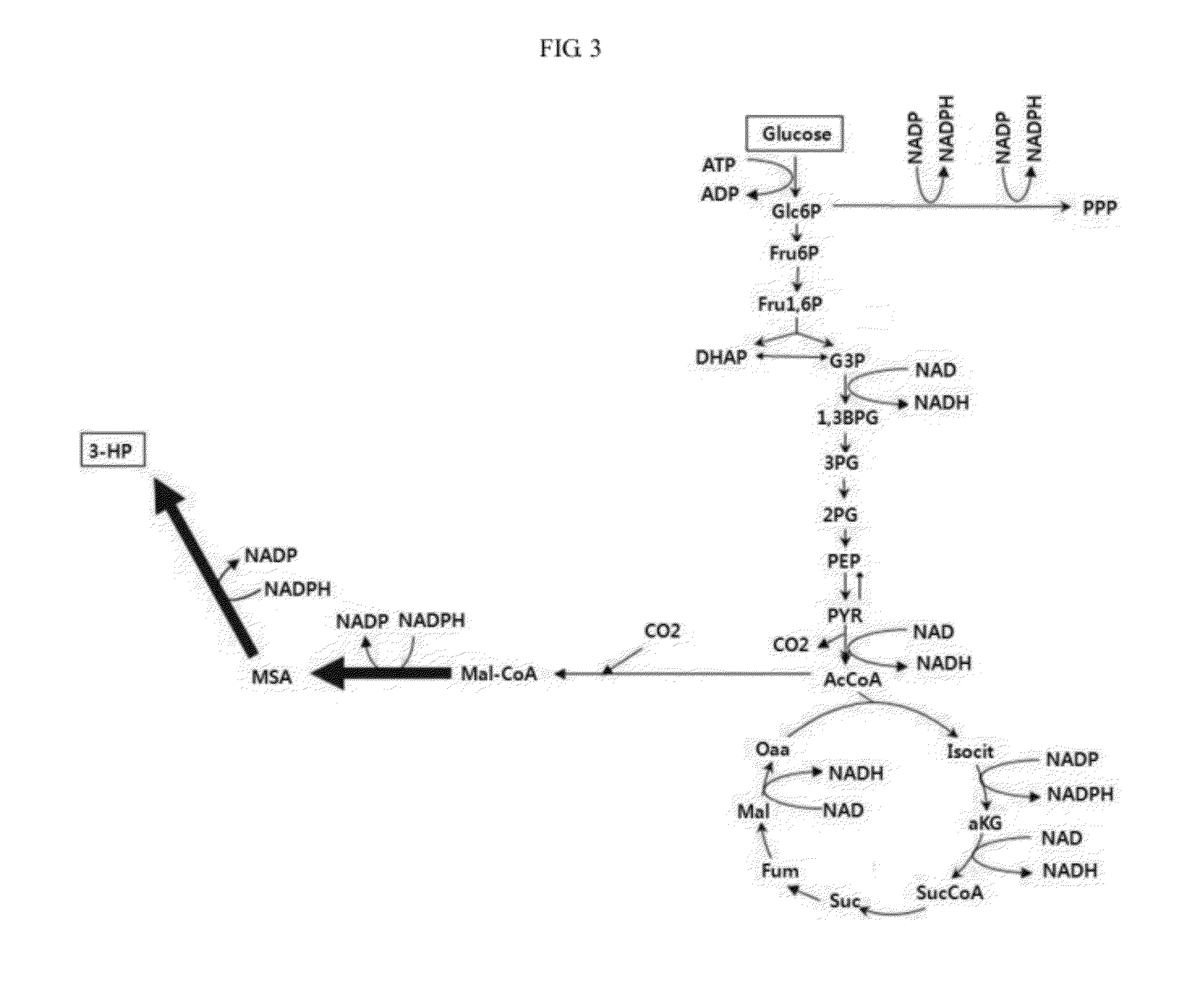
Methods for producing 3-hydroxypropionic acid and other products
ActiveUS20130071893A1Improve enzymatic activityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMicroorganism3-Hydroxypropionic acid
This invention relates to metabolically engineered microorganism strains, such as bacterial strains, in which there is an increased utilization of malonyl-CoA for production of a chemical product, which includes 3-hydroxypropionic acid.
Owner:CARGILL INC +1
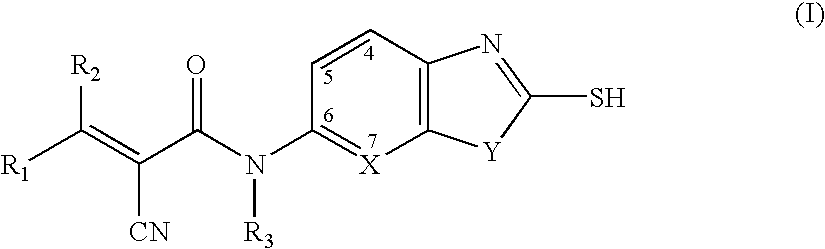
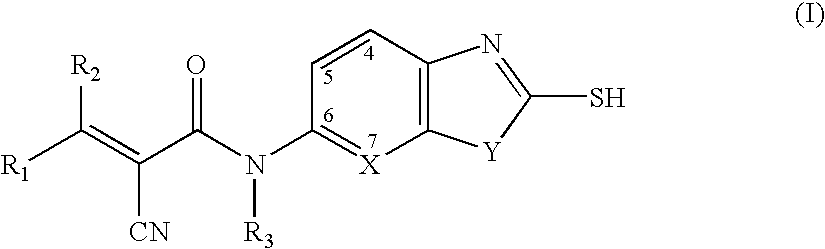
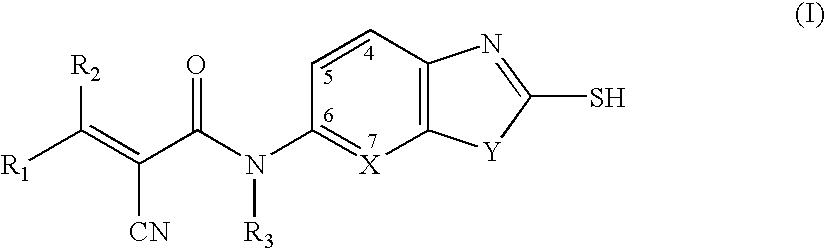
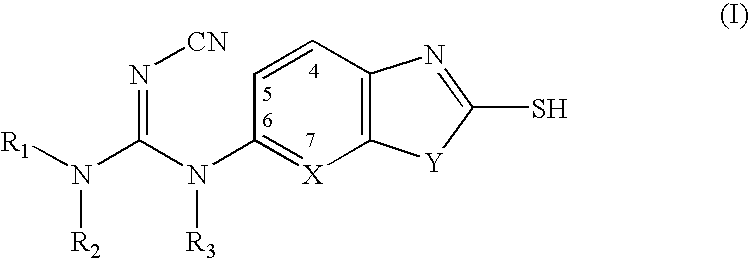
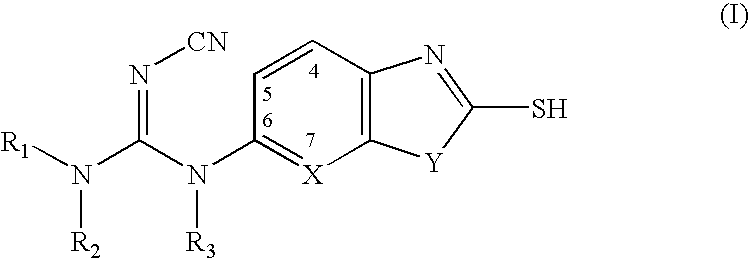
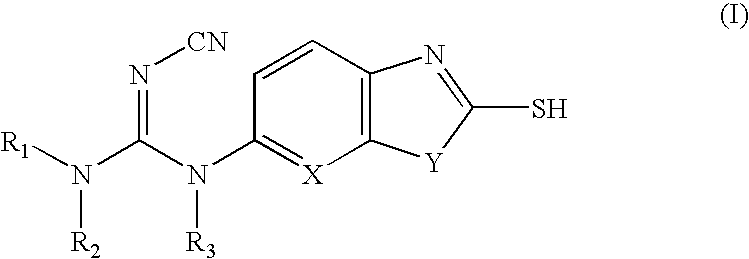
Heterocyclic compounds useful as malonyl-CoA decarboxylase inhibitors
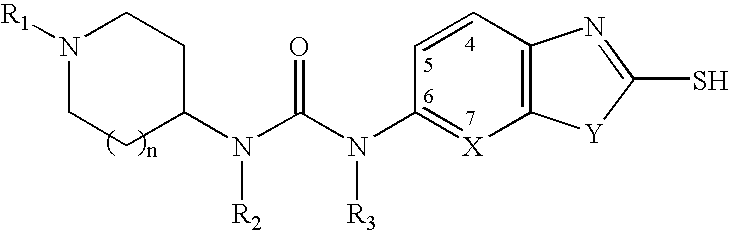
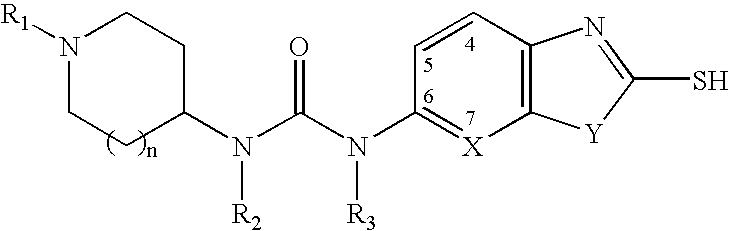
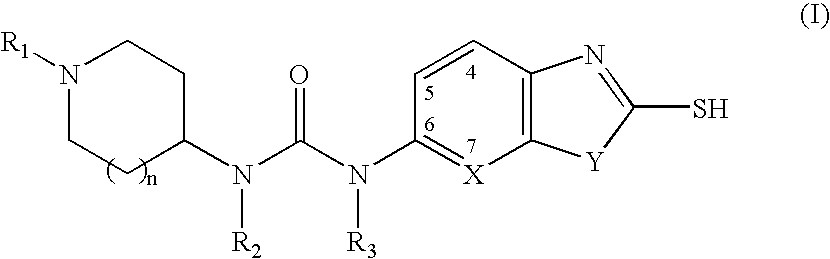
The present invention provides methods for the use of compounds as depicted by structure I, pharmaceutical compositions containing the same, and methods for the prophylaxis, management and treatment of metabolic diseases and diseases modulated by MCD inhibition. The compounds disclosed in this invention are useful for the prophylaxis, management and treatment of diseases involving in malonyl-CoA regulated glucose / fatty acid metabolism pathway. In particular, these compounds and pharmaceutical composition containing the same are indicated in the prophylaxis, management and treatment of cardiovascular diseases, diabetes, cancer and obesity.
Owner:CHUGAI PHARMA CO LTD
High throughput screening method for biological agents affecting fatty acid biosynthesis
InactiveUS6951729B1Reduce NADH consumptionReduce consumptionCompound screeningApoptosis detectionHigh-Throughput Screening MethodsScreening method
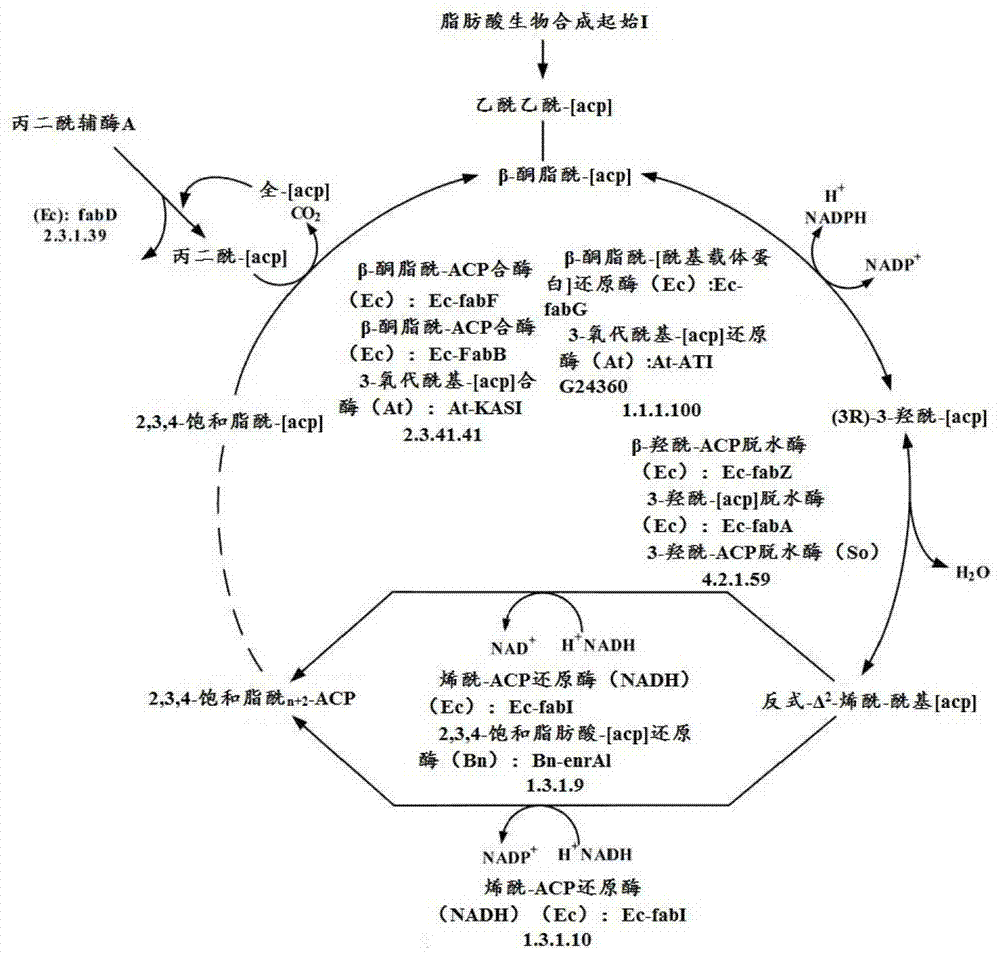
Provided is a screening method for compounds affecting fatty acid biosynthesis, the method comprising: providing a reaction mixture comprising: an acyl carrier moiety or enzymes and precursors sufficient to generate the acyl carrier moiety; a bacterial enzymatic pathway comprising at least two consecutively acting enzymes selected from the group consisting of: malonyl-CoA:ACP transacylase, beta-ketoacyl-ACP synthase III, NADPH dependent beta-ketoacyl-ACP reductase, beta-hydroxylacyl-ACP dehydrase and enoyl-ACP reductase; and substrates and cofactors required for the operation of the enzymes; contacting the reaction mixture with a prospective bioactive agent; conducting a high throughput measurement of the activity of the enzymatic pathway; and determining if the contacting altered the activity of the enzymatic pathway.
Owner:DEBIOPHARM INTERNATIONAL SA
Cyanoamide compounds useful as malonyl-CoA decarboxylase inhibitors
The present invention provides methods for the use of compounds as depicted by structure I, pharmaceutical compositions containing the same, and methods for the prophylaxis, management and treatment of metabolic diseases and diseases modulated by MCD inhibition. The compounds disclosed in this invention are useful for the prophylaxis, management and treatment of diseases involving in malonyl-CoA regulated glucose / fatty acid metabolism pathway. In particular, these compounds and pharmaceutical composition containing the same are indicated in the prophylaxis, management and treatment of cardiovascular diseases, diabetes, cancer and obesity.
Owner:CHUGAI PHARMA CO LTD
Polyunsaturated fatty acid production in heterologous organisms using pufa polyketide synthase systems
InactiveCN101573451AImprove the level ofReduce competitionMicrobiological testing/measurementAcyl Coenzyme A SynthetasesBiotechnology
Disclosed are novel acyl-CoA synthetases and novel acyltransferases, nucleic acid molecules encoding the same, recombinant nucleic acid molecules and recombinant host cells comprising such nucleic acid molecules, genetically modified organisms (microorganisms and plants) comprising the same, and methods of making and using the same. Also disclosed are genetically modified organisms (e.g., plants, microorganisms) that have been genetically modified to express a PKS-like system for the production of PUFAs (a PUFA PKS system or PUFA synthase), wherein the organisms have been modified to express an acyl-CoA synthetase, to express an acyl transferase, to delete or inactivate a fatty acid synthase (FAS) expressed by the organism, to reduce competition for malonyl CoA with the PUFA synthase or toincrease the level of malonyl CoA in the organism, and in one aspect, to inhibit KASII or KASIII. Additional modifications, and methods to make and use such organisms, in addition to PUFAs and oils o btained from such organisms, are disclosed, alone with various products including such PUFAs and oils.
Owner:DSM IP ASSETS BV
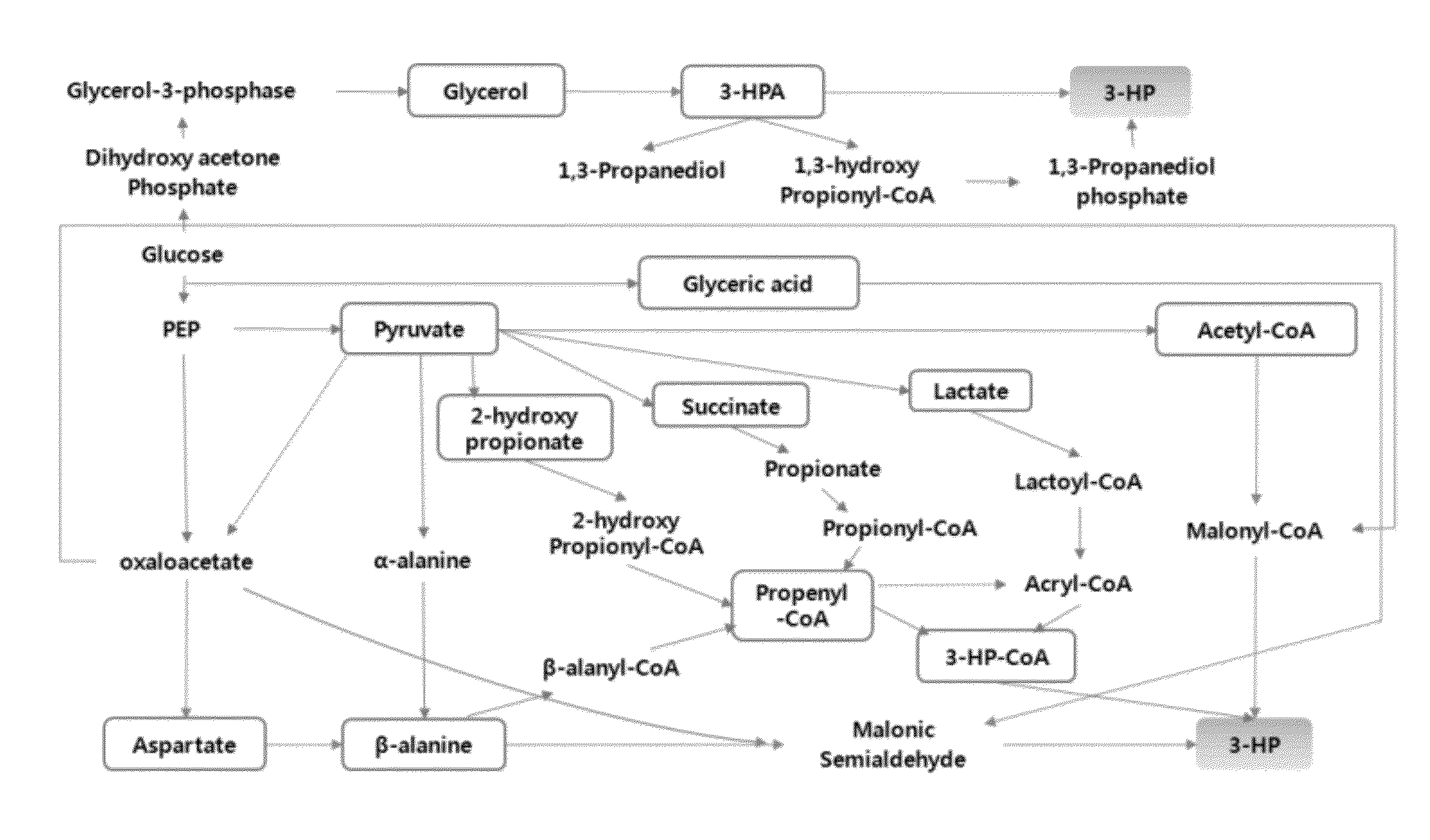
Genetic modification for production of 3-hydroxypropionic acid
InactiveUS20120329110A1Improve production yield and producibilityIncrease productivityFungiBacteriaLactate dehydrogenaseMetabolite
A method of increasing 3-HP production efficiency by inhibiting expression of a lactate dehydrogenase, a phosphotransacetylase, and an alcohol dehydrogenase in production of 3-HP using a malonic semialdehyde reduction pathway to prevent metabolite leak and increase a malonyl-CoA pool is disclosed.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
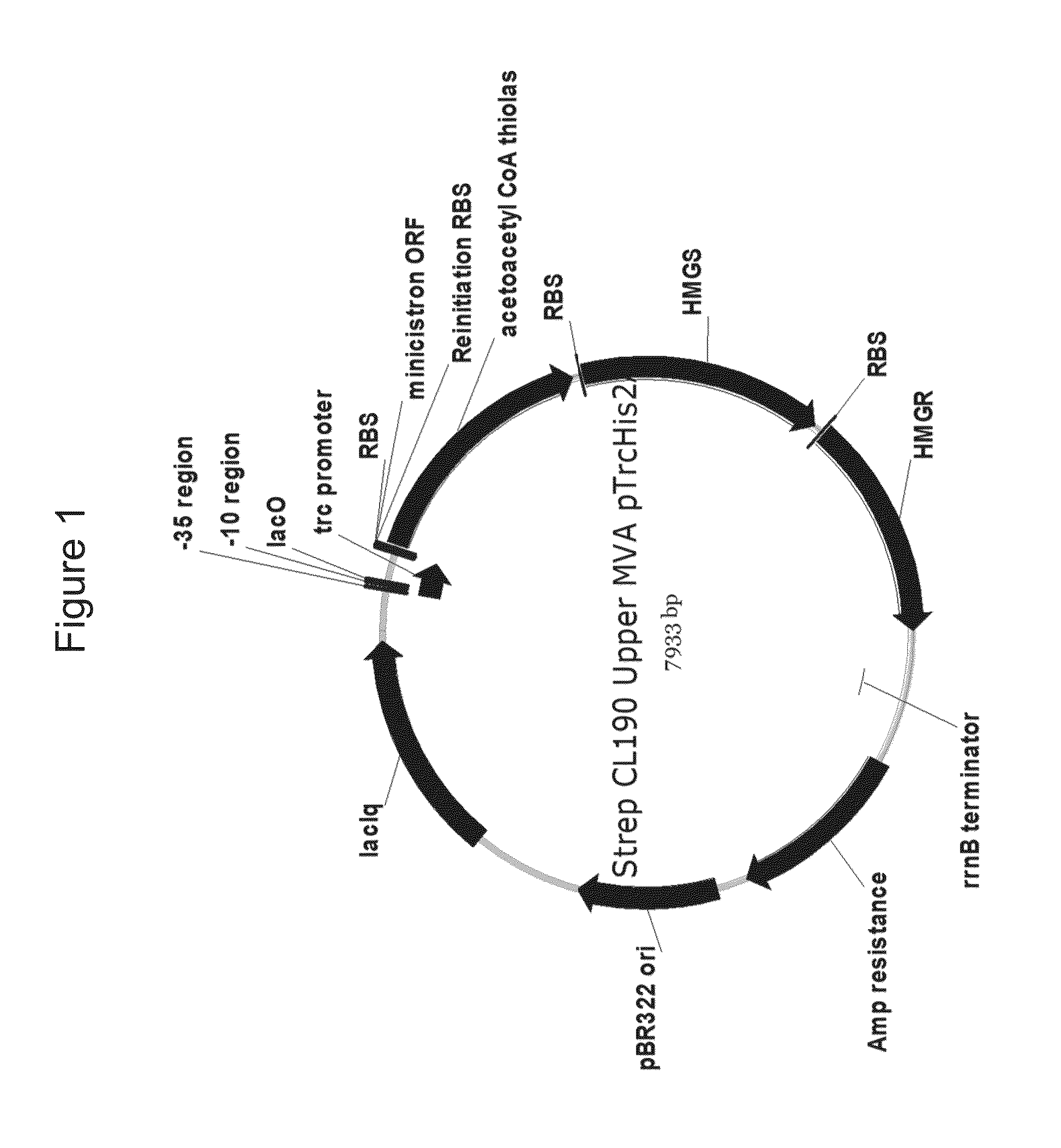
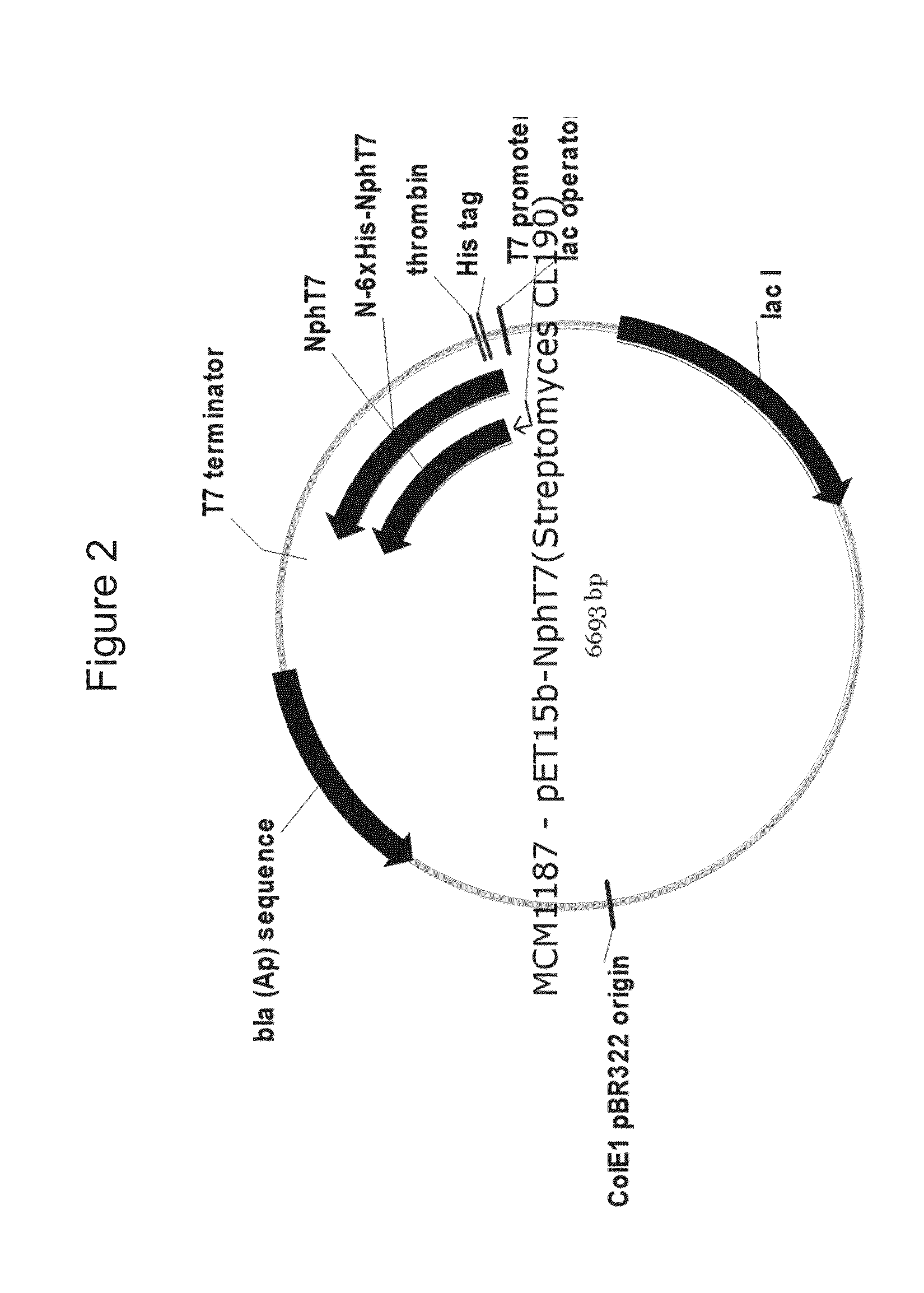
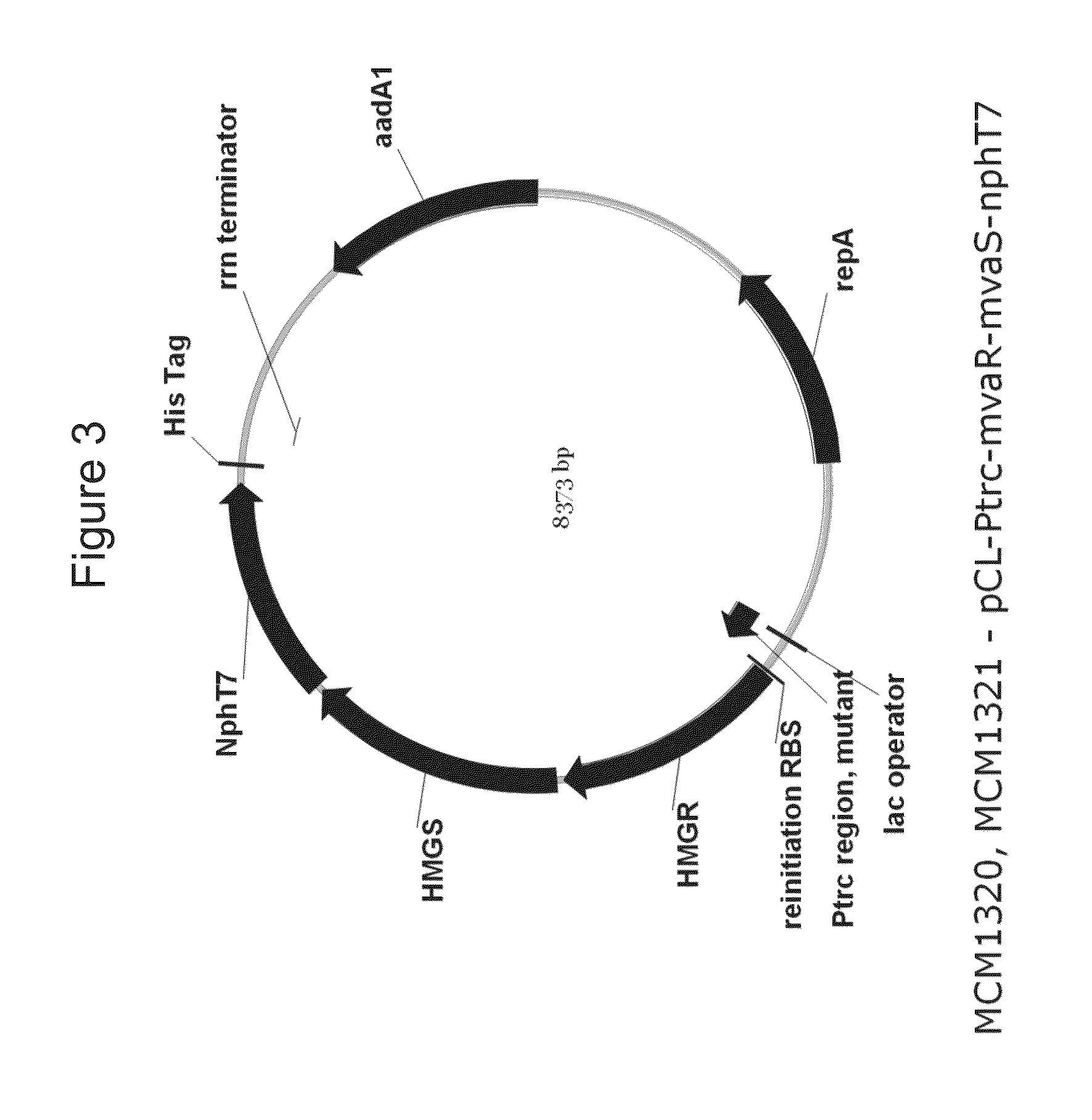
Production of isoprene, isoprenoid precursors, and isoprenoids using acetoacetyl-coa synthase
This invention relates to a recombinant microorganism capable of producing isoprene and isoprene production with the use of such recombinant microorganism with good efficiency. In this invention, the acetoacetyl-CoA synthase gene encoding an enzyme capable of synthesizing acetoacetyl-CoA from malonyl-CoA and acetyl-CoA and one or more genes involved in isoprene biosynthesis that enables synthesis of isoprene from acetoacetyl-CoA are introduced into a host microorganism.
Owner:THE GOODYEAR TIRE & RUBBER CO
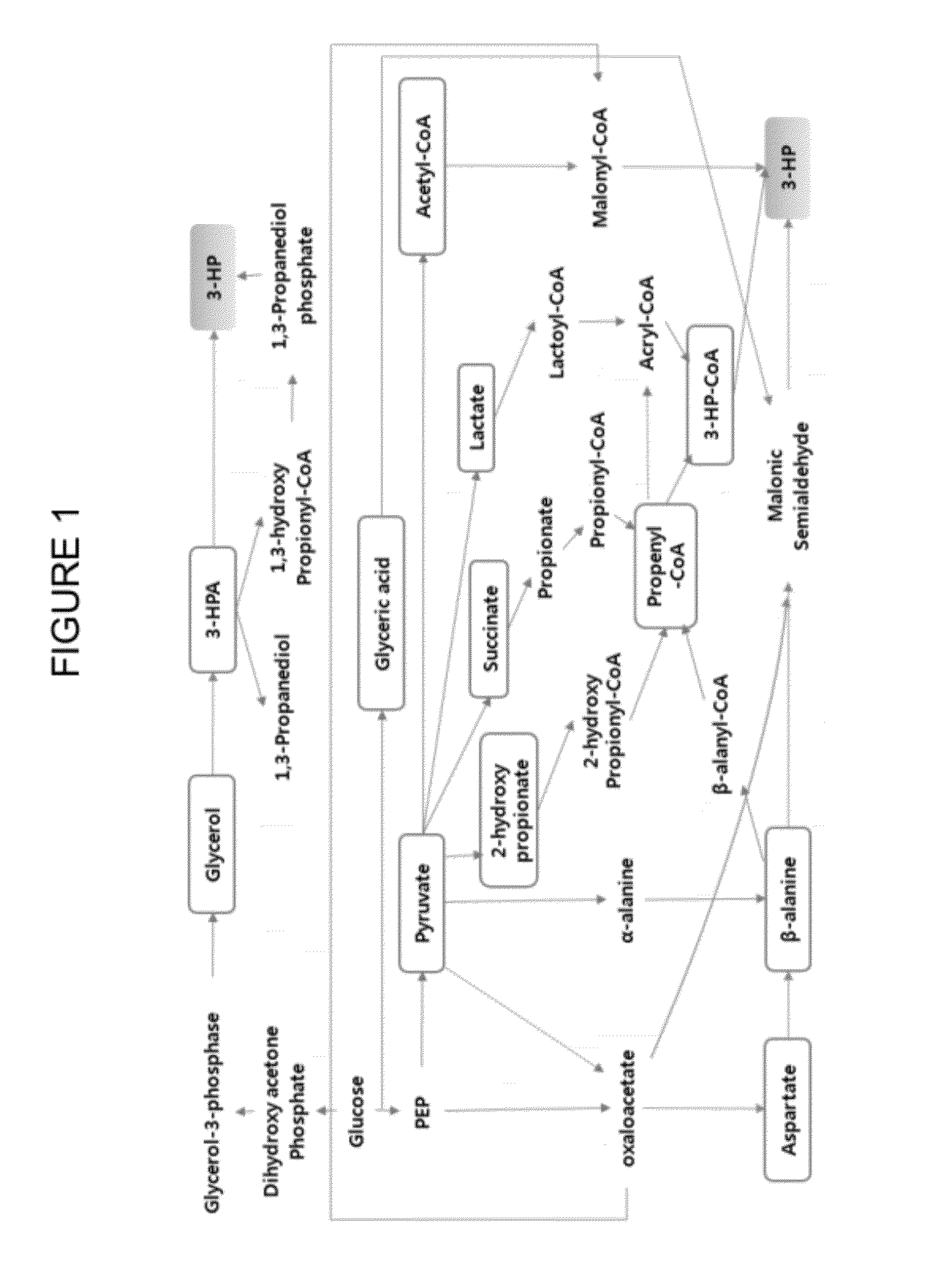
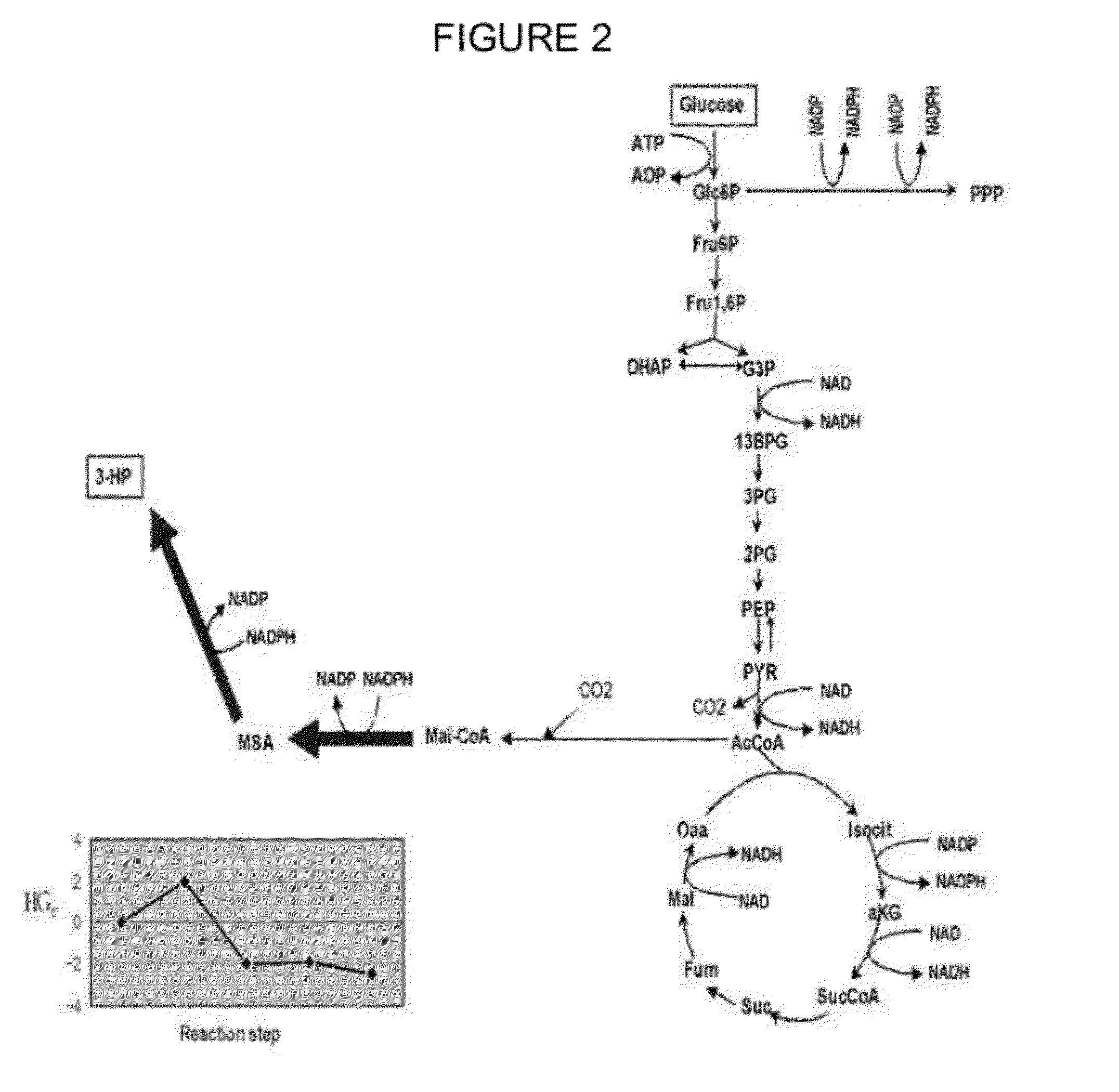
Method of producing 3-hydroxypropionic acid using malonic semialdehyde reducing pathway
A method of producing 3-hydroxypropionic acid (“3-HP”) with a high yield using a recombinant microorganism having an activity of reducing malonyl CoA into malonic semialdehyde and an activity of reducing malonic semialdehyde into 3-HP and / or an NADPH regeneration activity is provided.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method for producing 3-hydroxypropionic acid and other products
This invention relates to metabolically engineered microorganism strains, such as bacterial strains, in which there is an increased utilization of malonyl-CoA for production of a chemical product, which includes 3- hydroxypropionic acid.
Owner:OPX BIOTECH +1
Cyanoguanidine-based azole compounds useful as malonyl-CoA decarboxylase inhibitors
The present invention provides methods for the use of compounds as depicted by structure I, pharmaceutical compositions containing the same, and methods for the prophylaxis, management and treatment of metabolic diseases and diseases modulated by MCD inhibition. The compounds disclosed in this invention are useful for the prophylaxis, management and treatment of diseases involving in malonyl-CoA regulated glucose / fatty acid metabolism pathway. In particular, these compounds and pharmaceutical composition containing the same are indicated in the prophylaxis, management and treatment of cardiovascular diseases, diabetes, cancer and obesity.
Owner:CHUGAI PHARMA CO LTD
Production of fatty acids esters
A microbial cell is used for producing at least one fatty acid ester, wherein the cell is genetically modified to contain (i) at least one first genetic mutation that enables the cell to produce at least one fatty acid and / or acyl coenzyme A (CoA) thereof by increased enzymatic activity in the cell relative to the wild type cell of malonyl-CoA dependent and malonyl-ACP independent fatty acyl-CoA metabolic pathway, wherein the fatty acid contains at least 5 carbon atoms; and (ii) a second genetic mutation that increases the activity of at least one wax ester synthase in the cell relative to the wild type cell and the wax ester synthase has sequence identity of at least 50% to a polypeptide of SEQ ID NO: 1-8 and combinations thereof or to a functional fragment of any of the polypeptides for catalyzing the conversion of fatty acid and / or acyl coenzyme A thereof to the fatty acid ester.
Owner:CARGILL INC
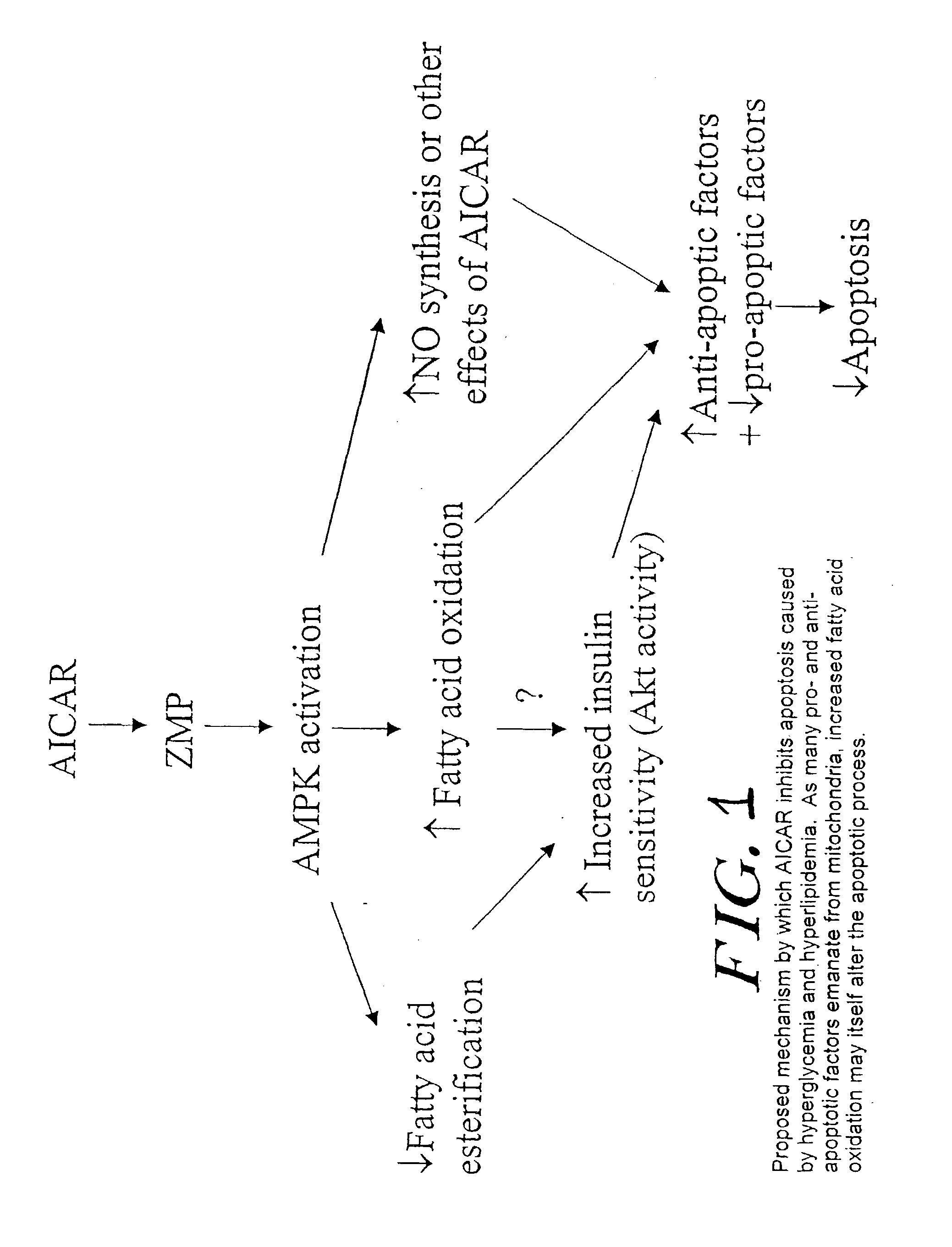
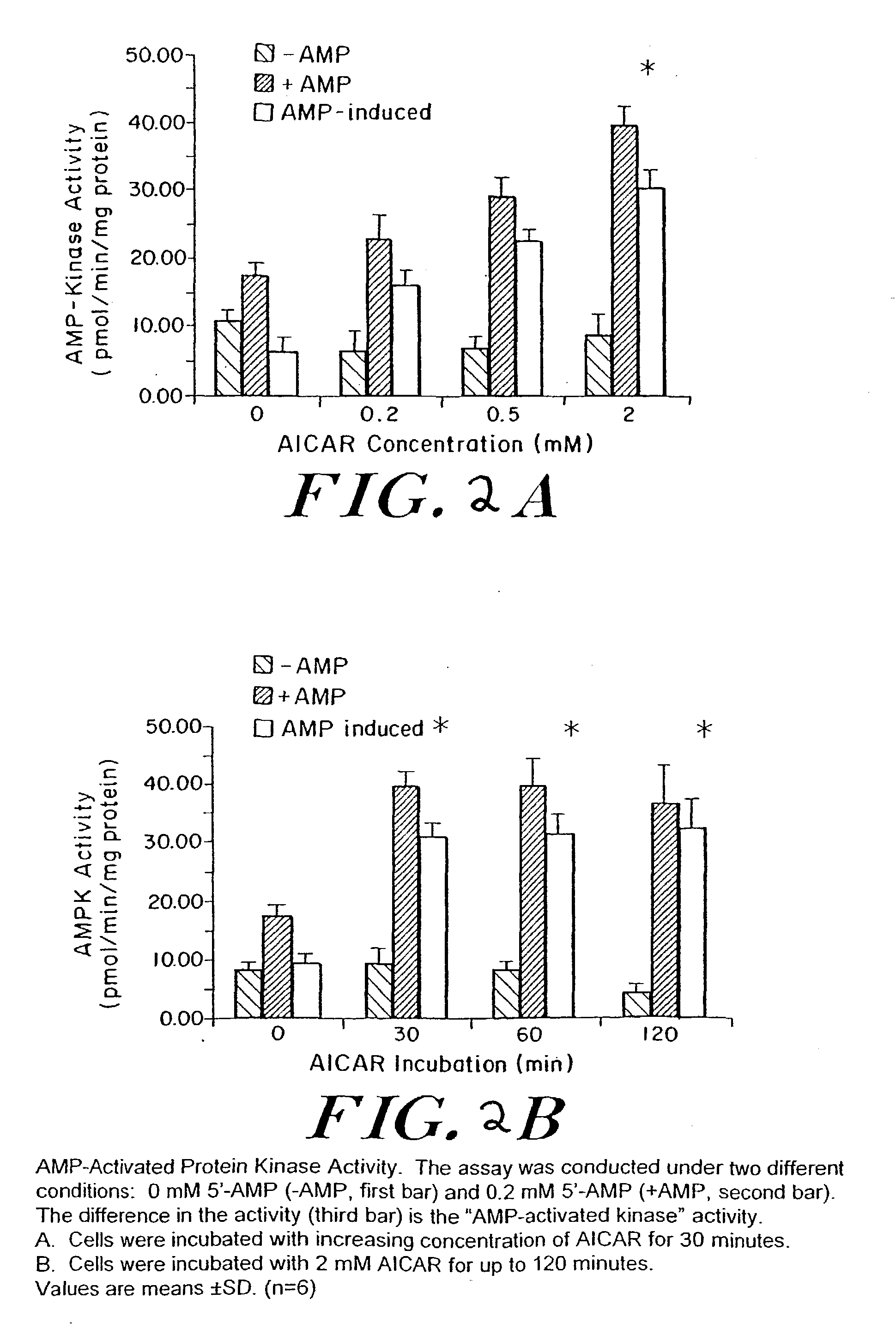
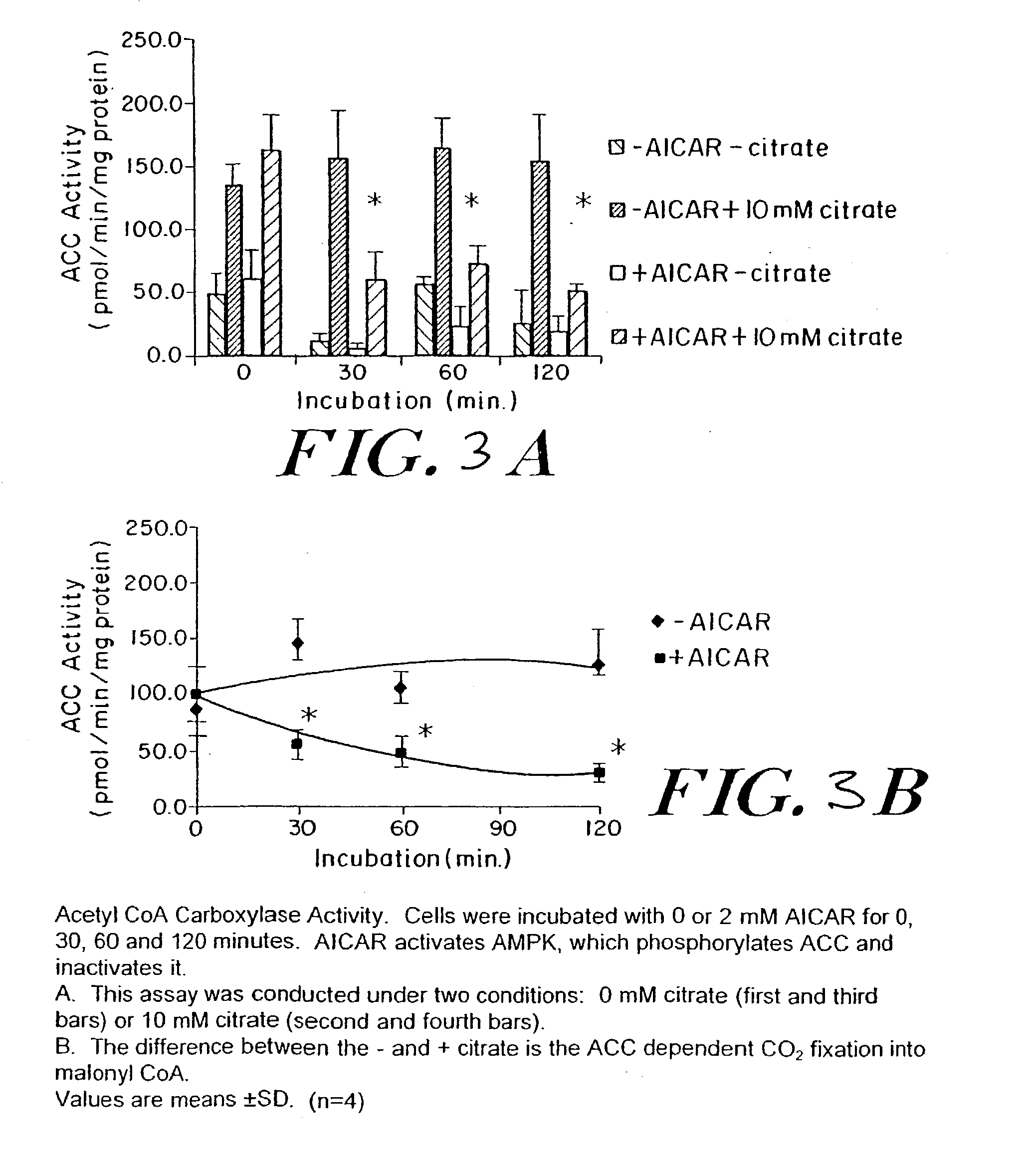
Methods fo treating conditions associated with insulin resistance with aicar, (5-amino-4-imidazole carboxamide riboside) and related compounds
InactiveUS20030212014A1Positive impact in reducing obesityIncrease insulin sensitivityBiocideCompound screeningMammalDisease cause
The long-term usage of AICR (5-aminio, 4-imidazole carboxamide riboside) to produce sustained metabolic and biological changes in mammals that overcome insulin resistance, i.e., increase insulin sensitivity, and result in benefits in diseases and conditions such as diabetes, hypertension, atherosclerosis, polycystic ovary syndrome and gallstones is described long-term usage of AICAR, particularly intermittent administration, e.g., three days per week, appears to have some of the positive effects of exercise, having an impact on the amount Of food consumed by a subject and resulting in reduced fat build-up and increase in muscle mass. Therefore, AICAR administration has a positive impact in reducing obesity. AICAR can also Prove useful in preventing or treating vascular diseases associated with hyperglycemia, high plasma levels of free fatty acids (FFA) and triglyceride, and insulin resistance by virtue of the fact that this agent activates fatty acid oxidation. Animal tests have Shown that chronic intermittent treatment with AICAR has not resulted in any noticeable toxic effects. AICAR and related compounds are activators of AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) and, furthermore, are effective at decreasing malonyl CoA levels in the animal.
Owner:UNIV BOSTON TRUSTEES OF THE +1
Production of Malonyl-CoA Derived Products Via Anaerobic Pathways
ActiveUS20130323766A1Low toxicityLower the volumeBacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganismHeterologous
The present invention provides for novel metabolic pathways to convert biomass and other carbohydrate sources to malonyl-CoA derived products, such as hydrocarbons and other bioproducts, under anaerobic conditions and with the net production of ATP. More specifically, the invention provides for a recombinant microorganism comprising one or more native and / or heterologous enzymes that function in one or more engineered metabolic pathways to achieve conversion of a carbohydrate source to, e.g., long-chain hydrocarbons and hydrocarbon derivatives, wherein the one or more native and / or heterologous enzymes is activated, upregulated, downregulated, or deleted. The invention also provides for processes to convert biomass to malonyl-CoA derived products which comprise contacting a carbohydrate source with a recombinant microorganism of the invention.
Owner:LALLEMAND HUNGARY LIQUIDITY MANAGEMENT LLC
Cloning of mulberry resveratrol synthase gene and construction of plant expression vector
InactiveCN103898130AIncrease contentImprove disease resistanceBacteriaEnzymesNicotiana tabacumCoumaric acid
The invention relates to cloning of a mulberry resveratrol synthase gene and construction of a plant expression vector. The gene has a nucleotide sequence shown by SEQ ID NO.7. Total RNA is extracted from fresh mulberry fruits, and the mulberry resveratrol synthase gene (MaRS) is cloned by using 3'RACE technology to obtain a complete gene sequence of 1496bp. A plant expression vector pCAMBIA2300-MaRS-Kana is constructed. The plant expression vector pCAMBIA2300-MaRS-Kana is transferred into agrobacterium C58 cells by electroporation, the activity of the enzyme coded by the cloned MaRS gene is verified by using a tobacco plant expression system, the MaRS gene can catalyze the combination of trans coumaric acid COA and malonyl-COA in tobacco to form resveratrol, and move the metabolic direction to downstream to synthesize a resveratrol derivative, and the gene is proved to be capable of improving the resveratrol content of a plant, therefore the MaRS gene has a development value of being applied to health food and beauty products. In addition, the MaRS gene can improve the disease resistance of the plant, thereby having a value of being applied to plant stress-tolerance gene engineering.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Fatty acid and derivatives production
At least one fatty acid and / or derivative thereof is produced from a gas containing H2, CO2, and O2 by providing a genetically modified hydrogen oxidizing bacterium in an aqueous medium; and contacting the aqueous medium with the gas containing H2, CO2 and O2 in a weight ratio of 20 to 70 (H2): 10 to 45 (CO2): 5 to 35 (O2); wherein the fatty acid contains at least 5 carbon atoms and wherein the hydrogen oxidizing bacterium is genetically modified relative to the wild type bacterium to increase the expression of enzyme E1 that is capable of catalyzing the conversion of acetyl CoA to acyl ACP via malonyl coA and to increase the expression of enzyme E2 that is capable of catalyzing the conversion of Acyl ACP to the fatty acid.
Owner:EVONIK DEGUSSA GMBH
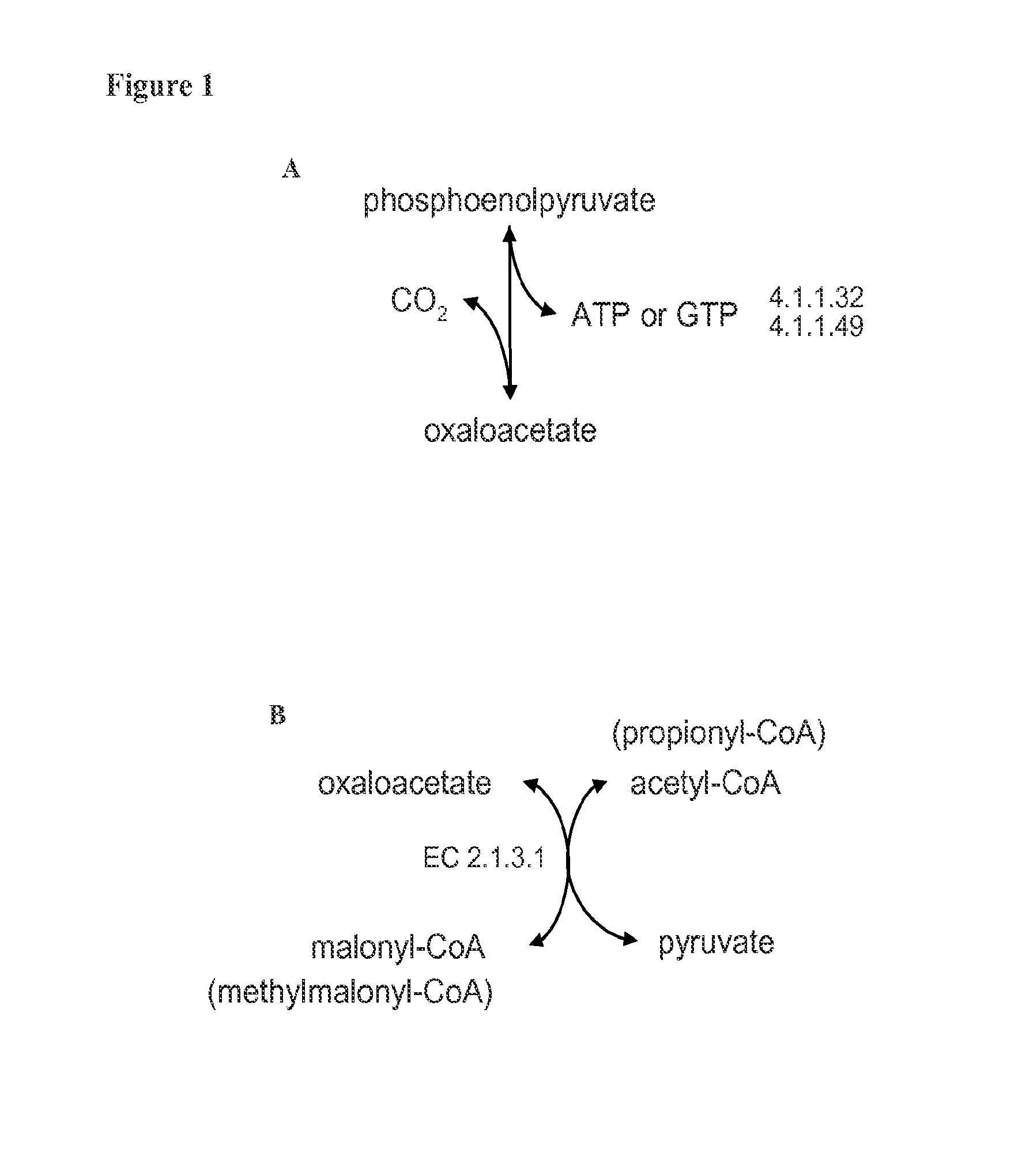
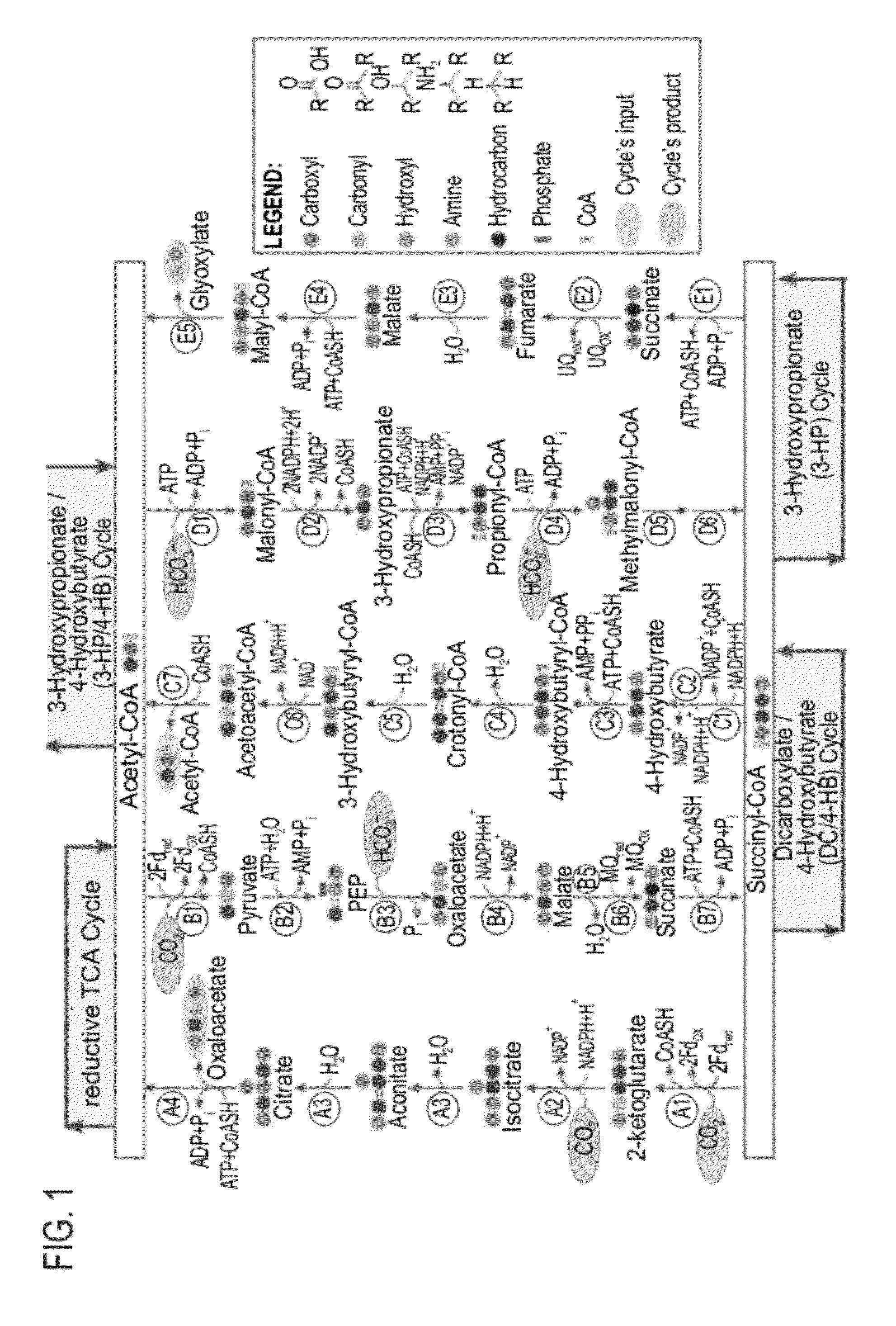
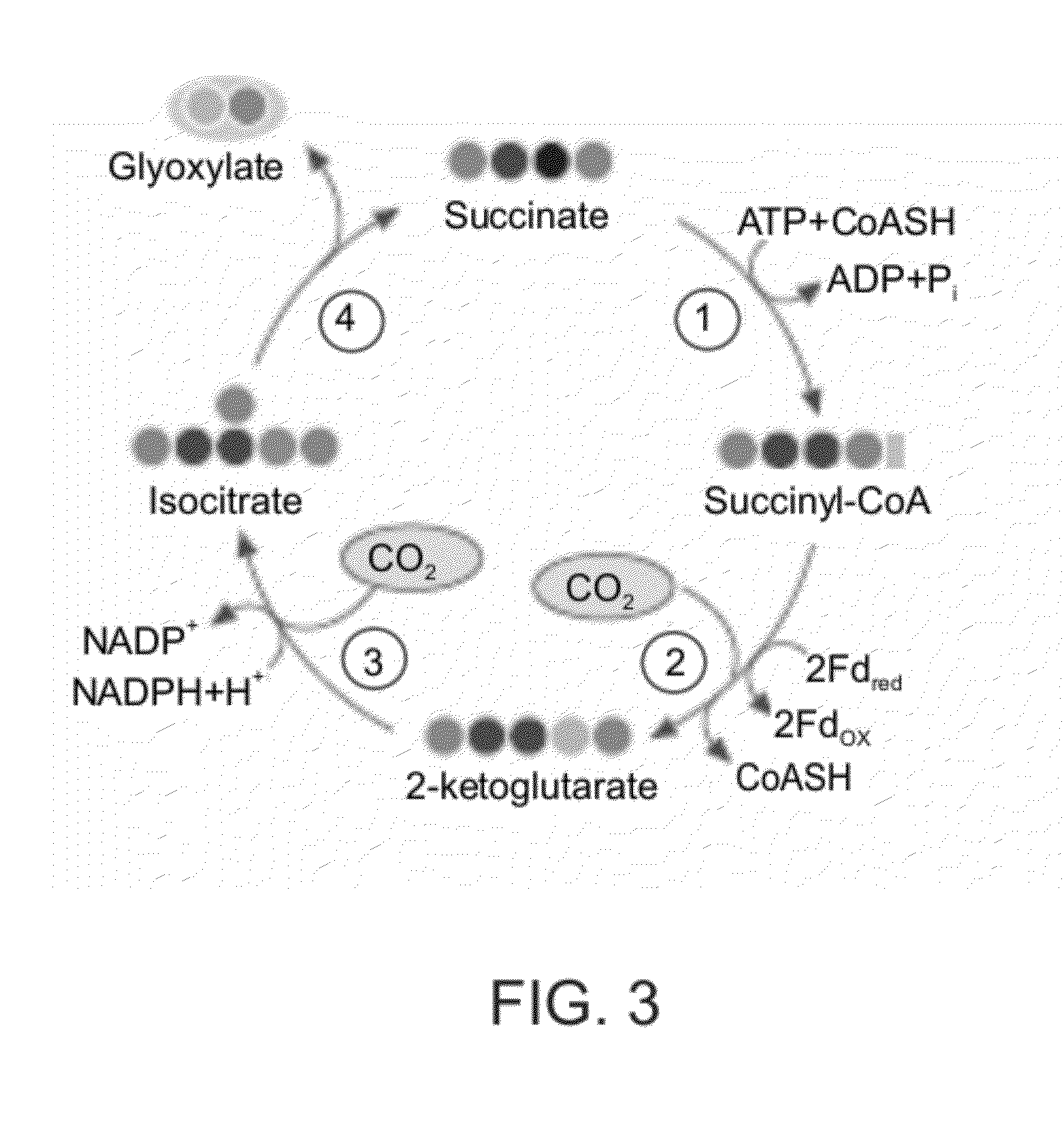
Enzymatic systems for carbon fixation and methods of generating same
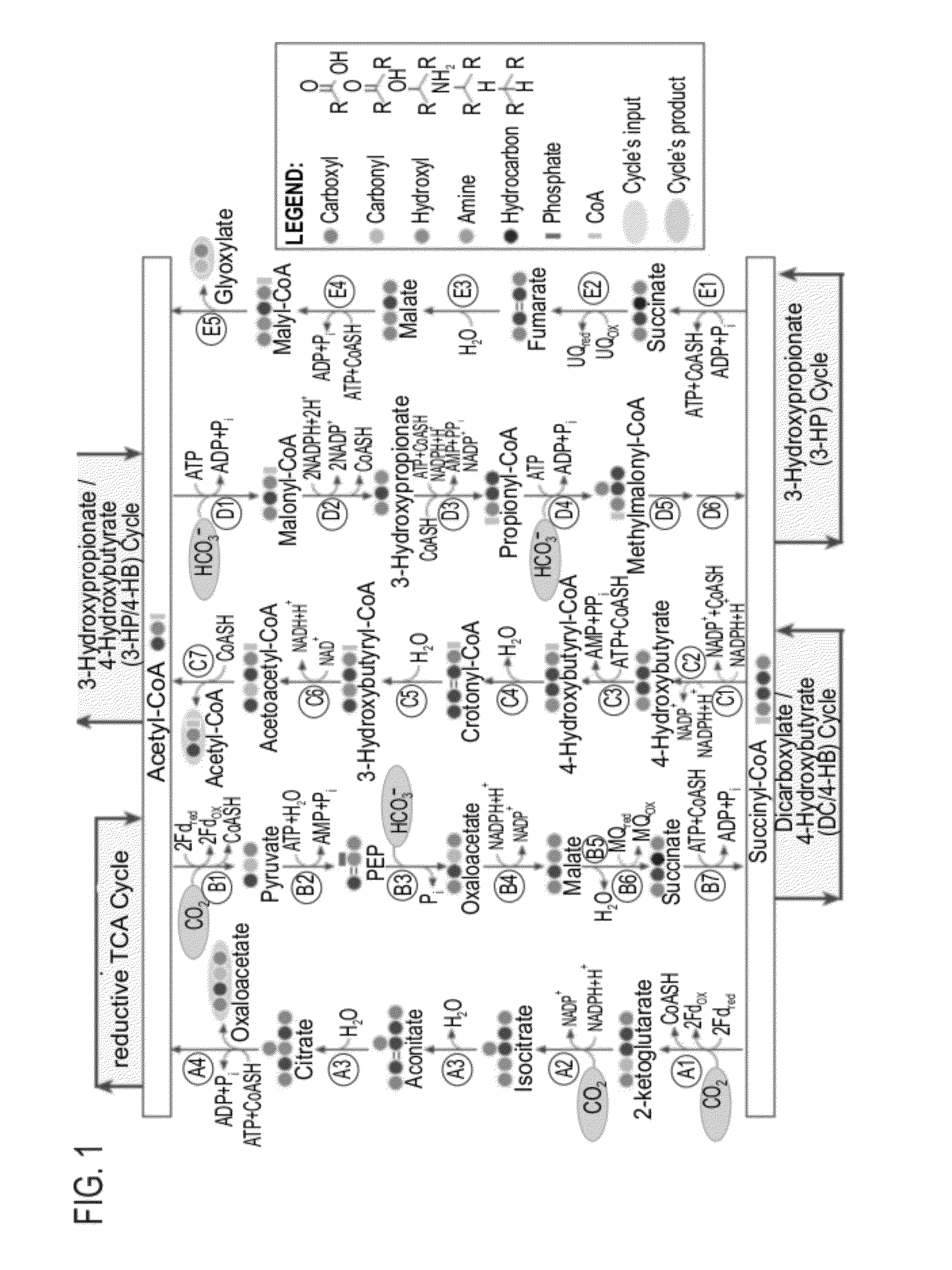
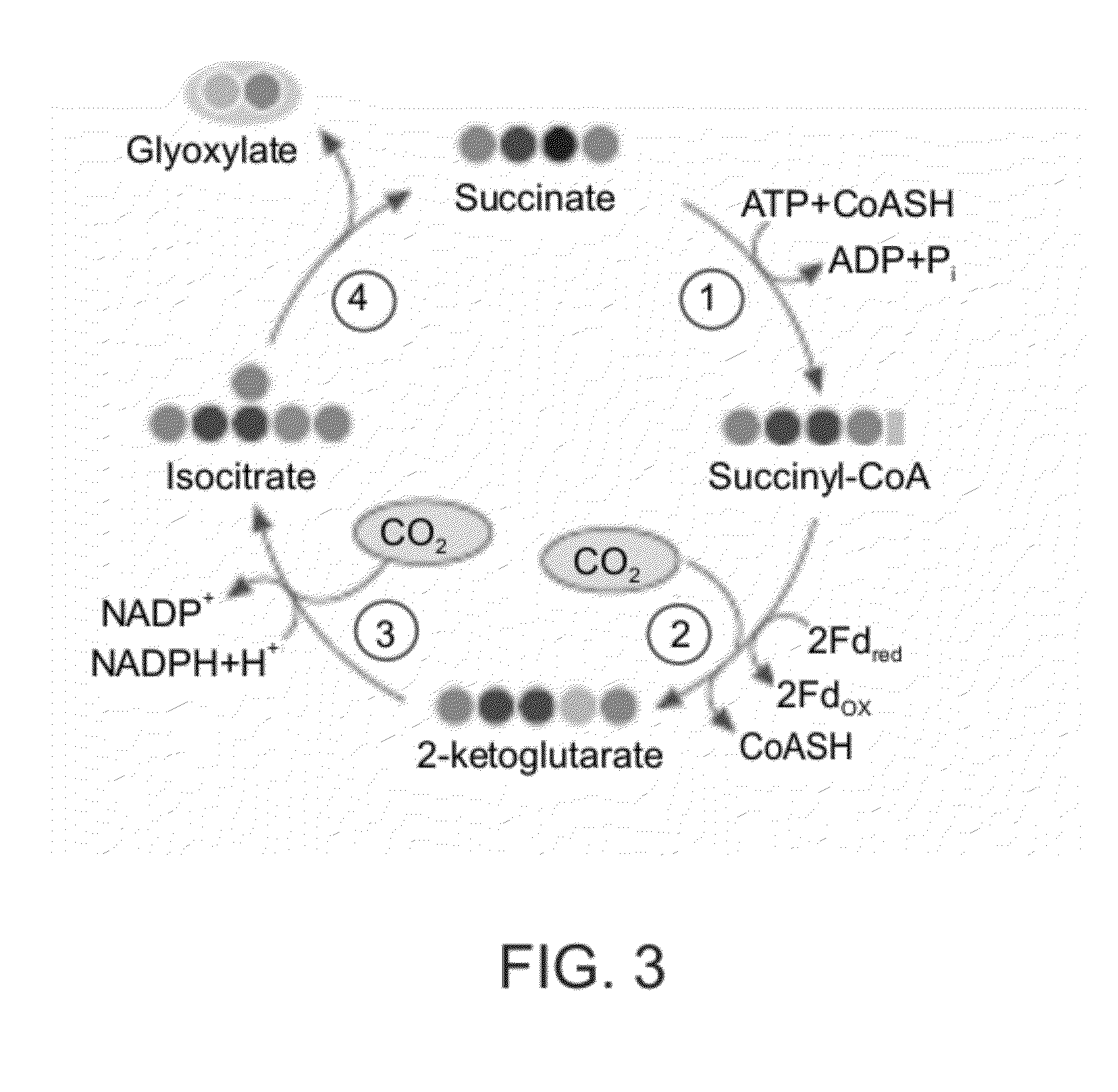
A system for carbon fixation is provided. The system comprises enzymes which catalyze reactions of a carbon fixation pathway, wherein at least one of the reactions of the carbon fixation pathway is a carboxylation reaction, wherein products of the reactions of the carbon fixation pathway comprise oxaloacetate and malonyl-CoA, wherein an enzyme which performs the carboxylation reaction is selected from the group consisting of phophoenolpyruvate (PEP) carboxlase, pyruvate carboxylase and acetyl-CoA carboxylase and wherein an export product of the carbon fixation pathway is glyoxylate. Additional carbon fixation pathways are also provided and methods of generating same.
Owner:YEDA RES & DEV CO LTD
Fatty acid and derivatives production
The present invention relates to at least one method of producing at least one fatty acid and / or derivative thereof from a gas comprising H 2 , CO 2 and O 2 the method comprising the steps of: (a) providing a genetically modified hydrogen oxidising bacterium in an aqueous medium; and (b) contacting the aqueous medium with a gas comprising H2, CO2 and O2 in a weight ratio of 20 to 70: 10 to 45: 5 to 35; wherein the fatty acid comprises at least 5 carbon atoms and wherein the hydrogen oxidising bacterium is genetically modified relative to the wild type bacterium to increase the expression of enzyme E 1 that is capable of catalysing the conversion of acetyl CoA to acyl ACP via malonyl coA and to increase the expression of enzyme E 2 that is capable of catalysing the conversion of Acyl ACP to the fatty acid.
Owner:EVONIK DEGUSSA GMBH
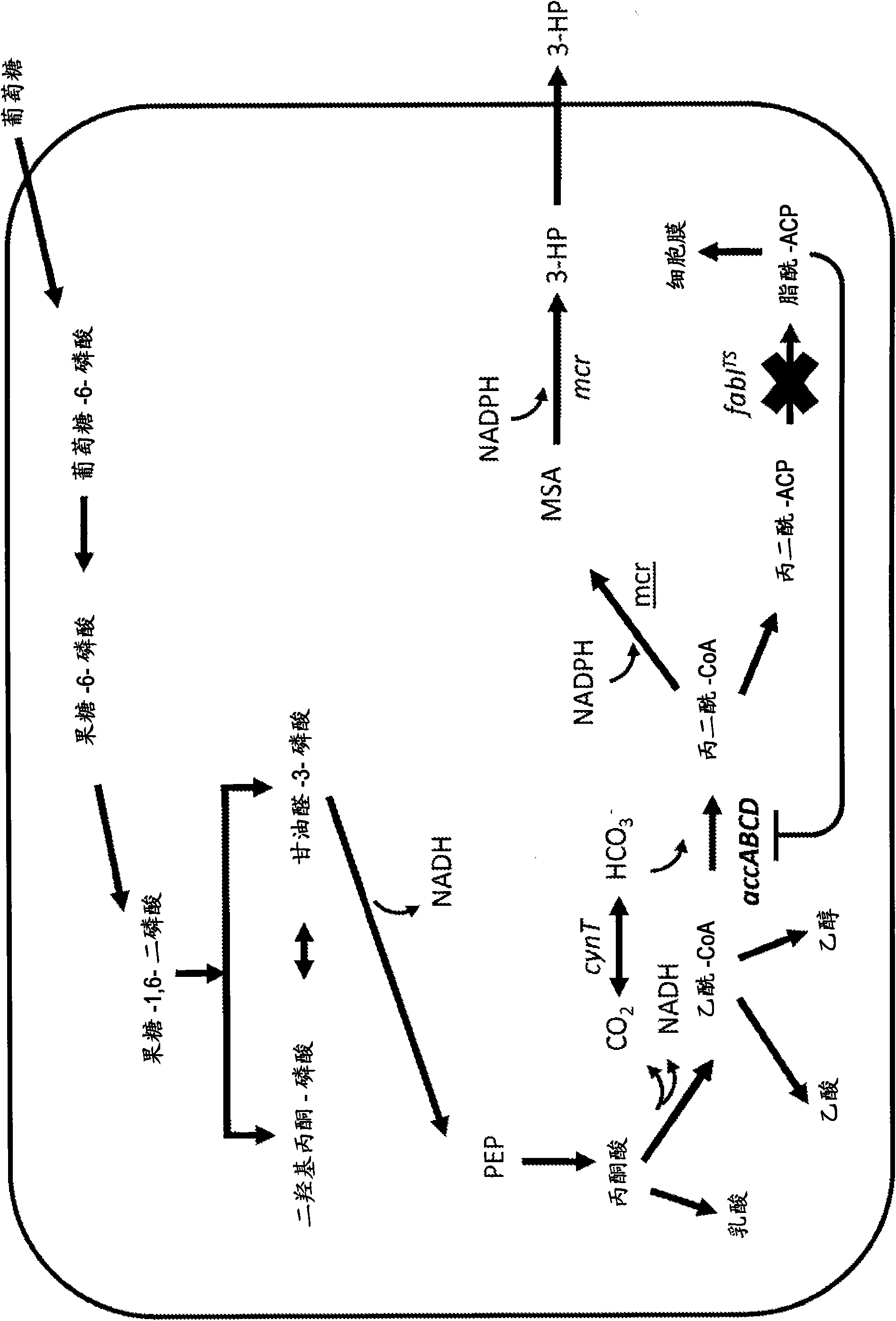
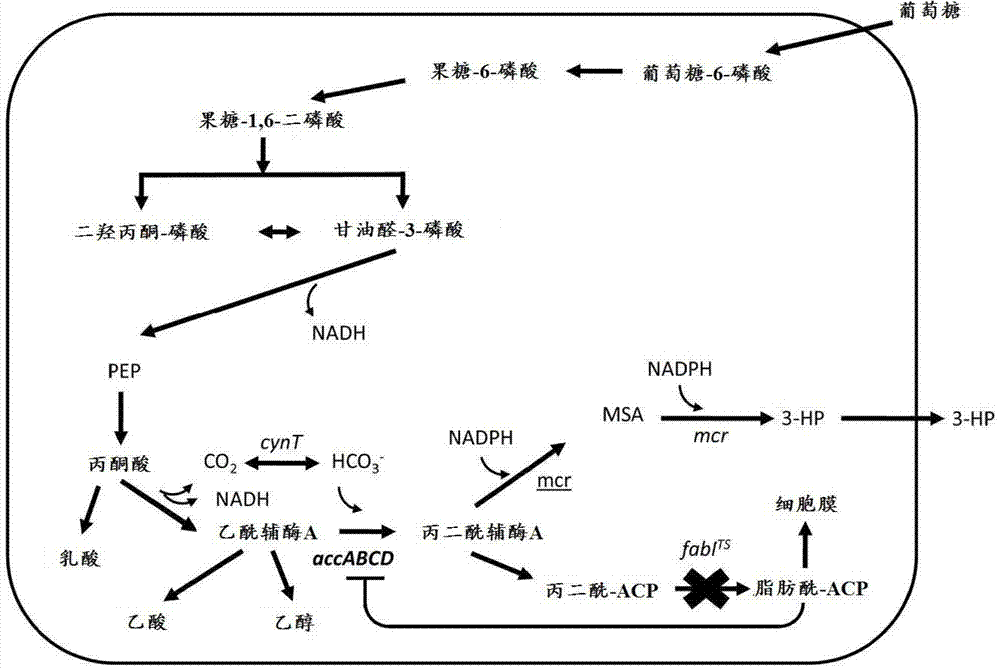
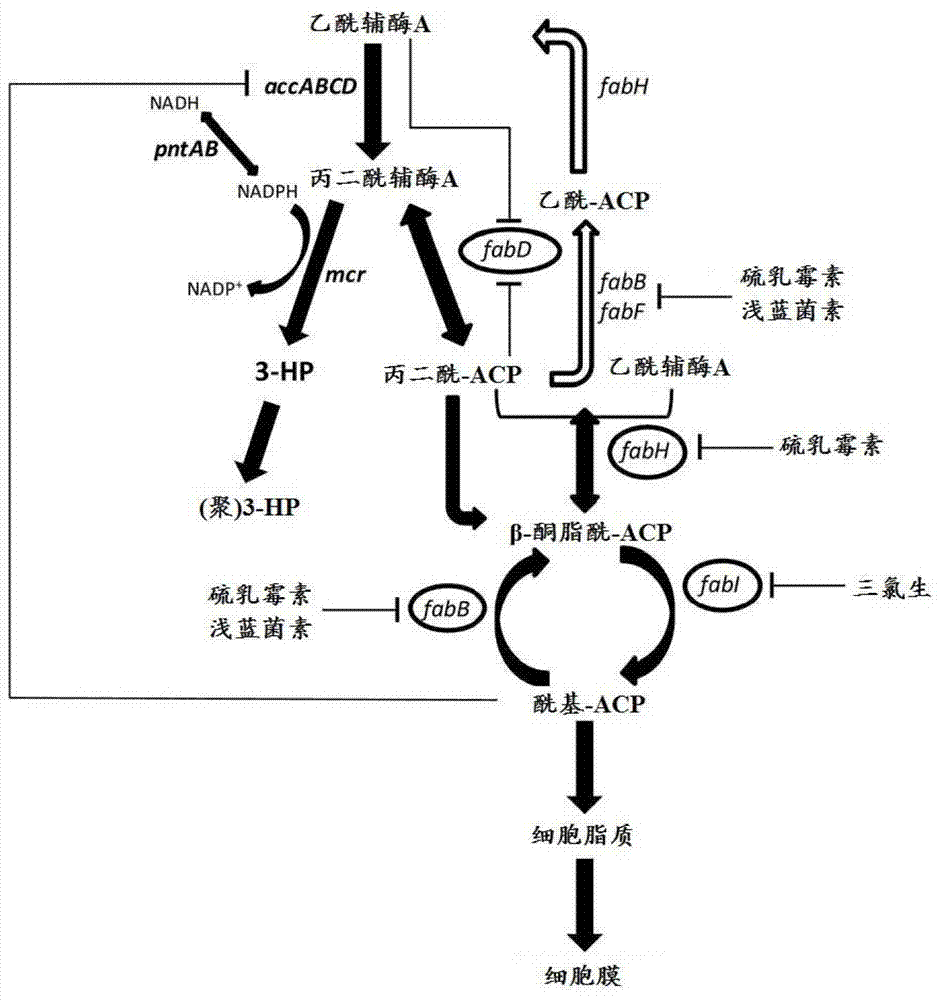
Construction method of engineering bacteria capable of dynamically regulating synthesis of 3HP (3-hydroxypropionic acid)
PendingCN107400652AReduce manufacturing costIncrease concentrationBacteriaMicroorganism based processesMalonic acidMicrobiology
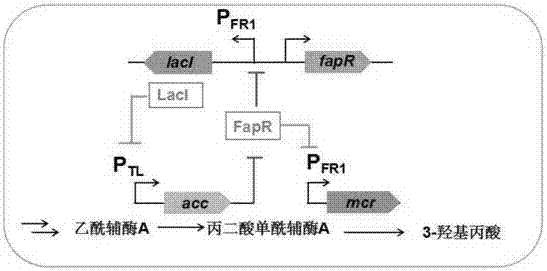
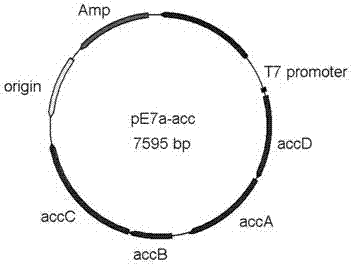
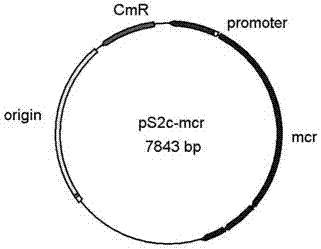
The invention relates to a construction method of engineering bacteria capable of dynamically regulating synthesis of 3HP (3-hydroxypropionic acid). The construction method is characterized in that a transcription factor FapR based on bacillus subtilis has the characteristic of response to malonyl CoA, an acc gene synthesizing malonyl CoA and a mcr gene converting malonyl CoA into 3HP in a 3HP synthesis pathway are arranged in the downstream position of a promoter, transcription of the two genes is dynamically regulated according to the concentration of malonyl CoA, the engineering bacteria synthesized from 3HP are dynamically regulated according to the concentration of malonyl CoA, the problems that malonyl CoA poisons bacteria and the 3HP synthesis efficiency is low at present are solved, and the technical support is provided for mass production of 3HP.
Owner:NORTHEAST FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
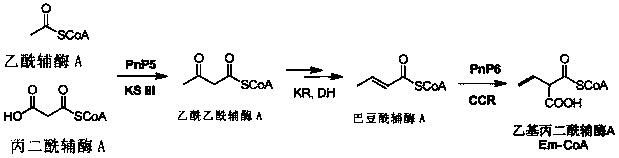
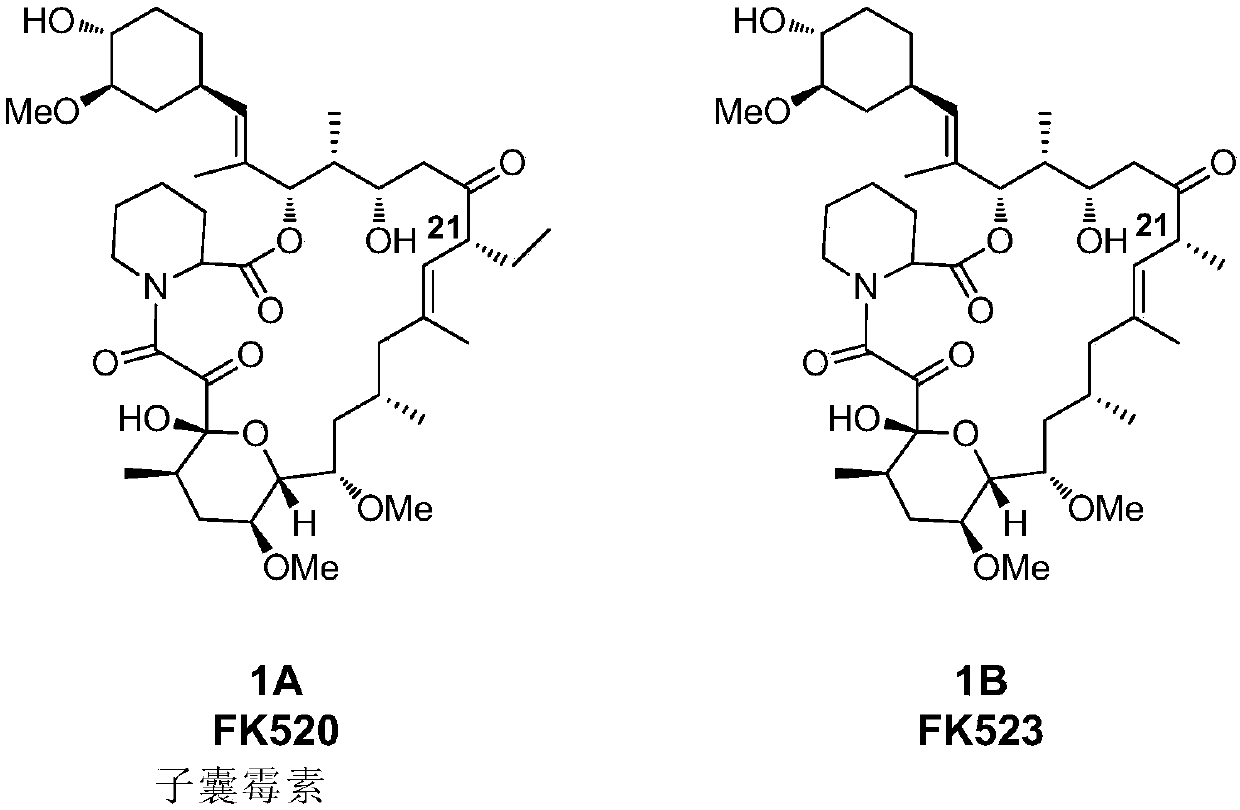
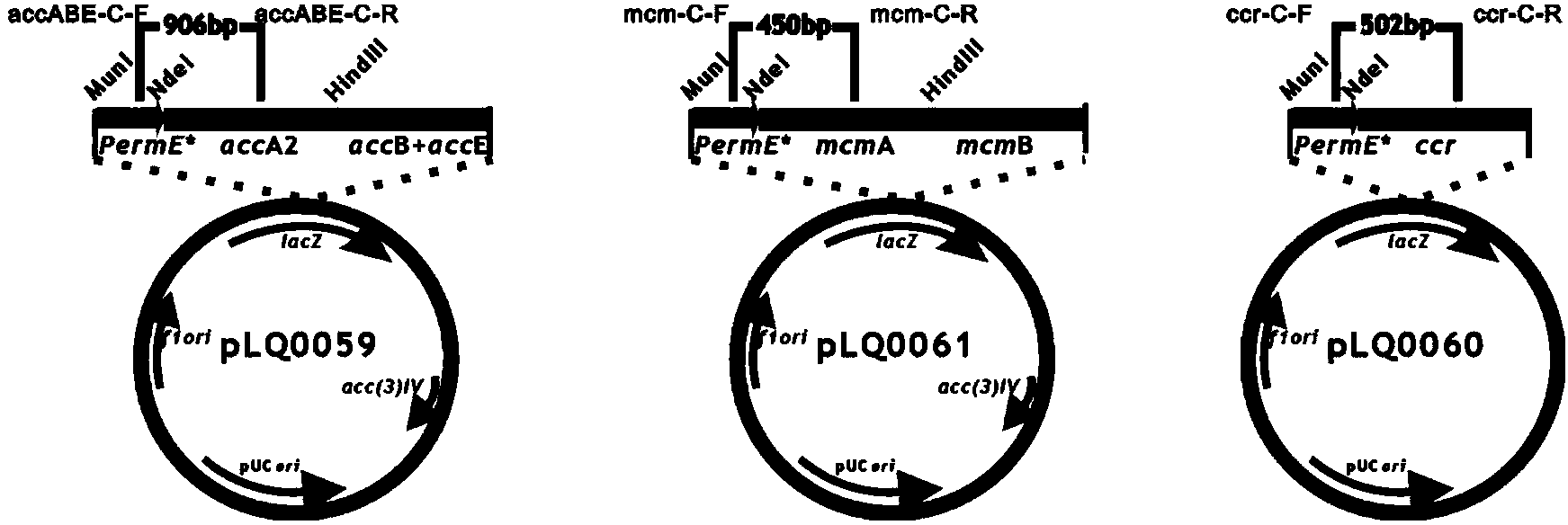
Method for constructing engineering strain with high yield of FK520 and strain with high yield of Streptomyces hygroscopicus
The invention provides an engineering strain with high yield of FK520 (ascomycin). A gene expression cassette is integrated in a genome of the strain, and the gene expression cassette expresses a protein encoded by a biosynthetic gene of ethyl malonyl coA. The yield of FK520 can be increased substantially by the transformed strain, and the proportion (mass ratio) of the main product FK520 to sideproduct FK523 is increased.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF ORGANIC CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
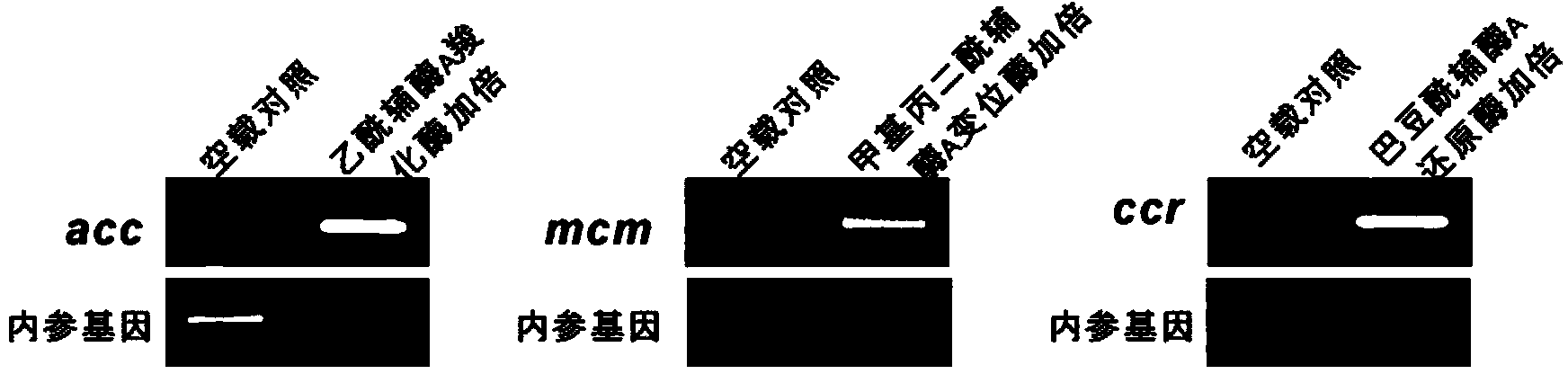
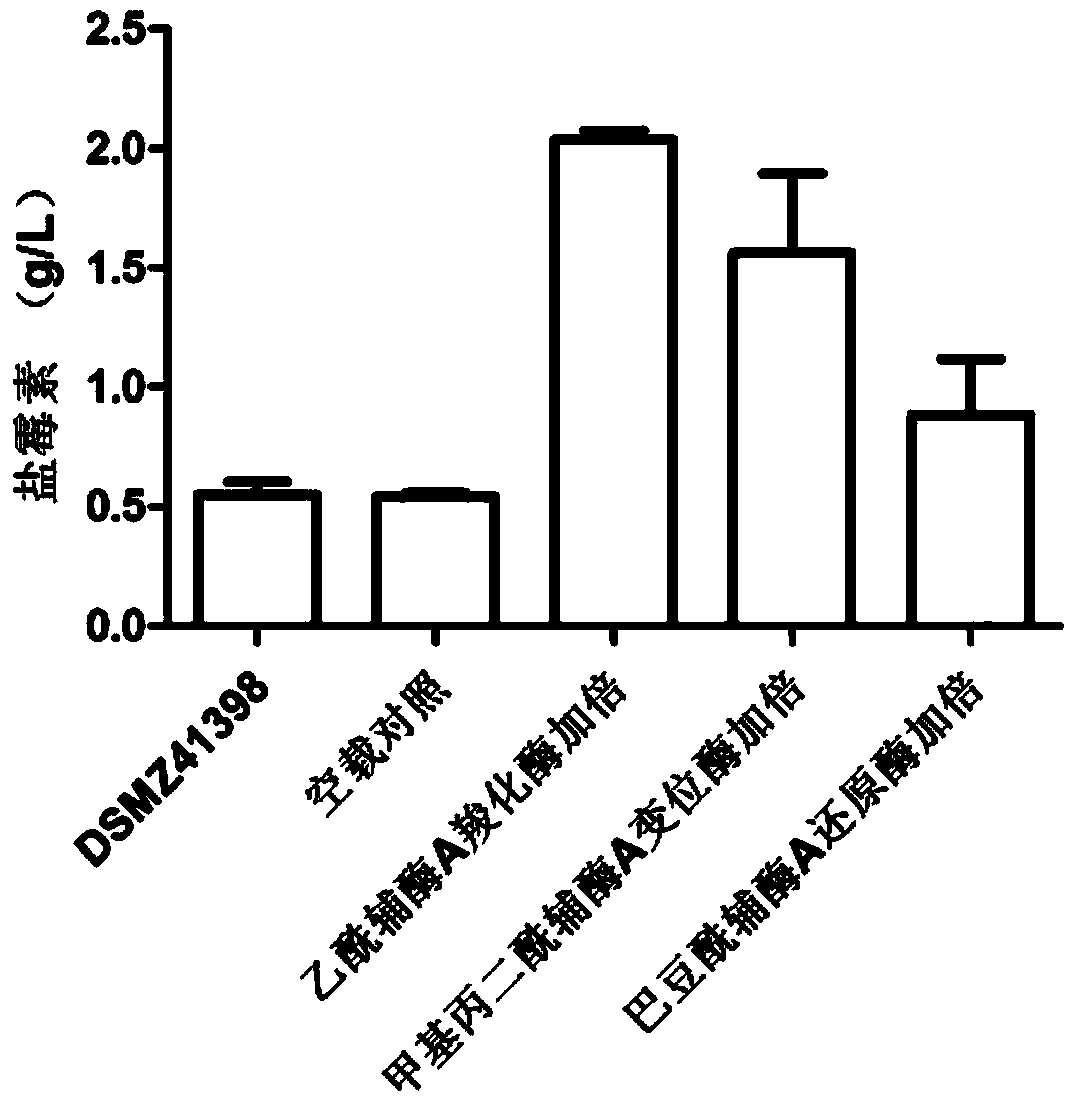
Method for improving fermentation level of salinomycin by increasing supply of precursors
ActiveCN104357506AIncrease supplyImprove fermentation yieldBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyAcyl-CoA carboxylase
The invention discloses a method for improving the fermentation level of salinomycin by increasing supply of precursors. The method comprises the following steps: doubling acetyl coA carboxylase genes from streptomyces coelicolor, methyl malonyl coA mutase genes from streptomyces albus DSMZ41398 and crotonoyl coA reductase genes from the streptomyces albus DSMZ41398 on the chromosomes of the streptomyces albus DSMZ41398 through an integrating vector pSET152 respectively to increase supply of three precursors required for synthesizing salinomycin so as to increase the salinomycin yield. According to the method, the final fermentation yield of engineering strain salinomycin is increased by 260% and the shake flask level of a lab reaches 2 g / L.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Microorganism production of high-valve chemical products, and related compositions, methods and systems
This invention relates to metabolically engineered microorganism strains, such as bacterial strains, in which there is an increased utilization of malonyl-CoA for production of a chemical product, which includes polyketides and 3-hydroxypropionic acid.
Owner:OPX BIOTECH +1
Enzymatic systems for carbon fixation and methods of generating same
ActiveUS20120301947A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsPyruvate synthesisAcetaldehyde
A system for carbon fixation is provided. The system comprises enzymes which catalyze reactions of a carbon fixation pathway, wherein at least one of the reactions of the carbon fixation pathway is a carboxylation reaction, wherein products of the reactions of the carbon fixation pathway comprise oxaloacetate and malonyl-CoA, wherein an enzyme which performs the carboxylation reaction is selected from the group consisting of phophoenolpyruvate (PEP) carboxlase, pyruvate carboxylase and acetyl-CoA carboxylase and wherein an export product of the carbon fixation pathway is glyoxylate. Additional carbon fixation pathways are also provided and methods of generating same.
Owner:YEDA RES & DEV CO LTD
Piperidine compounds useful as malonyl-CoA decarboxylase inhibitors
The present invention provides methods for the use of compounds as depicted by structure I, pharmaceutical compositions containing the same, and methods for the prophylaxis, management and treatment of metabolic diseases and diseases modulated by MCD inhibition. The compounds disclosed in this invention are useful for the prophylaxis, management and treatment of diseases involving in malonyl-CoA regulated glucose / fatty acid metabolism pathway. In particular, these compounds and pharmaceutical composition containing the same are indicated in the prophylaxis, management and treatment of cardiovascular diseases, diabetes, cancer and obesity.
Owner:CHUGAI PHARMA CO LTD
Microbial production of 3-hydroxypropionic acid
InactiveUS20160138056A1Increasing the flux towards cytosolic malonyl-CoAAvoid inactivationMicroorganismsOxidoreductasesMicroorganism3-Hydroxypropionic acid
A yeast cell having a reduced level of activity of NAD dependent glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) has at least one exogenous gene encoding NADP dependent GAPDH and / or has up-regulation of at least one endogenous gene expressing NADP dependent GAPDH, wherein combined expression of the enzymes NADP dependent GAPDH, PDC, ALD, ACS, ACC* and MCR in said host cell increases metabolic flux towards 3-HP via malonyl-CoA compared to an otherwise similar yeast cell lacking said genetic modification.
Owner:DANMARKS TEKNISKE UNIV
Microorganisms and methods for the production of fatty acids and fatty acid derived products
This invention relates to metabolically engineered microorganism strains, such as bacterial strains, in which there is an increased utilization of malonyl-CoA for production of a fatty acid or fatty acid derived product, wherein the modified microorganism produces fatty acyl-CoA intermediates via a malonyl-CoA dependent but malonyl-ACP independent mechanism.
Owner:CARGILL INC
Method using blue algae to synthesize phloretin
PendingCN109913508AEasy to buildReduce manufacturing costBacteriaMicroorganism based processesPropanoic acidChalcone synthase
The invention provides a technical method using 'photosynthetic bacteria', namely blue algae as the substrate organism to synthesize phloretin. The method mainly includes: exogenously expressing 4 coumarate Coenzyme A Ligase (4CL) and Chalcone synthase (CHS) which are two key enzymes for phloretin synthesis in the blue algae so as to use p-hydroxybenzene propanoic acid (also called phloretic acid)as the substrate to catalytically synthesize the phloretin, the 4CL catalyzes single-molecule p-hydroxybenzene propanoic acid to generate p-hydroxybenzene propionyl coenzyme A, the CHS catalyzes three-molecule malonyl coA and the single-molecule p-hydroxybenzene propionyl coenzyme A to synthesize the single-molecule phloretin. The method has the advantages that the phloretin is produced by usingone microorganism which can perform photosynthesis, the phloretin biological synthesizing approach which is cheap in raw material, simple in equipment, low in environment pollution and high in yield is created, and the method conforms to the direction of green production.
Owner:嘉兴欣贝莱生物科技有限公司
Heterocyclic compounds useful as malonyl-CoA decarboxylase inhibitors
InactiveUS7696365B2Organic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryDisease causeMalonyl coenzyme A decarboxylase
The present invention provides methods for the use of compounds as depicted by structure I, pharmaceutical compositions containing the same, and methods for the prophylaxis, management and treatment of metabolic diseases and diseases modulated by MCD inhibition. The compounds disclosed in this invention are useful for the prophylaxis, management and treatment of diseases involving in malonyl-CoA regulated glucose / fatty acid metabolism pathway. In particular, these compounds and pharmaceutical composition containing the same are indicated in the prophylaxis, management and treatment of cardiovascular diseases, diabetes, cancer and obesity.
Owner:CHUGAI PHARMA CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com