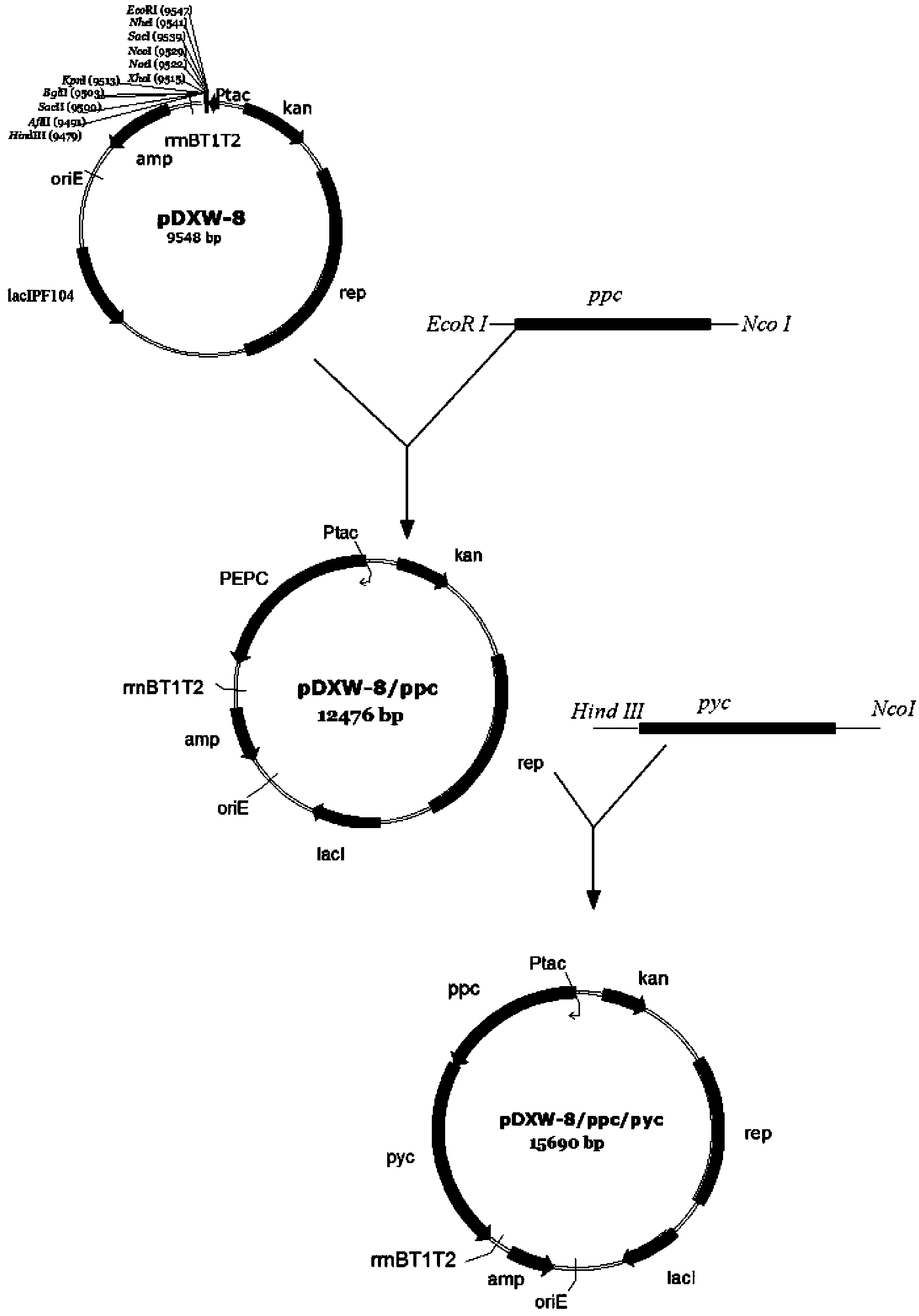
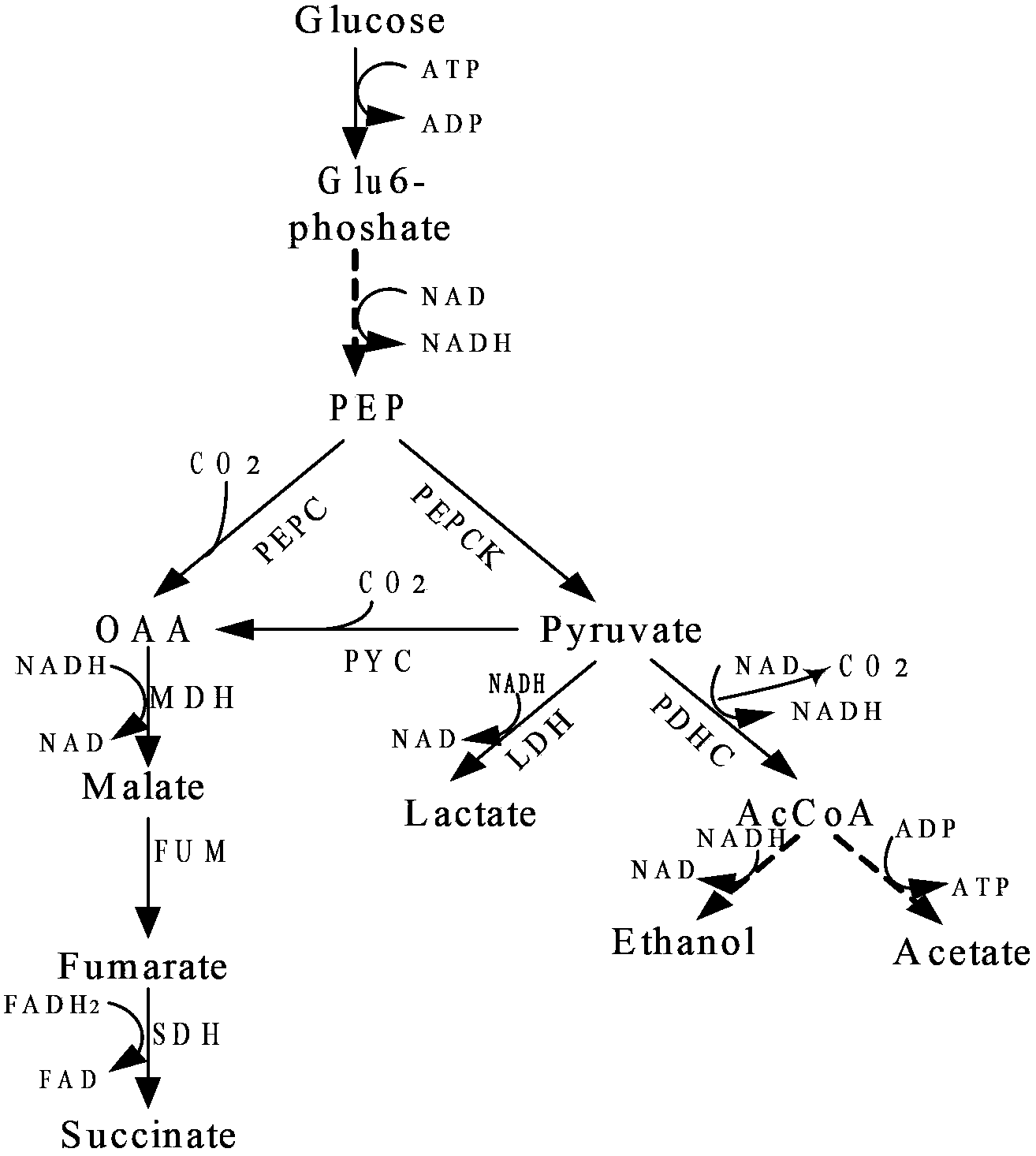
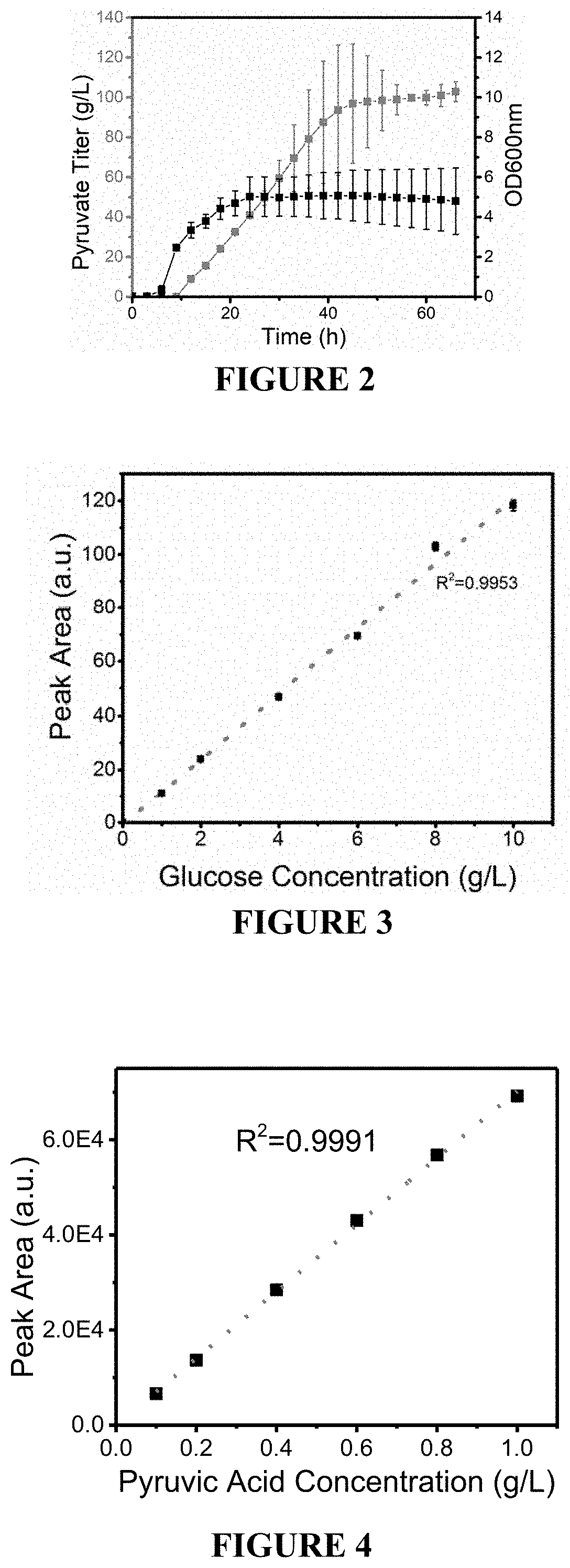
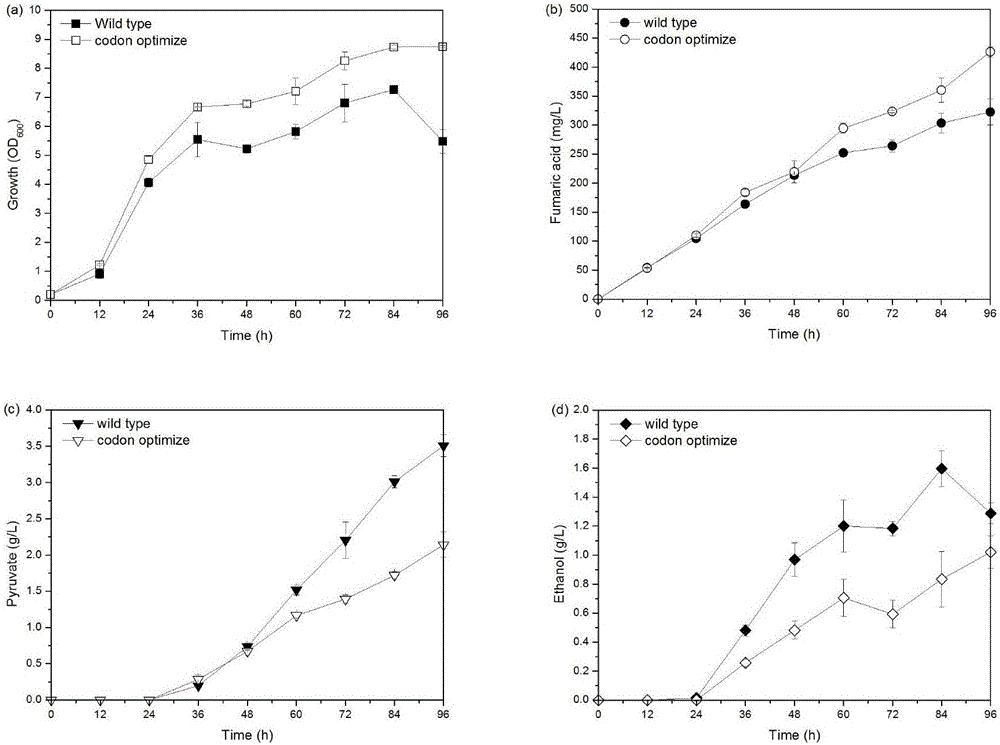
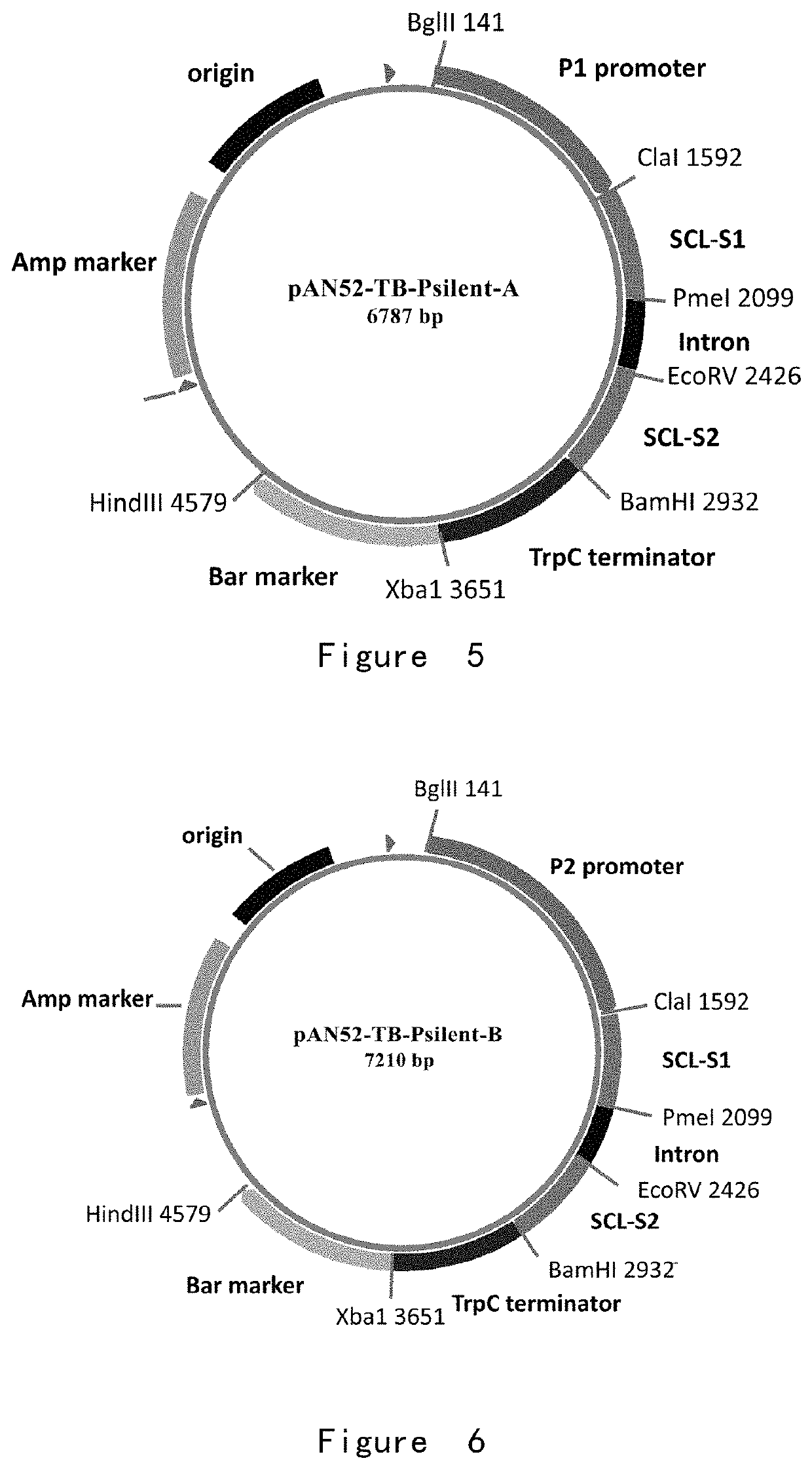
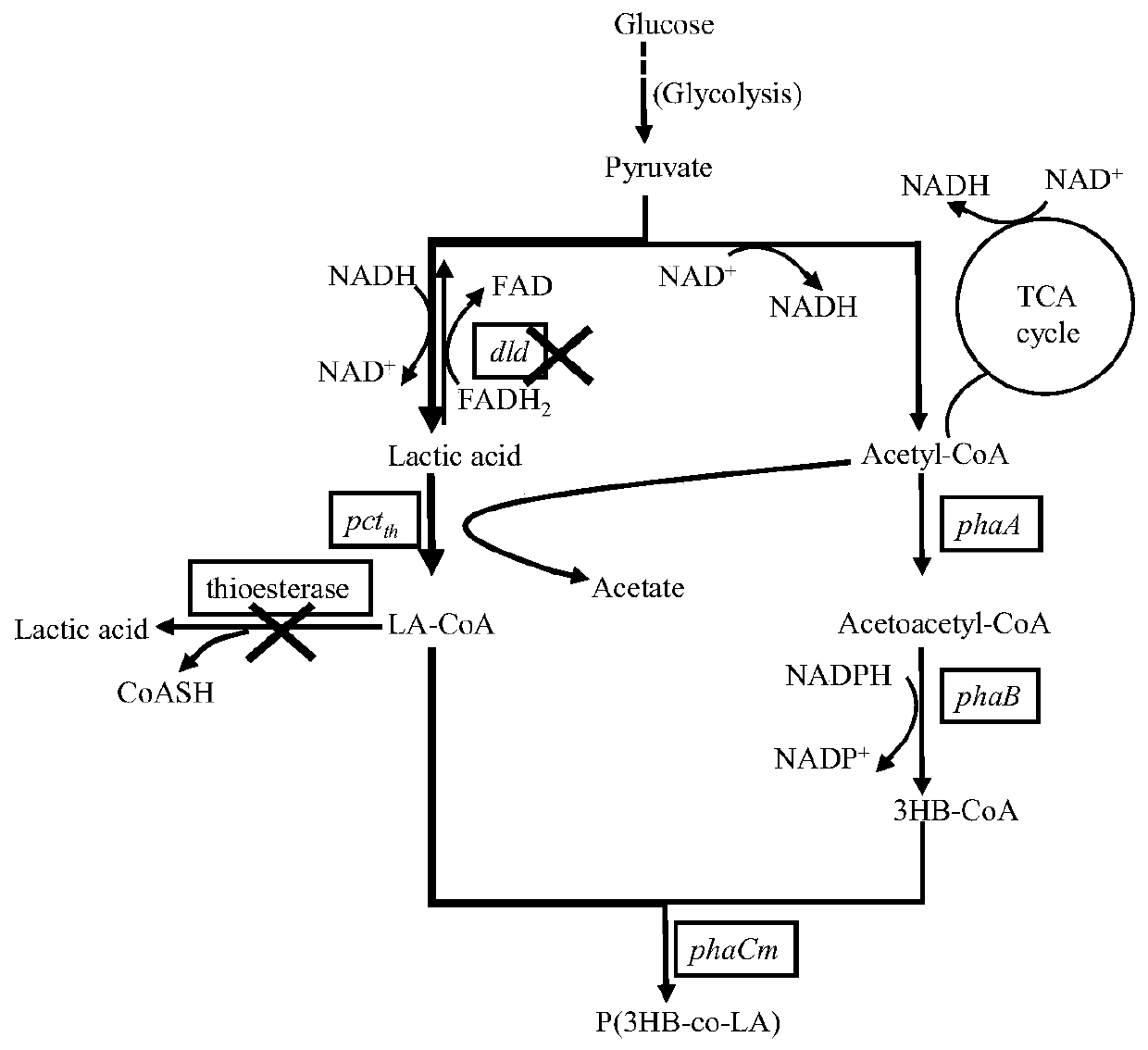
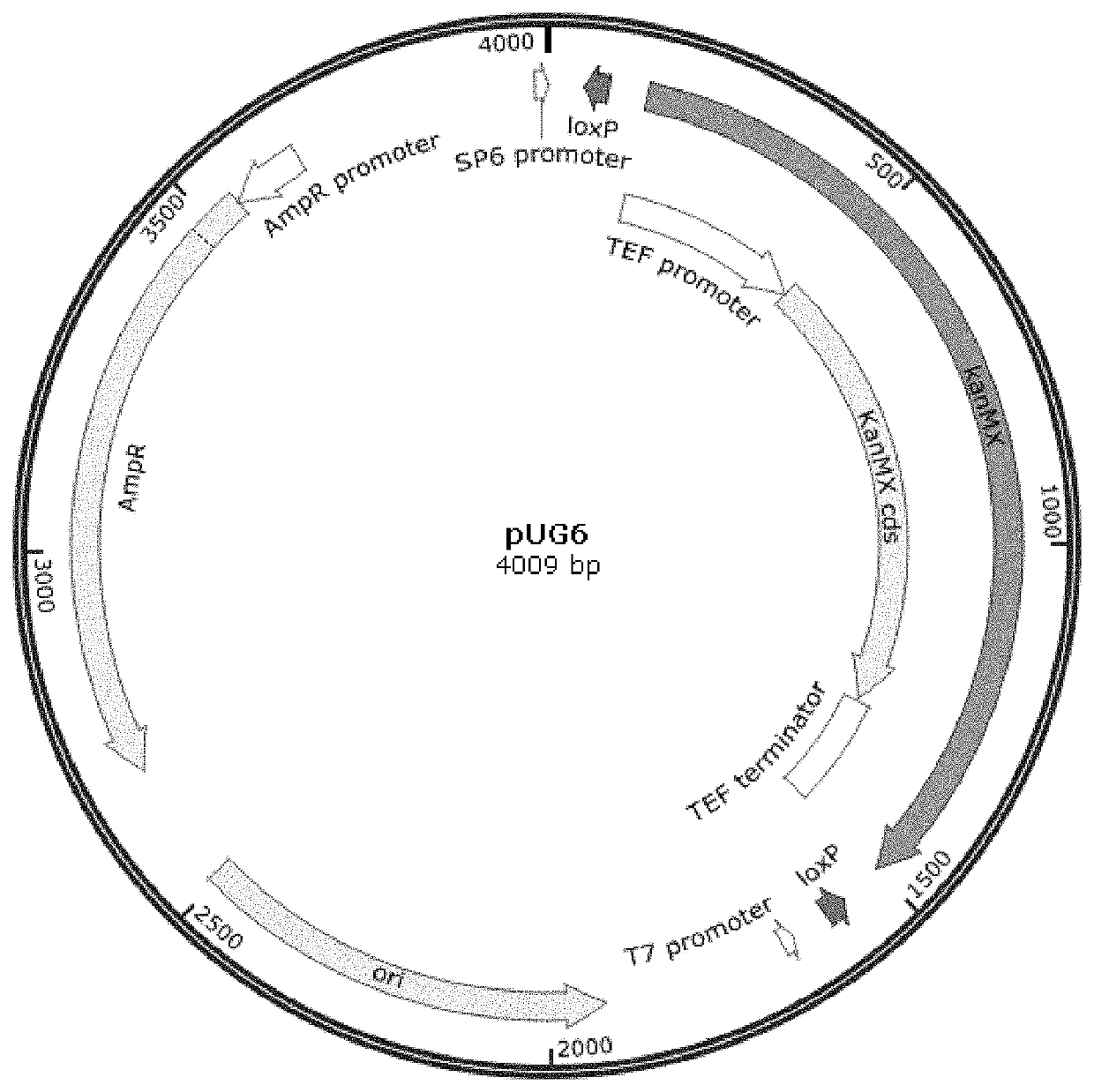
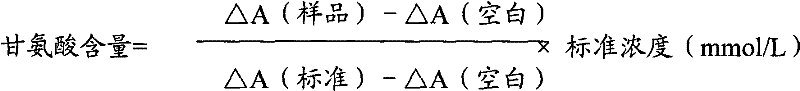Patents
Literature
83 results about "Pyruvate synthesis" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
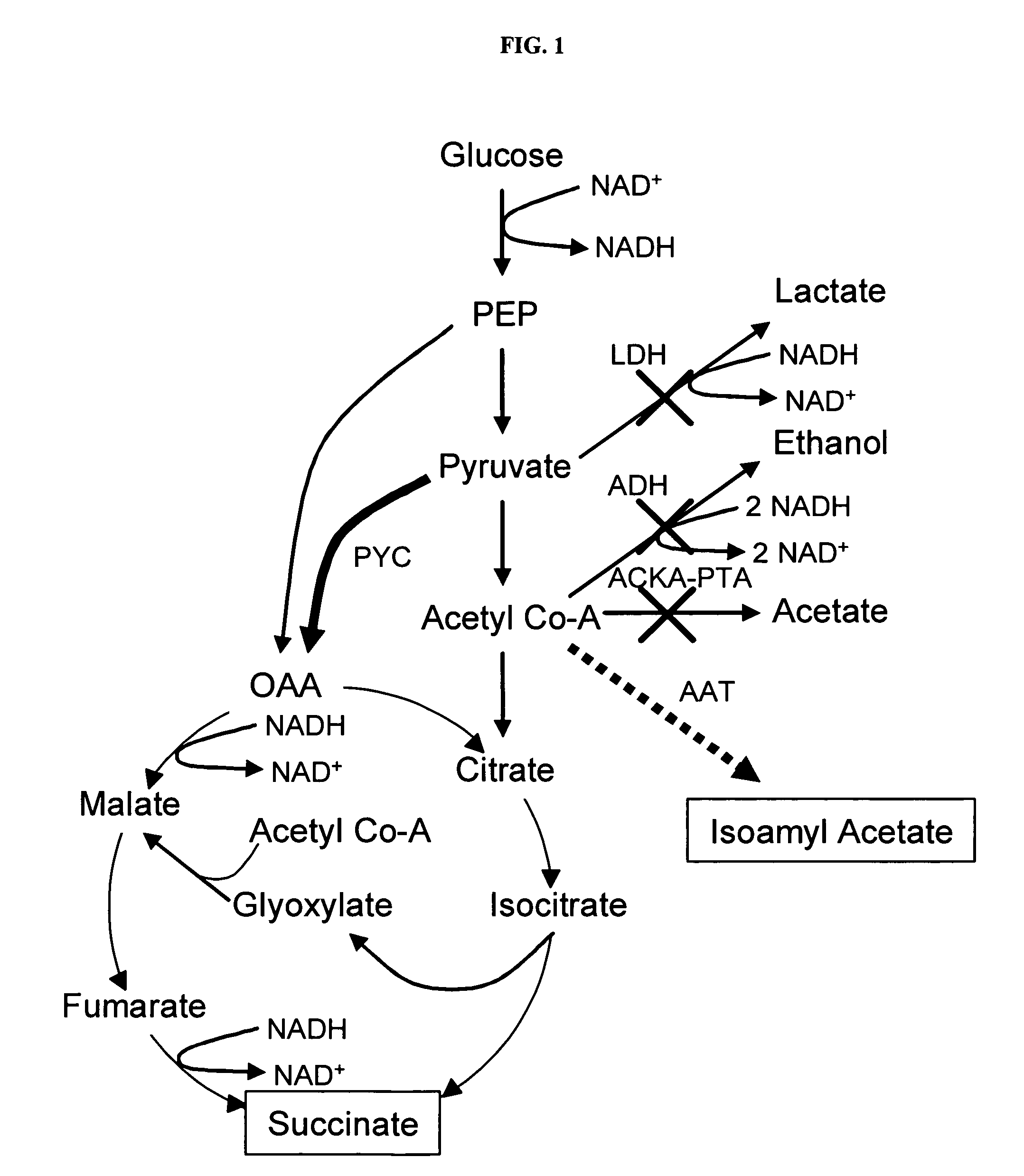
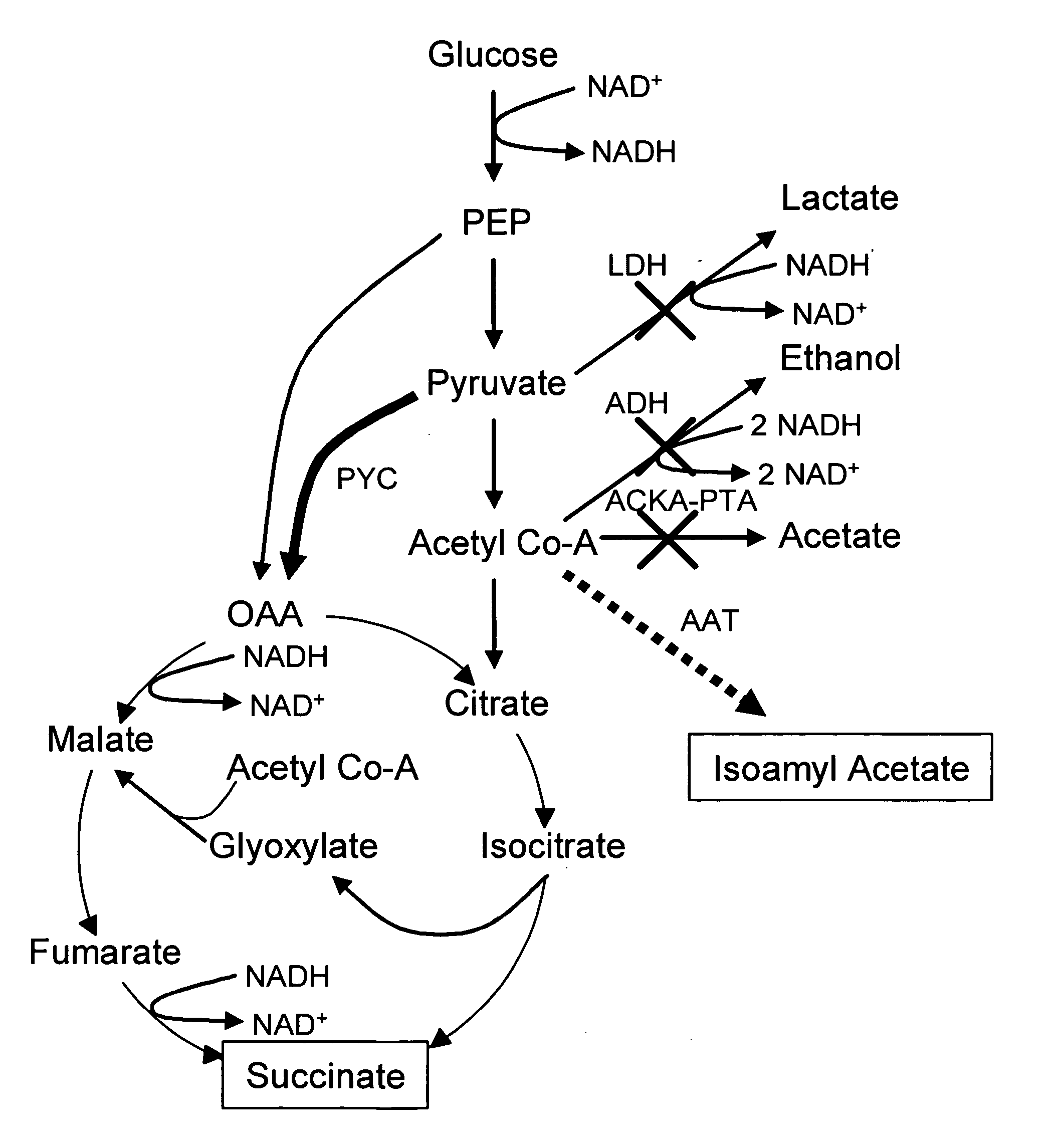
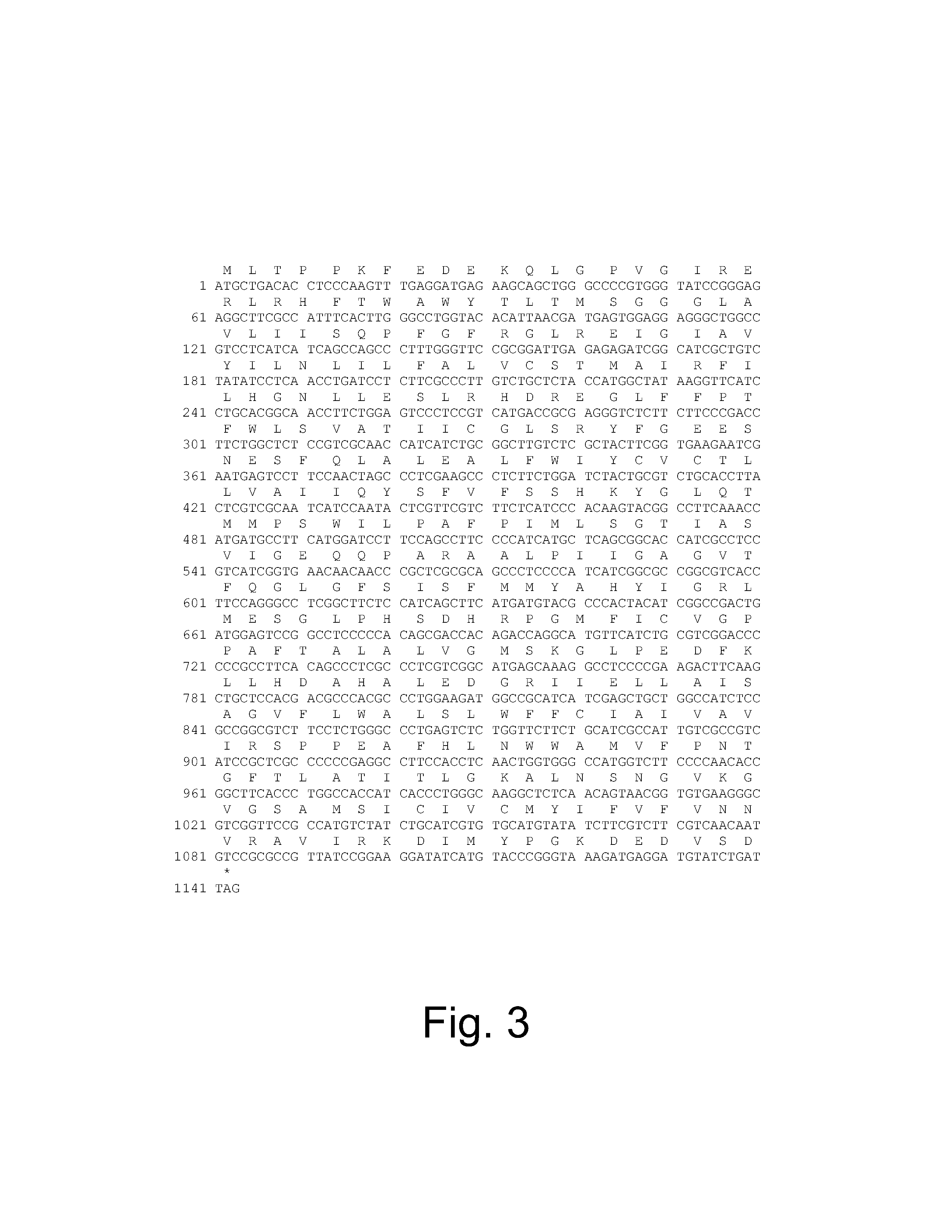
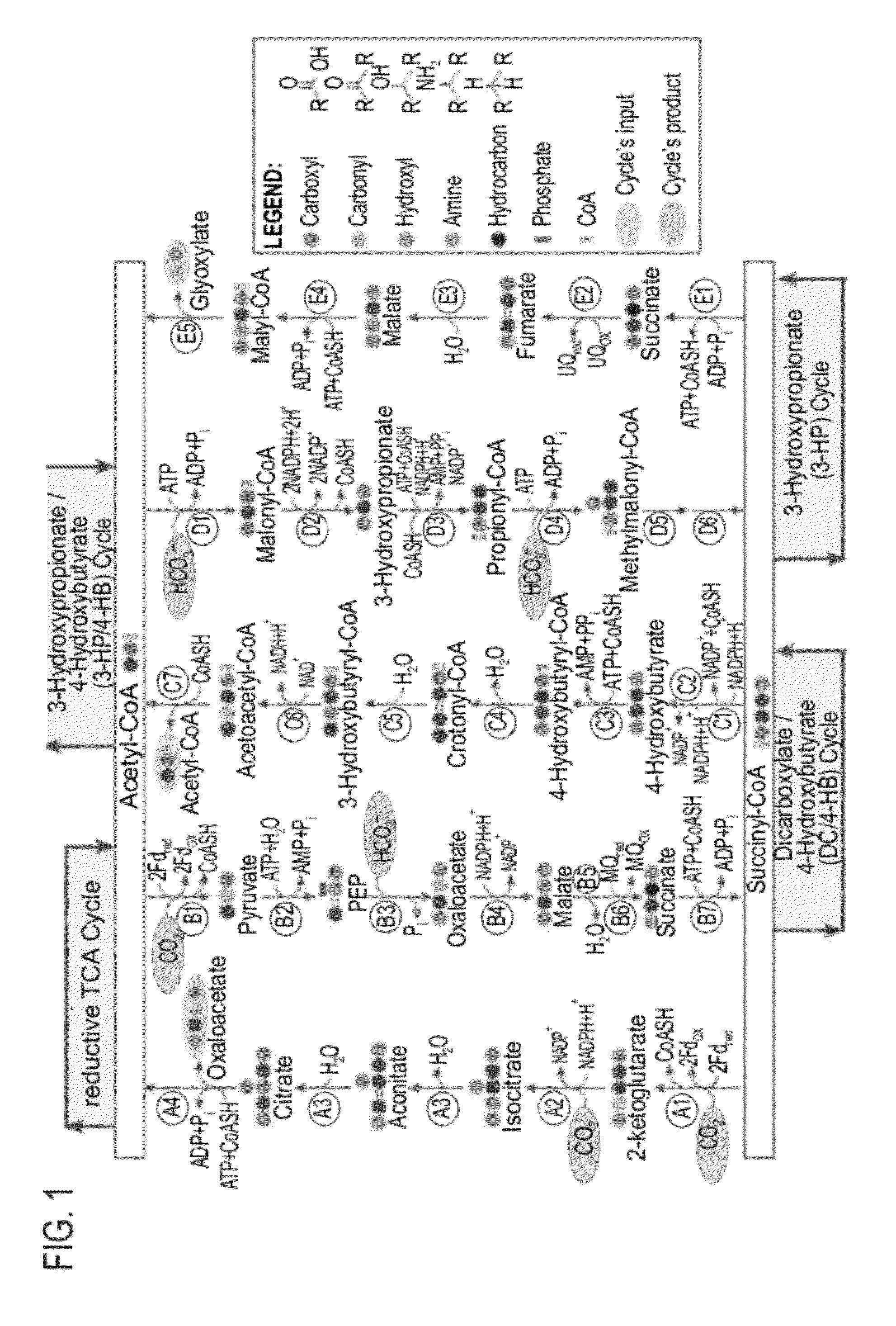
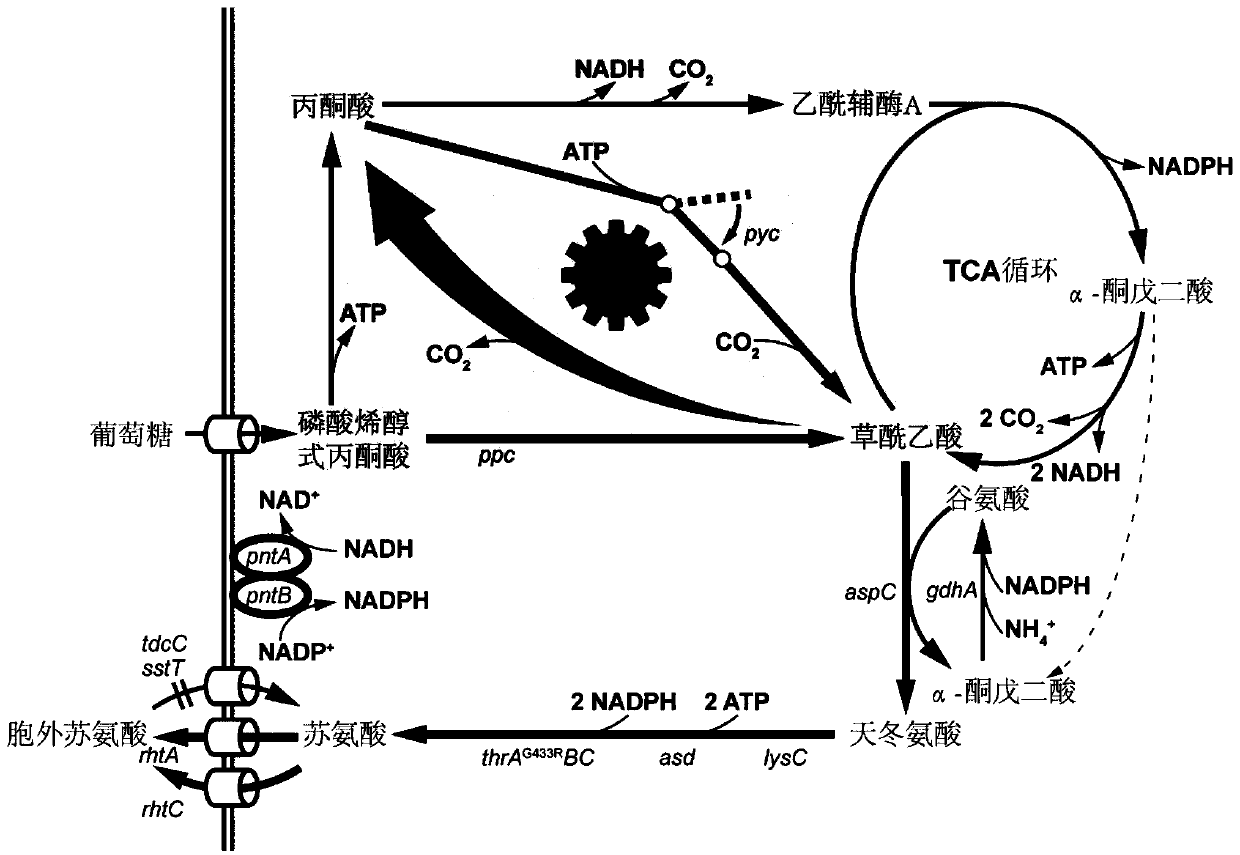
During gluconeogenesis, pyruvate carboxylase is involved in the synthesis of phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP) from pyruvate. Pyruvate is first converted by pyruvate carboxylase to oxaloacetate (OAA) in the mitochondrion requiring hydrolysis of one molecule of ATP.
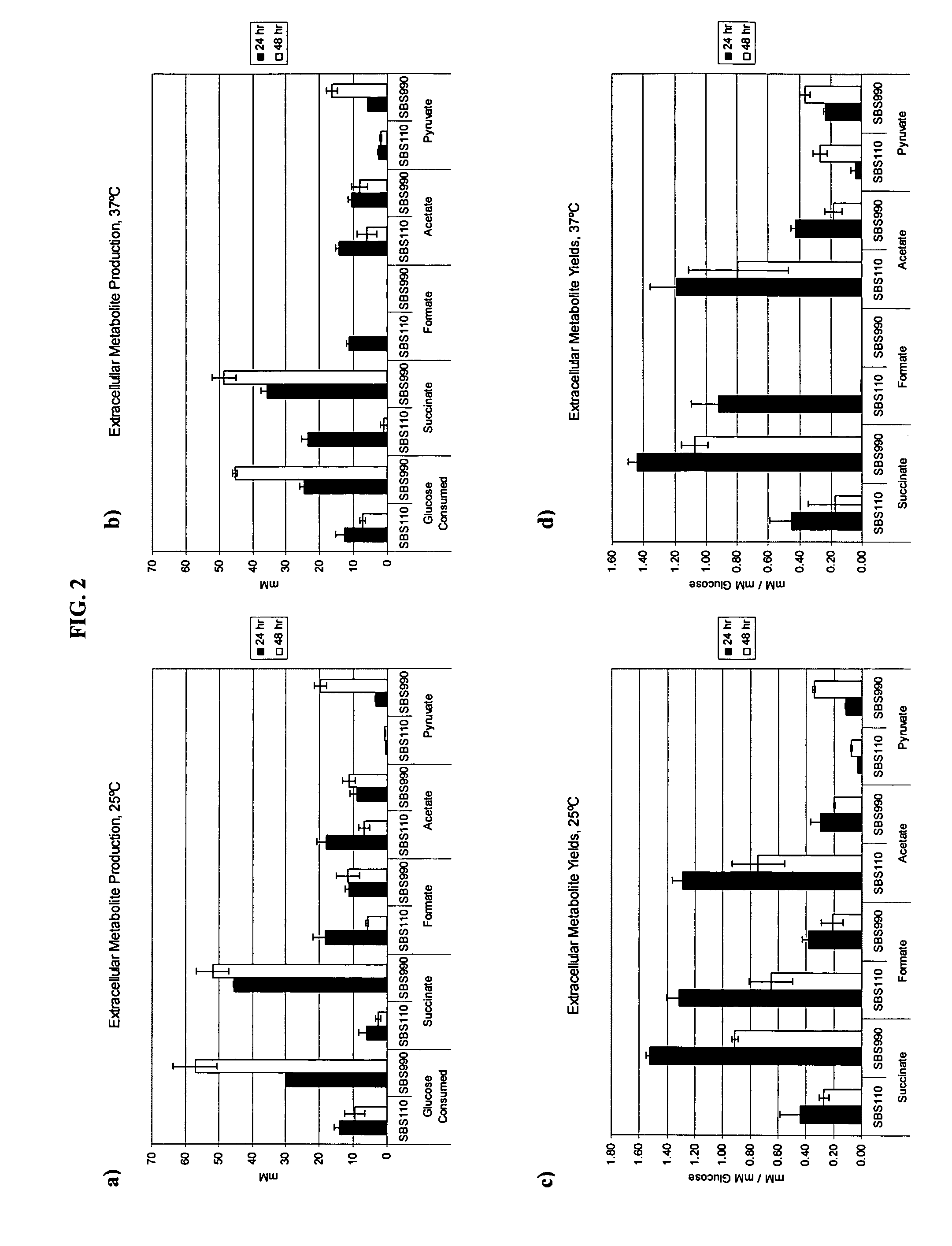
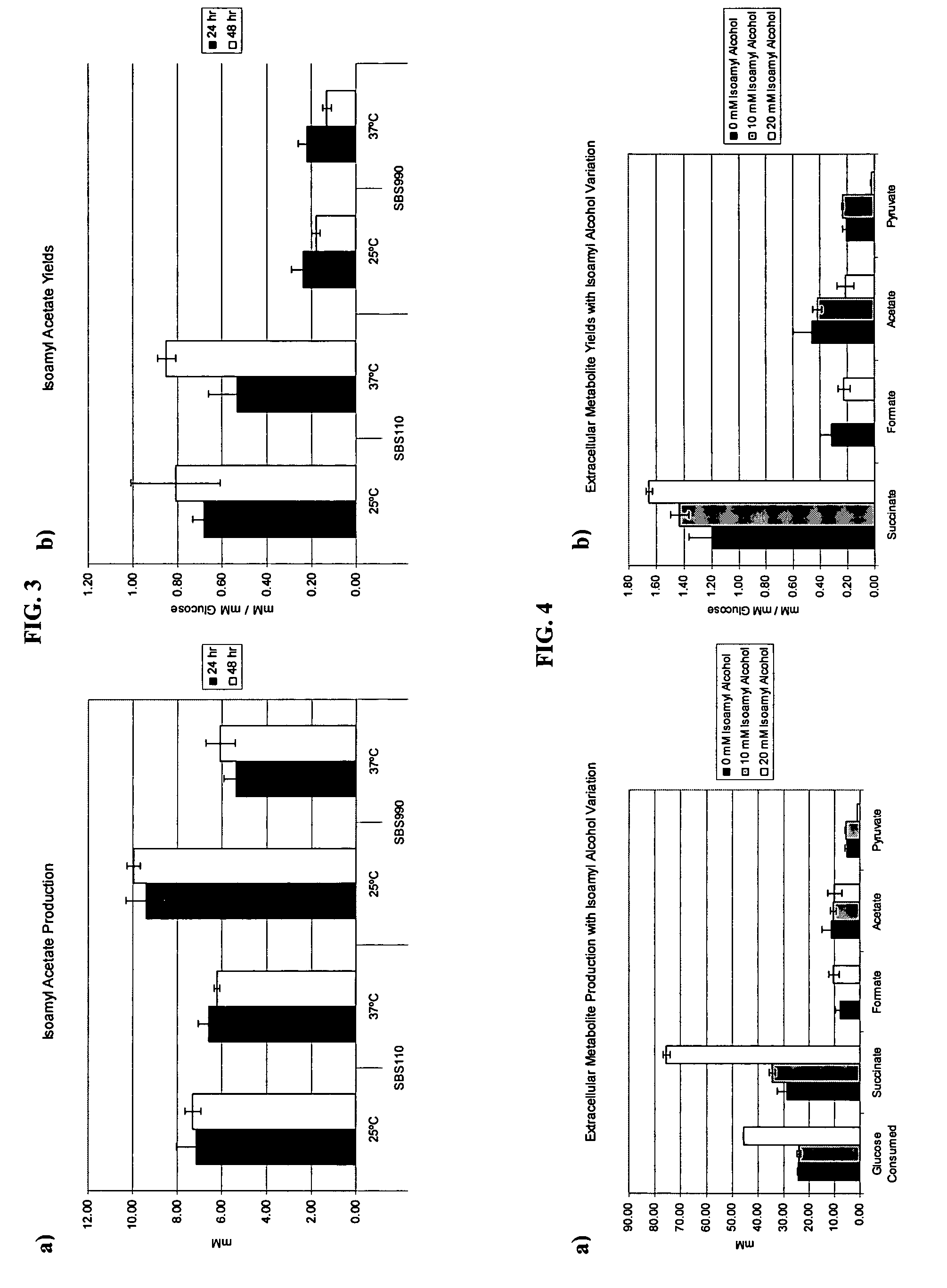
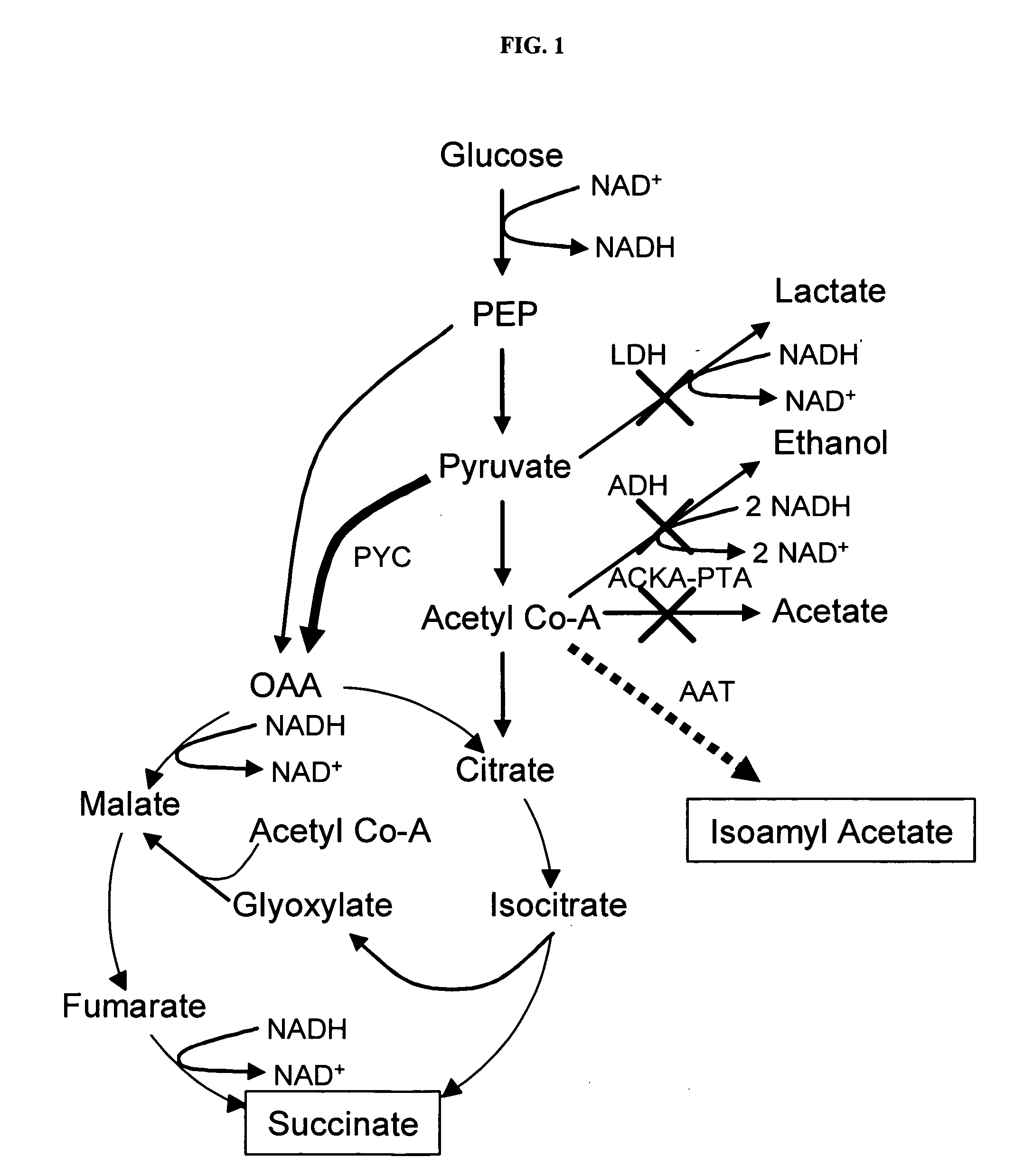
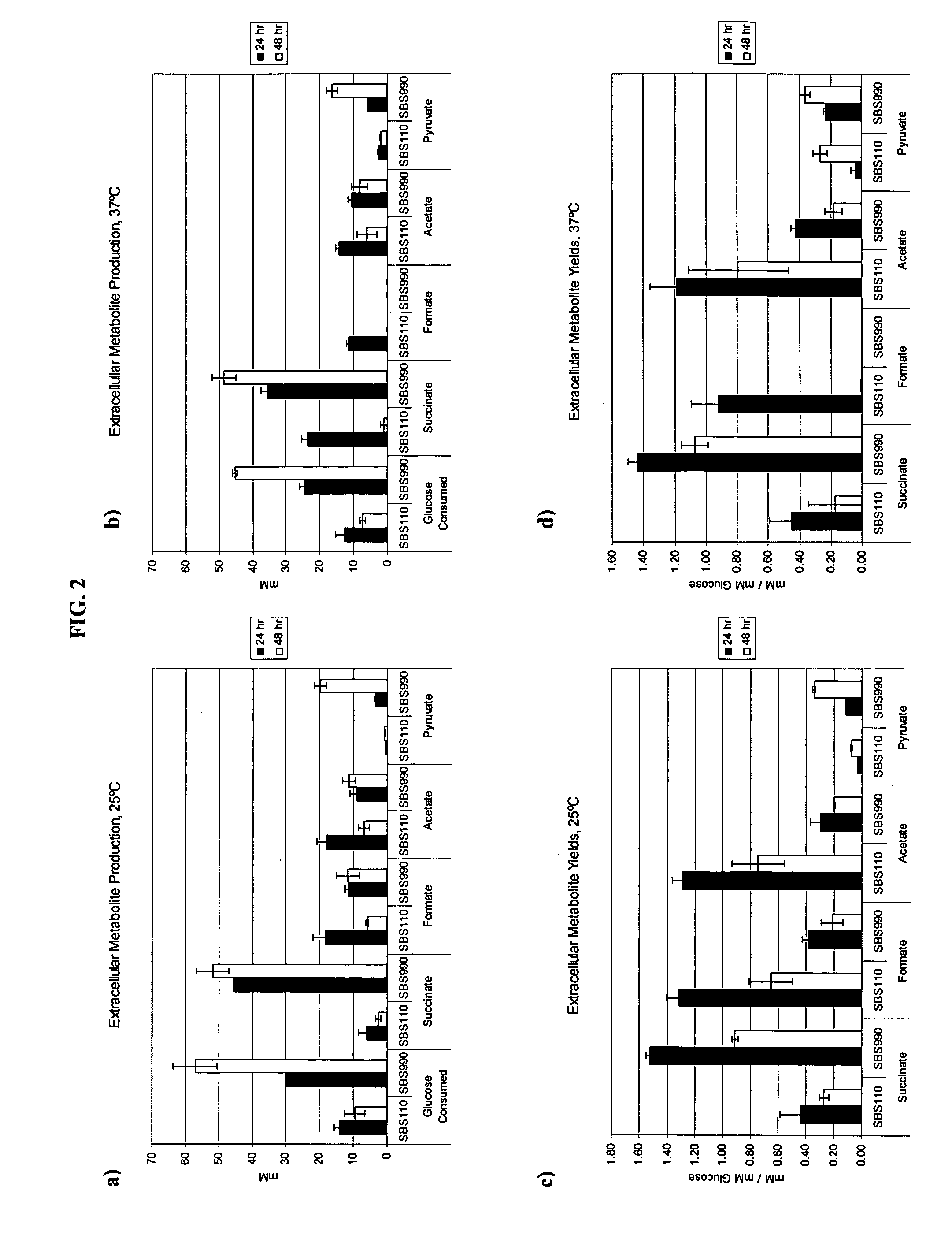
Simultaneous anaerobic production of isoamyl acetate and succinic acid
In vivo method of producing esters from acetyle coA, such as isoamyl acetate and succinate, has been developed by producing null mutants in pathways that use acetyl coA and by overexpressing products that use NADH and in order to maintain the proper redox balance between NADH and NAD+. The method is exemplified with null mutations in ldhA, adhE, ackA-pta and overexpression of pyruvate carboxylase and alcohol acetyltransferase. This strain produces higher levels of both isoamyl acetate and succinate.
Owner:RICE UNIV
Simultaneous anaerobic production of isoamyl acetate and succinic acid
InactiveUS20060141594A1Maximizing isoamyl acetate productionEasy to separateBacteriaTransferasesSuccinic acidPyruvate synthesis
In vivo method of producing esters from acetyle coA, such as isoamyl acetate and succinate, has been developed by producing null mutants in pathways that use acetyl coA and by overexpressing products that use NADH and in order to maintain the proper redox balance between NADH and NAD+. The method is exemplified with null mutations in ldhA, adhE, ackA-pta and overexpression of pyruvate carboxylase and alcohol acetyltransferase. This strain produces higher levels of both isoamyl acetate and succinate.
Owner:RICE UNIV
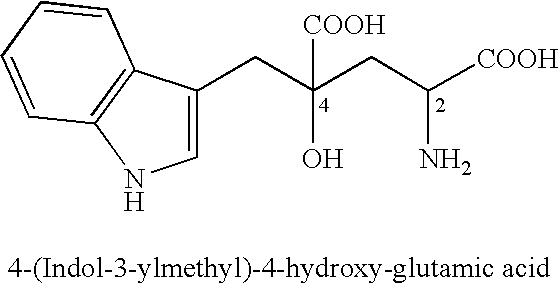
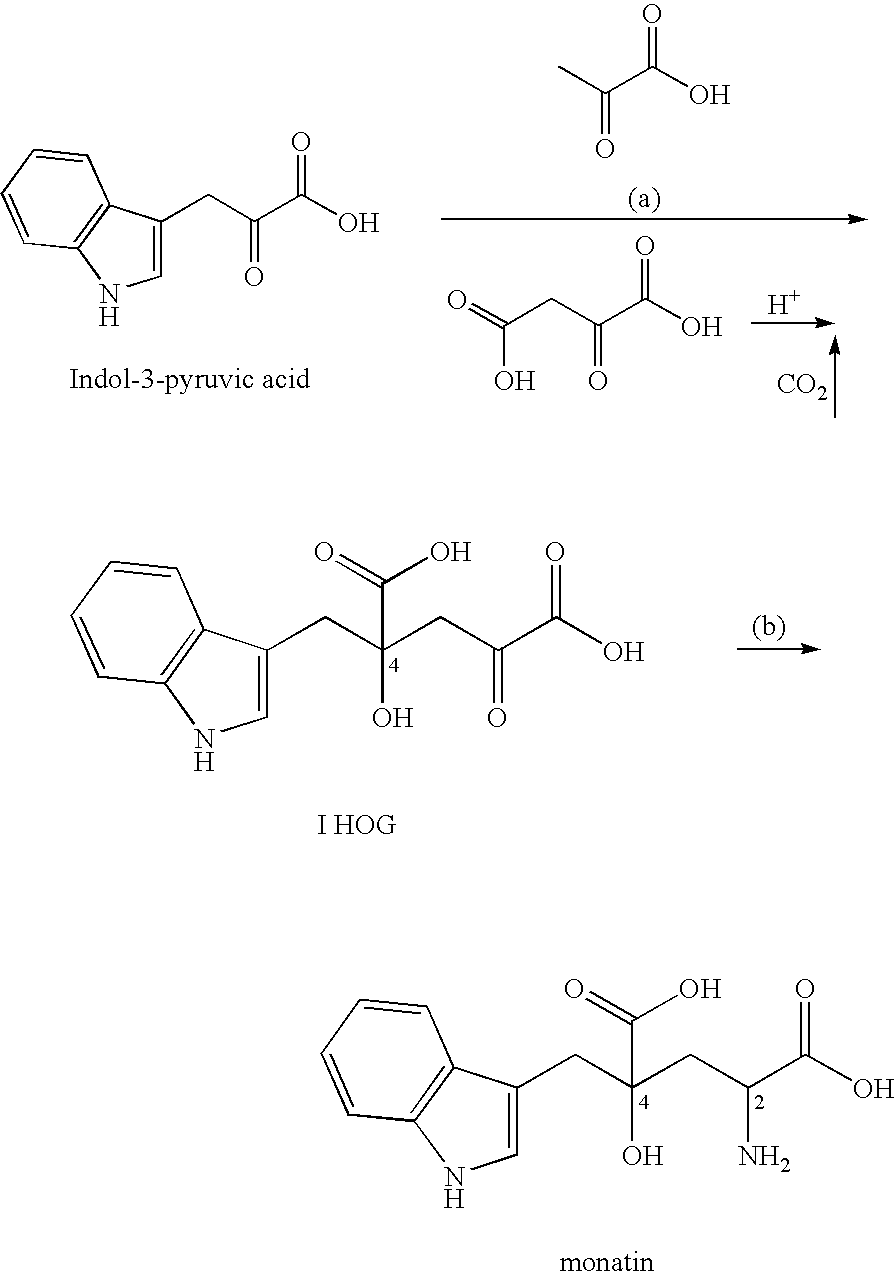
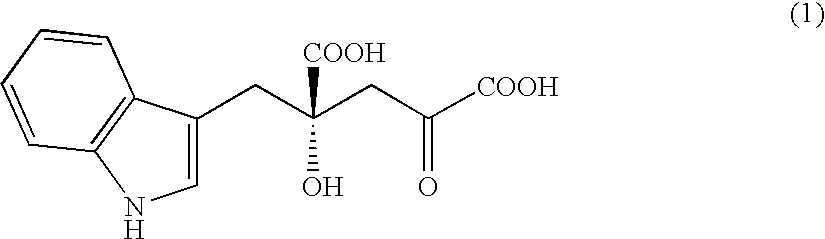
Novel aldolase, and method for producing optically active IHOG and monatin
The present invention relates to a method for producing optically active IHOG, which can in turn be used for the production of monatin. The present invention further relates to a method for producing optically active monatin, and aldolase used for these methods. As such, the present invention enables the synthesis of 4-(Indole-3-ylmethyl)-4-hydroxy-2-oxoglutaric acid with high optical purity, which is useful as an intermediate in the synthesis of optically active monatin, from indole pyruvic acid and pyruvic acid (or oxaloacetic acid).
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
High-yield fumaric acid Rhizopus delemar engineering bacterium and application thereof
InactiveCN103013843AExcess accumulation promotesOveraccumulation RealizedFungiMicroorganism based processesPyruvate synthesisBacterial strain
The invention discloses a high-yield fumaric acid Rhizopus delemar engineering bacterium and application thereof, and belongs to the field of genetic engineering. An encoded gene ScPYC1 of pyruvate carboxylase, which originates from saccharomyces cerevisiae, is overexpressed in a bacterial strain Rhizopus delemar NRRL1526 for producing the fumaric acid through a fermentation method, so that a recombinant bacterial strain R. delemar-pRS303H-PC, of which the activity of the pyruvate carboxylase is improved, is obtained, and the activity of the pyruvate carboxylase of the recombinant bacterial strain R. delemar-pRS303H-PC is improved by 5.4 times (reaches 4.59 U / mg protein); and glucose serves as the only carbon source, the output of the fumaric acid reaches 55.92 g / L and is 1.19 times of that of an original strain after the glucose is fermented for 72h, and the high-yield fumaric acid Rhizopus delemar engineering bacterium has a broad application prospect.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Methods for improving malic acid production in filamentous fungi
InactiveUS20110053233A1Reduce mitochondrial importImprove the level ofFungiPeptidesHeterologousNucleotide
The present invention relates to methods of producing a C4 dicarboxylic acid, comprising: (a) cultivating a filamentous fungal host cell comprising a polynucleotide selected from the group consisting of a heterologous first polynucleotide encoding a C4 dicarboxylic acid transporter, a heterologous second polynucleotide encoding a malate dehydrogenase, and a heterologous third polynucleotide encoding a pyruvate carboxylase; wherein the filamentous fungal host cell is capable of secreting increased levels of the C4 dicarboxylic acid compared to the filamentous fungal host cell without the heterologous polynucleotide when cultivated under the same conditions; and (b) recovering the C4 dicarboxylic acid. The present invention also relates to methods for increasing C4 dicarboxylic acid production, filamentous fungal host cells and malate dehydrogenase variants.
Owner:NOVOZYMES INC
Coryneform bacterium transformant and process for producing dicarboxylic acids using the same
ActiveUS7368268B2Improve productivityHigh expressionBacteriaSugar derivativesPyruvate synthesisGenetic engineering
The present invention provides an aerobic coryneform bacterium transformant in which a lactate dehydrogenase gene is disrupted, and a pyruvate carboxylase gene is recombined so as to be highly expressed by a genetic engineering method. The aerobic coryneform bacterium transformant of the present invention can produce dicarboxylic acids from saccharides at a high production rate.
Owner:RES INST OF INNOVATIVE TECH FOR THE EARTH
Corynebacterium glutamicum for producing high-yield succinic acid by utilizing straw hydrolysate, and construction and applicaitons
InactiveCN107012161AHigh final concentrationHigh yieldBacteriaMicroorganism based processesTransketolasePhosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase
The invention discloses a corynebacterium glutamicum for producing high-yield succinic acid by utilizing straw hydrolysate, and a construction and applications. The method comprises the following steps: (1) knocking out side products acetic acid and lactic acid formation pathway related genes from corynebacterium glutamicum ATCC 13032, and introducing anaplerotic pathway phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase and pyruvate carboxylase and phosphopentose pathway transketoaldehydase and transketolase on a strong promoter overexpression chromosome; and introducing xylose transport gene on the chromosome; and (2) expressing pyruvate carboxylase, succinic acid export protein and citrate synthase as well as xylose isomerase and xylulokinase on the corynebacterium glutamicum obtained in the step (1). 98.6gL<-1> of succinic acid can be anaerobically produced after 22.5h by utilizing mixed glucose and xylose in straw hydrolysate, with the yield of 0.98g succinic acid / g total sugar. The final concentration, yield and productivity of succinic acid achieve higher level, and the corynebacterium glutamicum has good industrial potential.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
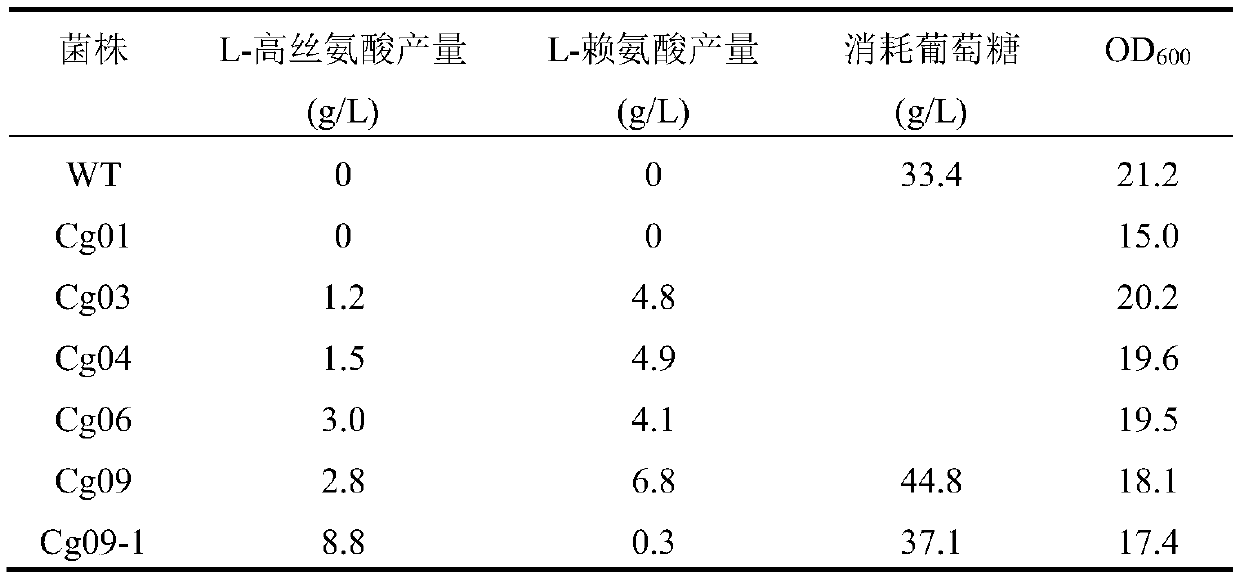
Construction and applications of corynebacterium glutamicum mutant strain for producing L-homoserine
The invention discloses construction and applications of a corynebacterium glutamicum mutant strain for producing L-homoserine, and belongs to the technical field of fermentation engineering. Corynebacterium glutamicum ATCC 13032 is taken as a starting strain to knock out regulatory protein McbR, homoserine kinase, transport protein MetD, phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase; the expression of isocitrate dehydrogenase is down regulated; transport protein BrnFE, aspartic semialdehyde dehydrogenase and homoserine dehydrogenase are overexpressed; and the expression of aspartate kinase, pyruvate carboxylase and the aspartate kinase I derived from escherichia coli are enhanced. Shake flask culture can be performed on the mutant strain for 48 h, and the yield of L-homoserine can reach 8.8 g / L.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Genetically engineered bacterium for producing L-aspartic acid through fermentation
ActiveCN106434510AGet Rid of Reliance on Petroleum-Based Fumaric AcidCarbon-nitrogen lyasesBacteriaEscherichia coliDry weight
The invention discloses a genetically engineered bacterium for directly producing L-aspartic acid through fermentation. The classification naming of the genetically engineered bacterium is Escherichia coli CM-AS-115, and the preservation number of the genetically engineered bacterium is CCTCC NO: M 2016457. The bacterial strain relates to inactivation of multiple genes, evolution, metabolism and domestication are simultaneously carried out on the bacterial strain which knockouts the multiple genes, and a mutant strain, namely, CM-AS-105, which has a lower respiratory quotient under the aerobic condition and of which the highest dry cell weight is 60-70% of dry weight of an original strain W1485 is obtained; meanwhile, the bacterial strain further relates to over expressions of two genes, wherein the two genes comprise an enol phosphate type pyruvate carboxylase encoding gene (ppc) and an aspartase encoding gene (aspA), and the obtained bacterial strain is CM-AS-115. The genetically engineered bacterium for directly producing L-aspartic acid through fermentation achieves a way of completely adopting renewable biomass resources such as starch and cellulose as raw materials to ferment and prepare the L-aspartic acid, and the way is green and environmentally friendly.
Owner:CHANGMAO BIOCHEMICAL ENG CO LTD
Enzymatic systems for carbon fixation and methods of generating same
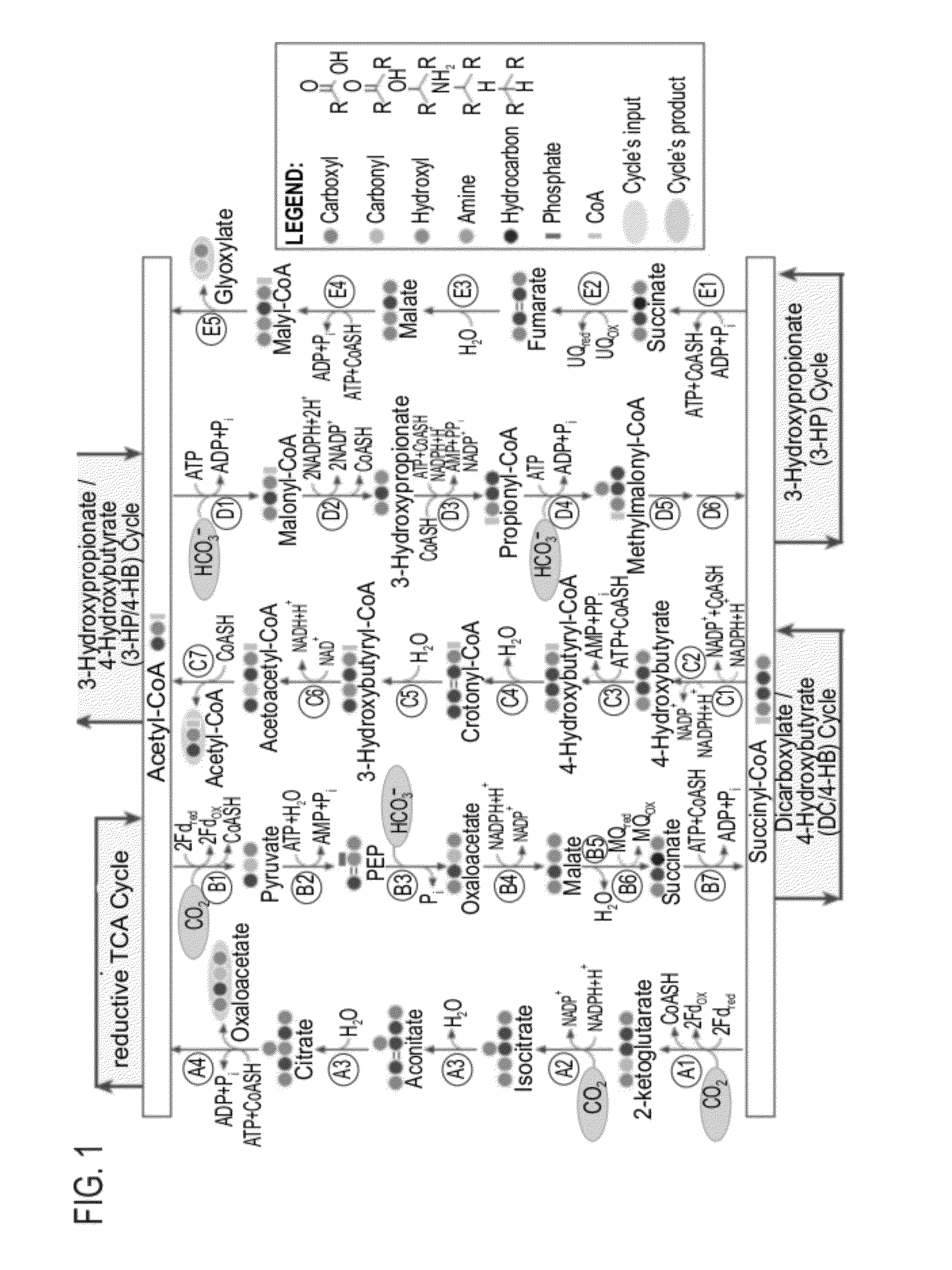
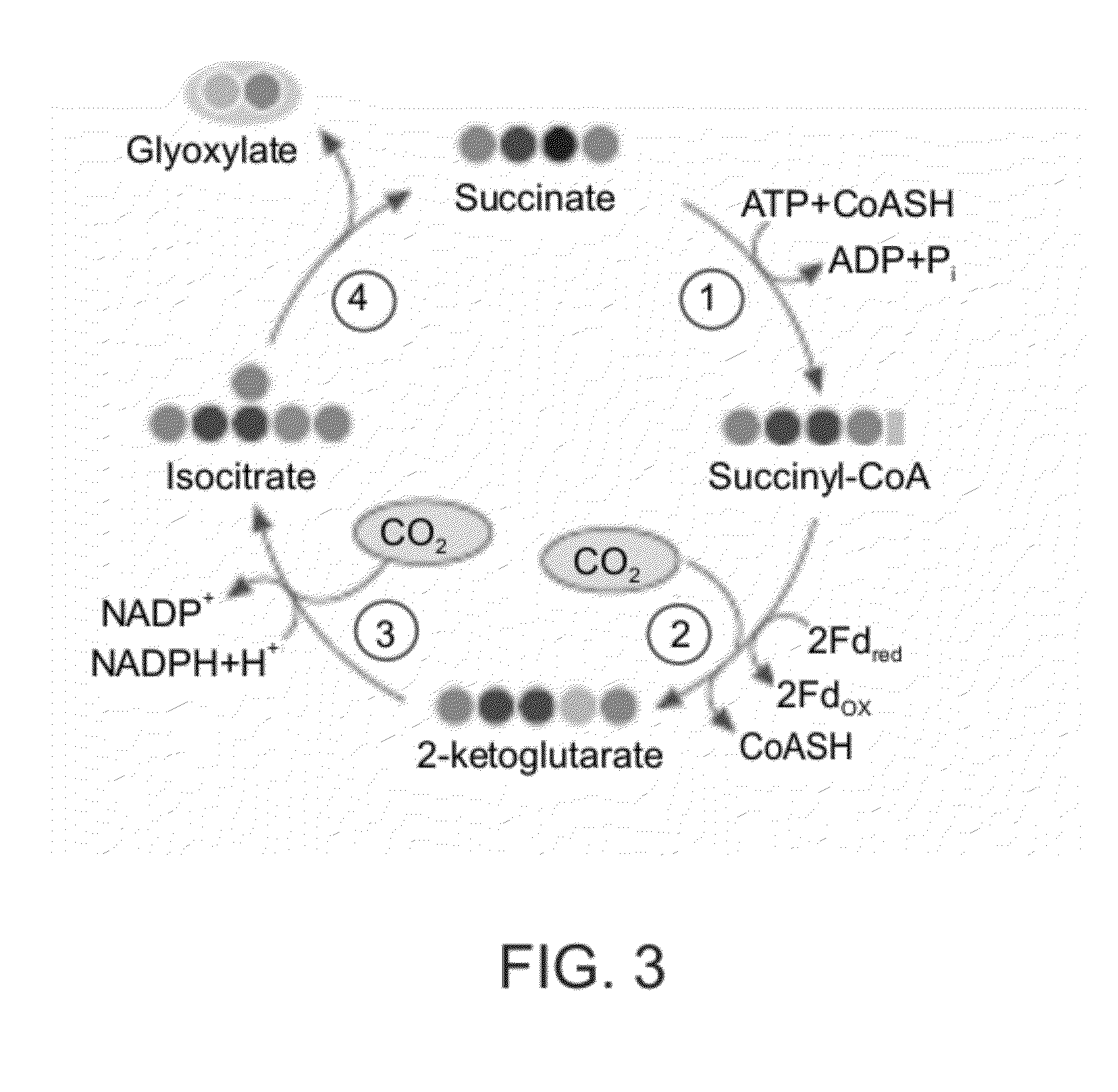
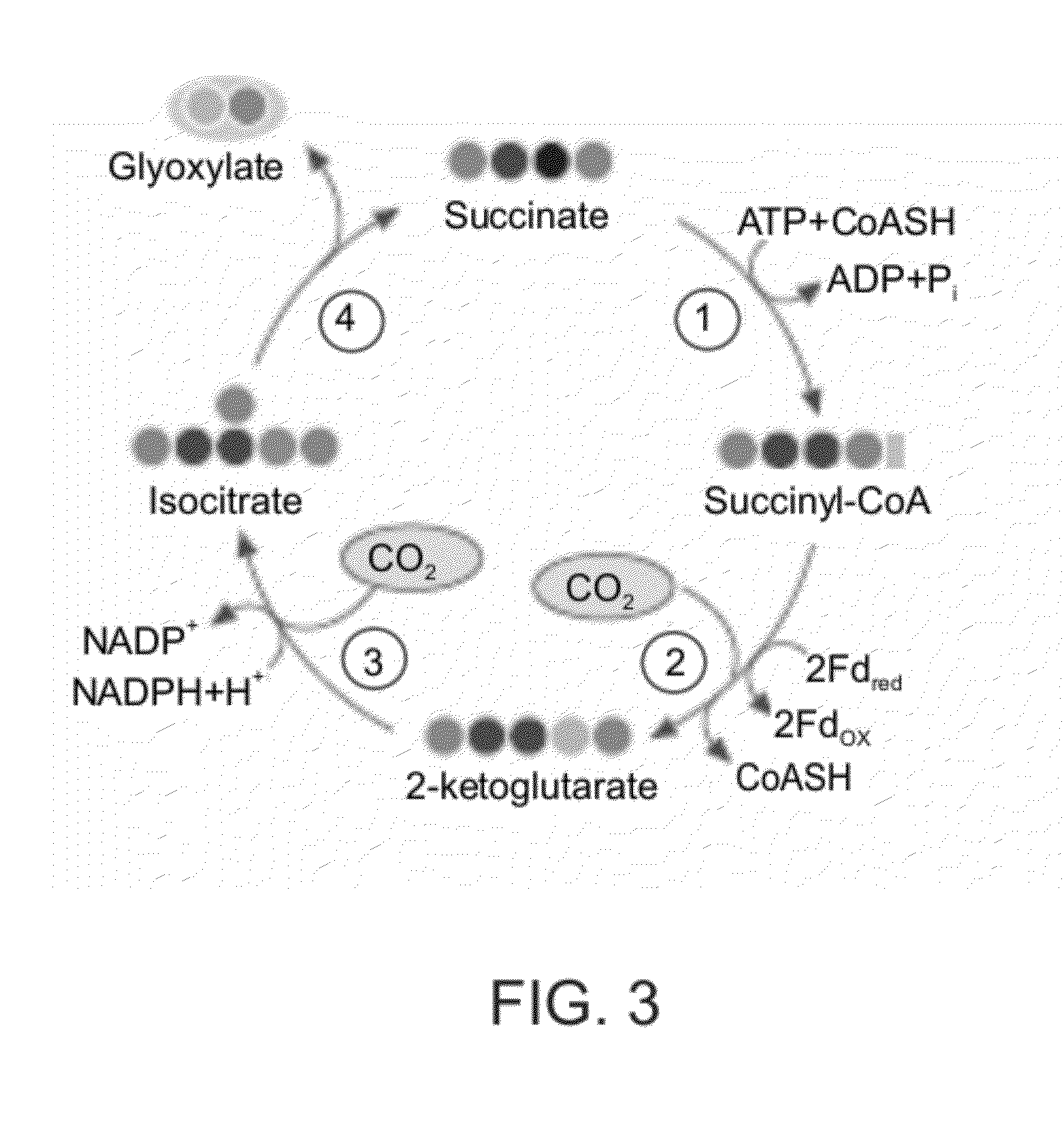
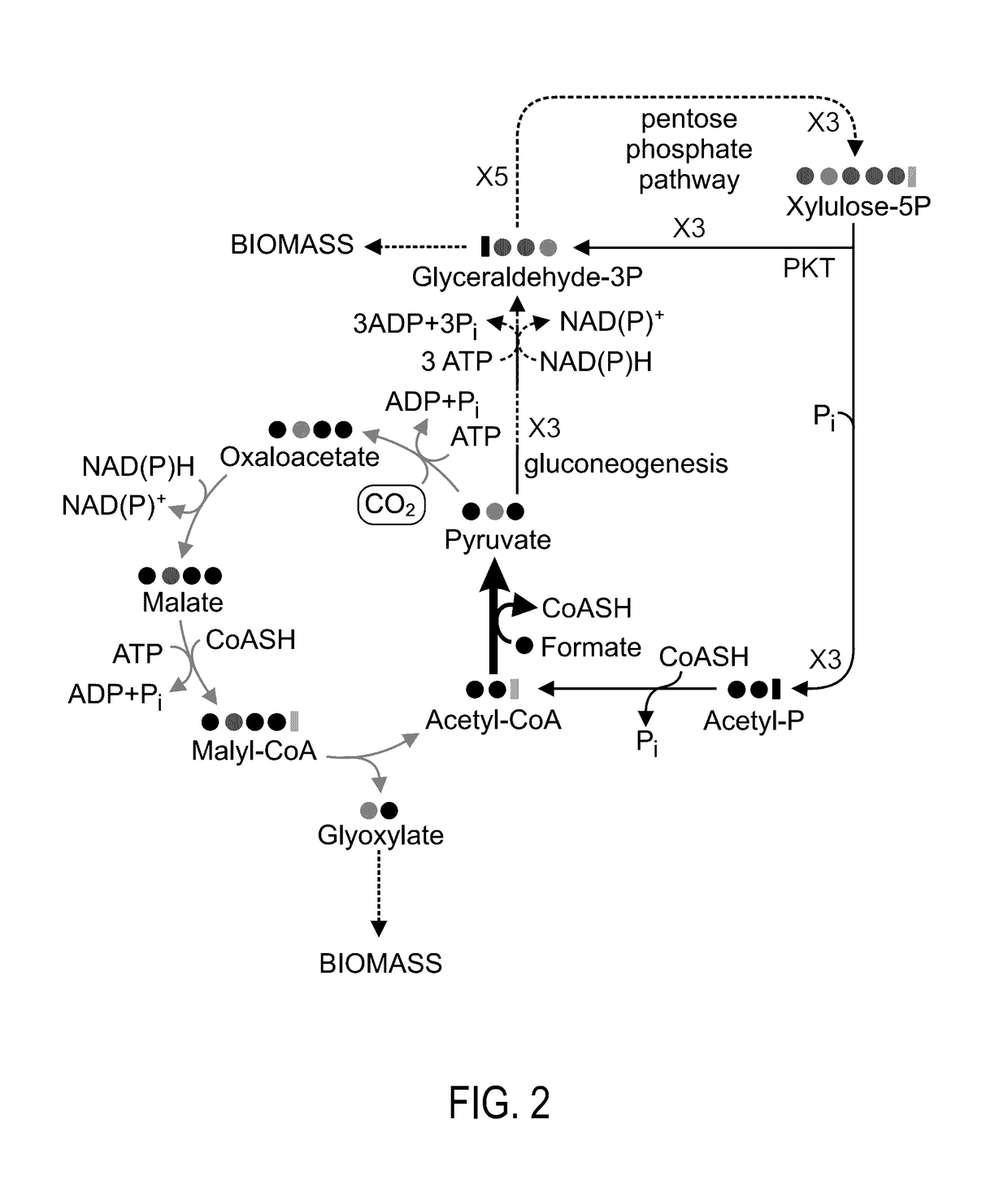
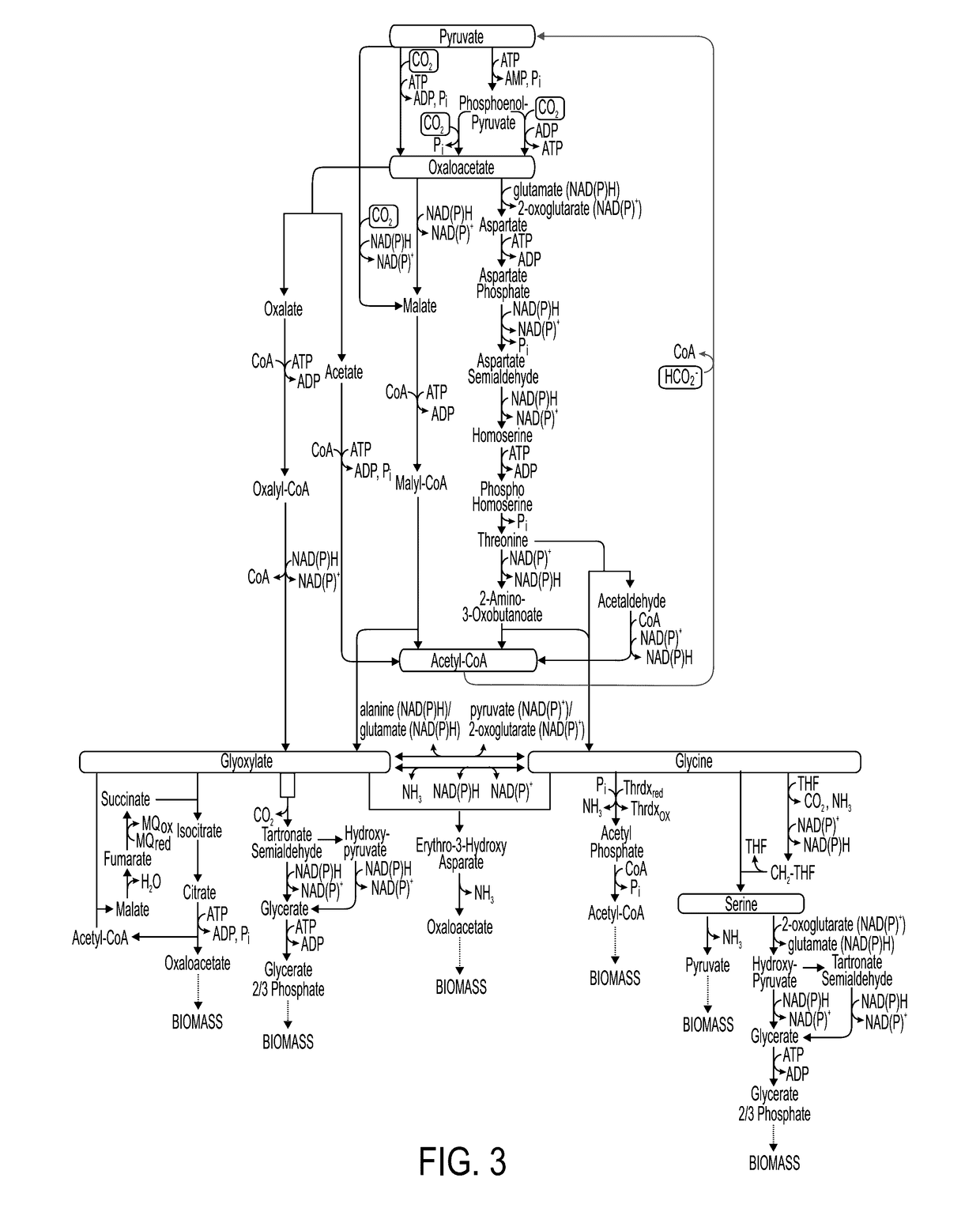
A system for carbon fixation is provided. The system comprises enzymes which catalyze reactions of a carbon fixation pathway, wherein at least one of the reactions of the carbon fixation pathway is a carboxylation reaction, wherein products of the reactions of the carbon fixation pathway comprise oxaloacetate and malonyl-CoA, wherein an enzyme which performs the carboxylation reaction is selected from the group consisting of phophoenolpyruvate (PEP) carboxlase, pyruvate carboxylase and acetyl-CoA carboxylase and wherein an export product of the carbon fixation pathway is glyoxylate. Additional carbon fixation pathways are also provided and methods of generating same.
Owner:YEDA RES & DEV CO LTD
Corynebacterium glutamicum engineering bacterium for highly producing succinic acid and building method thereof
InactiveCN103509747AIncrease productionReduce generationBacteriaMicroorganism based processesSaccharic acidPhosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase
The invention discloses a corynebacterium glutamicum engineering bacterium for anaerobic conversion to produce succinic acid, and a building method and application thereof, and belongs to the field of genetic engineering. A pyruvate carboxylase gene of the corynebacterium glutamicum and phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase from escherichia coli are cloned to corynebacterium glutamicum (ATCC13032); a lactate dehydrogenase gene of the corynebacterium glutamicum is knocked out in a homologous recombination manner. By adopting the lactic dehydrogenase-defective corynebacterium glutamicum for coexpression of a carboxylase gene, anaerobic production of succinic acid is carried out in a cell reutilization manner, so that the yield of succinic acid can be greatly improved; the yield can be up to 75g / L; the conversion rate of saccharic acid is 75%; the corynebacterium glutamicum engineering bacterium has a good application prospect; a fermentation model, especially a fermentation model for cell reutilization is built according to the optimum condition for biological transformation of succinic acid; the acid-production performance in repeated batch transformation process of cells can be basically kept stable.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
A genetically engineered bacterium for the production of l-theanine and its construction and application
ActiveCN109777763BIncrease enzyme activityGene expression is stableBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliEnzyme Gene
The invention belongs to the technical field of genetic engineering, and particularly relates to novel high-efficiency gamma-glutamyl methylamine synthetase and a plasmid-free genetic engineering bacterium for L-theanine production and construction and application thereof. The plasmid-free genetic engineering bacterium which performs denovo synthesis on L-theanine efficiently by taking cheap carbon sources such as glucose as a substrate is provided, escherichia coli serves as a host, and gamma-glutamyl methylamine synthase genes gmas-Mu copied three times are integrated on a genome of the escherichia coli; a glutamate dehydrogenase gene Cgl2079 is copied once; a pyruvate carboxylase gene Cgl0689 is copied once; a citrate synthase gene gltA is copied once, and the genetic engineering bacterium is obtained. After metabolic transformation of a system, the engineering bacterium can perform denovo synthesis on the L-theanine by taking the glucose as the raw material, the fermentation yieldand sugar-acid conversion rate are the highest values reported so far, in fermentation of a 5 L fermentor, the maximum production of the L-theanine can reach 60 g / L, and the sugar-acid conversion ratecan reach 40%.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Gene engineering bacterial strain generating succinic acid and method of producing succinic acid by fermentation of the gene engineering bacterial strain
The invention belongs to the technical field of biological engineering, relates to a gene engineering bacterial strain generating succinic acid and a method of producing succinic acid by fermentation of the gene engineering bacterial strain, particularly to a gene engineering bacterial strain generating succinic acid, namely Escherichia coli BA103, by high-efficiency use of glucose, a construction method of Escherichia coli BA103 and a method of producing succinic acid by Escherichia coli BA103. By expression of an exogenous pyruvate carboxylase, recombinant Escherichia coli can grow by use of glucose metabolism, so that the yield of succinic acid is greatly increased, the generation intensity is greatly improved, and the generation of pyruvic acid as a by-product is reduced.
Owner:NANJING TECH UNIV
Dibasic organic acid producing strain and preparation and application of same
ActiveUS20180171369A1Raise the level of fermentationReduce fermentation costsMicroorganismsTransferasesGlutaric acidRhizopus
Provided are an engineered strain for synthesizing a dibasic organic acid and preparation and application of same. The engineered strain introduces or up-regulates expression of a positive regulator gene for synthesis of a dibasic organic acid, and / or down-regulates expression of a negative regulator gene for synthesis of a dibasic organic acid, as compared with the origin strain of the engineered strain, the producing capability for producing the dibasic organic acid is improved. The dibasic organic acid comprises malic acid, succinic acid, fumaric acid, oxaloacetic acid, glutaric acid, and adipic acid; the expression product of the positive regulator gene comprises aspartate aminotransferase, glutamic acid-aspartate transporter, C4-dicarboxylic acid transporter, pyruvate carboxylase and malate dehydrogenase, glucose transporter; the expression product of the negative regulatory gene comprises succinyl-CoA synthase, and malic acid-alpha ketoglutarate transporter, and the original strain comprises myceliophthora thermophila, thielavia terrestris, aspergillus, and rhizopus.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Compositions and methods for the production of pyruvic acid and related products using dynamic metabolic control
ActiveUS20190390232A1Increase chanceImproved pyruvate productionOxidoreductasesAcyltransferasesBiotechnologyMicroorganism
The present disclosure is related to genetically engineered microbial strains and related bioprocesses for the production of pyruvate and related products. Specifically, the use of dynamically controlled synthetic metabolic valves to reduce the activity of enzymes known to contribute to pyruvate synthesis, leads to increased pyruvate production in a two-stage process rather than a decrease in production.
Owner:DUKE UNIV
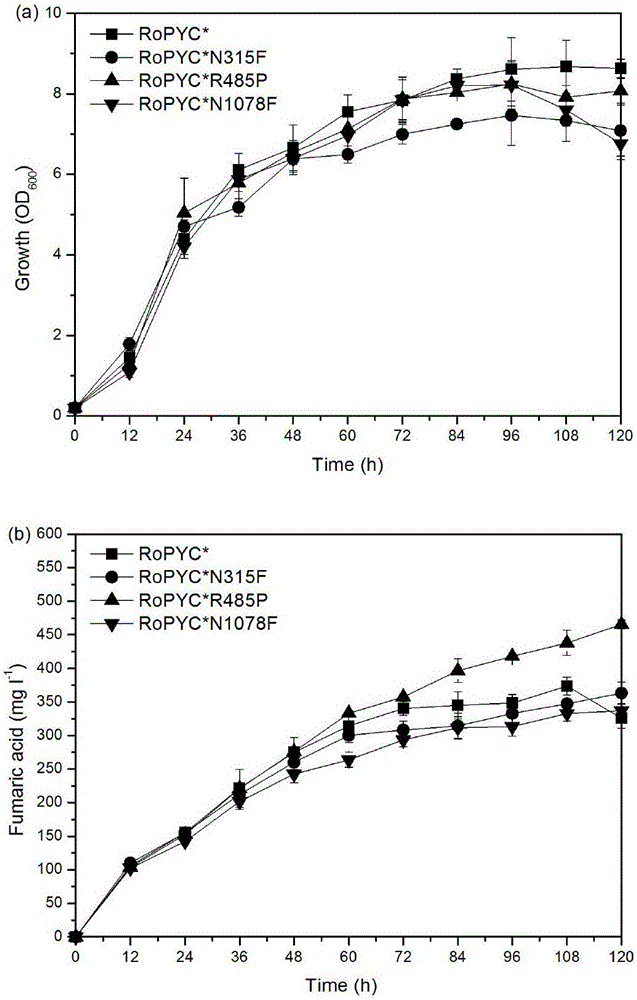
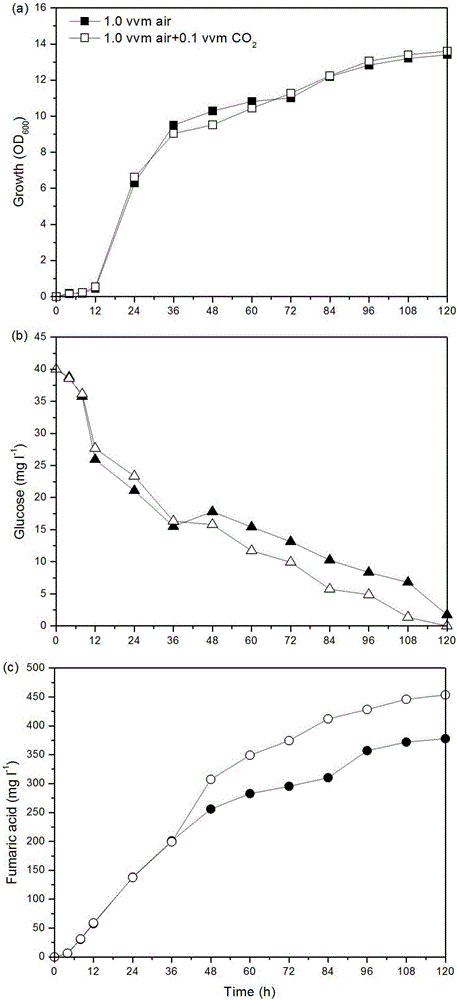
Method for improving yield of fumaric acid
The invention discloses a method for improving the yield of fumaric acid and belongs to the fields of genetic engineering and fermentation engineering. The method comprises the following steps: performing codon optimization on a pyruvate carboxylase gene RoPYC of rhizopus oryzae to obtain a gene RoPYC* and then mutating a R485 site of the gene RoPYC* into proline. In comparison with the yield after the expression of a wild type pyruvate carboxylase before codon optimization, the yield is improved by 24.6 percent; 10 percent of carbon dioxide is additionally introduced when genetically-engineered bacteria of an expression mutant is fermented for 36 hours in a fermentation tank of 7L, so that the yield of the fumaric acid reaches 453.6 mg / Lm and is improved by 20 percent through comparison. According to the method disclosed by the invention, a synthetic route through which a carbon metabolic flow enters the fumaric acid from pyruvic acid is effectively enhanced, so that conditions are created for the construction of engineering yeasts to efficiently produce the fumaric acid and other dicarboxylic acid, therefore, the industrial application value and the prospect are good.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Enzymatic systems for carbon fixation and methods of generating same
ActiveUS20120301947A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsPyruvate synthesisAcetaldehyde
A system for carbon fixation is provided. The system comprises enzymes which catalyze reactions of a carbon fixation pathway, wherein at least one of the reactions of the carbon fixation pathway is a carboxylation reaction, wherein products of the reactions of the carbon fixation pathway comprise oxaloacetate and malonyl-CoA, wherein an enzyme which performs the carboxylation reaction is selected from the group consisting of phophoenolpyruvate (PEP) carboxlase, pyruvate carboxylase and acetyl-CoA carboxylase and wherein an export product of the carbon fixation pathway is glyoxylate. Additional carbon fixation pathways are also provided and methods of generating same.
Owner:YEDA RES & DEV CO LTD
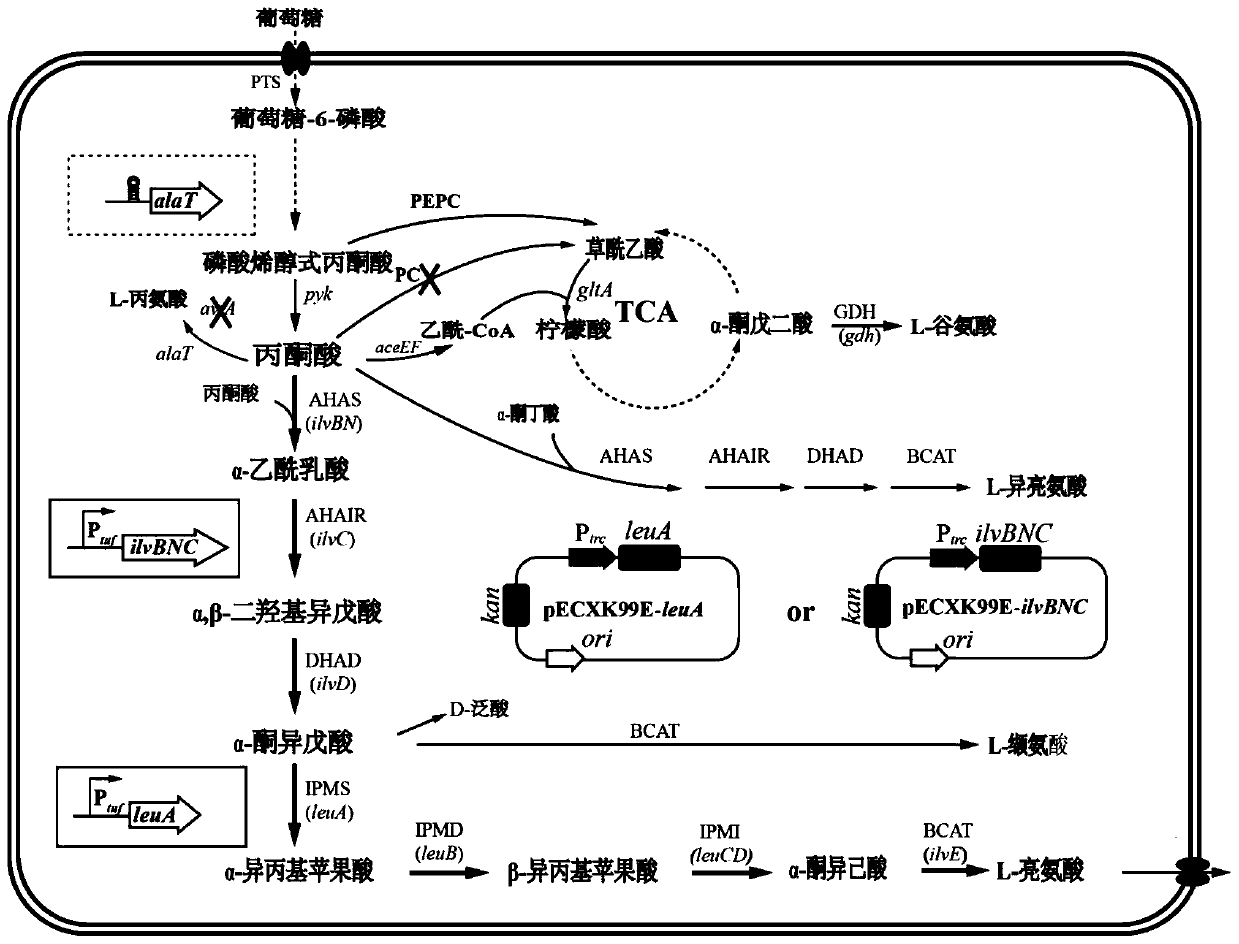
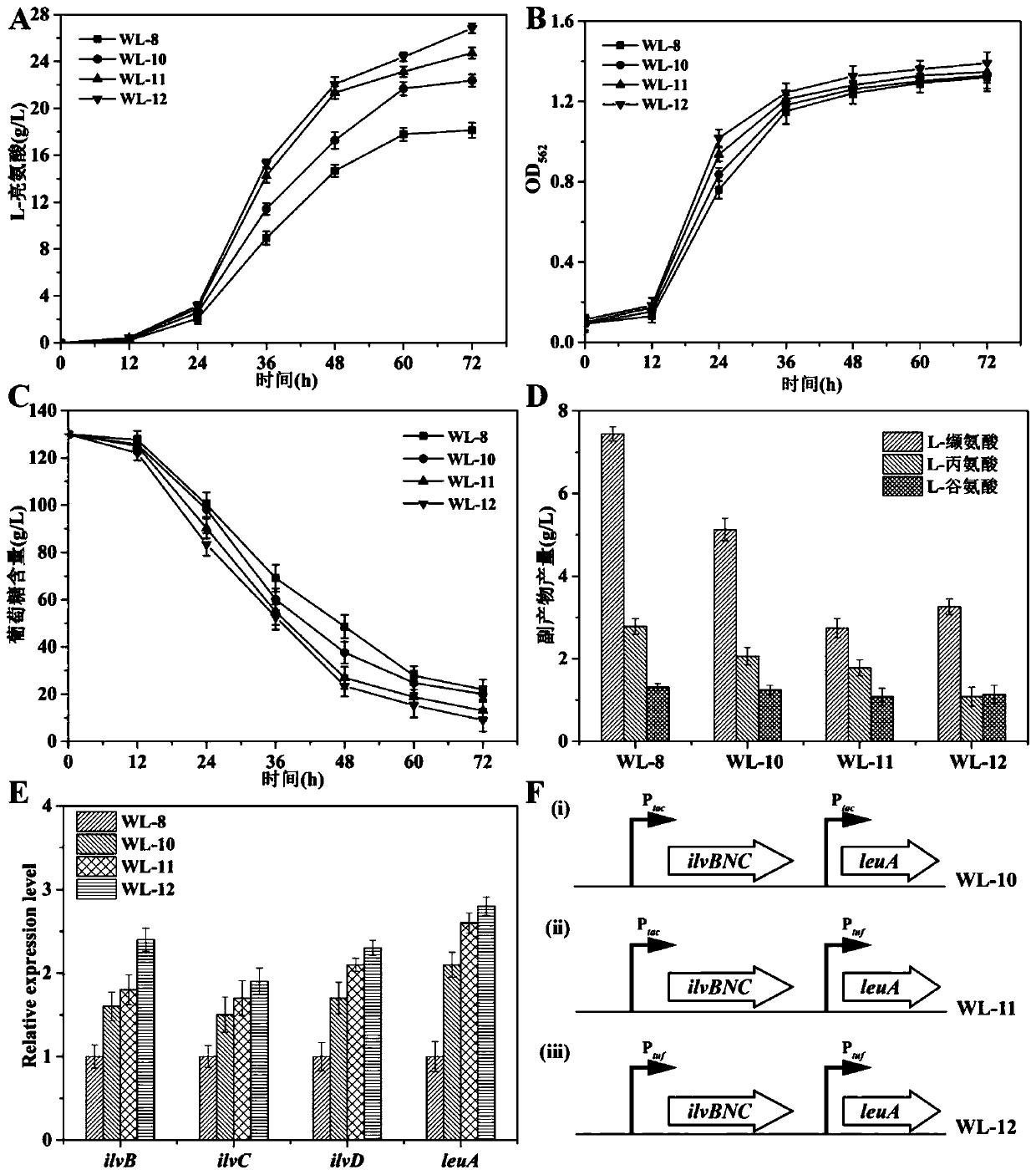
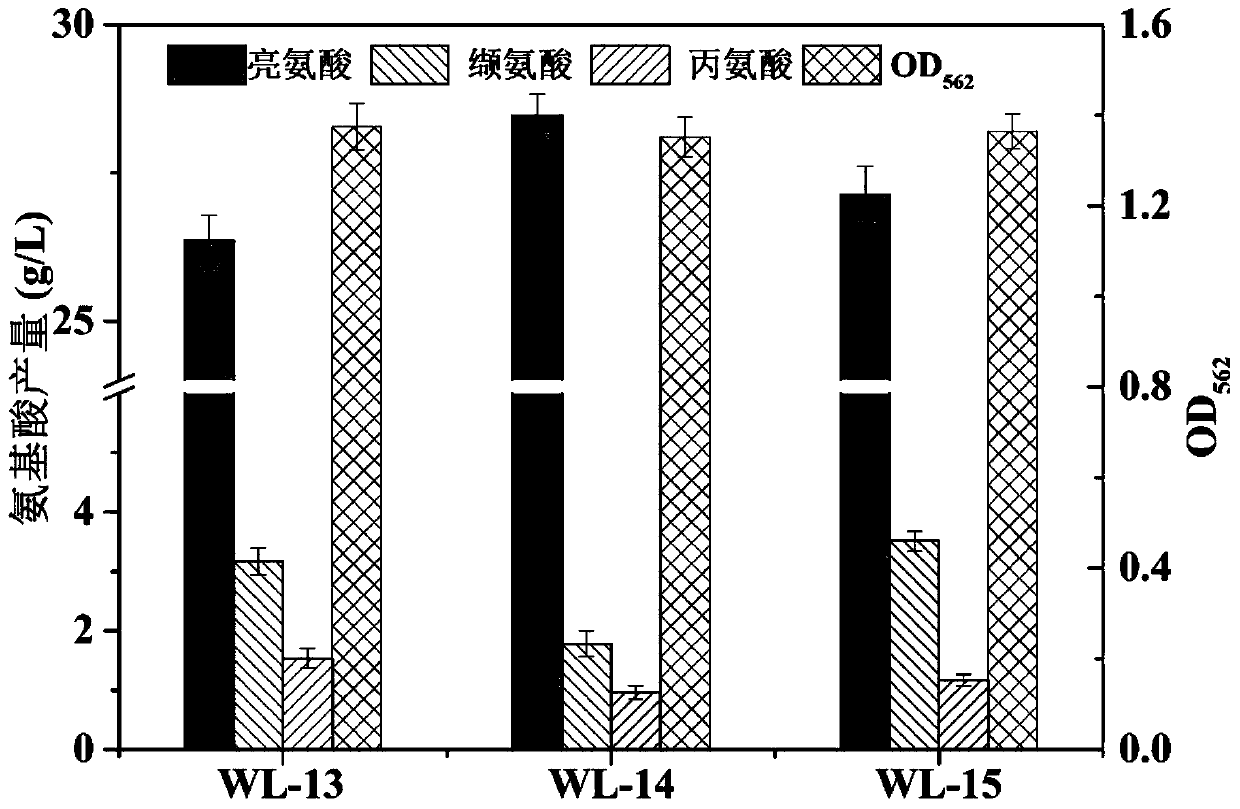
Recombinant corynebacterium glutamicum strengthening capability of synthesizing L-leucine from pyruvic acid and application of recombinant corynebacterium glutamicum
ActiveCN110982768AHigh yieldImprove conversion rateBacteriaStable introduction of DNAEnzyme GeneOperon
The invention relates to a method for strengthening capability of synthesizing L-leucine from pyruvic acid in corynebacterium glutamicum, and belongs to the field of genetic engineering. According tothe invention, a gene engineering method is applied, and in order to regulate and control an L-leucine anabolic flux, sequence sites of an ilvBNC operon and an leuA gene promoter are replaced by a Ptuf promoter; and meanwhile, the key enzyme gene isopropyl malate synthetase IPMS is overexpressed to further strengthen the anabolic flux of synthesizing leucine from pyruvic acid. An efficient L-leucine synthesis pathway is constructed, and the synthesis flux of L-valine in L-leucine producing bacteria of corynebacterium glutamicum is weakened. A recombinant strain WL-14 produces 28.47+ / -0.36 g / Lof leucine, which is 56.8% higher than leucine yield of an original strain WL-8; and the valine accumulation amount in the strain WL-14 is reduced to 1.78+ / -0.21 g / L.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
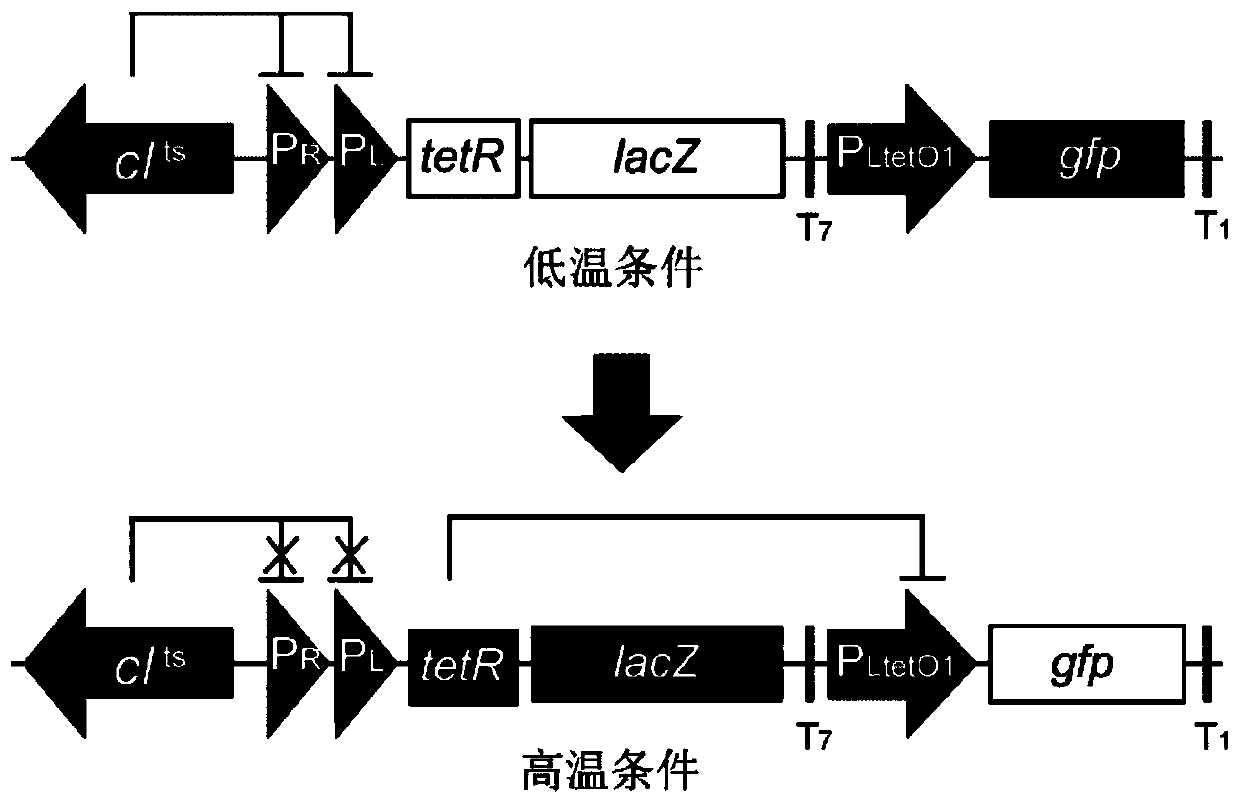
Temperature switch system and application thereof to increment of yield of amino acids
ActiveCN111363757AIncrease production capacityIncrease productionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesHeterologousThreonine
The invention relates to a temperature switch system and an application thereof to increment of yield of amino acids, in particular to a method for adjusting and controlling intracellular metabolism flow distribution to increment yield of threonine by using the temperature switch system, and belongs to the technical field of genetic engineering and microbial fermentation. The temperature switch system is used, so that the entire fermentation course is divided into two stages of cell growth and fermentation and production to be adaptive to intracellular environmental changes of different stagesin a fermentation process of an engineering bacterial strain. According to the system, the heterologous expression of pyruvate carboxylase is controlled, and through combination of a chemical property that oxaloacetic acid is thermo-sensitive and easy for decarboxylation, metabolism flows are rebalanced between pyruvate and oxaloacetic acid, a central metabolic pathway is dynamically regulated, and supply of reduced cofactors is guaranteed to promote production of L-threonine. The threonine mol conversion rate of obtained temperature control threonine production bacterial strains namely TWF106 / pFT24rp is 111.78% and the threonine mol conversion rate of obtained temperature control threonine production bacterial strains namely TW113 / pFT24rpal is 124.03%.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
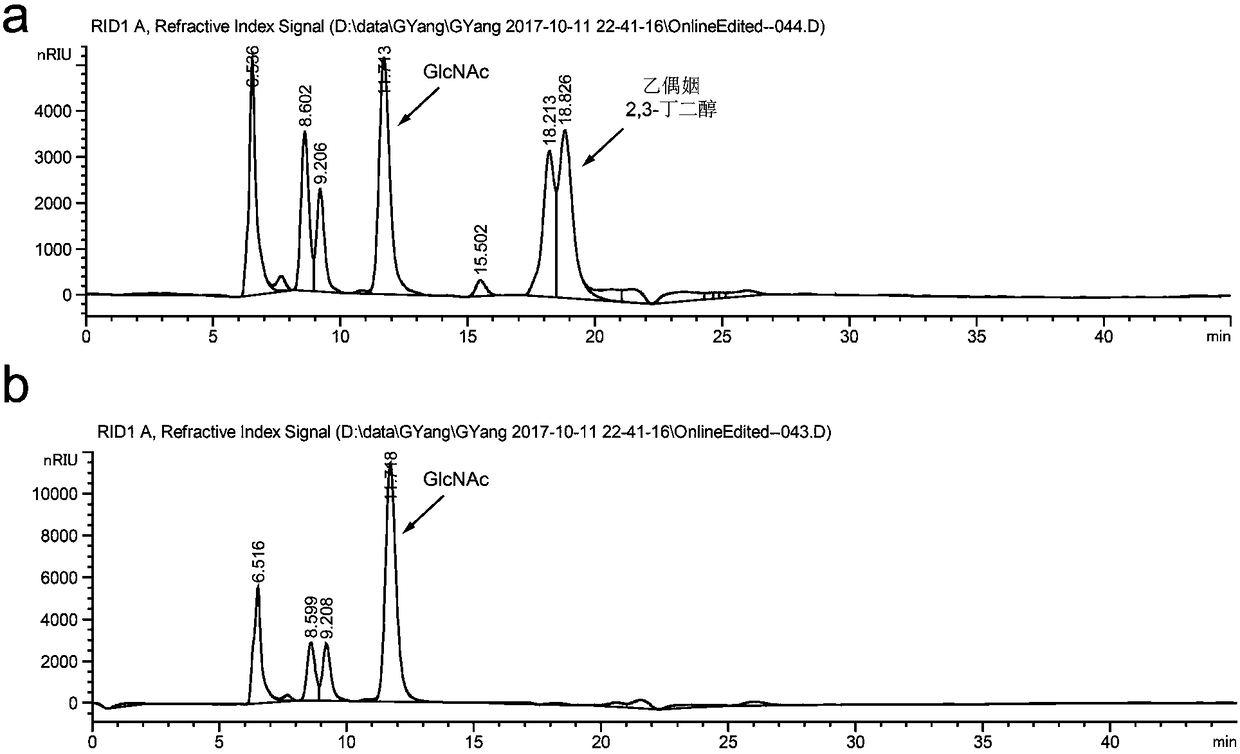
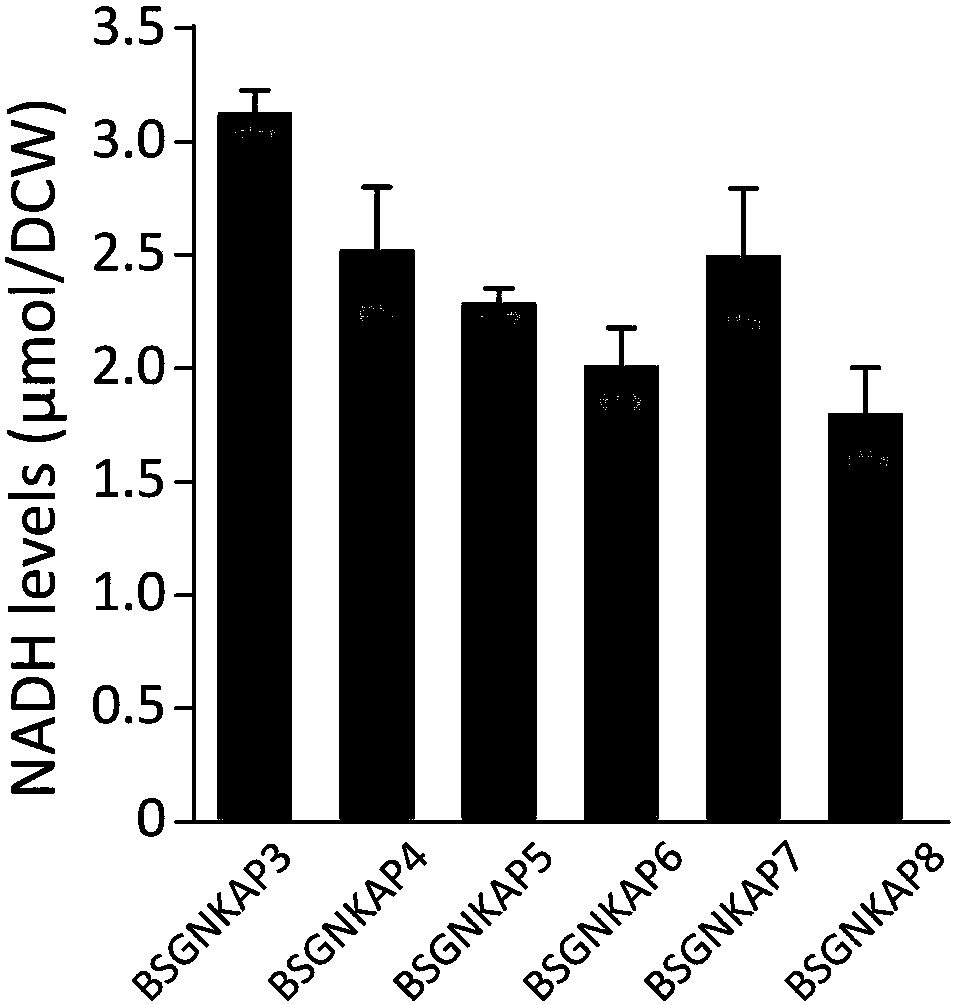
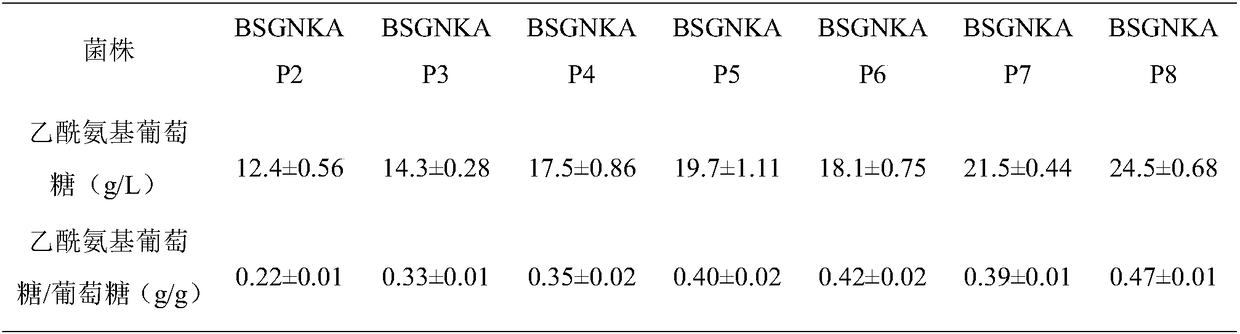
Method for promoting synthesis of bacillus subtilis acetylglucosamine
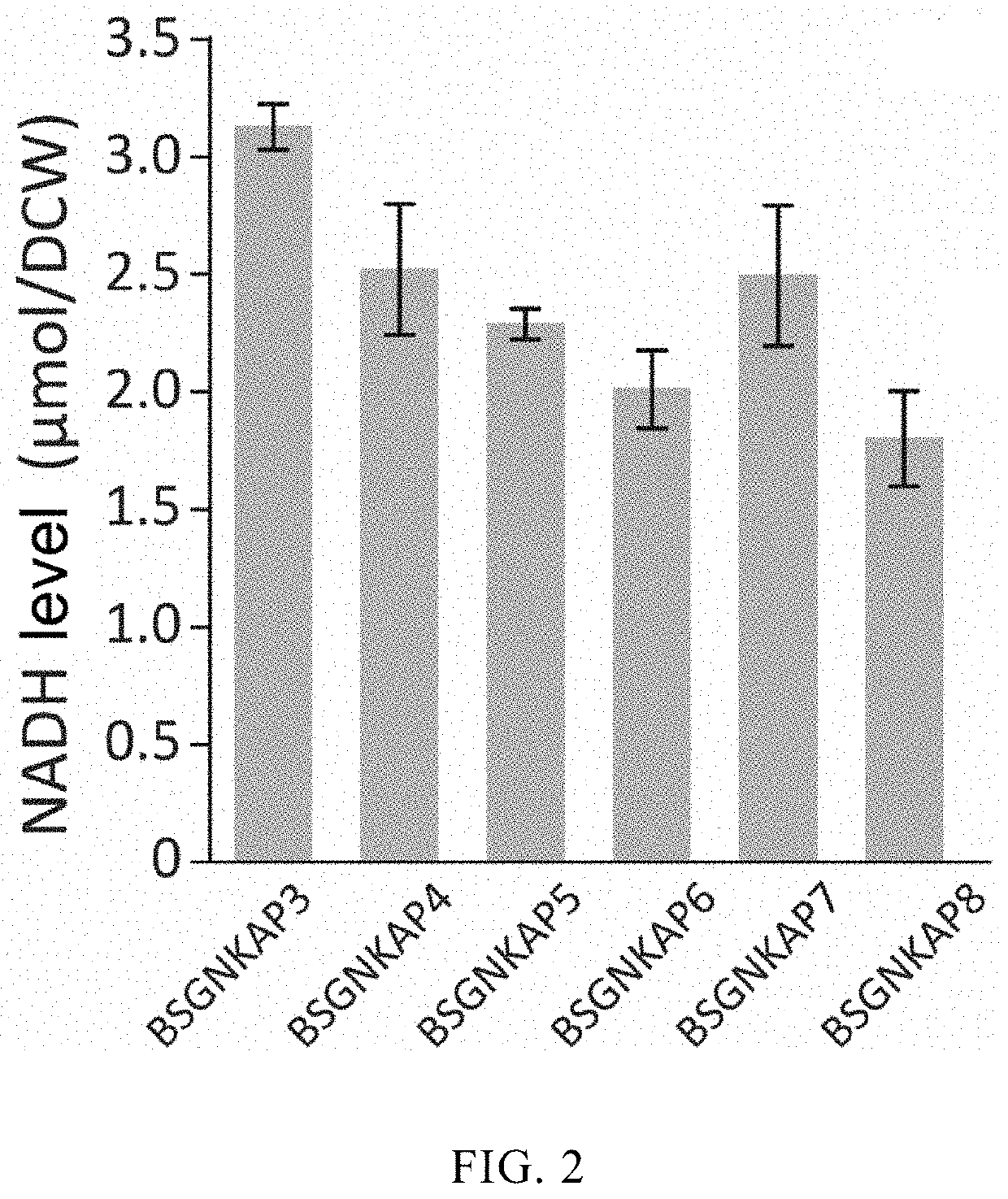
ActiveCN108424869AEasy to synthesizeInhibit synthesisBacteriaMicroorganism based processesQuinonePhosphate
The invention discloses a method for promoting synthesis of bacillus subtilis acetylglucosamine and belongs to the field of genetic engineering. The method is characterized in that a recombinant bacillus subtilis BSGNKAP2 is taken as a starting strain, and pyruvate carboxylase BalpycA from bacillus cereus is exogenously introduced, so that metabolism overflow of bacillus subtilis central carbon iseliminated and synthesis of acetoin as a byproduct is avoided; furthermore, five exogenous reductive metabolism reactions are introduced to replace a glycolytic pathway and a reaction of producing NADH in tricarboxylic acid cycle and reconstruct intracellular reductive metabolism, wherein the five exogenous reductive metabolism reactions specifically comprise glyceraldehydes-3-ferredoxin phosphate dehydrogenas, isocitric acid NAD<+> dehydrogenas, malic acid quinone dehydrogenas, ketonic acid ferredoxin oxidordeuctase and nitrogenase ferritin. In the shake-flask fermentation process of using acomplex medium, the yield of a recombinant strain BSGNKAP8 acetylglucosamine is 24.50g / L, and the yield of acetylglucosamine / glucose is 0.469g / L, which are 1.97 times and 2.13 times that of the starting strain BSGNKAP2.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Glycine Determination Method and Glycine Determination Kit
InactiveCN102298040AMicrobiological testing/measurementColor/spectral properties measurementsGlycinePyruvate synthase
The present invention relates to the measuring method of the content of glycine, the composition and the component of the reagent using enzyme cycle amplification method, enzyme colorimetric method and enzyme-linked method technology, the technical principle of its measuring is based on hydrogen cyanide synthase, pyruvate synthase, The series of catalyzed reactions of the malonate semialdehyde dehydrogenase is completed, and the invention also relates to a glycine determination kit. The determination method of the invention has high sensitivity and small error, so the determination method and the kit of the invention can be widely used in food inspection.
Owner:SUZHOU ANJ BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
Ammonia (ammonia ion) measuring method and ammonia (ammonia ion) diagnosing/measuring kit
InactiveCN102565367AMicrobiological testing/measurementColor/spectral properties measurementsPyruvate carboxylaseLactate dehydrogenase
The invention relates to a method for measuring ammonia (ammonia ion) content through an enzymatic colorimetric method and an enzyme coupling reaction technique, and the composition and the constituents of a reagent. The measuring technical principle of the method is fulfilled through the serial catalytic reactions of ammonia kinase, pyruvate carboxylase, and lactate dehydrogenase. The invention further relates to an ammonia (ammonia ion) diagnosing / measuring kit. The method provided by the invention has the advantages of high sensitivity and small error, so that the method and the kit provided by the invention can be widely applied to clinical medicine / food inspections.
Owner:SUZHOU ANJ BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
Recombinant strain of bacillus subtilis
ActiveUS20200032237A1Promoting acetylglucosamine synthesisEasy to useOxidoreductasesLigasesQuinoneCarbon metabolism
The invention relates to a recombinant strain of Bacillus subtilis, wherein pyruvate carboxylase BalpycA, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate ferredoxin dehydrogenase gor, isocitrate NAD+ dehydrogenase icd, malate quinone dehydrogenase mqo, pyruvate ferredoxin oxidoreductase porAB and nitrogenase ferritin cyh are integrated and expressed in the recombinant strain. The invention also discloses use of the recombinant strain in fermentation production of acetylglucosamine. The recombinant Bacillus subtilis of the invention eliminates the central carbon metabolism overflow of the Bacillus subtilis and balances the intracellular reducing force, and the fermentation yield of acetylglucosamine is greatly improved.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
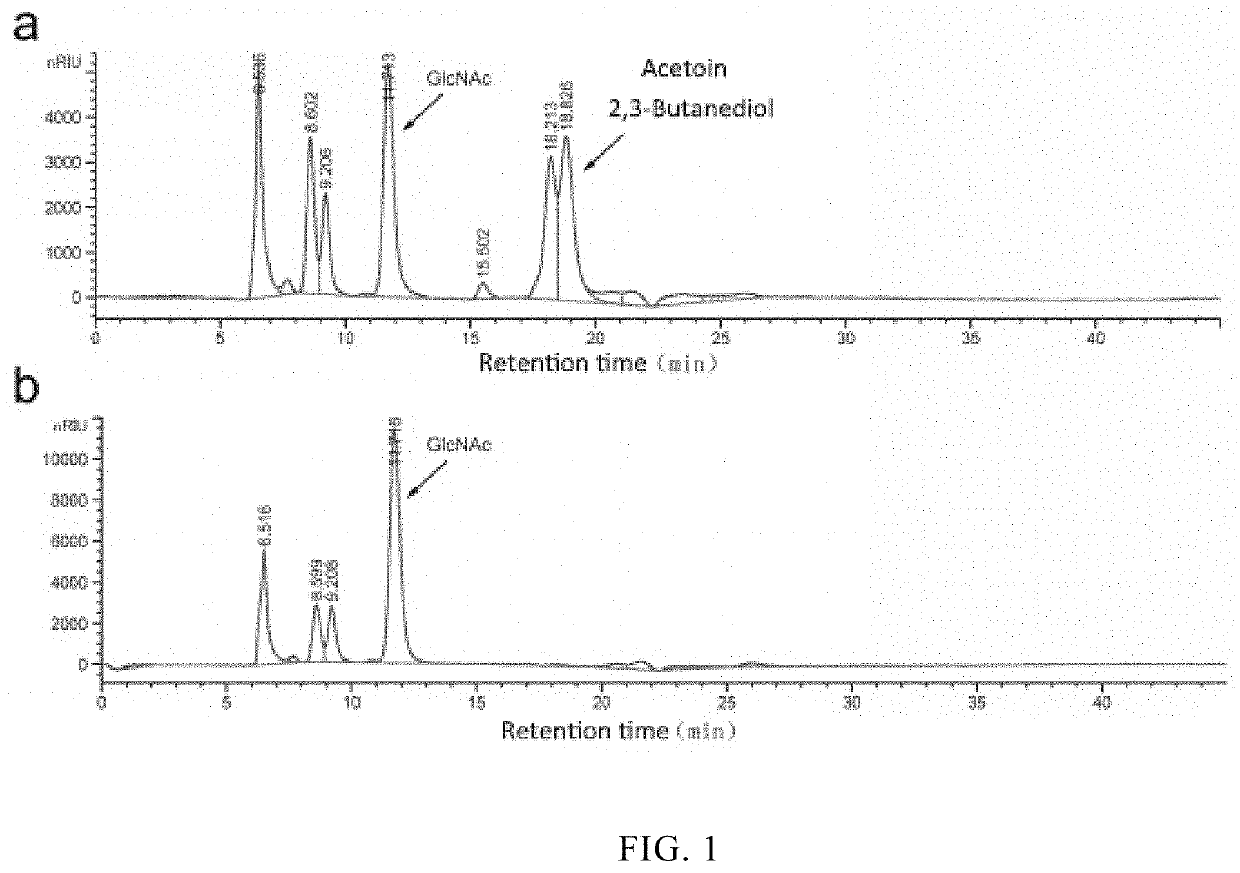
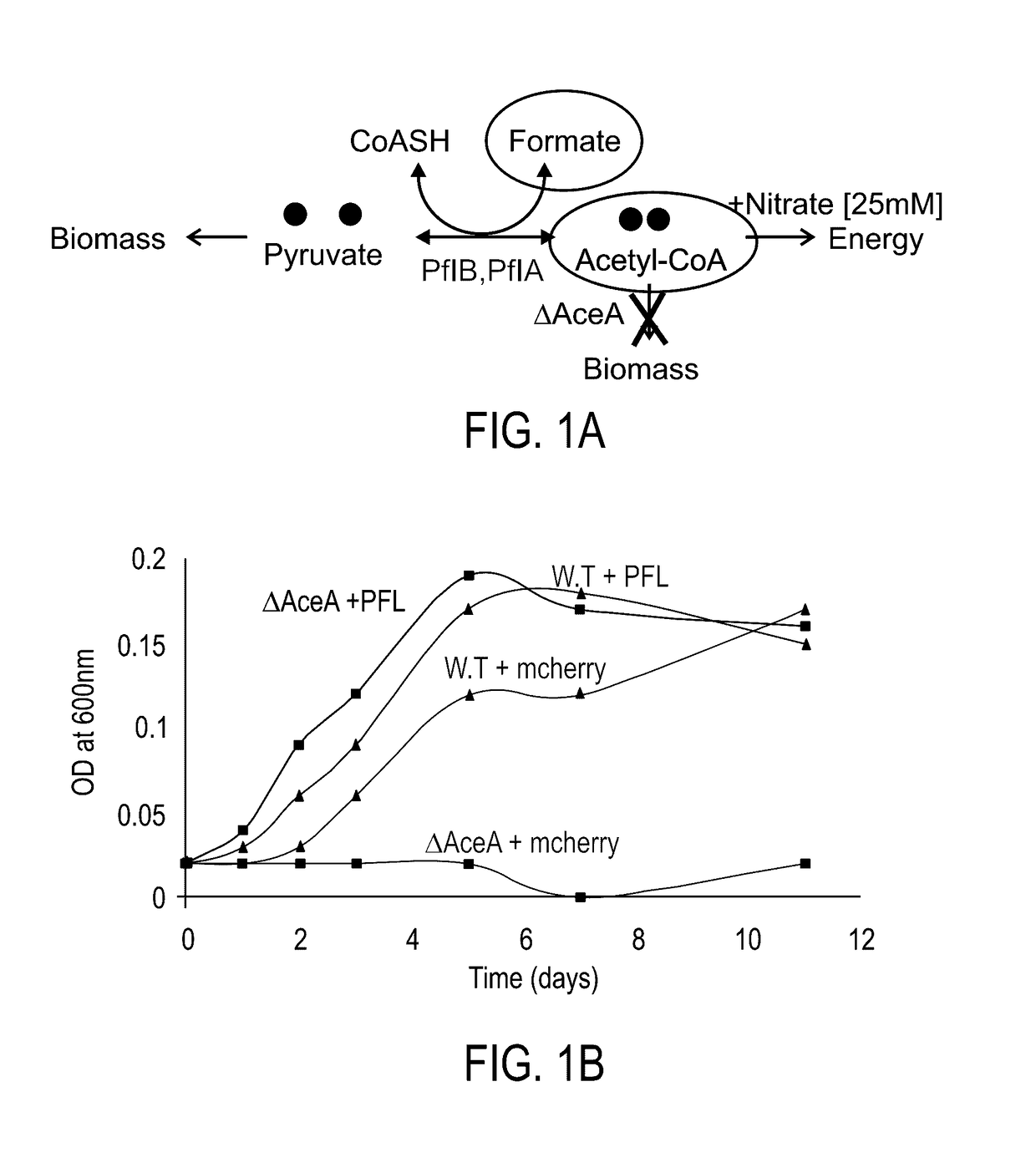
Use of enzymes which catalyze pyruvate synthesis from formate and acetyl-coa and bacteria expressing same
An isolated microorganism is disclosed being genetically modified to express pyruvate formate lyase (PFL) or 2-ketobutyrate formate lyase, wherein acetyl-CoA of the microorganism is converted to pyruvate in the presence of formate in a single step reaction, wherein the net flux of the reaction is in the direction of pyruvate synthesis.Uses of the microorganism and products comprising same are also disclosed.
Owner:YEDA RES & DEV CO LTD
Corynebacterium glutamicum high-producing l-proline and method for high-producing l-proline
ActiveCN114107141BIncrease productionImprove conversion rateBacteriaTransferasesPyruvate synthesisGlyceraldehyde
The invention provides a Corynebacterium glutamicum for producing L-proline, and a method for producing L-proline by using the strain. The L-proline-producing Corynebacterium glutamicum constructed by the present invention, wherein proline dehydrogenase / pyrrole-5-carboxylate dehydrogenase PutA is inactivated, glutamate kinase ProB, glutamate-5- Enhanced activity of semialdehyde dehydrogenase ProA, pyrrole-5-carboxylate dehydrogenase ProC, pyruvate carboxylase Pyc, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase GapN, L-proline efflux protein ThrE or SerE, The L-glutamate efflux protein MscCG is inactivated, and the L-proline yield, transformation rate and production intensity of the obtained strain are significantly improved compared with the starting strain, which can reduce the production cost of L-proline.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Plasmid-free and inducer-free genetically engineered bacterium for producing D-pantothenic acid and construction method
ActiveCN113278569ALittle side effectsPromote accumulationBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliPantothenate synthesis
The invention relates to a genetically engineered bacterium for producing D-pantothenic acid at high yield, a construction method and application of the genetically engineered bacterium to preparation of the D-pantothenic acid through microbial fermentation. According to the genetically engineered bacterium, related genes of an organic acid synthesis path of escherichia coli are blocked, so that side effects of organic acid are reduced and the accumulation of a pyruvic acid pool is increased; a pyruvic acid synthesis path gene pykA is enhanced and the accumulation of pyruvic acid is enhanced; negative feedback inhibition of a key enzyme is relieved and a bottleneck step of synthesizing the D-pantothenic acid is solved; the sugar uptake capability is improved and the accumulation of a precursor pyruvic acid is increased; over-expression genes lpd and ilvD are used for improving an expression condition of a main path synthesis path gene; finally, the engineered bacterium for producing the D-pantothenic acid at higher yield is obtained; an exogenous enzyme does not need to be introduced into a plasmid to enhance the enzyme activity of the key enzyme and the shake-flask fermentation yield reaches 3.99g / L; a repressor protein coding gene lacI is knocked out to form constitutive expression; after a culture medium is optimized, the shake-flask fermentation yield reaches 4.72g / L; materials are supplemented in batches in a 5L fermentation tank and fermentation is carried out; and the yield reaches 34.28g / L.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Mutant of pyruvate carboxylase gene promoter and application thereof
ActiveCN113755492AHigh promoter activityImprove expression strengthBacteriaMicroorganism based processesPromoter activityEnzyme Gene
The invention discloses a mutant of a corynebacterium glutamicum pyruvate carboxylase gene promoter and application of the mutant. The mutant has improved promoter activity in comparison with that of a wild type promoter. Therefore, the mutant can be used for enhancing the expression of a target gene, for example, the mutant is operably connected with a pyruvate carboxylase gene, so that the expression intensity of pyruvate carboxylase is enhanced, and the amino acid production efficiency of the strain is improved.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Dibasic organic acid producing strain and preparation and application of same
ActiveUS10781462B2Raise the level of fermentationLow costMicroorganismsTransferasesMyceliophthora thermophilaPyruvate synthesis
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Construction method and application of genetic engineering escherichia coli for increasing content of lactic acid components in polyhydroxybutyrate lactate
InactiveCN111363713AReduce wasteIncreased content of lactic acid componentsBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliHydroxybutyric acid
The invention discloses a construction method and an application of genetic engineering escherichia coli for increasing the content of lactic acid components in polyhydroxybutyrate lactate. The transformation pathway is that construction of a pyruvic acid synthesized polyhydroxybutyrate lactate metabolic pathway is carried out, and over-expression of related gene in 2-hydroxy propionyl-CoA synthesizing path is carried out to increase synthesis of LA-CoA; and the transformation pathway also comprises weakening of one or two of escherichia coli endogenous thioesterase ydiI and yciA, so as to reduce flowing of LA-CoA to a lactic acid synthesis pathway. According to the method disclosed by the invention, the La-CoA in escherichia coli can effectively flow to a synthesis module of a target product, the waste of the target product synthesis precursor La-CoA is reduced, the escherichia coli is transformed by analysis and regulation of the metabolic pathway via a gene engineering means, and the content of the lactic acid components in the polyhydroxy alkanoate produced by an obtained recombinant strain is obviously increased.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
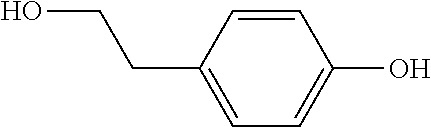
Method for constructing the recombinant yeasts for preparation of tyrosol and derivatives and its application
PendingUS20220213512A1Increase synthesisIncrease productionFungiGenetically modified cellsHydroxytyrosolTyrosol
A recombinant yeast is constructed by introducing an expressed gene of exogenous Fructose-6-phosphate phosphoketolase into a modified yeast cell, and the modified yeast cell is a yeast cell with a metabolic pathway for synthesizing tyrosol via Erythrose-4-phosphate and phosphoenolpyruvate. The present invention discloses for the first time that in the process of expressing Fructose-6-phosphate phosphoketolase in a yeast, Fructose-6-phosphate is synthesized into beta-D-Fructose 1,6-bisphosphate and also catalyzed into Erythrose-4-phosphate and Acetyl-phosphate, and Xylulose-5-phosphate is catalyzed into Glyceraldehydes-3-phosphate and Acetyl-phosphate, which change the metabolic flux distribution of carbon in the yeast, enhance the synthesis of Erythrose-4-phosphate as an important intermediate for the biosynthesis of tyrosol, optimize the metabolic pathway for synthesizing tyrosol, and increase the yields of tyrosol and its derivatives such as hydroxytyrosol.
Owner:SHANDONG HENGLU BIOTECH CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com