Construction method and application of genetic engineering escherichia coli for increasing content of lactic acid components in polyhydroxybutyrate lactate
A technology of polyhydroxybutyrate lactate and Escherichia coli, applied in the field of bioengineering, can solve the problem that the enzyme that degrades LA-CoA has not been reported, and achieves the effect of increasing the content of lactic acid components and reducing waste
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
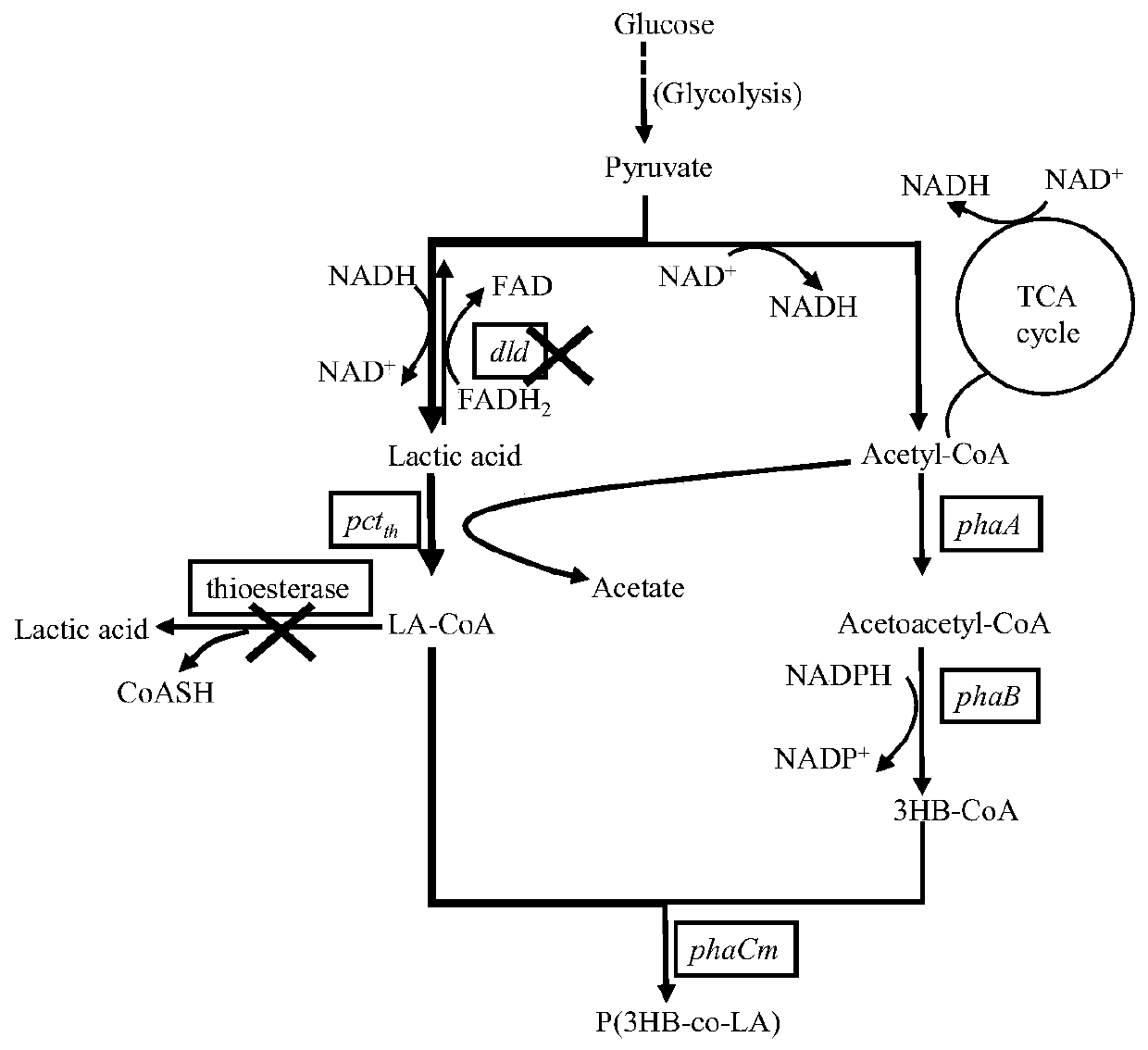
[0029] Example 1. Knockout gene dld prevents lactate from being converted into pyruvate
[0030] In the later stage of fermentation, lactic acid may synthesize pyruvate under the action of D-lactate dehydrogenase (dld), which reduces the lactic acid component in P(3HB-co-LA). Therefore, the gene dld was knocked out by Red recombination method, and the obtained strain was named WXJ01. The specific operation of gene knockout is as follows:
[0031] For the knockout of the gene dld, primers were firstly designed (primer sequences are shown in the table below), and a DNA fragment of about 1700 bp with kanamycin resistance was cloned by PCR. The plasmid pKD46 was introduced into the host bacteria through calcium transformation, and the recombinants were selected with ampicillin. Recombinant bacteria introduced with pKD46 were cultured at 30°C to OD 600 At about 0.3, L-arabinose was added for induction for 1 hour, and then 10% glycerol was used to prepare electroporation competen...
Embodiment 2
[0033] Example 2. Knockout gene ydiI weakens the degradation pathway of LA-CoA
[0034] The thioesterase in Escherichia coli has a degradative effect on LA-CoA, making LA-CoA move towards the fatty acid synthesis pathway, resulting in a decrease in the flux of LA-CoA synthetic polymers, which is ultimately unfavorable for the P(3HB-co- Synthesis of LA). Therefore, the present invention knocks out the endogenous thioesterase ydiI of Escherichia coli, weakens the degradation pathway of LA-CoA, and makes LA-CoA, as the direct precursor of P(3HB-co-LA), more towards the polymer synthesis pathway . On the basis of strain WXJ01, the gene ydiI was knocked out by Red recombination method, and the obtained strain was named WXJ02. The specific operation of gene knockout is the same as that of gene dld.
Embodiment 3
[0035] Example 3. Knockout gene yciA weakens the degradation pathway of LA-CoA
[0036] The thioesterase yciA and ydiI in Escherichia coli have similar properties, and both can degrade LA-CoA to form the corresponding fatty acid. Therefore, the present invention knocks out the gene yciA on the basis of the strain WXJ01, and the obtained strain is named WXJ021, which weakens LA-CoA. -The degradation of CoA makes it more towards the synthetic pathway of P(3HB-co-LA). The specific operation of gene knockout is the same as that of gene dld.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com