Plasmid-free and inducer-free genetically engineered bacterium for producing D-pantothenic acid and construction method
A technology of genetically engineered bacteria and pantothenic acid, applied in the field of metabolic engineering, can solve the problems of expensive precursors, uneconomical, difficult strain improvement, etc., to achieve the effect of removing negative feedback inhibition, strengthening pyruvate accumulation, and improving sugar uptake ability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
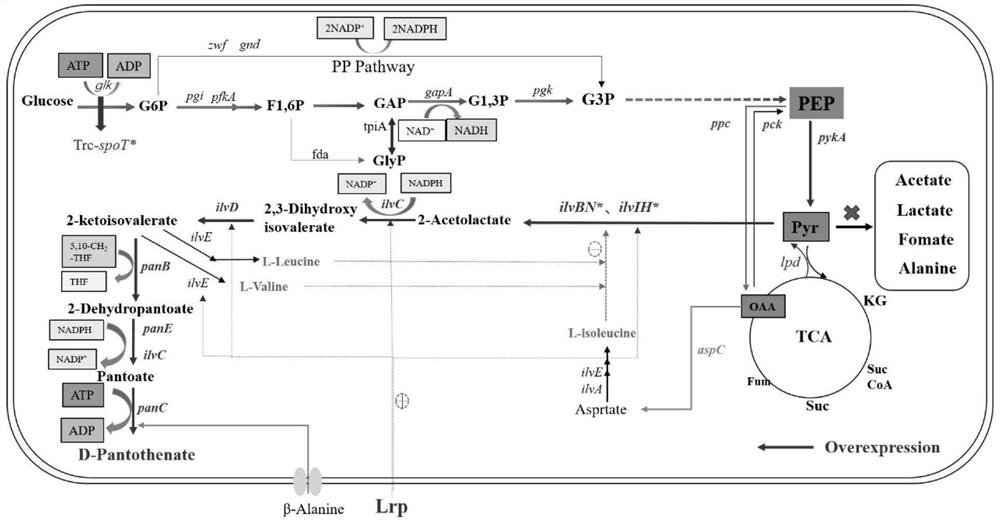
[0088] Example 1: Charge Trum DPA8 (E.COLI W3110 TRC-PANC / TRC-PANE / TRC-PANB / TRC-ILVC / ILVG * / ΔAVTA / ILVE * / COAA * Construction
[0089] (1) As the Escherichia.coli W3110, it is used as a strain using Crispr-Cas9 gene editing techniques, and the PANC gene promoter in the genome plant ESCHERICHIA.COLI W3110 genome is replaced with a TRC promoter to obtain recombinant strain Escherichia.coli W3110 / TRC- PANC, recorded as DPA1;
[0090] (2) Use the CRISPR-Cas9 gene editing technology to replace the PANE gene promoter in the strain DPA1 genome to TRC promoter to obtain recombinant strain Escherichia.coli W3110 / TRC-PANCPANE, remembered as DPA2;
[0091] (3) Use the CRISPR-Cas9 gene editing technique to replace the PANB gene promoter in the strain DPA2 genome with a TRC promoter to obtain recombinant strain Escherichia.coli W3110 / TRC-PANCPANEPANB, which is recorded as DPA3;
[0092] (4) Use crisPR-Cas9 gene editing techniques to replace the ILVC gene promoter in the stra...
Embodiment 2
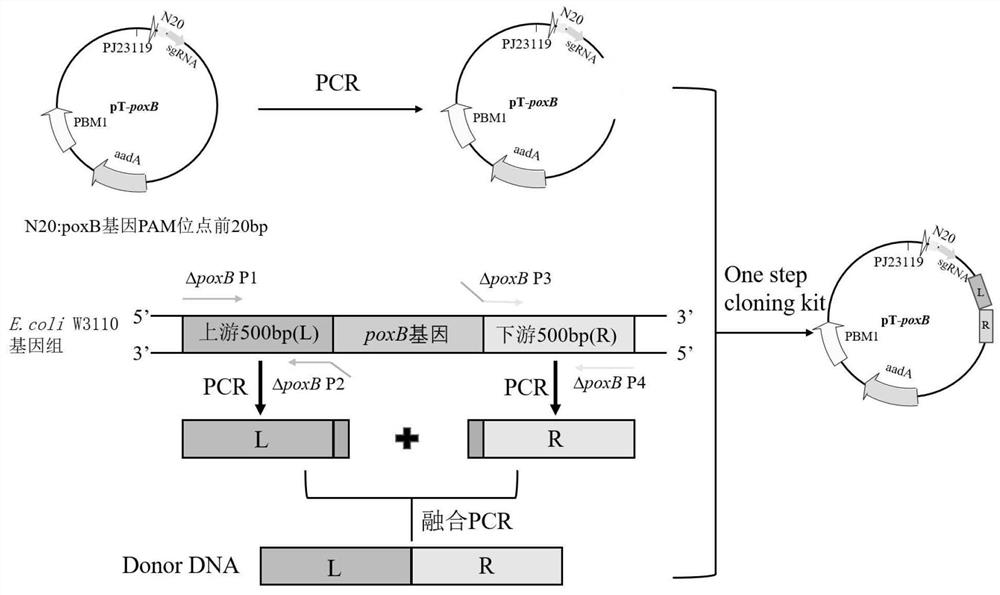
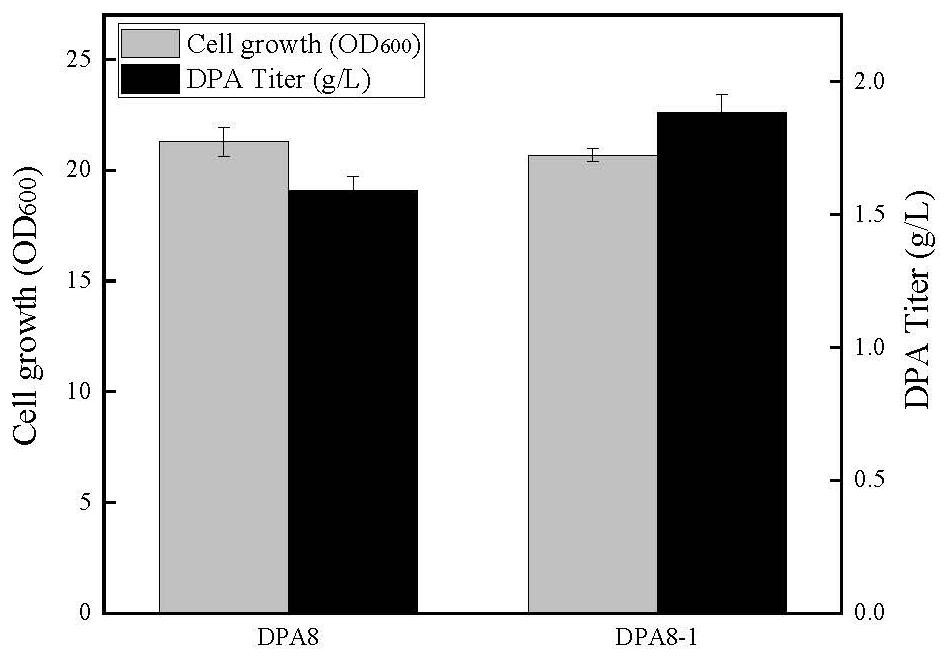
[0097] Example 2: Construction and shake flask fermentation of strain DPA8-1 knockout PoxB gene
[0098] Gene Engineering DPA8 (ie E.COLI W3110 TRC-PANC / TRC-PANE / TRC-PANB / TRC-ILVC / ILVG * / ΔAVTA / ILVE * / COAA * ) As starting strain, the use of CRISPR-Cas9 mediated gene editing technology (YuJiang et al.2015Multigene Editing in the Escherichia coli Genome via theCRISPR-Cas9 System.Applied Environmental Microbiology.81: 2506-2514), on acetic acid in the genome Gene Poxb is knocked out to reduce pyruvate synthesis acetic acid:
[0099](1) Constructing a PTarget-PoxB plasmid: Template as a PTARGET F plasmid (AddGene Plasmid # 62226), PT- △ PoxB F / PT- △ POXB R is amplified, and the obtained PCR product passes through DPN I at 37 ° C Insulation is 30 min, then transformed into E.Coli DH5α chemotactic admissions, magnificent maternal (SD) flat screen, sequencing and verifying the correct PTARGET-POXB plasmid for subsequent connection Donor DNA.
[0100] (2) Constructing a PTD...
Embodiment 3
[0108] Example 3: Construction of strain DPA8-2 knockout PTA gene
[0109] (1) Construction of PTarget- △ PTA plasmid: Template as a Ptarget F Plasmid (AddGene Plasmid # 62226), PTARGET-△ PTA F / PTARGET- △ PTA R is amplified, and the PCR product is incubated at 37 ° C through DPN I. Digestion 3 h, then transformed into E.Coli DH5α chemotactic cells, spectacular enzyme flat screen screening, sequencing and verifying the correct PTarget-PTA plasmid for subsequent connection Donordna.
[0110] (2) Constructing a PTD-PTA plasmid: Take the E.Coli W3110 genome as analog, ΔPTA P1, ΔPtAP2, ΔPTAP3 and ΔPTA P4 as primers, and the construction step is the same as in Example 2 (2) to obtain a PTD-ΔPTA plasmid. .
[0111] (3) Introduce PCAS plasmid (AddGene Plasmid # 62225) into the strain DPA8-1 perception obtained in Example 2, the strain DPA8-1 sensing state preparation method as in Example 2 (3).
[0112] (4) Constructing a strain DPA11 positive colonies, the construction method is the sa...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com