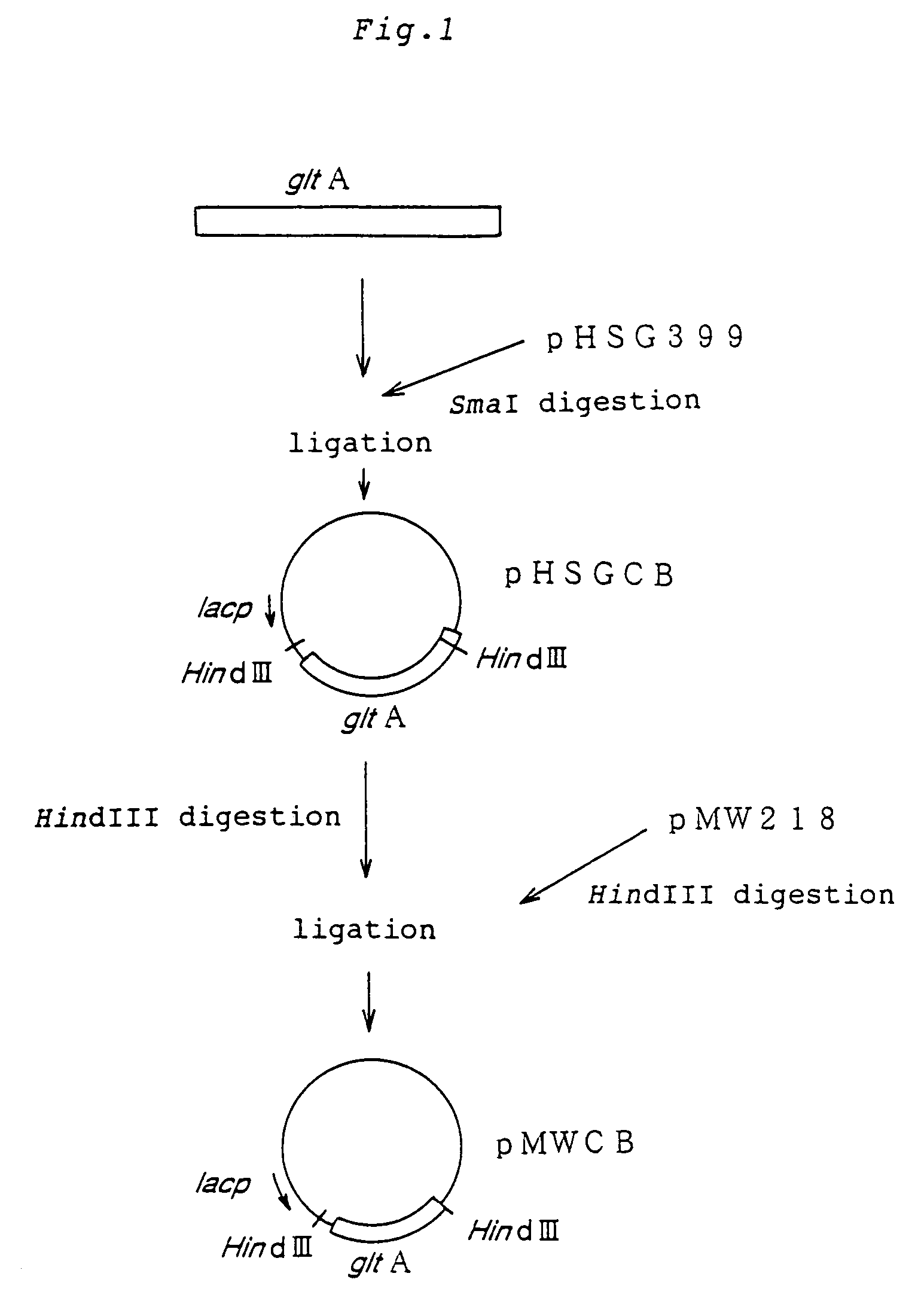
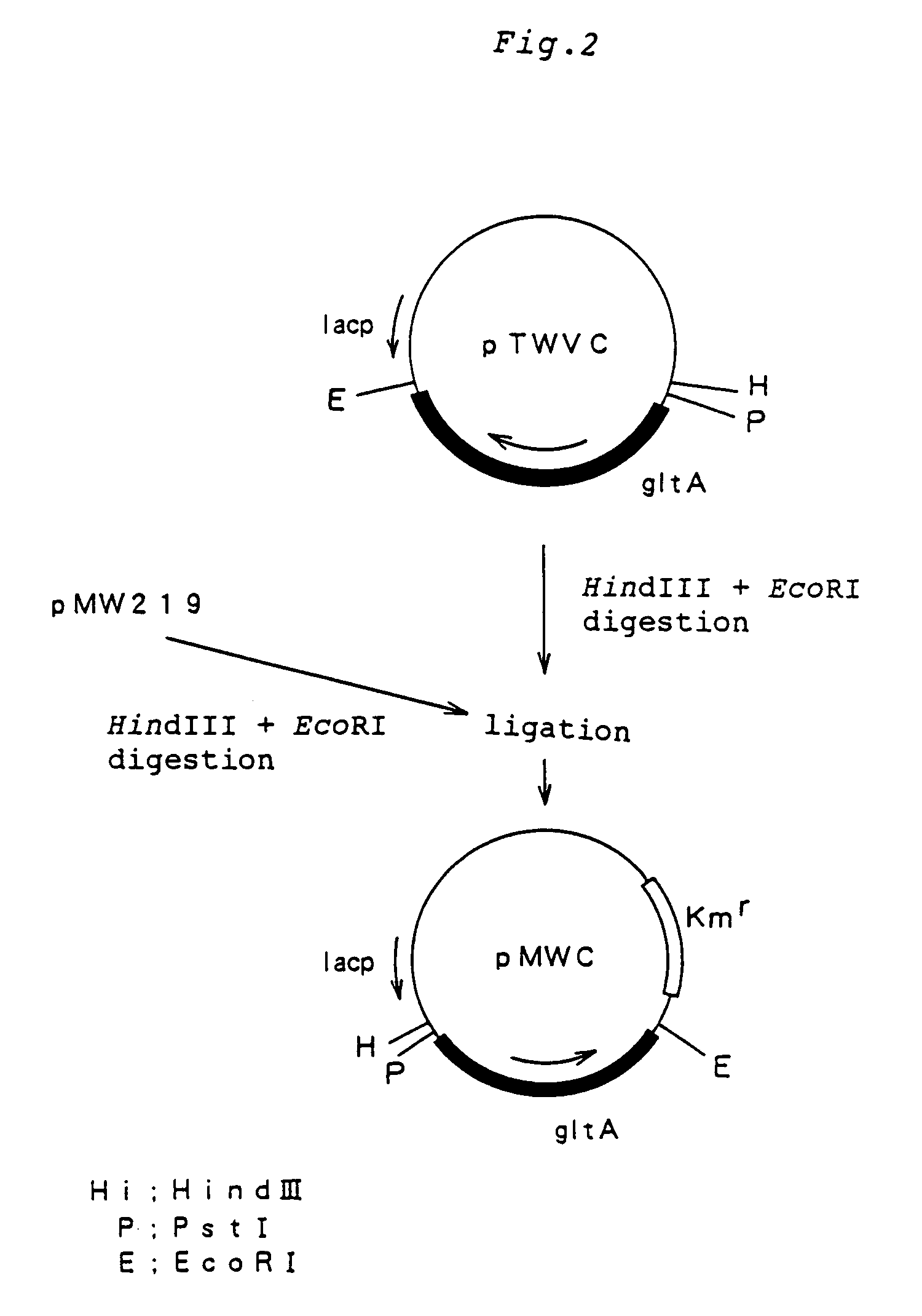
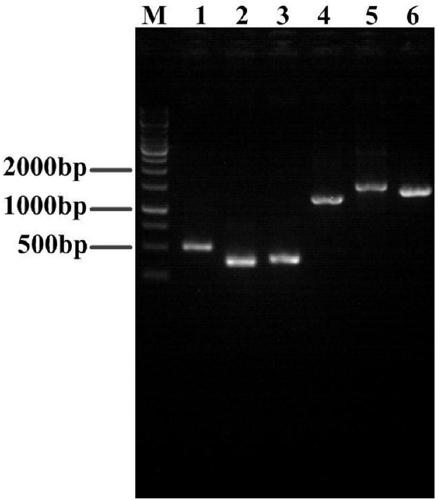
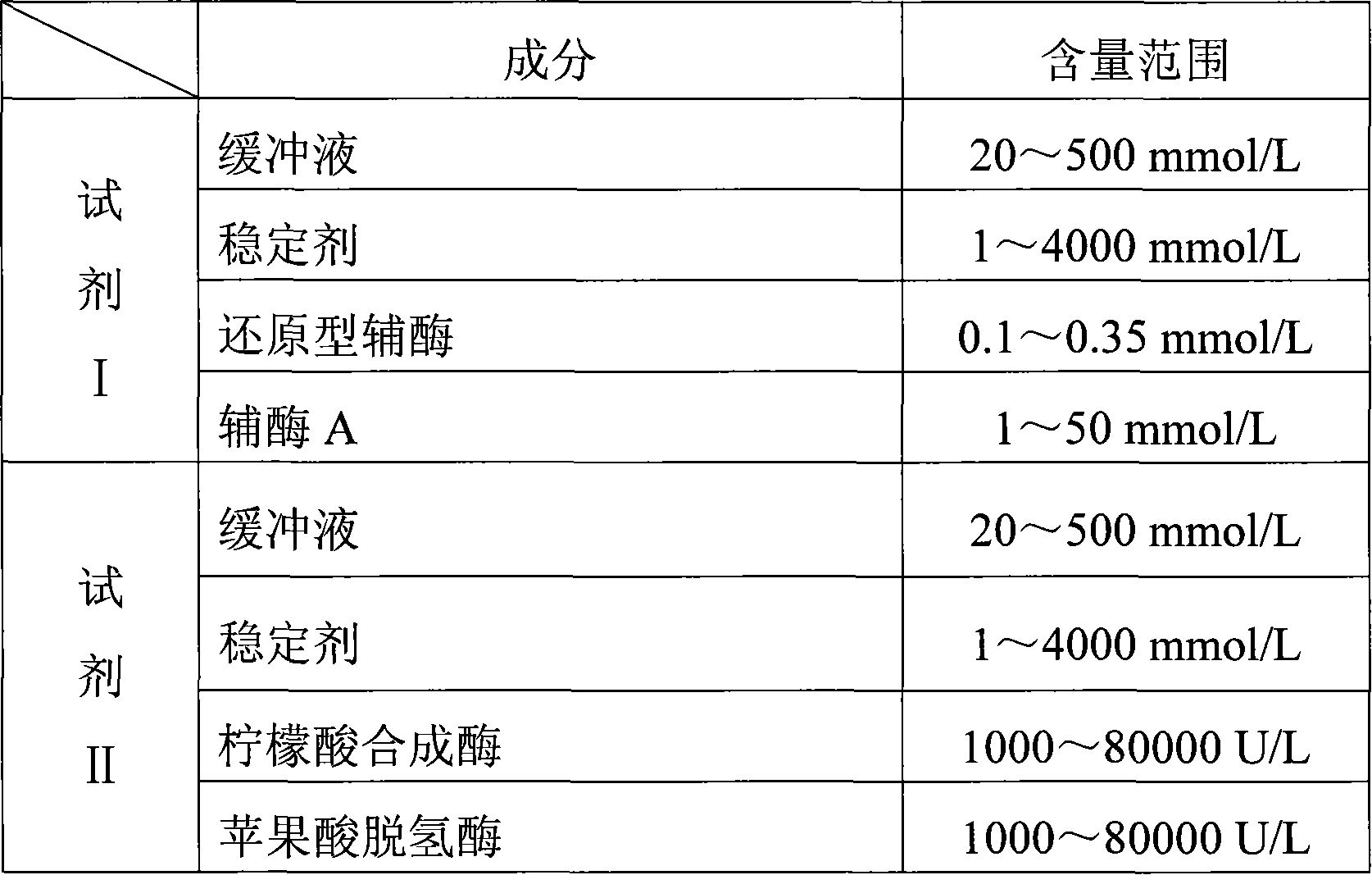
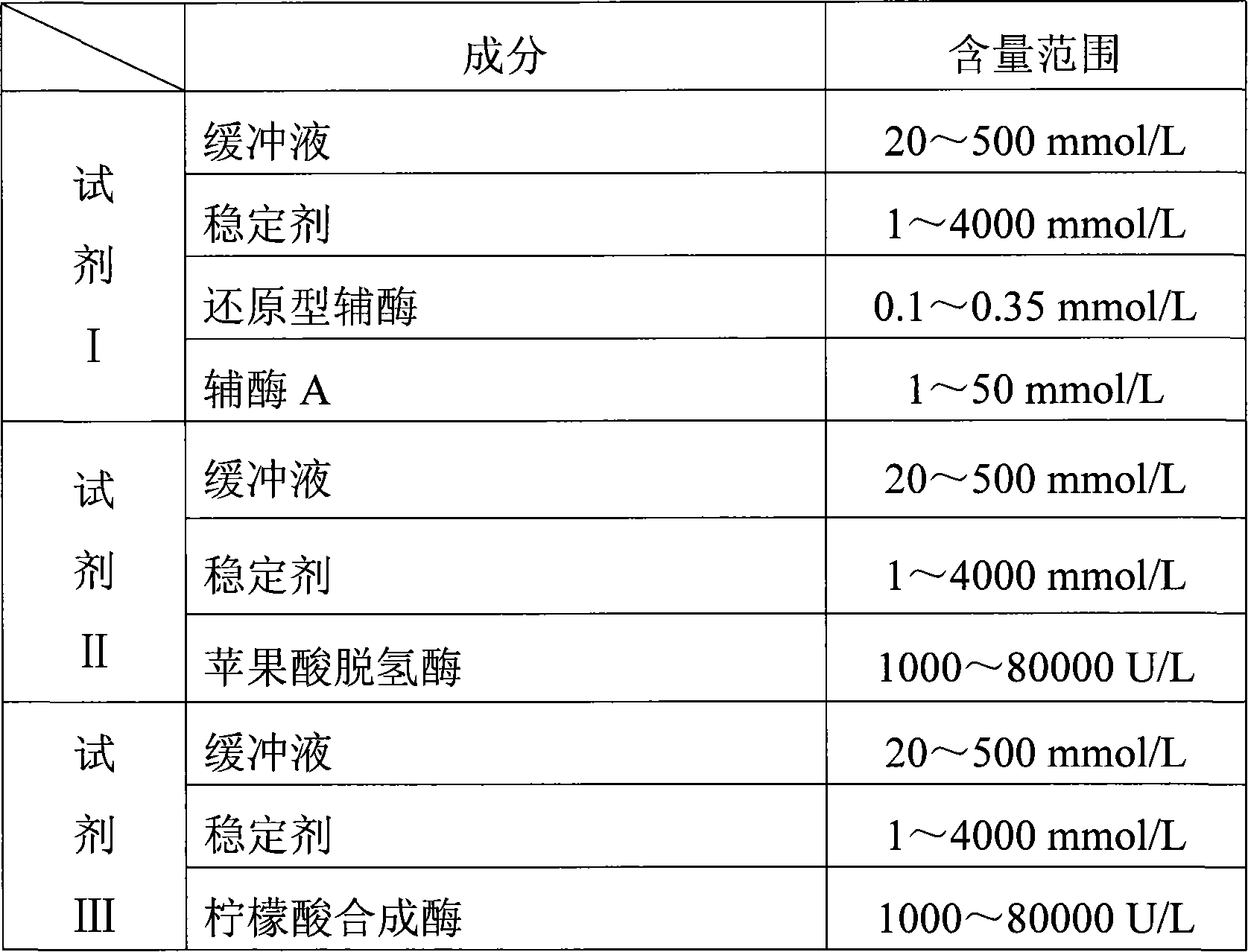
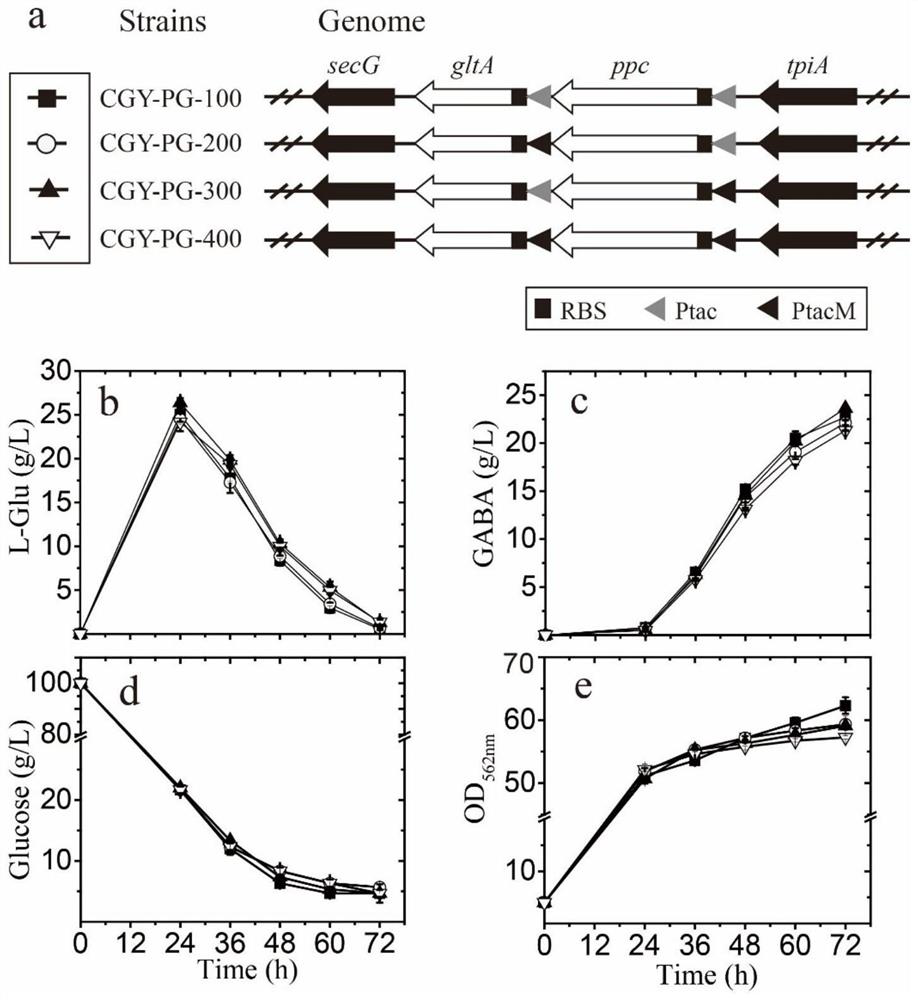
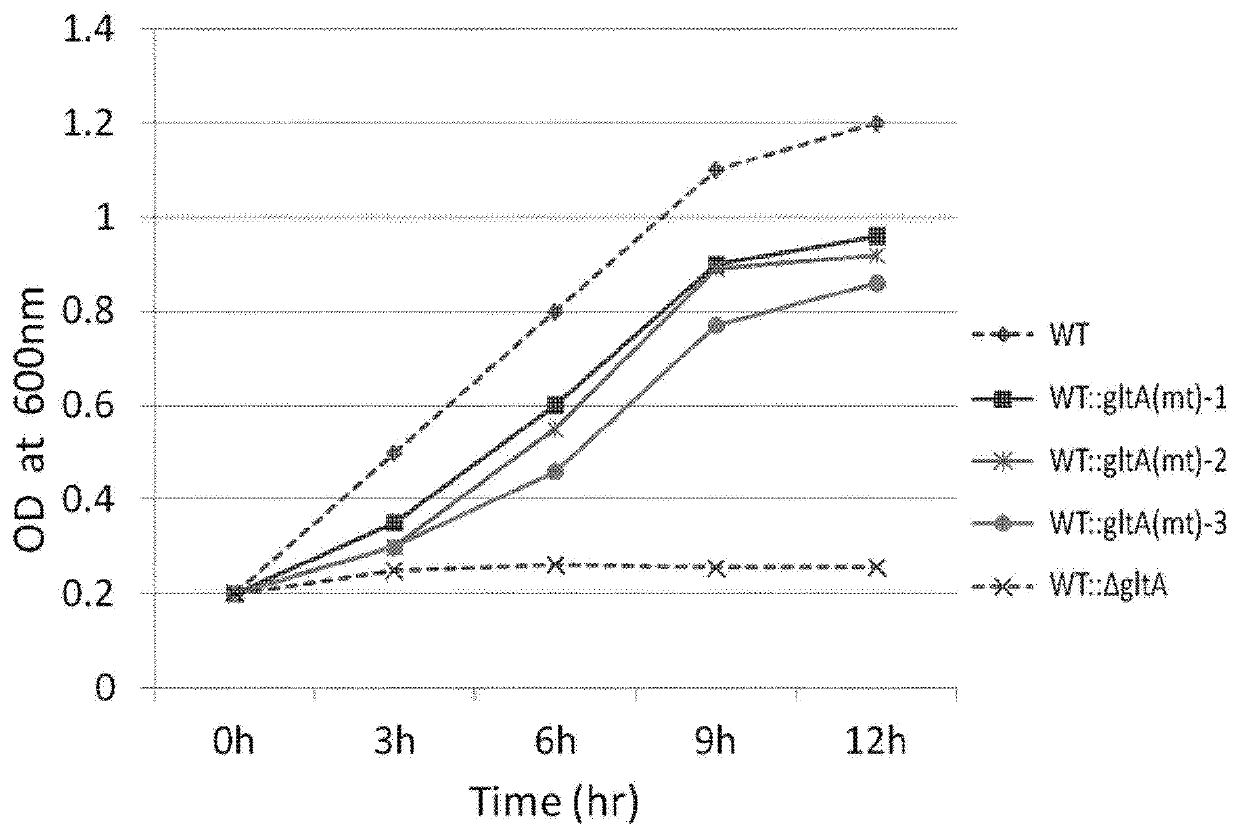
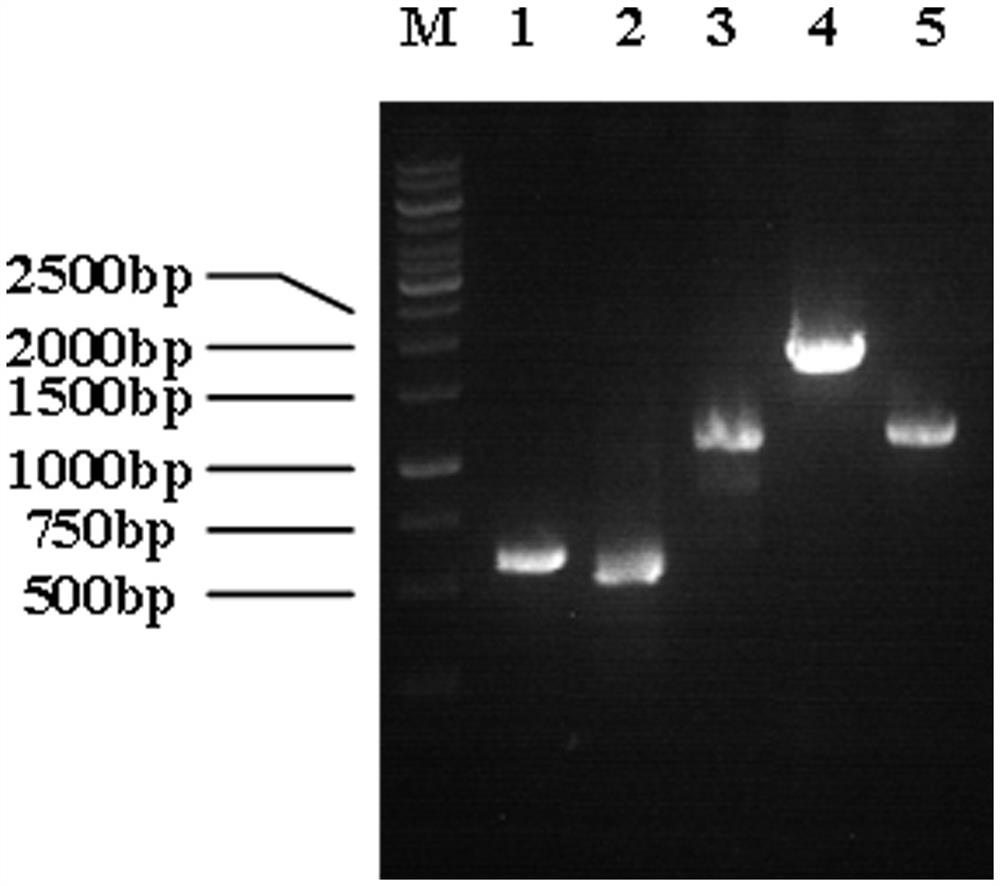
Patents
Literature
57 results about "Citrate synthase" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The enzyme citrate synthase E.C. 2.3.3.1 (previously 4.1.3.7)] exists in nearly all living cells and stands as a pace-making enzyme in the first step of the citric acid cycle (or Krebs cycle). Citrate synthase is localized within eukaryotic cells in the mitochondrial matrix, but is encoded by nuclear DNA rather than mitochondrial. It is synthesized using cytoplasmic ribosomes, then transported into the mitochondrial matrix.
L-glutamic acid producing bacterium and process for producing L-glutamic acid
InactiveUS7247459B1Less-efficient processing in expensiveProcess economyBacteriaSugar derivativesBacteroidesMicroorganism
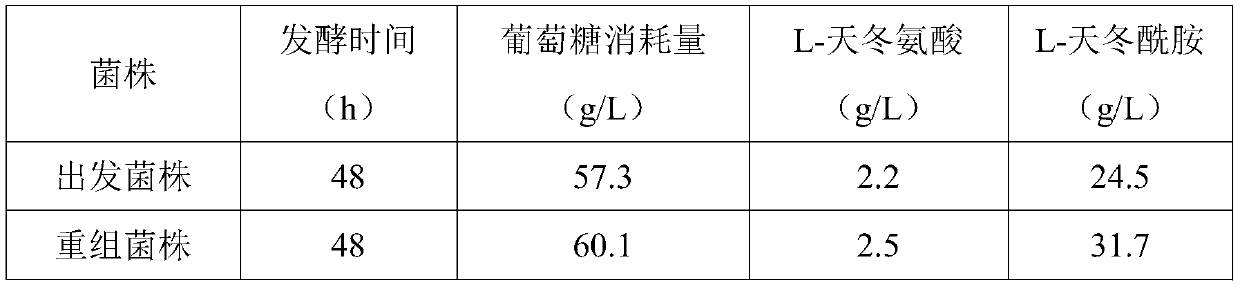
L-glutamic acid is produced by culturing in a medium a microorganism belonging to enterobacteria and having L-glutamic acid productivity, into which a citrate synthase gene derived from a coryneform bacterium is introduced to produce and accumulate L-glutamic acid in the medium and collecting the L-glutamic acid from the medium.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
Genetic engineering bacterium for L-theanine production and construction and application thereof
ActiveCN109777763AIncrease enzyme activityGene expression is stableBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliCitrate synthase
The invention belongs to the technical field of genetic engineering, and particularly relates to novel high-efficiency gamma-glutamyl methylamine synthetase and a plasmid-free genetic engineering bacterium for L-theanine production and construction and application thereof. The plasmid-free genetic engineering bacterium which performs denovo synthesis on L-theanine efficiently by taking cheap carbon sources such as glucose as a substrate is provided, escherichia coli serves as a host, and gamma-glutamyl methylamine synthase genes gmas-Mu copied three times are integrated on a genome of the escherichia coli; a glutamate dehydrogenase gene Cgl2079 is copied once; a pyruvate carboxylase gene Cgl0689 is copied once; a citrate synthase gene gltA is copied once, and the genetic engineering bacterium is obtained. After metabolic transformation of a system, the engineering bacterium can perform denovo synthesis on the L-theanine by taking the glucose as the raw material, the fermentation yieldand sugar-acid conversion rate are the highest values reported so far, in fermentation of a 5 L fermentor, the maximum production of the L-theanine can reach 60 g / L, and the sugar-acid conversion ratecan reach 40%.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Corynebacterium glutamicum for producing high-yield succinic acid by utilizing straw hydrolysate, and construction and applicaitons
InactiveCN107012161AHigh final concentrationHigh yieldBacteriaMicroorganism based processesTransketolasePhosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase
The invention discloses a corynebacterium glutamicum for producing high-yield succinic acid by utilizing straw hydrolysate, and a construction and applications. The method comprises the following steps: (1) knocking out side products acetic acid and lactic acid formation pathway related genes from corynebacterium glutamicum ATCC 13032, and introducing anaplerotic pathway phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase and pyruvate carboxylase and phosphopentose pathway transketoaldehydase and transketolase on a strong promoter overexpression chromosome; and introducing xylose transport gene on the chromosome; and (2) expressing pyruvate carboxylase, succinic acid export protein and citrate synthase as well as xylose isomerase and xylulokinase on the corynebacterium glutamicum obtained in the step (1). 98.6gL<-1> of succinic acid can be anaerobically produced after 22.5h by utilizing mixed glucose and xylose in straw hydrolysate, with the yield of 0.98g succinic acid / g total sugar. The final concentration, yield and productivity of succinic acid achieve higher level, and the corynebacterium glutamicum has good industrial potential.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Carrier for enhancing aluminum-tolerance of plant, and method for establishing the same
InactiveCN102199620ALarge amount of synthesisPromote growthVector-based foreign material introductionPhosphoenolpyruvate carboxylaseNicotiana tabacum
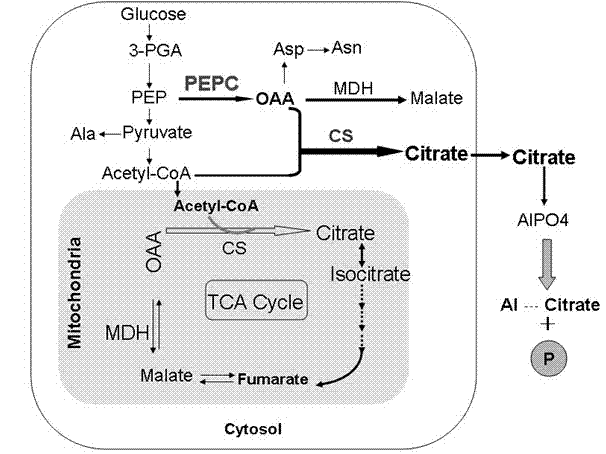
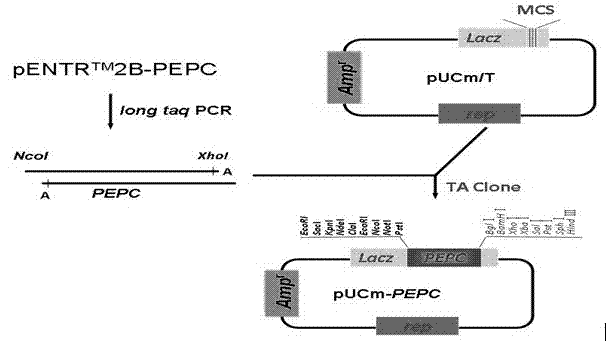
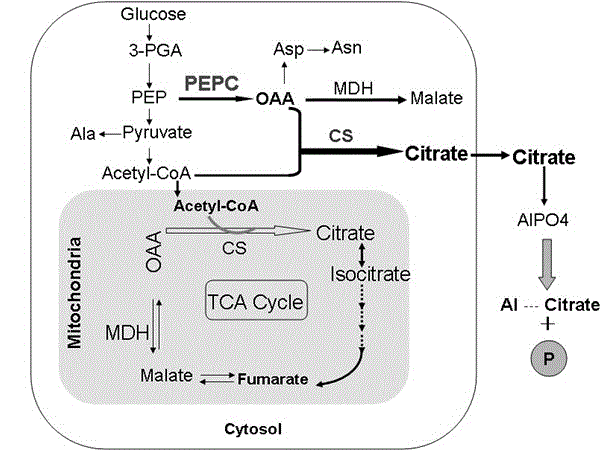
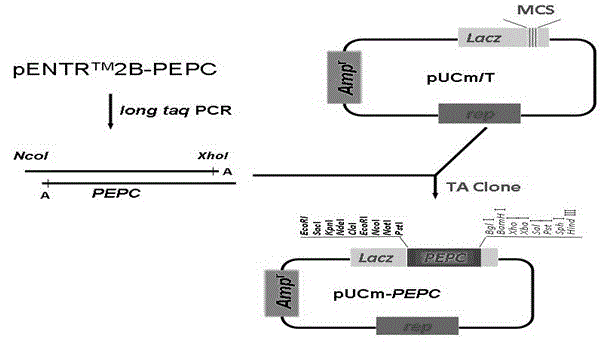
The invention provides a carrier for enhancing aluminum-tolerance of a plant, and a method for establishing the same. The carrier is a plant expression vector having photoinduction promoters and phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase (PEPC) genes. The method for establishing the carrier comprises the following steps: searching for the sequence of the full length gene of Synechococcus vulcanus PEPC in GenBank and designing a pair of primers with sequences as described in the specification; recovering and purifying PEPC full length gene segments and connecting the segments to a pUCm-T vector; establishing an entry vector pENTER*-PrbcS-PEPC; establishing a plant expression vector pH2-35S-PrbcS-PEPC. In the invention, the activity of citrate synthase of tabacoo with transgenic PEPC and CS genes is 2.4 to 2.6 times that of wild tobacco, and the activity of phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase of such tabacco is 2.2 to 2.4 times that of wild tobacco. The special-purpose carrier provided in the invention can exert great influence on the improvement of aluminum-tolerance of a plant, and particularly, can significantly promote aluminum-tolerance of plants grown in acid red soil in southern China, thereby providing a novel approach for variety improvement of plants.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH +1
Genetic engineering bacterium for producing glycollic acid by acetic acid, and building method and application thereof
ActiveCN107603998AIncrease productionHigh yieldBacteriaMicroorganism based processesMalate synthaseAcetyl Coenzyme A Synthetase
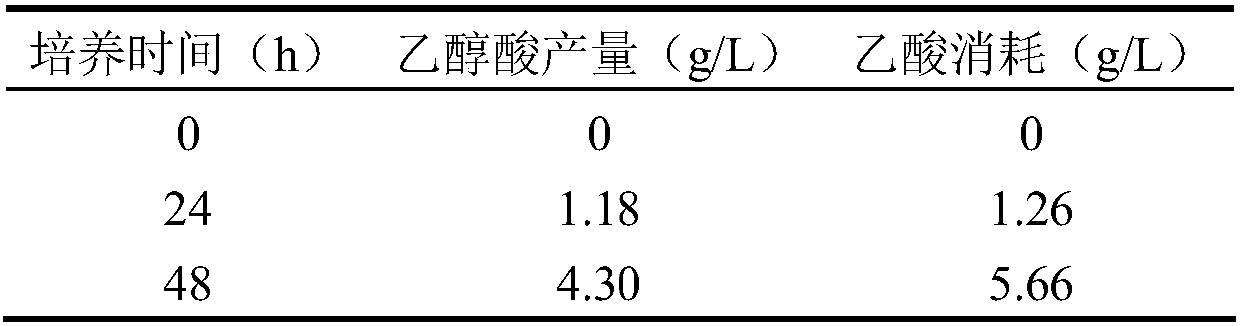
The invention discloses a genetic engineering bacterium for producing glycollic acid by acetic acid, and a building method and application thereof. A method for preparing the genetic engineering bacterium for producing glycollic acid provided by the invention comprises the following steps of improving the expression and / or activity of acetylcoenzyme A synthetase, phosphotransacetylase, acetokinase, citrate synthase, isocitrate lyase, isocitrate dehydrogenase kinase and glyoxylate reductase in the recipient bacterium; reducing the expression and / or the activity of malate synthase, glycolate oxidase and isocitrate lyase repressor protein in the recipient bacterium, so that the engineering bacterium for producing the glycollic acid is obtained. The recipient bacterium is a bacterium capable of using acetic acid as a carbon source for growth. The prepared genetic engineering bacterium uses acetic acid as the carbon source for producing the glycollic acid; in addition, the production quantity and yield of the glycollic acid in shaking culture can reach the relatively high level; relatively good industrial application prospects are realized.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
A genetically engineered bacterium for the production of l-theanine and its construction and application
ActiveCN109777763BIncrease enzyme activityGene expression is stableBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliEnzyme Gene
The invention belongs to the technical field of genetic engineering, and particularly relates to novel high-efficiency gamma-glutamyl methylamine synthetase and a plasmid-free genetic engineering bacterium for L-theanine production and construction and application thereof. The plasmid-free genetic engineering bacterium which performs denovo synthesis on L-theanine efficiently by taking cheap carbon sources such as glucose as a substrate is provided, escherichia coli serves as a host, and gamma-glutamyl methylamine synthase genes gmas-Mu copied three times are integrated on a genome of the escherichia coli; a glutamate dehydrogenase gene Cgl2079 is copied once; a pyruvate carboxylase gene Cgl0689 is copied once; a citrate synthase gene gltA is copied once, and the genetic engineering bacterium is obtained. After metabolic transformation of a system, the engineering bacterium can perform denovo synthesis on the L-theanine by taking the glucose as the raw material, the fermentation yieldand sugar-acid conversion rate are the highest values reported so far, in fermentation of a 5 L fermentor, the maximum production of the L-theanine can reach 60 g / L, and the sugar-acid conversion ratecan reach 40%.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
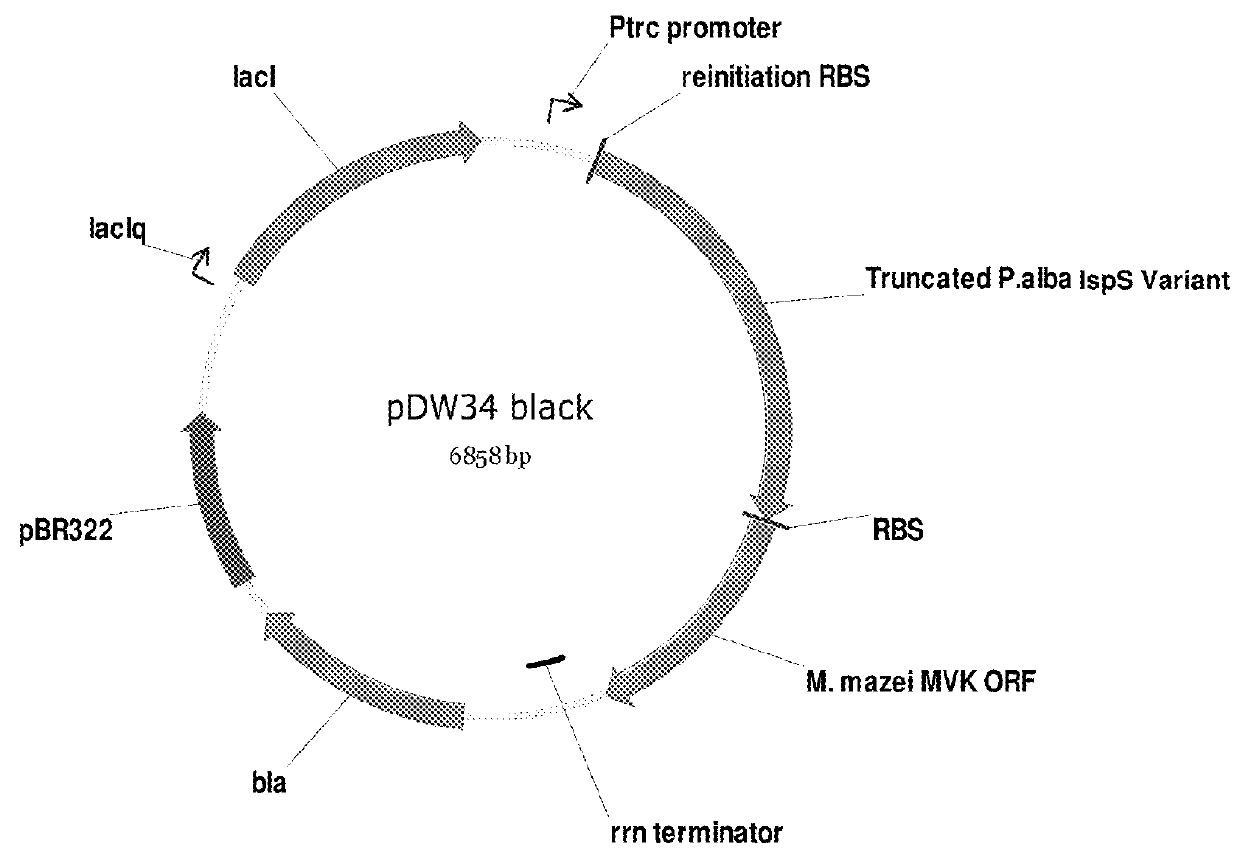
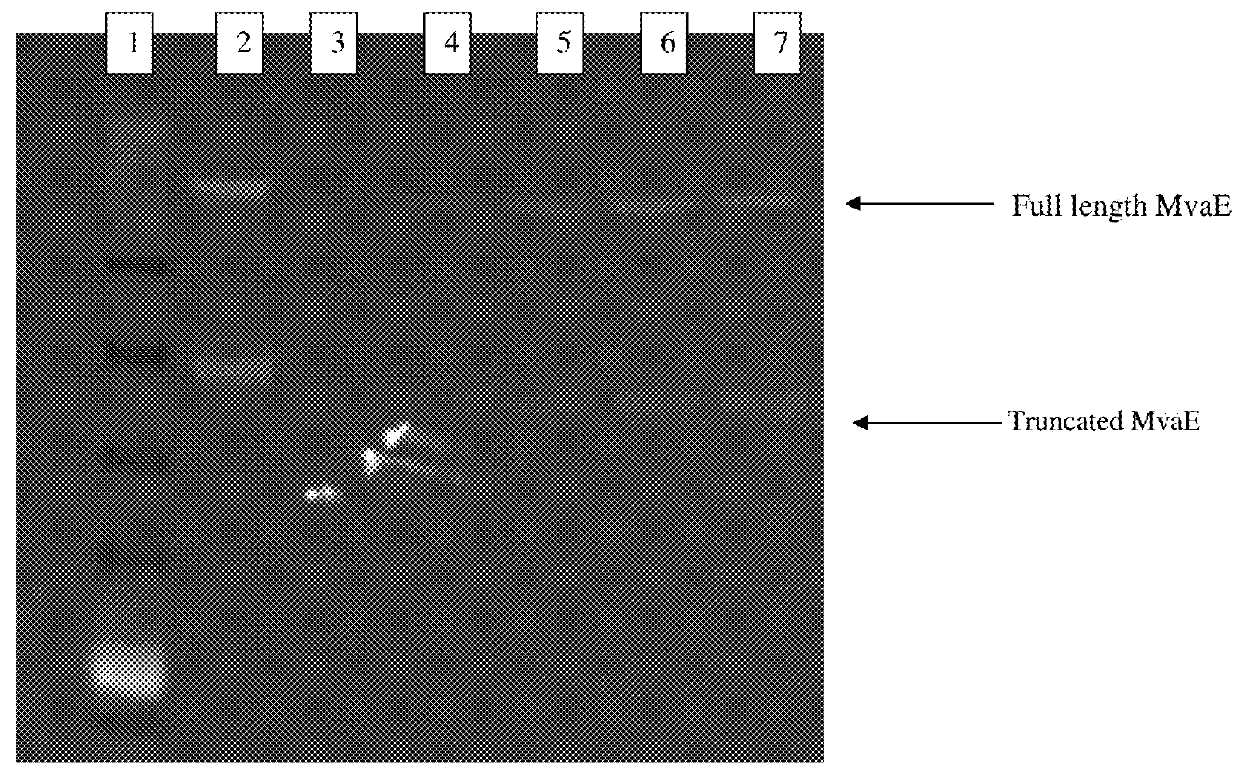
Recombinant microorganisms for enhanced production of mevalonate, isoprene, and isoprenoids
ActiveUS20160032323A1Reduce the amount of solutionHigh activityBacteriaHydrolasesHeterologousCitrate synthase
The invention features compositions and methods for the increased production of mevalonate, isoprene, isoprenoid precursor molecules, and / or isoprenoids in microorganisms by engineering a microorganism for increased carbon flux towards mevalonate production in the following enzymatic pathways: (a) citrate synthase, (b) phosphotransacetylase, (c) acetate kinase, (d) lactate dehydrogenase, (e) malic enzyme, and (f) pyruvate dehydrogenase such that one of more of the enzyme activity is modulated. In addition, production of mevalonate, isoprene, isoprenoid precursor molecules, and / or isoprenoids can be further enhanced by the heterologous expression of the mvaE and mvaS genes (such as, but not limited to, mvaE and mvaS genes from the organisms Listeria grayi DSM 20601, Enterococcus faecium, Enterococcus gallinarum EG2, and Enterococcus casseliflavus).
Owner:DANISCO US INC +1
Kit for and method for content determination of acetyl coenzyme A
ActiveCN104293884AHigh detection sensitivitySimple and fast operationMicrobiological testing/measurementPyrrolidinonesCitrate synthase
The invention discloses a kit and a method for content determination of acetyl coenzyme A. The kit comprises a reagent I, a reagent II, a reagent III, a reagent IV and a reagent V, wherein the reagent I is prepared from Tris-HCl, polyvinylpyrrolidone, mercaptoethanol, phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride and glycerinum; the reagent II is prepared from malic dehydrogenase; the reagent III is prepared from citrate synthase; the reagent IV is prepared from malic acid and an oxidation type coenzyme I; and the reagent V is prepared from Tris-HCl. The malic dehydrogenase can be used for catalyzing malic acid and the oxidation type coenzyme I to generate oxaloacetic acid and a reduced coenzyme I; the citrate synthase is used for catalyzing acetyl coenzyme A and oxaloacetic acid to generate citric acid and a coenzyme A; by virtue of a coupled reaction of the malic dehydrogenase and the citrate synthase, the content of the acetyl coenzyme A and the generation rate of the reduced coenzyme I are in a direct proportion; the climbing speed of the light absorption value at 340nm reflects the content of the acetyl coenzyme A. The kit disclosed by the invention is simple and convenient to operate, high in detection sensitivity and high in recovery rate, and the cost of the reagents is remarkably lowered. The detection steps are further simplified, so that the kit is simpler and more convenient and efficient to test.
Owner:SUZHOU COMIN BIOTECH
Related gene for high-yield L-leucine, construction method for engineering bacteria and application
ActiveCN109456987AImprove growth traitsGood characterBacteriaMicroorganism based processesSaccharic acidAgricultural science
The invention relates to a related gene for high-yield L-leucine, a construction method of engineering bacteria and application. The construction method for the engineering bacteria comprises the following steps: (1) integrating a leuA mutant gene to a cgl1135 pseudogene locus, wherein the leuA mutant gene is as shown in sequence 1; (2) integrating an ilvBN mutant gene to a cgl1890 pseudogene locus, wherein the ilvBN mutant gene is as shown in sequence 2; and (3) replacing a citrate synthase primary promoter by a PCP_2928 specific promoter, wherein the PCP_2928 specific promoter is as shown insequence 3. By adopting the technical scheme provided by the invention, 32 g / L L-leucine can be produced by fermenting for 30 hours in a shaking flask, and 60 g / L L-leucine can be produced by fermenting for about 50 hours in a 5L fermenting tank; the maximum production intensity can reach 1.5 g / (L*h); the saccharic acid conversion rate is 30 percent; and the production level is the highest levelfor producing the L-leucine by the fermenting method reported at present.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for measuring citric acid concentration and citric acid diagnose reagent kit
InactiveCN101082575AFree from pollutionHigh precisionMicrobiological testing/measurementColor/spectral properties measurementsCITRATE ESTERCoupling
The invention relates to a kind of enzyme colorimetric method and a method of the coupling method measuring the density of citric acid and a diagnosis reagent box applying the citrate synthetase and coupling malic dehydrogenase enzymatic reaction continues monitoring method / ratio colorimetric method. The reaction of citrate synthetase enzymolysis citric acid generates oxaloacetic acid and then through the effect of coupling malic dehydrogenase at last oxidizes the reduced coenzyme (there is a absorption peak at the site of 340nm) becoming the coenzyme (there is a absorption peak at the site of 340nm) so we can assay the degree / speed of the fall-way absorbance at the place of 340nm. It can measure and calculate the density of citric acid by measuring the degree / speed of the fall-way absorbance at the place of 340nm. The method has high specificity and it is not polluted by the endogenous and exogenous object and the test result is precise and accurate. The invention can get the array result by the ultraviolet / visible light analytic instrument so it is convenience to extend and apply.
Owner:SUZHOU ANJ BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
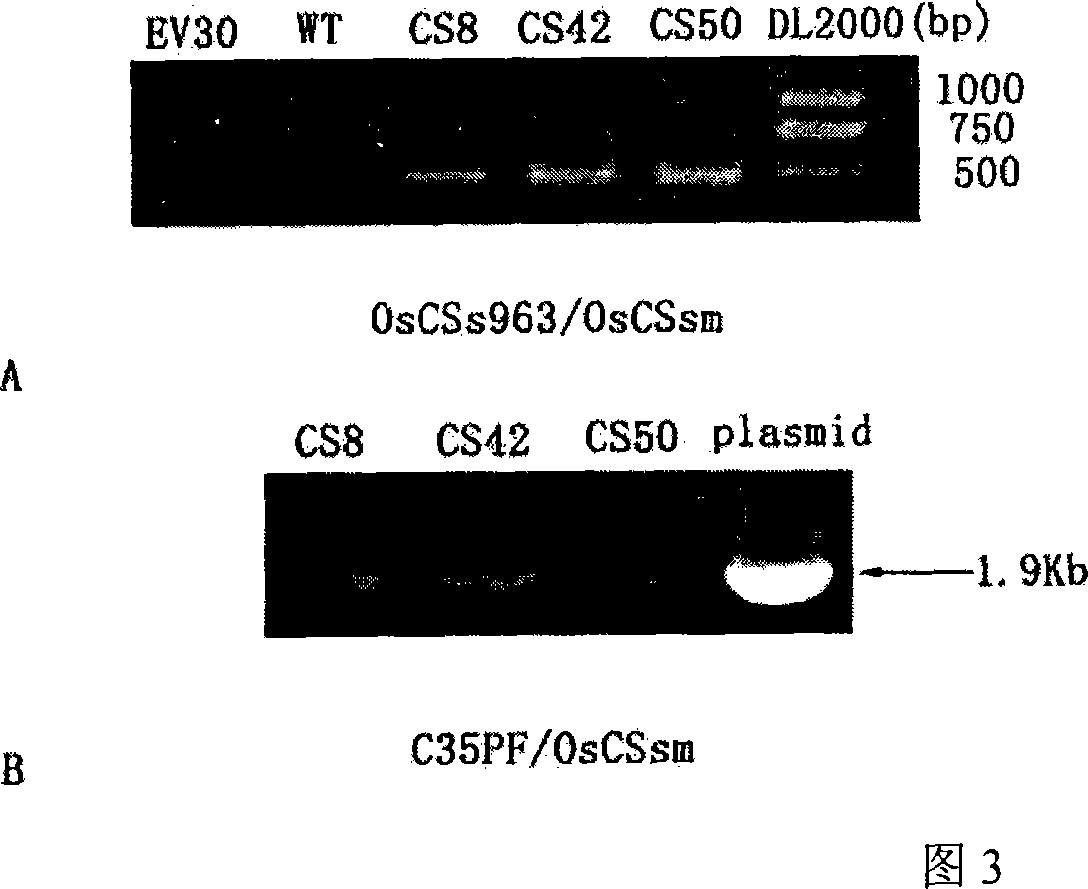
Rice OsCS coded sequence and application thereof
The invention relates to a code sequence expressing citrate synthase in the rice and an application improving plant citric acid secretory and plant aluminium toxin immunity in the gene engineering technique field, which also relates to a recombinant expression vector of the gene, a conversion plant cell of expression vector, the transgenosis plant of the gene developed by the conversion cell. The gene expression in the plant improves the citric acid secretory quantity of the transgenosis plant, which enhances the aluminium toxin immunity.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
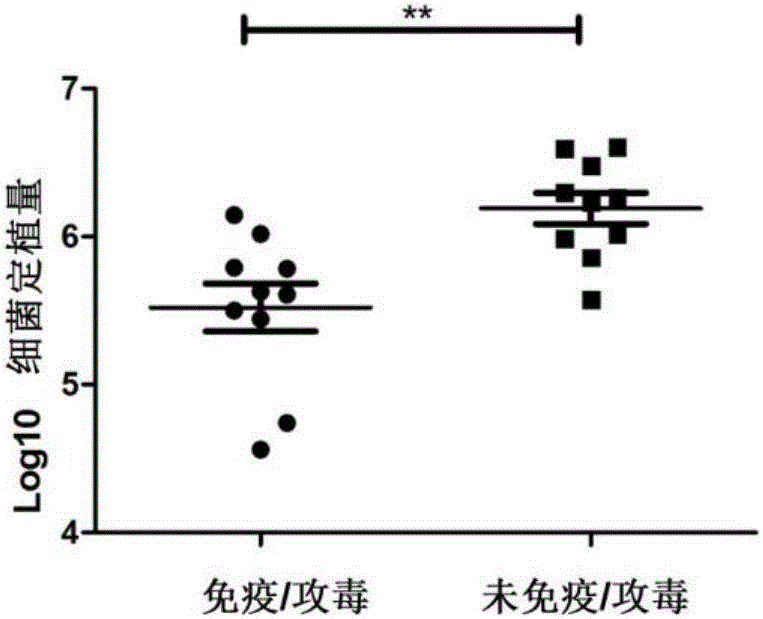
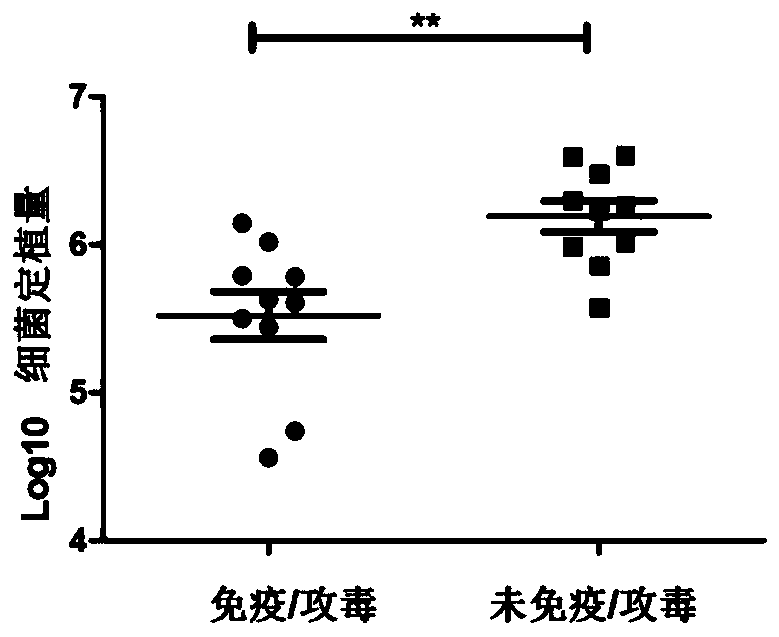
Helicobacter pylori dominant antigen assembly based on CD4+T cell immunity and screening method
InactiveCN106480003AImprove cleanlinessMild immunopathological damageAntibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsProtective antigenScreening method
The invention relates to a helicobacter pylori dominant antigen assembly based on CD4+T cell immunity and a preparation method. The dominant antigen assembly comprises the following three components and homologous protein of the three components: inosine monophosphate dehydrogenase, type II citrate synthase and urease B subunit, wherein the amino acid sequences are shown as SEQ ID NO.1, SEQ ID NO.2 and SEQ ID NO.3. The screened dominant antigen assembly based on CD4+T cell immunity has the obvious immune protection effect, has the protection effect superior to that of H.pylori holoprotein antigen, has strong capacity of scavenging helicobacter pylori, and causes extremely slight pathological injuries. The three immunity dominant antigens provided by the invention can induce the body to generate strong immune response reaction aiming at antigens, therefore, through the means of inducing the body to generate the response aiming at the immunoprotecive dominant antigens, or directly immunizing the body by adopting the protective antigens, the effective immune protection effect can be achieved on the helicobacter pylori infection, and the scheme can be used for the further study on the preventive and therapeutic polyvaccines of helicobacter pylori.
Owner:ARMY MEDICAL UNIV
Method for cultivating phosphor highly active paddy rice utilizing inverted citrate synthetase gene
InactiveCN1500875AImprove patienceShort cyclePlant genotype modificationAngiosperms/flowering plantsGenetically modified riceRice plants
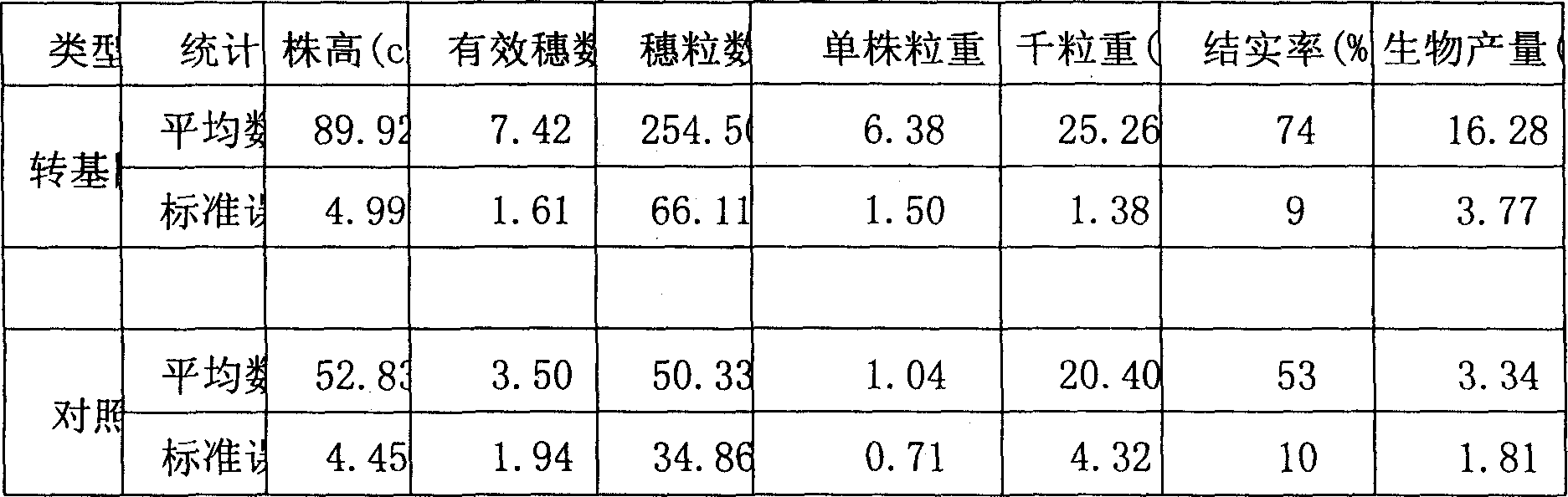
The present invention belongs to the field of genetic engineering and new plant variety breeding technology, and features that Citrate synthase from bacteria is introduced into rice acceptor, and by means of report gene, PCR detection and molecular hybridization to identify transgenic plant, examine the soil null phosphate absorbing case and agricultural character of filial plant, select transgenic rice plant line with obviously increased stooling, increased yield and low phosphate tolerance, and further breed high efficiency phosphate rice variety and create new resource for breeding.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Method for producing itaconic acid in escherichia coli
InactiveCN107723317AComplete structureChange structureMicroorganism based processesFermentationEscherichia coliAconitase
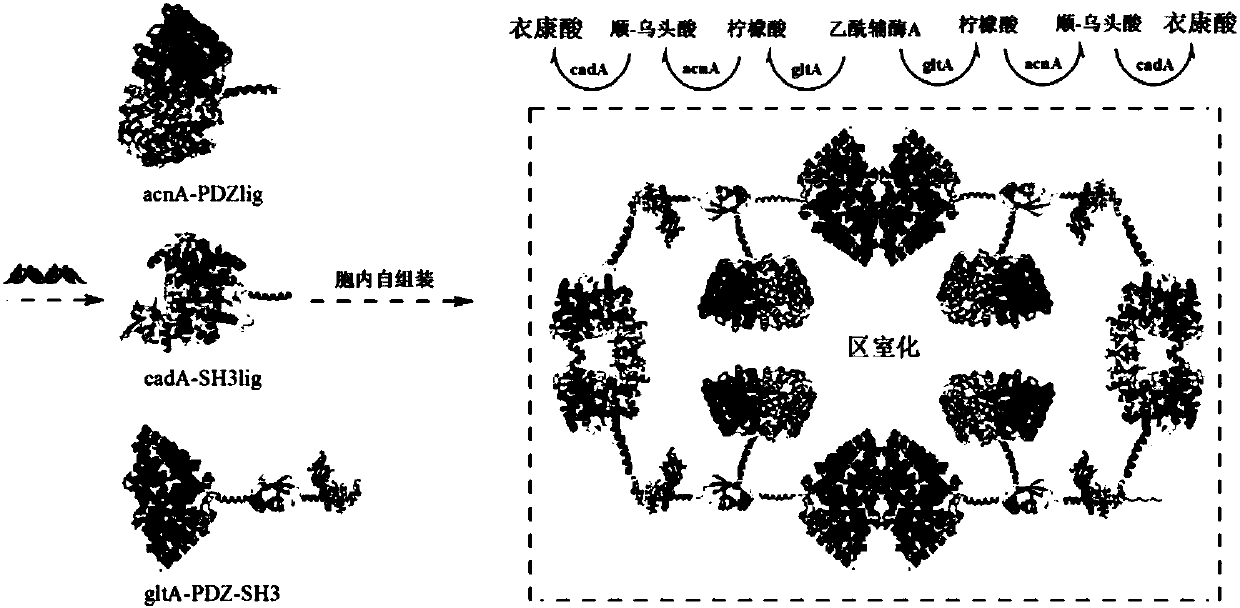
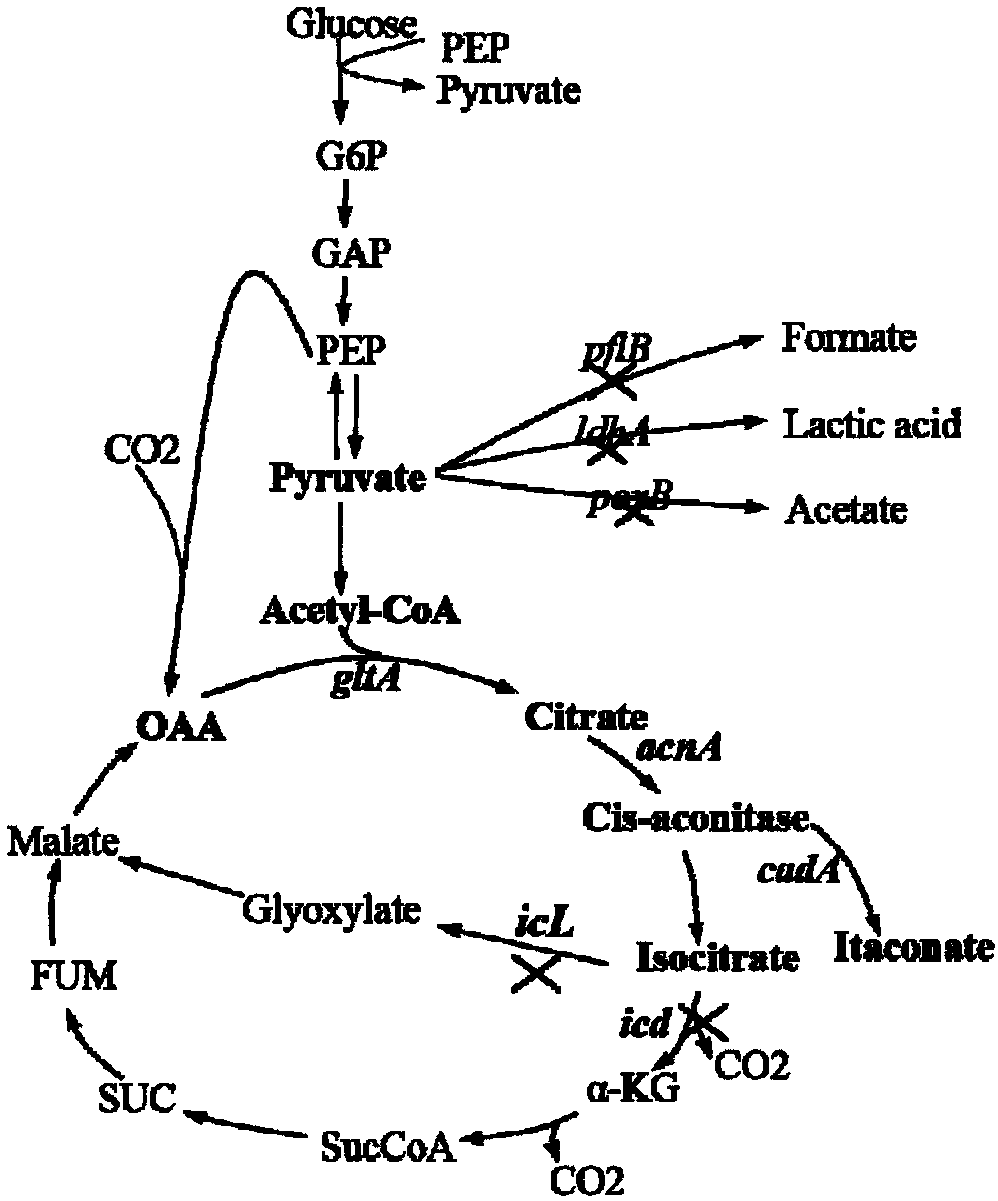
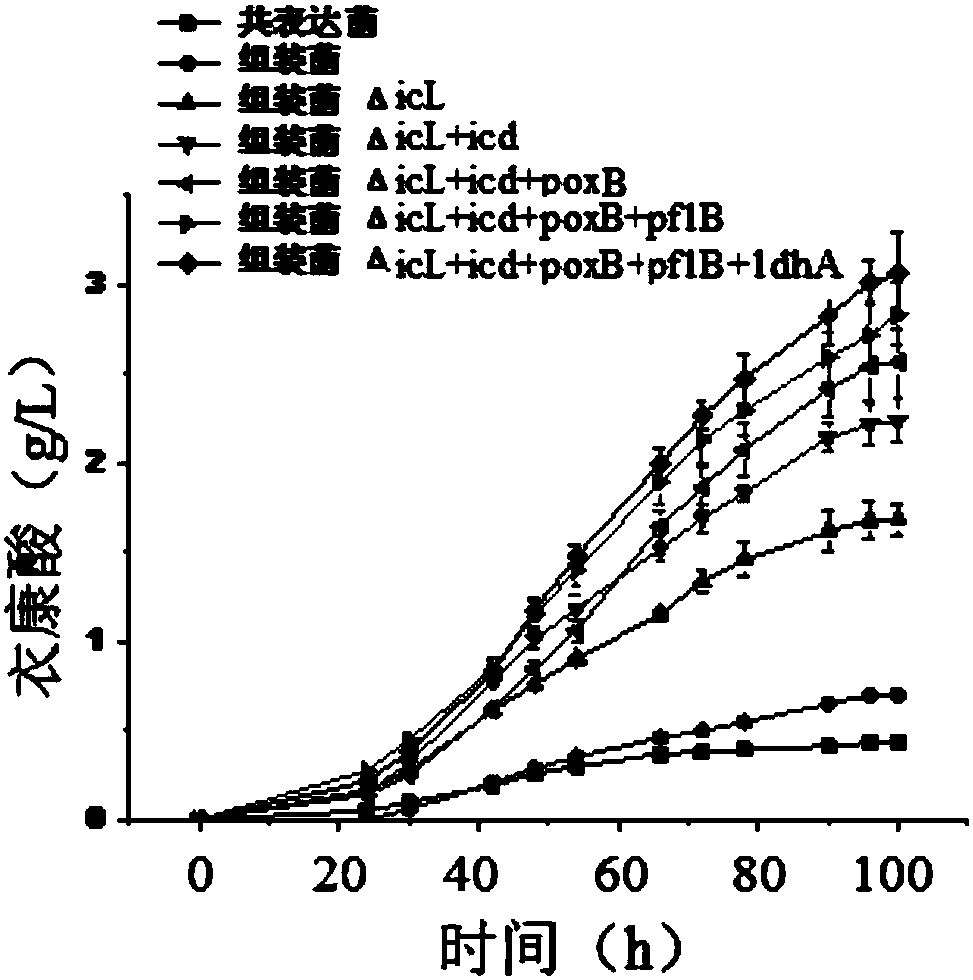
The invention provides a method for producing itaconic acid in escherichia coli, belonging to a method for efficiently producing itaconic acid in escherichia coli by simultaneously utilizing a multi-enzyme assembly technology and a metabolic pathway transformation technology. The method for producing itaconic acid in escherichia coli comprises the following steps: (1) carrying out self-assembly onthree key enzymes for synthesizing itaconic acid in cells, thus forming a multi-enzyme complex, wherein the three key enzymes comprise citrate synthase gltA, cis-aconitase acnA and aconitate decarboxylase cadA; (2) carrying out metabolic pathway transformation on escherichia coli by adopting the Crispr / cas9 technology; and (3) transferring the multi-enzyme complex into escherichia coli after themetabolic pathway transformation, thus constructing an escherichia coli engineering bacterium, and producing itaconic acid through fermentation. According to the method, the three key enzymes for synthesizing itaconic acid are taken as assembly objects, meanwhile, the Crispr / cas9 technology is adopted for transforming the metabolic pathways, thus the efficient production of itaconic acid in escherichia coli is realized, and a new path is provided for the industrial production of itaconic acid.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Uses of bicyclol and pharmaceutically acceptable derivative thereof in prevention or treatment of drug-induced liver damage
InactiveCN109106711ARestoration of synthetase activityGene copy number gainDigestive systemHeterocyclic compound active ingredientsReticulum cellAutophagic death
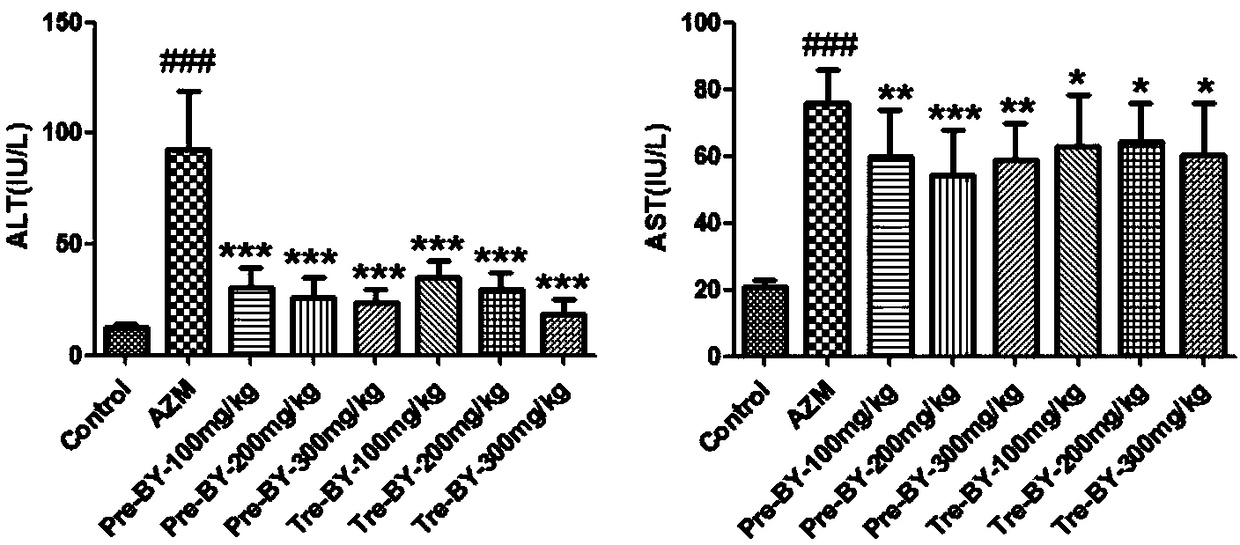
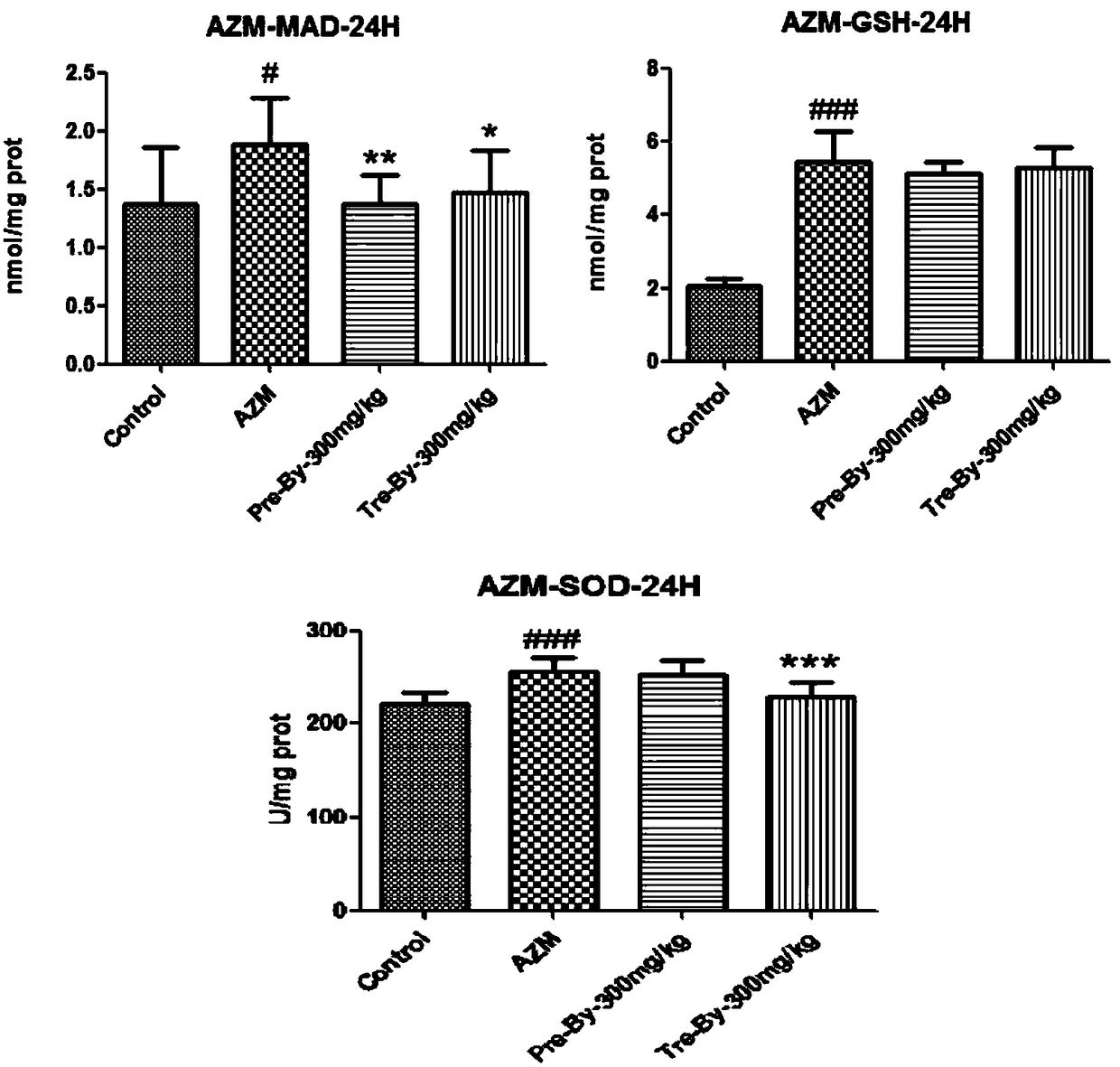
The invention belongs to the technical field of chemical medicines, and relates to uses of bicyclol and a pharmaceutically acceptable derivative thereof in prevention or treatment of drug-induced liver damage. According to the present invention, with the application of the bicyclol and the pharmaceutically acceptable derivative thereof to prevent or treat drug-induced liver damage, the ALT level and the AST level in serum can be significantly reduced, the activity of citrate synthase can be significantly restored, the liver mitochondrial gene copy number can be significantly increased, and theexpressions of liver autophagy gene, liver oxidative stress gene, liver endoplasmic reticulum stress gene and liver mitochondrial Sab gene can be significantly increased.
Owner:BEIJING UNION PHARMA FACTORY
Method for improving yield of glycolic acid in Escherichia coli
ActiveCN108315289AHigh yieldIncrease productionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliBatch fermentation
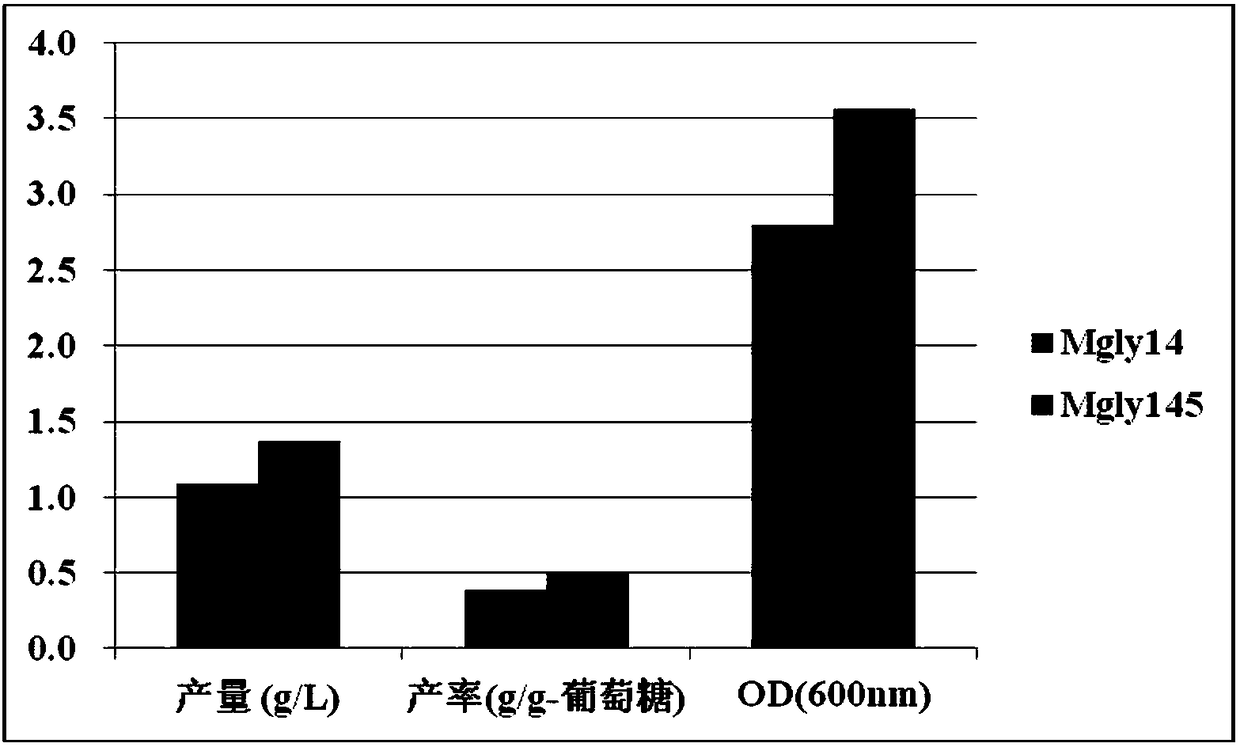
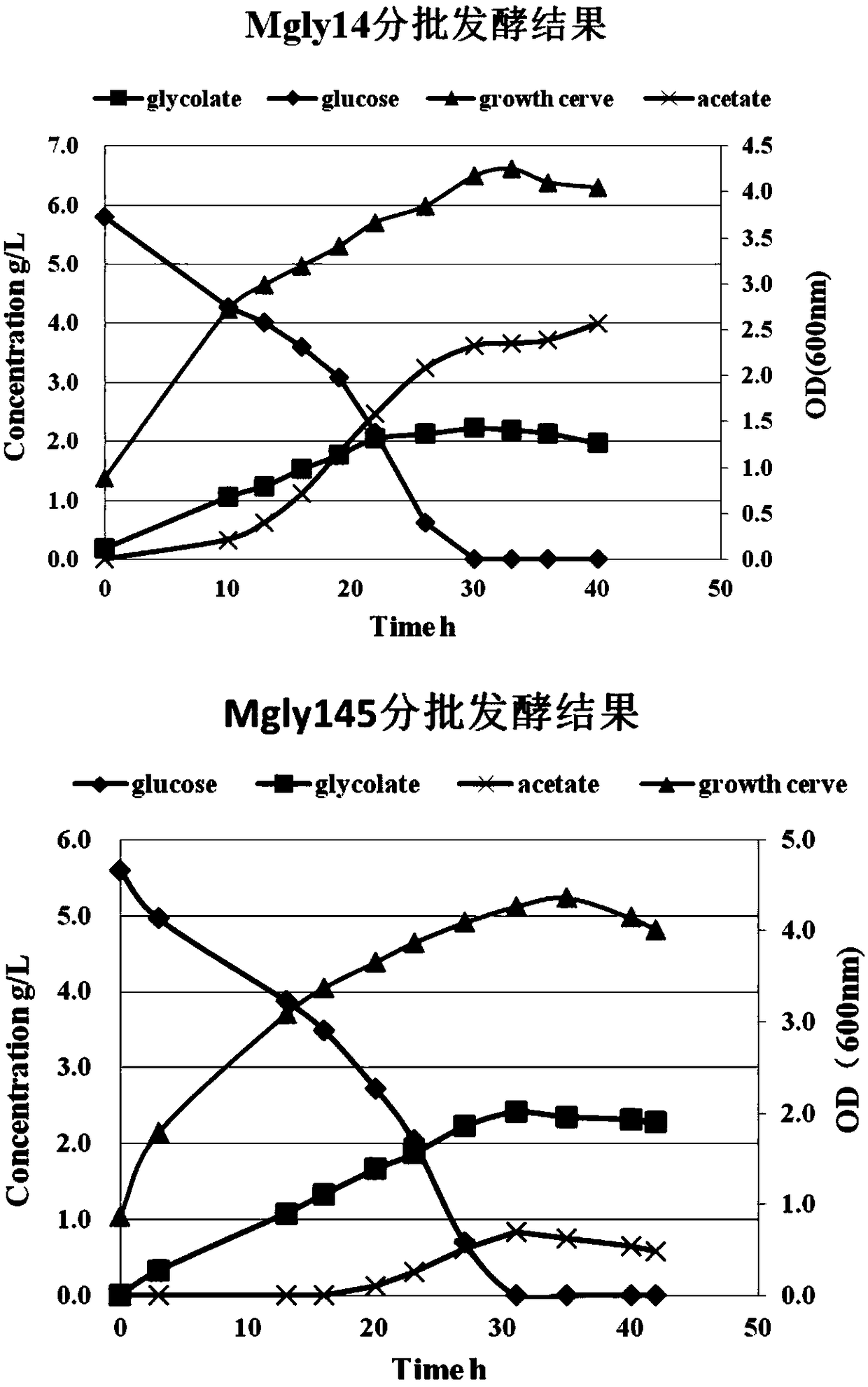
The invention discloses a method for improving a yield of glycolic acid in Escherichia coli and belongs to the technical field of bioengineering. According to the method disclosed by the invention, astrain of genetically engineered bacterium Mgly145 of citroyl synthetase shown in overexpression SEQ ID NO.1 is constructed; a glycolic acid yield of the genetically engineered bacterium in shake flask fermentation is 1.369g / L, and a productive rate is 0.504g / g-glucose; compared with genetically engineered bacterium Mgly14, the glycolic acid yield is improved by 30.9%; compared with Mgly14 in batch fermentation, the glycolic acid yield of the Mgly145 is improved by 8.8%, the productive rate is improved by 14.6%, and furthermore, acetic acid accumulation is reduced by 67.5%.
Owner:HUNAN NORCHEM PHARMACEUTICAL CO LTD
Deplating method for deplating brass surface tin-nickel coating
The invention relates to a deplating method for deplating a brass surface tin-nickel coating, and belongs to the technical field of electroplating. Prepared amino acid is mixed with hexose and fatty acid, acetylcoenzyme is added in the mixture and stirred, and after stirring is finished, the brass surface tin-nickel coating raw material is added in the mixture, active mud is introduced, and bottom aeration is carried out. After aeration is ended, citroyl synthetase and other enzymes are added, aeration treatment is carried out, and then a brass base body is taken out. The deplating method has the beneficial effects that the surface of brass is bright, the color of the base body is basically unchanged, no pin holes exist, and the corrosion volume is low; and meanwhile poisonous gas cannot be generated, and the environment is protected.
Owner:CHANGZHOU OPTICAL MATERIAL
Construction method of yarrowia lipolytica genetically engineered bacterium for producing citric acid or itaconic acid by using acetic acid
PendingCN113462588AEnvironmental protection methodFungiMicroorganism based processesCarboxylic acidCoenzyme A biosynthesis
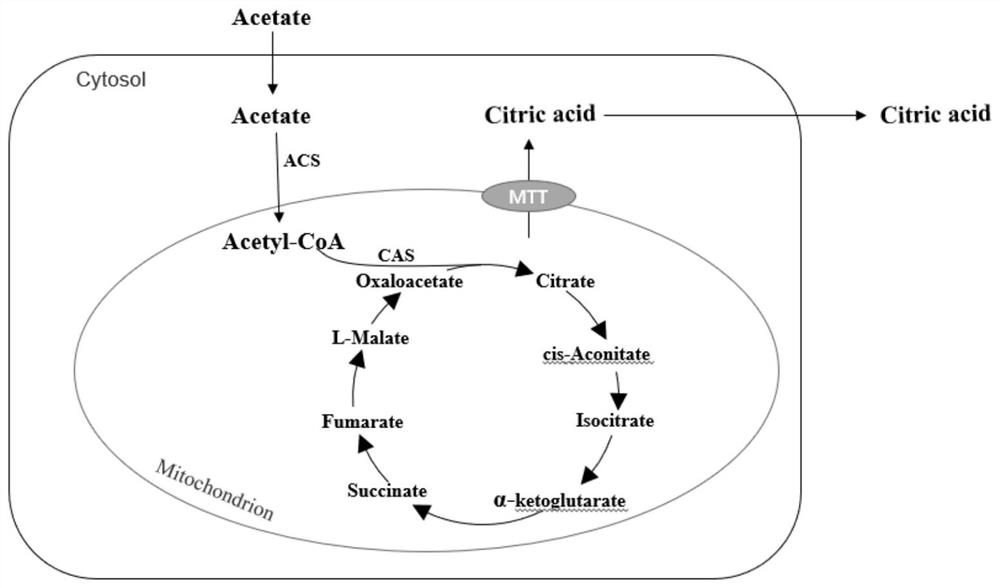
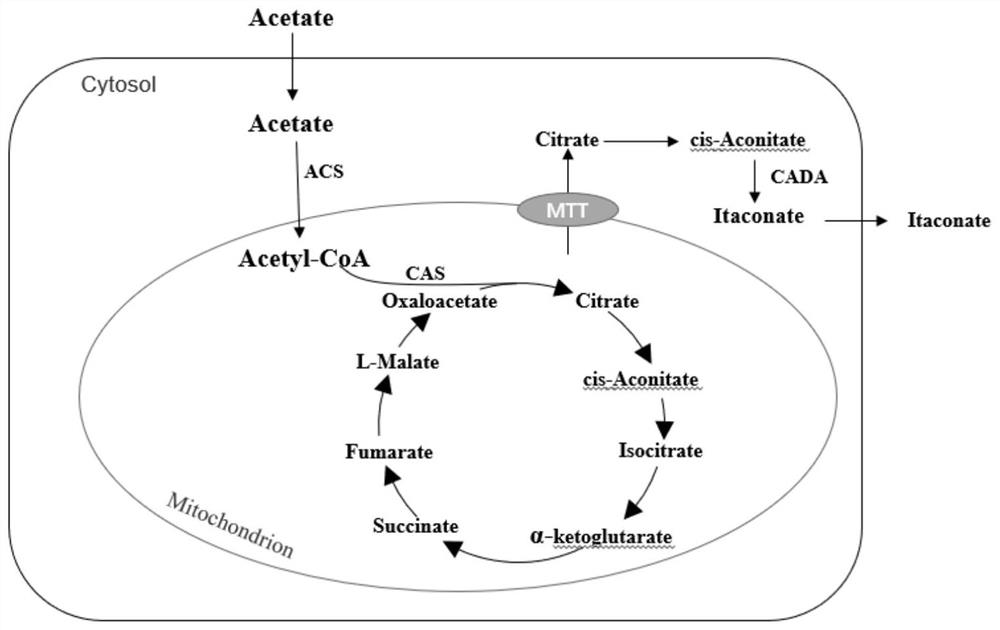
The invention relates to a construction method of yarrowia lipolytica genetically engineered bacterium for producing citric acid or itaconic acid by using acetic acid, and belongs to the field of gene engineering. The invention discloses a yarrowia lipolytica genetically engineered bacterium for producing citric acid or itaconic acid, which is prepared by the following steps: introducing a citric acid synthetase gene CAS, an acetyl-coenzyme A synthetase gene ACS, a mitochondrial carboxylic acid transporter gene MTT and a cis-aconitic acid decarboxylase gene CADA into leucine auxotrophic yarrowia lipolytica to construct and the yarrowia lipolytica genetically engineered bacterium YLA01 (containing genes CAS, ACS and MTT) and YLA02 (containing genes CAS, ACS, MTT and CADA) capable of metabolizing acetic acid. The yarrowia lipolytica genetically engineered bacterium constructed by the research can efficiently produce citric acid or itaconic acid by using acetic acid as a carbon source, and a good solution is provided for the waste acetic acid in the fermentation industry.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
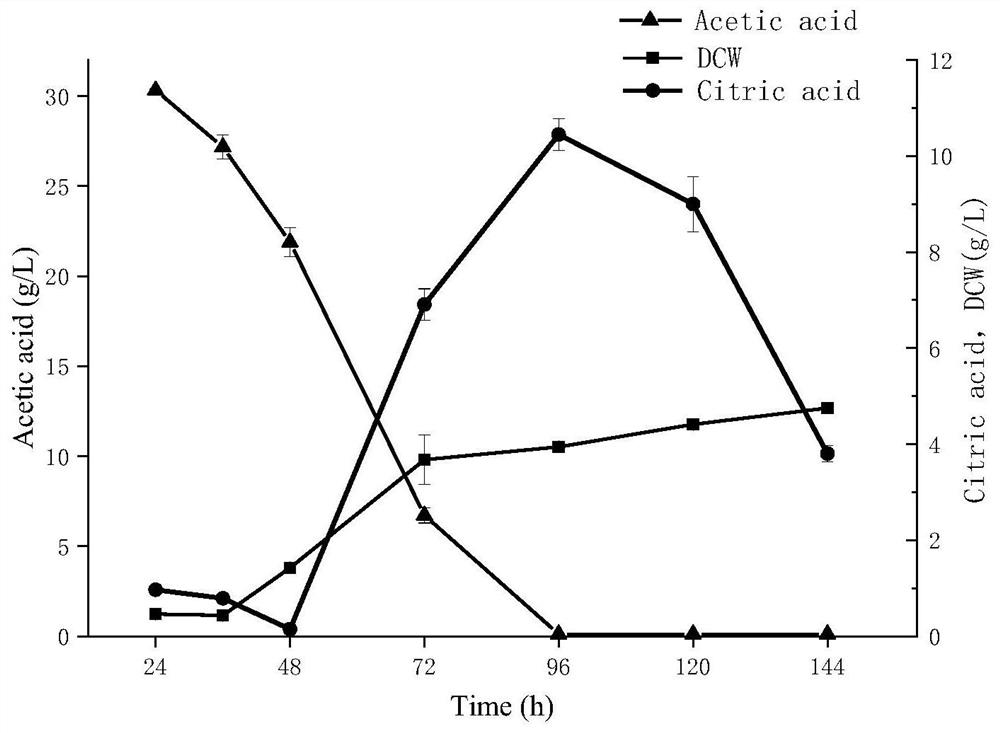
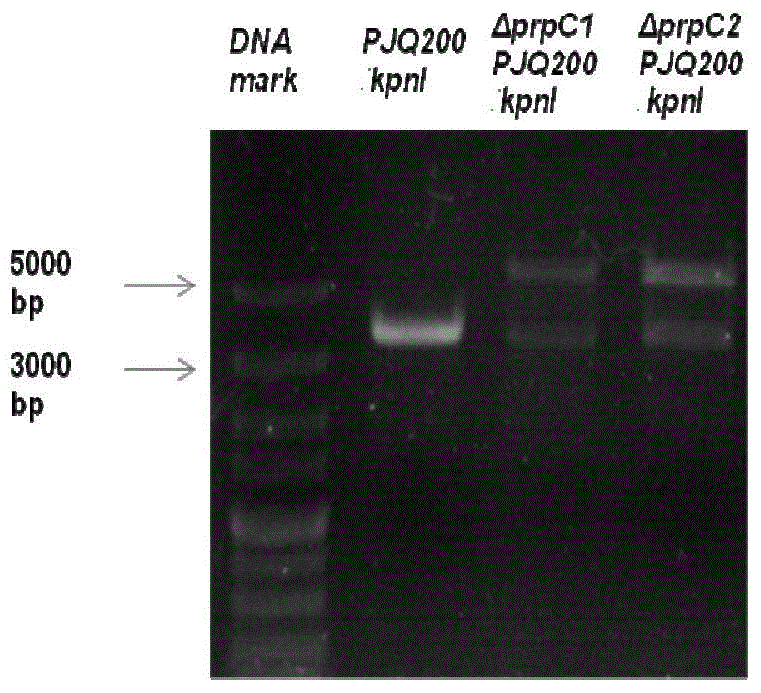
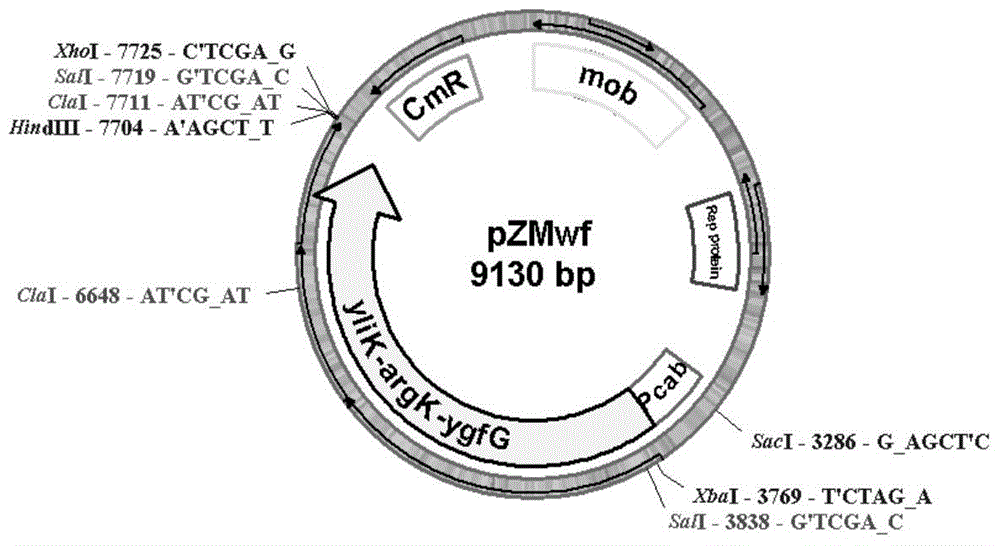
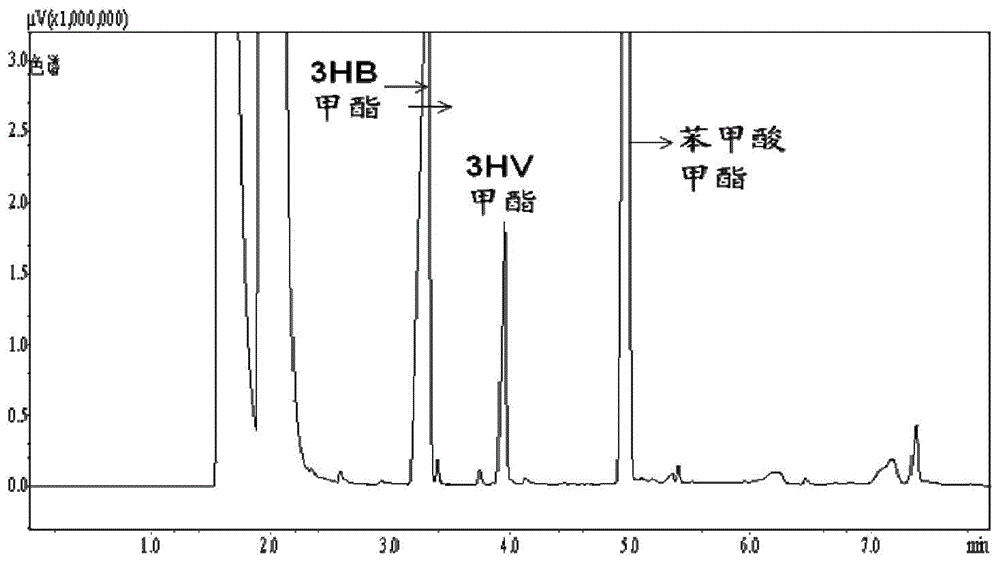
Genetically engineered bacterium for producing polyhydroxybutyric acid-valerate as well as construction method and application of genetically engineered bacterium
ActiveCN104450594AStrain SafeSave raw materialsBacteriaTransferasesHydroxybutyric acidCitrate synthase
The invention discloses a genetically engineered bacterium for producing polyhydroxybutyric acid-valerate as well as a construction method and application of the genetically engineered bacterium. The genetically engineered bacterium is a gene-deleted strain of ralstonia eutropha or is obtained by introducing a coding gene yliK of methylmalonyl-coA mutase, a coding gene argK of GTP kinase and a coding gene ygfG of methylmalonyl-coA decarboxylase to the ralstonia eutropha or the gene-deleted strain of the ralstonia eutropha; and the gene-deleted strain of the ralstonia eutropha is obtained by deleting at least one of a coding gene of 2-methyl citrate synthase-1 of the ralstonia eutropha and a coding gene of 2-methyl citrate synthase-2. In production of the polyhydroxybutyric acid-valerate, the recombinant bacterium constructed by the invention has the following advantages that the genetically engineered bacterium is safe in strain and relatively cheap in raw material, fermentation process is easy to control, and large-scale production is easy to realize.
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Citric acid synthesized enzyme gene and use thereof
InactiveCN1629295AImprove patienceShort cycleSugar derivativesFermentationGenetically modified riceEnzyme Gene
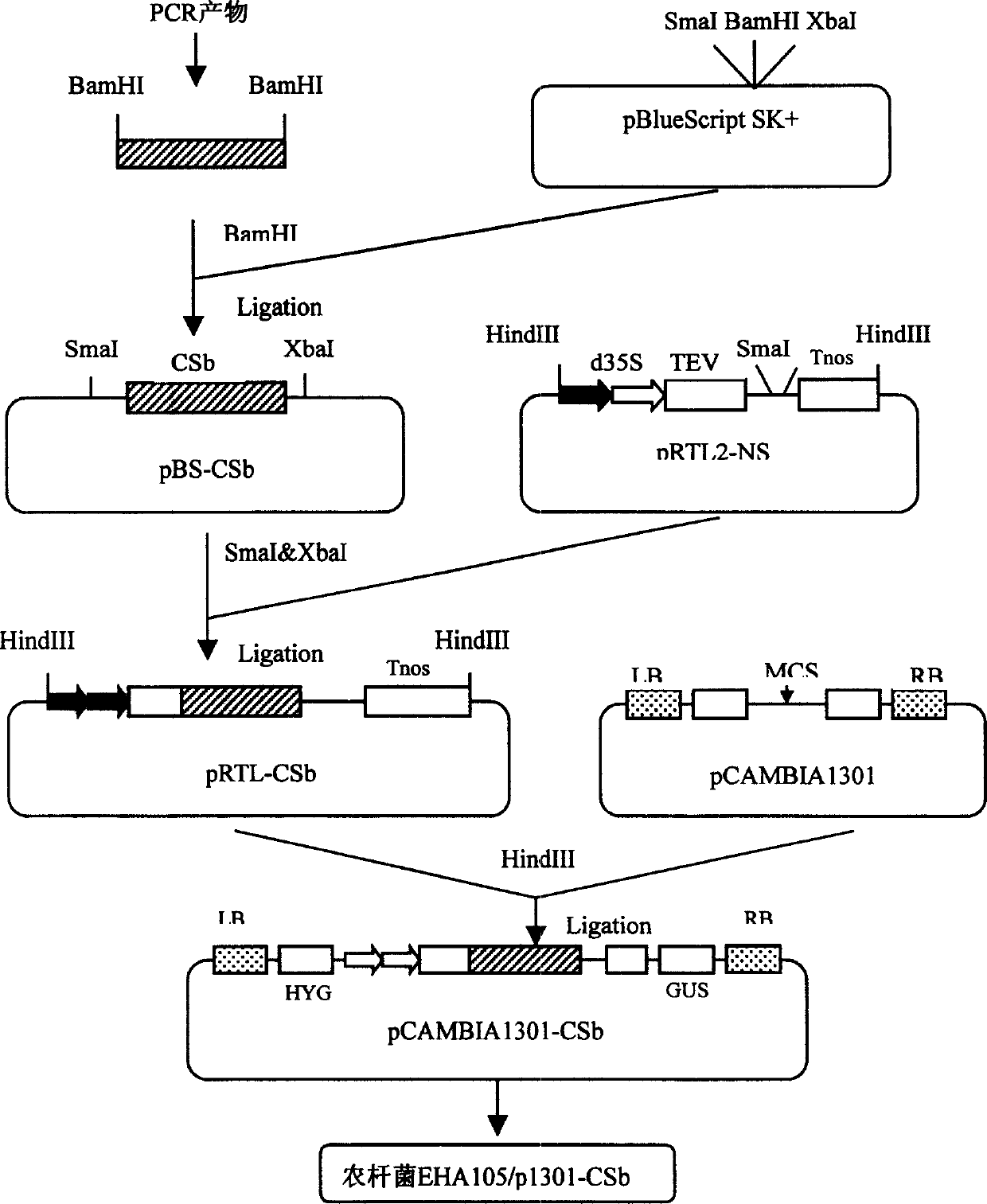
The invention discloses a novel citrate synthase gene and the use in rice improvement, which comprises, expanding coded sequence SEQ ID No.1 of citrate synthase gene (CS) from Pseudomonas sp. genome by means of PCR, appending plant gene highly performance expression element onto the two ends of the separated CS gene coded sequence, constructing super expression CS gene SEQ ID No.2, loading the SEQ ID No2 onto binary Ti-plasmid carrier pCAMBIA1301 suitable for agrobacteriocin mediated plant genetic conversion, constructing conversion carrier pCAMIA1301-CSb, leading the CS gene into rice receptor, identifying transgened strains, investigating the absorption state of the offspring strain to soil invalid phosphor, and breeding transgene strains with fine property.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Genetically engineered bacterium synthesizing L-asparaginate and construction method and application thereof
InactiveCN110218691AReduce consumptionPromote accumulationCarbon-nitrogen lyasesBacteriaBiotechnologyEscherichia coli
The invention discloses a genetically engineered bacterium synthesizing L-asparaginate. The genetically engineered bacterium is classified and named Escherichia coliDeltafumABCDeltaarcADeltaptsGDeltagltADeltaargG / pAA, and the preservation number of the genetically engineered bacterium is CCTCC NO:M2019170. The construction process of the genetically engineered bacterium comprises the steps that aspawn running strain fumarase encoding gene, a DNA transcription binding regulatory factor encoding gene, a glucose transport related gene, a citrate synthase encoding gene and an argininosuccinate synthase encoding gene are knocked out; an aspartase encoding gene and an asparagine synthetase A encoding gene are cloned to an expression plasmid, the recombinant plasmid is transformed into recombinant escherichia coli after gene knockout, and a target strain is obtained. The genetically engineered bacterium is synthesized into the L-asparaginate through fermentation, achieves a route for biosynthesizing and preparing the L-asparaginate by completely using glucose as a raw material, is efficient, green and environmentally friendly, and has economy.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
Construction of corynebacterium glutamicum independent of antibiotics and capable of efficiently producing gamma-aminobutyric acid
ActiveCN113583930AAvoid pollutionIncrease production capacityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesPhosphoenolpyruvate carboxylaseGlutamate decarboxylase
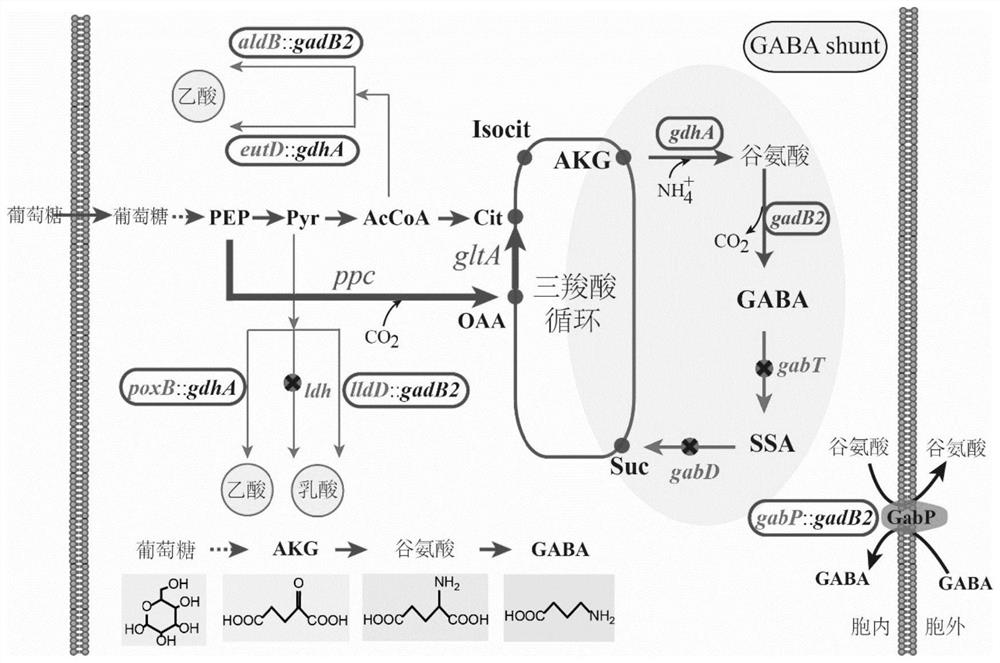
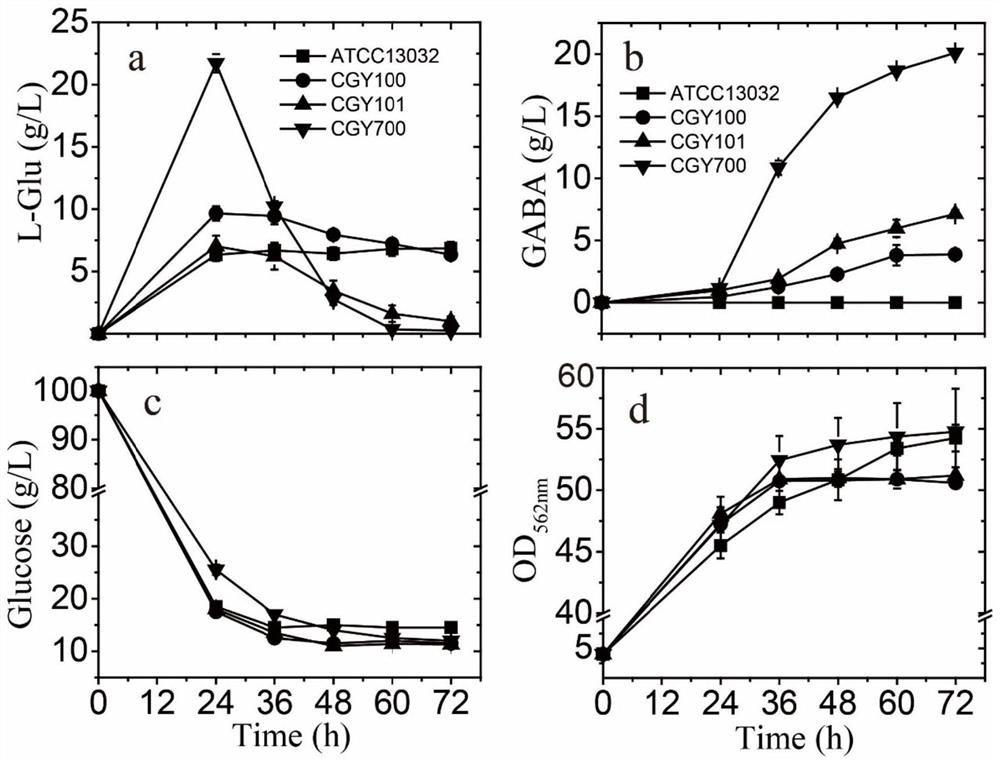
The invention discloses construction of corynebacterium glutamicum independent of antibiotics and capable of efficiently producing gamma-aminobutyric acid, and belongs to the technical field of genetic engineering and microbial fermentation. Corynebacterium glutamicum ATCC 13032 is used as a starting strain, a glutamate decarboxylase gene derived from Lactobacillus brevis is integrated into a Corynebacterium glutamicum genome to construct a production strain of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), and the GABA can be obtained by the strain by using glucose as a carbon source and utilizing a direct fermentation method. Gene expression regulation and control used in the method are all located in a genome and do not depend on a plasmid expression system, and therefore antibiotics do not need to be additionally added into a culture medium. Meanwhile, in the invention, the co-expression of phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase and citrate synthase is enhanced. Finally, the yield of the GABA obtained by a fed-batch fermentation method is 58.3 g / L.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Modified polypeptide with attenuated activity of citrate synthase and method for producing L-amino acid using the same
ActiveUS11499173B2Increase volumeBacteriaMicroorganism based processesCitrate synthaseOrganic chemistry
The present disclosure relates to a modified polypeptide with attenuated activity of citrate synthase and a method for producing an aspartate-derived L-amino acid using the modified polypeptide.
Owner:CJ CHEILJEDANG CORP
Genetically engineered bacterium for L-sarcosine production as well as construction method and application of genetically engineered bacterium
ActiveCN112522223AThe effect of enhancing gene expressionEnhance expressive abilityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesPhosphoenolpyruvate carboxylaseEscherichia coli
The invention discloses a genetically engineered bacterium for L-sarcosine production as well as a construction method and application of the genetically engineered bacterium. The genetically engineered bacterium is obtained by taking escherichia coli as a host, integrating and single copying imine reductase gene dpkA, single copying citrate synthase gene gltA, knocking out glyoxylic acid circulation inhibition gene iclR, knocking out malate synthase gene aceB, single copying isocitrate lyase gene aceA, single copying membrane combination transhydrogenase gene pntAB, knocking out 2-keto acid reductase gene ycdW, single copying phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase gene ppc, and knocking out pyruvate kinase gene pykF on a genome of the escherichia coli. After system metabolism transformation, theengineering bacteria can synthesize the L-sarcosine by taking glucose and methylamine as main raw materials, and the yield of the L-sarcosine can reach 10 g / L after fermentation is carried out in a 5L fermentation tank for 30 hours.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
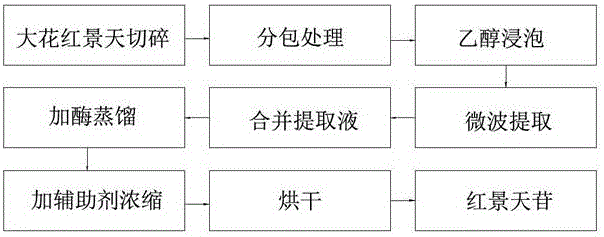
Process for extracting salidroside with assistance of ultrasonic waves
InactiveCN106317135AHigh extraction yieldHigh puritySugar derivativesSugar derivatives preparationSalidrosideUltrasonic assisted
The invention discloses a process for extracting salidroside with the assistance of ultrasonic waves. According to the process, the extraction of the salidroside in rhodiola crenulata can be assisted by adopting the ultrasonic waves; the rhodiola crenulata is extracted for four times by adopting four solvents; when the rhodiola crenulata is in a powder state, active ingredients are extracted more easily; the rhodiola crenulata is wrapped by adopting a medical non-woven fabric, and the active ingredients are extracted in virtue of the power of the ultrasonic waves, so that the extracting yield of the salidroside is improved; the process is simple in operation, and suitable for massive industrial production. Added citrate synthase can remove polysaccharides from the salidroside, so that the purity of the salidroside is improved, and the purity of the salidroside can reach 98 percent or above.
Owner:西藏自治区生产力促进中心
Ferrous ion diagnosis/determination reagent kit and method for determining ferrous ion concentration
InactiveCN101324608AFast measurementImprove accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementColor/spectral properties measurementsAconitaseCitrate synthase
The invention relates to a kit for diagnosing / mensurating ferrous ions by utilizing the technologies of the enzymic colorimetric method and the enzyme linked immunosorbent assay. The invention further relates to a method, a principle and the composition and the components of a reagent for mensurating the concentration of the ferrous ions, and belongs to the technology field of medical / food / environmental inspection and measurement. The main components of the kit include a buffer solution, cis-aconitic acid, coenzyme A, carbon dioxide, reduced coenzyme, aconitase, citrate synthetase, pyruvate dehydrogenase and a stabilizer. Through mixing a sample and the reagent by a certain volume ratio, an enzymatic reactions occurs, then the reactant is placed under an ultraviolet / visible light analyzer, and the velocity of the decrease in absorbance at 340nm of the dominant wavelength is detected, thereby mensurating the concentration of the ferrous ions.
Owner:SUZHOU ANJ BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
Generation of plants with altered oil content
Owner:AGRI GENETICS
Combination and screening method of dominant antigens of Helicobacter pylori based on CD4+ T cell immunization
InactiveCN106480003BImprove cleanlinessMild immunopathological damageAntibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsProtective antigenAntigen
The invention relates to a helicobacter pylori dominant antigen assembly based on CD4+T cell immunity and a preparation method. The dominant antigen assembly comprises the following three components and homologous protein of the three components: inosine monophosphate dehydrogenase, type II citrate synthase and urease B subunit, wherein the amino acid sequences are shown as SEQ ID NO.1, SEQ ID NO.2 and SEQ ID NO.3. The screened dominant antigen assembly based on CD4+T cell immunity has the obvious immune protection effect, has the protection effect superior to that of H.pylori holoprotein antigen, has strong capacity of scavenging helicobacter pylori, and causes extremely slight pathological injuries. The three immunity dominant antigens provided by the invention can induce the body to generate strong immune response reaction aiming at antigens, therefore, through the means of inducing the body to generate the response aiming at the immunoprotecive dominant antigens, or directly immunizing the body by adopting the protective antigens, the effective immune protection effect can be achieved on the helicobacter pylori infection, and the scheme can be used for the further study on the preventive and therapeutic polyvaccines of helicobacter pylori.
Owner:ARMY MEDICAL UNIV
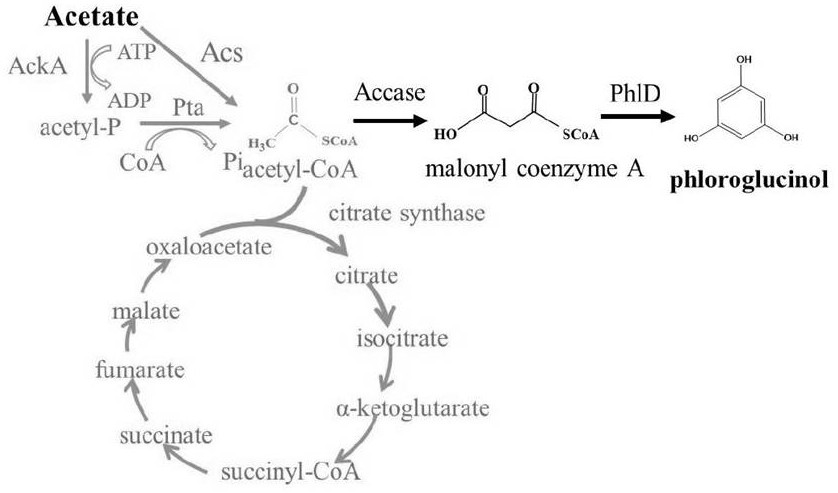
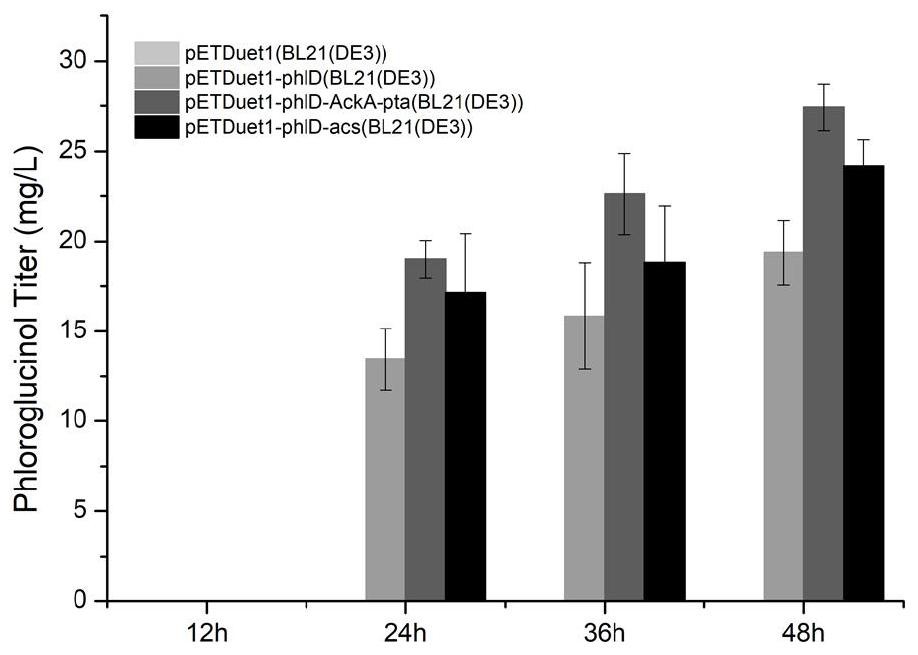
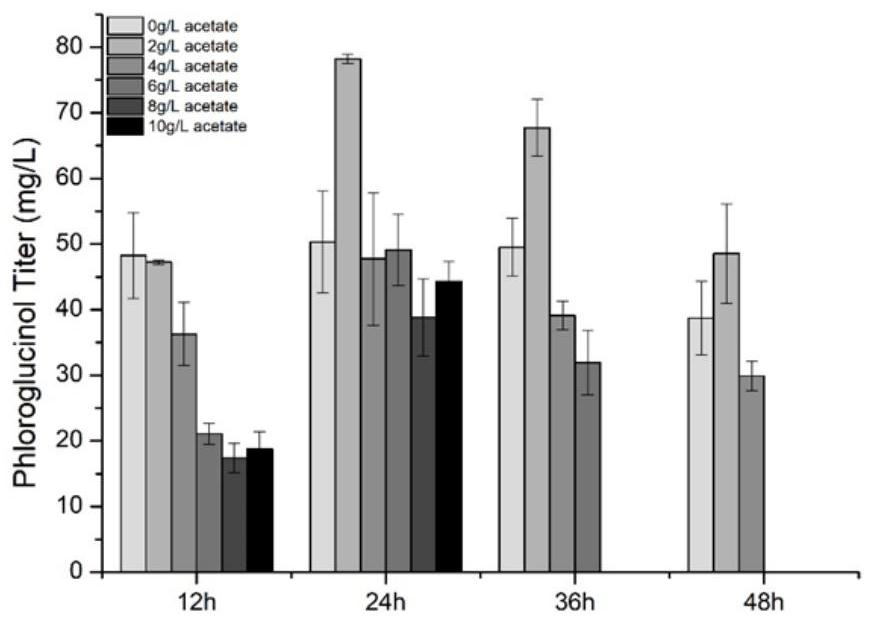
A kind of production method of phloroglucinol
ActiveCN110551769BIncrease productionMicroorganism based processesAcyltransferasesChemical synthesisCitrate synthase
As a high-value compound precursor, phloroglucinol has important application prospects in the fields of medical treatment and materials. Due to the disadvantages of traditional chemical synthesis methods in terms of cost and environmental protection, the present invention uses cheap and environmentally friendly acetic acid as a carbon source to realize the biosynthesis of phloroglucinol. The present invention first constructs two synthesis pathways using acetic acid as carbon source, verifies the feasibility of the method through fermentation, and determines that the pathway for expressing PhlD, AckA and Pta is the production pathway of phloroglucinol. The concentration of acetic acid and yeast extract in the M9 fermentation medium were respectively optimized to increase the production of phloroglucinol to 228mg / L. The feasibility of competitive pathway inhibition using CRISPR / dCas9 was demonstrated using the green fluorescent protein eGFP. Subsequent fermentation was carried out, and the expression level of citrate synthase in the competition pathway was reduced by CRISPRi, and the production of phloroglucinol was increased to 284mg / L. The invention proposes a novel production method of phloroglucinol, which provides a new strategy for the industrial production of phloroglucinol.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
A carrier and construction method for improving plant aluminum tolerance
InactiveCN102199620BLarge amount of synthesisPromote growthVector-based foreign material introductionPhosphoenolpyruvate carboxylaseNicotiana tabacum
The invention provides a carrier for enhancing aluminum-tolerance of a plant, and a method for establishing the same. The carrier is a plant expression vector having photoinduction promoters and phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase (PEPC) genes. The method for establishing the carrier comprises the following steps: searching for the sequence of the full length gene of Synechococcus vulcanus PEPC in GenBank and designing a pair of primers with sequences as described in the specification; recovering and purifying PEPC full length gene segments and connecting the segments to a pUCm-T vector; establishing an entry vector pENTER*-PrbcS-PEPC; establishing a plant expression vector pH2-35S-PrbcS-PEPC. In the invention, the activity of citrate synthase of tabacoo with transgenic PEPC and CS genes is 2.4 to 2.6 times that of wild tobacco, and the activity of phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase of such tabacco is 2.2 to 2.4 times that of wild tobacco. The special-purpose carrier provided in the invention can exert great influence on the improvement of aluminum-tolerance of a plant, and particularly, can significantly promote aluminum-tolerance of plants grown in acid red soil in southern China, thereby providing a novel approach for variety improvement of plants.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com