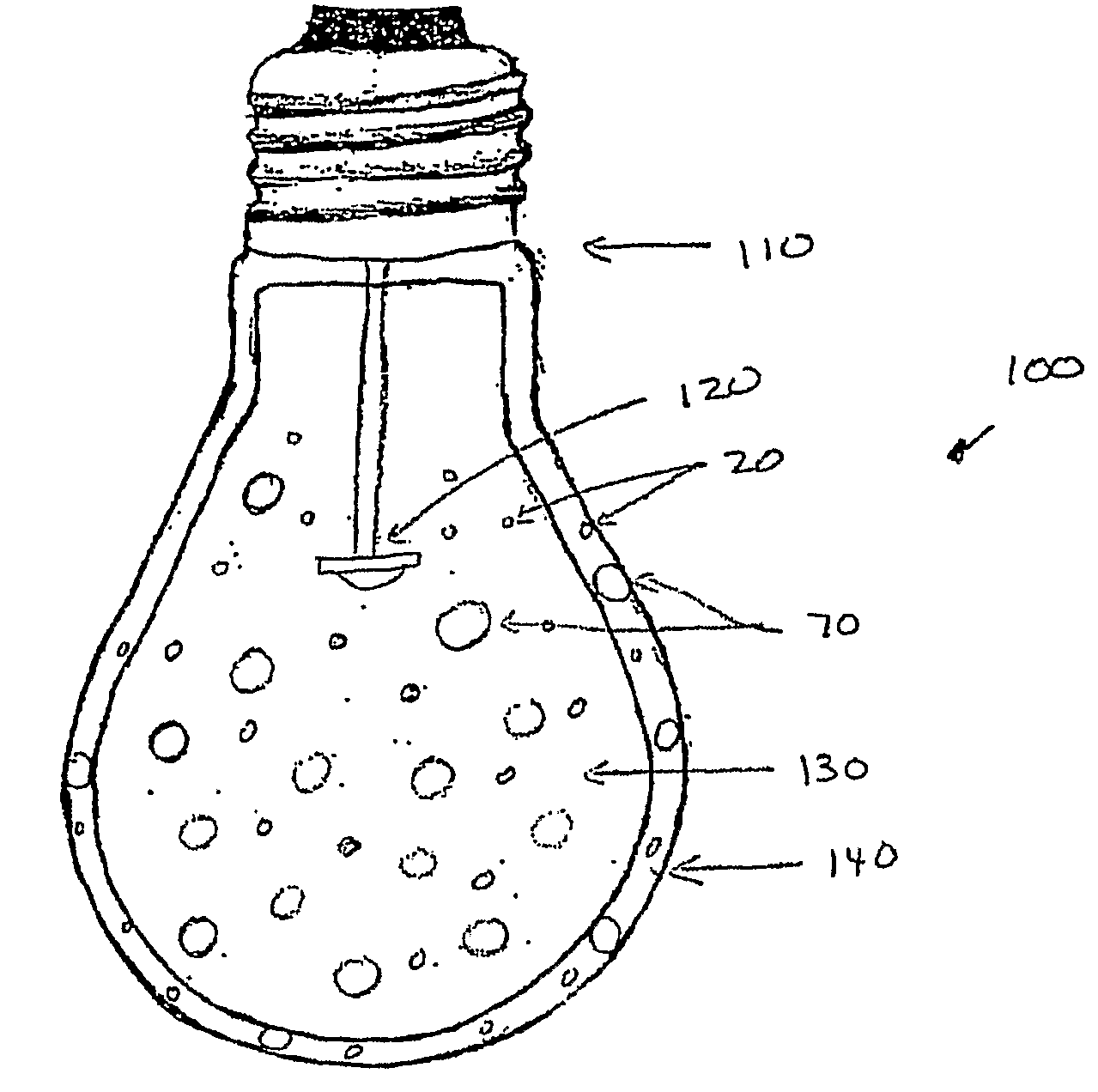
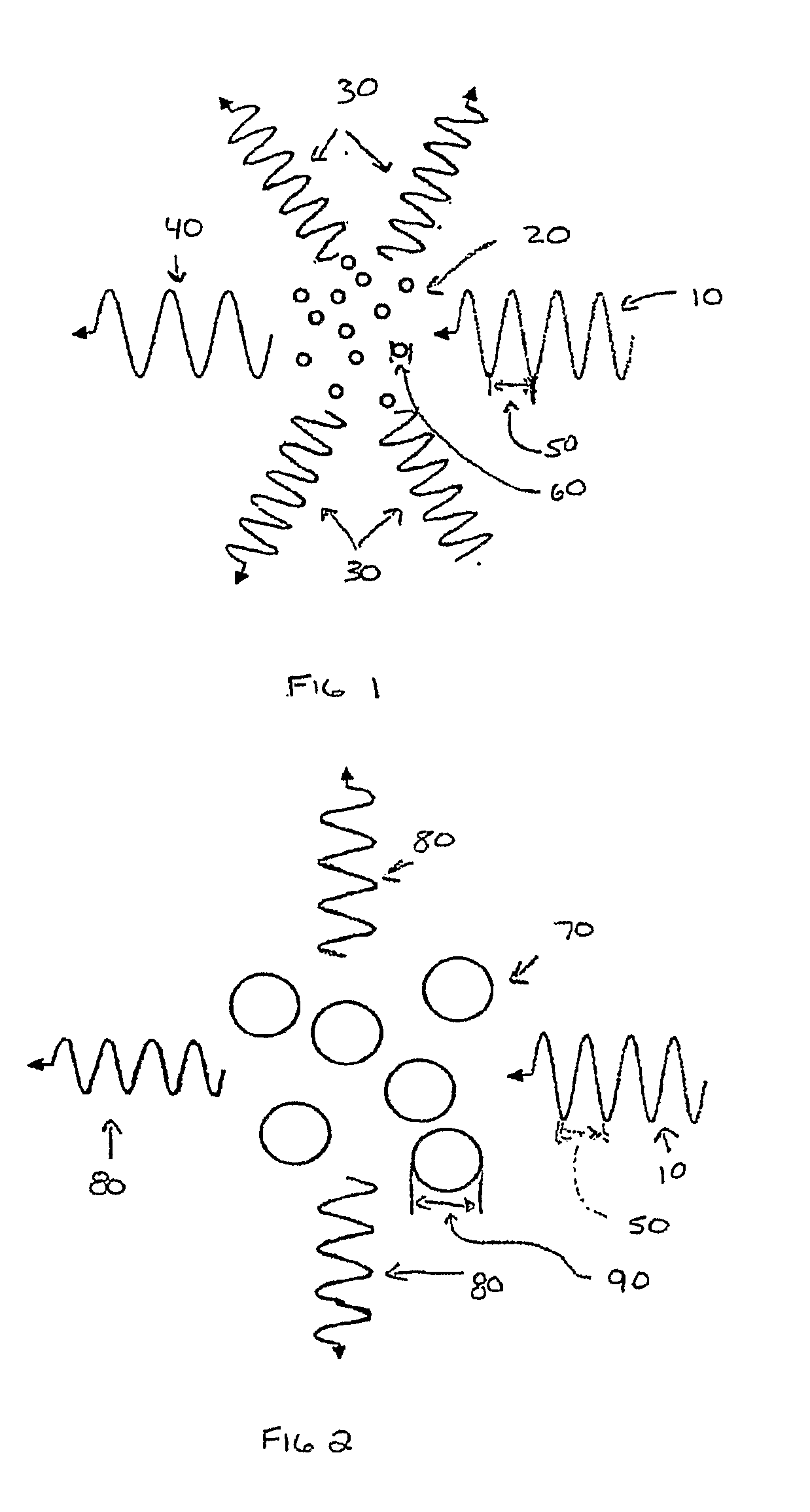
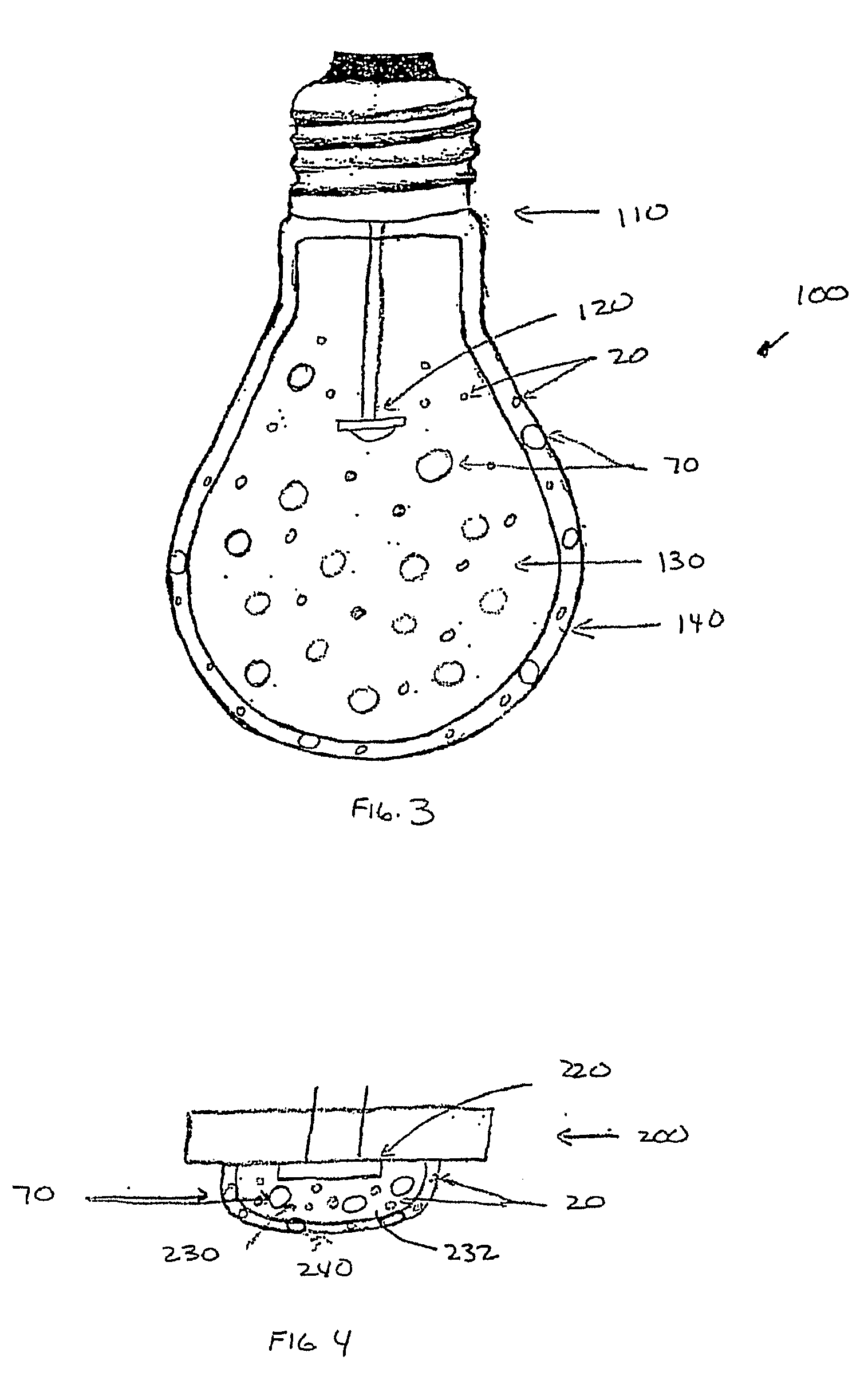
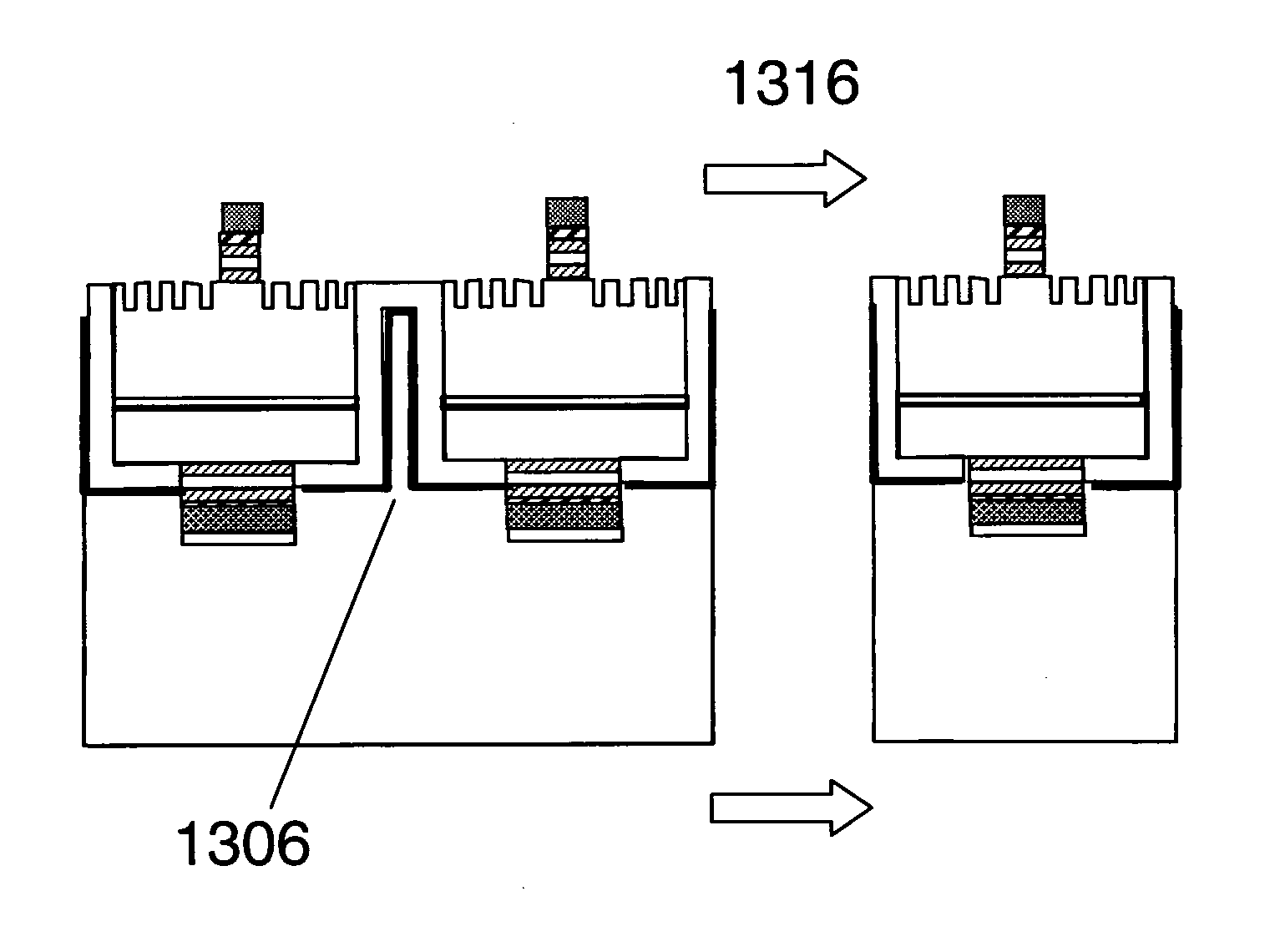
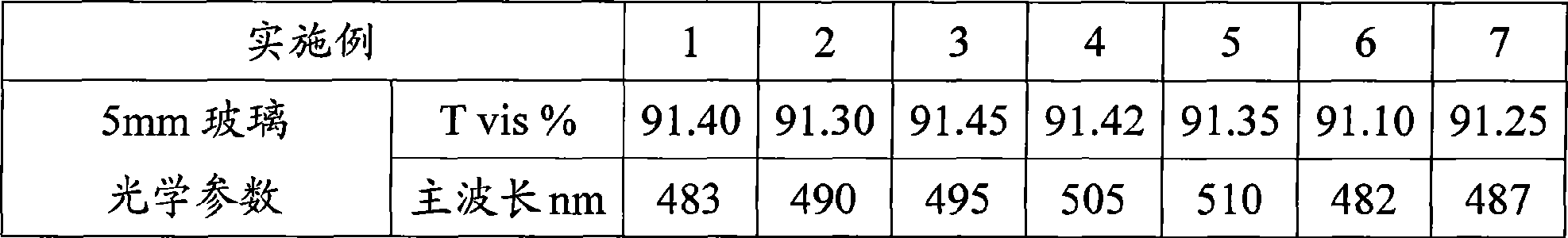Patents
Literature
628 results about "Dominant wavelength" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
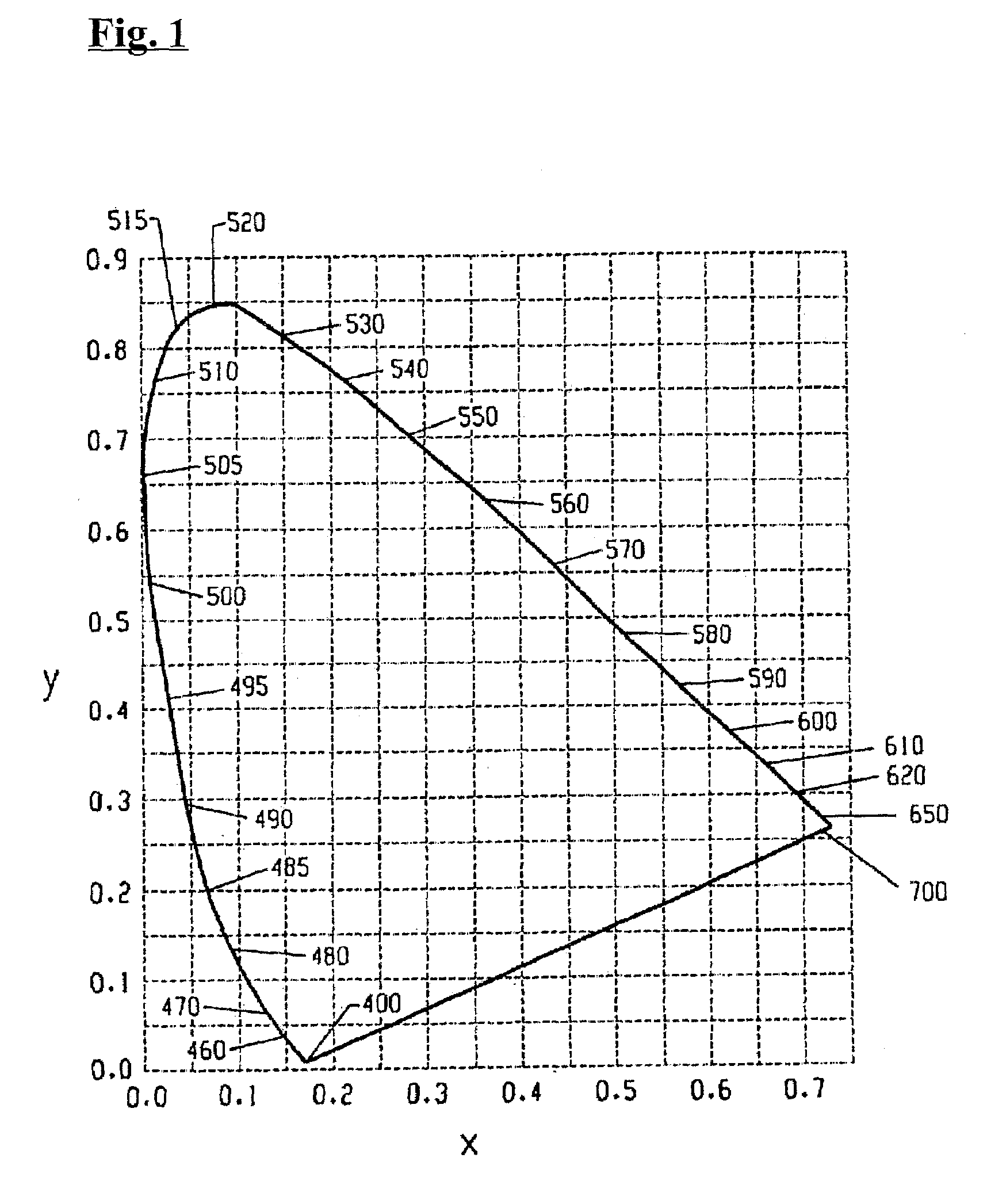
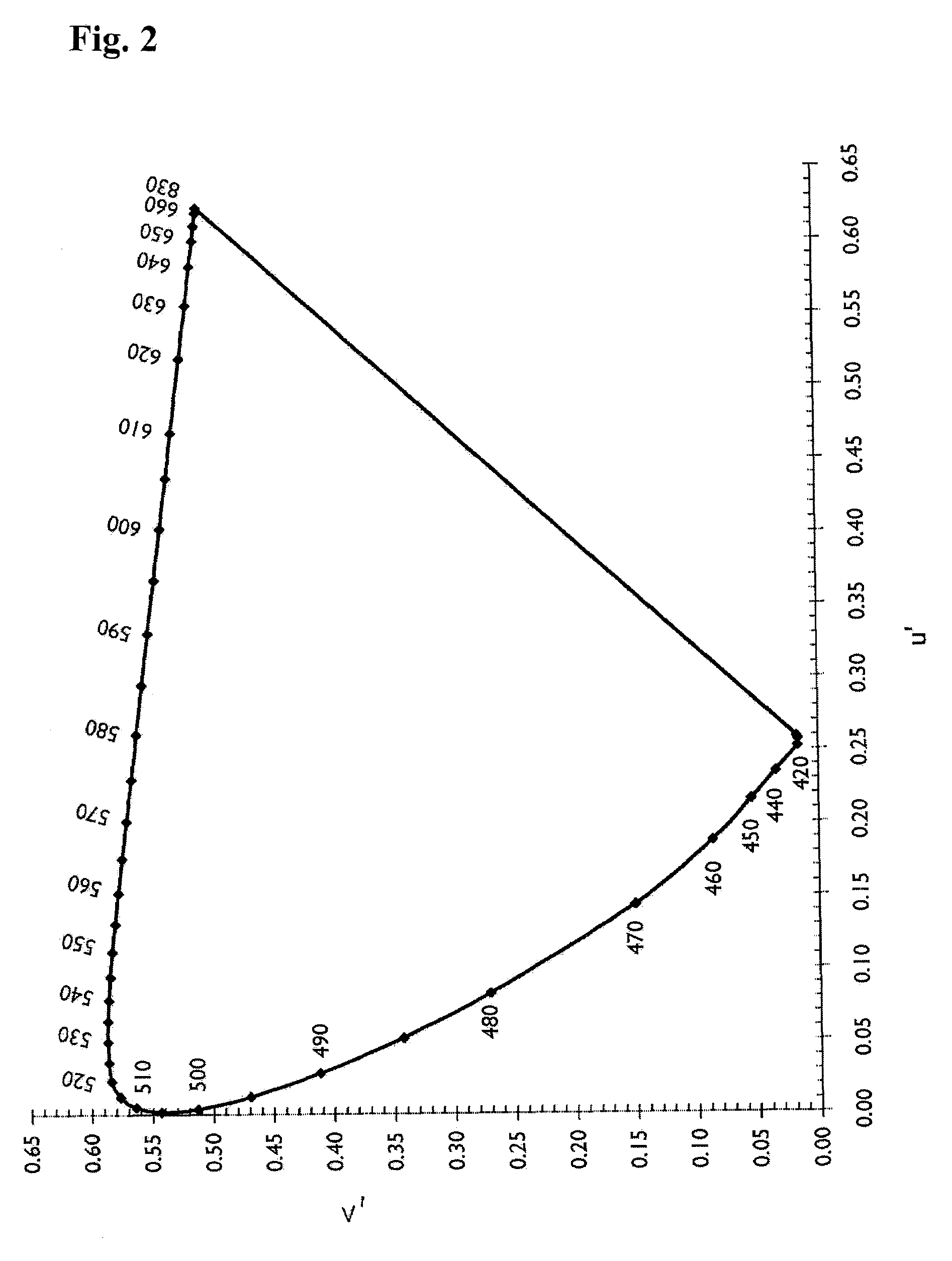
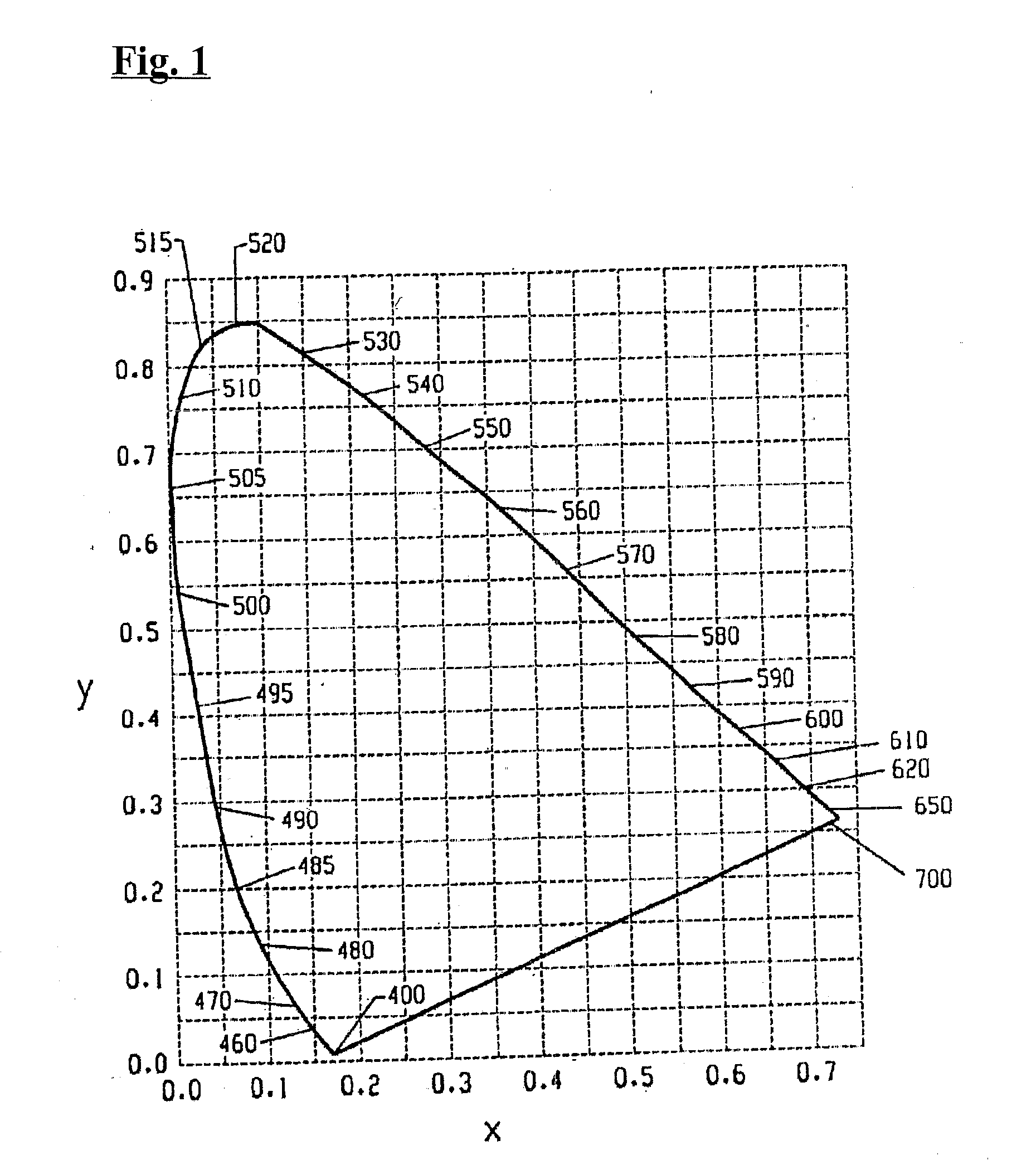
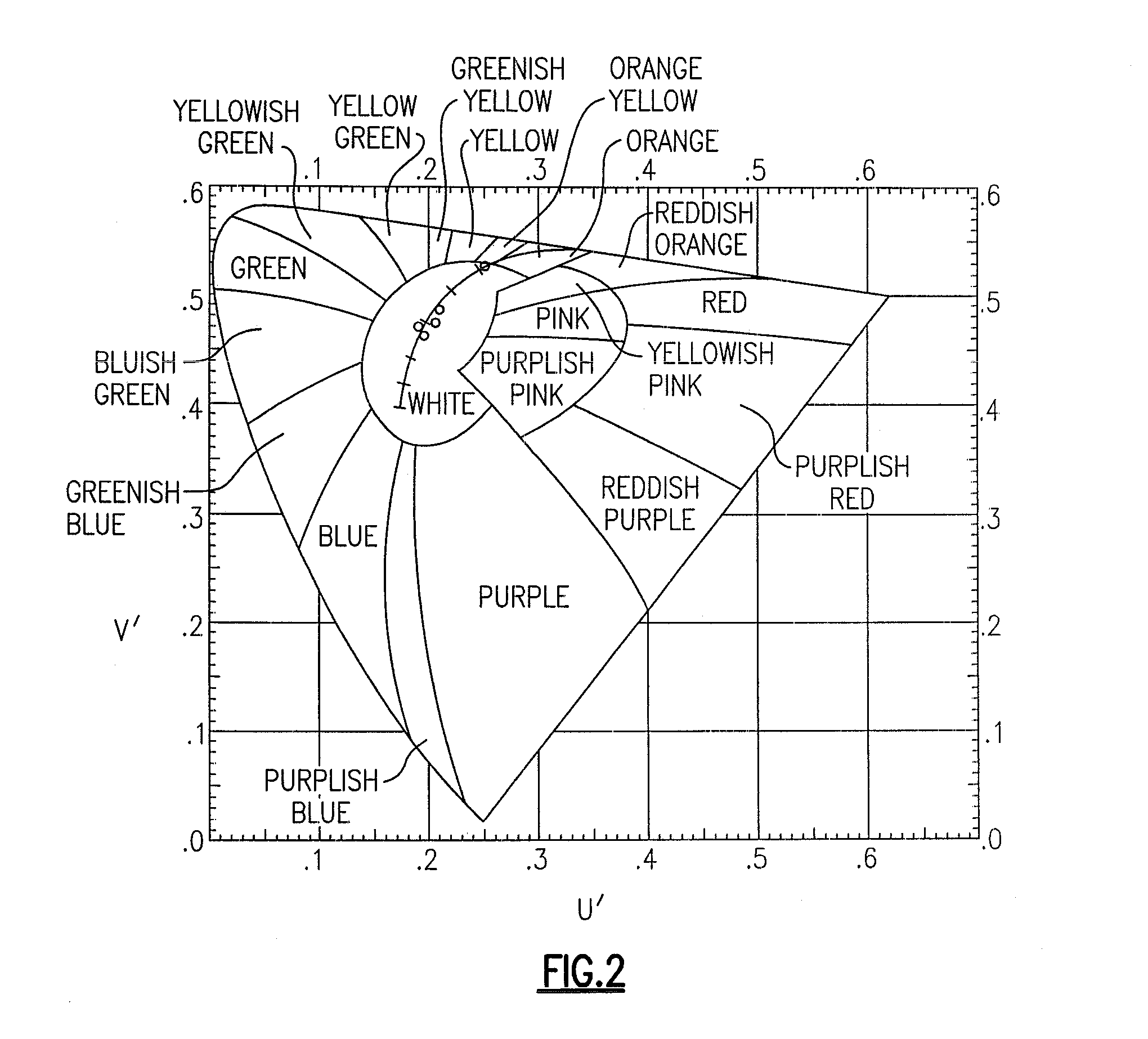
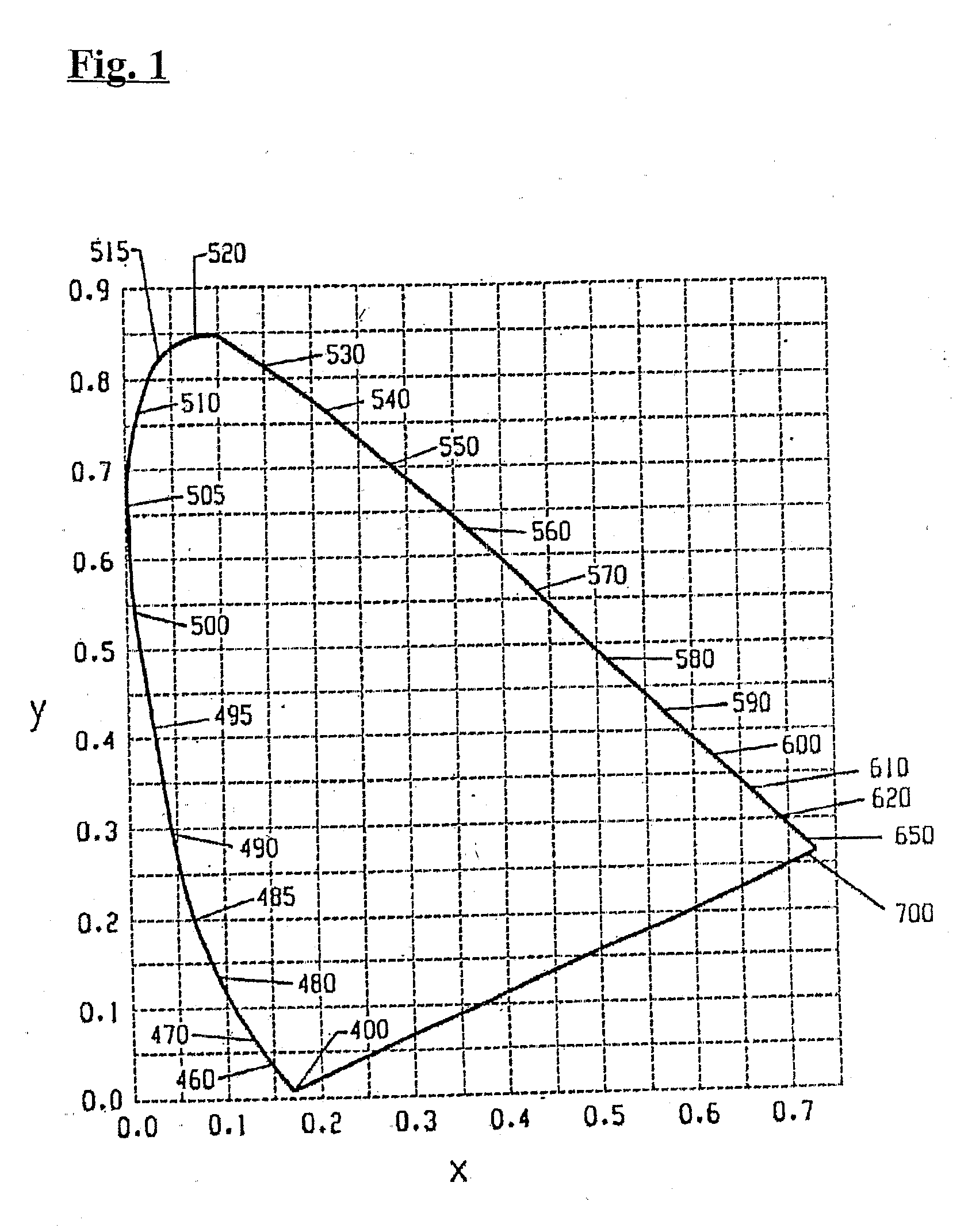
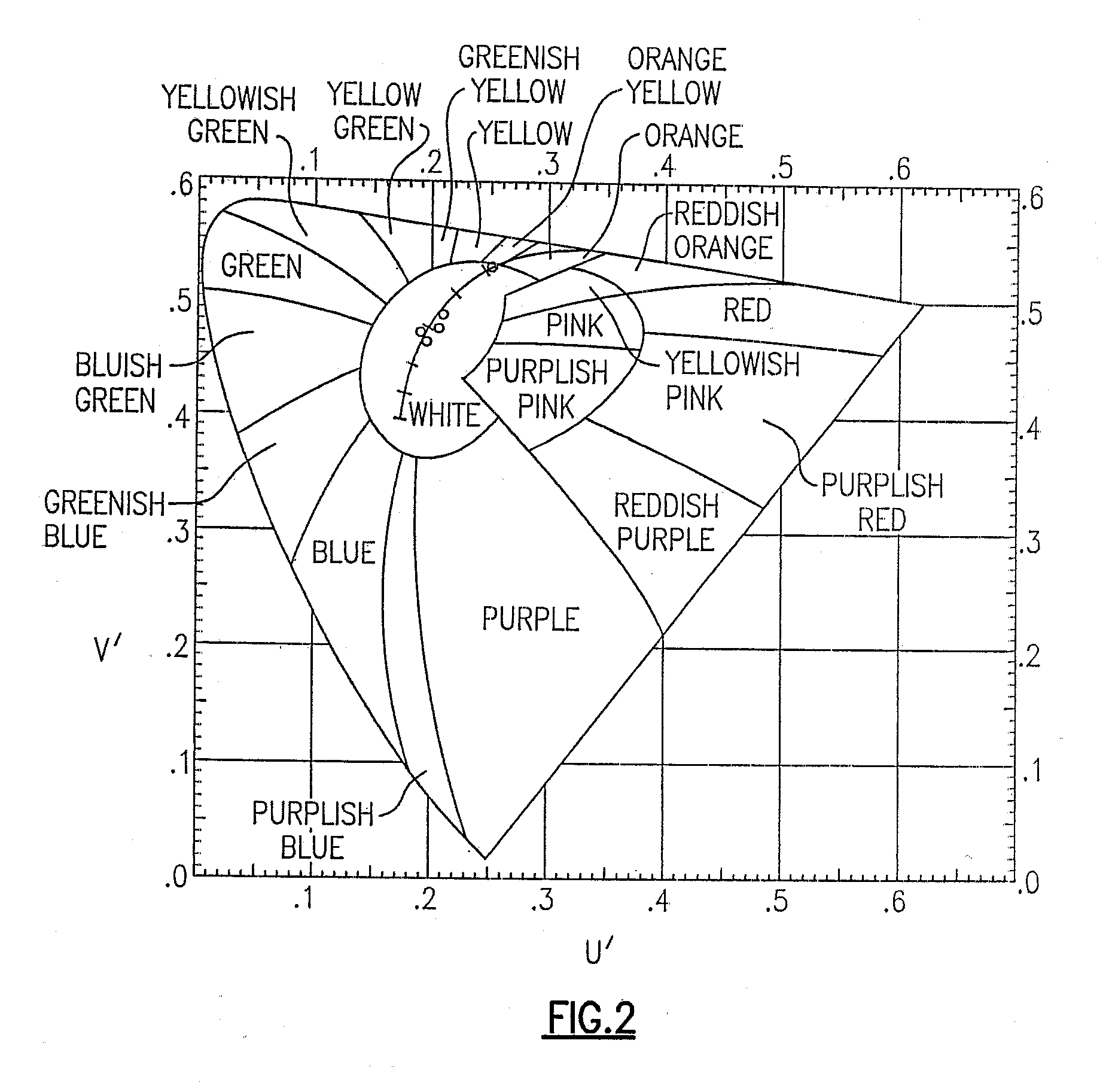
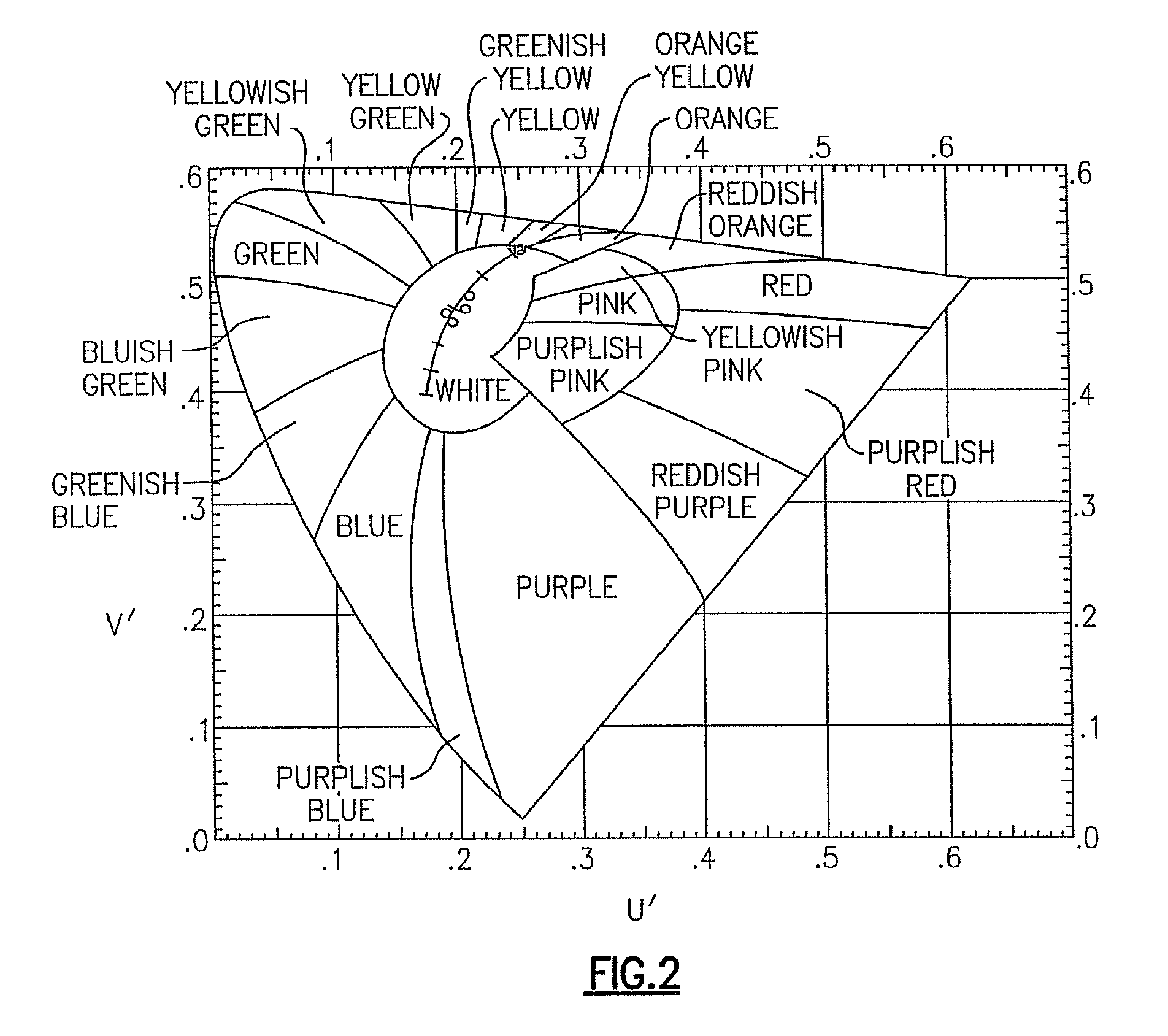
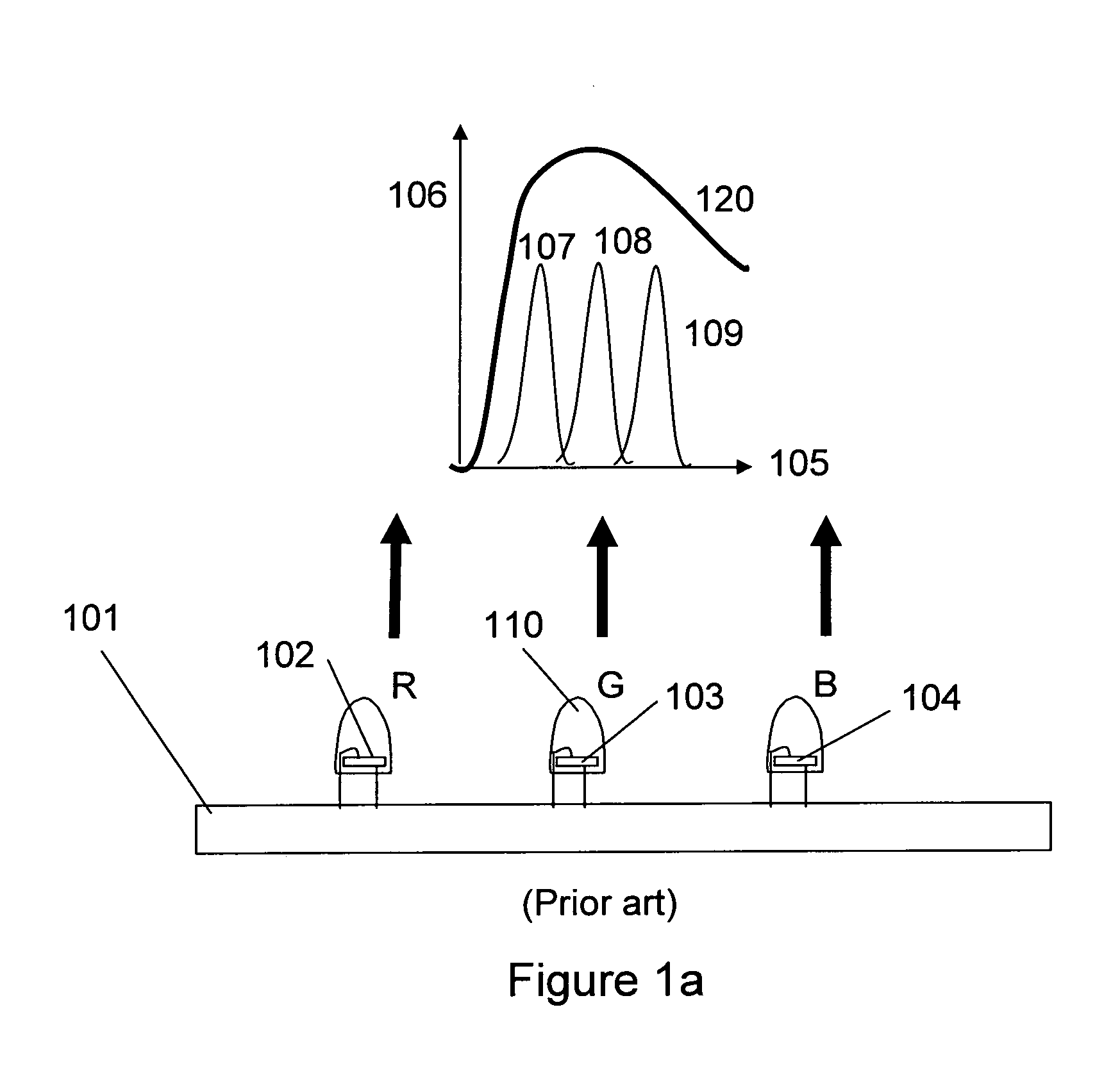
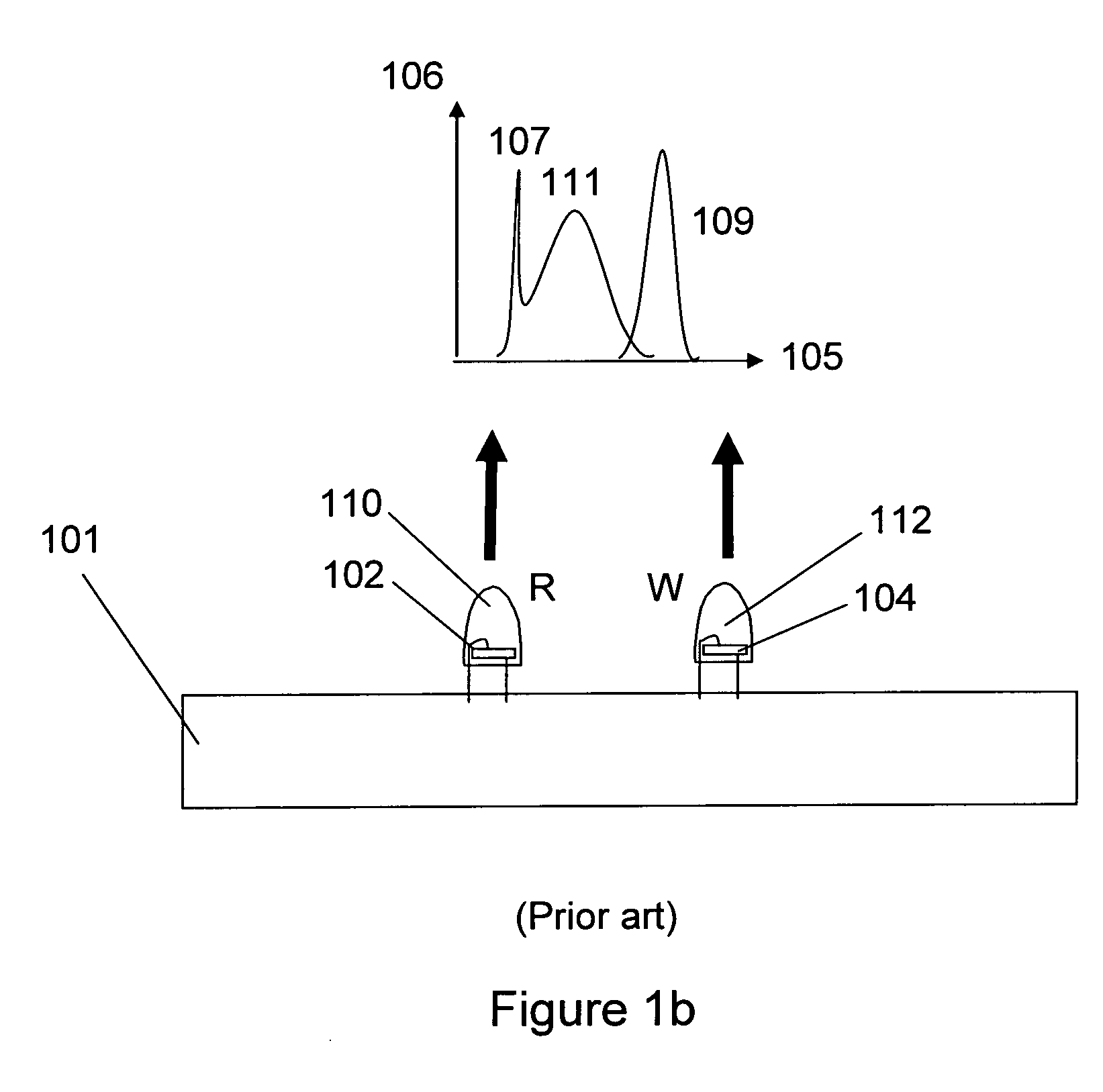
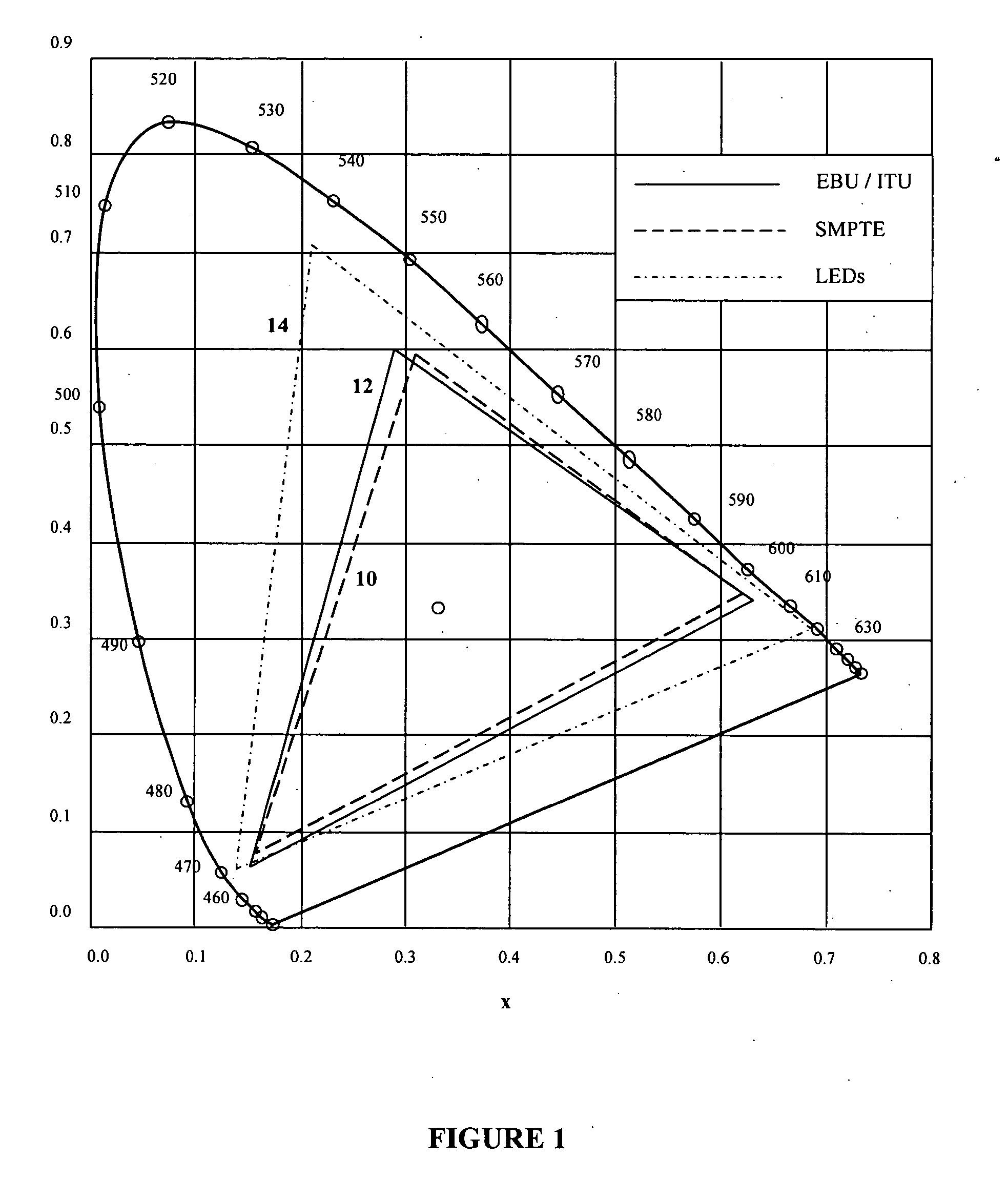
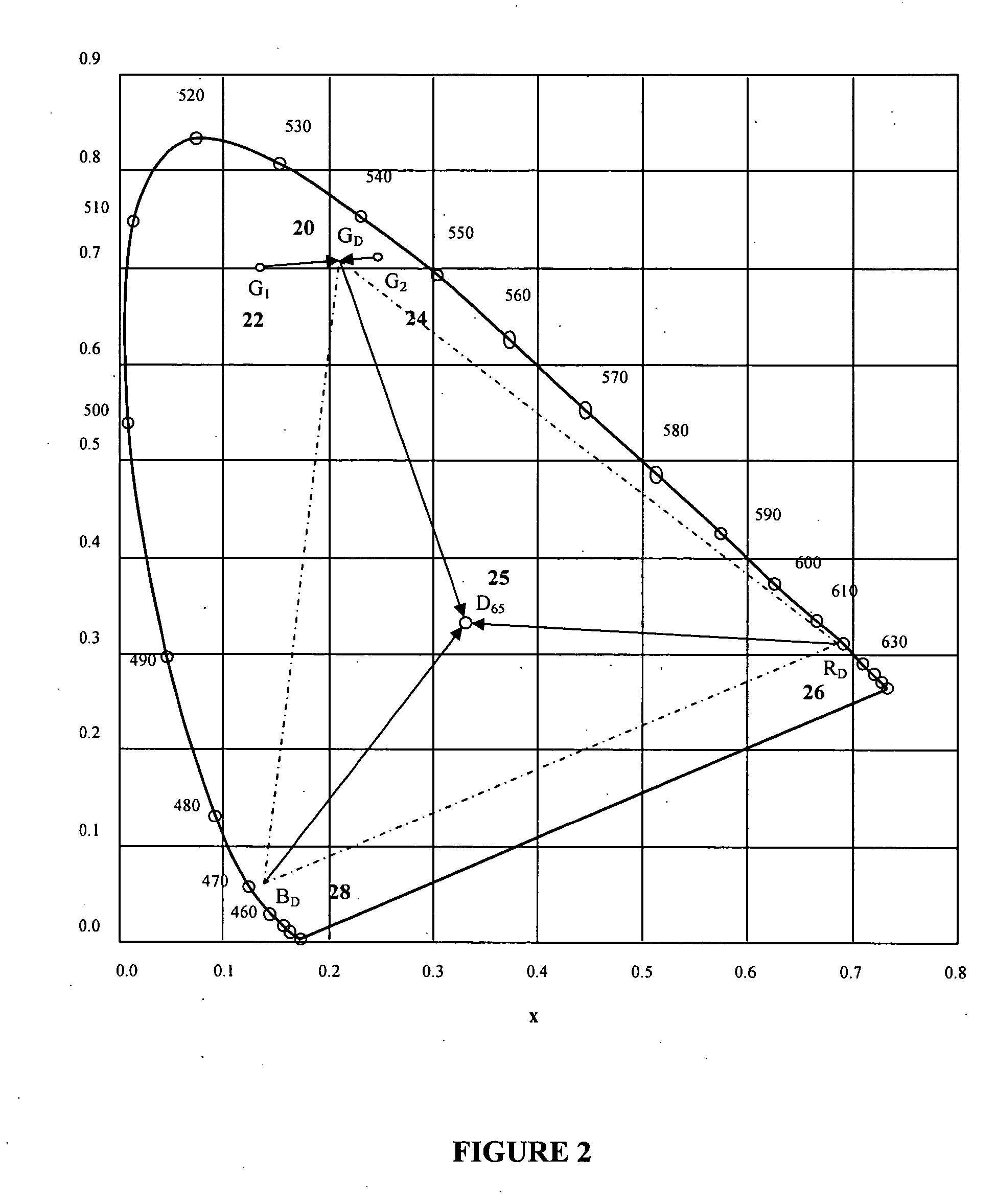
In color science, the dominant wavelength (and the corresponding complementary wavelength) are ways of characterizing any light mixture in terms of the monochromatic spectral light that evokes an identical (and the corresponding opposite) perception of hue. For a given physical light mixture, the dominant and complementary wavelengths are not entirely fixed, but vary according to the illuminating light's precise color, called the white point, due to the color constancy of vision.
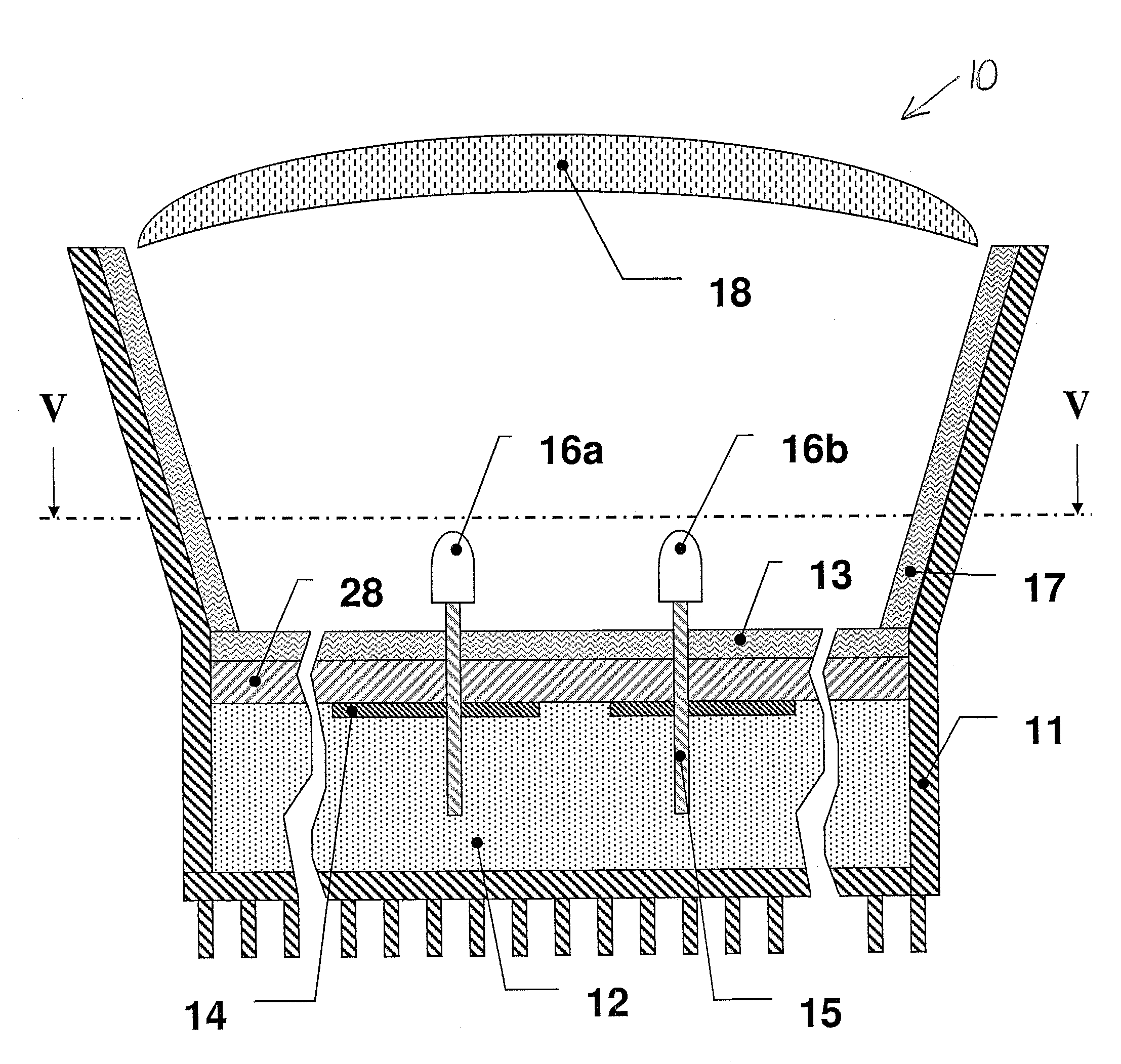
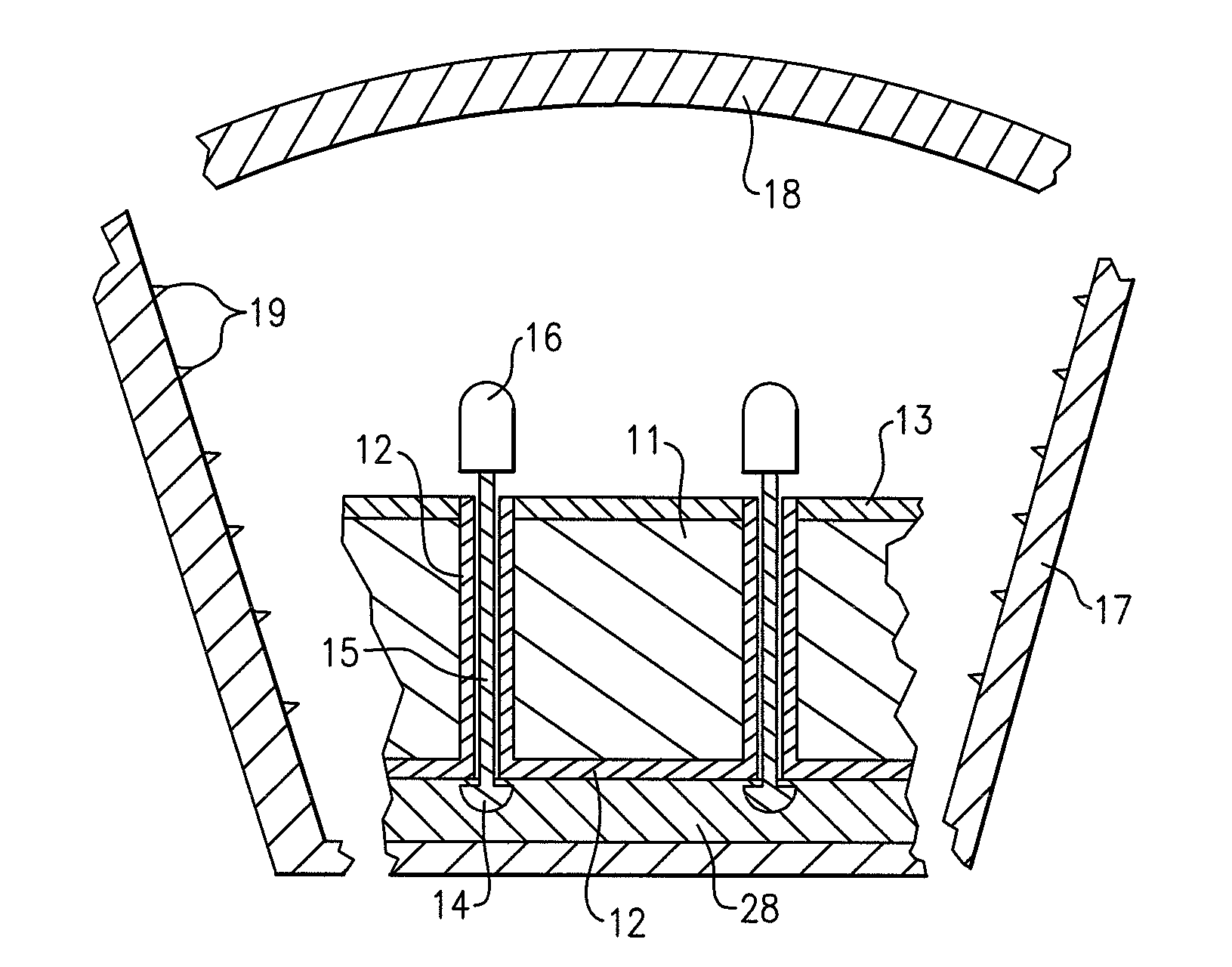
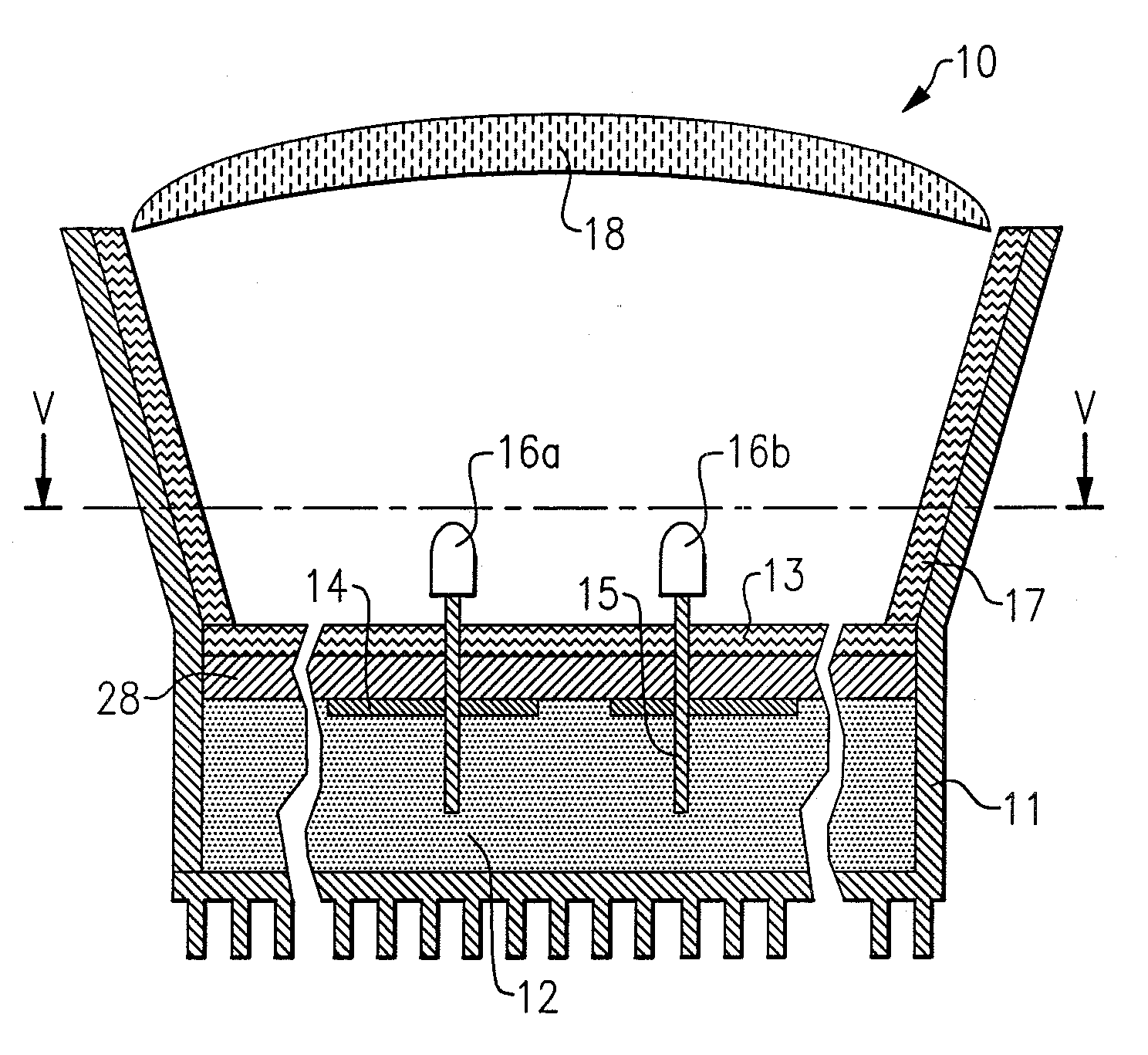
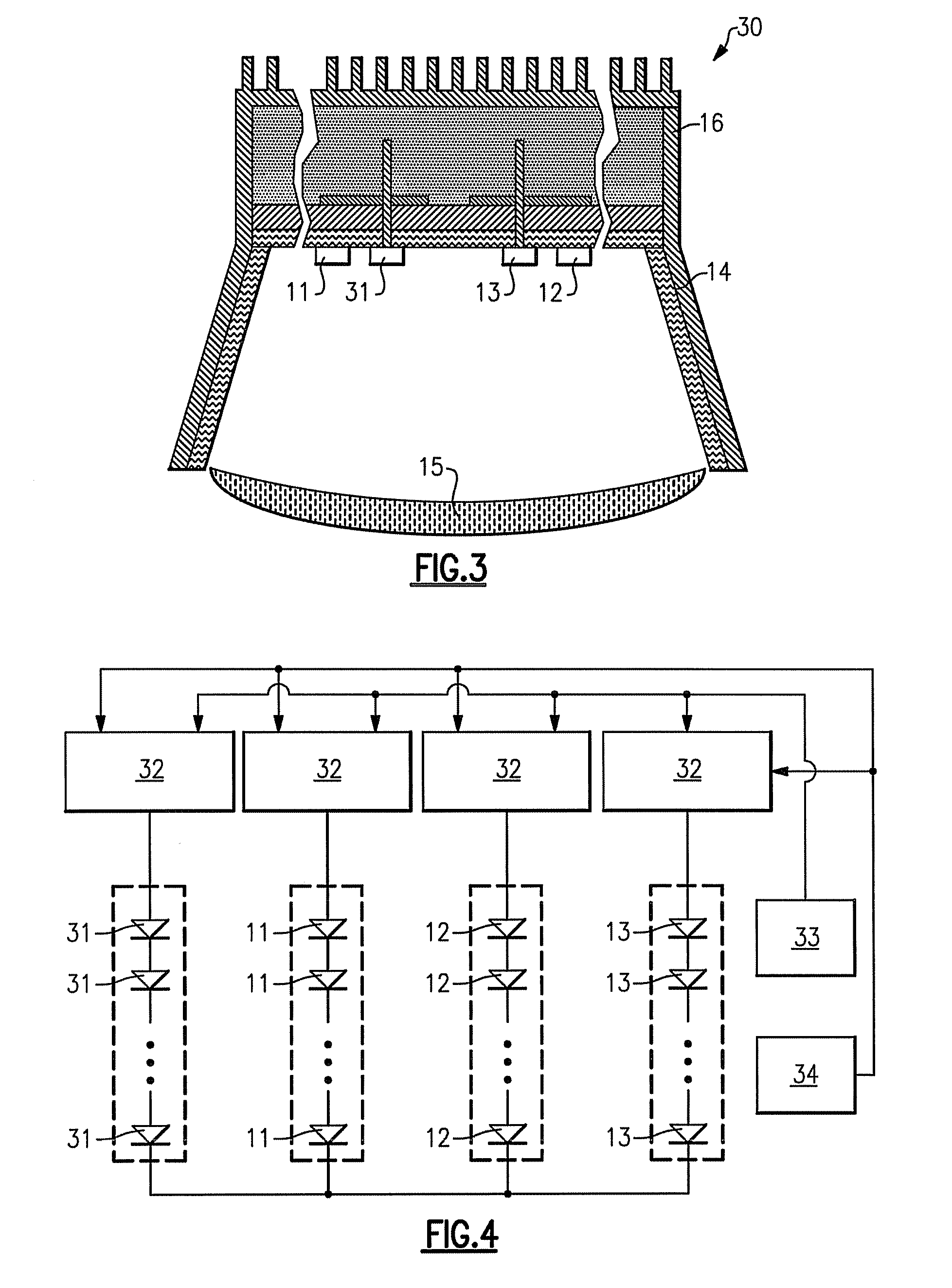
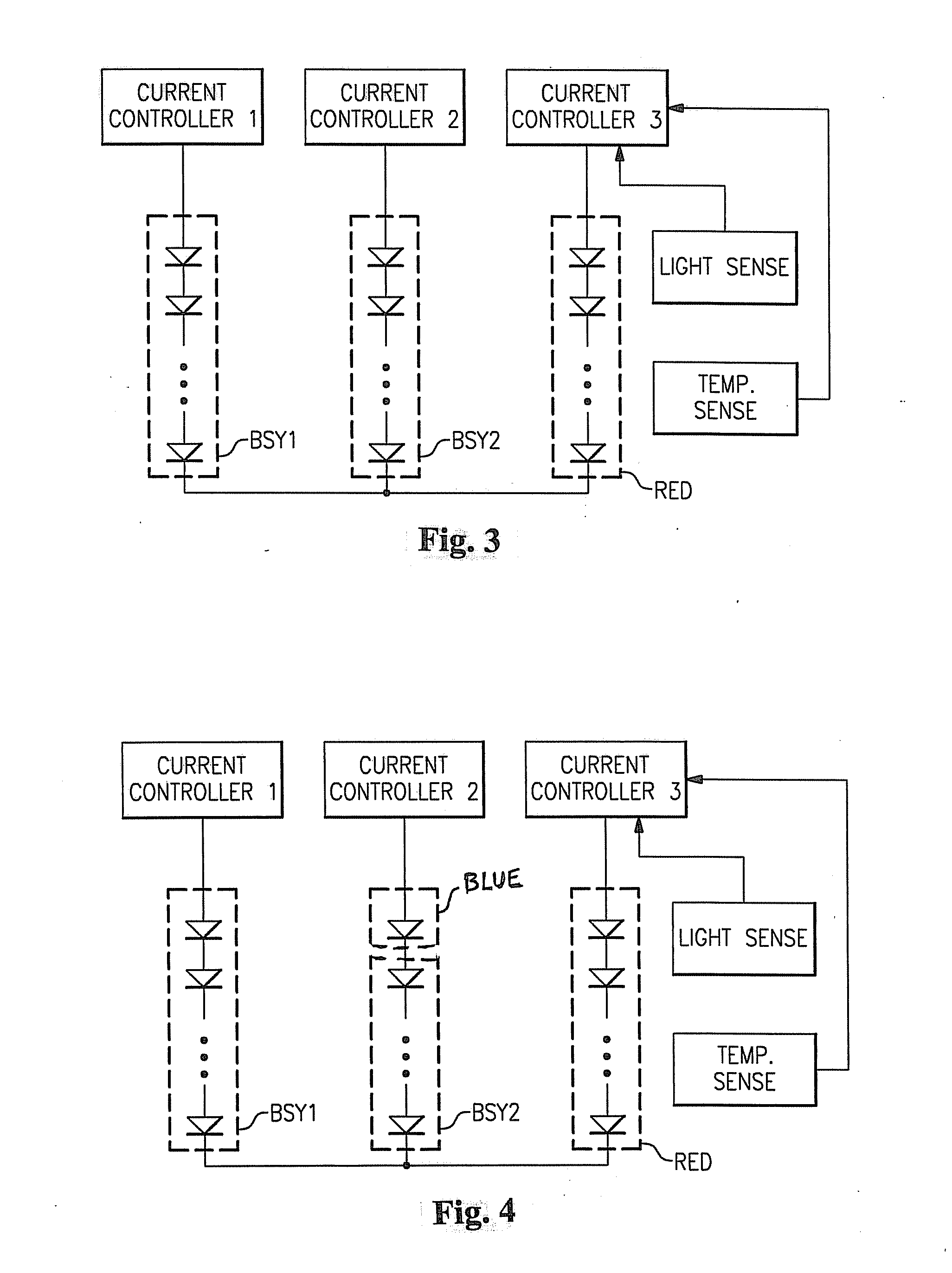
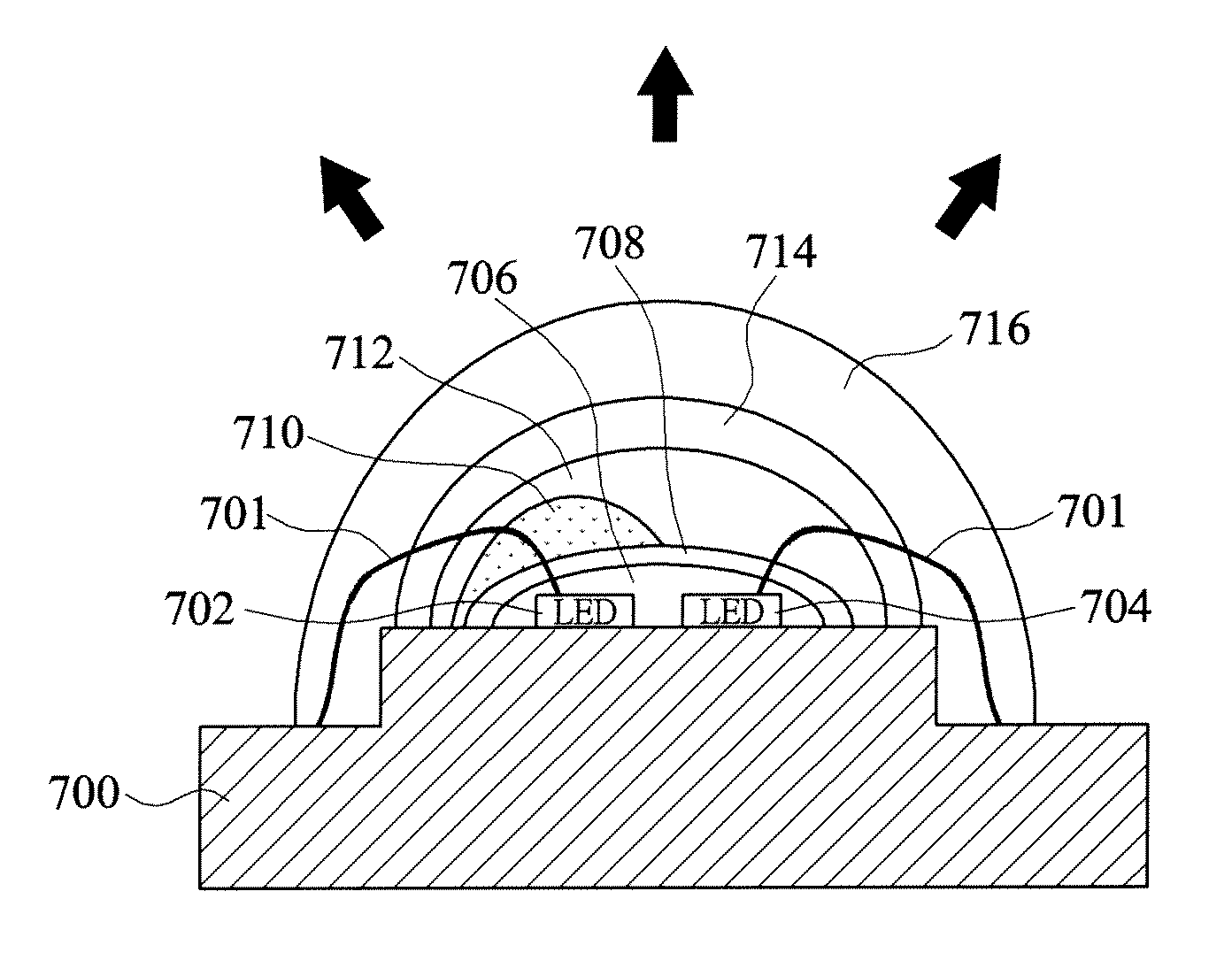
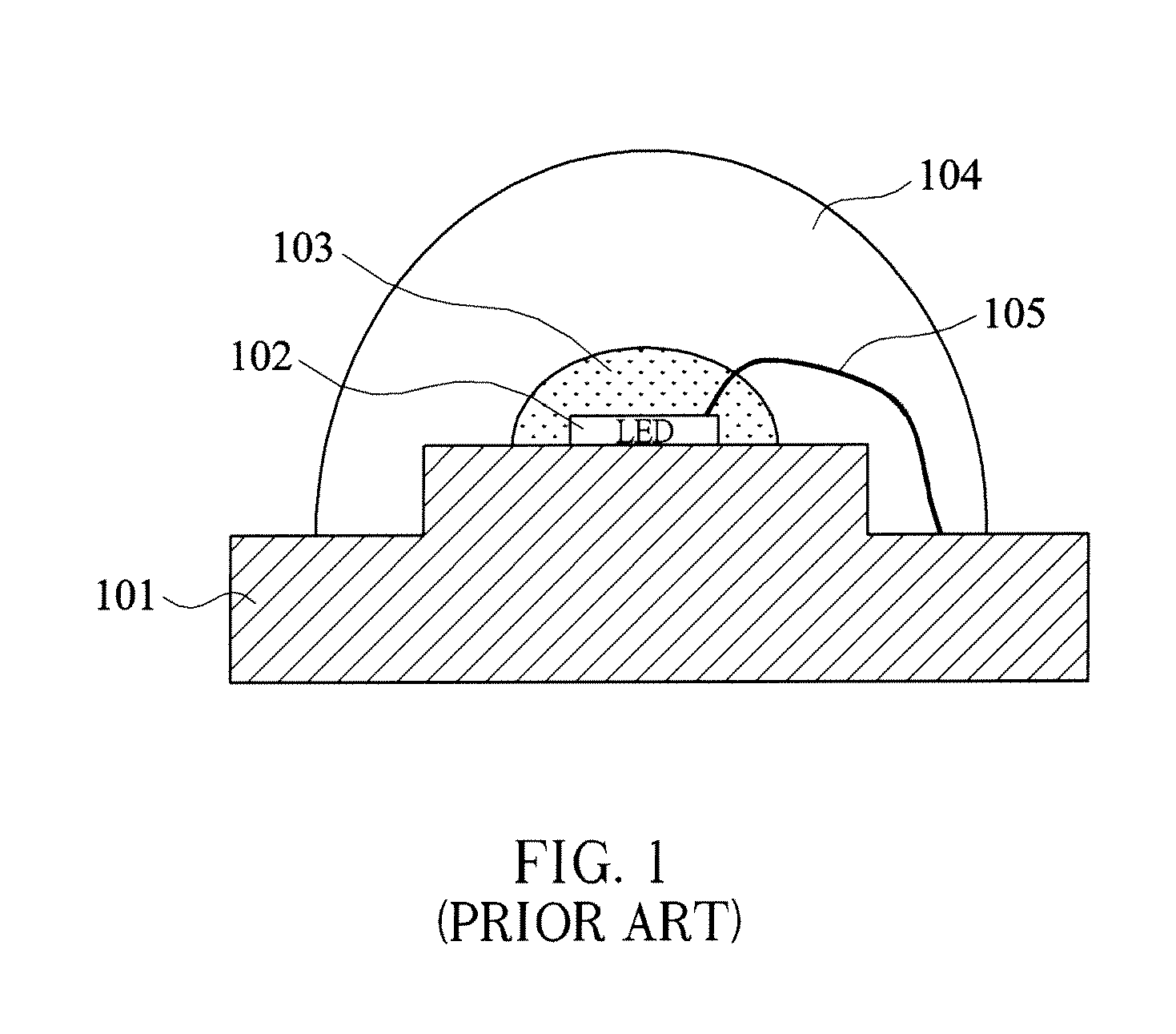
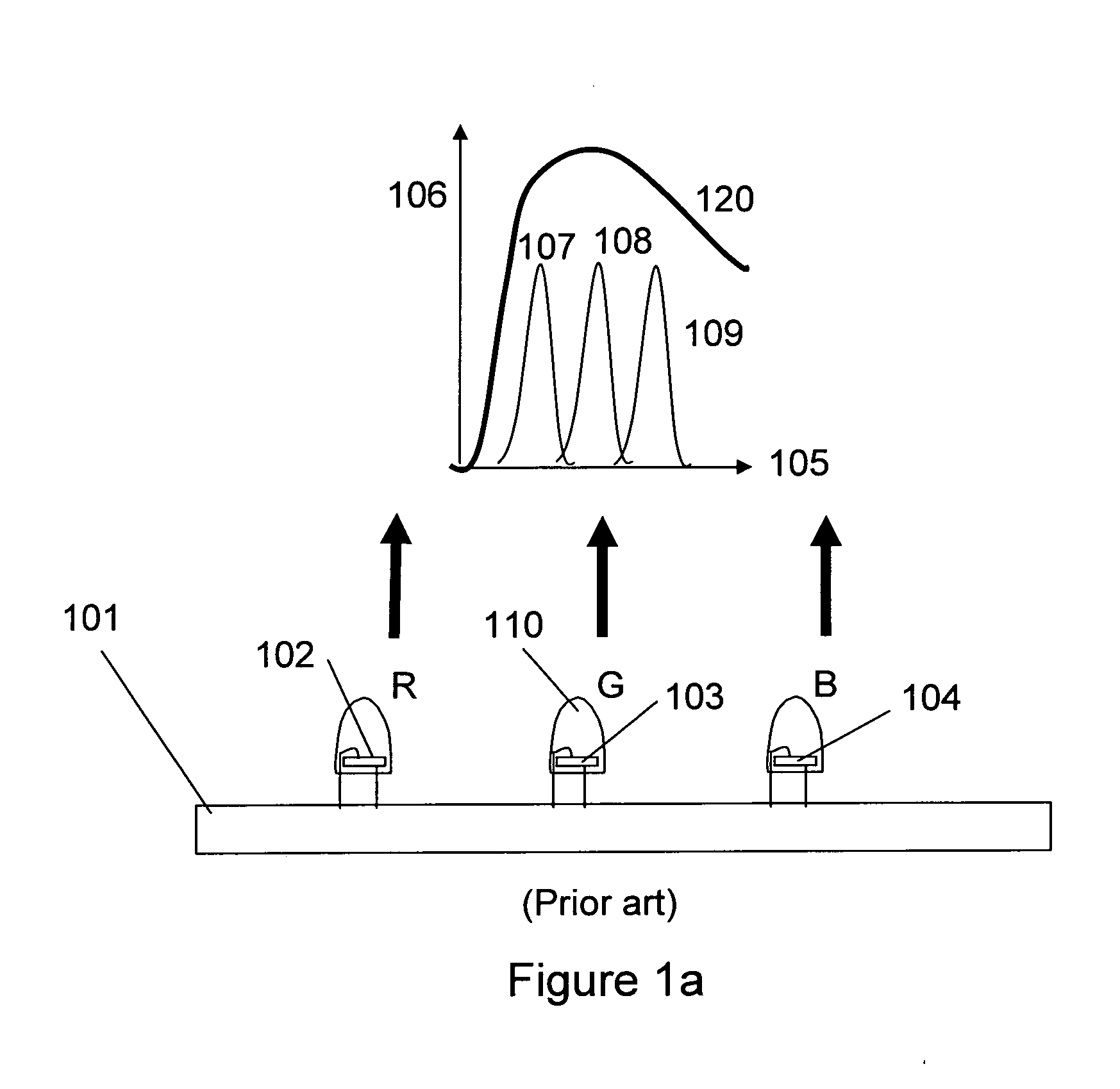
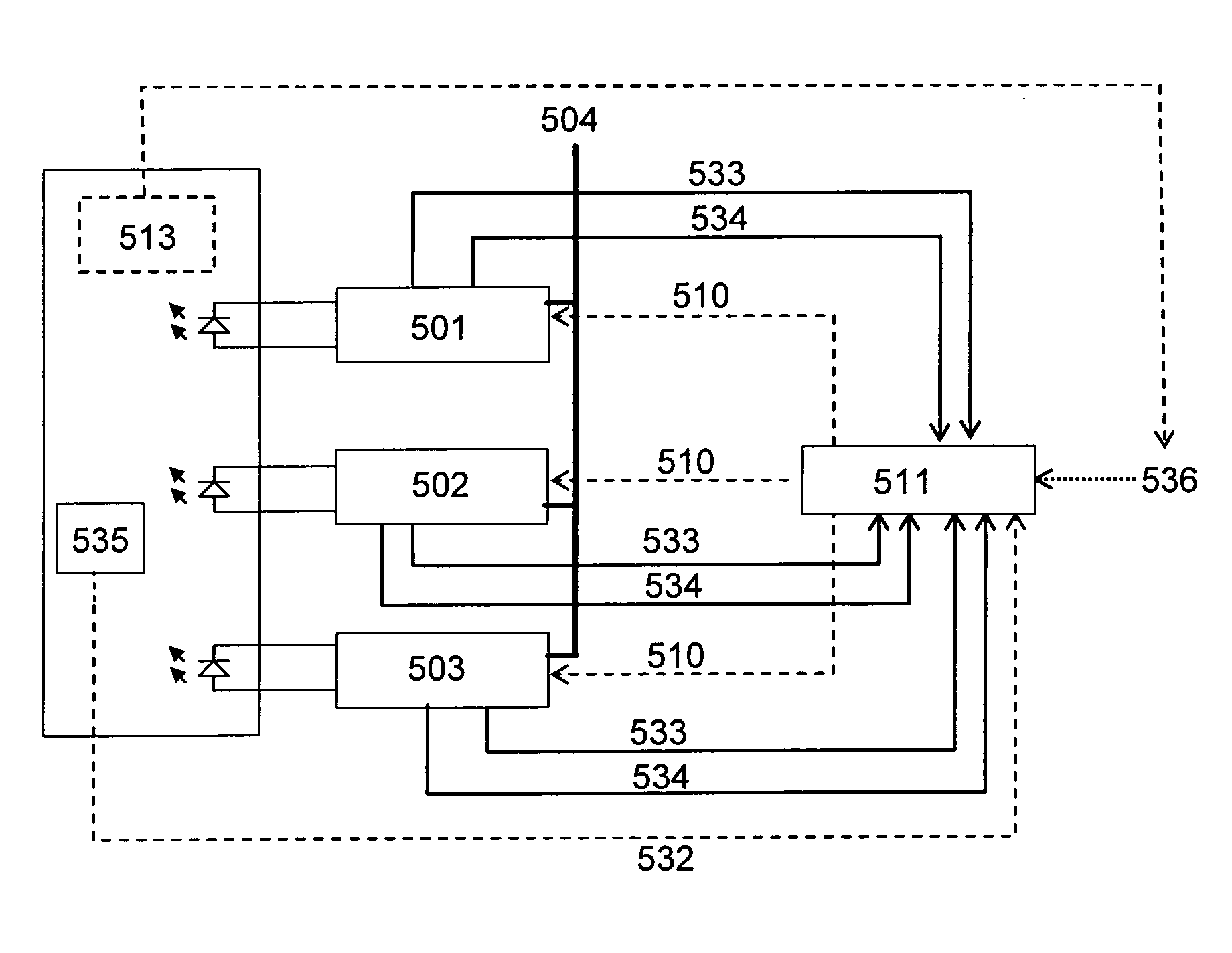
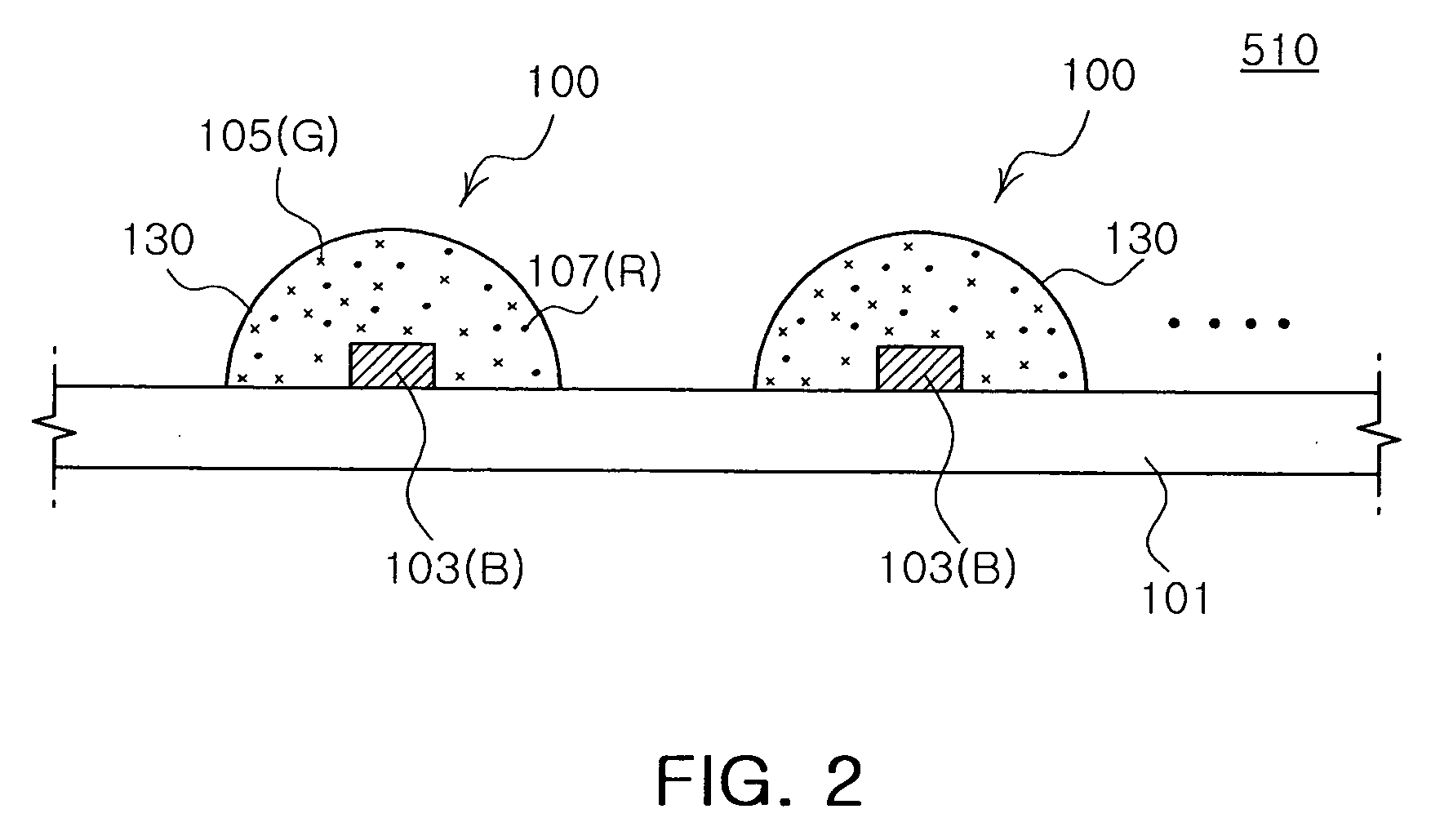
Lighting device and lighting method
ActiveUS7213940B1Low efficiencyImprove efficiencyPlanar light sourcesPoint-like light sourceEffect lightLength wave
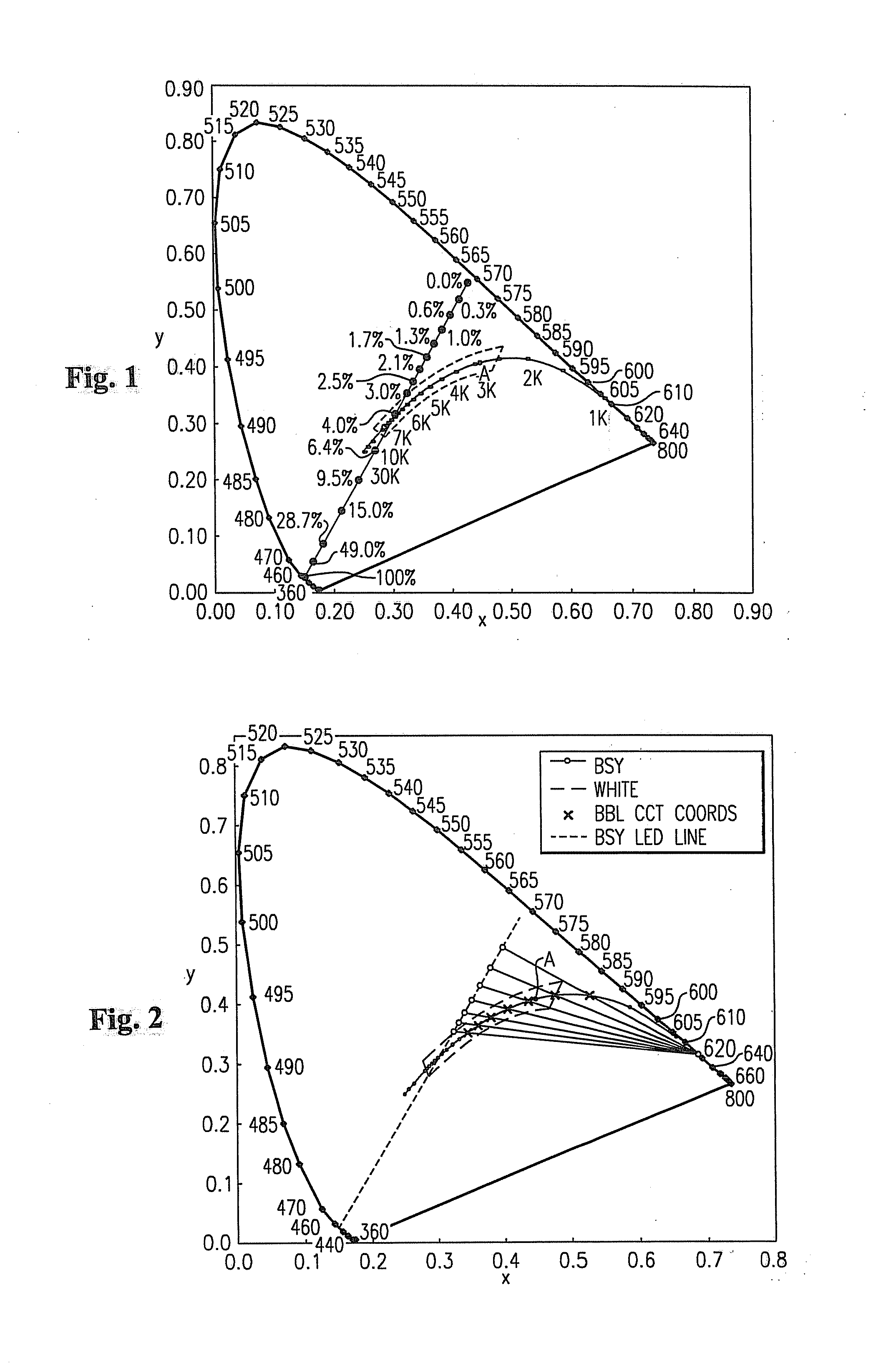
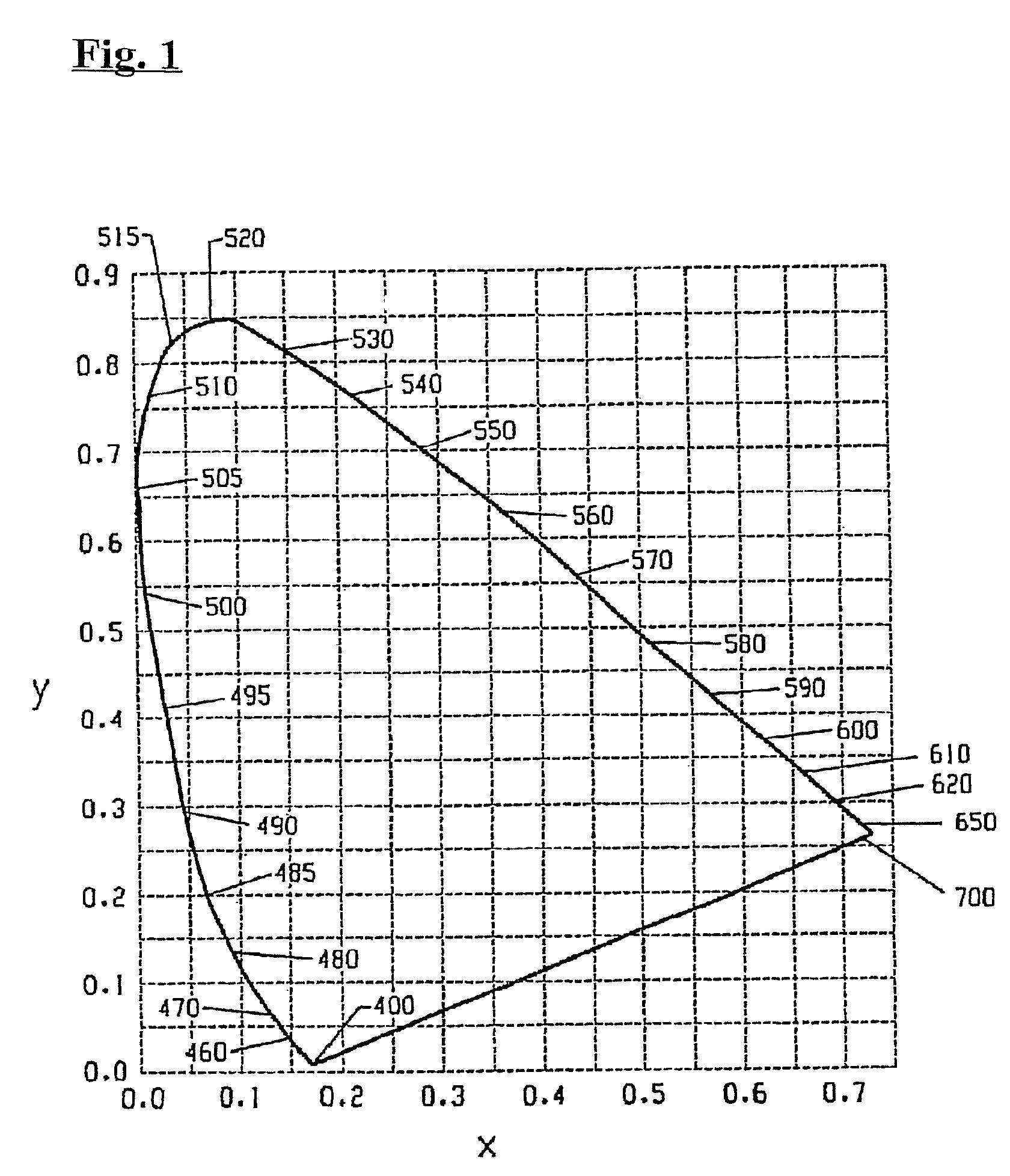
A lighting device comprising first and second groups of solid state light emitters, which emit light having dominant wavelength in ranges of from 430 nm to 480 nm and from 600 nm to 630 nm, respectively, and a first group of lumiphors which emit light having dominant wavelength in the range of from 555 nm to 585 nm. If current is supplied to a power line, a combination of (1) light exiting the lighting device which was emitted by the first group of emitters, and (2) light exiting the lighting device which was emitted by the first group of lumiphors would, in an absence of any additional light, produce a sub-mixture of light having x, y color coordinates within an area on a 1931 CIE Chromaticity Diagram defined by points having coordinates (0.32, 0.40), (0.36, 0.48), (0.43, 0.45), (0.42, 0.42), (0.36, 0.38). Also provided is a method of lighting.
Owner:IDEAL IND LIGHTING LLC
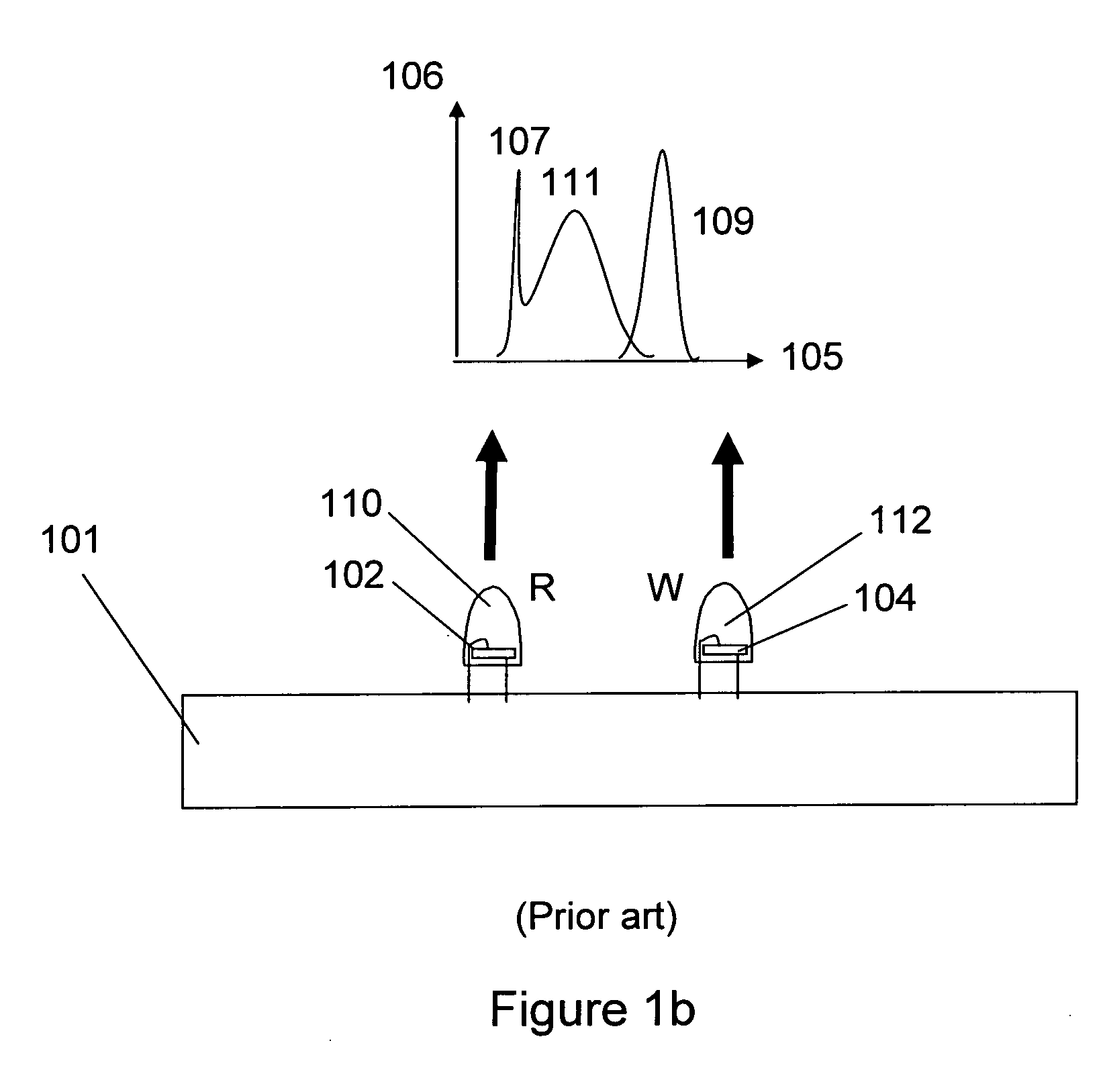
Lighting device and lighting method
ActiveUS20070278934A1Low efficiencyIncreased complexityDischarge tube luminescnet screensLamp detailsFluorescent lampMaterials science
A lighting device comprising a first group of solid state light emitters, with peak wavelength from 430 nm to 480 nm, and optionally a second group with dominant wavelength from 600 nm to 630 nm, and a first group of lumiphors which emit light having dominant wavelength from 555 nm to 585 nm. In some embodiments, if current is supplied to a power line, a combination of (1) light exiting the lighting device which was emitted by the first group of emitters, and (2) light exiting the lighting device which was emitted by the first group of lumiphors would, in an absence of any additional light, produce a sub-mixture of light having x, y color coordinates within an area on a 1931 CIE Chromaticity Diagram defined by points having coordinates (0.32, 0.40), (0.36, 0.48), (0.43, 0.45), (0.42, 0.42), (0.36, 0.38). Also provided is a method of lighting.
Owner:IDEAL IND LIGHTING LLC
Lighting device and lighting method
ActiveUS20080130285A1Excellent color renditionEffective limitDischarge tube luminescnet screensPoint-like light sourceLight equipmentEngineering
A lighting device comprising first and second groups of solid state light emitters, which emit light having wavelength in ranges of from 430 nm to 480 nm and from 600 nm to 630 nm, respectively, and a first group of lumiphors which emit light having dominant wavelength in the range of from 555 nm to 585 nm. If current is supplied to a power line, a combination of (1) light exiting the lighting device which was emitted by the first group of emitters, and (2) light exiting the lighting device which was emitted by the first group of lumiphors would, in an absence of any additional light, produce a sub-mixture of light having x, y color coordinates within an area on a 1931 CIE Chromaticity Diagram defined by points having coordinates (0.32, 0.40), (0.36, 0.48), (0.43, 0.45), (0.42, 0.42), (0.36, 0.38). Also provided is a method of lighting.
Owner:IDEAL IND LIGHTING LLC
High efficiency lighting device including one or more solid state light emitters, and method of lighting
ActiveUS20140078715A1Reduced CRI RaImprove efficiencySpectral modifiersSemiconductor devices for light sourcesLight equipmentMaterials science
A lighting device comprising first and second groups of solid state light emitters, that emit light having approximate dominant wavelength (in nm) of 441-448 (or 442-450, 444-455, 444-446, 442-445 or 444-452) and 555 nm to 585 nm, respectively. If the first and second groups are illuminated, a mixture of light would, in the absence of any additional light, have a color point within one or more of first, second, third, fourth and fifth areas on the 1931 CIE Chromaticity Diagram. In some embodiment, the lighting device further comprises a third group that emits light having approximate dominant wavelength (in nm) of 600-640 (or 605-610, 605-607, 600-606, 602-606 or 615-620). Also, methods of lighting.
Owner:IDEAL IND LIGHTING LLC
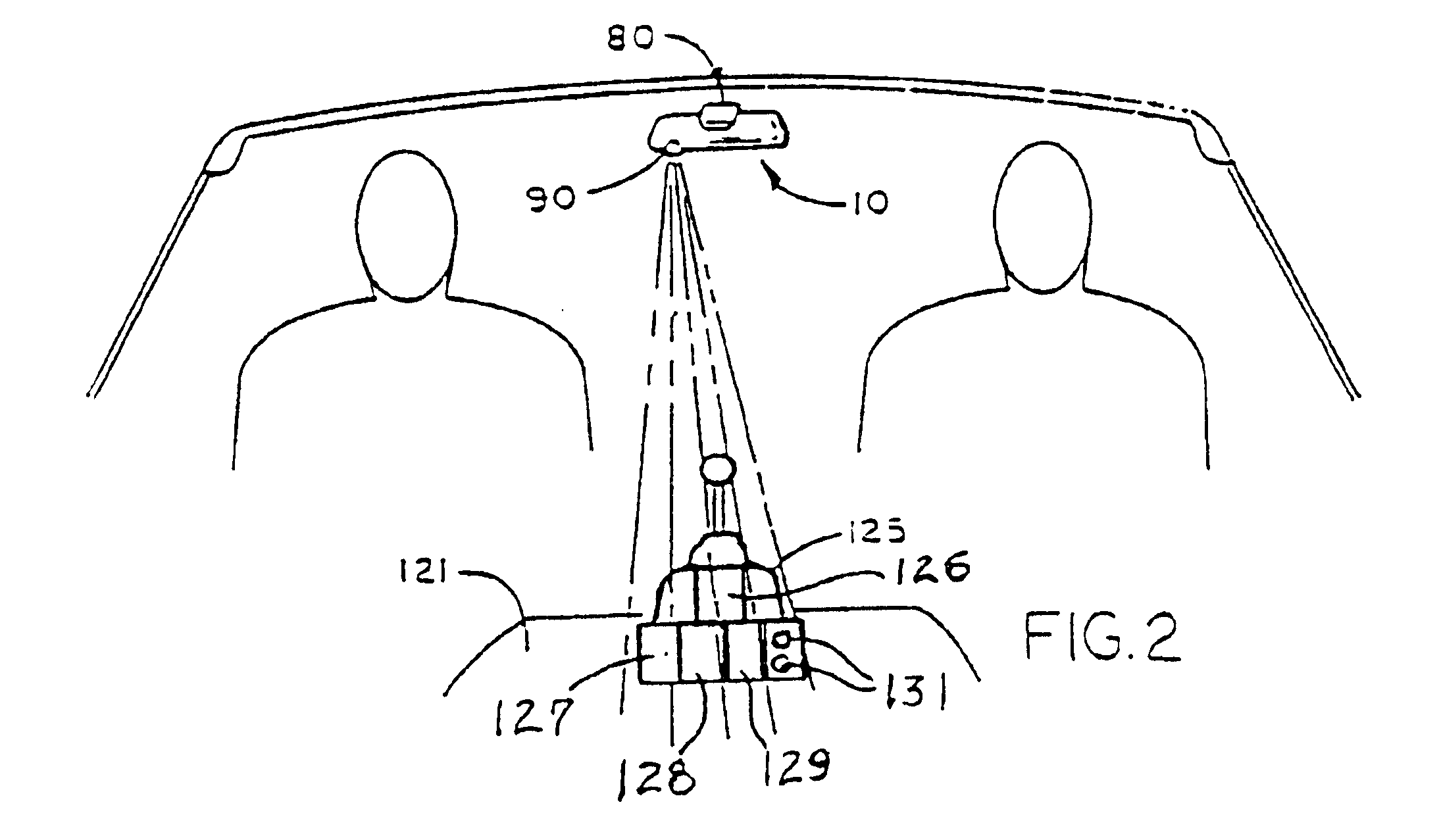
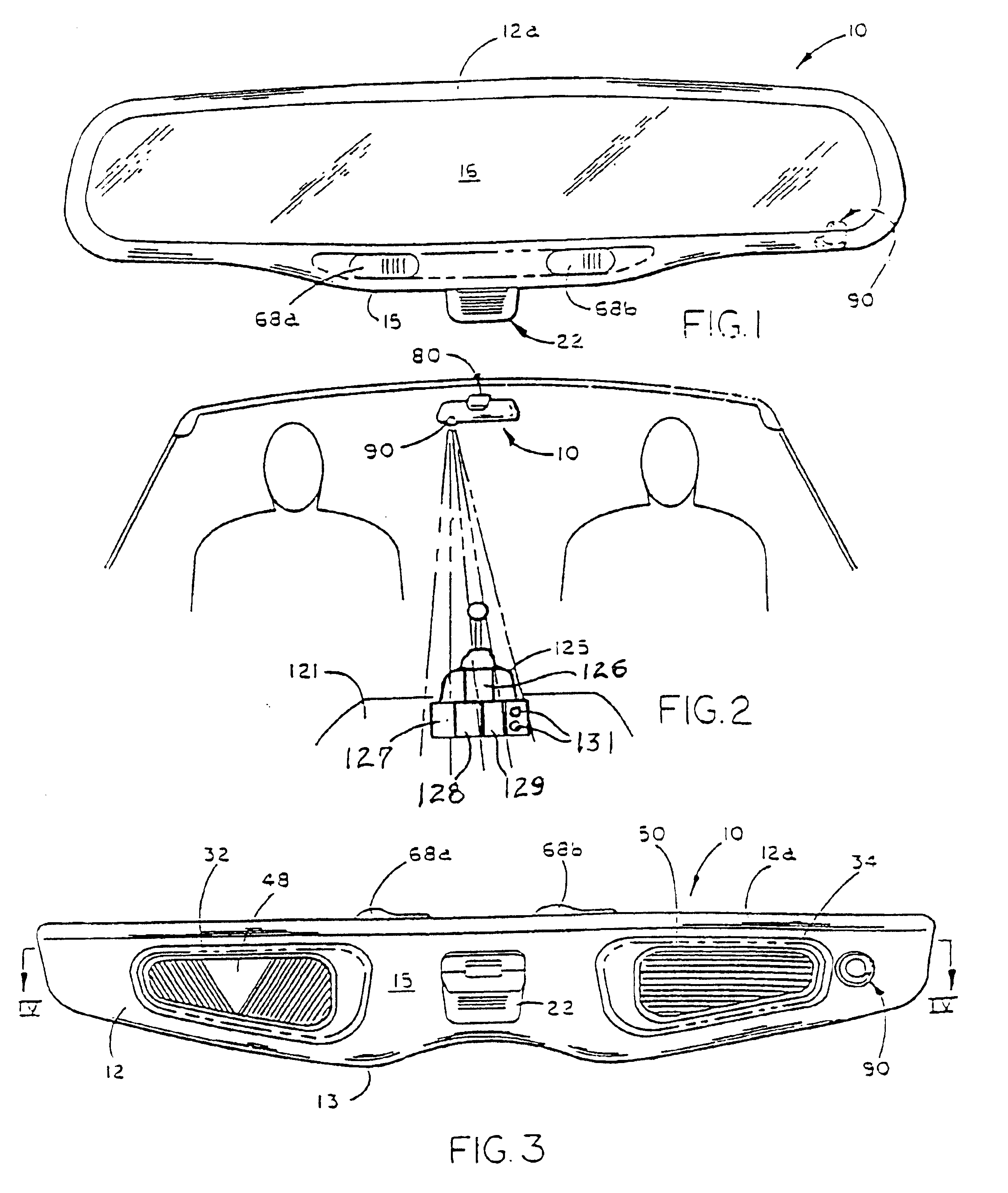
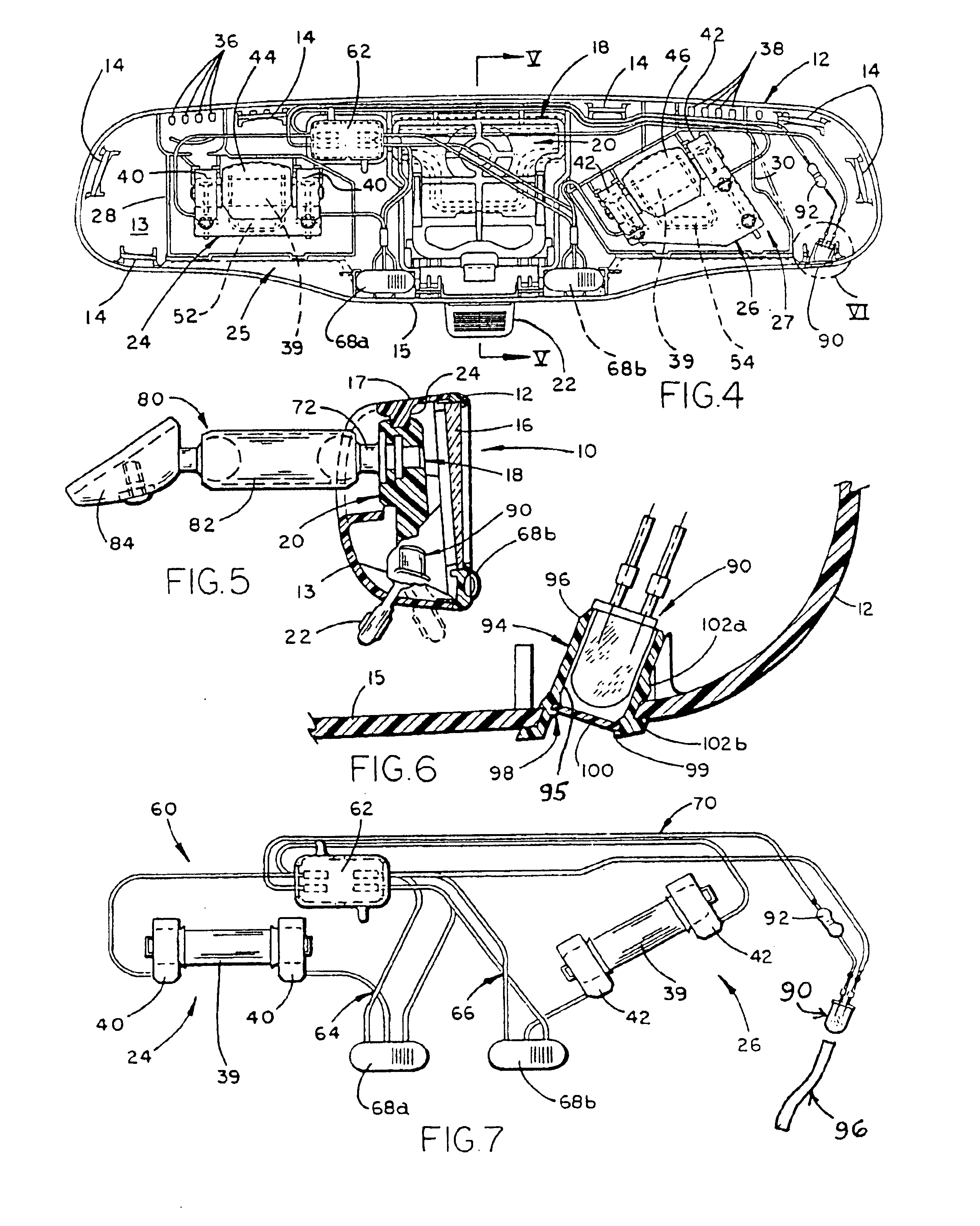
Interior mirror assembly for a vehicle incorporating a solid-state light source
InactiveUS6848817B2Eliminate needAvoids causing glareLighting circuitsLighting support devicesLuminous intensityEngineering
Illumination of a portion of a vehicle interior is provided by an interior rearview mirror assembly incorporating a solid-state light source comprising a light emitting diode (LED) which emits light generally downwardly from the assembly. In one form of the invention, the mirror case of the rearview mirror assembly includes at least one of an opening, a light conduit, and a fiberoptic element through which the LED emits light. In another form, the LED preferably has a luminous intensity of at least 500 mcd when operated at a forward current of 20 mA. The LED preferably has a dominant wavelength of at least about 530 nm. The light emitted by the LED may be selected from green, orange, yellow, amber, reddish-orange, red and blue. The vehicle interior portion may include at least one of a shift lever console and a floor console.
Owner:BOS BRENT J +2
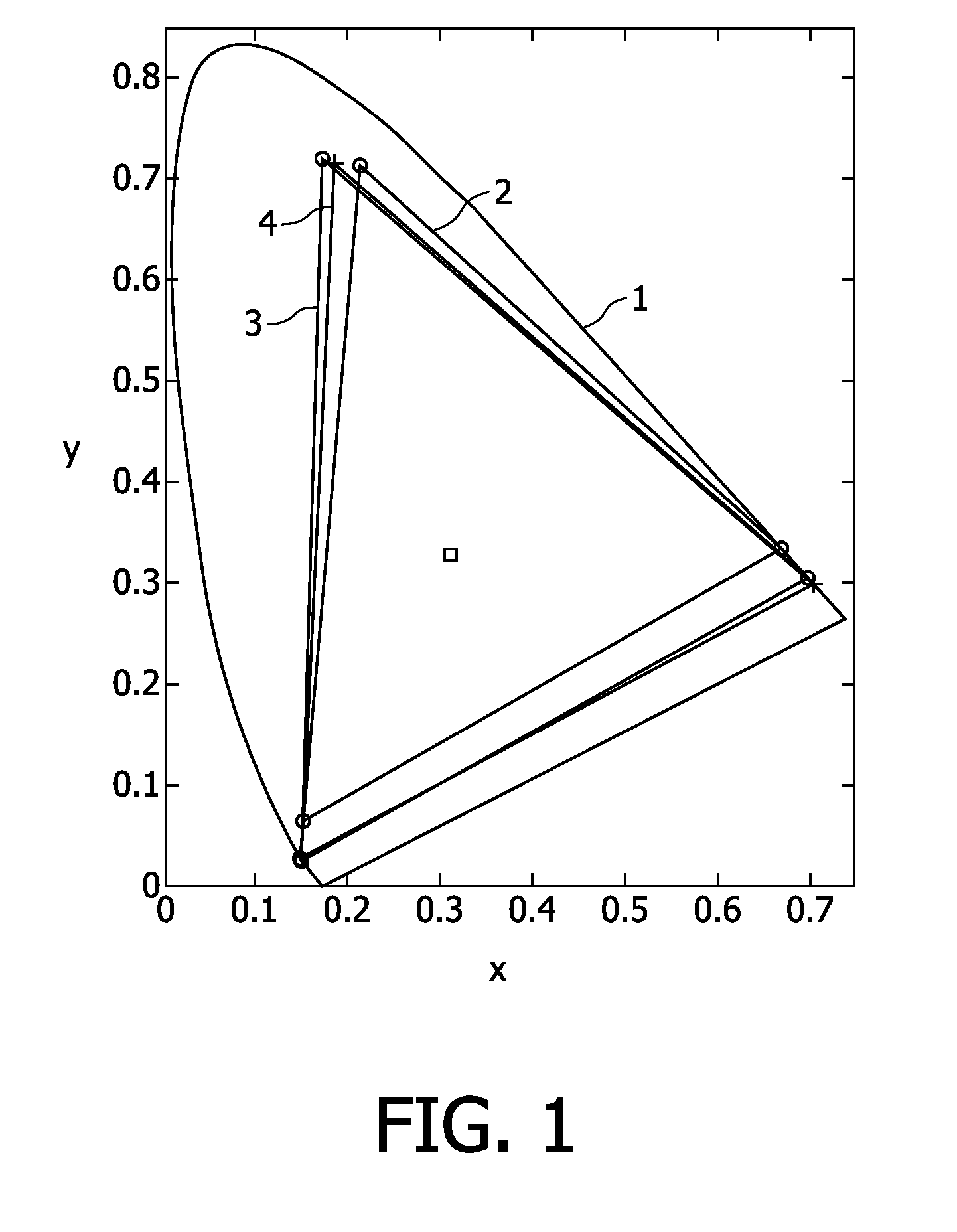
White light emitting device and white light source module using the same
ActiveUS20080128735A1High color reproductionImprove color uniformitySolesElectroluminescent light sourcesPhosphorGreen-light
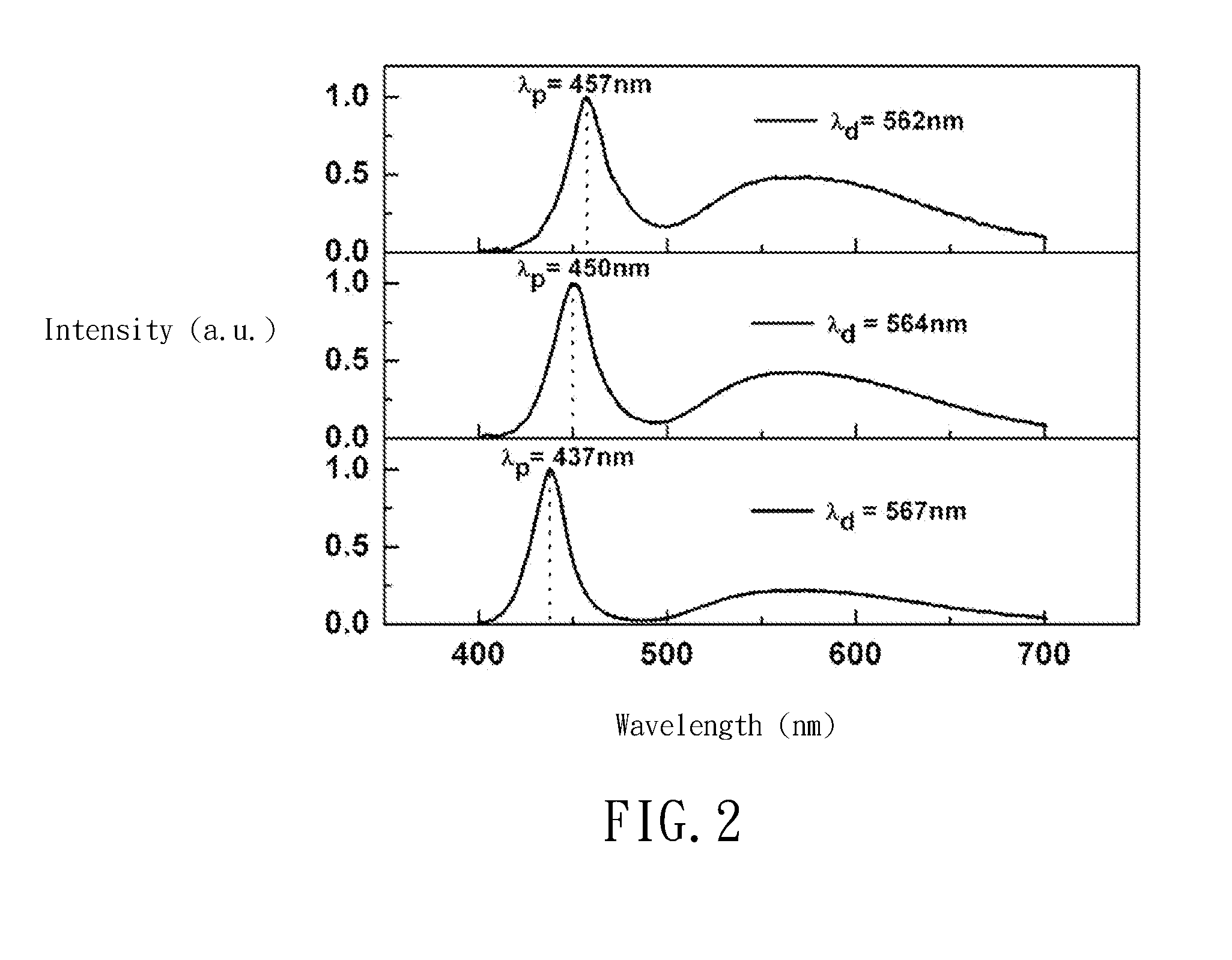
A white light emitting device including: a blue light emitting diode chip having a dominant wavelength of 443 to 455 nm; a red phosphor disposed around the blue light emitting diode chip, the red phosphor excited by the blue light emitting diode chip to emit red light; and a green phosphor disposed around the blue light emitting diode chip, the green phosphor excited by the blue light emitting diode chip to emit green light, wherein the red light emitted from the red phosphor has a color coordinate falling within a space defined by four coordinate points (0.5448, 0.4544), (0.7079, 0.2920), (0.6427, 0.2905) and (0.4794, 0.4633) based on the CIE 1931 chromaticity diagram, and the green light emitted from the green phosphor has a color coordinate falling within a space defined by four coordinate points (0.1270, 0.8037), (0.4117, 0.5861), (0.4197, 0.5316) and (0.2555, 0.5030) based on the CIE 1931 color chromaticity diagram.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
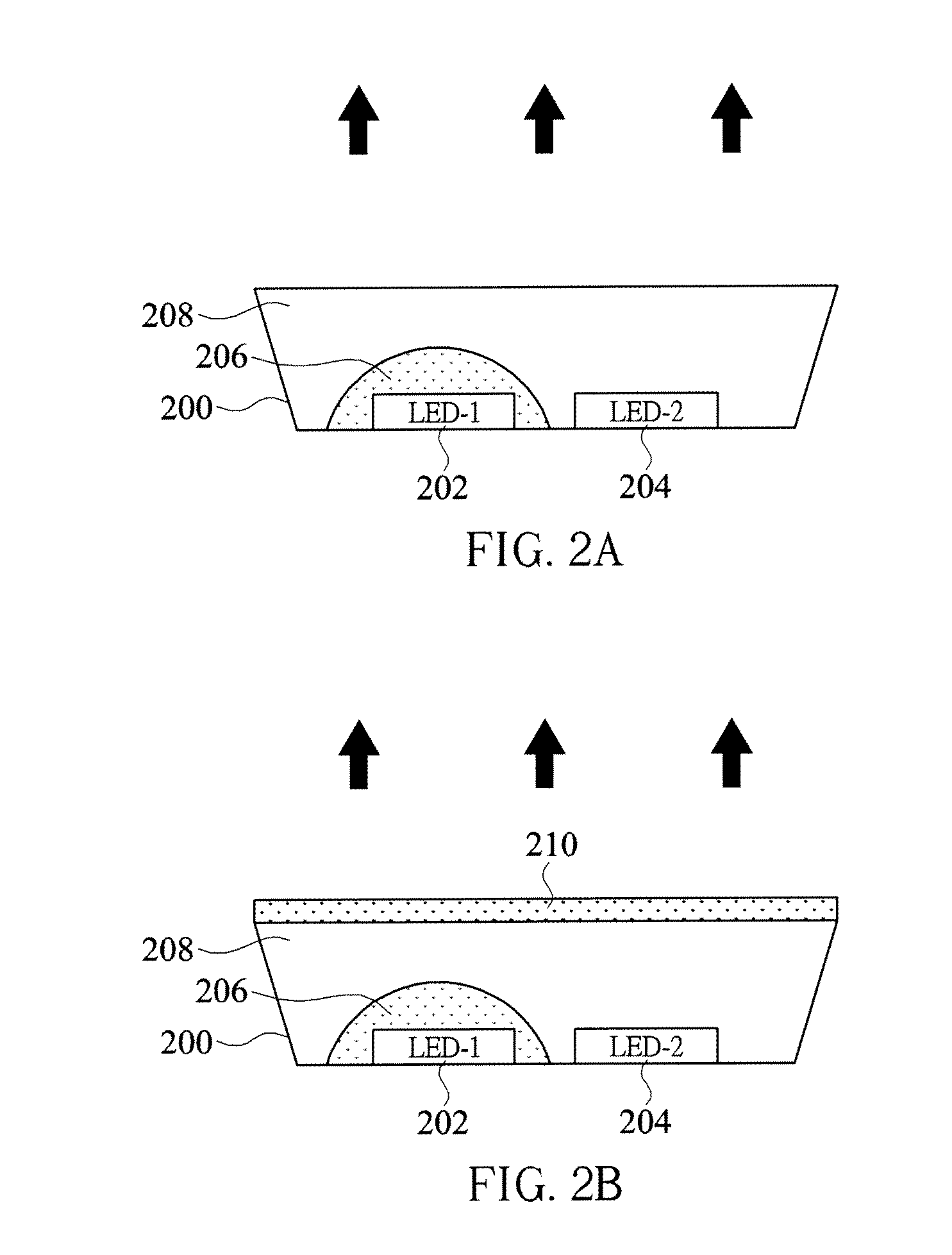
Lighting device having first, second and third groups of solid state light emitters, and lighting arrangement
ActiveUS20110031894A1Sharp contrastPlanar light sourcesLight source combinationsLength waveLight emitter
Owner:IDEAL IND LIGHTING LLC
White light emitting device and light source module for liquid crystal display backlight using the same
InactiveUS20080180948A1High color reproductionImprove material stabilityElectroluminescent light sourcesGas discharge lamp usageLiquid-crystal displayPhosphor
A white light emitting device including: a blue LE chip having a dominant wavelength of 430 to 455 nm; a red phosphor disposed around the blue light emitting diode chip, the red phosphor excited by the blue light emitting diode chip to emit red light; and a green phosphor disposed around the blue light emitting diode chip, the green phosphor excited by the blue LED chip to emit green light, wherein the red light emitted from the red phosphor has a color coordinate falling within a space defined by four coordinate points (0.5448, 0.4544), (0.7079, 0.2920), (0.6427, 0.2905) and (0.4794, 0.4633) based on the CIE 1931 chromaticity diagram, the green light emitted from the green phosphor has a color coordinate falling within a space defined by four coordinate points (0.1270, 0.8037), (0.4117, 0.5861), (0.4197, 0.5316) and (0.2555, 0.5030) based on the CIE 1931 color chromaticity diagram, and the red phosphor includes a phosphor represented by (Sr, Ba, Ca)AlSiN3:Eu and the green phosphor includes a phosphor represented by (Sr, Ba, Ca)2SiO4:Eu.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
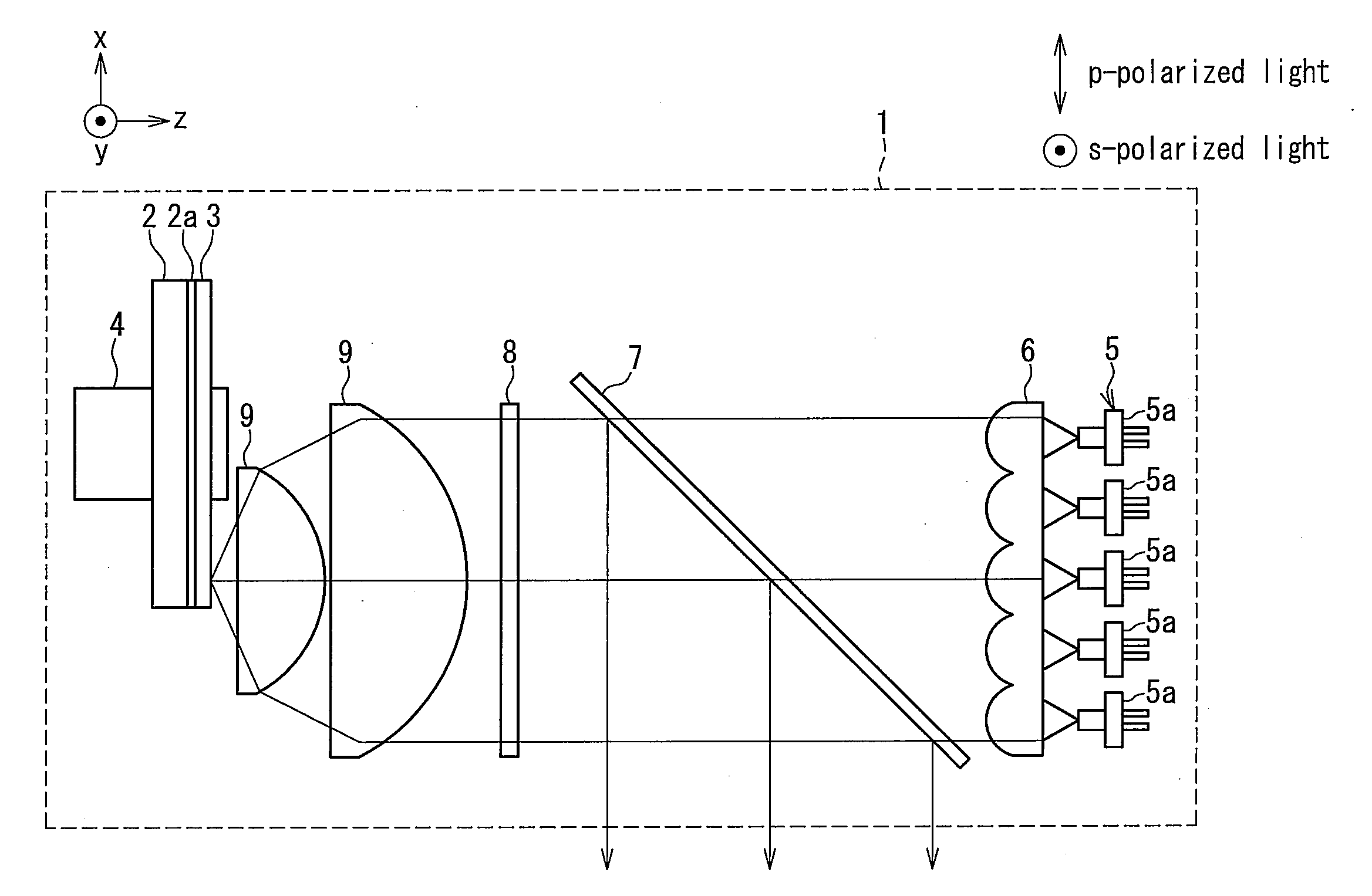
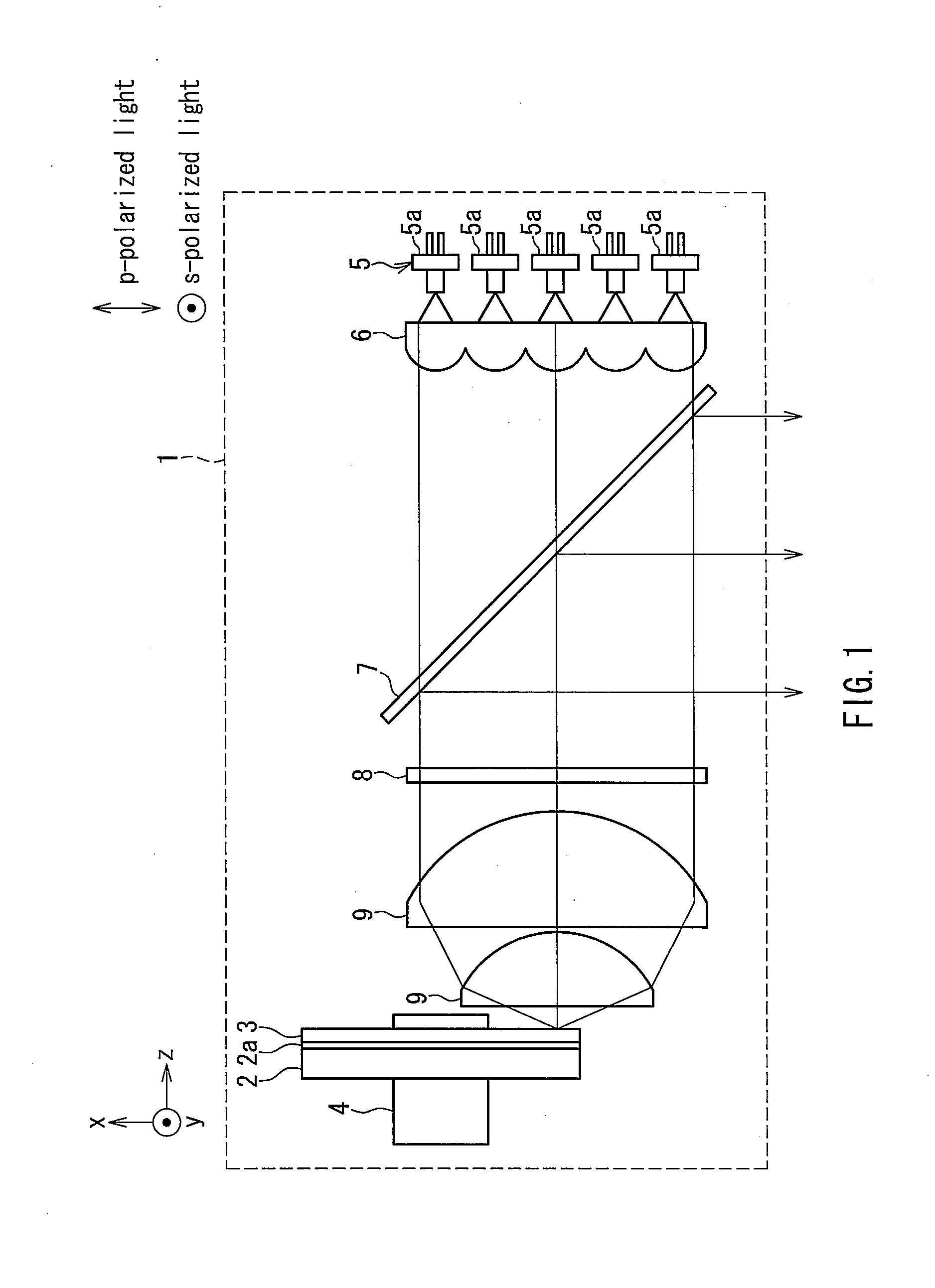
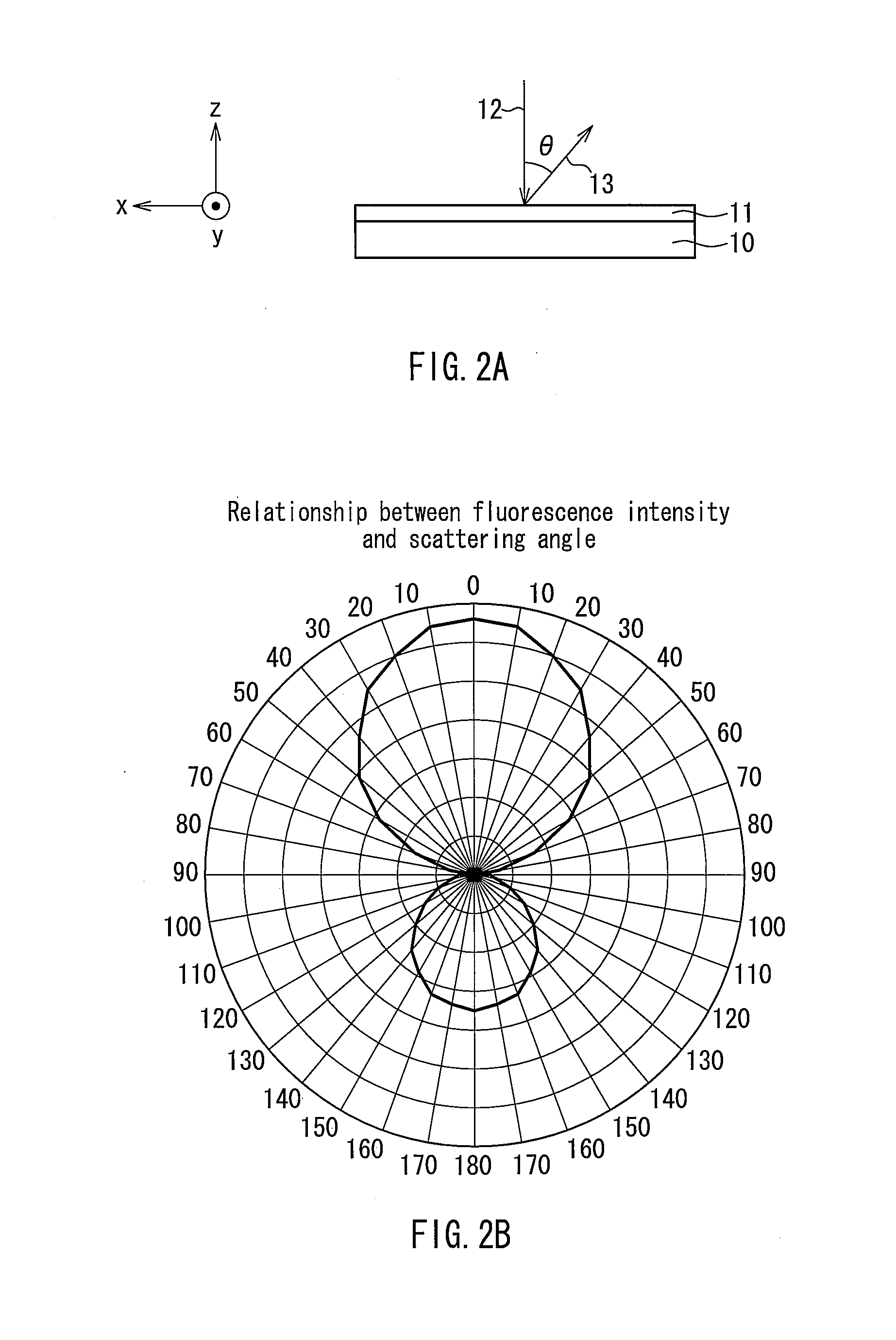
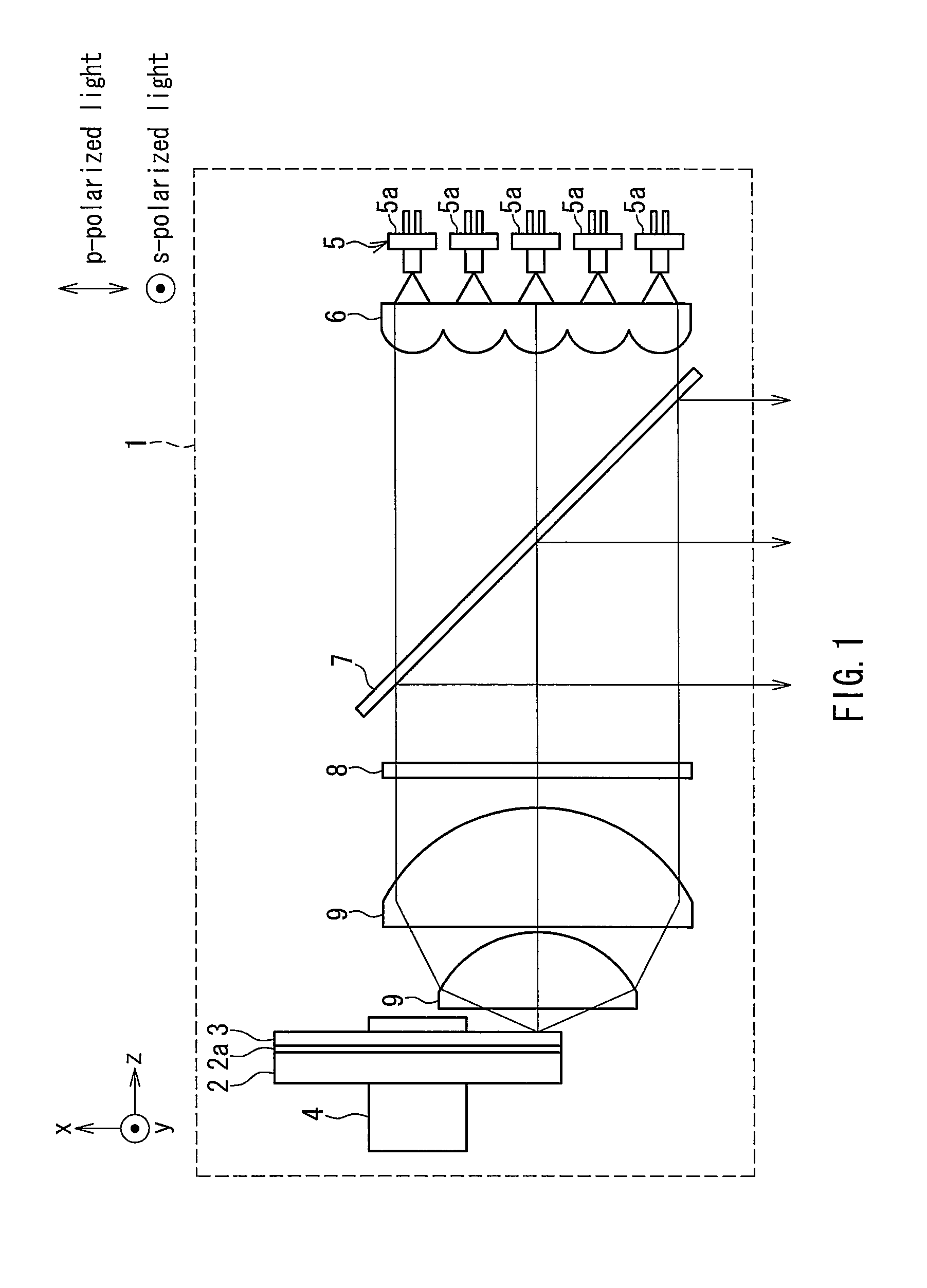
Light source device and image display apparatus
ActiveUS20120127435A1Efficient extractionEfficiently propagatingElectric circuit arrangementsProjectorsFluorescencePhosphor
A light source device includes a phosphor layer formed on a base, and an excitation light source exciting the phosphor. A dichroic mirror is arranged between the phosphor layer and the excitation light source and inclined with respect to a propagation direction of excitation light from the excitation light source. An incident region of the excitation light and an exiting region of fluorescence emitted from the phosphor belong to a space on the same side with respect to the surface with the phosphor layer disposed. In a dominant wavelength of the excitation light, the dichroic mirror has a spectral characteristic of transmitting 50% or more of light of a p-polarized component and reflecting 50% or more of light of a s-polarized component. Fluorescence emitted from the phosphor layer can be extracted highly efficiently and propagated by a compact and simple optical system.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Lighting device and method of making
ActiveUS20110279015A1Improve performanceReduce capacityLight source combinationsDischarge tube luminescnet screensPhosphorWhite light
A lighting device comprising first and second groups of non-white light sources emitting light outside a first area on a 1976 CIE Chromaticity Diagram bounded by a curves 0.01 u′v′ above and below the blackbody locus and within a second area enclosed by saturated light curves from 430 to 465 nm and from 560 to 580 nm and segments from 465 to 560 nm and from 580 to 430 nm and a supplemental light emitter in the range of 600 to 640 nm. Also, a lighting device, comprising a first string of non-white phosphor converted light sources with excitation sources having dominant wavelengths that differ by at least 5 nm, a second string of non-white light sources, and a third string of supplemental light emitters in the range of 600 to 640 nm.
Owner:IDEAL IND LIGHTING LLC
White-light emitting devices with stabilized dominant wavelength
InactiveUS20110279998A1Stabilizing dominant wavelength of a white-lightDrawback can be obviatedSpectral modifiersSemiconductor devicesPhosphorTransmittance
The disclosure provides a dominant wavelength stabilized white light emitting device and a method for stabilizing dominant wavelength of a white-light light emitting device. The light emitting device includes light-emitting diode chips, a phosphor resin layer disposed above the diode chip, and an optical filter disposed above the resin with a gap interposed between the phosphor resin layer and the optical filter. The phosphor resin layer contains a phosphor that is excited by light of the first wavelengths to emit light of second wavelengths. The optical filter reflects light of wavelength shorter than the peak wavelength and transmitting light of the second wavelengths with a modulated transmittance in a range of the first wavelengths.
Owner:NAT TAIWAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
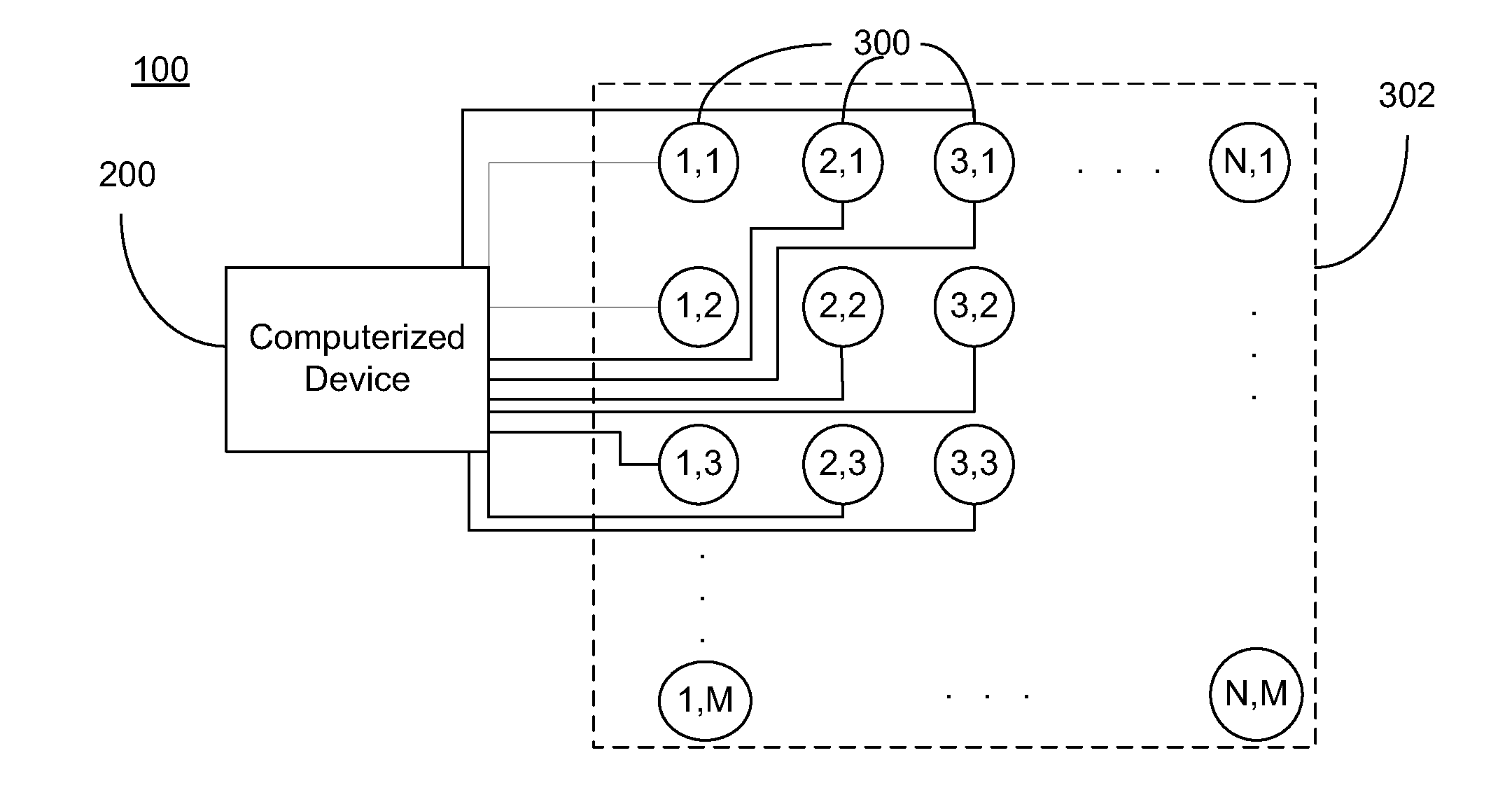
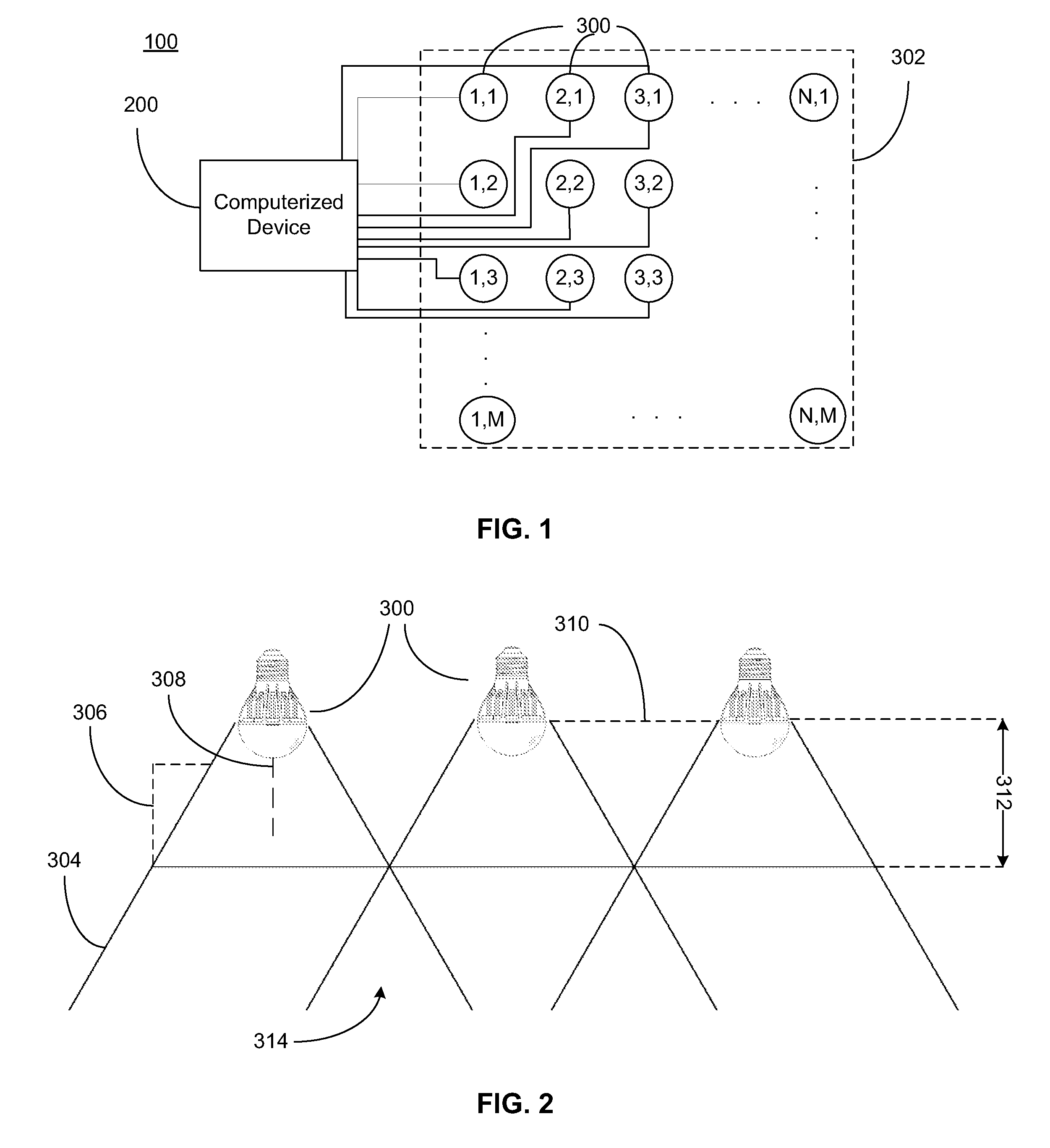
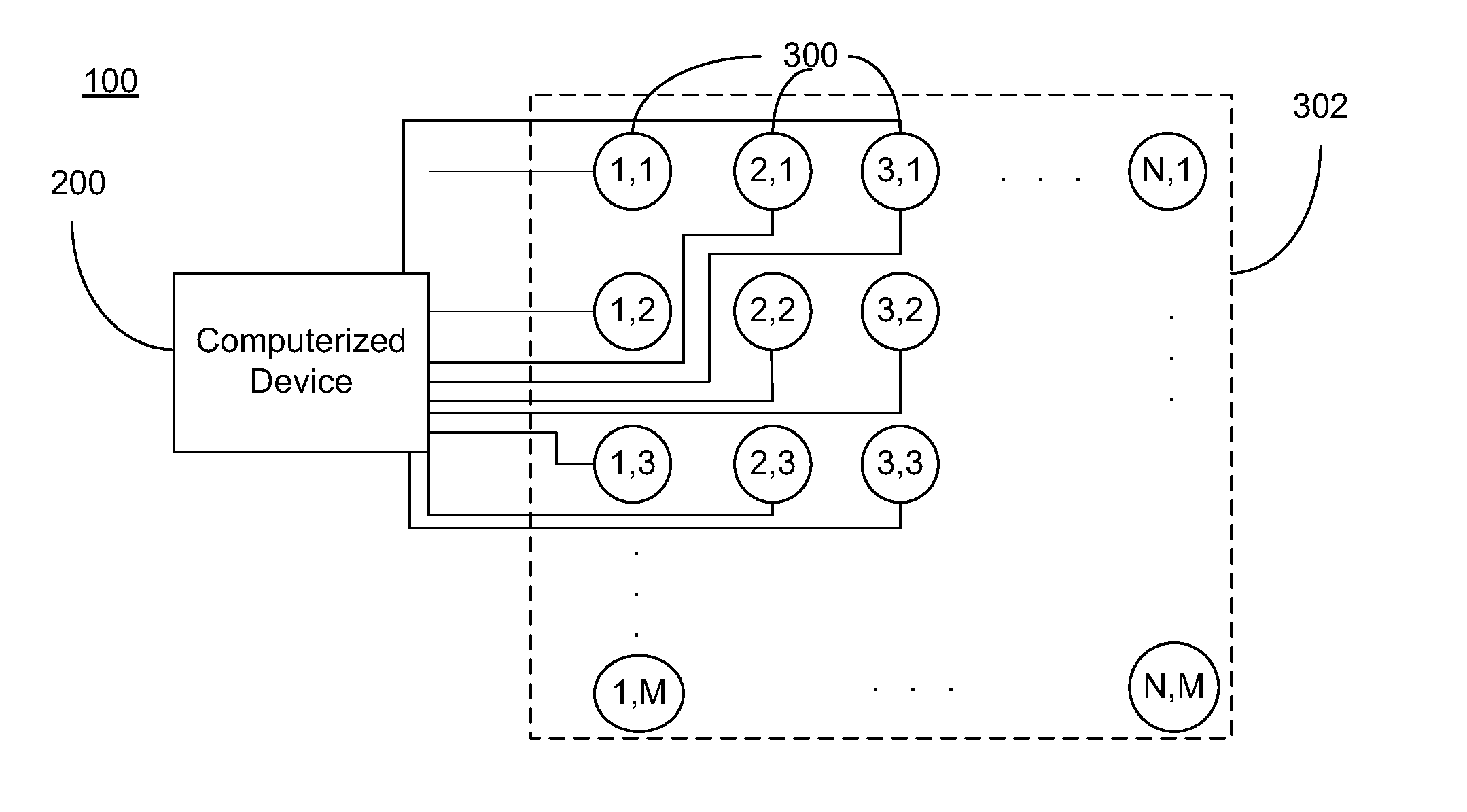
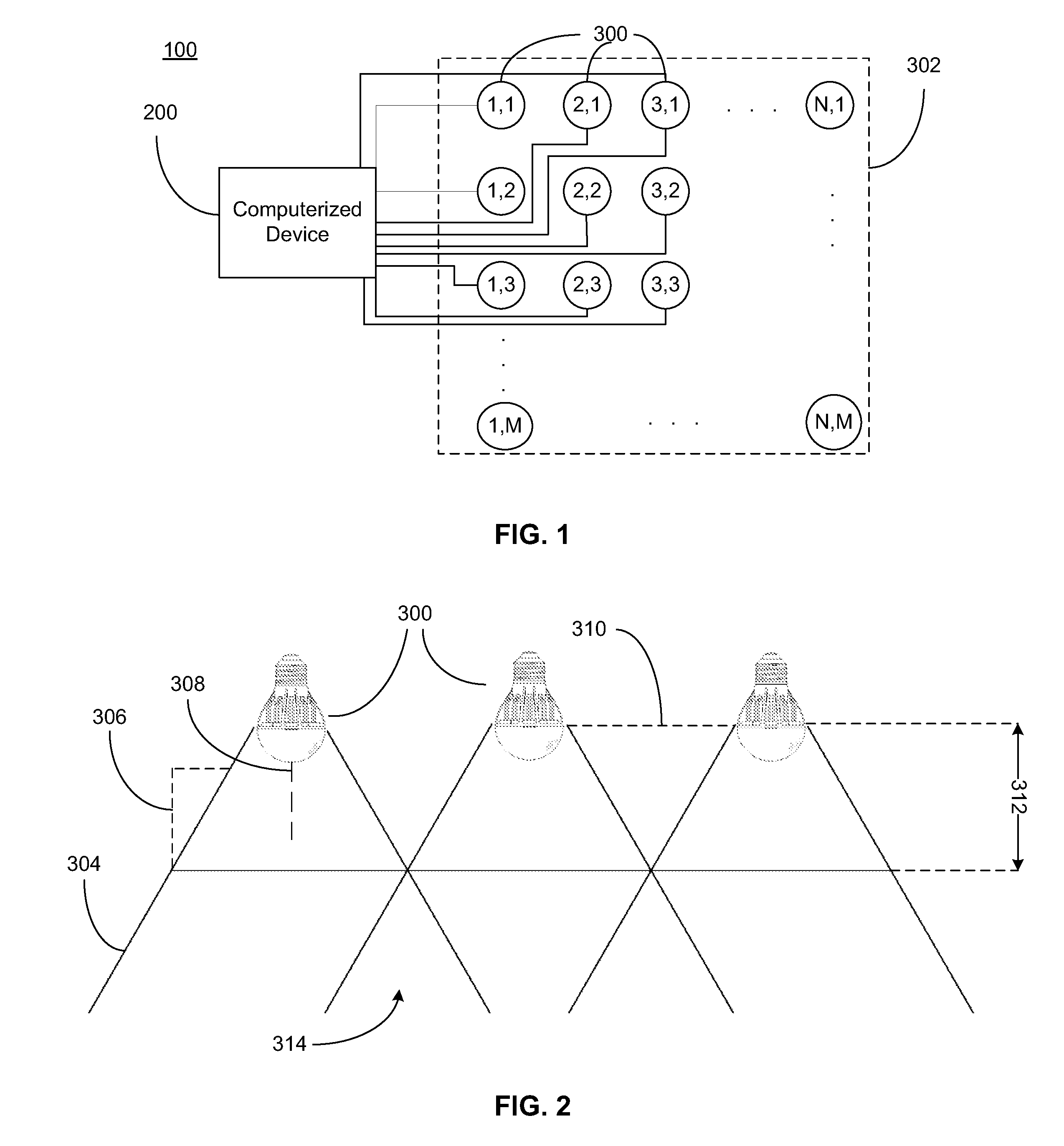
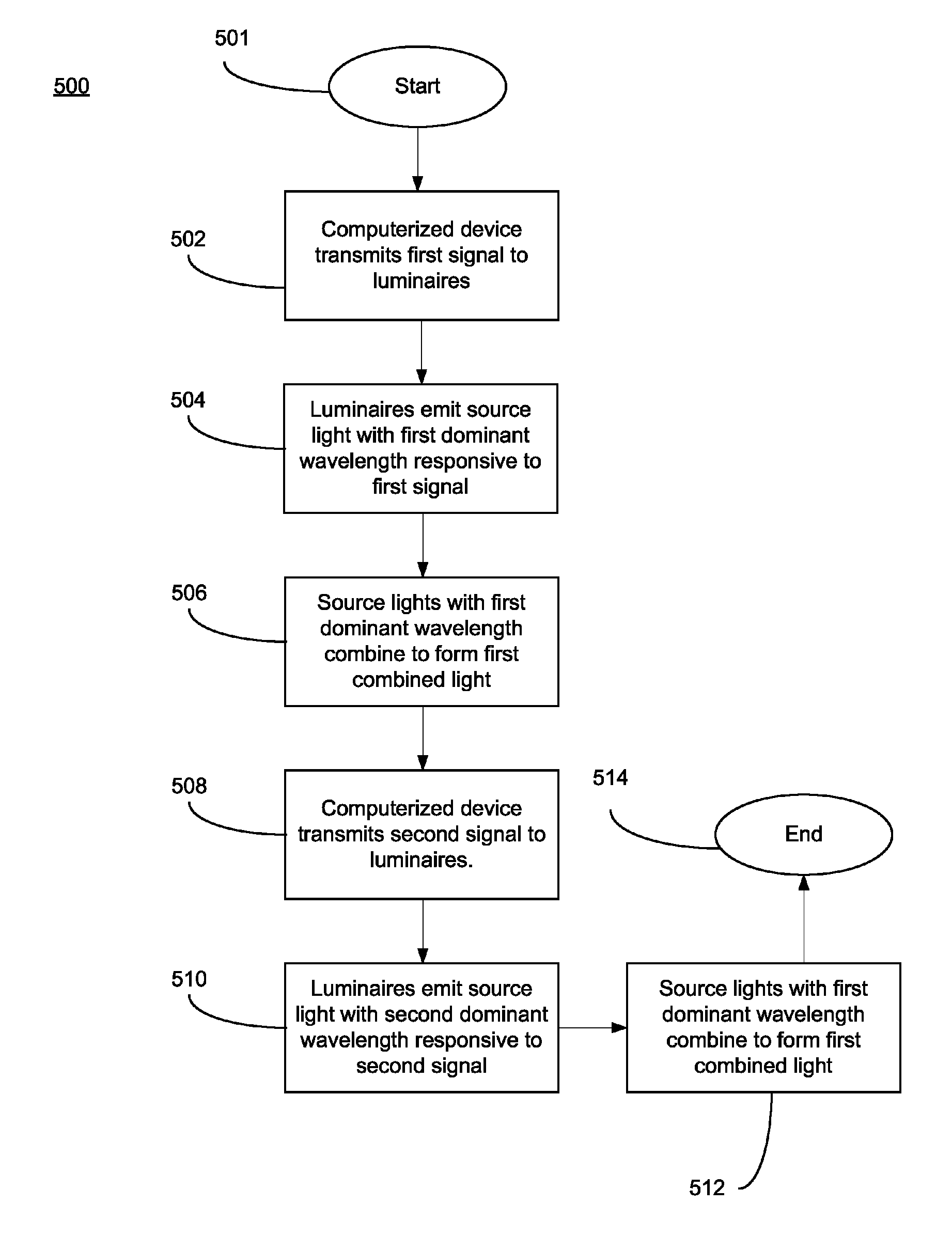
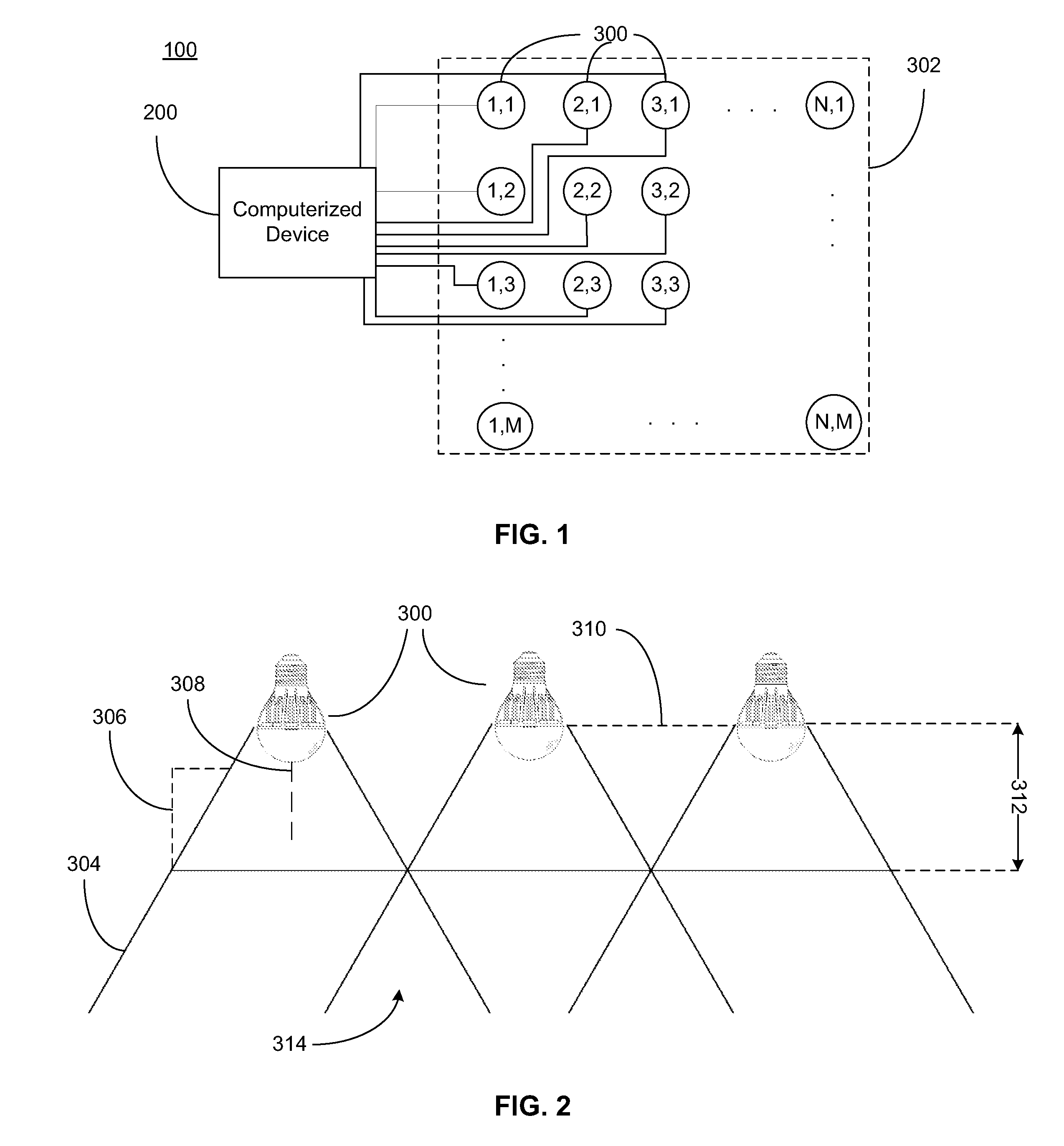
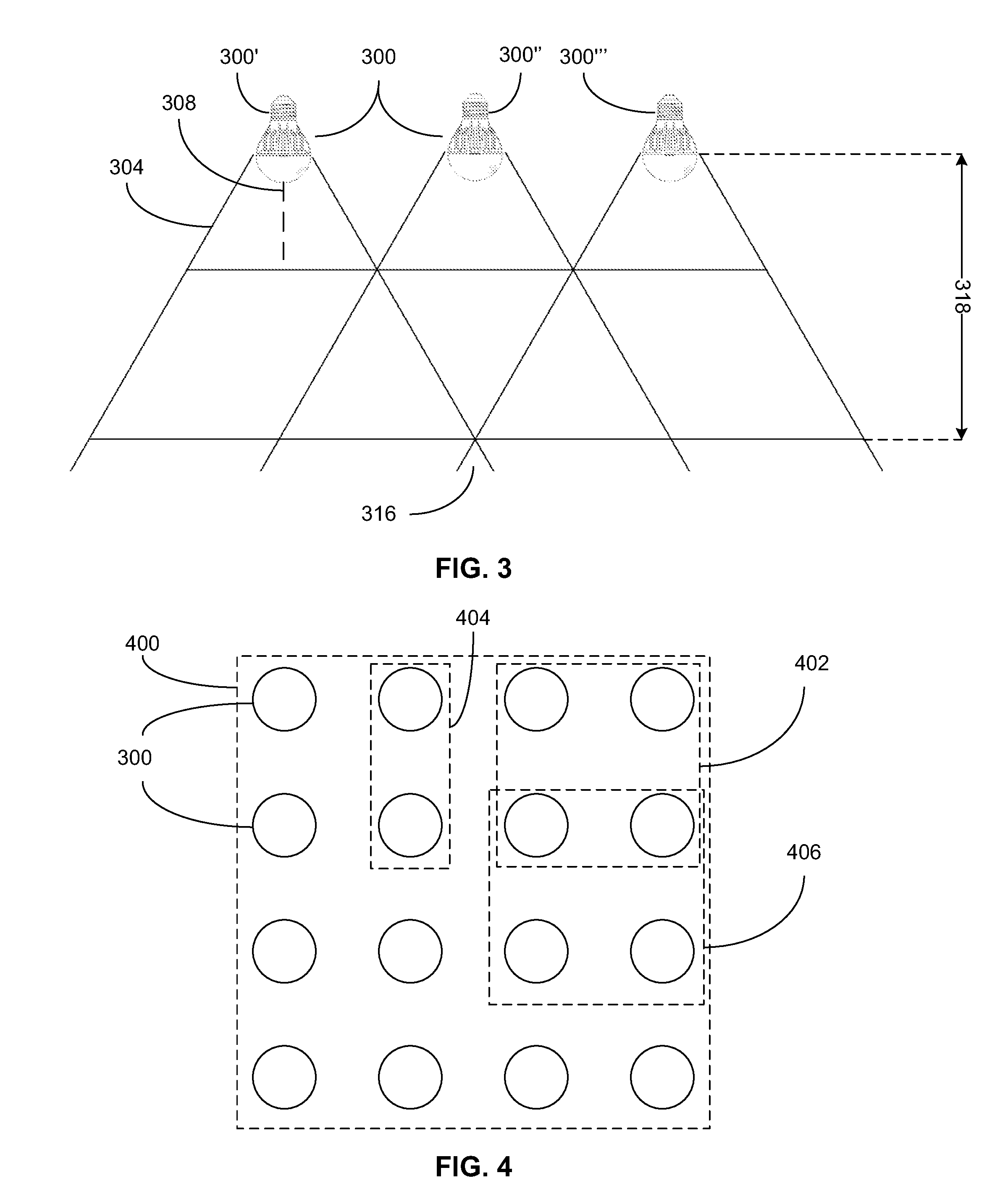
System for generating non-homogenous biologically-adjusted light and associated methods
A lighting system including a plurality of luminaires capable of generating polychromatic light having a dominant wavelength in the visible spectrum and arranged into an array and a computerized device electrically coupled to the plurality of luminaires so as to selectively operate each individual luminaire to produce source light varying with each other and with time. The computerized device operates the luminaire such that each luminaire emits a source light, the source lights combining to form a combined light having selected characteristics. Each of the plurality of luminaires may be operable to emit light having increased spectral opponency, thereby reducing melatonin suppression. The source lights, when perceived directly, recreate a lighting scenario having varying lighting characteristics.
Owner:HEALTHE INC
Light emitting device with high color rendering index and high luminescence efficiency
InactiveUS20100264432A1High color rendering indexImprove luminous efficiencySolid-state devicesSpectral modifiersHigh colorNitrogen oxide
A light emitting device comprises two light-emitting diode (LED) groups, a group of luminophor layers, and an input terminal. The first LED group includes at least one blue LED emitting light having a dominant wavelength in a range between 400 nm and 480 nm, and the second LED group includes at least one red-orange LED emitting light having a dominant wavelength in a range between 610 nm and 630 nm. The group of luminophor layers, which are selected from one of silicates, nitrides, and nitrogen oxides, are positioned above the first LED group and partially converts the light emitted by the first LED group into light having a dominant wavelength in a range between 500 nm and 555 nm. The input terminal is connected to the two LED groups for providing desired electric energy thereto.
Owner:SEMILEDS OPTOELECTRONICS CO LTD
High colour quality luminaire
InactiveUS20120038280A1Low costUniform chromaticity propertyLight source combinationsElectroluminescent light sourcesSemiconductor materialsEffect light
A colour tunable lighting module is described which includes at least three solid state lighting emitters (such as light emitting diodes) and at least two wavelength converting elements (such as phosphors). The three solid state lighting emitters are formed of the same semiconductor material system and the light generated by them has dominant wavelengths in the blue-green-orange range of the optical spectrum. The two wavelengths converters are used re-emit some of the light from two of the emitters in broader spectra having longer dominant wavelengths, while the third emitter is selected to emit light at a wavelength between the dominant wavelengths of the light from the two emitters and the two converters. A control system may be employed to monitor and control the module and the lighting module can be optimised for tunable high colour quality white light applications.
Owner:PHOTONSTAR LED
System for generating non-homogenous light and associated methods
A lighting system including a plurality of luminaires capable of generating polychromatic light having a dominant wavelength in the visible spectrum and arranged into an array and a computerized device electrically coupled to the plurality of luminaires so as to selectively operate each individual luminaire to produce source light varying with each other and with time. The computerized device operates the luminaire such that each luminaire emits a source light, the source lights combining to form a combined light having selected characteristics. The source lights, when perceived directly, recreate a lighting scenario having varying lighting characteristics.
Owner:HEALTHE INC
Lighting device and lighting method
ActiveUS7828460B2Excellent color renditionEffective limitDischarge tube luminescnet screensPoint-like light sourceEffect lightLength wave
Owner:IDEAL IND LIGHTING LLC
High colour quality luminaire
InactiveUS8783901B2Low costWell defined chromaticity propertyLight source combinationsLighting support devicesSemiconductor materialsEffect light
A color tunable lighting module is described which includes at least three solid state lighting emitters (such as light emitting diodes) and at least two wavelength converting elements (such as phosphors). The three solid state lighting emitters are formed of the same semiconductor material system and the light generated by them has dominant wavelengths in the blue-green-orange range of the optical spectrum. The two wavelengths converters are used re-emit some of the light from two of the emitters in broader spectra having longer dominant wavelengths, while the third emitter is selected to emit light at a wavelength between the dominant wavelengths of the light from the two emitters and the two converters. A control system may be employed to monitor and control the module and the lighting module can be optimized for tunable high color quality white light applications.
Owner:PHOTONSTAR LED
Backlighting apparatus and method
InactiveUS20060290624A1Desired chromaticityElectrical apparatusStatic indicating devicesEffect lightPhysics
The present invention provides a method and apparatus for generating light having a desired chromaticity, wherein two or more light-emitting elements which emit light having a dominant wavelength different from the dominant wavelength of a desired chromaticity can be used to generate light having the desired chromaticity. In particular, the dominant wavelength of one light-emitting element is selected to be greater than that of the dominant wavelength of the desired chromaticity and the dominant wavelength of a second light-emitting element is selected to be less than the dominant wavelength of the desired chromaticity. Two or more light-emitting elements configured in this manner can be employed to generate one of each of the three or more display primaries required for a specific lighting application, for example backlighting of a display panel.
Owner:TIR TECH LP
White light emitting device and white light source module using the same
ActiveUS20080265269A1High color reproductionImprove color uniformitySolesDischarge tube luminescnet screensGreen-lightBlue light emitting diode
A white light emitting device including: a blue light emitting diode chip having a dominant wavelength of 443 to 455 nm; a red phosphor disposed around the blue light emitting diode chip, the red phosphor excited by the blue light emitting diode chip to emit red light; and a green phosphor disposed around the blue light emitting diode chip, the green phosphor excited by the blue light emitting diode chip to emit green light, wherein the red light emitted from the red phosphor has a color coordinate falling within a space defined by four coordinate points (0.5448, 0.4544), (0.7079, 0.2920), (0.6427, 0.2905) and (0.4794, 0.4633) based on the CIE 1931 chromaticity diagram, and the green light emitted from the green phosphor has a color coordinate falling within a space defined by four coordinate points (0.1270, 0.8037), (0.4117, 0.5861), (0.4197, 0.5316) and (0.2555, 0.5030) based on the CIE 1931 color chromaticity diagram.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
System for generating non-homogenous light and associated methods
A lighting system including a plurality of luminaires capable of generating polychromatic light having a dominant wavelength in the visible spectrum and arranged into an array and a computerized device electrically coupled to the plurality of luminaires so as to selectively operate each individual luminaire to produce source light varying with each other and with time. The computerized device operates the luminaire such that each luminaire emits a source light, the source lights combining to form a combined light having selected characteristics. The source lights, when perceived directly, recreate a lighting scenario having varying lighting characteristics.
Owner:HEALTHE INC
Method of Light Dispersion and Preferential Scattering of Certain Wavelengths of Light-Emitting Diodes and Bulbs Constructed Therefrom
InactiveUS20090200939A1Little and no loss in light intensityDischarge tube luminescnet screensPoint-like light sourceLight dispersionLength wave
A method for preferential scattering of certain wavelengths of light and / or dispersing light in an LED or LED bulb. The method includes emitting light from at least one LED die, and scattering the light from the at least one LED die by dispersing a plurality of particles having a size a fraction of at least one dominant wavelength of the light from the at least one LED die in the LED outer shell or in an LED bulb or in an at least one shell of an LED bulb. Alternatively, the method includes emitting light from the at least one LED die, and dispersing the light from the at least one LED die by distributing a plurality of particles having a size one to a few times larger than a dominant wavelength of the light from the LED in an outer shell, or body of the LED bulb.
Owner:SWITCH BULB CO INC
LED with enhanced light extraction
ActiveUS20100283075A1Improve light extractionImproved non-symmetrical emissionSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesLight emitting deviceSemiconductor
A light emitting device having a plurality of light extracting elements defined on an upper surface of a semiconductor layer of the device, wherein the light extracting elements are adapted to couple light out of the device and to modify the far field emission profile of the device. Each element comprises an elongate region having a length at least twice its width and also greater than the effective dominant wavelength of light generated in the device. The elongate region extends orthogonal to the upper surface but not into the light emitting region of the device and may be oriented at an angle of less than 45° relative to one of a pair of basis axis defining a plane parallel to the semiconductor layer. Each elongate region is spatially separated from neighbouring elongate regions such that it perturbs light generated in the light emitting region independently of the neighbouring regions.
Owner:LUMILEDS HLDG BV
Ultra-white float glass
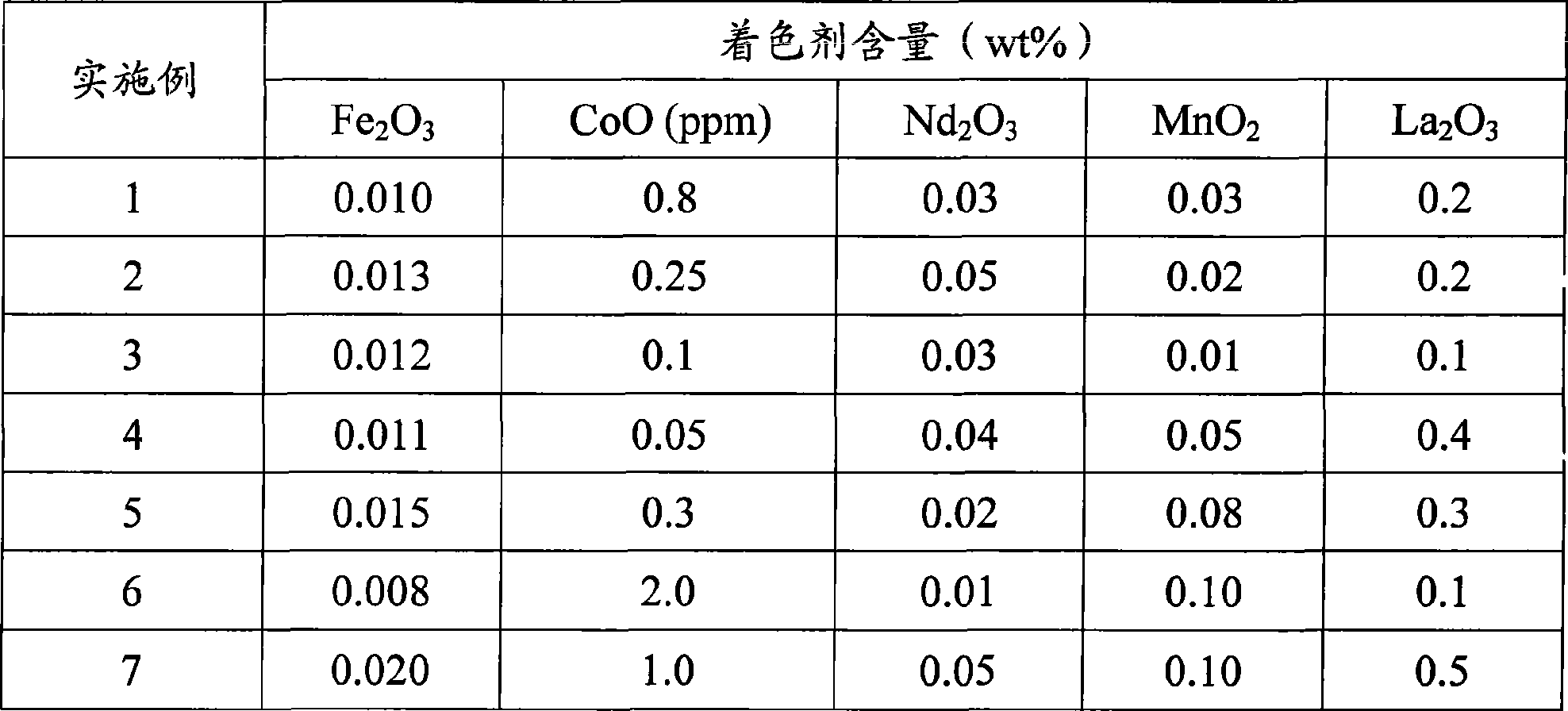
The invention relates to super-white float glass comprising a basic glass part and a colorant part, wherein the basic glass part comprises the following components: 65 to 75 weight percent of SiO2, 10 to 20 weight percent of Na2O, 5 to 15 weight percent of CaO, 0 to 5 weight percent of MgO, and 0 to 5 weight percent of Al2O3; and the colorant part comprises the following components counted by weight of the basic glass: 0 to 0.02 weight percent of Fe2O3, 0 to 2ppm of CoO, 0 to 5 weight percent of Nd2O3, 0 to 5 weight percent of La2O3, and 0 to 0.1 weight percent of MnO2. The finished product of the super-white float glass has the dominant wavelength range of between 480 and 510nm under the condition of the conversion into 5mm equivalent thickness, the visible light transmission rate of above 91 percent, and the light blue edge color.
Owner:CSG HOLDING
Blue laser pumped green light source for displays
The invention relates to light sources and displays incorporating blue laser pumped light sources that provide green light. According to a first aspect of the invention, a green light source includes a semiconductor diode laser emitting light in an optical path having a dominant wavelength within the blue spectral region, a substrate positioned in the optical path of the semiconductor diode laser, and a material coupled to the substrate. The material is selected to absorb light emitted by the semiconductor diode laser and, in response, to emit light having a dominant wavelength within the green spectral region. According to a second aspect of the invention, an apparatus includes a lighting module for a display, the lighting module includes an array of red laser light sources, an array of blue laser light sources, and an array of green light sources according to the first aspect of the invention.
Owner:CORP FOR LASER OPTIC RES
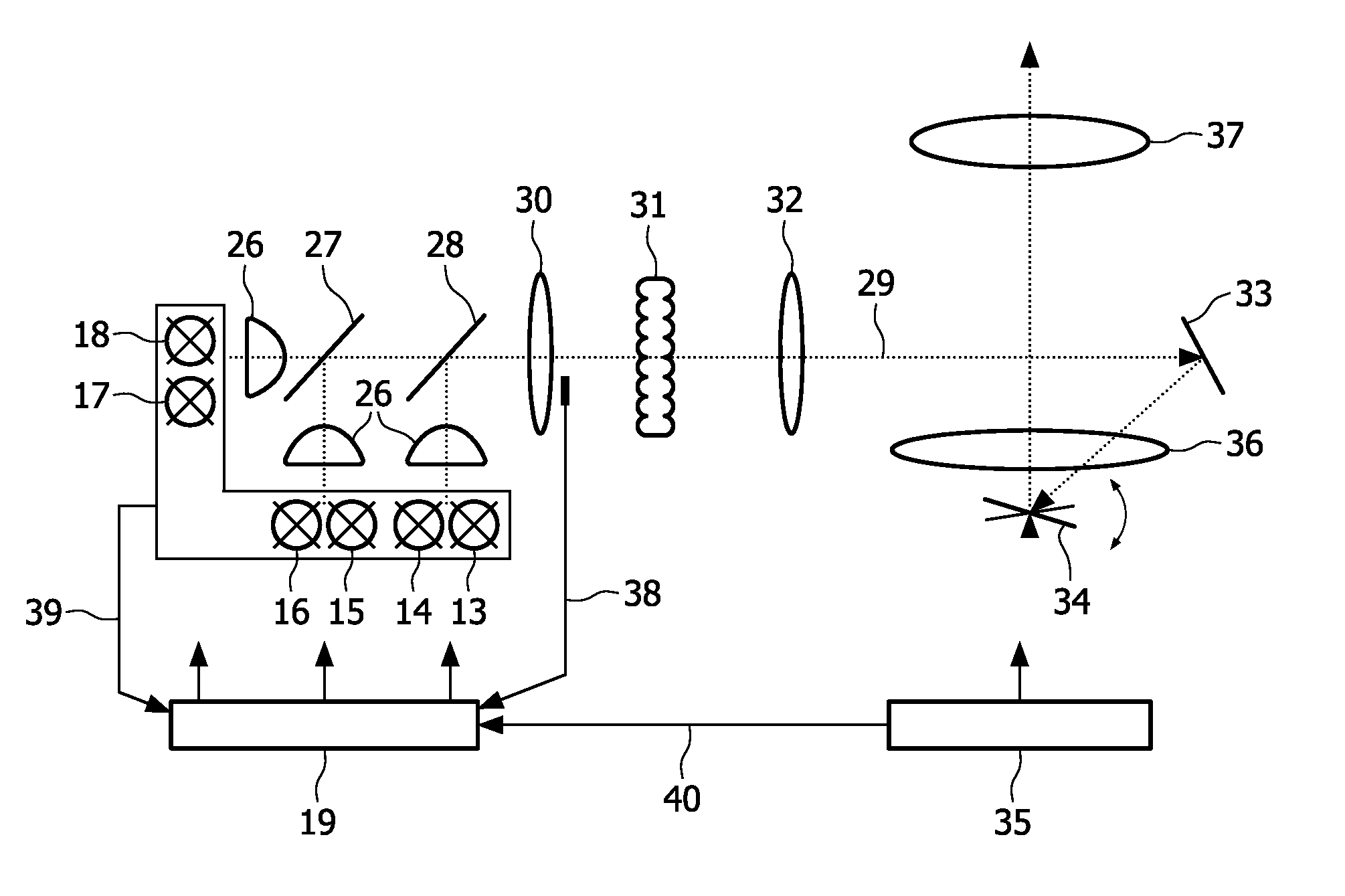
Light source device and image display apparatus
ActiveUS8562146B2Efficient extractionEfficiently propagatingElectric circuit arrangementsProjectorsPhosphorFluorescence
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
System and method for generating light by color mixing
InactiveUS20100072900A1Simple methodElectrical apparatusElectroluminescent light sourcesGamutPeak value
The present invention relates to a method of generating light with a predetermined chromaticity value of a color gamut by color mixing of the light emitted by a plurality of light sources, each of which emits light with a primary color, the light sources being capable of emitting light with at least three primary colors, wherein at least a first and a second light source are used to emit light of at least one primary color. The object to provide a simple method of generating light with a predetermined and constant chromaticity value of a color gamut by color mixing of the light emitted by a plurality of light sources, which can even be advantageously used in display applications sequentially displaying primary colors, is achieved in that said first and said second light source emit light with different peak and / or dominant wavelengths, the chromaticity of the primary color generated by color mixing of the light emitted from said first and said second light source being adjusted to a predetermined and constant chromaticity value by controlling the ratio of intensities of said first and said second light source, and said chromaticity value of said primary-color light generated by color mixing is used to generate light by color mixing with the light of other primary color light sources.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
White position taillight for aircraft
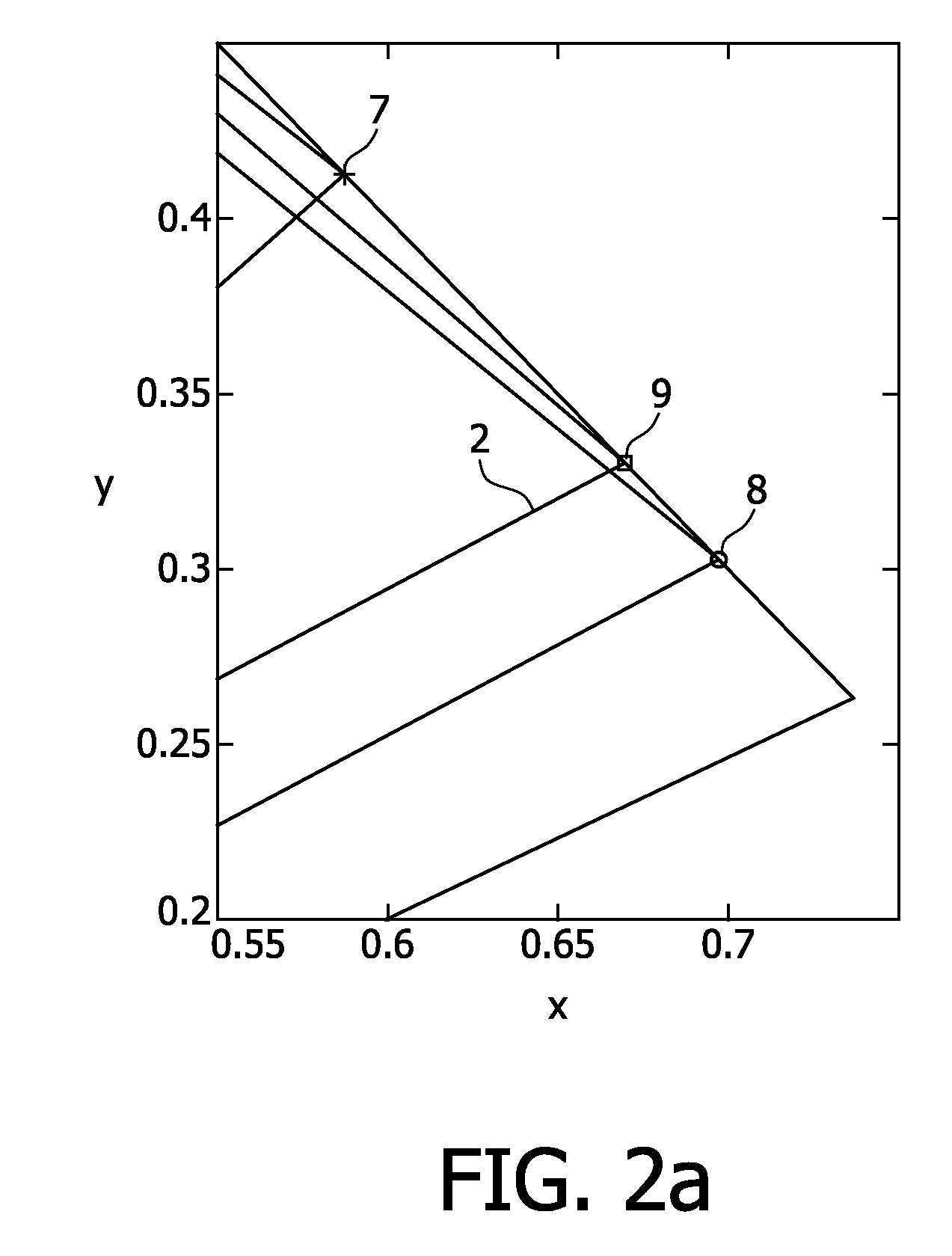
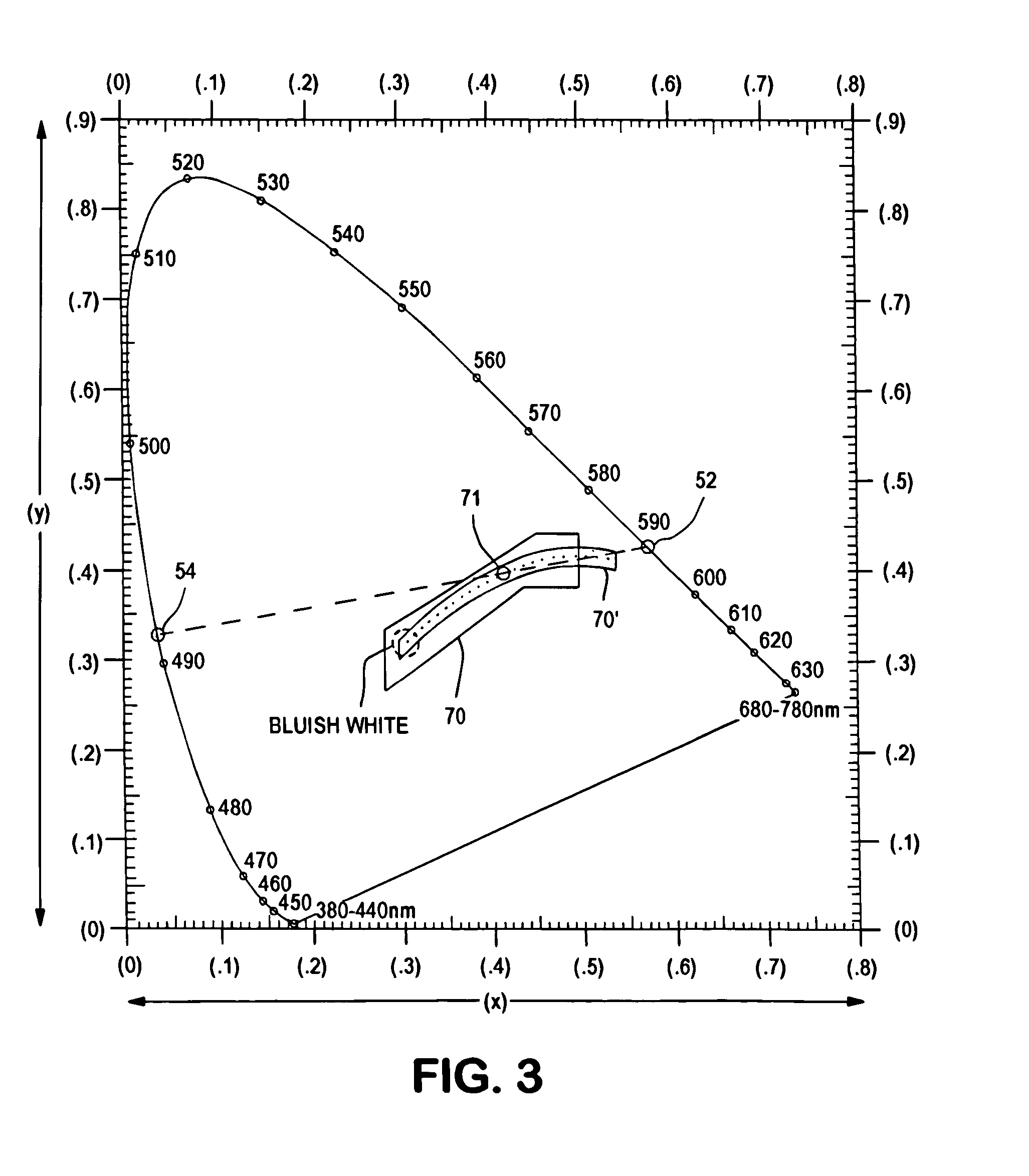
InactiveUS7118261B2Much of lightNon-electric lightingLighting support devicesNight visionLuminous flux
An aircraft position light employs selected colored LEDs to produce a white appearing warning light with a reduced light component in the amplification spectrum of night vision imaging equipment. A combination of amber and cyan LEDs are selected to produce approximately three amber flux units for every cyan flux unit resulting in a white composite light. Both of the selected LEDs have dominant wavelengths of less than 600 nm.
Owner:WHELEN ENGINEERING COMPANY
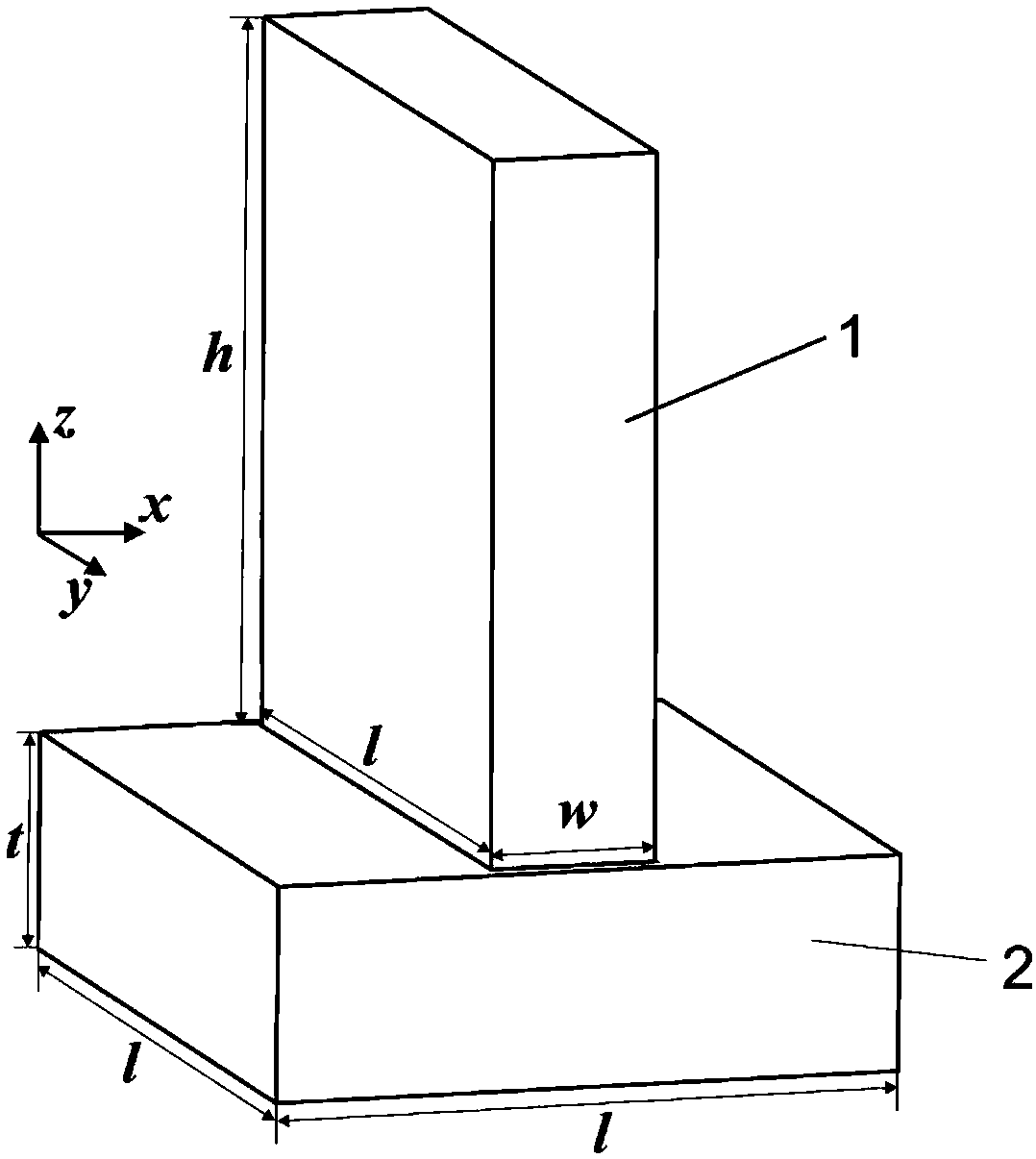
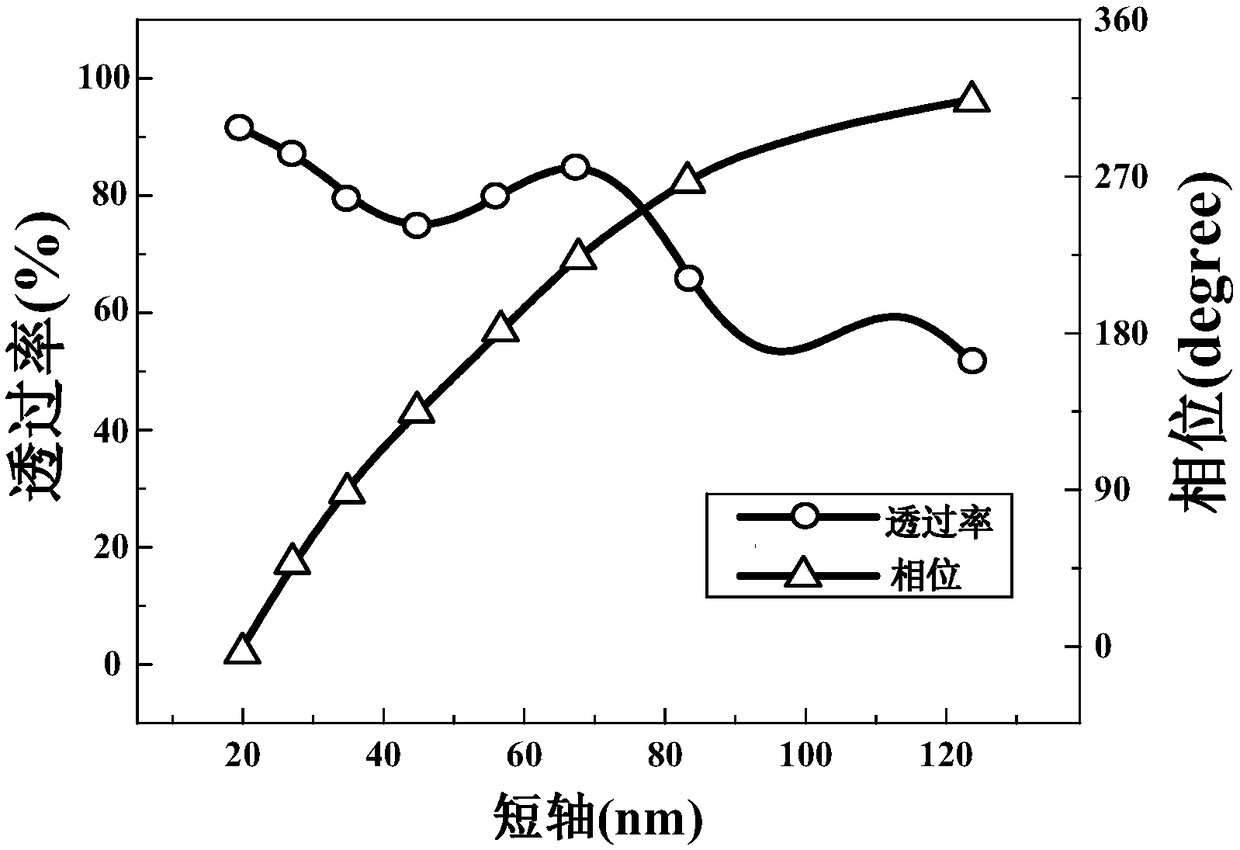
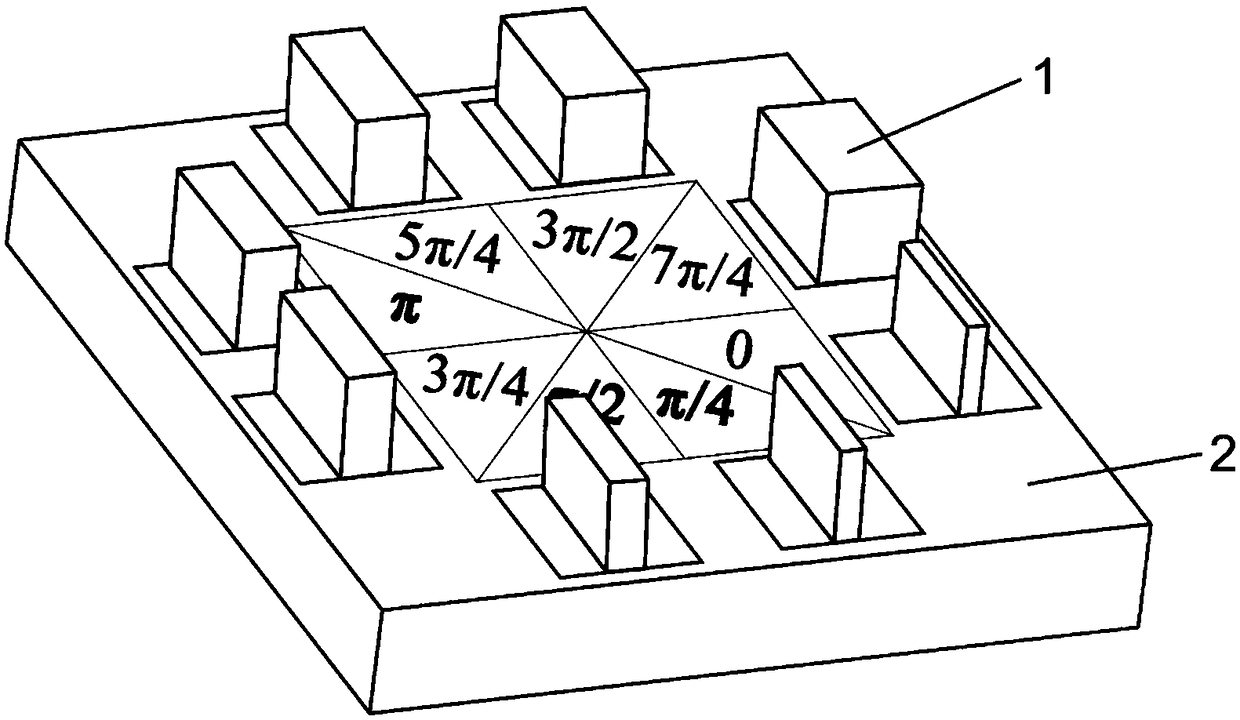
Polarization multiplexing holographic imaging method based on transmission type all-medium metasurface
The invention belongs to the technical field of micro-nano optics, polarization optics and optical holographic, and discloses a polarization multiplexing holographic imaging method based on a transmission type all-medium metasurface. A response main wavelength <lambda> is determined; geometric parameters of a unit structure are determined; a GS phase recovery algorithm is adopted to obtain phase distribution of the unit structure responding to the main wavelength; the pixel point of each element is expanded into a 2*2 array by adopting a Dammann grating method, and the obtained each pixel unitcomprises information responding to horizontal polarized light and information responding to vertical polarized light; and a synthesized silicon nano-antenna array is irradiated by horizontal polarized light and vertical polarized light with the wavelength of <lambda>, and different holographic images are reconstructed. According to the method, phase modulation of 0-2 <pi> can be realized only bychanging the size of the short axis of the silicon nano-antenna, and an embossment phase modulation structure of any step number can be realized equivalently; and a simple process, high processing error tolerance and quite high stability and reliability are achieved.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCIENCES
Image sensor unit and image reader
InactiveUS20120154876A1Data stabilityPaper-money testing devicesOptical light guidesIlluminanceLight guide
An illumination device includes a light guide made of plastic, and a light source including a light emitting element whose dominant wavelength is a light emission wavelength in an infrared region, and identifies a banknote. White reference plates are provided at positions that are at opposite ends of a rod lens array and cover respective areas external to an image region across the banknote. A correction coefficient is acquired by calculation. The calculation is made by correcting an illuminance such that IR correction data is substantially identical to IR reference data preliminarily stored in a memory circuit in a signal processor on the basis of IR white reference data representing a white reference illuminance generated from light reflected from the white reference plates. The correction coefficient is used for correcting IR image data when the banknote is read.
Owner:CANON COMPONENTS INC
Lighting device having first, second and third groups of solid state light emitters, and lighting arrangement
A lighting device comprising first, second and third groups of solid state light emitters, the first group emitting light having a dominant wavelength of 430 to 490 nm, the second group at 525 to 575 (in some devices 540 to 575 nm), the third group at 610 to 640 nm. In some devices, wavelength of light from emitters in first and second groups, and light from second and third groups, differs by at least 70 nm. Some devices emit light having CRI Ra of at least 70 when first, second and third groups of emitters are illuminated. Also, a lighting arrangement comprising first, second and third groups as above, in addition to a fourth emitter emitting light of dominant wavelength outside the ranges for the first, second and third groups, and not more than 10 nm different from a dominant wavelength of a color on an item to be illuminated.
Owner:IDEAL IND LIGHTING LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com