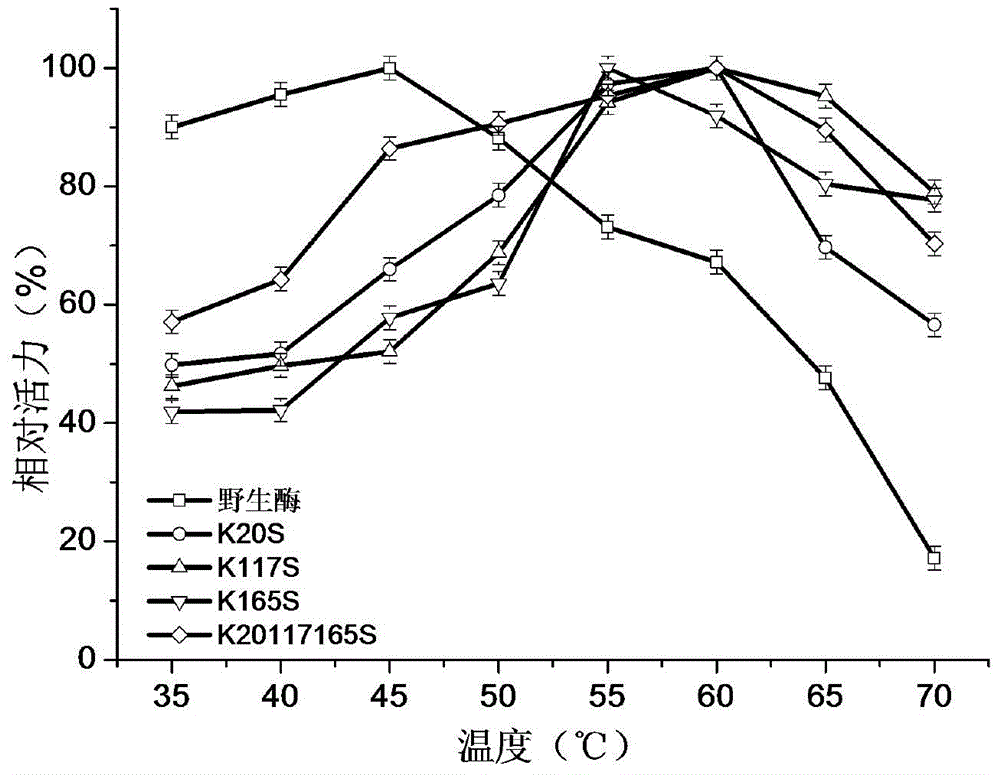
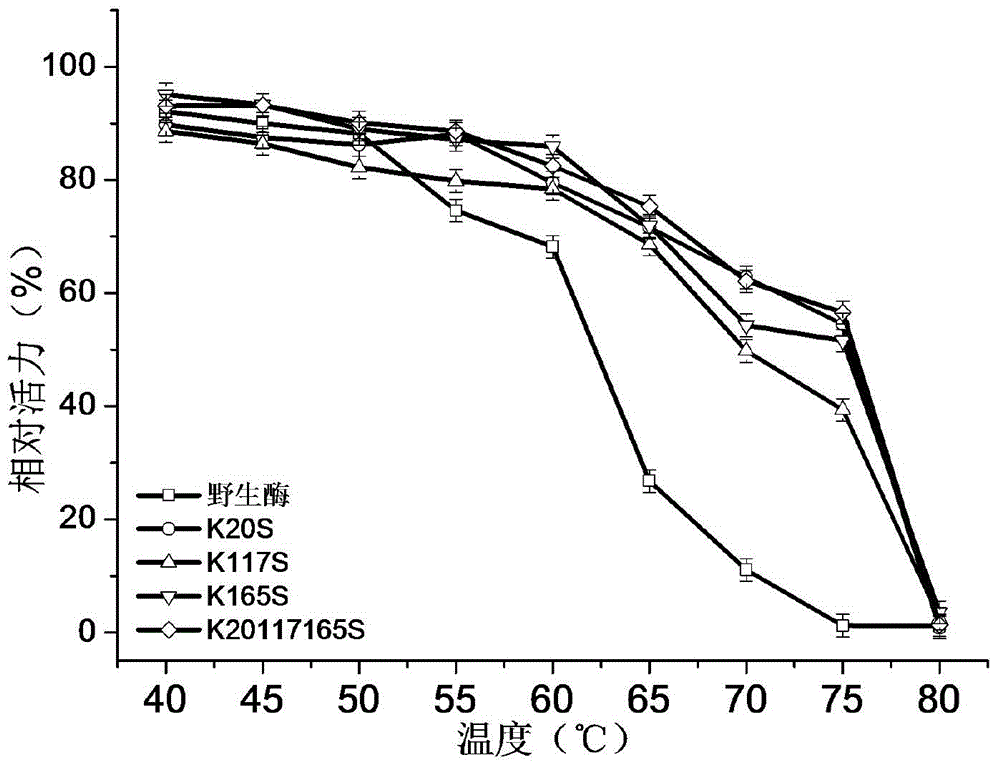
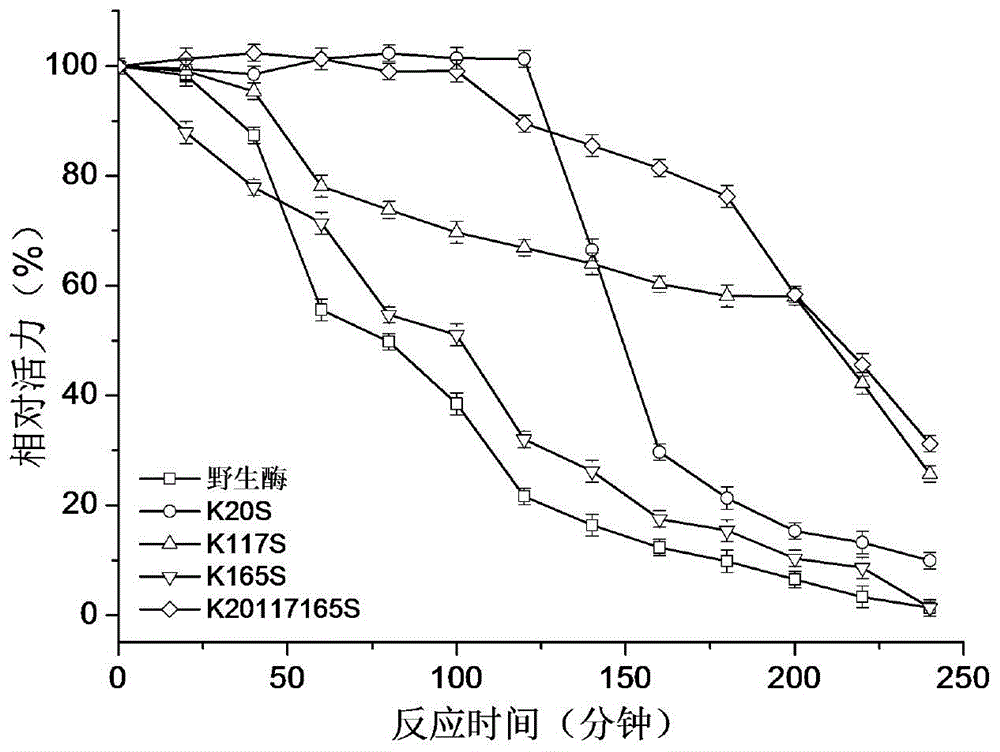
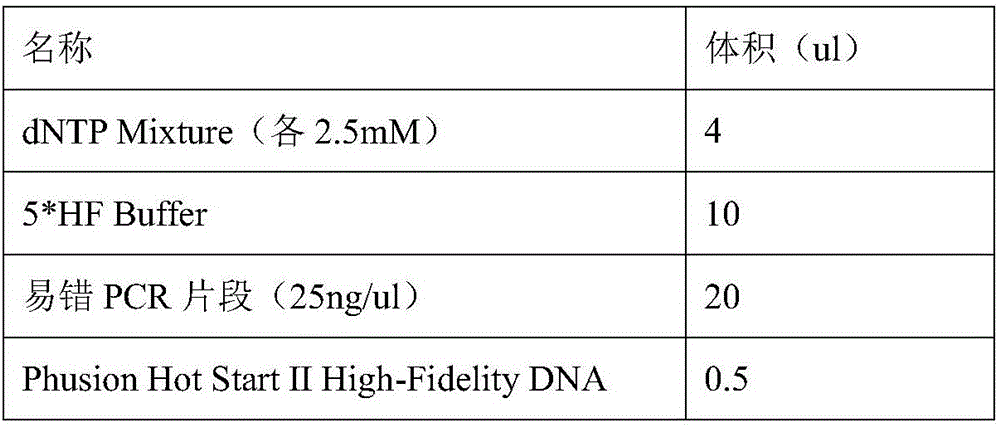
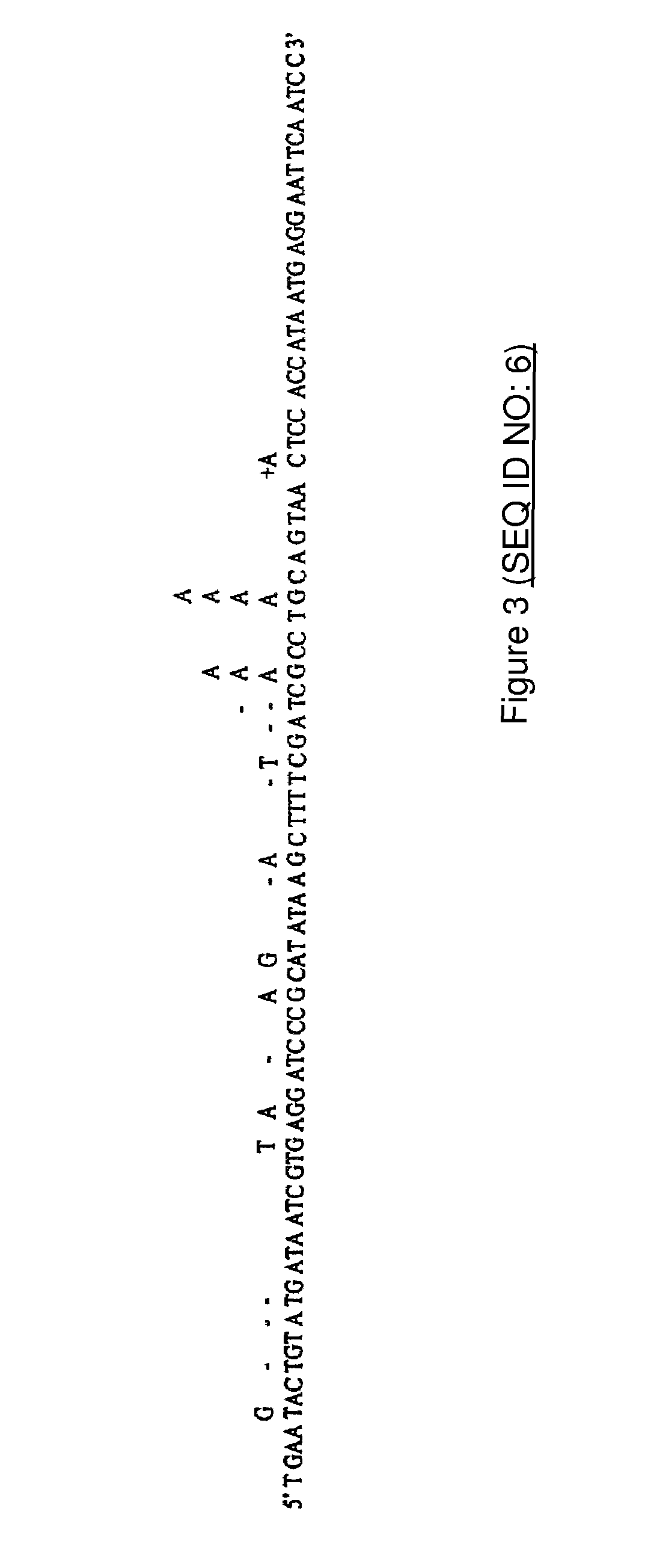
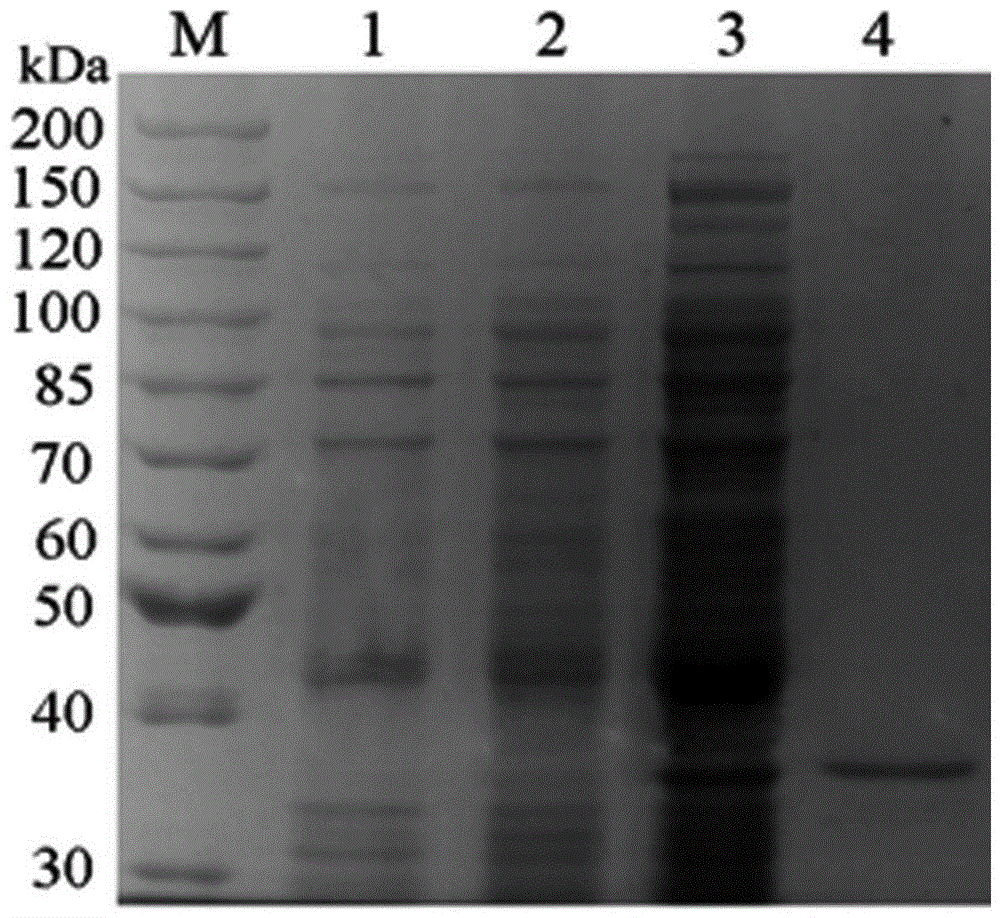
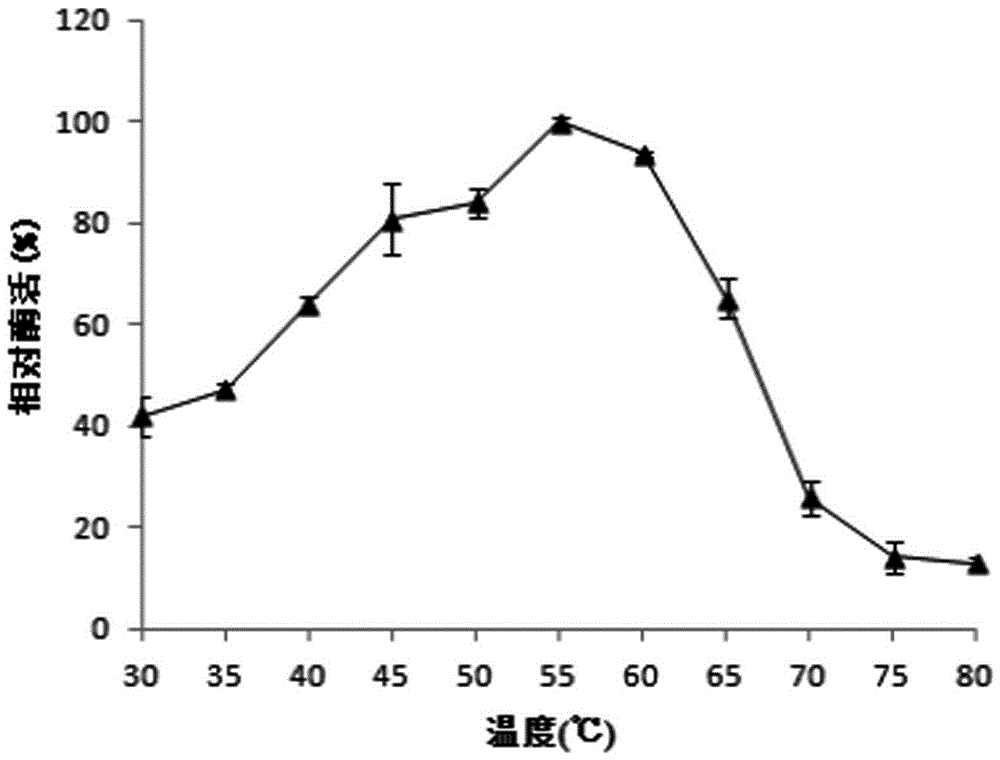
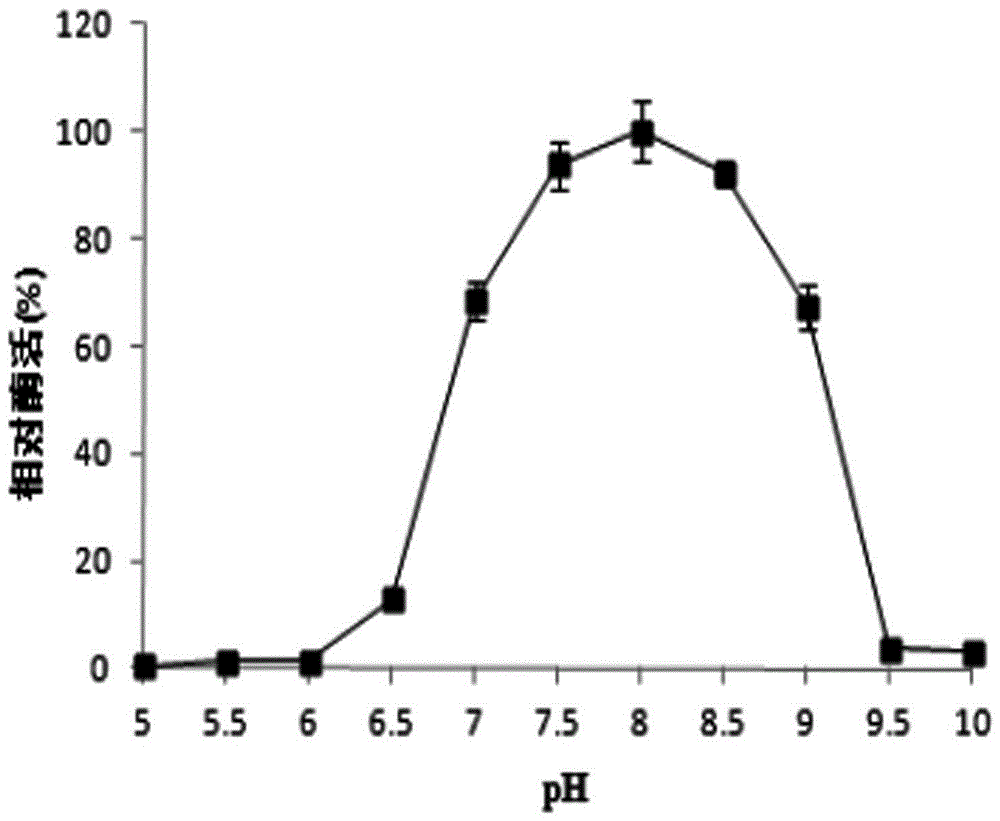
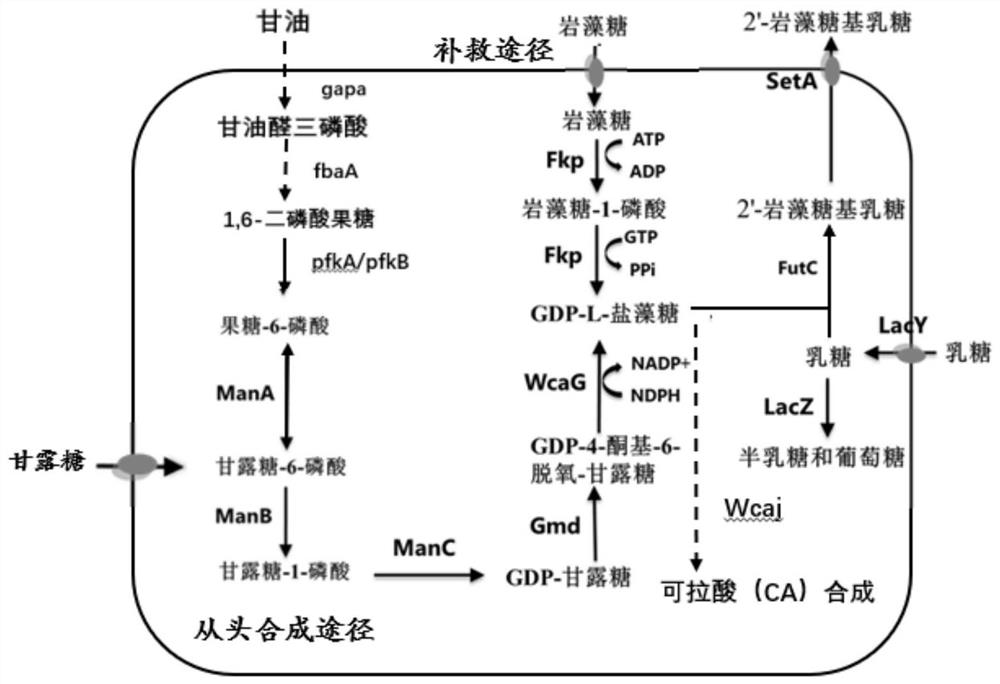
Patents
Literature
91 results about "Mutase" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A mutase is an enzyme of the isomerase class that catalyzes the movement of a functional group from one position to another within the same molecule. In other words, mutases catalyze intramolecular group transfers. Examples of mutases include bisphosphoglycerate mutase, which appears in red blood cells and phosphoglycerate mutase, which is an enzyme integral to glycolysis. In glycolysis, it changes 3-phosphoglycerate to 2-phosphoglycerate. In particular it moves phosphate groups within a single molecule, for instance: phosphoglycerate mutase.
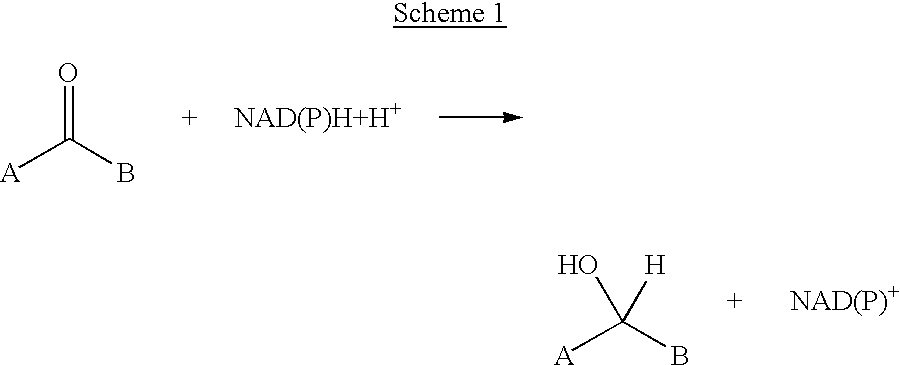
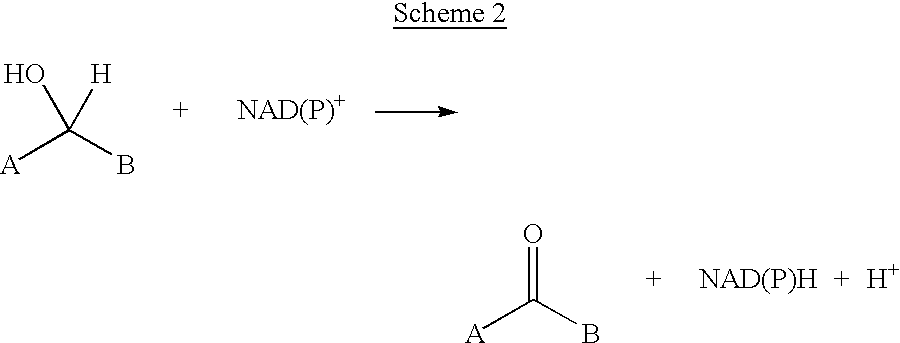
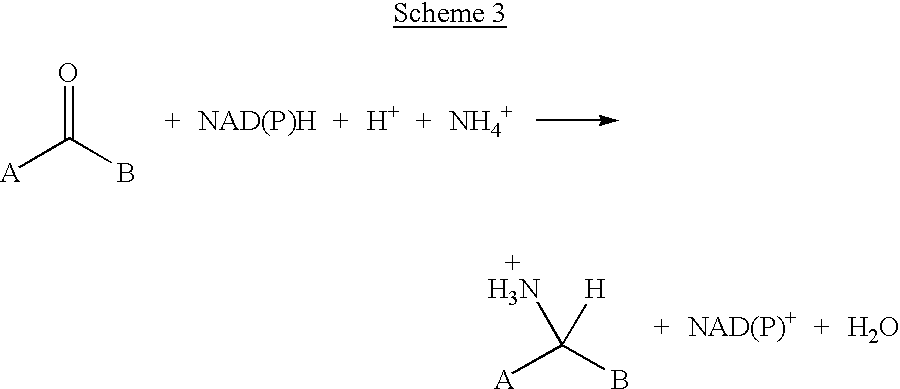
Method for reductive amination of a ketone using a mutated enzyme
Methods for chemically transforming compounds using a mutated enzyme are provided, and more particularly a method for the production of an amino acid from a target 2-ketoacid, the production of an amine from a target ketone and the production of an alcohol from a target ketone. The methods comprise creating a mutated enzyme that catalyzes the reductive amination or transamination of the target 2-ketoacid or ketone or the reduction of the ketone and providing the mutated enzyme in a reaction mixture comprising the target 2-ketoacid or ketone under conditions sufficient to permit the formation of the desired amino acid, amine or alcohol to thereby produce the amino acid, amine or alcohol.
Owner:CODEXIS INC
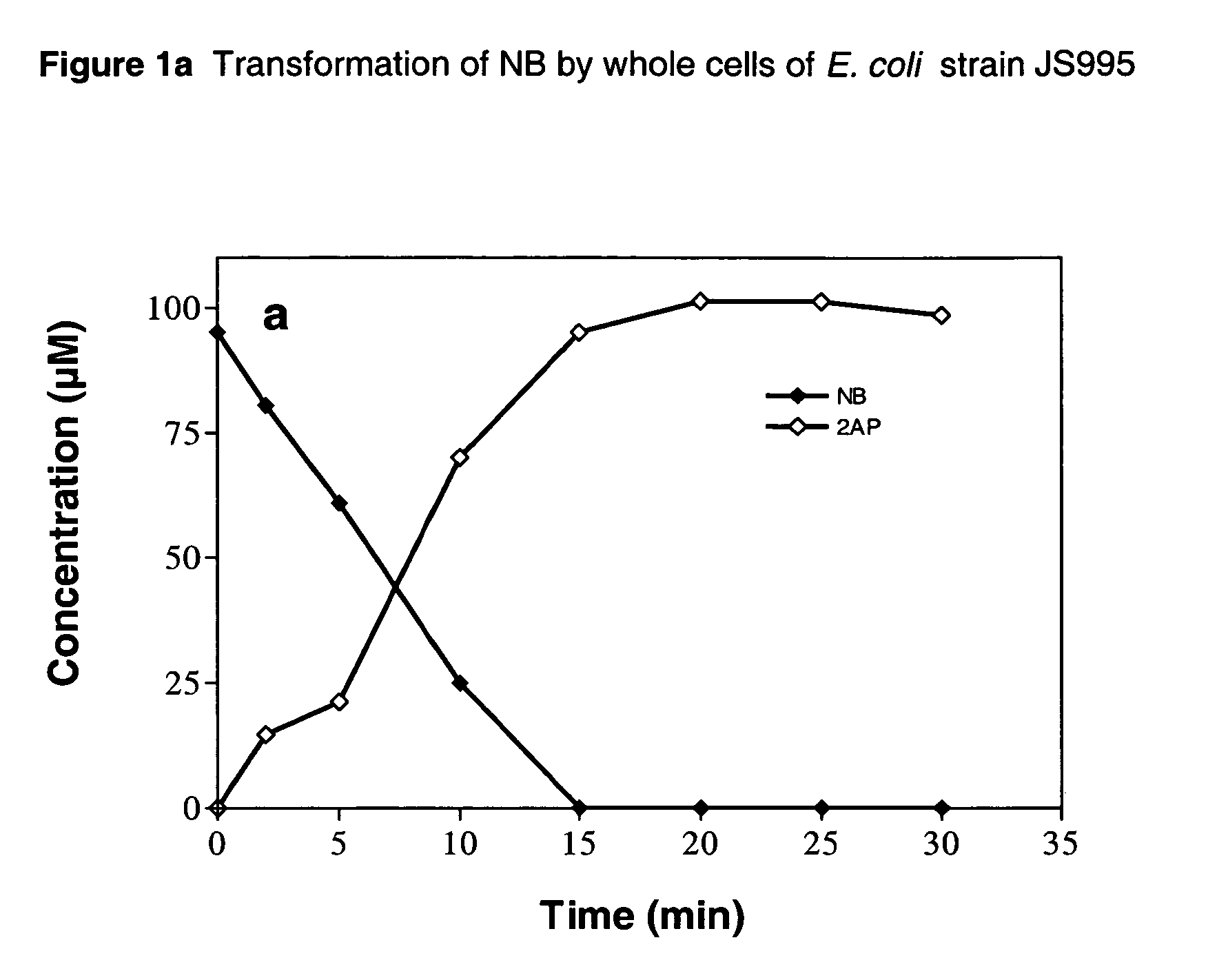
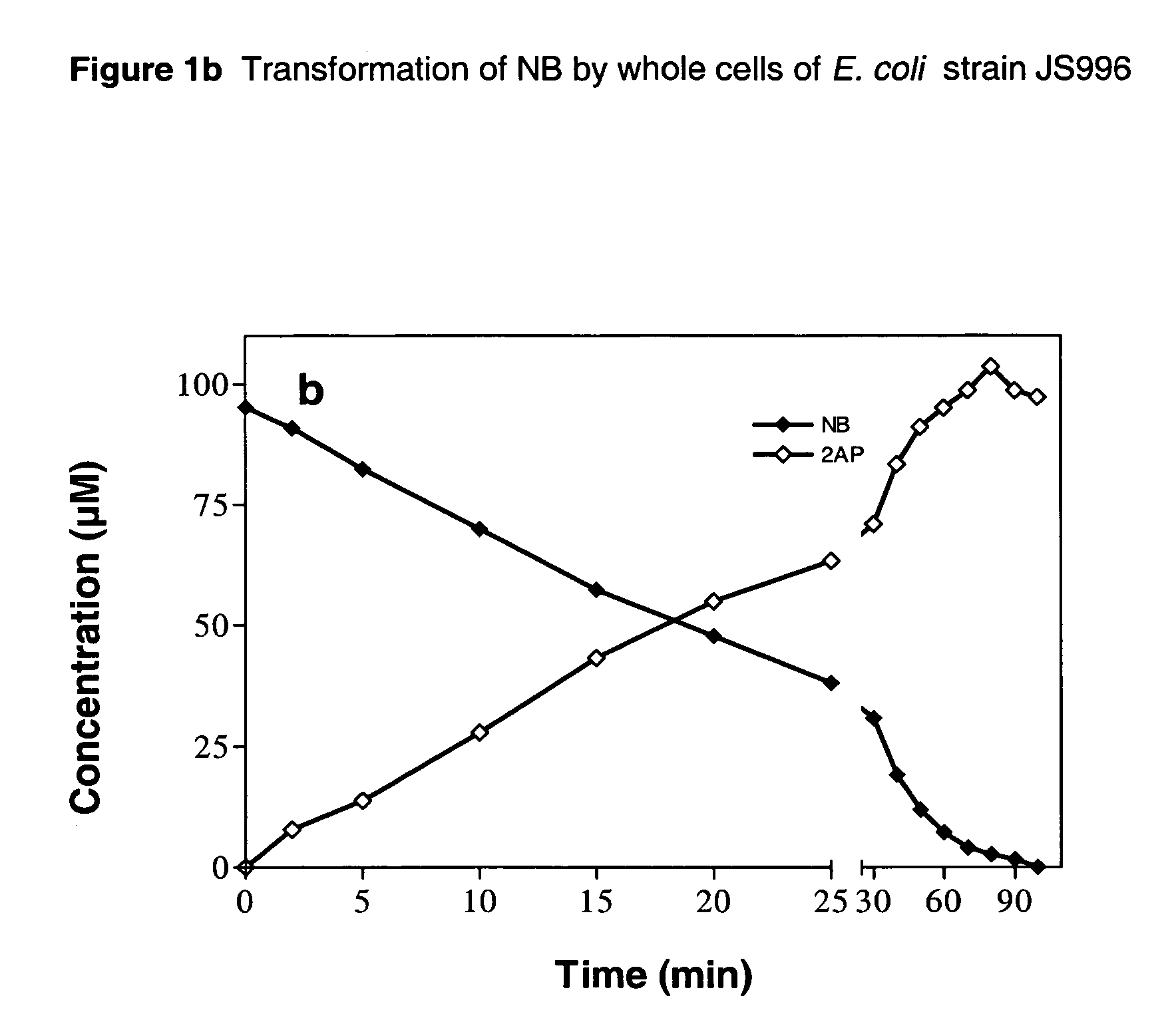
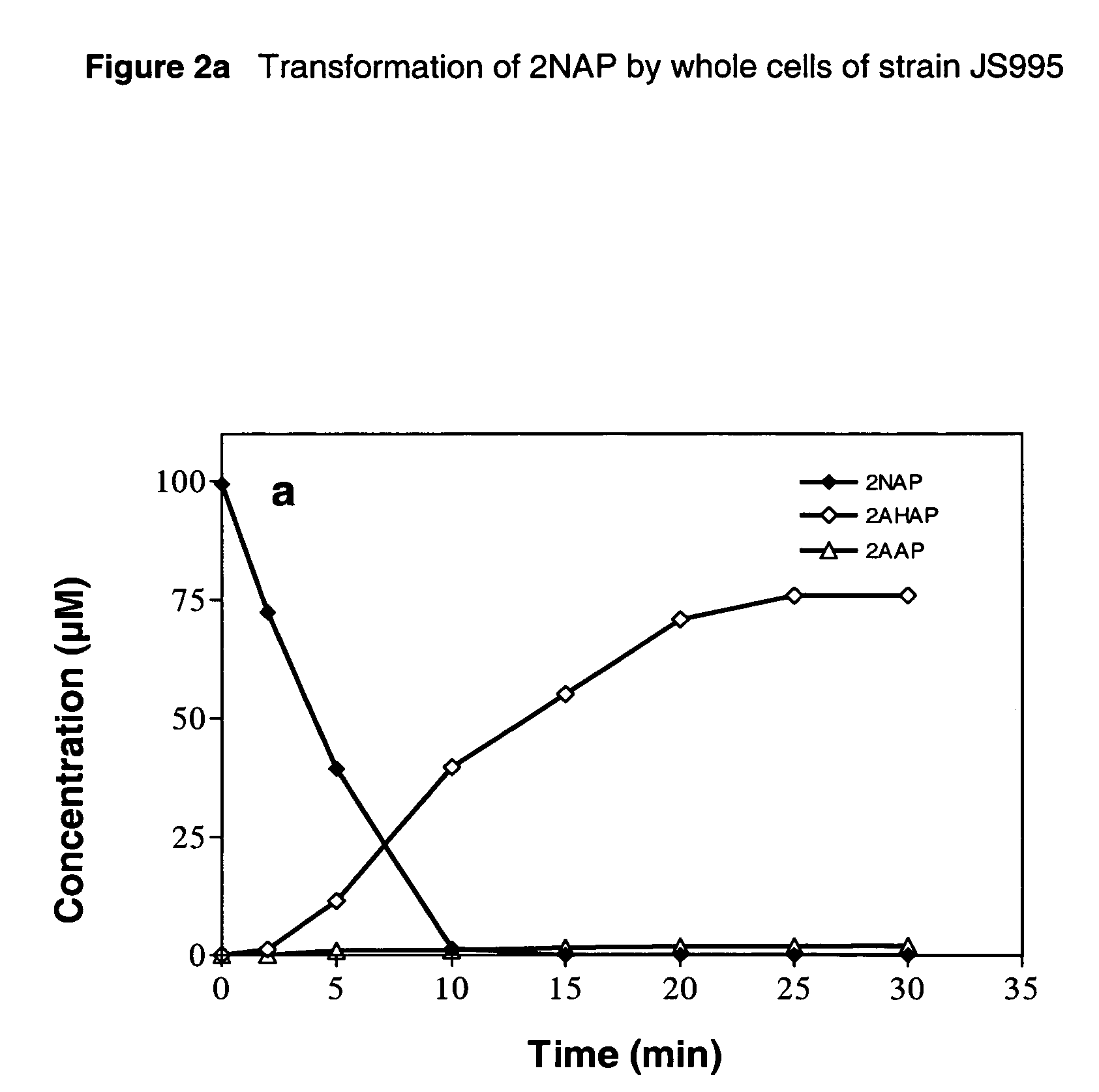
Biological process for the conversion of nitroarenes to ortho-aminophenols using recombinant E. coli strains
A process for biological production of ortho-aminophenols from nitroaromatic compounds using recombinant E. Coli strains. The process uses an enzyme system that makes use of a nitroreductase enzyme that initially reduces the nitroarene to the hydroxylaminoarene and a mutase enzyme that converts the hydroxylaminoarene to an ortho-aminophenol.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESETNED BY THE SEC OF THE AIR FORCE
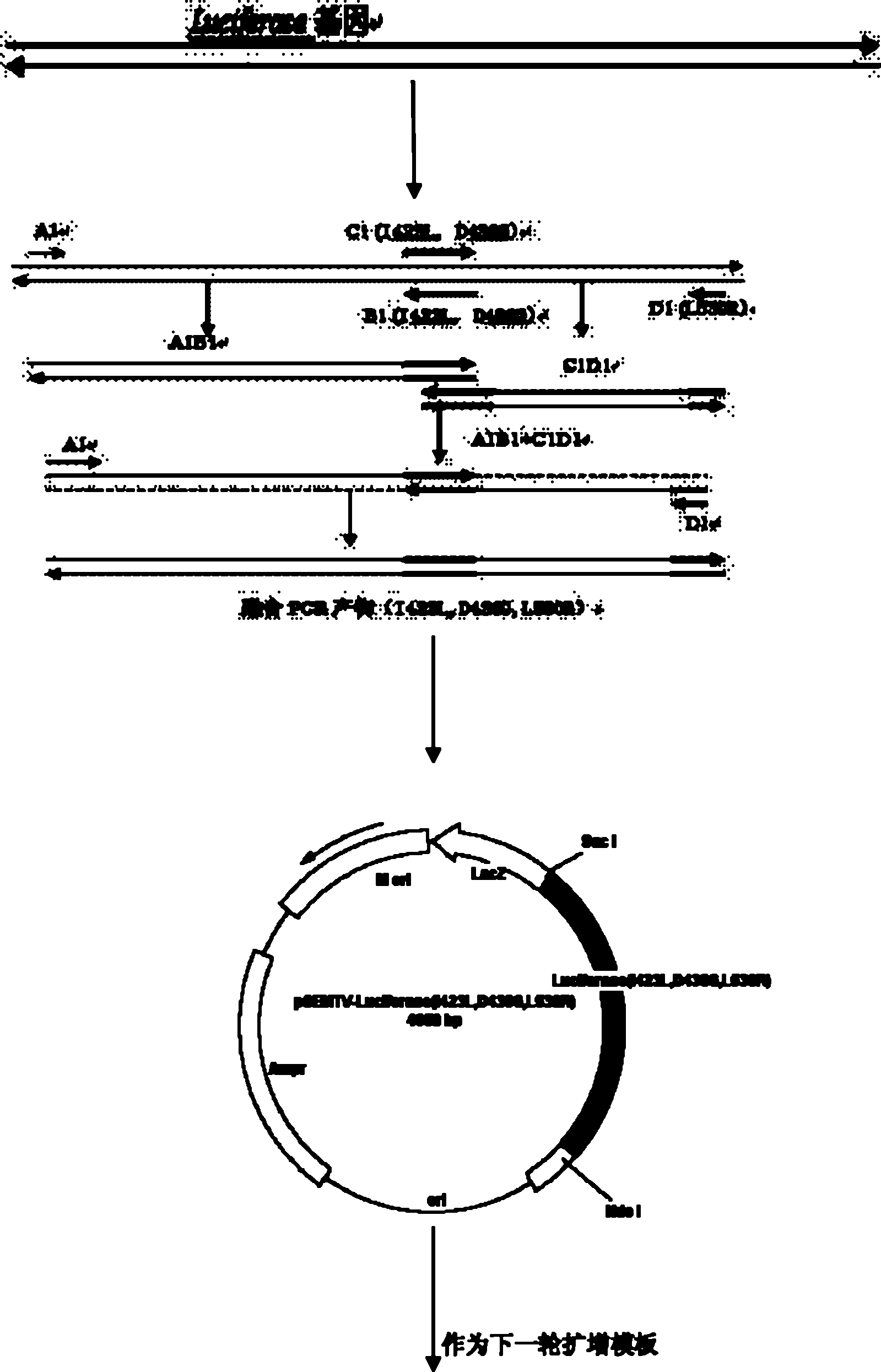
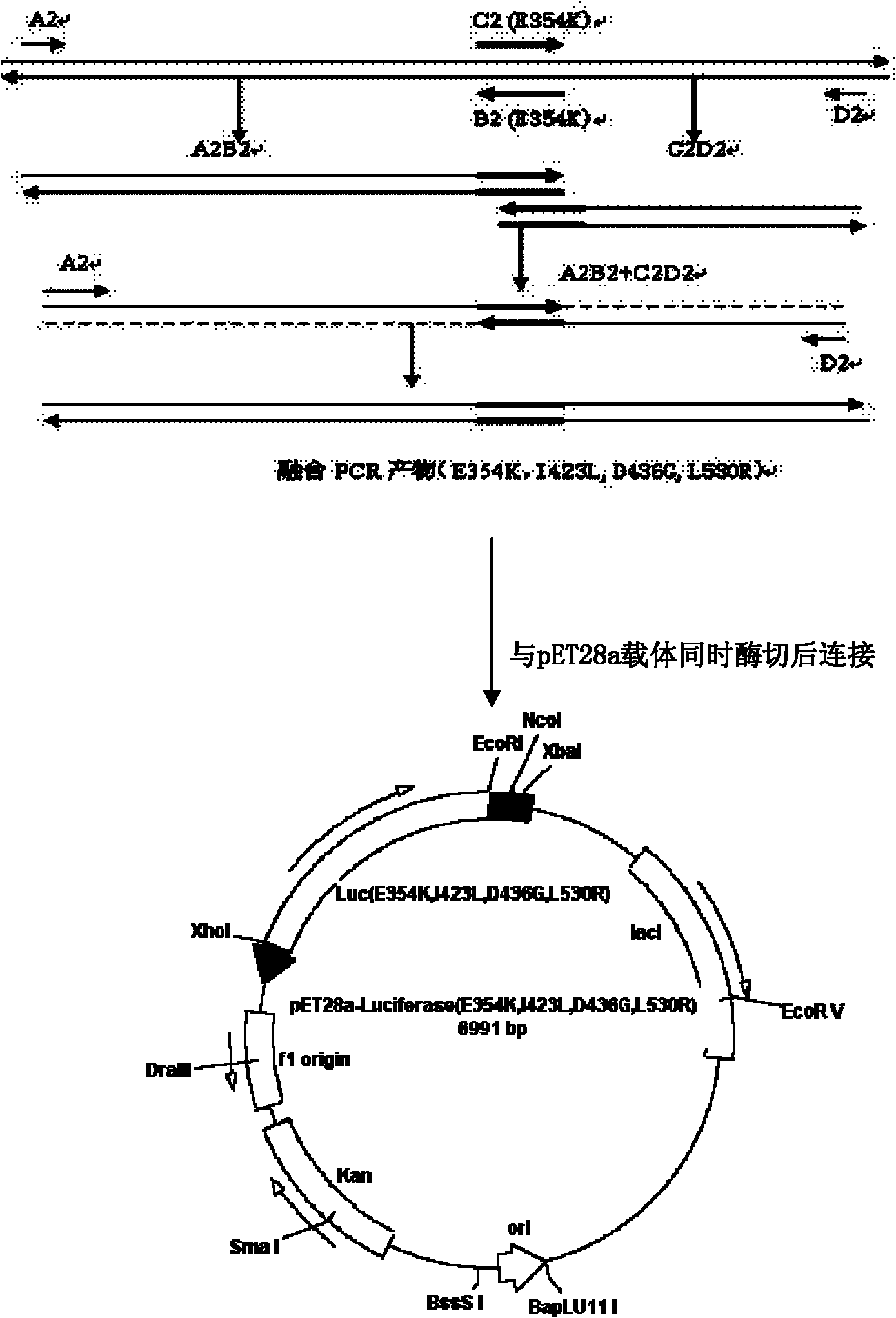
Gene encoding of firefly luciferase, its preparation method and application
InactiveCN102191213AImprove thermal stabilityMeet application requirementsBacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementEscherichia coliCompetent cell
The invention relates to a gene encoding of firefly luciferase, its preparation method and application, which comprises the following steps: 1. introducing mutation sites of mutant enzymes; 2. identifying recombinant plasmids; 3. sequencing to obtain polymerase chain reaction (PCR) fragment with 1060 mutation sites; 4. obtaining escherichia by using restriction endonucleasecoli purifying after recovering and purifying through gel; 5. identifying recombinant plasmids to obtain a separating protein gene; 6. culturing escherichia coli, 7. converting recombinant plasmids into BL21 competent cell to obtain bacterial strain capable of expressing mutant enzymes, 8. culturing the obtained BL21 expression bacterial strain; 9. centrifuging bacteria liquid of protein, centrifuging to obtain supernatant through ultrasonic fragmentation; 10. determining to obtain firefly luciferase with high heating stability and high enzyme activity. The invention relates to application of firefly luciferase gene on foodstuff, medicine, thalline detection. The luminous intensity of the mutant enzyme is about 15 to 20 times than that of wild type, and the mutant enzyme has good heat stability than that of the wild type.
Owner:WUHAN INST OF VIROLOGY CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Process of preparing D-amino acid oxydase
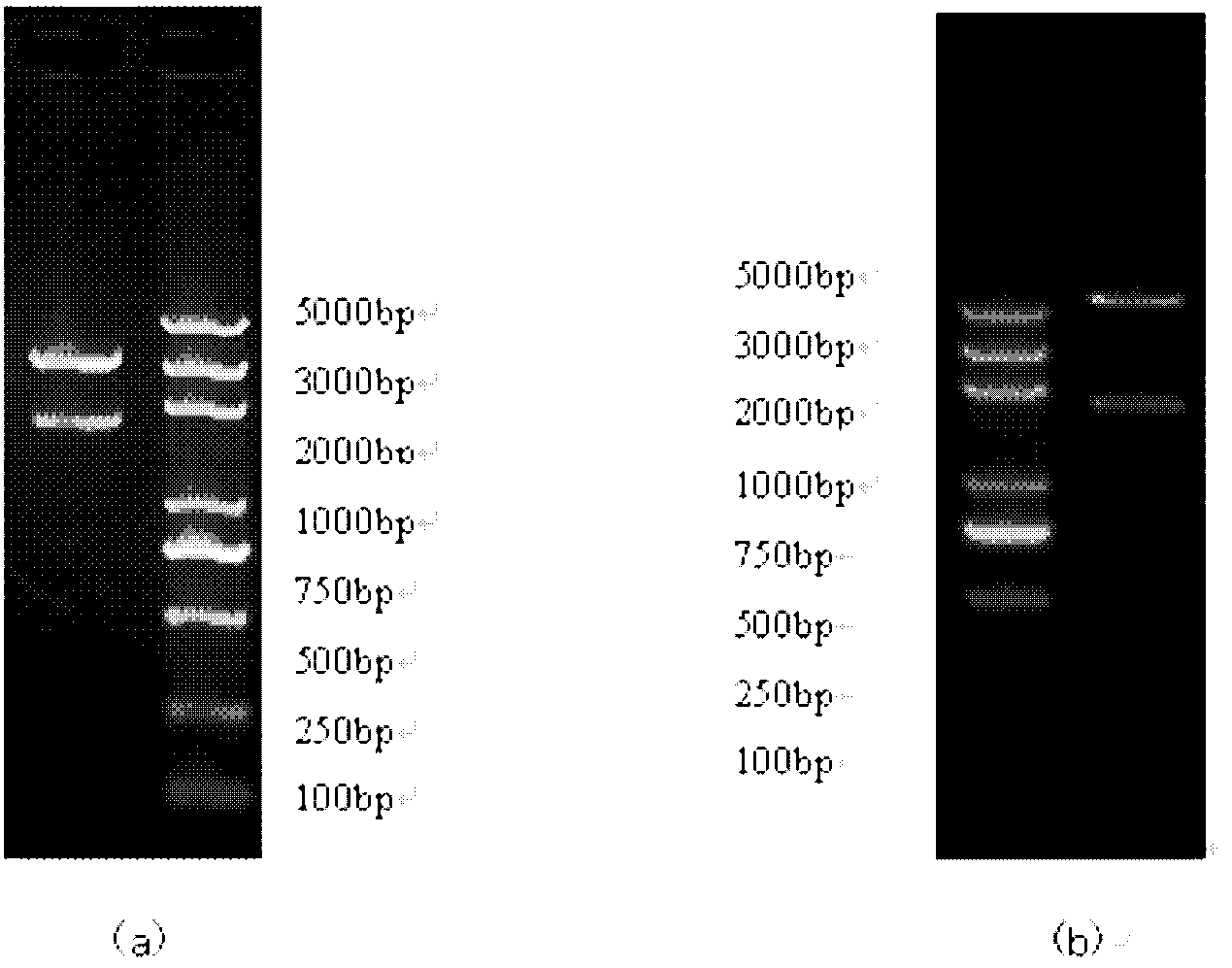
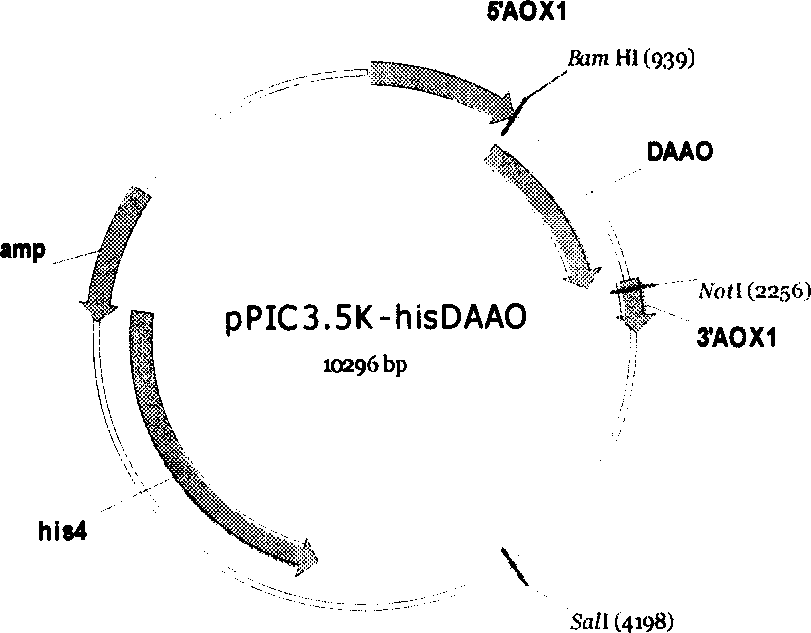
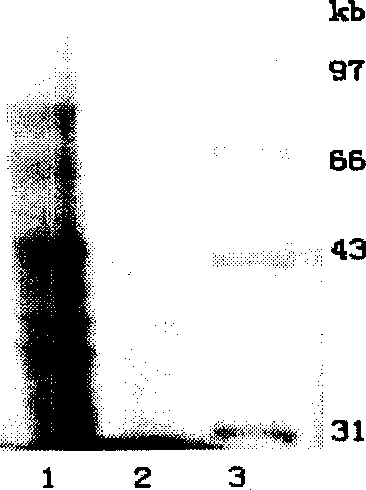
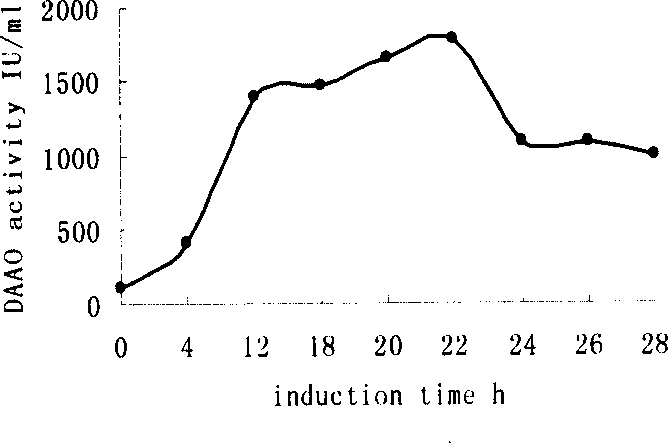
The invention is a method of preparing D-amino acid oxidase, relating to a method of preparing flavo-enzyme D-amino acid oxidase. Concretely, it relates to a method of highly efficiently producing mutational D-amino acid oxidase by constructing recombinant engineering strains. It reconstructs wild D-amino acid oxidase coming from Trigonopsis variablilis by means of gene engineering, fuses a segment of Histag at N end and C end of the wild enzyme, and further implements high-efficiency fast separation of mutational enzyme by affinity chromatography. The expression level of the enzyme in fermentation liquor is 4000IU / mL, higher than that of the wild enzyme, and the recovery ratio of Ni-column affinity chromatography is 50%. The purified enzyme can be used in making high-efficient oxidation conversion of cephalosporin C- to produce glutaryl-7-ACA and be used together with GL-7-ACA to produce 7-ACA.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
1,3-1,4-Beta-glucanase mutant
ActiveCN104130988AImprove activity stabilityImprove thermal stabilityBacteriaWort preparationMutaseGlucanase
Owner:无锡正元生物科技有限公司
Glucose 6 phosphate dehydrogenase mutant
ActiveCN106190996AIncreased specific enzyme activityImprove thermal stabilityBiological material analysisOxidoreductasesMutantSorbitol-6-phosphate dehydrogenase
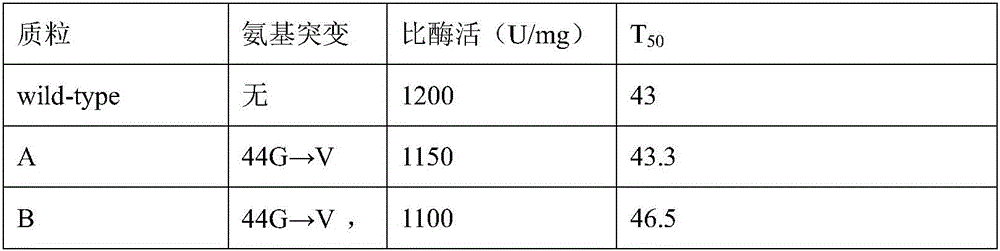
The invention relates to a glucose 6 phosphate dehydrogenase mutant. The mutant is obtained by mutating 44th-site glycine into valine and 319th-site glycine into valine in a glucose 6 phosphate dehydrogenase of which the amino acid sequence is disclosed as SEQ ID No.1; and compared with the glucose 6 phosphate dehydrogenase of which the amino acid sequence is disclosed as SEQ ID No.1 before mutation, the mutant has higher heat stability. The glucose 6 phosphate dehydrogenase mutant has the advantages of high heat stability and high inhibition rate; and the mutant enzyme can be used as a raw material for multiple small molecule detection kits, so that the obtained kit has higher stability and sensitivity.
Owner:NINGBO MEDICAL SYSTEM BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
Recombinant bacterium for generating inosine, preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN106906174AIncrease productionEasy to separate and purifyBacteriaMicroorganism based processesMutaseInosine
The invention relates to a recombinant bacterium for generating inosine. Compared with an original strain, the recombinant bacterium has the weakened phosphopentose mutase activityor inactivated transphosphorylase. The original strain is a strain capable of accumulating inosine. The invention finds an improving target for increasing the fermenting yield of inosine and establishing the corresponding recombinant bacterium. A test proves that the inosine yield of the recombinant bacterium can be obviously increased and the accumulation volume of the side product hypoxanthine can be reduced.
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Mutant enzyme and application thereof
Disclosed is a novel enzyme that exhibits glucose dehydrogenase activity. Furthermore, disclosed is a novel method pertaining to enzyme modification. The mutant enzyme comprises an amino acid sequence wherein one or at least two amino acids selected from the group consisting of (1)-(13) below are replaced with another amino acid in the amino acid sequence of a microorganism-derived glucose oxidase: (1) the amino acid corresponding to the amino acid at position 115 of the amino acid sequence indicated by SEQ ID NO: 1; (2) the amino acid corresponding to the amino acid at position 131 of the amino acid sequence indicated by SEQ ID NO: 1; (3) the amino acid corresponding to the amino acid at position 132 of the amino acid sequence indicated by SEQ ID NO: 1; (4) the amino acid corresponding to the amino acid at position 193 of the amino acid sequence indicated by SEQ ID NO: 1; (5) the amino acid corresponding to the amino acid at position 353 of the amino acid sequence indicated by SEQ ID NO: 1; (6) the amino acid corresponding to the amino acid at position 436 of the amino acid sequence indicated by SEQ ID NO: 1; (7) the amino acid corresponding to the amino acid at position 446 of the amino acid sequence indicated by SEQ ID NO: 1; (8) the amino acid corresponding to the amino acid at position 472 of the amino acid sequence indicated by SEQ ID NO: 1; (9) the amino acid corresponding to the amino acid at position 511 of the amino acid sequence indicated by SEQ ID NO: 1; (10) the amino acid corresponding to the amino acid at position 535 of the amino acid sequence indicated by SEQ ID NO: 1; (11) the amino acid corresponding to the amino acid at position 537 of the amino acid sequence indicated by SEQ ID NO: 1; (12) the amino acid corresponding to the amino acid at position 582 of the amino acid sequence indicated by SEQ ID NO: 1; (13) the amino acid corresponding to the amino acid at position 583 of the amino acid sequence indicated by SEQ ID NO: 1.
Owner:AMANO ENZYME INC
2 '-fucosyllactose high-yield strain and preparation method and application thereof
The invention discloses a 2 '-fucosyllactose high-yield strain as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The preservation number of the strain is CGMCC No.19557. Escherichia coli E.coliBL21 (DE3) is used as a production host, and phosphomannose mutase (manB), mannose-1-phosphate phosphate guanylyltransferase (manC), GDP-mannose-4, 6-dehydratase (gmd), GDP-L-fucose synthase (flc) and alpha-1,2- fucosyltransferase (futC) are overexpressed so as to construct a synthesis path of the 2'-FL; substrate supply is improved by overexpressing sucrose transporter and lactose transporter onthe basis, the production capacity of 2 '-FL is further improved, efficient expression of 2'-FL in escherichia coli is realized, the 2 '-FL high-yield strain is improved.
Owner:江苏华燕集团有限公司
Method for preparing glutamic acid decarboxylase mutant by utilizing ramachandran map information and mutant thereof
InactiveCN104694524AIncrease reaction rateEase of industrial productionFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionBiotechnologyGlutamate decarboxylase
The invention discloses a method for preparing a glutamic acid decarboxylase mutant by utilizing ramachandran map information and a mutant thereof. The method comprises the following steps of: constructing a three-dimensional structural model of glutamic acid decarboxylase, carrying out dihedral angle reasonable evaluation to generate a ramachandran map, and determining an amino acid residue site in an unreasonable conformation area from the ramachandran map; designing a site-specific mutation primer aiming at the site, and carrying out site-specific PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) amplification by taking a glutamic acid decarboxylase gene as a template so as to obtain a site-specific mutation library; and screening the glutamic acid decarboxylase mutant from the site-specific mutation library. Enzyme is rationally designed through structural information provided by the ramachandran map; in combination with a site-specific mutation technology, the mutation probability is effectively increased; the time is saved; the experimental efficiency is increased; mutant enzyme the catalytic activity of which is superior to wild type enzyme can be obtained by screening; the mutant enzyme is capable of increasing the reaction rate for generating gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) by catalyzing L-glutamic acid or sodium salts thereof; and thus, industrial production of GABA is easily carried out.
Owner:NINGBO INST OF TECH ZHEJIANG UNIV ZHEJIANG
Method for extracting superoxide dismutase from erythrocyte
The invention discloses a method for extracting super oxide mutase from red blood cells, which comprises the following procedures: carrying out anti-coagulation treatment for fresh animal blood, collecting in a centrifugal way red blood cells, haemolyting, thermal modifying, settling by stages through acetone, freezing dry to get crude SOD, separating the crude SOD by ion exchanging separation and / or molecular sieve separation to get refined SOD. The invention has completely eliminates chloroform alcohol, just uses thermal modification and stage-by-stage settlement through acetone to separate crude SOD with high activity. The method can maintain to the max. extent the original SOD activity, and the yield rate is higher than prior chloroform alcohol method. The invention is easy to operate and is applicable for industrialized production.
Owner:抚顺丹阳生物科技股份有限公司
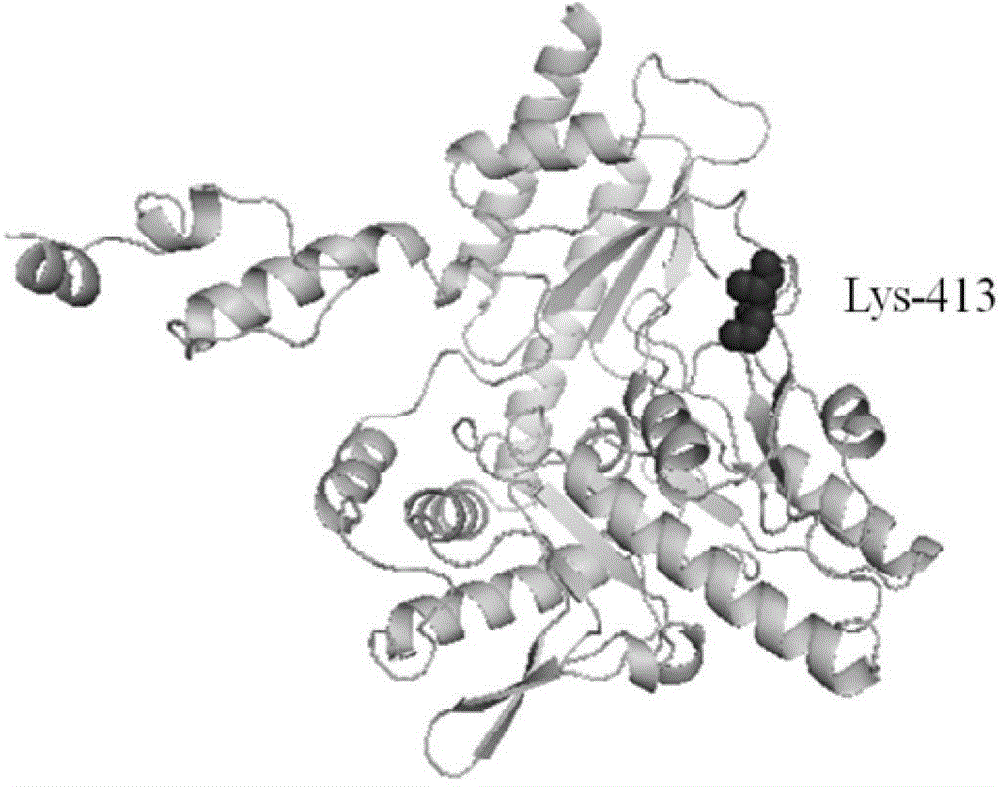
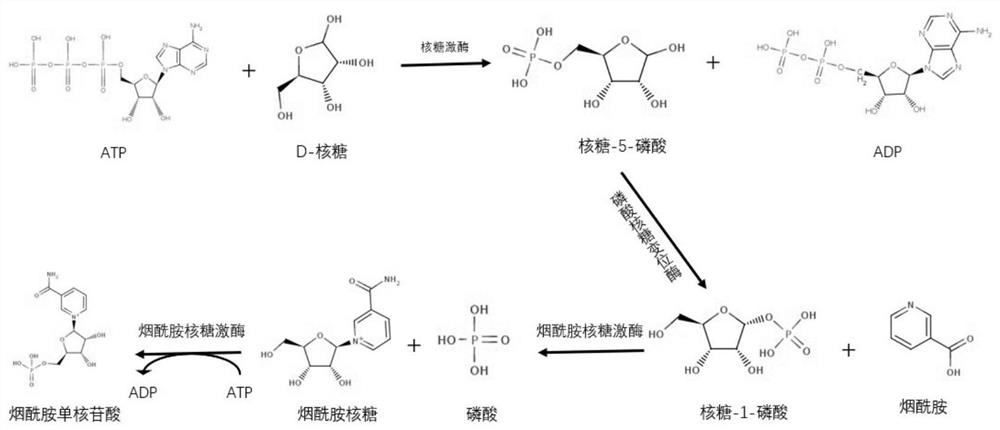
Method for synthesizing nicotinamide mononucleotide based on enzyme method
ActiveCN112877386ASolve the problem of enzymatic preparationMild reaction conditionsFermentationMutaseNicotinamide riboside
The invention provides a method for synthesizing nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN) based on an enzymic method, which comprises the following steps: taking D-ribose, nicotinamide and ATP (adenosine triphosphate) as substrates, and synthesizing the nicotinamide mononucleotide by a one-pot method under the coupling catalytic action of ribose kinase, phosphoribose mutase and nicotinamide ribose kinase. The method for preparing the NMN opens up a new way for synthesizing the NMN by an enzyme method. The three enzymes can be recycled, and the method is low in cost, energy-saving, environment-friendly and suitable for large-scale industrial production.
Owner:HUNAN FLAG BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
D-carboxamide hydrolase mutant and its uses
InactiveCN1995336AIncrease enzyme activityShow potential application valueBacteriaHydrolasesTyrosineThreonine
The invention discloses four mutants of D-carbamoyl hydrolase and application to manufacture D-p-hydroxybenzene glycine in the biological engineering domain, which is characterized by the following: mutating the amino acid at 18th position of mutation enzyme 1 from alanine into threonine and tyrosine at 30th position of mutation enzyme 2 to asparagine; switching the lysine at 30th of mutation enzyme 2 into glutacid; overlapping three mutation positions; obtaining the mutation enzyme 4.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF BIOLOGICAL SCI CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for producing recombinant high-activity manganese superoxide mutase
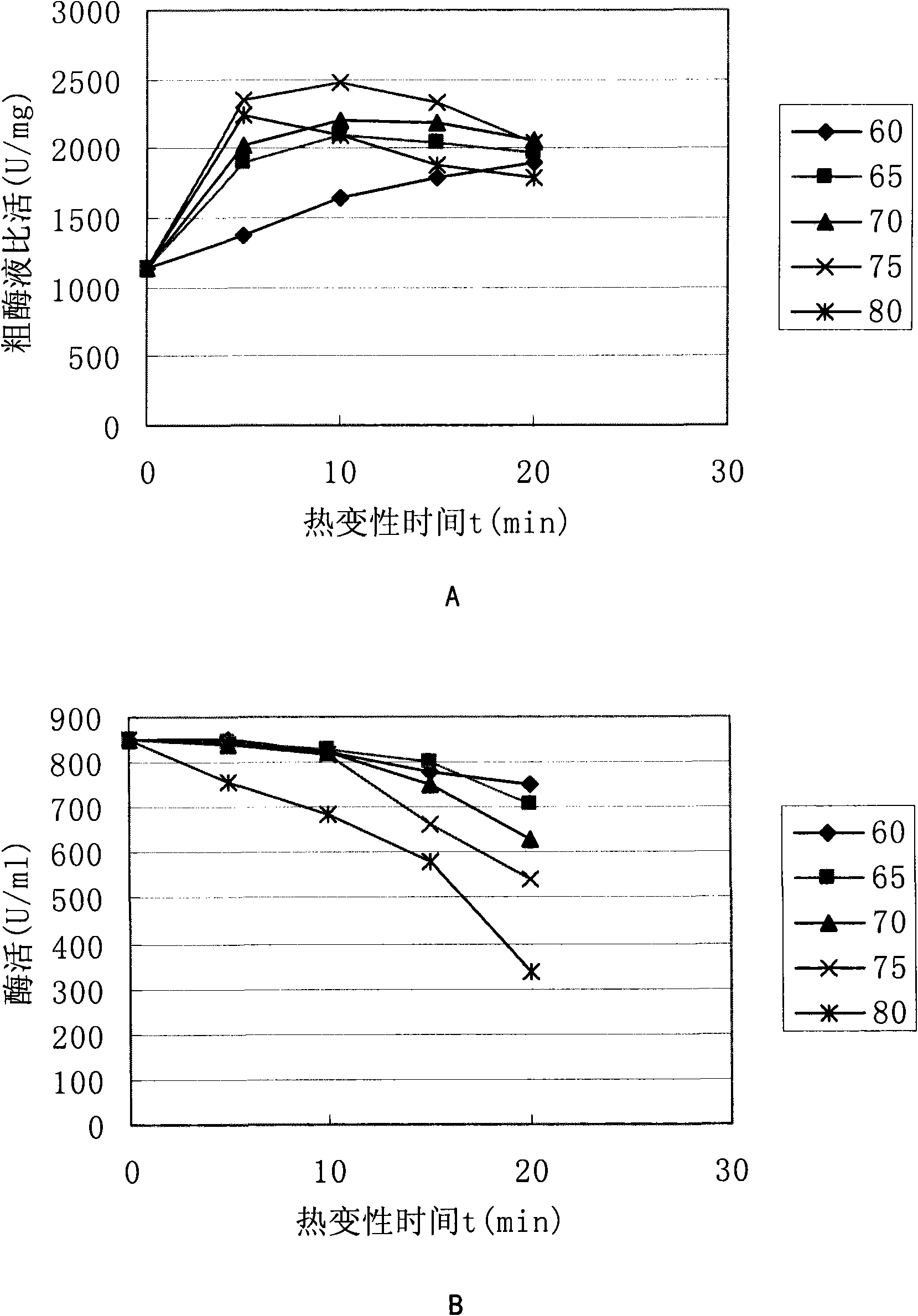
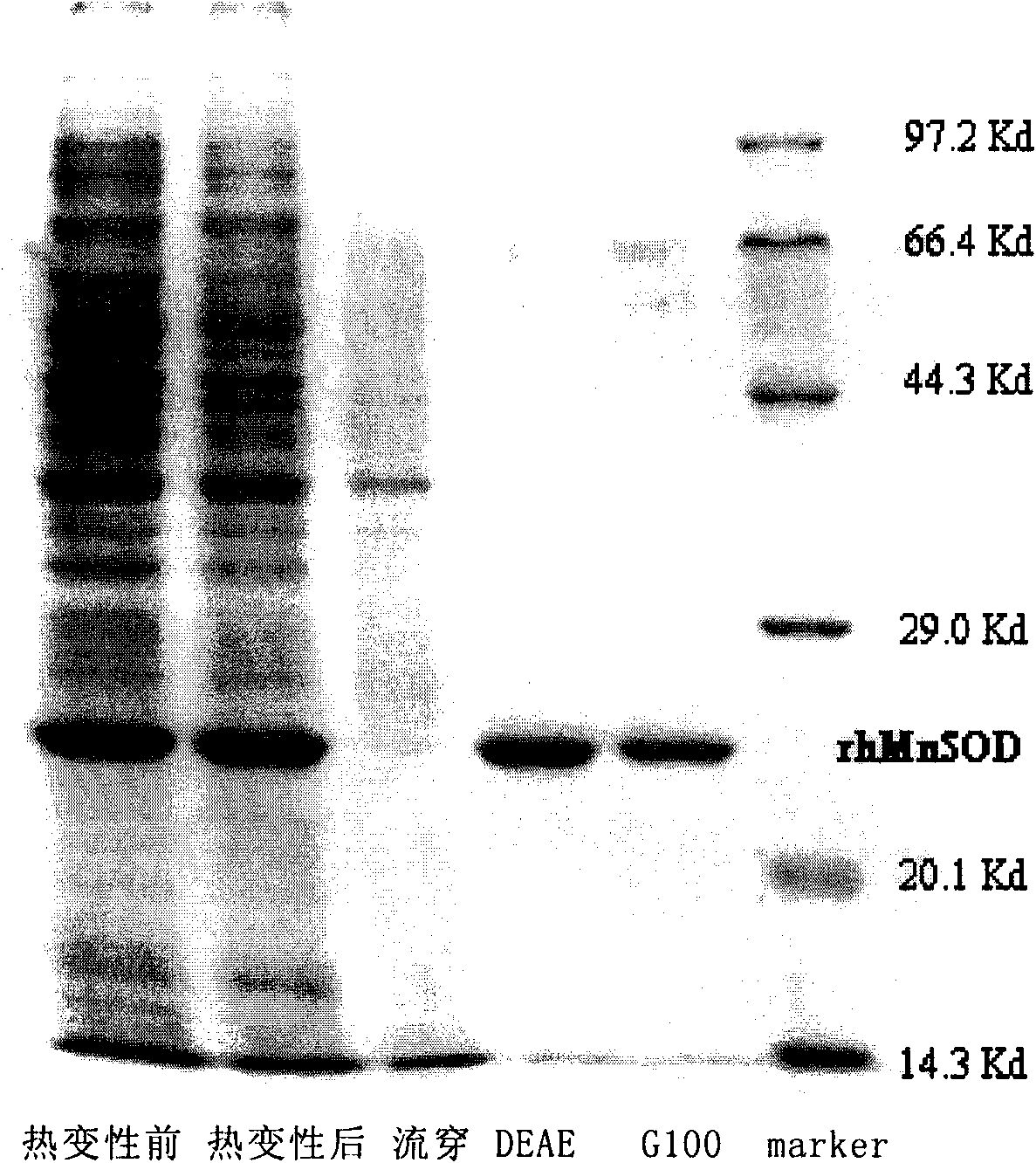
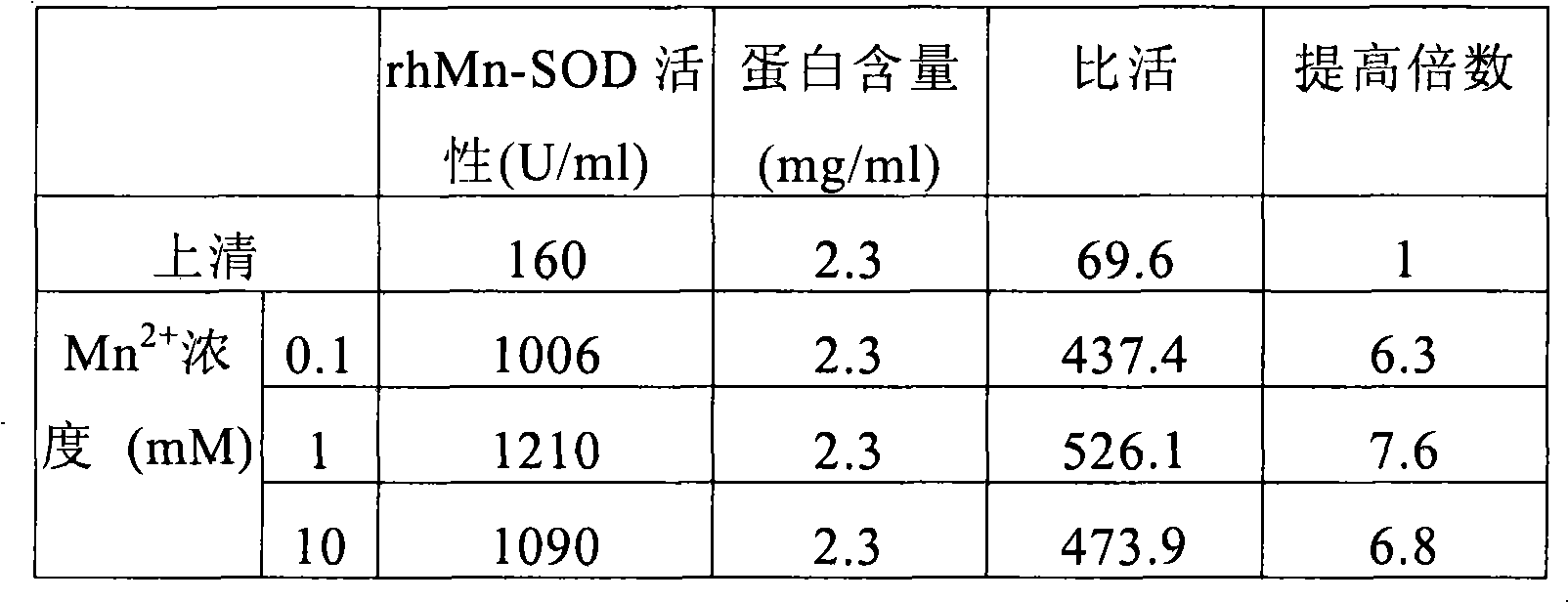
InactiveCN101955918AMicroorganism based processesOxidoreductasesThermal denaturationProtein solution
The invention relates to a method for producing recombinant high-activity manganese superoxide mutase. In the method, soluble expression manganese superoxide mutase is recombined, cell supernatant is subjected to thermal denaturation, protein solution is purified, and the product of the purification is activated by manganese ions at a proper concentration. The method can produce high-activity manganese superoxide mutase.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Glucose dehydrogenase mutant with improved specific enzyme activity of catalytic xylose
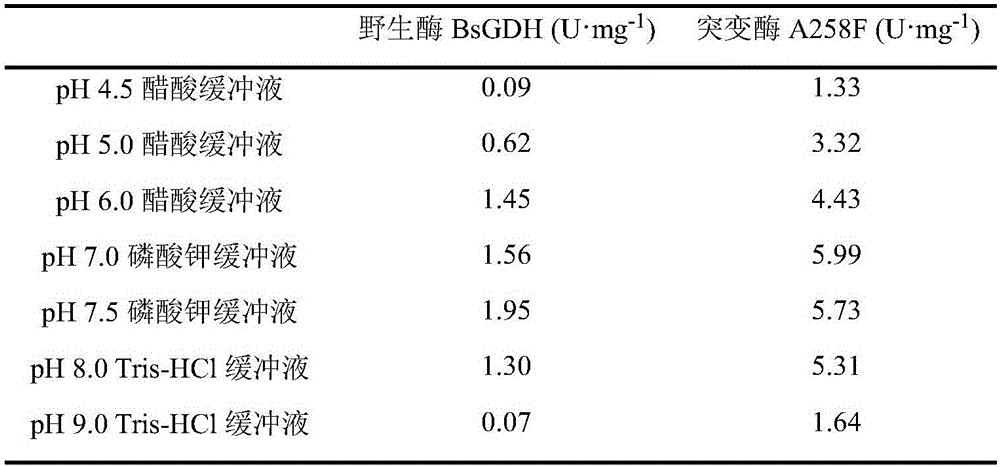
ActiveCN106754776ASolve problems that cannot be effectively usedReduce manufacturing costBacteriaOxidoreductasesGenetic engineeringCompanion animal
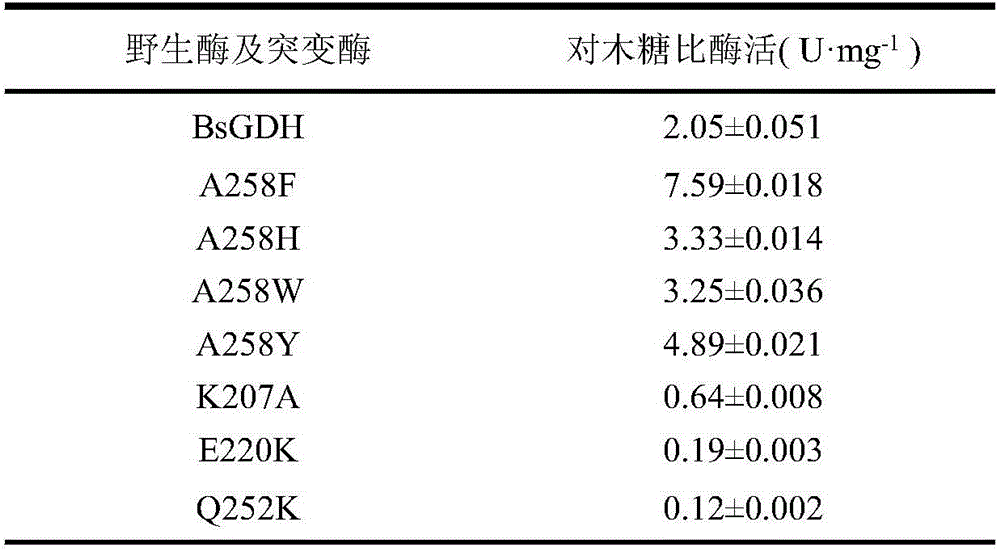
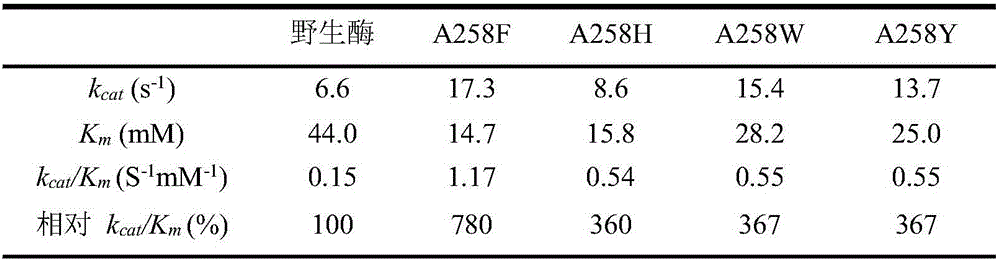
The invention discloses a glucose dehydrogenase mutant with improved specific enzyme activity of catalytic xylose and belongs to the technical field of genetic engineering. A recombinant strain E.coli BL21(DE3) / pET-GDH (A258F) containing a target gene is successfully built. A mutate enzyme A258F is subjected to induced expression through the recombinant strain E.coli BL21(DE3) / pET-GDH (A258F); and a crude enzyme fluid is purified through His-Trap affinity chromatography to obtain a pure enzyme A258F. Through optimizing an enzyme activity determination condition, the specific enzyme activity of the A258F in a potassium phosphate buffer solution of pH 7.0 at 55 DEG C reaches 7.59U.mg<-1>. A novel substrate is provided for a coenzyme cycle of glucose dehydrogenase for asymmetric transformation reaction by the work; the problem that a xylose resource cannot be effectively utilized is solved; reduction of the production cost is facilitated; an excellent strain is provided for xylose utilization in industry; and a foundation is laid for transformation of the substrate specificity of the enzyme through a gene engineering method.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
1,3-1,4-beta-glucanase mutant
ActiveCN104862290AImprove thermal stabilityMaintain catalytic activityBacteriaFermentationGlucanaseMutase
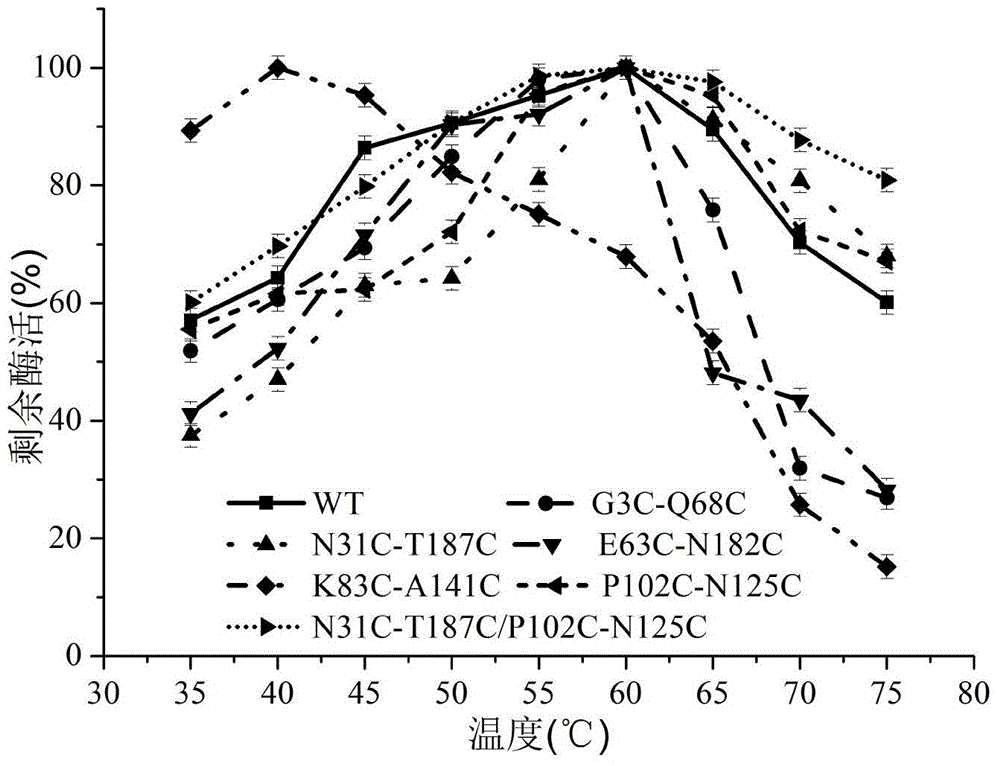
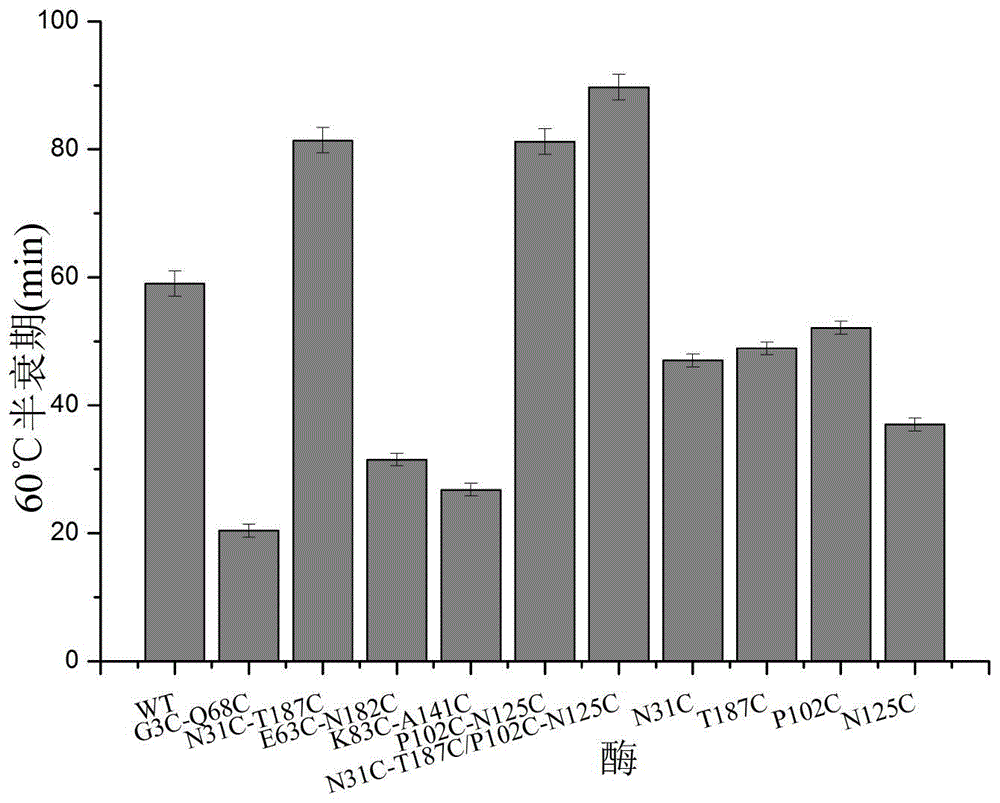
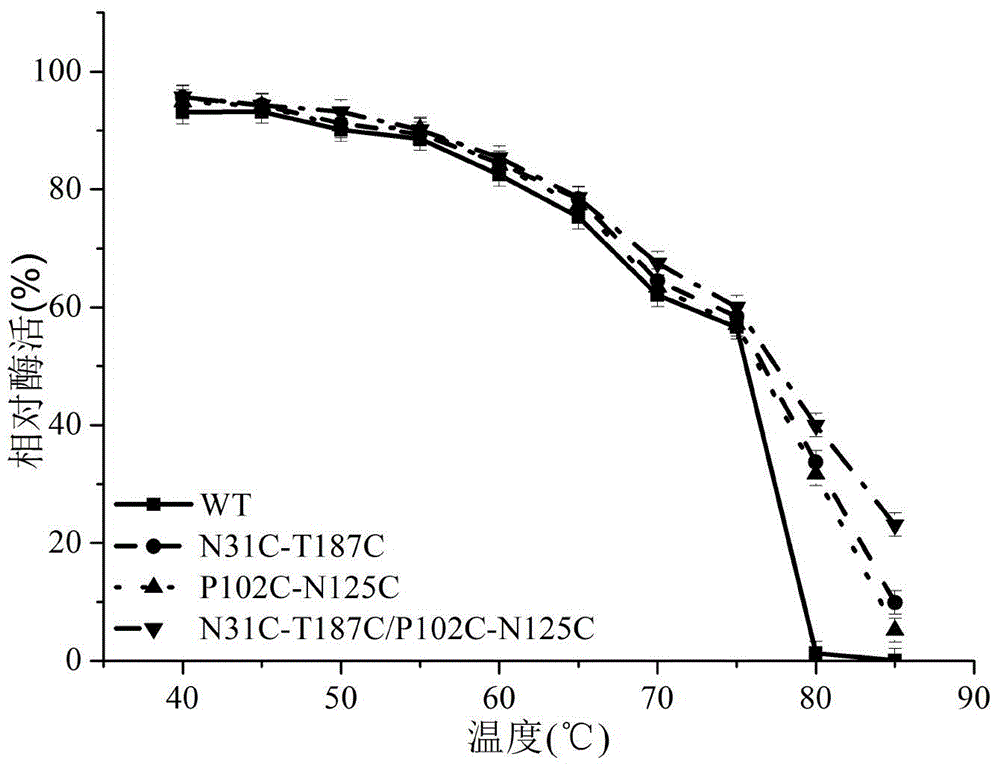
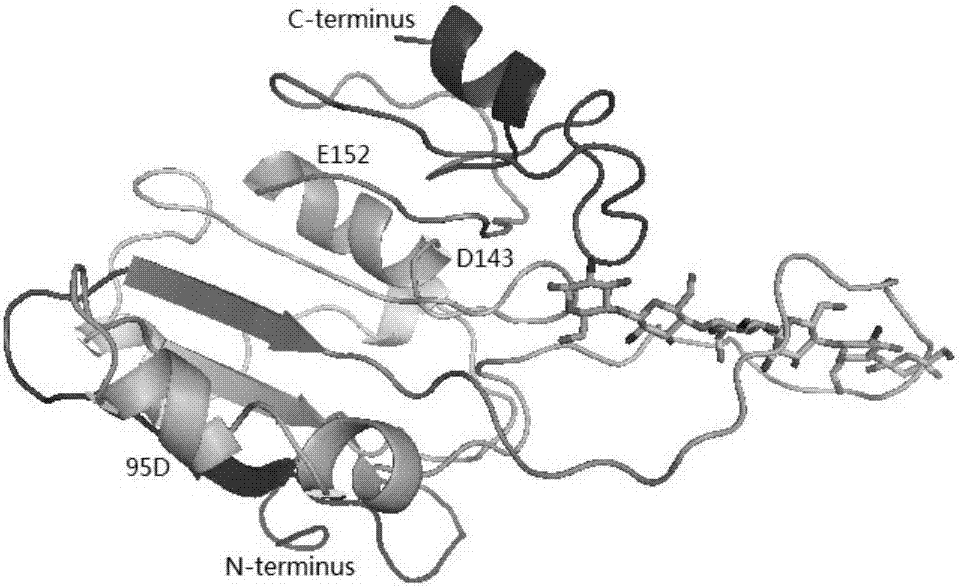
The invention discloses a 1,3-1,4-beta-glucanase mutant, belonging to the fields of genetic engineering and enzyme engineering. According to the invention, for the 1,3-1,4-beta-glucanase mutant sourced from modified bacillus terquilensis CGX5-1, the 31st asparagine, 187th threonine, 102nd proline and 125th asparaginate are subjected to an overlap extension PCR method to become cysteine to respectively obtain single mutants N31C-T187C and P102C-N125C. Two mutation sites are integrated and mutated to obtain N31C-T187C / P102C-N125C double disulfide bond mutant enzymes. Three mutant enzymes show good thermal stability. Compared with wild enzymes, the mutant enzymes is beneficial to industrial application.
Owner:SHANGHAI BAILANG BIOTECHOLOGY
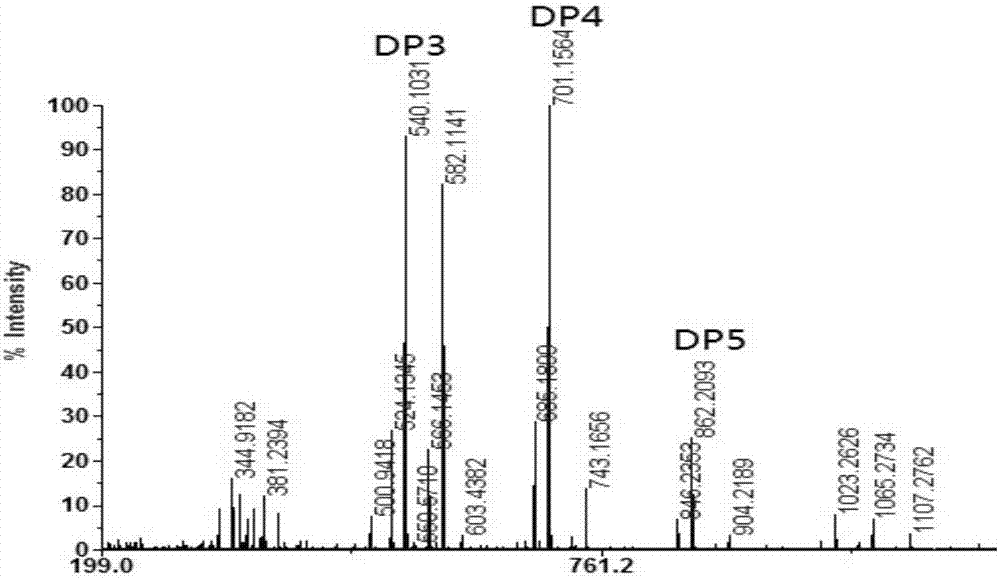
Recombinant aspergillus flavus chitosanase and encoding gene, as well as preparation and application
The invention provides preparation of a high-effective aspergillus flavus (Aspergillus sp.Y2K) chitosan endonuclease mutant. The mutation enzyme can be used for hydrolyzing chitosan to produce oligosaccharide or monosaccharide. The method mainly includes the following steps: 1) cloning a DNA sequence of a matured recombinant chitosanase gene, with mutation at two loci A286G and C287T, onto an expression vector pPICZ[alpha]A of pichia pastoris; and 2) integrating the recombinant plasmid to pichia pastoris host bacteria X-33 through an electric-conversion process to form the recombinant chitosanase mutant which can high-effectively secrete and express and high-effectively degrade chitosan and is high in purity. Compared with a non-mutation enzyme, the chitosan endonuclease mutant is increased in activity by three times. The chitosan endonuclease is widely applied to the fields of foods, medicines, bio-resources, etc.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for producing super oxide mutase complex enzyne at large scale using grain seed
InactiveCN1587395AIncrease vitalityVitality is controllable and the effect is goodPeptide/protein ingredientsUltrafiltrationPeroxidaseSlurry
The method of producing superoxide dismutase complex enzyme at large scale with grain seeds features that the production process includes screening, disinfecting and washing grain seeds; soaking in hot water and germinating; grinding into coarse slurry and adding buffering liquid; adding cellulase, pulping into fine slurry and adding calcium chloride; separating liquid from solid, press filtering and centrifuging the filtrate to collect centrifuged liquid; ultrafiltering, adding amylase and concentrating with neutral ultrafiltering film to reach required SOD concentration. The present invention has the advantages of extracting SOD, peroxidase and hydrogen peroxidase, less impurity protein in product, high enzyme activity, etc.
Owner:陈欣
DNA polymerase for improving synthesis efficiency of catalytic DNA
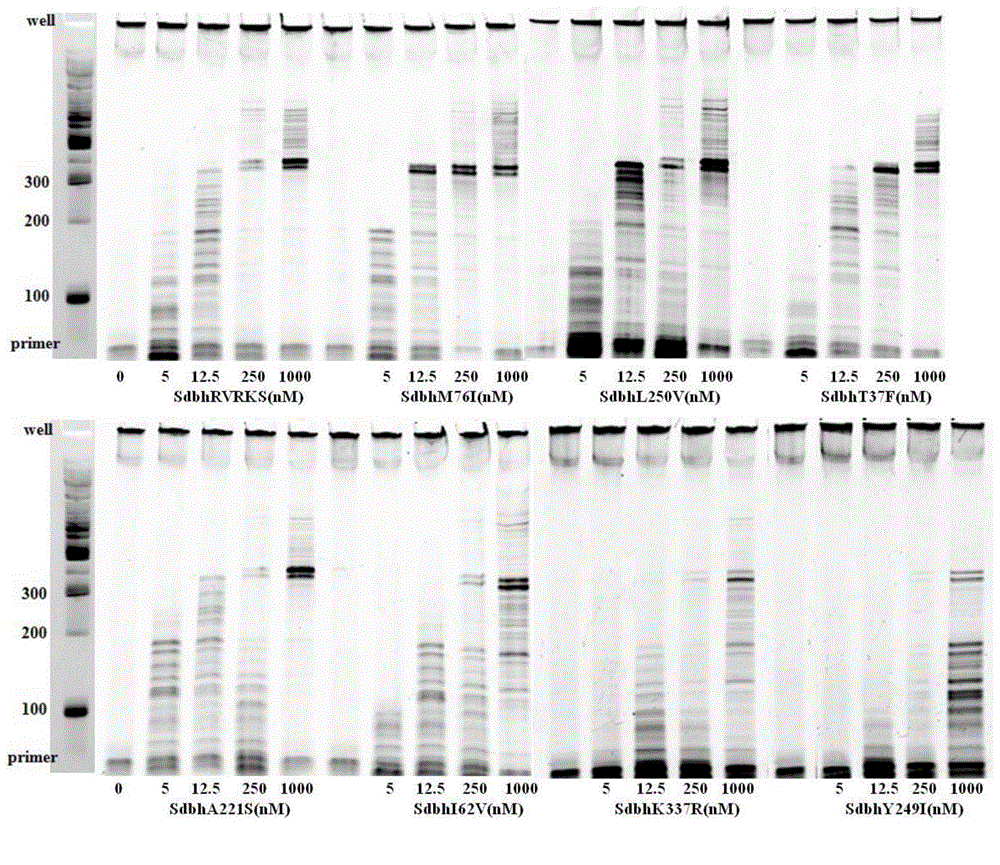
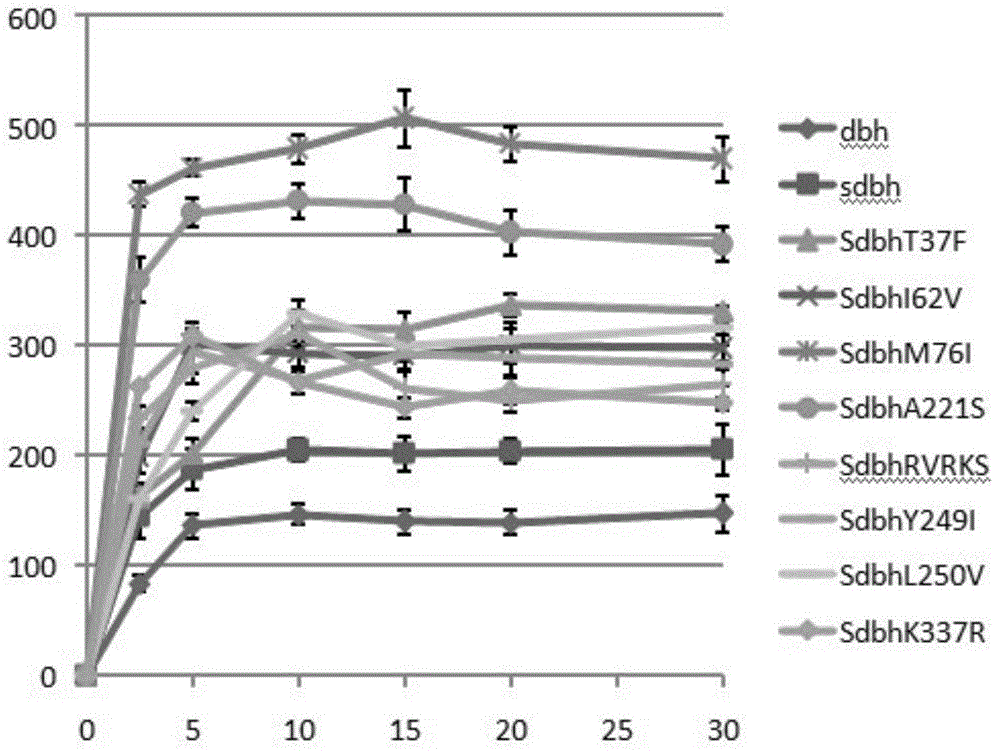
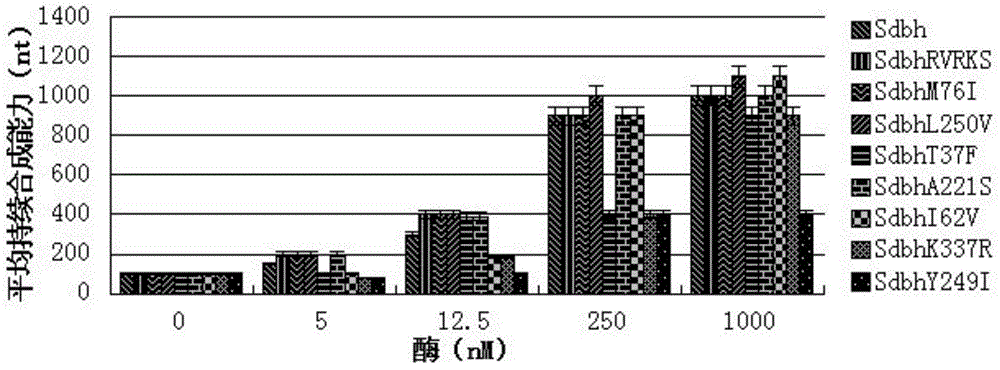
The invention discloses DNA polymerase for improving the synthesis efficiency of catalytic DNA and belongs to the technical field of biological engineering. The DNA polymerase is prepared by the following steps of: firstly mutating the 241-245th amino acids KSKIP of Dhb into RVRKS, or mutating the 250th-site L into V, or mutating the 221th-site A into S, or mutating the 76-site M into I, then fusing Sso7d by flexible linker at the N end of a mutant and constructing out Dbh with improvement of the nucleotide doping efficiency, i.e., four positive mutants such as SdhbM76I, Sdbh A221S, Sdbh KSKIP(241-245)RVRKS and Sdbh L250V. Simultaneously, the invention also provides a method for enhancing the continuous synthesis capability by non-conservative sites of a mutant enzyme.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Use of mutagenic DNA polymerase for producing random mutations
ActiveUS7670809B2Improve heat resistanceImprove effectivenessMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationRandom mutationMutase
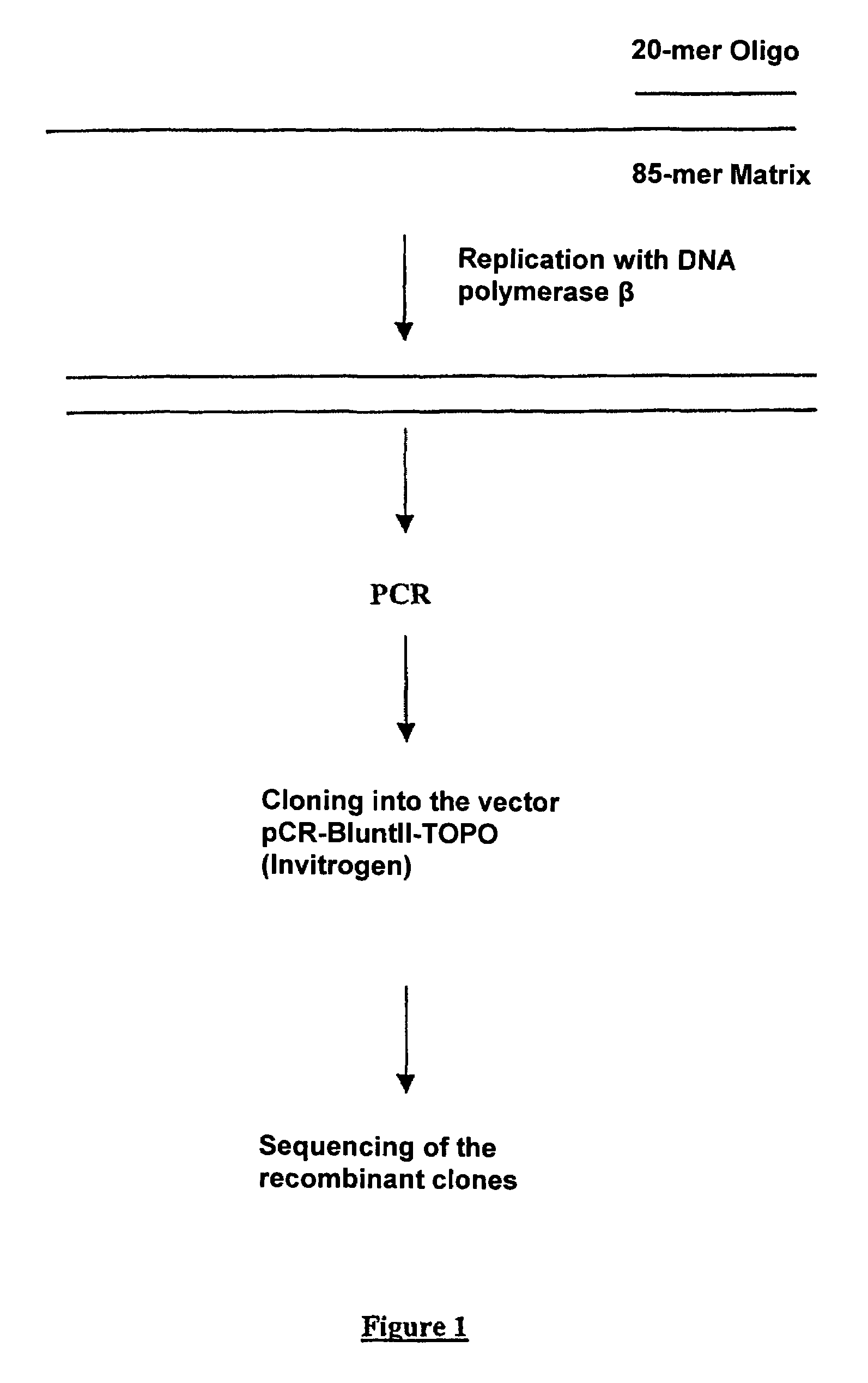
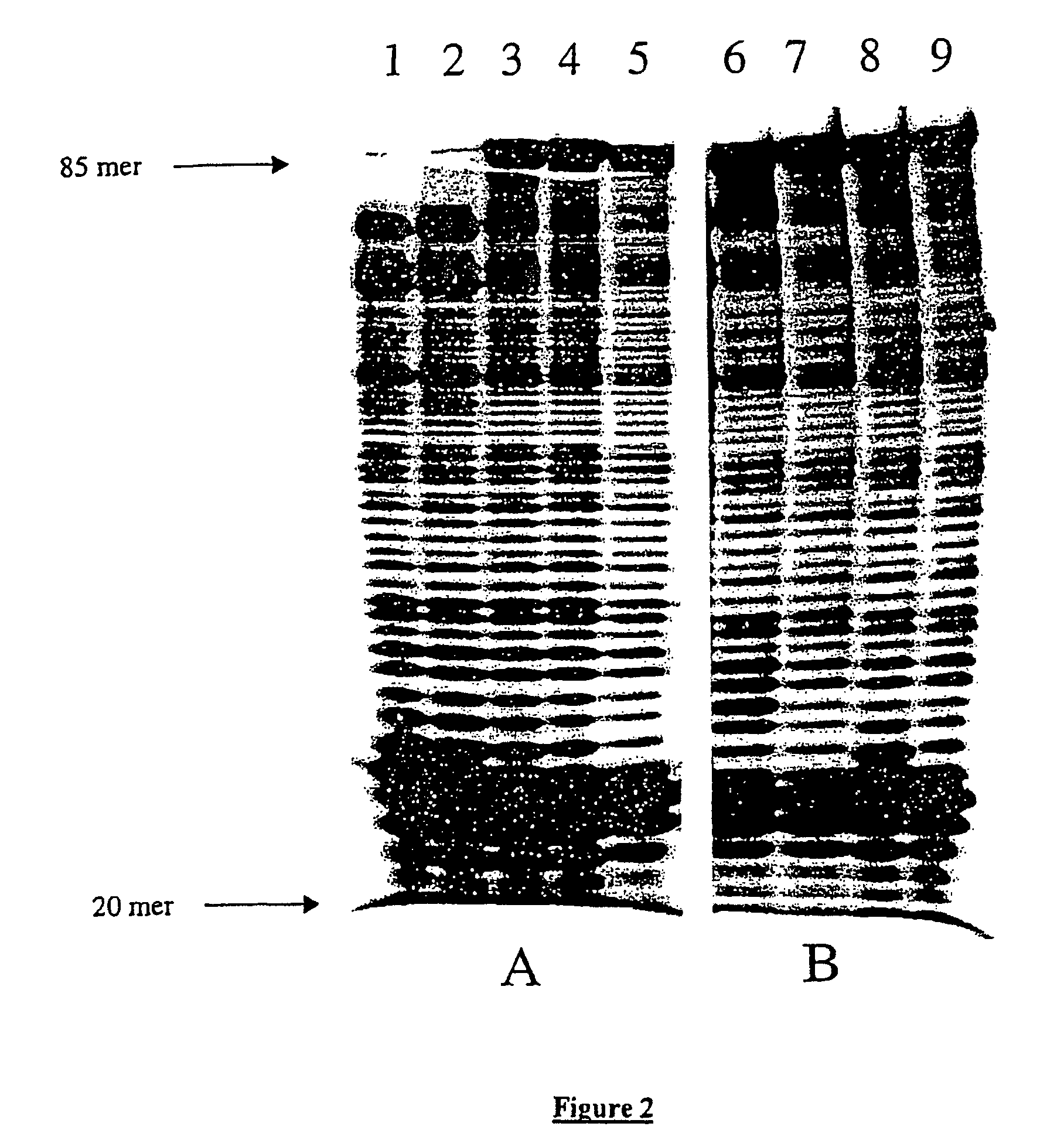
The invention concerns a method for random mutagenesis comprising the replication of a DNA sequence in the presence of an efficient amount of at least a mutase, for example a Pol β, the random mutagenesis rate being at least of the order of 1 mutation for 400 base pairs. The replication product, optionally recombined and amplified, is cloned in an expression vector so as to generate mutated polypeptides which will be selected on the basis of the desired property or properties.
Owner:LABE FR DU FRACTIONNEMENT & DES BIOTECH SA
Tagatose-producing bacillus subtilis genetic engineering bacteria and method for preparing tagatose
ActiveCN112342179BEasy to manufactureGood for catalytic applicationsBacteriaHydrolasesTagatoseEngineered genetic
The invention discloses a tagatose-producing Bacillus subtilis genetically engineered bacterium and a method for preparing tagatose. The genetically engineered bacterium comprises constructing a single-expression or co-expression thermostable α-glucan phosphorylase, thermostable glucose phosphate Mutase, thermostable glucose phosphate isomerase, thermostable 6‑phosphate tagatose epimerase, and thermostable 6‑phosphate tagatose phosphatase. Starch can be effectively converted into tagatose by using the genetically engineered bacteria. Compared with the existing methods for producing tagatose, the method of the present invention has the advantages of being suitable for whole cell recycling, high safety performance, high yield, simple production process, low cost and easy large-scale preparation.
Owner:天津怡和生物科技有限责任公司
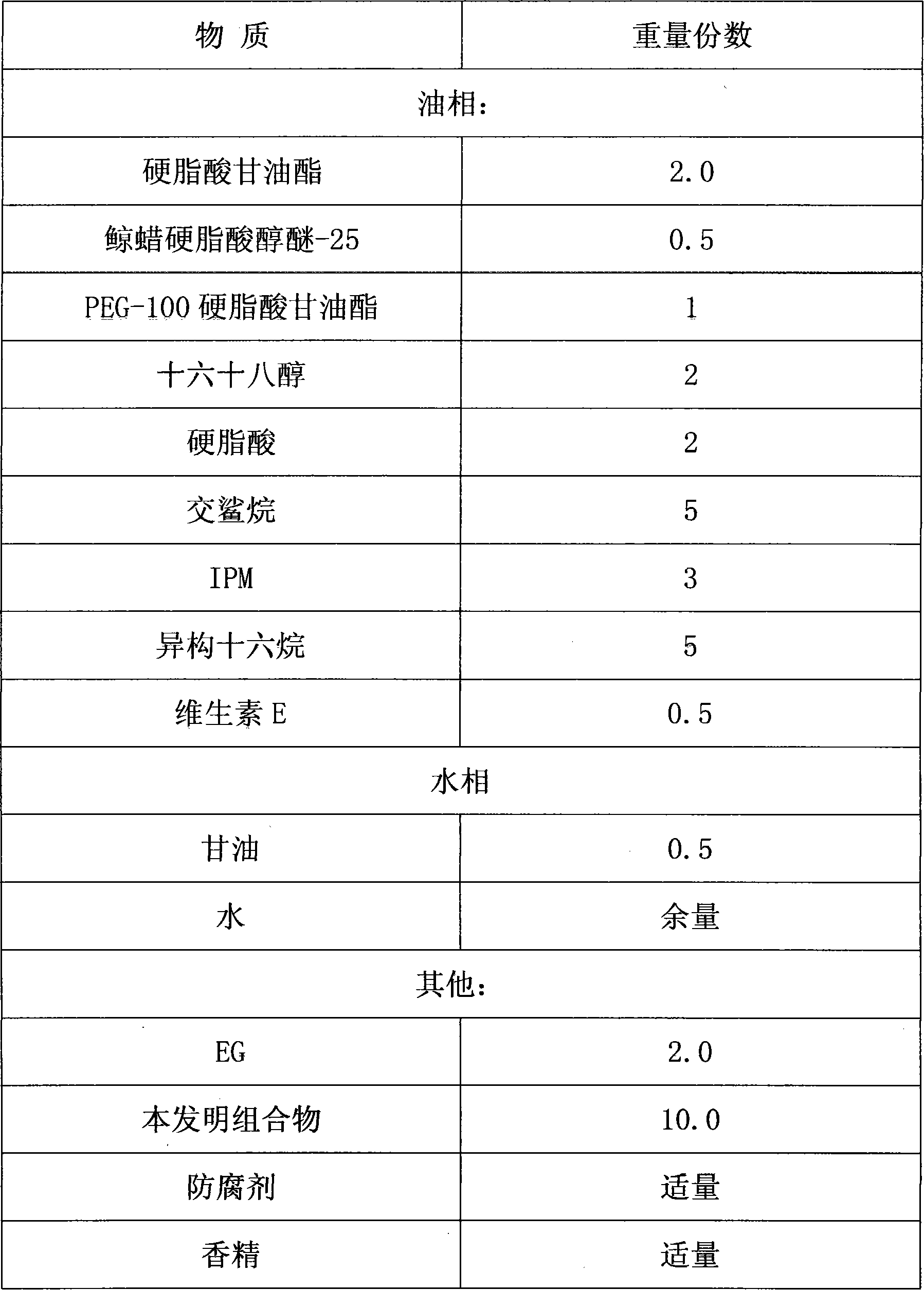
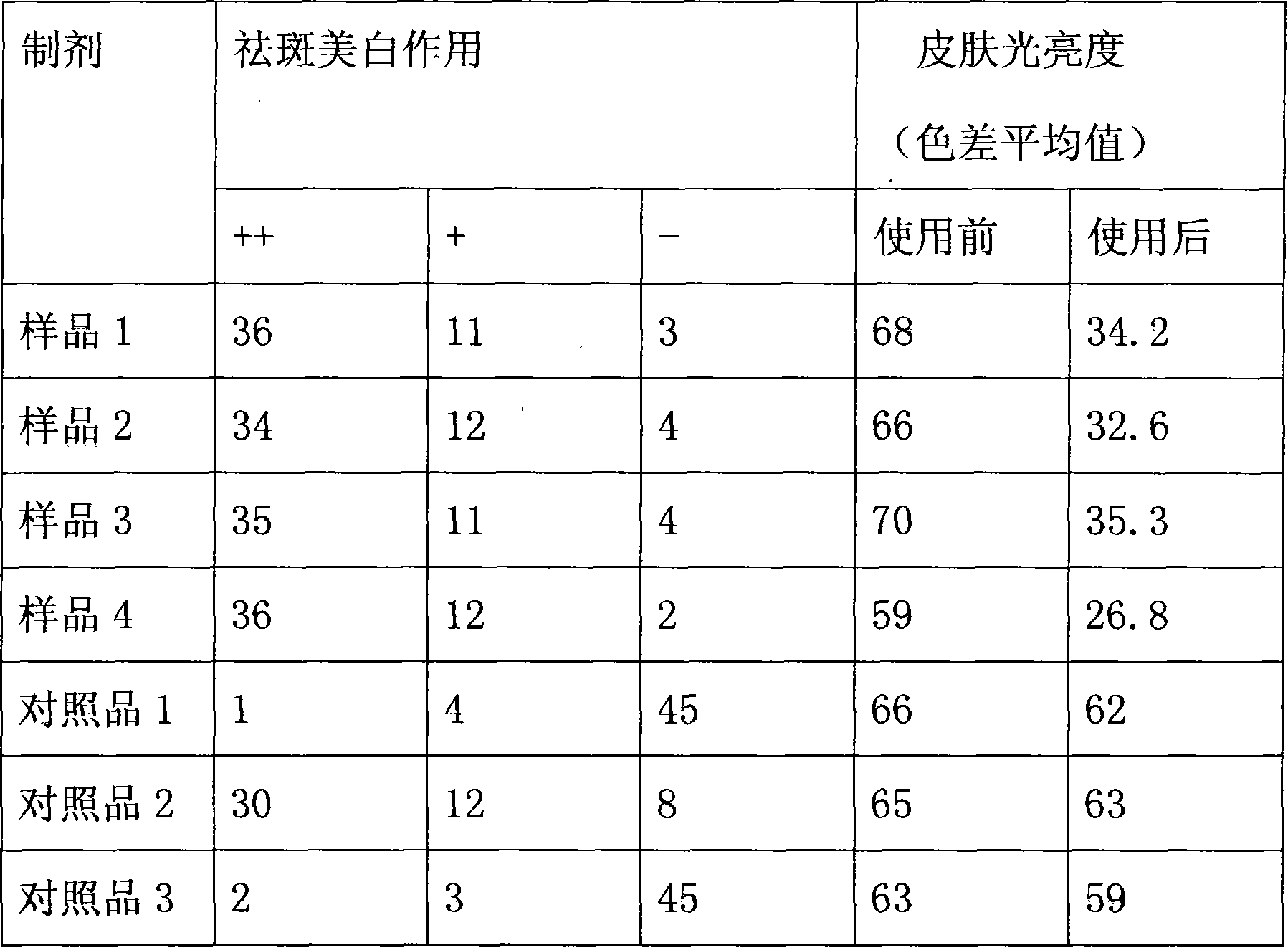
Skin whitening composition
InactiveCN101606890AInhibitionAllergies do not causeCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsMutaseGlabridin
The invention discloses a skin whitening composition, which is characterized by comprising the following components in portion by weight: 10 to 30 portions of undecylenoyl phenylalanine, 1 to 10 portions of glabridin and 20 to 80 portions of dibasic alcohol. The invention aims to overcome the defects existing in the prior art and provide the composition which is used for whitening cosmetics and can reduce the generation of melanin by inhibiting the generation of alpha-melanocyte stimulating hormone, tyrosinase, dopa mutase and DHICA oxidase. When the skin whitening composition is used for cosmetics, the cosmetics has obviously effects of removing freckles, whitening the skin and preventing and improving darkening, dark side, spots and freckles of the skin caused by sun exposure, ageing and the like.
Owner:中山市嘉丹婷日用品有限公司
Phenylalanine amino mutase mutant derived from pantoea agglomerans
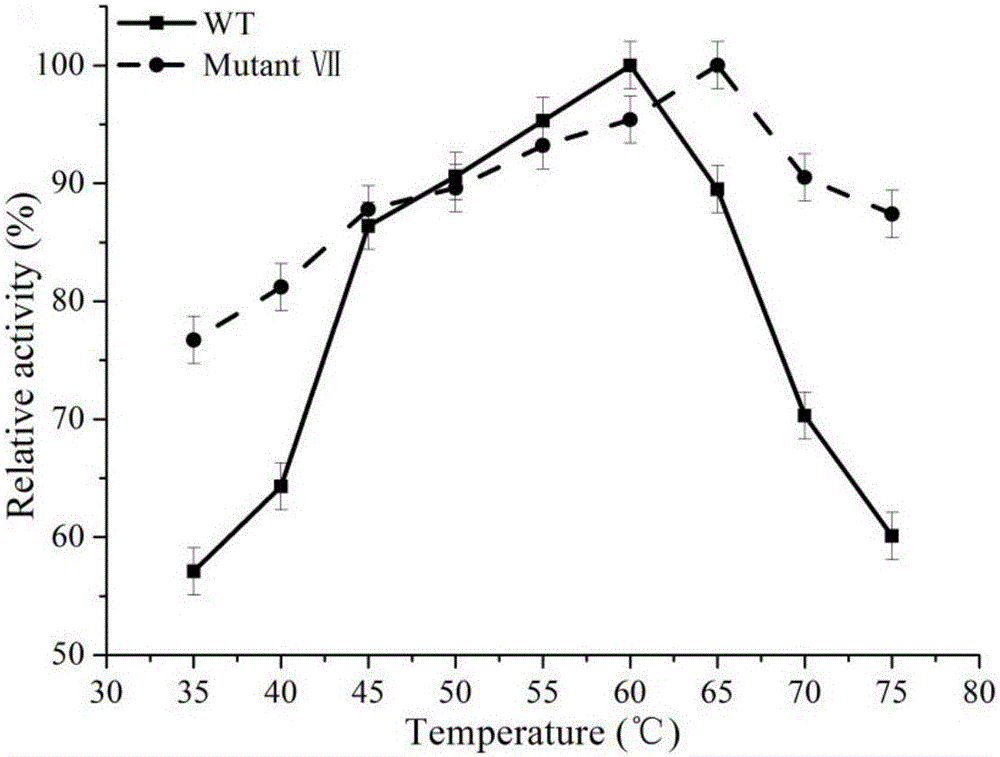
ActiveCN108004225AImprove thermal stabilityGood enzymatic propertiesBacteriaTransferasesEnterobacter agglomeransPantoea agglomerans
The invention discloses a phenylalanine amino mutase mutant derived from pantoea agglomerans, and belongs to the technical field of enzyme engineering. The sequence of the phenylalanine amino mutase mutant is shown in SEQ ID NO.2, and the mutant enzyme still has 60% residual enzyme activity after being processed at 50 DEG C for one hour and has higher temperature stability compared with wild enzyme. Meanwhile, the mutant also has better pH stability, and is good for future industrial production.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Mutant YqhD enzyme for the production of a biochemical by fermentation
ActiveUS8969053B2Increase productionHigh catalytic efficiencySugar derivativesBacteria1,4-ButanediolMicroorganism
Owner:METABOLIC EXPLORER
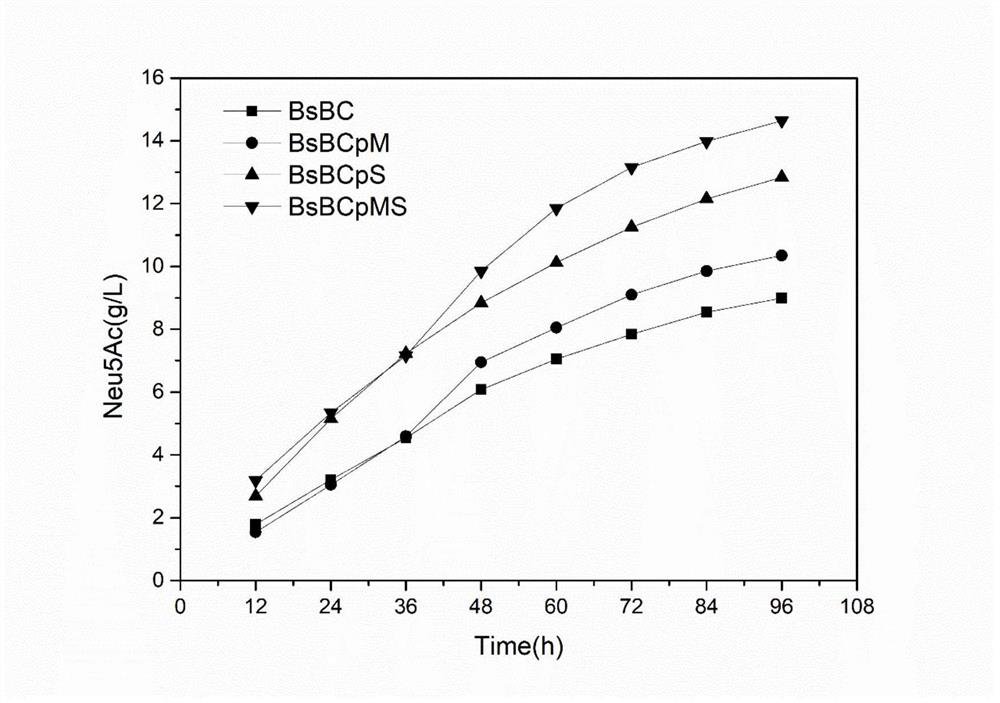
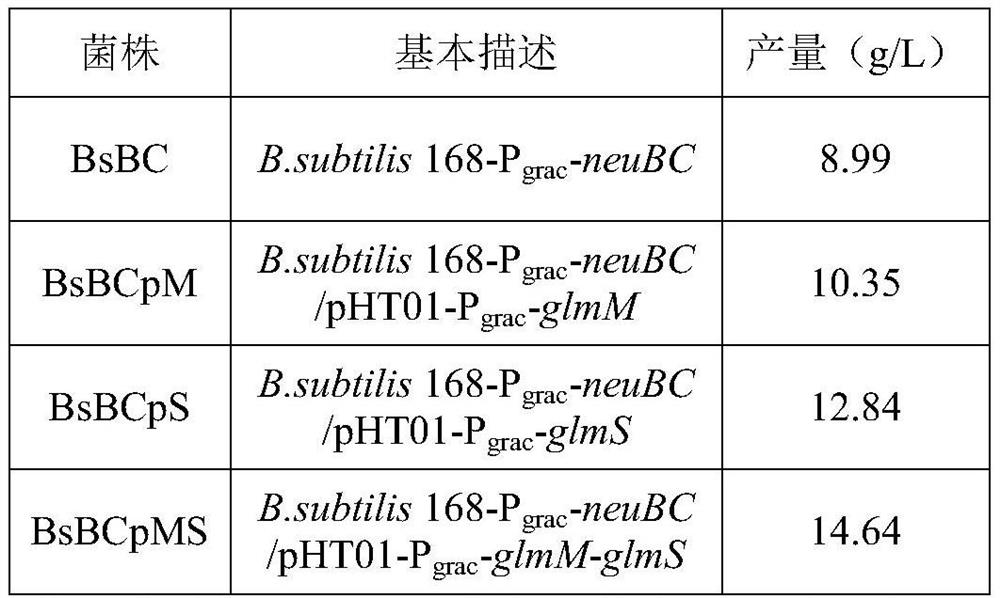
Recombinant bacillus subtilis with high yield of N-acetylneuraminic acid, and construction method and application of recombinant bacillus subtilis
PendingCN113249285AHas industrial production valueSimple production processBacteriaTransferasesBiotechnologyGenetic engineering
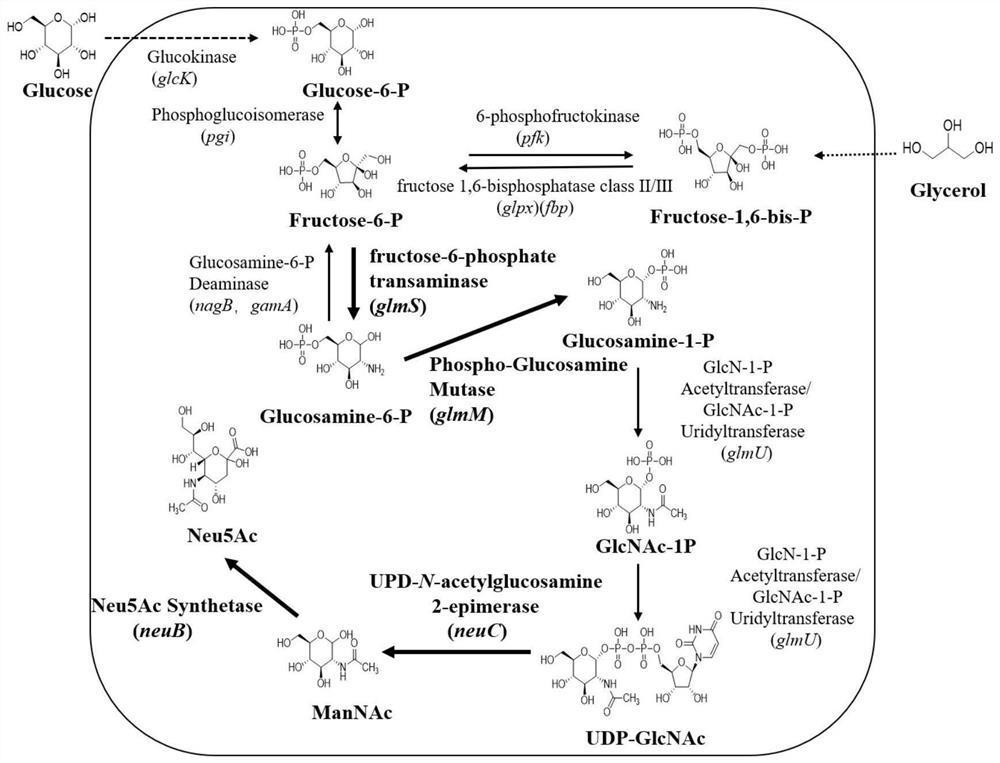
The invention relates to the technical field of bioengineering, in particular to recombinant bacillus subtilis with high yield of N-acetylneuraminic acid, and a construction method and application of the recombinant bacillus subtilis. According to the recombinant bacillus subtilis with high yield of N-acetylneuraminic acid, bacillus subtilis is taken as an expression host; an N-acetylneuraminic acid synthetase gene neuB and an N-acetylglucosamine 2-epimerase gene neuC are integrated onto a bacillus subtilis genome to be stably expressed; and then overexpression on a glucosamine phosphate mutase gene glmM and a fructose 6-phosphate transaminase gene glmS is carried out on a plasmid. According to the invention, a gene engineering technology is adopted to modify the B.subtilis so as to directly synthesize the N-acetylneuraminic acid by using glycerol as the substrate; the production process is simple; environmental protection and no endotoxin are provided; and the method can be used in the food field, and has industrial production value.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
1,3-1,4-beta-glucanase mutant
ActiveCN105671022AImprove thermal stabilityMaintain catalytic activityBacteriaWort preparationGlucanaseMutase
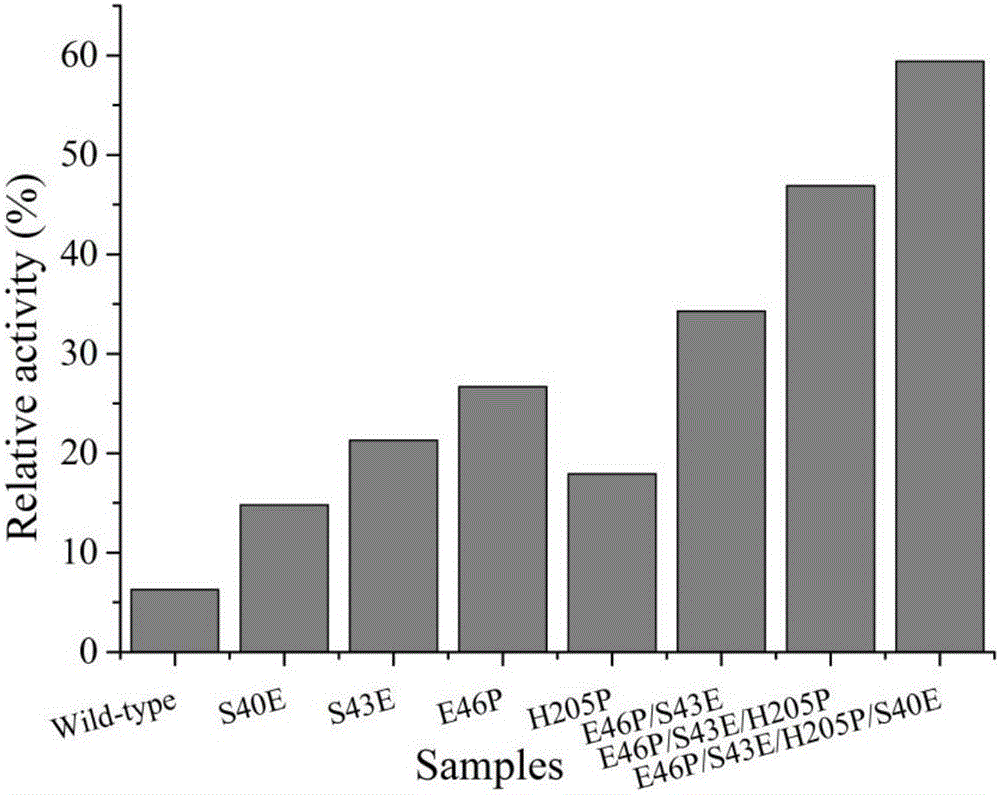
The invention discloses a 1,3-1,4-beta-glucanase mutant and belongs to the field of gene engineering and enzyme engineering.40-bit serine and 43-bit serine, 46-bit glutamic acid and 205-bit histidine of 1,3-1,4-beta-glucanase from bacillus terquilensis CGX 5-1 are mutated into glutamic acid, glutamic acid, praline and praline respectively through an iterative saturation mutation method, and finally four strains of single mutants and three strains of compound mutants are obtained.Seven strains of mutate enzyme all represent better heat stability, and particularly S40E / S43E / E46P / H205P mutate enzyme has extremely good heat stability.Compared with wild enzyme, the mutate enzyme can be used in the industry more easily.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Method for preparing inositol by multi-enzyme reaction system expressed by edible microorganisms
ActiveCN109913489AAvoid the possibility of contaminationReduce manufacturing costHydrolasesTransferasesEscherichia coliInositol monophosphatase
The invention discloses a method for preparing inositol by a multi-enzyme reaction system expressed by edible microorganisms. The method has the advantages that strains for the food industry serve asmulti-enzyme expression systems to produce isoamylase, glucan phosphorylase, glucose phosphate mutase, inositol-3-phosphate synthase and inositol monophosphatase, which are required for catalyzing starch and derivatives thereof, so that the possibility of contaminating the inositol by toxic protein, antigenic protein or endotoxin generated by escherichia coli in a production process is avoided fundamentally, a strict and complicated purification process is avoided, and the production cost is reduced.
Owner:CHENGDU BOHAODA BIOLOGICAL TECH CO LTD
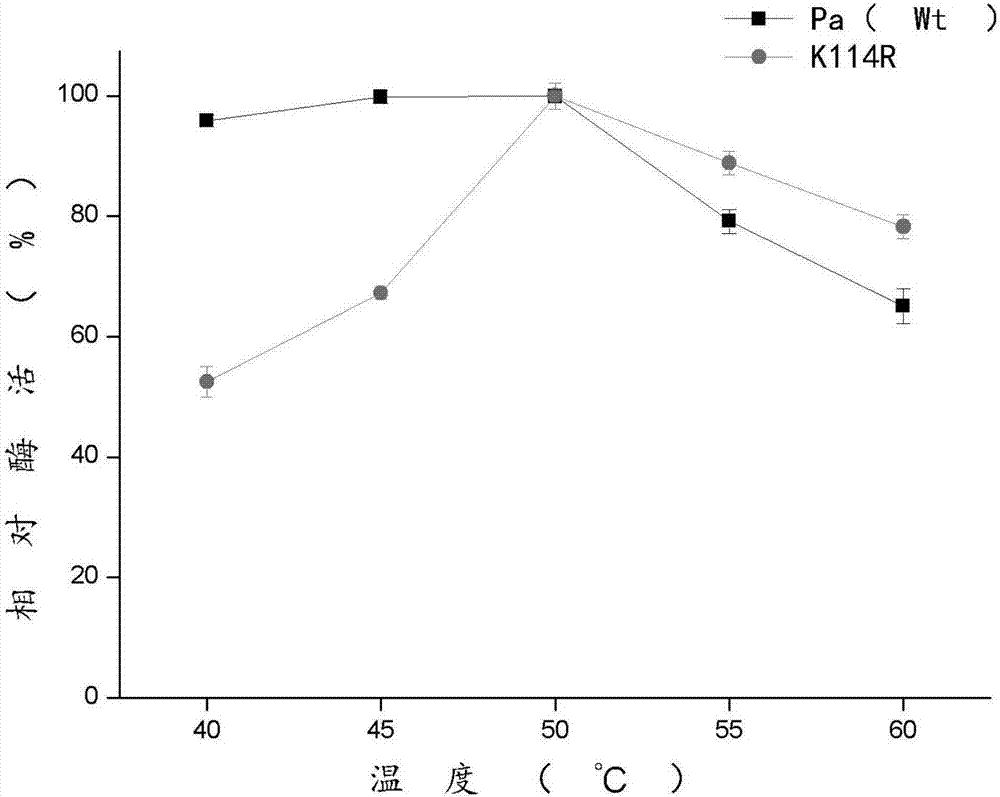
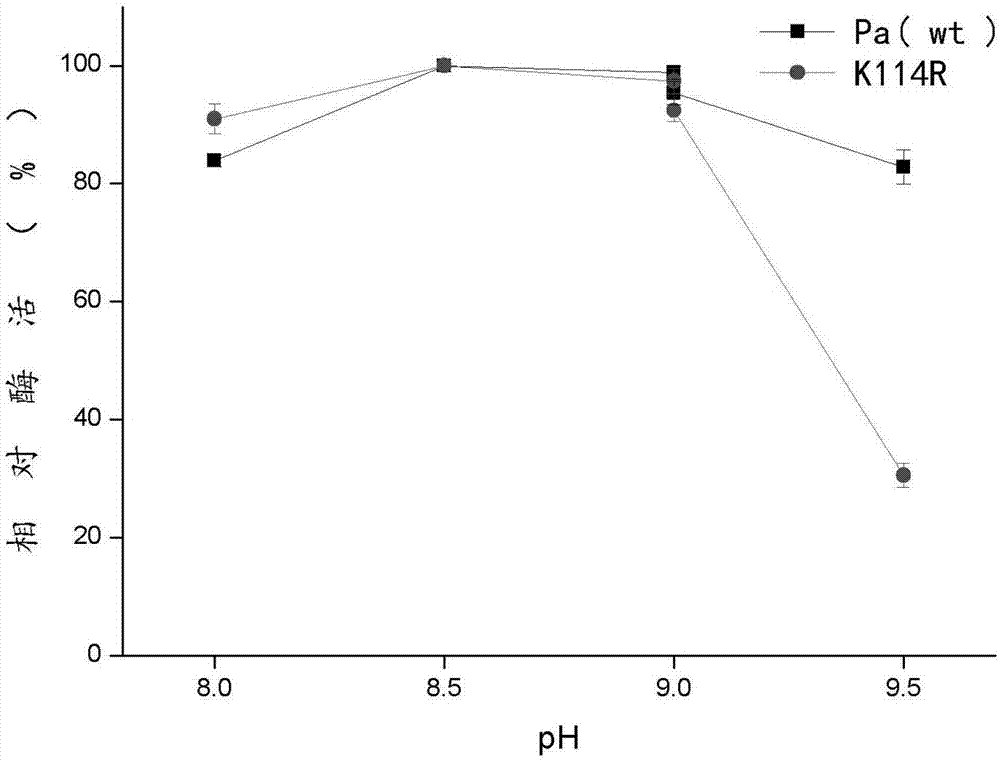
Thermally stable mutant aromatic sulfatase and its gene and use
ActiveCN106399334ARealize large-scale productionImprove thermal stabilityHydrolasesFermentationHeterologousReaction temperature
The invention discloses thermally stable mutant aromatic sulfatase and its gene and use. Through an error-prone PCR technology, random mutagenesis is introduced, a P. carrageenovora aromatic sulfatase mutant library is constructed and through screening, the mutant aromatic sulfatase with improved thermal stability is obtained. The result shows that compared with WT, H260L thermal stability is obviously improved. Based on potassium p-nitrophenyl sulfate as a substrate, the H260L has the optimal reaction temperature of 55 DEG C and pH of 8.0. The H260L is stable in the pH range of 6.0-9.0. EDTA has a strong inhibitory effect on the activity of the mutant enzyme and it is proved that a metal ion produces an important effect in the catalytic process of the mutant sulfatase. H260L has good tolerance to a detergent and has a gracilaria lemaneiformis crude polysaccharide sulfuric acid group desulfurization rate of 82%. The invention also discloses genetic engineering bacteria containing the mutant aromatic sulfatase gene. The genetic engineering bacteria realize the heterologous expression of the sulfatase and provide a good foundation for the industrial production and application of the sulfatase.
Owner:JIMEI UNIV
Recombinant escherichia coli for synthesizing 2 '-fucosyllactose by using mannose and application of recombinant escherichia coli
PendingCN114276971AImprove conversion rateImprove carbon source utilizationBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliHigh mannose
The invention relates to a method for constructing recombinant escherichia coli, synthesizing GDP-fucose by using mannose, further producing 2 '-fucosyllactose and improving the utilization rate of mannose, and belongs to the field of microbial metabolism engineering. The engineering bacterium takes escherichia coli as a starting strain, a Plac promoter sequence and lacI and lacZ genes in a lac operon sequence are knocked out, wcaG, gmd and lacy genes are overexpressed on 1acI and lacZ gene loci, then a phosphomannose isomerase coding gene manA is knocked out on a genome, a phosphomannose mutase coding gene manB and alpha-(1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 8, 8, 8, 8, 8, 8, 8, 8, 8, 8, 8, 8, 8, 8, 8, 8, 8, 8, 8, 8, 8, 8, 8, 8, 8, 8, 8, 8, 8, 8, 8, 8, 8, 8, 8, 8, 8, 8, 8, 8, 8 and (2) obtaining a fucosyl transferase coding gene futC and a mannose-1-phosphate guanine transferase coding gene manC. According to the fermentation strategy for producing the 2 '-fucosyllactose through the de novo synthesis route of the 2'-fucosyllactose, the utilization rate of a carbon source for producing the 2 '-fucosyllactose through escherichia coli fermentation can be greatly increased.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY +1
Inhibitors of UDP-galactopyranose mutase thwart mycobacterial growth
ActiveUS8273778B2Improve efficiencyAntibacterial agentsBiocidePathogenic microorganismVirulent characteristics
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com