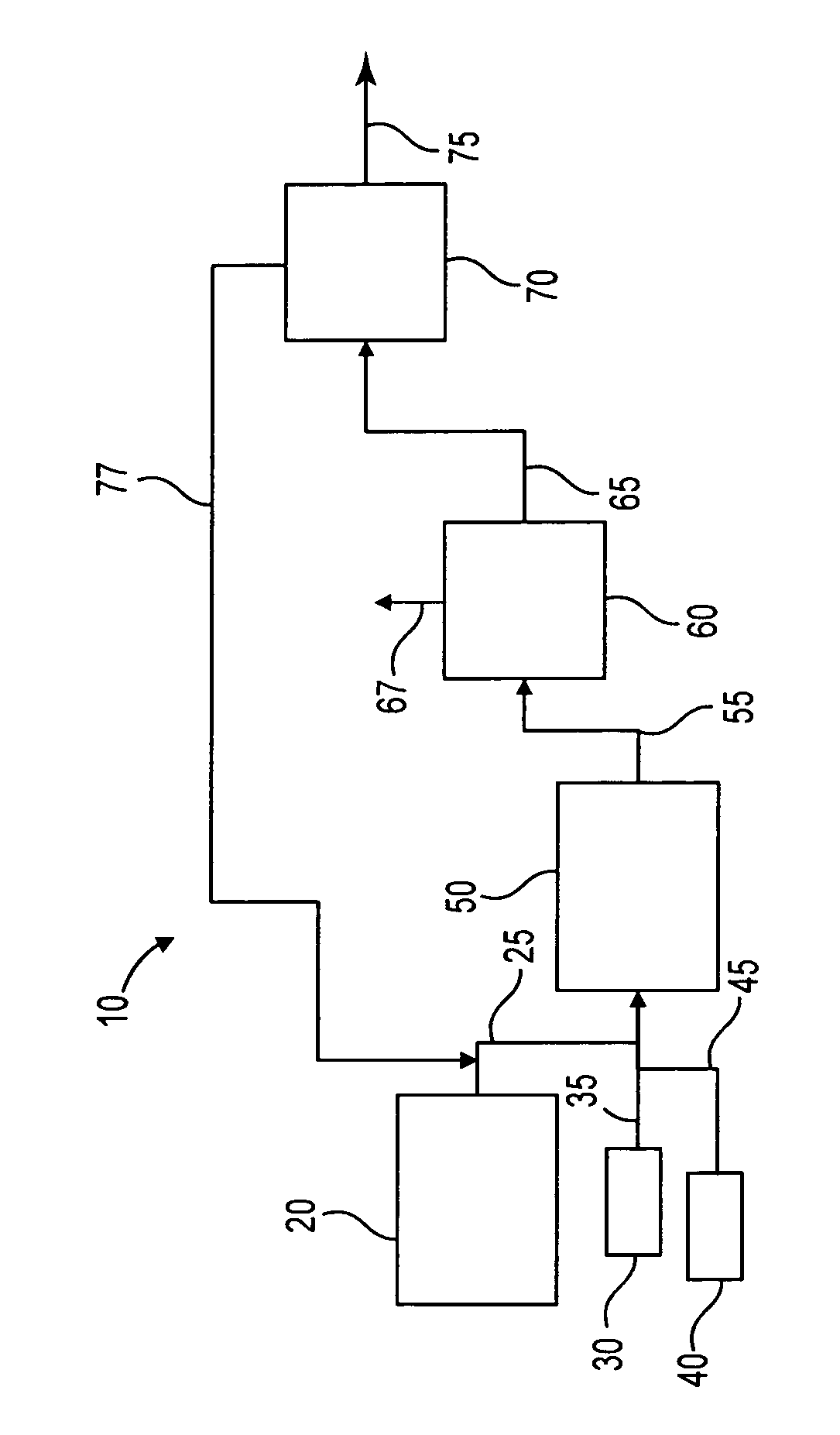
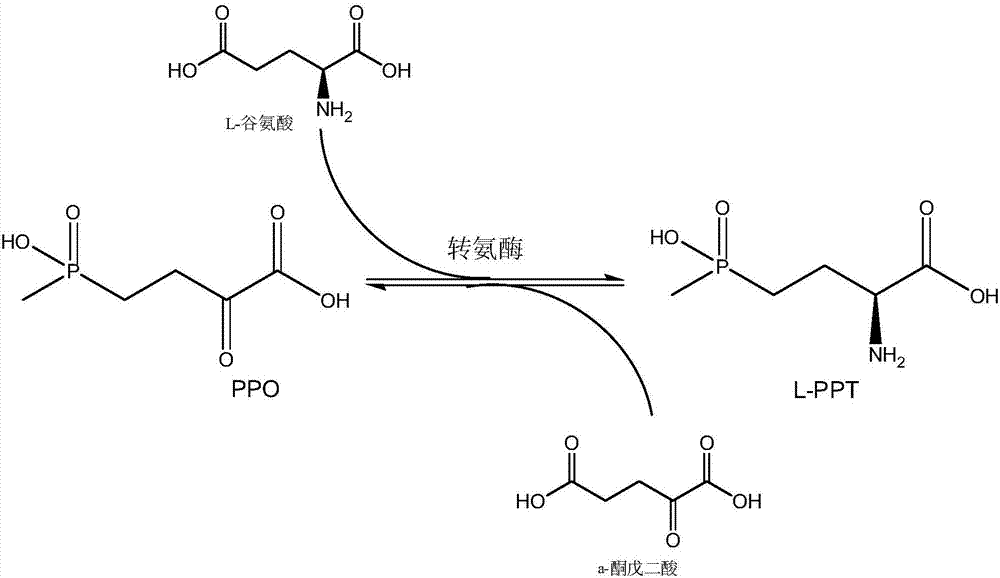
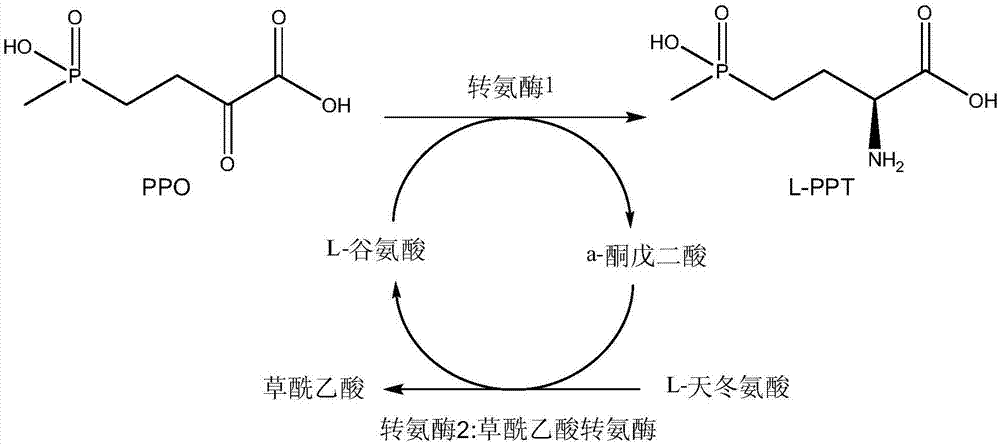
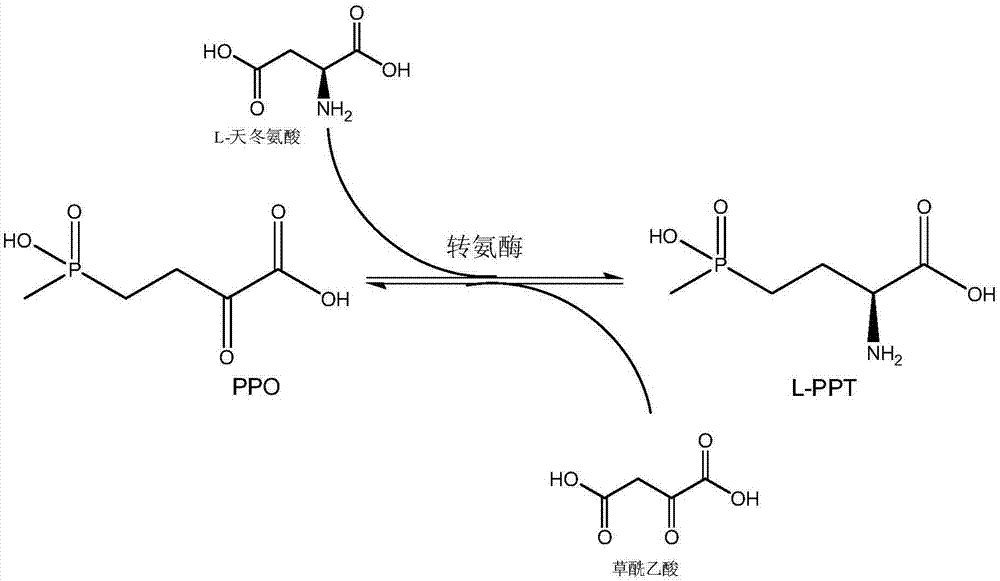
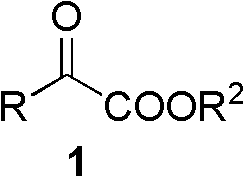
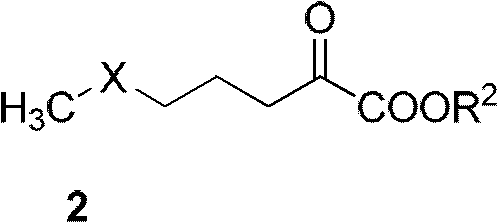
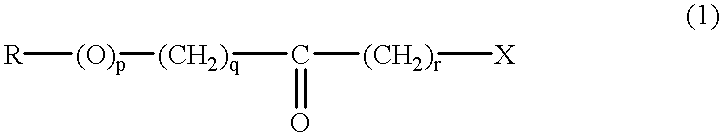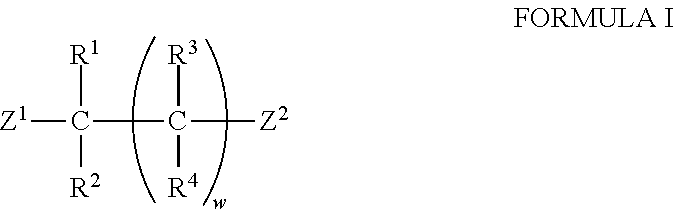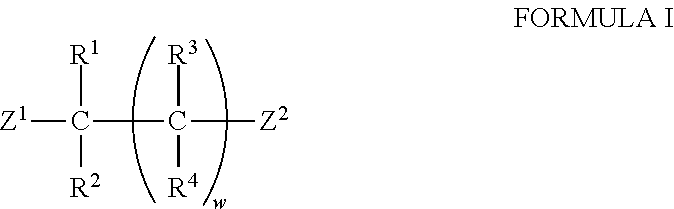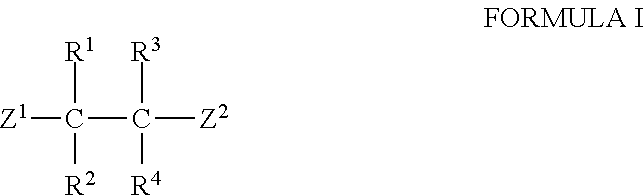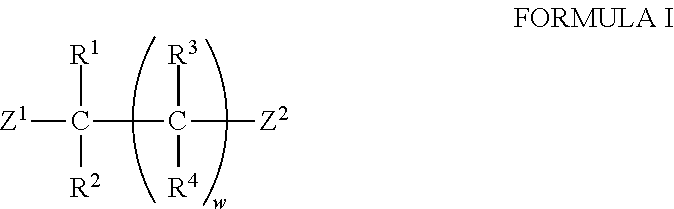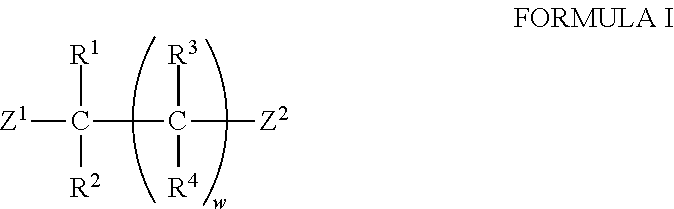Patents
Literature
72 results about "Transamination" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
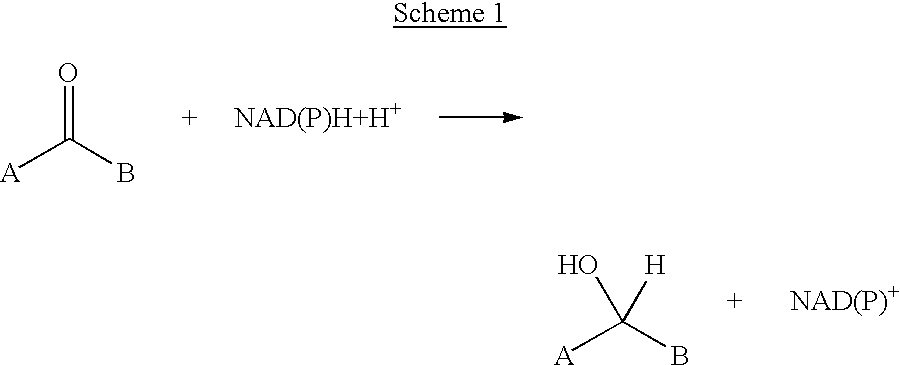
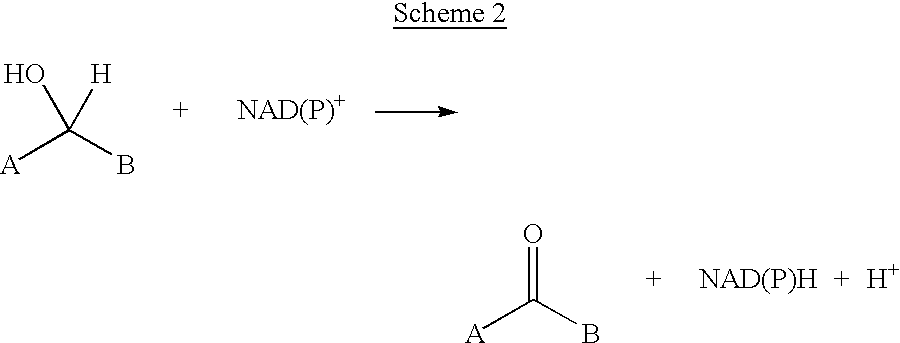
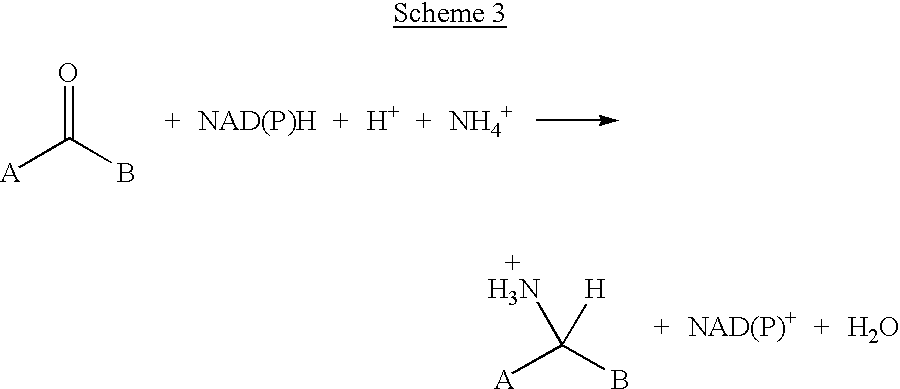
Transamination, a chemical reaction that transfers an amino group to a ketoacid to form new amino acids. This pathway is responsible for the deamination of most amino acids. This is one of the major degradation pathways which convert essential amino acids to non-essential amino acids (amino acids that can be synthesized de novo by the organism).
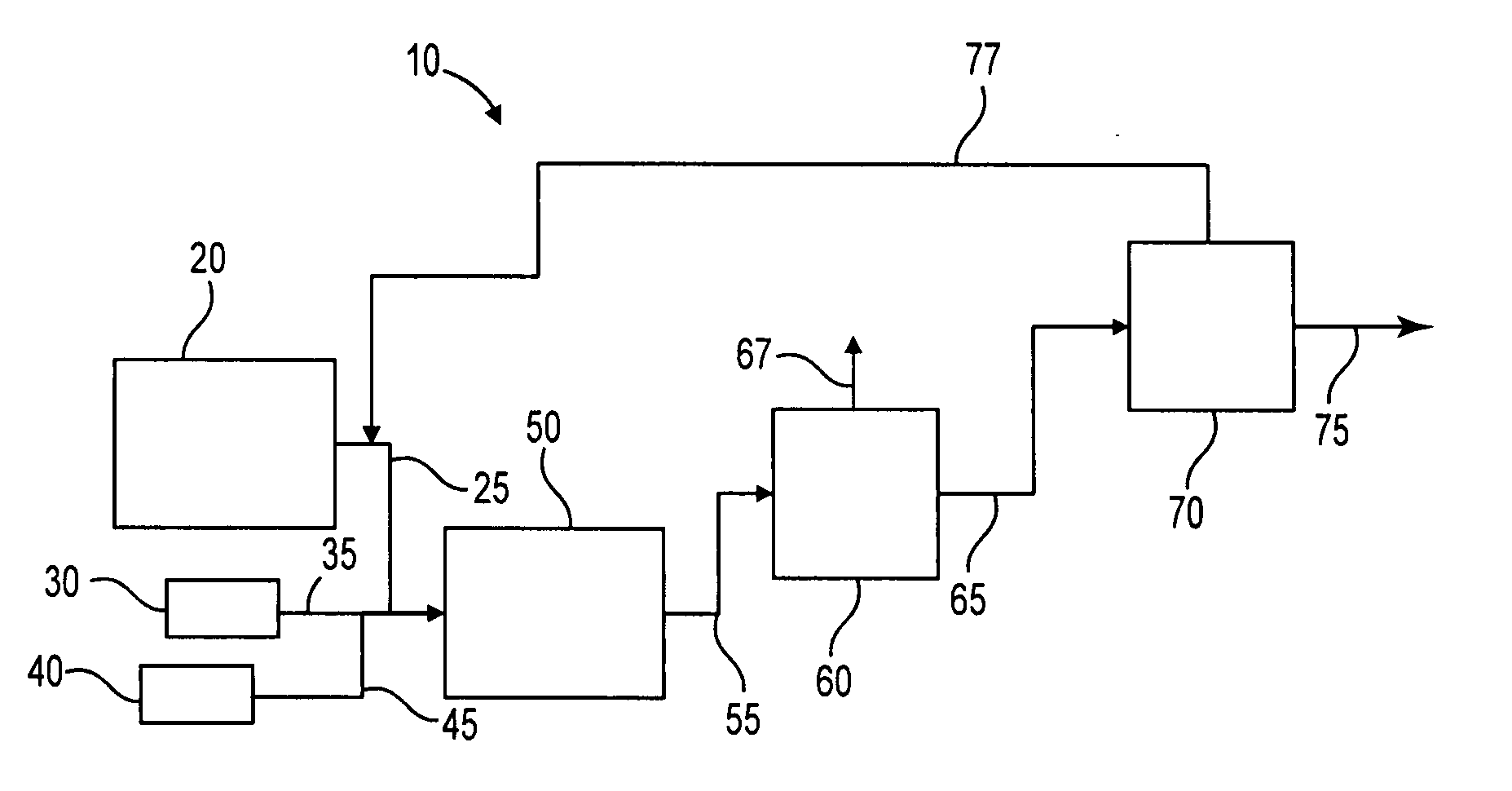
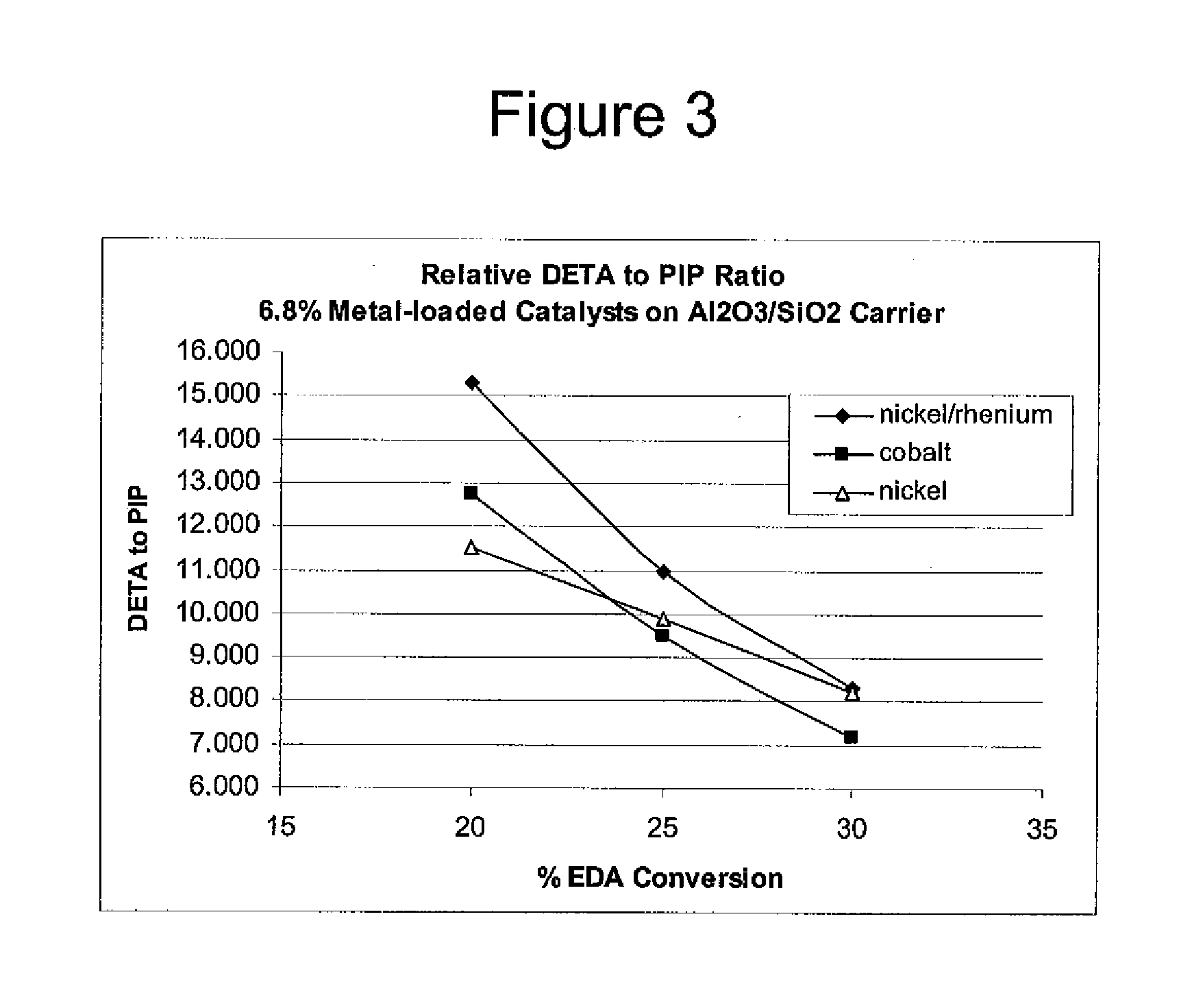
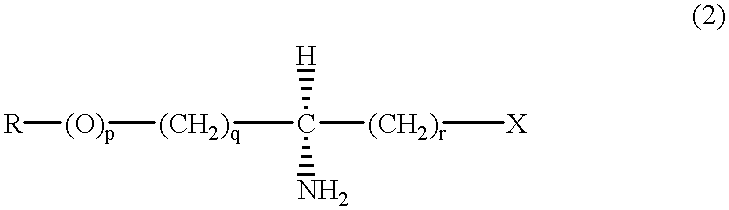
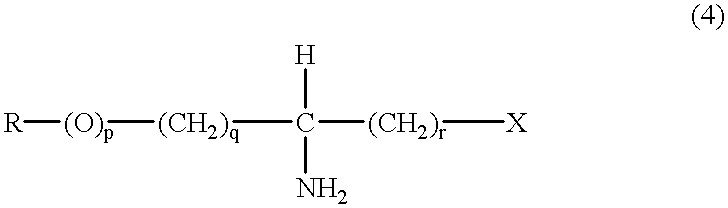
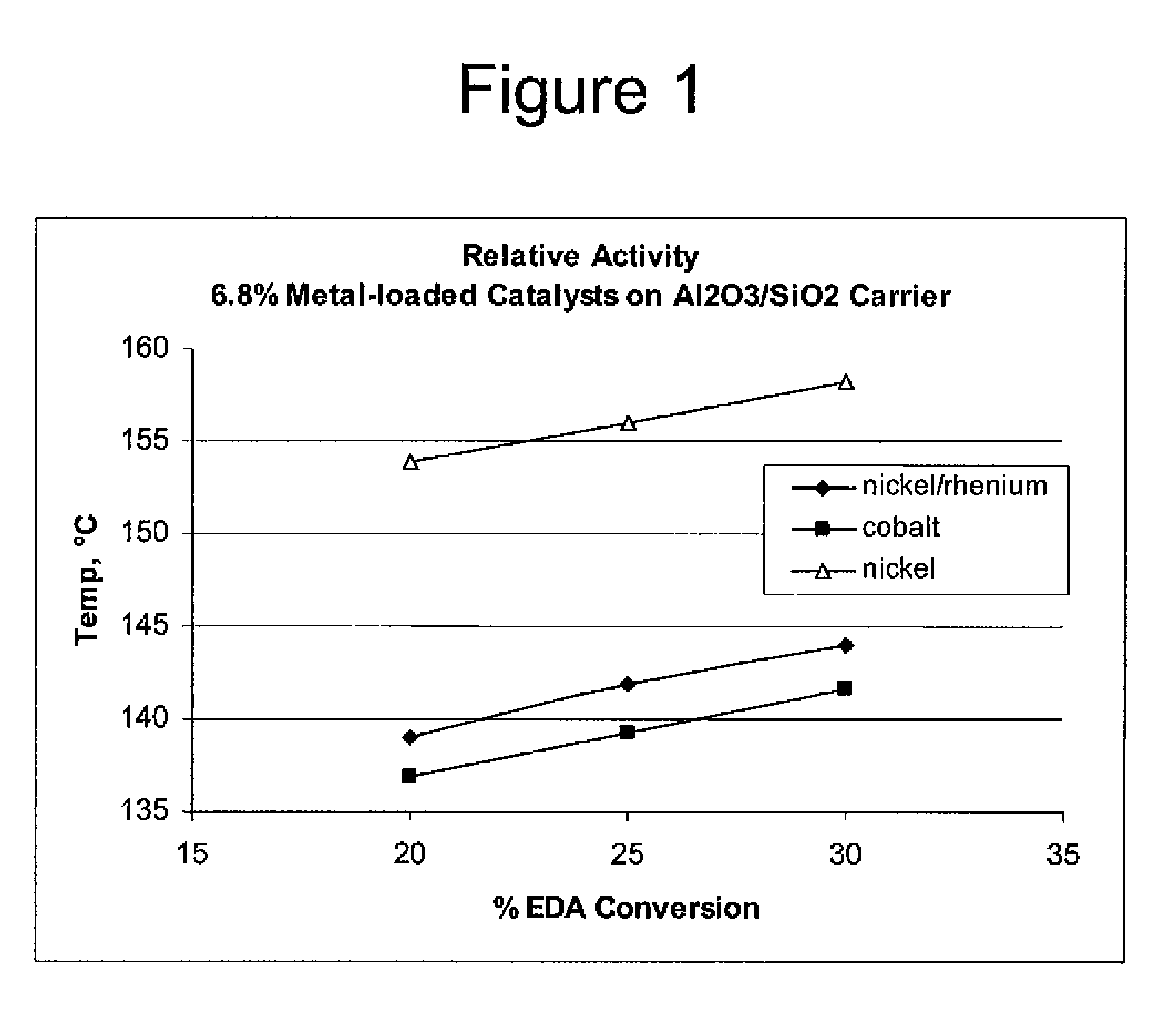
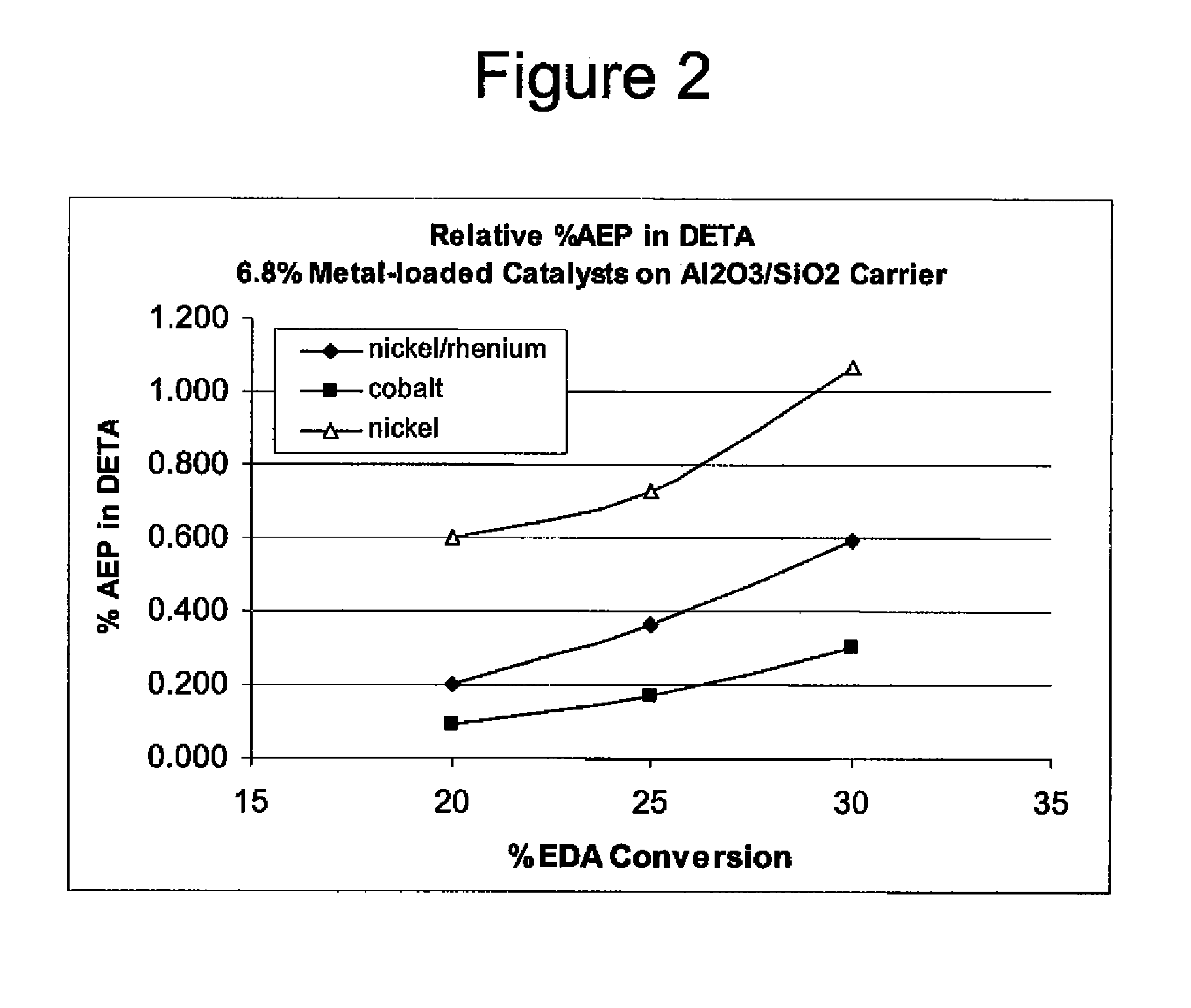
Process to selectively manufacture diethylenetriamine (DETA) or other desirable ethylenamines via continuous transmination of ethylenediamine (EDA), and other ethyleneamines over a heterogeneous catalyst system
ActiveUS20100087683A1Quantity maximizationQuantity minimizationOrganic compound preparationAmino compound preparation by disproportionationEthylenediamineDiethylenetriamine
The present invention reacts ethylenediamine with one or more additional ethyleneamines in the presence of a transamination catalyst to provide a different, preferably more desirable product mix of one or more ethyleneamines.
Owner:UNION CARBIDE CORP
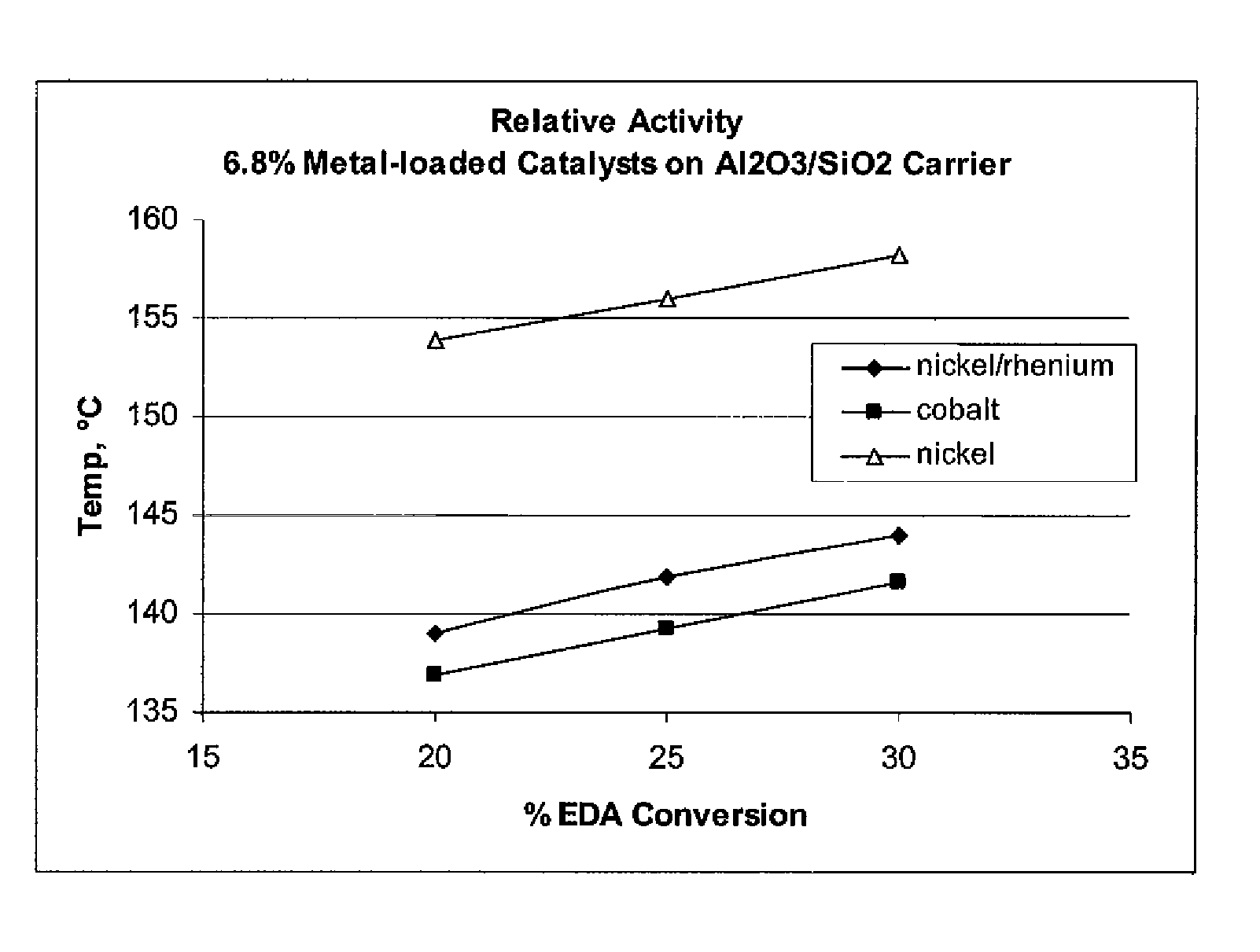
Low metal loaded, alumina supported, catalyst compositions and amination process
ActiveUS20100137642A1Good choiceMinimizingOther chemical processesOrganic compound preparationRheniumAmination
The present invention provides catalyst compositions useful for transamination reactions. The catalyst compositions have a catalyst support that includes transitional alumina, use a low metal loading (for example, less than 25 wt. %), and do not require the presence of rhenium. The catalyst compositions are able to advantageously promote transamination of a reactant product (such as the transamination of EDA to DETA) with excellent activity and selectivity, and similar to transaminations promoted using a precious metal-containing catalyst.
Owner:UNION CARBIDE CORP
Production method of L-glufosinate
ActiveCN105603015AImprove conversion rateSimple separation processTransferasesMicroorganism based processesButyric acidHydroxy compound
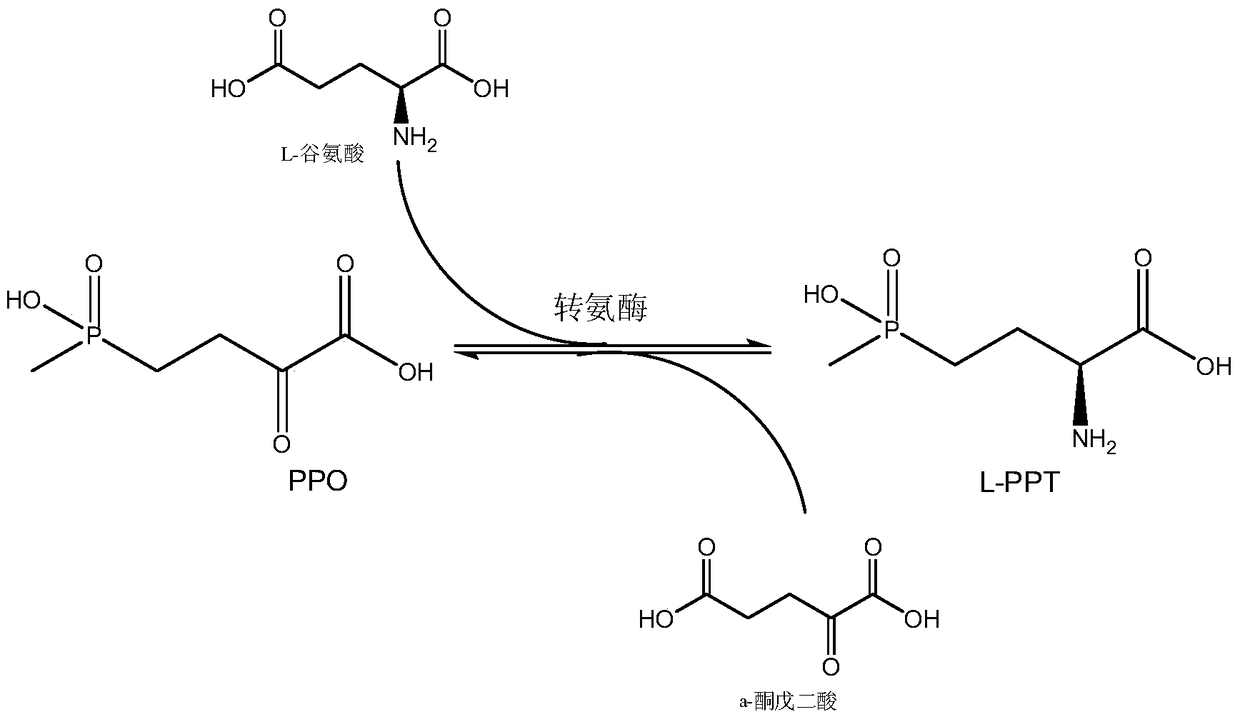
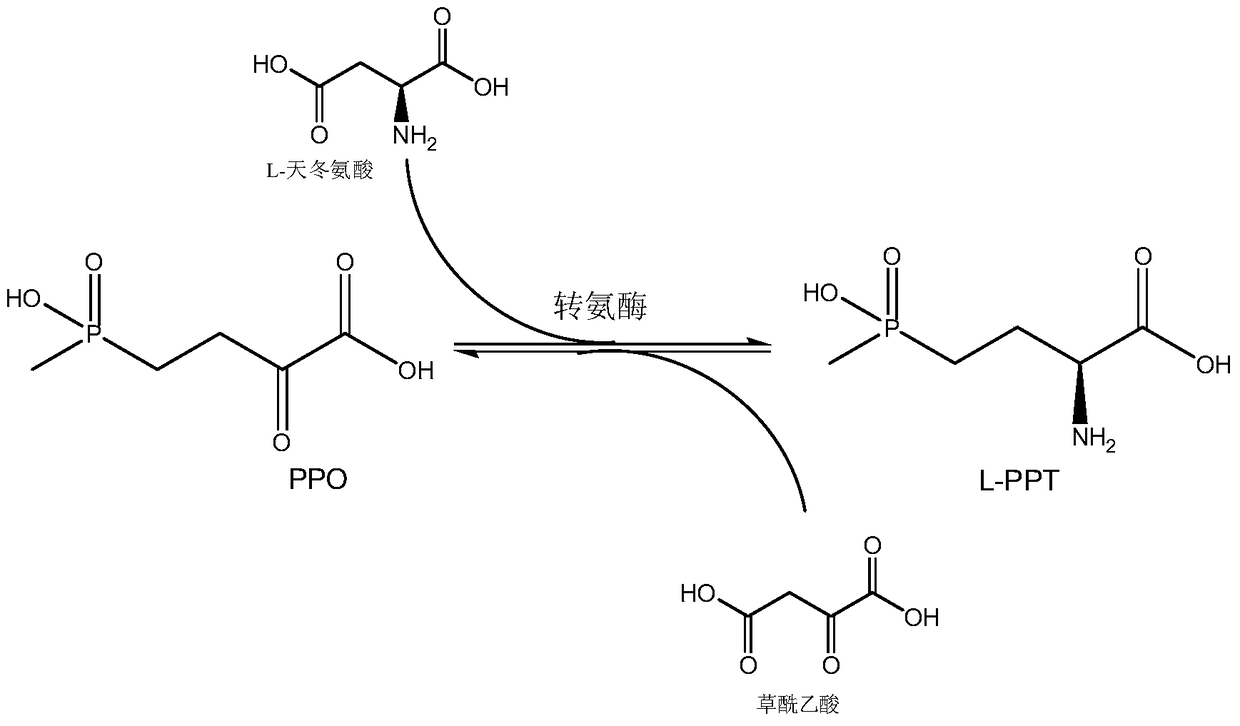
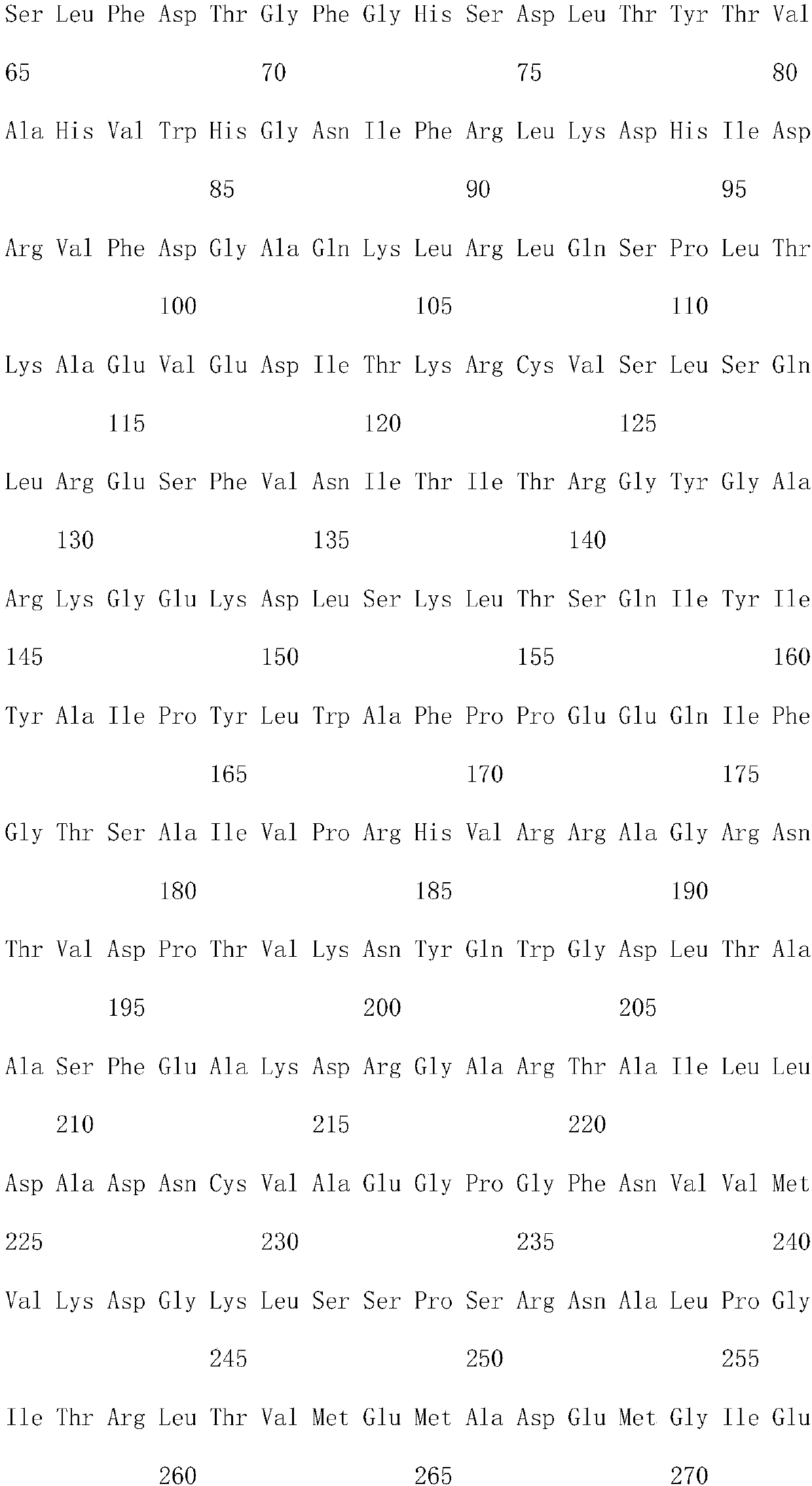
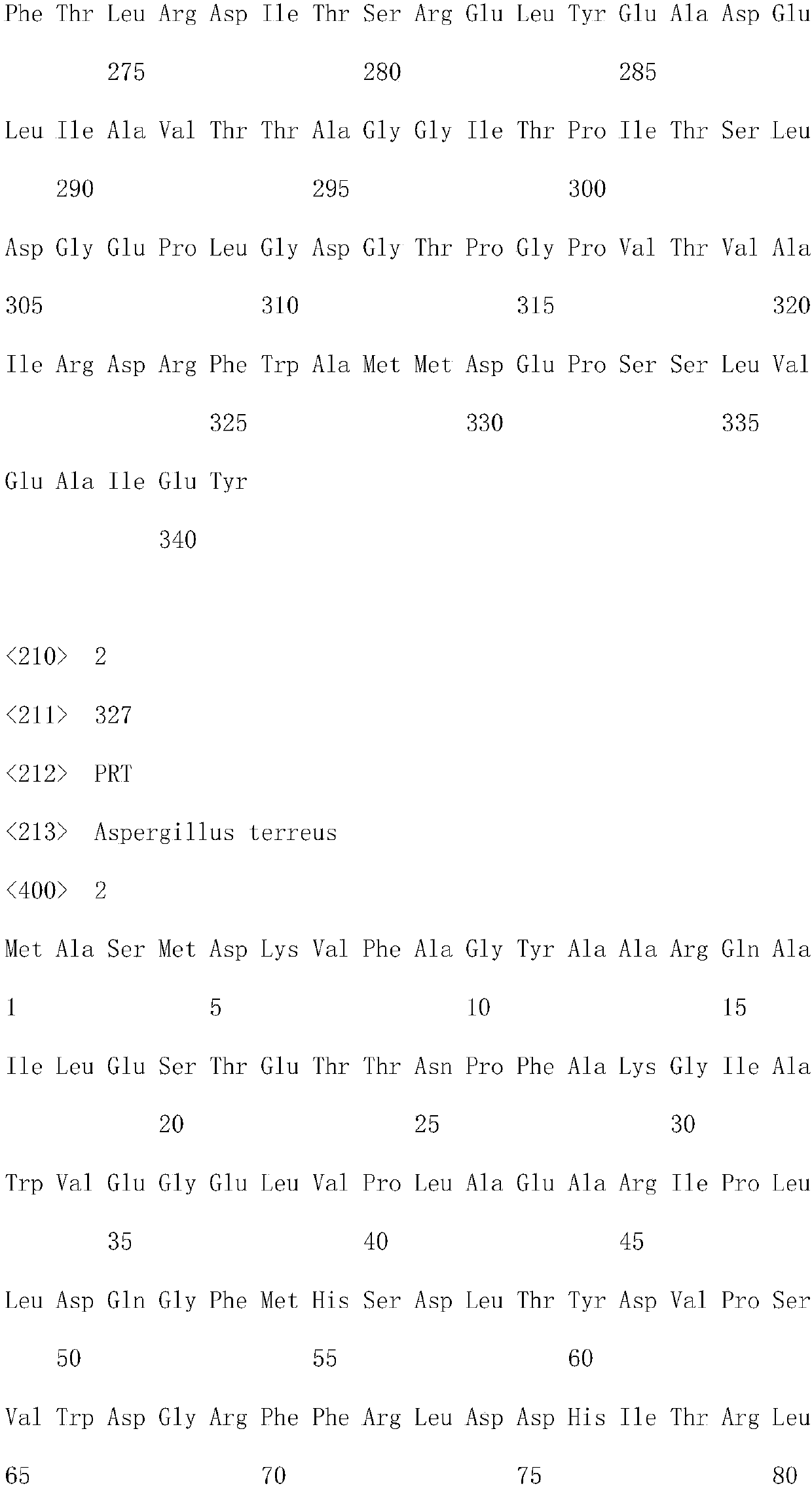
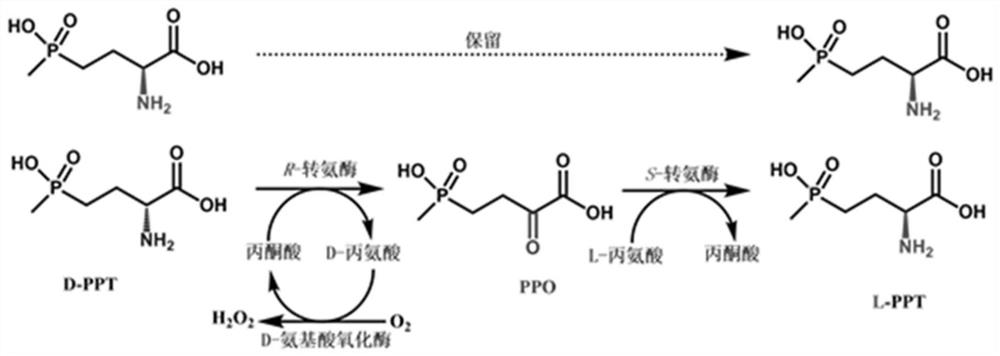
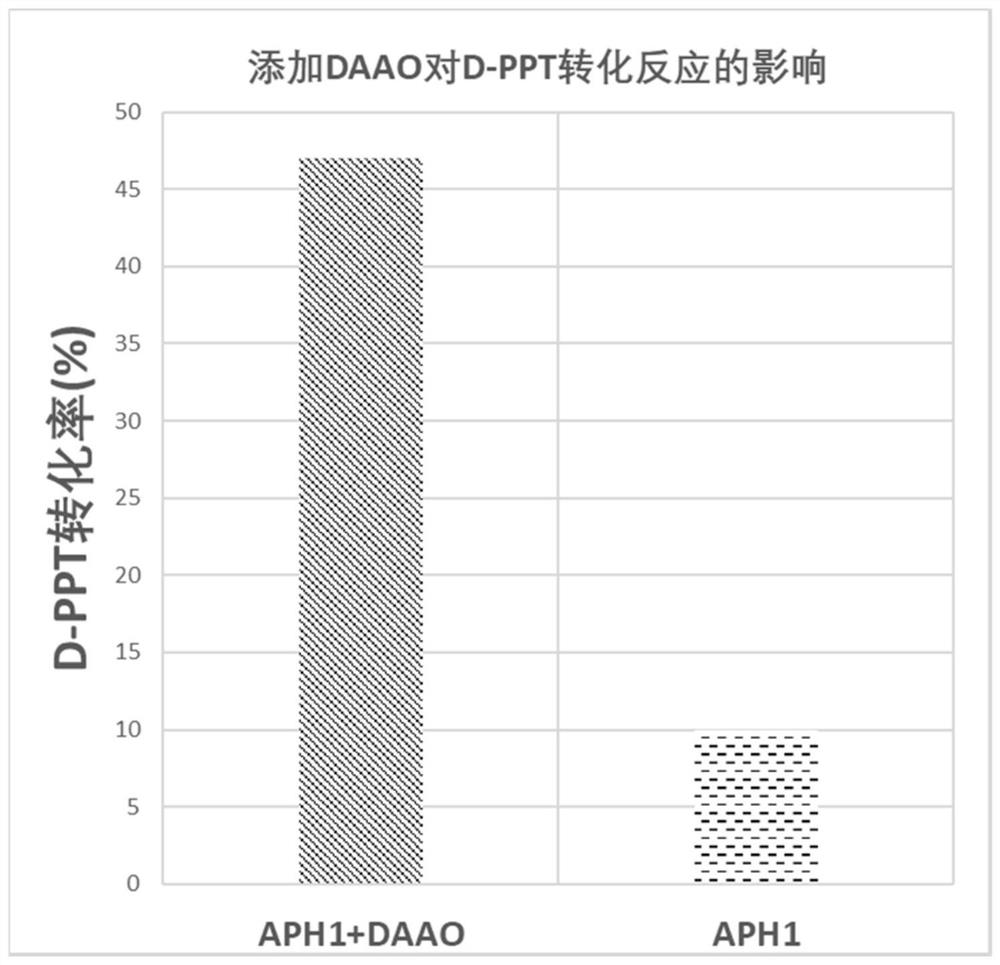
The invention discloses a production method of L-glufosinate. The method includes the steps that with 2-carbonyl-4-(hydroxyl methyl phosphoryl) butyric acid and salt thereof being a substrate, isolated transaminase or a cell catalysis substrate of in-vitro expression transaminase reacts with an amino donor under the condition that the amino donor exists, so that L-glufosinate is obtained, wherein the amino donor is alanine, and the amino acid sequence of transaminase is shown in SEQ ID NO.1-3. With 2-carbonyl-4-(hydroxyl methyl phosphoryl) butyric acid and salt thereof being the substrate and alanine being the amino donor, the transamination reaction occurs through the specific transaminase catalysis substrate, the substrate can be completely converted into L-glufosinate, and the conversion rate of raw materials is high and can reach 100%.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
(S)-alpha-phenethylamine: pyruvate transaminase
Relating to an enzyme capable of efficiently converting a ketone compound to an optically active amino compound by transamination, and a process for preparing an optically active amino compound using the enzyme. An (S)-alpha-phenethylamine:pyruvate transaminase, which acts on (S)-alpha-phenethylamine and a ketone compound, thereby catalyzing transamination for forming acetophenone and an amino compound corresponding to the ketone compound; a process for preparing an optically active amino compound using the transaminase; and a method for culturing a microorganism for producing the above transaminase, comprising adding to a medium one or more compounds selected from the group consisting of propylamine, 1-butylamine, 2-butylamine, 2-pentylamine, isopropylamine and isobutylamine as an inducer for the enzyme when a microorganism for producing (S)-alpha-phenethylamine:pyruvate transaminase is cultured.
Owner:KANEKA CORP
Low metal loaded, alumina supported, catalyst compositions and amination process
ActiveUS8293676B2Reduce metal contentRemarkable activityOrganic compound preparationOther chemical processesRheniumAmination
The present invention provides catalyst compositions useful for transamination reactions. The catalyst compositions have a catalyst support that includes transitional alumina, use a low metal loading (for example, less than 25 wt. %), and do not require the presence of rhenium. The catalyst compositions are able to advantageously promote transamination of a reactant product (such as the transamination of EDA to DETA) with excellent activity and selectivity, and similar to transaminations promoted using a precious metal-containing catalyst.
Owner:UNION CARBIDE CORP
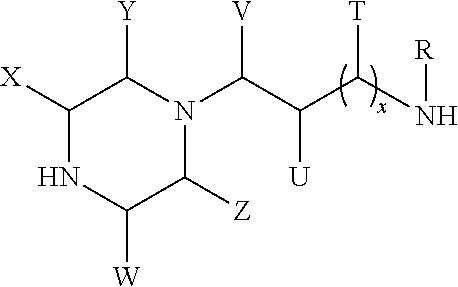
Methods of making cyclic, n-amino functional triamines
The present invention provides strategies for making cyclic triamines. Reactant media including certain precursors and / or certain types of catalysts can be converted into cyclic triamines with improved conversion and selectivity. The strategies can be incorporated into reactions that involve transamination schemes and / or reductive amination schemes. In the case of transamination, for instance, using transamination to cause ring closure of higher amines in the presence of a suitable catalyst leads to desired cyclic triamines with notable conversion and yield. In the case of reductive amination, reacting suitable polyfunctional precursors in the presence of a suitable catalyst also yields cyclic triamines via ring closure with notable selectivity and conversion. Both transamination and reductive amination methodologies can be practiced under much milder temperatures than are used when solely acid catalysts are used. Preferred embodiments can produce reaction mixtures that are generally free of salt by-products.
Owner:UNION CARBIDE CORP
Method for reductive amination of a ketone using a mutated enzyme
Methods for chemically transforming compounds using a mutated enzyme are provided, and more particularly a method for the production of an amino acid from a target 2-ketoacid, the production of an amine from a target ketone and the production of an alcohol from a target ketone. The methods comprise creating a mutated enzyme that catalyzes the reductive amination or transamination of the target 2-ketoacid or ketone or the reduction of the ketone and providing the mutated enzyme in a reaction mixture comprising the target 2-ketoacid or ketone under conditions sufficient to permit the formation of the desired amino acid, amine or alcohol to thereby produce the amino acid, amine or alcohol.
Owner:CODEXIS INC
Process to selectively manufacture diethylenetriamine (DETA) or other desirable ethyleneamines via continuous transamination of ethylenediamine (EDA), and other ethyleneamines over a heterogeneous catalyst system
ActiveUS8383860B2Quantity maximizationQuantity minimizationOrganic compound preparationAmino compound preparation by disproportionationEthylenediamineHomogeneous catalysis
The present invention reacts ethylenediamine with one or more additional ethyleneamines in the presence of a transamination catalyst to provide a different, preferably more desirable product mix of one or more ethyleneamines.
Owner:UNION CARBIDE CORP
Method for producing L-glufosinate-ammonium by using transaminase and ethylene-forming enzyme
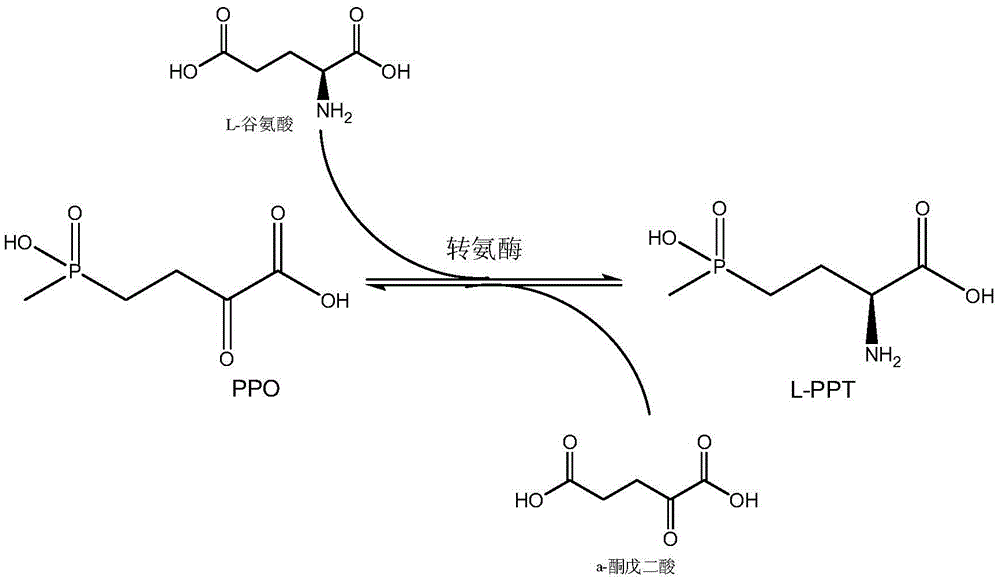
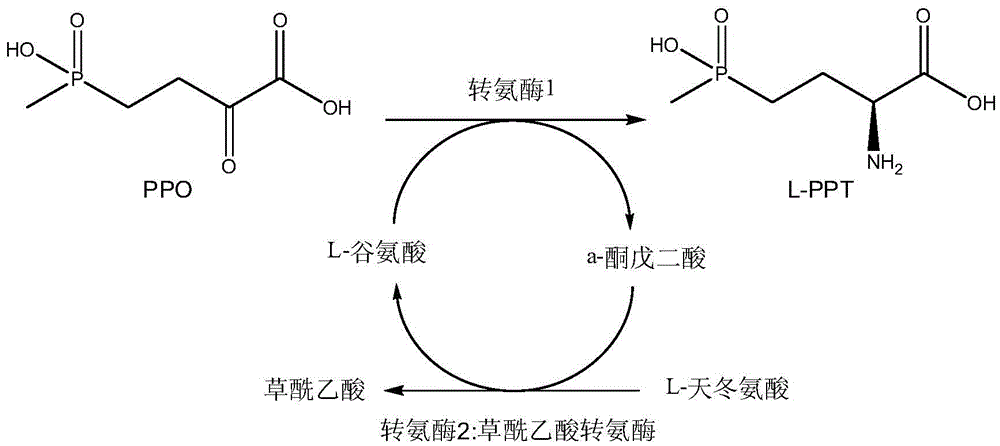
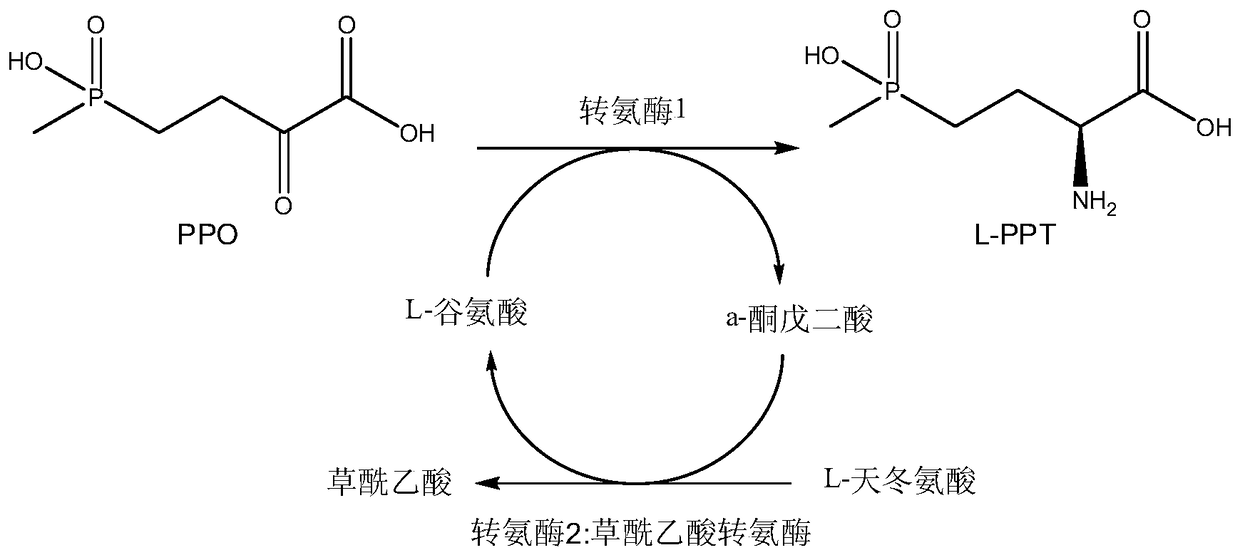
The invention discloses a method for producing L-glufosinate-ammonium by using transaminase and an ethylene-forming enzyme. According to the method, 2-carbonyl-4-(hydroxyl methyl phosphoryl) butyric acid or salt thereof is taken as a raw material, and the L-glufosinate-ammonium is obtained through a catalytic reaction of the transaminase and the ethylene-forming enzyme under the condition of taking glutamic acid or salt thereof as an amidogen donor. According to the method, the 2-carbonyl-4-(hydroxyl methyl phosphoryl) butyric acid or the salt thereof is taken as a substrate, and the L-glufosinate-ammonium is obtained through the co-catalysis of the transaminase and the ethylene-forming enzyme under the condition of taking the glutamic acid or the salt thereof as the amidogen donor, so that by-product alpha-dibasic ketonic acid after a transamination reaction is completely converted into carbon dioxide and ethylene through catalysis of the ethylene-forming enzyme, under the condition of guaranteeing few using amount of the raw materials, the conversion rate of the raw materials is obviously improved, the cost of the raw materials is reduced, the subsequent purification technology is simplified, and the product total recovery is improved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
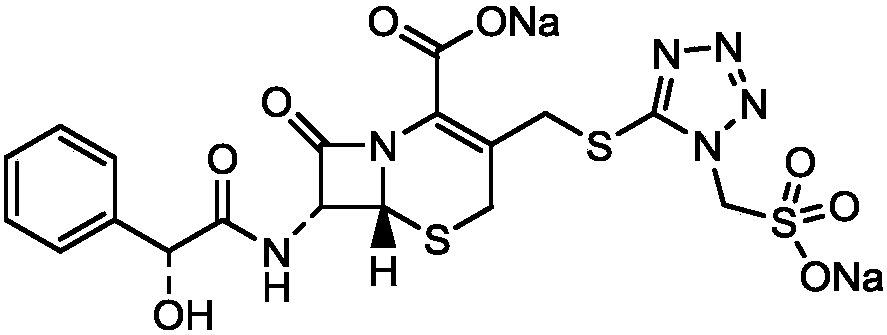
Method for crystallizing and producing cefpiramide sodium crystals
The invention discloses a method for crystallizing and producing cefpiramide sodium crystals. The method comprises the steps that: (a) cefpiramide acid and an transamination agent are dissolved in a solvent I, wherein the transamination agent is any one selected from triethylamine, diisopropylamine, and isopropylamine; and a temperature is controlled, and the materials are stirred until completely dissolved; (b) a salt-forming agent is added into a solvent II, wherein when the salt-forming agent is sodium ethylhexanoate, the solvent II is an acetone solvent, and when the salt-forming agent is sodium hydroxide, the solvent II is any one or a mixture of two selected from methanol and tetrahydrofuran; and the materials are stirred until completely dissolved; (c) the salt-forming agent solution is uniformly added into the solution of cefpiramide amine salt; the temperature is controlled, and crystal seeds are added; curing crystallization is carried out; acetone is added into the crystallization system for regulating the pH value of the crystallization system and for carrying out solvent-out crystallization; and filtering, washing, and drying are carried out, such that the cefpiramide sodium crystals are obtained. The method provided by the invention has the advantages of simple operation, uniform crystals, high purity, low impurity content, good stability, easy storage, and the like.
Owner:NORTH CHINA PHARMA HEBEI HUAMIN PHARMA
A process for the identification and preparation of a (r)-specific omega-transaminase
The present invention relates to a process for the identification and preparation of a (r)-specific omega-transaminase, in particular a processes for the screening, preparation and characterization of (R)-selective omega-transaminases, to transaminases obtained thereby and their uses in various transamination processes.
Owner:LONZA LTD
Transamination of nitrogen-containing compounds to high molecular weight polyalkyleneamines
ActiveUS9000217B2Easy to customizeHigh molecular weightOrganic compound preparationAmino compound preparation by disproportionationDehydrogenationAlkyl amine
A process for preparing high molecular weight acyclic polyamines comprising providing a reaction mixture that includes at least a first component comprising a first organic, nitrogen-containing compound that contains at least two non-tertiary amine groups separated from one another by a ternary or higher carbon atom spacing that can be transaminated in the presence of a hydrogenation / dehydrogenation catalyst to form a mixture of higher molecular weight, acyclic polyamines while minimizing the formation of cyclic polyamines.
Owner:DOW GLOBAL TECH LLC
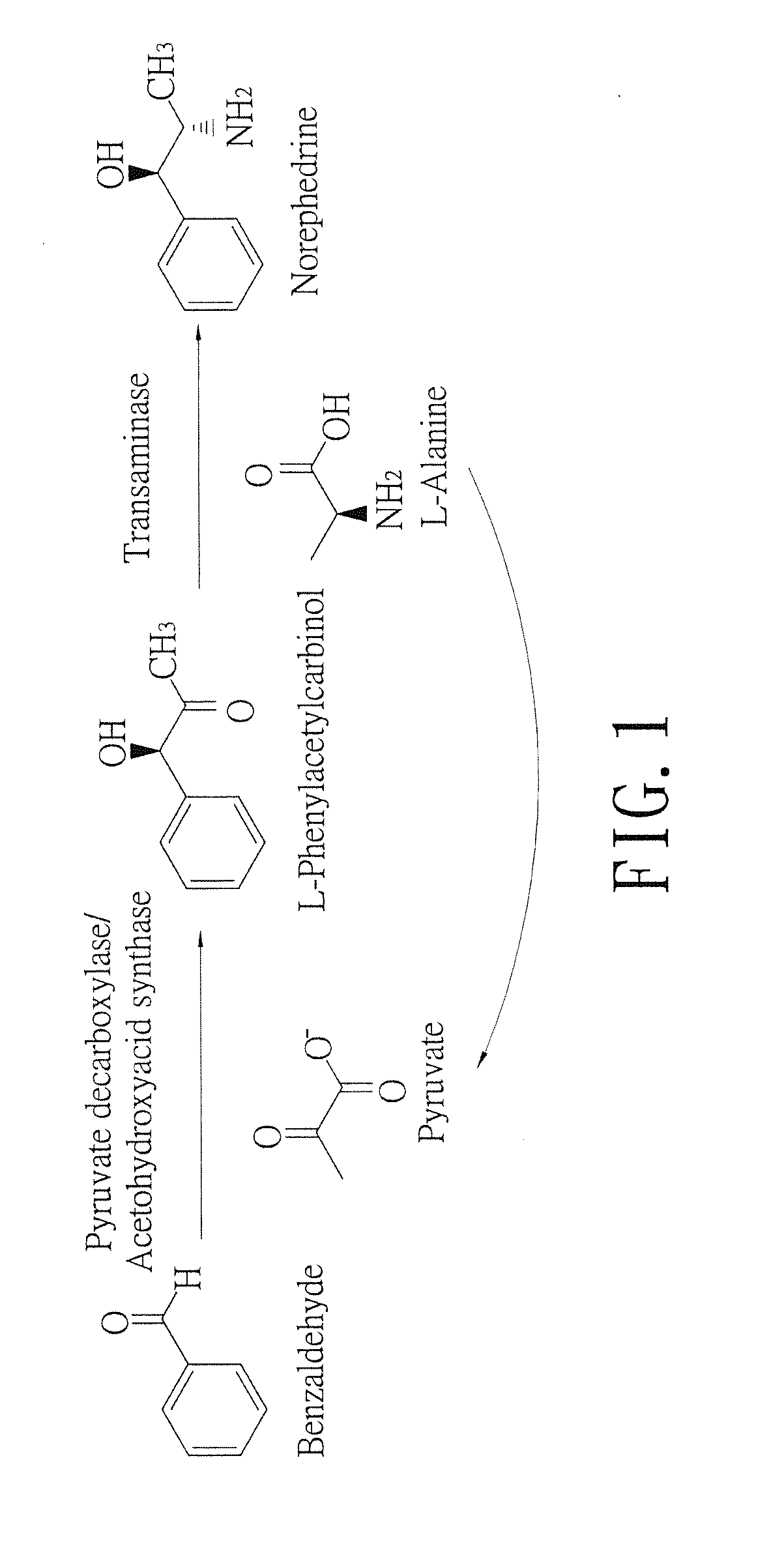
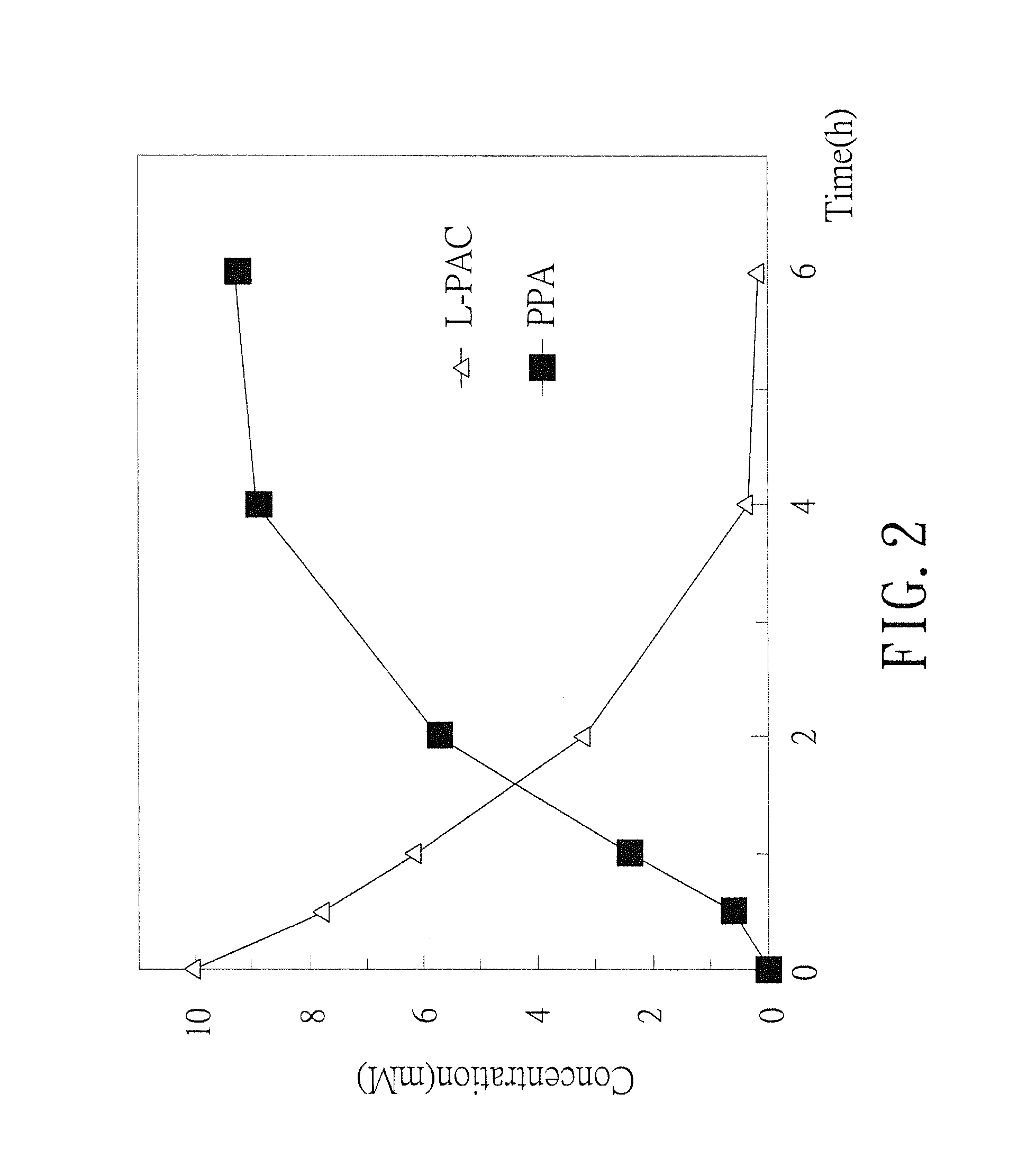
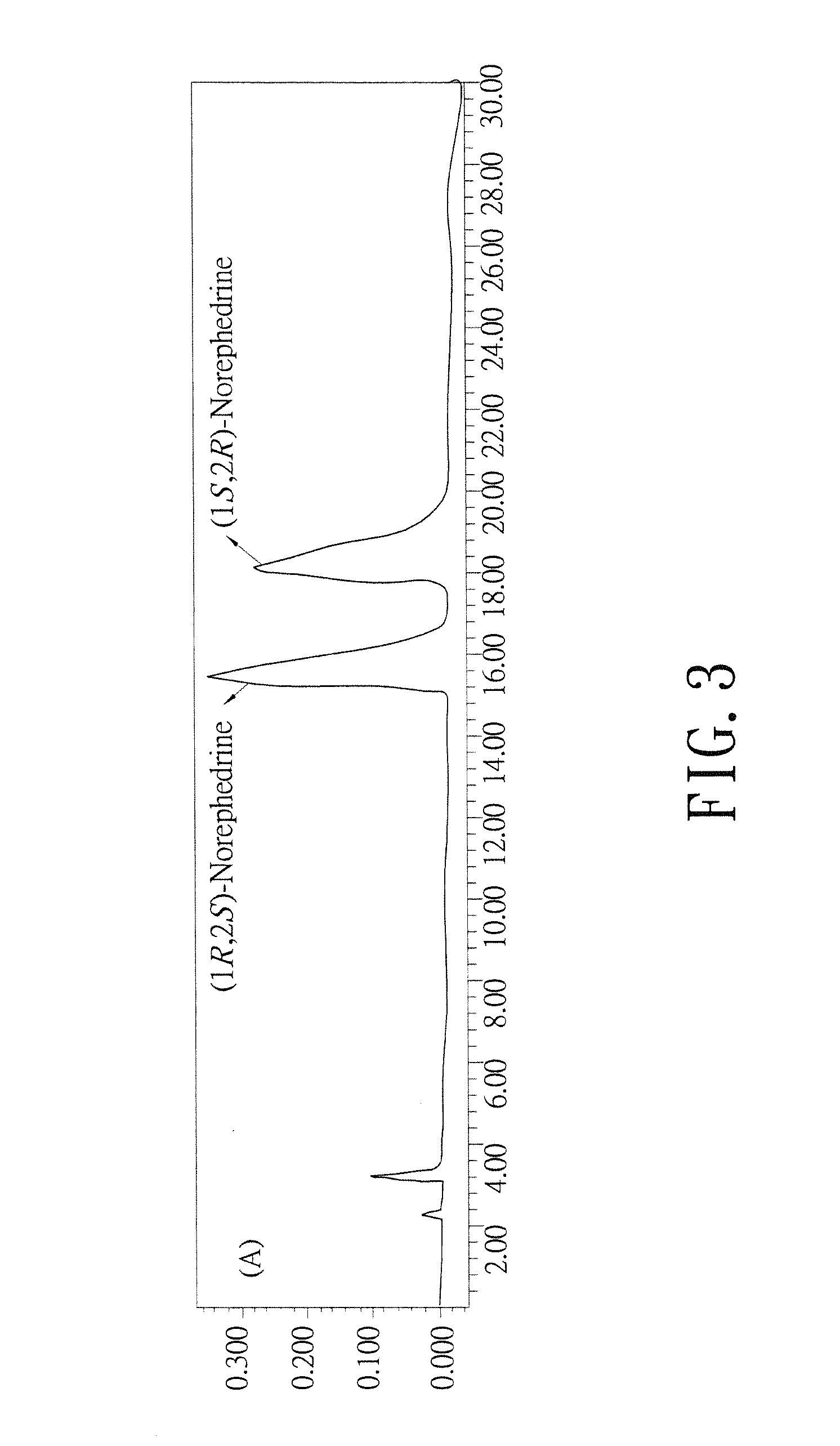
Biosynthesis methods of norephedrine with specific optical activities
InactiveUS20130309732A1Reduce formationLower reaction costTransferasesFermentationBenzaldehydeD-norephedrine
A biosynthesis method of norephedrine with specific optical activities is revealed to convert and generate optical isomers with specific optical activities by biocatalysis. A two-step biotransformation reaction is carried by a whole-cell biocatalyst for converting reaction substrates, benzaldehyde and pyruvate, to L-phenylacetylcarbinol (L-PAC) in the first step and the yield of the L-PAC is 99%, and then an amino donor (L-alanine) is added and the transamination of the L-PAC is catalyzed by a transaminase with optical specificity for biosynthesizing the norephedrine with high optical purity. The pyruvate is produced from the amino donor, L-alanine, by the transamination in the reaction system, so that the pyruvate is regenerated in the reaction system without being added again.
Owner:HUNGKUANG UNIV
Transamination of nitrogen-containing compounds to make cyclic and cyclic/acyclic polyamine mixtures
A transamination process is described to prepare polyamine product mixtures from reactants comprising mixed nitrogen-containing compounds with binary carbon spacing between nitrogen-containing groups (a binary component). A second nitrogen-containing component with a second carbon atom spacing between nitrogen-containing groups may also be employed. The molar ratio between the binary and second components can be adjusted to customize the product composition for desired end uses.
Owner:DOW GLOBAL TECH LLC
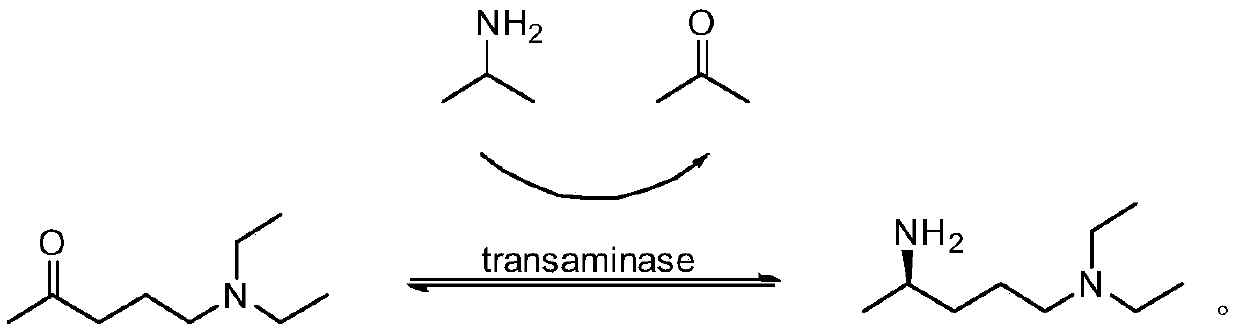
Preparation method of (R)-N1,N1-diethyl-1,4-pentanediamine
The present invention belongs to the technical field of chiral amine preparations and particularly relates to a preparation method of chiral amine (R)-N1,N1-diethyl-1,4-pentanediamine. A synthesis ofthe (R)-N1,N1-diethyl-1,4-pentanediamine comprises the following steps: using 5-diethylamino-2-pentanone as a raw material and catalyzing the 5-diethylamino-2-pentanone with an amino group donor isopropylamine to conduct a transamination reaction under catalysis of omega-transaminase ATA-117 and coenzyme pyridoxal phosphate to produce the(R)-N1,N1-diethyl-1,4-pentanediamine. The product prepared by the provided method is good in stereoselectivity and produced enantiomer by-products are less than 0.5%; after purification by distillation, purity reaches 99.3% or more and single impurity reachesstarting raw material indexes of raw material medicines; and a total yield can reach as high as 70-85%, the yield is obviously higher than that of traditional process, and the preparation method has avery good industrial application prospect.
Owner:暨明医药科技(苏州)有限公司
Transamination of nitrogen-containing compounds to high molecular weight polyalkyleneamines
ActiveUS20130225864A1High molecular weightEasy to customizeOrganic compound preparationAmino compound preparation by disproportionationHigh carbonNitrogen
A process for preparing high molecular weight acyclic polyamines comprising providing a reaction mixture that includes at least a first component comprising a first organic, nitrogen-containing compound that contains at least two non-tertiary amine groups separated from one another by a ternary or higher carbon atom spacing that can be transaminated in the presence of a hydrogenation / dehydrogenation catalyst to form a mixture of higher molecular weight, acyclic polyamines while minimizing the formation of cyclic polyamines.
Owner:DOW GLOBAL TECH LLC
A kind of production method of L-glufosinate-ammonium
ActiveCN105603015BImprove conversion rateSimple separation processTransferasesMicroorganism based processesButyric acidHydroxy compound
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Process for the separation of organic compounds
ActiveUS10730022B2Improve stabilityEfficient and stable processingAmino compound purification/separationMembranesOrganic acidSimple Organic Compounds
Owner:VLAAMSE INSTELLING VOOR TECHNOLOGISCH ONDERZOEK NV VITO
Novel chiral open-chain pyridoxamine catalyst and synthesis method and application thereof
InactiveCN106083703AImprove biological activitySynthesis shortcutOrganic compound preparationOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsHydrogenHalogen
The invention relates to a novel chiral open-chain pyridoxamine catalyst and a synthesis method and application thereof. The structural general formula of the pyridoxamine catalyst is shown in the specification, wherein R1, R2, R3 and R4 are one of hydrogen, C1-24 alkyl, C1-24 alkyl containing substituent groups, substances shown in the specification and halogen, the substituent groups on C1-24 alkyl are a substance shown in the specification or a substance shown in the specification or a substance shown in the specification or O-Rw or S-Rw' or halogen, and Rx, Rx', Ry, Ry', Ry'', Rz, Rz', Rw and Rw' are one of hydrogen, methyl, ethyl, n-propyl, isopropyl, n-butyl, tertiary butyl, cyclopentyl, cyclohexyl, cycloheptyl, phenyl, benzyl, (1-phenyl)ethyl, 1-naphthyl, 2-naphthyl and halogen. Compared with the prior art, the pyridoxamine catalyst can achieve rapid and efficient synthesis of chiral amino acid, the preparation raw materials are easy to obtain, reaction conditions are mild, cost is low, and when the novel chiral open-chain pyridoxamine catalyst is used for a transamination reaction, the conditions are mild, and the reaction is stable.
Owner:SHANGHAI NORMAL UNIVERSITY
A kind of transaminase and its application in the synthesis of sitagliptin intermediate
ActiveCN105018440BEasy to recycleHigh optical purityBacteriaTransferasesSitagliptin PhosphateRecombinase
The invention provides a new aminotransferase, a gene of the new aminotransferase, a recombinant expression vector containing the gene, a recombinant expression transformant, a recombinase, a preparation method of the recombinase, and application of the aminotransferase to preparation of active chiral amine by performing asymmetrical transamination on a carbonyl compound. The aminotransferase is derived from mycobacterium (mycobacterium vanbaalenii) PYR-1, and is applied to preparation of (R)-3-amino-4-(2, 4, 5-trifluorophenyl)-methyl butyrate. Compared with other preparation methods, the preparation methods provided by the present invention have the advantages that catalyzed and prepared products are high in concentration, enantioselectivity is high, reaction conditions are mild, operations are simple and convenient, enlargement is easy and the like, so that the industrial application prospect in production of sitagliptin phosphate is excellent.
Owner:弈柯莱(台州)药业有限公司
Synthetic method of alpha-amino acid with photolytic activity
InactiveCN102766058AMild reaction conditionsEasy to operateOrganic compound preparationAmino-carboxyl compound preparationAmino estersBenzylamine
The invention belongs to an amino acid compound, especially to a synthetic method of alpha-amino acid with photolytic activity by asymmetric biomimetic transamination. The synthetic method comprises the following steps of: using alpha-keto ester and benzylamine as raw materials, using cinchona alkaloid derived chiral base A or chiral base B as a catalyst to catalyze alpha-keto ester with different structures by one kettle way to carry out asymmetric transamination, carrying out post-treatment such as hydrolysis, extraction, column chromatography and the like, synthesizing to prepare alpha-amino ester with photolytic activity, and finally carrying out hydrolysis to obtain (chiral)alpha-amino acid with photolytic activity. Enantiomeric excess value (ee value) can be as high as 92%.
Owner:INST OF CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Progressive decarbonizing method of nitride fiber
ActiveCN106995947AImprove mechanical propertiesImprove performanceFibre chemical featuresFiberAmidogen
The invention provides a progressive decarbonizing method of nitride fiber. The method comprises the steps of carrying out substitution reaction of ammonia gas at 300 to 650 DEG C so as to introduce amidogen for removing most of H and methyl, and then utilizing transamination reaction of the ammonia gas at 650 to 950 DEG C for eliminating alkyl participating in the reaction. Through controlling ammonia gas involvement occasion and involvement degree, progressive decarbonizing of the fiber is realized, the occurrence of a large number of nanometer defects is avoided, nitride ceramic fiber with excellent performance is obtained, and the mechanical property of the obtained fiber is improved.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
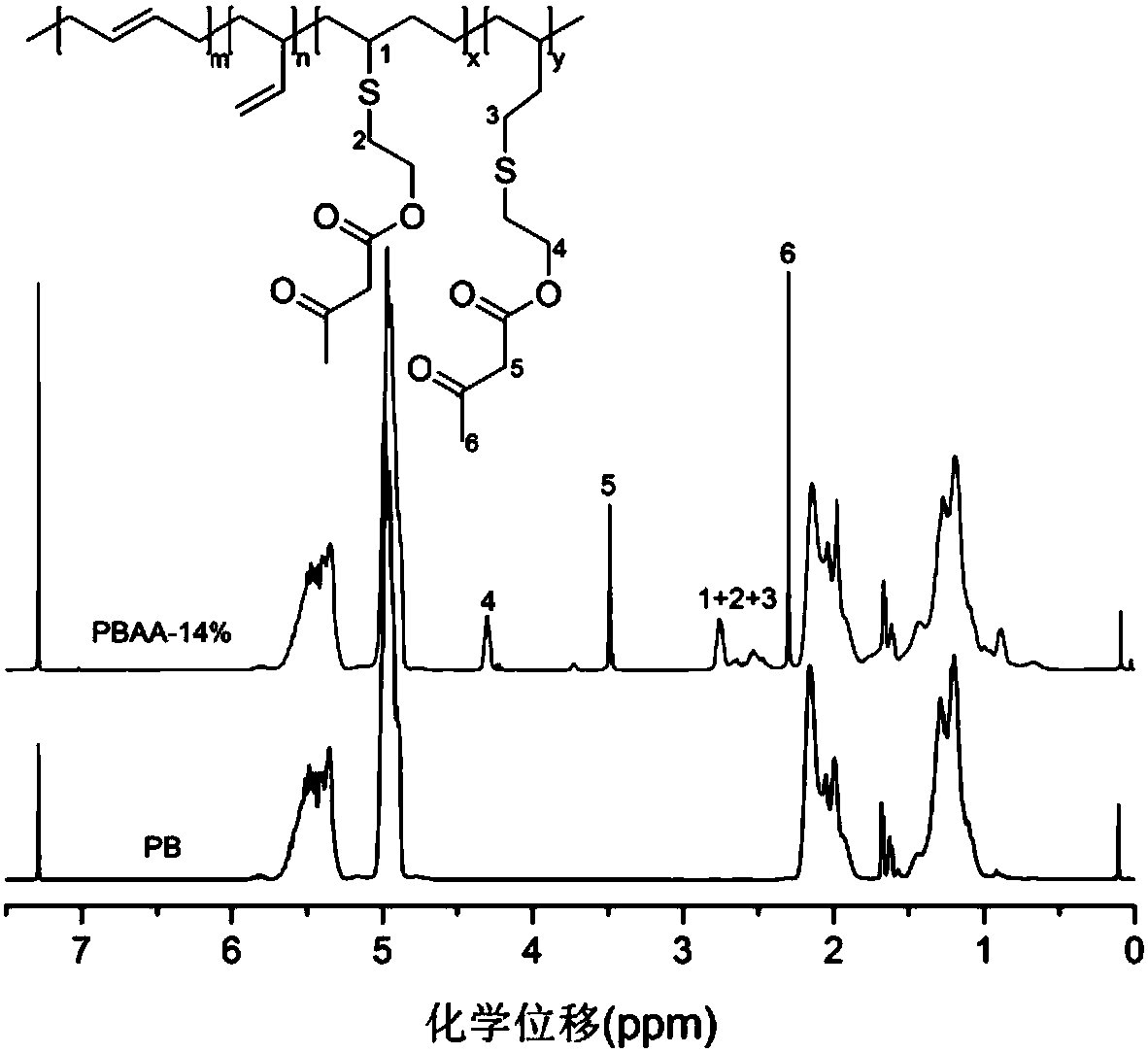
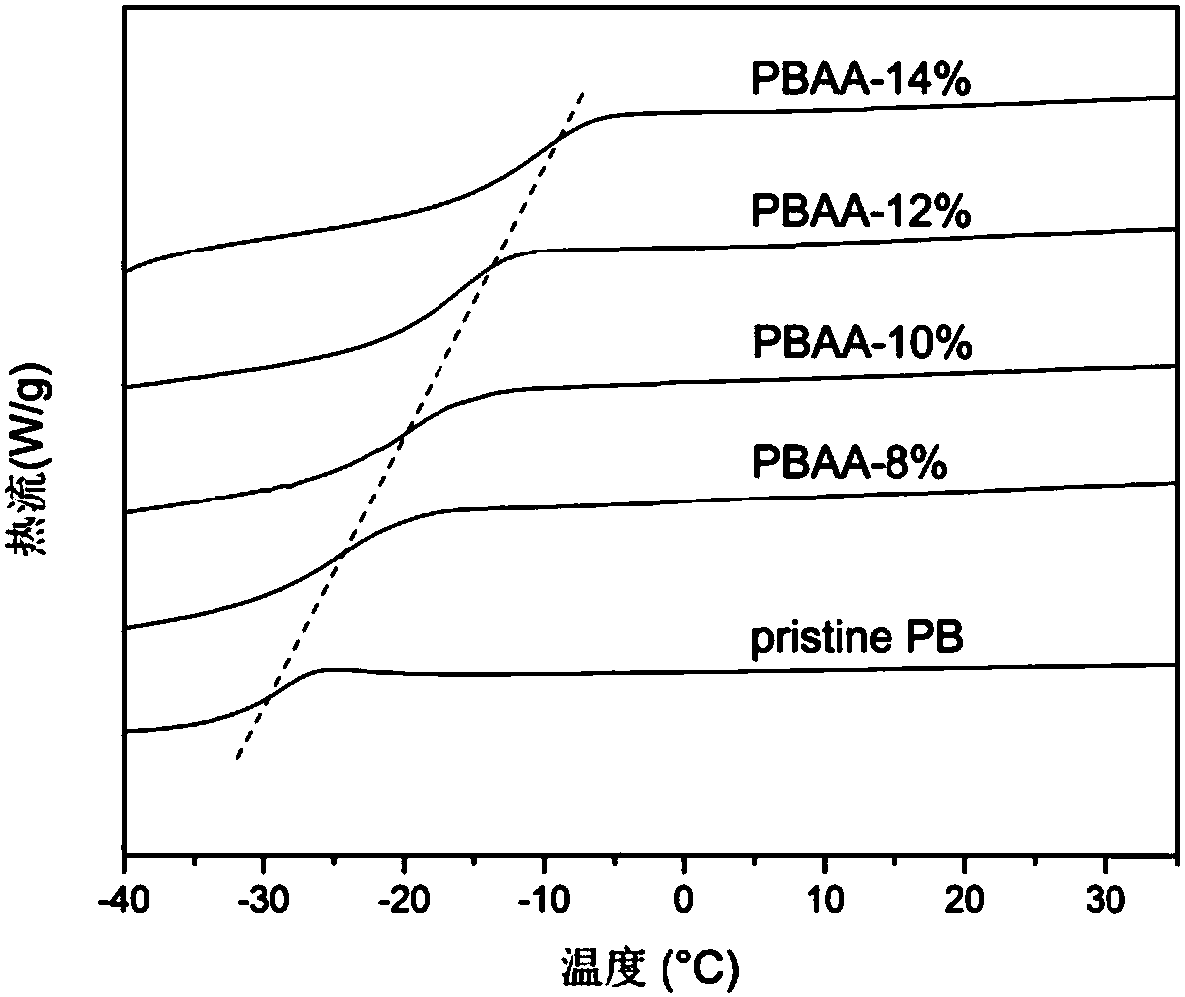
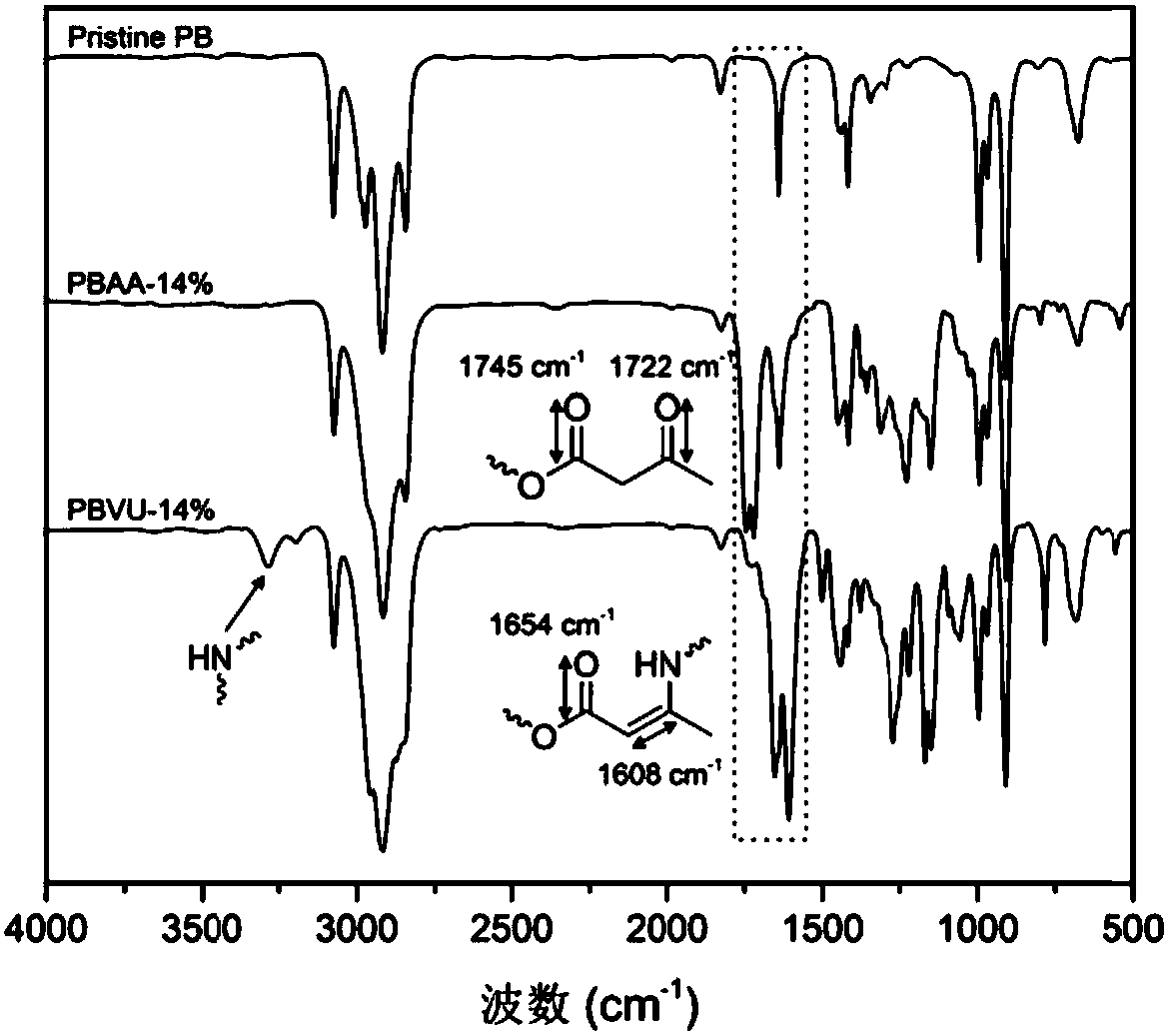
Method for preparing crosslinked elastomer capable of being reprocessed by utilizing transamination
The invention belongs to the technical field of functional materials, and in particular relates to a method for preparing a crosslinked elastomer capable of being reprocessed by utilizing transamination. A dynamic exchange reaction based on the transamination of the method makes the crosslinked elastomer have reprocessability; and the method comprises the following steps: firstly, through a thiol-ene ''click'' chemical modification method, a reaction of thiol and double bonds in an unsaturated elastomer is utilized to introduce hydroxyl; secondly, the introduced hydroxyl is further modified into acetoacetyl; and finally, a polyamine compound is added as a crosslinking agent to form a chemically-crosslinked network structure. According to the method disclosed by the invention, since an m-vinyl carbamate bond formed by a reaction of amino with the acetoacetyl can be subjected to transamination under certain conditions, the prepared crosslinked elastomer has reprocessability; and the method has very good practical value in the recovery and reuse process of elastomers.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
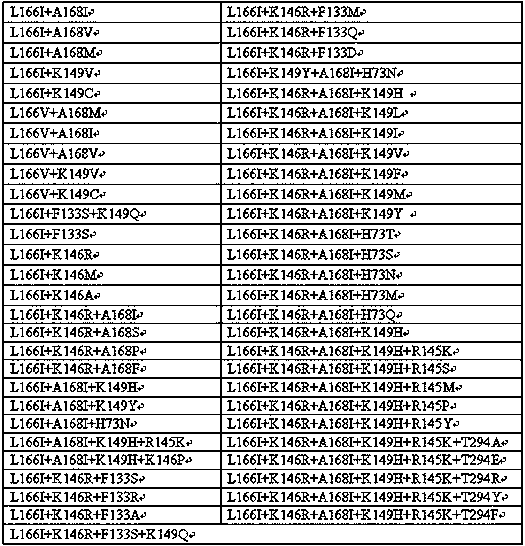
Transaminase mutant and application thereof
ActiveCN111235127AHigh catalytic activitySuitable for industrial productionTransferasesMicroorganism based processesKetoneChiral amine
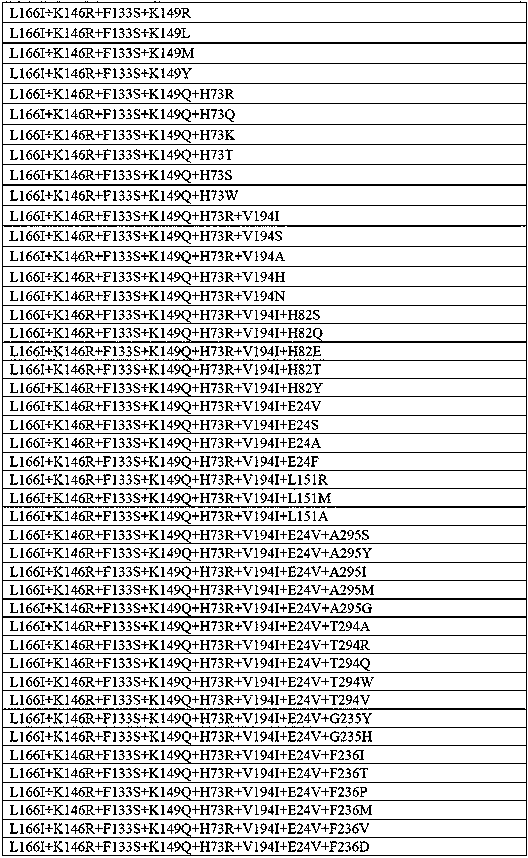
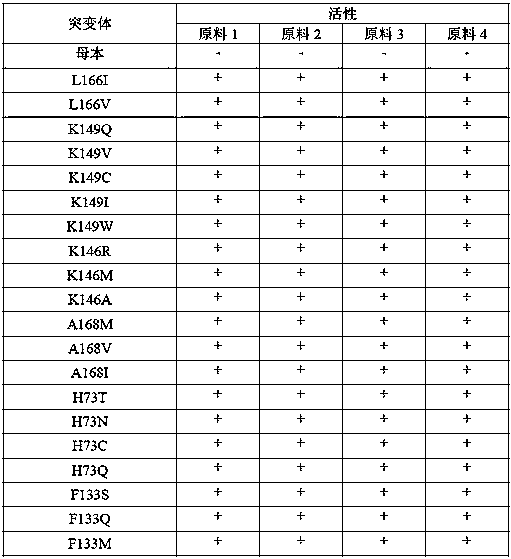
The invention provides a transaminase mutant and application thereof. Compared with an amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO:1, an amino acid sequence of the transaminase mutant includes at least oneof the following mutation sites: L166, K149, K146, A168, H73, F133, H82, E24, V194, T294, A295, G235 and F236. The transaminase mutant has improved catalytic activity for transamination reaction of ketone substrates and is suitable for industrial production of chiral amines.
Owner:ASYMCHEM LAB TIANJIN
Synthesis method of chiral amine
InactiveCN112458123ACatalyzed reaction volume is smallShort synthetic routeTransferasesFermentationKetoneCombinatorial chemistry
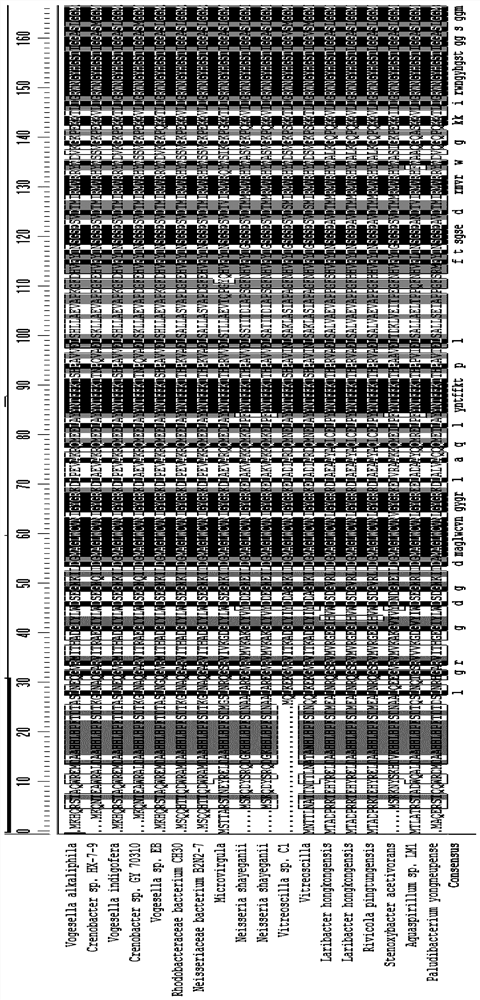
The invention provides a synthesis method of chiral amine. According to the synthesis method, transaminase is used for performing transamination reaction on a ketone substrate shown as a formula I under the action of an amino donor to obtain a chiral amine compound; in the formula I, the transaminase is transaminase with a conservative amino acid sequence region; the conservative amino acid sequence region at least comprises a region 1 and a region 2; the conservative amino acid sequence of the region 1 is MAGLWCVN; and the conservative amino acid sequence of the region 2 is YNTFFKT. The large-steric-hindrance chiral amine is synthesized by adopting transaminase with a specific conservative amino acid sequence region; the enzyme catalysis reaction volume is small; the synthesis route is short; the product yield is high; high-cost noble metal catalysis is not needed for synthesis conditions; furthermore, three wastes are greatly reduced; and the production cost is reduced.
Owner:ASYMCHEM LAB TIANJIN
Method for refining cefonicid dibenzyl ethylenediamine salts
ActiveCN109232610AHigh purityLess impuritiesOrganic compound preparationAmino compound preparationEthylenediamineIon exchange
The invention discloses a method for refining cefonicid dibenzyl ethylenediamine salts and belongs to the technical field of medicines. The method comprises the following steps: performing ion exchange on crude cefonicid salts with resins, decoloring the salts with a decoloring agent, carrying out a salt forming reaction with a transamination agent, and crystallizing by a precipitator, thereby obtaining the refined cefonicid dibenzyl ethylenediamine salts. The cefonicid dibenzyl ethylenediamine salt prepared by the method disclosed by the invention is high in purity, less in impurity and low in color grade, and the refining method disclosed by the invention has the advantages of being simple in process, energy-saving, environmental-friendly, suitable for large-scale industrial production and the like.
Owner:NORTH CHINA PHARMA HEBEI HUAMIN PHARMA
Method for preparing amine compound having multiple chiral centers
ActiveCN107805648AHigh purityEfficient productionFermentationTert-Butyloxycarbonyl protecting groupEthyl group
The invention discloses a method for preparing an amine compound having multiple chiral centers. The method is characterized in that a compound with the formula shown in the description reacts with anamino donor under the action of transaminase to generate another compound with the formula shown the description; and in the formulas, R1 and R2 are a methyl group or an ethyl group respectively, R3is a tert-butyloxycarbonyl group or a benzyloxycarbonyl group, and n is zero or one. The transaminase stereoselectively transaminates a ketone compound used as a raw material to efficiently produce chiral amine, and selective resolution is carried out to obtain the chiral amine compound having multiple chiral centers; and the method has the characteristics cheap substrate and high product purity,and is suitable for being promoted in the industrial production of chiral amine.
Owner:ASYMCHEM LIFE SCI TIANJIN
Method for preparing L-glufosinate-ammonium by using biological multi-enzyme coupling method
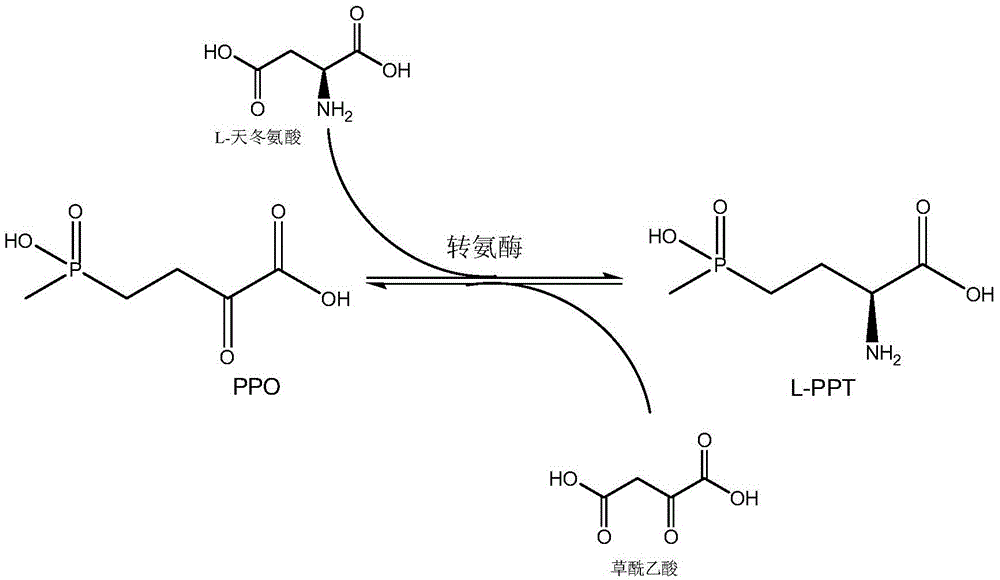
The invention relates to a method for preparing L-glufosinate-ammonium by using a biological multi-enzyme coupling method. The method comprises the following steps of: a) in the presence of (R)-transaminase and an amino receptor, performing transamination reaction on D, L-glufosinate-ammonium to obtain 2-carbonyl-4-[hydroxyl (methyl) phosphono] butyric acid and an amino-added product of the amino receptor; and b) in the presence of (S)-transaminase and an amino donor, performing transamination reaction on the 2-carbonyl-4-[hydroxyl (methyl) phosphono] butyric acid obtained in the step a) to obtain L-glufosinate-ammonium and a deamination product of the amino donor. The method provided by the invention can realize efficient resolution of high-concentration D, L-glufosinate-ammonium to prepare L-glufosinate-ammonium.
Owner:YONGNONG BIOSCI +2
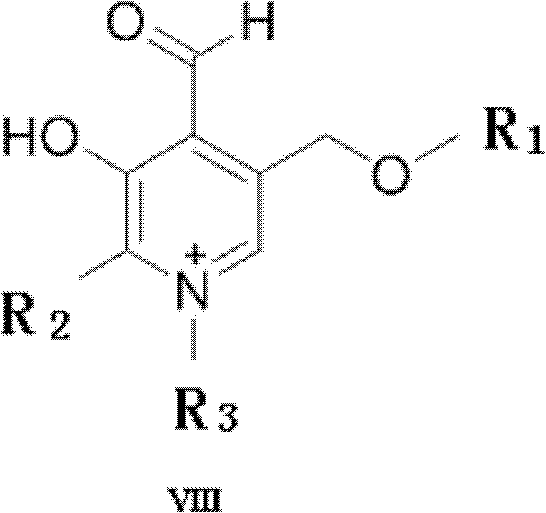
Pyridoxal derivative for pegylation modification of N terminal of protein and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN102952067AImprove transamination efficiencyFavorable for PEGylationCarrier-bound/immobilised peptidesTert-leucineValine
The invention overcomes the problems of long reaction time and low yield of the existing transamination method involving pyridoxal, and provides a designed and synthesized pyridoxal derivative for improving the transamination efficiency of N-terminal amino acid of protein, particularly the high-steric hindrance amino acids such as leucine, isoleucine, and valine. The pyridoxal derivative is characterized by having a structure shown by the formula VIII. The pyridoxal derivative disclosed by the invention improves the transamination efficiency of the N-terminal amino acid of the protein, particularly the transamination reaction of the polypeptide containing high-steric hindrance amino acids (Leu, Ile and Val) at N terminal, thereby being favorable for further pegylation modification of protein.
Owner:JIANGSU SINOCOMPOUND CATALYST
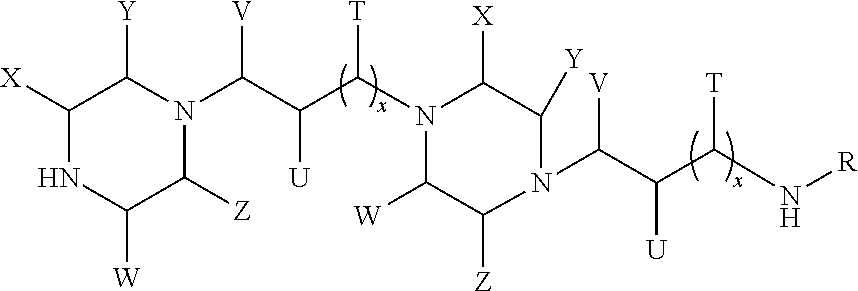
Formation of higher molecular weight cyclic polyamine compounds from cyclic polyamine compounds
ActiveUS20150011762A1High molecular weightReduce compoundingOrganic chemistryPolyamine CompoundNitrogen
The present invention provides strategies for making higher weight, cyclic polyamines from lower molecular weight, cyclic polyamine starting compounds via transamination. The higher molecular weight, cyclic polyamines are structurally similar to the lower molecular weight, cyclic polyamine starting compounds. The reactants used in the present invention include a cyclic polyamine component that comprises at least two amine groups separated from one another by at least a binary carbon atom spacing, and that can be transaminated to form a higher molecular weight, cyclic polyamine compound. The higher molecular weight, cyclic polyamine has at least two cyclic rings joined to one another through a nitrogen-containing hydrocarbyl group. Each of the cyclic rings contains two amine groups separated from one another by binary carbon atom spacing.
Owner:DOW GLOBAL TECH LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com