Synthesis method of chiral amine
A synthesis method and technology of chiral amines, applied in the field of chiral amine synthesis, can solve the problems of harsh reaction conditions and high cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0051] Example 1 Screening of wild-type transaminase
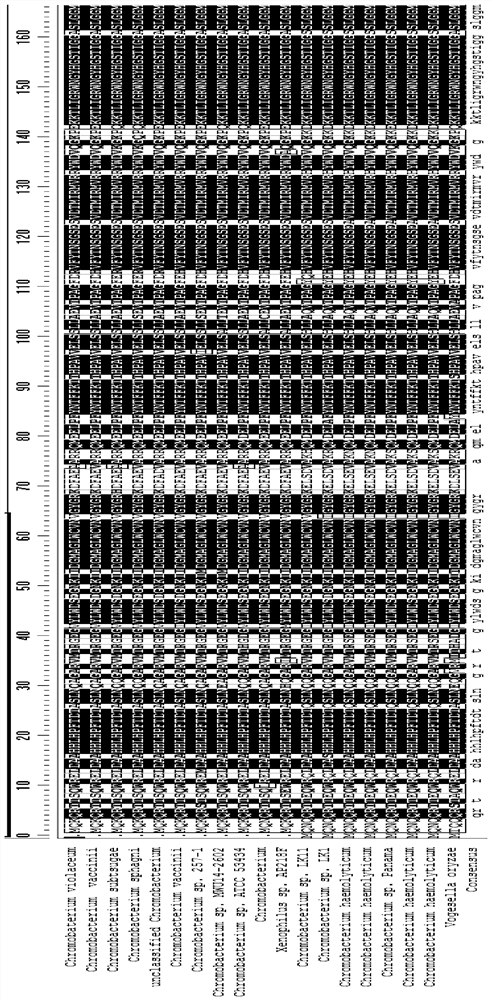
[0052] This embodiment chooses the source and source Chromobaterium violaceum The maternal transaminases belong to the same genus but different species, and the amino acid sequence is more than 82% homologous to the wild-type transaminase (see Table 1 for details) compared with SEQ ID NO: 1, and its catalytic activity was tested. Similar to transaminases, these wild-type transaminase strains catalyze the synthesis of the target bulky substrate (substrate 1) with an efficiency of 0.01% to 1%. The specific results are shown in Table 1.
[0053] Among them, the detailed process of CvTA wild-type transaminase catalyzing substrate 1 is as follows: 1 mL system includes 1 mg substrate 1, 0.1 mg PLP, 1 mg isopropylamine hydrochloride, 50 mg enzyme powder, pH8.0 100 mM phosphate buffer solution, reacted for 40 h.
[0054] The catalytic process of the following other enzymes is the same as above.
[0055] Table 1: Sourced from ...
Embodiment 2
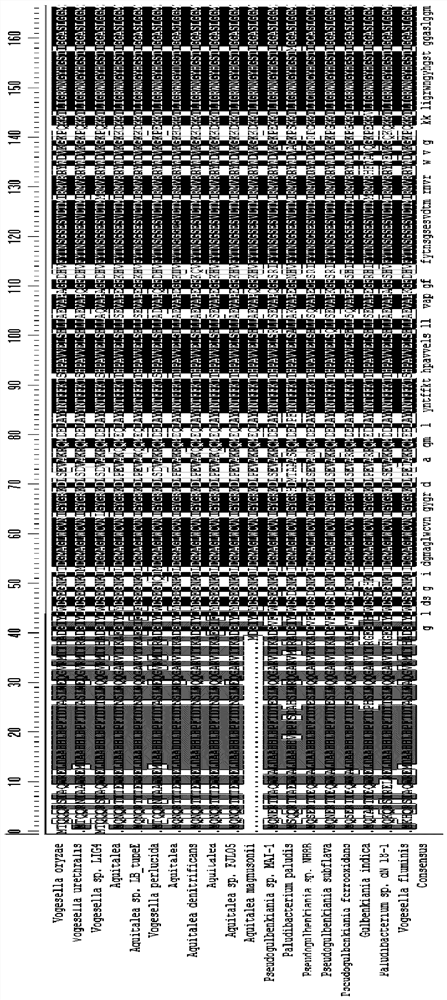
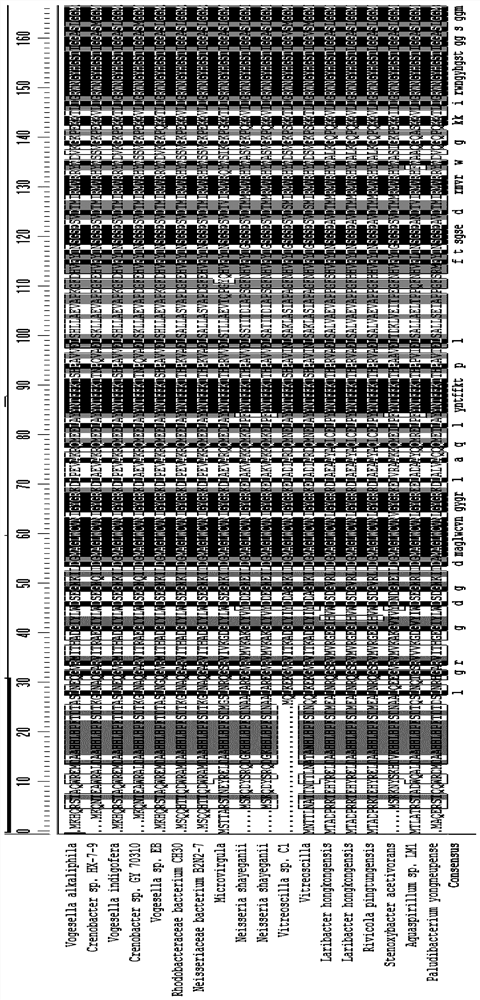
[0060] In addition to transaminases derived from Chromobacterium, the present application also tested transaminases from other sources with 69% to 87% homology to Chromobaterium violaceum. The specific information is listed in Table 2.
[0061] The amino acid sequences between the 54th to 63rd and the 84th to 96th among the wild-type transaminases from different sources in this example also show high conservation. These wild-type transaminases have been tested to show that they also have 0.01%~1% catalytic activity for the target large steric hindrance substrate (substrate 1).
[0062] Table 2: Other transaminases with less homology to Chromobaterium violaceum but derived from different genera.
[0063]
[0064]
[0065] In the above table, + means that the conversion rate is between 0.01% and 0.1%, ++ means that the conversion rate is between 0.1 and 0.5%, and +++ means that the conversion rate is between 0.5 and 1%.
[0066] The different aminotransferase bacterial s...
Embodiment 3
[0068] In order to further confirm that this type of transaminase with the above-mentioned conserved amino acid region affects the catalytic activity of large steric hindrance substrates, the inventors initially Chromobaterium violaceum Conserved amino acid region 1 in the source transaminase (the specific sequence is DGMAGL WC The amino acids W and C in VNVGYGR) were mutated by A. It was found that the catalytic efficiency of substrate 1 was improved after these conservative amino acids were mutated. The conversion rate is improved to between 1~5% (concrete reaction process is recorded in the same embodiment 1).
[0069] In order to confirm that transaminases from other species have the same mutation at the conserved site, the conversion rate of the substrate is improved. The inventors also performed the same mutation on transaminases from other sources. The test results are shown in the table below.
[0070] table 3:
[0071]
[0072] In the above table, ++++ means th...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com