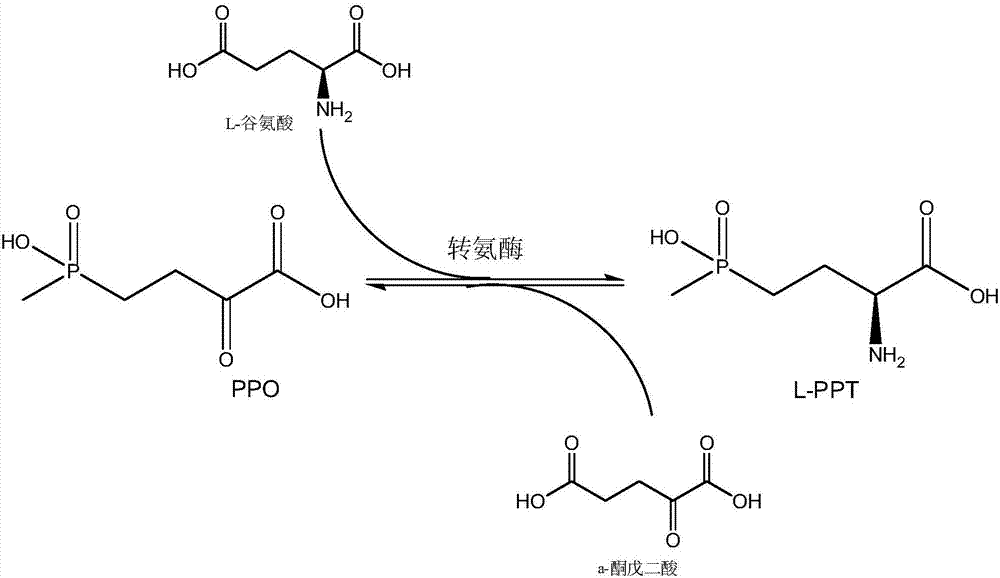
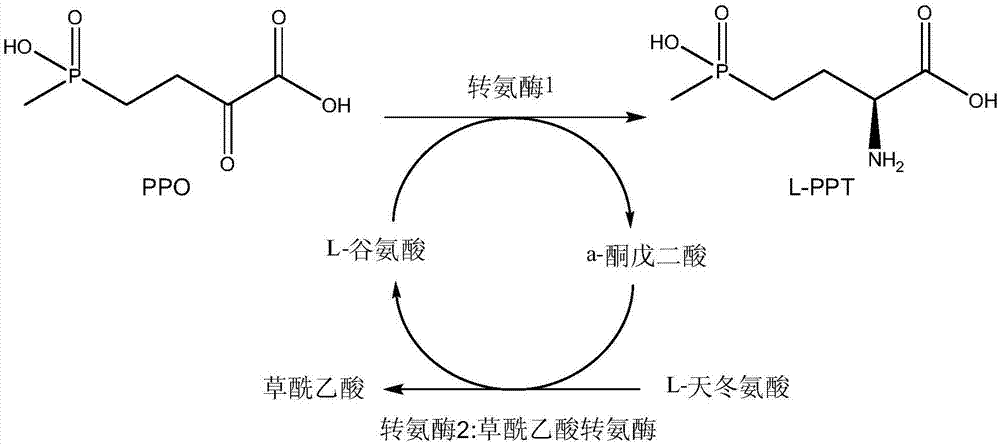
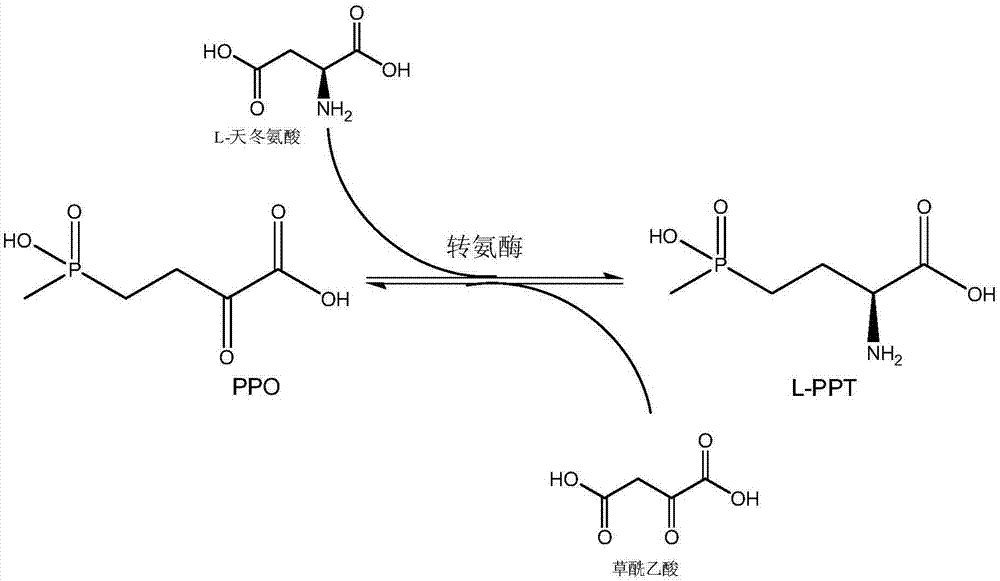
Method for producing L-glufosinate-ammonium by using transaminase and ethylene-forming enzyme
An ethylene synthase and transaminase technology is applied in a new process for producing L-glufosinate-ammonium, in the field of improving the production efficiency of optically pure L-glufosinate-ammonium, and can solve the problems of low process efficiency, long time consumption, large alanine consumption and the like , to achieve the effect of simplifying the refining process, simple reaction process and reducing the cost of raw materials
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0050] 1.1 Construction of genetically engineered bacteria expressing transaminase
[0051] Transaminase genes were cloned from the genomes of Bacillus subtilis 168, Bacillus magaterium YYBM1, Escherichia coli K12W3110, Bacillus stearothermophilus and Streptomyces sp. DSM 40736 respectively, according to the corresponding genomic DNA sequences ( GenBank accession numbers are CP010052.1, CP001982.1, CP012868.1, AE016877.1 and EFL35314.1) to design corresponding PCR upstream primers and downstream primers.
[0052] Primers for transaminases from Bacillus subtilis:
[0053] BS-F sequence: 5'-CCC GAGCTC ATGAGTCAAAACAACAGCAAGCATCA-3'(SacI)
[0054] BS-R sequence: 5'-CCC AAGCTT TTAAGCTCGCAGGCCCGCCT-3' (HindIII)
[0055] Primers for transaminases from Bacillus magaterium:
[0056] BM-F sequence: 5'-CGC GGATCC ATGAGTCAAACTTTTAGCAA-3' (BamHI)
[0057] BM-R sequence: 5'-CCC AAGCTT TTACACTTCAACCGTTTGCT-3' (HindIII)
[0058] Primers for transaminases derived from E.coli:
[...
Embodiment 2
[0099] 2.1 Culture of microorganisms
[0100] Composition of LB liquid medium: peptone 10g / L, yeast powder 5g / L, NaCl 10g / L, dissolved in deionized water and then constant volume, sterilized at 121°C for 20min, ready for use.
[0101] The genetically engineered bacteria E.coli BL21(DE3) containing transaminase gene and ethylene synthase were inoculated into 5 mL LB liquid medium containing 50 μg / mL kanamycin, and cultured with shaking at 37°C for 12 hours. Transfer to 500mL fresh LB liquid medium also containing 50μg / mL Kan, shake culture at 37°C until OD 600 When it reaches about 0.8, add IPTG to its concentration of 0.1mM, and induce culture at 18°C for 16h. After the cultivation, the culture solution was centrifuged at 10,000 rpm for 10 min, the supernatant was discarded, and the bacterial cells were collected, and stored in a -70°C ultra-low temperature refrigerator until use.
[0102] 2.2 Preparation of pure enzyme
[0103] The bacterial cells collected after the cul...
Embodiment 3
[0111] Embodiment 3 contrasts the reaction effect of transaminase and ethylene synthetase coupling
[0112] 3.1 Qualitative reaction of whole cells
[0113] Configure substrate solution: quantitatively weigh PPO, L-glutamic acid, L-arginine, FeSO 4 And pyridoxal phosphate into the beaker, adjust pH=8.5 with 30% ammonia water, add in the volumetric flask, and use deionized water to make the final concentration of PPO 20mM, the final concentration of L-glutamic acid is 20mM, L-Arg concentration is 5mM, Fe 2+ Concentrations were 2 mM and pyridoxal phosphate 1 mM.
[0114] After the cultivation, the bacteria were collected by centrifugation, the supernatant was discarded, and the activity of the bacteria was measured after washing the bacteria. Mix transaminase (derived from Escherichia coli, GenBank accession number CP012868.1) and ethylene synthase (derived from Pseudomonas syringae, GenBank accession number D13182.1) according to the ratio of activity 1:1, For transaminase,...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Pre-denatured | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Extend | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com