Recombinant escherichia coli for synthesizing 2 '-fucosyllactose by using mannose and application of recombinant escherichia coli
A technology of fucosyllactose and Escherichia coli, applied in the field of microbial metabolic engineering, can solve the problems of low utilization rate of carbon source, high cost, no industrial production, etc., and achieve the effect of improving utilization rate of carbon source and conversion rate.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0088] The construction of embodiment 1 chassis bacterium bacterial strain L
[0089] Strain E.coli K12 MG1655ΔlacIZ::P trc - Build of wcaG-gmd-lacy
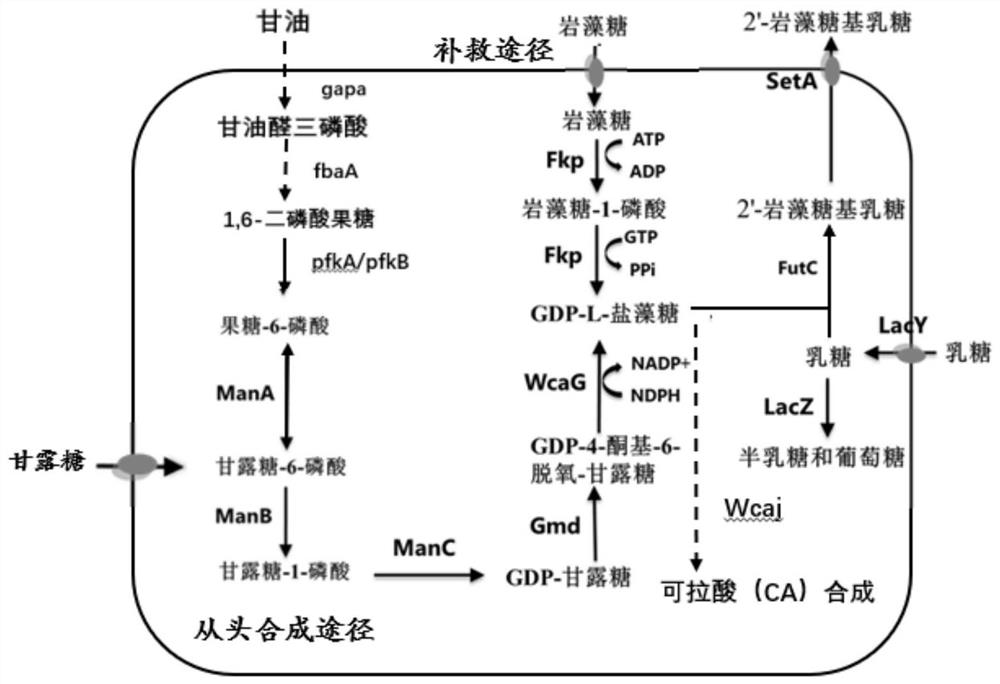
[0090] Taking Escherichia coli MG1655 as the original strain, the P in the lac operon sequence was knocked out lac Promoter sequence and lacI, lacZ gene, and use P on the lacI, lacZ gene locus trc The promoter overexpresses wcaG, gmd, and lacy genes. P trc The promoter is P trp promoter and P lac The spliced promoter of the promoter has a ratio of P lac Promoter higher transcription efficiency.
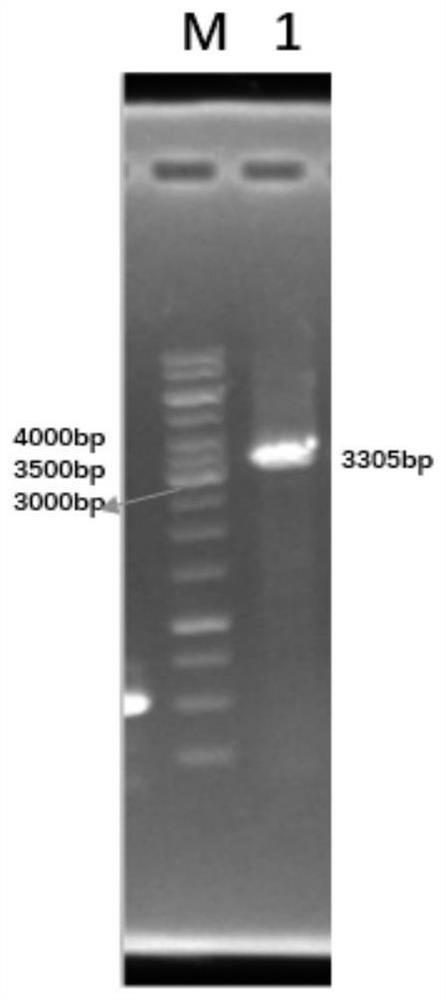
[0091] The method used to construct this strain is λRed recombination. The main purpose is to construct a two-step homologous recombination fragment, and use pKD46 (GenBank: MF287367) as a homologous recombination plasmid to carry out gene knockout and integration. The homologous recombination fragment in the first step includes upstream and downstream homology arms, chloramphenicol resistance gene and sacB gene. The second-...
Embodiment 2
[0104] Embodiment 2: the construction of bacterial strain L1 (knockout manA gene)
[0105] The strain L1 was constructed, and the strain L constructed in Example 1 was used as the chassis strain, and the manA (phosphomannose isomerase) gene on the genome was knocked out.
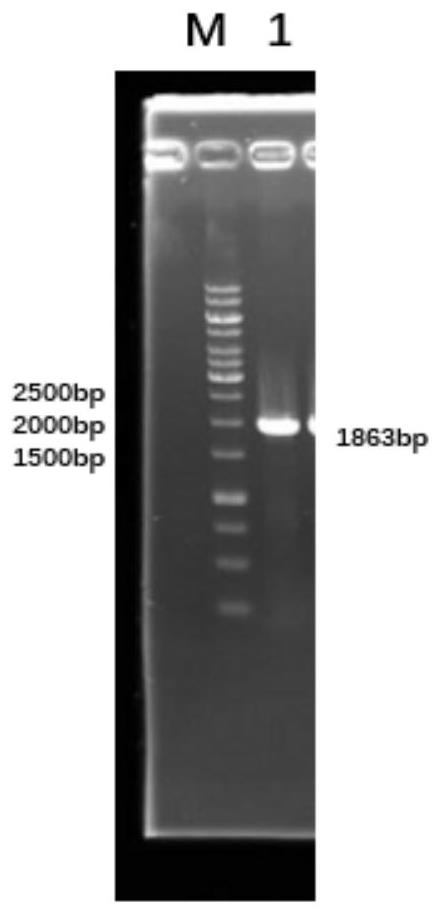
[0106] The method used to construct this bacterial strain is λRed recombination technology. The main purpose is to construct a two-step homologous recombination fragment, and use pKD46 (GenBank: MF287367) as a homologous recombination plasmid to carry out gene knockout and integration. The homologous recombination fragment in the first step includes upper and lower homology arms, chloramphenicol resistance gene and sacB gene. The second-step homologous recombination fragment contains upstream and downstream homology arms.
[0107] The specific method is described in detail below:
[0108] 1. The first step is the construction of the homologous recombination fragment up-cat-sacB-down. Construct the cat-sa...
Embodiment 3
[0118] Embodiment 3: Construction of bacterial strain L2 (knockout wcaj gene)
[0119] Construct strain L2, use strain L1 as the chassis strain, knock out the UDP-glucolipid carrier transferase coding gene (Wcaj) on the genome, and use cas9 to construct this strain. It is mainly to construct the homologous recombination fragment in the first step, including the upstream and downstream homology arms, chloramphenicol resistance gene and N20 gene (SEQ ID NO.15), and then electroporate into the chassis strain that needs to be knocked out. After the selection medium with different resistances grew out, the Escherichia coli that was successfully recombined in the first step was induced to express the Pcago plasmid to produce cas9 protein to screen the fragments that were successfully recombined. The specific method is described in detail below:
[0120]1. The first step is the construction of the homologous recombination fragment up-cat-N20-down. The cat-N20 gene fragment was cons...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com