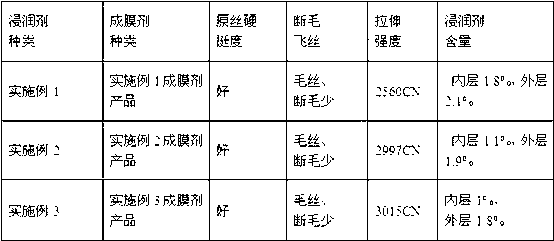
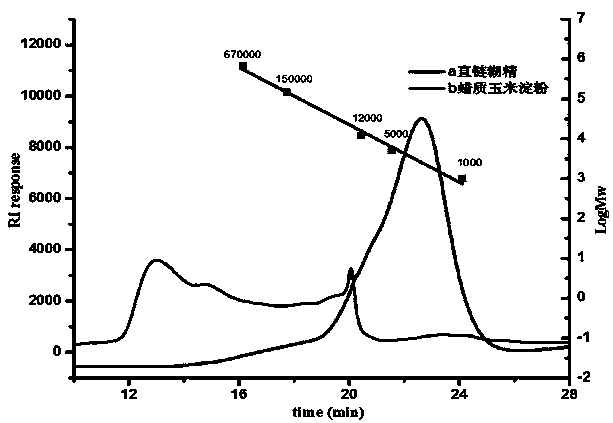
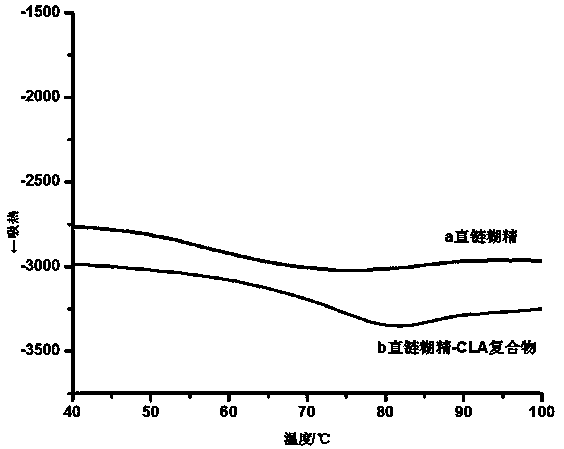
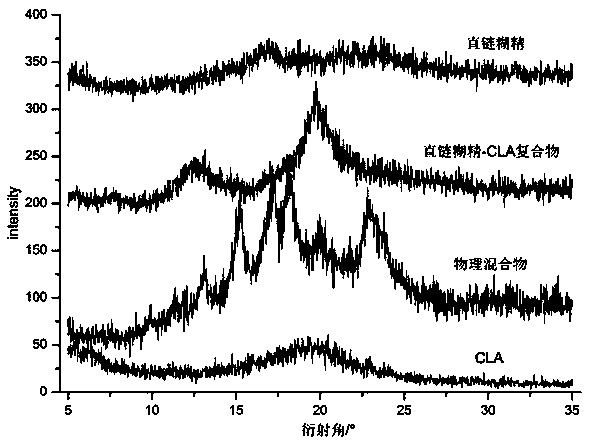
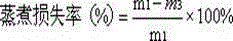Patents
Literature
96 results about "Isoamylase" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Isoamylase (EC 3.2.1.68, debranching enzyme, glycogen alpha-1,6-glucanohydrolase) is an enzyme with systematic name glycogen 6-alpha-D-glucanohydrolase. This enzyme also readily hydrolyses amylopectin.
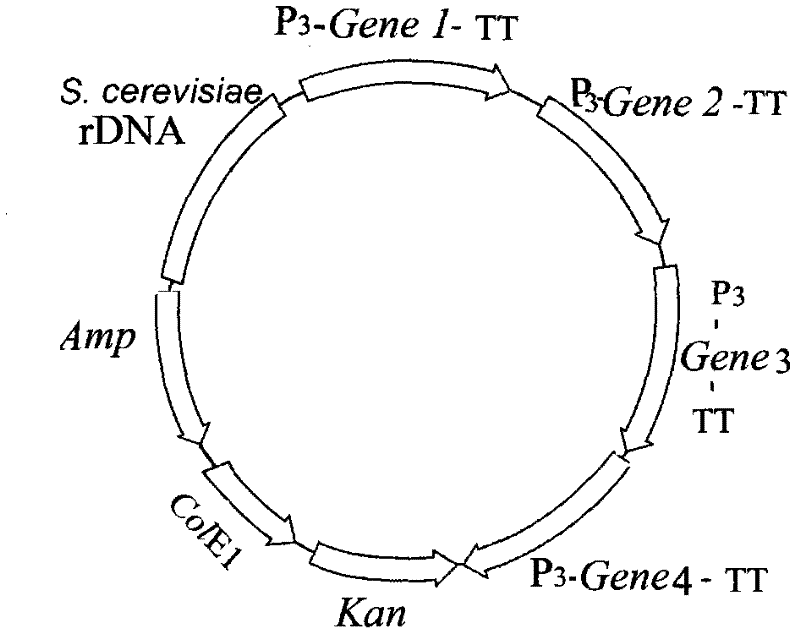
Nucleic acid molecules which code for enzymes derived from wheat and which are involved in the synthesis of starch
Nucleic acid molecules are described which encode enzymes involved in starch synthasis in plants. These enzymes are wheat isoamylases.The invention furthermore relates to vectors and host cells which contain the above-described nucleic acid molecules, in particular to transformed plant cells and plants which can be regenerated from these and which have an increased or reduced activity of the isoamylases according to the invention.
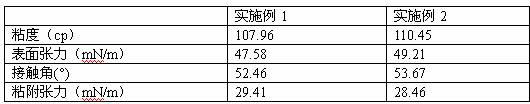
Owner:BASF AGRICULTURAL SOLUTIONS SEED LLC
Pig feed complex enzyme preparation and preparing method thereof
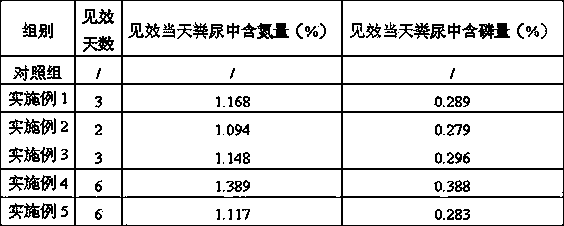
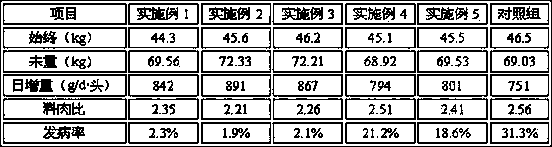
ActiveCN104000051AFast growthGood for healthAnimal feeding stuffAccessory food factorsBiotechnologyFeed conversion ratio
Owner:河源双胞胎饲料有限公司
Preparation method of starch type film-forming agent for glass fiber wetting agent
InactiveCN102304188ALow thermal decomposition temperatureReduce carbon residueFermentationGlass fiberFiltration
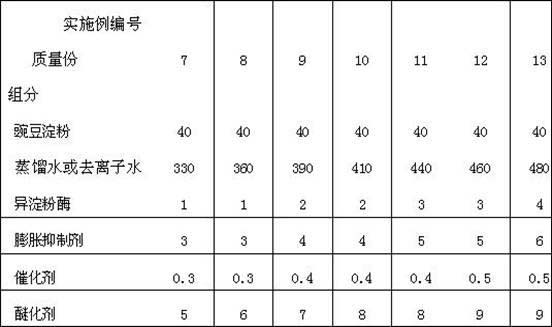
The invention discloses a preparation method of a starch type film-forming agent for a glass fiber wetting agent, which is characterized by comprising the following steps: feeding 40 mass parts of pea starch into a reaction vessel, adding 300-500 mass parts of water, heating to 75-90 DEG C while stirring, carrying out gelation reaction for 0.5-2 hours, and then cooling to 35-50 DEG C; adjusting the pH value to 4-6.5, adding 1-4 mass parts of isoamylase, reacting for 6-30 hours, and then heating to 75-90 DEG C to carry out enzyme inactivation for 5-30 minutes; cooling to 30-55 DEG C, adding 3-6 mass parts of expansion inhibitor, and keeping the temperature for 10-20 minutes; and adding 0.3-0.5 mass part of catalyst and 4-10 mass parts of etherifying agent, reacting for 10-24 hours, adjusting the pH value to 6-8, cooling to room temperature, then carrying out vacuum filtration, and drying the solid to obtain the film-forming agent product. The product is used for a glass fiber wetting agent, and has the characteristics of good film forming performance, convenient post treatment process and the like.
Owner:SOUTHWEAT UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Starch-based hydration heat regulation material preparation method
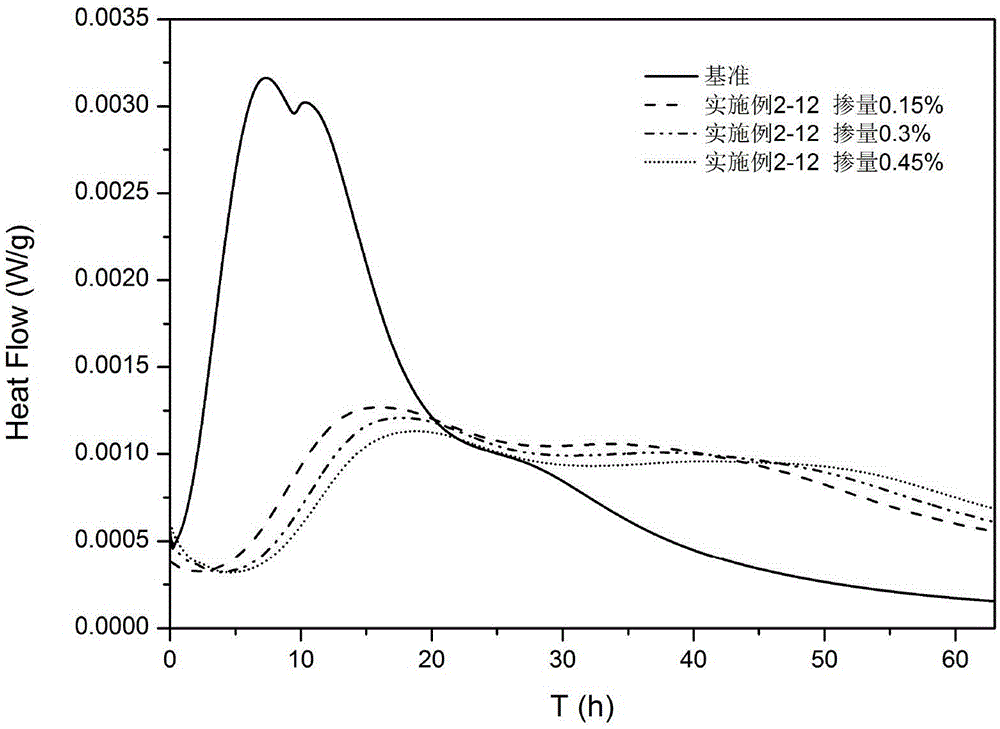
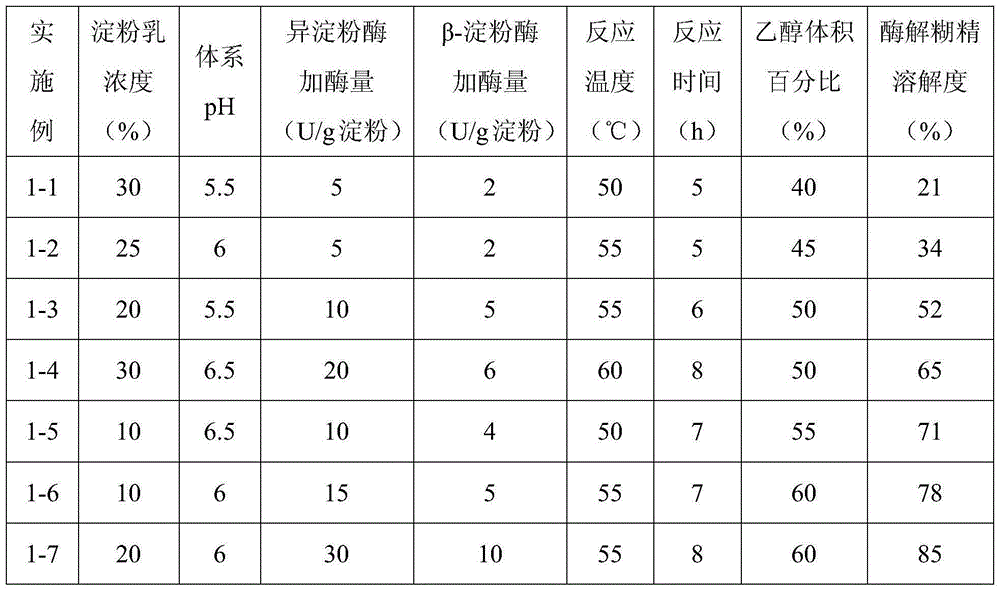
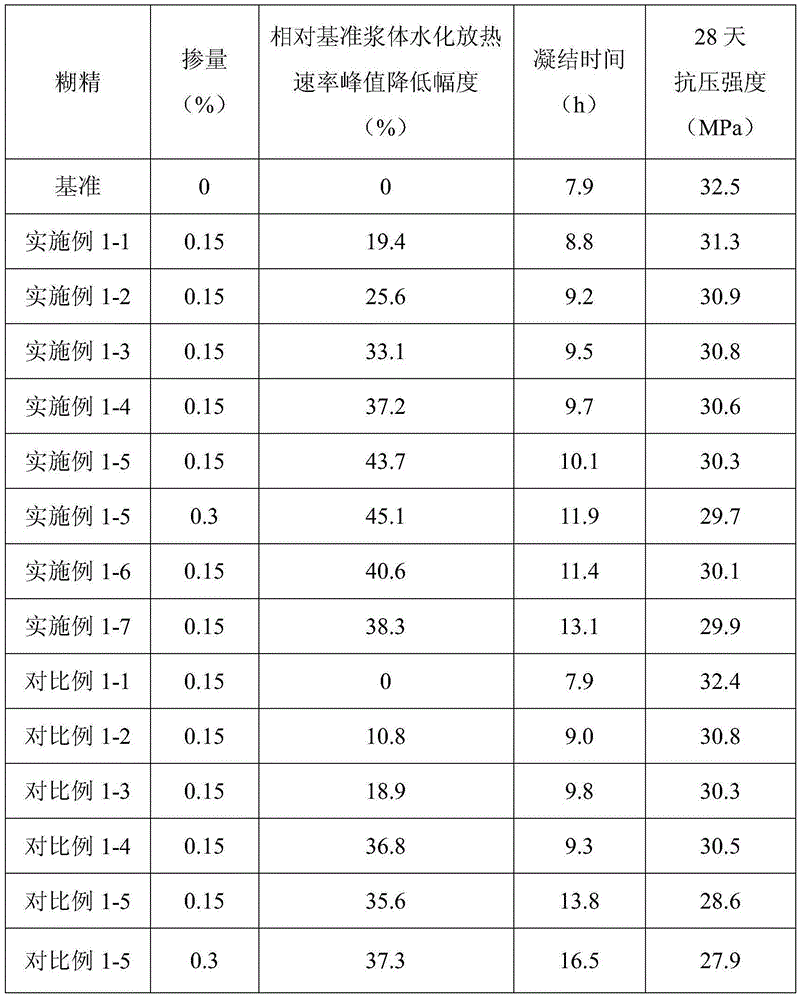
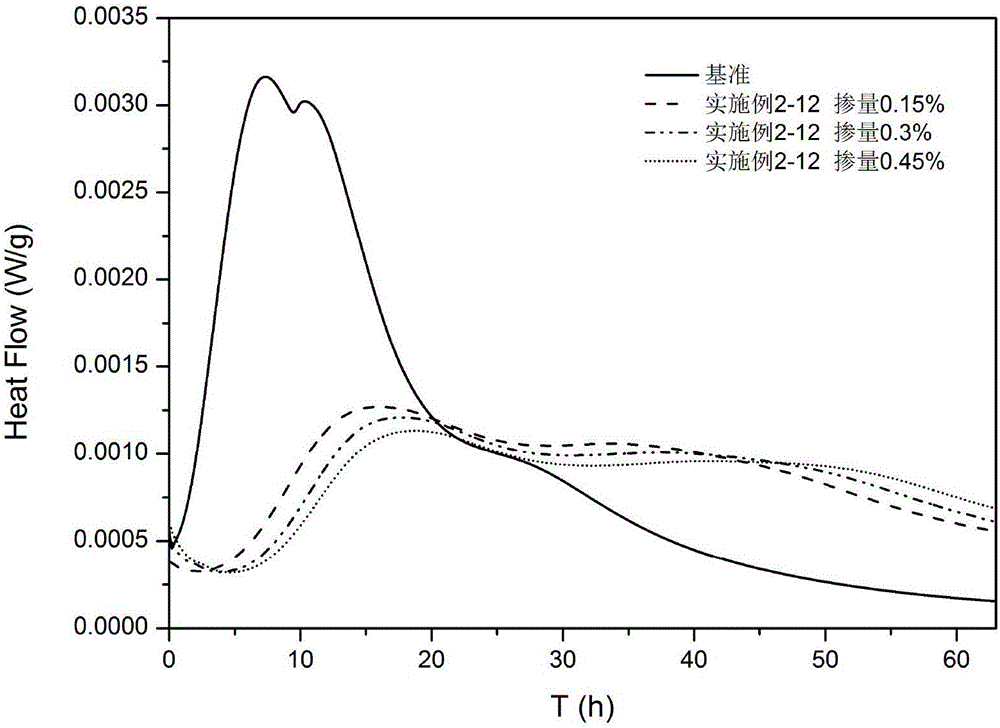
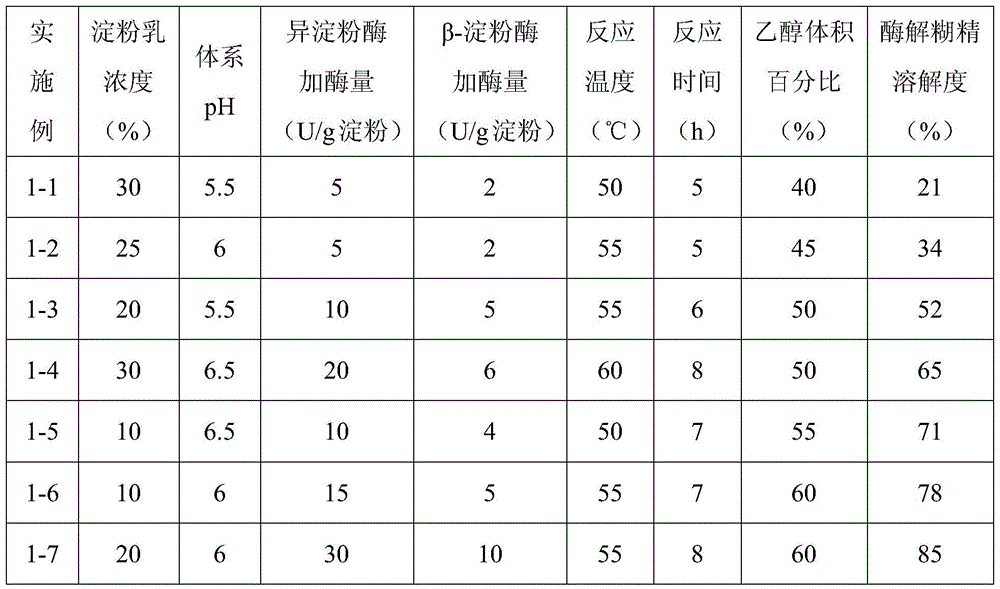
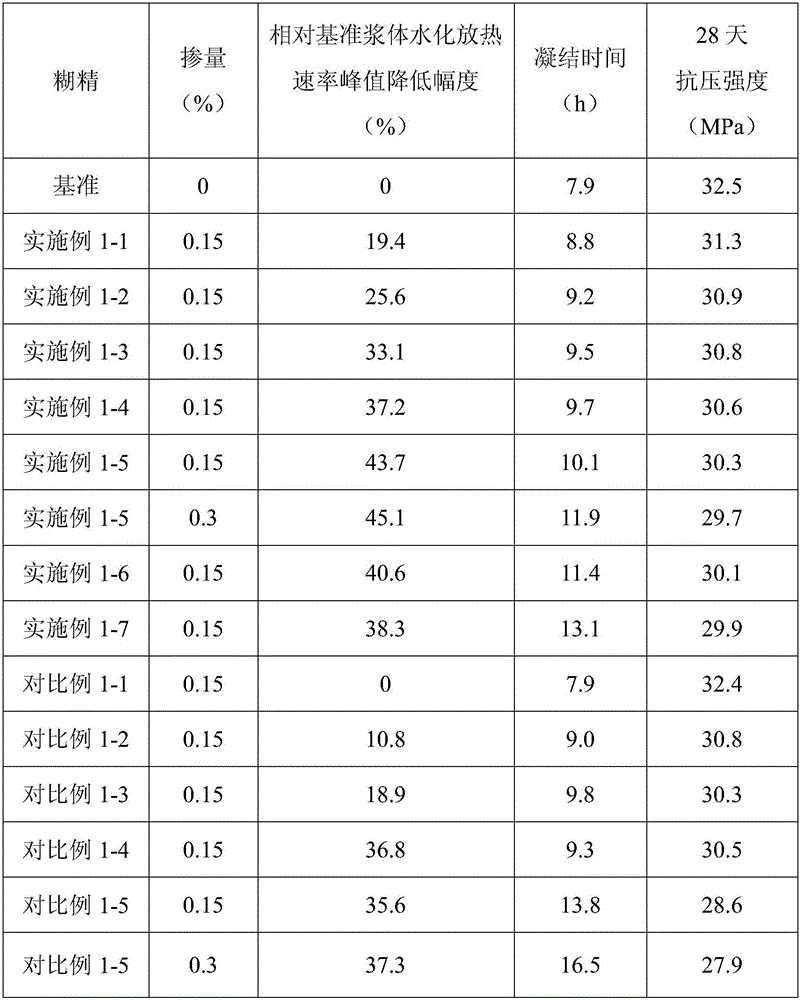
The present invention provides a starch-based hydration heat regulation material preparation method, which comprises: 1, preparing enzymolysis dextrin: adding water to corn starch, blending into starch milk, placing the corn milk in a boiling water bath, heating to achieve a completely pasting state, cooling to a room temperature, adjusting the pH value to 5.5-6.5, adding isoamylase and beta-amylase, carrying out a hydrolysis reaction, adjusting the pH value to less than or equal to 3.0 after completing the reaction, inactivating the enzyme, adjusting the pH value to a neutral pH value, cooling to a room temperature, adding ethanol to the reaction solution, stirring, filtering, drying the filtrate, and crushing so as to obtain the enzymolysis dextrin; and 2, preparing the starch-based hydration heat regulation material: adding water to the enzymolysis dextrin prepared in the step 1, blending into a dextrin solution, adding an emulsifier, carrying out an emulsifying reaction, filtering, drying the solid, and crushing so as to obtain the finished product. According to the present invention, the method has characteristics of simple process and low cost, and the prepared hydration heat regulation material has characteristics of stable performance, effective reduction of the cement hydration heat release rate peak value, and substantial no influence on the medium-late stage strength of concrete.
Owner:安徽省友邦混凝土有限公司
Preparation method and application of crosslinking-enzymolysis composite superfine modified starch adsorbent
InactiveCN105642244AIncrease surface areaHigh pore volumeOther chemical processesWater/sewage treatment by sorptionEmulsionFreeze-drying
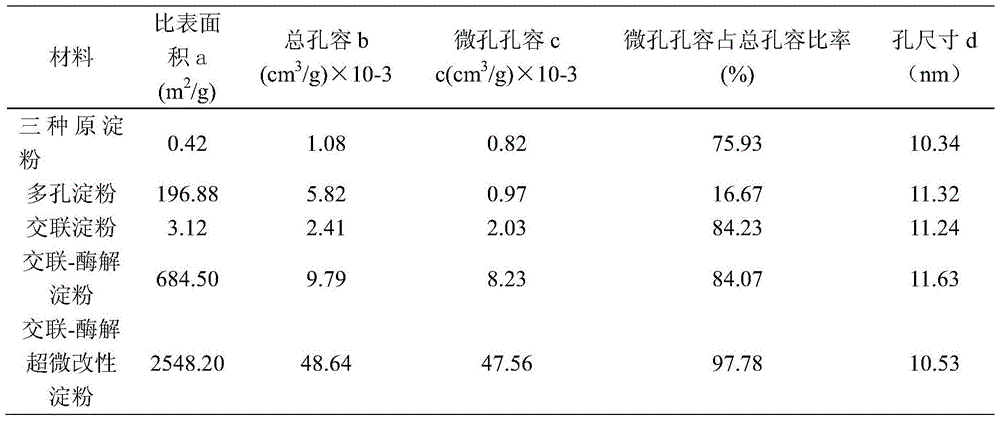
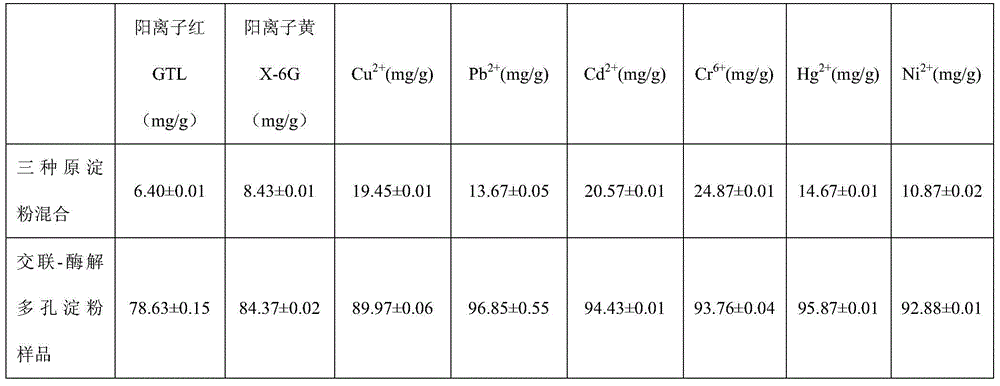
Provided is a preparation method of a crosslinking-enzymolysis composite superfine modified starch adsorbent. The method comprises the steps that 1, corn, sweet potatoes and potatoes are superfinely ground into superfine starch with the granule size of 10-50 micrometers through a superfine grinder separately; 2, the three kinds of superfine starch are mixed to be uniform according to the mass ratio of 1:4:3, water is added into the materials, stirring is conducted, and starch emulsion is obtained; 3, the pH of the starch emulsion is adjusted to be 7.5-8.5, a certain amount of sodium tripolyphosphate solution is added, and crosslinking is conducted for 1-1.5 h at the temperature of 75 DEG C-80 DEG C; 4, centrifugal dewatering is conducted on crosslinked starch emulsion, the dewatered starch emulsion is washed with deionized water, and freeze drying is conducted; 5, the crosslinked starch is added with water and blended into starch emulsion again, the pH is adjusted to be 6.5-7.5, alpha-amylase and isoamylase are added, and an enzymolysis reaction is conducted for 12-15 h at the temperature of 50 DEG C; 6, the starch emulsion subjected to enzymolysis is centrifuged, washed and dried and then sieved through a 40-100-mesh sieve, and the crosslinking-enzymolysis composite superfine modified starch is obtained. The modified starch significantly increases the specific surface area of porous starch, improves the mechanical strength of the porous starch and improves the adsorption capacity of the porous starch on harmful ingredients, especially, heavy metal elements.
Owner:ANHUI AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Production of recombinant mixed isoamylases, alpha amylases and glucoamylases
ActiveCN102286443ASave raw materialsSave human resourcesMicroorganism based processesEnzymesBacillus licheniformisHordeum vulgare
The invention discloses a method for producing the mixture of isoamylase, alpha-amylase and glucamylase and belongs to the field of biological technology. The method comprises: firstly, amplifying an isoamylase gene out of the genome of bacillus amyloliquefaciens, an alpha-amylase gene out of the genome of bacillus licheniformis, an alpha-amylase gene out of the genome of barley and a glucamylase gene out of the genome of aspergillus niger; secondly, constructing a bacillus subtilis expression vector containing the isoamylase gene, a pichia stipitis expression vector containing two alpha-amylase genes and a saccharomyces cerevisiae expression vector containing the glucamylase gene; thirdly, constructing engineering bacteria, namely transforming the genome of bacillus subtilis through the bacillus subtilis expression vector, transforming the genome of pichia stipitis through the pichia stipitis expression vector, and transforming the genome of the saccharomyces cerevisiae through the saccharomyces cerevisiae expression vector; and finally, allowing the fermentation engineering bacteria to produce the mixture of recombinant isoamylase, alpha-amylase and glucamylase. The mixed use of the enzymes can obviously improve the action under which starch can be hydrolyzed into glucose. The production of the mixed enzymes has the advantage that the change from the production of isoamylase, alpha-amylase and glucamylase by several steps regularly into production by one step obviously reduces energy consumption and lowers production cost.
Owner:INST OF TROPICAL BIOSCI & BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF TROPICAL AGRI SCI +1
Processing method of lotus seed starch-lipid compound nanoparticles
ActiveCN106832435AIncrease production capacityHigh degree of compoundMaterial nanotechnologyFermentationMonoglycerideSide chain
The invention relates to a processing method of lotus seed starch-lipid compound nanoparticles and belongs to the field of modified starch processing. The method comprises the following steps of: by taking the lotus seed starch and glyceryl monostearate as raw materials, hydrolyzing the raw materials through alpha-amylase and isoamylase; performing high pressure microjet homogenization compounding; performing short-time low-temperature regenerating crystallization; performing washing and centrifugalization; performing freezing and drying; and performing crushing and packaging to prepare the lotus seed starch-lipid compound nanoparticles. According to the principle provided by the invention, side chain branches of branch chain starch are cut based on a double enzyme synergetic enzymatic hydrolysis technology to form a lot of long-chain straight-chain starch; the length of the chain section of the straight-chain starch is reduced by means of high pressure microjet homogenization to accelerate short-chain fragments to be compounded with monoglyceride; the nanoparticles are generated by means of short-time low-temperature regenerating crystallization. The method provided by the invention overcomes the defects that a conventional acid hydrolysis preparation method is time-consuming, low in yield, relatively high in grain size of nanoparticles and the like. Compared with a conventional acid hydrolysis method, the yield of the nanoparticles is increased by 30-45%, and the grain sizes are distributed in a range of 60-120nm.
Owner:FUJIAN AGRI & FORESTRY UNIV
A method for preparing an esterified starch film former for glass fiber wetting
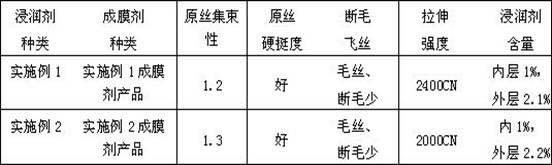
The present invention discloses a method for preparing an esterified starch film former for glass fiber wetting, and the method is characterized in that the product of the esterified starch film former for glass fiber wetting is obtained by: placing corn starch into a reactor, adding water, heating to a temperature of 70-90 DEG C under stirring, reacting for 0.5- 2h, and cooling to 30-60 DEG C; adjusting a pH value to 4-7, adding isoamylase, after reacting for 0.5-6h, heating to a temperature of 80-90 DEG C for 20 min for enzyme deactivation, and filtering to remove the enzyme and obtain a reaction solution; and cooling the reaction solution to a temperature of 25-55 DEG C, adding an acid anhydride, adding an alkaline catalyst, maintaining the pH value being 7-10, reacting for 2-10h, adjusting the pH value to be 6-7, cooling to the room temperature, suction filtering, and drying a solid. The product of the film former has the advantages of a good film forming property and an easy post-treatment process, and has excellent effects of bundling and protecting the glass fiber in the production process of the glass fiber.
Owner:SOUTHWEAT UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Production method for powder containing crystalline alpha, alpha-trehalose dihydrate
ActiveCN103946386AHigh crystallinityEfficient use ofSugar derivativesDisaccharidesFractionationGenus Arthrobacter
Provided is a production method whereby it is possible to produce a powder containing crystalline trehalose dihydrate with starch as a starting material with high powder-to-starch yields. More specifically, provided is a production method for a powder containing crystalline alpha, alpha-trehalose dihydrate and having at least 98.0mass% of alpha, alpha-trehalose on an anhydrous basis, said method including: a step in which liquefied starch is subjected to the actions of a starch debranching enzyme, cyclomaltodextrin glucanotransferase, an alpha-glycosyl trehalose producing enzyme derived from a micro-organism belonging to the genus arthrobacter, and a trehalose releasing enzyme derived from a micro-organism belonging to the genus arthrobacter, and then to the action of glucoamylase, to obtain an alpha, alpha-trehalose-containing saccharide solution; a step in which alpha, alpha-trehalose dihydrate is crystallized from the saccharide solution; and a step in which the crystallized alpha, alpha-trehalose dihydrate is extracted by centrifugation, aged, and dried. The production method is characterized in that a natural or recombinant enzyme derived from a micro-organism belonging to the genus paenibacillus or a variant of such an enzyme is used as the cyclomaltodextrin glucanotransferase such that the content of alpha, alpha-trehalose in the saccharide solution is over 86.0mass% on an anhydrous basis, without having to undergo a column chromatography fractionation step.
Owner:HAYASHIBARA CO LTD
A kind of preparation method of starch-based hydration heat regulating material
ActiveCN105060762BImprove performanceDoes not affect mid and late strengthProcess engineeringHydrolysis
The present invention provides a starch-based hydration heat regulation material preparation method, which comprises: 1, preparing enzymolysis dextrin: adding water to corn starch, blending into starch milk, placing the corn milk in a boiling water bath, heating to achieve a completely pasting state, cooling to a room temperature, adjusting the pH value to 5.5-6.5, adding isoamylase and beta-amylase, carrying out a hydrolysis reaction, adjusting the pH value to less than or equal to 3.0 after completing the reaction, inactivating the enzyme, adjusting the pH value to a neutral pH value, cooling to a room temperature, adding ethanol to the reaction solution, stirring, filtering, drying the filtrate, and crushing so as to obtain the enzymolysis dextrin; and 2, preparing the starch-based hydration heat regulation material: adding water to the enzymolysis dextrin prepared in the step 1, blending into a dextrin solution, adding an emulsifier, carrying out an emulsifying reaction, filtering, drying the solid, and crushing so as to obtain the finished product. According to the present invention, the method has characteristics of simple process and low cost, and the prepared hydration heat regulation material has characteristics of stable performance, effective reduction of the cement hydration heat release rate peak value, and substantial no influence on the medium-late stage strength of concrete.
Owner:安徽省友邦混凝土有限公司
Acidic heat-resisting isoamylase genetic engineering bacterium and application thereof
ActiveCN102559568AIncrease enzyme activityHas starch amylopectin hydrolysis activityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesChemical synthesisGenetic engineering
The invention relates to an acidic heat-resisting isoamylase genetic engineering bacterium and an application thereof, belonging to the field of enzyme engineering. According to the invention, a Tfu_1891 encoding gene sequence of isoamylase is obtained by chemical synthesis; culture is carried out in an industrial fermentation culture medium by taking pT7-7 as an expression vector and E.coli BL21 (DE3) as an expression host; and by virtue of inductive recombination, the fermentation vigor of the isoamylase reaches 3185U / mL. The recombinase has hydrolysis activity of a starch alpha-1,6 glucoside bond; the optimum temperature is 40-50 DEG C, and the optimum pH value is 5.5; after heat preservation is carried out for 30 hours at the temperature of 50 DEG C, the enzyme activity of the recombinase still maintains more than 50%; the recombinase has starch debranching activity and can hydrolyze branched starch in starch so as to form amylose; and the recombinase is combined with alpha-cyclodextrin glucosyltransferase to be used, thereby obviously improving the conversion rate of cyclodextrin and being suitable for industrial production of cyclodextrin.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Digestion-resistant starch as well as preparation method and applications thereof
ActiveCN107418988AImprove featuresEnhance resiliencePharmaceutical non-active ingredientsFermentationPullulanaseSlurry
The invention discloses digestion-resistant starch as well as a preparation method and applications thereof, belonging to the field of deeply processing starch. The preparation method comprises the following steps: preparing starch slurry from 5-15% of starch and a phosphate buffer solution and then gelatinizing, adding into an enzymatic membrane reactor, performing enzymolysis and ultrafiltration sequentially by utilizing ultrafiltration membranes respectively with cut-off molecular weight of 1000Da and 100000Da and immobilized pullulanase or isoamylase, wherein the vigor of the immobilized enzyme is 10-55ASPU / g starch; adding fat-soluble phenol derivatives into the cut-off filtrate, compounding under a pressure filed and then washing with ethanol, and drying to obtain a product. The digestion-resistant starch is a compound of starch and fat-soluble phenol derivatives, has digestion-resistant, anti-oxidization and bacteriostatic activity, can be used for functional active substances to control released carrier materials, and is beneficial to stability of functional factors in a delivery system.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Extraction method of effective components of Chinese angelica
InactiveCN102381962AQuality assuranceReduce wasteCarboxylic compound separation/purificationReflux extractionCellulose
The invention relates to an extraction method of effective components of Chinese angelica. The extraction method comprises the following steps: 1, Chinese angelica is crushed; 2, crushed Chinese angelica is added to a solvent A solution with the pH value of 5.5; 3, cellulase with the concentration of 0.3mg.mL<-1> is added to the solution obtained in step 2; 4, the solution obtained in step 3 is subjected to enzymatic hydrolysis for 6h at a constant temperature of 55DEG C; 5, isoamylase with the concentration of 0.3mg.ml<-1> is added to the solution obtained in step 4; 6, a solution obtained in step 5 is subjected to enzymatic hydrolysis for 6h at a constant temperature of 55DEG C; 7, the solution obtained in step 6 is subjected to reduced pressure filtration after completing the enzymatic hydrolysis, and the obtained filtrate is preserved in a dark place; 8, the filter residue obtained by filtering in step 7 is used for extracting ligustilide, an eight time solvent B is added each time, reflux extraction is twice carried out for 2h, the obtained first filtrate and the obtained second filtrate are mixed to obtain a mixed filtrate which is a ligustilide solution, and the ligustilide solution is preserved in a low temperature dark place; 9, the filter residue obtained in step 8 is used for extracting angelica polysaccharides, an fifteen time solvent C is added to the filter residue to extract; 10, the filtrate obtained in step 9 is concentrated to obtain a concentrate; and 11, a solvent D is added to the concentrate obtained in step 10 until that the concentration of the solvent D reaches 75% to obtain a deposition, and the deposition is centrifuged by a centrifuge to obtain the angelica polysaccharides.
Owner:LANZHOU UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Nucleic acid molecules encoding wheat enzymes involved in starch synthesis
InactiveUS6897358B2Increased substance permeabilityImprove breathabilityDough treatmentBacteriaPlant cellStarch synthesis
The invention relates to nucleic acid molecules which code for enzymes and which are involved in the synthesis of starch in plants. These enzymes concern isoamylases derived from wheat. The invention also relates to vectors and host cells which contain the described nucleic acid molecules, especially transformed plant cells and plants which can be regenerated therefrom, which exhibit an increased or reduced activity of the inventive isoamylases.
Owner:BASF AGRICULTURAL SOLUTIONS SEED LLC
Enzyme silk noodle preparation method, wherein alum is replaced by starch branched chain hydrolytic enzymes
The invention discloses an enzyme silk noodle preparation method, wherein alum is replaced by starch branched chain hydrolytic enzymes, and belongs to the technical of food engineering and enzyme engineering. According to the enzyme silk noodle preparation method, plant starch is taken as a raw material; based on a traditional silk noodle preparation method, a starch branched chain hydrolytic enzyme action period is increased after starch gelatinization period in silk noodle preparation, wherein after starch gelatinization, the temperature of an obtained starch gelatinization liquid is reduced to a temperature suitable for the action of the starch branched chain hydrolytic enzymes, and pullulanase, isoamylase, and the like, which are capable of hydrolyzing starch branched chain alpha-1,6 glucosidic bonds are added, and appropriate thermal insulation is carried out; or the starch branched chain hydrolytic enzymes can be added before gelatinization, and after starch gelatinization, the obtained starch gelatinization liquid is subjected to appropriate thermal insulation at the temperature suitable for the action of the starch branched chain hydrolytic enzymes. The other steps are the same as that of the traditional silk noodle preparation method. The enzyme silk noodle preparation method without using alum is provided, food safety of the added starch branched chain hydrolytic enzymes is higher than that of alum, and using amount is less, and compared with the prior art, application of food additives can be reduced, and enlarged production is convenient to realize.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Preparation method of straight chain dextrin embedded conjugated linoleic acid microcapsules
ActiveCN103990424AAvoid Potential ToxicitySmall molecular weightMicroballoon preparationMicrocapsule preparationSolubilityFreeze-drying
A preparation method of straight chain dextrin embedded conjugated linoleic acid microcapsules comprises the following steps: dissolving waxy starch in water, heating for gelatinizing, cooling, adding isoamylase for complete debranching, centrifuging, and freeze-drying to obtain straight chain dextrin powder; and dissolving the straight chain dextrin powder, placing the obtained straight chain dextrin solution at a crystallization temperature, dissolving conjugated linoleic acid (CLA) in a preheated anhydrous ethanol solution, adding the obtained CLA solution into the solution, carrying out heat insulation stirring for a certain time, taking out, cooling to room temperature, centrifuging, washing the obtained precipitate by using an anhydrous ethanol / water mixed solution to remove uncompounded CLA, centrifuging, and carrying out vacuum drying on the finally obtained precipitate to obtain a microcapsule embedding material containing the CLA. The method improves the solubility of the straight chain dextrin and CLA compound, the oxidation stability of the CLA and the bioavailability in an aqueous solution, so the problems of low dissolvability of the straight chain starch compound, and easy automatic oxidation and low bioavailability of the CLA are solved, and the microcapsules can be added to functional nutrition reinforcement foods and staple foods as a nutrition reinforcement agent.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Preparation method of tubular starch derivative
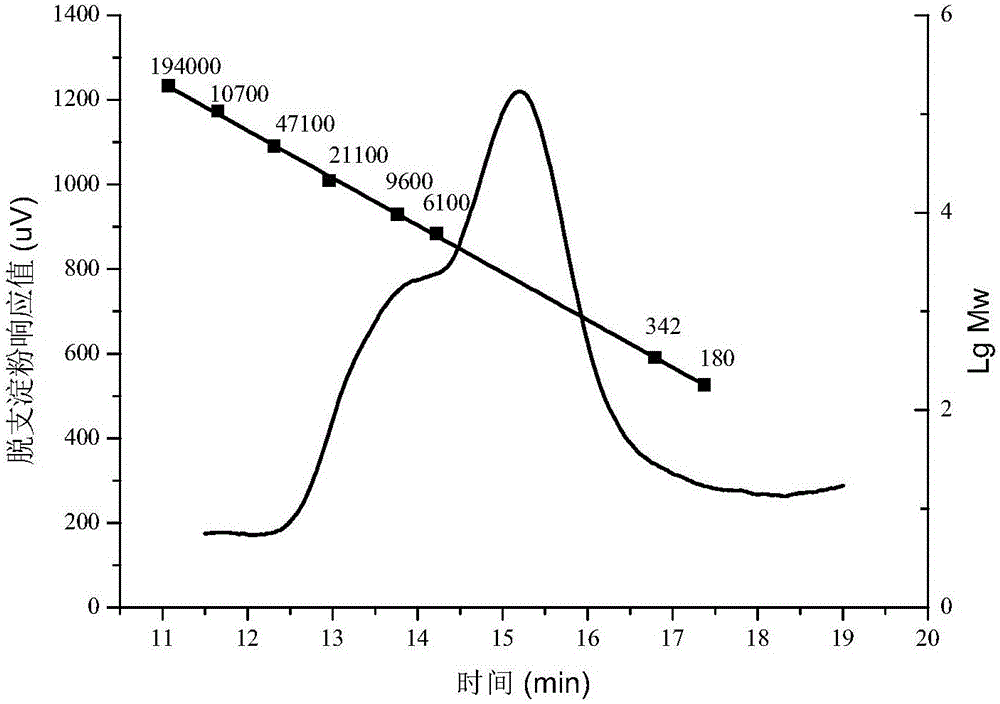
ActiveCN103436572ASolve the problem of low out-of-branch efficiencyHigh yieldFermentationSolubilityAlcohol
The invention discloses a preparation method of tubular starch derivative, and belongs to the technical field of modified starch processing. The invention relates to tubular starch derivative, which has a narrow polymerization degree range and is prepared through combination of ultrasonic de-cluster starch, isoamylase debranching, and alcohol step precipitation fractionation technologies. The method comprises the main steps that waxy rice starch is selected as a raw material, and then tubular starch derivative products, with the polymerization degree (DP) being 20 to 32, are obtained through gelatinization, ultrasonic de-cluster (ultrasonic processing is performed for 3s, and then ultrasonic processing is stopped for 3s, the total time is 15 to 20min, the frequency of ultrasonic wave used is 20kHz, and the power is 200W), isoamylase debranching (the reaction pH is 3.5 to 5.0, the reaction temperature is 37 DEG C, and the reaction time is 12 to 16h), alcohol step precipitation fractionation and drying. The method has the advantages of simple processes, low cost, narrow polymerization degree range of the tubular starch derivative products obtained, good embedment characteristic, stable quality and high solubility.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Preparation method of water-chestnut fermented beverage
ActiveCN104026688ASimple processReduce processing costsNatural extract food ingredientsFood ingredient functionsBiotechnologyBifidobacterium
The invention provides a preparation method of a water-chestnut fermented beverage. The preparation method comprises the following steps: cleaning water-chestnut with water; carrying out ultrahigh-pressure treatment at 15-25MPa for 10-60 minutes; crushing, grinding into thick liquid; carrying out enzymolysis at 80-95 DEG C for 30-50 minutes, wherein 4-6U / g of alpha-amylase and 1-4U / g of isoamylase is added for enzymolysis; saccharifying: adding 80-120U / g of glucamylase for enzymolysis at 75-80 DEG C, wherein enzymolysis lasts for 60-120 minutes; fermenting till the fermented acidity is 65-750T, wherein bifidobacterium and lactic acid bacteria are added and mixed at a weight ratio of (1-1.5) to (1-2), and the inoculum size of the mixed strain is 3-5%, the fermentation temperature is 35-45 DEG C; carrying out high-pressure homogenizing under 20-30Mpa at room temperature for 1-3 times; and finally blending.
Owner:江西仁仁健康微生态科技有限公司
Microwave-specific food package bag and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveCN104709567AHigh strengthStrong enoughBio-packagingClimate change adaptationPlastic packagingHigh humidity
The invention provides a microwave-specific food package bag and a manufacturing method thereof. The manufacturing method comprises the steps that air holes are formed in a plastic package body, film brei is brushed on the air holes, and the food package bag is obtained when the film brie is dried; the manufacturing method of the film brei comprise the steps that the corn starch and the crosslinked starches are mixed according to the proportion of 4:1, and starch slurry with 25% concentration is prepared when the mixed starches dissolve in water; the PH value is adjusted; the calcium chloride solution with 3.6% concentration is added into the starch slurry, and the starch slurry is stirred and heated to 70 DEG C; the starch slurry is cooled to 45 DEG C rapidly when the starch slurry is pasted fully, and the isoamylase is added into the pasted starch slurry according to the proportion that adding 50 ug isoamylase to per g of gram of starch; stirring is conducted for 3 hours, the isoamylase with equal amount is added further, stirring is conducted for 6 hours, and power brei is prepared after filtrating through a gauze. According to the microwave-specific food package bag and the manufacturing method thereof, starch film can melt gradually under a high-temperature and high-humidity environment, so that the food package bag can ventilate automatically.
Owner:NINGBO HOLLY PRINTING
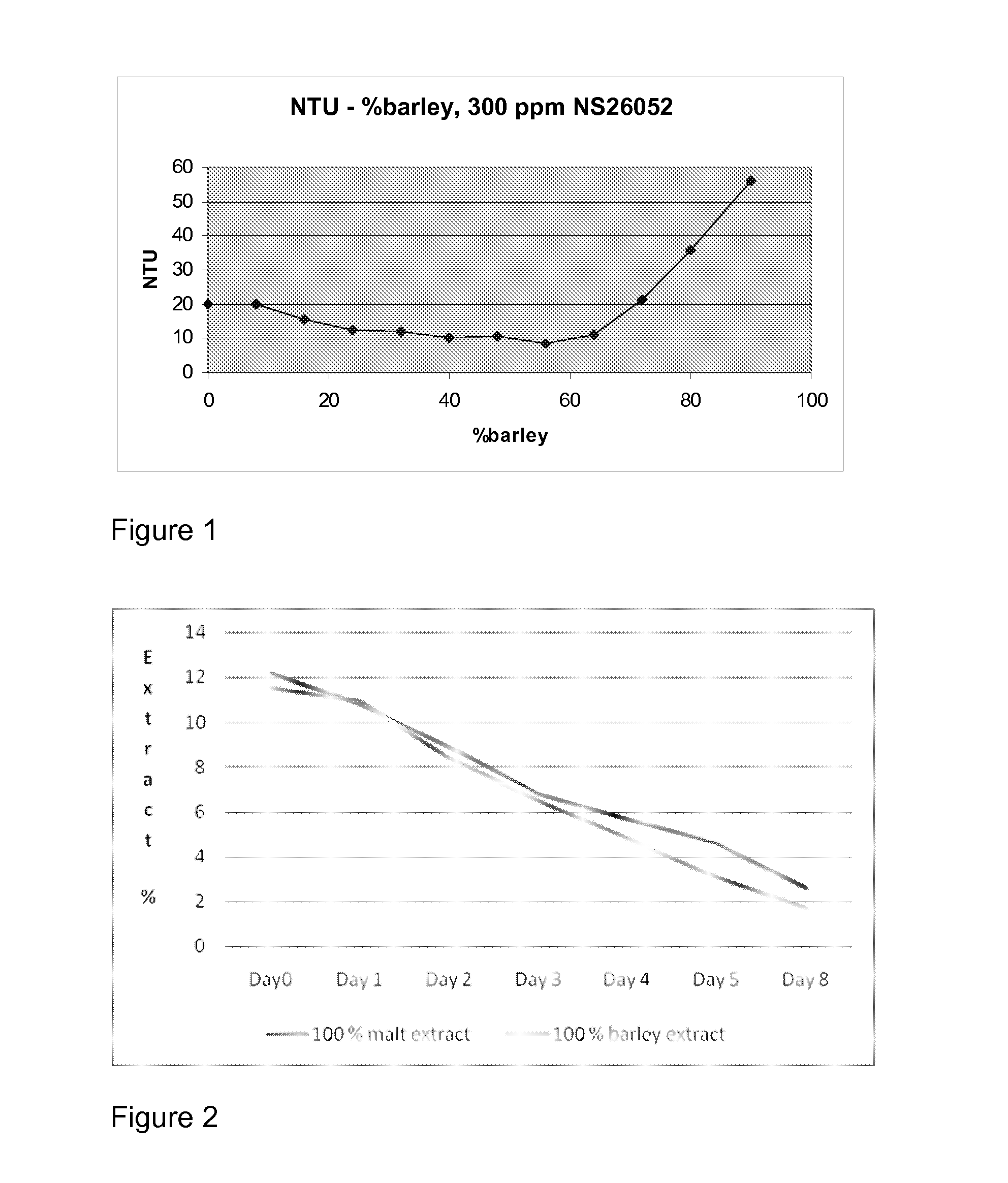
Brewing Process
The invention relates to a process for the production of wort, comprising the enzymatic treatment of gist in up to 100% unmalted (grain) form, for further processing into high quality beverage products. By the addition of a combination of exogenous enzymes (α-amylase, isoamylase / pullulanase, FAN generating activity (proteases) and beta-glucanase activity) to the mash and by the simultaneously thermal activation of the maltose-generating endogenous β-amylase, it is possible to obtain a wort based on up to even 100% barley. The invention further relates to a process for the production of a high quality beer or beer product and to the high quality beer produced according to the process.
Owner:NOVOZYMES AS
Method for improving resistance and yield of resistant dextrin
The invention discloses a method for improving the resistance and yield of resistant dextrin, and belongs to the field of preparation of water-soluble dietary fibers. The method includes the steps that pyrodextrin is subjected to enzymatic hydrolysis with isoamylase, enzymatic hydrolysis with alpha-amylase, and enzymatic hydrolysis with transglucosidase in turn; after enzymatic hydrolysis, ethanolis added to the enzymatic hydrolysate for alcohol precipitation to obtain resistant dextrin. According to the method, by adding a step of enzymatic hydrolysis with the isoamylase, a small branch chain in the pyrodextrin becomes a plurality of small linear chains under the action of the isoamylase, the alpha-amylase can completely break alpha-1,4 glycosidic bonds in the pyrodextrin, and the resistance of the resistant dextrin is improved; the content of small molecules of glucose or maltose in the enzymatic hydrolysate is increased to a certain extent, further more small molecules of glucose and maltose are provided for the transglucosidase, the content of alpha-1,6 glycosidic bonds is increased, and the resistance of the resistant dextrin is further improved. The method is convenient to operate and has a low cost, and the obtained resistant dextrin product has good resistance and high yield, and is suitable for industrial application.
Owner:SHANDONG FOOD & FERMENT IND RES & DESIGN INST
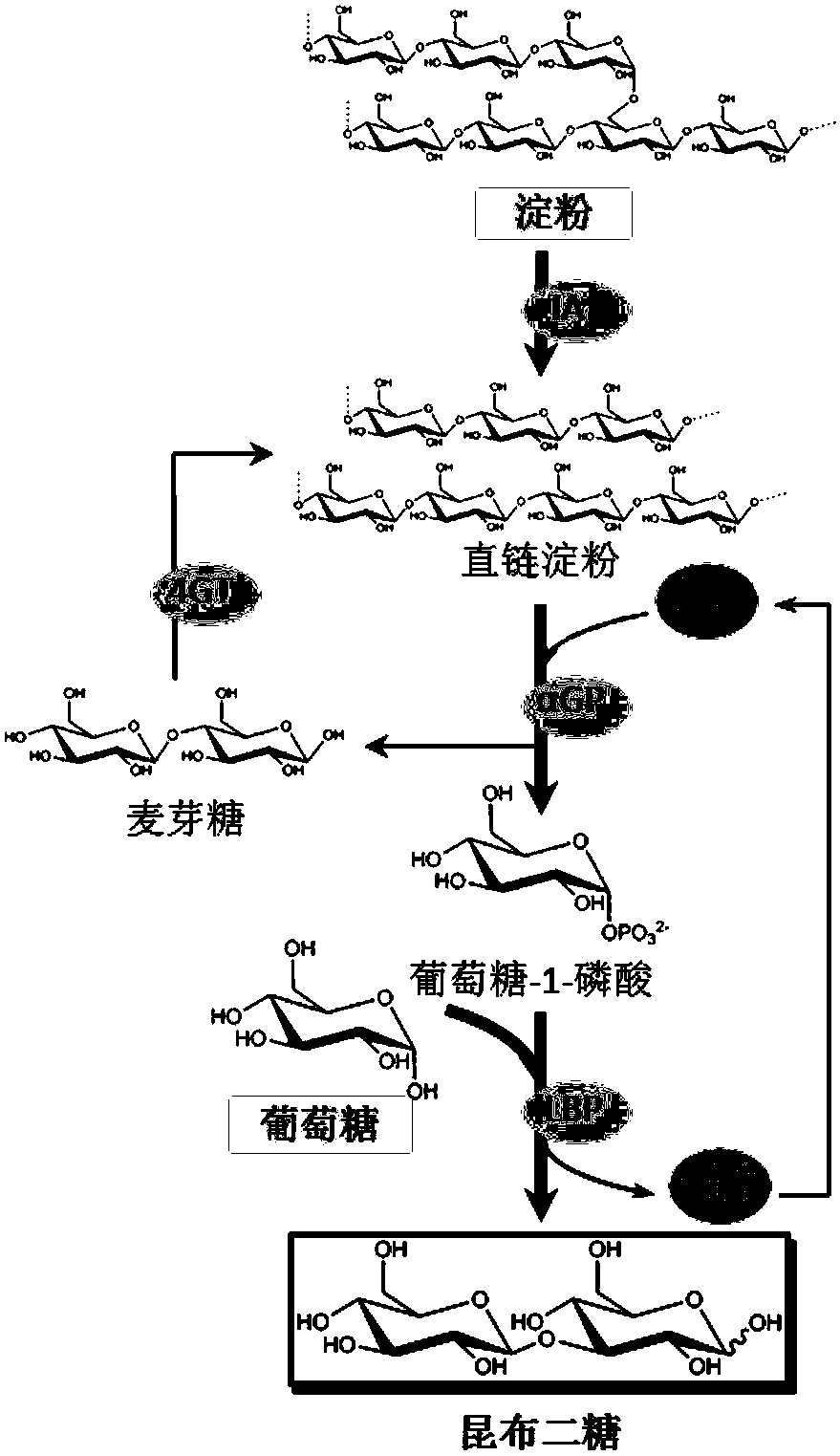
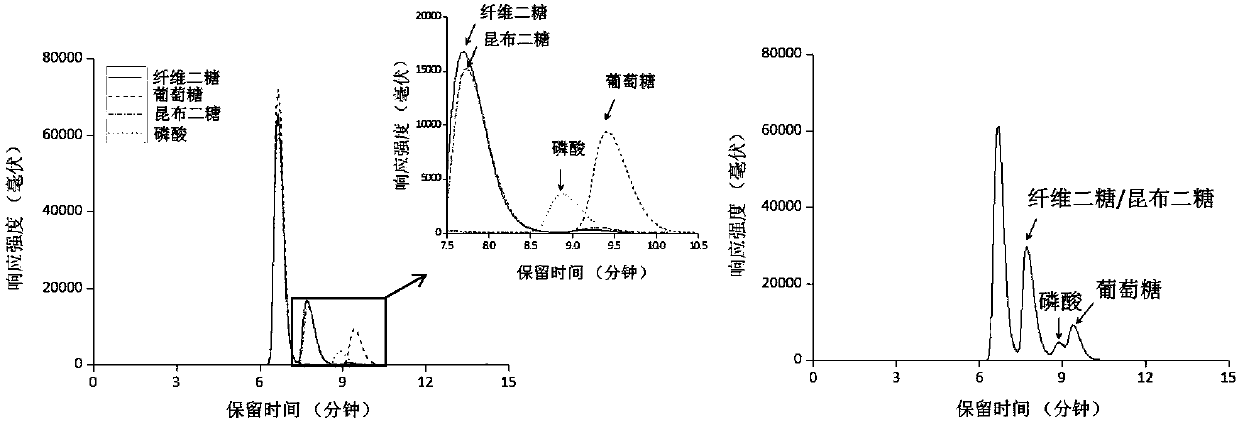
Method for preparing laminaribiose
ActiveCN109706200AIncrease profitReduce separation costFermentationPhosphoric acidLaminaribiose phosphorylase
The invention discloses a method for constructing an in vitro multienzyme molecule machine and preparing laminaribiose by multienzyme cascade catalyzing, and belongs to the field of preparation of enzyme catalysis of laminaribiose. The preparation method of the laminaribiose disclosed by the invention comprises the following steps of converting glucose units in starch into glucose-1-phosphoric acid through glucanphosphorylase, and performing synthesis on the glucose-1-phosphoric acid and glucose through laminaribiose phosphorylase to obtain the laminaribiose. In the process, other auxiliary enzymes, such as isoamylase and glucantransferase, for enabling the starch to be subjected to complete phosphorus desorption are added, so that the utilization rate of the starch and the final concentration of the laminaribiose can be increased. The technical method has the advantages that substrates are cheap and easy to obtain, the production cost is low, the yield of products is high, and separation and purification are simple. The large-scale production of the laminaribiose can be realized.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Method for producing γ-cyclodextrin by simultaneous use of γ-cyclodextrin glycosyltransferase and isoamylase
The present invention provides a method for the production of γ-CD, comprising making a starch slurry, incubating with γ-CGTase and isoamylase simultaneously for γ-CD production, forming a complex of γ-CD and an organic complexant, and purifying γ-CD from the complexant. The present invention provides a simple and cost-effective method for producing high purity γ-CD, which has a short production cycle, a high conversion rate, and is adaptable to large-scale industrial production.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Preparation method of high amylose
The invention discloses a preparation method of high amylose. The preparation method comprises the following steps: accurately weighing the amount of amylose (on a dry basis) at a concentration of 0.02 mol / L and acetic acid sodium acetate buffer solution of a certain pH value, gelatinizing by boiling water bath for some time, placing in a certain temperature of the thermostatic shock water bath pot for 12 min, adding the appropriate amount of isoamylase and pullulanase, oscillating in the thermostatic water bath for some time, and terminating the reaction in boiling water bath for 30 minutes; centrifuging at 10,000 rpm for 10 minutes, taking the supernatant, and freeze-drying to get excellent high amylose. The preparation method adopts the complex enzyme composed of isoamylase and pullulanin to act on the ordinary starch to obtain high amylose, has the advantages of simplicity, high efficiency and no pollution, and has good practical value.
Owner:李郑松
Plants with modified starch metabolism
InactiveCN101970668AExpand production potentialImprove digestibilityTransferasesPlant peptidesSucroseSaccharum
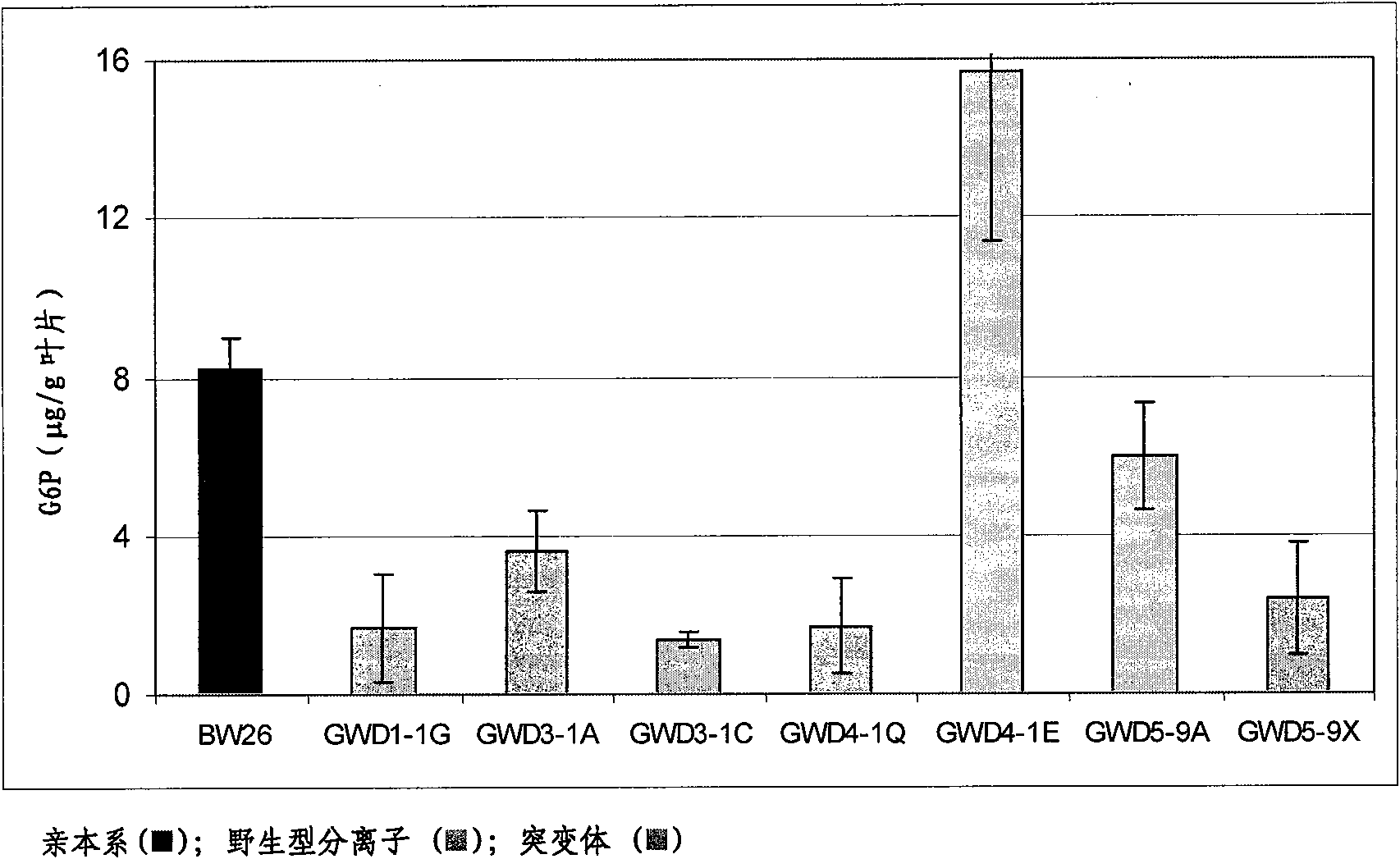
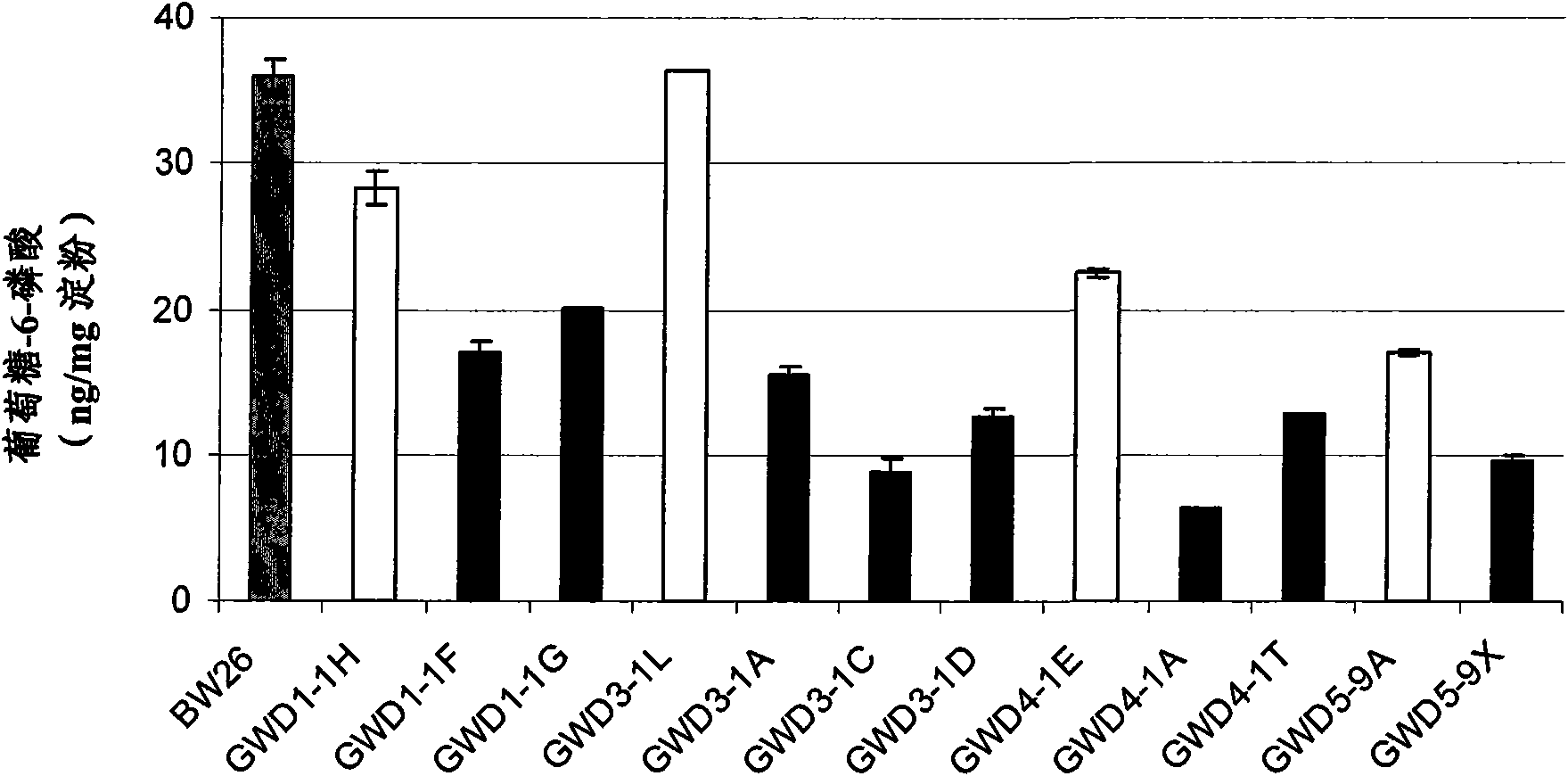
The specification provides methods of obtaining a genetically modified plant which has increased production potential compared to a control plant, the method comprising the steps of i) obtaining a plurality of plants at least one of which comprises in its genome a heterologous polynucleotide, ii) identifying from the plurality of plants a plant which has increased production potential relative to the control plant and comprises the heterologous polynucleotide, and iii) selecting the genetically modified plant, wherein the polynucleotide comprises a transcriptional control sequence operably linked to a nucleic acid sequence which encodes an agent that modifies endogenous starch phosphorylation and / or starch degradation in the plant. In some embodiments, the plant has increased endogenous glycosylase or increased digestibility compared to a control plant. In some specific embodiments, the endogenous starch phosphorylation and / or starch degradation is modified by modifying expression or activity of one or more enzymes selected from the group consisting of alpha-amylase (EC 3.2.1.1), beta-amylase (EC 3.2.1.2), glucoamylase (EC 3.2.1.3), starch phosphorylase (EC2.4.1.1), glycosylase (EC 3.1.33), sucrase-isomaltase (EC 3.2.10), amylomaltase (EC 2.4.1.25), maltase (EC 3.2.1.20), isoamylase, and a-glucan, water dikinase (GWD, EC 2.7.9.4).
Owner:COMMONWEALTH SCI & IND RES ORG +1
Isolation of SU1, a starch debranching enzyme, the product of the maize gene sugary1
InactiveUS20050204425A1Sugar derivativesOther foreign material introduction processesGMO PlantsAmino acid
SU1, a starch debranching enzyme active in maize endosperm (Zea mays), and the cDNA and genomic sequences encoding SU1 are disclosed. The amino acid sequence is significantly similar to that of bacterial isoamylases, enzymes that hydrolyze α-(1→6) glycosidic bonds. Amino acid sequence similarity establishes SU1 as a member of the α-amylase superfamily of starch hydrolytic enzymes. Also disclosed are antibodies reactive with the SU1 protein, methods of producing antibodies to the SU1 protein, methods of producing fusion proteins including SU1 as well as recombinant SU1 and methods of producing transgenic plants with a modified Su1 gene. The native or expressed SU1 protein can serve as a replacement for the bacterial and fungal enzymes currently used in the starch processing industry.
Owner:IOWA STATE UNIV RES FOUND
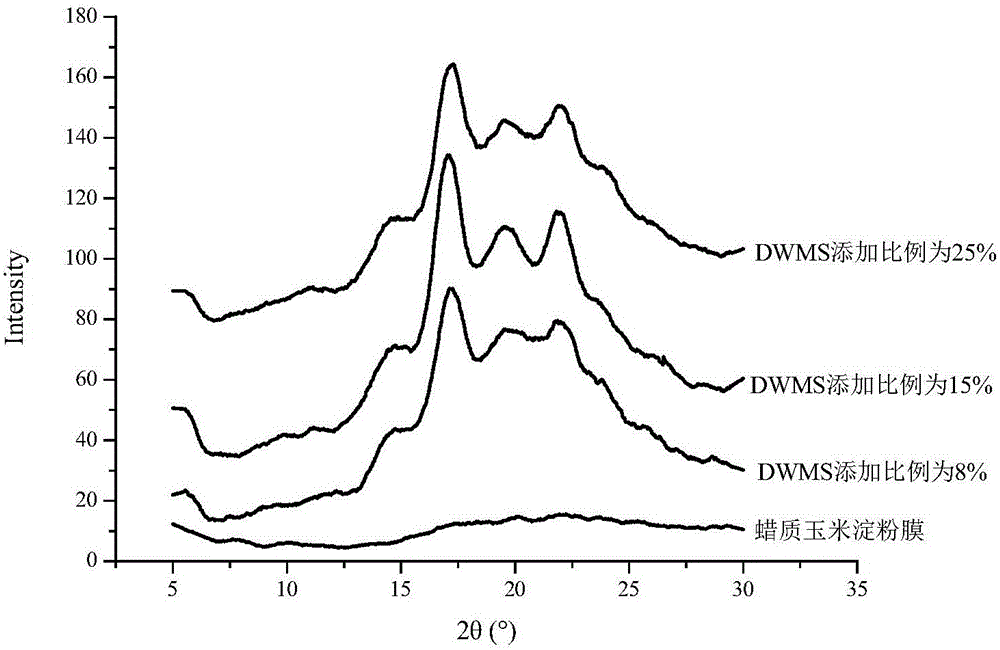
Preparation method of high-solubility waxy maize starch film
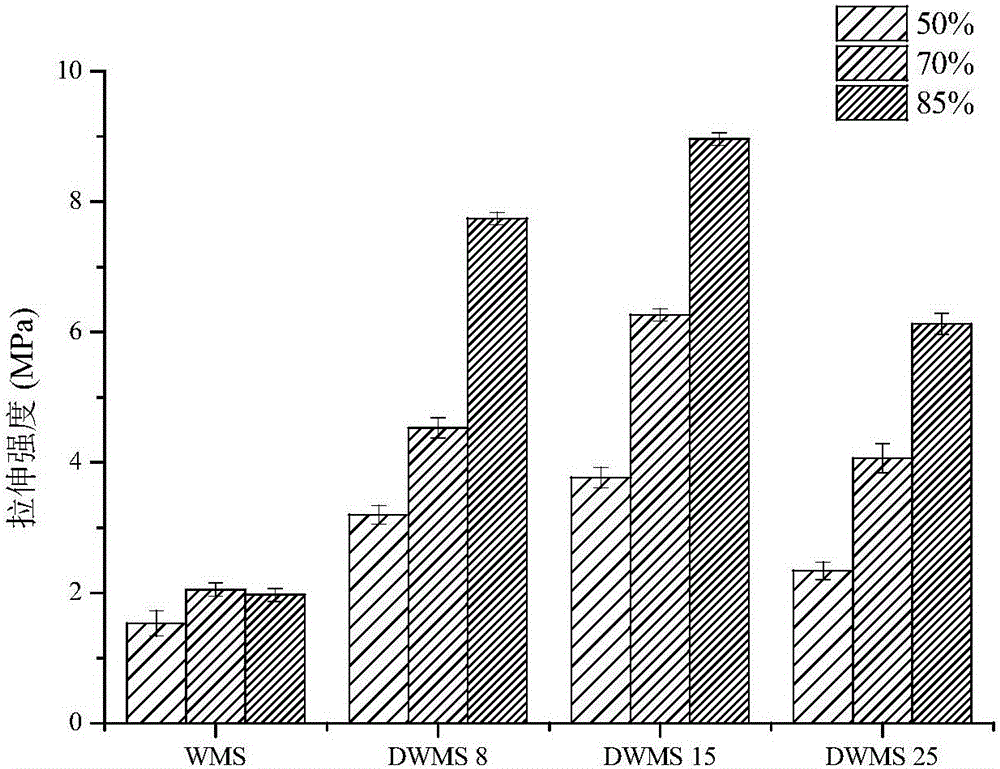
The invention discloses a preparation method of a high-solubility waxy maize starch film. The preparation method comprises the following steps: dispersing waxy maize starch into water; carrying out pre-gelatinization to completely gelatinize the starch and then cooling; adding isoamylase and completely debranching; concentrating, freezing and drying to obtain debranched waxy maize starch (DWMS); mixing the DWMS with the waxy maize starch and drying under certain humidity to form a film, so as to prepare the starch film with high mechanical strength and solubility and good heat sealing property and barrier property; the problems that the mechanical property of the waxy maize starch film is relatively weak and the solubility of a starch film with high content of amylose is poor can be solved at the same time. Moreover, in a production process, all used reagents are food-grade reagents so that the high-solubility waxy maize starch film can be used as a good edible food packaging film and is used for packaging instant foods including instant noodle seasonings or instant coffee and the like.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Method for preparing modified starch-type glass fiber impregnating compound
The invention discloses a method for preparing a modified starch-type glass fiber impregnating compound, which belongs to the field of glass fiber production. The method comprises the following steps:isoamylase is used for performing enzymatic hydrolysis on buckwheat starch, an etherification reaction is carried out, modified starch is taken as a film forming agent, the viscosity is enhanced, thecaking degree is also increased, an auxiliary film forming agent is added, the bonding cluster force is increased, the modified starch and amylose are mixed, so that the dispersion degree of the filmforming agent on the glass fiber and intensity of the glass fiber are increased, a silane coupling agent is used for modification of quartz sand, microbe is used for decomposition of plant oil to generate a lipophilic ester group, the self-crosslinking effect on the microbe is generated, the compatibility between the quartz sand and a polymer is enhanced, the uniform dispersion intensity is improved, the bonding intensity of the film forming agent on the glass fiber is increased, a proper amount of an emulsifier is added, the surface tension is effectively reduced, the glass fiber surface iseasily wetted by the impregnating compound, and the mechanical strength and caking property of the modified starch-type glass fiber impregnating compound are enhanced.
Owner:周荣
Seed-crystal-induction-and-dual-enzyme composite preparation method for RS3 type long-shaped-rice-based resistant starch
InactiveCN106480132AIncrease amylose contentIncrease contact areaFermentationDevitrificationResistant starch
The invention relates to a seed-crystal-induction-and-dual-enzyme composite preparation method for RS3 type long-shaped-rice-based resistant starch. Pregelatinization processing is carried out on long-shaped-rice-based starch by using a microwave technology and stepwise debranching enzymolysis is carried out on the starch after microwave processing by using isoamylase and pullulanase; after increasing of the content of amylose in a raw material system, an RS3 type potato resistant starch seed crystal is added, so that aggregation and recrystallization of the long-shaped-rice amylose are carried out rapidly on a low-supersaturation-degree condition to generate RS3 type long-shaped-rice-based resistant starch. The prepared resistant starch has characteristics of short devitrification time, high yield, and centralized crystal grain size distribution; and thus the long-shaped rice additional value is improved and the application field is expanded. Moreover, the starch material employed in the method is available; production can be carried out throughout the year without being limited by seasons; the processing cost is reasonable; and the prepared product has the broad market prospects.
Owner:HUNAN AGRICULTURAL UNIV
Food product containing starch gel, starch granule, production method and use thereof
ActiveUS9005681B2Well formedImproved gelling abilityDough treatmentBaking mixturesAlgluceraseCyclodextrin
Here is provided a method of producing a starch gel-containing food, the method comprising the steps of: treating starch granules with an enzyme at a temperature of about 10° C. or higher and about 70° C. or lower to obtain an enzyme-treated starch; mixing a food material, the enzyme-treated starch and water to obtain a mixture; heating the mixture thereby gelatinizing the enzyme-treated starch in the mixture; and cooling the mixture containing the gelatinized enzyme-treated starch thereby gelling the starch to obtain a starch gel-containing food, wherein the enzyme is selected from the group consisting of amyloglucosidase, isoamylase, α-glucosidase, α-amylase having a characteristic capable of improving a gel forming ability of a starch, and cyclodextrin glucanotransferase.
Owner:GLICO NUTRITION
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com