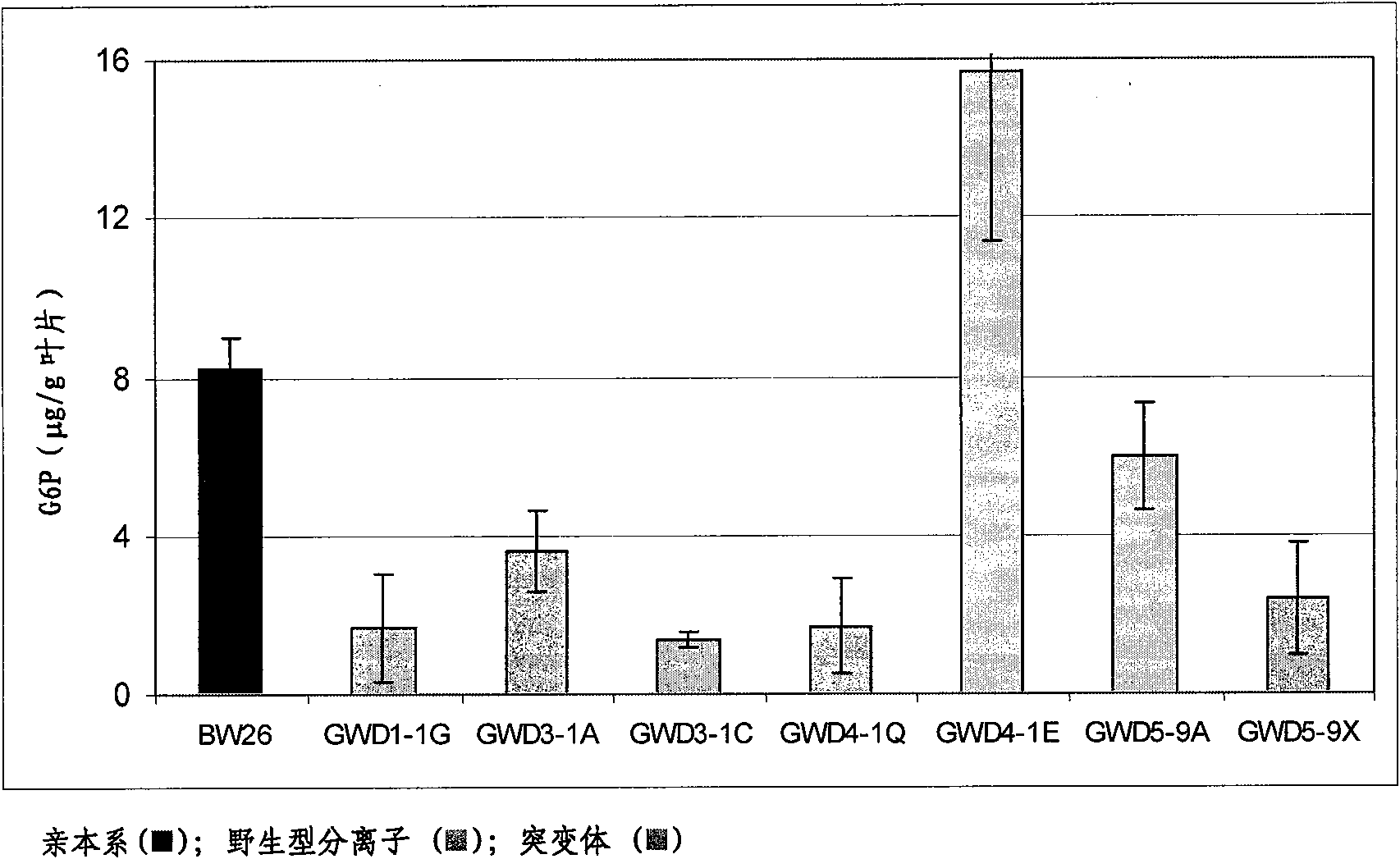
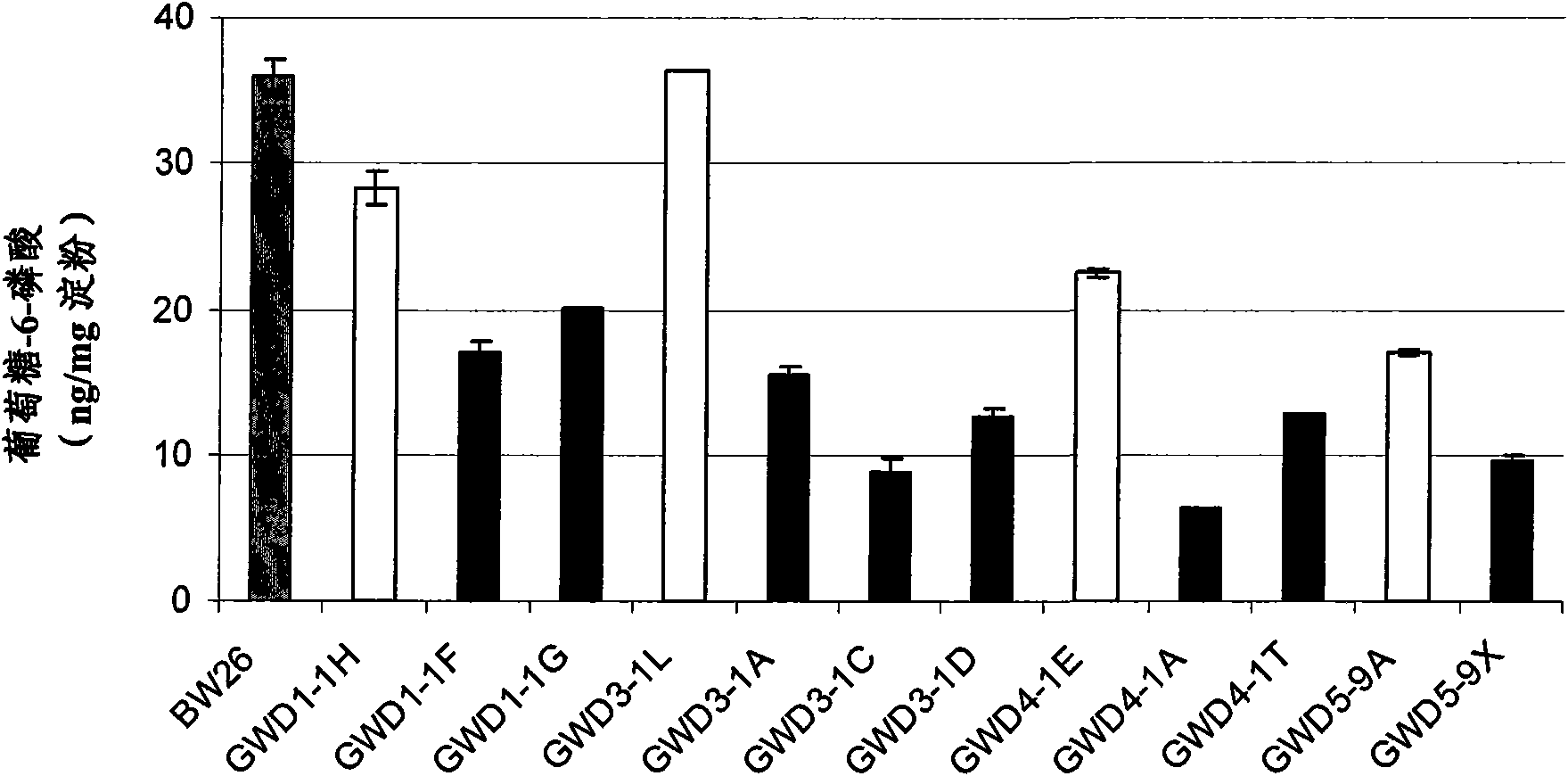
Plants with modified starch metabolism
A crop, amylase technology, applied in the fields of plant peptides, food science, plant products, etc., can solve the problem of the lag of wheat transformation efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0263] Embodiment 1 Materials and methods
[0264] Extraction of starch from cereals
[0265] The mature grains were pulverized with a small pulverizer of Metefem (prototype), and the pulverized material was passed through a 0.5 mm sieve. The semolina obtained was weighed and 50% by weight of water was added to soften the result. The dough is obtained by mechanically mixing water and flour. Excess water was added to extract starch from gluten, and then the starch suspension was filtered through 100 μm filter paper to remove residue. Repeat the extraction 4 times or until no starch remains in the dough. The starch was granulated by centrifugation (5,000 rpm, 10 minutes, 4°C). The covering albumen is removed and the starch is resuspended in excess water. Repeat the wash 3 times. The extracted starch was freeze-dried in a FTS freeze dryer (Model No.FD-3-55D-MP). Using this method, 10 g of grain yields approximately 6 g of flour and 3 g of starch.
[0266] Extraction of st...
Embodiment 2
[0292] Identification of GWD and PWD Genes in Example 2 Wheat and Other Cereals
[0293] The amino acid sequence (Accession No. AAK11735) used for the potato R1 protein sequence and the Arabidopsis PWD protein (NP_194176) were used as query sequences in the NCBI database, and the wheat EST sequence was queried using the BLASTN program. Seventeen ESTs (listed below) were identified and aligned to form a sequence of 2273 base pairs (SEQ ID NO: 1).
[0294] dbj|CJ626658.1|CJ626658 Y.Ogihara unpublished cDNA library.
[0295] gb|CV773056.1|FGAS067452 Triticum aestivum FGAS library.
[0296] dbj|CJ694861.1|CJ694861 Y.Ogihara unpublished cDNA library.
[0297] gb|CA743865.1|wrils.pk006.k23 wrils Triticum aestivum cDNA.
[0298] gb|BQ240991.1|TaE05010D07R Ta05 Triticum aestivum cDNA.
[0299] dbj|CJ696711.1|CJ696711 Y.Ogihara unpublished cDNA library.
[0300] dbj|CJ730334.1|CJ730334 Y.Ogihara unpublished cDNA library.
[0301] gb|BQ237936.1|Ta05010D07F TaE05 Triticum aestivum ...
Embodiment 3
[0317] Example 3 Production of Transformed Plants Containing Structures That Suppress GWD Gene Expression
[0318] To examine the effects of inhibiting GWD gene expression, gene constructs capable of expressing double-stranded RNA molecules used to inhibit partial homologs of wheat GWD were designed, targeting a conserved region consistent with the starch-binding domain.
[0319] This construct contains the wheat Bx17 HMW glutenin gene promoter for expression of dsRNA, which acts as a tissue-specific promoter, preferably expressed in the cereal endosperm. Therefore, it is predicted that inhibition of gene expression may occur primarily in the endosperm.
[0320] The suppressor gene construct was assembled in the following pBx17IRcasNOT cloning vector. This vector contains the following components in order: from the wheat HMWG Bx17 gene, as reported by Reddy et al. (1993), including the endosperm-specific promoter of the first 1897 nucleotides of the Bx17 genome sequence, its ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com