Patents
Literature
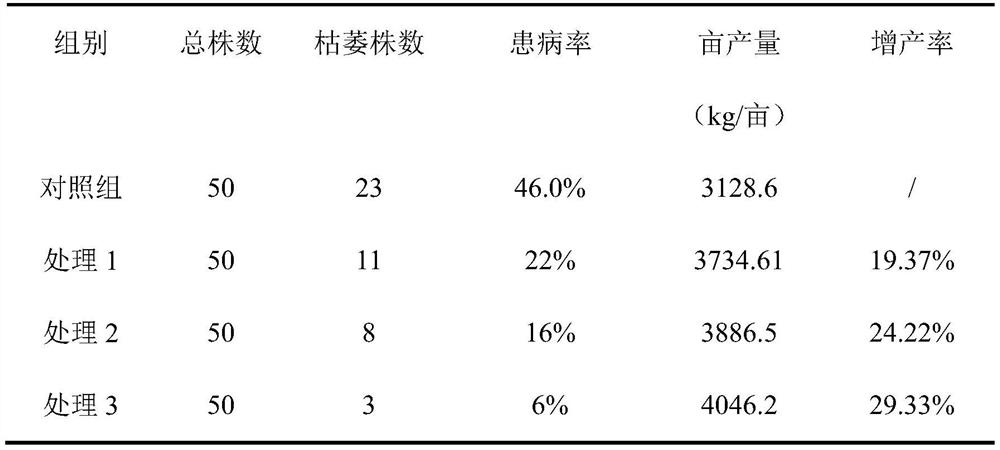
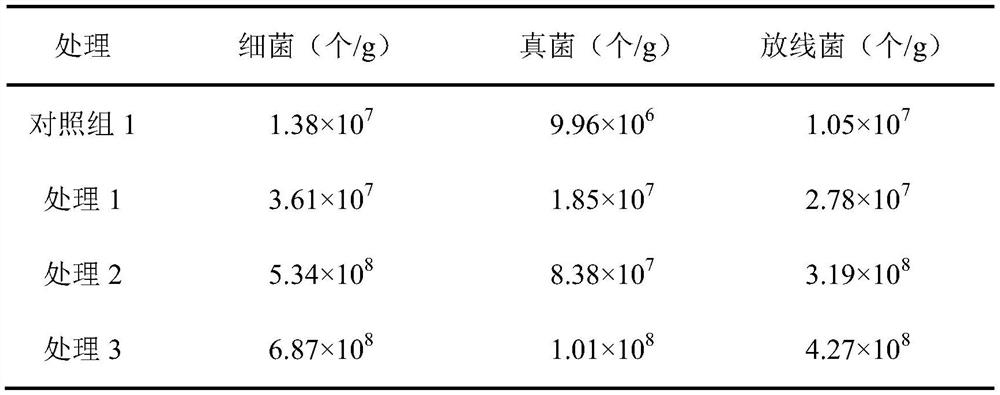
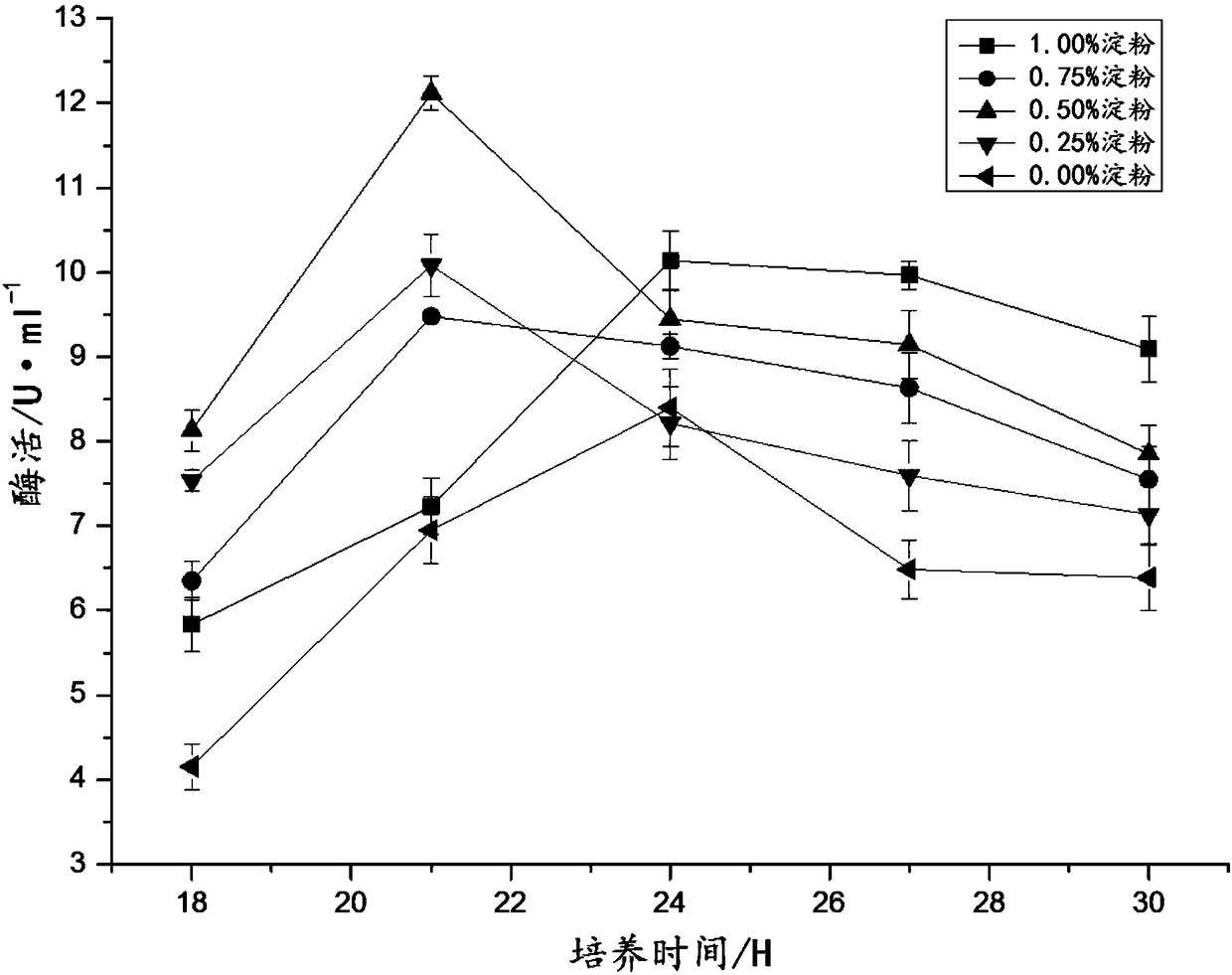
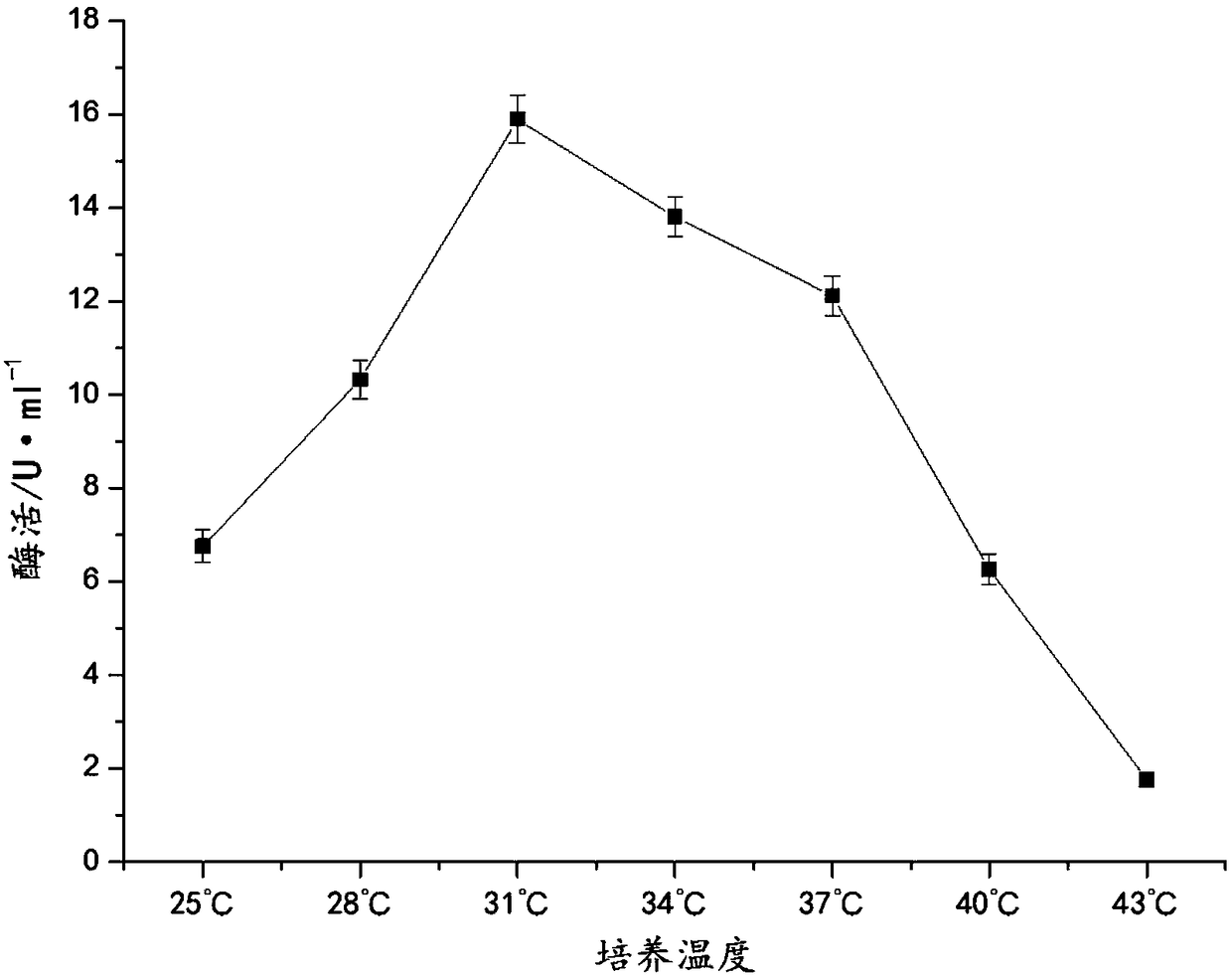
68 results about "Starch degradation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
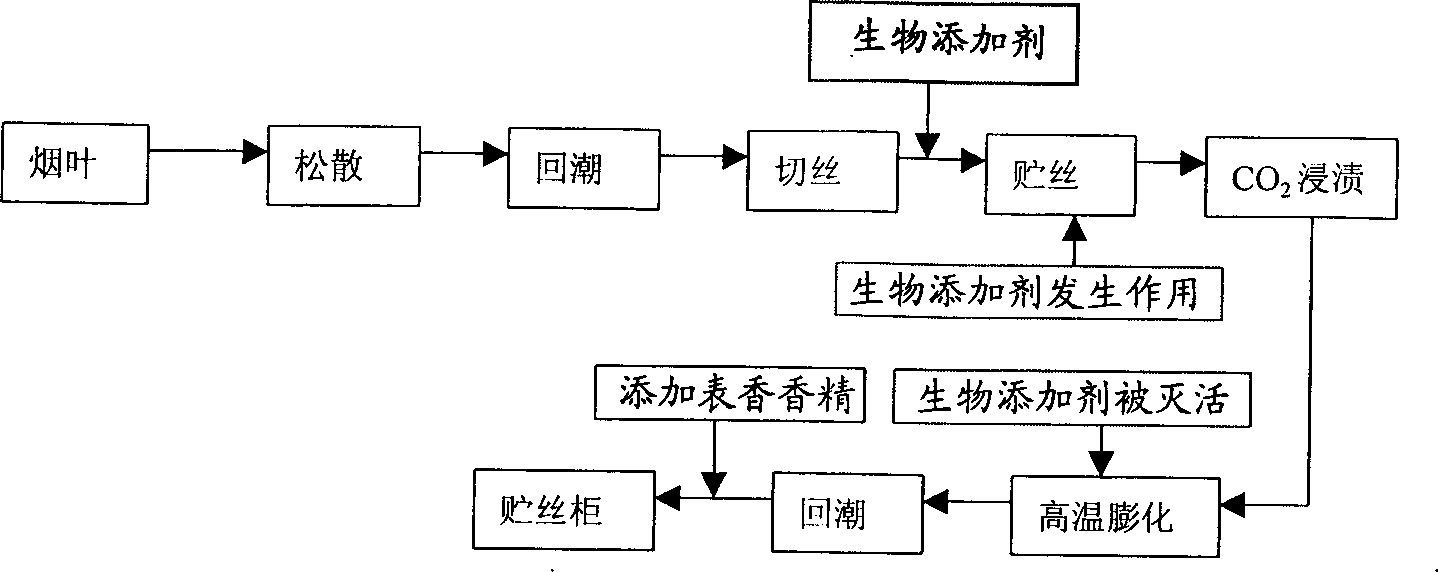
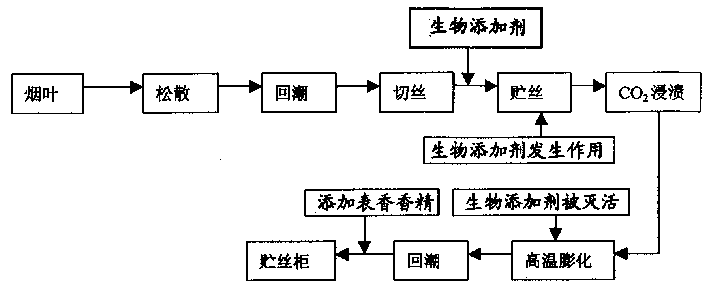
Compound microbial agent as well as processing method and application thereof
ActiveCN103756941AGood decomposition effectImprove decomposition effectBacteriaSolid waste disposalFiberProtein Degradations
The invention relates to a compound microbial agent which comprises compound bacteria for decomposing kitchen wastes and auxiliary materials for solid fermentation, wherein the compound bacteria comprise 10-15 parts of cellulose degradation bacteria, 15-30 parts of starch degradation bacteria, 15-20 parts of protein degradation bacteria, 15-20 parts of grease degradation bacteria, 10-15 parts of bacillus subtilis and 5-15 parts of pseudomonas aeruginosa; the auxiliary materials comprise 50-60 kg of wheat bran, 15-20 kg of bean pulp, 0.4-0.6 kg of magnesium sulfate, 0.4-0.6 kg of potassium dihydrogen phosphate, 0.1-0.2 kg of disodium hydrogen phosphate and 8-10 kg of glucose. The inoculation amount of the compound bacteria in the auxiliary materials is 0.8%-1%, and the compound bacteria is subjected to solid fermentation to obtain the compound microbial agent. The compound microbial agent has a good decomposing effect on greases, proteins and fiber substances and can be tolerant to salt with a certain concentration; optimally, the degradation rate can reach more than 90%.
Owner:BEIJING GREEN ENERGY ENVIRONMENTAL ENG
Methods for increasing starch content in plants
ActiveUS20090119800A1High in starchImprove the level ofAnimal feeding stuffOther foreign material introduction processesFree sugarGenetically engineered
Methods and compositions for increasing the starch content in green tissues of a plant are provided. The method comprises down-regulating me activity of starch degradation enzymes in a plant. The resulting transgenic plants of the invention have increased starch content in green tissues and exhibit a starch excess phenotype. In one embodiment the method involves manipulating a monocot plant to down-regulate the activity of a starch degradation enzyme. The plants are useful for improving the yield of free sugars from plant biomass and increase dried green tissue storage stability.
Owner:AGRIVIDA
Additive for flue-cured tobacco, prepn. method and application thereof
ActiveCN1723811AAccelerate the speed of alcoholizationReduce contentTobacco treatmentLiquid productVitamin C
An additive of flue-cured tobacco is prepared from the protein degradation enzyme, starch degradation enzyme, pectin degradation enzyme, poly-phenol oxidase, cellulose, VC and potassium tartrate through adding them to water, stirring for dissolving and filtering to obtain the liquid product. It can be sprayed onto the leaves of tobacco to decreasing the content of organic high-molecular substances in tobacco leaf and improving its quality.
Owner:YUNNAN REASCEND TOBACCO TECH GRP
Novel process for producing distilled spirit by carrying out extrusion pretreatment on distilled spirit raw materials and adopting liquid-state method
InactiveCN103243001AComplete gelatinizationGelatinization stabilityAlcoholic beverage preparationChemical structureLiquid state
The invention relates to a novel process for producing distilled spirit by pretreating distilled spirit raw and auxiliary materials by means of an extrusion technology and carrying out liquid-state method fermentation. The raw and auxiliary materials for distilled spirit production are pretreated by using the extrusion technology, and reasonable parameters of a distilled spirit raw material extrusion technology and reasonable parameters for liquid-state method distilled spirit production by using the raw materials puffed by extrusion are provided. According to the distilled spirit raw materials pretreated by using the extrusion technology, the compounding effect among materials is better, starch degradation and albuminous degeneration can be performed more thoroughly, so that the utilization rate of the raw materials is increased, and the distilled spirit fermentation cycle is shortened compared with that of the traditional process; and in addition, the flavor, the liquor yield and other multiple qualities of the finished-product distilled spirit are greatly promoted. According to the novel method for brewing by pretreating the distilled spirit raw materials by extrusion, the energy consumption can be saved, the cost is reduced, the raw material utilization rate and the distilled spirit yield are increased, and the fermentation cycle is shortened; and meanwhile, due to multiaspect comprehensive effects, such as sufficient heat effect, mechanical effect and chemical structure modification effect, the yield and quality of the finished-product distilled spirit are greatly promoted.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
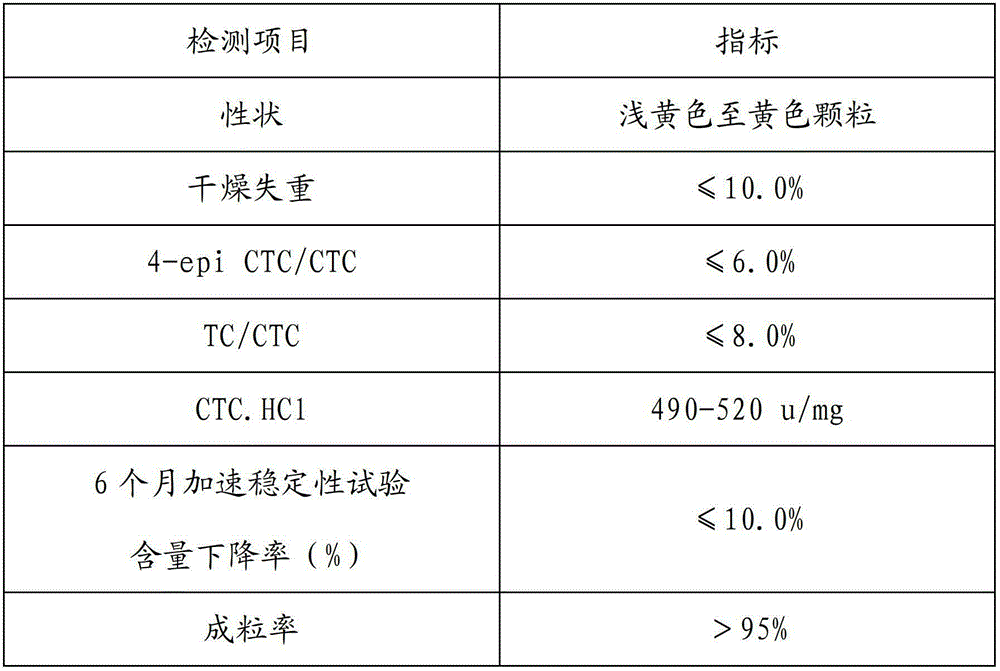
Formula of aureomycin hydrochloride premix granule and granulating process
ActiveCN102716092AReduce generationHigh granulation rateTetracycline active ingredientsPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsChlortetracycline hclStarch degradation
The invention discloses a formula of aureomycin hydrochloride premix granule, which is characterized in that the following components are included: 80 percent or less than 80 percent of aureomycin hydrochloride, 80 percent or less than 80 percent of soluble starch or starch degradation products, 20 percent or less than 20 percent of carbohydrates, and 30 percent or less than 30 percent of purified water. The invention further discloses a granulating process. After the adoption of the formula and the granulating process, the invention achieves that the aureomycin hydrochloride premix granule is uniform, has a mellow appearance, is unanimous in tincture and high in percentage of ripened grains, the stability of product quality is excellent, the normal working conditions during the aureomycin hydrochloride premix granulating process can be ensured, and the improvement to production efficiency and quality is facilitated.
Owner:PUCHENG CHIA TAI BIOCHEM
Bacterium-enzyme combined preparation containing bacillussubtilis strain xp and application of bacterium-enzyme combined preparation in accelerating starch degradation in tobacco stem
ActiveCN103756944AReview Score IncreaseIncrease in total ratingBacteriaTobacco treatmentBiotechnologyMicroorganism
The invention belongs to the technical field of microorganisms and particularly relates to a bacillussubtilis strain xp producing amylase. A classification designation of the bacillussubtilis strain xp is Bacillussubtilis. The collection number of the strain in China Center for Type Culture Collection (CCTCC) is CCTCC NO: M2011452. The invention further discloses a bacterium-enzyme combined preparation prepared by the strain xp, and an application of the bacterium-enzyme combined preparation in accelerating starch degradation in a tobacco stem.
Owner:CHINA TOBACCO HENAN IND
Biomass environment-friendly non-chlorine deicing and snow-melting agent and preparation method thereof
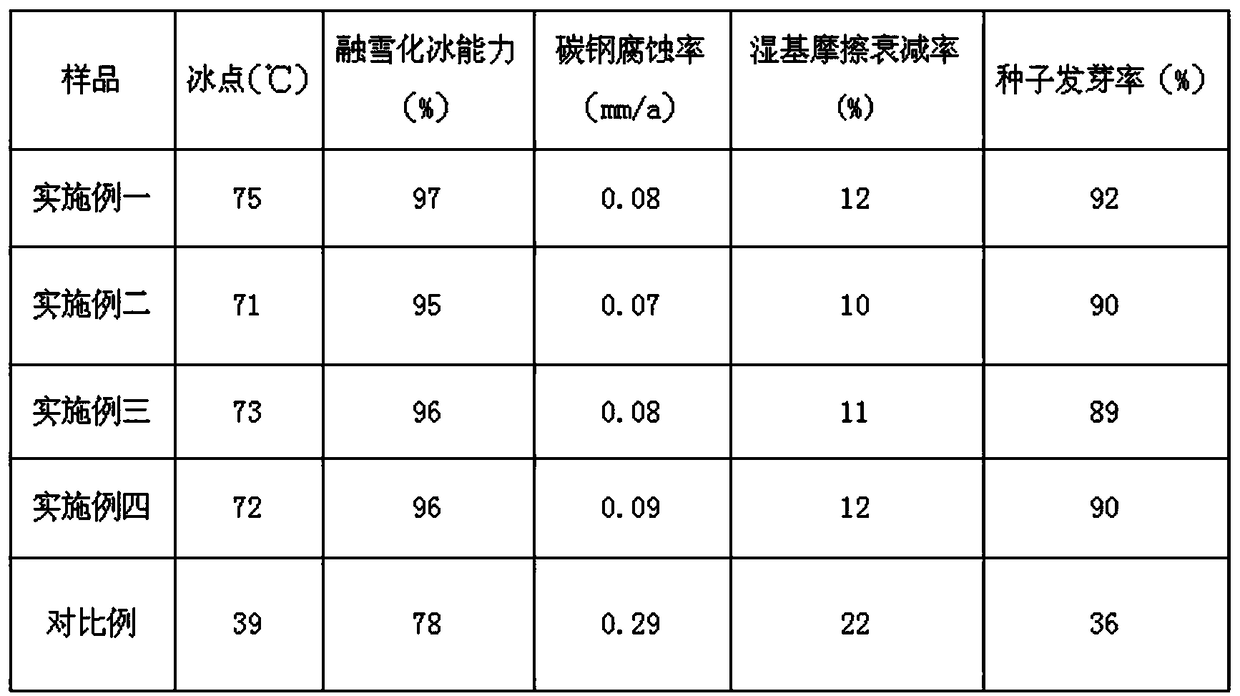
InactiveCN109266310ALittle effect on germination rateStrong ability to melt snow and iceOther chemical processesSnow meltingMonoglyceride citrate
The invention belongs to the field of deicing and snow-melting agents, and discloses a biomass environment-friendly non-chlorine deicing and snow-melting agent and a preparation method thereof. The deicing and snow-melting agent is prepared from 10-30 parts of tap water, 15-35 parts of glucose degradation product, 6-20 parts of starch degradation product, 8-18 parts of saccharose, 7-18 parts of monoglyceride citrate and 2-5 parts of corrosion inhibitor; the preparation method comprises the steps that firstly, the glucose degradation product and the starch degradation product are prepared; thenthe tap water is added into a reaction kettle, the temperature rises to 60-80 DEG C, the glucose degradation product and the starch degradation product are added, and mixing reaction is carried out for 1-3 h; then the saccharose, the monoglyceride citrate and triisopropanolamine are added in sequence, and full stirring and mixing reaction is carried out for 1-2 h; and lastly, after the reactant is mixed uniformly and dissolved into one phase, cooling and discharging are carried out. The biomass environment-friendly non-chlorine deicing and snow-melting agent and the preparation method thereofhave the advantages that the obtained product has strong snow-melting and deicing abilities and a weak corrosive effect, the raw material is basically biomass, the biodegradability is high, and the biomass environment-friendly non-chlorine deicing and snow-melting agent belongs to an environment-friendly product.
Owner:黄山九星环保科技股份有限公司
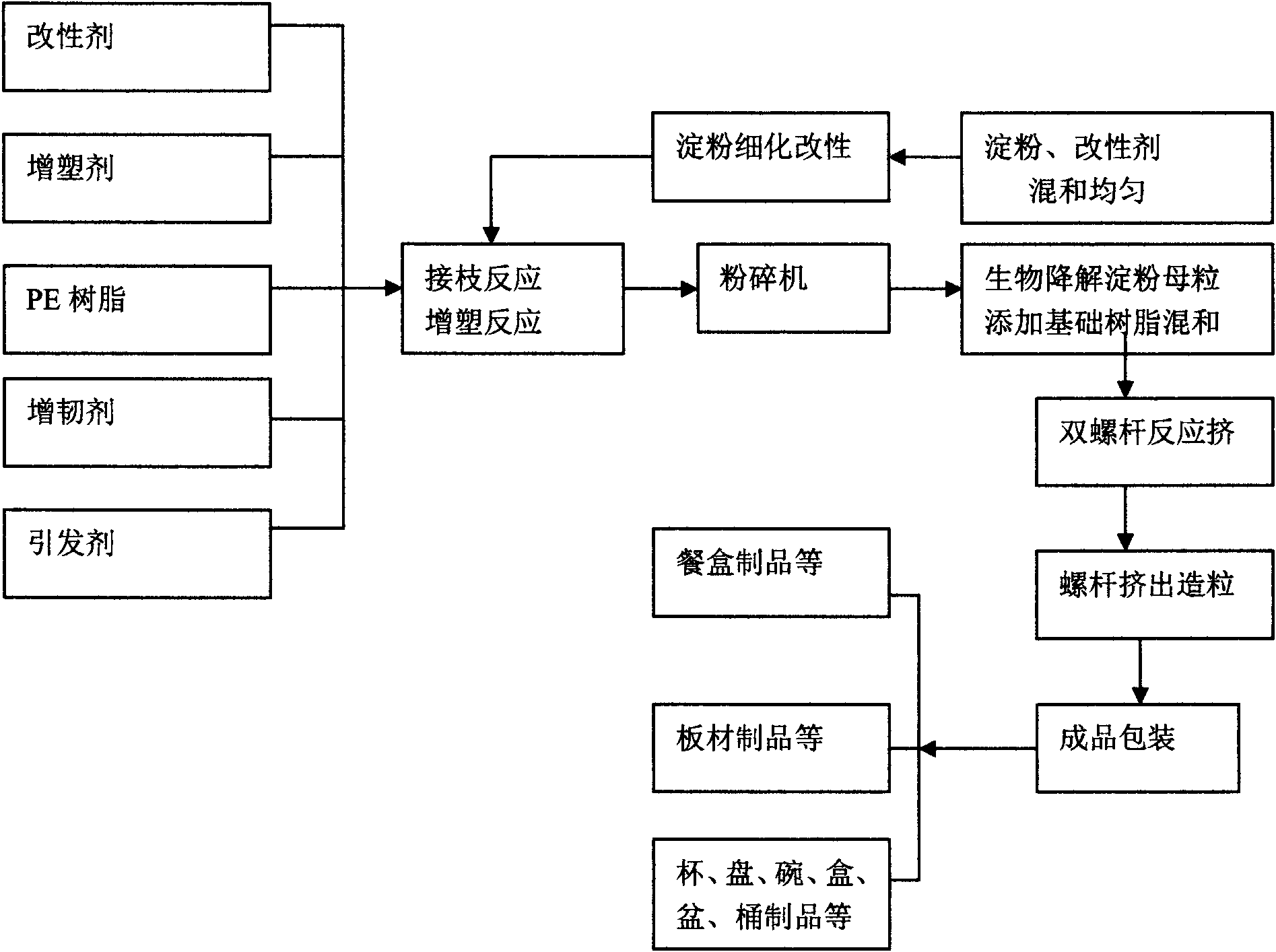
Biological starch-based (sheet) degradation master batch
The invention discloses a biological starch degradation plastic master batch, comprising the following components by weight percent: 70%-80% of refined starch, 7%-10% of flexibilizer, 0.5%-2% of initiator, 4%-7% of modifier, 1%-3% of plasticizer and 3%-6% of lubrication processing aid. The invention further discloses a preparation method thereof.
Owner:梁雄辉
Deinking of waste paper
InactiveUS20020179261A1Good deinking effectSpeed up the processPaper recyclingPulping with organic solventsStarch degradationEnzyme
In the production of pulp and paper from starch-containing paper, the deinking effect can be improved by including treatment with both a starch-degrading enzyme and a pectate lyase. The process comprises enzyme treatment during or after disintegration of the paper to produce pulp, followed by separation of ink particles.
Owner:NOVOZYMES AS +1
Bacterium-enzyme combined preparation containing bacillussubtilis strain xp and application of bacterium-enzyme combined preparation in accelerating starch degradation in tobacco sheet
ActiveCN103756946AImprove the level ofIncrease in total ratingBacteriaTobacco treatmentBiotechnologyMicroorganism
The invention belongs to the technical field of microorganisms and particularly relates to a bacillussubtilis strain xp producing amylase. A classification designation of the bacillussubtilis strain xp is Bacillussubtilis. The collection number of the strain in China Center for Type Culture Collection (CCTCC) is CCTCC NO: M2011452. The invention further discloses a bacterium-enzyme combined preparation prepared by the strain xp, and an application of the bacterium-enzyme combined preparation in accelerating starch degradation in a tobacco sheet.
Owner:CHINA TOBACCO HENAN IND
Tobacco-swelling biological additive and its prepn. and application
A biological additives to expand tobacco and its producing method and applications are disclosed whose compositions and contents are tobacco leaf protein degradation enzyme of 0.1-10%, starch degradation enzyme of 1.0-10%, pectin degradation enuzyme of 0.2-10%, polyose degradation enzyme of 0.5-20%, fiber modifier of 0.5-20%, polyphenol oxidation degradution enzyme of 0.1-5%, carbon chain enzyme of 0.1-10%, vitamin C of 0.1-5% and water of 100%. The invented additives can be added into tabocco after the tabocco is remoistened and cut into pieces but before the tabocco is expanded with adding quantity as 0.2-5% of tobacco pieces weight at the temperature of 30 degree c to 50 degree C. The present invention can not bring negative influence to tobacco but can decrease the composition contents which is harmuful in smoking.
Owner:YUNNAN REASCEND TOBACCO TECH GRP
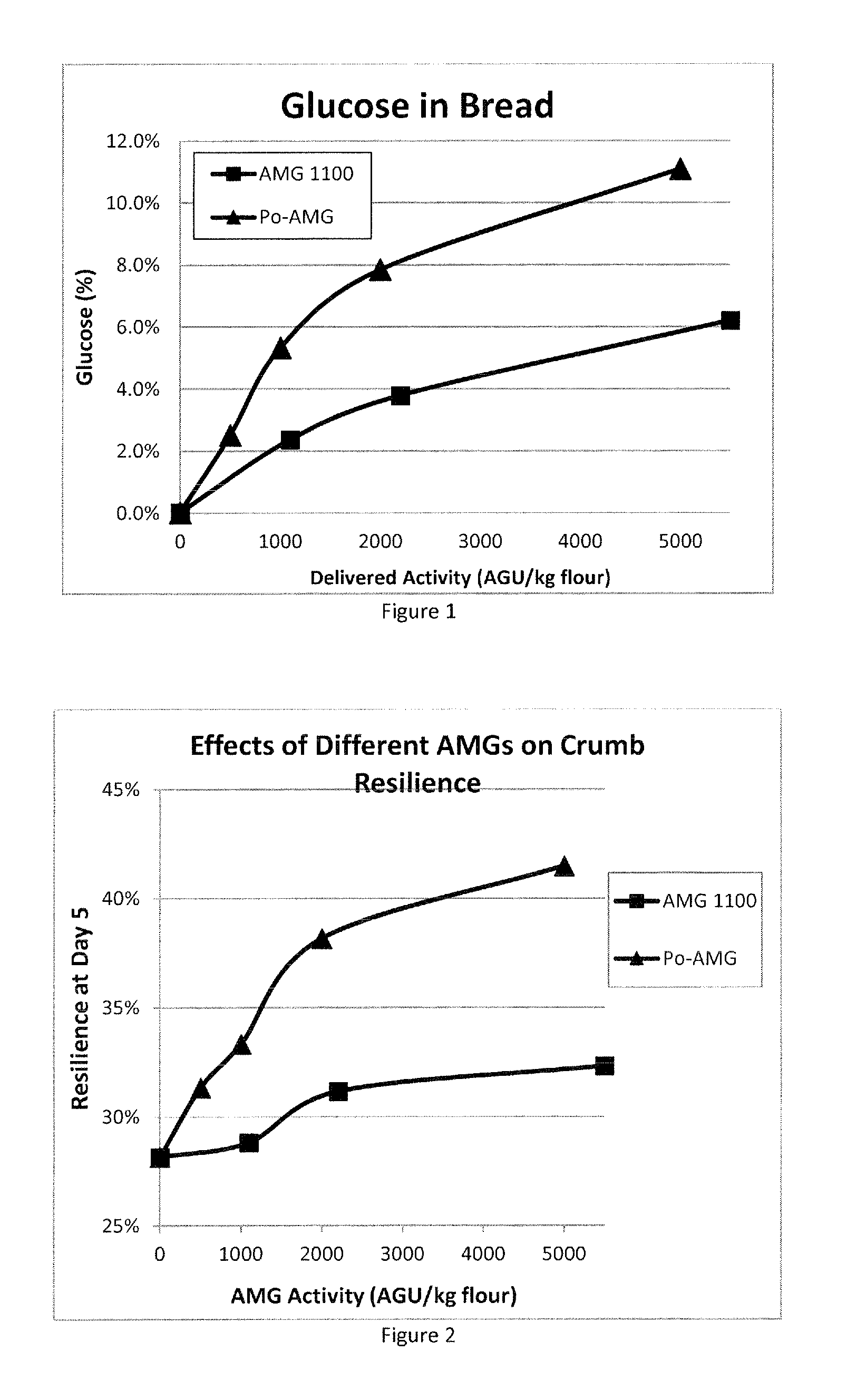
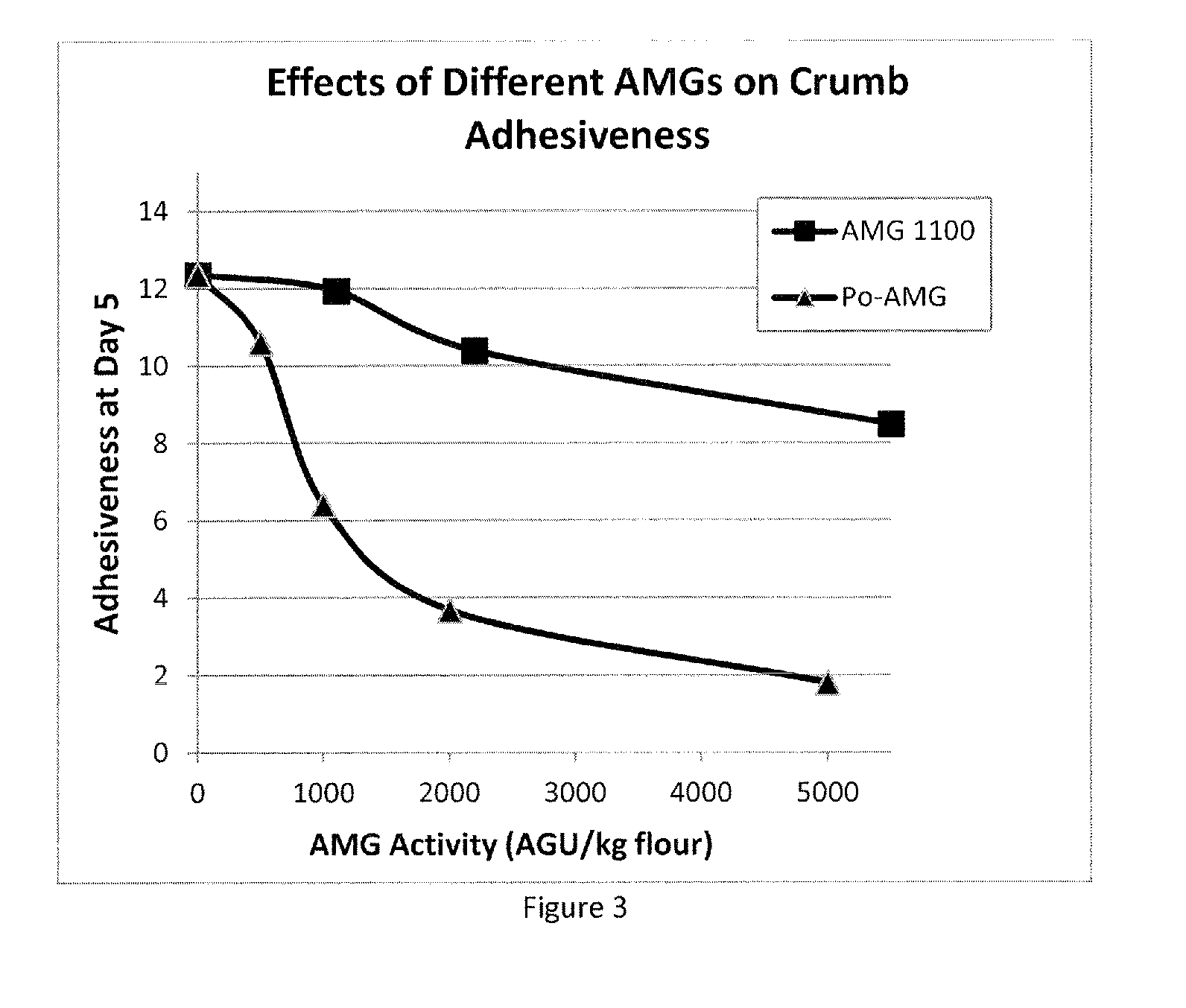
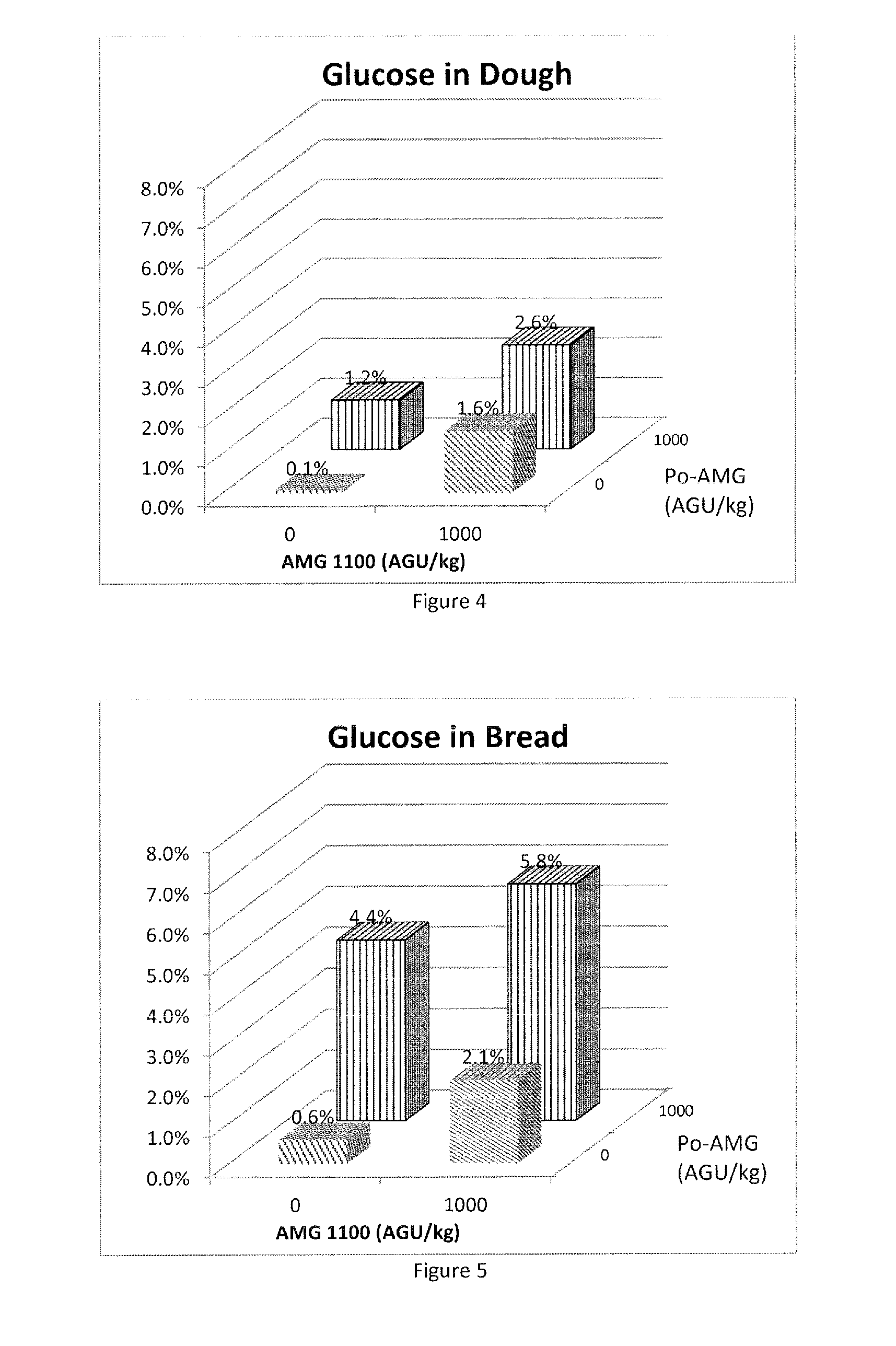
Method of Producing a Baked Product with Alpha-Amylase, Lipase and Phospholipase
ActiveUS20160135472A1Low elastic modulusEconomical to useMilk preparationDough treatmentPhospholipaseAlpha-amylase
The present invention provides a method of producing a baked product having reduced crumb elasticity, said method comprising adding a raw starch degrading alpha-amylase, a lipase and a phospholipase to dough ingredients comprising flour, water, and yeast and mixing to prepare a dough; leavening the dough; and baking the dough to obtain the baked product.
Owner:NOVOZYMES AS
Starch degradation/graft polymerization composition, process, and uses-thereof
Disclosed herein are starch stabilized polymeric emulsions. Persulfate salts degrade starch to give it suitable characteristics, and then also, essentially simultaneously, initiate polymerisation with monomers. This permits a single reaction condition to be used for both the degradation step and the polymerization step, and avoids the need for use of metallic ions such as iron.
Owner:BASF AG
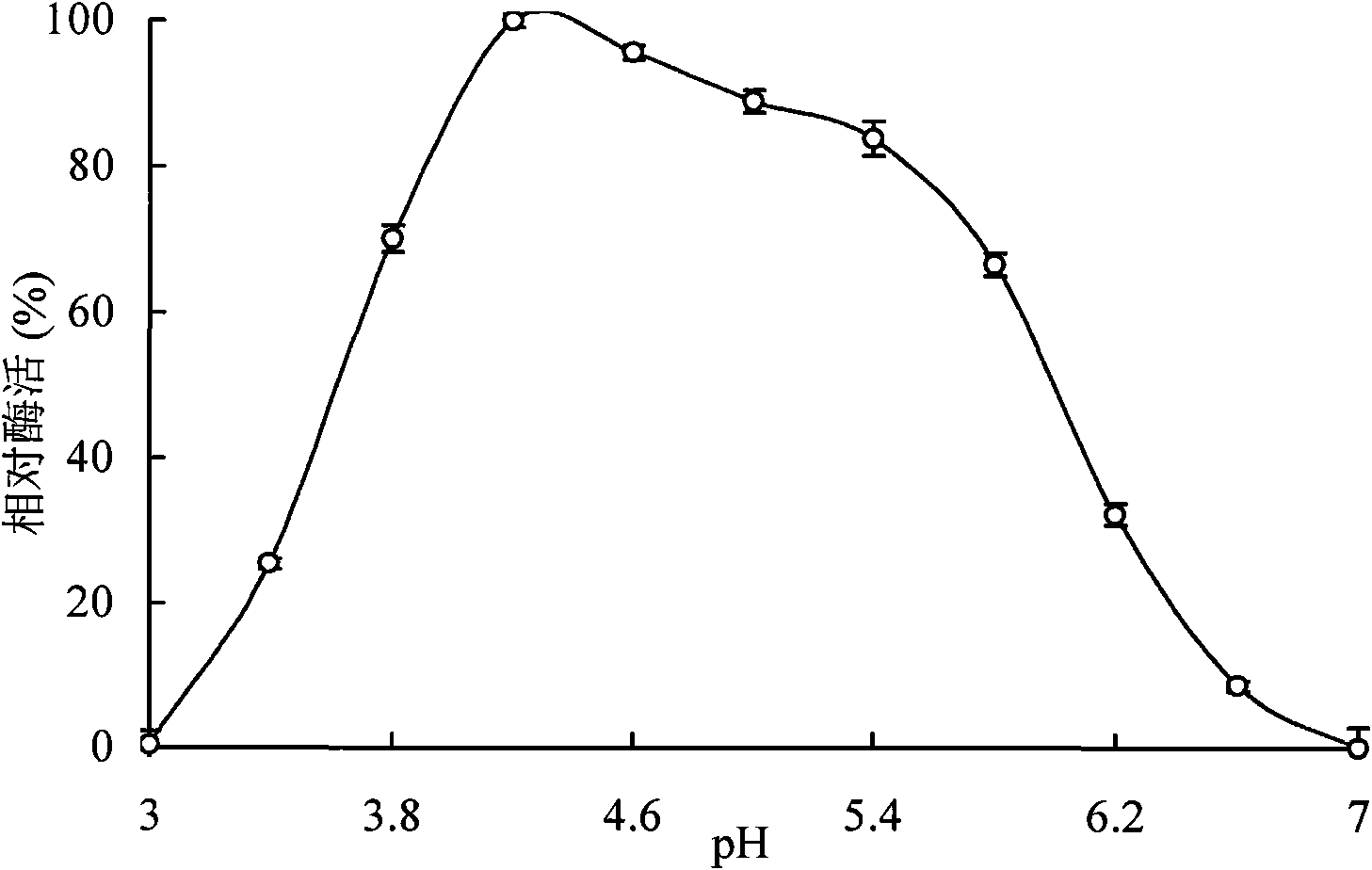
Acid amylase AMYA4 and gene and application thereof
The invention relates to the field of gene engineering, in particular to acid amylase AMYA4 and gene and application thereof. The amino acid sequence of the acid amylase AMYA4 is expressed as SEQ ID NO.1. The optimal pH value of the AmyA4 is 4.2, the optimal temperature is 75 DEG C, and the AmyA4 has high activity at the temperature of between 55 and 75 DEG C and has strong raw starch degrading capability at the same time. The zymology properties meet the process requirement for preparing sugar by a double-enzyme method, so the acid amylase has great application potential. In the process for preparing sugar by simulating the double-enzyme method, no matter paste starch or raw starch is used as a substrate, the starch can reach good hydrolysis rate under the action of matching commercial saccharifying enzyme, so the AmyA4 has huge application potential.
Owner:INST OF ANIMAL SCI OF CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
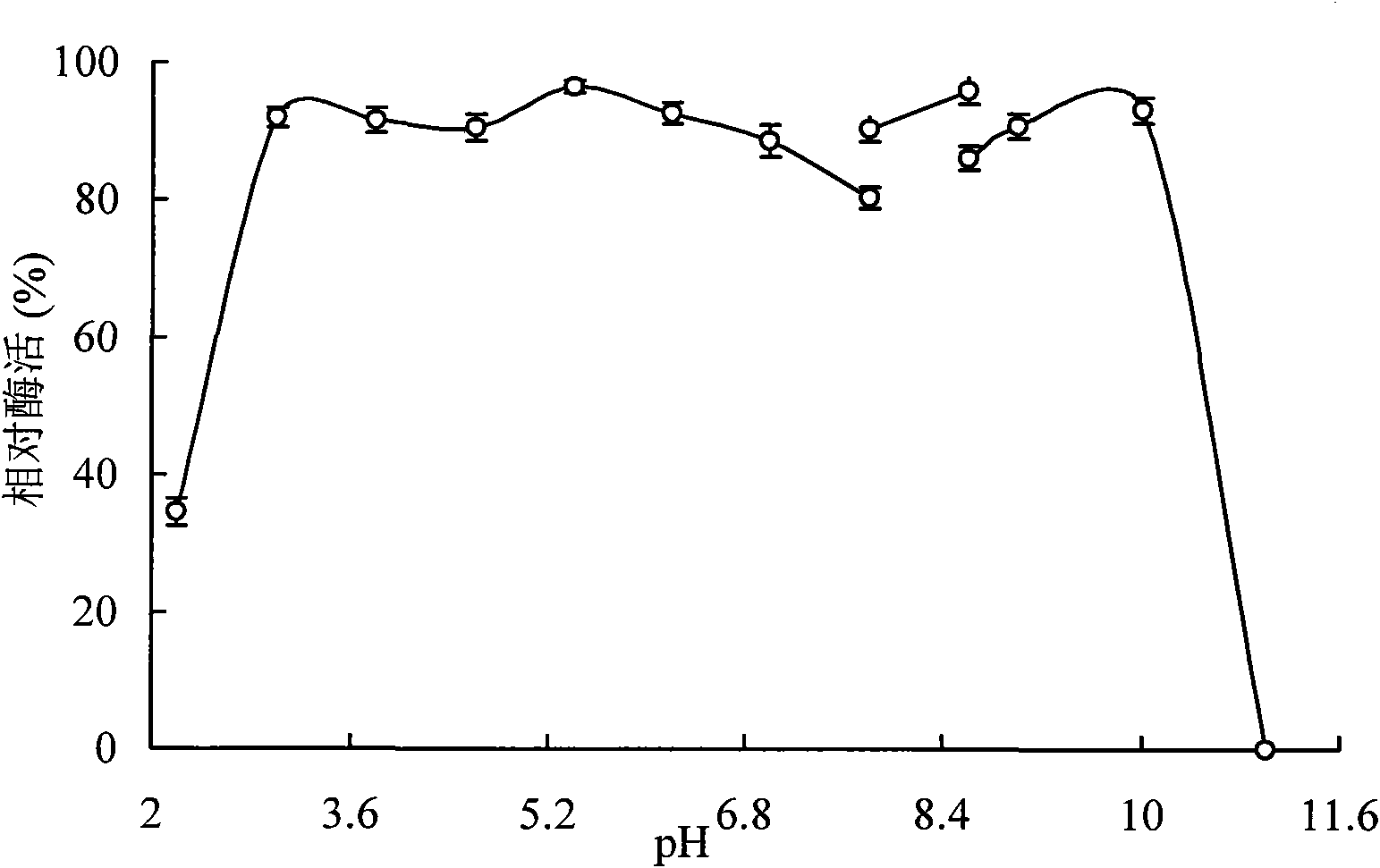
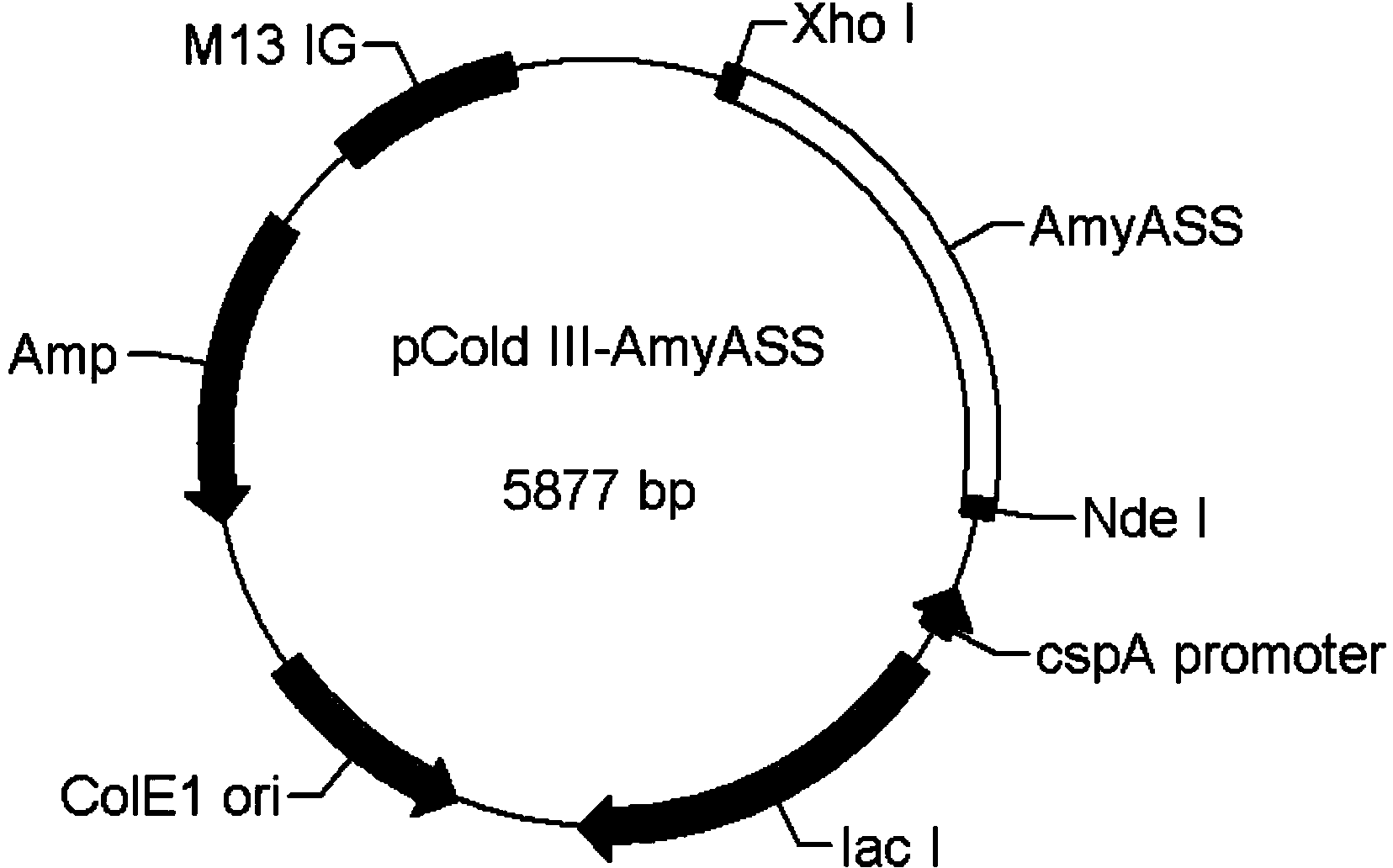
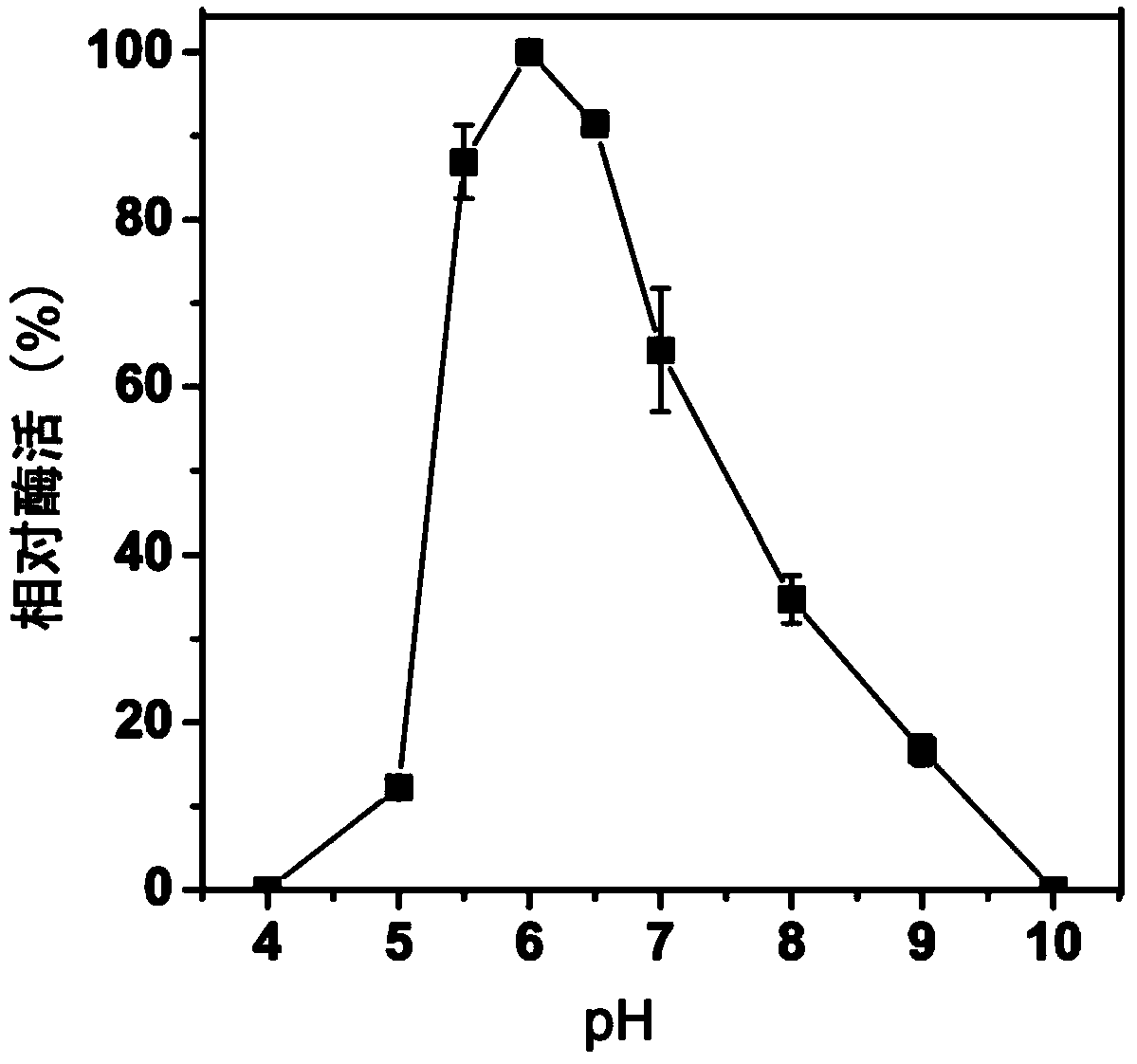
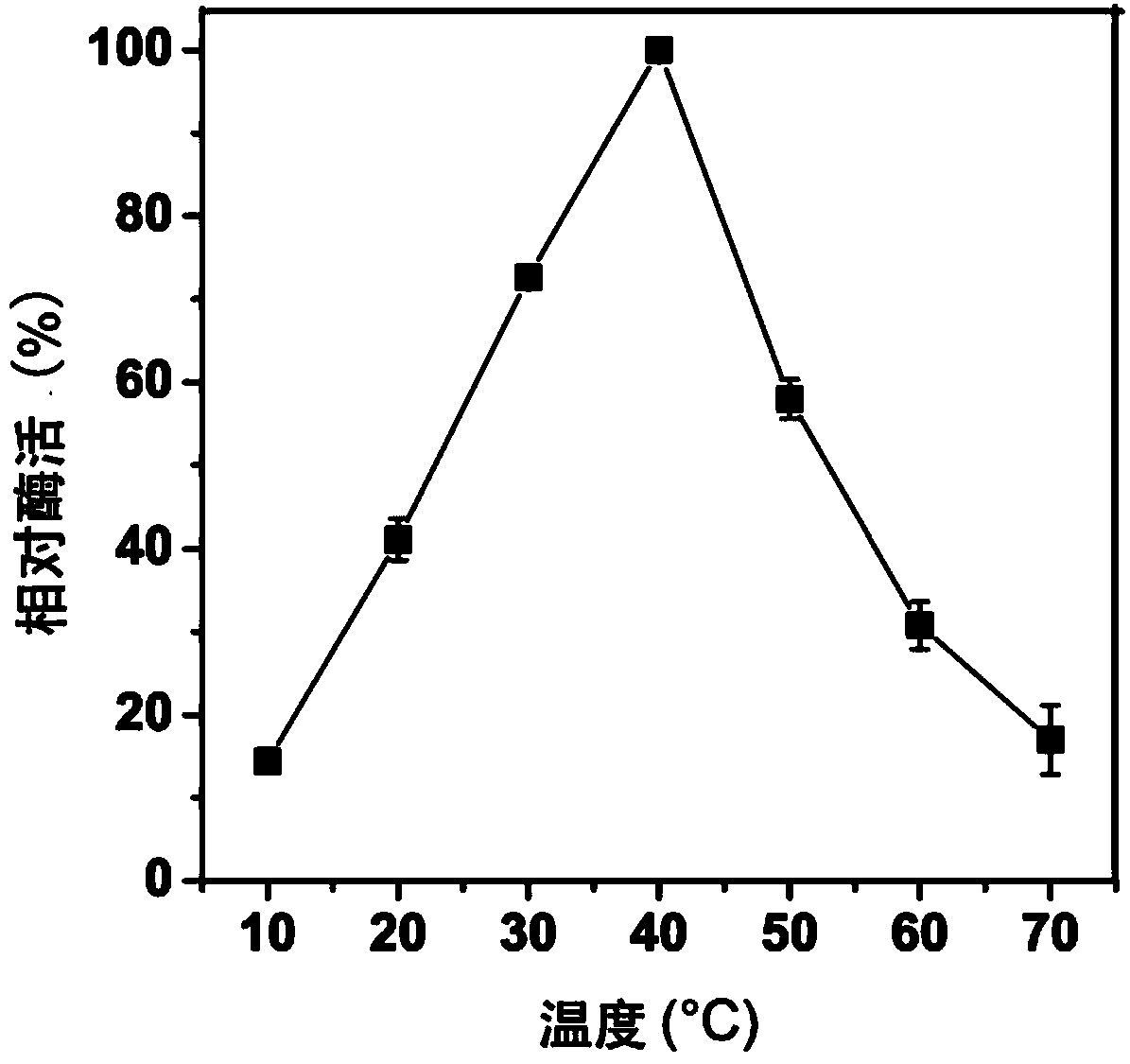
Alpha-amylase Amy ASS and application of alpha-amylase Amy Ass in raw starch degradation
The invention discloses alpha-amylase. A gene sequence of the amylase is shown in SEQ ID NO:2; an amino acid sequence encoded by the gene sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO:1; the gene sequence SEQ ID NO:2 can successfully express the alpha-amylase in an inclusion body form in escherichia coli. By adopting the alpha-amylase obtained by the inclusion body renaturation operation disclosed by the invention, the protein purity can be up to over 85%, and the renaturation rate can be up to over 50%. The alpha-amylase disclosed by the invention can be applied to rapid degradation of raw starch, and is especially applicable to degradation of rice raw starch.
Owner:ANHUI UNIVERSITY
Sugar-producing and texture-improving bakery methods and products formed therefrom
InactiveUS20160007618A1Function increaseImprove performanceMilk preparationDough treatmentAlgluceraseAdded sugar
Novel yeast-raised and other bakery products and methods of making those products are provided. The products are formed from dough comprising a thermally-stable amyloglucosidase, and a raw starch degrading amyloglucosidase and / or an anti-staling amylase. The level of added sugar included in the dough can be substantially reduced, and even eliminated, while still achieving a sweet product. Additionally, the resulting bakery product is free of, or at least substantially free of, fructose. The final baked product will also have improved texture properties, including superior firmness, resilience, and adhesiveness and can be made with a reduced amount of yeast.
Owner:CARAVAN INGREDIENTS
Methods for increasing starch content in plant cobs
InactiveUS20120054915A1High in starchImprove the level ofSugar derivativesBiofuelsFree sugarTransgene
Methods and compositions for increasing the starch content in cob tissues of a plant are provided. The method comprises down-regulating the activity of starch degradation enzymes in a plant. The resulting transgenic plants of the invention have increased starch content in cob tissues. In one embodiment the method involves manipulating a monocot plant to down-regulate the activity of a starch degradation enzyme in cob tissues. The plants are useful for improving the yield of free sugars from plant biomass.
Owner:SYNGENTA PARTICIPATIONS AG
Plants with modified starch metabolism
InactiveCN101970668AExpand production potentialImprove digestibilityTransferasesPlant peptidesSucroseSaccharum
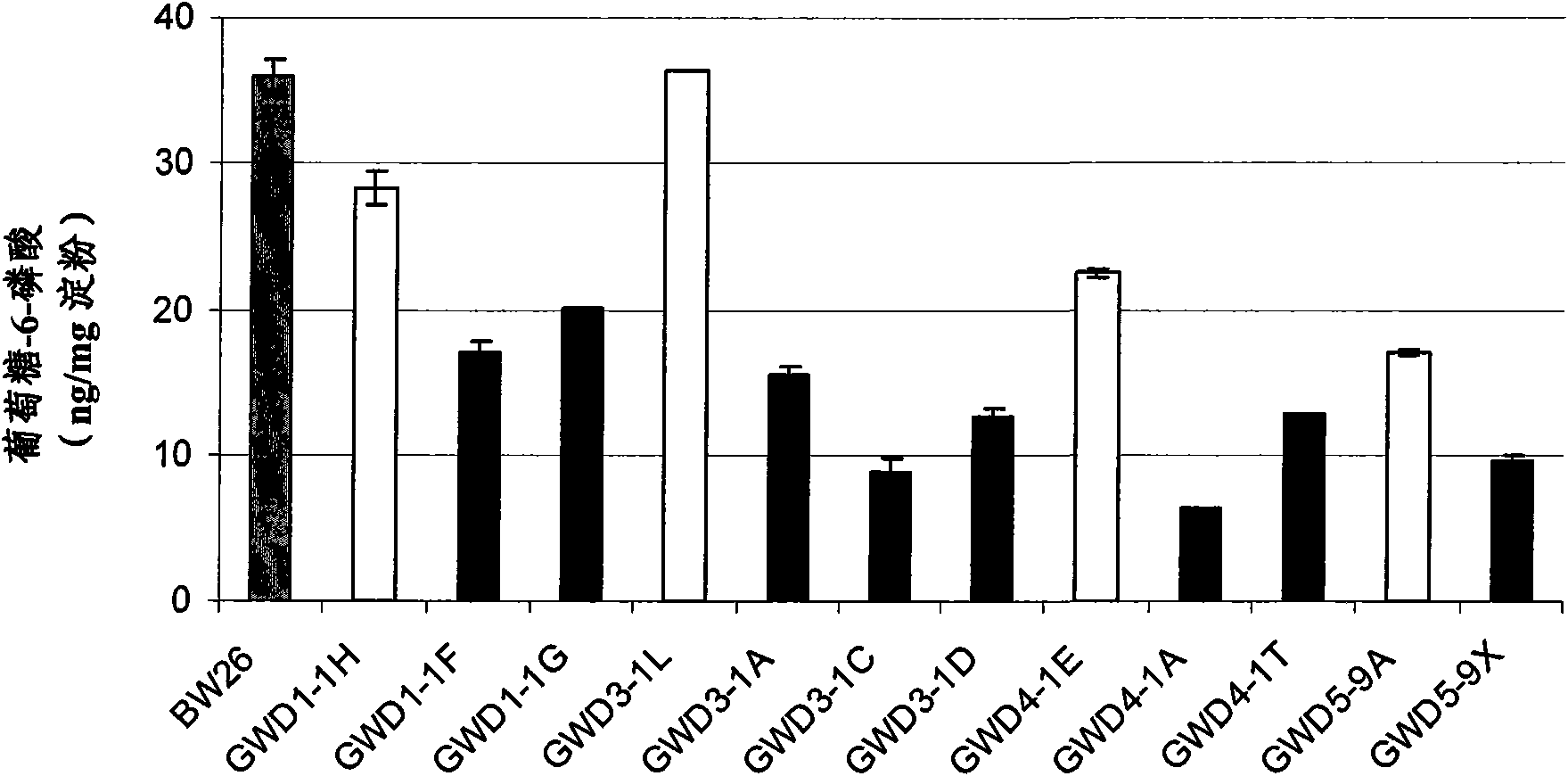
The specification provides methods of obtaining a genetically modified plant which has increased production potential compared to a control plant, the method comprising the steps of i) obtaining a plurality of plants at least one of which comprises in its genome a heterologous polynucleotide, ii) identifying from the plurality of plants a plant which has increased production potential relative to the control plant and comprises the heterologous polynucleotide, and iii) selecting the genetically modified plant, wherein the polynucleotide comprises a transcriptional control sequence operably linked to a nucleic acid sequence which encodes an agent that modifies endogenous starch phosphorylation and / or starch degradation in the plant. In some embodiments, the plant has increased endogenous glycosylase or increased digestibility compared to a control plant. In some specific embodiments, the endogenous starch phosphorylation and / or starch degradation is modified by modifying expression or activity of one or more enzymes selected from the group consisting of alpha-amylase (EC 3.2.1.1), beta-amylase (EC 3.2.1.2), glucoamylase (EC 3.2.1.3), starch phosphorylase (EC2.4.1.1), glycosylase (EC 3.1.33), sucrase-isomaltase (EC 3.2.10), amylomaltase (EC 2.4.1.25), maltase (EC 3.2.1.20), isoamylase, and a-glucan, water dikinase (GWD, EC 2.7.9.4).
Owner:COMMONWEALTH SCI & IND RES ORG +1
Method for squeezing auxiliary materials of enzyme added beer, processing installation, and saccharification method
InactiveCN101050406ACompletely degradedHigh reducing sugar contentWort preparationStarch degradationEnzyme
This invention discloses processing method, processing apparatus and saccharification method for beer adjunct added with enzyme preparation by squeezing and cooking. This invention provides squeezing and cooking apparatus for adding enzyme preparation to beer adjunct, reasonable parameters of squeezing and cooking system for adding enzyme preparation to beer adjunct, and saccharification method for beer adjunct added with enzyme preparation. During the saccharification process, the mash of beer adjunct added with enzyme preparation has such advantages as adequate starch degradation, short saccharification time, and high extract yield. Compared with the present double-mash saccharification method and enzyme addition saccharification method, the method in this invention omits beer adjunct cooking and pasting process and apparatus, and adds malt powder and beer adjunct powder or mince added with enzyme preparation into the water in the saccharification pot simultaneously for saccharification, which can save energy, lower cost, and increase beer productivity.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV OF TECH
Polypeptides with starch debranching activity
Polypeptides comprising a catalytic starch debranching domain and a starch binding domain are disclosed. The polypeptides comprising the starch binding domain have an improved functionality in raw starch degradation compared with same catalytic unit in same amount but without the starch binding domain.
Owner:NOVOZYMES INC
Methods for increasing starch content in plant cobs
InactiveCN102405291AHigh in starchIncrease valueBiofuelsOther foreign material introduction processesFree sugarTransgene
Methods and compositions for increasing the starch content in green tissues of a plant are provided. The method comprises down-regulating the activity of starch degradation enzymes in a plant. The resulting transgenic plants of the invention have increased starch content in green tissues and exhibit a starch excess phenotype. In one embodiment the method involves manipulating a monocot plant to down-regulate the activity of a starch degradation enzyme. The plants are useful for improving the yield of free sugars from plant biomass and increase dried green tissue storage stability.
Owner:SYNGENTA PARTICIPATIONS AG
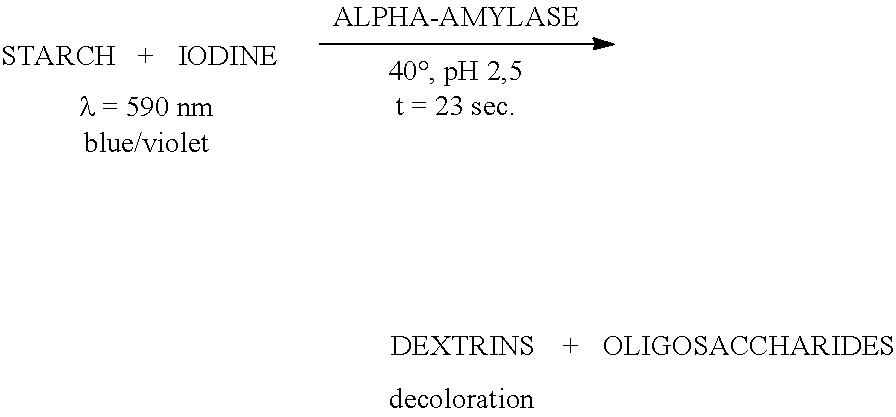
Enzymic starch catabolin and its preparing process
A process for preparing the starch catabolin by enzyme method includes such steps as adding cross-linking agent to raw starch, heating to gelatinizing temp, amorphous treating, and enzymic degrading under the action of microbes, medium-temp alpha-amylase, or high-temp alpha-amylase. Its advantages are simple equipment and condition, easy control and low cost and energy consumption.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Recombinant saccharomyces cerevisiae utilizing starch and secreting antibacterial peptide
InactiveCN106591351AAchieve growthGrowth inhibitionFungiTransferrinsAlpha-amylaseAntibacterial peptide secretion
The invention discloses a recombinant saccharomyces cerevisiae utilizing starch and secreting antibacterial peptide. The recombinant saccharomyces cerevisiae contains a multigene coexpression vector capable of utilizing starch and secreting antibacterial peptide. The vector contains an alpha-amylase gene, a glucoamylase gene and an antibacterial peptide gene. During expression of the antibacterial peptide gene, the recombinant saccharomyces cerevisiae plays a synergistic role of starch degradation through coexpression of amylase and glucoamylase in starch degradation enzyme, thus realizing degrading utilization of starch matrix by recombinant bacteria to reach thallus growth, ethanol production or antibacterial peptide secretion, etc. Therefore, the recombinant yeast constructed by the invention can be utilized to realize starch degradation utilization, yeast thallus growth, alcohol conversion, sundry bacteria growth inhibition and other purposes synchronously in starch matrix based feed adding, industrial alcohol production and kitchen waste degradation.
Owner:SHANDONG YISHENG LIVESTOCK & POULTRY BREEDING CO LTD +1
Composite microbial agent and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN111849829AImprove stress resistanceIncrease productionBiocidePlant growth regulatorsContinuous croppingBacillus licheniformis
The invention discloses a composite microbial agent and a preparation method and application thereof. The composite microbial agent is prepared by uniformly mixing a cellulose decomposition strain, alignin decomposition strain, protein and a starch degradation strain, wherein the cellulose decomposition strain is one or more of ginseng bacillus, bacillus megatherium and bacillus aryabhattai, thelignin decomposition strain is Klebsiella, and the protein and starch degradation strains are one or more of bacillus thuringiensis, lysine borate bacillus, bacillus licheniformis and bacillus acidophilus. According to the invention, the microbial agent is selected to prevent and treat greenhouse vegetable continuous cropping obstacles, and related functional microorganisms are utilized to condition the nutritional status and microbial structure of the continuous cropping soil, so that the stress resistance of crops is improved, and the purpose of eliminating the continuous cropping obstaclescan be achieved.
Owner:陕西均良土壤环境技术有限责任公司
Lactobacillus plantarum with high yield of amylase and applications of lactobacillus plantarum
The invention discloses lactobacillus plantarum with high yield of amylase. The strain is lactobacillus plantarum, is preserved in the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center (CGMCC),and is assigned with the accession number of CGMCC No.14177, and the preservation date is May 19, 2017. The strain is separated from fermented old dough, is obtained through plate spreading, preliminary screening and secondary screening, and is identified through morphology, physiology and biochemistry and molecular biology. Culturing is carried out in an MRS culture medium (with the pH being 6) with 0.5% starch replacing 0.5% glucose for 21h at 31 DEG C, and the amylase activity of the fermented liquor is 15.89+ / -0.51 U / mL. The invention further discloses applications of the strain in solid fermentation of potato powder and applications of the strain in decomposition of starch. The strain can be used for fermentation of starchy raw materials including whole potato flour, and has the obvious degradation effect for starch.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Thermophilic acidic raw starch alpha-amylase mutant capable of improving cornstarch degradation capability as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN108823186APromote degradationSimple processBacteriaMicroorganism based processesAlpha-amylaseMutant
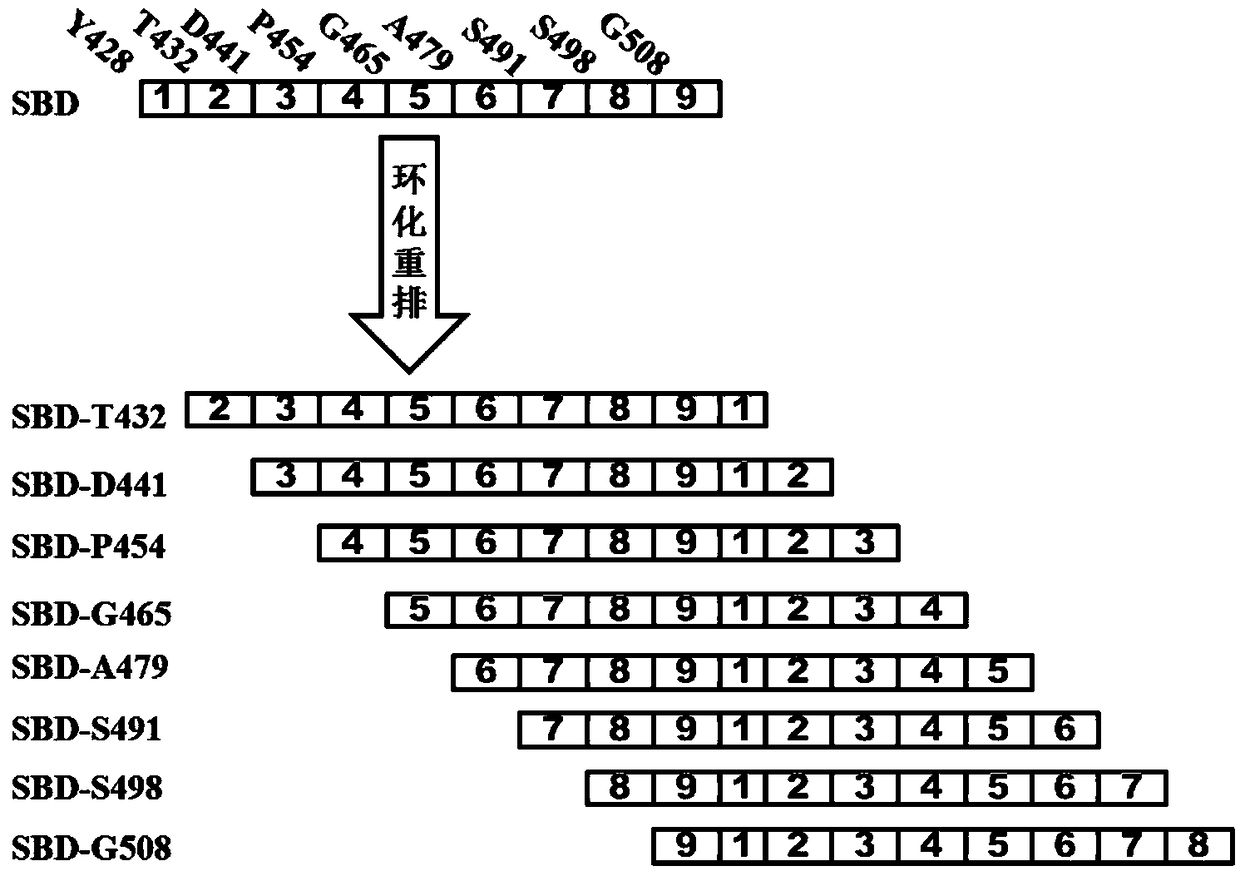
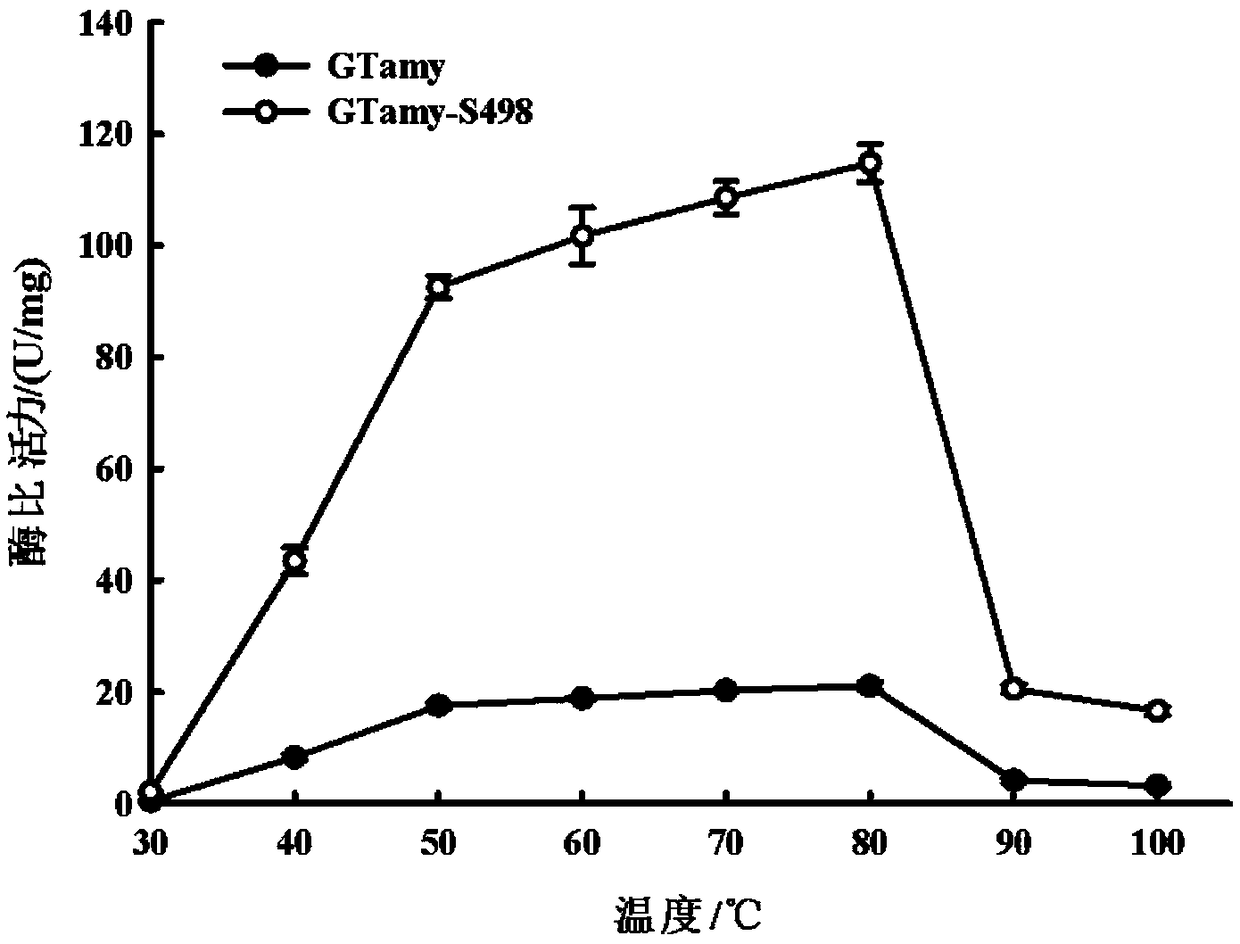
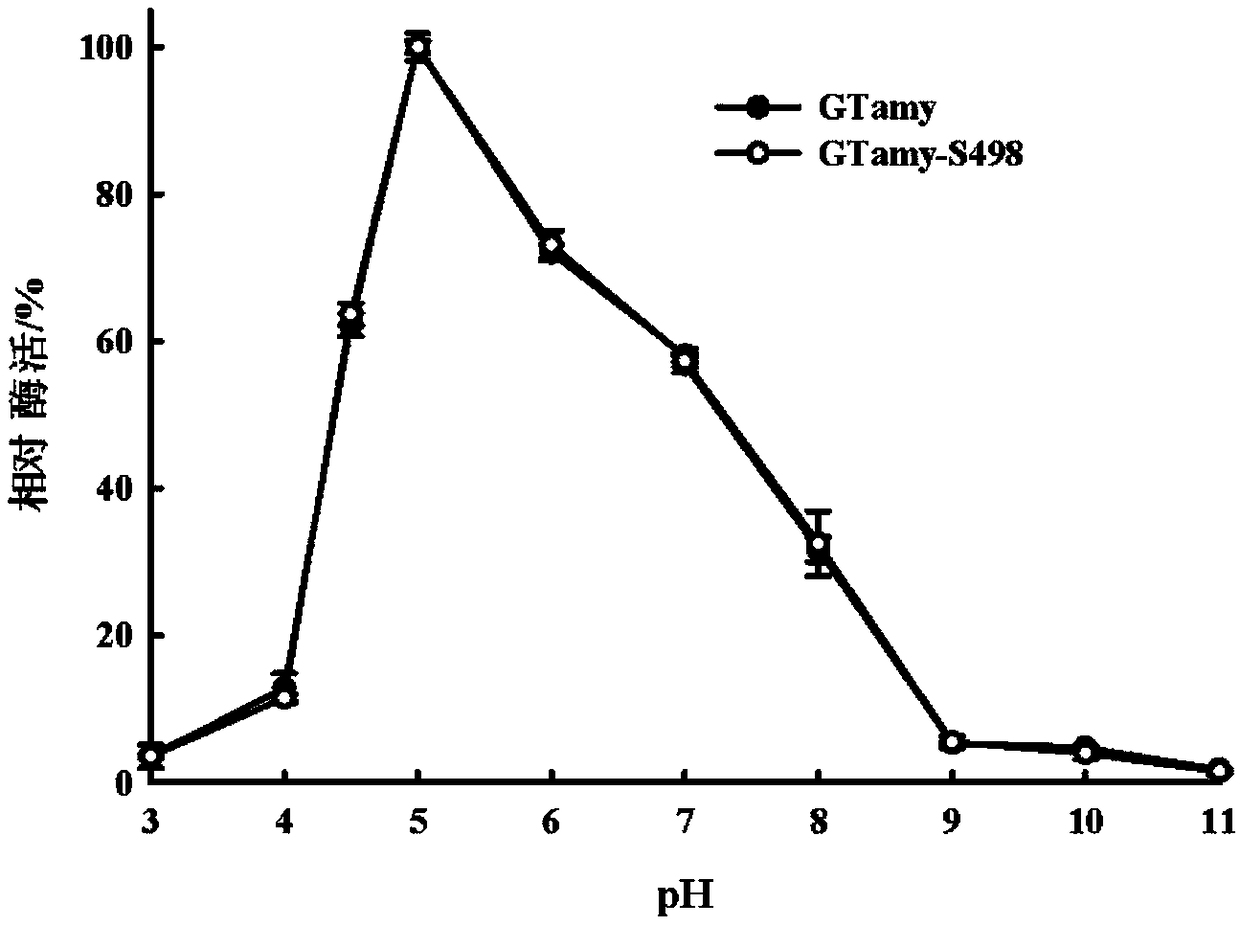
The invention discloses a thermophilic acidic raw starch alpha-amylase mutant capable of improving the cornstarch degradation capability as well as a preparation method and application thereof and belongs to the field of genetic engineering and enzyme engineering. According to the thermophilic acidic raw starch alpha-amylase mutant, an SBD structure domain of raw starch alpha-amylase GTamy is subjected to cyclic rearrangement mutation; then SBD in the GTamy is replaced with an SBD cyclic rearrangement mutant, so as to construct a GTamy cyclic rearrangement mutant. The enzyme activity of the GTamy cyclic rearrangement mutant to the cornstarch is compared to screen a raw starch alpha-amylase mutant GTamy-S498 with the cornstarch degradation capability which is remarkably improved. The enzymeactivity of the raw starch alpha-amylase mutant GTamy-S498 provided by the invention on the cornstarch is improved to 114.77 U / mg from 21.08 U / mg of a control group (before mutation) and is improvedby 5.44 times. The cornstarch degradation capability of the raw starch alpha-amylase mutant GTamy-S498 is remarkably improved and the enzymatic property meets the requirements of a starch liquefactiontechnology and is more suitable for the starch liquefaction technology.
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY JIANGXI ACADEMY OF SCI
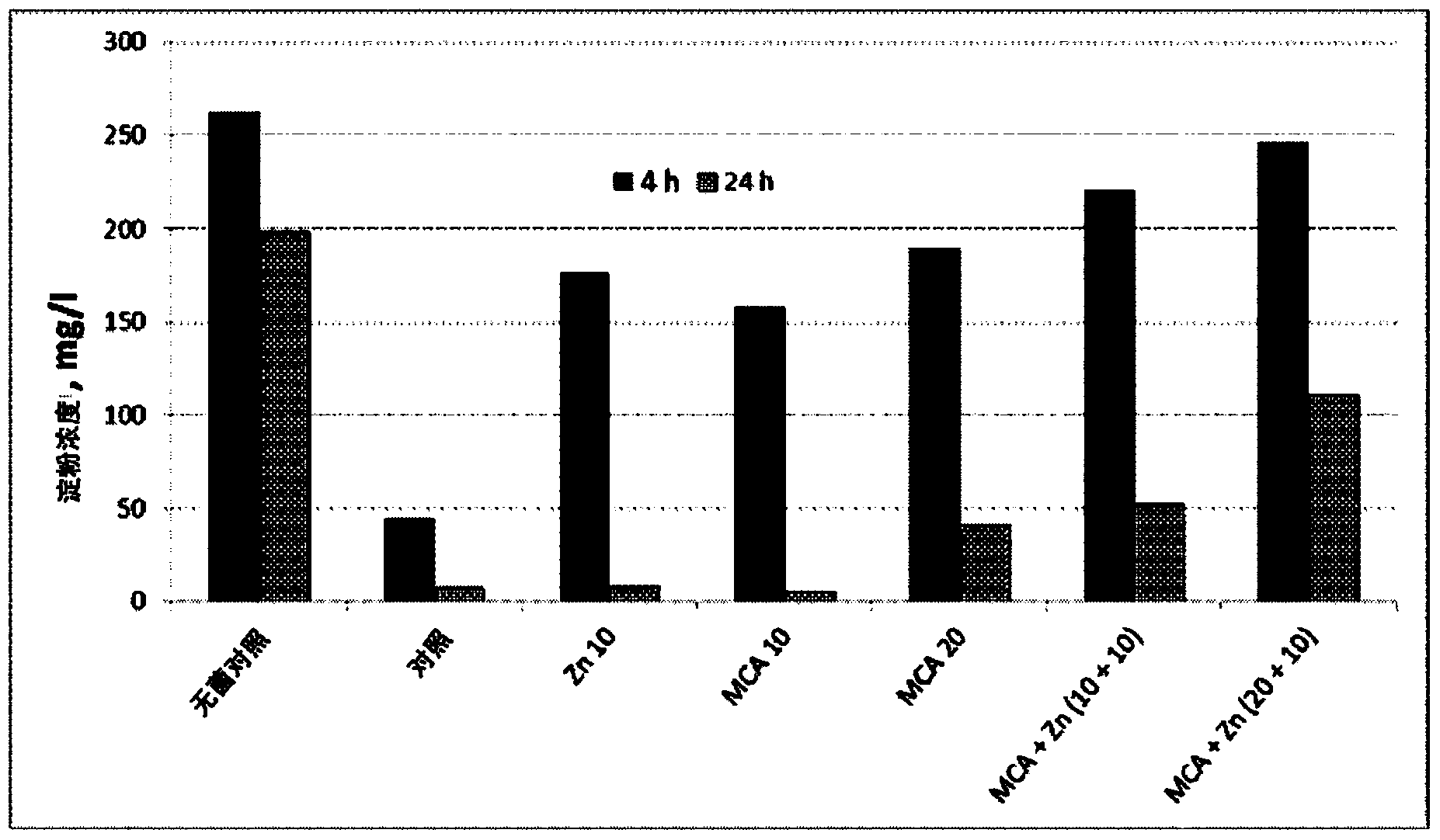
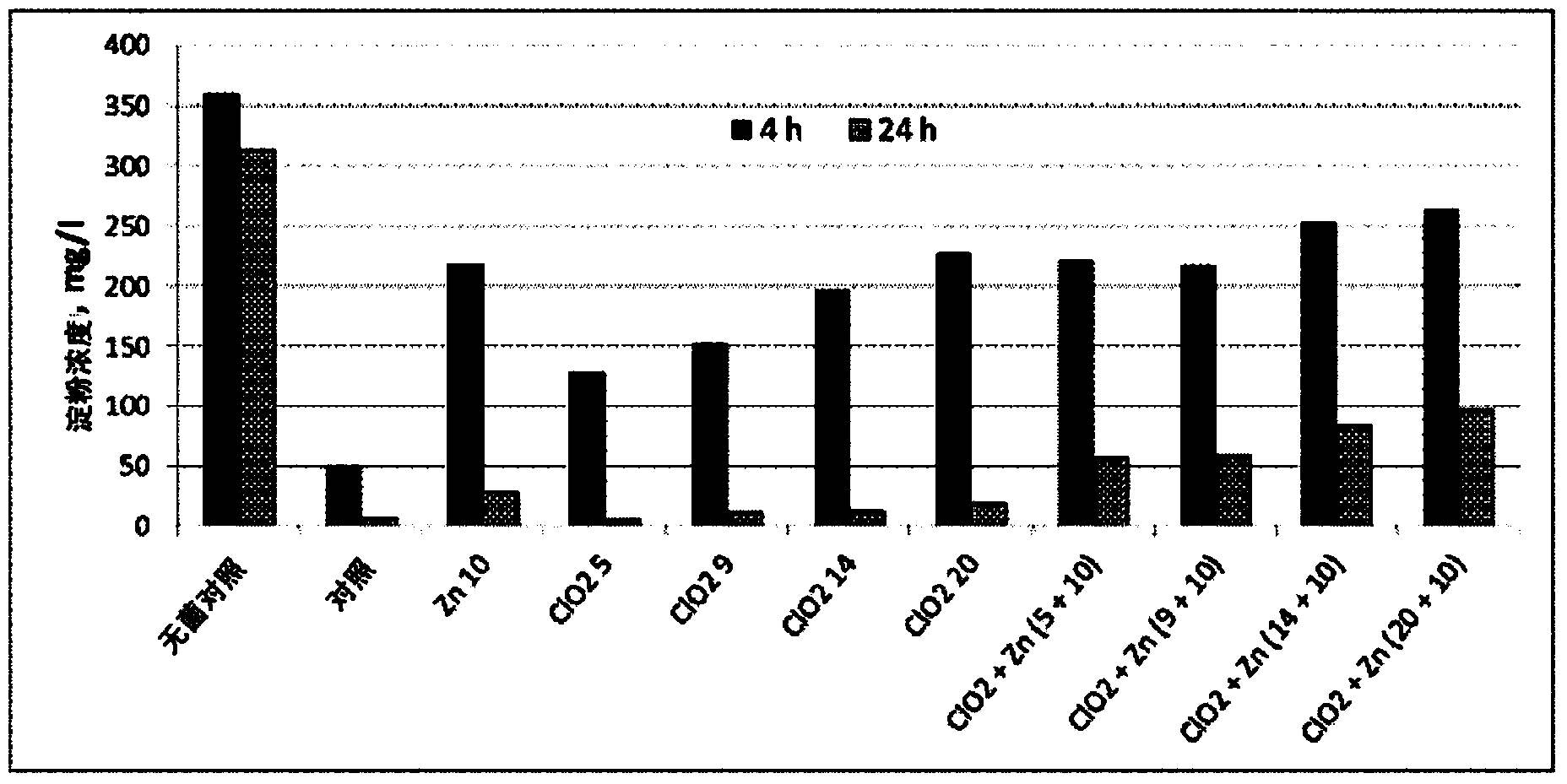
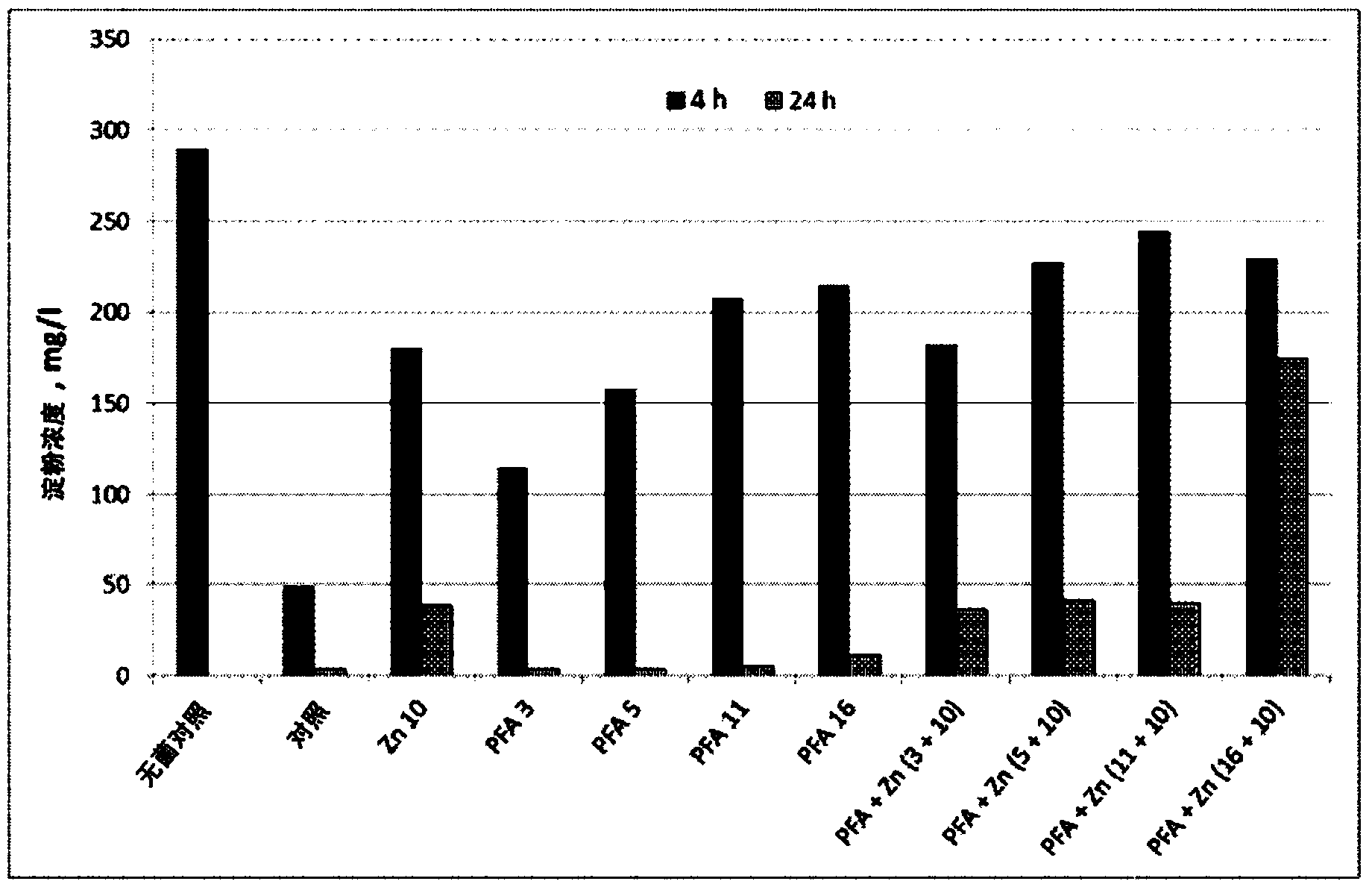
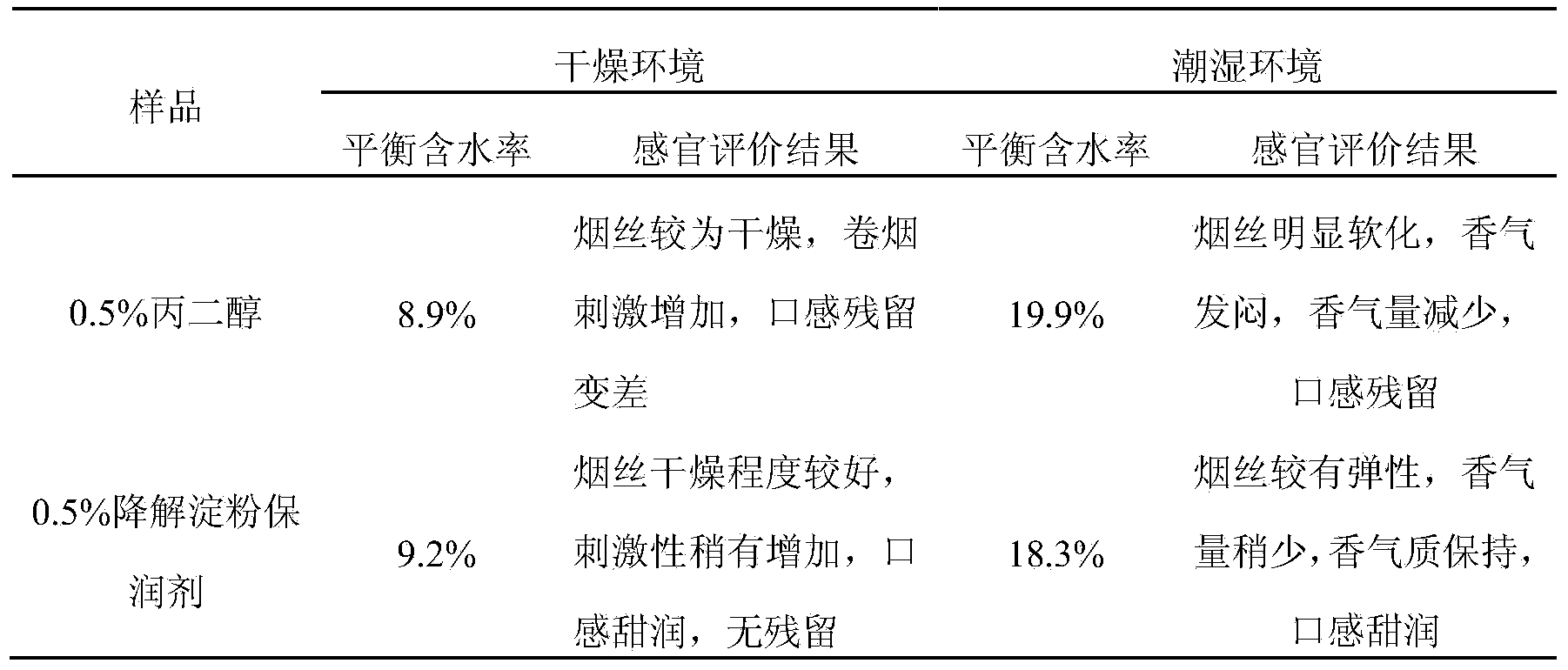
Preparation method of degraded starch tobacco humectant with mixed hydrolysis degrees
The invention discloses a preparation method of degraded starch tobacco humectant with mixed hydrolysis degrees. The preparation method comprises the following steps of (1) adding starch into water with 4-times mass, stirring and mixing the starch and water, heating the mixture to 70 to 100 DEG C, and maintaining the temperature for 1h to 2h so as to enable the starch to be adequately gelatinized; (2) adding hydrochloric acid solution, uniformly stirring, heating the mixture to 60 to 90 DEG C to be reacted for 0.5h to 5h, cooling the mixture, adding alkali to neutralize the excessive acid to be neutral to obtain a starch degradation product with different hydrolysis degrees; (3) compounding the short-time hydrolyzed starch, the appropriately-hydrolyzed starch and the long-time hydrolyzed starch according to a ratio to obtain the mixed degraded starch tobacco humectant. The prepared humectant is rich in polyol and good in moistening effect; by containing polysaccharide molecules of different sizes, the prepared humectant can be better affined with pores in different sizes on the surface of tobacco, the film forming property is good, and the moistening and dampproof effect can be better realized.
Owner:CHINA TOBACCO ANHUI IND CO LTD +1
Methods for increasing starch content in plant cobs
InactiveUS20140283215A1High in starchIncrease valueBiofuelsOther foreign material introduction processesFree sugarTransgene
Methods and compositions for increasing the starch content in cob tissues of a plant are provided. The method comprises down-regulating the activity of starch degradation enzymes in a plant. The resulting transgenic plants of the invention have increased starch content in cob tissues. In one embodiment the method involves manipulating a monocot plant to down-regulate the activity of a starch degradation enzyme in cob tissues. The plants are useful for improving the yield of free sugars from plant biomass.
Owner:SYNGENTA PARTICIPATIONS AG
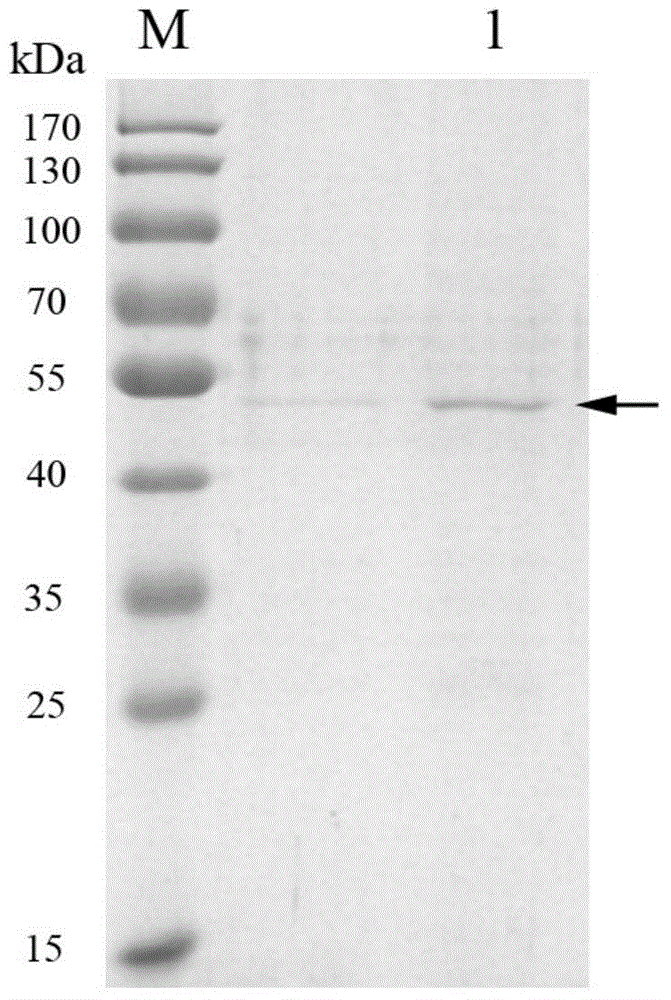
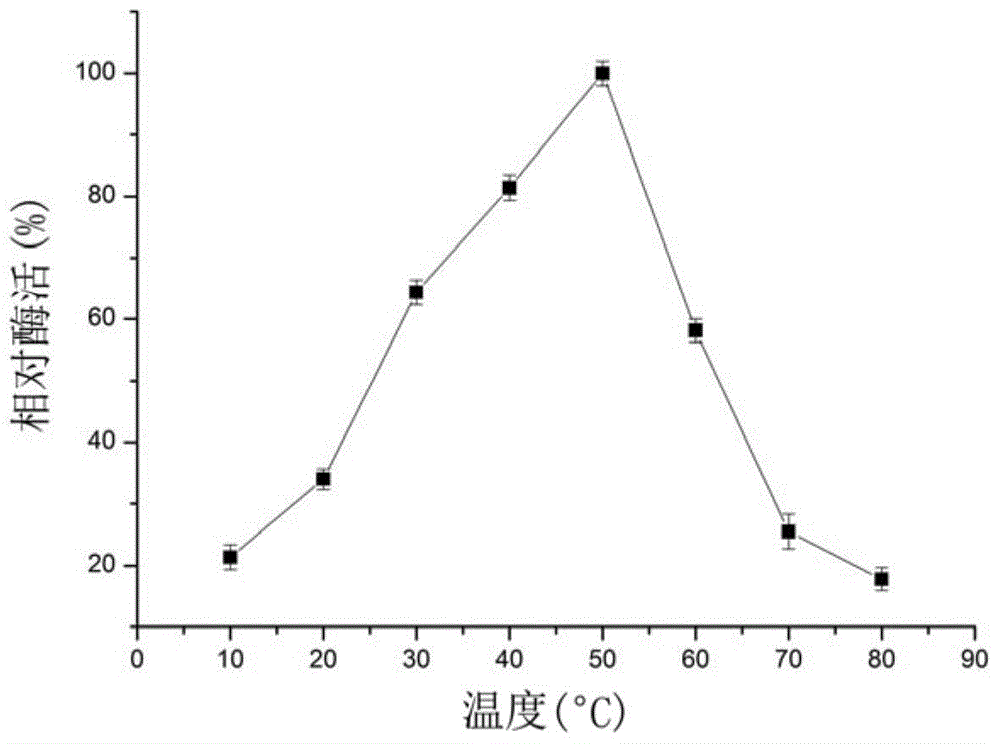
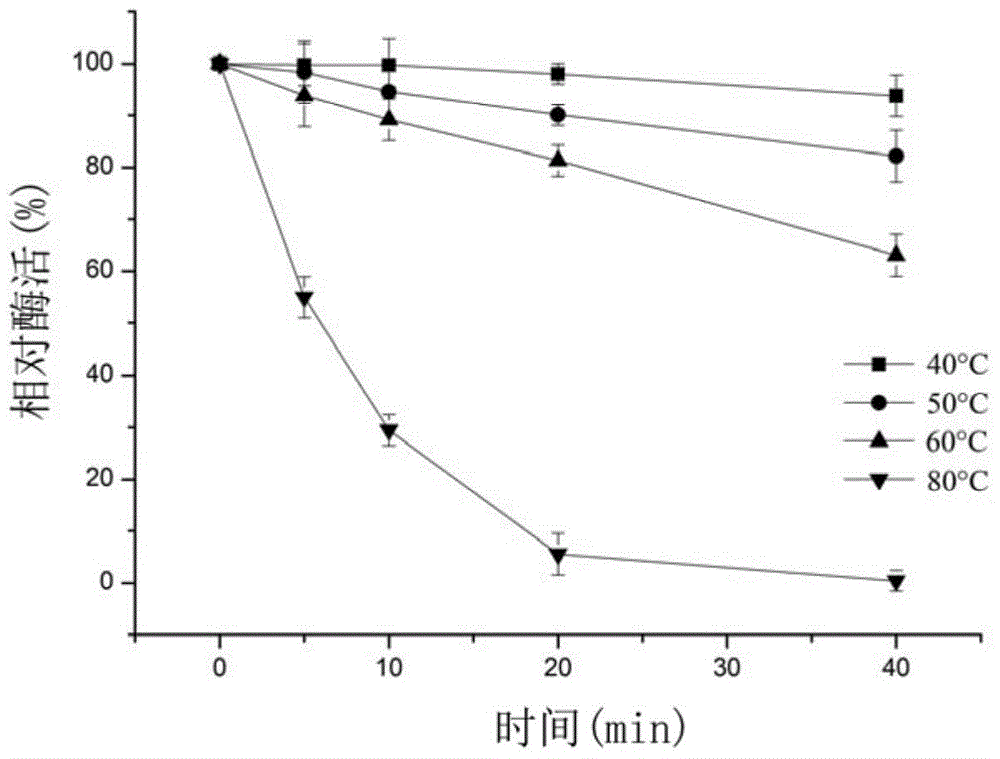
Alpha-amylase Amy16, as well as gene and application thereof
ActiveCN104560914AGuaranteed stabilityOvercome inactivation and other deficienciesBacteriaFermentationAlpha-amylaseFermentation
The invention discloses alpha-amylase Amy16, as well as a gene and application thereof, and relates to amylase. The alpha-amylase Amy16 is separated from flammeovirga pacifica H2. The alpha-amylase Amy16 is prepared by the following steps: cloning an alpha-amylase gene amy16, and inserting the alpha-amylase gene amy16 into an expression vector to construct a recombinant expression vector carrying the alpha-amylase gene amy16; converting the recombinant expression vector containing the alpha-amylase gene amy16 into Escherichia coli BL21, and selecting a positive clone in the converted Escherichia coli BL21 for fermentation cultivation in a culture medium; centrifugally collecting fermented Escherichia coli BL21 cells, resuspending the Escherichia coli BL21 cells in a lysis buffer for lysis, centrifuging the lysed suspension, and collecting supernatant; purifying the obtained supernatant to obtain the alpha-amylase Amy16. The alpha-amylase Amy16 can be applied to the preparation of a starch degradation agent.
Owner:THIRD INST OF OCEANOGRAPHY STATE OCEANIC ADMINISTATION
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com