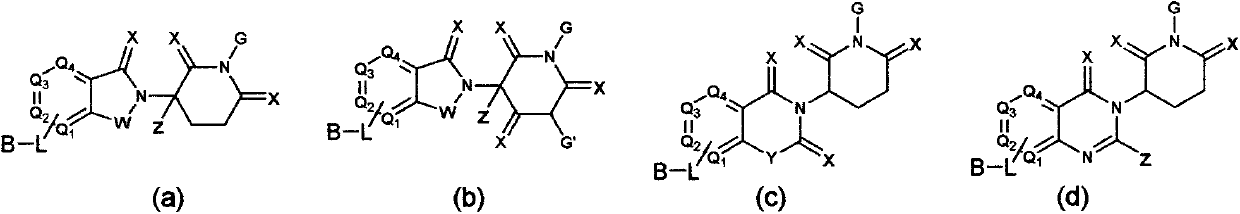
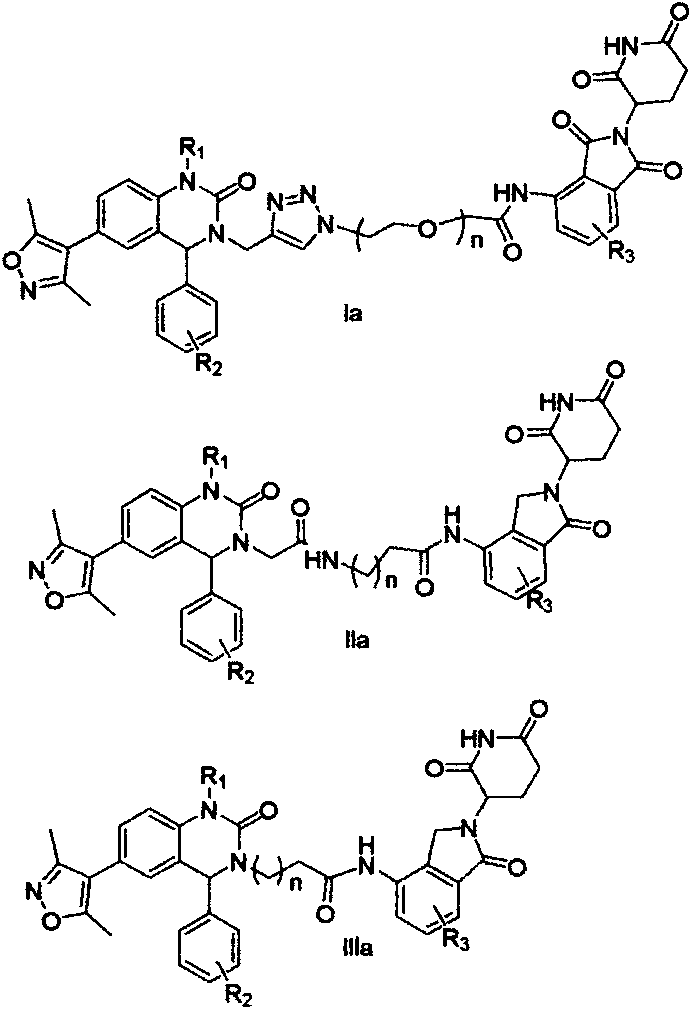
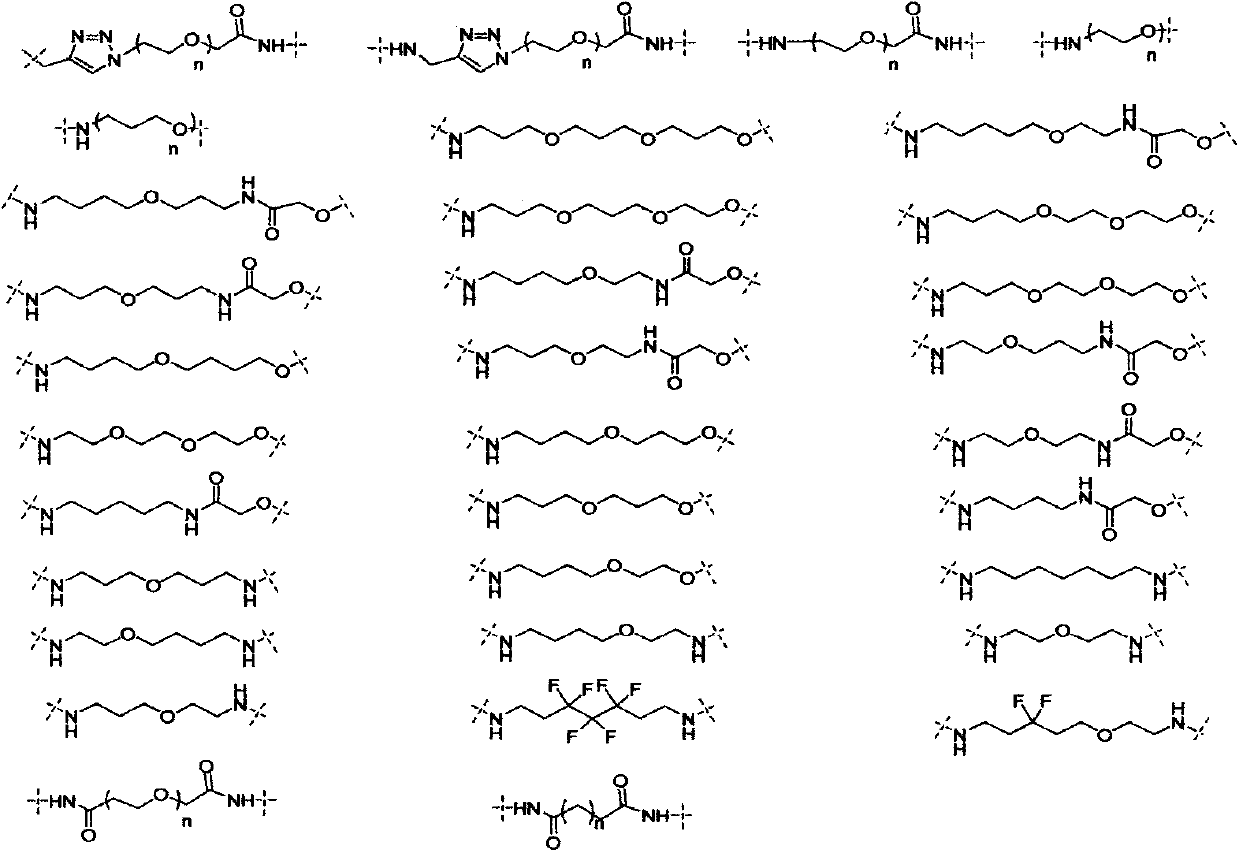
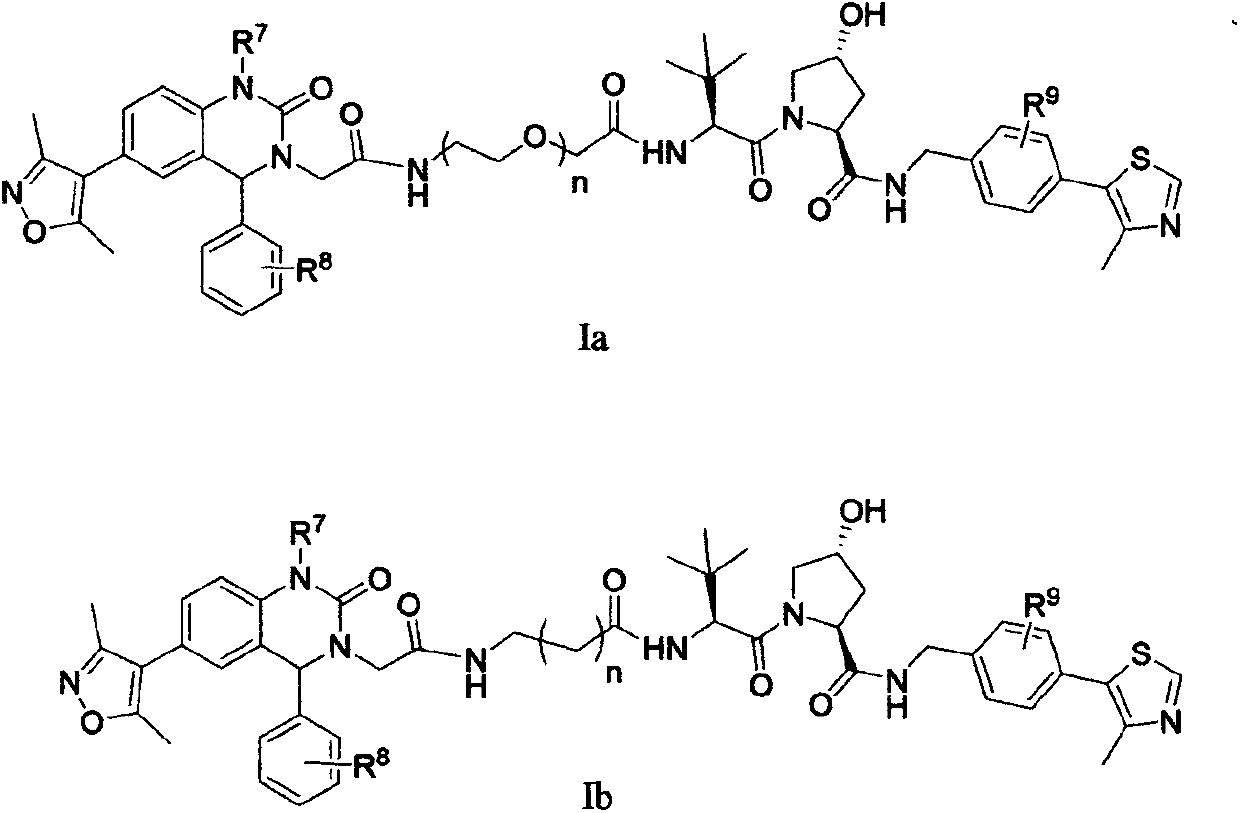
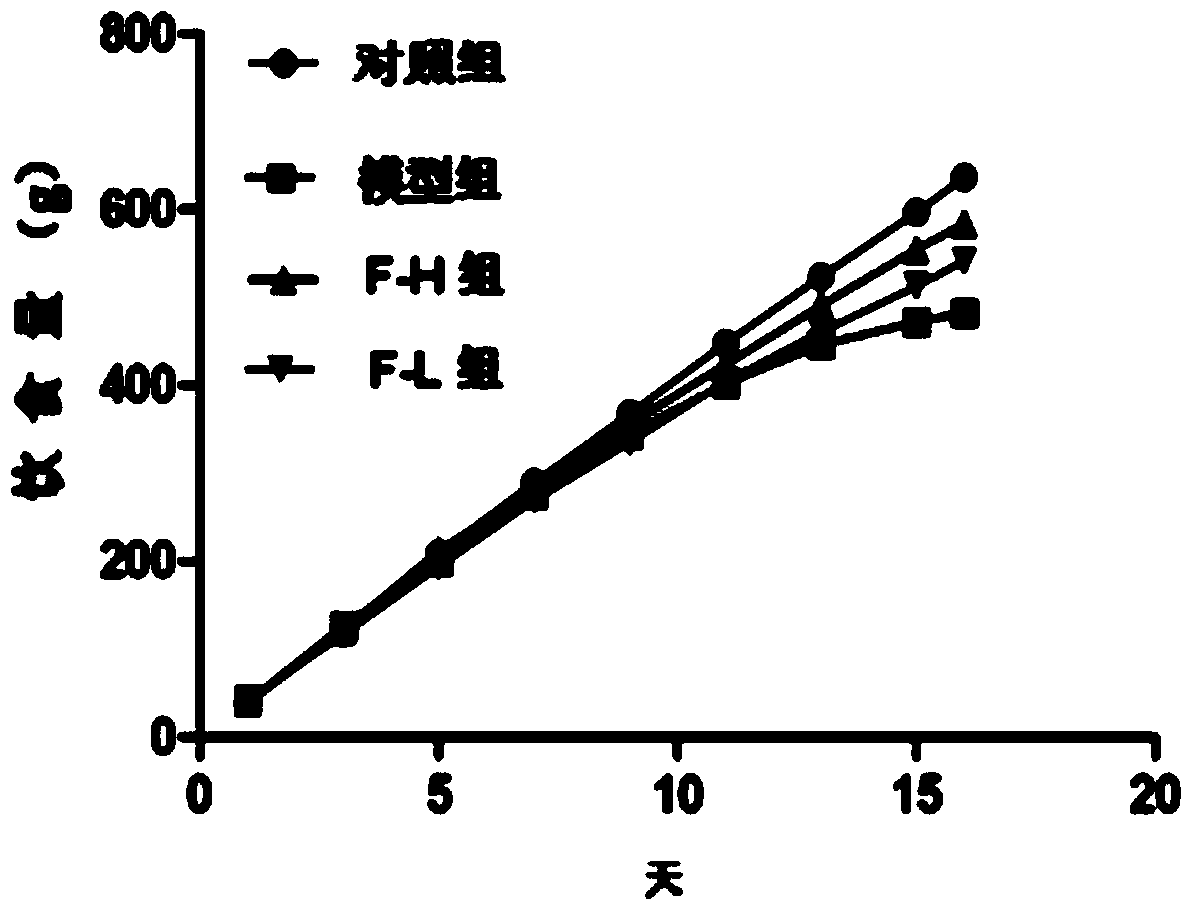
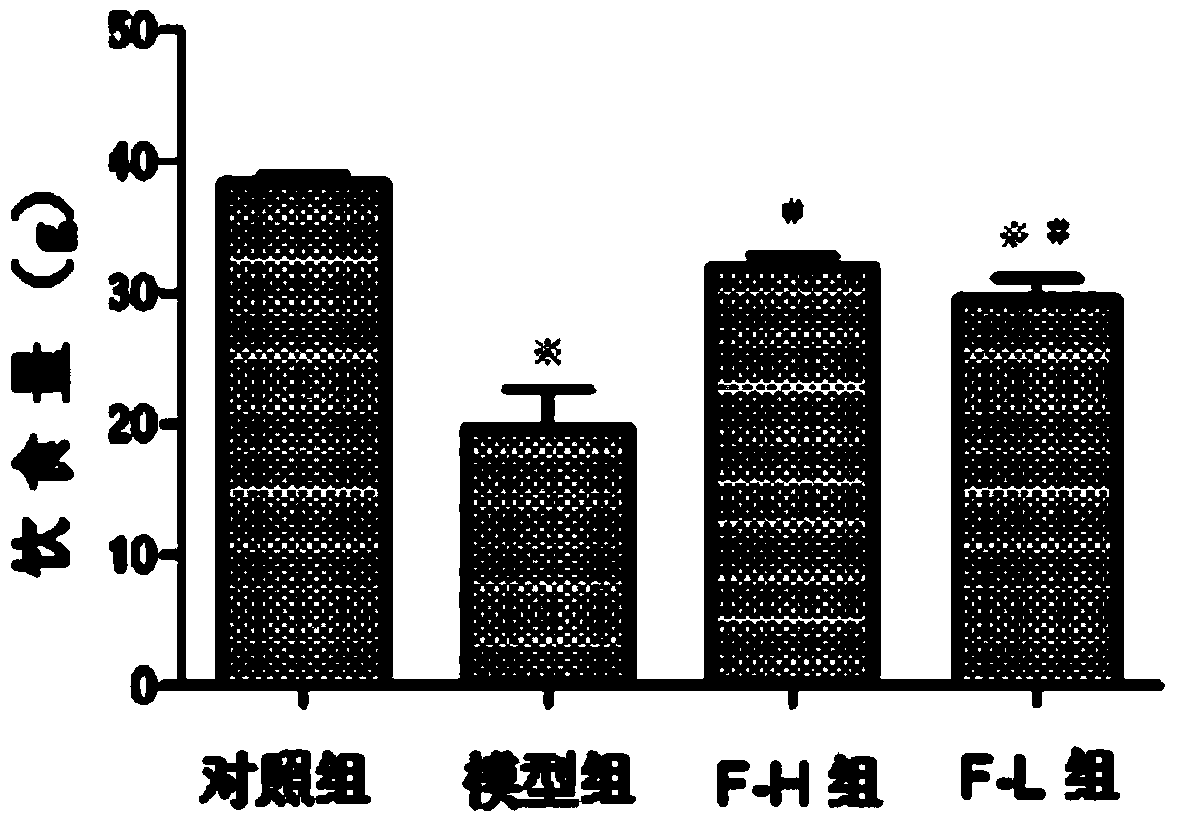
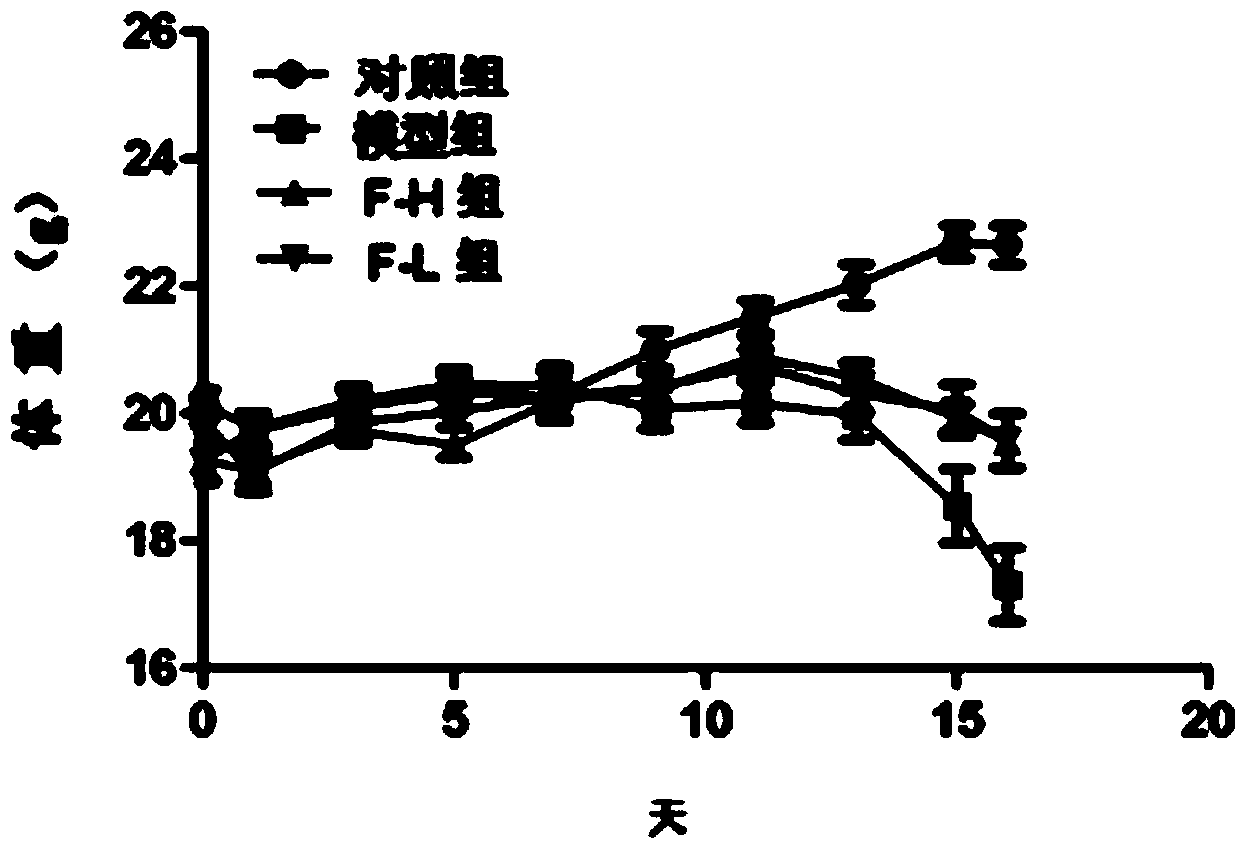
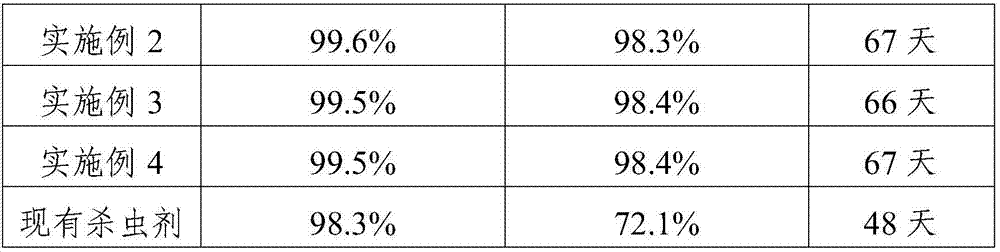
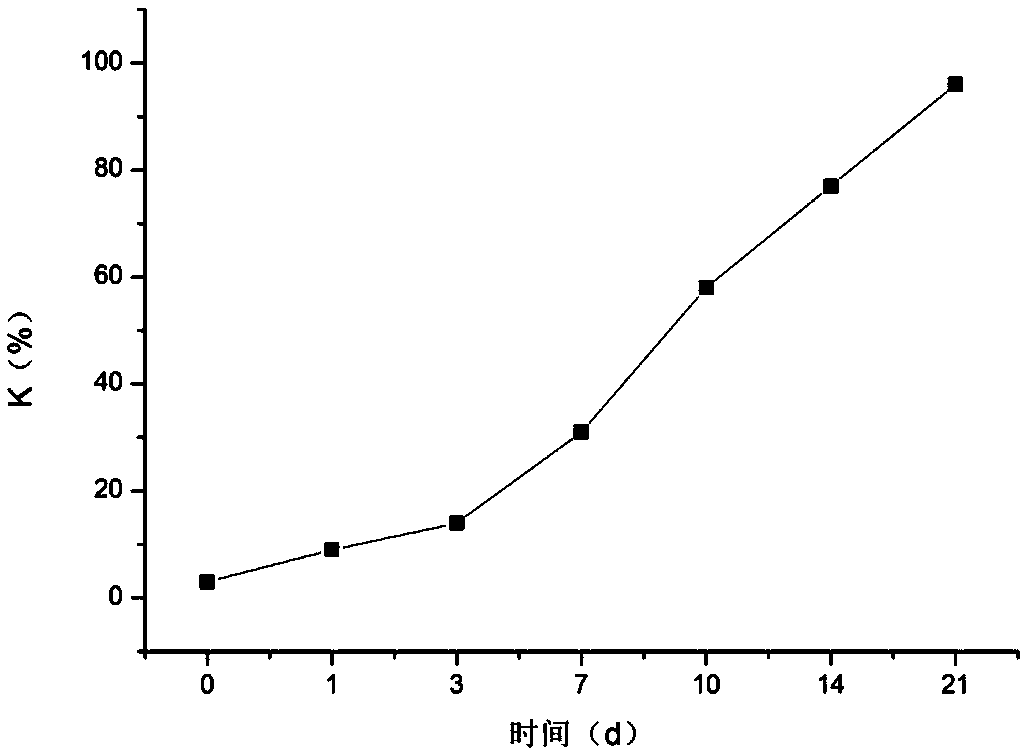
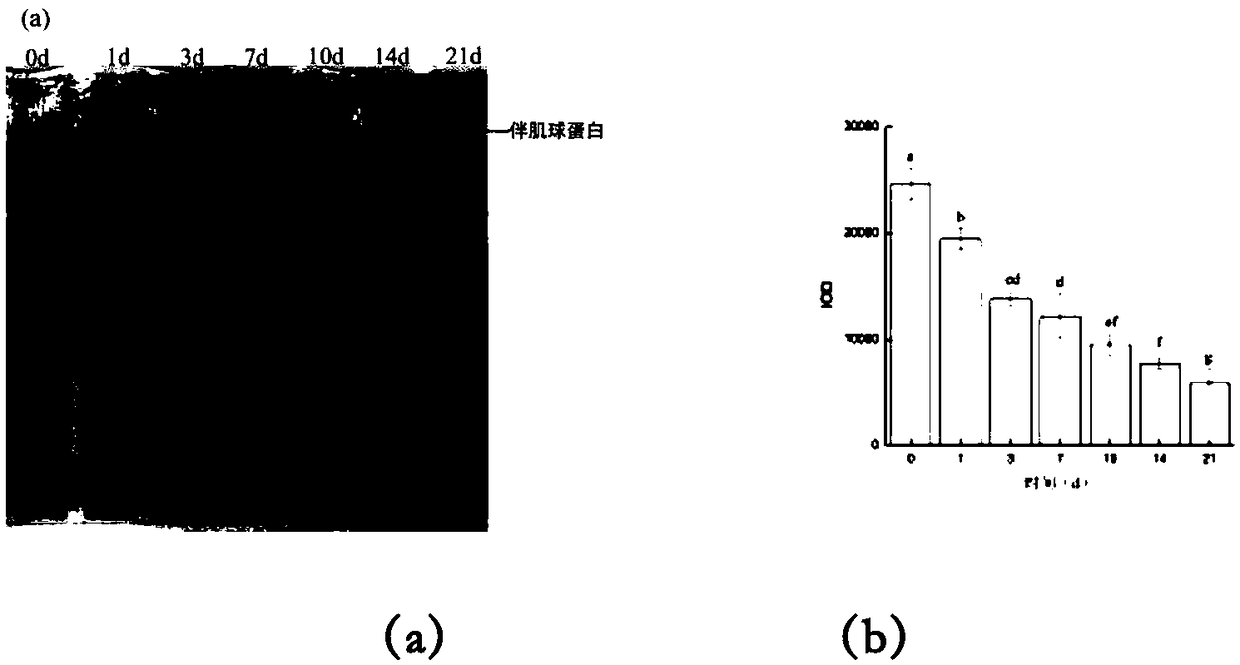
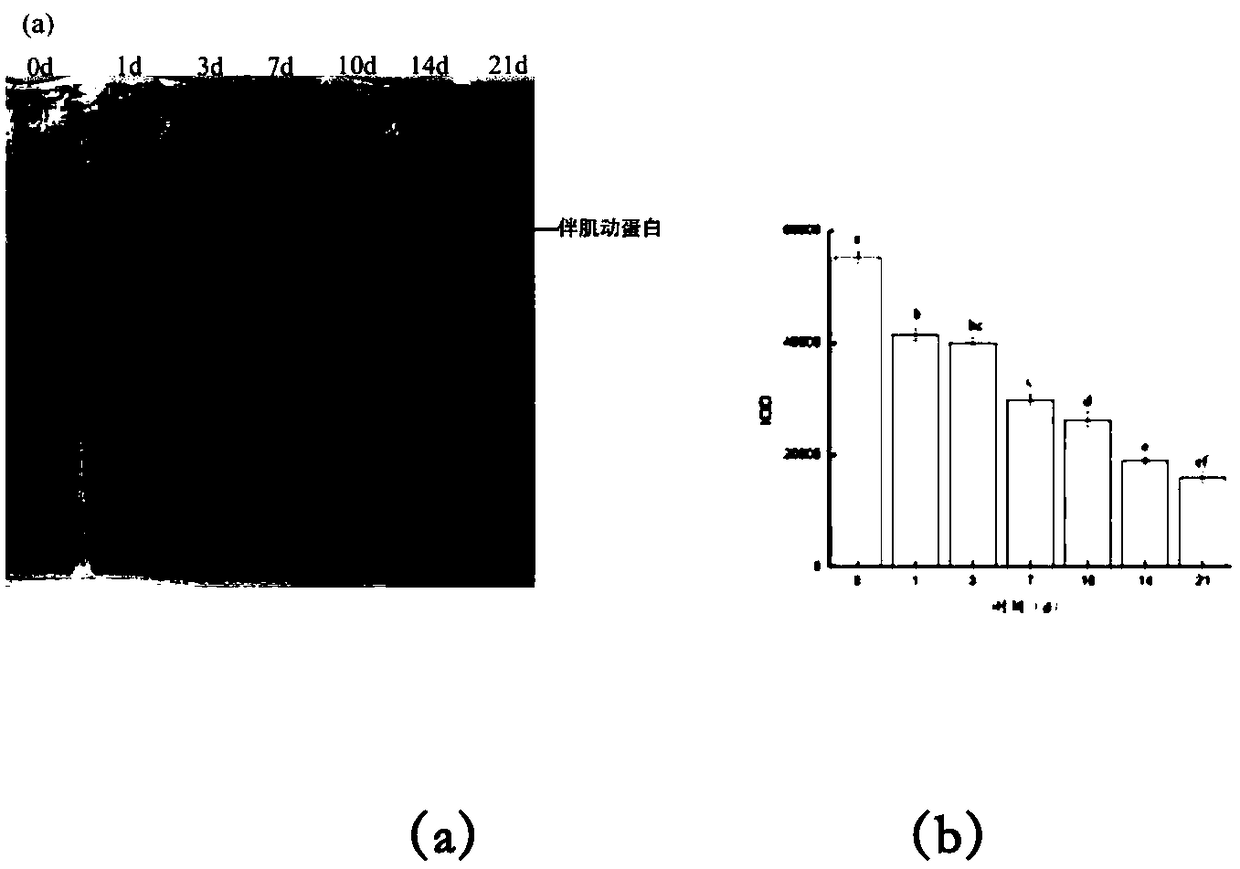
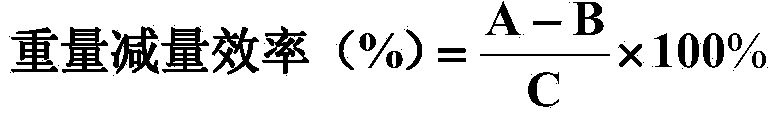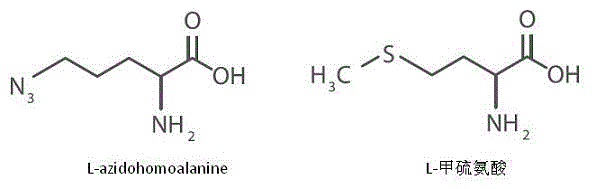Patents
Literature
38 results about "Protein Degradations" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
This process, known as protein degradation or proteolysis, takes place constantly inside of cells. Protein levels must stay within specific levels for cells to function properly, so cells have a variety of ways to digest these molecules.
Phosphatase inhibitor sample collection system
InactiveUS20050124965A1Organic active ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementProtein DegradationsProteinase activity
A collection container and a method for collecting a biological sample, particularly whole blood, includes at least one stabilizing agent in an amount effective to stabilize and inhibit protein degradation and / or fragmentation. The stabilizing agent is able to stabilize proteases in the biological sample, particularly at the point of collection, by inhibiting protein degradation and / or fragmentation in the sample when the sample is stored. The stabilizing agent comprises or consists of one or more protease inhibitors.
Owner:BECTON DICKINSON & CO
Method for Rapidly Screening Microbial Hosts to Identify Certain Strains with Improved Yield and/or Quality in the Expression of Heterologous Proteins
ActiveUS20100137162A1High yieldQuality improvementLibrary screeningMicroorganism librariesHeterologousProtein Degradations
The present invention provides an array for rapidly identifying a host cell population capable of producing heterologous protein with improved yield and / or quality. The array comprises one or more host cell populations that have been genetically modified to increase the expression of one or more target genes involved in protein production, decrease the expression of one or more target genes involved in protein degradation, or both. One or more of the strains in the array may express the heterologous protein of interest in a periplasm compartment, or may secrete the heterologous protein extracellularly through an outer cell wall. The strain arrays are useful for screening for improved expression of any protein of interest, including therapeutic proteins, hormones, a growth factors, extracellular receptors or ligands, proteases, kinases, blood proteins, chemokines, cytokines, antibodies and the like.
Owner:PFENEX
Compound microbial agent as well as processing method and application thereof
ActiveCN103756941AGood decomposition effectImprove decomposition effectBacteriaSolid waste disposalFiberProtein Degradations
The invention relates to a compound microbial agent which comprises compound bacteria for decomposing kitchen wastes and auxiliary materials for solid fermentation, wherein the compound bacteria comprise 10-15 parts of cellulose degradation bacteria, 15-30 parts of starch degradation bacteria, 15-20 parts of protein degradation bacteria, 15-20 parts of grease degradation bacteria, 10-15 parts of bacillus subtilis and 5-15 parts of pseudomonas aeruginosa; the auxiliary materials comprise 50-60 kg of wheat bran, 15-20 kg of bean pulp, 0.4-0.6 kg of magnesium sulfate, 0.4-0.6 kg of potassium dihydrogen phosphate, 0.1-0.2 kg of disodium hydrogen phosphate and 8-10 kg of glucose. The inoculation amount of the compound bacteria in the auxiliary materials is 0.8%-1%, and the compound bacteria is subjected to solid fermentation to obtain the compound microbial agent. The compound microbial agent has a good decomposing effect on greases, proteins and fiber substances and can be tolerant to salt with a certain concentration; optimally, the degradation rate can reach more than 90%.
Owner:BEIJING GREEN ENERGY ENVIRONMENTAL ENG
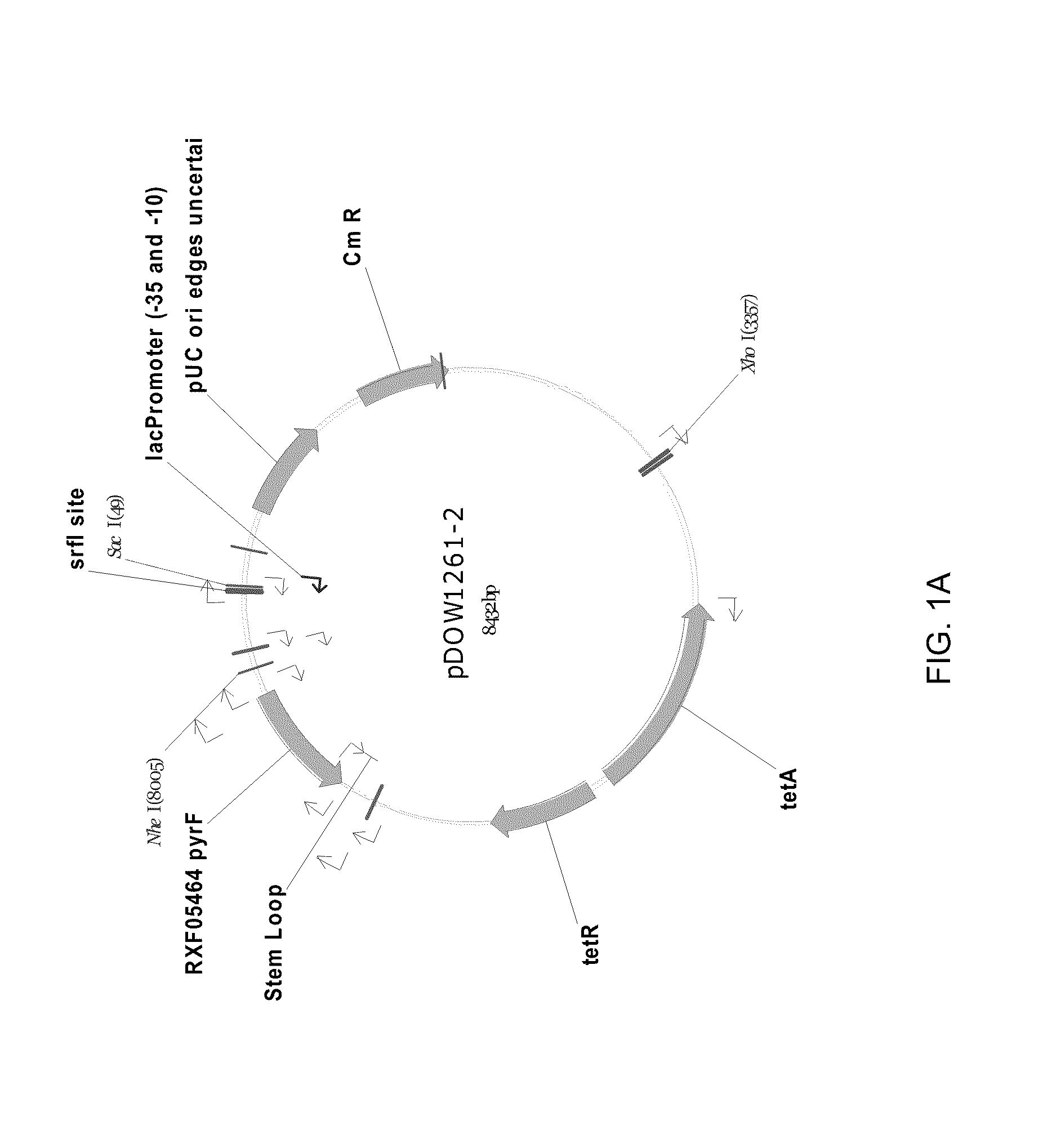
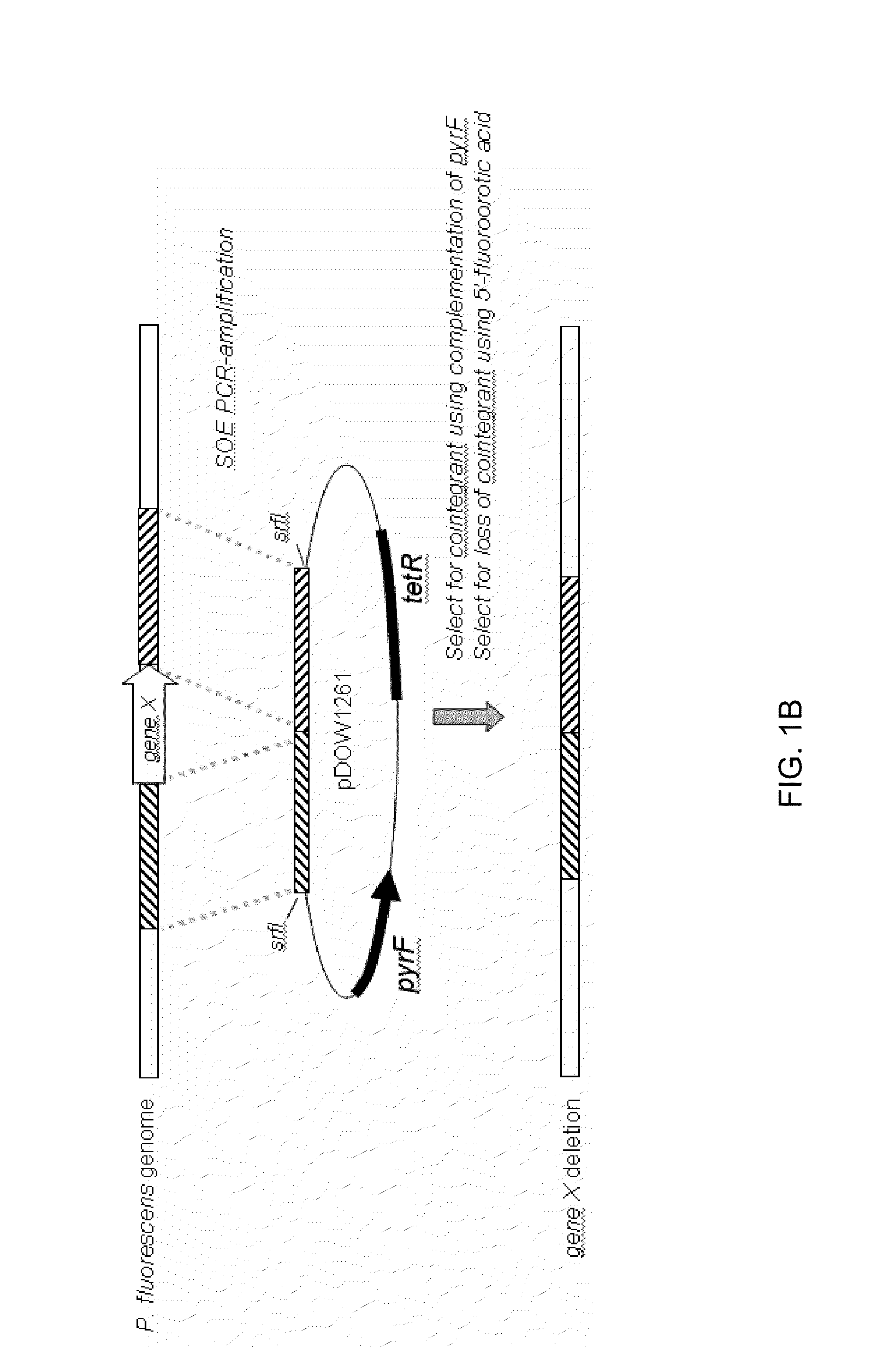
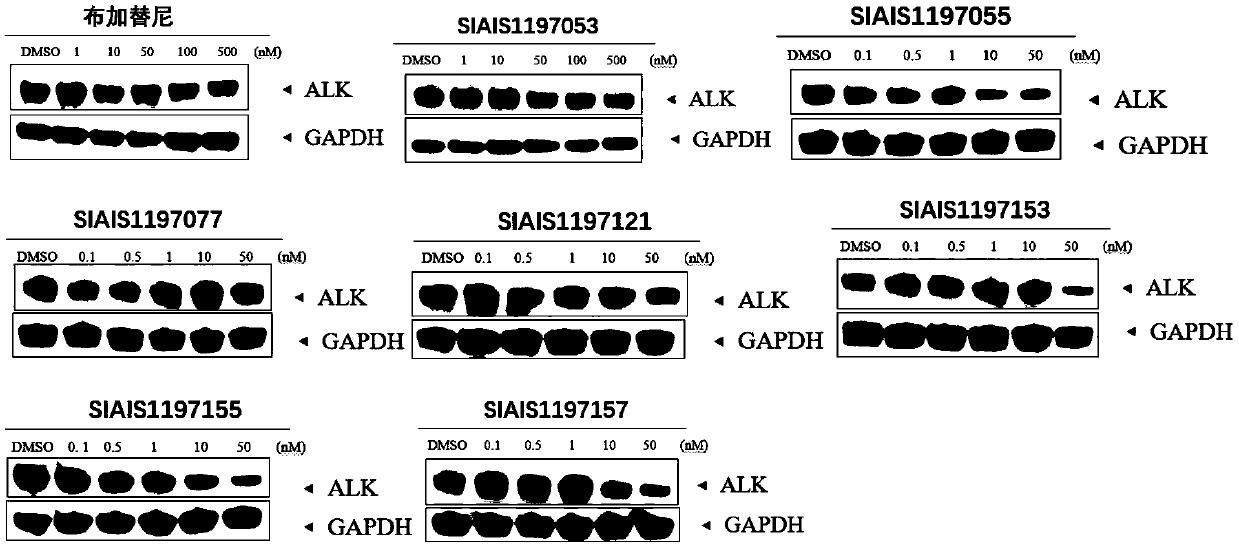
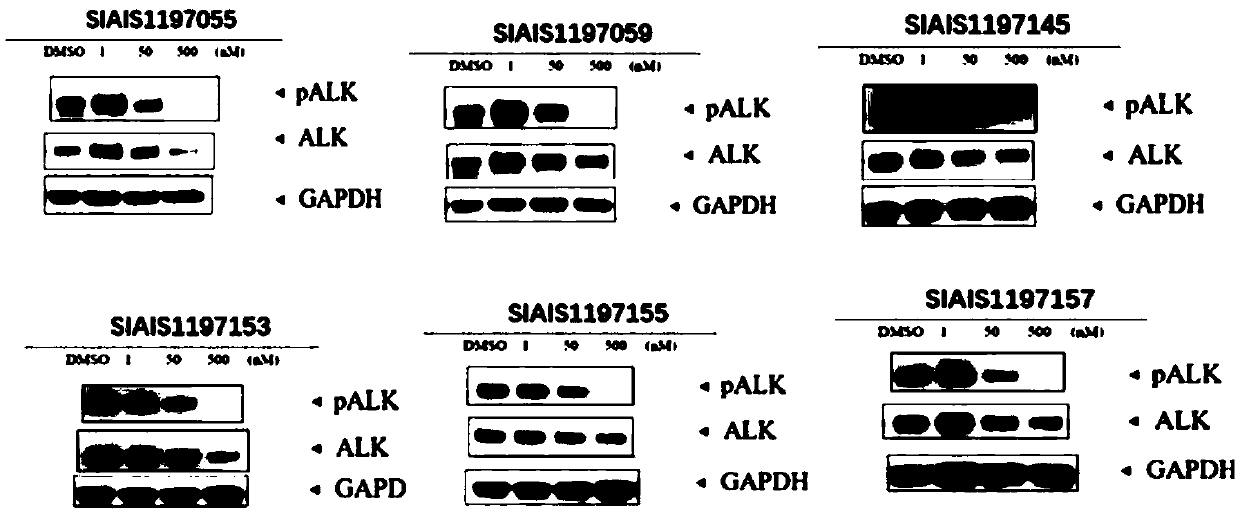
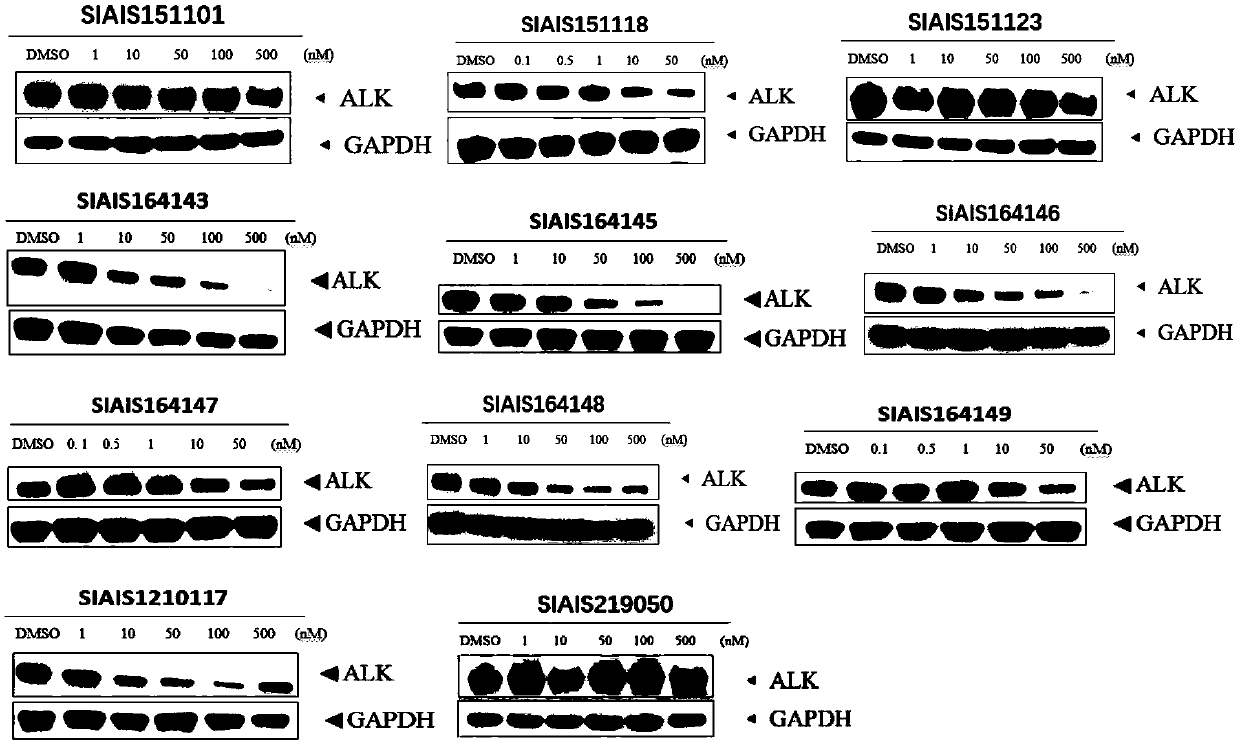
ALK (anaplastic lymphoma kinase) protein degradation agent and anti-tumor application thereof
ActiveCN109912655AGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsProtein DegradationsAbnormal tissue growth
The invention discloses a compound in a formula (I) and an anti-tumor application thereof. The compound in the formula (I) has degradation and inhabitation functions on ALK target protein and mainly comprises four parts, the first part ALK-TKIs is a compound with ALK tyrosine kinase inhabitation activity; the second part LIN is different linkers; the third part ULM (ubiquitin ligase binding moiety) of VHL, CRBN or other protease micromolecular ligand with a ubiquitination function; the fourth part group A is carboxyl or deficiency and covalently binds ALK-TKIs with LIN and covalently binds LINwith ULM. A series of designed and synthesized compounds have wide pharmacological activity, have functions of degrading ALK protein and inhibiting ALK activity and can be applied to related tumor therapy.
Owner:SHANGHAI TECH UNIV
Method for rapidly screening microbial hosts to identify certain strains with improved yield and/or quality in the expression of heterologous proteins
ActiveUS9580719B2High expressionReduce expressionLibrary screeningMicroorganism librariesHeterologousADAMTS Proteins
The present invention provides an array for rapidly identifying a host cell population capable of producing a heterologous protein with improved yield and / or quality. The array comprises one or more host cell populations that have been genetically modified to increase the expression of one or more target genes involved in protein production, decrease the expression of one or more target genes involved in protein degradation, or both. One or more of the strains in the array may express the heterologous protein of interest in a periplasm compartment or may secrete the heterologous protein extracellularly through an outer cell wall. The strain arrays are useful for screening for improved expression of any protein of interest including therapeutic proteins, hormones, growth factors, extracellular receptors or ligands, proteases, kinases, blood proteins, chemokines, cytokines, antibodies and the like.
Owner:PELICAN TECH HLDG INC
Cereblon ligand-induced BET degradation-based bifunctional molecule and preparation and application thereof
The invention relates to a novel preparation method of a bifunctional molecule and a pharmaceutically acceptable salt, hydrate or prodrug thereof and application of these compounds and a medicinal composition thereof in treatment of diseases such as tumors, inflammation and immunity. The bifunctional molecule is a protein degradation-targeted complex (PROTACs), and is capable of selectively inducing BET protein degradation. A BET protein small-molecule inhibitor is connected with a cereblon protein ligand in an E3 ubiquitin ligase complex to obtain the bifunctional molecule.
Owner:CHINA PHARM UNIV
Cereblon ligand mediated novel BET protein degradation bifunctional molecules, preparation and application thereof
The invention relates to a preparation method of new bifunctional small molecules and pharmaceutically acceptable salts, hydrates or prodrugs thereof, and application of the compounds and pharmaceutical compositions thereof in treatment of tumors, inflammation, immunity and other diseases. The bifunctional small molecules involved in the invention are protein degradation targeting chimeras (PROTACs), and can selectively induce BET protein degradation. According to the invention, a connecting arm is employed to connect a BET protein small molecule inhibitor and a cereblon protein ligand in theE3 ubiquitin ligase complex so as to obtain the bifunctional small molecules.
Owner:CHINA PHARM UNIV
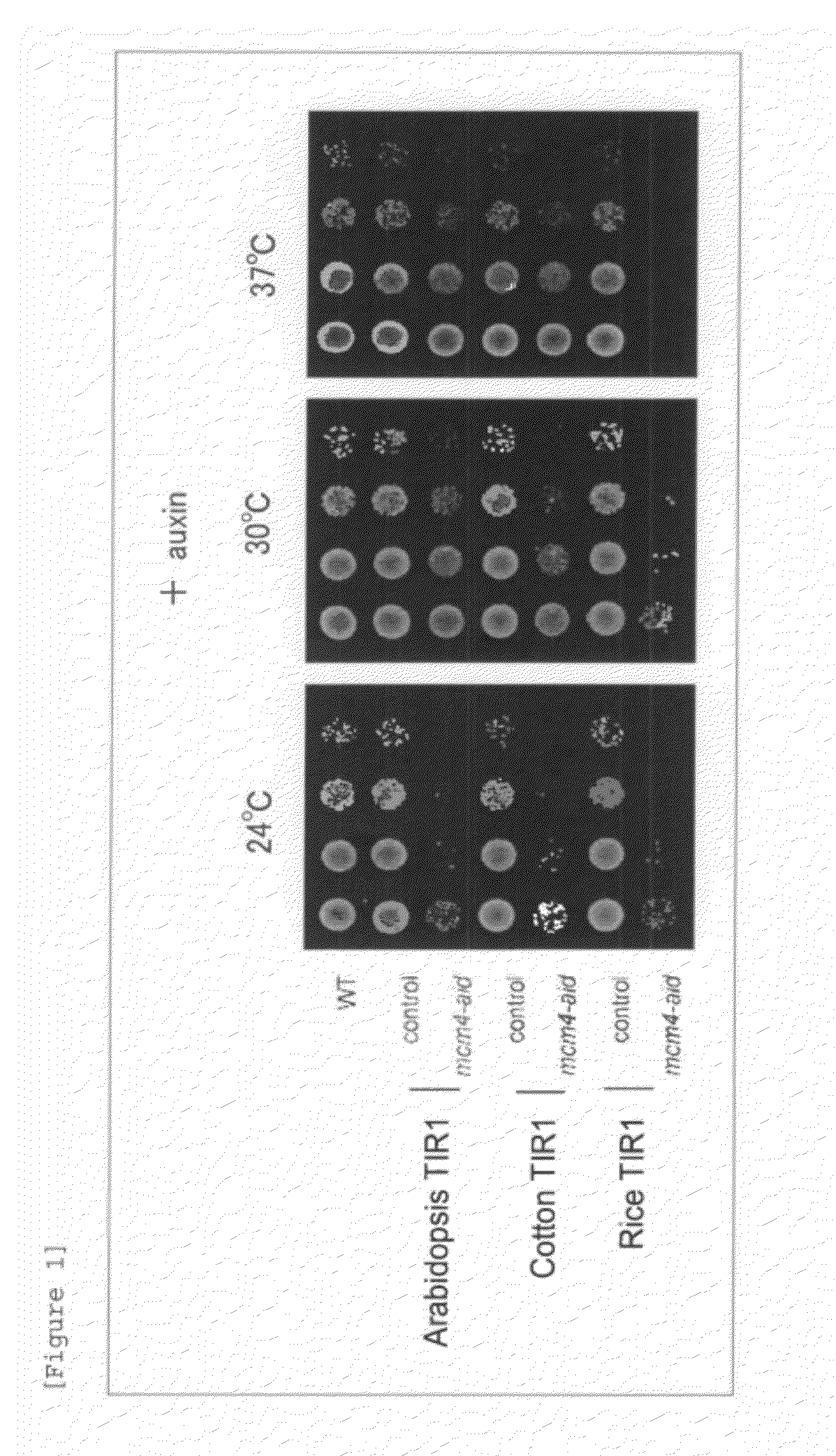
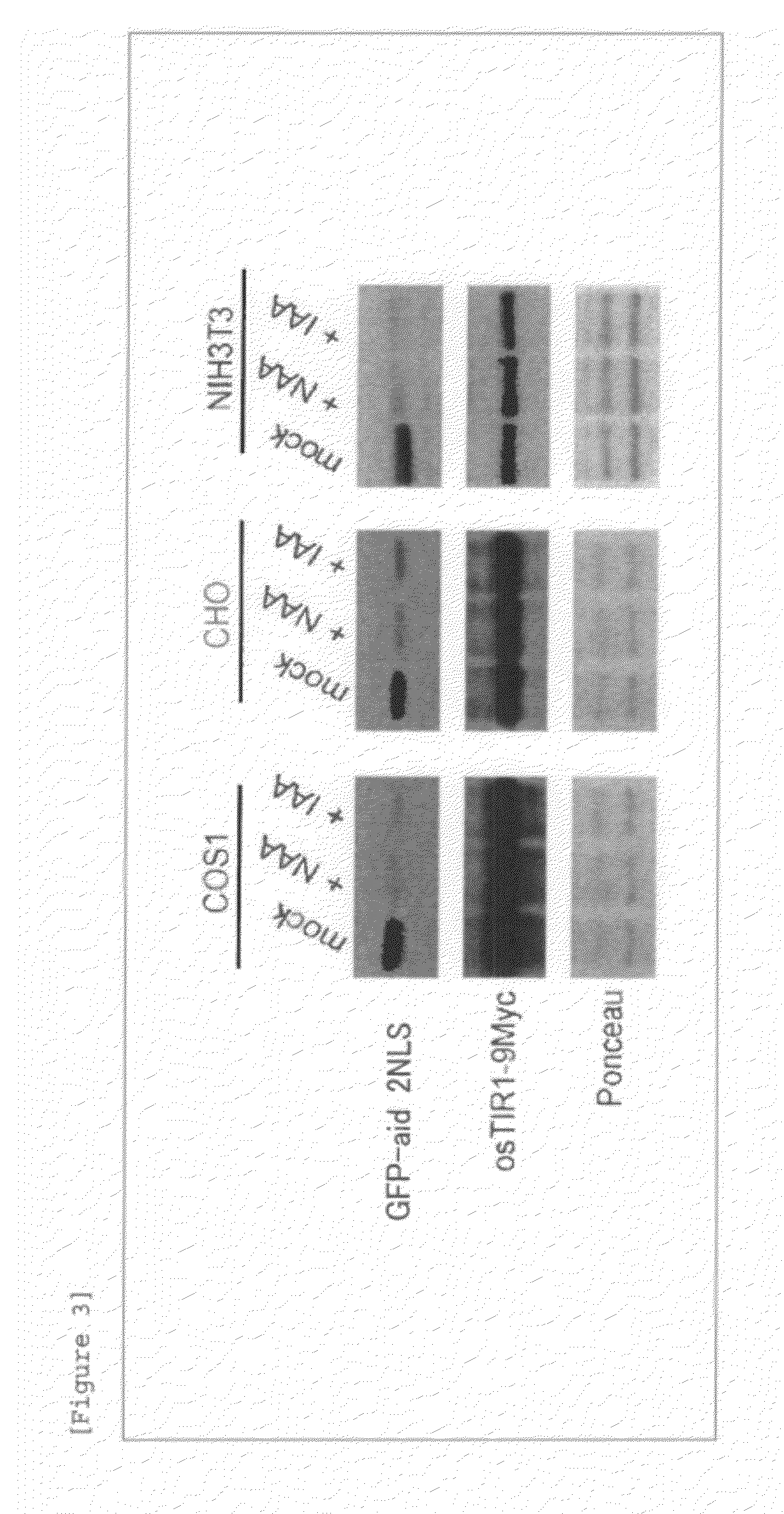
Method for inducing degradation of protein in mammalian cell
Provided is a system which can induce the degradation of a protein of interest in a mammalian cell system reliably and stably within a short time. A mammalian cell inducible for protein degradation, the degradation of a protein of interest being induced by an auxin, in which the mammalian cell has both a TIR1 family protein gene from rice and a chimeric gene expressing a protein of interest labeled with a plant Aux / IAA family protein.
Owner:OSAKA UNIV
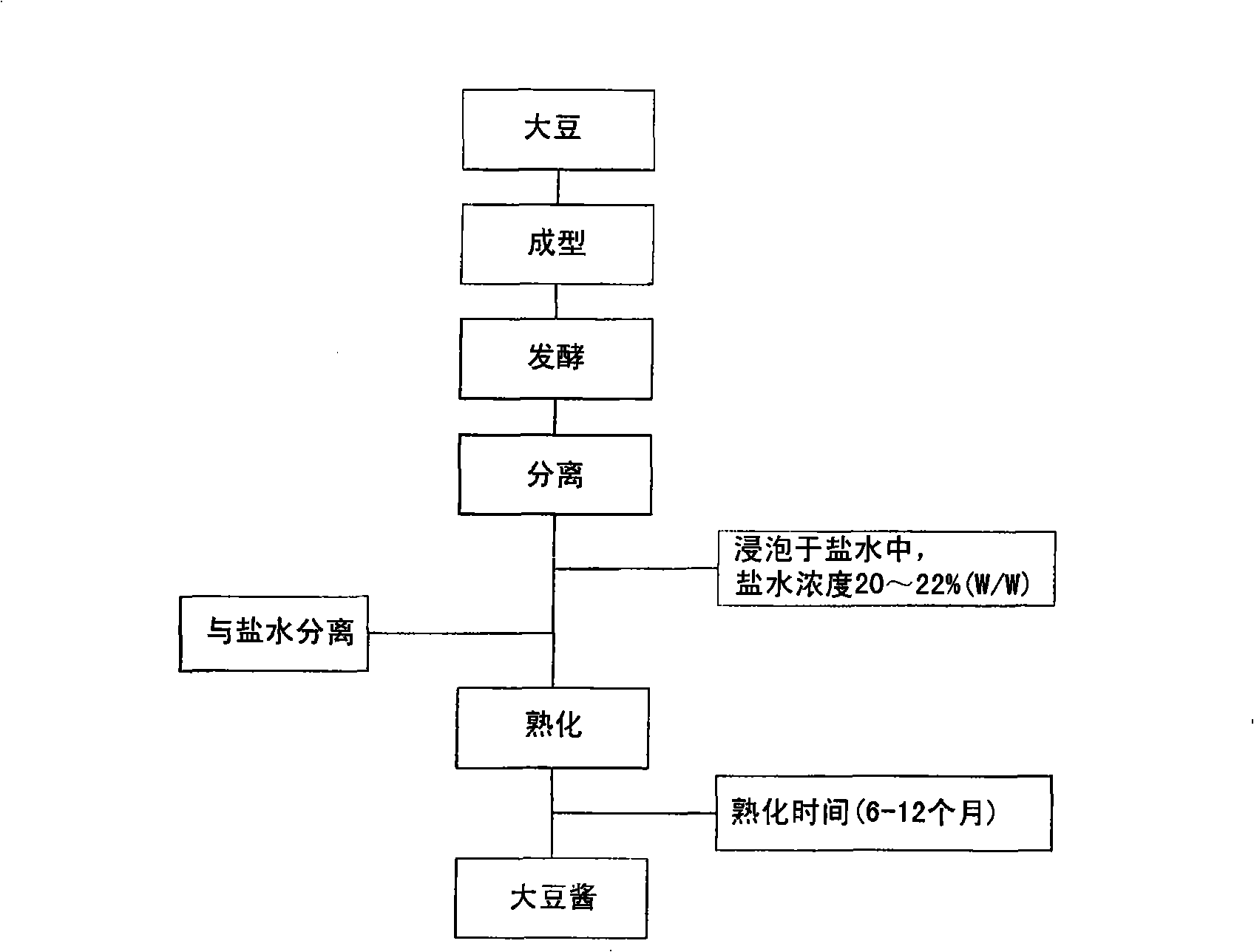
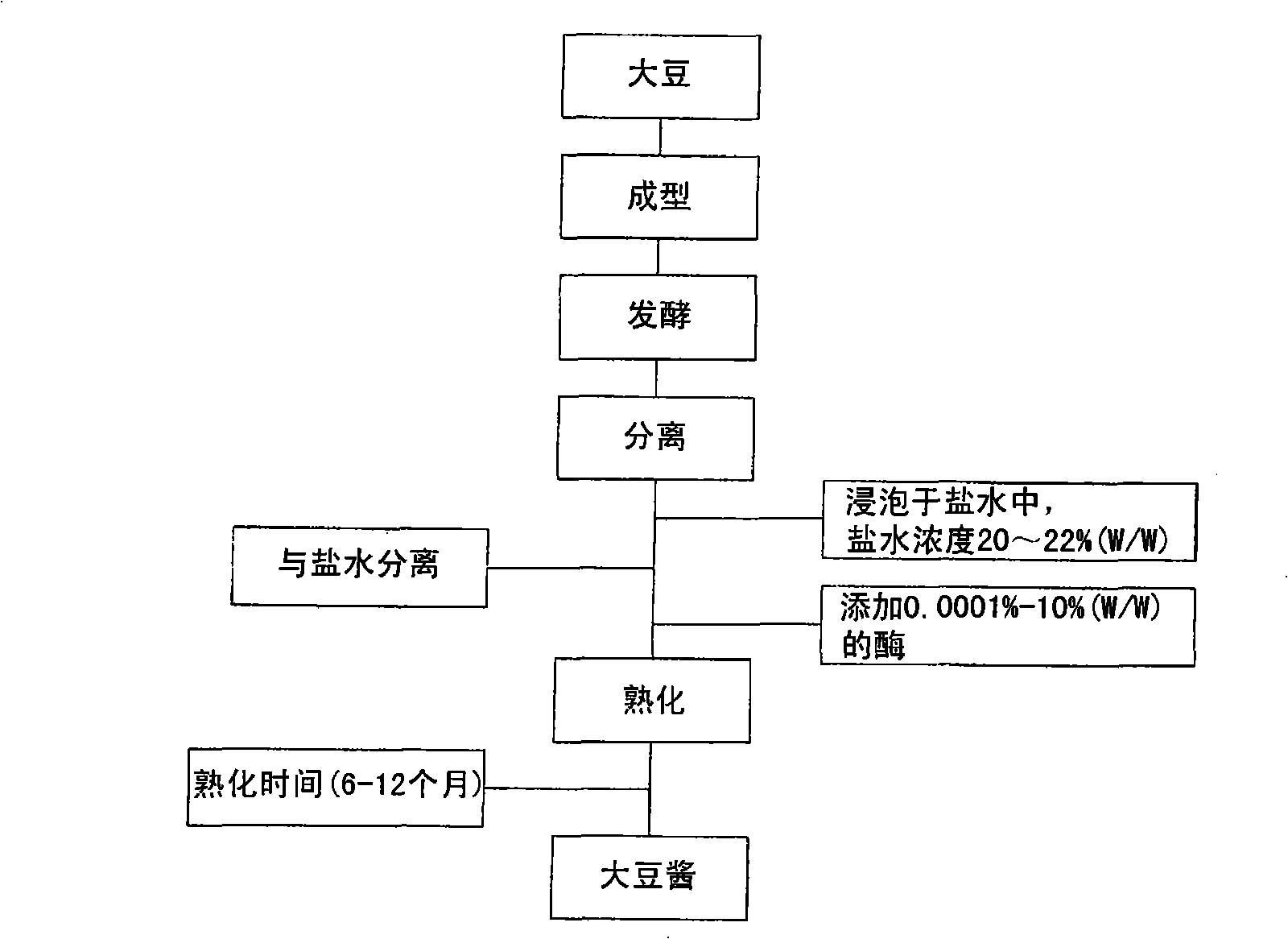
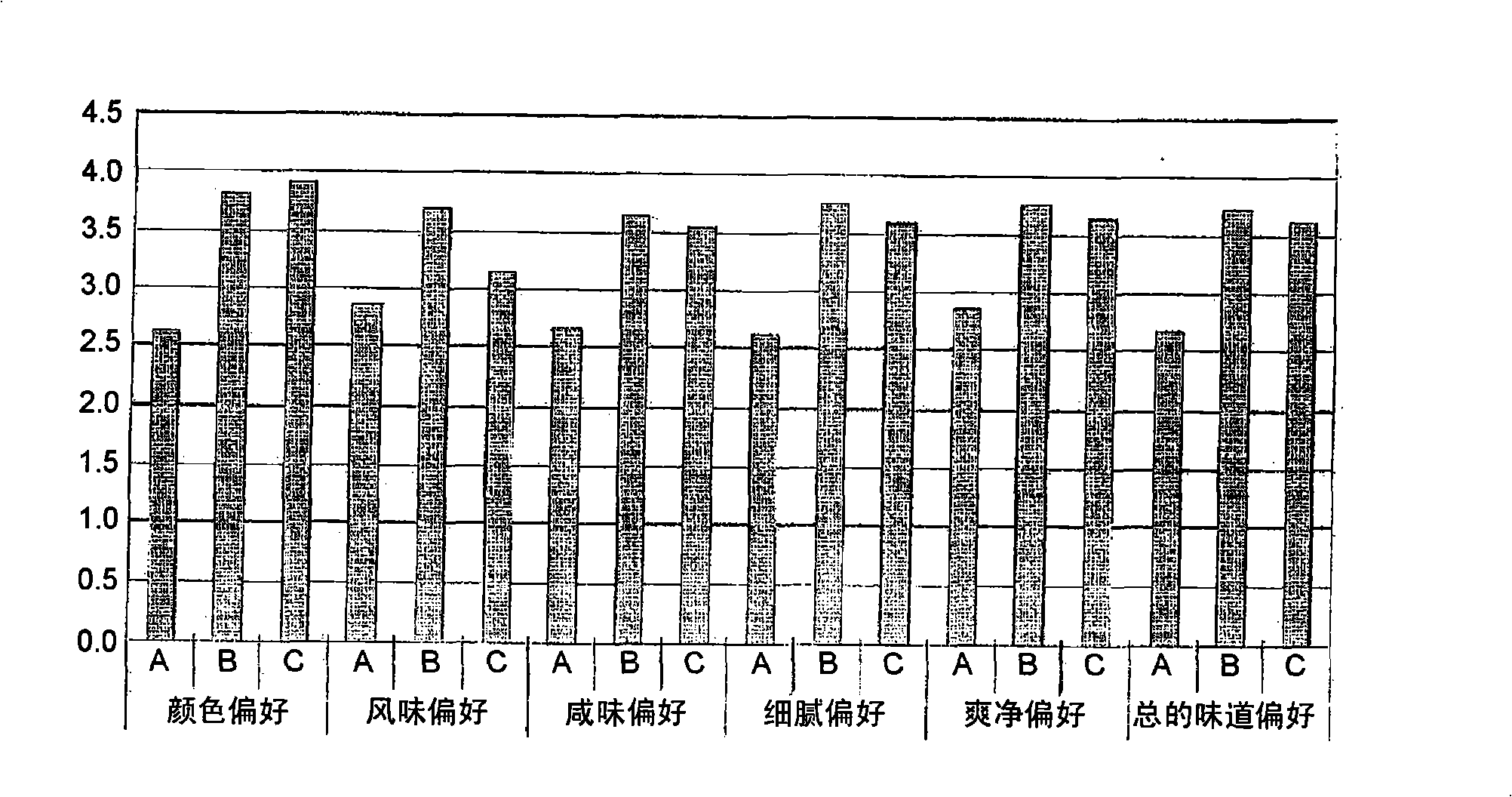
Manufacturing method of soybean paste by protease and its processed products
InactiveCN101346071AQuality improvementRipe fastMicroorganism based processesNatural extract food ingredientsProtein DegradationsProduction rate
The present invention relates to a method of manufacturing soybean paste characterized by the addition of a protease during the production of the soybean paste to accelerate aging and enhance the quality of the soybean paste prepared thereby. More precisely, the present invention relates to a method of manufacturing soybean paste comprising the step of adding single protease or a protease complex prepared by mixing at least two different proteases selected from a group consisting of protease originating from Aspergillus oryzae, having excellent protein degradation capacity; protease originating from Bacillus spp. and plant proteases such as those originating from papaya and pineapple. According to the present invention, by the addition of a protease with excellent protein degradation capacity, a soybean paste with unique tastes and flavors can be prepared with reduced aging time and increased production efficiency.
Owner:CJ CHEILJEDANG CORP
Method for screening of cell-protecting agent
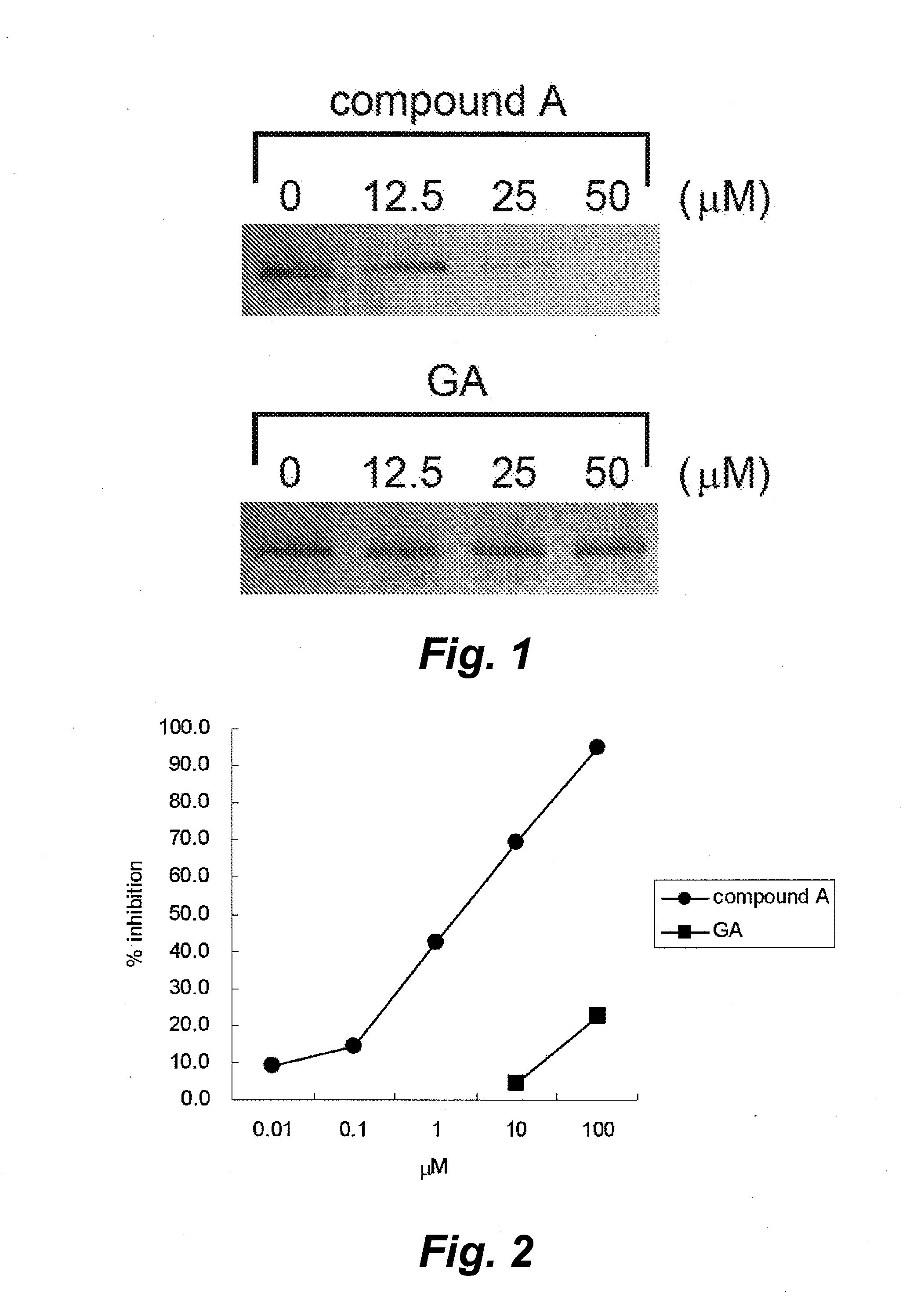
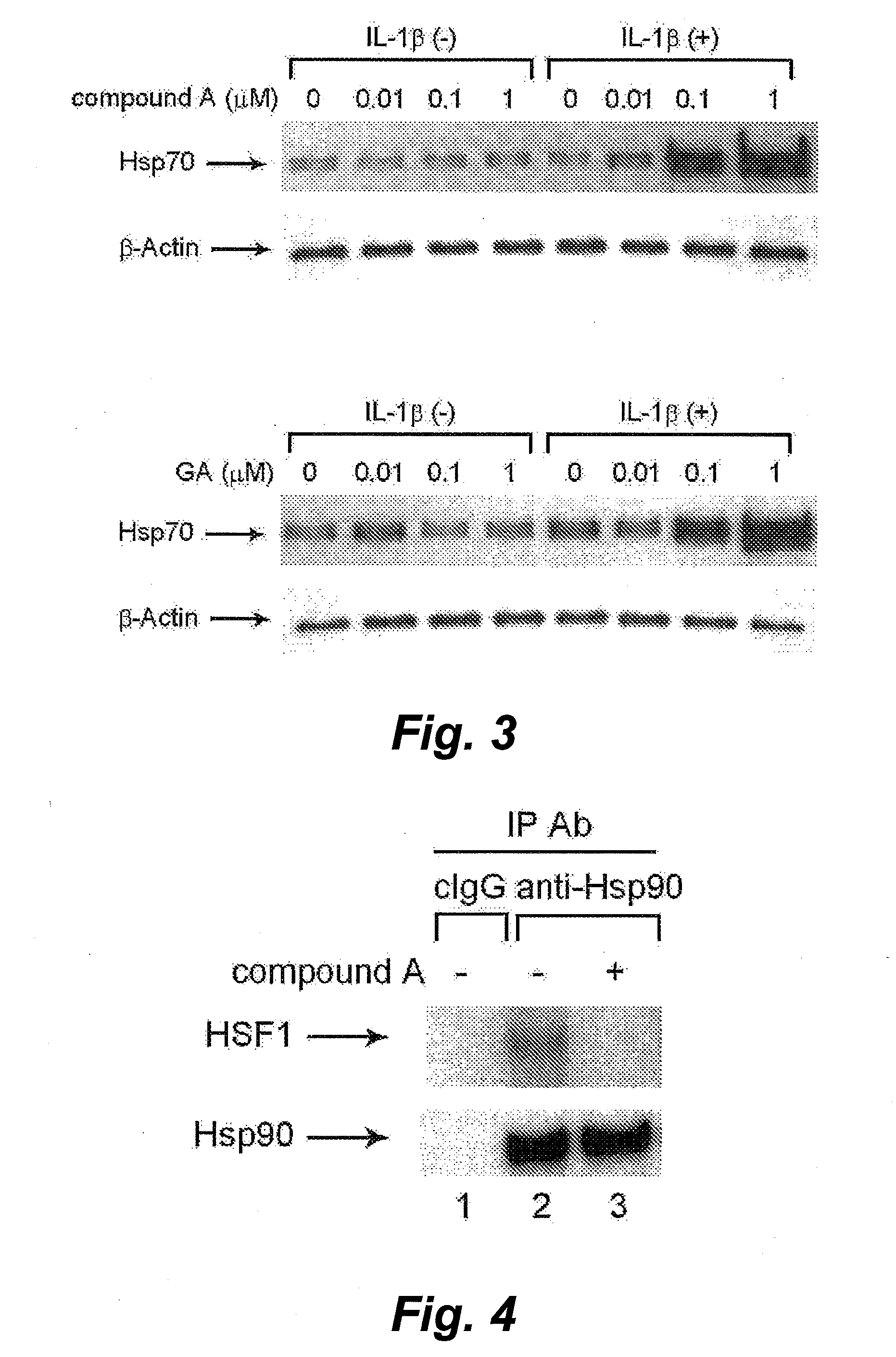
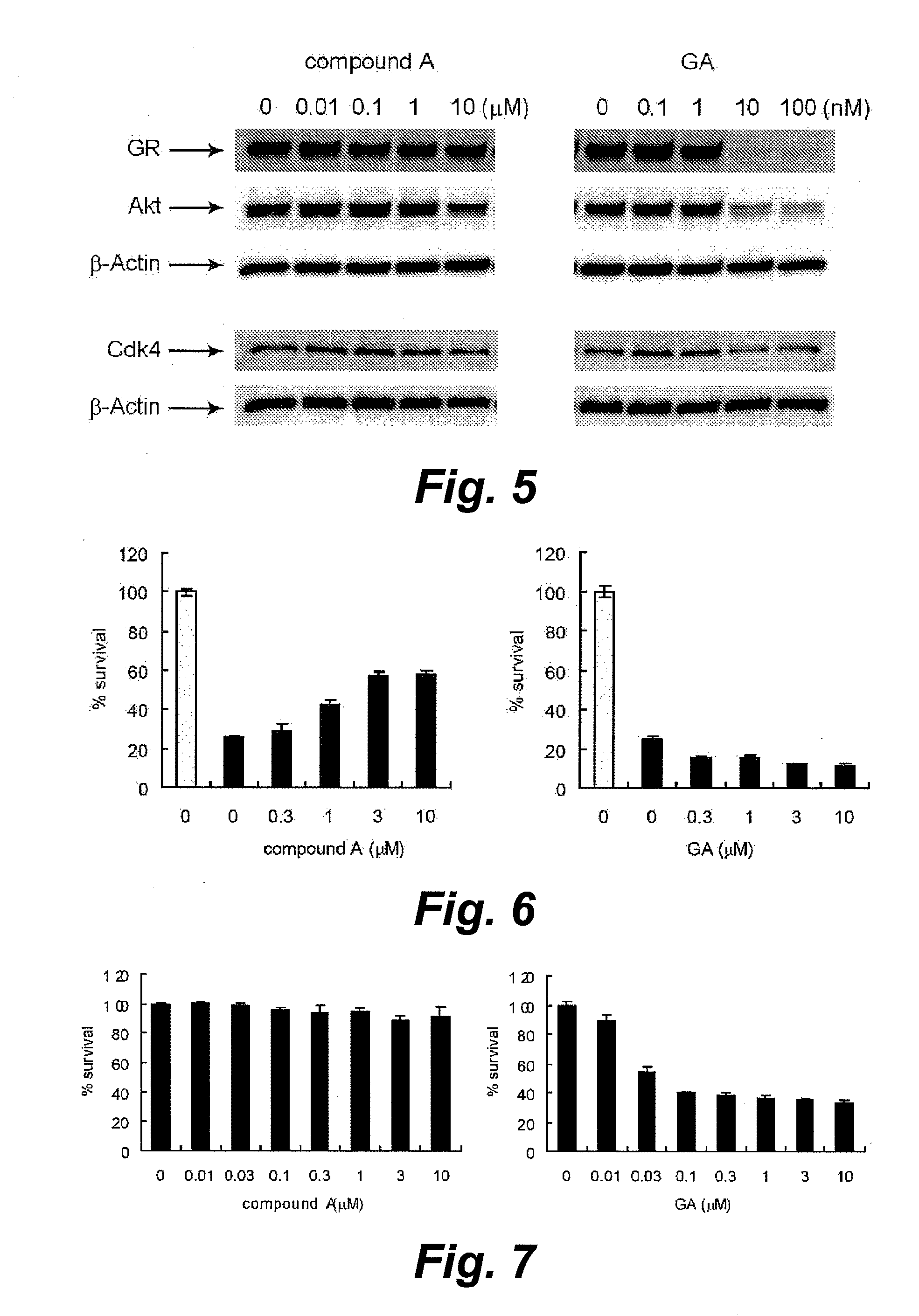
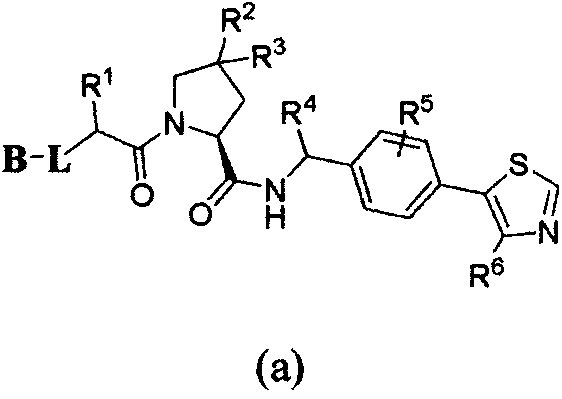
InactiveUS20100279311A1Minimize cytotoxicityEasy to getCompound screeningNervous disorderProtein DegradationsScreening method
The invention provides a screening method and screening kit for a cell protecting agent. Specifically, the invention provides a method for screening a cell protecting agent showing an Hsp90-binding activity and a heat shock protein expression-inducing activity but having no Hsp90 client protein degradation-promoting activity. The method comprises the following steps (1) to (3): (1) measuring the binding property of a test compound to Hsp90; (2) measuring the activity of a test compound to induce the expression of a heat shock protein, or measuring the activity of a test compound to disrupt an Hsp90 / HSF-1 complex, by using a cell capable of expressing the heat shock protein; and (3) measuring the activity of a test compound to induce the degradation of an Hsp90 client protein by using a cell capable of expressing the Hsp90 client protein. The invention further provides specifically a kit for screening a cell protecting agent, comprising (1) Hsp90; (2) a reagent for measuring the heat shock protein expression-inducing activity; (3) an imidazothiazine derivative; and (4) a reagent for quantifying an Hsp90 client protein.
Owner:TAKEDA PHARMA CO LTD
Bifunctional molecules for induction of BET degradation based on VHL ligand and BET inhibitor, preparation and application thereof
The invention relates to a preparation method of new bifunctional small molecules and pharmaceutically acceptable salts, hydrates or prodrugs thereof, and application of the compounds and pharmaceutically compositions thereof in treatment of tumors, inflammation, immunity and other diseases. The bifunctional small molecules involved in the invention are protein degradation targeting chimeras (PROTACs), and can selectively induce BET (Bromo-and Extra-terminal) protein degradation. According to the invention, a carbon chain or polyethylene glycol chain truss arm is utilized to connect the 3, 5-dimethyl isoxazole BET protein small molecule inhibitor with the von Hippel-Lindau (VHL) protein ligand in an E3 ubiquitin ligase complex so as to obtain the bifunctional small molecules.
Owner:CHINA PHARM UNIV
A novel function of a Bacillus subtilis GGT protein degradation product and antimicrobial peptide identification for the product
ActiveCN108929866AActive against Streptomyces scabiesBiocideDisinfectantsProtein DegradationsAntimicrobial peptides
The invention relates to a novel function of a Bacillus subtilis GGT protein degradation product, namely an anti-Streptomyces scabies application. The invention also provides antimicrobial peptides from Bacillus subtilis GGT protein. That the known Bacillus subtilis GGT protein after degradation has an anti-Streptomyces scabies activity is found, and the antimicrobial peptide sequences are identified from a degradation product of the Bacillus subtilis GGT protein, thus providing a novel way of thinking for biological control of potato common scab.
Owner:HEILONGJIANG BAYI AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
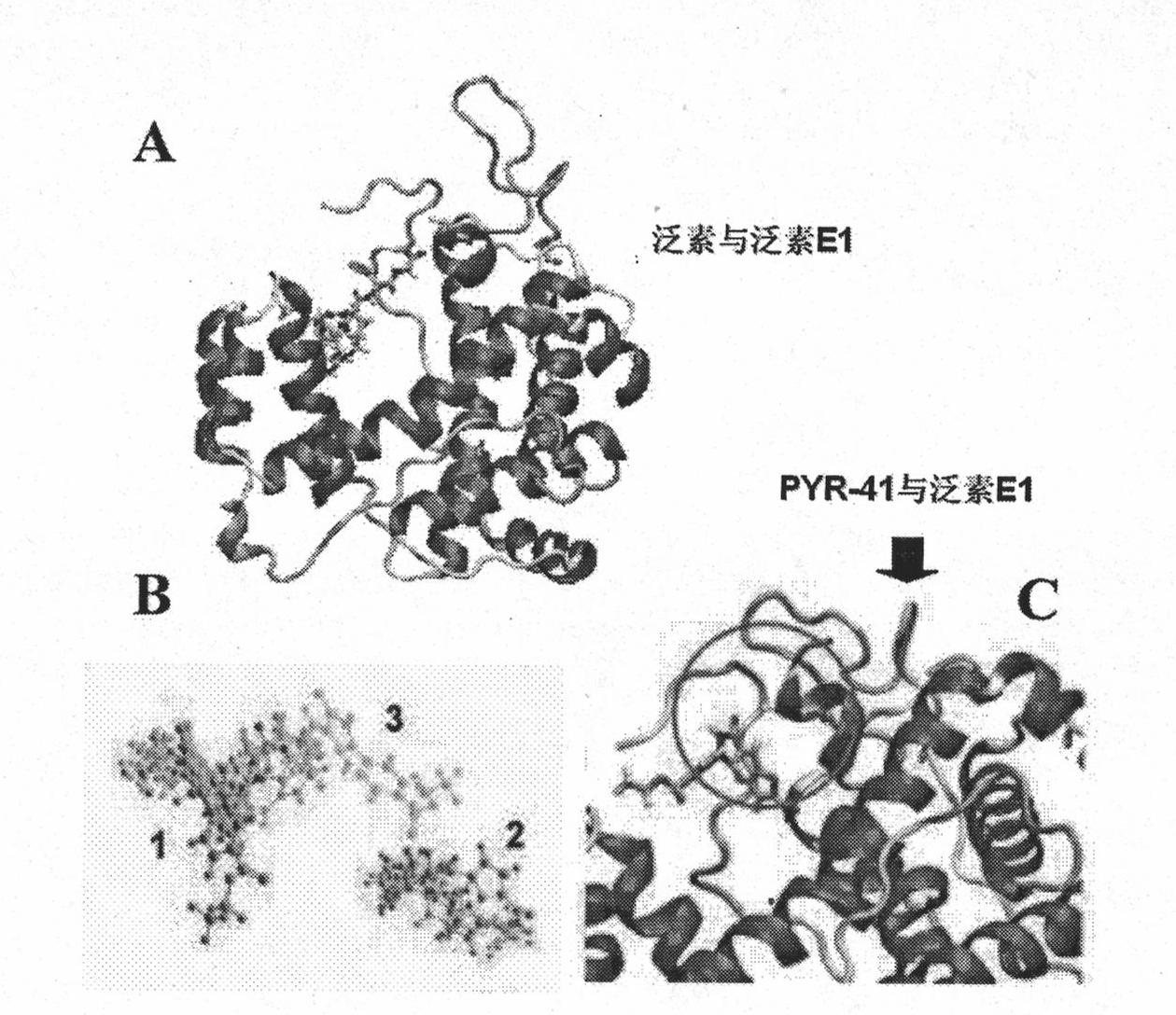
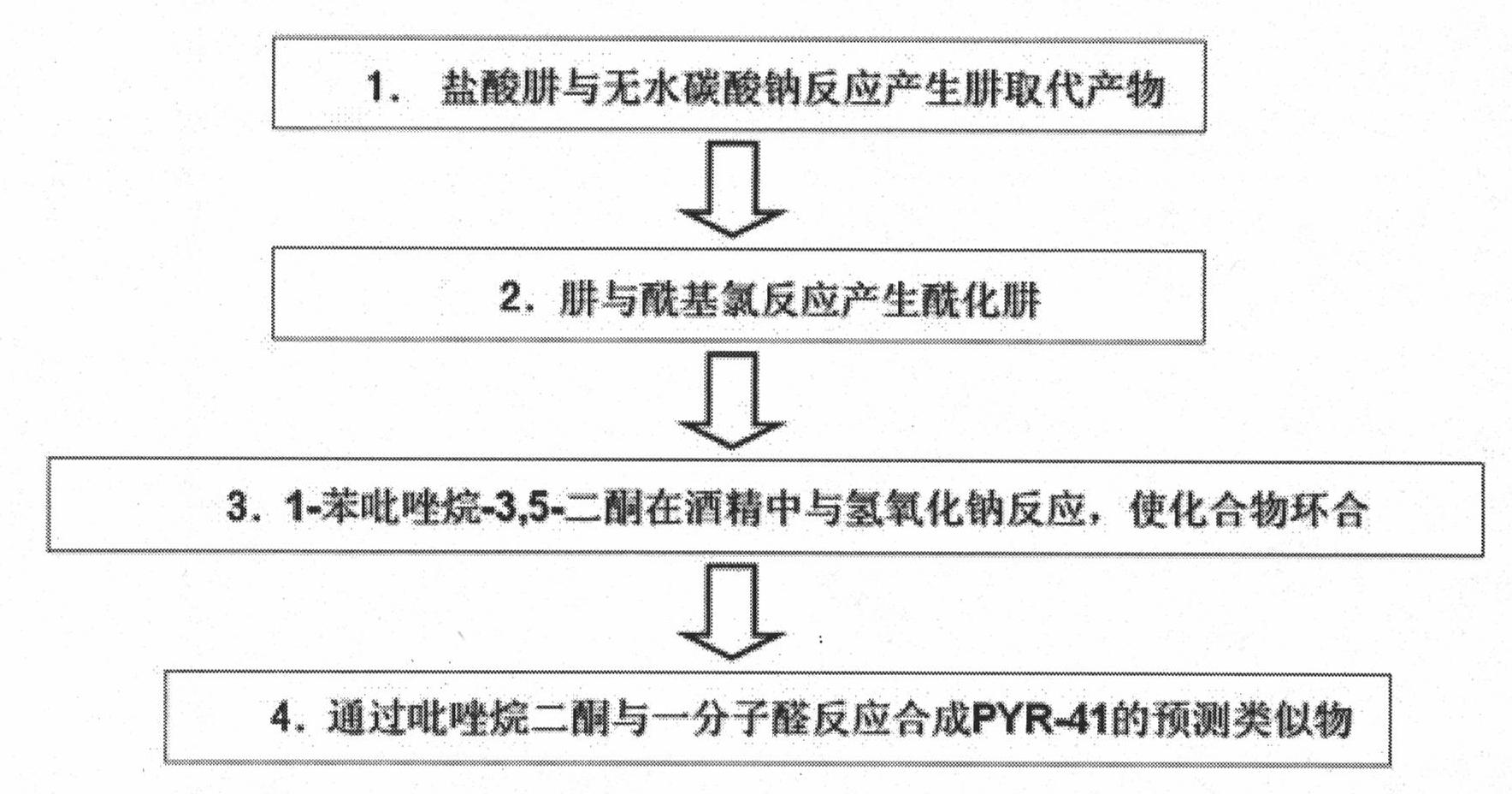
Ubiquitin E1 inhibitor and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101961331AEasy to passGood water solubilityOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryFuranProtein Degradations
The invention relates to an ubiquitin E1 inhibitor and a preparation method thereof. Series compound Y-1-benzene pyrazole silane-3,5-diketone and relevant derivative (such as 4-(4-ethyoxyl-3-methoxybenzylidene)-1-benzene pyrazole silane-3,5-diketone, and the like) with different alternative groups are prepared by a liquid-phase organic synthesis method according to the structure of PRY-41(4(4-(5-nitro-furan group-methylene]-3,5-dioxo-pyrazolidine-1-radical)-ethyl benzoate). The ubiquitin E1 inhibitor can be used for inhibiting protein degradation mediated by ubiquitination and nondegradation of ubiquitination, and can kill transformed cells containing p53 in the process of blocking up the NFkB activity by the inhibitor, that is to say, the inhibitor possibly has the potential property of treating tumor and can be used as an important tool for researching ubiquitin proteinase system mechanism.
Owner:西安杰诺瓦生物科技有限公司
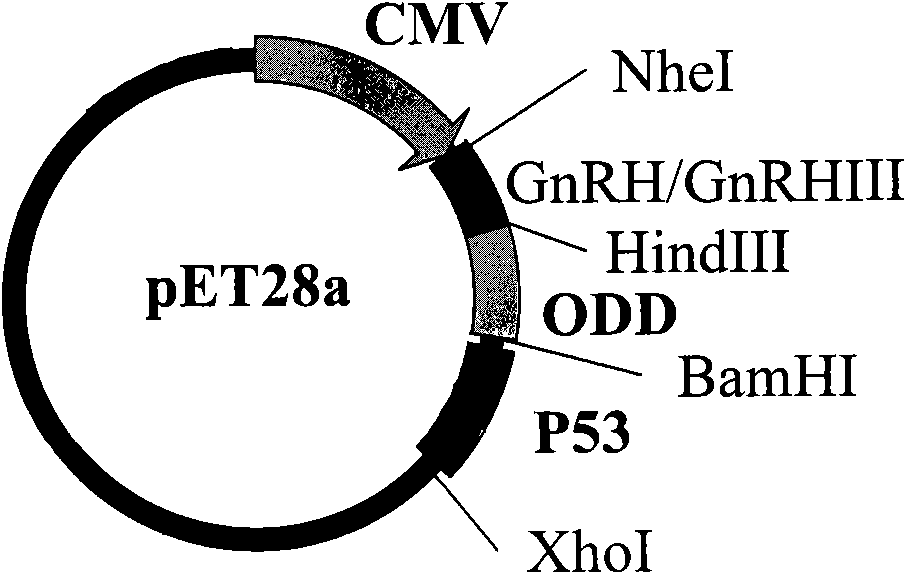
Recombinant fusion proteins containing p53 genes, recombinant and application thereof
InactiveCN101684472AGrowth inhibitory effectAvoid damageBacteriaPeptide/protein ingredientsProtein DegradationsHypoxia-inducible factors
The invention relates to a fusion gene which comprises a GnRH gene sequence, a p53 gene sequence and an optional gene sequence of an oxygen-dependent protein degradation structural domain (ODD) of a hypoxia-inducible factor between the GnRH gene sequence and the p53 gene sequence. The invention also relates to recombinant fusion proteins, an expression recombinant of the fusion genes, engineeringbacteria obtained from the expression recombinant and pharmaceutical applications of the expression recombinant and the fusion proteins. A function of resisting tumor of p53 can be efficiently improved according to the invention.
Owner:INST OF PHARMACOLOGY & TOXICOLOGY ACAD OF MILITARY MEDICAL SCI P L A
Flavonoids compound, preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN104161767AInhibit the inflammatory responseAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsDiseaseProtein Degradations
The invention provides a flavonoids compound, a preparation method and an application of the flavonoids compound in medicine for prevention and treatment of cachexia. The compound has a structure shown in a structural formula (I) as follows. The provided flavonoids compound can be used for preparing the medicine for treating human and animal cachexia, and cachexia relative to a plurality of diseases can be treated, lowered body weight due to skeletal muscle atrophy and fat degradation atrophy can be effectively alleviated, tumour burden can be obviously mitigated, protein degradation is inhibited, and cytokine TNF-a and IL-6 level can be increased.
Owner:SHANGHAI SIXTH PEOPLES HOSPITAL
Method for detecting degradation of protein in cells
InactiveCN104155452AAccurate degradationBiological testingFluorescence/phosphorescenceDiseaseProtein Degradations
The invention belongs to the field of biochemistry, and relates to a method for detecting the degradation of protein in cells. The method comprises the following steps: (1) marking methionine of newly synthesized protein in the cells with azide small molecule groups by utilizing an methionine analogue; (2) lysing the cells at different time points, and coupling specific molecules which can be identified to the azide small molecule groups through CuAAC reaction; and (3) quantifying target protein which is coupled with the molecules which can be identified in the step (2) by directly utilizing an HTRF (Homogeneous Time-Resolved Fluorescence) resonance principle in a reaction system so as to determine the degradation rate of the target protein. The method is a new protein degradation measurement method which is free from the need of an isotope or cytotoxin, is compatible with high-throughput screening, and can be used for screening related disease protein degradation medicines in pharmaceutical industry, screening specific related protein degradation signals in academia, and the like.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
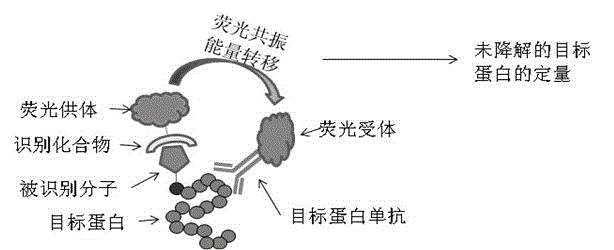
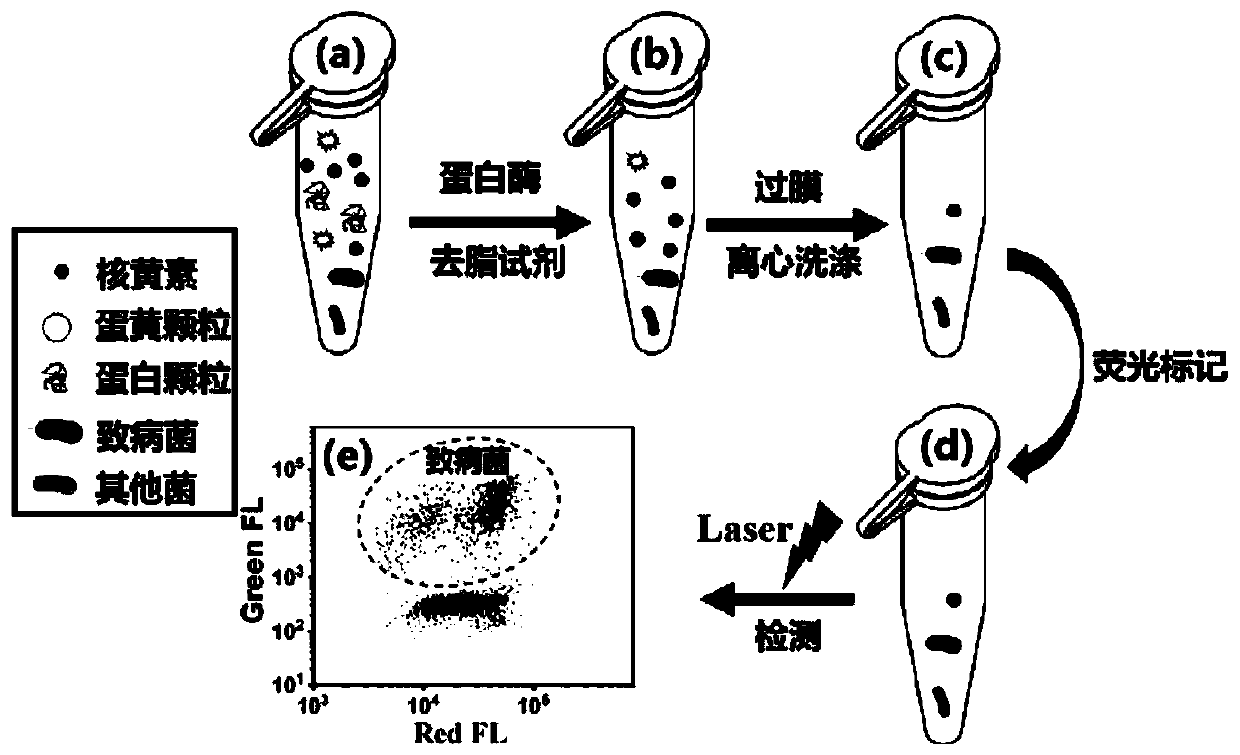
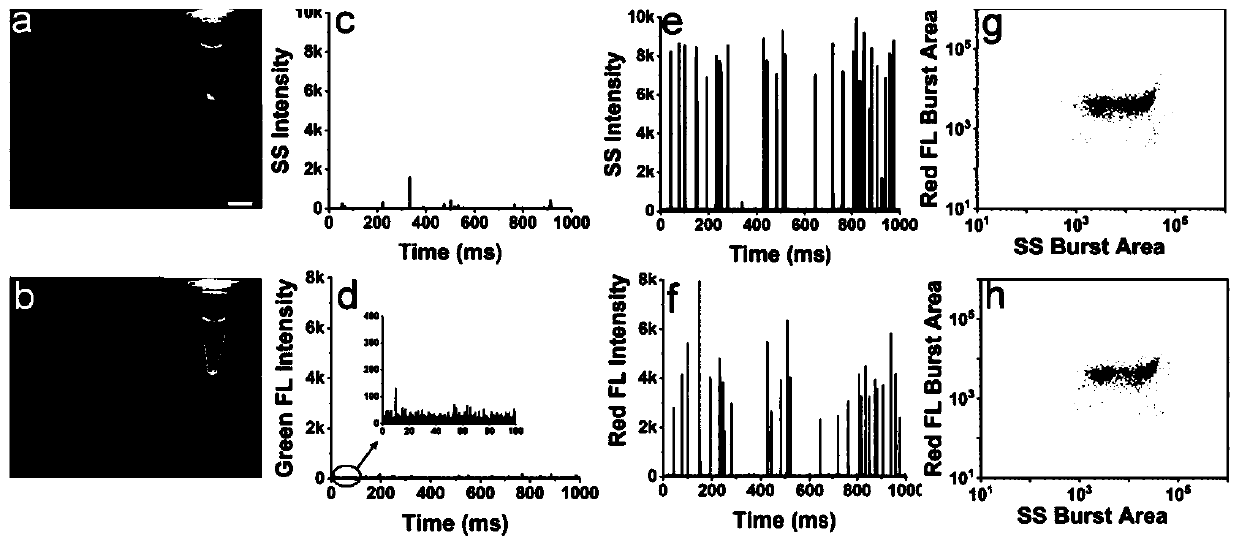
Method for quantitative detection of pathogenic bacteria and total bacterial count in edible raw egg
PendingCN110218763AReduce background fluorescence signalAchieving identifiabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceProtein DegradationsFluorescence
The invention relates to a method for quantitative detection of pathogenic bacteria and total bacterial count in an edible raw egg. The method comprises the following steps that S1, a to-be-detected edible raw egg sample is homogenized; S2, after an egg liquid sample is diluted, protein degradation treatment and degreasing treatment are carried out; S3, the treated egg liquid sample is subjected to membrane filtration; S4, the filtered egg liquid sample is subjected to centrifugal washing and supernatant removal, and the centrifuged precipitates are suspended by a suspending medium; S5, a specific pathogenic bacterium probe is used for performing first fluorescence labeling on an egg liquid suspension solution, and a nucleic acid dye is used for performing second fluorescence labeling on the egg liquid suspension solution; S6, the fluorescence of particles in a detection and sample loading suspension solution is detected by using high-sensitivity flow cytometry. The method is suitablefor detection of various edible raw egg and egg liquid samples, and can simultaneously and quantitatively detect target pathogenic bacteria and total bacterial count in the samples, including variouspathogenic bacteria, nonpathogenic bacteria and the like.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Protein degradation inducing tag and usage thereof
ActiveUS20180164289A1Induce degradationCompound screeningApoptosis detectionProtein DegradationsNin one binding protein
Provided are: a protein degradation inducing tag which is a molecule that has affinity with proteases and does not inhibit degradation of a protein by proteases; a protein degradation inducing molecule that is a conjugate of at least one protein degradation inducing tag and at least one protein binding molecule that binds to a protein; and a usage of those.
Owner:TOKYO UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE
Biological insecticide for preventing and controlling high mountain cnaphalocrocis medinalis guenee
InactiveCN107372661ANo side effectsDestroy body structureBiocideDead animal preservationProtein DegradationsSide effect
The invention provides a biological insecticide for preventing and controlling high mountain cnaphalocrocis medinalis guenee, and relates to the field of insecticides. The biological insecticide is prepared from the following raw materials in parts by weight: 33 to 42 parts of SYP-9080 (Silvchongxian'an), 12 to 23 parts of sodium fluosilicate, 15 to 25 parts of deltamethrin, 10 to 15 parts of nicotine, 8 to 14 parts of rhizoma cyrtomii, 5 to 10 parts of ruby sulfur, 20 to 35 parts of protein-degradation enzyme and 18 to 25 parts of octadecyl sodium sulfate. In the formula, the protein-degradation enzyme can damage the body structure of the cnaphalocrocis medinalis guenee, and act through being matched with the rhizoma cyrtomii and the ruby sulfur; the cnaphalocrocis medinalis guenee at different age levels can be killed; the drug effect durability is high; meanwhile, side effects cannot be generated on rice.
Owner:福建小薇金匙科技孵化有限公司
Method for evaluating fish meat freshness based on skeleton protein degradation
PendingCN109142495AAvoid damageSmall amount of sampleComponent separationMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansProtein DegradationsEcological environment
The invention discloses a method for evaluating the fish meat freshness based on skeleton protein degradation. The method comprises the steps that polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis is adopted for determining light density values IOD of skeleton proteins of fish meat samples under different storage days; the efficient liquid chromatography is adopted for determining triphosadenine degradation product concentrations of the fish meat samples under different storage days, and a freshness index K value is calculated; the light density values IOD and the K value are combined, a least square supportvector machine is utilized, and a prediction model for the fish meat freshness index K value is built. By adopting combination of titin, nebula and TnT representation skeleton protein as the fish meat freshness evaluation index, the sampling amount is small, and damage to detection samples is small; no other chemical index needs to be combined, and damage to ecological environment is small; the detection steps are simple, the detection time is saved, and online real-time monitoring can be achieved; the detection level reaches the molecular level, and the accuracy is high.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Fermented microalgae vegetable protein composite beverage and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN108371215AProtein colorRetain nutrientsMilk substitutesFood scienceProtein DegradationsAdditive ingredient
The invention belongs to the field of foods, and discloses a fermented microalgae vegetable protein composite beverage and a preparation method thereof. The method comprises the following steps: adding soybean powder, microalgae powder, other vegetable protein powder and anhydrous glucose to water, and conducting melting, hydration, homogenization, sterilization and browning so as to obtain a preliminarily fermented base material; adding kombucha gluconacetobacter and lactic acid bacteria into the preliminarily fermented base material for fermentation, and conducting demulsification, homogenization and cooling to obtain a fermented base material after reaching fermentation end; and diluting the fermented base material by 1.5 times, adding lactic acid and ingredients, and conducting homogenization to obtain the fermented microalgae vegetable protein composite beverage. The beverage not only reserves the nutritional ingredients of plant protein beverages, but also contains active lacticacid bacteria and kombucha, and can inhibit harmful microbes in human bodies. The method utilizes the acid production, aroma generation and deodorization of lactic acid bacteria to carry out protein degradation and acid production on plant seed kernel emulsions. The finished product is milk white in color and fine in taste, and has mild sourness and a refreshing flavor.
Owner:FOSHAN UNIVERSITY
Production technology of sunflower seed peptide powder
InactiveCN106889303AAvoid degradationImprove immunityVegetable proteins working-upProtein DegradationsEnzymatic hydrolysis
The invention discloses a production process of sunflower seed peptide powder, which uses defatted sunflower seed meal as raw material, undergoes enzymatic hydrolysis, impurity removal, vacuum concentration, and spray drying to obtain sunflower seed peptide powder; the invention provides a sunflower seed peptide The production process of sunflower seed powder solves the problem of high-fat sunflower seed protein degradation, and can degrade various nutrients in defatted sunflower seed meal to produce nutritious sunflower seed peptide powder that can be directly absorbed by the human body.
Owner:杨富元
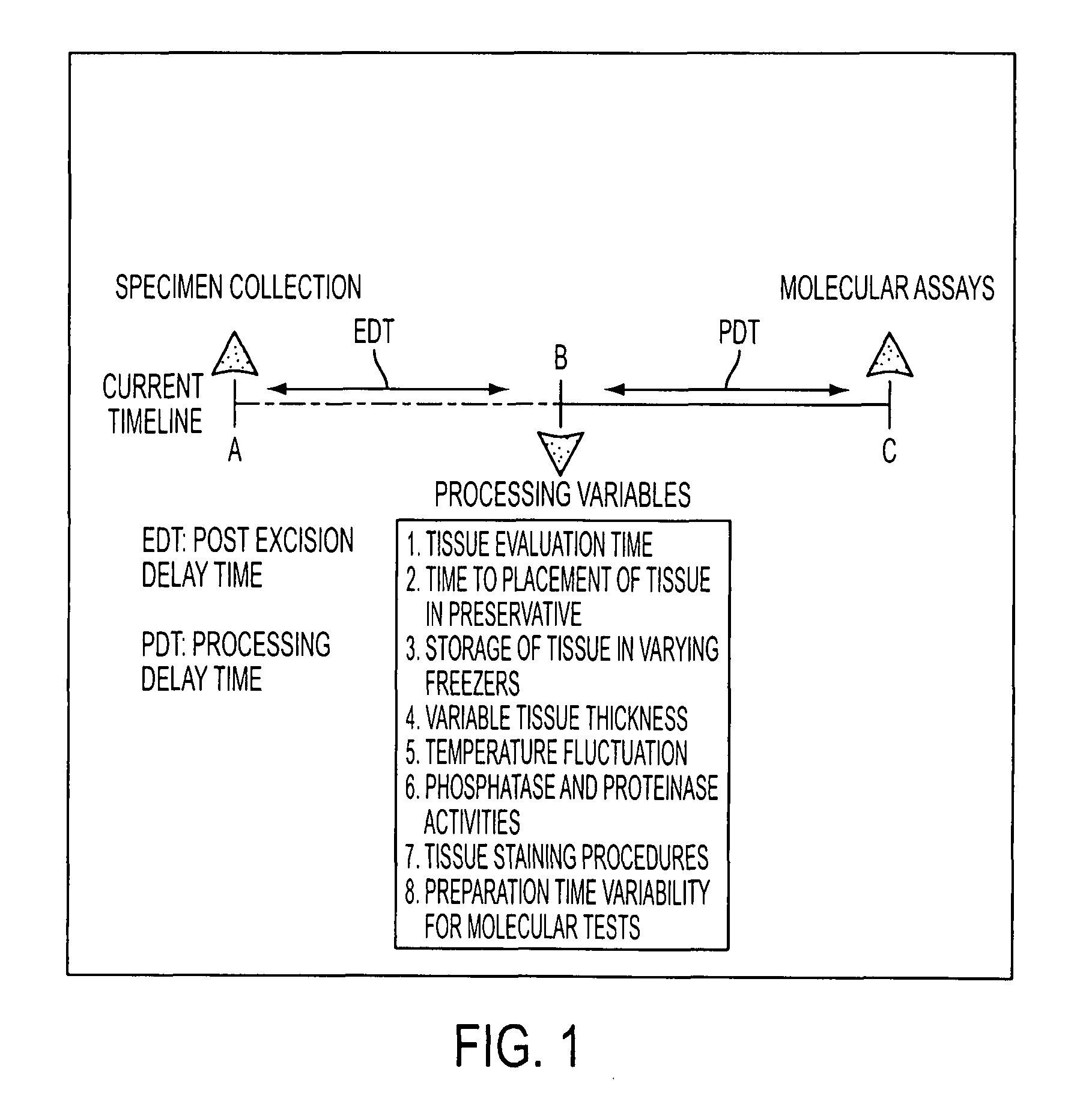
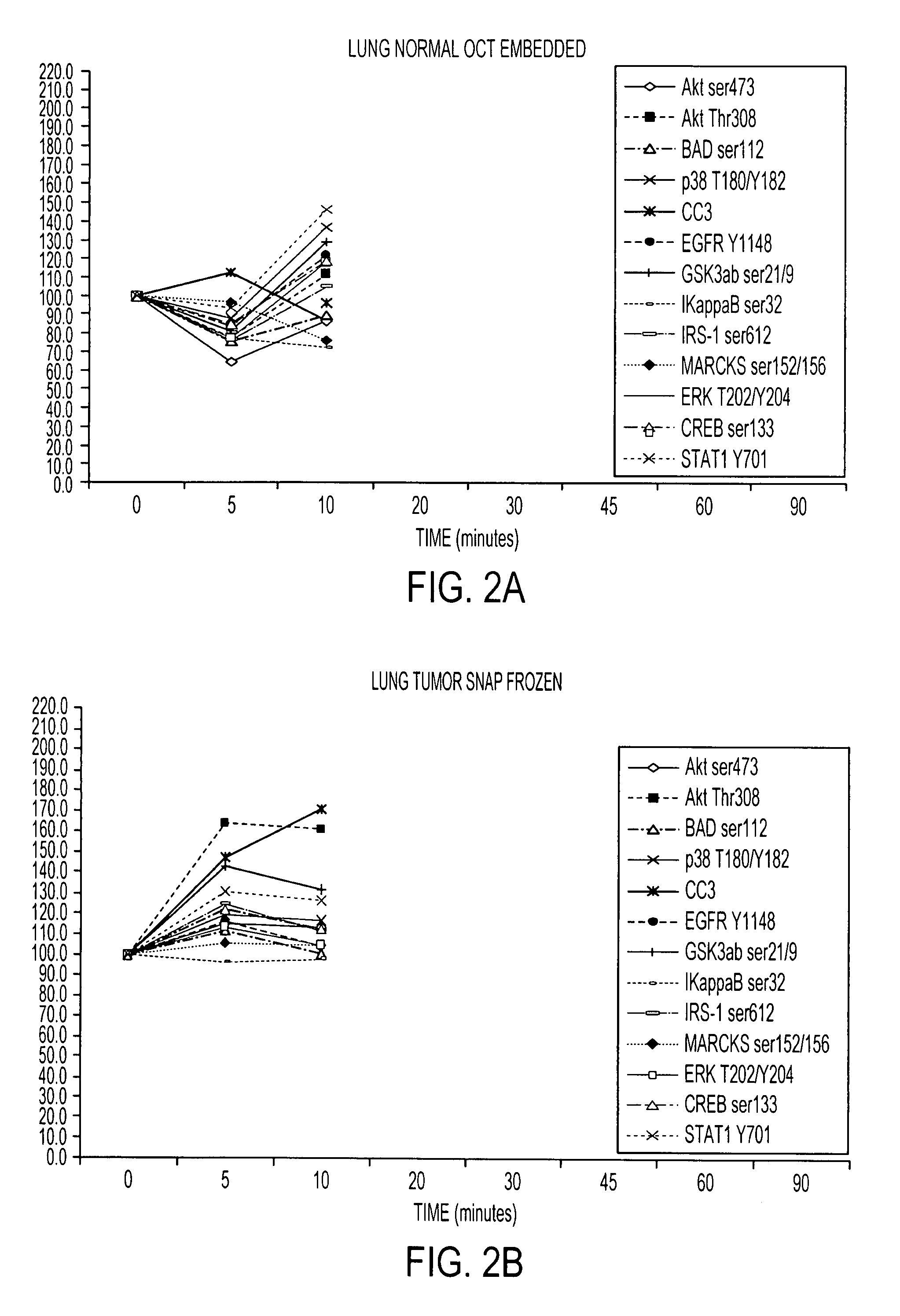
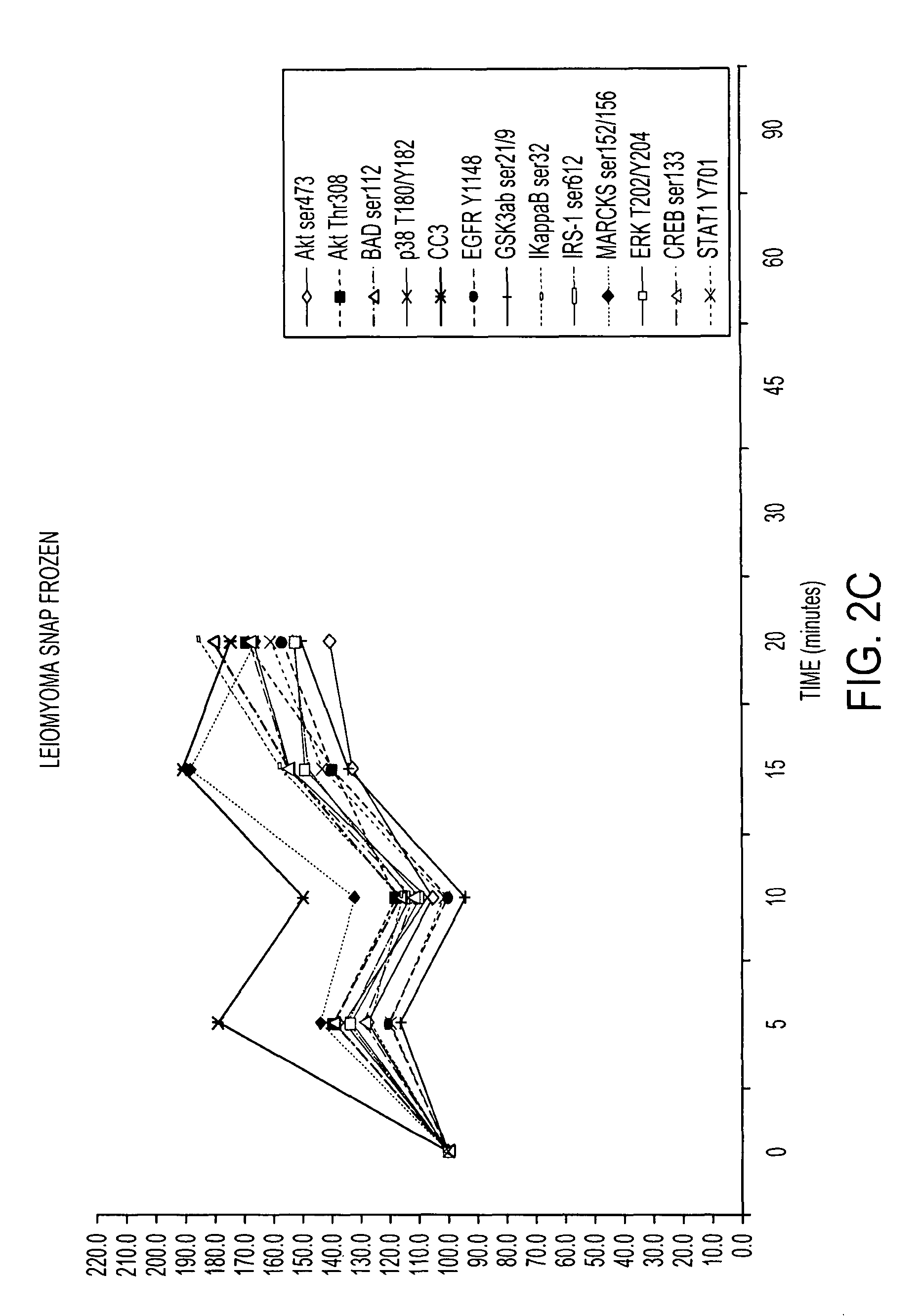
Tissue preservation and fixation method
ActiveUS8460859B2Material nanotechnologyPreparing sample for investigationProtein DegradationsPopulation sample
This invention relates, e.g., to a composition that, at room temperature, when contacted with a sample comprising phosphoproteins, can fix and stabilize cellular phosphoproteins, preserve cellular morphology, and allow the sample to be frozen to generate a cryostat frozen section suitable for molecular analysis. The composition comprises (1) a fixative that is effective to fix the phosphoproteins, and that has a sufficient water content to be soluble for a stabilizer and / or a permeability enhancing agent); (2) a stabilizer, comprising (a) a kinase inhibitor and (b) a phosphatase inhibitor and, optionally, (c) a protease (e.g., proteinase) inhibitor; and (3) a permeability enhancing agent (e.g. PEG). Methods are described for preserving phosphoproteins, using such a composition. Also described are endogenous surrogate markers for monitoring protein degradation, including the loss of posttranslational modifications (such as phosphorylation), e.g. the following removal of a cell or tissue from a subject; and exogenous molecular sentinels (e.g. phosphoproteins attached to magnetic nanoparticles) that allow one to evaluate the processing history of a cellular or tissue population sample.
Owner:GEORGE MASON UNIVERSITY
Coating phosphoric acid for feeds
InactiveCN101999532AEasy to produceInhibit sheddingAnimal feeding stuffAccessory food factorsProtein DegradationsPhosphoric acid
The invention discloses coating phosphoric acid for feeds, which consists of an outer stomach coating layer and an inner tablet core layer containing phosphoric acid. The tablet core, accounting for 100 percent, comprises the following components: 30-70 percent of phosphoric acid and 30-70 percent of silicon dioxide, wherein the mass of the stomach coating layer accounts for 5-20 percent of the total mass of the coating phosphoric acid, and the granularity of the coating phosphoric acid is 40-80 meshes. The coating phosphoric acid has no phenomenon of dripping and breakage in the processes of production, machining and stirring and mixing of feeds, and cannot be reacted with alkali components and starch substances in the feeds to cause the problems of moisture absorption, blocking and easy deterioration of the feeds. After piglets are fed, the tablet core is completely released in one hour after entering the stomach; after the phosphoric acid is dissolved and released, chloride is converted into hydrochloric acid to reduce pH values of stomach contents and improve the protein degradation capability by pepsase, so that the starch polysaccharide is hydrolyzed to monosaccharide, thereby improving feed digestibility, effectively reducing nonnutritive diarrhea and obviously improving the production performance of the piglets, therefore, the coating phosphoric acid for feeds has the optimal economic benefit.
Owner:广州市正百饲料科技有限公司
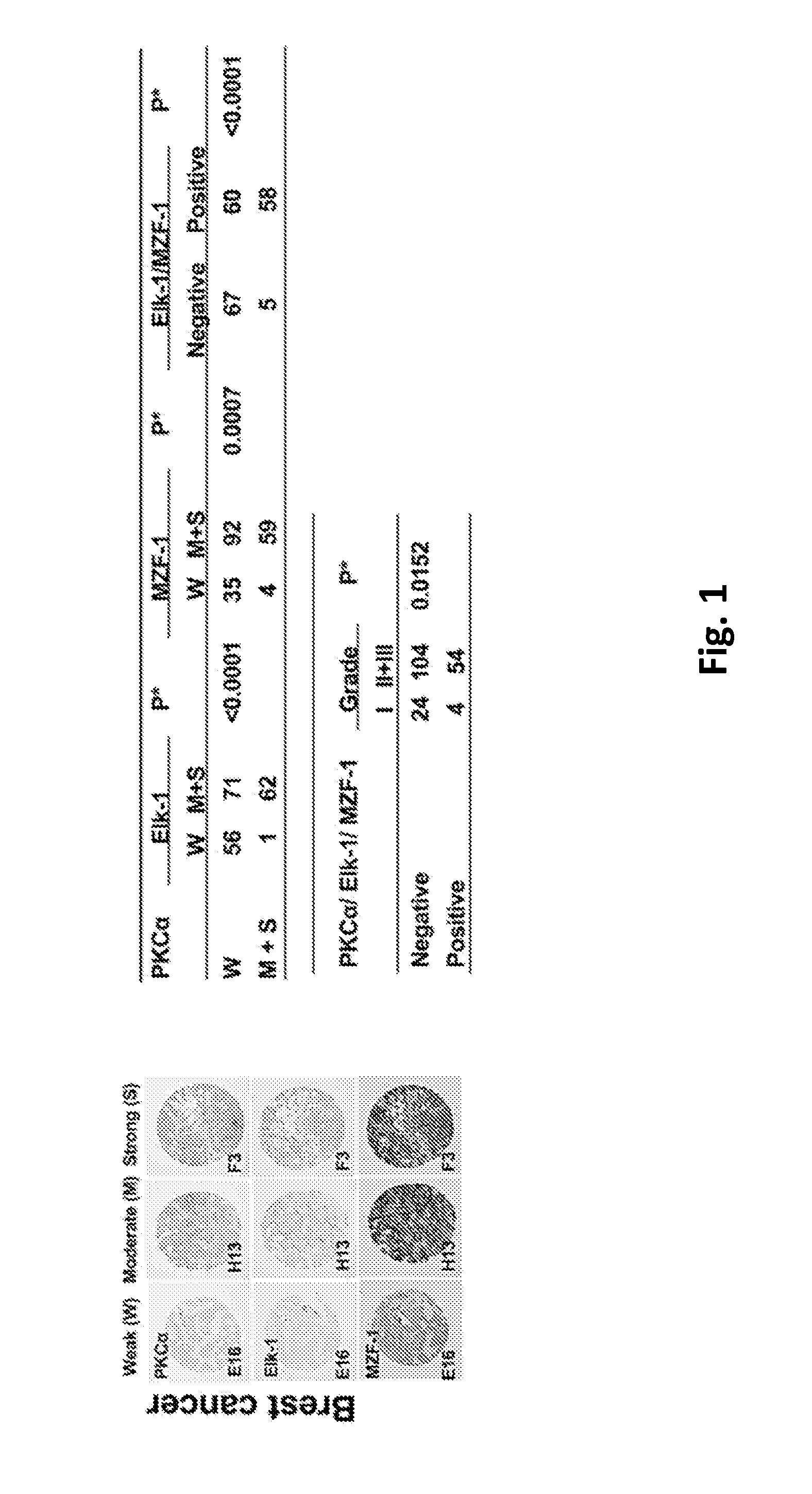
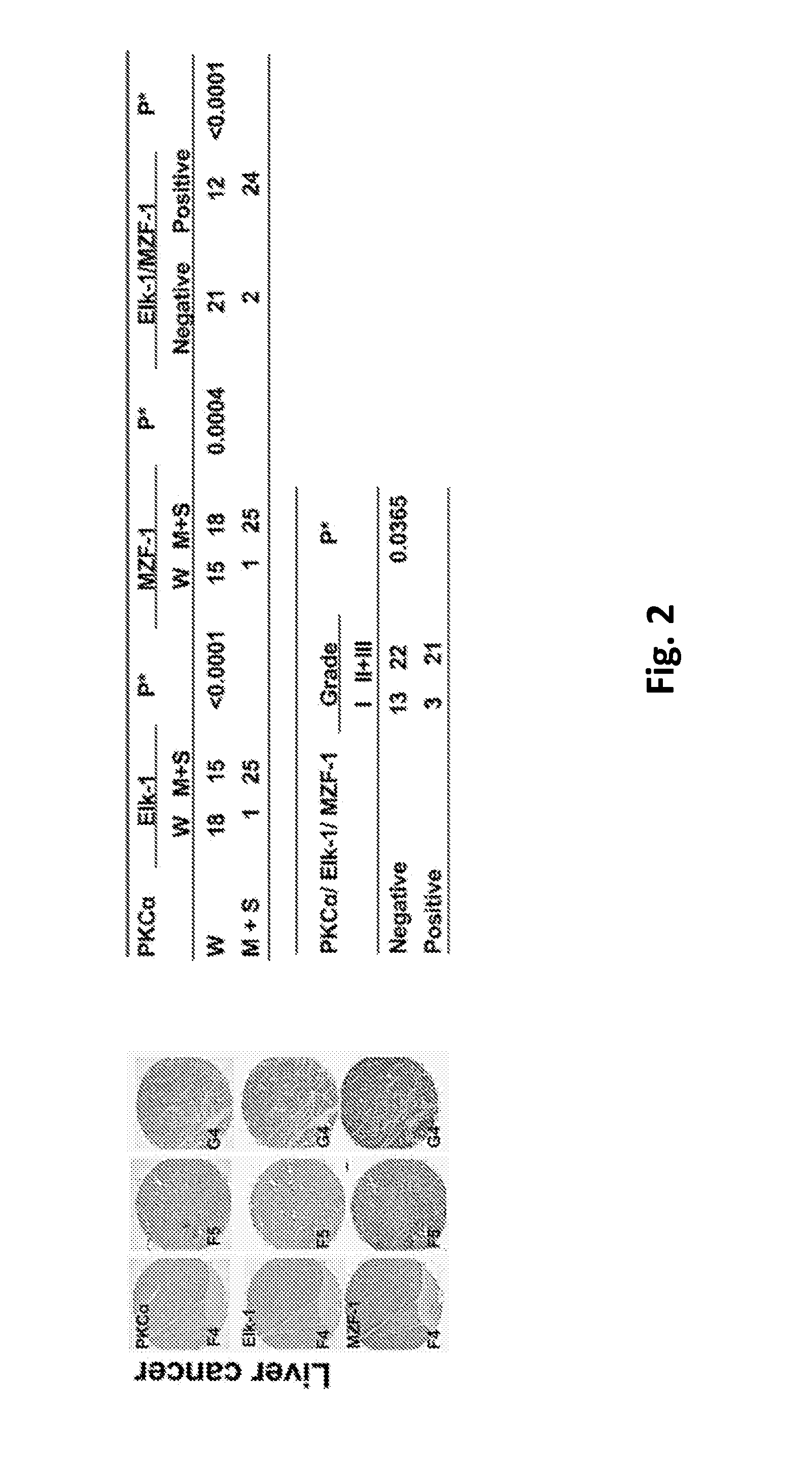
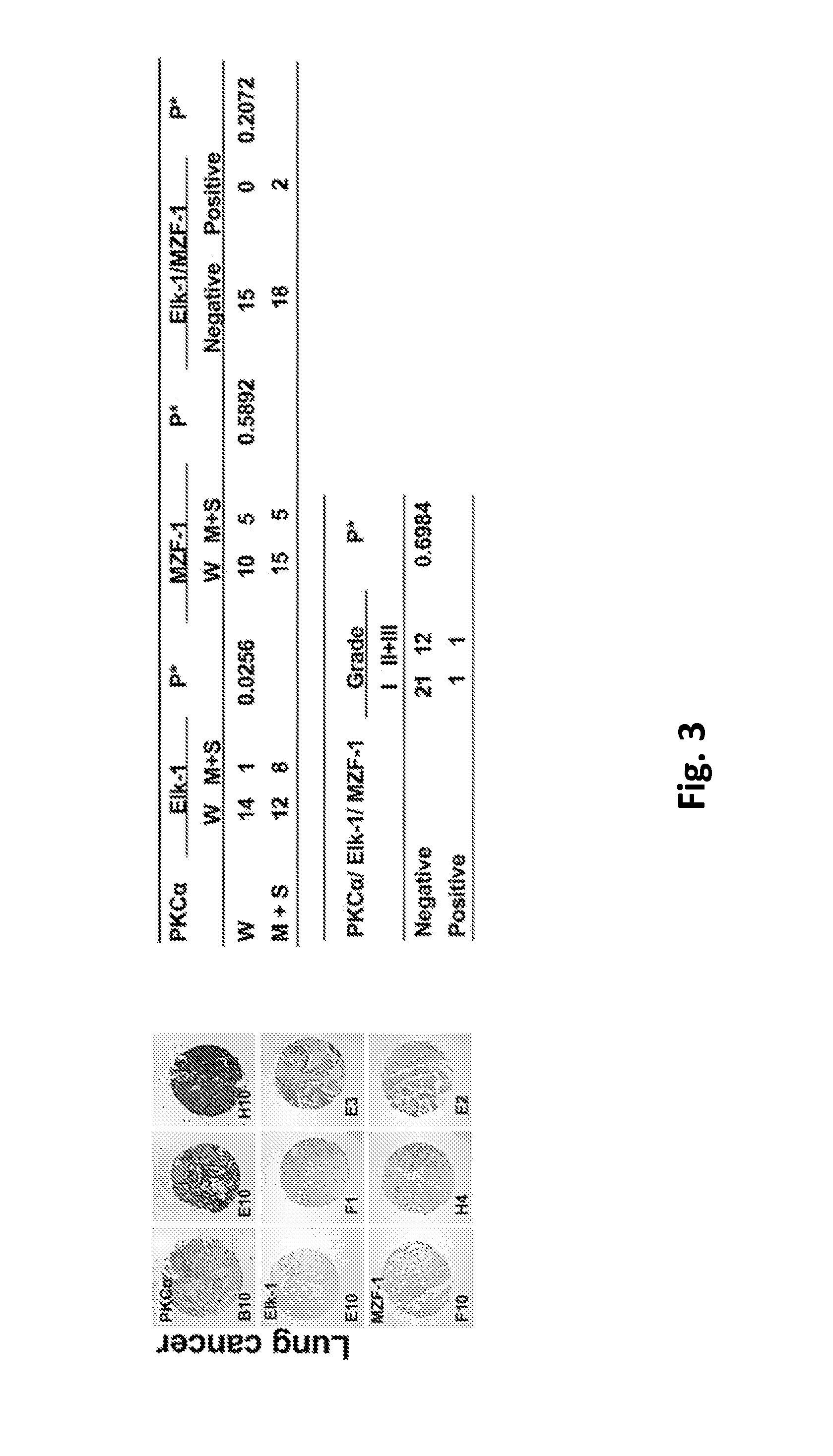
Pharmaceutical composition inhibiting interaction between MZF-1 and Elk-1
InactiveUS20160362463A1Reduce tumor volumePolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifPeptide/protein ingredientsProtein DegradationsCancer cell
This invention discloses a peptide, which inhibits the interaction between of MZF-1 and Elk-1 and further inhibits cancers. Both myeloid zinc finger 1 (MZF-1) and Ets-like protein-1 (Elk-1) expressions correlate to PKCα expression in cancer cells. Furthermore, it is the interaction between the acidic domain of MZF-1 and the heparin-binding domain of Elk-1 which facilitated their heterodimeric complex formation before their binding to the PKCα promoter. Blocking the formation of the heterodimer changed Elk-1 nuclear localization, MZF-1 protein degradation, their DNA-binding activities, and subsequently the expression of PKCα in cancer cells. Thus, migration, tumorigenicity, and epithelial-mesenchymal transition potential of cancer cells decreased, suggesting that the Elk-1 / MZF-1 heterodimer is considered as a mediator of PKCα in TNBC cell malignancy. The obtained data also suggest that the next therapeutic strategy in the treatment of cancer will come from the blocking of Elk-1 / MZF-1 interaction through the saturation of Elk-1 or MZF-1 binding domains, such as through the application of cell-penetrating HIV transactivating regulatory protein-fused peptides.
Owner:CHINA MEDICAL UNIVERSITY(TW)
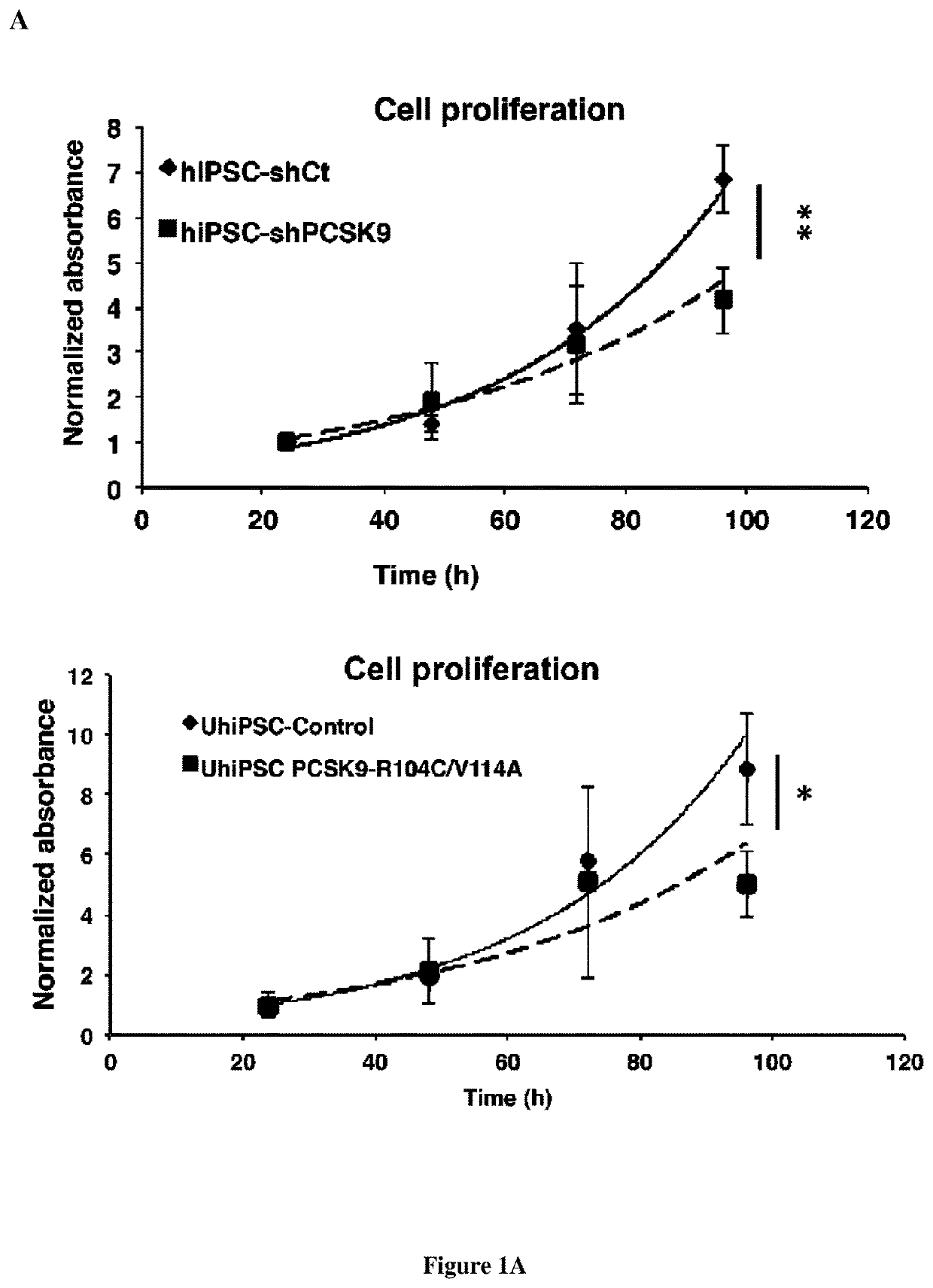
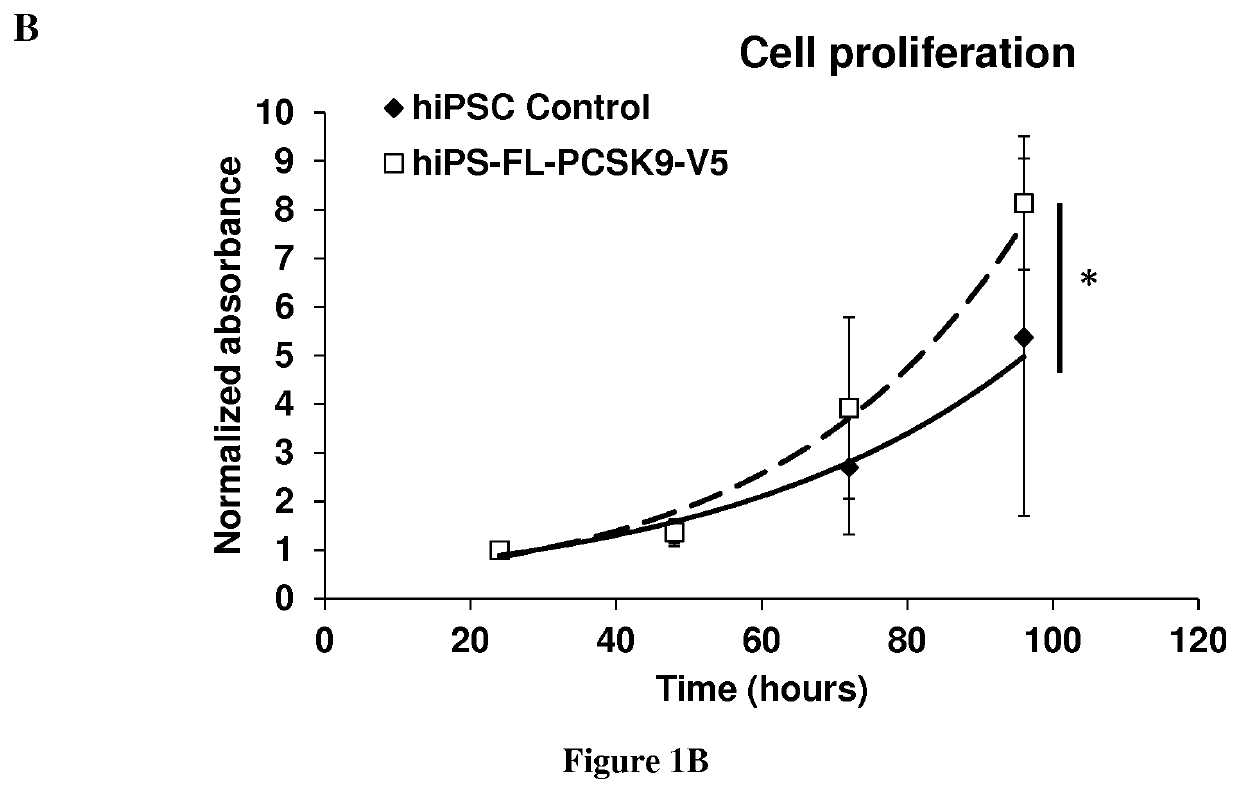
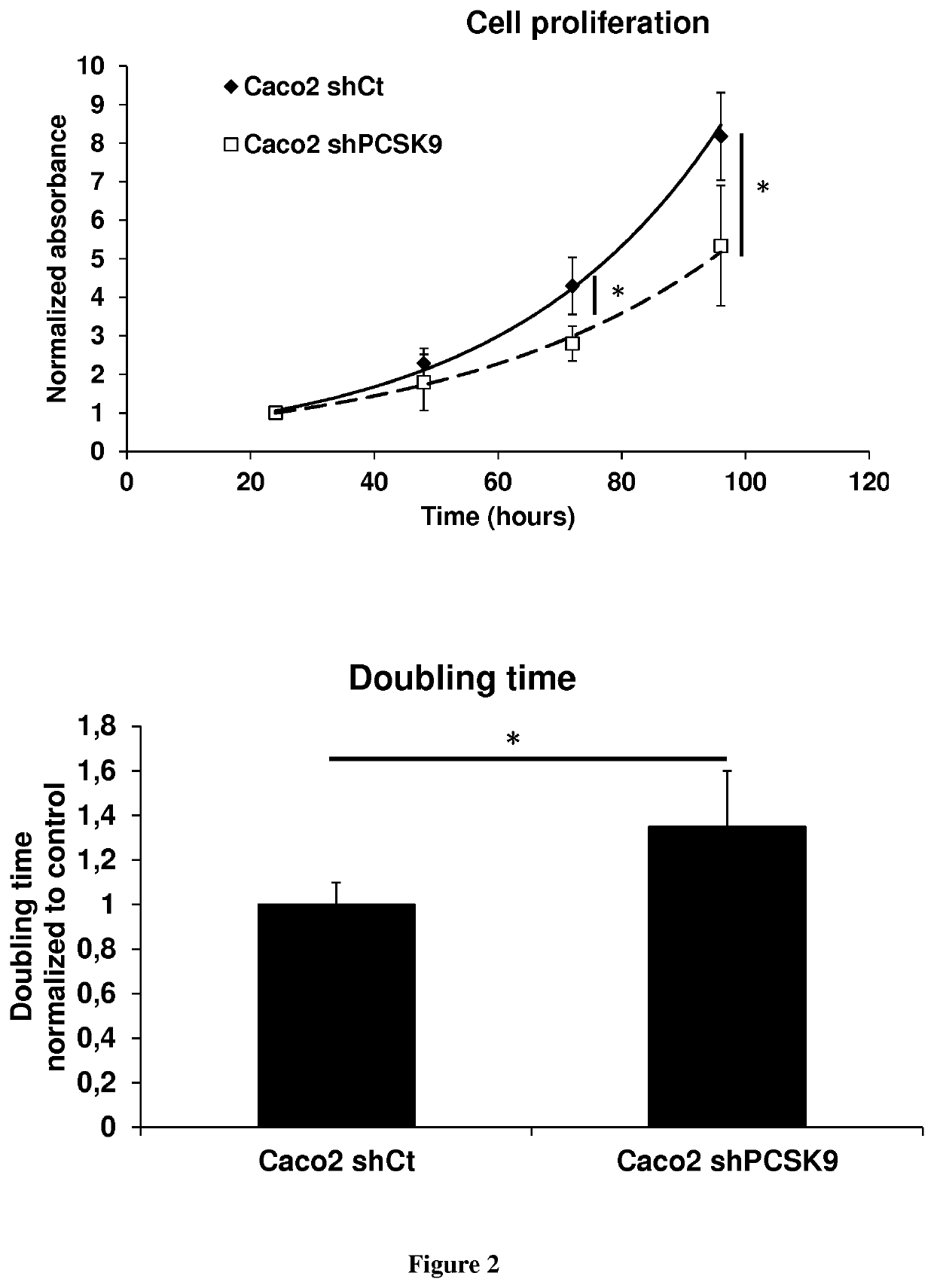
Methods and pharmaceutical compositions for modulating stem cells proliferation or differentiation
InactiveUS20190345500A1Increase productionEasier for the immune system to recognise and destroyOrganic active ingredientsAntibody ingredientsProtein DegradationsSignal Pathways
The present invention relates to a method for modulating stem cells proliferation or differentiation comprising a step of contacting said stem cells with an effective amount of an activator or inhibitor of a proprotein convertase subtilisin kexin 9 (PCSK9). Inventors performed a global transcriptomic analyses in hiPSCs and showed that PCSK9 inhibition by shRNA and the intracellular PCSK9-R104C / V114A mutation negatively regulate the NODAL signaling pathway and its targets. This regulation was manifested in drastic reduction P-SMAD2 / total SMAD2 protein level. This was accompanied by reduced proliferation rate where hiPSC-shPCSK9 and hiPSC-R104C / V114A demanded >1.3-fold more time to double compared to their control counterparts. They showed that PCSK9 was regulating this signaling pathway through direct physical interaction with DACT2, an intracellular attenuator of NODAL receptor and favoring its protein degradation. Thus, these findings allow to understand the differentiation and proliferation of cells.
Owner:INST NAT DE LA SANTE & DE LA RECHERCHE MEDICALE (INSERM) +4
Production technology of cashew peptide powder
InactiveCN106889299AAvoid degradationImprove immunityProtein composition from vegetable seedsVegetable proteins working-upProtein DegradationsEnzymatic hydrolysis
The invention discloses a production process of cashew nut peptide powder, which uses degreased cashew nut meal as raw material, undergoes enzymatic hydrolysis, impurity removal, vacuum concentration, and spray drying to obtain cashew nut peptide powder; the production process of cashew nut peptide powder provided by the invention , solve the degradation problem of high-fat cashew nut protein, degrade various nutrients in defatted cashew nut meal, and make it produce nutritious cashew nut peptide powder that can be directly absorbed by the human body.
Owner:艾华仲
Process for fermenting stinky preserved soybeans
InactiveCN106174038AUnique flavorModerate contentFood ingredient as taste affecting agentProtein DegradationsTotal amino acids
The invention relates to the technical field of bean food processing, and particularly relates to a process for fermenting stinky preserved soybeans. The process comprises the following steps: washing high-quality soybeans, drying in the air, roasting, soaking, and mixing with little yellow croaker to ferment for 5-7 days in a sealed condition; separating soybeans from little yellow croaker, steaming, inoculating one or more of aspergillus niger, rhizopus oryzae and glucoamylase in the steamed soybeans, seasoning the fermented soybeans, filling into cans, and pasteurizing to obtain a finished product. The stinky preserved soybeans prepared by the process have unique flavor and mellow taste, and can be used for promoting elimination of heavy metals in a body. According to the stringy fermented soybeans, the protein is increased by 30-35 percent, the total amino acid is increased by 22-26 percent, the large molecular weight protein degradation rate is more than 99.2 percent, and the small molecular protein is more than 50.1 percent of soluble protein. The stinky preserved soybeans can be stored for 8 months at normal temperature when chemical preservative is not added.
Owner:张红
Production technology of peanut peptide powder
InactiveCN106889301AAvoid degradationImprove immunityProtein composition from vegetable seedsProtein DegradationsEnzymatic hydrolysis
The invention discloses a production process of peanut peptide powder, which uses defatted peanut meal as raw material, undergoes enzymatic hydrolysis, impurity removal, vacuum concentration, and spray drying to obtain peanut peptide powder; the production process of peanut peptide powder provided by the invention , solve the degradation problem of high-fat peanut protein, degrade various nutrients in defatted peanut meal, and make it produce peanut peptide powder that can be directly absorbed by the human body and rich in nutrition.
Owner:张世禄
Method for Determining Ubiqutin Chain Length
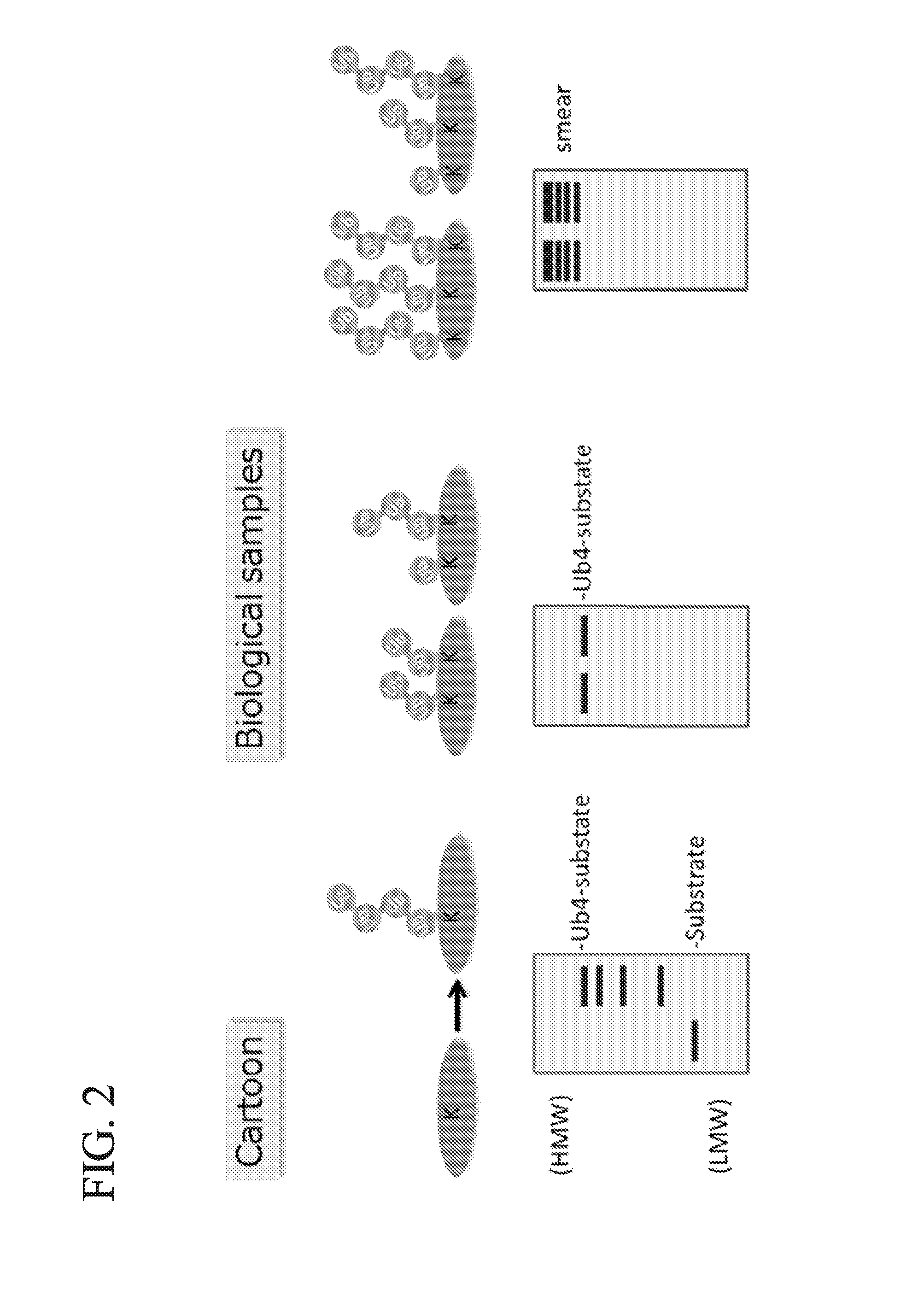
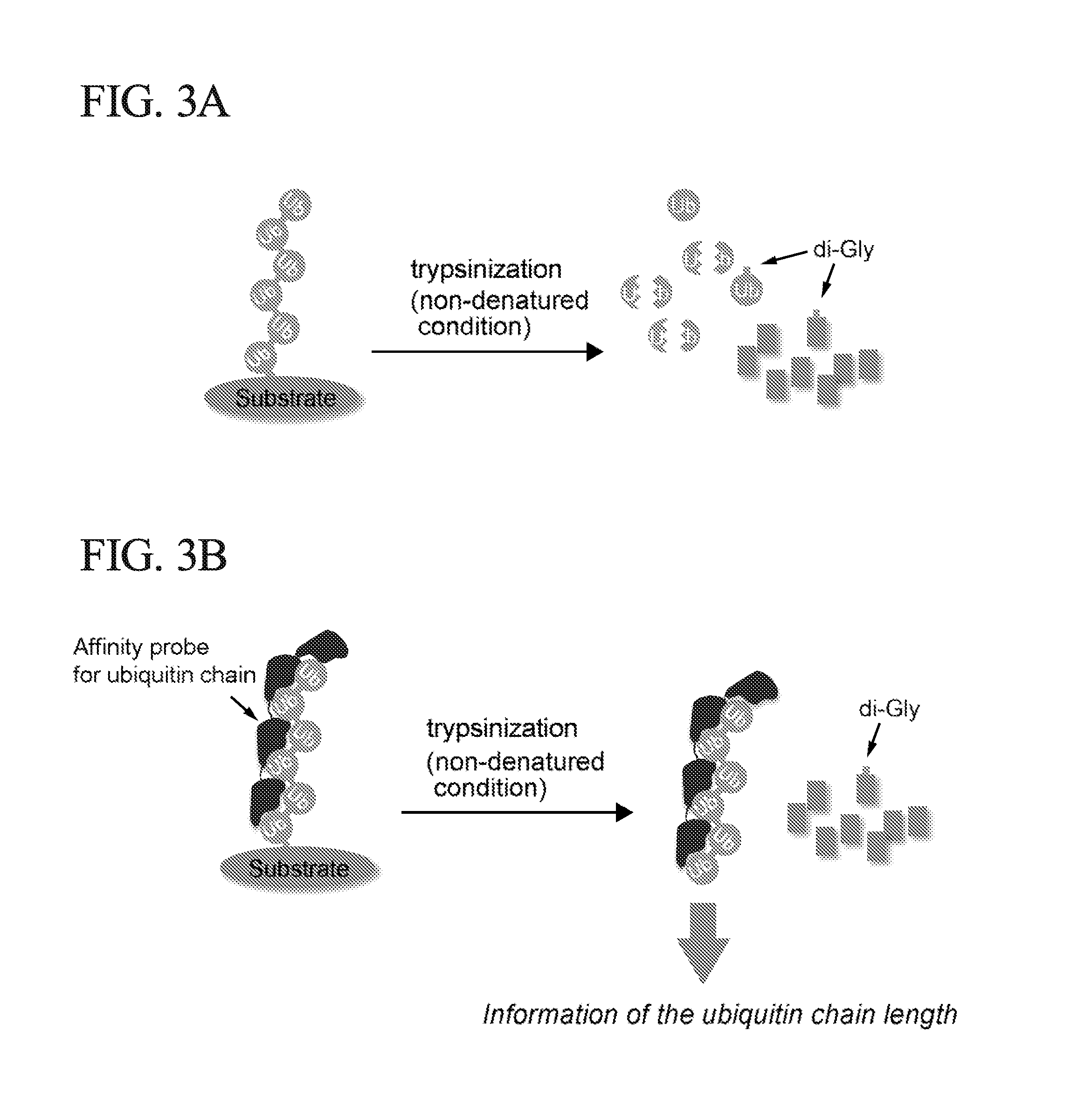
ActiveUS20150132779A1Used to determineDepsipeptidesPeptide preparation methodsProtein DegradationsProteasome Inhibition
Protein ubiquitylation, an essential post-translational modification, regulates almost every cellular process including protein degradation, protein trafficking, signal transduction, and DNA damage response in eukaryotic cells. The diverse functions of ubiquitylation are thought to be mediated by distinct chain topologies resulting from eight different ubiquitin linkages, chain lengths, and complexities. Currently, ubiquitin linkages are generally thought to be a critical determinant of ubiquitin signaling. However, ubiquitin chain lengths, another key element of ubiquitin signaling, have not been well documented especially in vivo situation during past three decades from the discovery of ubiquitin. The reason of this was simply because no method has been available for determination of ubiquitin chain length in endogenous ubiquitylated substrates. In the present invention, a practical technique for determining the actual length of substrate-attached polyubiquitin chains from biological samples is established. Using the method, the mean length of substrate-attached polyubiquitin chains was determined and the robustness of ubiquitin chain length regulation in cells is investigated. The following is a summary of findings in this invention: 1. A method for determining ubiquitin chain length was developed and this method was named ‘ubiquitin protection from trypsinization’ (Ub-ProT). 2. Using Ub-ProT, it was determined that the mean length of substrate-attached ubiquitin chains is in the dimer to decamer range. 3. By quantitative proteomics, it was found that the mean lengths of five major types of ubiquitin chains can be divided into two groups. 4. Proteasome-inhibition did not alter the mean length of substrate-attached polyubiquitin chains, indicating that cells have a robust system for regulating ubiquitin chain length.
Owner:TOKYO METROPOLITAN INST OF MEDICAL SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com