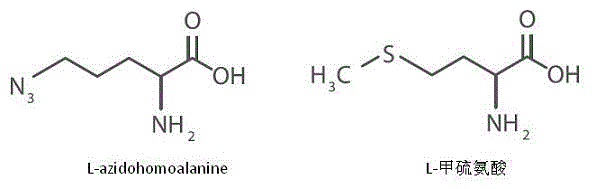Method for detecting degradation of protein in cells
A protein and cell technology, applied in the field of biochemistry, can solve the problems of high laboratory requirements, blocking, high cytotoxicity of cycloheximide, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0031] Example 1 Methionine Labeling of Newly Synthesized Proteins in Cells by Azide Small Molecule Groups
[0032] In various cells such as STHdh of experimental mice, methionine is an essential amino acid for protein synthesis. L-azidohomoalanines are methionine analogues with an azido group. Spread the same number of cells in several culture dishes, culture with complete culture medium for 24 hours, remove the complete culture medium, and wash once with PBS. The cells were starved for one hour using the methionine-free medium purchased from Life Technologies to completely consume the original methionine in the cells, and then the azido-containing methionine analog L -azidohomoalanine, so that the final concentration in the culture medium is 1‰, culture for 12 hours, during the 12 hours, the newly synthesized protein in the cells is labeled with L-azidohomoalanine, so as to have an azide group; collect the first time point after 12 hours Wash the cells in the remaining cul...
Embodiment 2
[0034] The biotin molecule is coupled to the azide small molecule group of the protein by CuAAC reaction:
[0035] The CuAAC reaction refers to the cycloaddition reaction of copper catalyzed azide and terminal alkyne, using copper ions to catalyze the reaction of the azide group of the protein that has been labeled with the azide group but not degraded with the terminal alkyne with biotin , to achieve protein labeling with biotin.
[0036] The reaction was carried out according to the specific operation steps of the Click-iT Reaction Kit purchased from Life Technologies. Add up to 50uL of protein lysate to the EP tube (up to 200ug of protein), add 100uL of Click-iT reaction buffer, add water to make up to a total volume of 160uL, Vortex for 5s, add 10uL of Click-iT Component B (CuSO 4 ), Vortex for 5s, add 10uL click it reaction buffer additive 1, Vortex for 5s, place for 2-3 min, but no more than 5 min, add 20uL Click-iT reaction buffer additive 2, Vortex for 5s, place t...
Embodiment 3
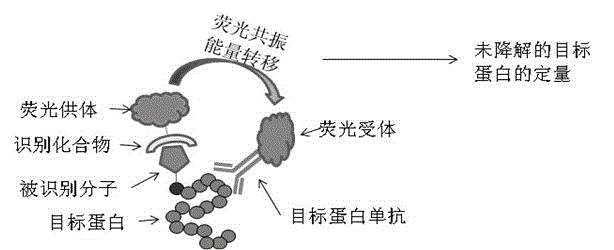
[0038] Quantification of target proteins coupled with biotin molecules using the principle of homogeneous time-resolved fluorescence resonance:
[0039] Streptavidin (Streptavidin) and biotin (Biotin) have specific binding properties, adding fluorescent group-labeled streptavidin and target protein antibody in the reaction, using the principle of homogeneous time-resolved fluorescence resonance ( HTRF), to perform high-throughput, high-precision, and specific quantification of undegraded but labeled target proteins, thereby accurately detecting protein degradation.
[0040] Add a certain amount of biotin-labeled protein samples into a 384-well plate, add Streptavidin-D2 labeled with fluorescent receptor D2 (1.4 ng / μl ) and Terbium Cryptate-labeled target protein-specific antibody (2B7-Tb, 0.023 ng / μl), after incubation for 1 to 2 hours, detect fluorescence resonance signals on a PerkinElmer Envision instrument, only those labeled with biotin , and the protein that can be spec...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com