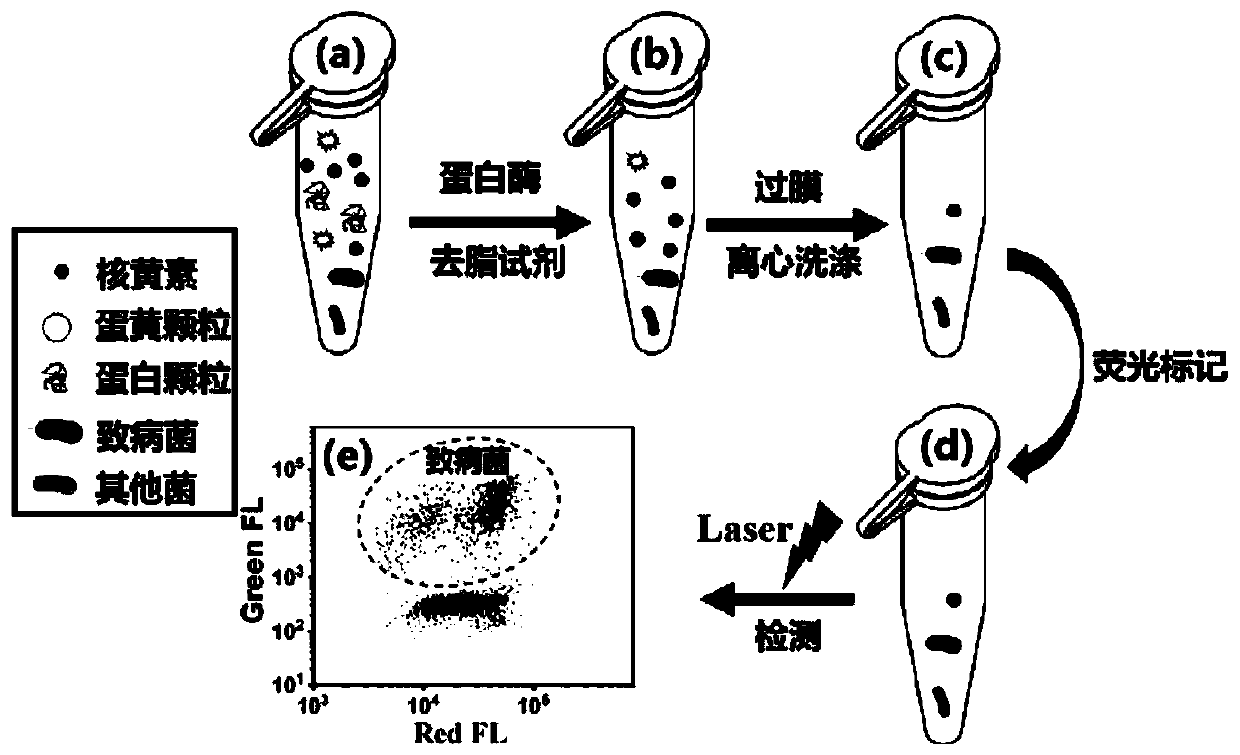
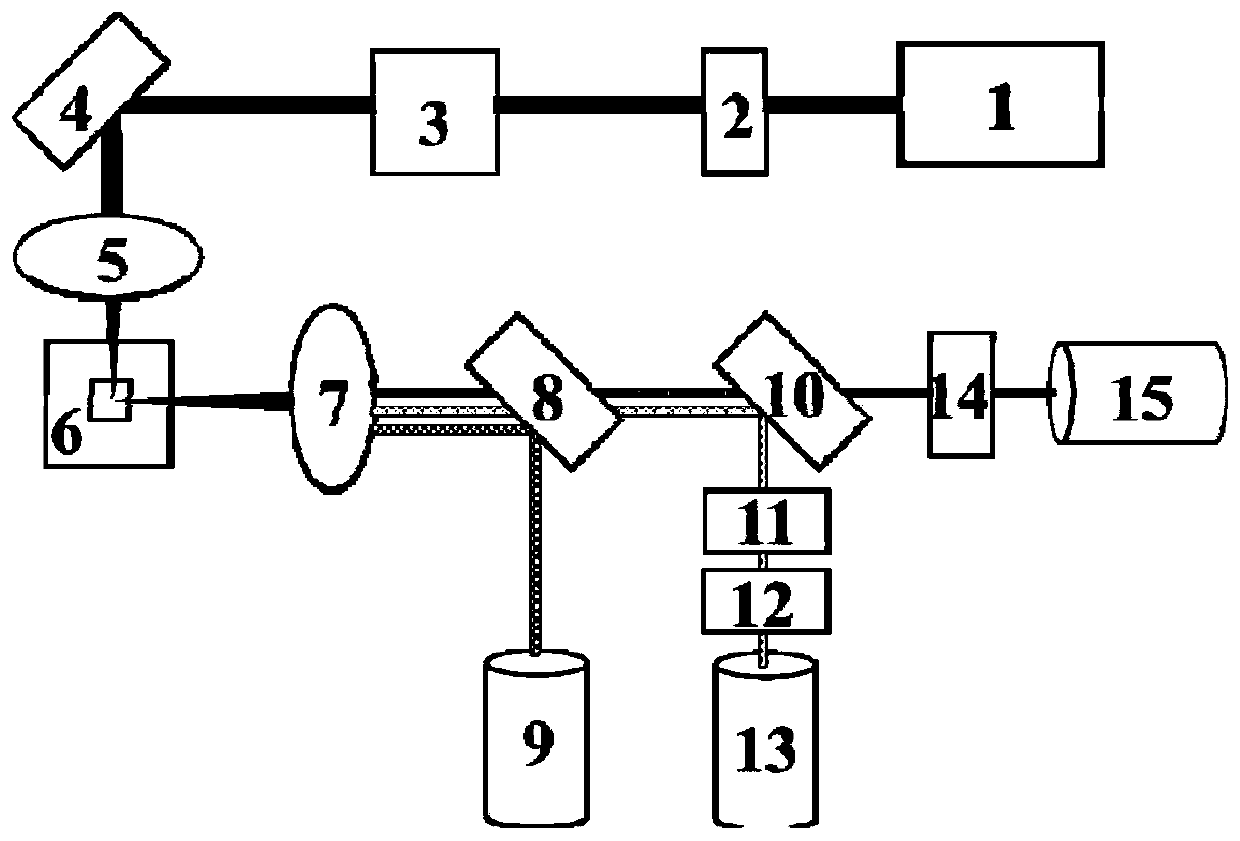
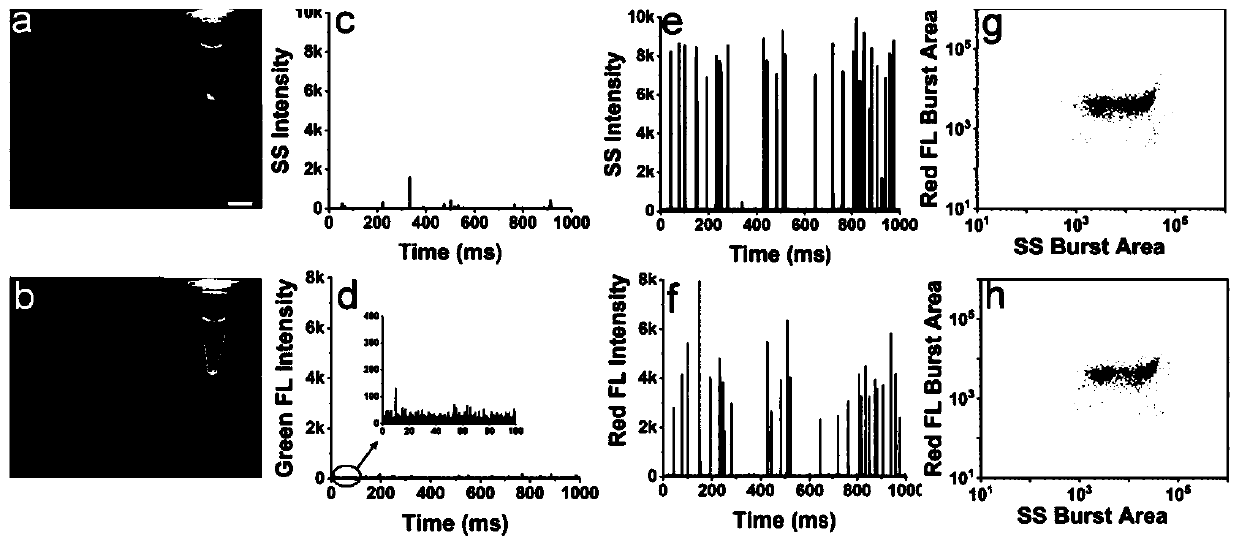
Method for quantitative detection of pathogenic bacteria and total bacterial count in edible raw egg
A technology for quantitative detection and pathogenic bacteria, applied in the field of food hygiene, can solve the problems of difficult detection, high false positive rate, and low detection signal-to-noise ratio.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0083] This example is used to illustrate the effectiveness of the pretreatment method for edible raw eggs and the influence of the pretreatment method on the detection of bacteria. The pretreatment experimental bacteria were obtained from laboratory culture.
[0084] The edible raw egg sample sampling plan used in this example is: put fresh eggs on a sterile ultra-clean bench, wipe the eggshells with 75% by volume ethanol, disinfect the eggshells, and then carefully break the eggshells, The egg content was placed in a 250mL sterile Erlenmeyer flask, shaken at 250rpm for 10min at 4°C, and a sterile egg liquid sample was prepared.
[0085] Take 0.1 mL of the sterile egg liquid sample prepared above, add 630 μL of PBS, 70 μL of proteinase K (20 mg / mL), and 200 μL of Triton X-100 (10 volume %), the total volume is 1 mL, that is, the egg liquid is diluted 10 times. The final concentration of the enzyme was 1.4 mg / mL, the final concentration of the degreasing reagent was 2% by volu...
Embodiment 2
[0090] This example is used to illustrate the comparison between the detection results of bacteria artificially added to edible raw eggs by the method provided by the present disclosure and the detection results of the traditional plate culture method.
[0091] In this experiment, the method of preparing egg liquid samples by eating raw egg samples is consistent with that in Example 1. Sampling of fresh eggs was carried out using the protocol in Example 1, and the bacterial culture method consistent with Example 1 was used to cultivate Escherichia coli K12.
[0092] The method for preparing the sterile egg liquid sample used in this example is: take 1 mL of the prepared Escherichia coli K12 bacterial liquid sample, centrifuge it and resuspend it in 1 mL of sterile raw egg sample, vortex and mix well, and obtain the sterile egg liquid sample .
[0093] Take 0.1 mL of the prepared sterile egg liquid sample, add 630 μL of PBS, 70 μL of proteinase K (20 mg / mL), and 200 μL of Trit...
Embodiment 3
[0098] This example is used to illustrate that the detection result of the ratio of target pathogenic bacteria and non-pathogenic bacteria artificially added to edible raw eggs by the method provided in the present disclosure is consistent with the actual addition ratio.
[0099] In this example, Alexa Fluor 488-labeled Salmonella typhimurium-specific monoclonal antibody probes were used for the first fluorescent labeling. The antibody was purchased from abcam with a product number of ab8247, and the antibody specifically recognized lipopolysaccharide (LPS) of Salmonella typhimurium. , Alexa Fluor 488 was purchased from Thermo Fisher, the product number is A2000, and the method of binding Alexa Fluor 488 to the antibody refers to the labeling strategy of Thermo Fisher, see Thermo Fisher A30006 method.
[0100] In this experiment, the method of preparing egg liquid samples by eating raw eggs is consistent with that in Example 1. The concentration of non-pathogenic bacteria mode...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| volume | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com