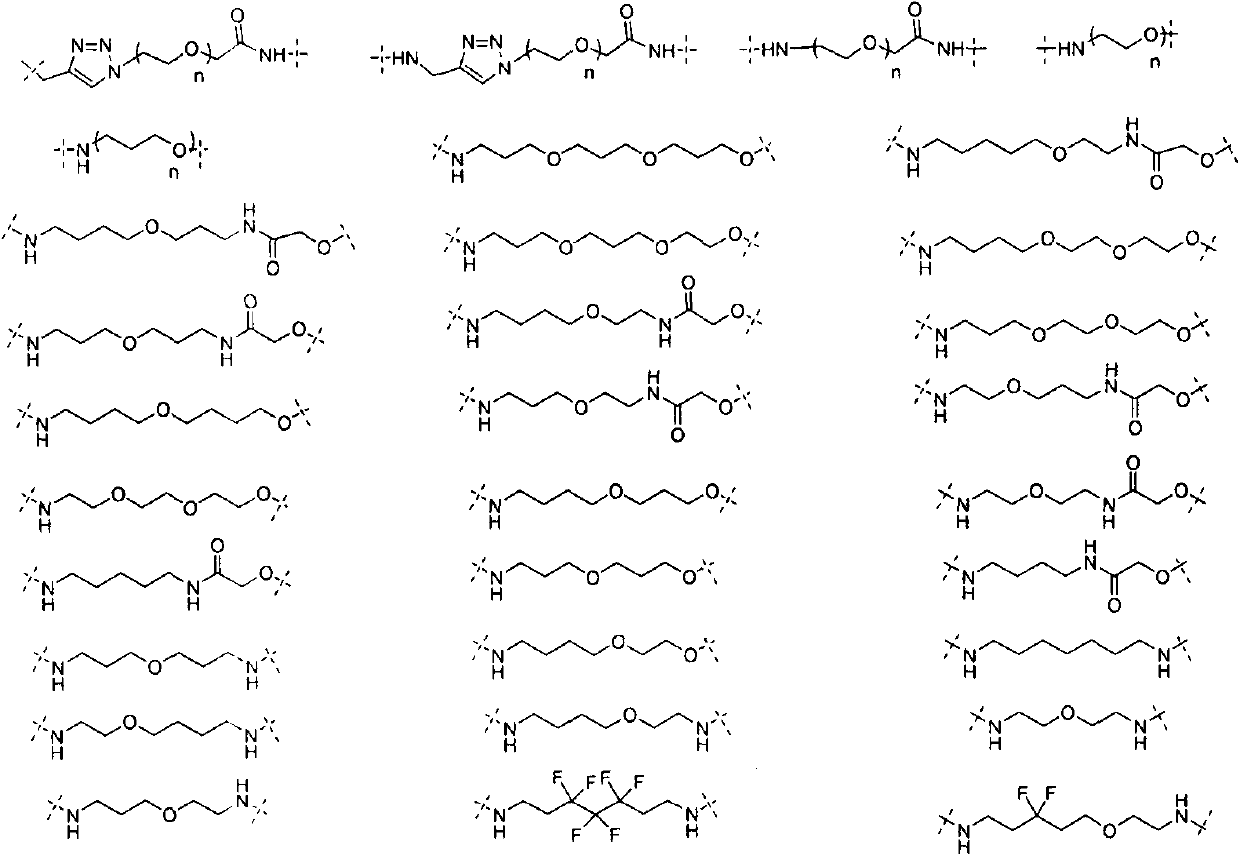
Patents
Literature
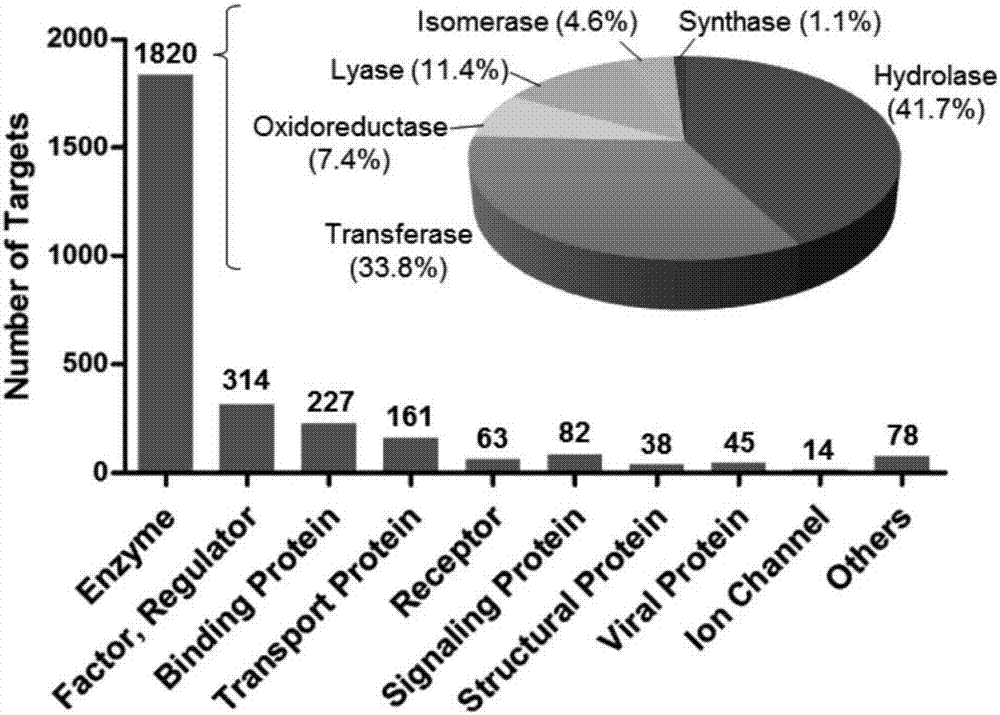
140 results about "Protein ligand" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In biochemistry, a protein ligand is an atom, a molecule or an ion which can bind to a specific site on a protein. Alternative names used to mean a protein ligand are affinity reagents or protein binders. To date, antibodies are the most widely used protein ligands in life-science investigations, however, other molecules such as protein scaffolds, nucleic acids, peptides are also being used. Main methods to study protein–ligand interactions are principal hydrodynamic and calorimetric techniques, and principal spectroscopic and structural methods such as Fourier transform spectroscopy Raman spectroscopy Fluorescence spectroscopy Circular dichroism Nuclear magnetic resonance Mass spectrometry Atomic force microscope Paramagnetic probes Dual Polarisation Interferometry Other techniques include: fluorescence intensity, bimolecular fluorescence complementation, FRET / FRET quenching surface plasmon resonance, Bio-Layer Interferometry, Coimmunopreciptation indirect ELIS, equilibrium dialysis, gel electrophoresis, far western blot, fluorescence polarization anisotropy, electron paramagnetic resonance, Microscale Thermophoresis
Mutant protein
InactiveUS20060194950A1Improve stabilityIncreased pH-valuesBacteriaSerum immunoglobulinsMutated proteinComplementarity determining region
Owner:GE HEALTHCARE BIO SCI CORP
Mutated immunoglobulin-binding protein
ActiveUS20050143566A1Improve stabilityIncreased pH-valuesSerum immunoglobulinsComponent separationComplementarity determining regionChemical stability
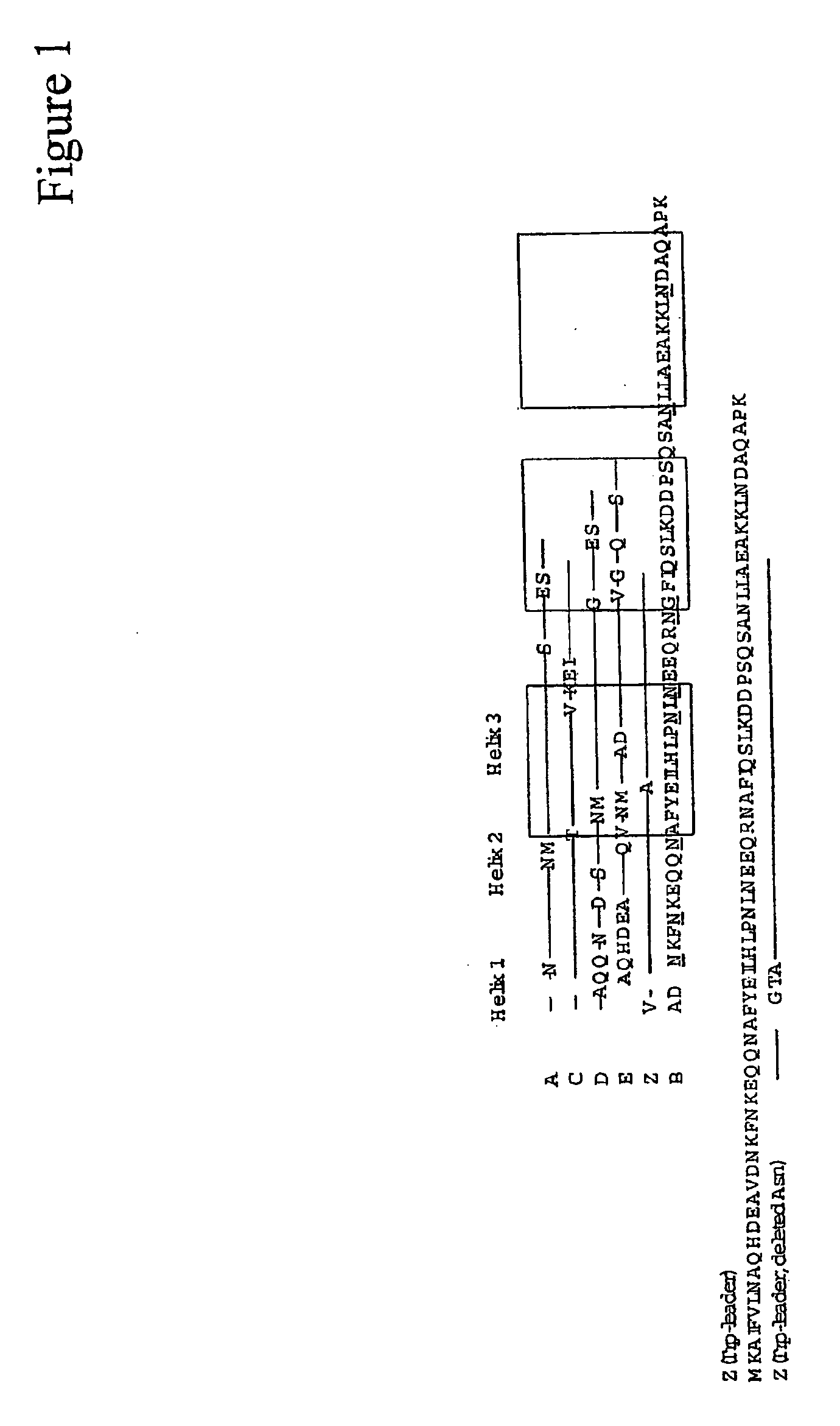
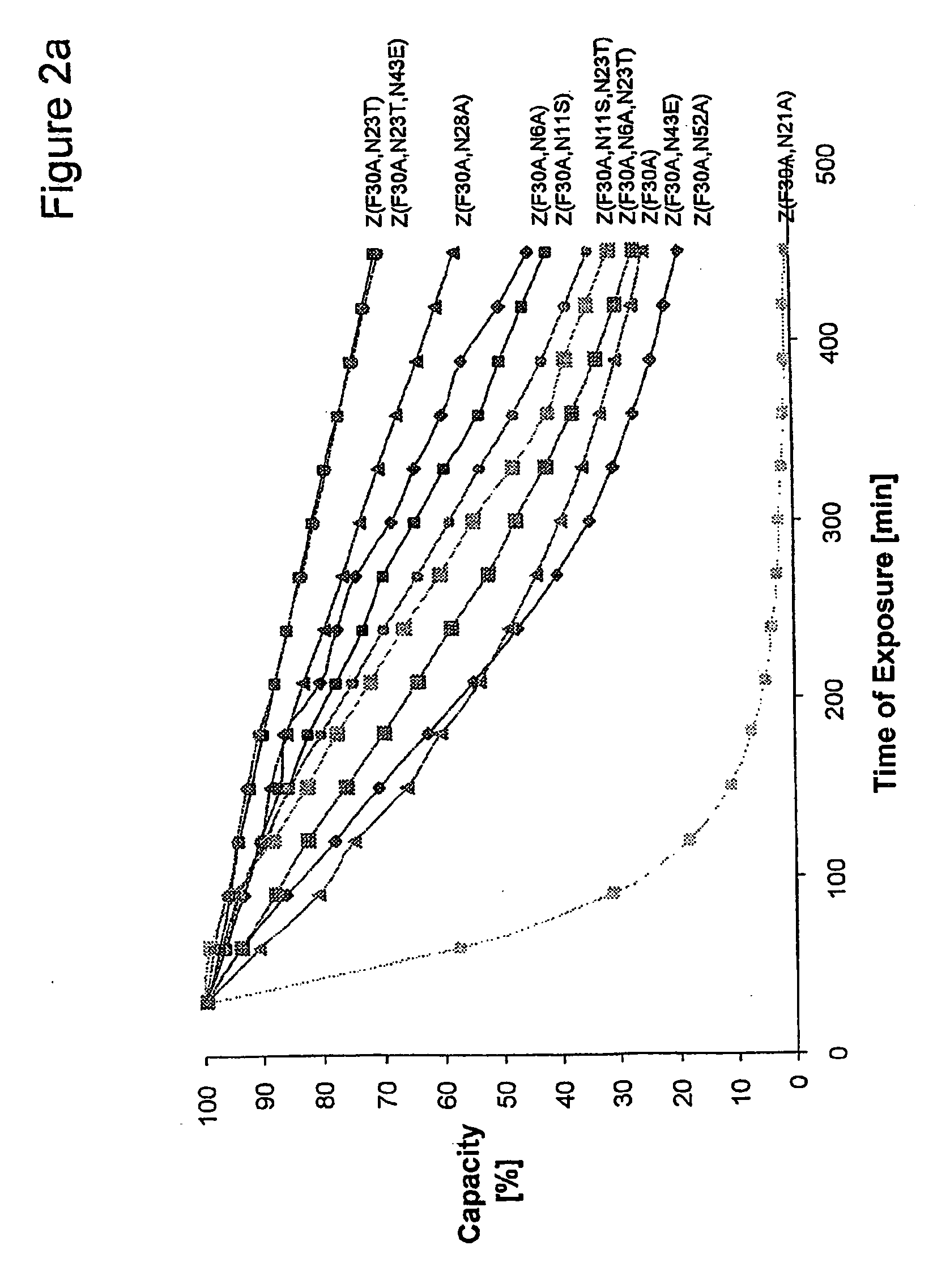
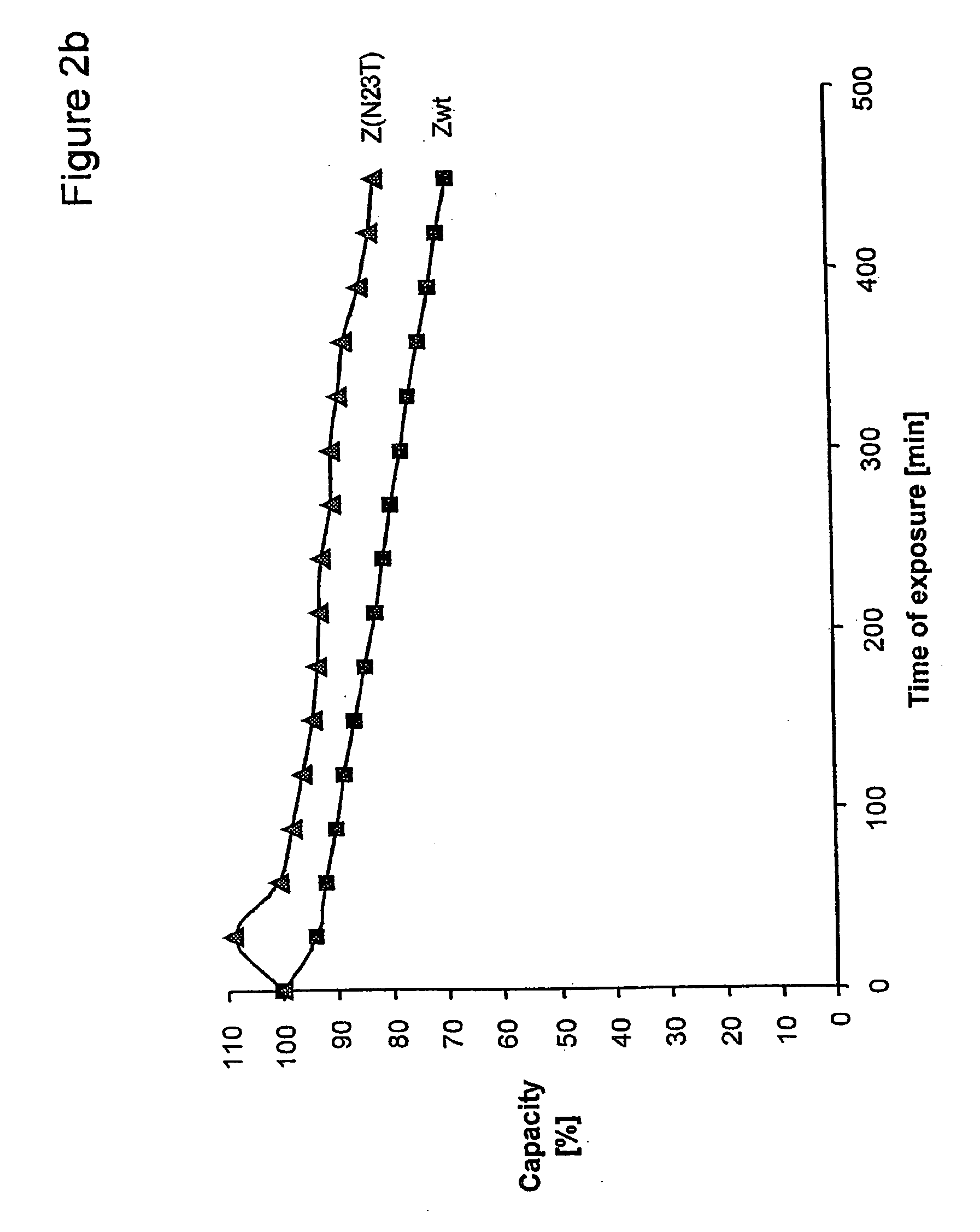
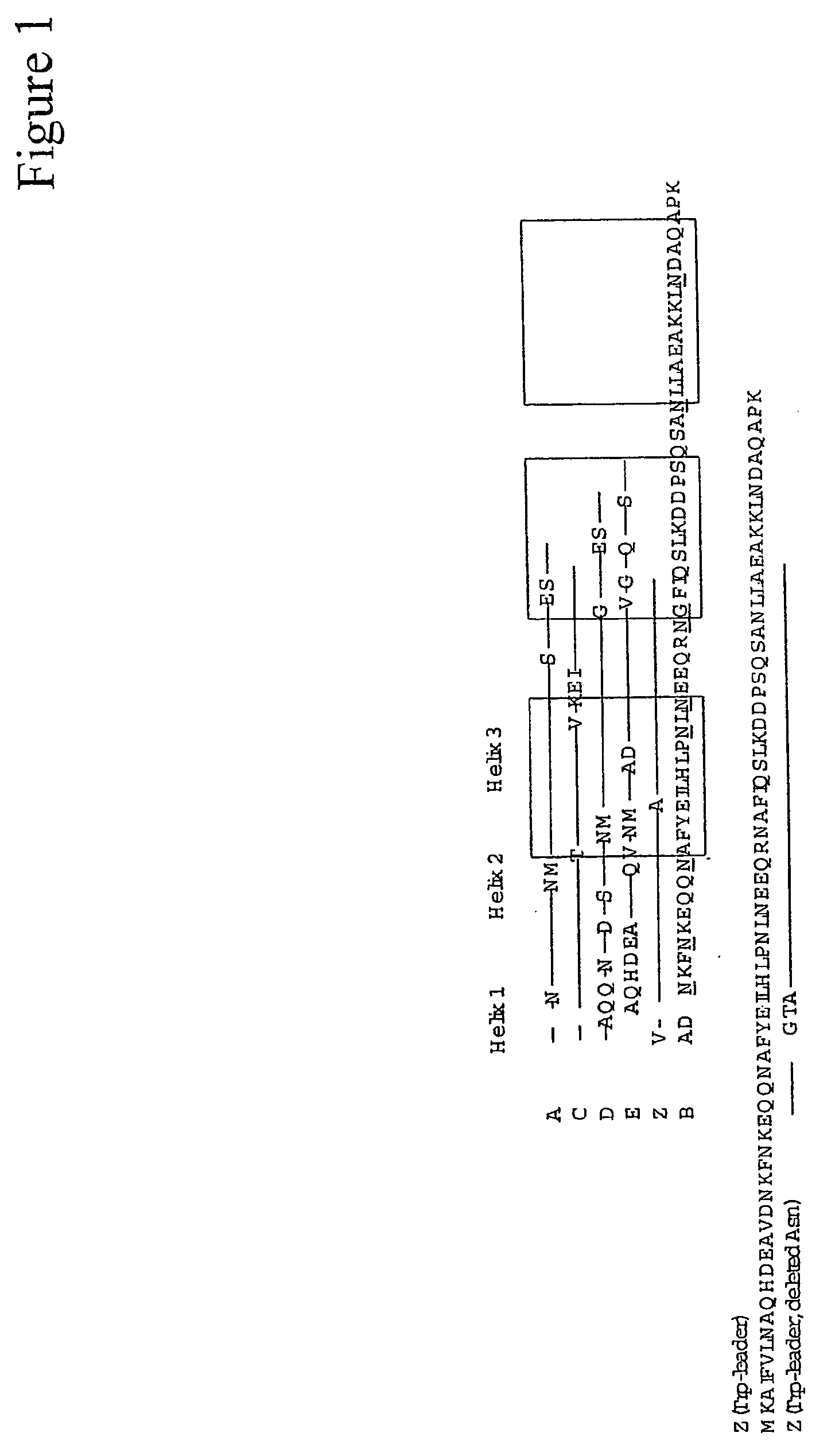
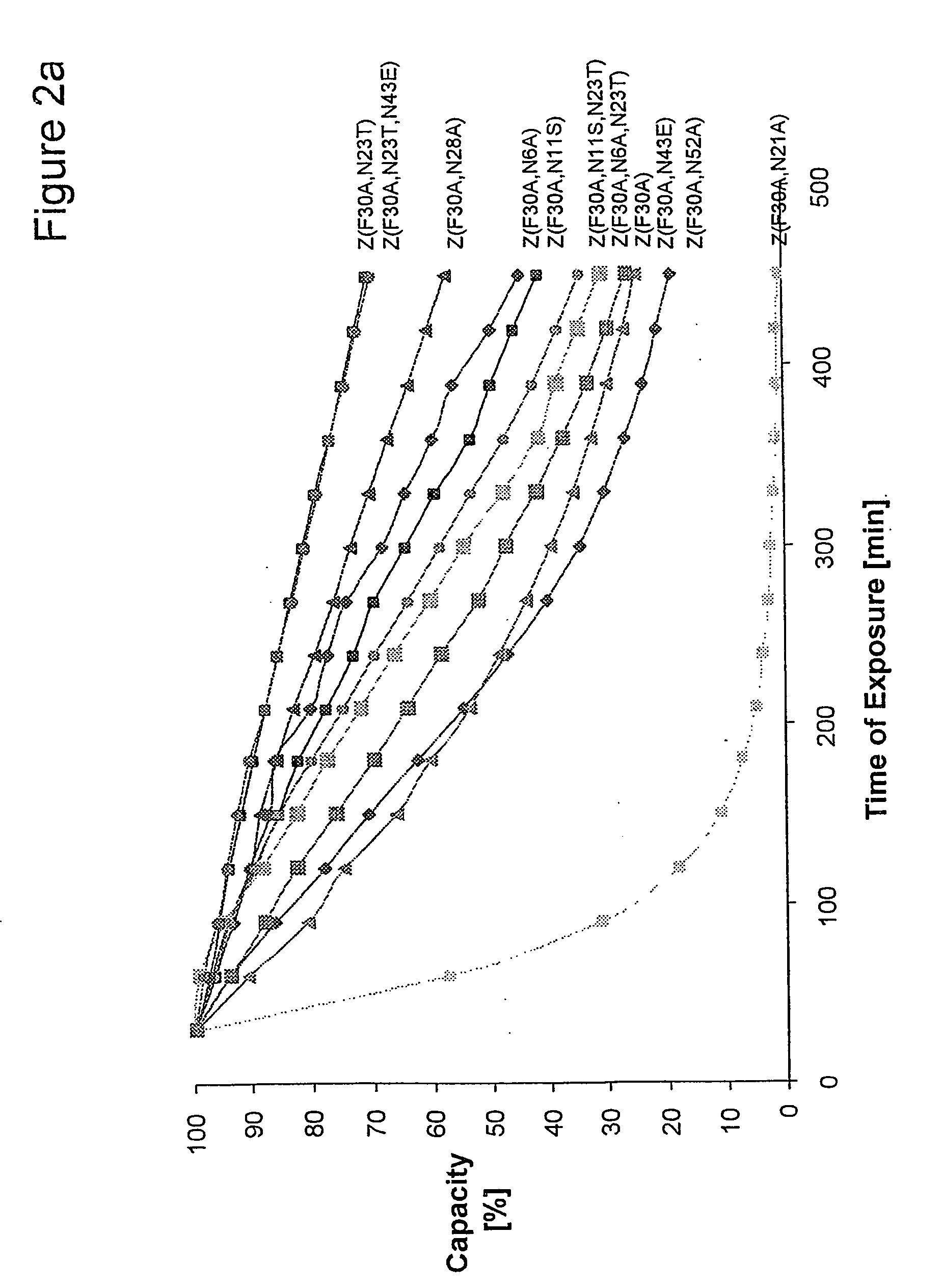
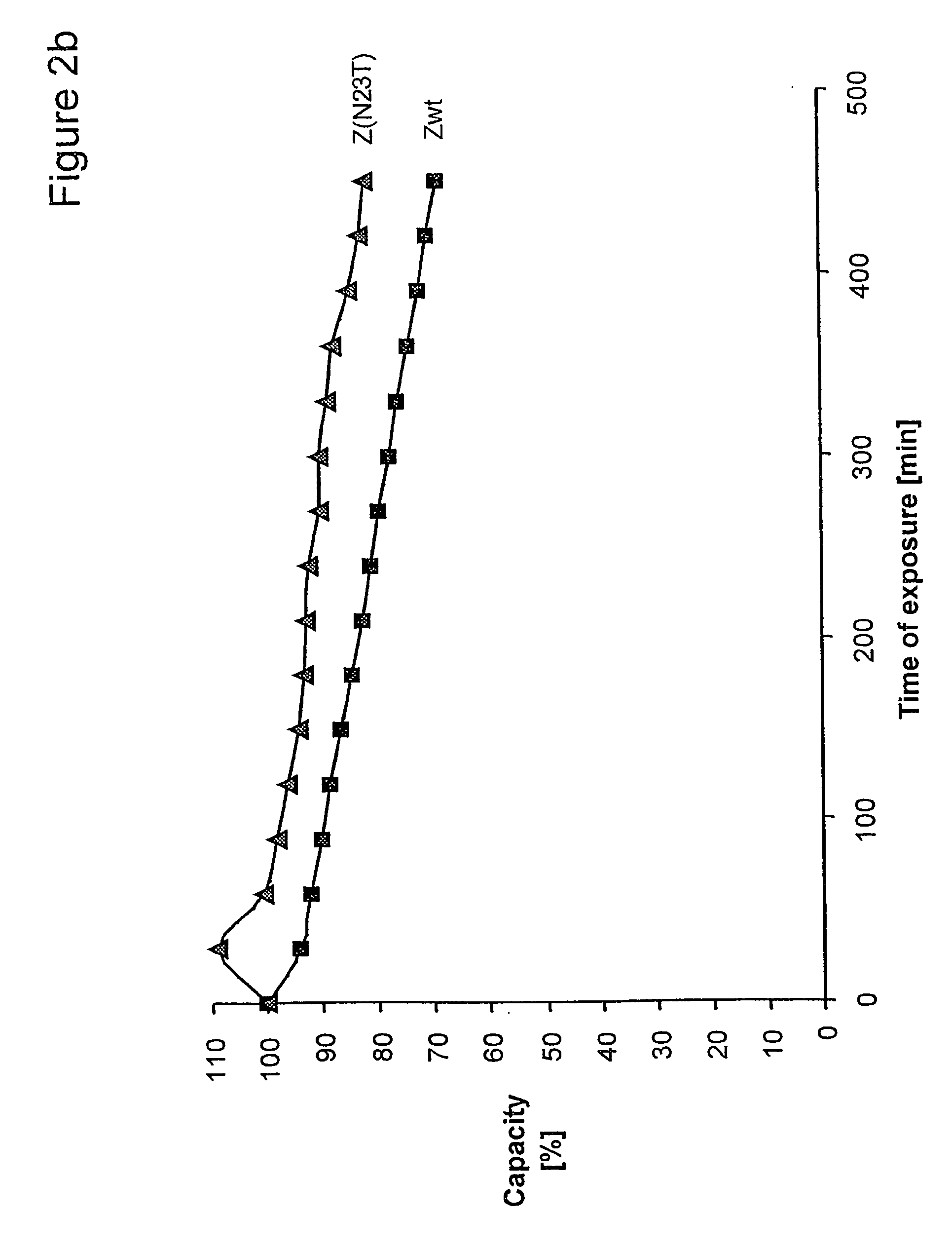
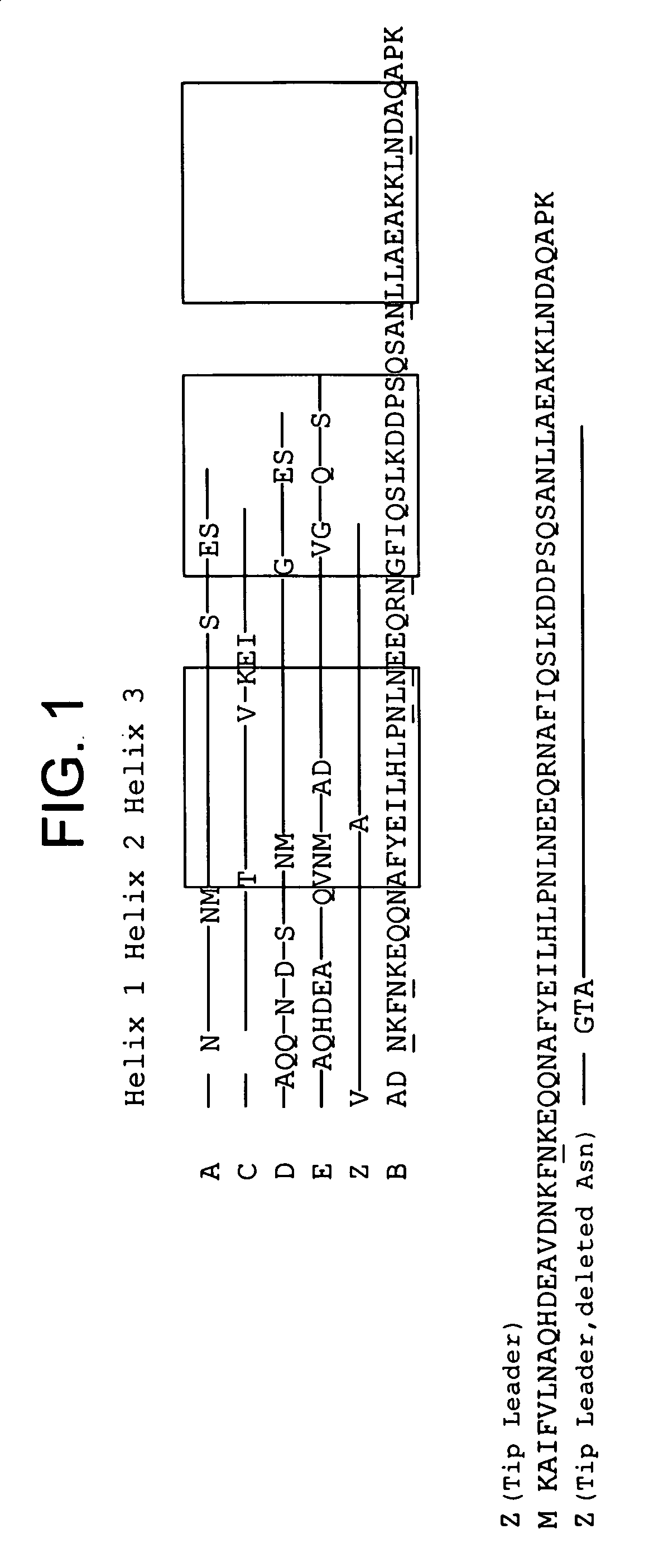
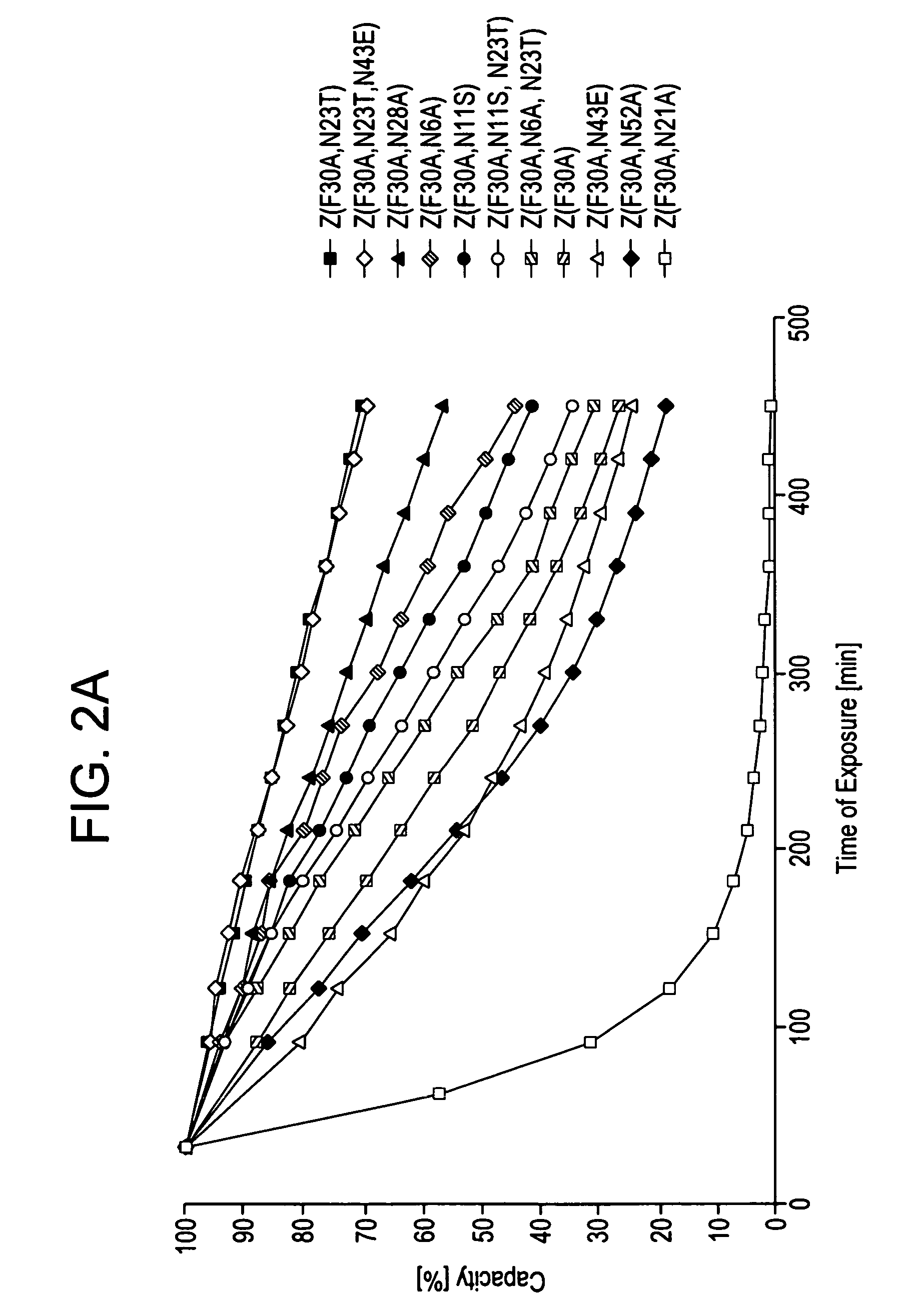
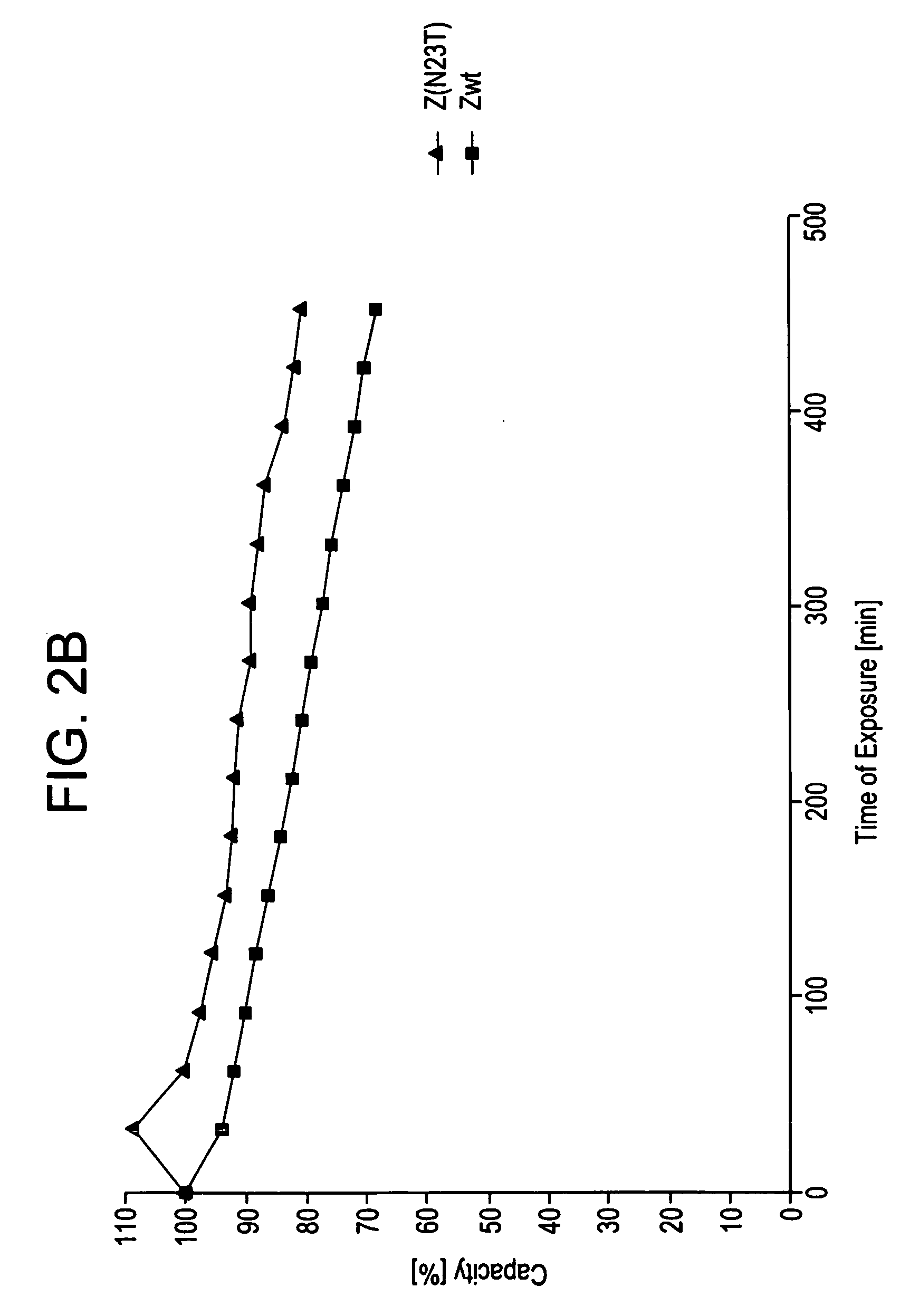
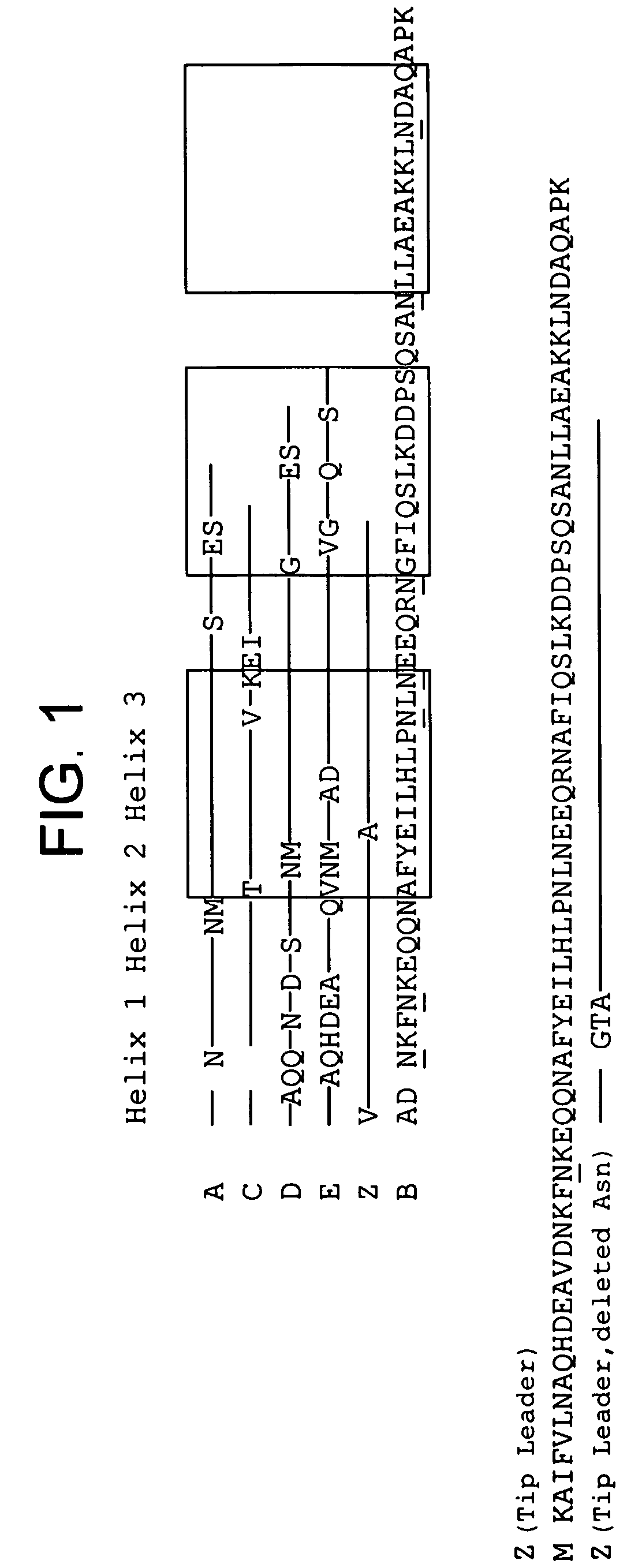
The present invention relates to an immunoglobulin-binding protein, wherein at least one asparagine residue has been mutated to an amino acid other than glutamine or aspartic acid, which mutation confers an increased chemical stability at pH-values of up to about 13-14 compared to the parental molecule. The protein can for example be derived from a protein capable of binding to other regions of the immunoglobulin molecule than the complementarity determining regions (CDR), such as protein A, and preferably the B-domain of Staphylococcal protein A. The invention also relates to a matrix for affinity separation, which comprises an immunoglobulin-binding protein as ligand coupled to a solid support, in which protein ligand at least one asparagine residue has been mutated to an amino acid other than glutamine.
Owner:CYTIVA BIOPROCESS R&D AB
Protein ligands
ActiveUS20060194955A1Retention characteristicReduce leakageImmunoglobulins against animals/humansBiological testingComplementarity determining regionStaphylococcus
The present invention relates to the use of an alkali-stable protein, wherein at least one asparagine residue has been mutated to an amino acid other than glutamine or aspartic acid, which mutation confers an increased chemical stability at pH-values of up to about 13-14 compared to the parental molecule. The protein can for example be derived from a protein capable of binding to other regions of the immunoglobulin molecule than the complementarity determining regions (CDR), such as protein A, and preferably the B-domain of Staphylococcal protein A. The invention also relates to a matrix for affinity separation, which comprises an immunoglobulin-binding protein as ligand coupled to a solid support, in which protein ligand at least one asparagine residue has been mutated to an amino acid other than glutamine.
Owner:CYTIVA BIOPROCESS R&D AB
Method of affinity separation and ligands for use therein
Methods of affinity separation wherein the affinity ligand is an immobilized proteinaceous ligand wherein one or more of its asparagine (Asn) residues has been modified. Methods of making a stabilized combinatorial protein by a) modification of Asn residues within a protein molecule to increase stability of the protein in alkaline conditions, and b) randomization of a protein molecule to modify its binding characteristics, and combinatorial proteins wherein in a step separate from the randomization step, the stability of the protein in alkaline conditions has been increased by modifying one or more of its Asn residues.
Owner:AFFIBODY TECH AB
Β-turn peptidomimetic cyclic compounds
InactiveUS6881719B2Easy to manageReduce deliveryOrganic active ingredientsTetrapeptide ingredientsDiseaseNeurotrophin Receptor p75
Proteolytically stable small molecule β-turn peptidomimetic compounds have been identified as agonists or antagonists of neurotrophin receptors, such as TrkA. A compound of particular interest binds the immunoglobulin-like C2 region of the extracellular domain of TrkA, competes the binding of another TrkA ligand, affords selective trophic protection to TrkA-expressing cell lines and neuronal primary cultures, and induces the differentiation of primary neuronal cultures. The small β-turn peptidomimetic compounds of the invention can activate a tyrosine kinase neurotrophin receptor that normally binds a relatively large protein ligand. Such compounds that bind the extracellular domain of Trk receptors are useful pharmacological agents to address disorders where Trk receptors play a role, by targeting populations selectively.
Owner:TEXAS A&M UNIVERSITY +1
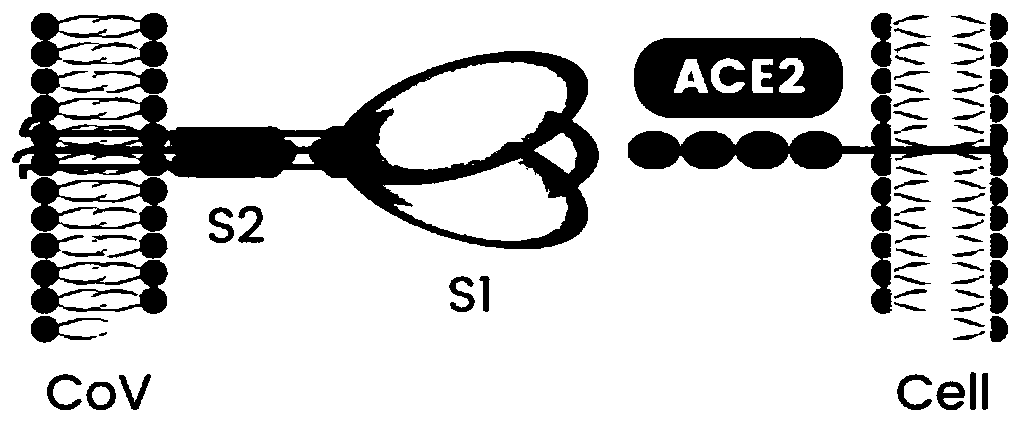
Coronavirus rapid detection kit based on S protein ligand and ACE2 receptor competitive chromatography
ActiveCN111273016AImmunochromatographic fastEasy immunochromatographyCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsReceptorBlood plasma
Owner:浙江诺迦生物科技有限公司 +1
Protein ligands
ActiveUS7709209B2Retention characteristicReduce leakageImmunoglobulins against animals/humansBiological testingComplementarity determining regionChemical stability
Owner:CYTIVA BIOPROCESS R&D AB
Soluble, stable form of HDM2, crystalline forms thereof and methods of use thereof
InactiveUS20050037383A1Improve solubilityImprove stabilitySugar derivativesPeptide/protein ingredientsProtein–ligand complexCrystallization
The present invention discloses modified Hdm2 proteins that are soluble. In addition, the present invention discloses nucleic acids that encode the modified Hdm2 proteins of the present invention. The invention also provides crystals of modified Hdm2 proteins that are suitable for X-ray crystallization analysis. The present invention also discloses methods of using the modified Hdm2 proteins and crystals thereof to identify, select and / or design compounds that may be used as anticancer agents. The present invention further discloses compounds that bind to modified Hdm2 proteins in protein-ligand complexes.
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME CORP
Affinity chromatography matrices and methods of making and using the same
ActiveUS20070207500A1Highly specificFast and economicalPeptide/protein ingredientsOther chemical processesAntibody Affinity ChromatographyChromatography
The invention provides methods of coupling protein ligands to a solid support. The invention also provides affinity chromatography matrices and methods of using affinity chromatography matrices to purify a target molecule.
Owner:MILLIPORE CORP
Quantum mechanics based method for scoring protein-ligand interactions
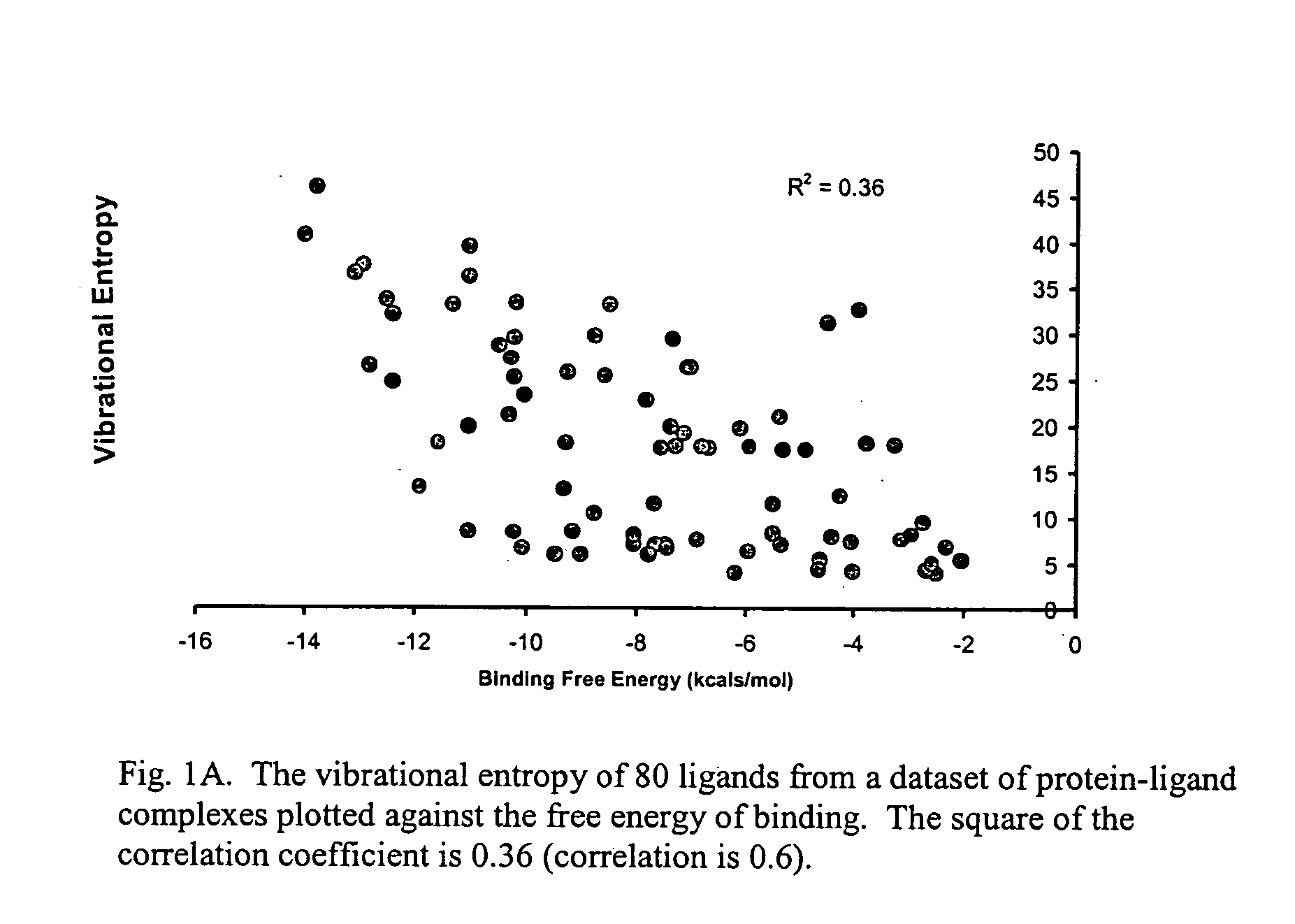
The present invention provides for the first time a quantum mechanics-based method for scoring protein-ligand interactions and binding affinity predictions, using quantum mechanical Hamiltonians and / or a combined quantum mechanical / molecular mechanical approach, and Poisson-Boltzmann (PB)-based solvation methods. Also provided is a method for using quantum mechanics to describe the enthalpic and solvation effects of binding. The method comprises comparing the calculated binding affinities to experimental values in order to measure the success of the method. The methods disclosed herein may further be used to score protein and drug or protein and inhibitor interactions. The present method can predict the free energy of binding of protein-ligand complexes with high accuracy so as to enable lead optimization, thus serving as a powerful tool in computational drug design.
Owner:PENN STATE RES FOUND
Support for affinity chromatography and method for isolating immunoglobulin
InactiveUS9040661B2Peptide/protein ingredientsSerum immunoglobulinsImmunglobulin eImmobilized protein
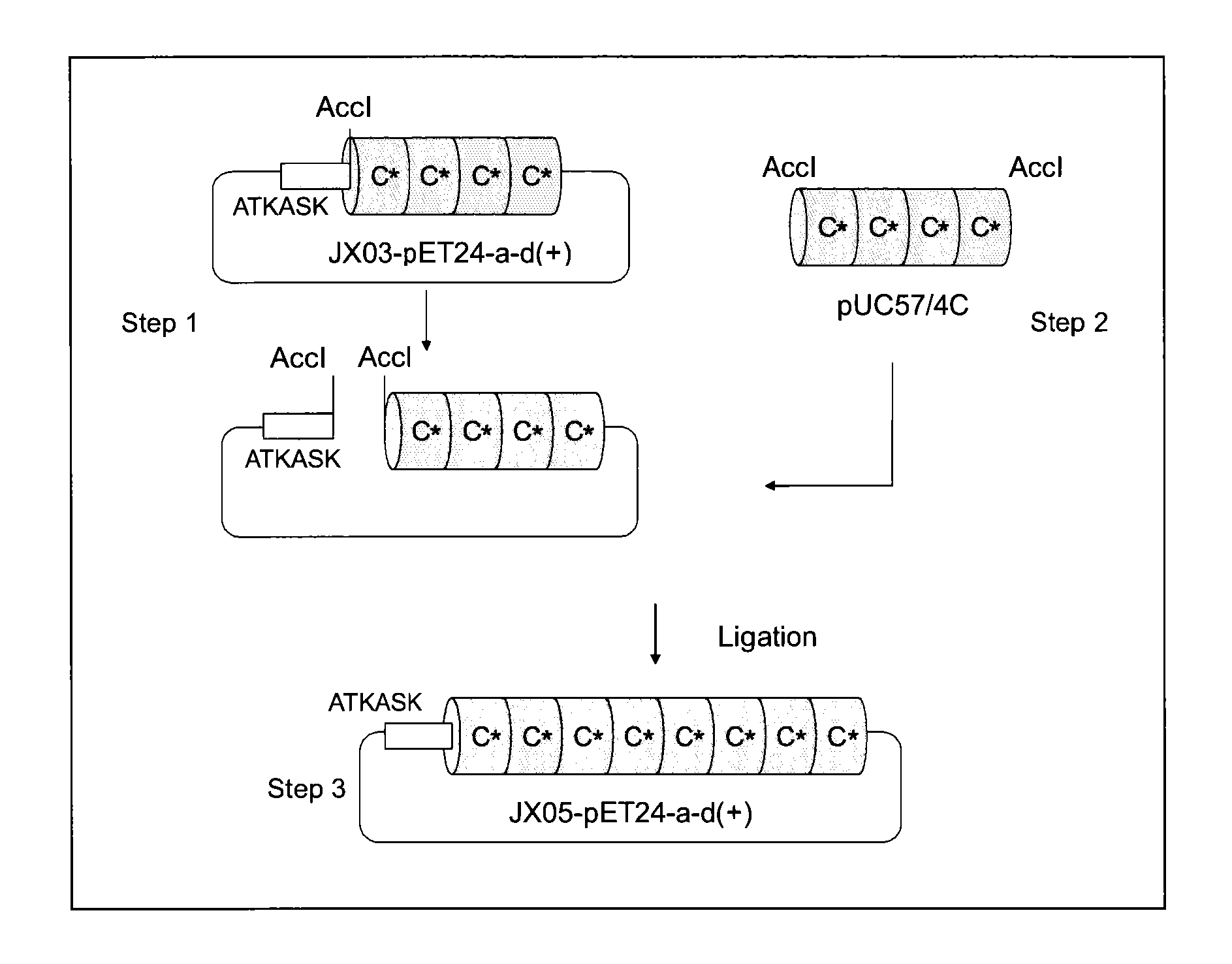
Provided are a support for affinity chromatography which has excellent alkali resistance, and a method for isolating immunoglobulin. A support for affinity chromatography, containing an immobilized protein ligand represented by the following formula (1):R—R2 (1)wherein R represents a polypeptide consisting of 4 to 30 amino acid residues that contains an amino acid sequence represented by ATK or ASK; and R2 represents a polypeptide consisting of 50 to 500 amino acid residues containing an immunoglobulin-binding domain consisting of an amino acid sequence represented by SEQ ID NO: 1 or SEQ ID NO: 2, the partial sequence thereof, or an amino acid sequence having 70% or more identity to these sequences; with the proviso that a terminus at which R2 binds to R is C-terminus or N-terminus of the immunoglobulin-binding domain.
Owner:JSR CORPORATIOON +1
Protein-ligand affinity predicting method based on molecule descriptors
InactiveCN102930181AReduce dependenceImprove predictive abilitySpecial data processing applicationsCrystal structureConjugate gradient method
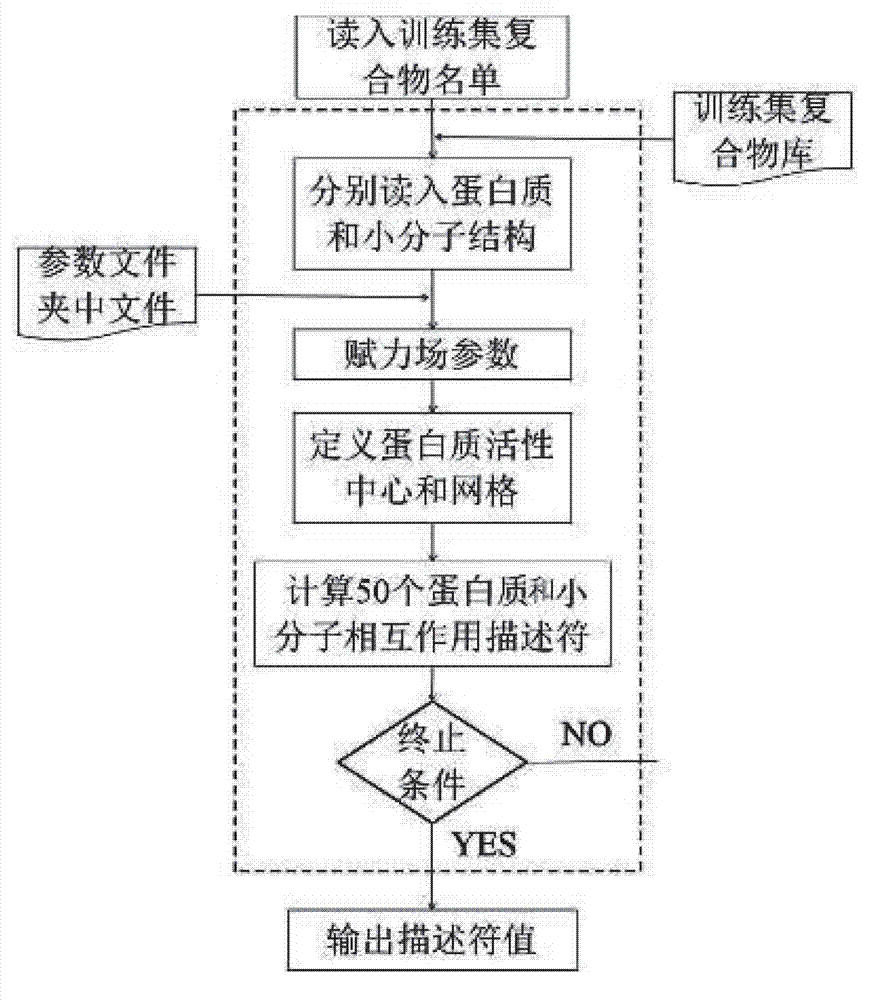
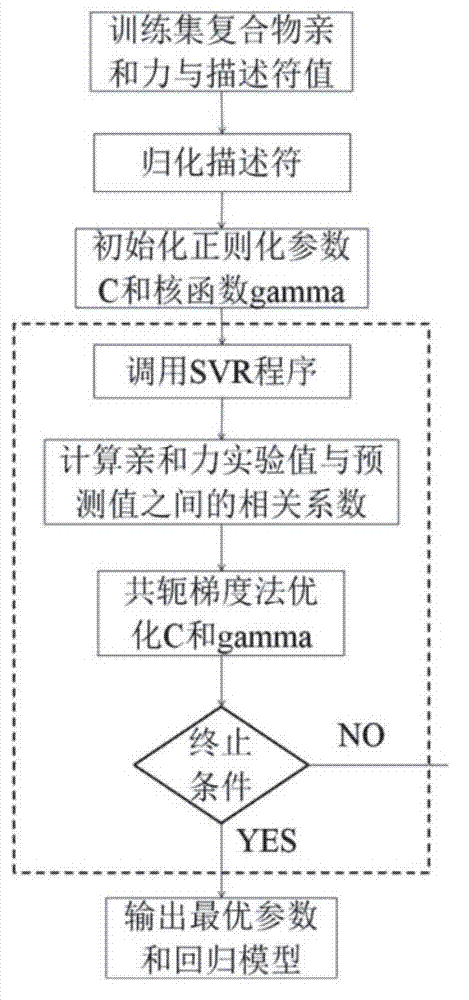
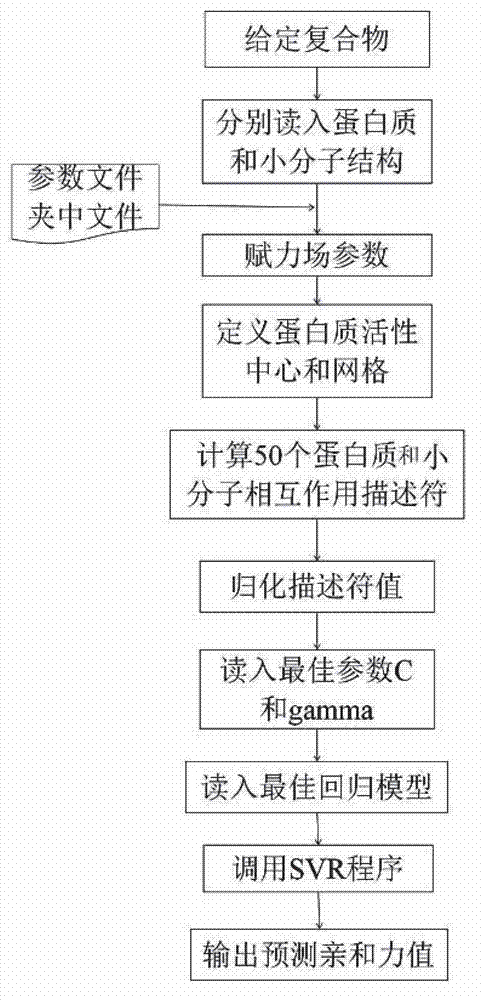
Disclosed is a protein-ligand affinity predicting method based on molecule descriptors. The protein-ligand affinity is reflected through construction of perfect and systematic molecule descriptors, and the relation between the descriptors and the affinity is constructed through a supporting vector regression (SVR) mode. The method includes the steps of training set preparation: preparing a large amount of data containing the crystal structure and the affinity of a protein-ligand complex; construction and calculation of the molecule descriptors: constructing 50 kinds of molecule descriptors which belong to nine categories, and calculating concrete values of all the complex descriptors in the training set; regression model construction: fitting the relation between the descriptors and the affinity through the SVR mode, and introducing a conjugate gradient method to optimize a penalty factor C and a kernel function parameter; and novel scoring function building which is used for predicting the affinity of the complex. The method has the advantages of being high in prediction capacity, small in target dependence, high in homolog sensitivity and the like.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
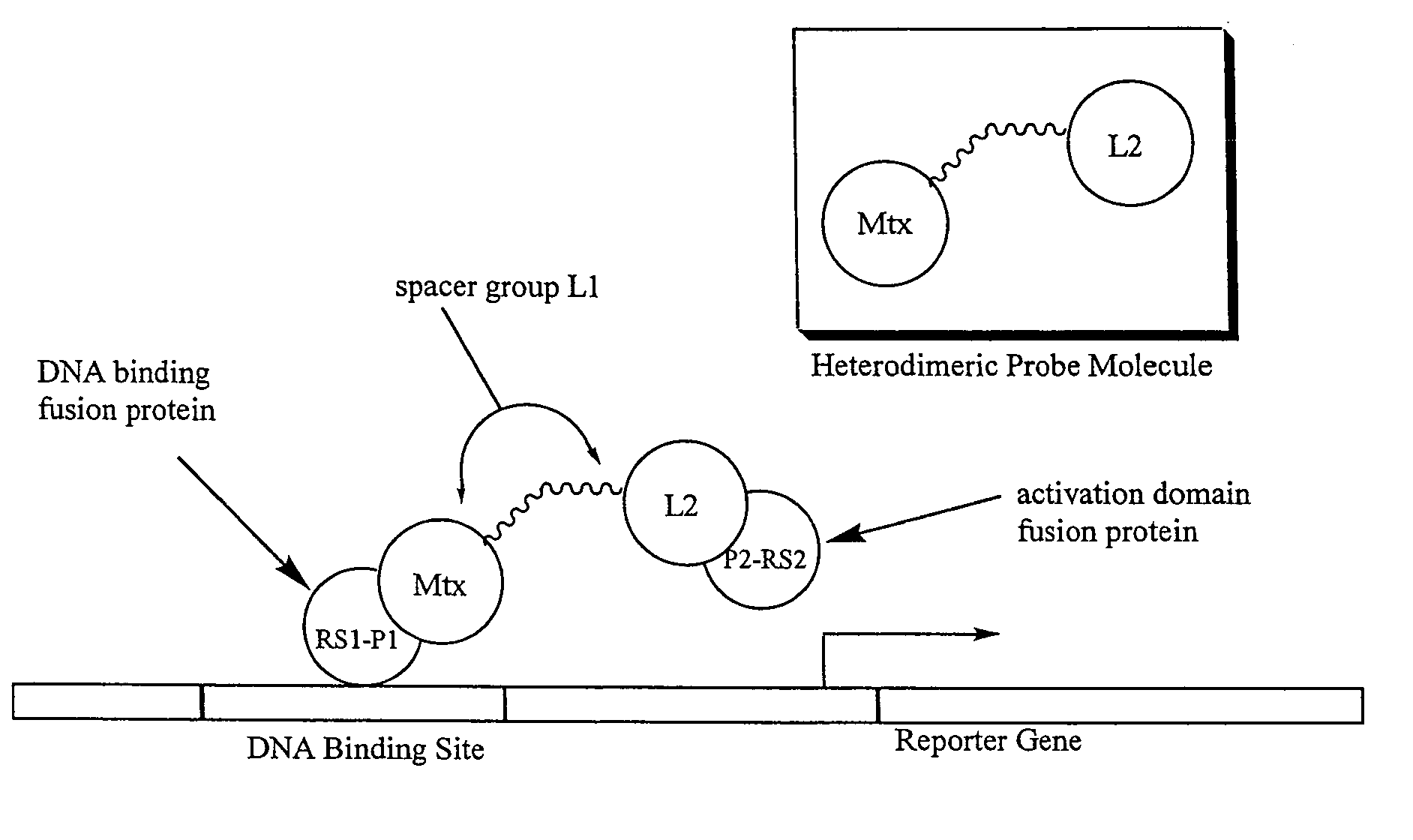
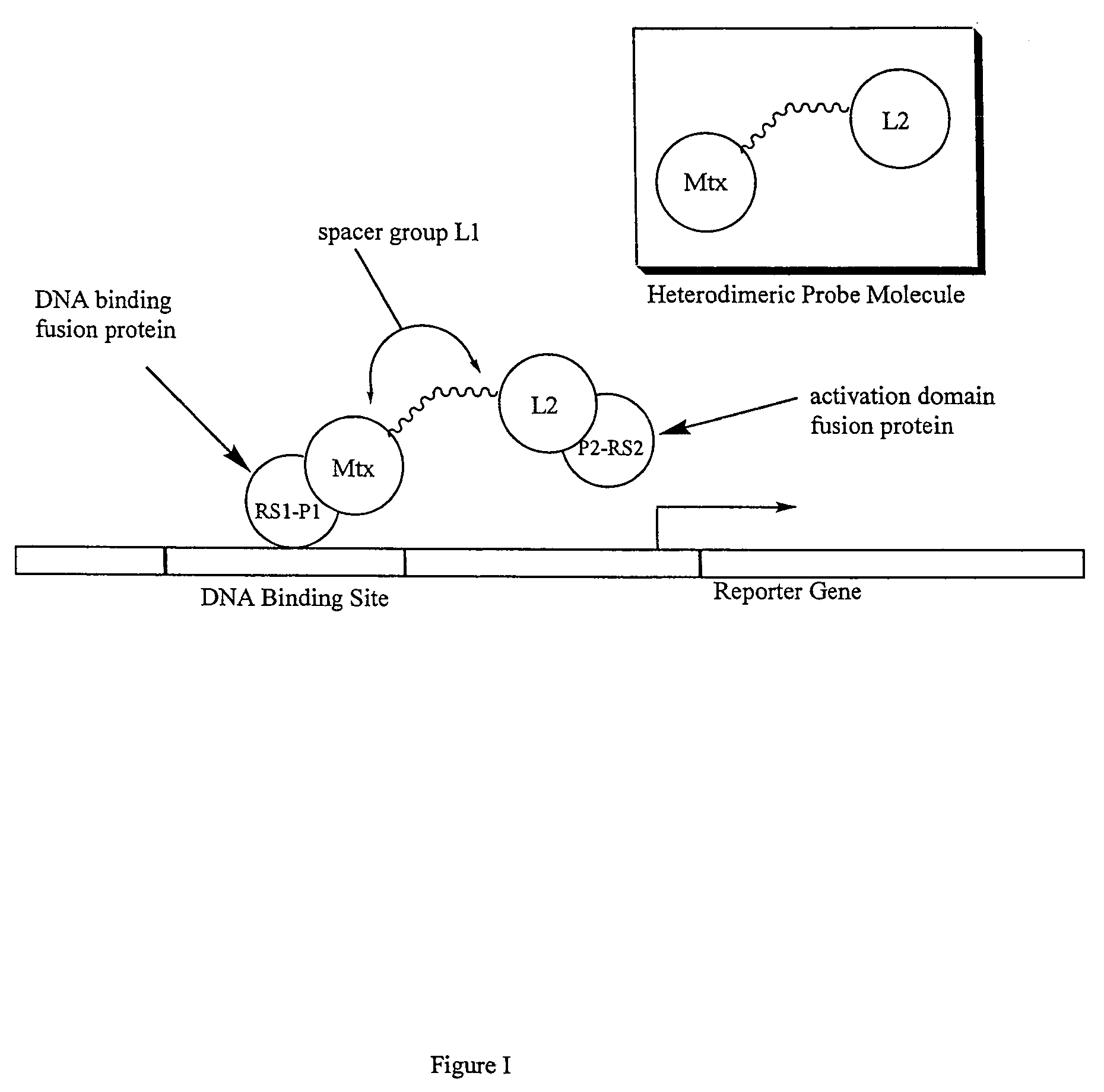
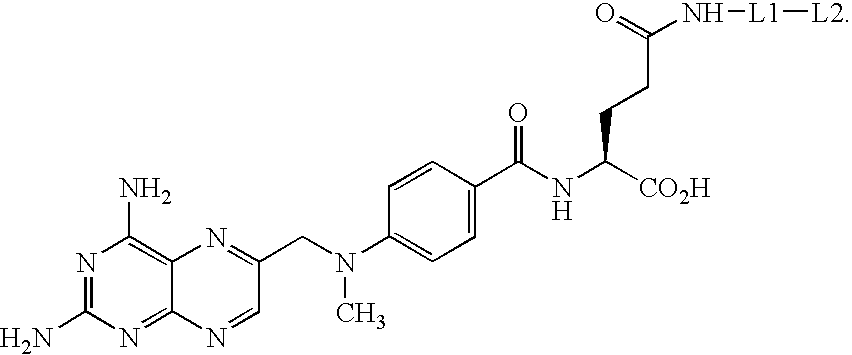
Synthesis of methotrexate-containing heterodimeric molecules
InactiveUS7230101B1Improve membrane permeabilityEffective isolationBiocideOrganic chemistryProtein targetCombinatorial chemistry
The present invention relates to novel compositions of methotrexate-containing heterodimeric probe molecules, also known as chemical inducers of dimerization (CID), useful in three-hybrid assays. The invention further relates to synthesis of said compositions and their intermediates. Another aspect of the invention is a method for using the heterodimeric probe molecules described herein in drug screens to identify potential protein targets to a given ligand, optimize protein-ligand interactions, or identify potential ligands for a given protein target. In certain embodiments, the invention contemplates the synthesis of the following methotrexate-containing heterodimeric probe:
Owner:AGGENIX
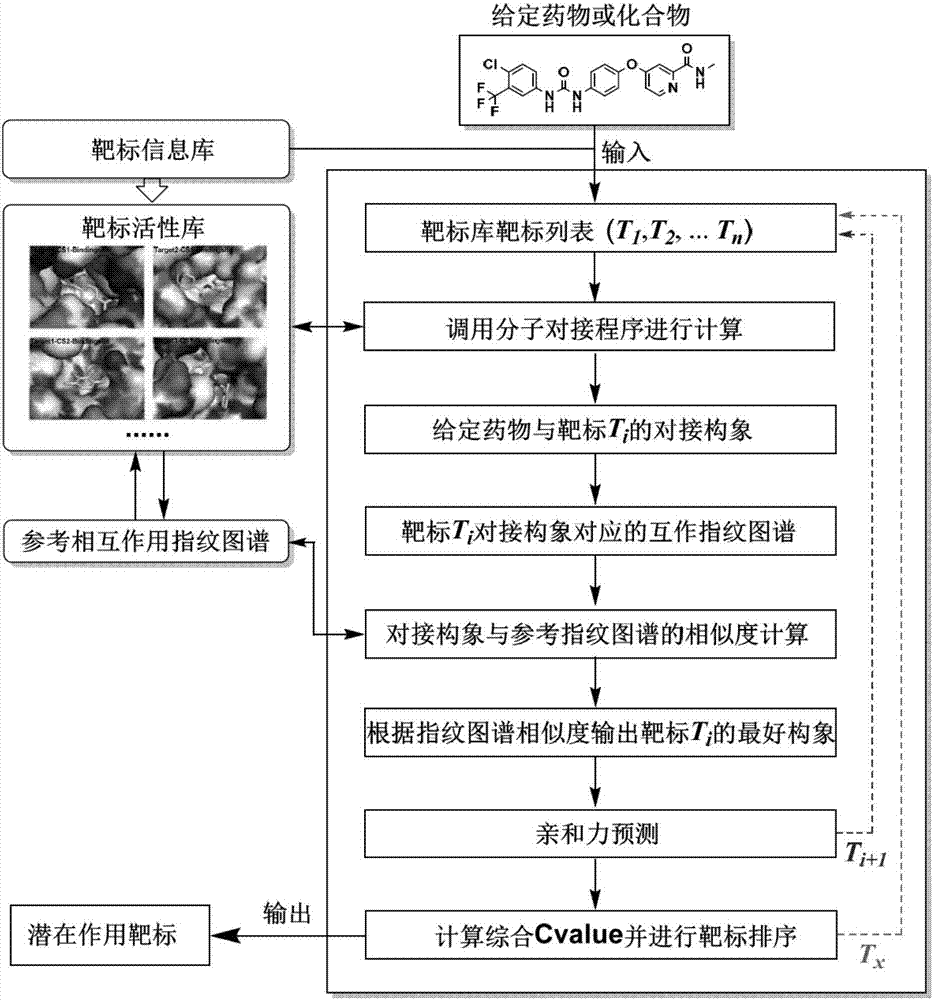
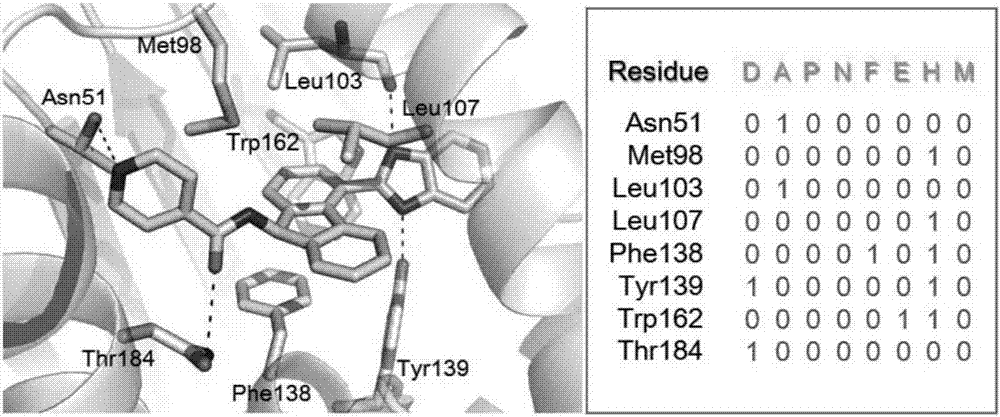
Protein-ligand interaction fingerprint spectrum-based drug target prediction method
InactiveCN107038348AImprove forecast accuracyOvercome the disadvantage of low prediction success rateBiostatisticsProteomicsMacromolecular dockingCrystal structure
The invention discloses a protein-ligand interaction fingerprint spectrum-based drug target prediction method. The method comprises the steps of collecting a large amount of diversified target and ligand complex crystal structures; building a reference protein-ligand interaction fingerprint spectrum model; predicting a possible combination mode of a to-be-tested drug and each target by molecular docking; building a drug and target interaction fingerprint spectrum model; and calculating the similarity between a fingerprint spectrum and the reference interaction fingerprint spectrum model, and the affinities of the drug and targets, sorting the targets of a target library by integrating docking scoring, the fingerprint spectrum similarity and the affinities, and outputting a potential target of the drug. According to the method, drug and target interaction modes are sorted and predicted by adopting an interaction fingerprint spectrum method, so that the shortcoming of relatively low success rate of predicting the drug and target interaction modes due to the molecular docking is overcome; and the targets are sorted by adopting a comprehensive index Cvalue, and the advantages of various methods are brought into play, so that the prediction accuracy of the drug target is radically improved.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
MHC-peptide complex binding ligands
InactiveUS7718777B2Reduce appearance problemsDecreased and stabilization sizeFungiBacteriaImmunoglobulin heavy chainWAS PROTEIN
Disclosed are protein ligands comprising an immunoglobulin heavy chain variable (VH) domain and an immunoglobulin light chain variable (VL) domain, wherein the proteins bind a complex comprising an MHC and a peptide, do not substantially bind the MHC in the absence of the bound peptide, and do not substantially bind the peptide in the absence of the MHC, and the peptide is a peptide fragment of gp100, MUC1, TAX, or hTERT. Also disclosed are methods of using and identifying such ligands.
Owner:TECHNION RES & DEV FOUND LTD
System and methods for electrophoretic separation of proteins on protein binding membranes
ActiveUS7326326B2Increase capacityEasy to separateSludge treatmentVolume/mass flow measurementProteinHeat generation
Proteins can be rapidly separated to a high degree of resolution by electrophoresis on polymeric membranes that have high protein binding capacity. The electrophoretic separation is carried out in a low conductivity, water-miscible organic solvent buffer. The low conductivity of the organic solvent buffer minimizes heat generation, and the water-miscible nature of the organic solvent buffer permits the analysis of hydrophobic and low molecular weight proteins as well as hydrophilic proteins. When electrophoresis is conducted under non-denaturing conditions, it allows the detection of enzymatic activities, protein-protein interactions and protein-ligand interactions.
Owner:TEMPLE UNIVERSITY
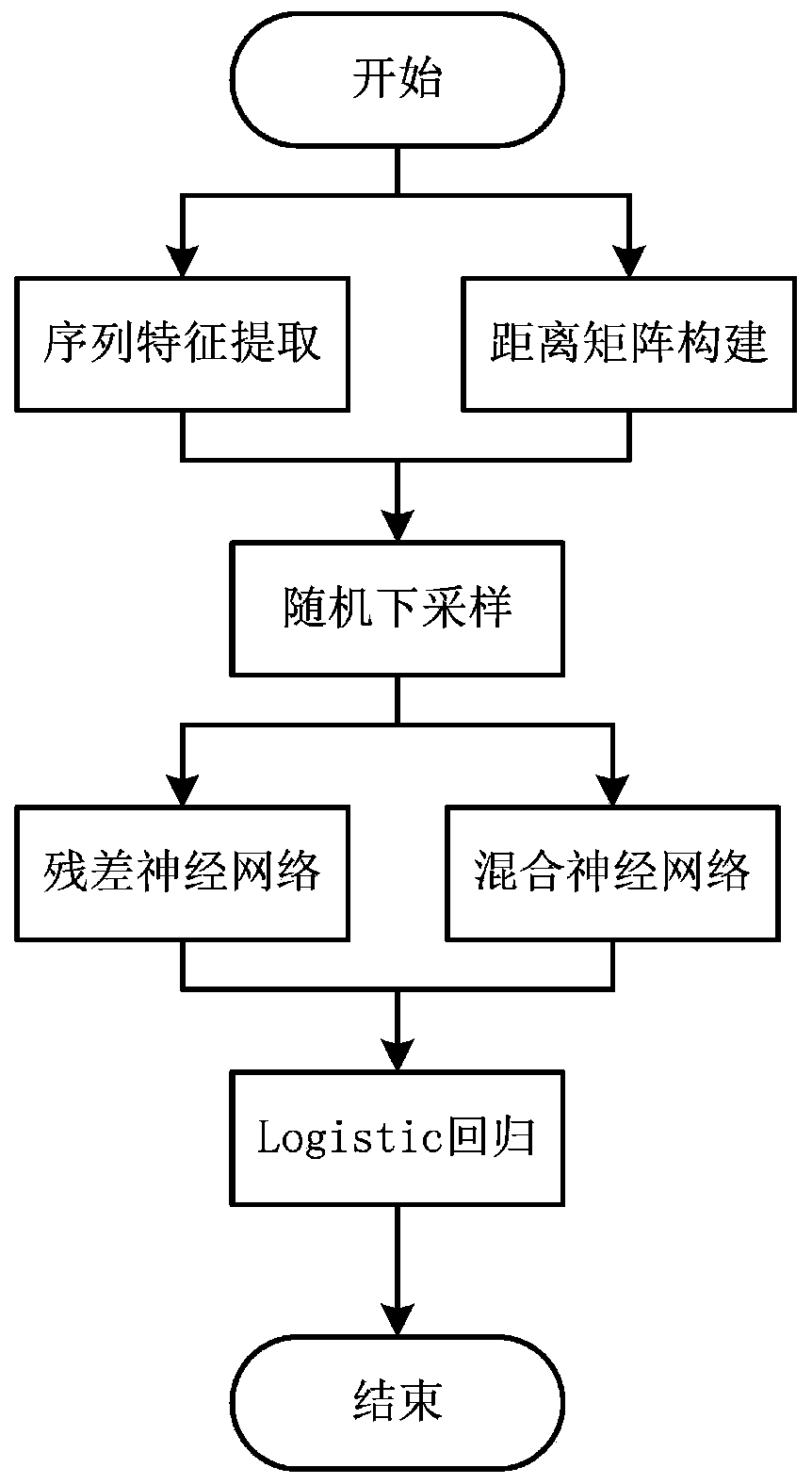
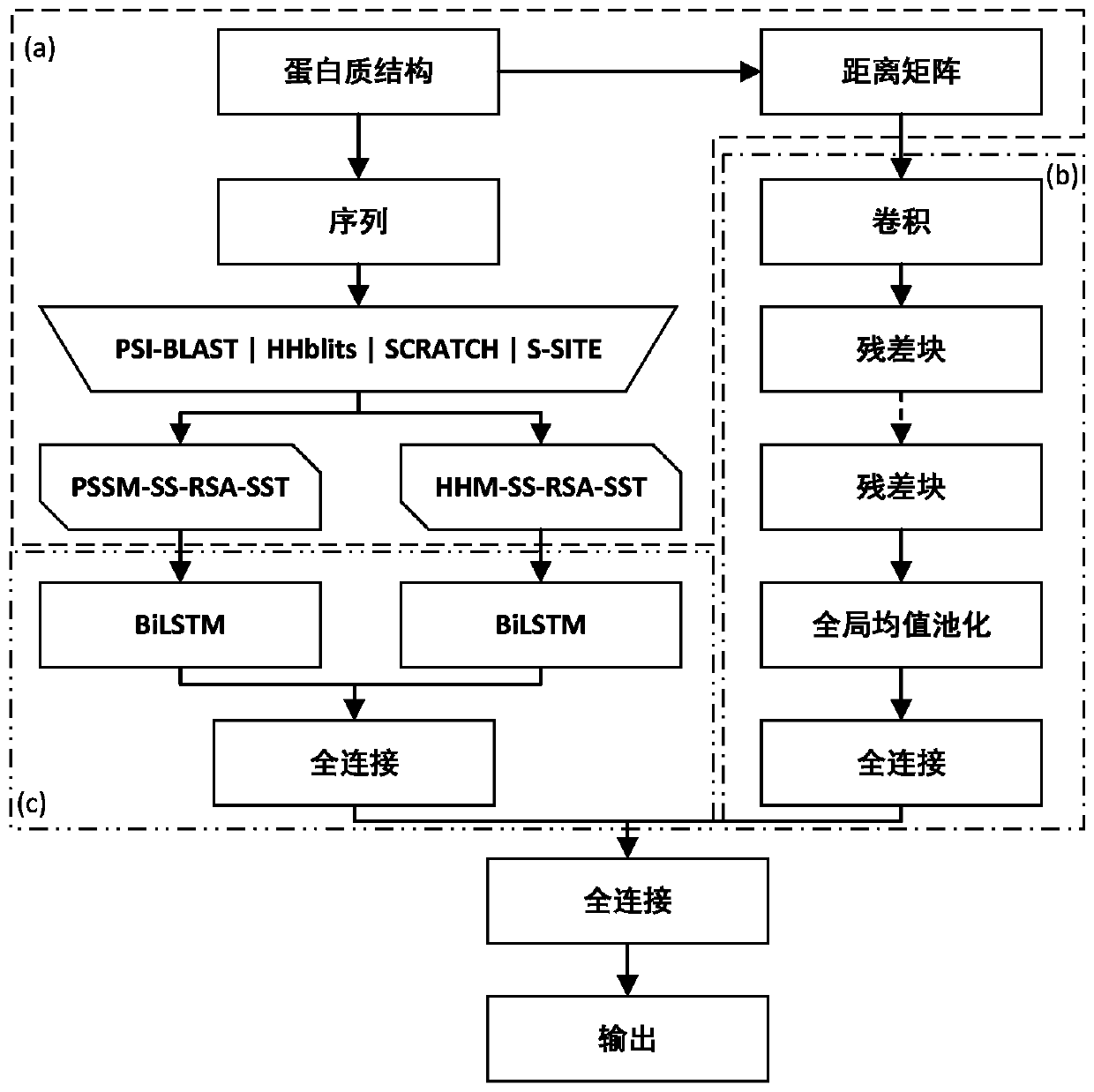
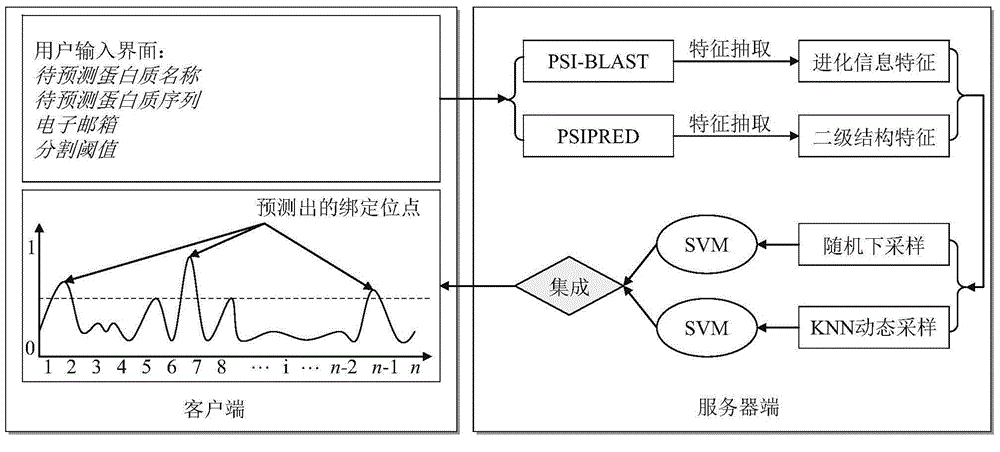
Protein-ligand binding site prediction algorithm based on deep learning
ActiveCN110689920AReduce the impactImprove forecast accuracyBiostatisticsProteomicsPrediction algorithmsBinding site
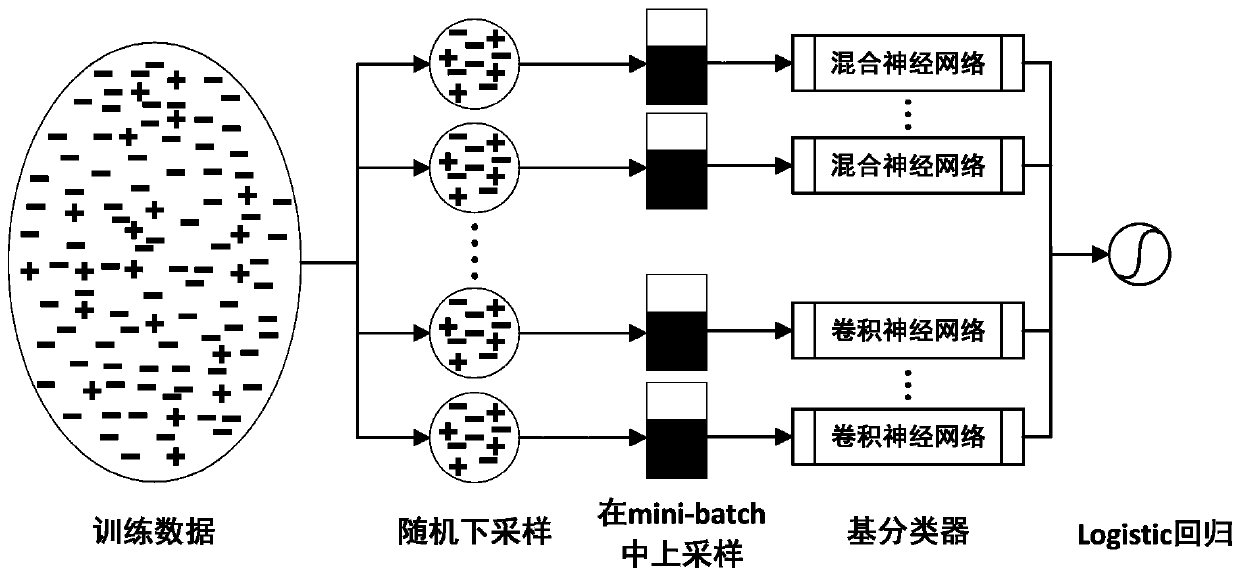
The invention discloses a protein-ligand binding site prediction algorithm based on deep learning. For protein to be predicted, the algorithm comprises the steps of: firstly, extracting sequence features and a distance matrix; distributing the sequence features to each residue through adoption of a sliding window method; and inputting the features corresponding to the residues into a residual neural network and a hybrid neural network one by one, and inputting output results of the residual neural network and the hybrid neural network into a Logistic regression classifier to obtain a final result, namely the binding probability corresponding to each residue in the protein. According to the method, a classic bidirectional long-short-term memory network and a residual neural network are fused, the fused network can process heterogeneous protein sequences and structural data at the same time, and complementarity of sequence features and structural features is mined. Compared with an existing method, the protein-ligand binding site prediction algorithm has higher prediction precision, and has good generalization performance for data sets of different ligands.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
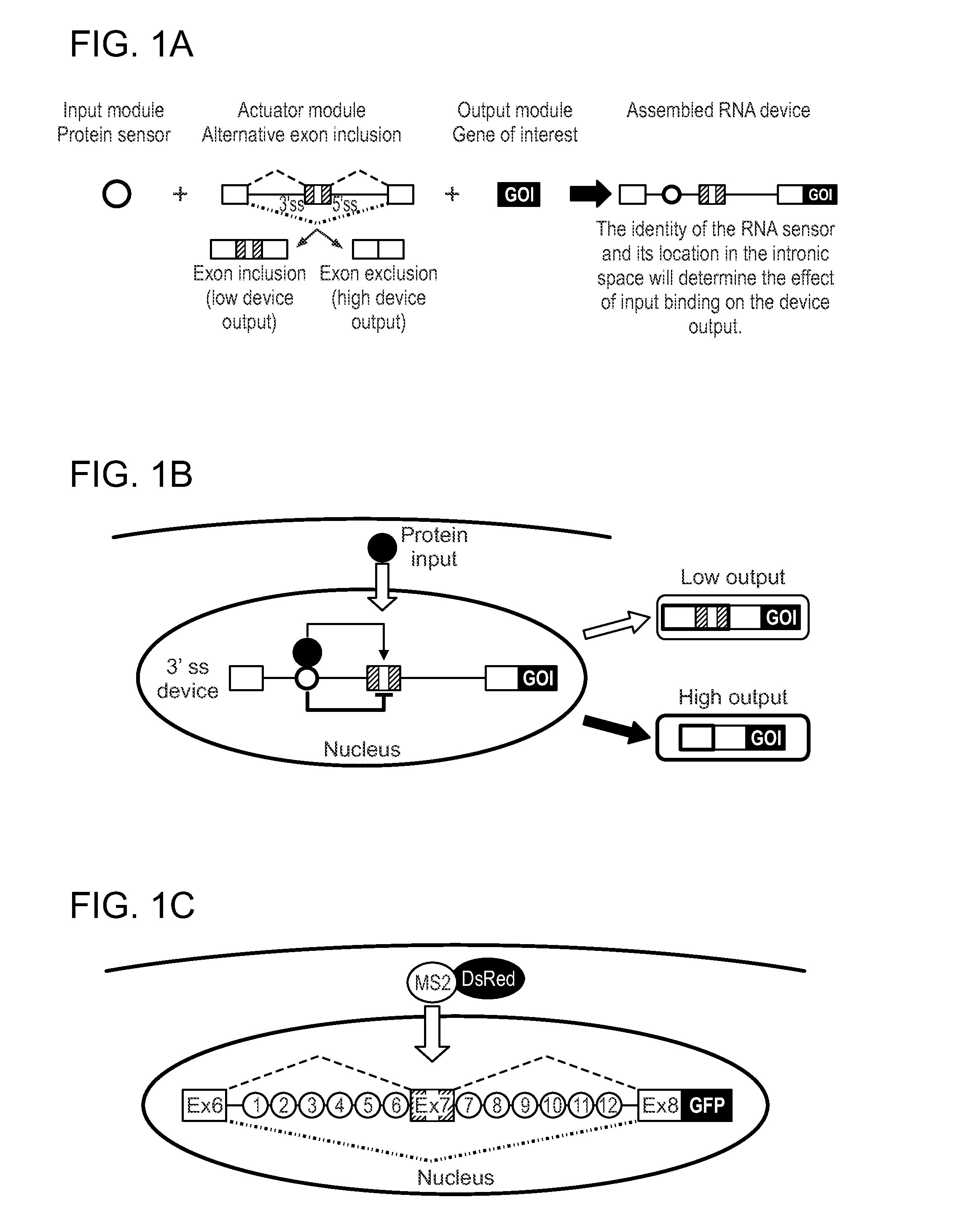
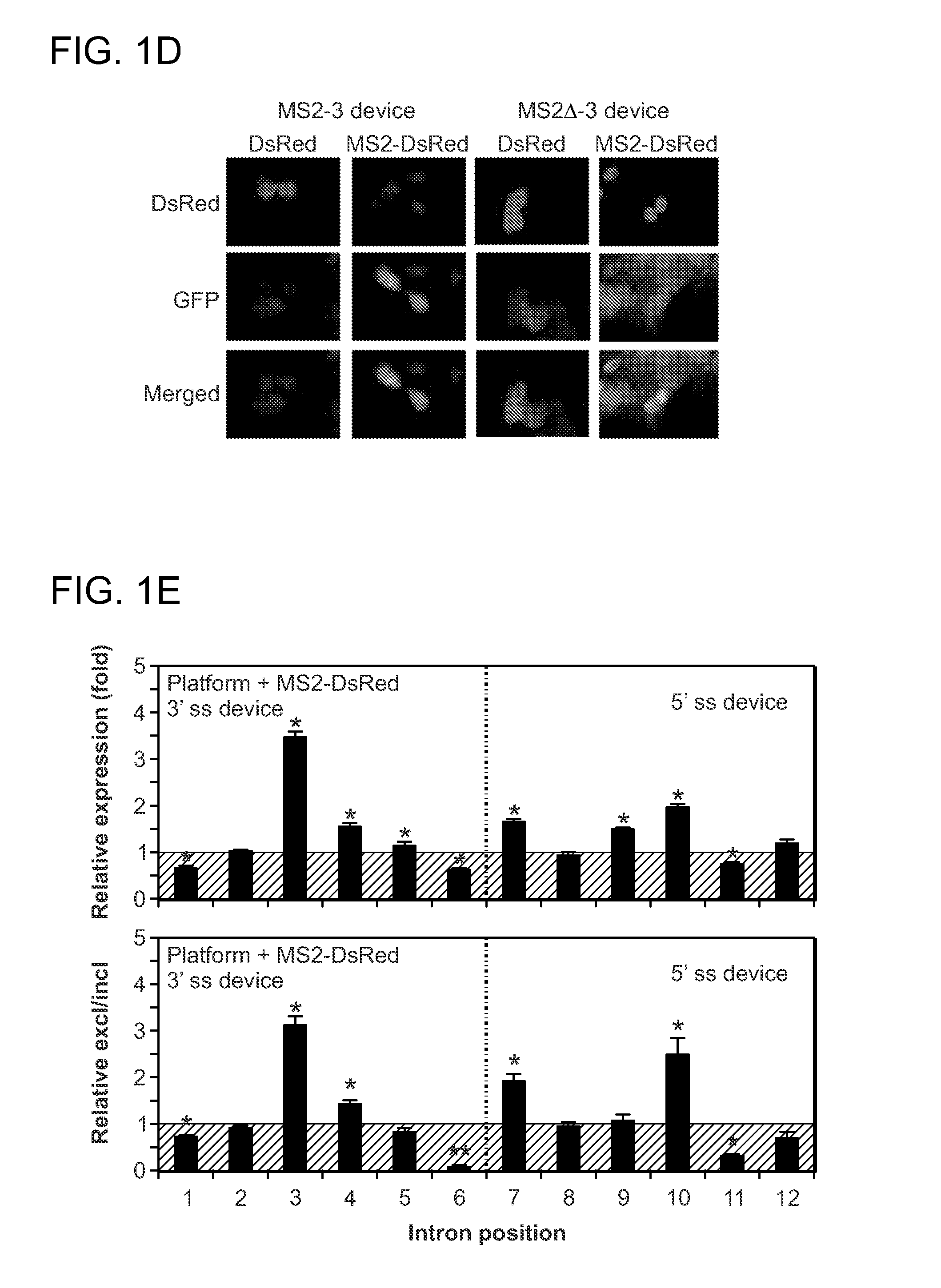
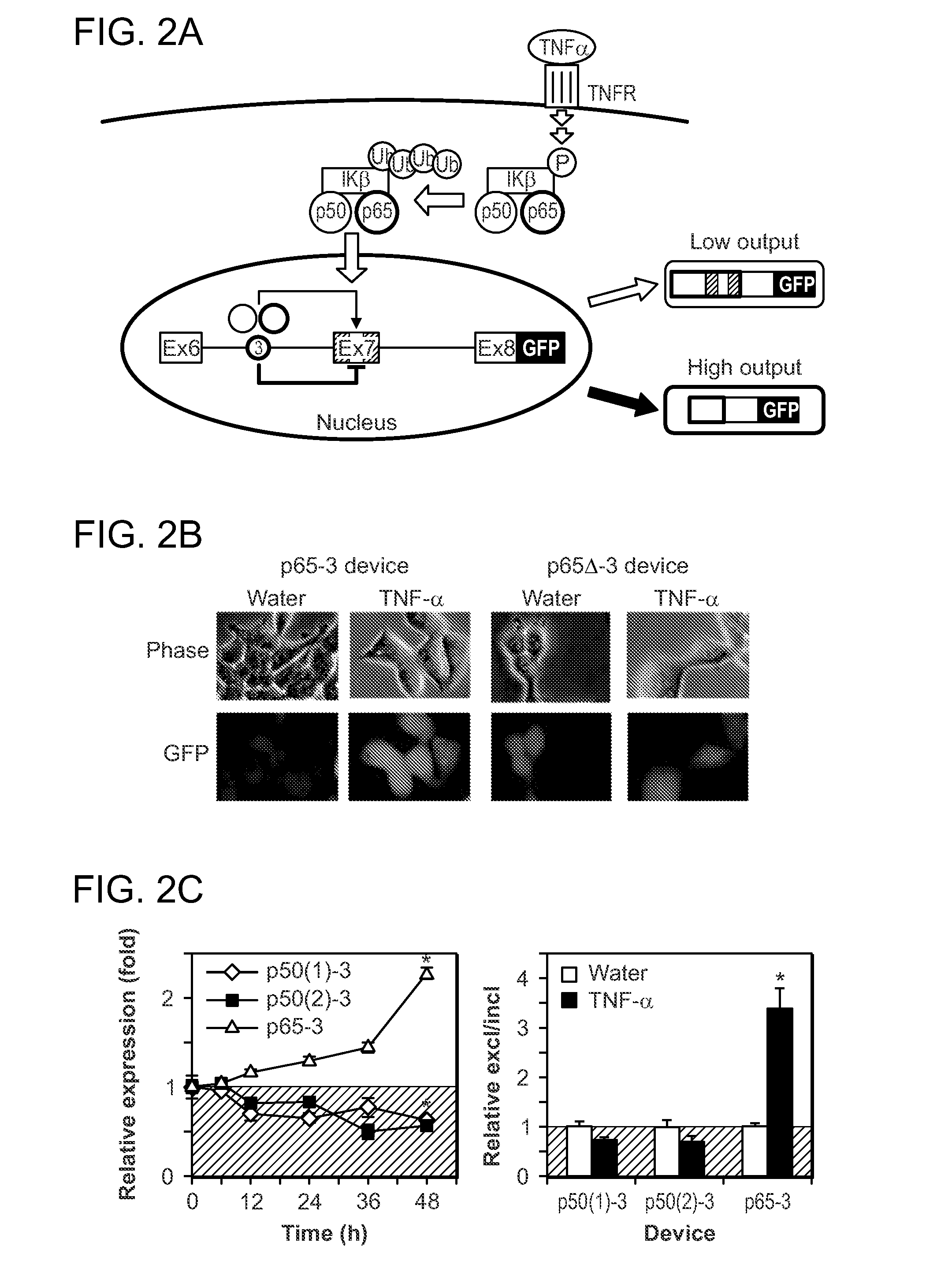
Protein-Responsive RNA Control Devices and Uses Thereof
ActiveUS20110111411A1Modulating the expression of the GOI in the cellAltered expressionSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementAlternative splicingBiology
The invention described herein relates to an RNA-based control device that senses the presence and / or concentration of at least one protein ligand, preferably through its protein-binding aptamer domain, and regulates a target gene expression through alternative splicing of the target gene in which the RNA-based control device is integrated. The device has uses in therapeutic as well as diagnostic applications.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Solid phase for mixed-mode chromatographic purification of proteins
ActiveUS20130102761A1High yieldEfficient extractionChromatographic cation exchangersPeptide preparation methodsSupport matrixPhysical chemistry
Proteins are purified by a mixed-mode chromatography system formed by attaching a ligand with cation exchange and hydrophobic functionalities to a large-pore support matrix, the only linkage between the ligand and the support matrix being a chain having a backbone of no more than three atoms between the hydrophobic group and the support matrix.
Owner:BIO RAD LAB INC
Bifunctional molecules and their use in the disruption of protein-protein interactions
InactiveUS7220552B1Peptide/protein ingredientsMammal material medical ingredientsProtein targetProtein insertion
Bifunctional inhibitor molecules and methods for their use in the inhibition of protein—protein interactions are provided. The subject bifunctional inhibitor molecules are conjugates of a target protein ligand and a blocking protein ligand, where these two moieties are optionally joined by a linking group. In the subject methods, an effective amount of the bifunctional inhibitor molecule is administered to a host in which the inhibition of a protein—protein interaction is desired. The bifunctional inhibitor molecule simultaneously binds to its corresponding target and blocking proteins to produce a tripartite complex that inhibits the target protein—protein interaction. The subject methods and compositions find use in a variety of applications, including therapeutic applications.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
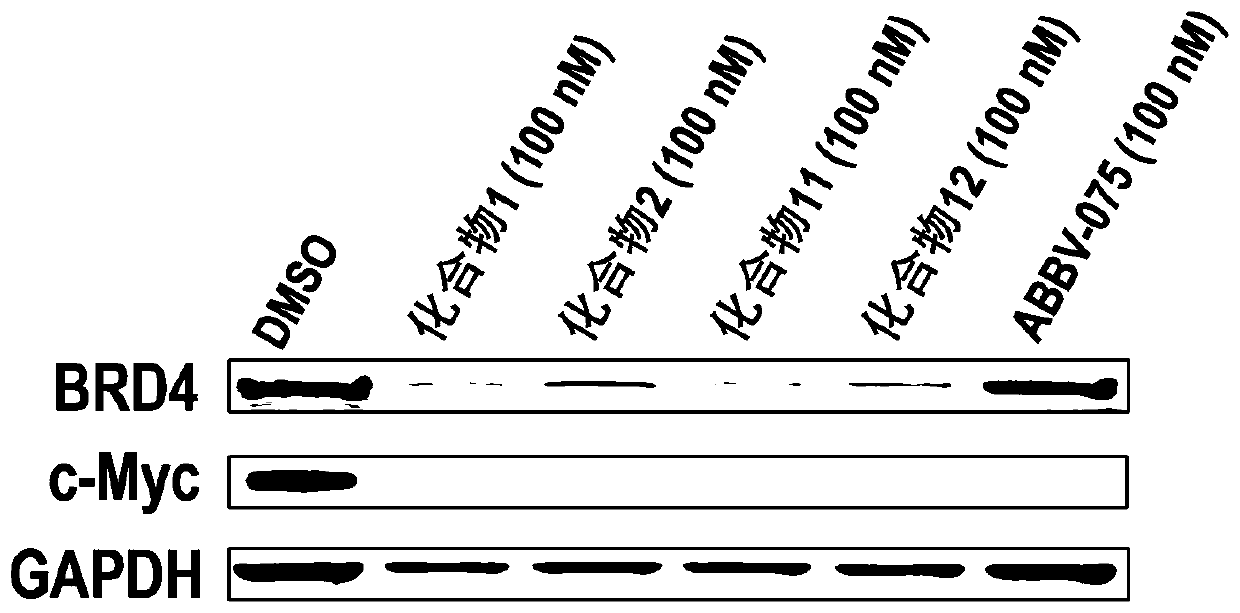
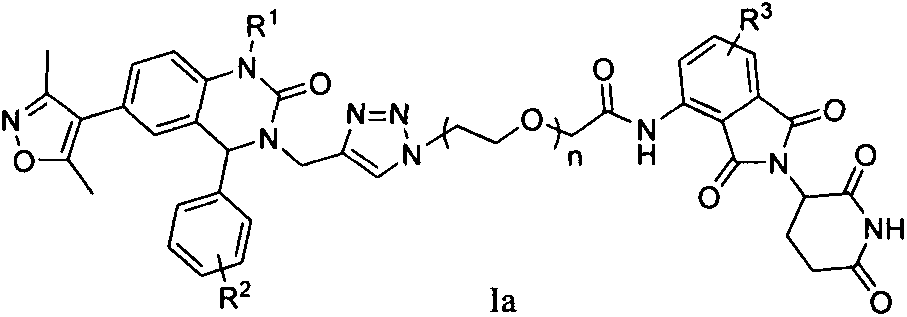
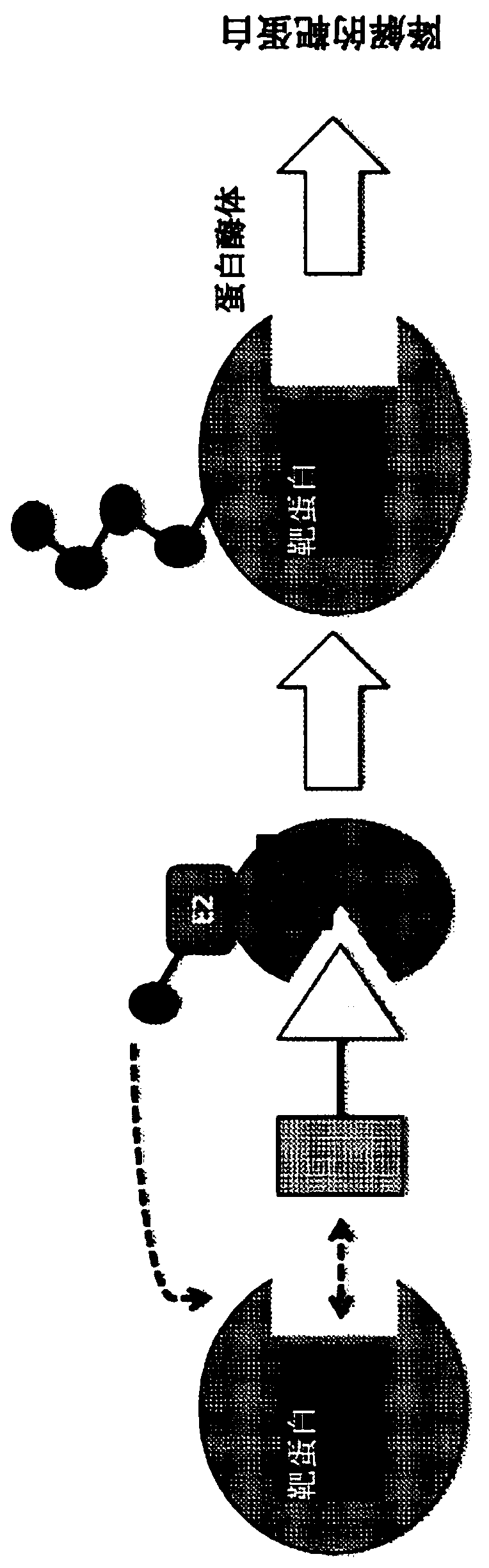
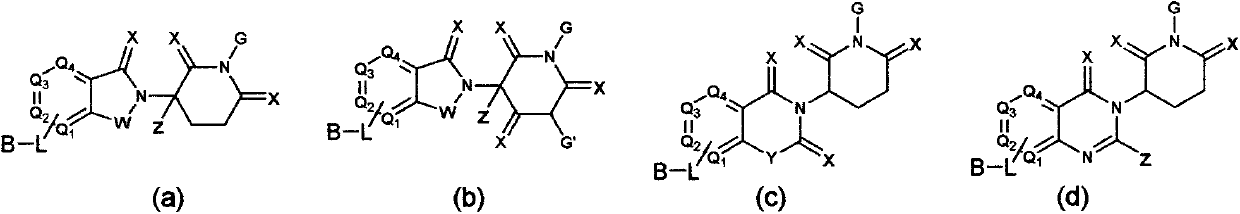
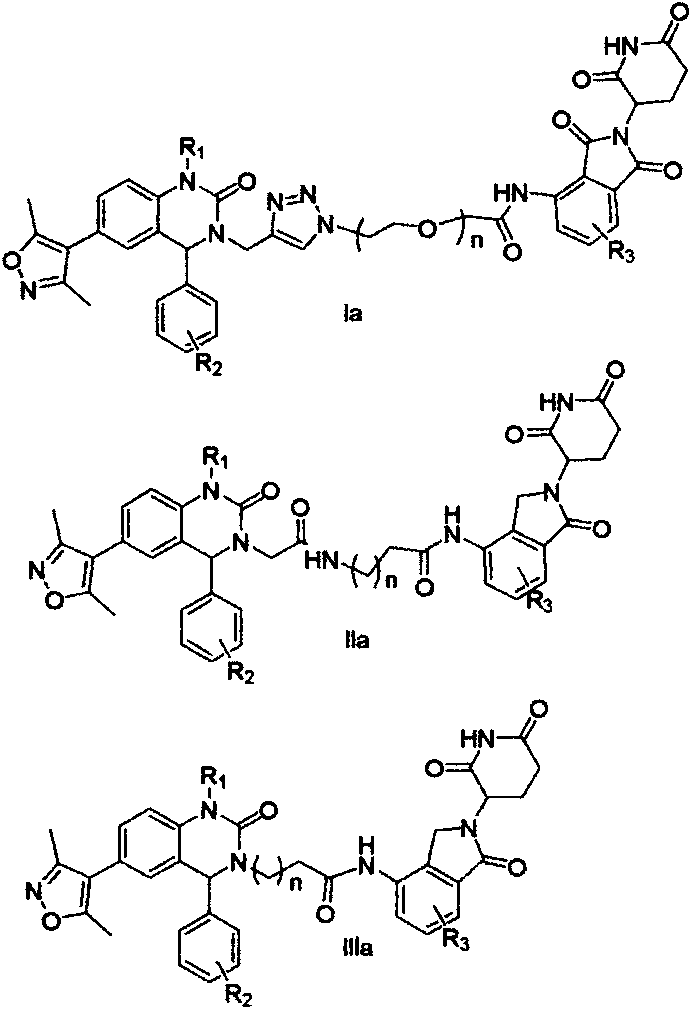
Bifunctional molecule based on VHL ligand induced BET degradation as well as preparation and application thereof
The invention relates to a new bifunctional small molecule, a preparation method of pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, hydrate or prodrug and application of the compounds and medicinal compositions in treating diseases such as tumor, inflammation and immune diseases. The bifunctional small molecule provided by the invention is a protein degradation targeted combo (PROTACs) which can selectively induce BET protein degradation. According to the invention, a BET protein small molecular inhibitor is connected with a von Rippel-Lindau (VHL) protein ligand in E3 ubiquitin ligase complex by a connecting arm to obtain the bifunctional small molecule.
Owner:CHINA PHARM UNIV
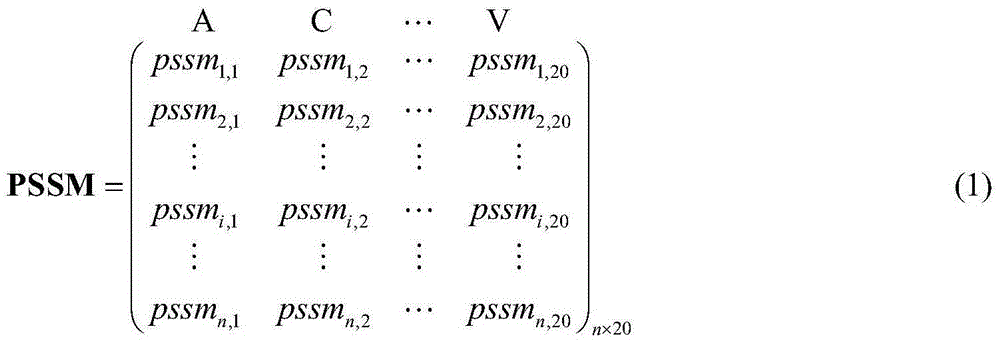
Sampling learning based protein-ligand binding site prediction method
ActiveCN104992079AImprove forecast accuracyImprove interpretabilitySpecial data processing applicationsBinding siteMachine learning
The invention provides a sampling learning based protein-ligand binding site prediction method. The method comprises the steps of: firstly, utilizing PSI-BLAST and PSIPRED programs to obtain evolutionary information and secondary structure information of protein, and using a slide window technology to extract characteristics of each amino acid residue (sample); secondly, utilizing a random down-sampling technology to perform random down-sampling on non-binding site samples, and using obtained non-binding site sample subsets and binding site sample set to train an SVM for predicting all to-be-predicted samples; thirdly, according to characteristic information of each to-be-predicted sample, utilizing a KNN dynamic sampling learning technology to perform sampling learning on binding site samples and the non-binding site samples respectively, and combining binding site sample subsets and the non-binding site sample subsets after sampling to train a specific SVM for predicting the to-be-predicted samples; and finally, using a threshold based integration technology to integrate the two trained SVMs. The method has the advantages that: firstly, the use of the random down-sampling and KNN dynamic sampling learning technologies can effectively reduce the scale of training sets and accelerate the model training speed; secondly, the use of the KNN dynamic sampling learning technology can train different SVM models for different to-be-predicted samples and effectively infuse the difference among the to-be-predicted samples; and thirdly, the use of the SVM integration technology effectively reduces the information loss caused by sampling learning and improves the model prediction precision.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Cereblon ligand-induced BET degradation-based bifunctional molecule and preparation and application thereof
The invention relates to a novel preparation method of a bifunctional molecule and a pharmaceutically acceptable salt, hydrate or prodrug thereof and application of these compounds and a medicinal composition thereof in treatment of diseases such as tumors, inflammation and immunity. The bifunctional molecule is a protein degradation-targeted complex (PROTACs), and is capable of selectively inducing BET protein degradation. A BET protein small-molecule inhibitor is connected with a cereblon protein ligand in an E3 ubiquitin ligase complex to obtain the bifunctional molecule.
Owner:CHINA PHARM UNIV
Tetrahydronaphthalene and tetrahydroisoquinoline derivatives as estrogen receptor degraders
The present disclosure relates to bifunctional compounds, which find utility as modulators of estrogen receptor (target protein). In particular, the present disclosure is directed to bifunctional compounds, which contain on one end at least one of a Von Hippel-Lindau ligand, a cereblon ligand, Inhibitors of Apoptosis Proteins ligand, mouse double-minute homolog 2 ligand, or a combination thereof, which binds to the respective E3 ubiquitin ligase, and on the other end a moiety which binds the target protein, such that the target protein is placed in proximity to the ubiquitin ligase to effect degradation (and inhibition) of target protein. The present disclosure exhibits a broad range of pharmacological activities associated with degradation / inhibition of target protein. Diseases or disorders that result from aggregation or accumulation of the target protein are treated or prevented with compounds and compositions of the present disclosure.
Owner:ARVINAS OPERATIONS INC
Methods and systems for predicting protein-ligand coupling specificities
The invention provides methods and systems for predicting or evaluating protein-ligand coupling specificities. A pattern recognition model can be trained by selected sequence segments of training proteins which have a specified ligand coupling specificity. Each selected sequence segment is believed to include amino acid residue(s) that may contribute to the ligand coupling specificity of the corresponding training protein. Sequence segments in a protein of interest can be similarly selected and used to query the trained model to determine if the protein of interest has the same ligand coupling specificity as the training proteins. In one embodiment, the pattern recognition model employed is a hidden Markov model which is trained by concatenated cytosolic domains of GPCRs which have interaction preference to a specified class of G proteins. This trained model can be used to evaluate G protein coupling specificity of orphan GPCRs.
Owner:WYETH LLC
Cereblon ligand mediated novel BET protein degradation bifunctional molecules, preparation and application thereof
The invention relates to a preparation method of new bifunctional small molecules and pharmaceutically acceptable salts, hydrates or prodrugs thereof, and application of the compounds and pharmaceutical compositions thereof in treatment of tumors, inflammation, immunity and other diseases. The bifunctional small molecules involved in the invention are protein degradation targeting chimeras (PROTACs), and can selectively induce BET protein degradation. According to the invention, a connecting arm is employed to connect a BET protein small molecule inhibitor and a cereblon protein ligand in theE3 ubiquitin ligase complex so as to obtain the bifunctional small molecules.
Owner:CHINA PHARM UNIV
Pyrrolopyridone double-functional molecule compound based on Cereblon ligand induced BET degradation
The invention relates to a novel pyrrolopyridone double-functional molecule, and pharmaceutically acceptable salts, hydrates, prodrug thereof, and a pharmaceutical composition taking the novel pyrrolopyridone double-functional molecule as an active component, and applications of the above compounds and the pharmaceutical composition in treatment or prevention of tumor, inflammation, and immunity diseases. The double-functional molecule is a proteolytic targeting chimera (PROTAC); the preparation method is mature; connecting arms are adopted to connect BET protein small molecular inhibitors andCereblon protein ligand in E3 ubiquitin ligase complex so as to obtain the double-functional molecule; the obtained compound is capable of realizing selective induction of BET protein degradation; and the tumor prevention effect is obvious.
Owner:JIANGSU PROVINCE INST OF TRADITIONAL CHINESE MEDICINE +1
Pyrrolopyridone bifunctional molecular compound based on VHL ligand-induced BET degradation
The invention relates to a novel kind of pyrrolopyridone bifunctional molecule and its pharmaceutically acceptable salt, hydrate and prodrug and a pharmaceutical composition using the compounds as active ingredients, and application in the preparation of these compounds and their pharmaceutical composition and in the treatment or prevention of tumors, inflammation, diseases related immunity, etc.The bifunctional molecule involved in the invention is a proteolytic targeting chimera (PROTAC). A small molecule inhibitor of BET protein and a Von Hippel-Lindau (VHL) protein ligand in E3 ubiquitinligase complex are linked by a connecting arm to obtain the bifunctional molecule. The obtained compound can selectively induce the degradation of BET protein, and has significant anti-tumor effect.
Owner:JIANGSU PROVINCE INST OF TRADITIONAL CHINESE MEDICINE +1
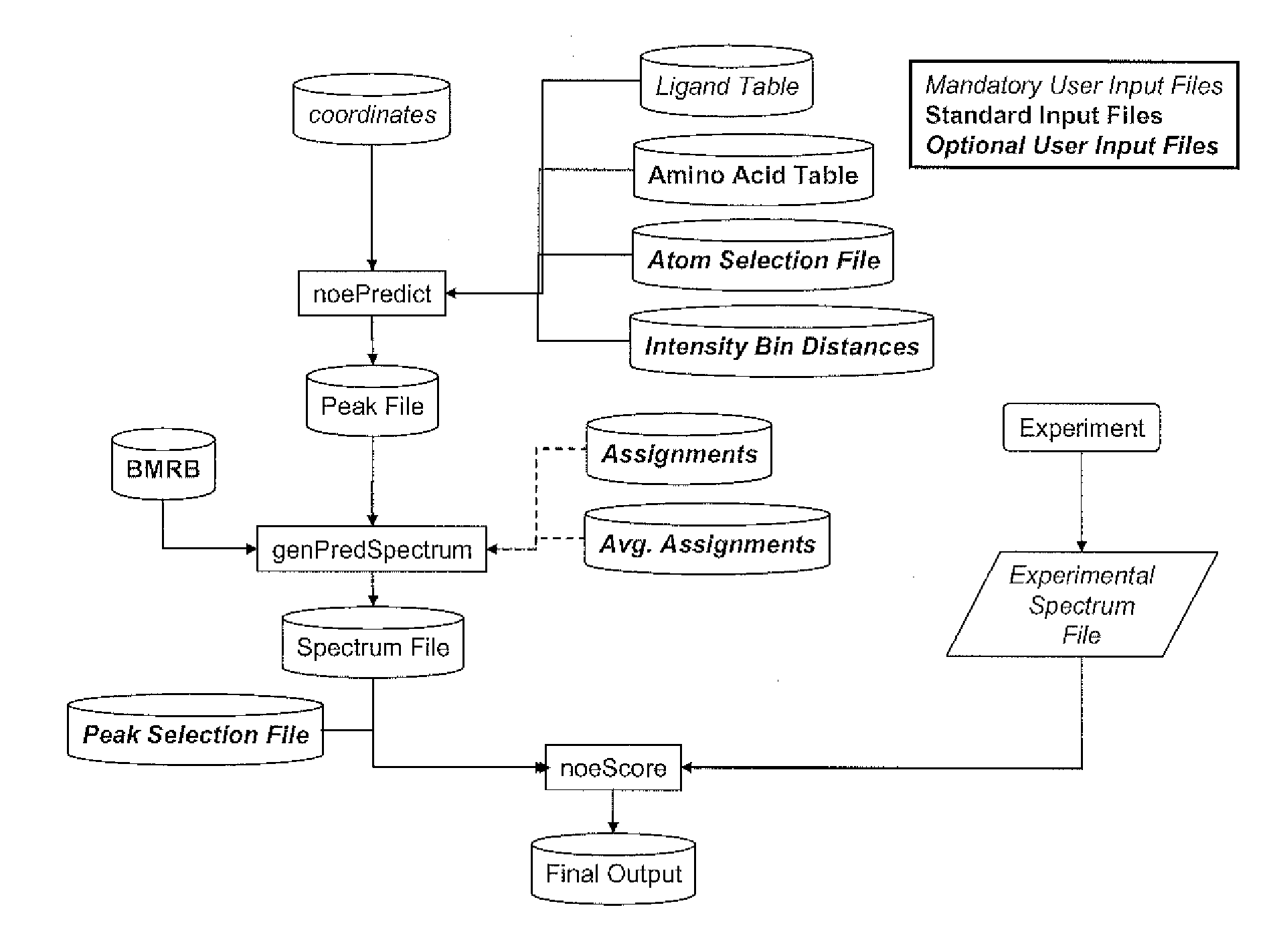
Protein-ligand noe matching for high-throughput structure determination
ActiveUS20120143580A1Facilitates in effortImprove attributesAnalogue computers for chemical processesSpecial data processing applicationsNuclear Overhauser effectAnalytical chemistry
A method of enhancing the throughput and applicability of NMR-based structure determination of protein-ligand complexes is disclosed. The method circumvents the need for protein sequence-specific resonance assignments and combines NMR data analysis and ligand docking methods into an integrated process. In one embodiment, NMR data is used to filter docking results to identify the most consistent binding modes, thereby providing structural information in a high-throughput fashion without the need for assigning protein resonances. Trial assignments for protein-ligand nuclear Overhauser effect (NOE) interactions are also produced by the method.
Owner:BRISTOL MYERS SQUIBB CO
Hydrogels of water soluble polymers crosslinked by protein domains
A stimuli-responsive, hybrid hydrogel wherein the bulk of the polymer is made up of relatively inexpensive water soluble polymer strands crosslinked by protein domains. The responsiveness of the gel is controlled or modulated by the protein component.The physical and biological properties of the hydrogel are determined by specifically designed or engineered protein domains.The crosslinking of the protein domains to the water soluble polymers is by means of non-covalent bonding such as chelation or coordination bonding, biotin-avidin bonding, protein—protein interaction and protein-ligand interaction, or by means of covalent bonding. Methods of making and using the polymer-protein hydrogels are disclosed in this application.
Owner:UNIV OF UTAH RES FOUND
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com