Sampling learning based protein-ligand binding site prediction method
A technology of binding sites and prediction methods, which is applied in the fields of instruments, computing, and electrical digital data processing, etc., can solve problems such as poor interpretability, insufficient consideration of differences, and poor versatility, so as to improve prediction accuracy, Fairness and rationality, and the effect of improving interpretability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0017] In order to better understand the technical content of the present invention, the present invention will be further described below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings.
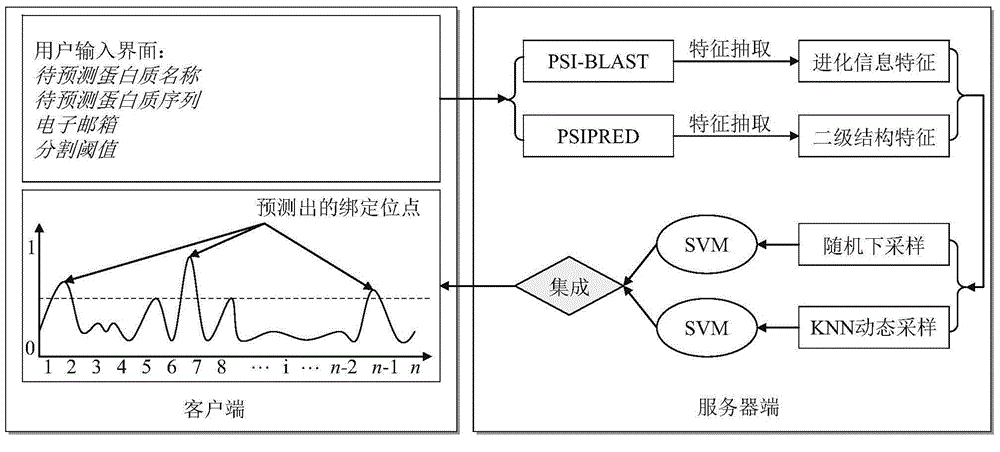
[0018] figure 1 A schematic diagram of the system structure of the prediction method of the present invention is given. combine figure 1 As shown, according to an embodiment of the present invention, a method for predicting protein-ligand binding sites based on sampling learning includes the following steps:
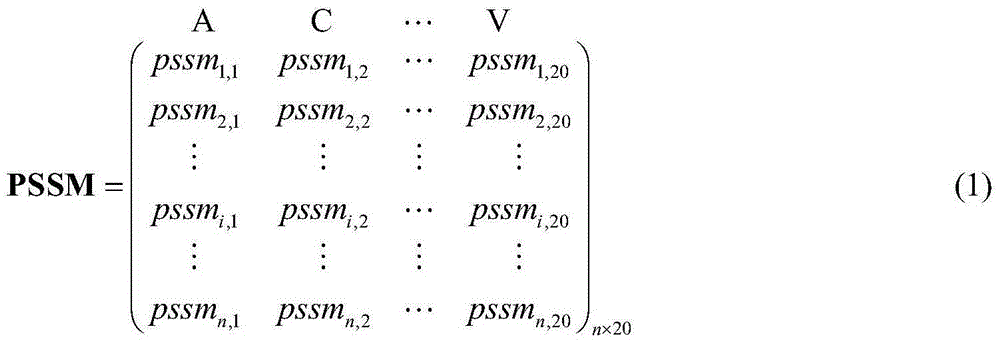
[0019] First, use the PSI-BLAST and PSIPRED programs to obtain the evolutionary information matrix (Position Specific Scoring Matrix, PSSM) and secondary structure prediction probability matrix (Predicted Secondary Structure, PSS) of the training protein respectively; Construct the eigenvector of each amino acid residue with the secondary structure prediction probability matrix, and then serially combine the eigenvectors of the above two kinds of information to obtain the final eigenv...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com