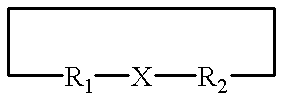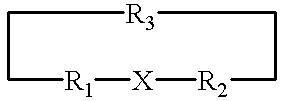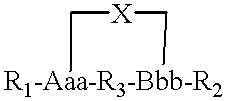Patents
Literature
548 results about "Protein secondary structure" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
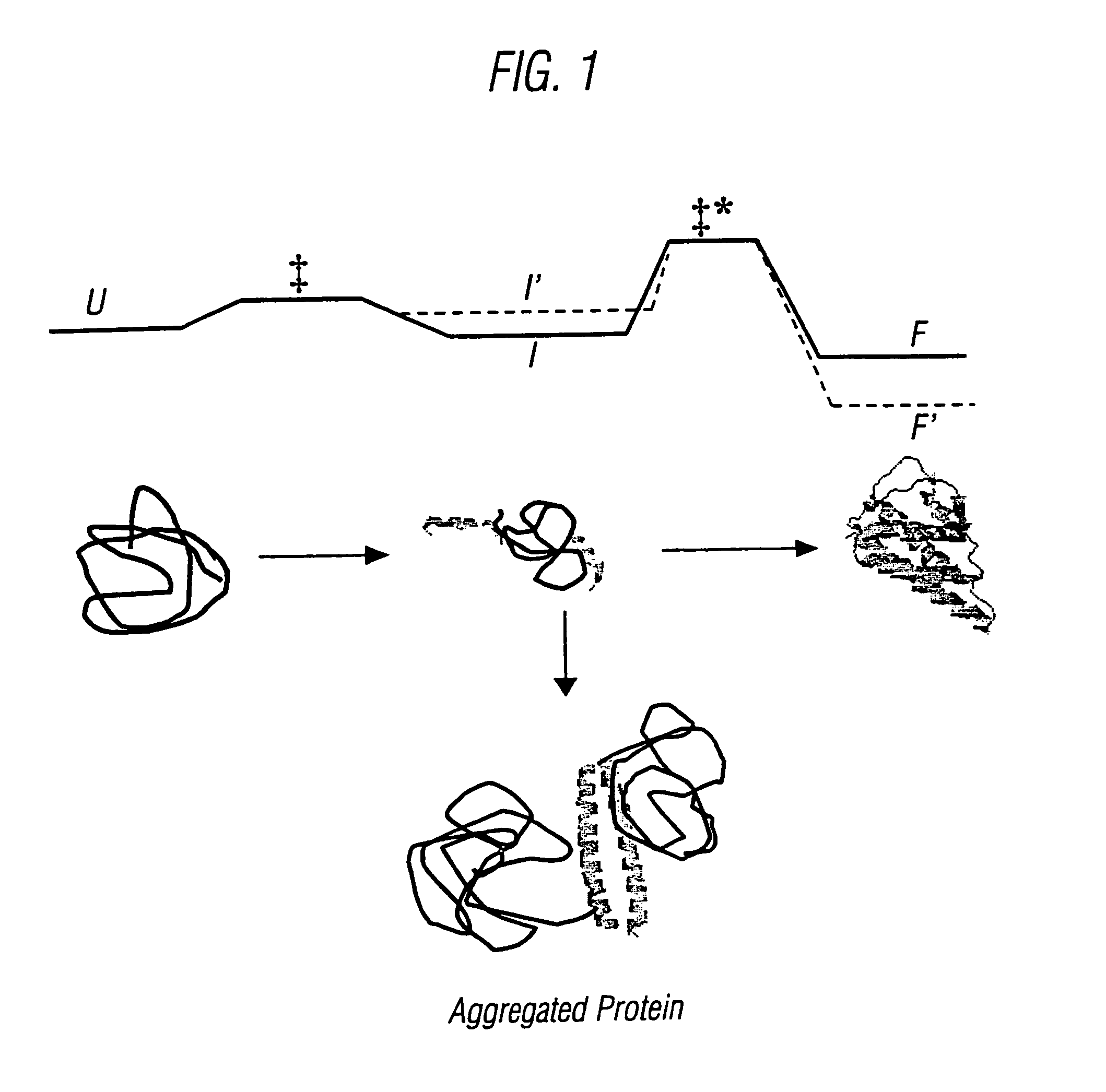
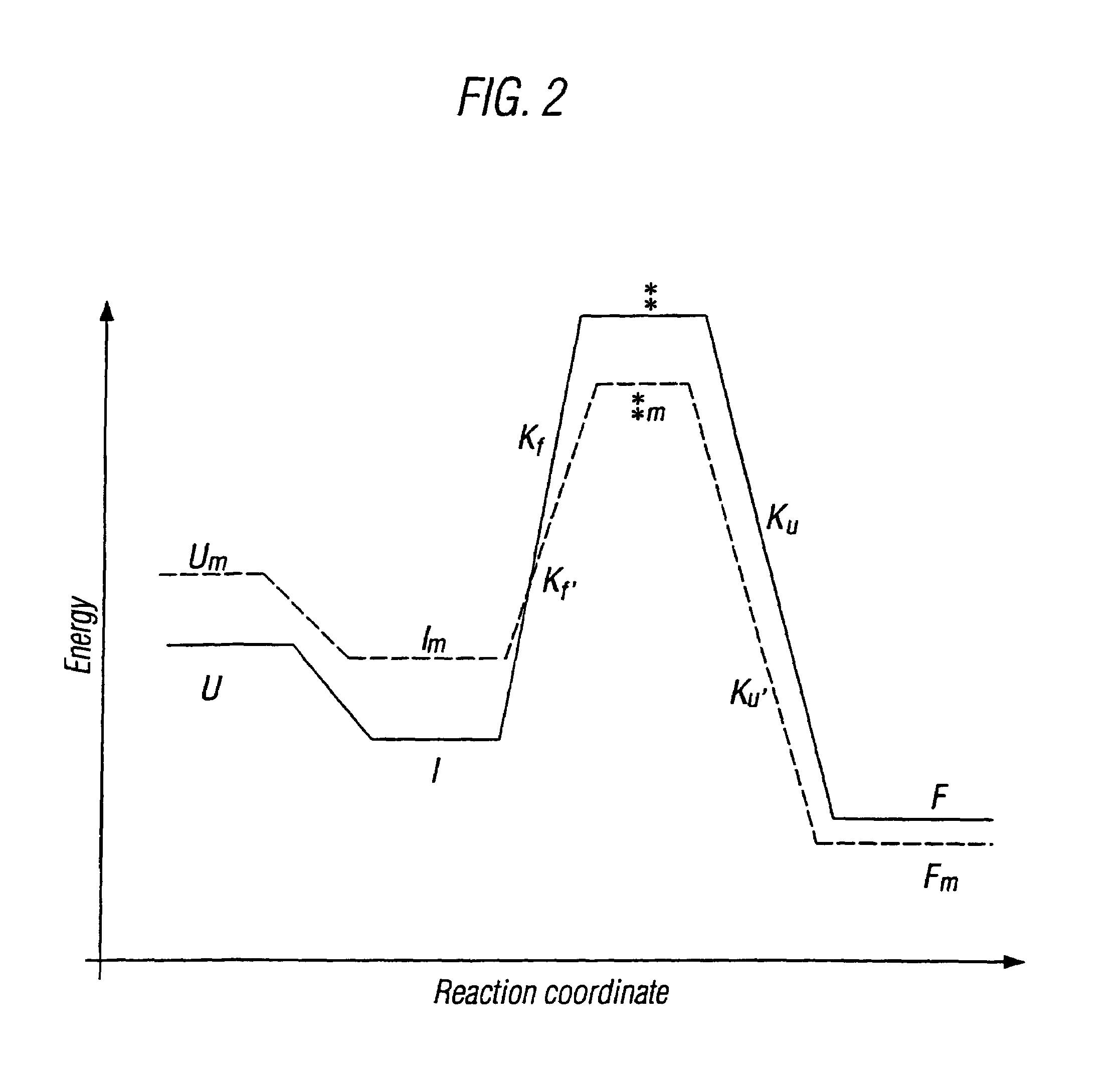
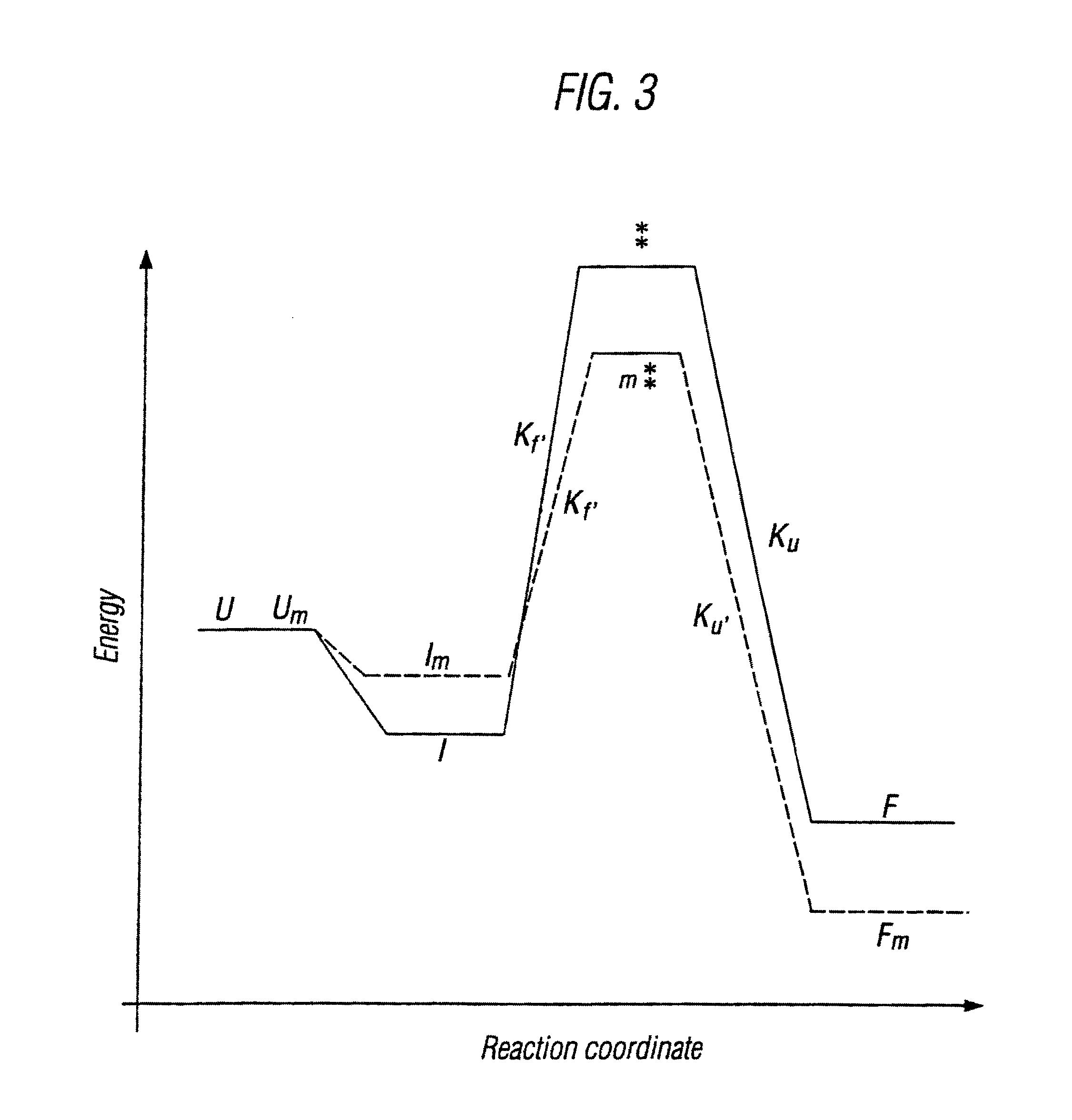
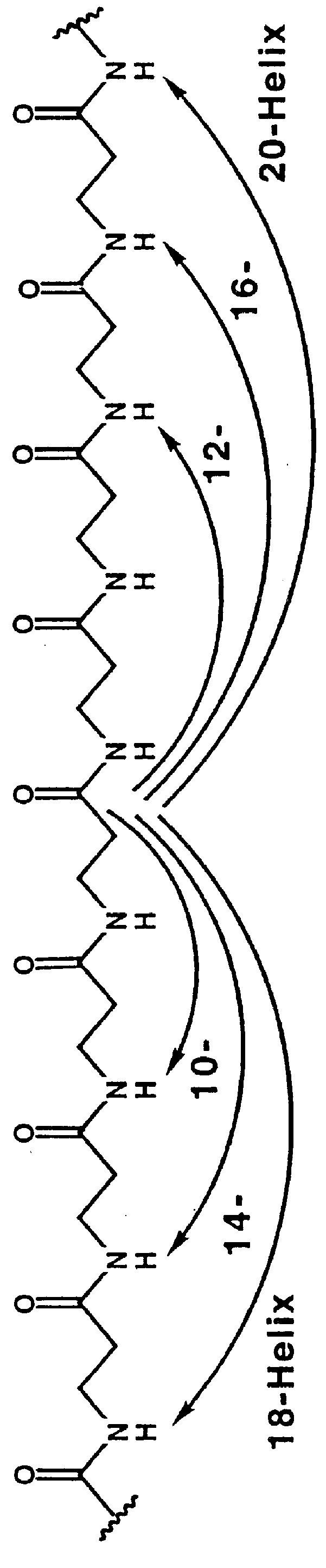
Protein secondary structure is the three dimensional form of local segments of proteins. The two most common secondary structural elements are alpha helices and beta sheets, though beta turns and omega loops occur as well. Secondary structure elements typically spontaneously form as an intermediate before the protein folds into its three dimensional tertiary structure.
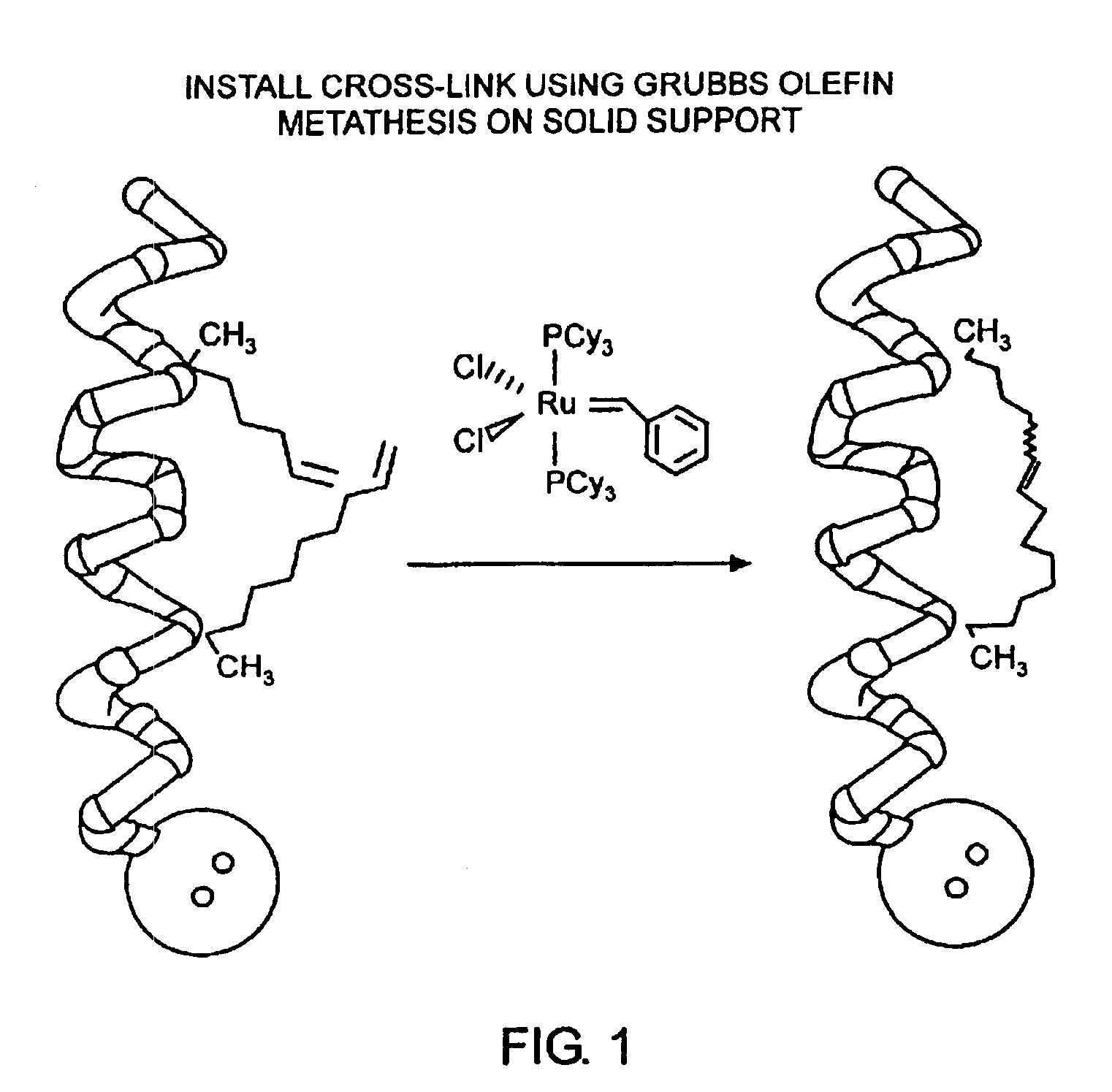
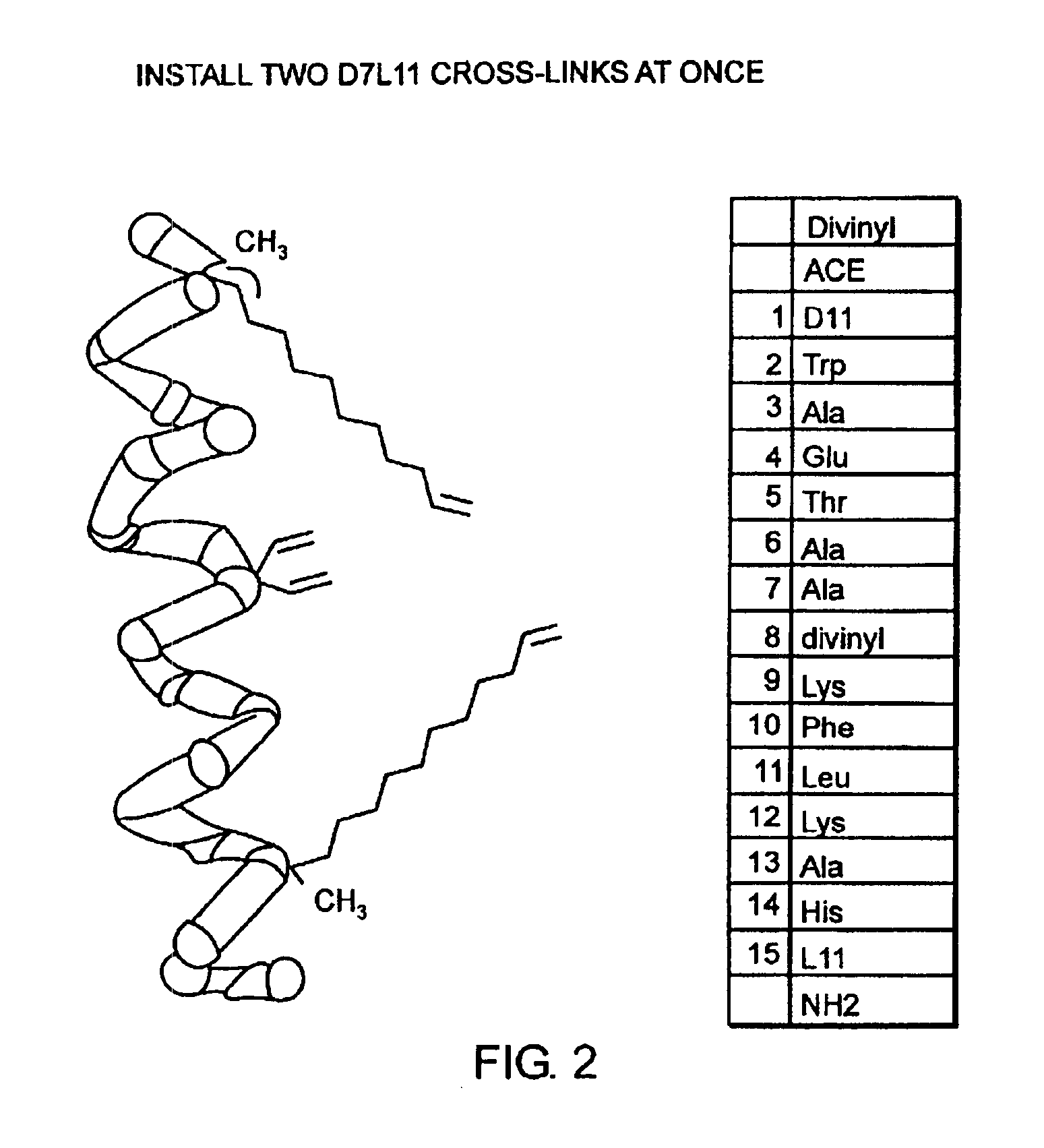
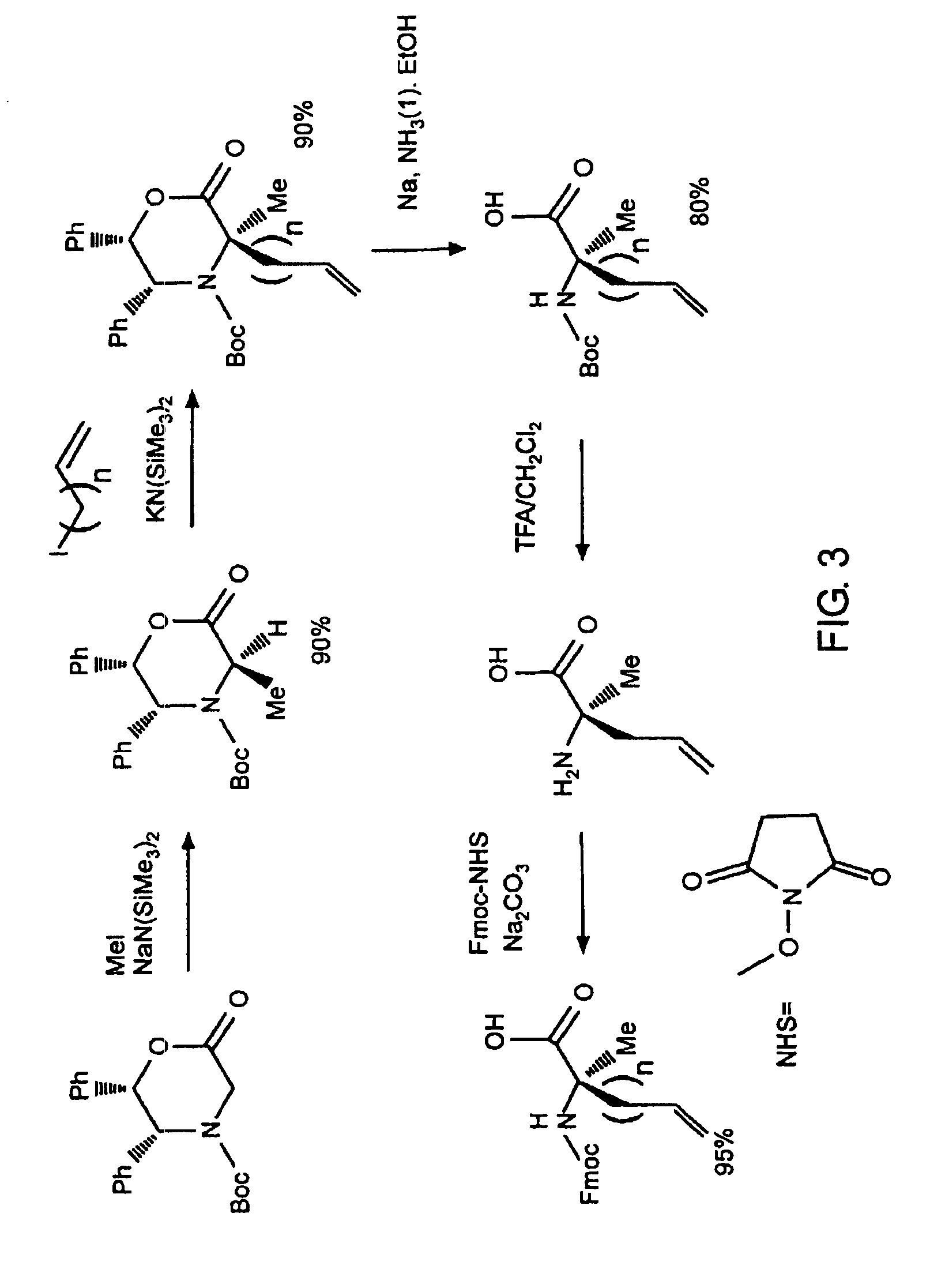
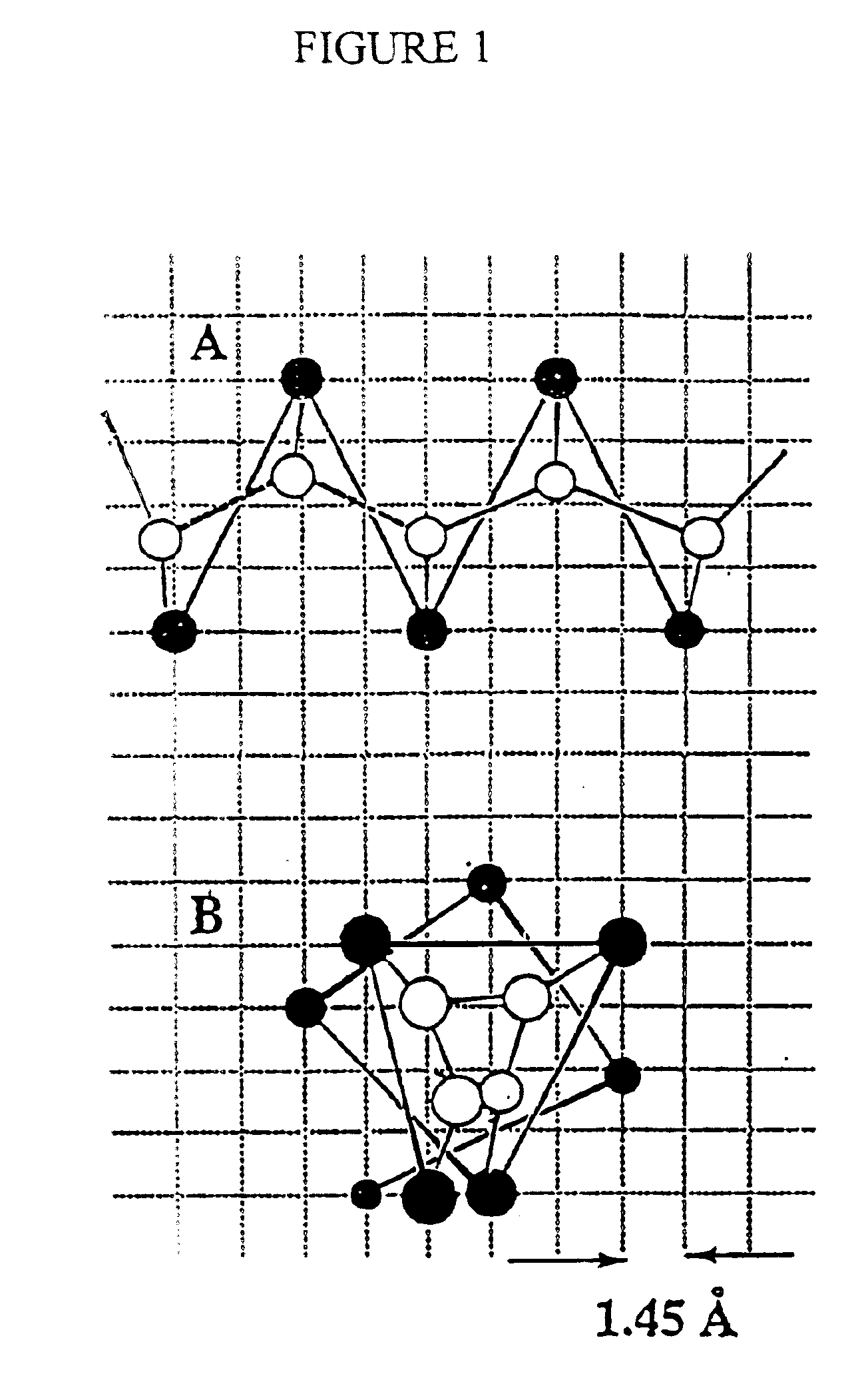
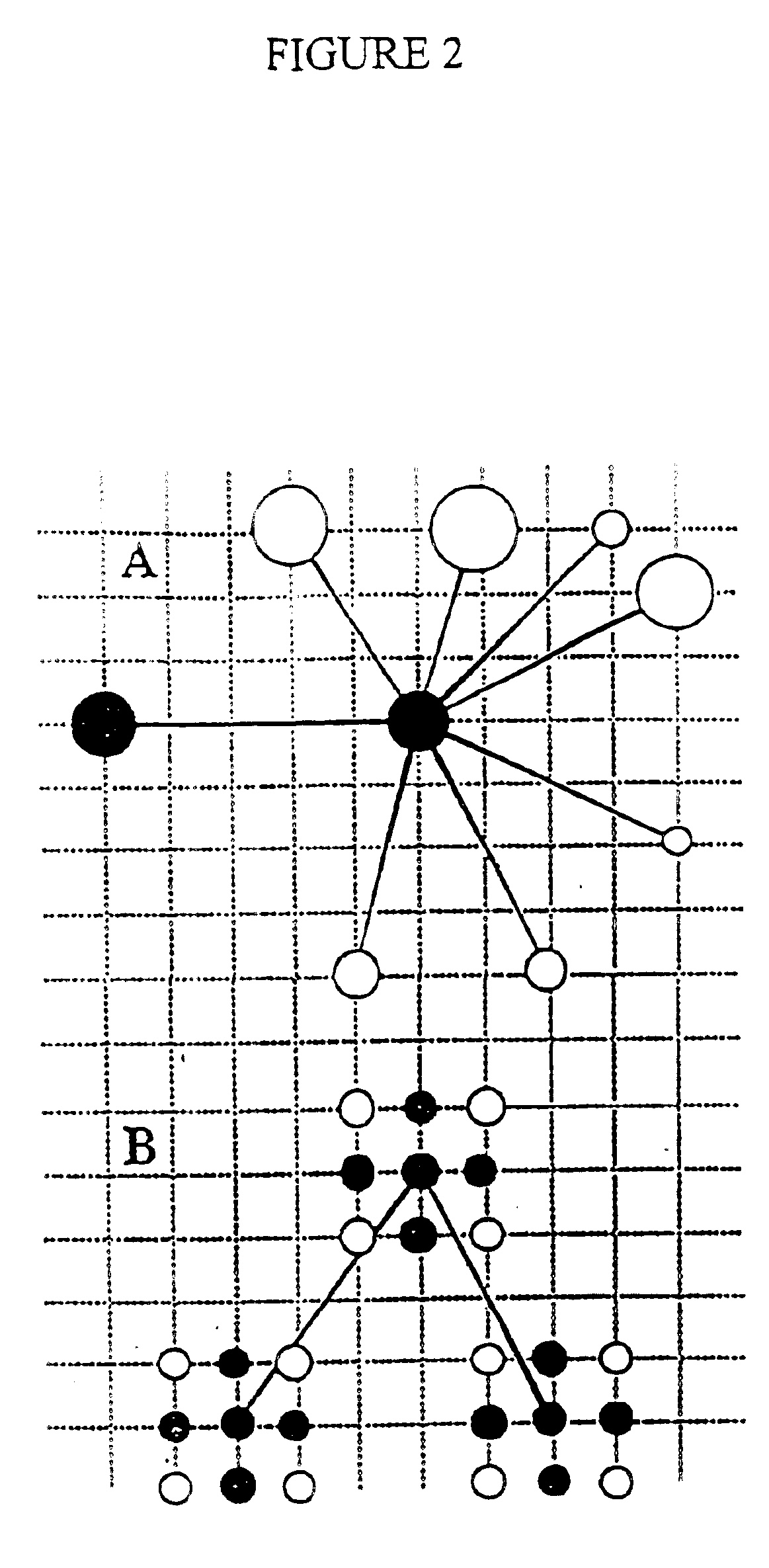
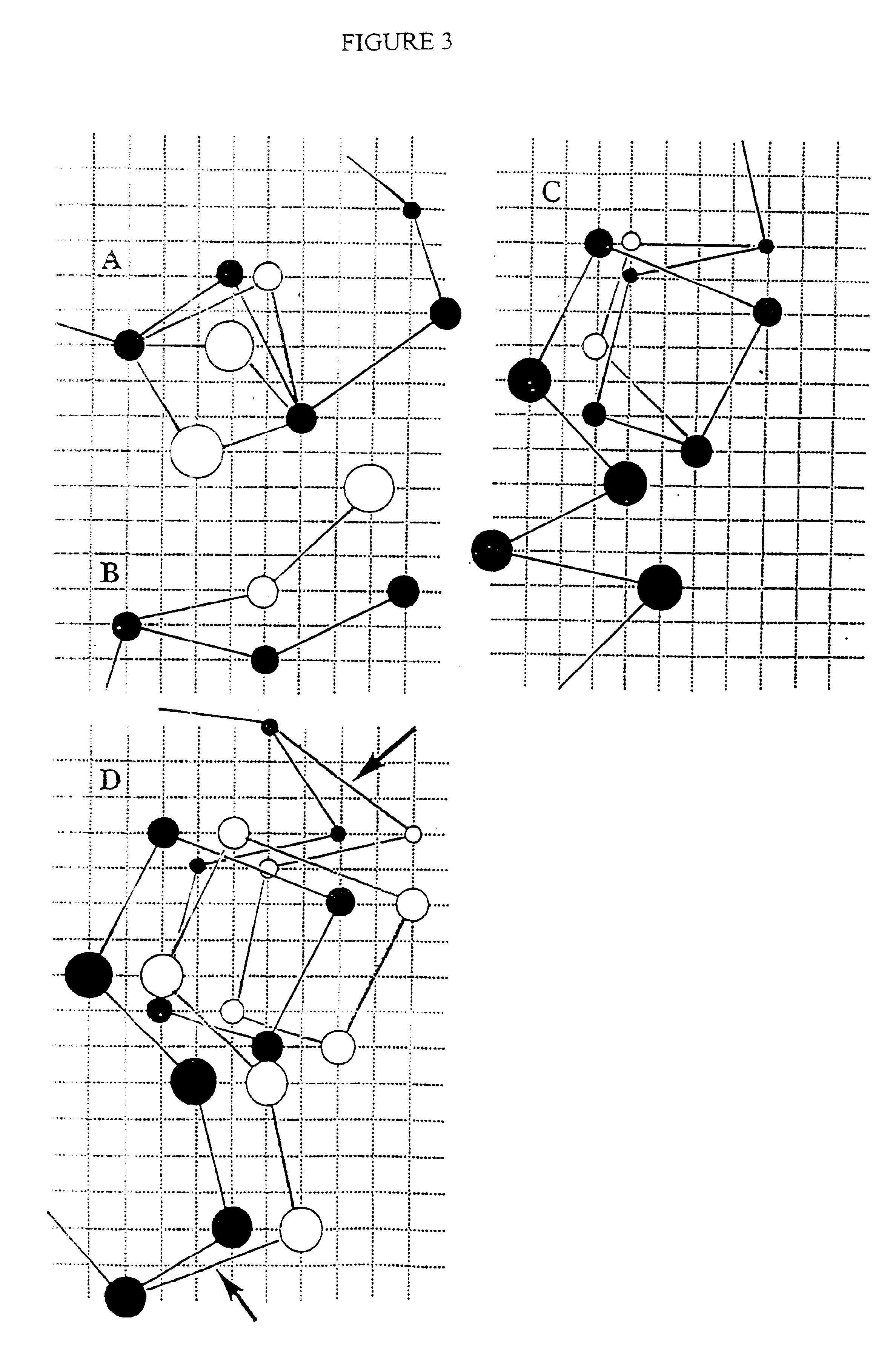
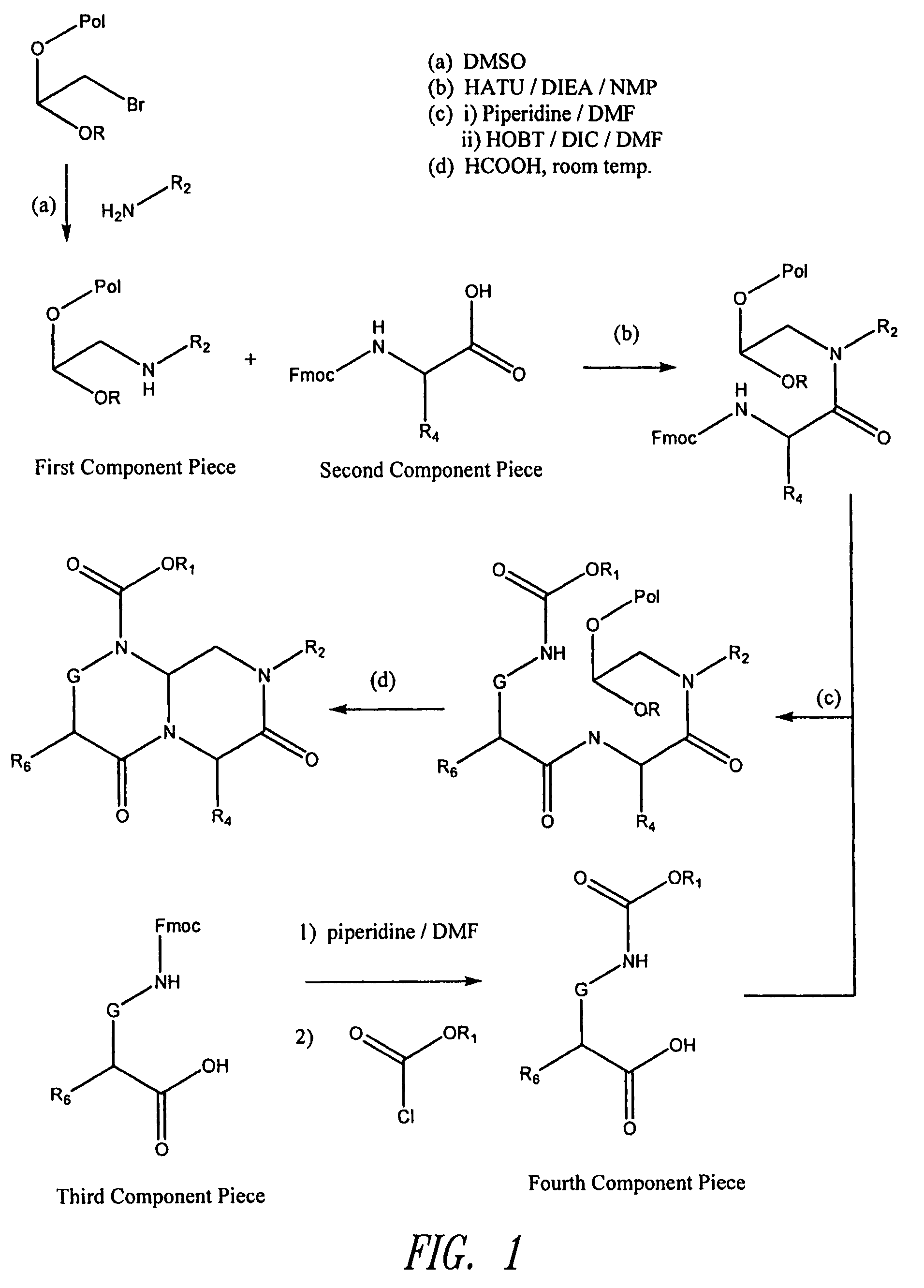
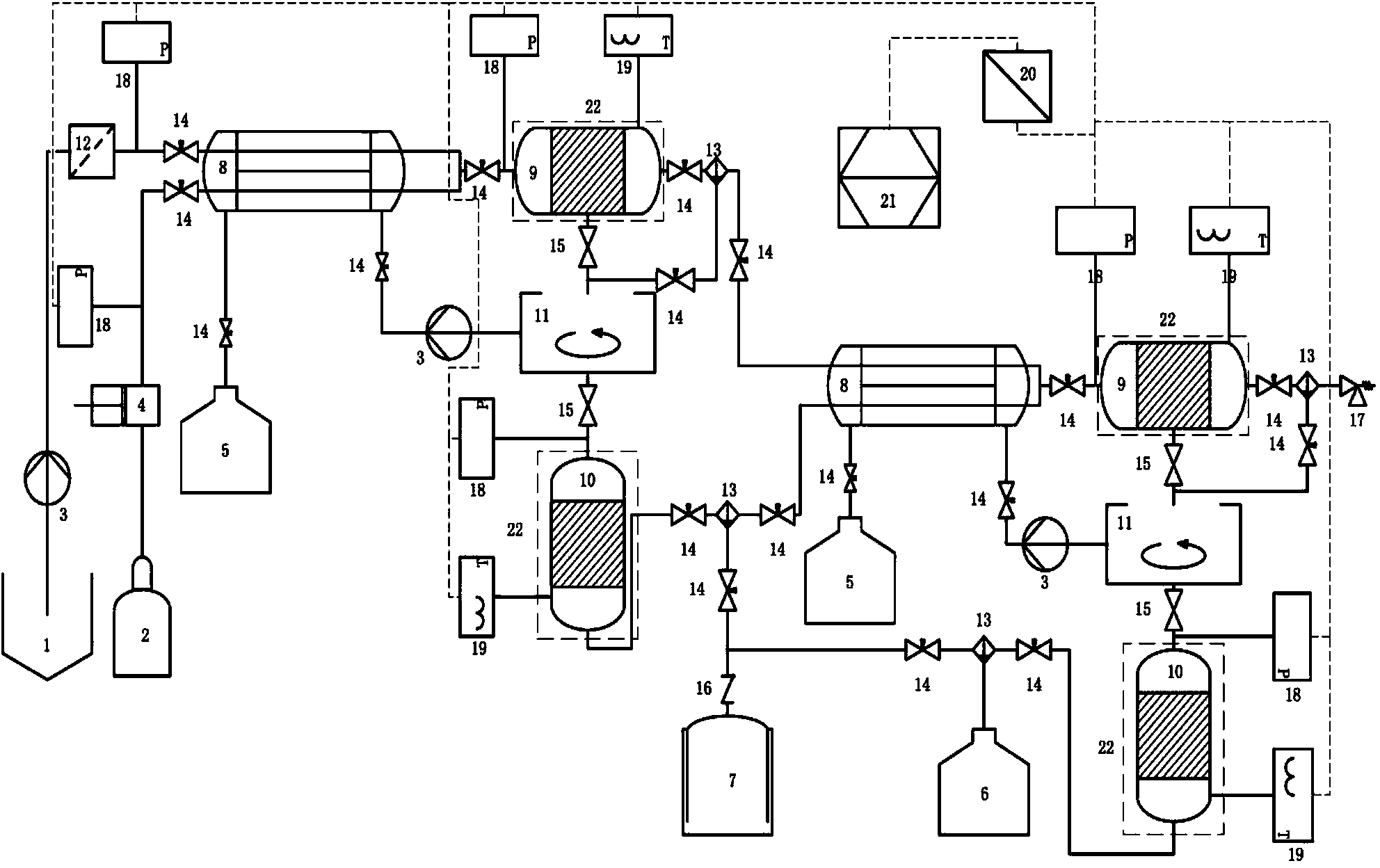
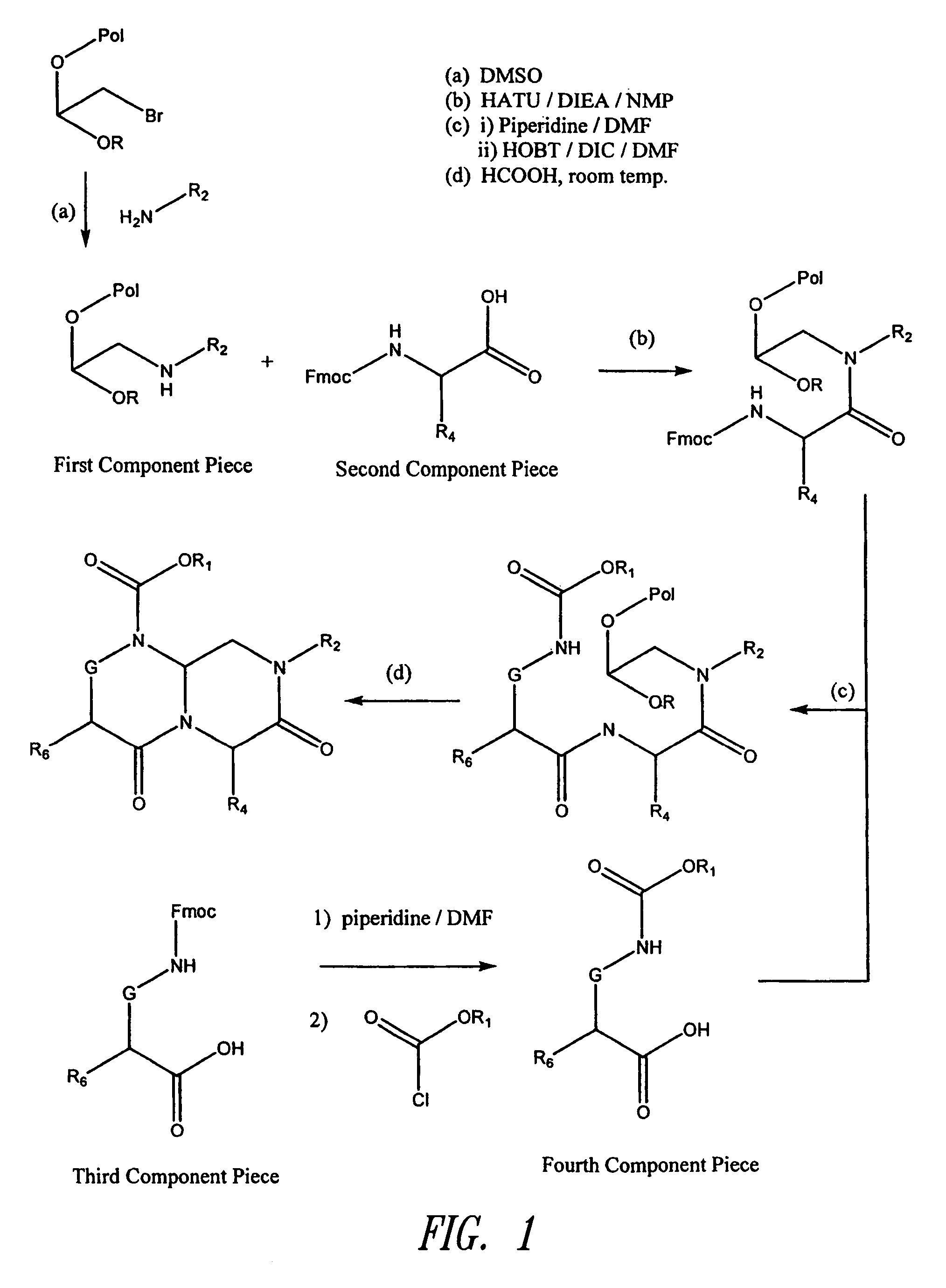
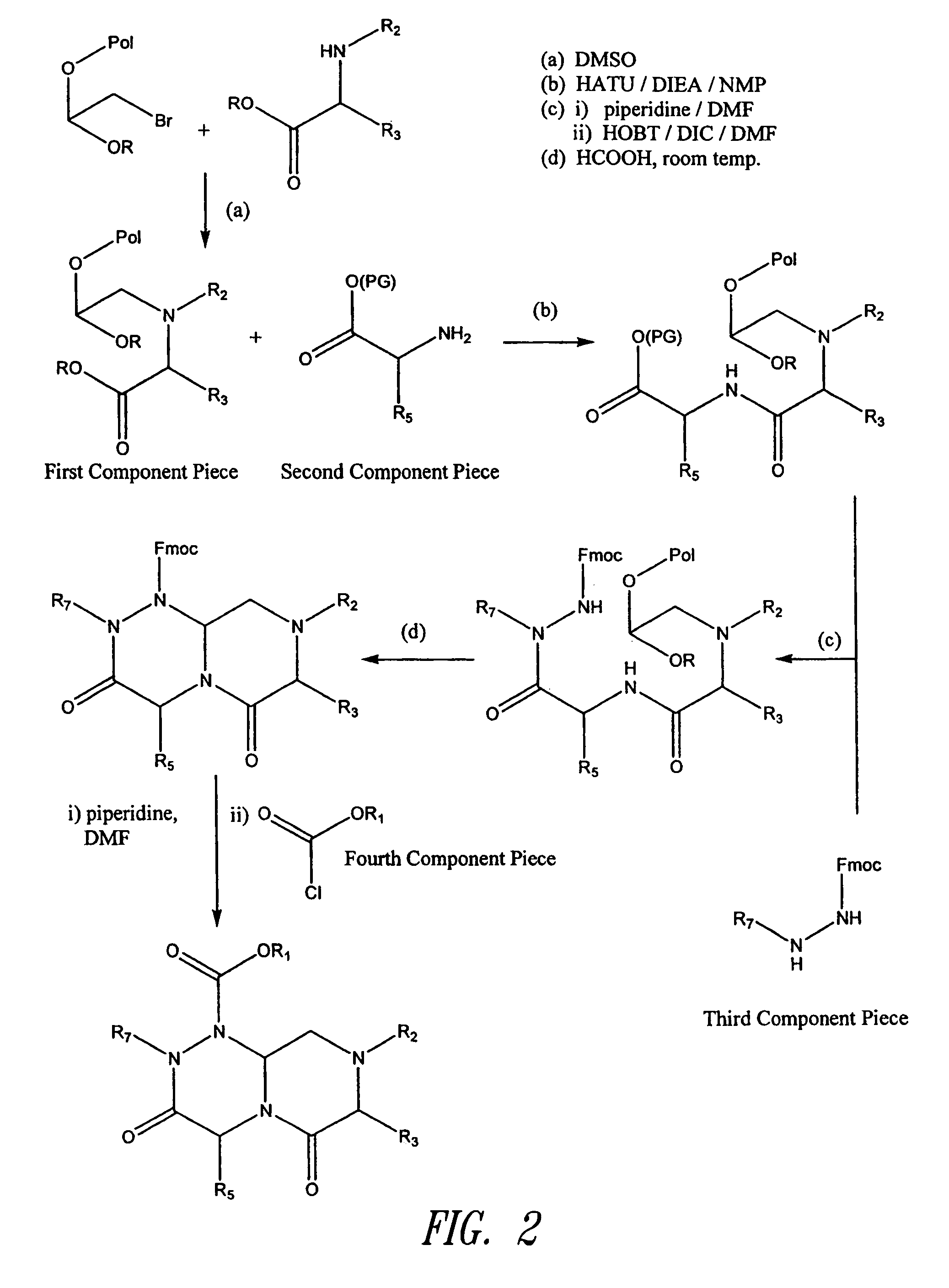
Stabilized compounds having secondary structure motifs
InactiveUS7192713B1Peptide-nucleic acidsGroup 8/9/10/18 element organic compoundsCrystallographyCarbon–carbon bond
The present invention provides novel stabilized crosslinked compounds having secondary structure motifs, libraries of these novel compounds, and methods for the synthesis of these compounds libraries thereof. The synthesis of these novel stabilized compounds involves (1) synthesizing a peptide from a selected number of natural or non-natural amino acids, wherein said peptide comprises at least two moieties capable of undergoing reaction to promote carbon-carbon bond formation; and (2) contacting said peptide with a reagent to generate at least one crosslinker and to effect stabilization of a secondary structure motif. The present invention, in a preferred embodiment, provides stabilized p53 donor helical peptides. Additionally, the present invention provides methods for disrupting the p53 / MDM2 binding interaction comprising (1) providing a crosslinked stabilized α-helical structure; and (2) contacting said crosslinked stabilized α-helical structure with MDM2.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
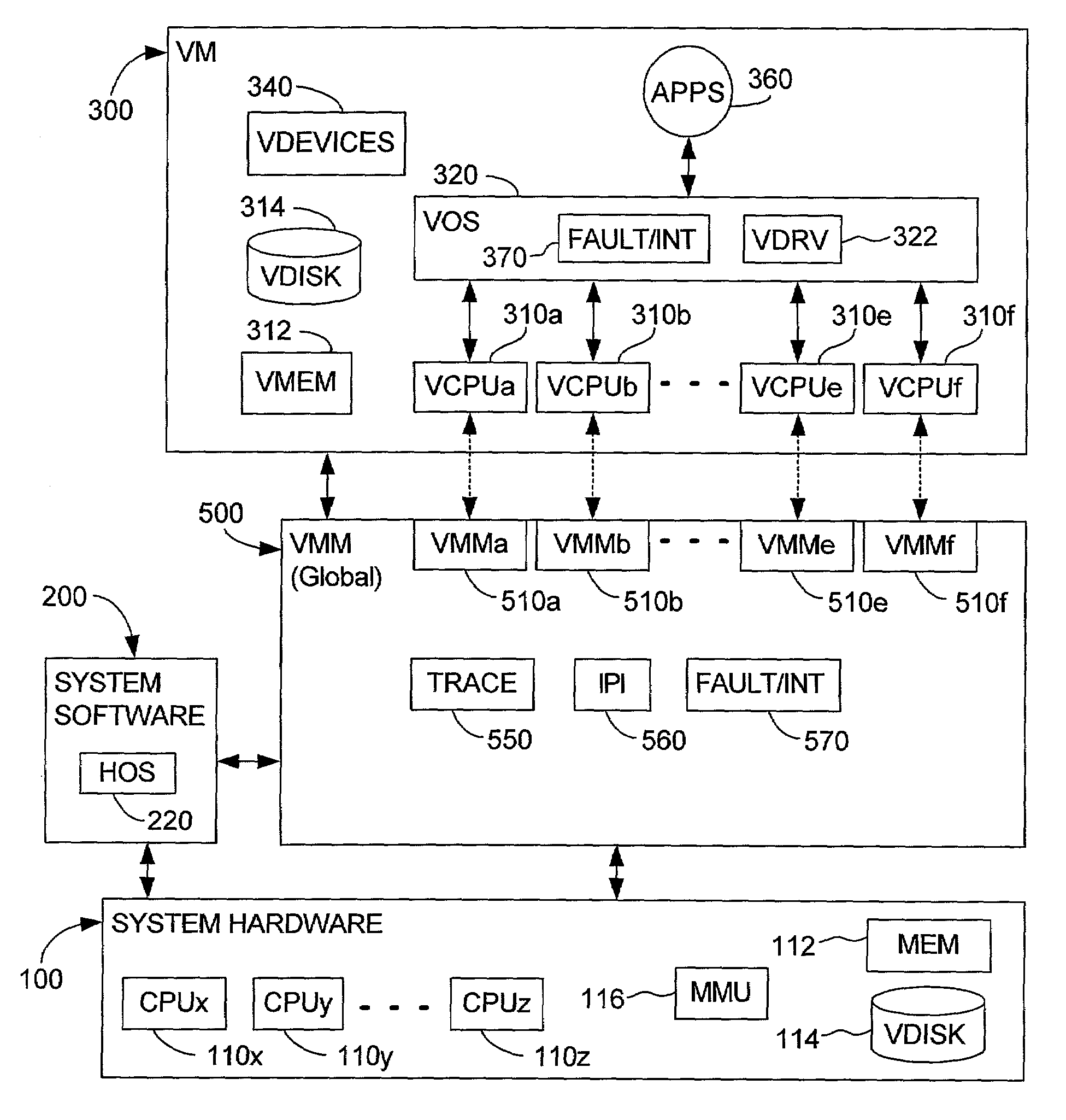
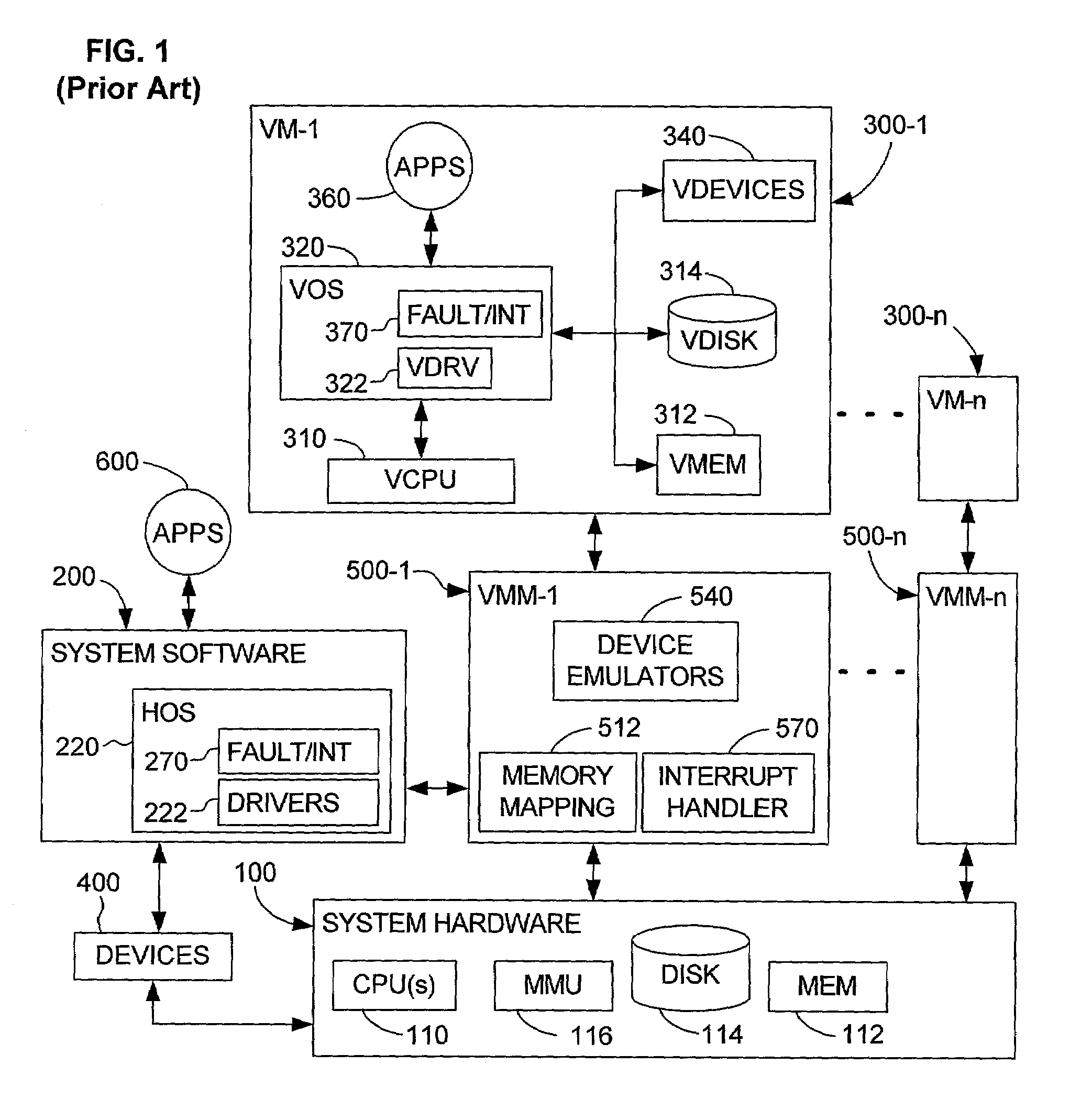
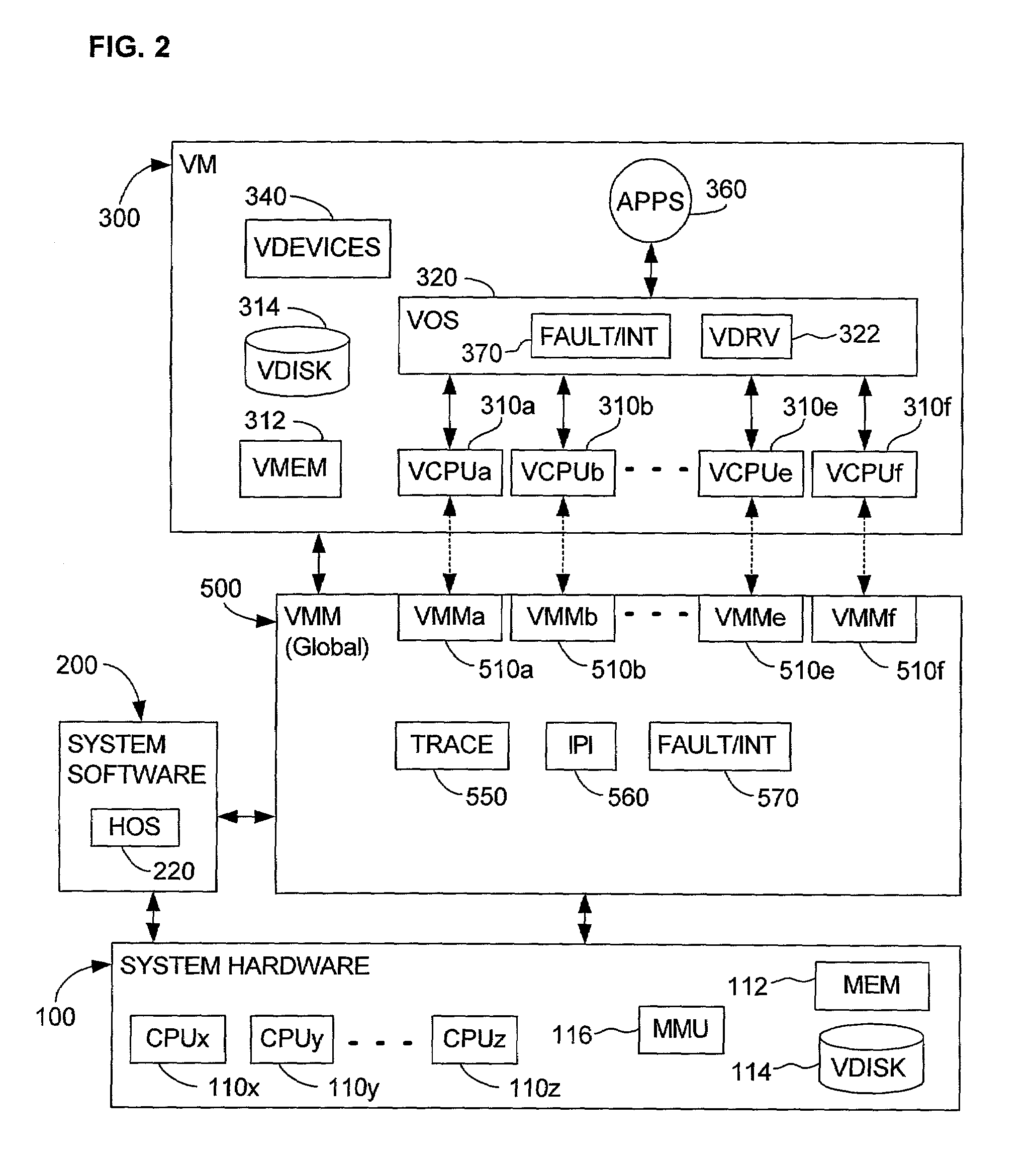
System and method for detecting access to shared structures and for maintaining coherence of derived structures in virtualized multiprocessor systems
A computer system includes at least one virtual machine that has a plurality of virtual processors all running on an underlying hardware platform. A software interface layer such as a virtual machine monitor establishes traces on primary structures located in a common memory space as needed for the different virtual processors. Whenever any one of the virtual processors generates a trace event, such as accessing a traced structure, then a notification is sent to at least the other virtual processors that have a trace on the accessed primary structure. In some applications, the VMM derives and maintains secondary structures corresponding to the primary structures, such as where the VMM converts, through binary translation, original code intended to run on a virtual processor into code that can be run on an underlying physical processor of the hardware platform. In these applications, the VMM may rederive or invalidate the secondary structures as needed upon receipt of the notification of the trace event. Different semantics are provided for the notification, providing different choices of performance versus guaranteed consistency between primary and secondary structures. In the preferred embodiment of the invention, a dedicated sub-system is included within the VMM for each virtual processor; each sub-system establishes traces, senses trace events, issues the notification, and performs other operations relating specifically to its respective virtual processor.
Owner:VMWARE INC
Classification of nucleic acid templates
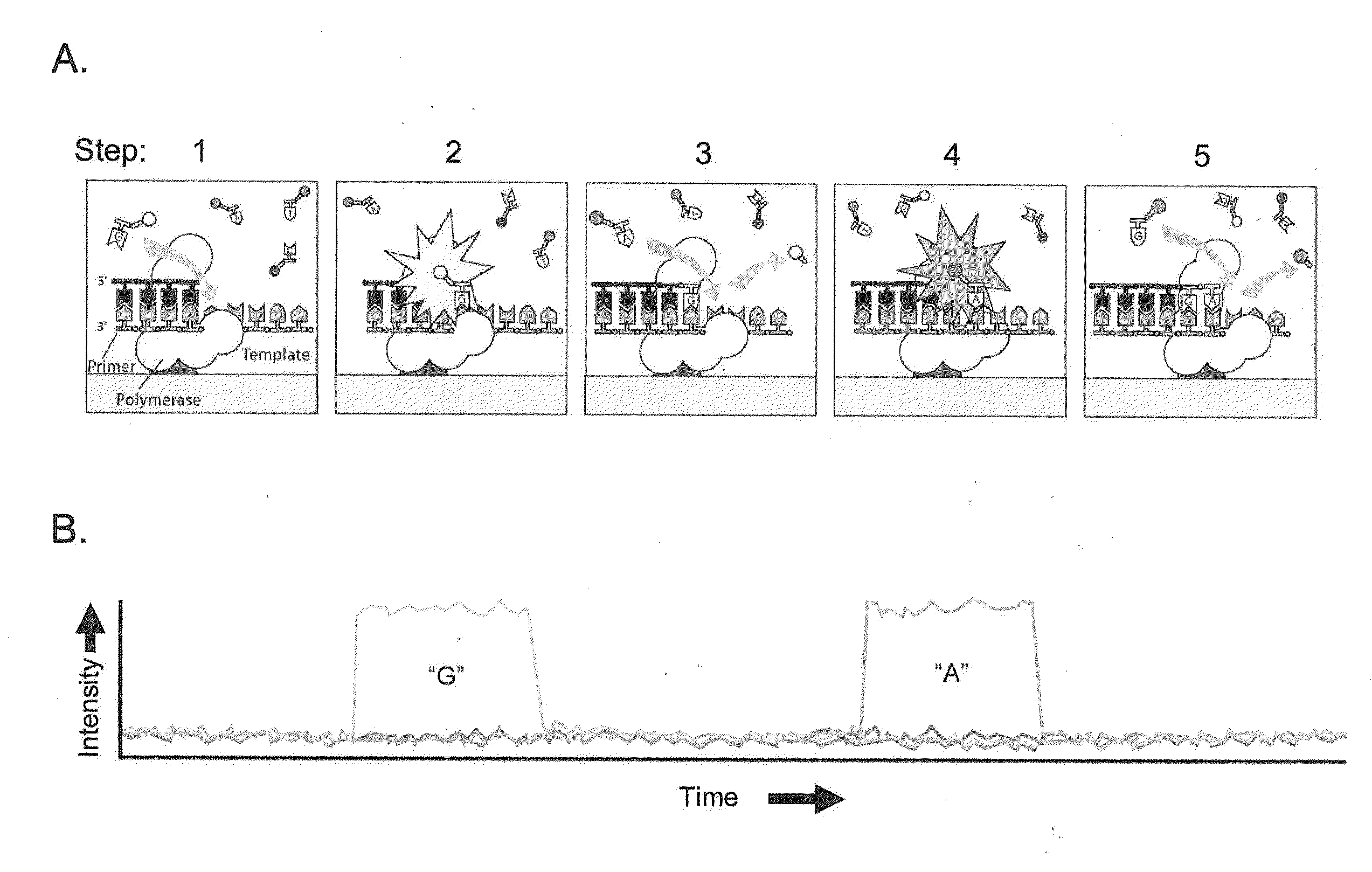
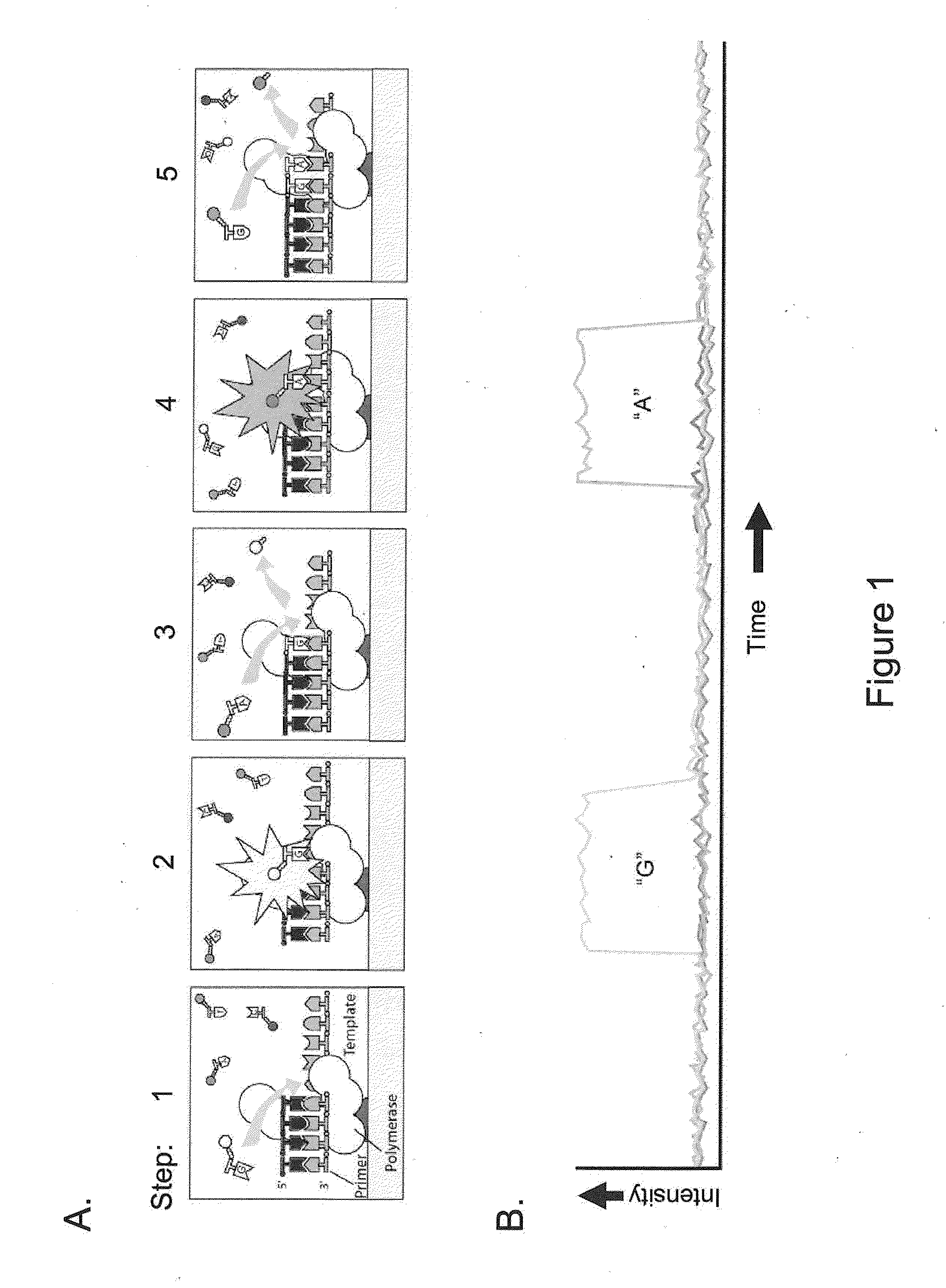
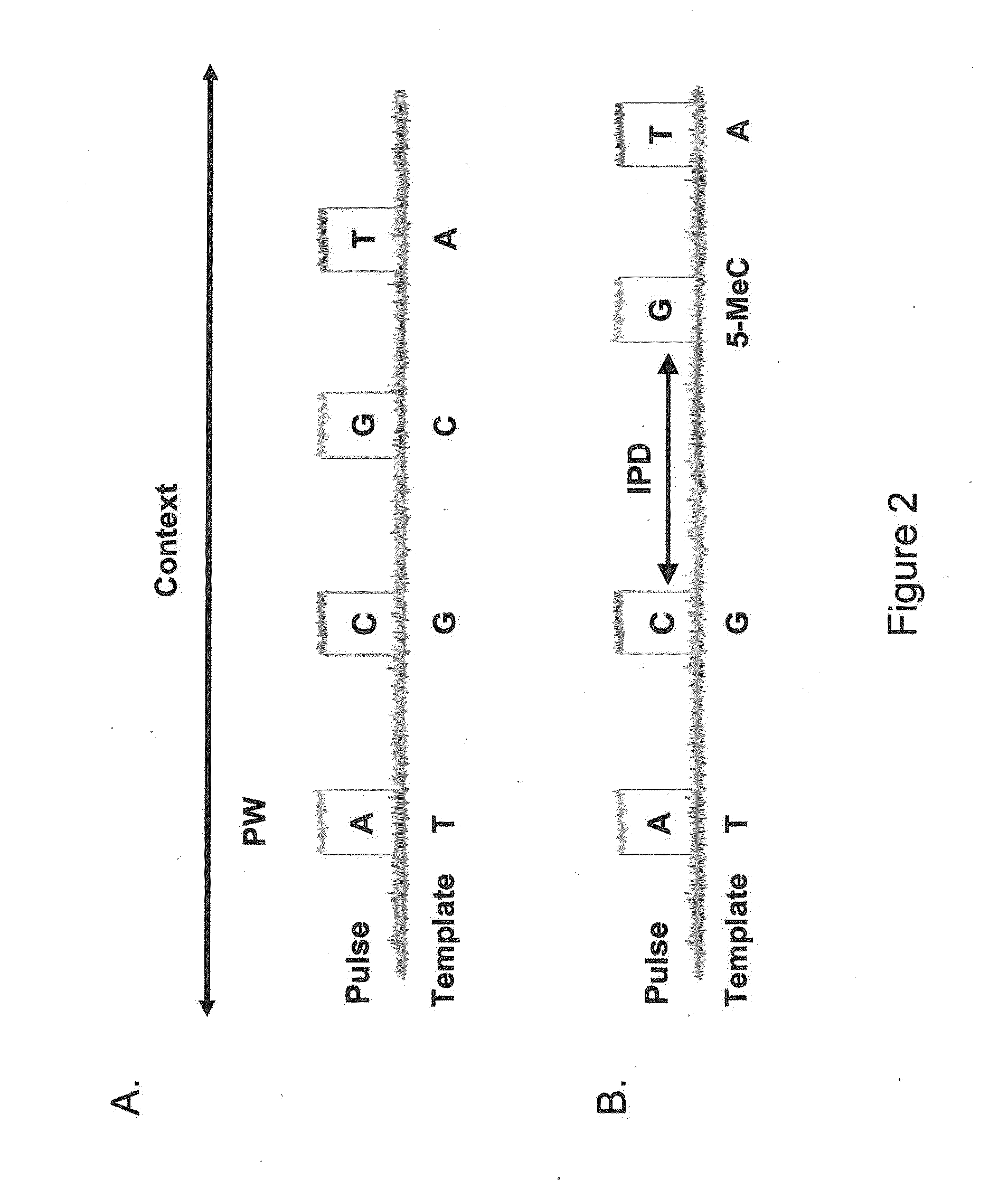
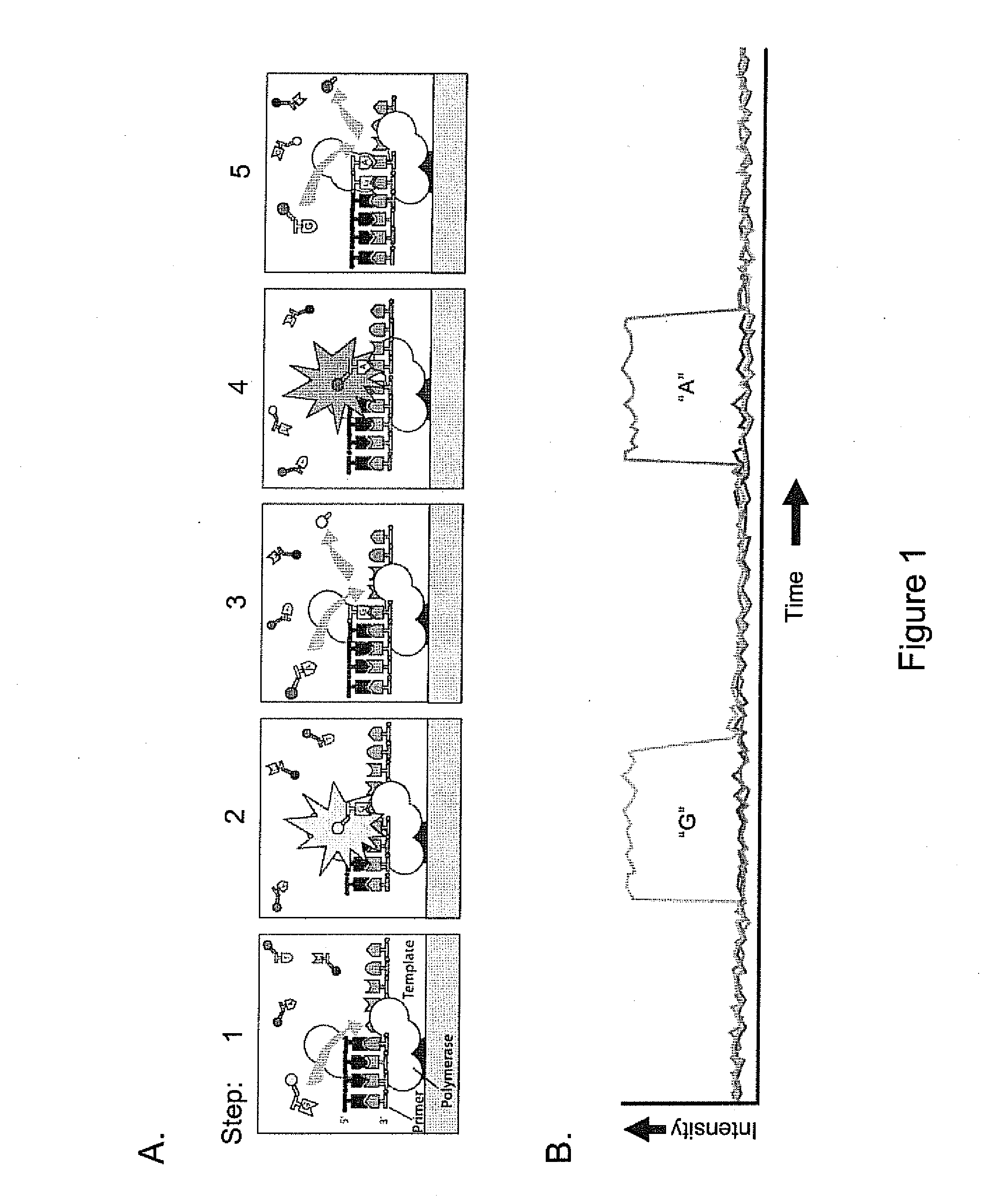
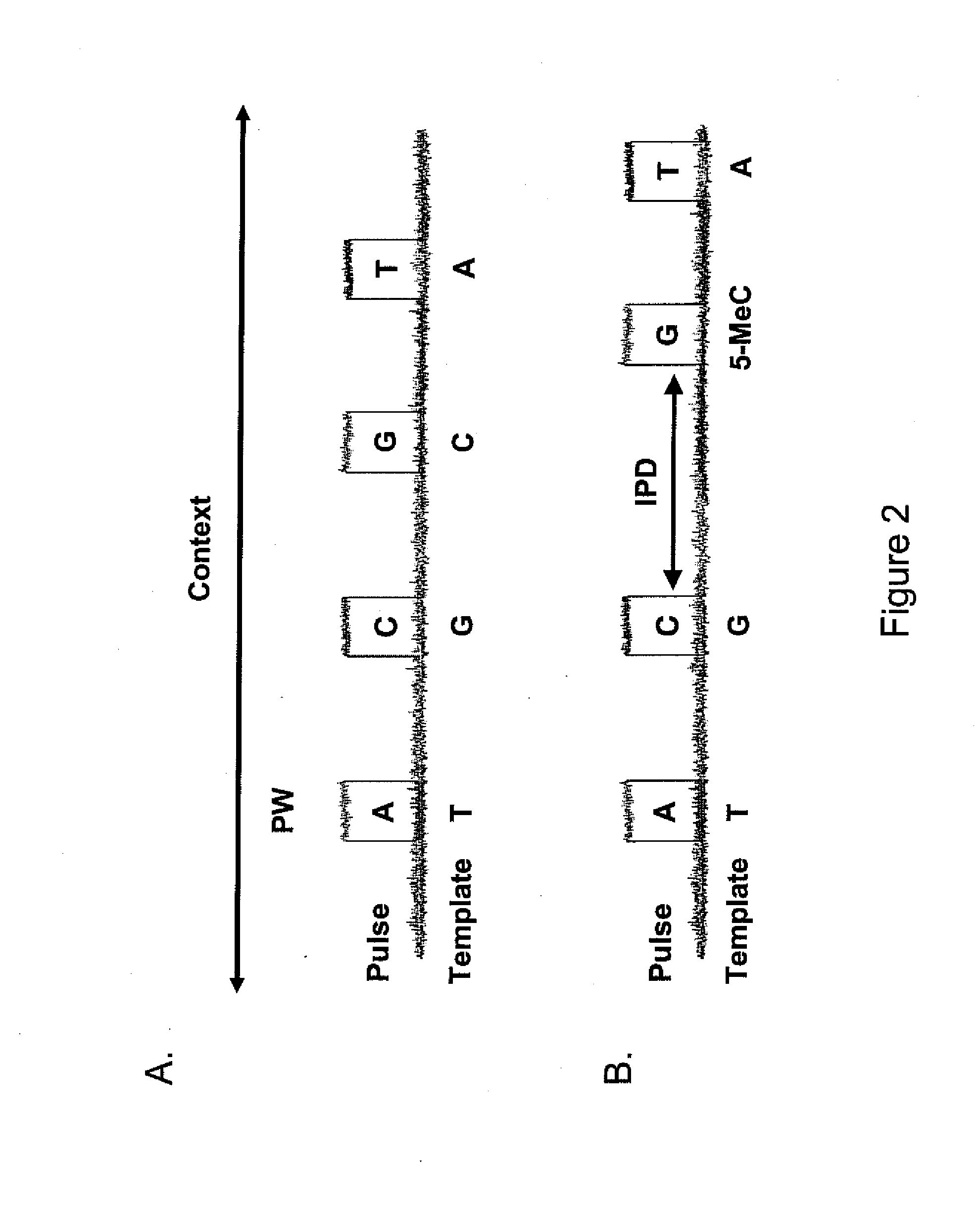
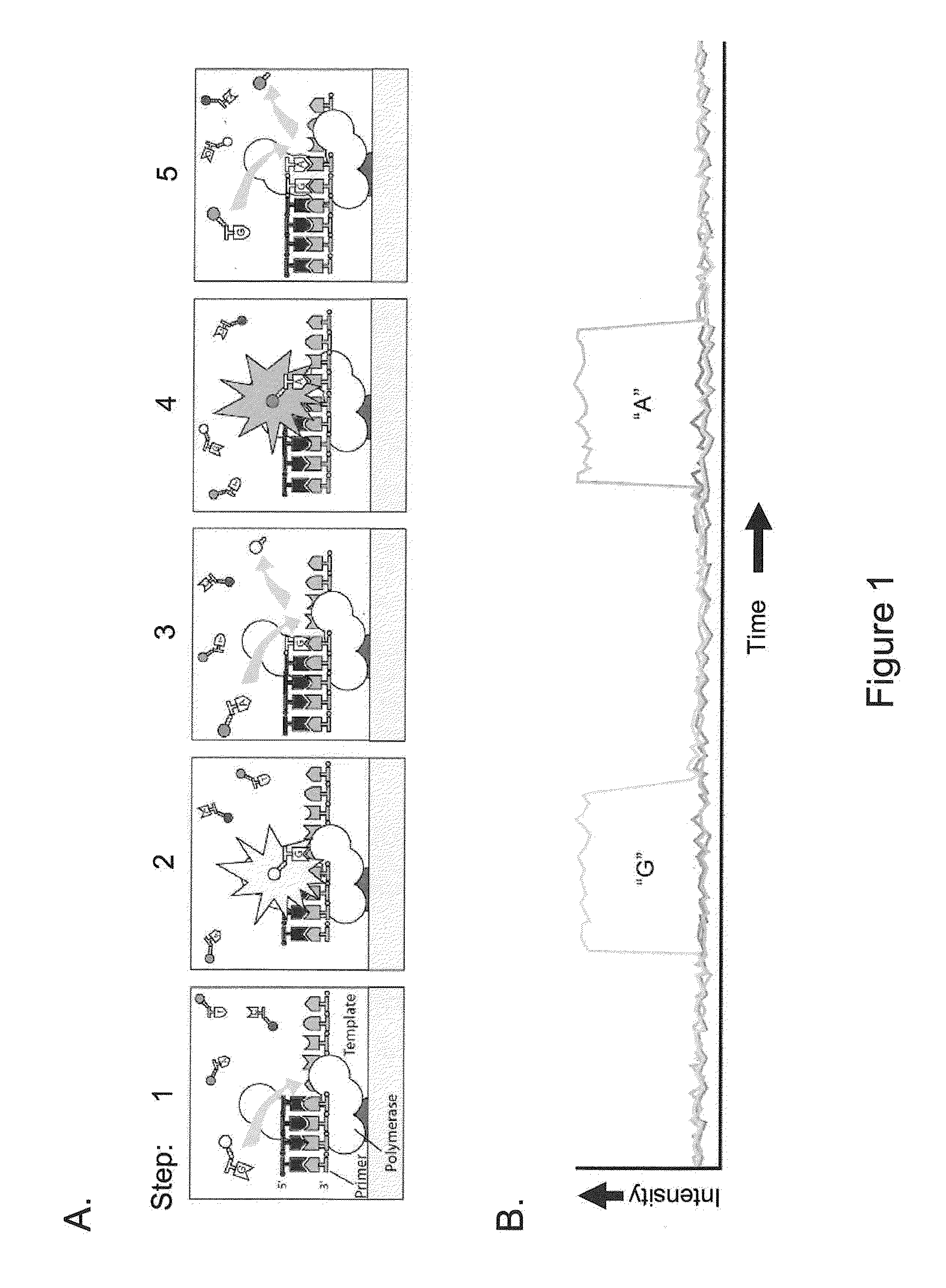
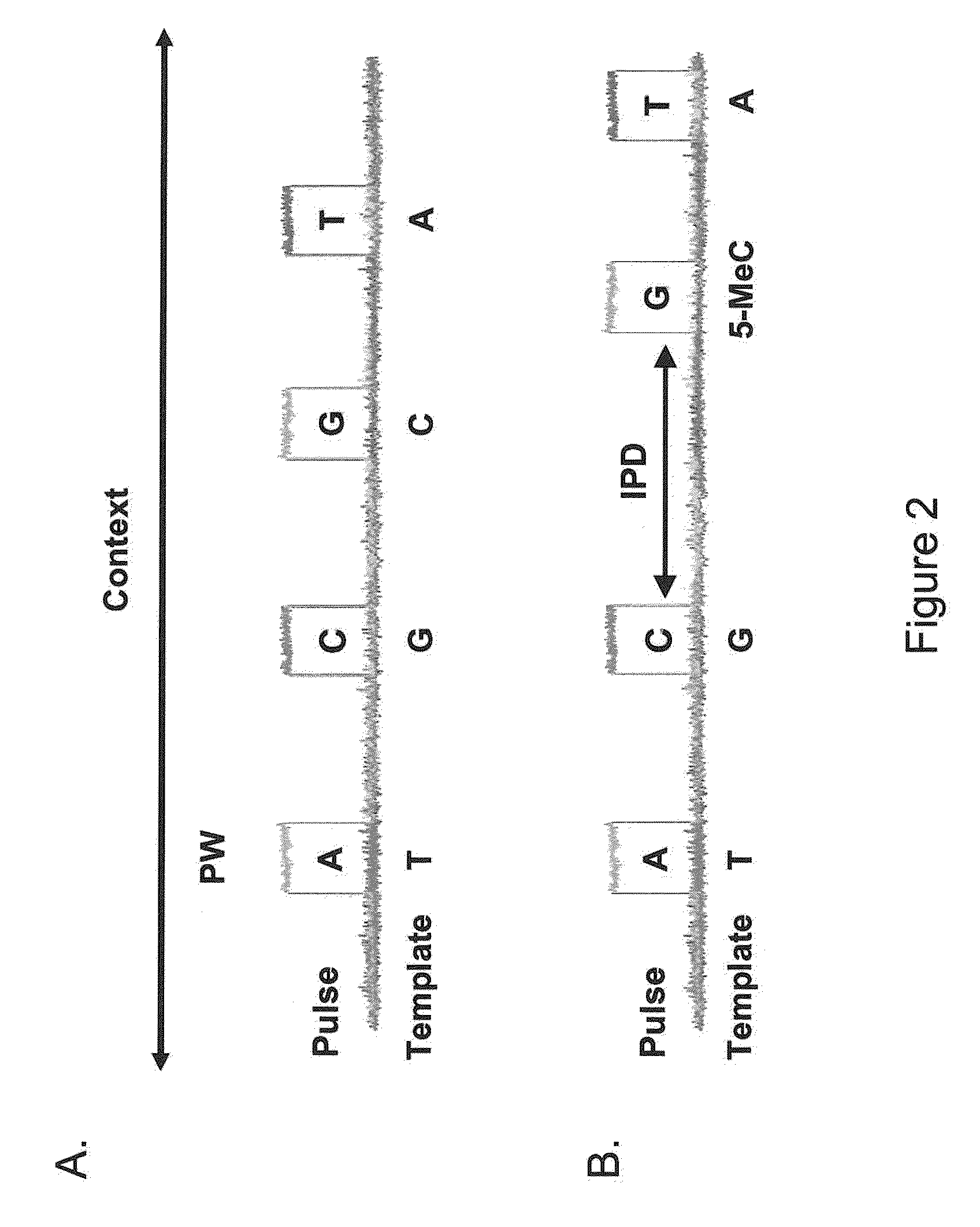
ActiveUS20110183320A1Convenient introductionImprove responseMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleic acid sequencingProtein secondary structure
Methods, compositions, and systems are provided for characterization of modified nucleic acids. In certain preferred embodiments, single molecule sequencing methods are provided for identification of modified nucleotides within nucleic acid sequences. Modifications detectable by the methods provided herein include chemically modified bases, enzymatically modified bases, abasic sites, non-natural bases, secondary structures, and agents bound to a template nucleic acid.
Owner:PACIFIC BIOSCIENCES
Classification of Nucleic Acid Templates
ActiveUS20100221716A1High densityMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleic acid sequencingProtein secondary structure
Methods, compositions, and systems are provided for characterization of modified nucleic acids. In certain preferred embodiments, single molecule sequencing methods are provided for identification of modified nucleotides within nucleic acid sequences. Modifications detectable by the methods provided herein include chemically modified bases, enzymatically modified bases, abasic sites, non-natural bases, secondary structures, and agents bound to a template nucleic acid.
Owner:PACIFIC BIOSCIENCES
Prion-free collagen and collagen-derived products and implants for multiple biomedical applications; methods of making thereof
InactiveUS6197935B1Preserve integrityPeptide/protein ingredientsImmunoglobulinsIn vivo biocompatibilityCollagen VI
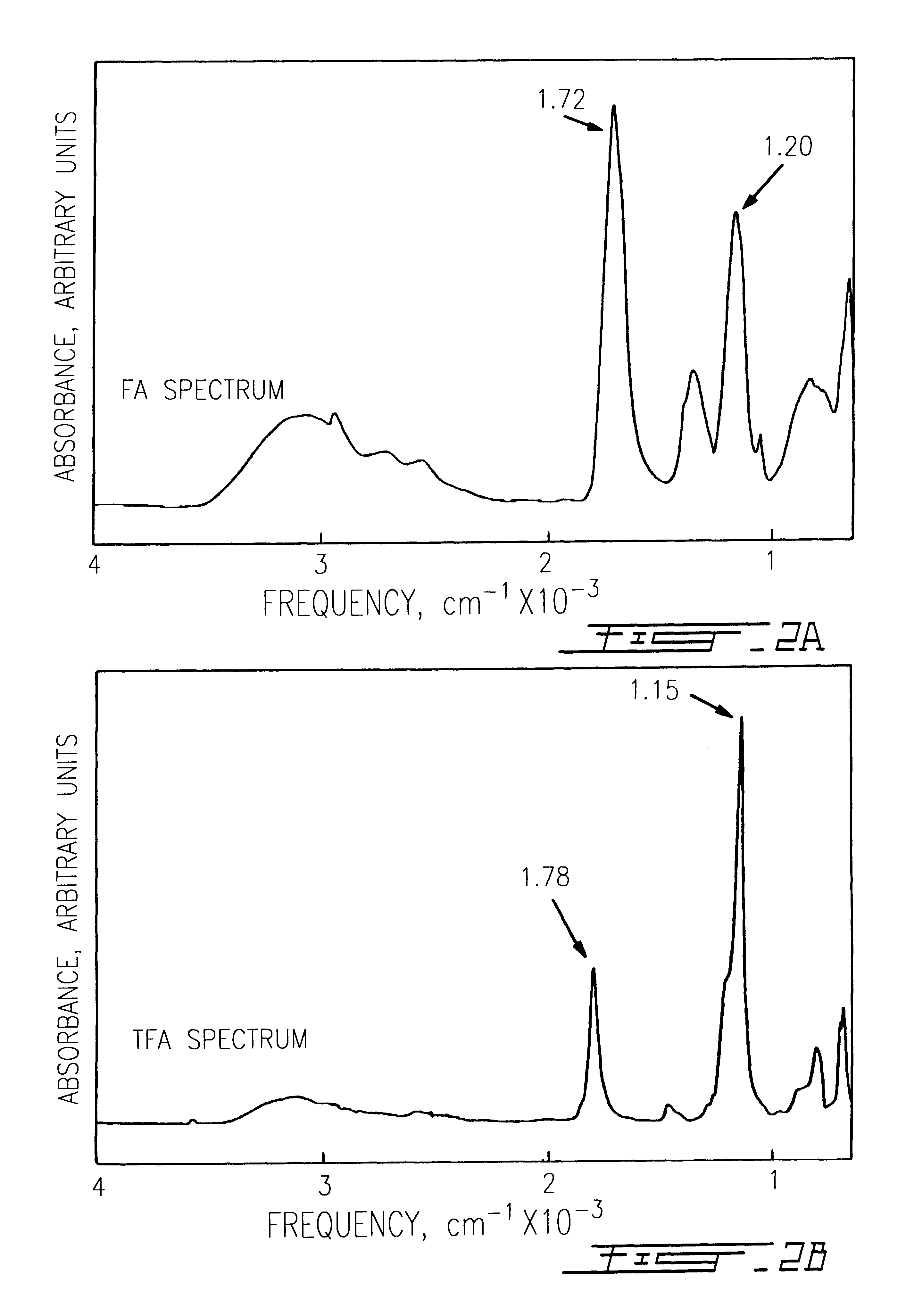
The use of collagen as a biomedical implant raises safety issues towards viruses and prions. The physicochemical changes and the in vitro and in vivo biocompatibility of collagen treated with heat, and by formic acid (FA), trifluoroacetic acid (TFA), tetrafluoroethanol (TFE) and hexafluoroiso-propanol (HFIP) were investigated. FA and TFA resulted in extensive depurination of nucleic acids while HFIP and TFE did so to a lesser degree. The molecules of FA, and most importantly of TFA, remained within collagen. Although these two acids induced modification in the secondary structure of collagen, resistance to collagenase was not affected and, in vitro, cell growth was not impaired. Severe dehydrothermal treatment, for example 110° C. for 1-3 days under high vacuum, also succeeded in removing completely nucleic acids. Since this treatment also leads to slight cross-linking, it could be advantageously used to eliminate prion and to stabilize gelatin products. Finally, prolonged treatment with TFA provides a transparent collagen, which transparency is further enhanced by adding glycosaminoglycans or proteoglycans, particularly hyaluronic acid. All the above treatments could offer a safe and biocompatible collagen-derived material for diverse biomedical uses, by providing a virus or prion-free product.
Owner:UNIV LAVAL
Device with multi-structural contact elements
A contact device with resilient contact elements is disclosed. The resilient contact elements have primary structures and secondary structures. The primary structures and secondary structures have contact surfaces for engaging a working surface. The primary structures are preferably molded structures with hardness value between 10 to 90 Shores A. The secondary structures are nodules, squeegees, arrays of nodules or squeegees and matrices but are preferably bristle structures formed from plastic resins, wherein the device is configured clean dentition.
Owner:GAVNEY JR JAMES A
Multistack 3-dimensional high density semiconductor device and method for fabrication
InactiveUS6291858B1Function increaseHigh densitySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesLevel structureHigh density
A multistack 3-D semiconductor structure comprising a first level structure comprising a first semiconductor substrate and first active devices; and a second level structure comprising a SOI semiconductor structure bonded to the first level structure and further comprising second active devices; and wherein the first active devices are more heat tolerant than the second active devices is provided along with a method for its fabrication.
Owner:IBM CORP
Structurally determined cyclic metallo-constructs and applications
InactiveUS6331285B1Improve the level ofLess susceptible to proteolysisPeptide sourcesRadioactive preparation carriersProtein secondary structureMedicinal chemistry
A metallo-construct, which may be a peptide, is provided for use as a biological, therapeutic, diagnostic imaging, or radiotherapeutic agent, and for use in library or combinatorial chemistry methods. The construct has a conformationally constrained global secondary structure obtained upon complexing with a metal ion. The peptide constructs are of the general formula:where X is a plurality of amino acids and includes a complexing backbone for complexing metal ions, so that substantially all of the valences of the metal ion are satisfied upon complexation of the metal ion with X, resulting in a specific regional secondary structure forming a part of the global secondary structure; and where R1 and R2 each include from 0 to about 20 amino acids, the amino acids being selected so that upon complexing the metal ion with X at least a portion of either R1 or R2 or both have a structure forming the balance of the conformationally constrained global secondary structure. All or a portion of the global secondary structure, which may be sychnologic or rhegnylogic, may form a ligand or mimic a known biological-function domain. The construct has substantially higher affinity for its target upon labeling with a metal ion.
Owner:PALATIN TECH INC
Modified cytokine
InactiveUS7112660B1Increase intrinsic stabilityIncrease of to proteolytic degradationPeptide/protein ingredientsPeptide preparation methodsProtein secondary structureSolvent
The invention relates to methods for the stabilisation of cytokines and to cytokines generated by such methods. The methods of the invention involve mutating the amino acid sequence of a cytokine so as to remove solvent-exposed hydrophobic residues, and / or mutating the amino acid sequence of the cytokine so as to stabilise one or more secondary structure elements in the molecule. These steps have the effect of destabilsing intermediates that are formed during the folding process, relative to the stability of the cytokine in its naturally folded state, so increasing the yield of the cytokine as produced in vitro.
Owner:BAYER SCHERING PHARMA AG +1
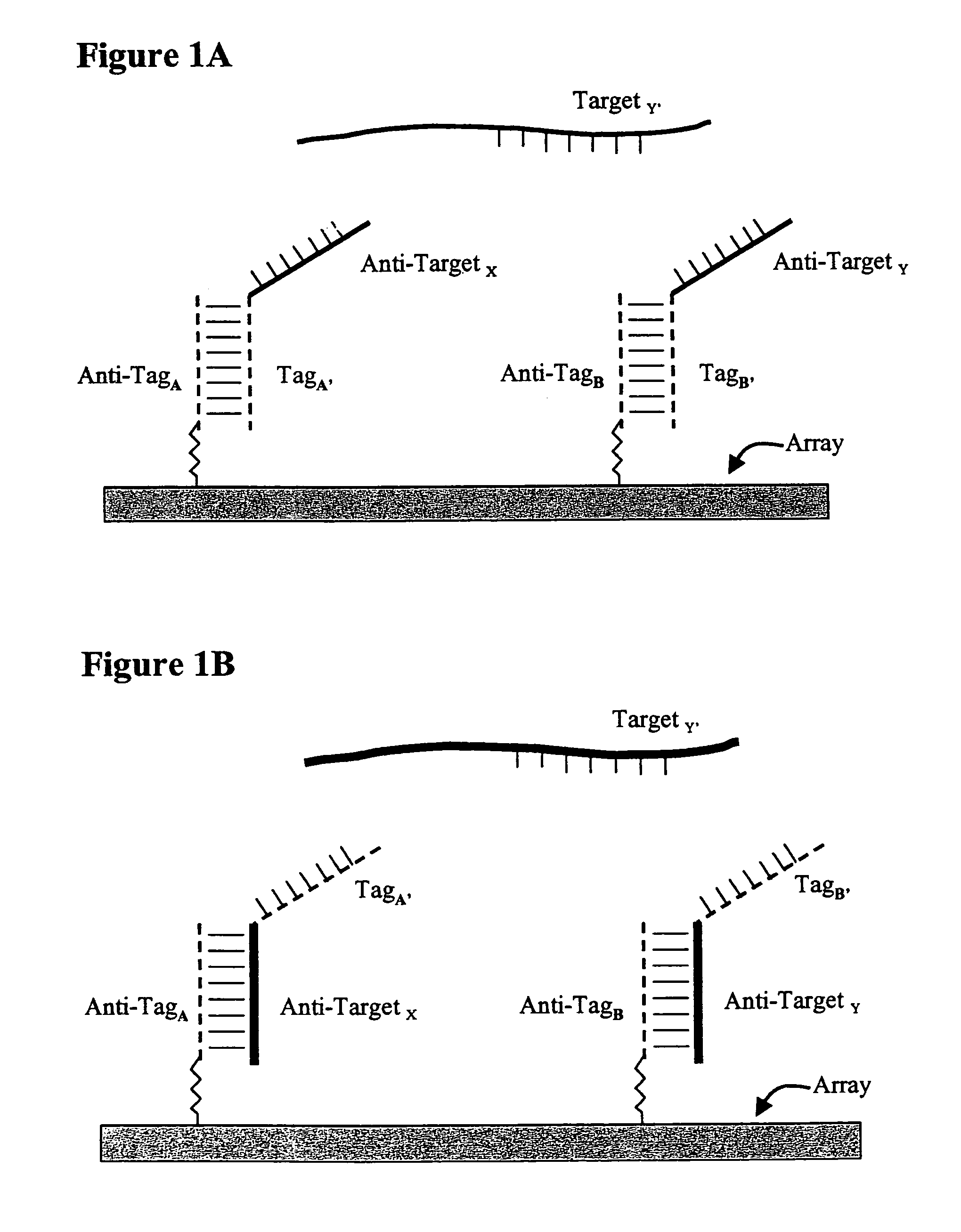
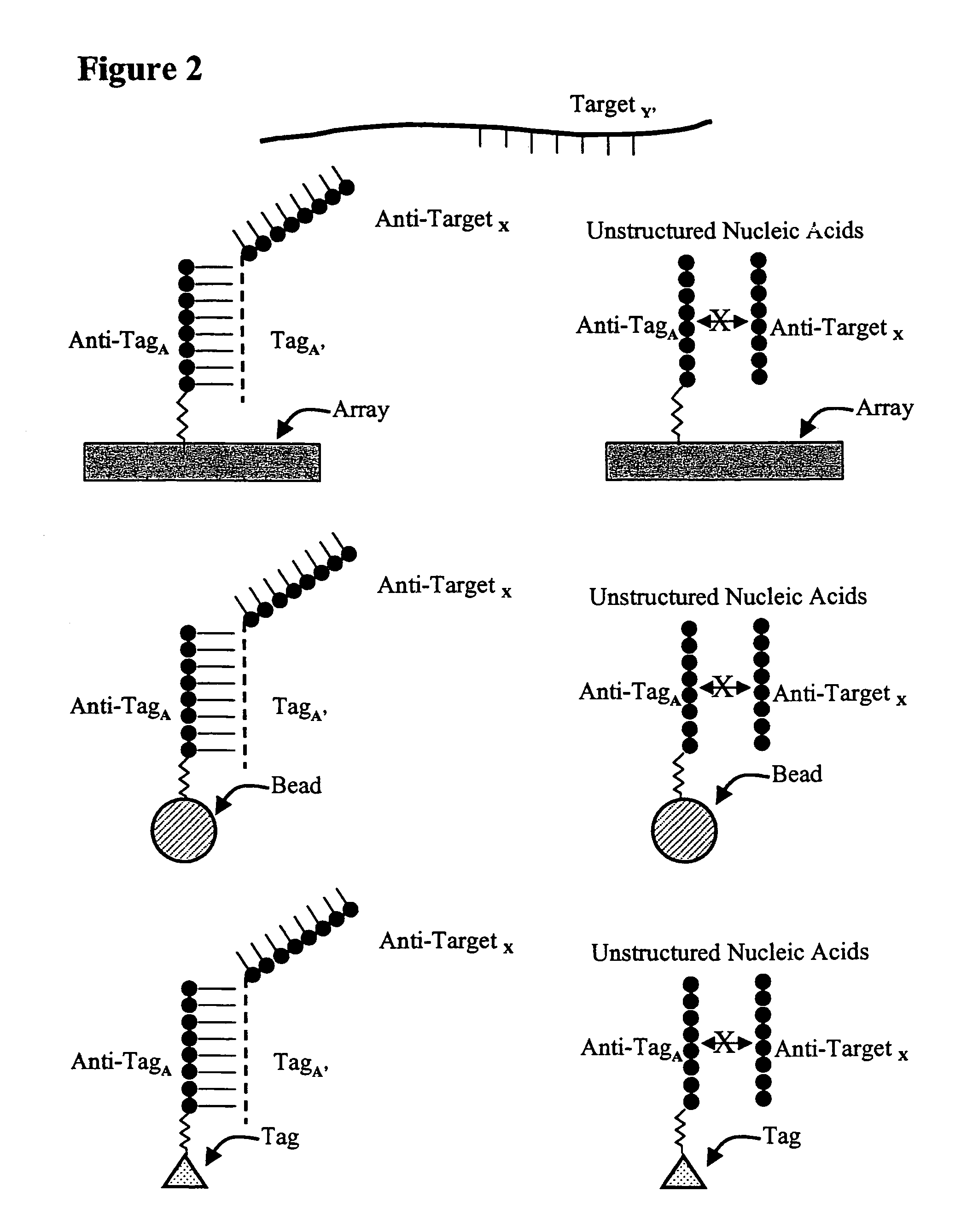
Use of unstructured nucleic acids in assaying nucleic acid molecules
InactiveUS7371580B2Reduce background signalHigh sensitivityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsProtein secondary structureCross hybridization
The present invention provides a system and methods for assaying nucleic acid molecules with reduced levels of background signal and enhanced specificity and sensitivity. In particular, the present invention provides a system and methods for detecting, sorting, tracking and characterizing nucleic acid molecules using hybridization assays with reduced levels of undesirable cross hybridization and reduced levels of intramolecular secondary structure.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
Oral care device with multi-structural contact elements
A contact device with resilient contact elements is disclosed. The resilient contact elements have primary structures and secondary structures. The primary structures and secondary structures have contact surfaces for engaging a working surface. The primary structures are preferably molded structures with hardness value between 10 to 90 Shores A. The secondary structures are nodules, squeegees, arrays of nodules or squeegees and matrices but are preferably bristle structures formed from plastic resins, wherein the device is configured clean dentition.
Owner:GAVNEY JR JAMES A
Beta -polypeptide foldamers of well-defined secondary structure
InactiveUS6060585AHigh conformational stabilityImprove stabilityOrganic compound preparationOrganic chemistry methodsProtein secondary structurePeptide backbone
Disclosed are beta -peptides containing cylcoalkyl, cycloalkenyl, and heterocylic substituents which encompass the alpha and beta carbons of the peptide backbone. The beta -peptides adopt stable helical and sheet structures in both the solid state and in solution. Method of generating combinatorial libraries of peptides containing beta -peptide residues and the libraries formed thereby are disclosed.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
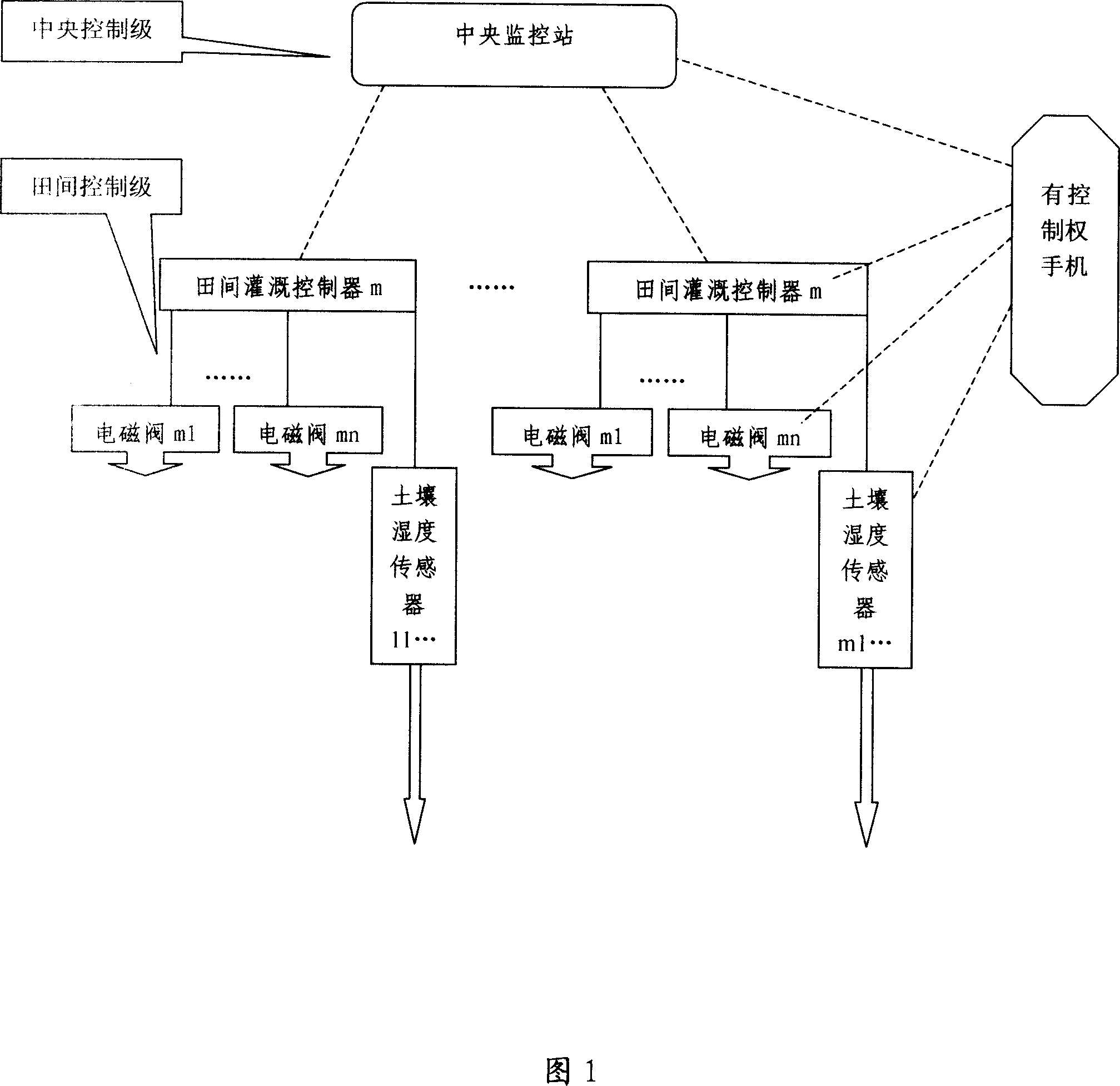
Remote controlled automated irrigation system based on public communication network and control method thereof
InactiveCN1951170AImprove scalabilityWide coverageData processing applicationsComputer controlAutomatic controlRemote control
The invention relates to a remote irrigation automatic method based on public communication network. Wherein, it has central control stage and field control stage; the central control stage is formed by central detecting station formed by central detector, public module and software; the field control stage is formed by several field irrigation controllers and several electromagnetic valves. The invention has the advantages that it can use irrigation software to complete automatic control and combine the parameter measurement and automatic irrigation, with automatic control, remote or hand control. And it can realize integrated management via communication network. The invention also can detect the condition, grow state of plants.
Owner:王光强 +1
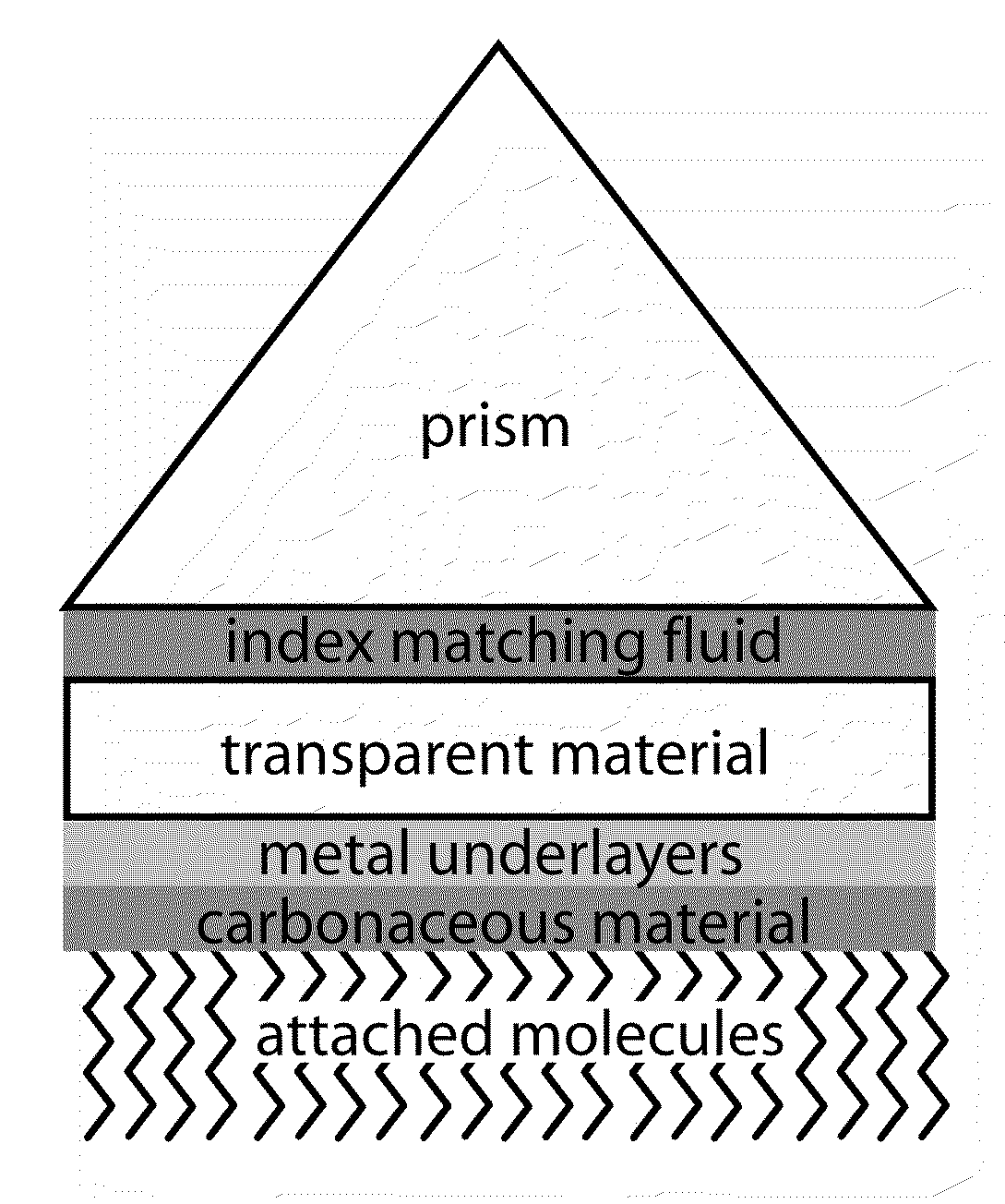
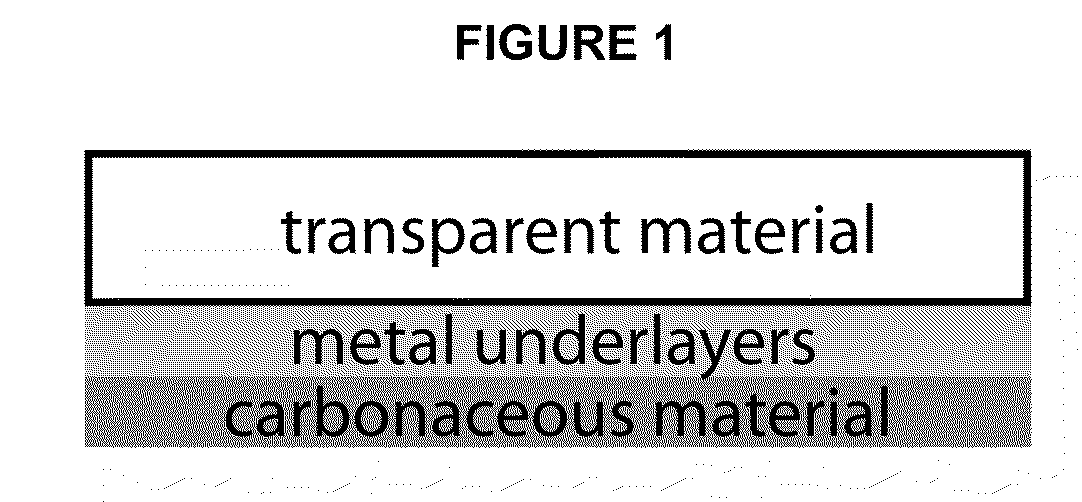
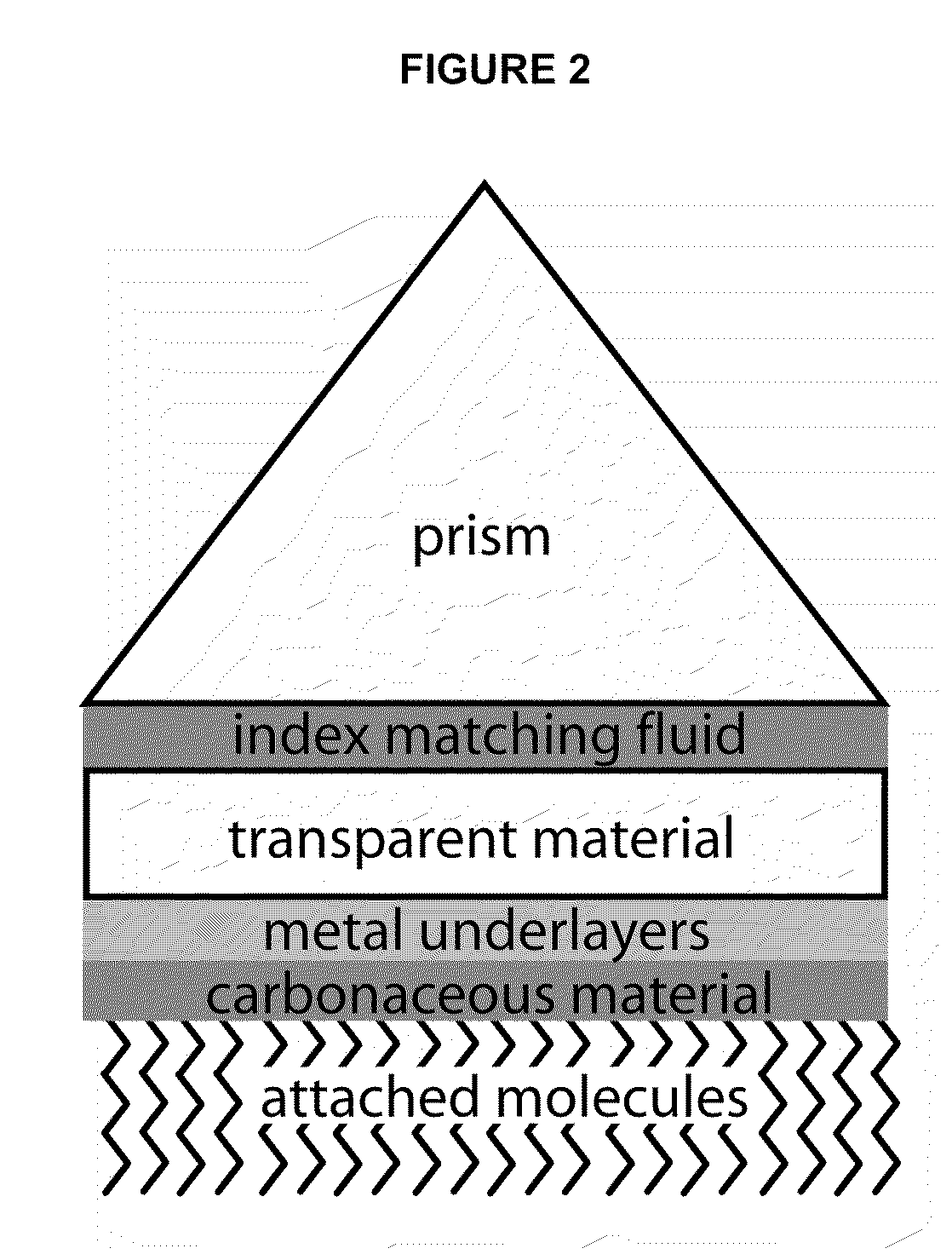
Surface plasmon resonance compatible carbon thin films
ActiveUS20090141376A1High refractive indexPrismsParticle separator tubesHigh-Density MicroarrayPhotolithography
SPR-compatible substrates for high density microarray fabrication and analyses are provided. Novel carbon-on-metal thin film substrate architecture permits the integration of surface plasmon resonance detection with photolithographically fabricated biomolecule arrays for the analysis of biomolecular interactions. The utility of the technology is shown in the analysis of specific DNA-DNA, DNA-RNA and DNA-protein binding interactions. These new substrates may be used to determine the secondary structure of RNA molecules, to probe the sequence-specific binding kinetics and affinity of proteins and small molecules, and as substrates for small-molecule combinatorial chemistry platforms for drug discovery applications.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
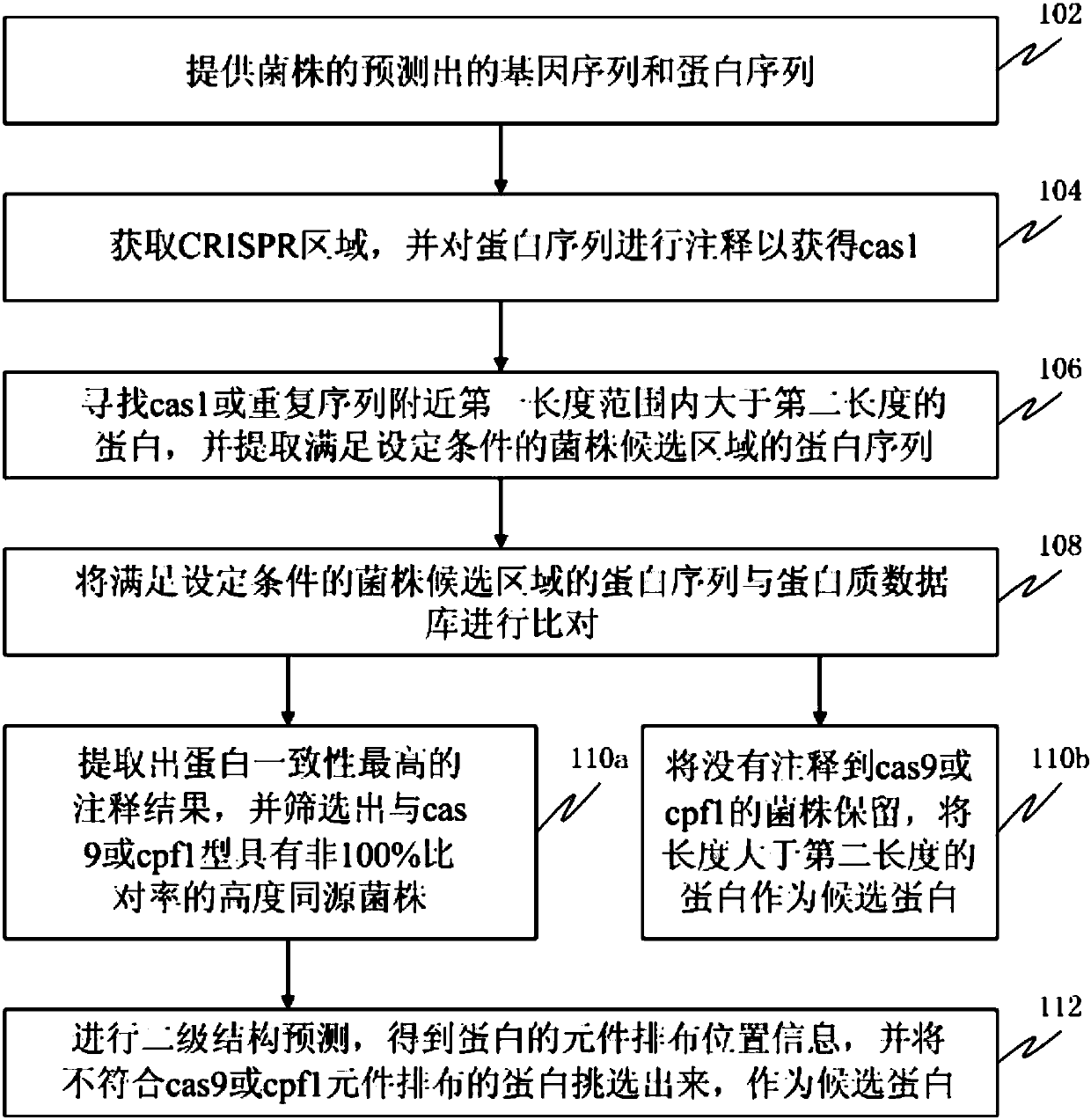
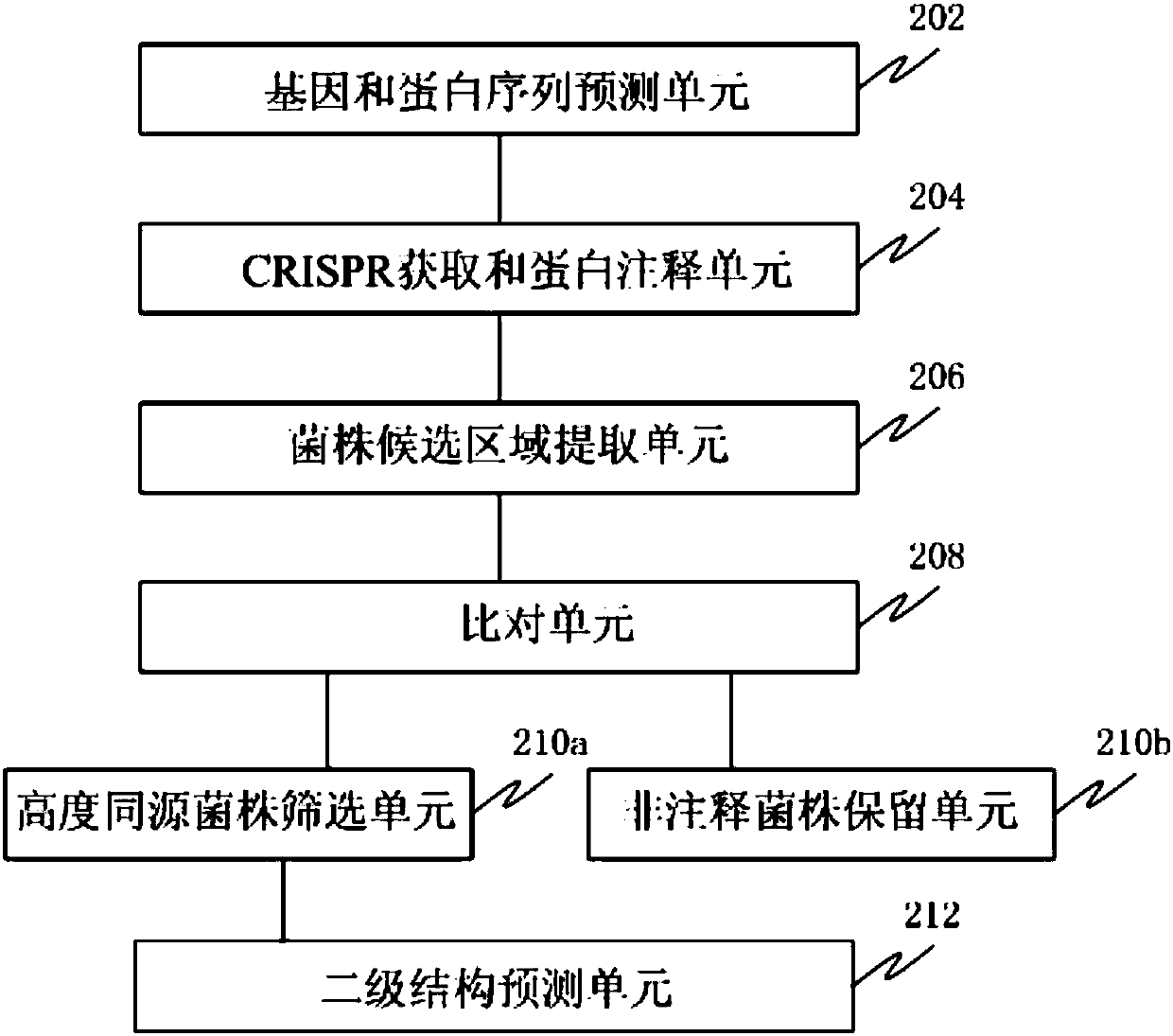
Screening method and device for novel CRISPR-Cas system
ActiveCN107784200AEffective positioningProteomicsGenomicsScreening methodProtein secondary structure
The invention discloses a screening method and device for a novel CRISPR-Cas system. The method comprises the following steps that the predicted gene sequences and protein sequences of strains are provided; CRISPR regions and proteins with cas1 annotation information are acquired; proteins larger than second length near cas1 or repetitive sequences in the range of first length are searched for, and protein sequences in candidate regions of the strains are extracted; a comparison is conducted; annotation result of the highest protein consistency is extracted, highly homologous strains of non 100% comparison ratio with cas9 or cpf1 type are screened out, a secondary structure prediction is conducted, arrangement position information of components of the proteins are acquired, proteins whichare not conformed to cas9 or cpf1 component arrangements are selected to serve as candidate proteins. The method can be used for analyzing single strain genome data so as to select strain proteins which may belong to the novel CRISPR-Cas system.
Owner:SHENZHEN HUADA GENE INST
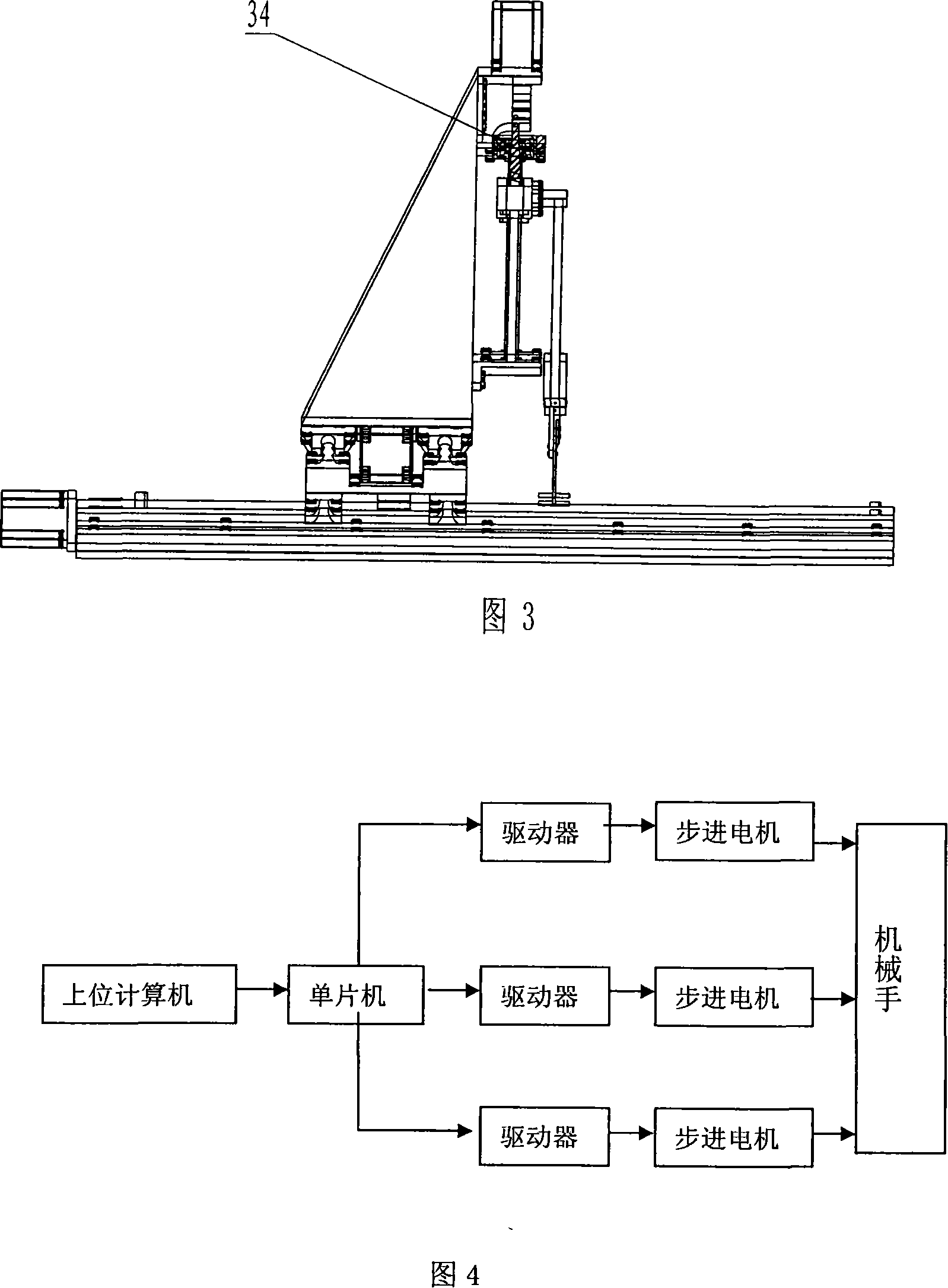
Three degrees of freedom right angle coordinate manipulator
InactiveCN101204812AFunction increaseReduce precisionProgramme-controlled manipulatorDistribution controlRectangular coordinates
The invention relates to a three-freedom rectangular coordinate manipulator, which essentially consists of a machinery part and a control part. The machinery part comprises the three mechanisms of X, Y and Z directions essentially finishing moving in a solid space range. Objects can be grabbed by adding a paw controlled by an electromagnet on the Z direction. The three motions are directly driven by a stepping motor and then a screw rob nut pair is utilized to switch the rotating motion of the motor into the linear motion of the nut. The paw is added on the Z direction to finish the motion of grabbing objects. The control part essentially comprises an upper position computer, a SCM, a driver, a stepping motor and an arm. A control system adopts a distribution structure. A distribution control system is provided with an upper position secondary structure and a lower position secondary structure. The invention has the advantages of wide application environment and multiple functions; besides, the manufacturing and processing precisions are a little lower than an industrial robot with a high cost performance; and a teaching robot has the advantages of small size and light weight. The teaching arm plays a very important role in teaching for the advantages of intuitionism, easy operation and integration.
Owner:沈孝芹
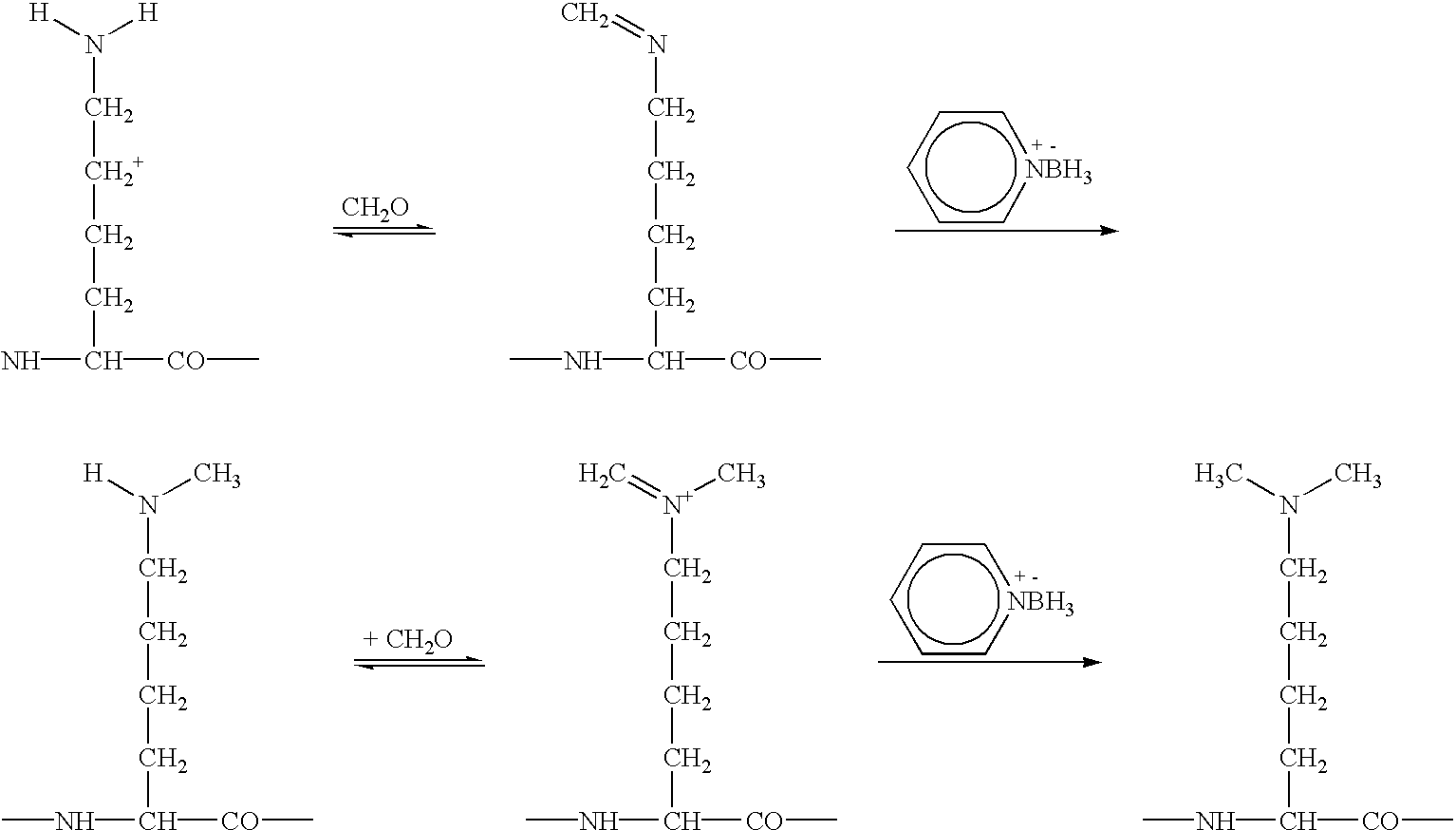
Non-naturally occurring synthetic lytic peptides
InactiveUS6559281B1Improve the immunityImprove stabilityPeptide-nucleic acidsPeptide/protein ingredientsLytic peptideCrystallography
Non-naturally occurring lytic peptides which contain a phenylalanine residue and one or more alanine, valine and lysine residues, and optionally contain chemically masked cysteine or serine residues possess an amphipathic structure which allows them to promote cell lysis in certain pathologic organisms, and particularly in prokaryotes. Peptides having a beta-pleated sheet secondary structure and lacking cysteine residues form one embodiment of these lytic peptides.
Owner:DEMEGEN
Fast preparation method of biological affinity copper nanometer cluster
InactiveCN104807795AImprove stabilityImprove solubilityFluorescence/phosphorescenceProtein solutionSynthesis methods
The invention relates to a fast preparation method of a biological affinity copper nanometer cluster, is applied to the detection of Hg<2+> content in a water sample, and belongs to the technical field of nanometer material preparation. A copper source solution and a protein solution are uniformly mixed; the pH of the solution is regulated to the alkalinity by alkali; oxidizing agents are dropped; heating incubation is carried out for a period of time; the copper nanometer cluster is prepared; the copper nanometer cluster is used for detecting the fluorescence intensity of an Hg<2+> standard solution or an Hg<2+> sample solution; the fluorescence intensity is substituted into a linear regression equation, and the Hg<2+> content in the sample is calculated. Due to strong oxidizing property and coordinating capability of oxidizing agents, the secondary structure in protein can be changed, copper-protein-oxidant complexes can be formed, the reducing capacity of the protein is enhanced, and the formation of the copper nanometer cluster is obviously accelerated. The copper nanometer cluster is used for the Hg<2+> detection in the water sample, and the method is obviously superior to the prior art in the aspects of analysis time, sensitivity, selectivity and cost.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Protein modeling tools
InactiveUS20030130797A1Rapid and computationally efficient generationEfficient representationDepsipeptidesPeptide preparation methodsProtein modellingSide chain
The invention provides a new, efficient method for the assembly of protein tertiary structure from known, loosely encoded secondary structure constraints and sparse information about exact side chain contacts. The method is based on a new method for the reduced modeling of protein structure and dynamics, where the protein is described by representing side chain centers of mass rather than alpha-carbons. The model has implicit, built-in multi-body correlations that simulate short- and long-range packing preferences, hydrogen bonding cooperativity, and a mean force potential describing hydrophobic interactions. Due to the simplicity of the protein representation and definition of the model force field, the Monte Carlo algorithm is at least an order of magnitude faster than previously published Monte Carlo algorithms for three-dimensional structure assembly. In contrast to existing algorithms, the new method requires a smaller number of tertiary constraints for successful fold assembly; on average, one for every seven residues as compared to one for every four residues. The reliability and robustness of the invention make it useful for routine application in model building protocols based on various (and even very sparse) experimentally-derived structural constraints.
Owner:SKOLNICK JEFFREY +1
Reverse-turn mimetics and method relating thereto
InactiveUS7671054B1Efficient implementationPromoting neurite outgrowthBiocideOrganic chemistryWide areaUlcerative colitis
Conformationally constrained compounds that mimic the secondary structure of reverse-turn regions of biologically active peptides and proteins as well as their prodrugs are disclosed. Such reverse-turn mimetic structures and prodrugs have utility over a wide range of fields, including use as diagnostic and therapeutic agents. Libraries containing the reverse-turn mimetic structures of this invention are also disclosed as well as methods for screening the same to identify biologically active members. The invention also relates to the use of such compounds and prodrugs for inhibiting or treating disorders modulated by Wnt-signaling pathway, such as cancer, especially colorectal cancer, restenosis associated with angioplasty, polycystic kidney disease, aberrant angiogenesis disease, rheumatoid arthritis disease, tuberous sclerosis complex, Alzheimer's disease, excess hair growth or loss, or ulcerative colitis.
Owner:JW PHARMA CORP
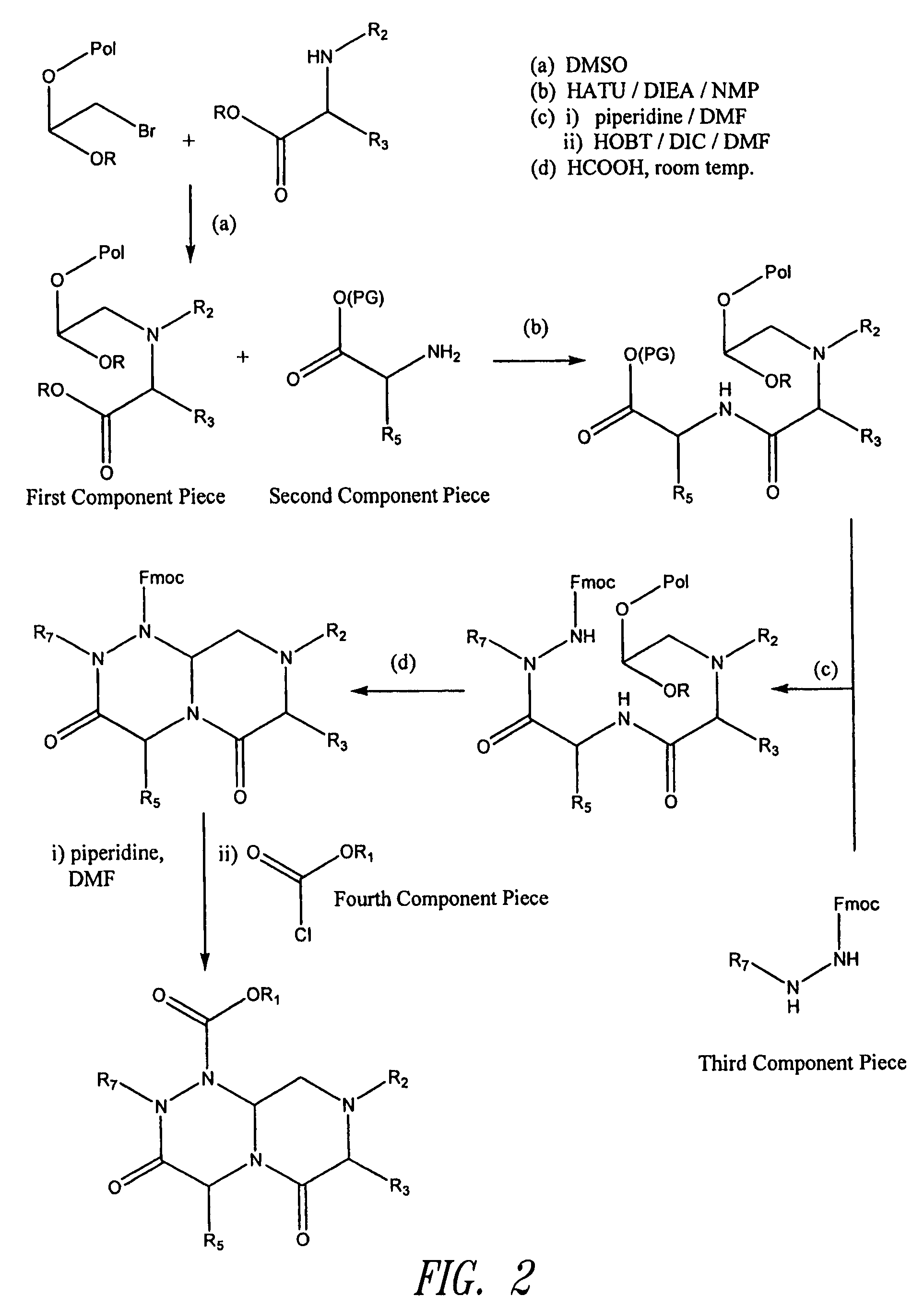
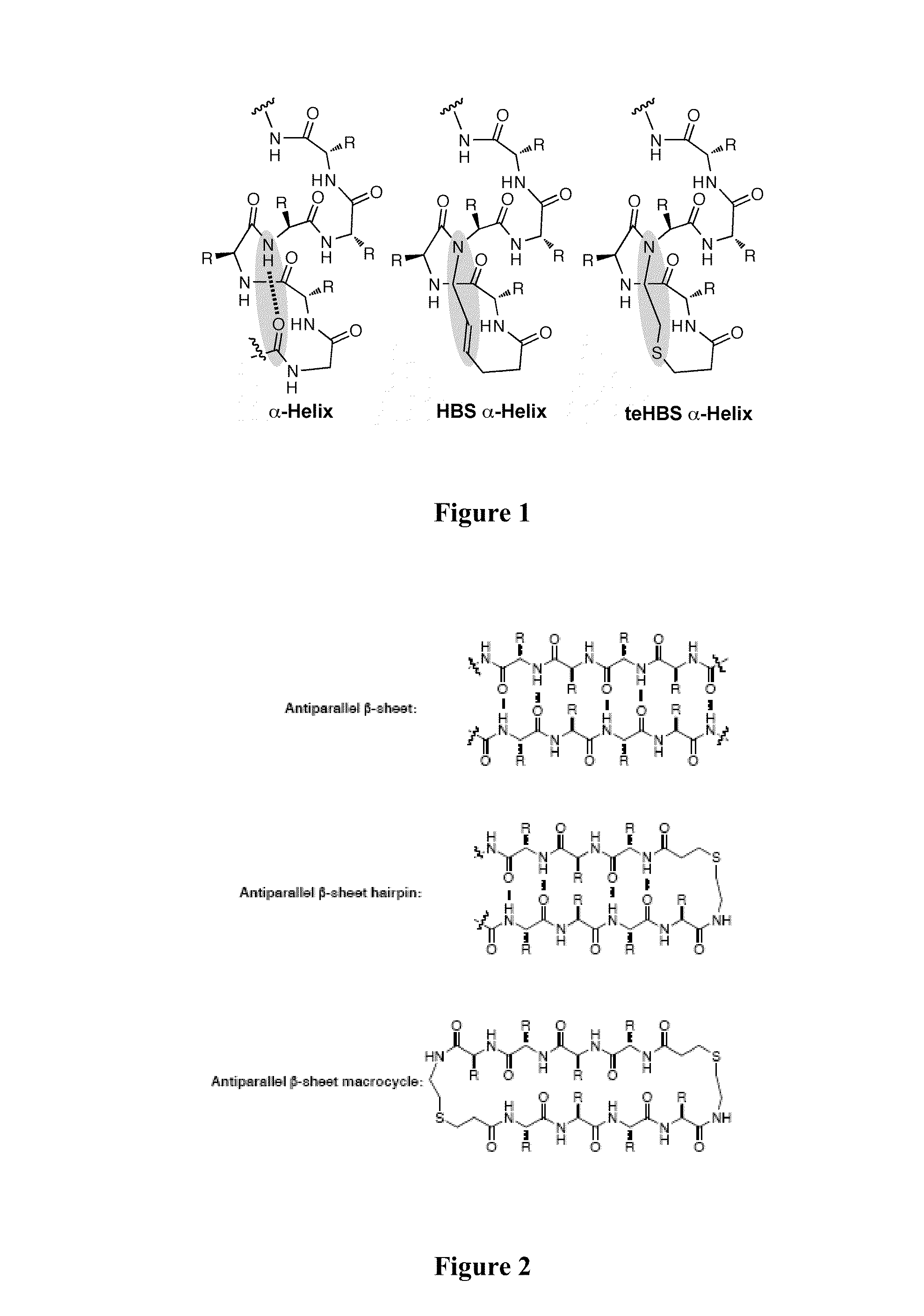
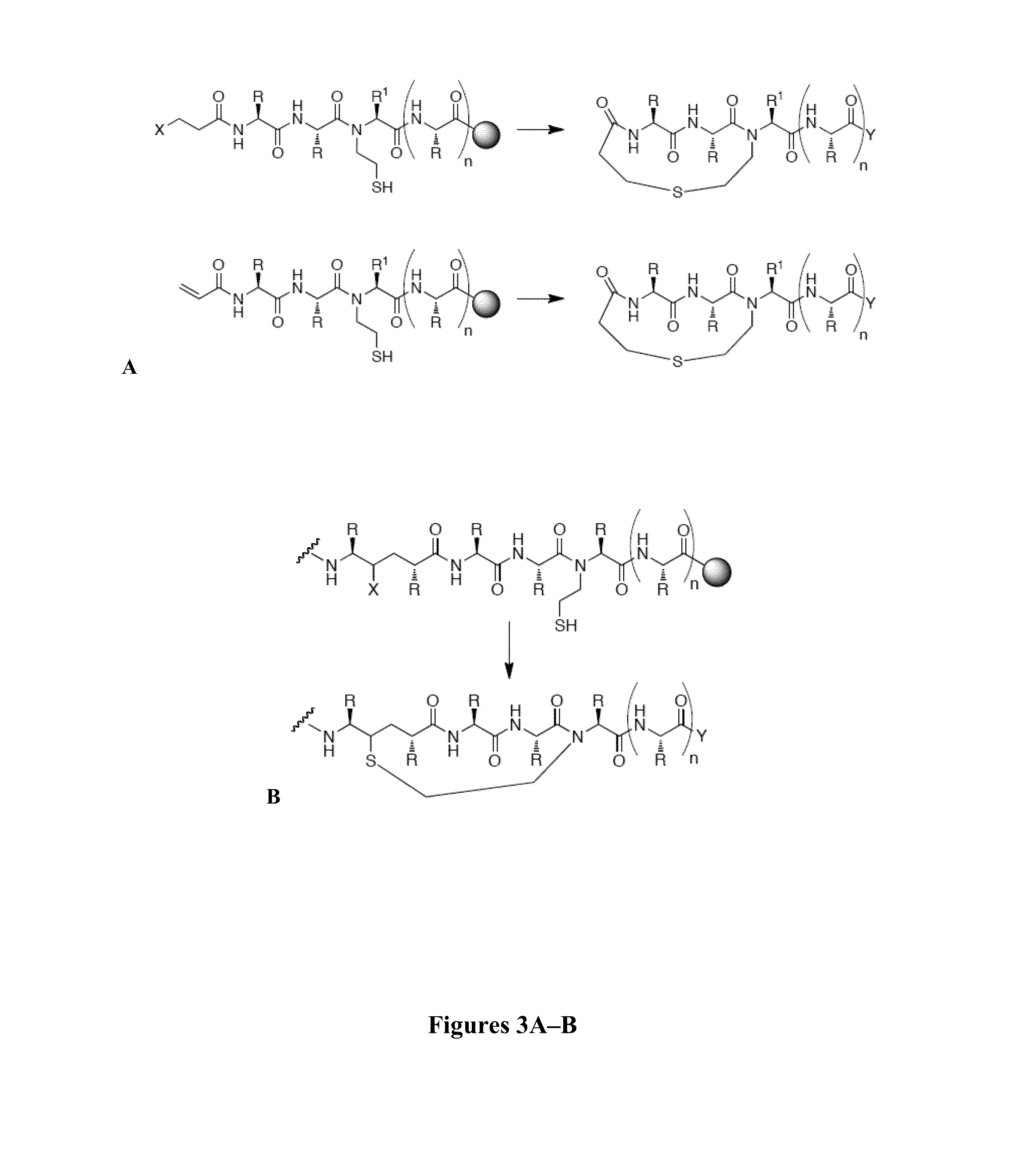
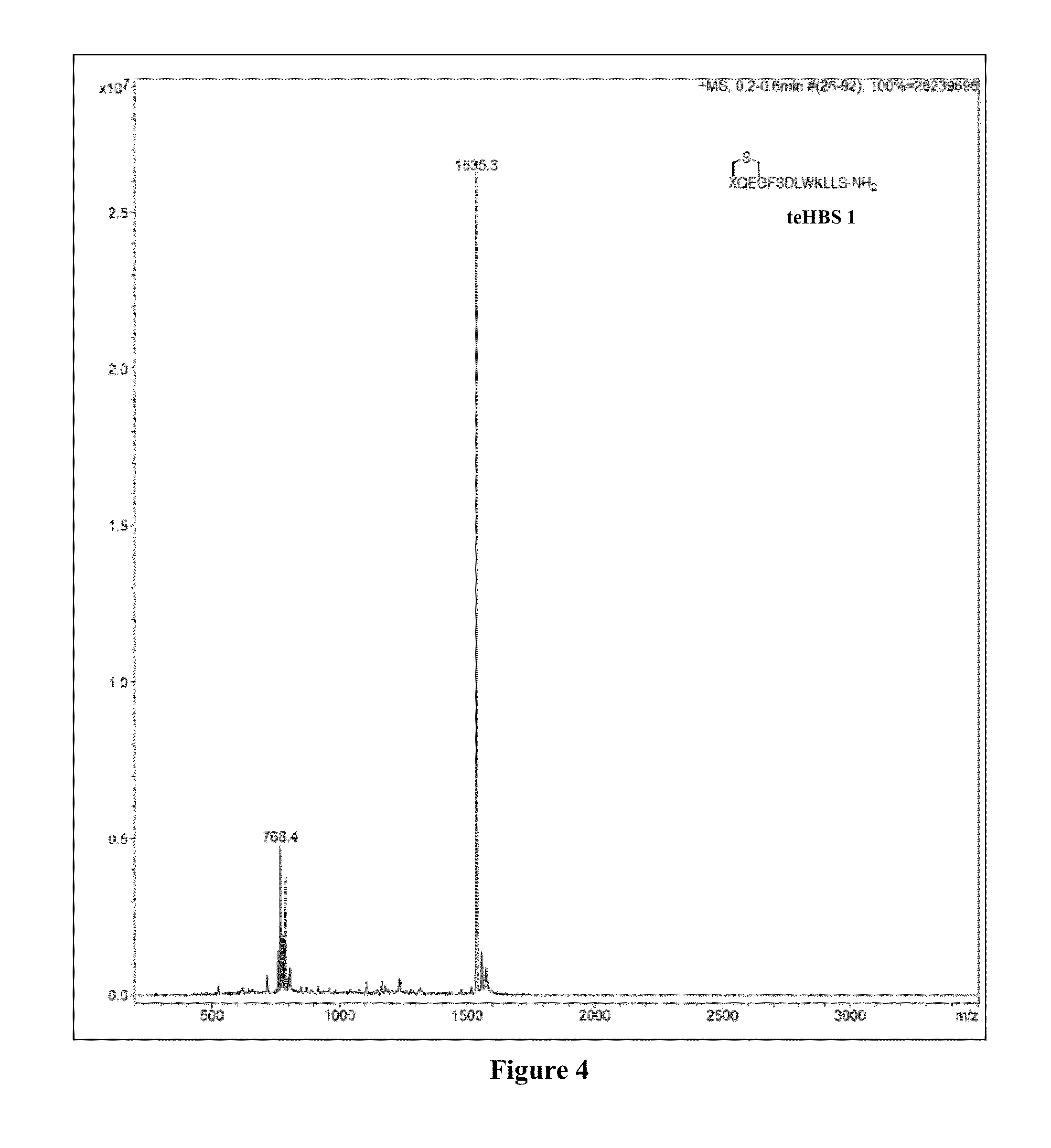
Thioether-, ether-, and alkylamine-linked hydrogen bond surrogate peptidomimetics
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
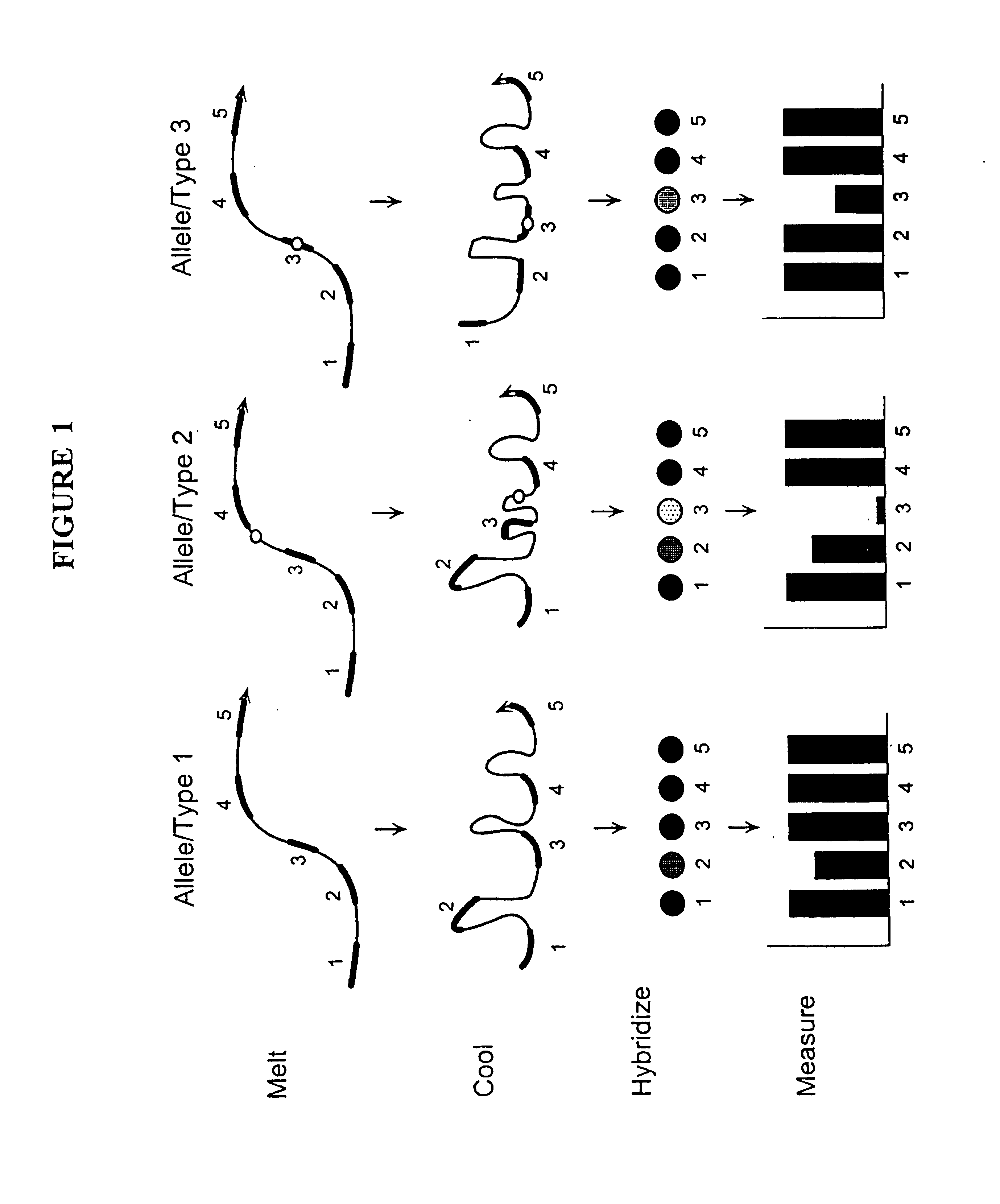
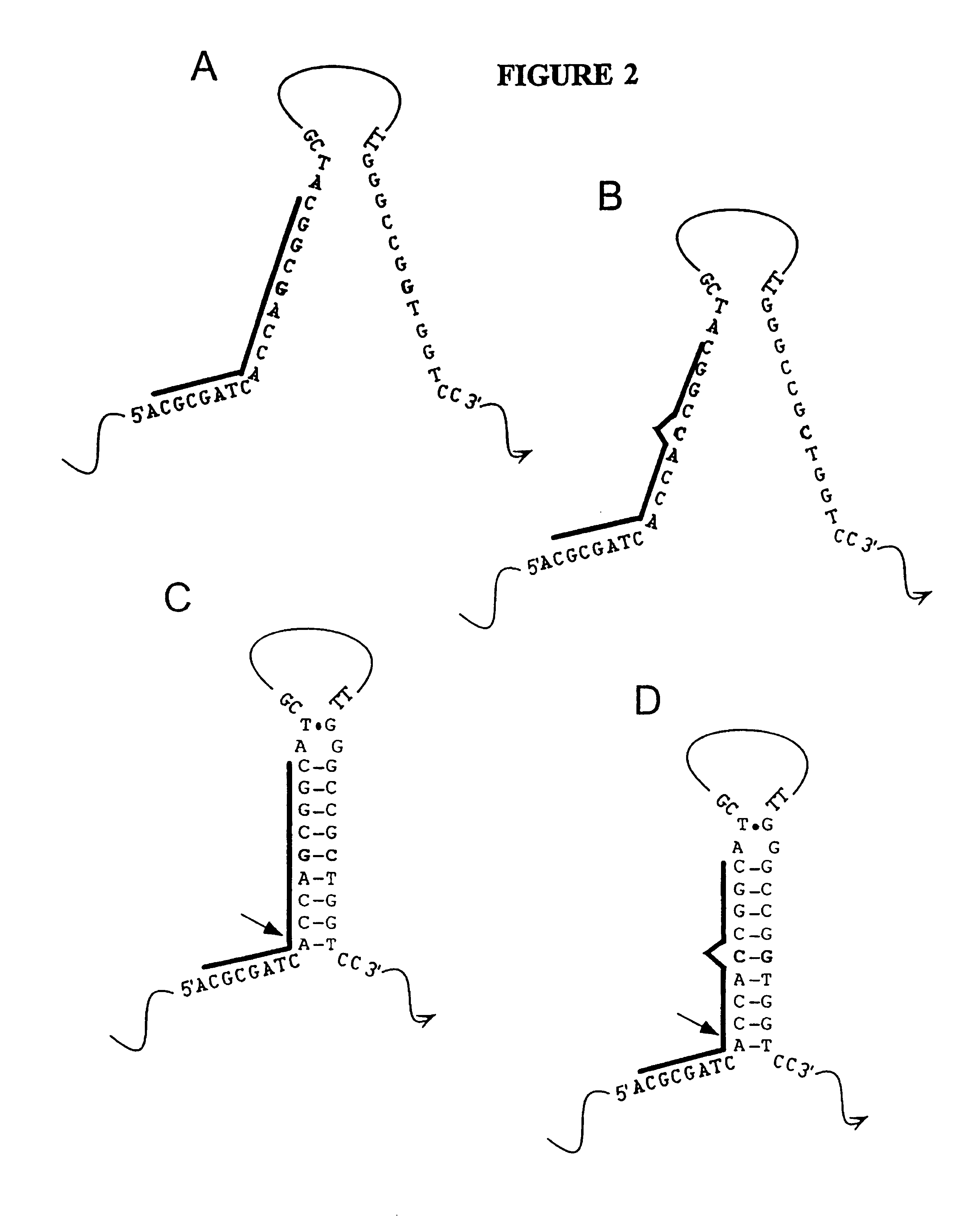
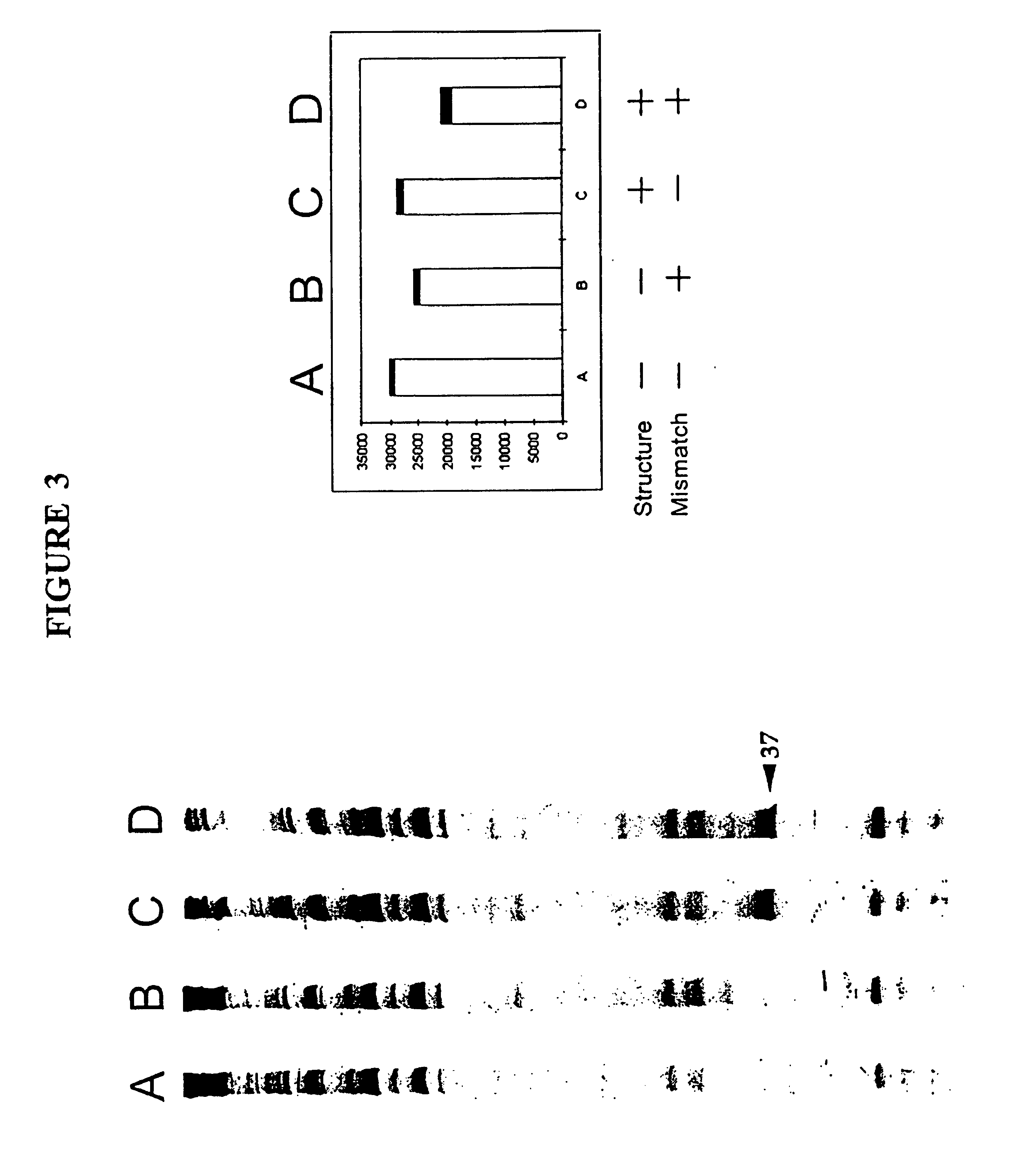
Nucleic acid accessible hybridization sites
InactiveUS7060436B2Quick checkQuick identificationSugar derivativesBacteriaProtein secondary structureNucleic acid sequencing
The present invention relates to methods and compositions for analyzing nucleic acids, and in particular, methods and compositions for detection and characterization of nucleic acid sequences and sequence changes. The present invention also provides methods and compositions for identifying oligonucleotides with desired hybridization properties to nucleic acid targets containing secondary structure.
Owner:GEN PROBE INC
Methods for identifying nucleic acid modifications
ActiveUS9175338B2Microbiological testing/measurementProtein secondary structureNucleic acid sequencing
Methods, compositions, and systems are provided for characterization of modified nucleic acids. In certain preferred embodiments, single molecule sequencing methods are provided for identification of modified nucleotides within nucleic acid sequences. Modifications detectable by the methods provided herein include chemically modified bases, enzymatically modified bases, abasic sites, non-natural bases, secondary structures, and agents bound to a template nucleic acid.
Owner:PACIFIC BIOSCIENCES
Methods for reducing stress on composite structures
InactiveUS20080115454A1Relieve pressureEfficient propulsion technologiesBuilding componentsProtein secondary structureEngineering
Methods for reducing stress on composite structures involving providing a primary composite structure having a circumference, providing at least one mounting flange operably connected to the primary composite structure about the circumference to form a joint, and providing a secondary structure operably connected to the primary composite structure at the mounting flange such that when stresses on the primary composite structure exceed a maximum capacity level delamination or separation of the mounting flange from the primary structure occurs at the joint, and the secondary structure remains operably connected to the mounting flange.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Medical implant
ActiveUS20110098814A1Improve securityConvenient ArrangementDilatorsToysProtein secondary structureBiomedical engineering
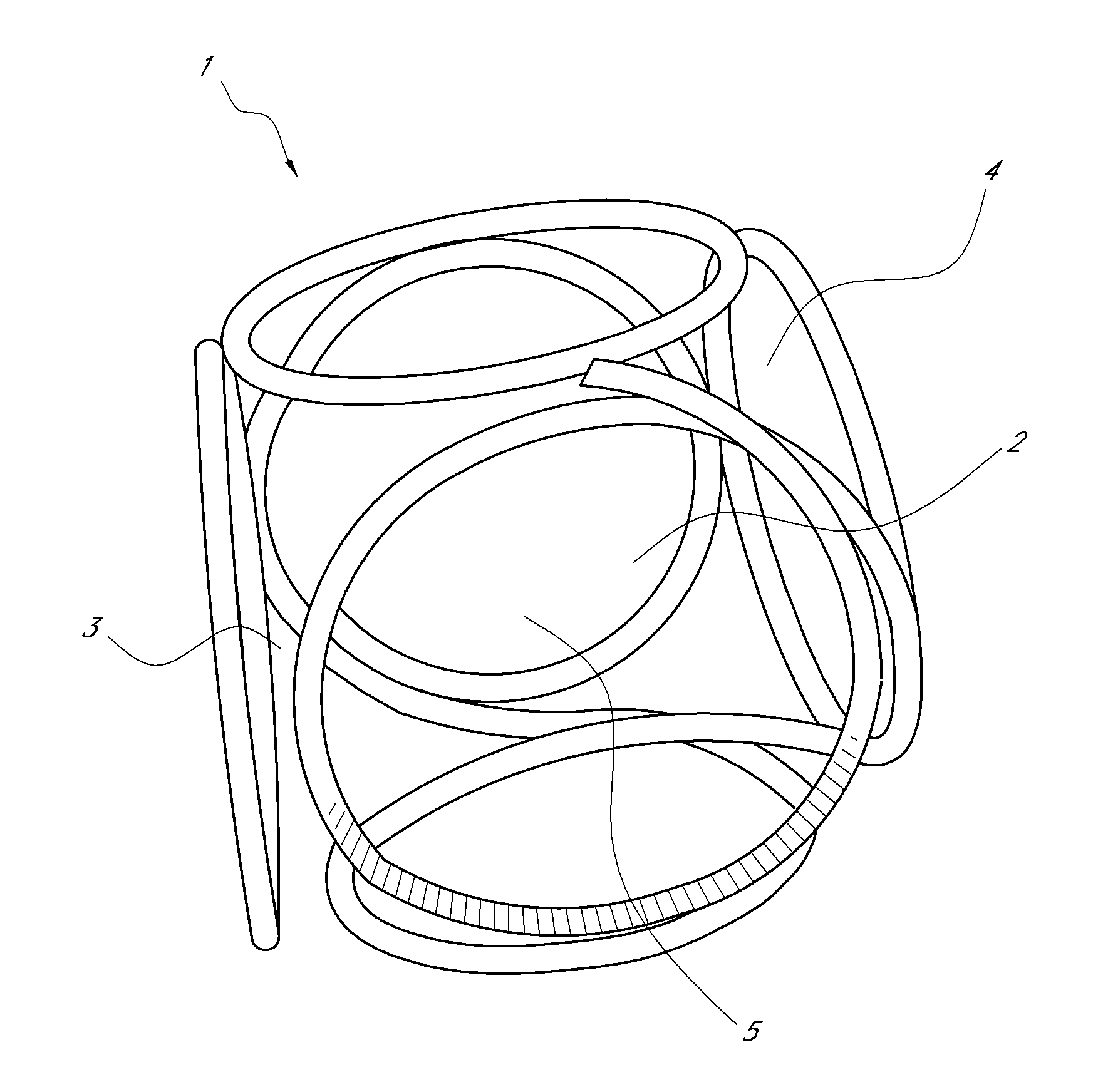
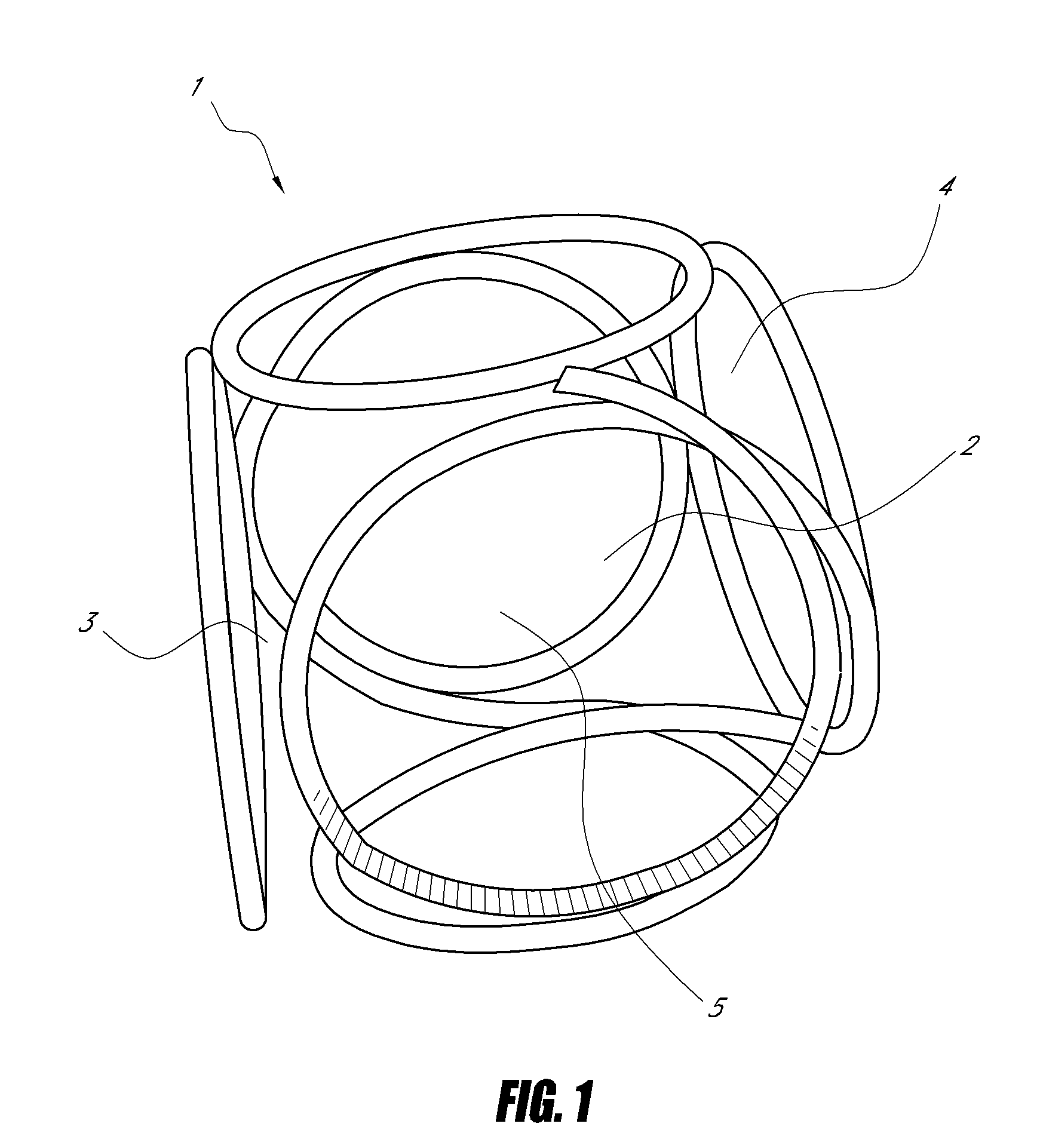
The invention relates to a medical implant in the form of an elongated helix wherein at least one part of the helix is preformed in such a manner that it has a secondary structure of identically sized loops which it assumes during implantation at the placement site, with said structure in turn forming at the placement site during implantation a polyhedral tertiary structure, and the polyhedron being provided with at least one additional loop.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Reverse-turn mimetics and method relating thereto
Conformationally constrained compounds that mimic the secondary structure of reverse-turn regions of biologically active peptides and proteins are disclosed. Such reverse-turn mimetic structures have utility over a wide range of fields, including use as diagnostic and therapeutic agents. Libraries containing the reverse-turn mimetic structures of this invention are also disclosed as well as methods for screening the same to identify biologically active members. The invention also relates to the use of such compounds for inhibiting or treating disorders modulated by Wnt-signaling pathway, such as cancer, especially colorectal cancer, restenosis associated with angioplasty, polycystic kidney disease, aberrant angiogenesis disease, rheumatoid arthritis disease, tuberous sclerosis complex, Alzheimer's disease, excess hair growth or loss, or ulcerative colitis.
Owner:JW PHARMA CORP
Method for preparing silk fibroin three-dimensional porous material
The invention relates to a porous material and a method for preparing the same and discloses a method for preparing a silk fibroin three-dimensional porous material. The method comprises the following steps of: slowly concentrating a water solution of silk fibroin, uniformly mixing the water solution of silk fibroin with alcohol, and freezing and drying the misture to directly obtain a water-insoluble silk fibroin porous support material; regulating and controlling the secondary structure and the mechanical properties of the porous support by selectively using after-treatment means, and controlling the porosity, the pore diameter and the like of the porous material by changing the parameters of silk fibroin concentration, freezing temperature and the like; and finally, soaking the silk fibroin porous support material in water to remove alcohol. The invention has mild preparation process conditions, no addition of any cross-linking agent, any hole making agent and other toxic organic solvents, simple, convenient and controllable process and easy realization of industrialization; the biocompatibility of silk fibroin can be effectively maintained, and the silk fibroin can be applied to the tissue repair of bone, cartilage, anadesma, nerves, skin and the like, the drug controlled-release carriers and the like.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
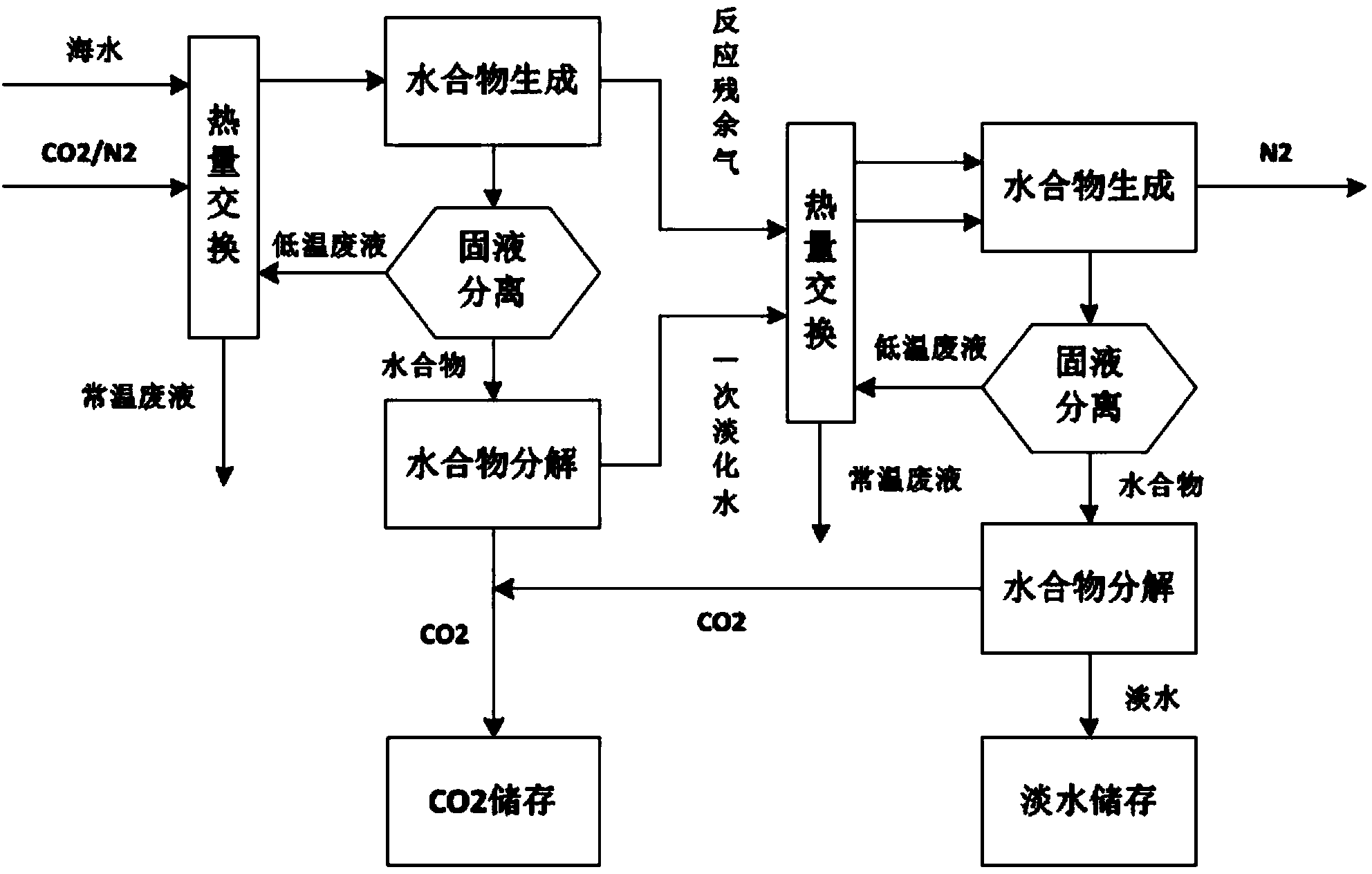
Carbon dioxide capturing and seawater desalting co-production device and method based on hydrate method
The invention provides a carbon dioxide capturing and seawater desalting co-production device and method based on a hydrate method, belonging to the technical field of hydrate application. The carbon dioxide capturing and seawater desalting co-production device comprises a gas-water conveying part, a hydrate generation and decomposition control part and a product storing and discharging part. The hydrate generation and decomposition control part comprises a front-grade structure and a rear-grade structure; a hydrate generation condition is gas supersaturation. A first-grade hydrate generates residual gas and decomposed water to be used as second-grade raw materials; after two grades of treatment, fresh water is obtained and stored; N2 is discharged to atmosphere by a gas exhausting safety valve; carbon dioxide is introduced into a gas tank to be stored. The carbon dioxide capturing and seawater desalting co-production device is applicable to the co-production of carbon dioxide capturing and seawater desalting of a fossil fuel power station in a coastal region, so as to meet the requirements of the carbon dioxide capturing of a smoke CO2 / N2 power station; a heat exchanger is used for pre-cooling so that the cold loss is reduced and the energy utilization rate is improved; the reaction speed is increased by high-speed agitation in a hydrate generation process; emissions comprise the N2 and concentrated seawater and have no pollution to the environment.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Reverse-turn mimetics and method relating thereto
Conformationally constrained compounds that mimic the secondary structure of reverse-turn regions of biologically active peptides and proteins are disclosed. Such reverse-turn mimetic structures have utility over a wide range of fields, including use as diagnostic and therapeutic agents. Libraries containing the reverse-turn mimetic structures of this invention are also disclosed as well as methods for screening the same to identify biologically active members. The invention also relates to the use of such compounds for inhibiting or treating disorders modulated by Wnt-signaling pathway, such as cancer, especially colorectal cancer, restenosis associated with angioplasty, polycystic kidney disease, aberrant angiogenesis disease, rheumatoid arthritis disease, tuberous sclerosis complex, Alzheimer's disease, excess hair growth or loss, or ulcerative colitis.
Owner:JW PHARMA CORP
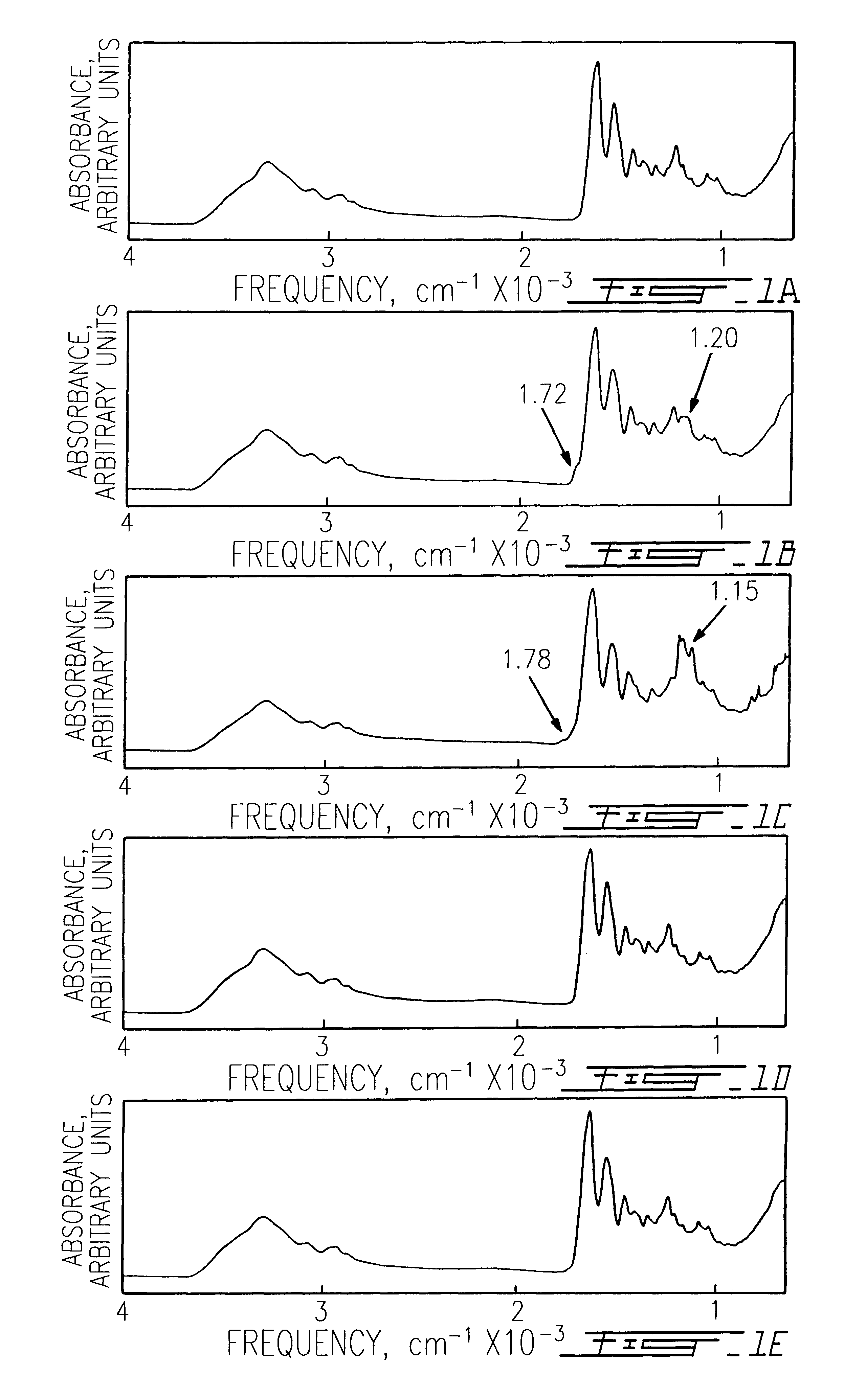
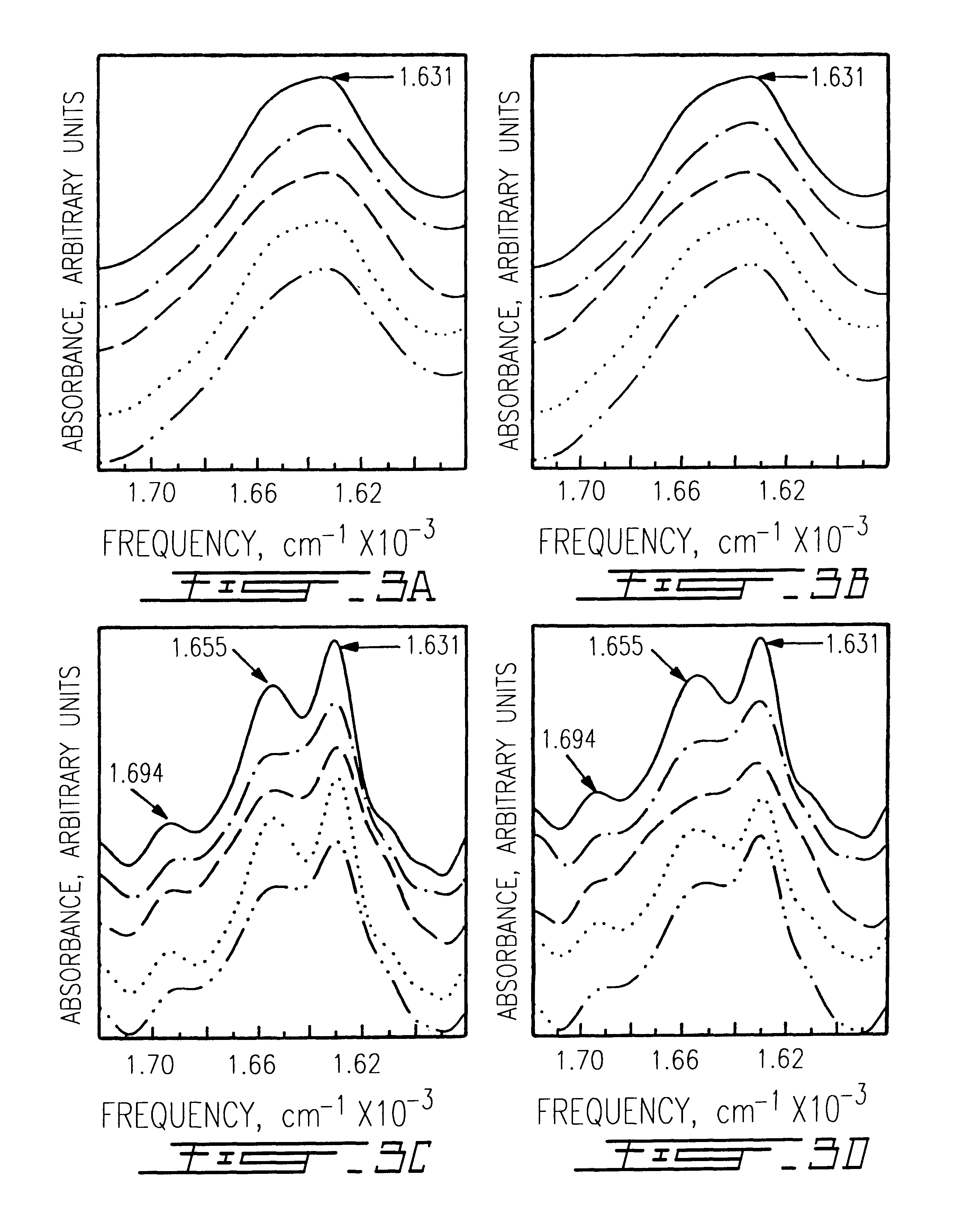
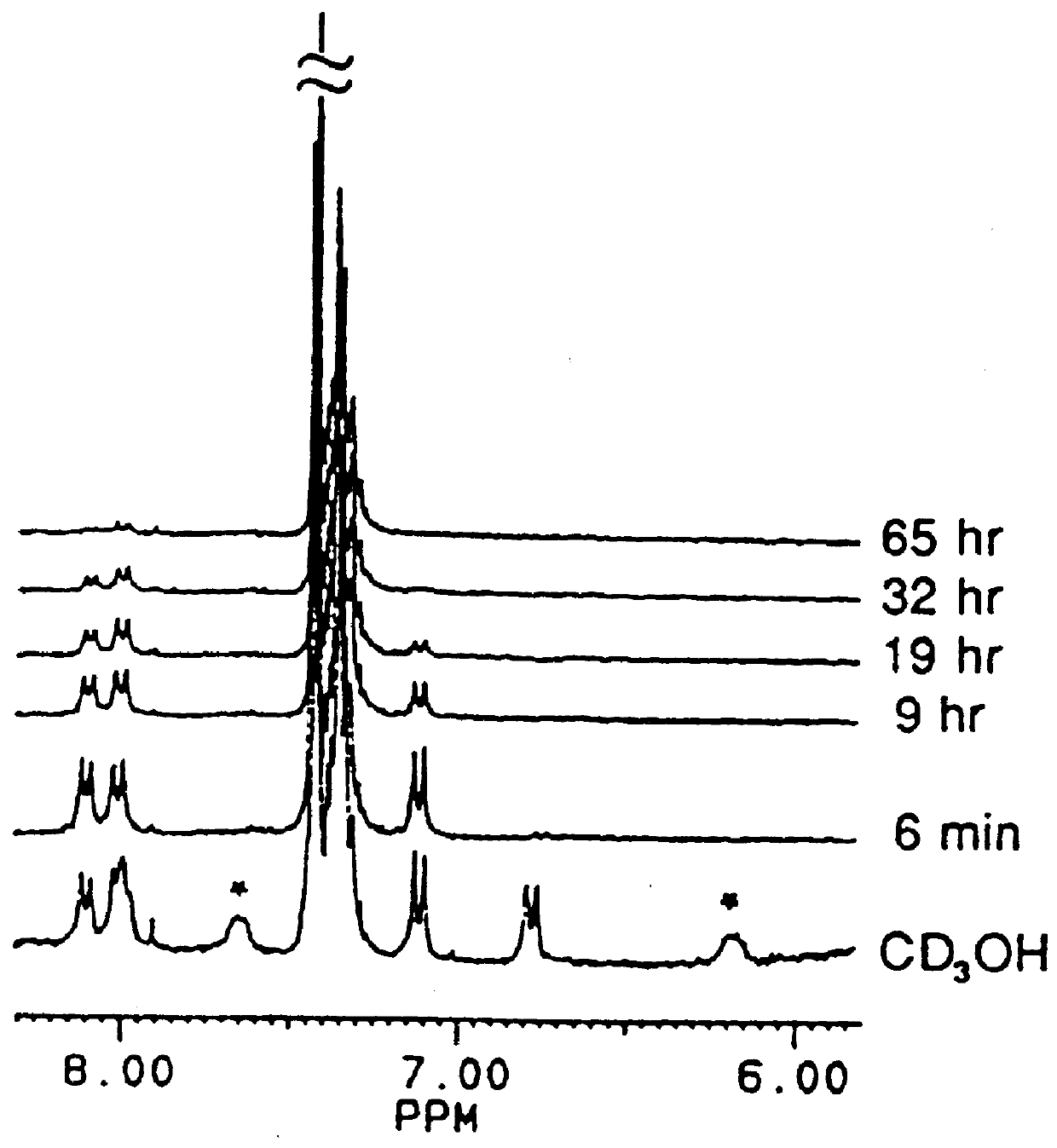
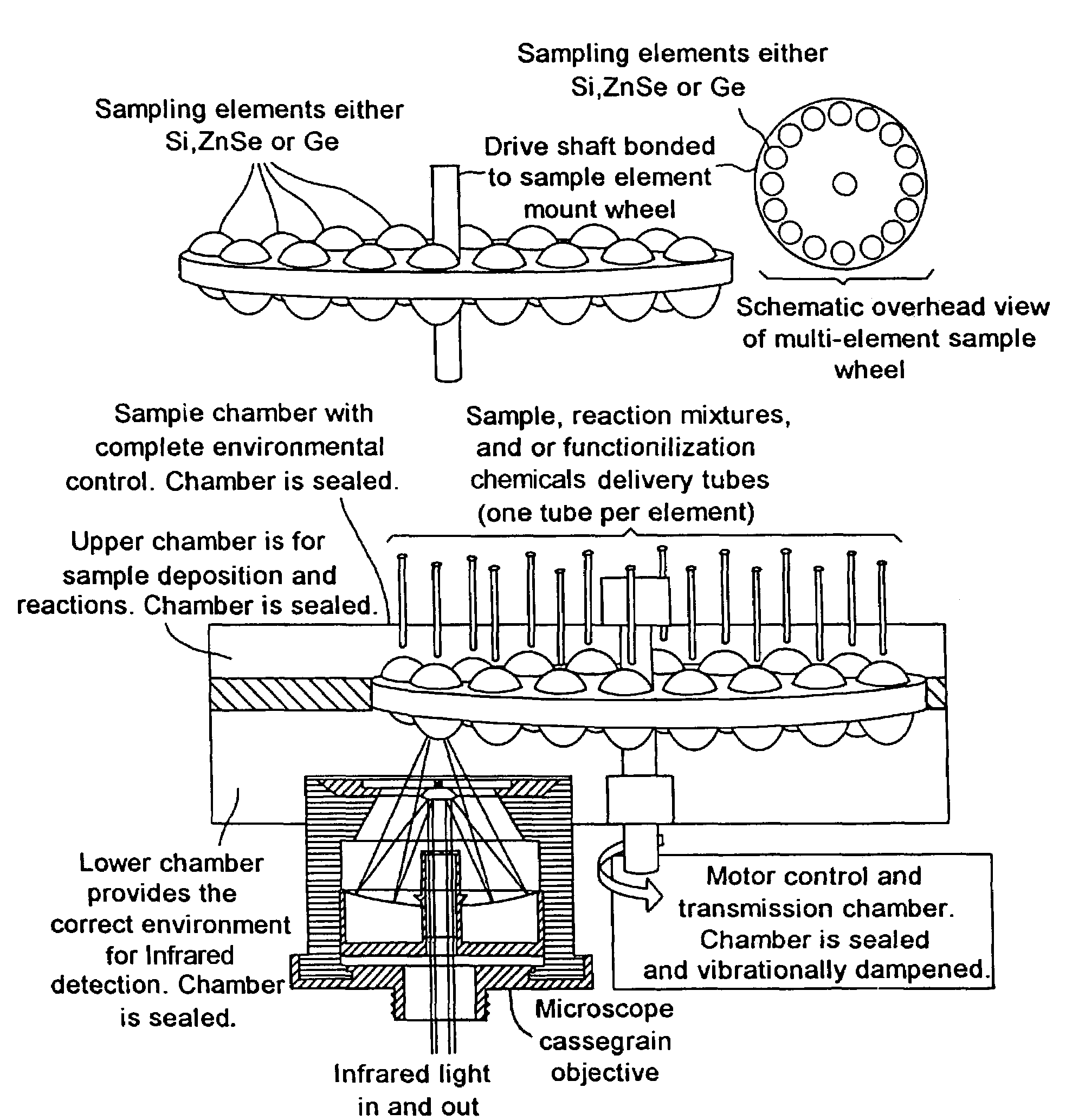
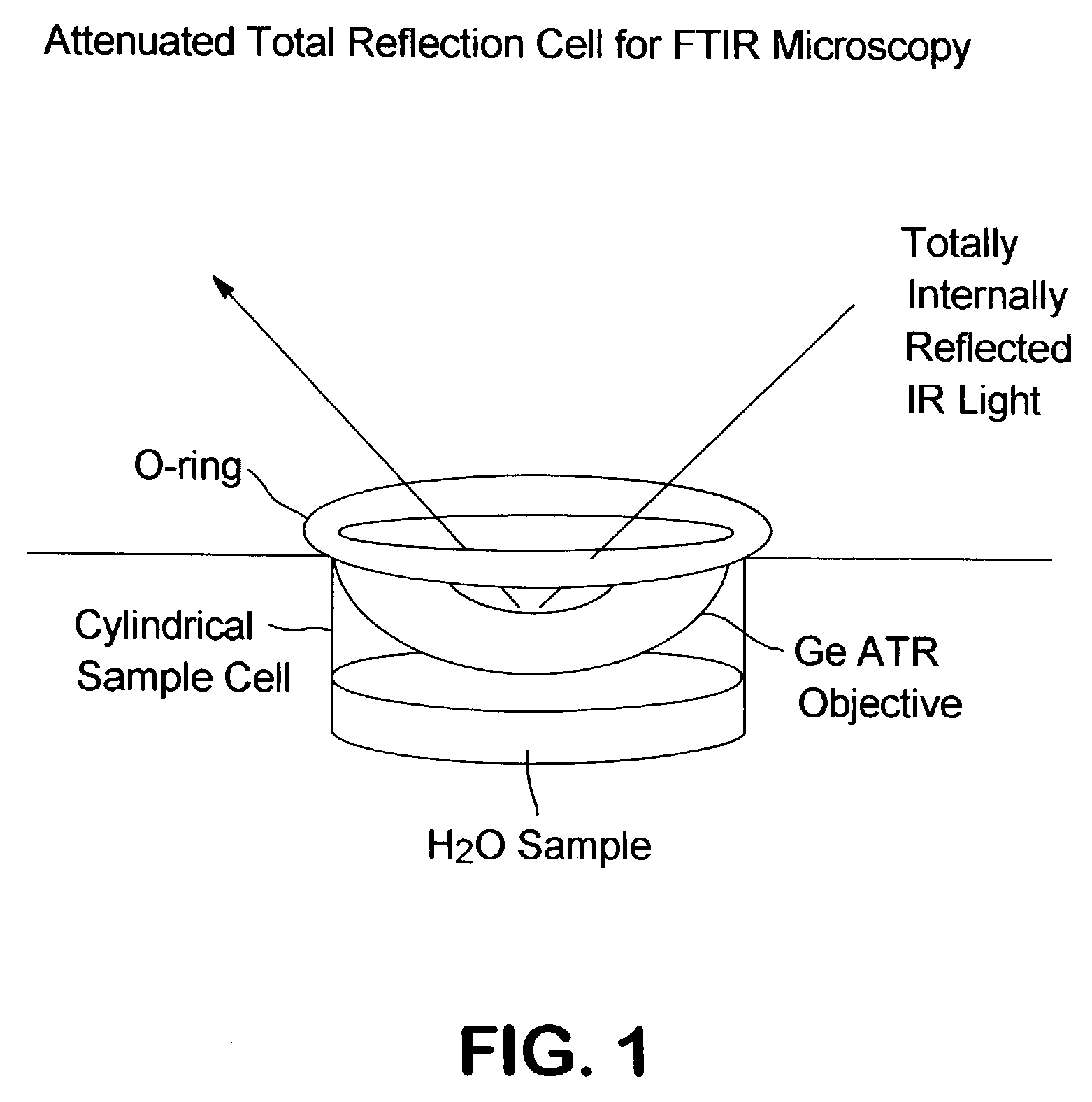
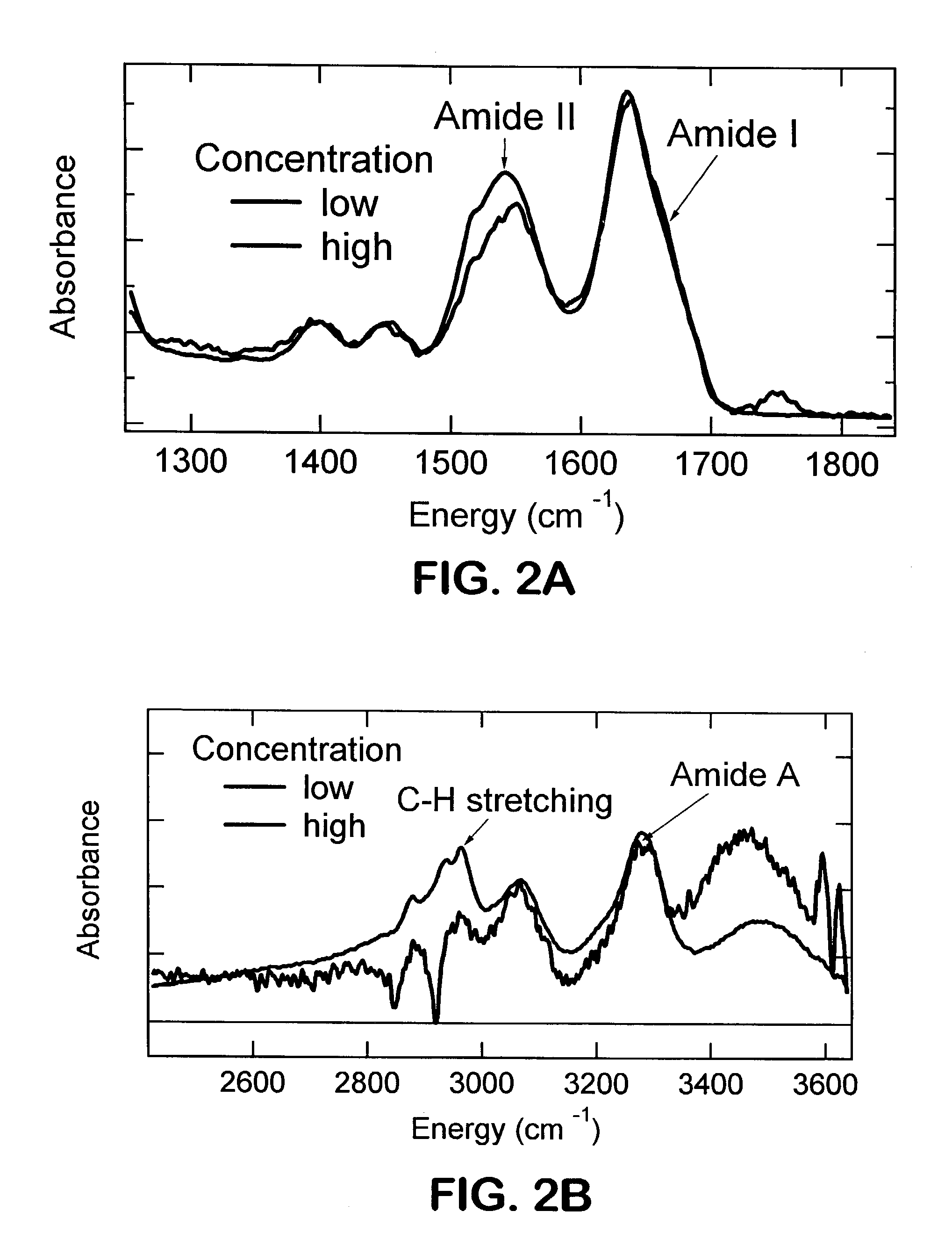
Single pass attenuated total reflection fourier transform infrared microscopy apparatus and method for identifying protein secondary structure, surface charge and binding affinity
InactiveUS7255835B2Facilitate acquisitionFacilitate dataBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsReflectivityFourier transform
Apparatus and method for acquiring an infrared spectrum of a sample having or suspected to have an amide I band, an amide II band, an amide III band, an amide A band, an OH stretching region or a combination thereof. A representative method includes providing a sample; providing an internal reflecting element (IRE) with a functionalized tip; contacting the sample with the IRE to form a sample-IRE interface; directing a beam of infrared (IR) radiation through the IRE under conditions such that the IR radiation interacts with the sample-IRE interface once; recording a reflectance profile over a range of preselected frequencies, whereby an infrared spectrum of the of a sample having or suspected of having an amide I band, an amide II band, an amide III band, an amide A band, an OH stretching region or a combination thereof, disposed in an aqueous solution is acquired. Representative apparatus includes an internal reflecting element (IRE) comprising a reflection face located on the IRE at a region of intended contact between the IRE and a solublized sample; an infrared radiation source for supplying an evanescent wave of infrared radiation and directing the same from the outside of the IRE to the inside thereof so as to cause the infrared radiation to be incident on the reflection face, wherein the infrared radiation is reflected from the reflection face once; a sample cell; a functionalized tip comprising a surface-immobilized probe that partially or completely fills the volume exposed to the evanescent wave; and a detector for detecting the once-reflected infrared radiation.
Owner:NORTH CAROLINA STATE UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com