Patents
Literature
148 results about "Biomedical implant" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
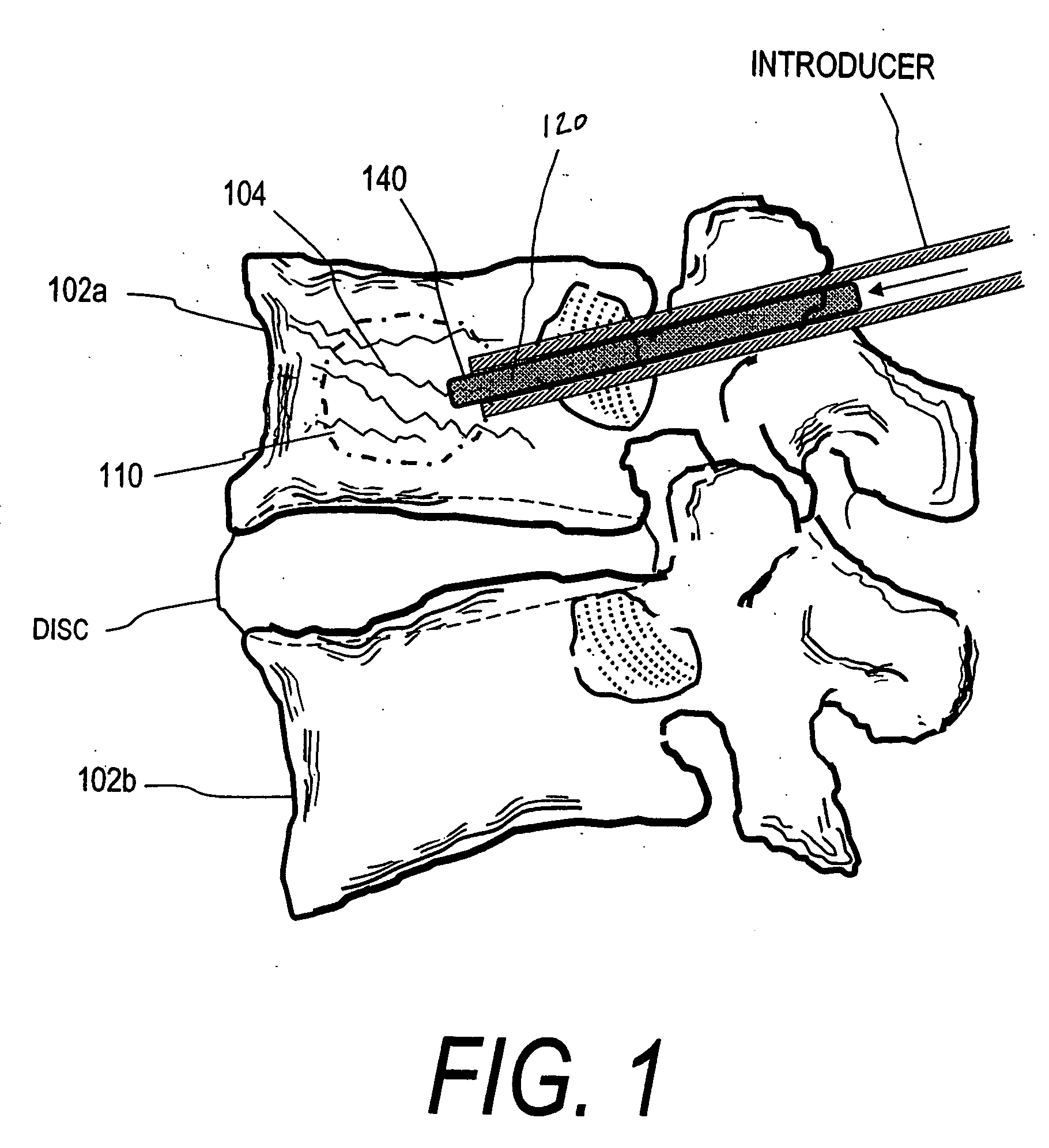
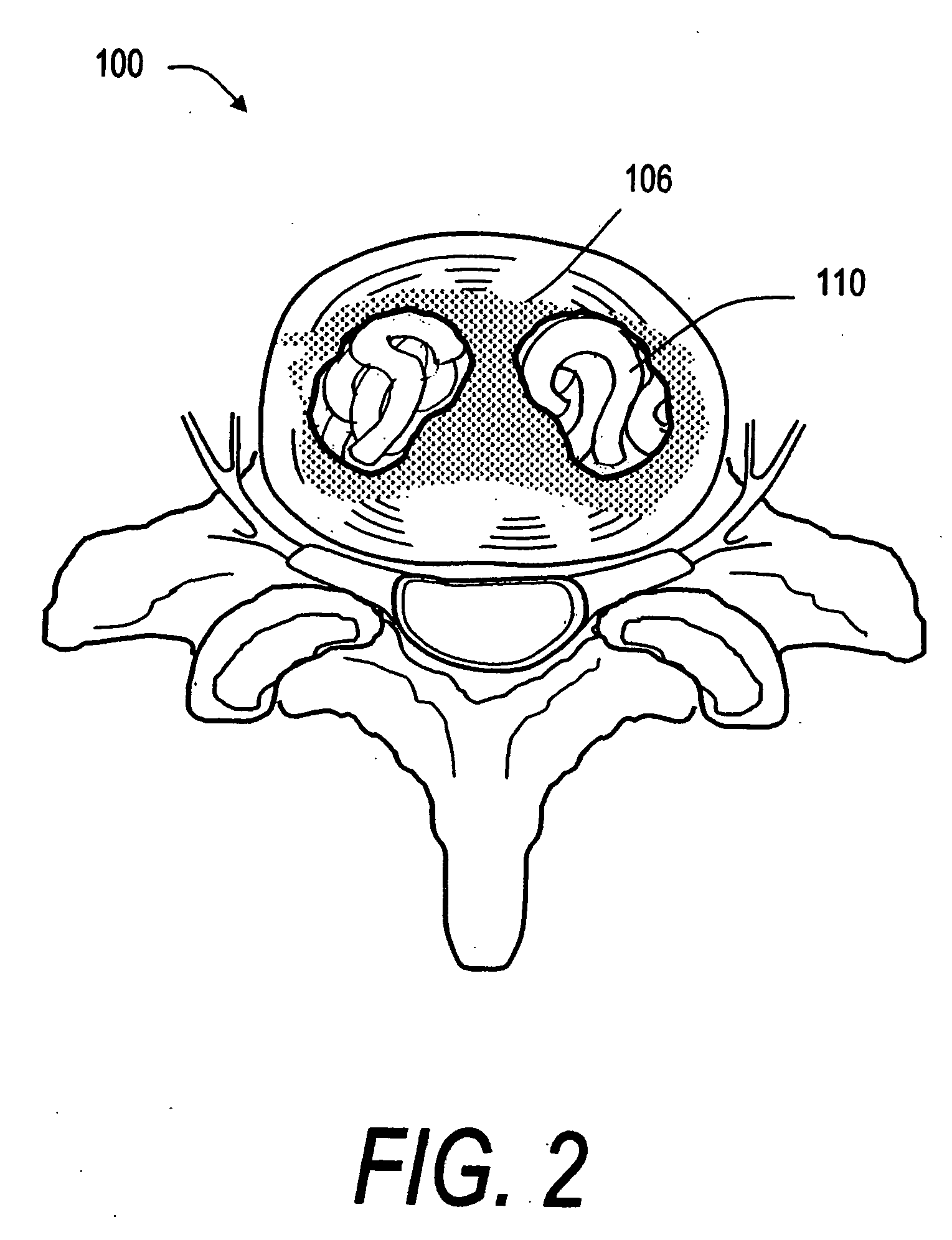
Implants and methods for treating bone
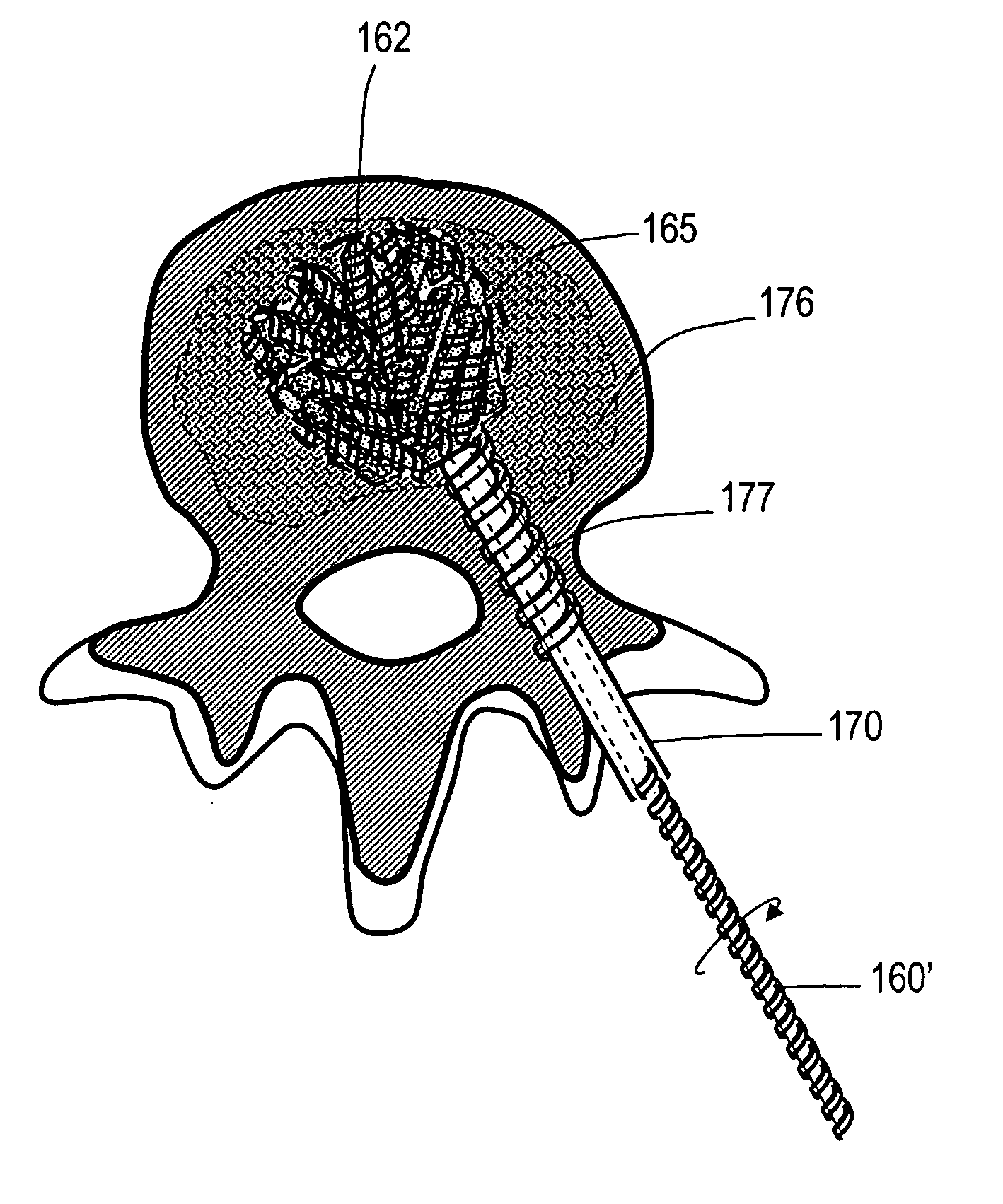
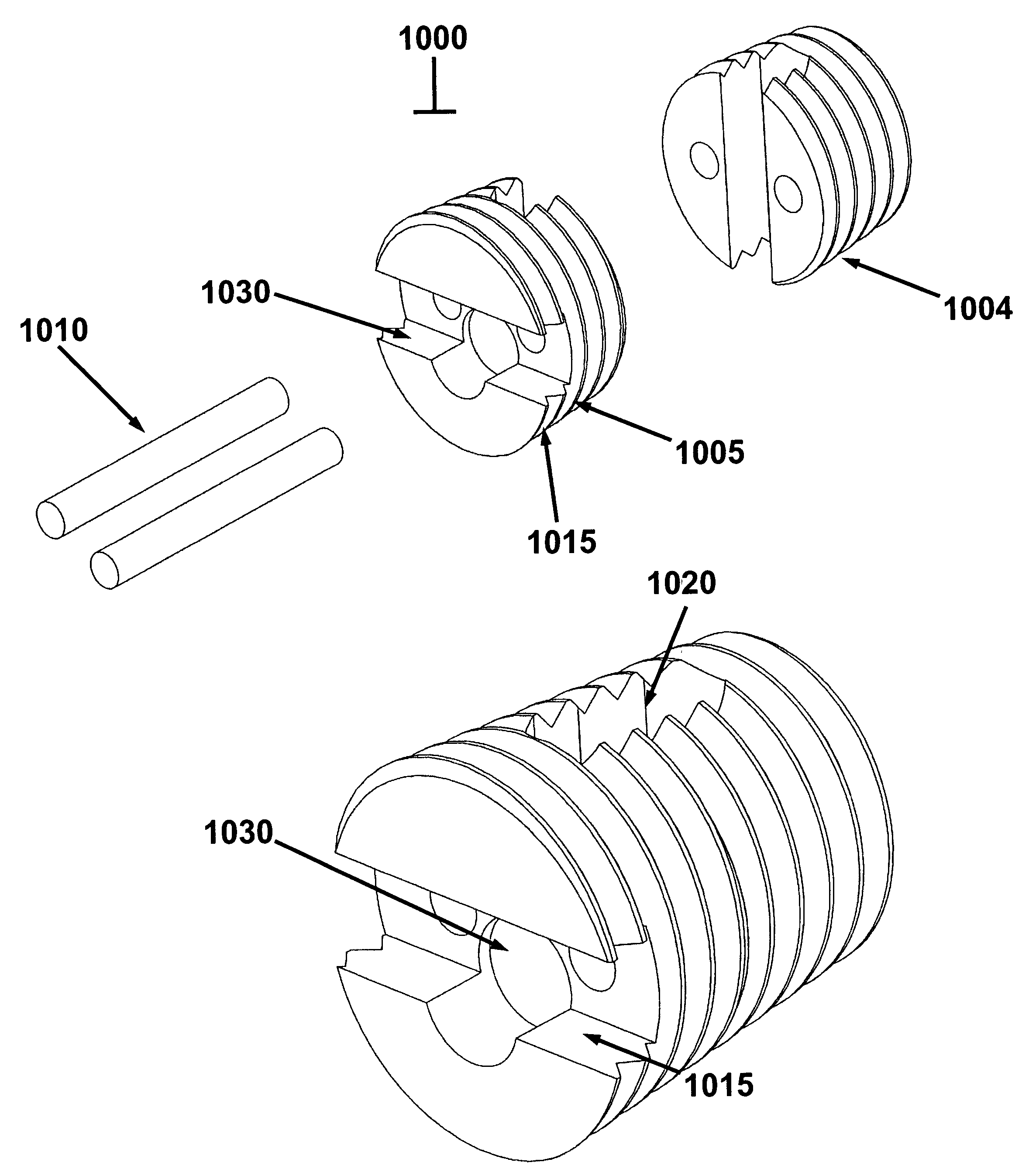
This invention relates to biomedical implants for filling, supporting or treating bone. In one embodiment, the implant comprises an electrospun polymer scaffold that is thereafter plated with a metal to provide a selected high modulus. Such an implant can be fabricated with a selected porosity for tissue ingrowth. The implant can be further provided with a varied modulus along the length of the implant body for inducing bending of the implant for packing in a bone. In another embodiment, the implant is fabricated in an elongated configuration for introducing into bone to treat a vertebral fracture. In another embodiment, the implant can be configured with helical threads for helically driving the implant into a bone.
Owner:DFINE INC
Nanotechnology for drug delivery, contrast agents and biomedical implants
A nanocomposite structure comprising a nanostructured filler or carrier intimately mixed with a matrix, and methods of making such a structure. The nanostructured filler has a domain size sufficiently small to alter an electrical, magnetic, optical, electrochemical, chemical, thermal, biomedical, or tribological property of either filler or composite by at least 20%.
Owner:PPG IND OHIO INC
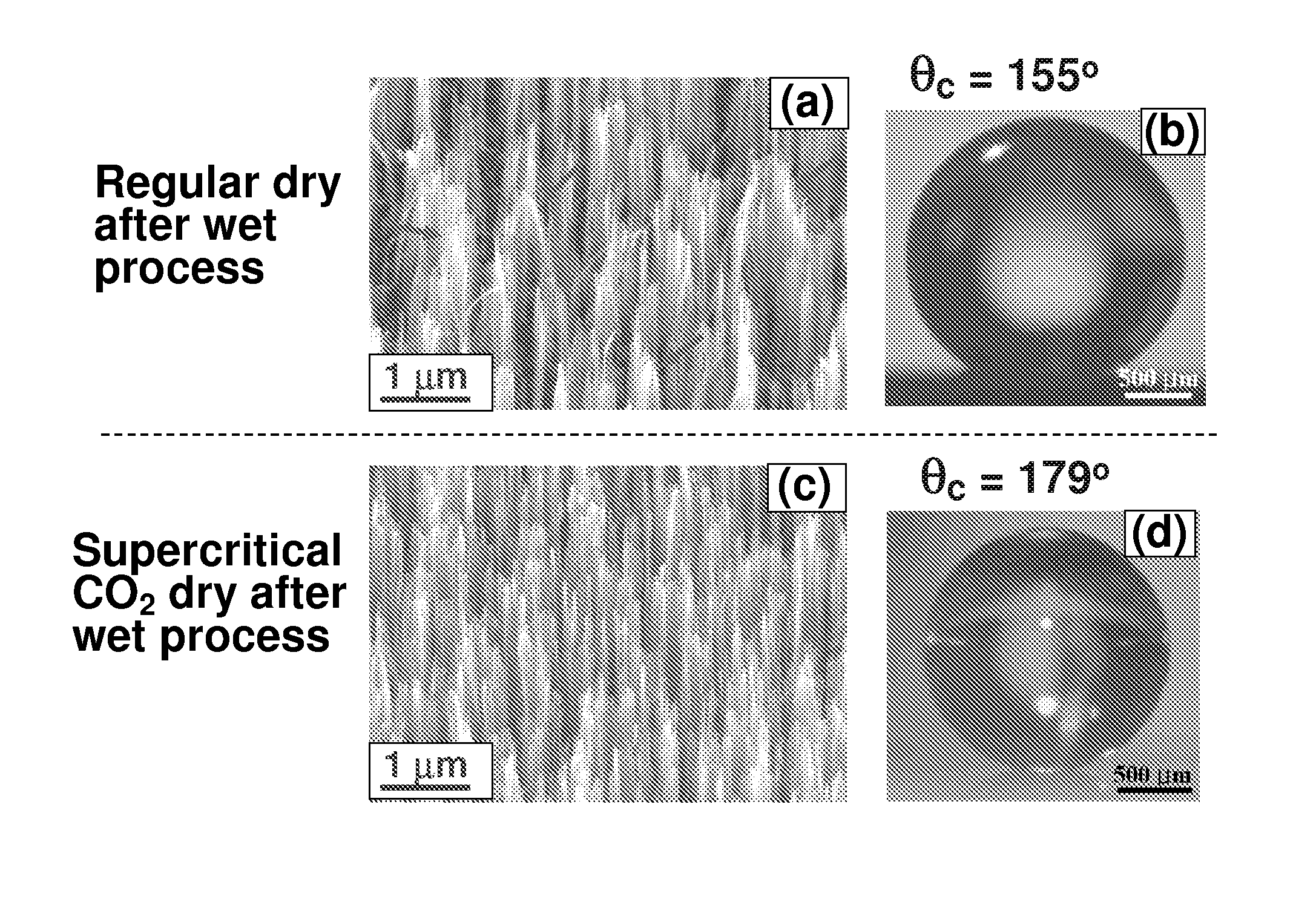
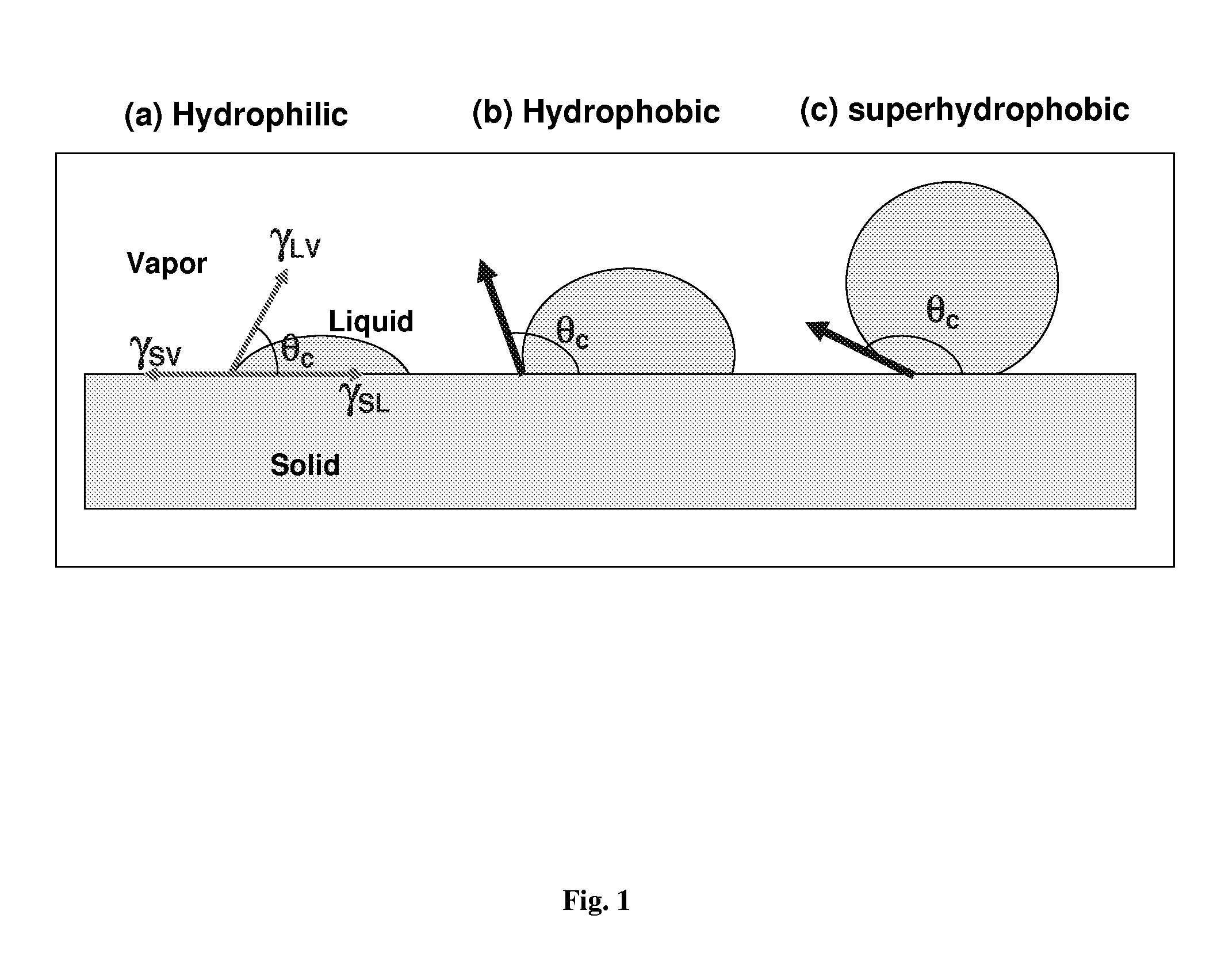
Nanostructured superhydrophobic, superoleophobic and/or superomniphobic coatings, methods for fabrication, and applications thereof
Systems, techniques and applications for nanoscale coating structures and materials that are superhydrophobic with a water contact angle greater than about 140° or 160° and / or superoleophobic with an oil contact angle greater than about 140° or 160°. The nanostructured coatings can include Si or metallic, ceramic or polymeric nanowires that may have a re-entrant or mushroom-like tip geometry. The nanowired coatings can be used in various self-cleaning applications ranging from glass windows for high-rise buildings and non-wash automobiles to pipeline inner surface coatings and surface coatings for biomedical implants.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Compositions and methods for biomedical applications
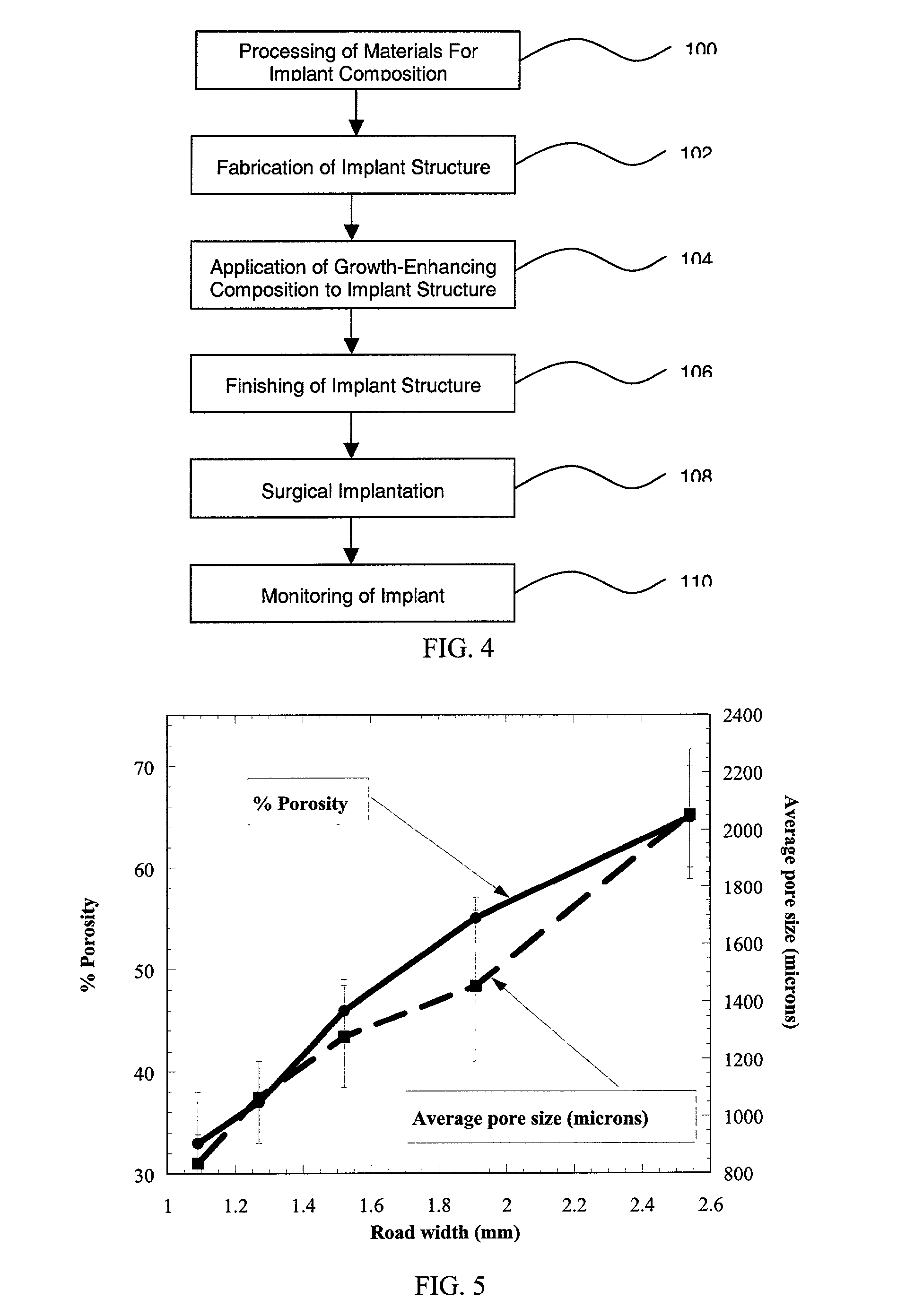
InactiveUS20020143403A1Large average pore sizeIncrease widthBone implantSpinal implantsBiomedical engineeringBiomedical implant
The present invention relates to biomedical implants for bone substitution and replacement applications. The implant includes a strong, porous polymeric or thermoplastic compositions and growth-enhancing compositions.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
Biomimetic hydrogel materials
Novel biomimetic hydrogel materials and methods for their preparation. Hydrogels containing acrylamide-functionalized carbohydrate, sulfoxide, sulfide or sulfone copolymerized with a hydrophilic or hydrophobic copolymerizing material selected from the group consisting of an acrylamide, methacrylamide, acrylate, methacrylate, vinyl and a derivative thereof present in concentration from about 1 to about 99 wt %. and methods for their preparation. The method of use of the new hydrogels for fabrication of soft contact lenses and biomedical implants.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Prion-free collagen and collagen-derived products and implants for multiple biomedical applications; methods of making thereof
InactiveUS6197935B1Preserve integrityPeptide/protein ingredientsImmunoglobulinsIn vivo biocompatibilityCollagen VI
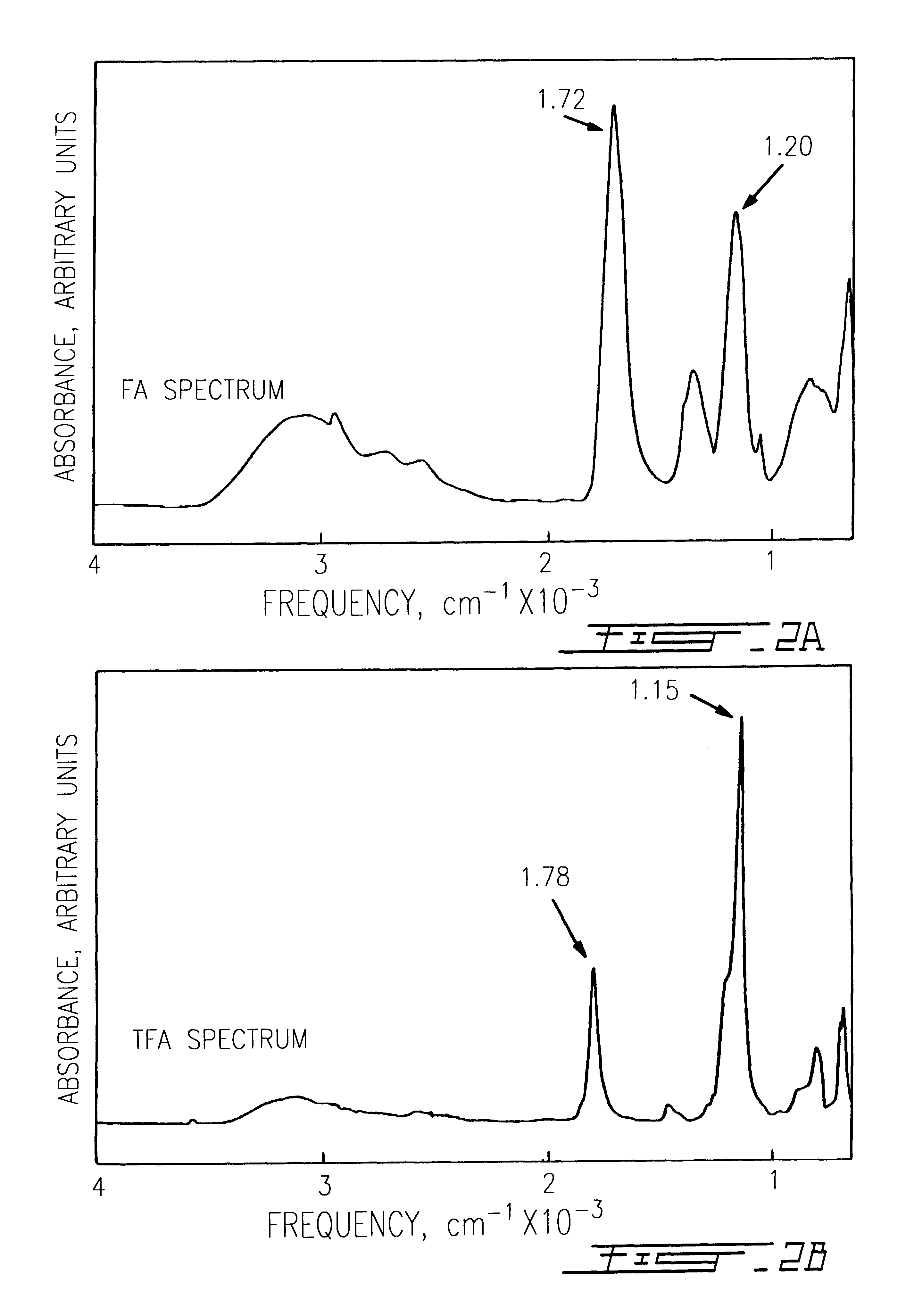
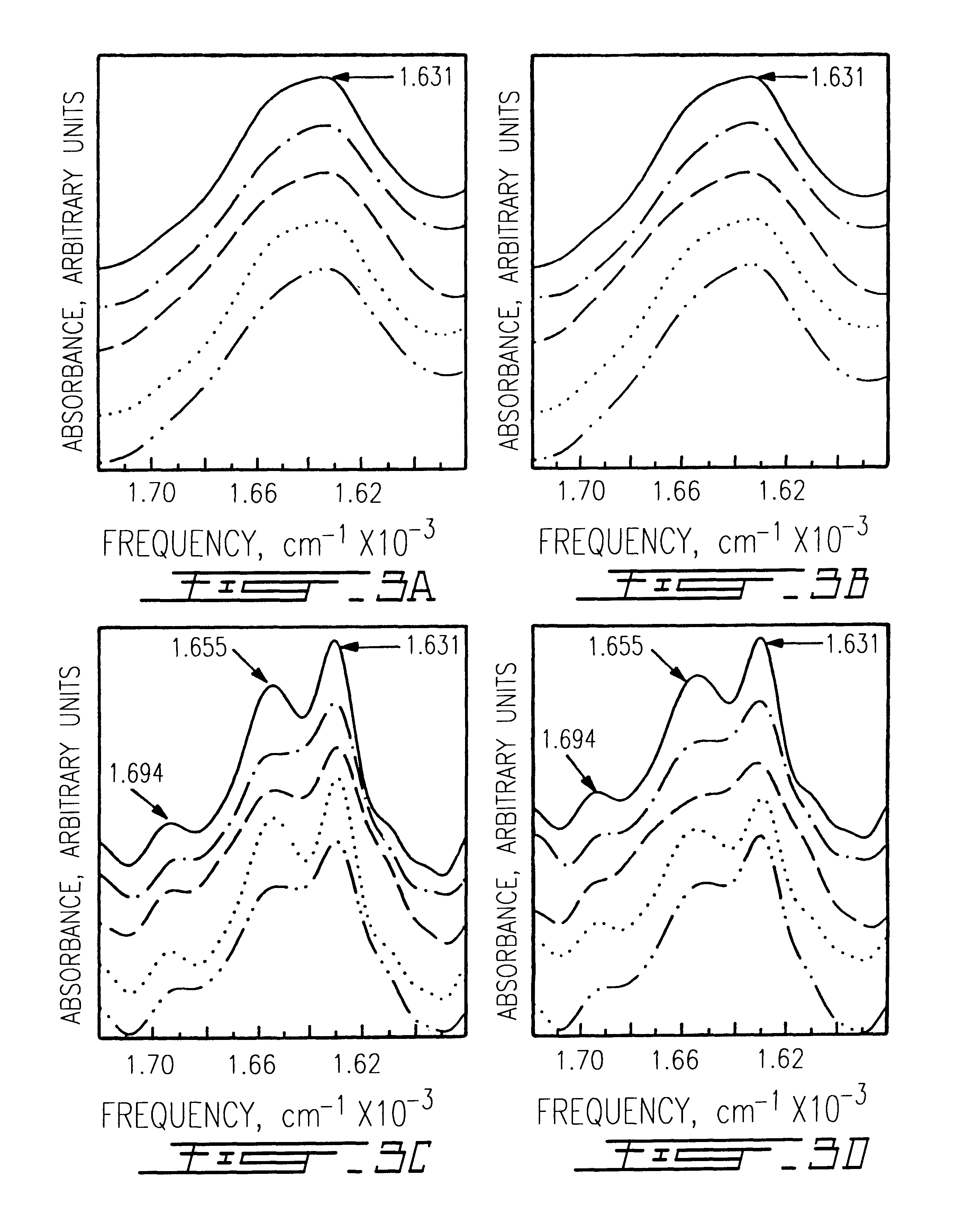
The use of collagen as a biomedical implant raises safety issues towards viruses and prions. The physicochemical changes and the in vitro and in vivo biocompatibility of collagen treated with heat, and by formic acid (FA), trifluoroacetic acid (TFA), tetrafluoroethanol (TFE) and hexafluoroiso-propanol (HFIP) were investigated. FA and TFA resulted in extensive depurination of nucleic acids while HFIP and TFE did so to a lesser degree. The molecules of FA, and most importantly of TFA, remained within collagen. Although these two acids induced modification in the secondary structure of collagen, resistance to collagenase was not affected and, in vitro, cell growth was not impaired. Severe dehydrothermal treatment, for example 110° C. for 1-3 days under high vacuum, also succeeded in removing completely nucleic acids. Since this treatment also leads to slight cross-linking, it could be advantageously used to eliminate prion and to stabilize gelatin products. Finally, prolonged treatment with TFA provides a transparent collagen, which transparency is further enhanced by adding glycosaminoglycans or proteoglycans, particularly hyaluronic acid. All the above treatments could offer a safe and biocompatible collagen-derived material for diverse biomedical uses, by providing a virus or prion-free product.
Owner:UNIV LAVAL
Cervical tapered dowel
Disclosed herein are biomedical implants, and methods of using same, that are derived from bone. Particularly exemplified are implants having a tapered dowel shape that are useful for implantation in the spine, and especially in the cervical region of the spine. The taper of the implants disclosed herein provides an advantage over conventional implants, as it creates the proper support and angulation to maintain the proper curvature of the spine. Optionally, the implants taught herein are associated with osteogenic materials or other biomedical substances.
Owner:RTI BIOLOGICS INC
Biodegradable osteogenic porous biomedical implant with impermeable membrane
InactiveUS20100161074A1Facilitate mechanical shaping and fillingFacilitate and enhance proliferationDental implantsSurgical adhesivesBone tissueBone growth
A biomedical implant is disclosed with osteogenic factors and a solid impermeable membrane occluding a portion of its surface for the generation of new bone growth at the target site of the implant. The implant is porous, bioresorbable, and forms a three dimensional architectural scaffold for the formation of new bone tissue. The implant is formed with a polymer or collagen, bone morphogenetic protein and ceramic particles.
Owner:WARSAW ORTHOPEDIC INC
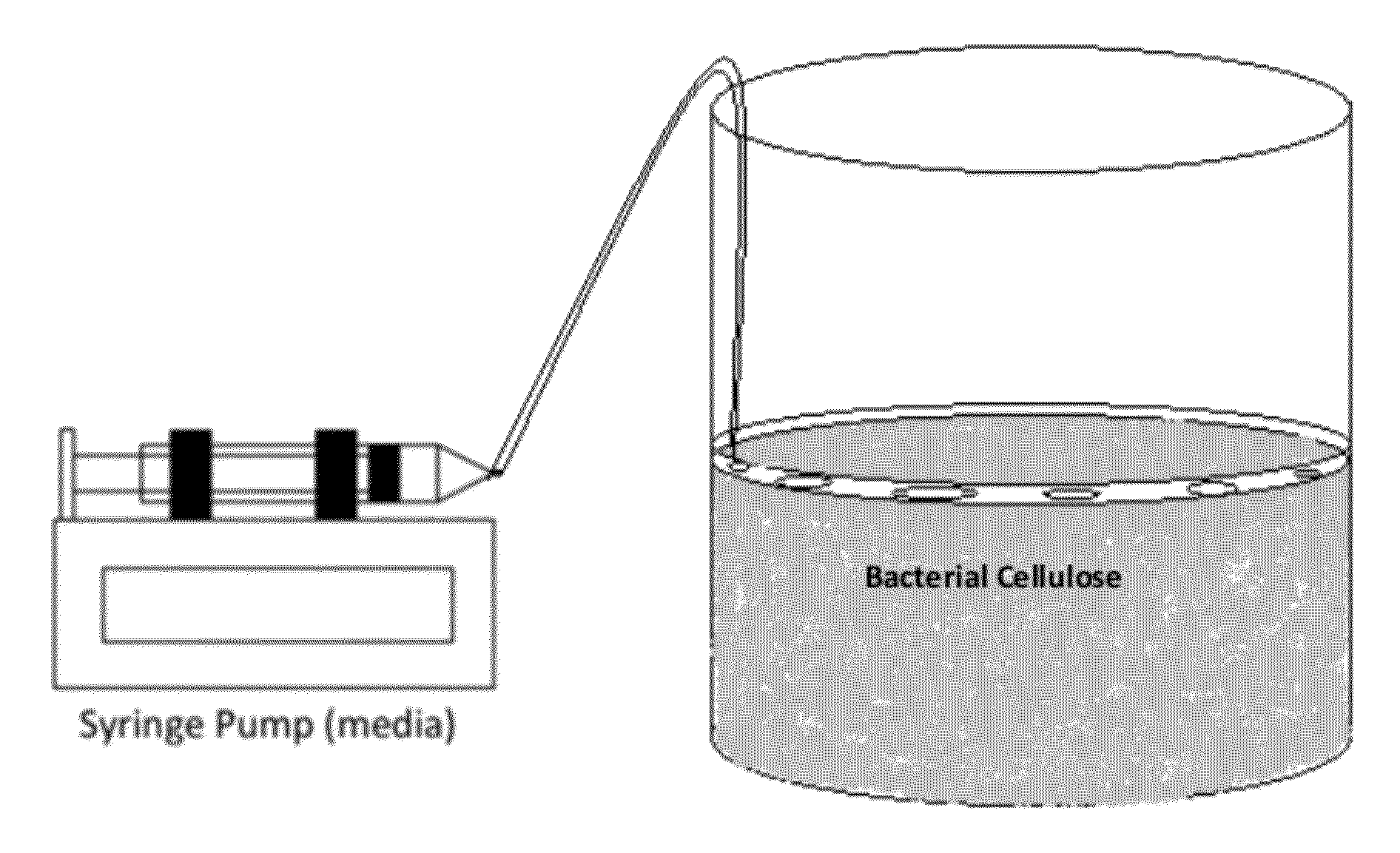
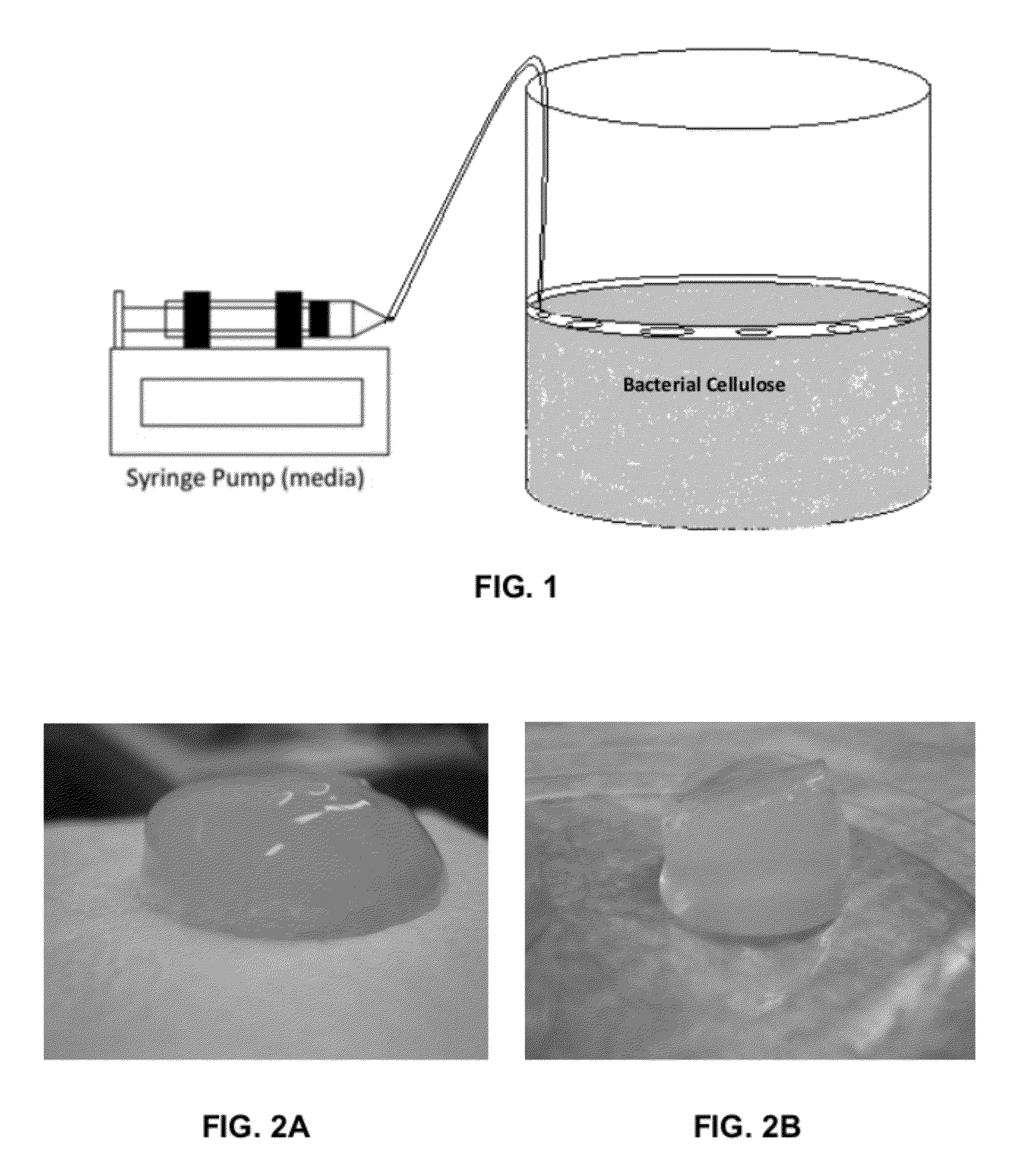
Three-dimensional bioprinting of biosynthetic cellulose (BC) implants and scaffolds for tissue engineering
InactiveUS8691974B2Optimize thicknessStrength optimizationOrganic active ingredientsSugar derivativesInterconnectivityPorosity
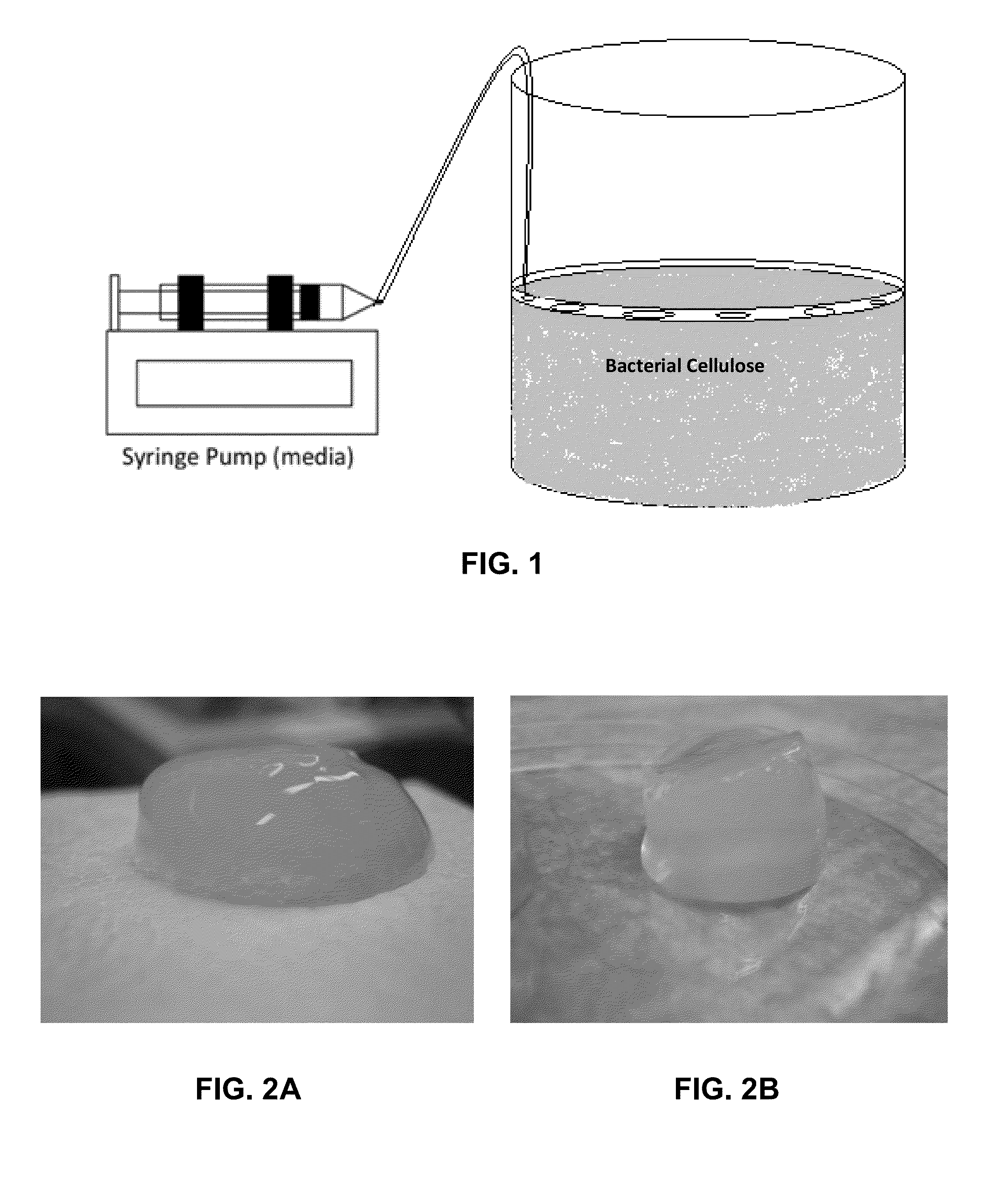
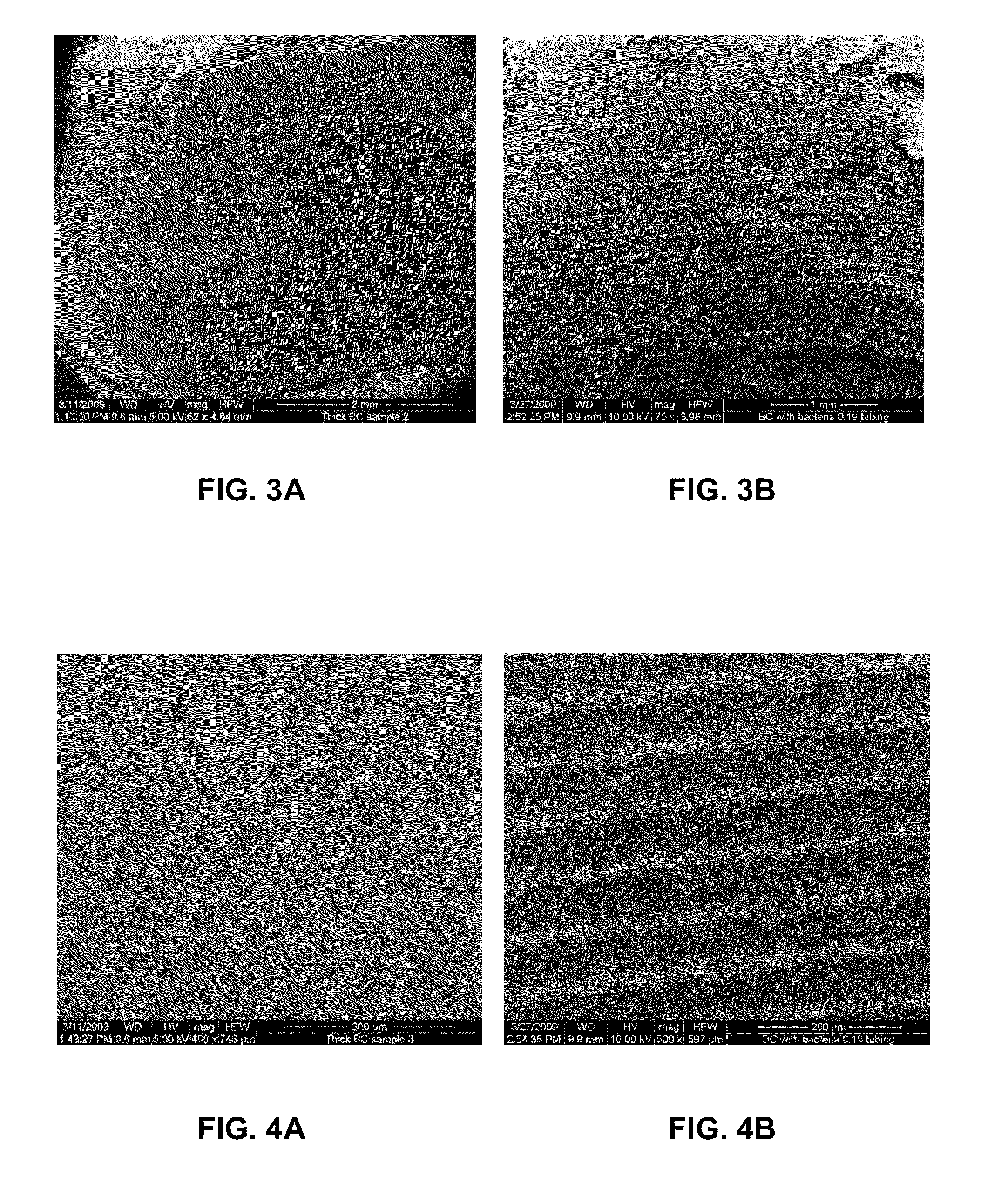
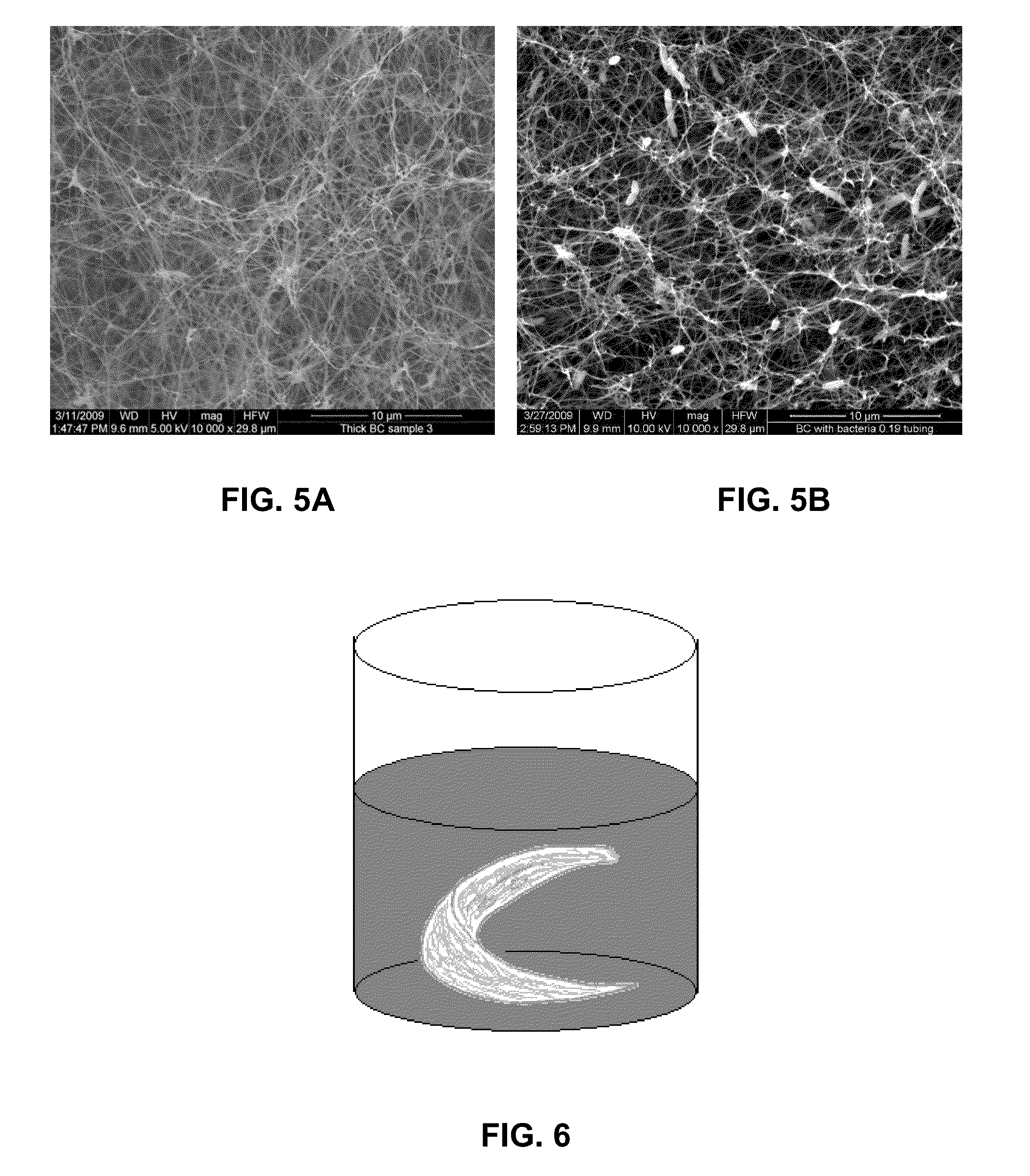
A novel BC fermentation technique for controlling 3D shape, thickness and architecture of the entangled cellulose nano-fibril network is presented. The resultant nano-cellulose based structures are useful as biomedical implants and devices, are useful for tissue engineering and regenerative medicine, and for health care products. More particularly, embodiments of the present invention relate to systems and methods for the production and control of 3-D architecture and morphology of nano-cellulose biomaterials produced by bacteria using any biofabrication process, including the novel 3-D Bioprinting processes disclosed. Representative processes according to the invention involve control of the rate of production of biomaterial by bacteria achieved by meticulous control of the addition of fermentation media using a microfluidic system. In exemplary embodiments, the bacteria gradually grew up along the printed alginate structure that had been placed into the culture, incorporating it. After culture, the printed alginate structure was successfully removed revealing porosity where the alginate had been placed. Porosity and interconnectivity of pores in the resultant 3-D architecture can be achieved by porogen introduction using, e.g., ink-jet printer technology.
Owner:VIRGINIA TECH INTPROP INC
Multilayered cellular metallic glass structures
ActiveUS20120077052A1High yield strengthGood molding effectMedical devicesVehicle componentsEnergy absorptionHoneycomb like
Multi-layered cellular metallic glass structures and methods of preparing the same are provided. In one embodiment, the cellular metallic glass structure includes at least one patterned metallic glass sheet and at least one additional sheet. The at least one patterned metallic glass sheet may include multiple sheets connected together to form a group of sheets, and the structure may include a group of sheets sandwiched between two outer sheets. The patterned metallic glass sheets may be patterned by thermoplastically forming two- and / or three-dimensional patterns in the metallic glass sheets. The metallic glass cellular structures are useful in a wide variety of applications, including but not limited to blast protection applications, energy absorption applications, structural support applications, biomedical implant applications, heat exchanger applications, thermal management applications, electrical shielding applications, magnetic shielding applications, and debris and radial
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Biomedical implantable material and methods of producing the same
The present invention relates to improved biomedical implantable material comprising a plurality of pores, of which one or more of the pores are interconnected below the surface of the material. The improved biomedical implantable material may be used in biomedical implant devices such as orthopedic implants, spinal implants, neurocranial implants, maxillofacial implants, and joint replacement implants. The present invention also relates to a method of preparing an improved biomedical implantable material, comprising subjecting an implantable material to a pore-forming treatment and optionally further subjecting the material to a surface-modifying treatment. The biomedical implantable material may be used in other applications, which as applications where two surfaces are contacted and bonding between the surfaces is required.
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND
Three-dimensional bioprinting of biosynthetic cellulose (BC) implants and scaffolds for tissue engineering
InactiveUS20120190078A1Improve the level ofOptimize thicknessPharmaceutical delivery mechanismCell culture supports/coatingFiberPorosity
A novel BC fermentation technique for controlling 3D shape, thickness and architecture of the entangled cellulose nano-fibril network is presented. The resultant nano-cellulose based structures are useful as biomedical implants and devices, are useful for tissue engineering and regenerative medicine, and for health care products. More particularly, embodiments of the present invention relate to systems and methods for the production and control of 3-D architecture and morphology of nano-cellulose biomaterials produced by bacteria using any biofabrication process, including the novel 3-D Bioprinting processes disclosed. Representative processes according to the invention involve control of the rate of production of biomaterial by bacteria achieved by meticulous control of the addition of fermentation media using a microfluidic system. In exemplary embodiments, the bacteria gradually grew up along the printed alginate structure that had been placed into the culture, incorporating it. After culture, the printed alginate structure was successfully removed revealing porosity where the alginate had been placed. Porosity and interconnectivity of pores in the resultant 3-D architecture can be achieved by porogen introduction using, e.g., ink-jet printer technology.
Owner:VIRGINIA TECH INTPROP INC
Inorganic structures with controlled open cell porosity and articles made therefrom
Structural inorganic cellular materials with controlled open porosity are produced by foaming fine particulate-laden aqueous solutions into stable, uniform, dodecahedral froth structures which are dried and sintered by microwave energy or high voltage instant electrical discharge. Porous open cell biomedical implants such as niobium or tantalum acetabular caps with engineered osteoconductive porosity are among the products achievable.
Owner:BILLIET ROMAIN LOUIS +1
Zn-Li series zinc alloy as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN107460371AImprove mechanical propertiesHigh strengthSuture equipmentsProsthesisZinc alloysMechanical property
The invention discloses a Zn-Li series zinc alloy as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The Zn-Li series zinc alloy comprises Zn and Li; and based on weight percent, the mass percent content of the Li in the zinc alloy accounts for 0 to 30%, but not including 0. The preparation method of the Zn-Li series zinc alloy comprises the following steps: (1) mixing the Zn and the Li to obtain a mixture; (2) treating the mixture according to the following step a) or step b) and then cooling the mixture to obtain the zinc alloy: a) under the protection of a CO2 and SF6 atmosphere, carrying out smelting or sintering on the mixture; and b) under the protection of a vacuum atmosphere, dissolving hydrogen gas into the mixture and carrying out the smelting. The zinc alloy prepared by the preparation method disclosed by the invention has an excellent mechanical property and can provide a long-term effective supporting force in vivo; and the zinc alloy has excellent cellular compatibility, blood compatibility and tissue and organ compatibility and can be used for preparing biomedical implant materials.
Owner:PEKING UNIV +1
Cyclic Impact-Sliding Fatigue Wear Testing Instrument
ActiveUS20110314894A1Acceleration measurementMaterial strength using repeated/pulsating forcesWear testingContact pressure
This invention deals with a testing instrument that is used to investigate failure behavior of items subject to impact and sliding forces. The testing instrument produces an impact motion and a sliding motion in each testing cycle with maximum contact pressure similar to actual stresses applied to the items during real applications. The invented instrument simulates wear conditions and failure behaviors of biomedical implants, components, tools and coatings which are observed in practical applications.
Owner:NIE YINING +1
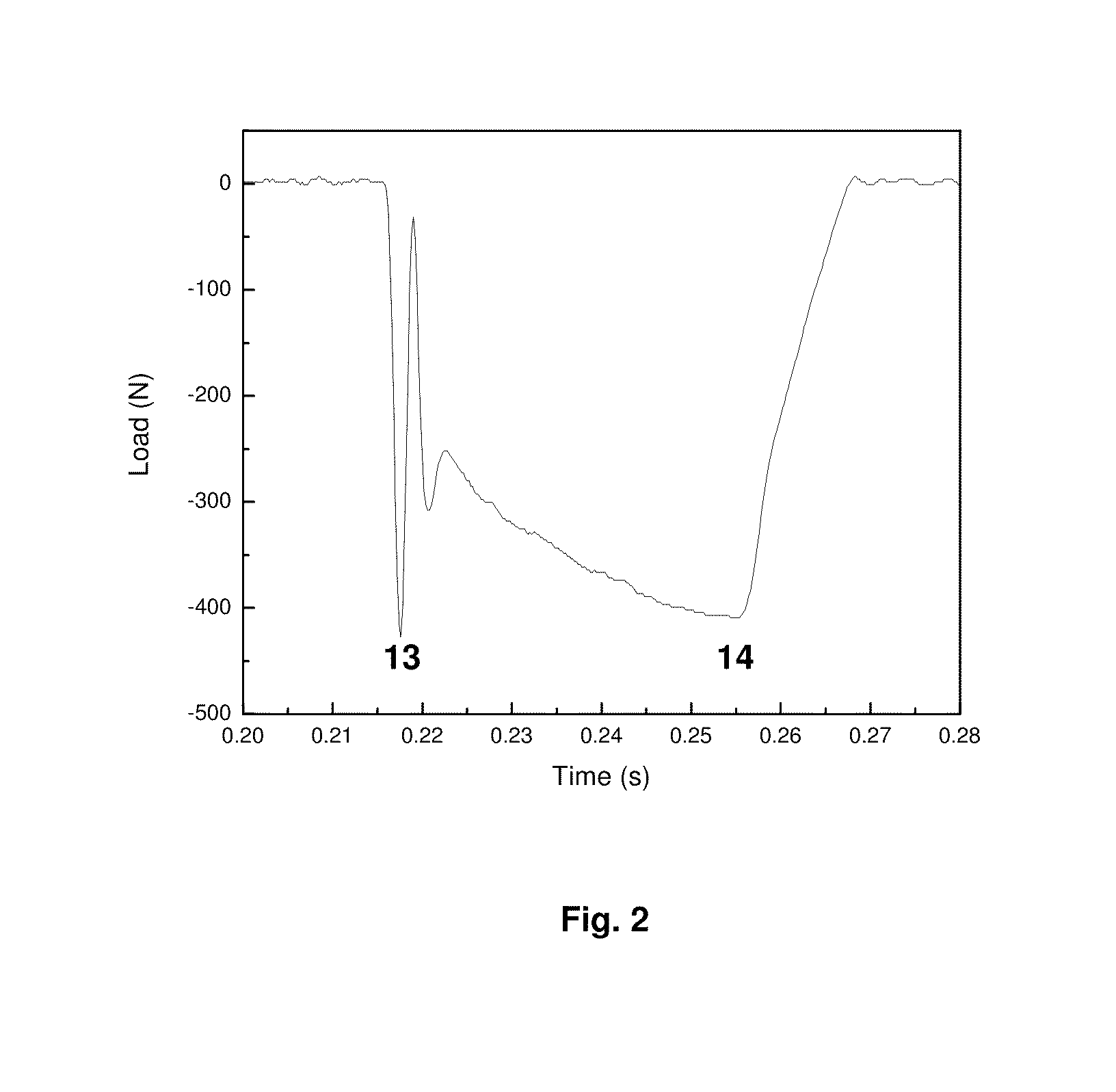
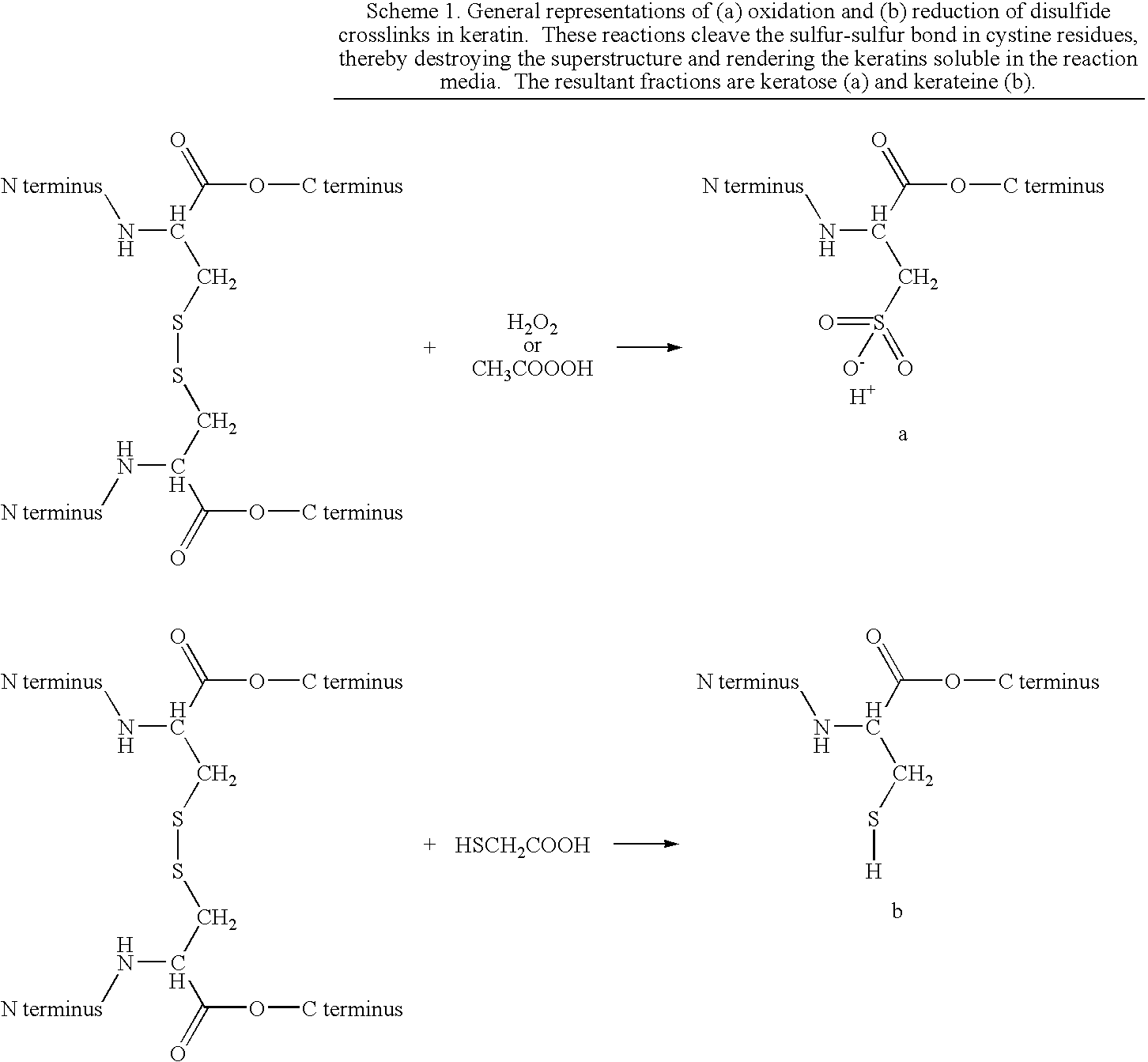
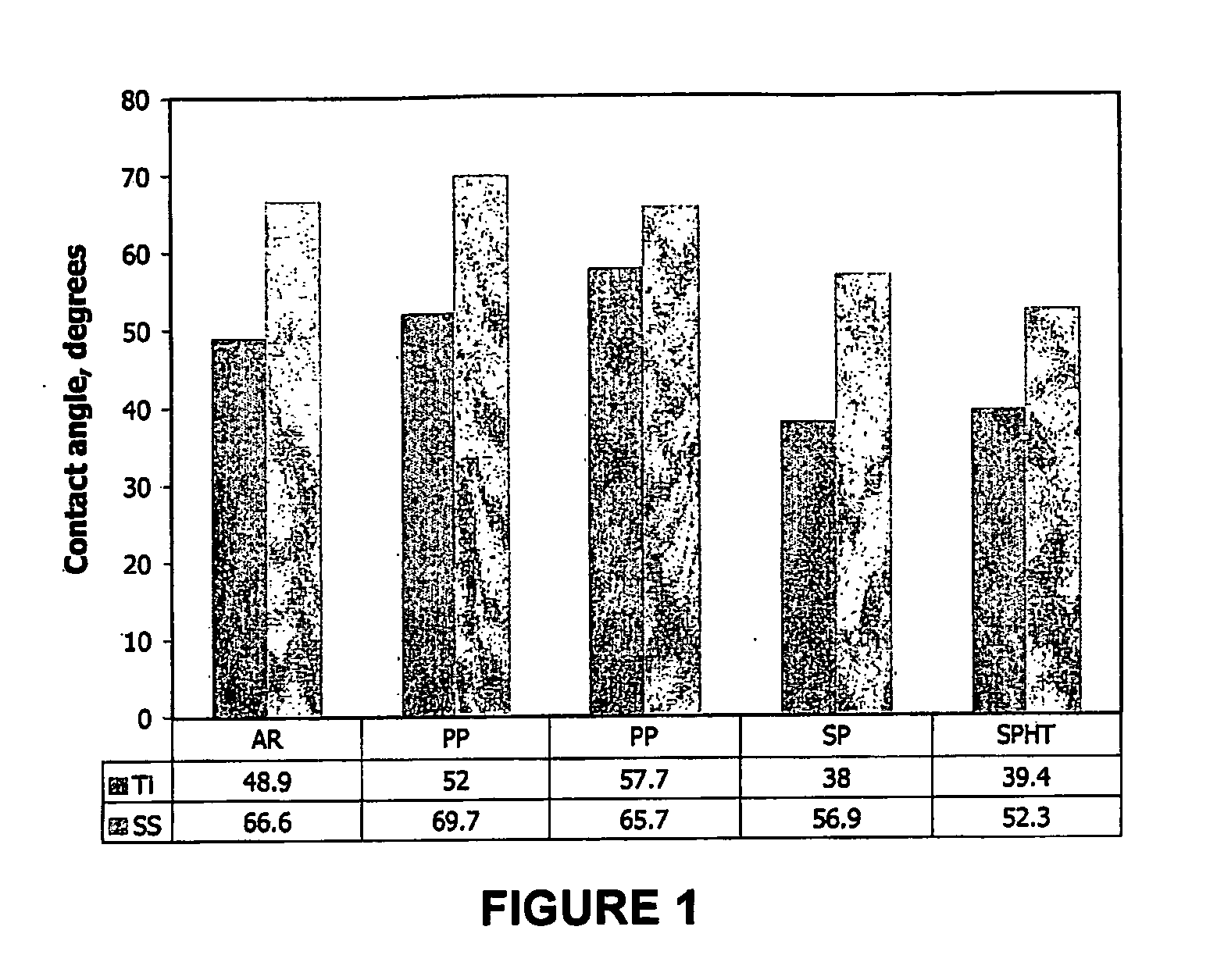
Coatings and Biomedical Implants Formed From Keratin Biomaterials
ActiveUS20090004242A1Inhibit blood coagulationPeptide/protein ingredientsSurgeryFractionationBlood coagulations
Methods are provided to produce optimal fractionations of charged keratins that have superior biomedical activity. Also provided are medical implants coated with these keratin preparations. Further provided are methods of treating blood coagulation in a patient in need thereof.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
Bioactive Coating of Biomedical Implants
InactiveUS20080071382A1Easy to fixHigh densityBone implantPharmaceutical containersPlasma GasesSilica coating
A method of forming a bioactive coating on a biomedical implant, the method including the step of contacting at least part of the surface of the implant prior to implantation with a plasma gas containing a reactive hydroxylating oxidant species. The step of contacting the surface of the implant prior to implantation with a plasma gas containing a reactive hydroxylating oxidant species may be preceded by a step of exposing the implant to an organosilane or organosilicate species to form a silica coating on at least part of the implant prior to contact with the oxidant species.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTH AUSTRALIA
Method to improve hydroxyapatite implantation and stimulate bone regeneration
InactiveUS20020127261A1Favorable to tissue growth of tissueReduced affinityBone implantJoint implantsApatiteTissue Compatibility
Hydroxyapatite is treated by a combination of nitridation and the application of bone morphogenetic protein to improve the tissue compatibility and affinity of the hydroxyapatite, rendering the hydroxyapatite more useful as a material for biomedical implants.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Medical degradable and absorbable Mg-Sr-Ca series magnesium alloy implant and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to a medical degradable and absorbable Mg-Sr-Ca series magnesium alloy implant and a preparation method thereof. The medical implant is made of a Mg-Sr-Ca series alloy, wherein strontium is 0 to 5 percent (but not 0) of the weight of the Mg-Sr-Ca series alloy; calcium is 0 to 2 percent (but not 0) of the weight of the Mg-Sr-Ca series alloy; a small amount of one or more of trace elements, namely manganese, zirconium, tin, rare earth and yttrium may be contained, and are not more than 2 percent of weight of the Mg-Sr-Ca series alloy; and the balance is magnesium. In-vivo and in-vitro tests prove that the Mg-Sr-Ca series alloy implant is nontoxic, has high histocompatibility, and is a reliable biomedical implant material.
Owner:浙江海圣医疗器械股份有限公司
Material and method to prevent low temperature degradation of zirconia in biomedical implants
ActiveUS7037603B2Ceramic layered productsNatural mineral layered productsHigh fractureThermal treatment
Owner:ALFRED E MANN FOUND FOR SCI RES
Zn-Mn series zinc alloy and preparing method and application thereof
ActiveCN107460372AImprove mechanical propertiesHigh strengthSuture equipmentsTissue regenerationHydrogenBiocompatibility Testing
The invention discloses a Zn-Mn series zinc alloy and a preparing method and application thereof. The Zn-Mn series zinc alloy comprises Zn and Mn, wherein by weight percent, the mass percent of Mn in the zinc alloy ranges from 0% to 30%, however the mass percent of the Mn cannot be 0. The preparing method comprises following steps: firstly, Zn and Mn are mixed, and a mixture is obtained; secondly, the mixture is treated according to the step of a or b, cooling is carried out, and the zinc alloy is obtained, wherein under the CO2 and SF6 atmosphere protection, the mixture is smelted or sintered, and under the vacuum atmosphere protection, hydrogen is dissolved in the mixture to be smelted. The prepared Zn-Mn series zinc alloy is excellent in mechanical property, long-term effective mechanical support is provided in the machine body, the excellent cellular biocompatibility, blood compatibility and tissue and organ compatibility can be achieved, and the alloy can be used for preparing of biomedical implant materials.
Owner:PEKING UNIV +1
Preparation method of titanium surface porous structure layer bioactive ceramic membrane with low elasticity modulus
InactiveCN103088348AImprove stress distributionIncrease pressureCoatingsProsthesisMicro arc oxidationPlasma electrolytic oxidation
The invention discloses a preparation method of a titanium surface porous structure layer bioactive ceramic membrane with low elasticity modulus, and relates to the field of biomedical implant, especially the preparation technology of a biomedical implant made of a titanium or titanium alloy material. The method comprises steps of: first preparing a porous structure layer on a matrix structure of a pure titanium or titanium alloy implant with a solid structure by using a powder metallurgy method; then forming a titanium dioxide membrane containing calcium and phosphorus on a hole surface of the porous structure layer by a micro-arc oxidation method; and finally, preparing a hydroxyl apatite layer on a hole external surface of the porous structure layer by an electrodeposition method. The invention can realize formation of porous structure layer on the surface of the pure titanium or titanium alloy implant with solid structure, and reduce elastic modulus on the implant surface; meanwhile, the implant is endowed with high biological activity through implantation of a hydroxyapatite layer, and can be used in the field of biological medicine.
Owner:INST OF METAL RESEARCH - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Surface treatment of biomedical implant for improved biomedical performance
The invention provides a method of preparing a biomedical implant comprising the steps of providing a biomedical implant comprising a metal and having a surface, wherein the surface comprises a metal oxide layer, contacting the biomedical implant with a composition comprising an alkaline earth element, disrupting the metal oxide layer on the surface of the biomedical implant, and adhering the alkaline earth element to the surface of the biomedical implant.
Owner:CABOT MICROELECTRONICS CORP
Injection zone markers for biomedical implants
A mammary implant and method of making are provided herein. The implant includes an outer shell configured to retain fluid therein, an injection element coupled to the outer shell and adapted to receive therethrough an injection device for injecting fluid into the outer shell, and an injection marker zone made of a material having ultrasonically detectable markers incorporated therein. The markers are a plurality of microcavities that are located relative to the injection element so that, when ultrasonically detected, such detection indicates a location of the injection element.
Owner:MENTOR WORLDWIDE
Zn-Li-Mg-system zinc alloy and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN108277386AImprove mechanical propertiesGood mechanical propertiesImpression capsSurgeryZinc alloysBiomedical implant
The invention discloses a Zn-Li-Mg-system zinc alloy and a preparation method and application thereof. The zinc alloy comprises, by weight, 0-1% of Li, 0-1% of Mg and the balance Zn, wherein the masspercents of Li and Mg are not zero. The zinc alloy prepared by the preparation method is excellent in mechanical performance, can provide long-term and effective supporting force in a body, has excellent cellular and blood compatibility, and can be applied to preparation of biomedical implants.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Medical implanted titanium alloy with low elastic modulus and high fatigue strength and preparation method
The invention relates to a medical implanted titanium alloy with low elastic modulus and high fatigue strength and a preparation method. The medical implanted titanium alloy comprises, by weight, 30-33% of Nb, 1-6% of Zr, 2-4% of Mo, 0.20-0.40% of O, and the balance Ti. The preparation method of the medical implanted titanium alloy specifically comprises the steps that smelting is conducted by using a vacuum non-consumable electric-arc furnace to obtain an alloy ingot with uniform ingredients, solution treatment is conducted at 850-950 DEG C after the alloy ingot is subjected to hot forging into bar materials, and water cooling is conducted to the room temperature; then cold rolling deformation processing is conducted, and the deformation quantity is 80-90%; and finally, aging heat treatment is conducted, the heating temperature of the aging heat treatment is 400-500 DEG C, and the heat preservation time is 1-12 h. According to the medical implanted titanium alloy with the low elasticmodulus and the high fatigue strength and the preparation method, after cold rolling and heat treatment, the strength is significantly higher than that of a current most-widely-applied medical implanted titanium alloy Ti-6Al-4V, the fatigue strength is comparable to Ti-6Al-4V, the elastic modulus is only 52% of Ti-6Al-4V, the biocompatibility and the mechanical compatibility are more excellent, and the medical implanted titanium alloy can be applied to preparation of biomedical implants.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
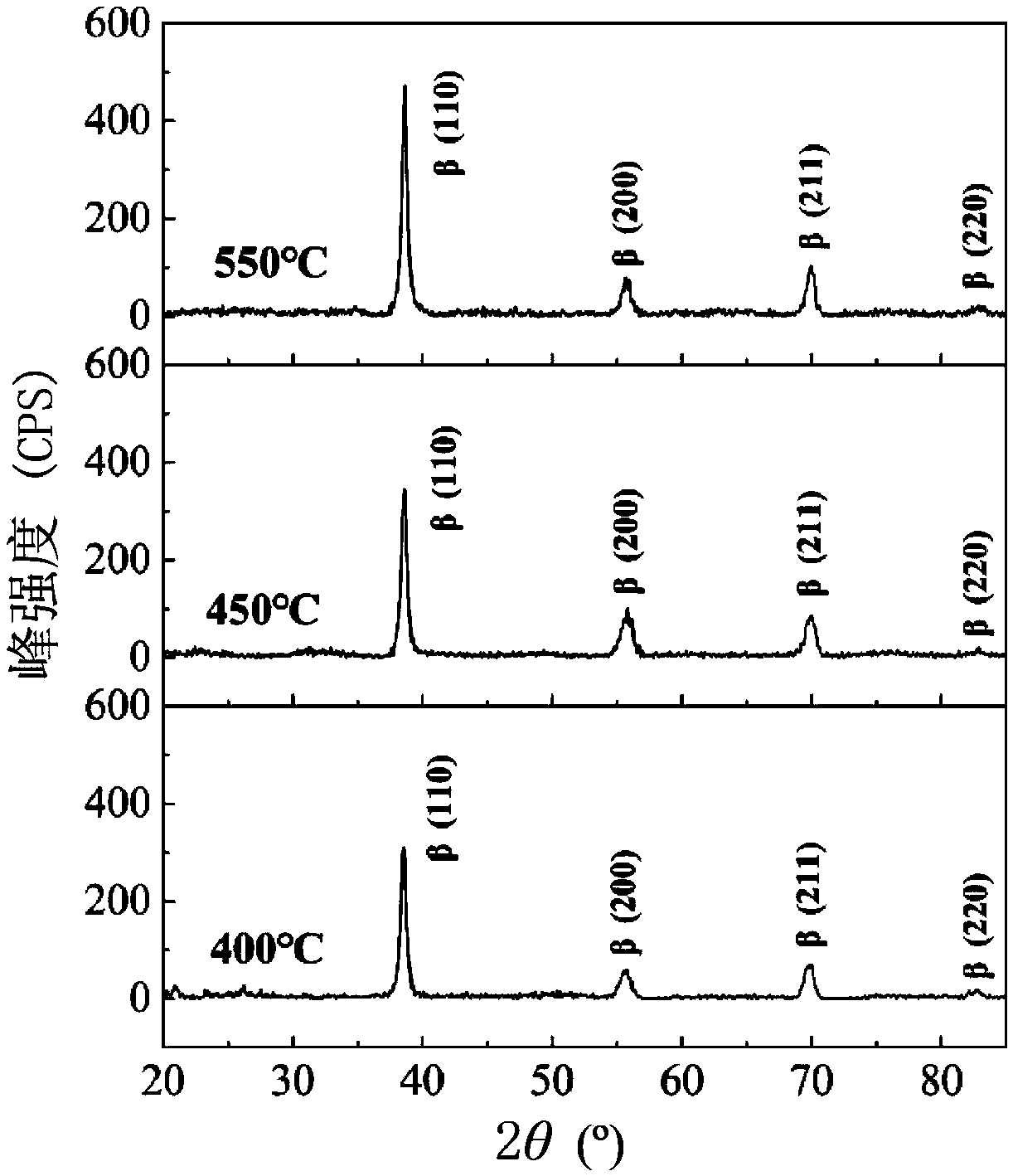
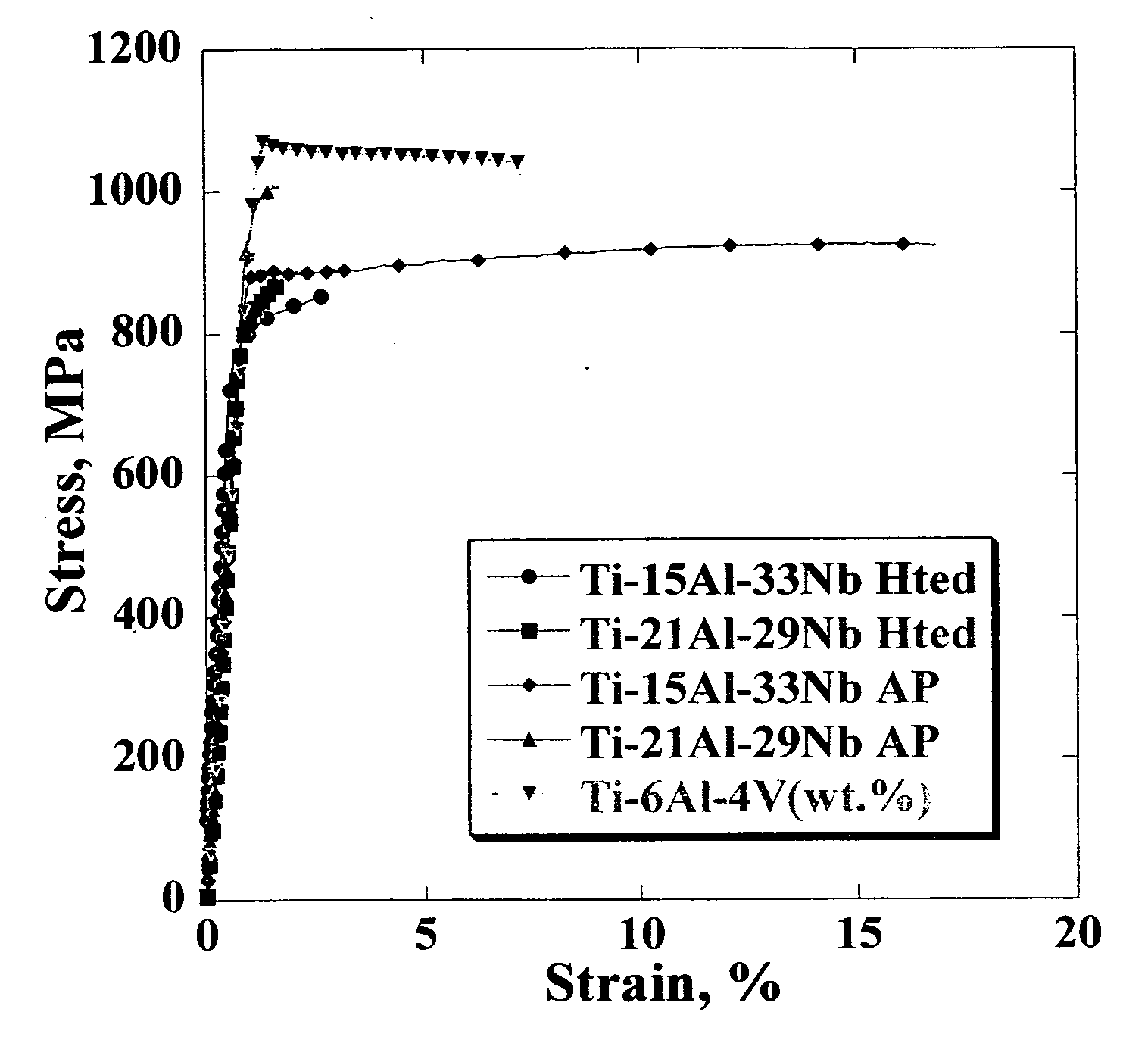
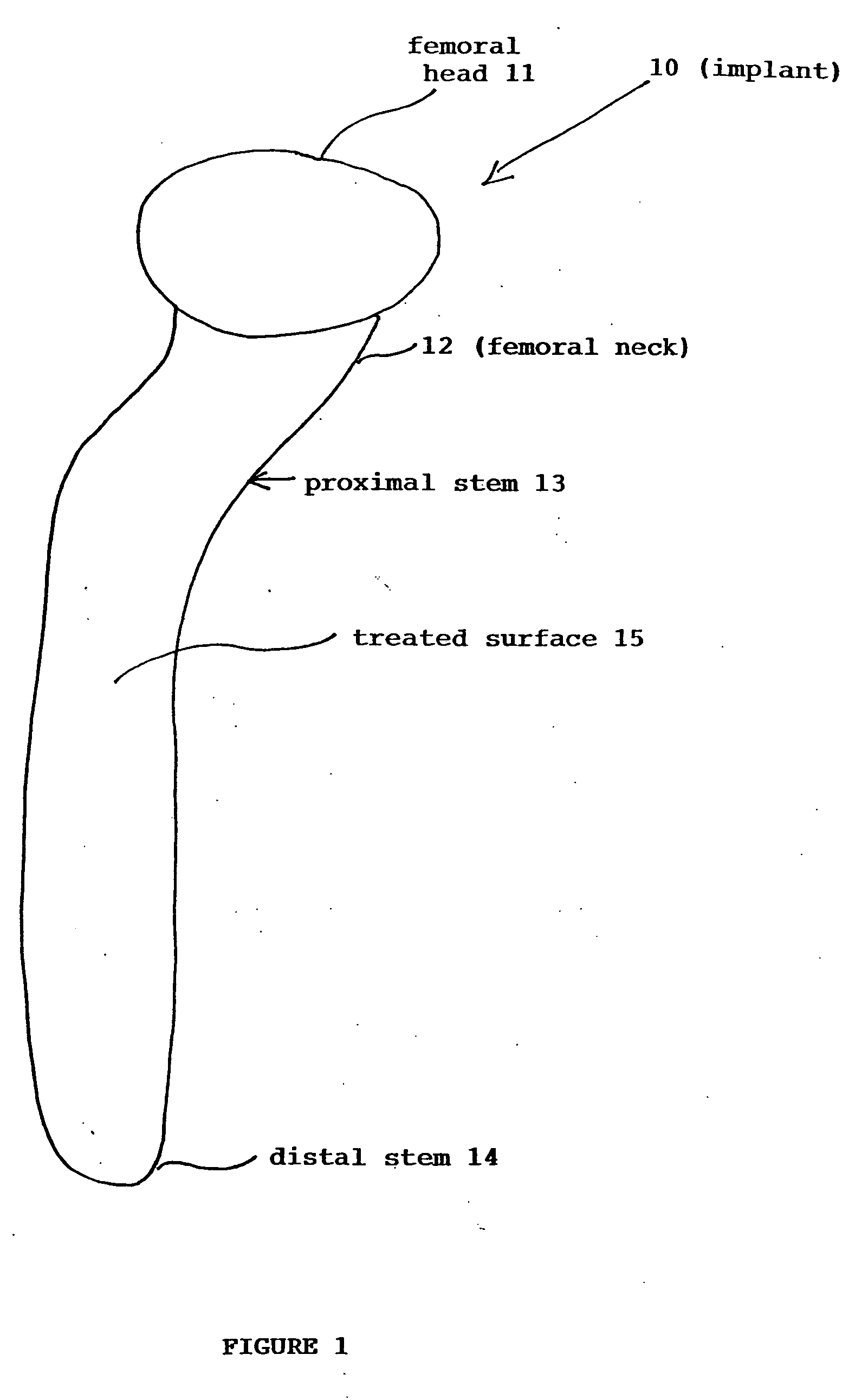
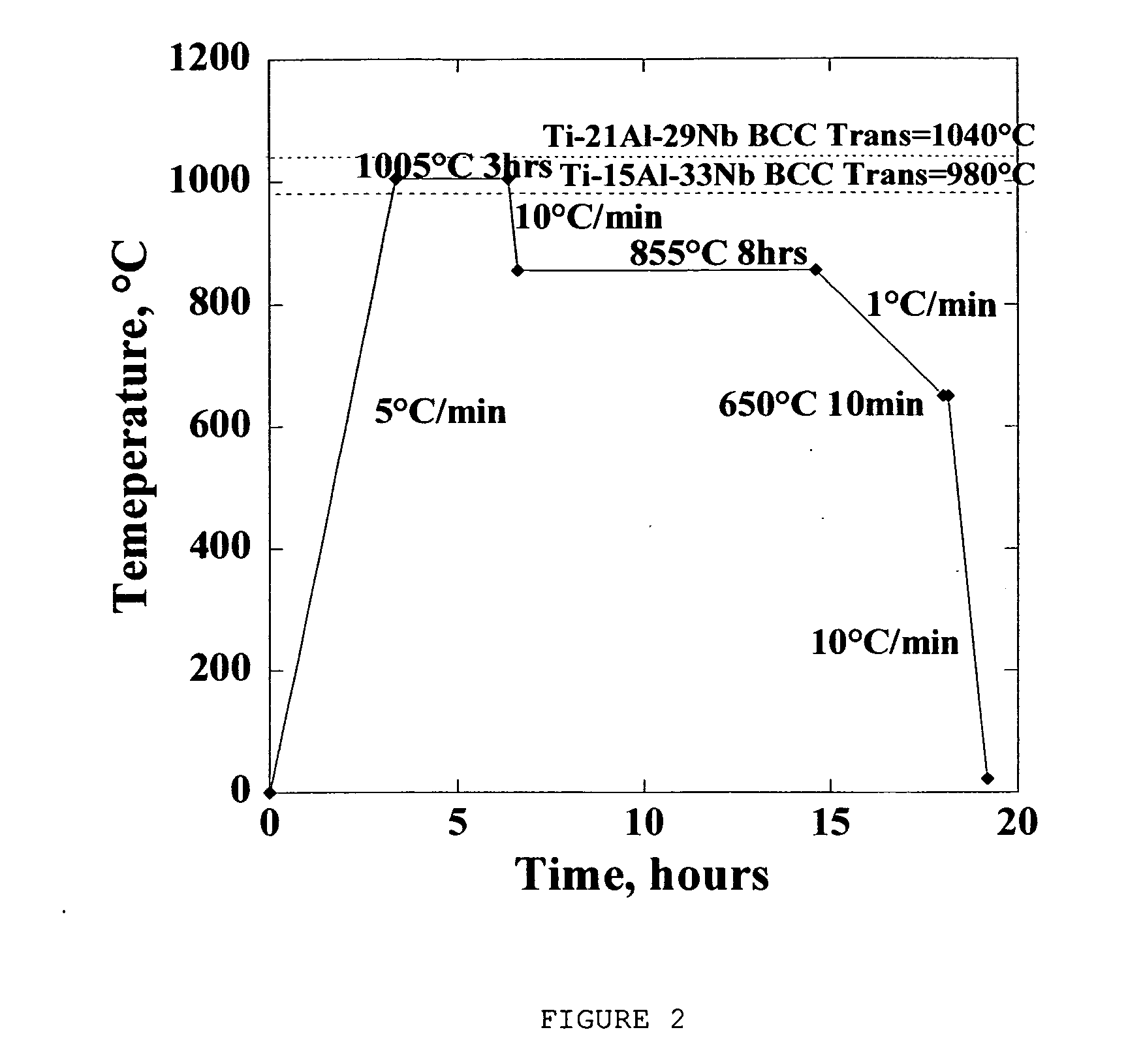
Ti, Al and Nb alloys
Ti(x %)Al(y %)Nb alloys as implants for biomedical implant apparatus, where x is between about 45 and 54% by atoms, y is between about 15 to 25% by atoms are described. The implants are useful for prosthesis implanted into the body of a human, or lower mammals and in various structures.
Owner:BOARD OF TRUSTEES OPERATING MICHIGAN STATE UNIV
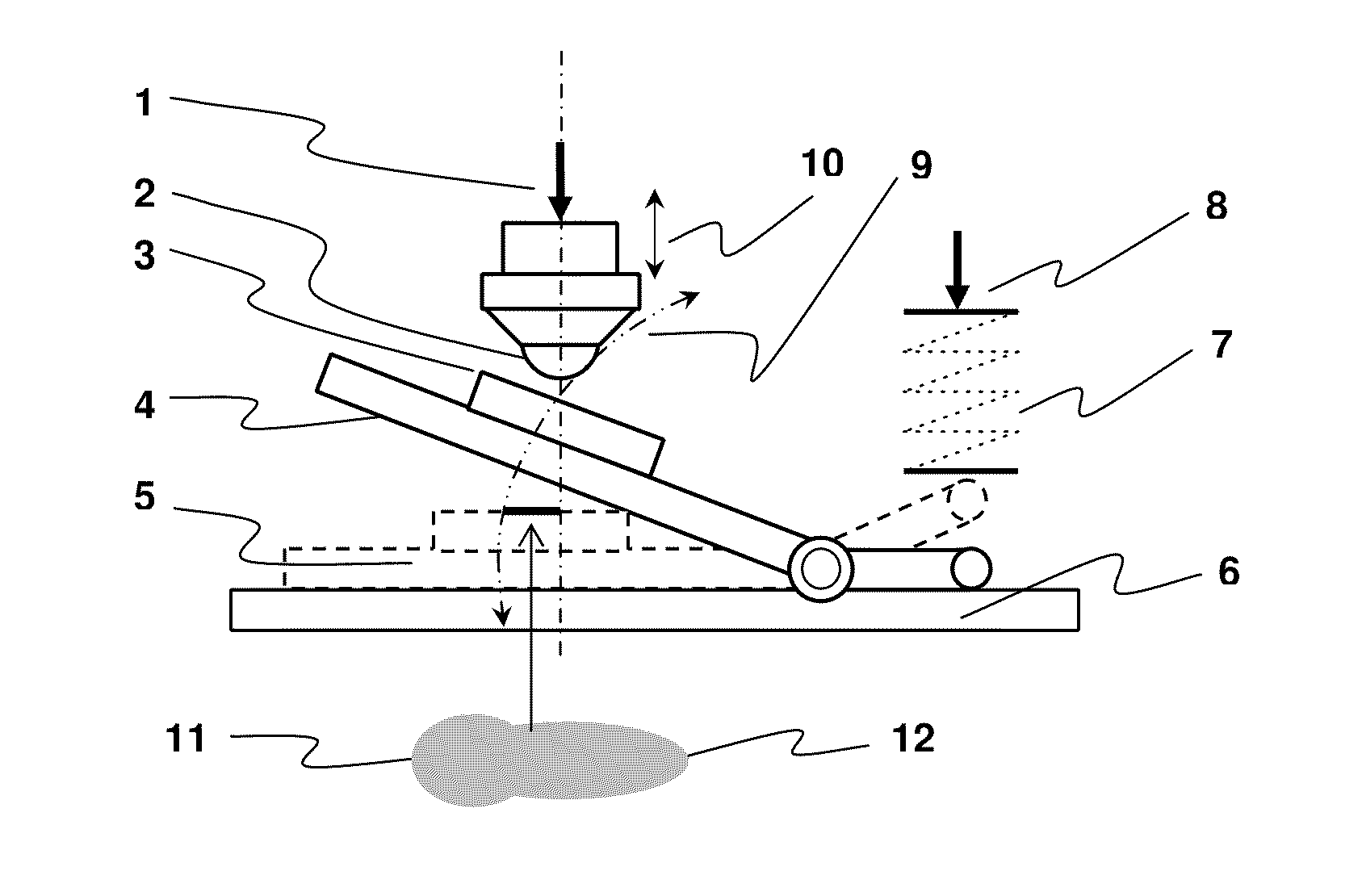
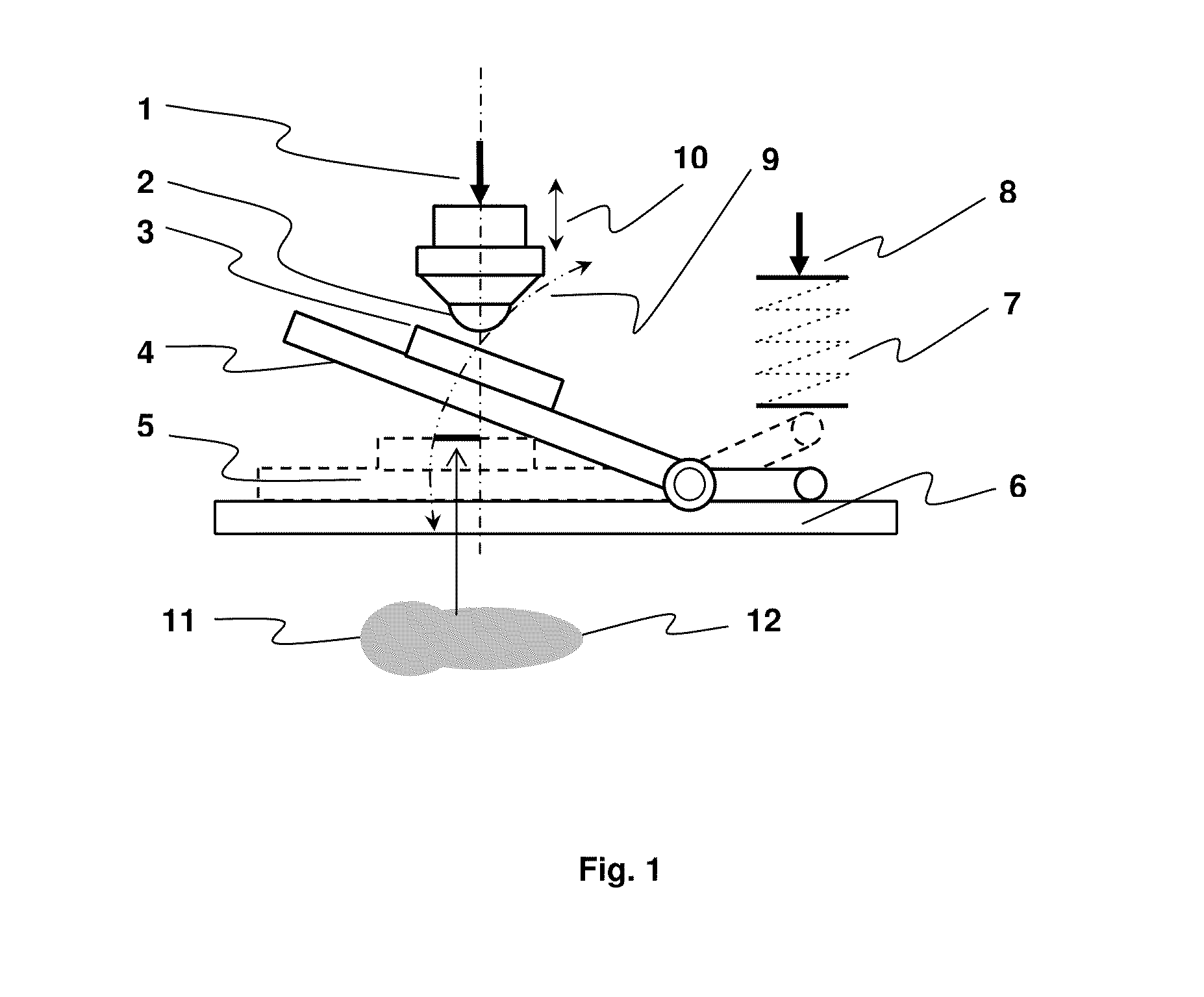
Method for preparing hydroxylapatite coating by cold spraying
InactiveCN101591777AHigh bonding strengthGood biological stabilityPressure inorganic powder coatingFull recoveryApatite
The invention discloses a method for preparing a hydroxylapatite coating by cold spraying, which belongs to the field of implant processing and preparation in biomedical material engineering. The method adopts cold spraying equipment to spray dried hydroxylapatite powder onto a matrix of a biomedical implant metal material with the surface subjected to sand blasting treatment, thereby obtaining the hydroxylapatite coating with high crystallinity and good biological stability. The method can effectively avoid the thermal decomposition of sprayed powder, namely hydroxylapatite during the processing, can reduce the non-crystallization and hydroxyl loss, has small influence on an organization structure of the material, retains a structure of the originally spayed HA powder, and does not generate impurity phases. The hydroxylapatite powder used by the sprayed powder can realize the full recovery, which saves the powder for spraying in a large quantity. The method can prepare the hydroxylapatite coating on the surfaces of implant metal materials to ensure that the surfaces of biologically inert metal matrixes have biological activity, and can prepare medical implant devices such as dental roots, artificial joints and the like.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
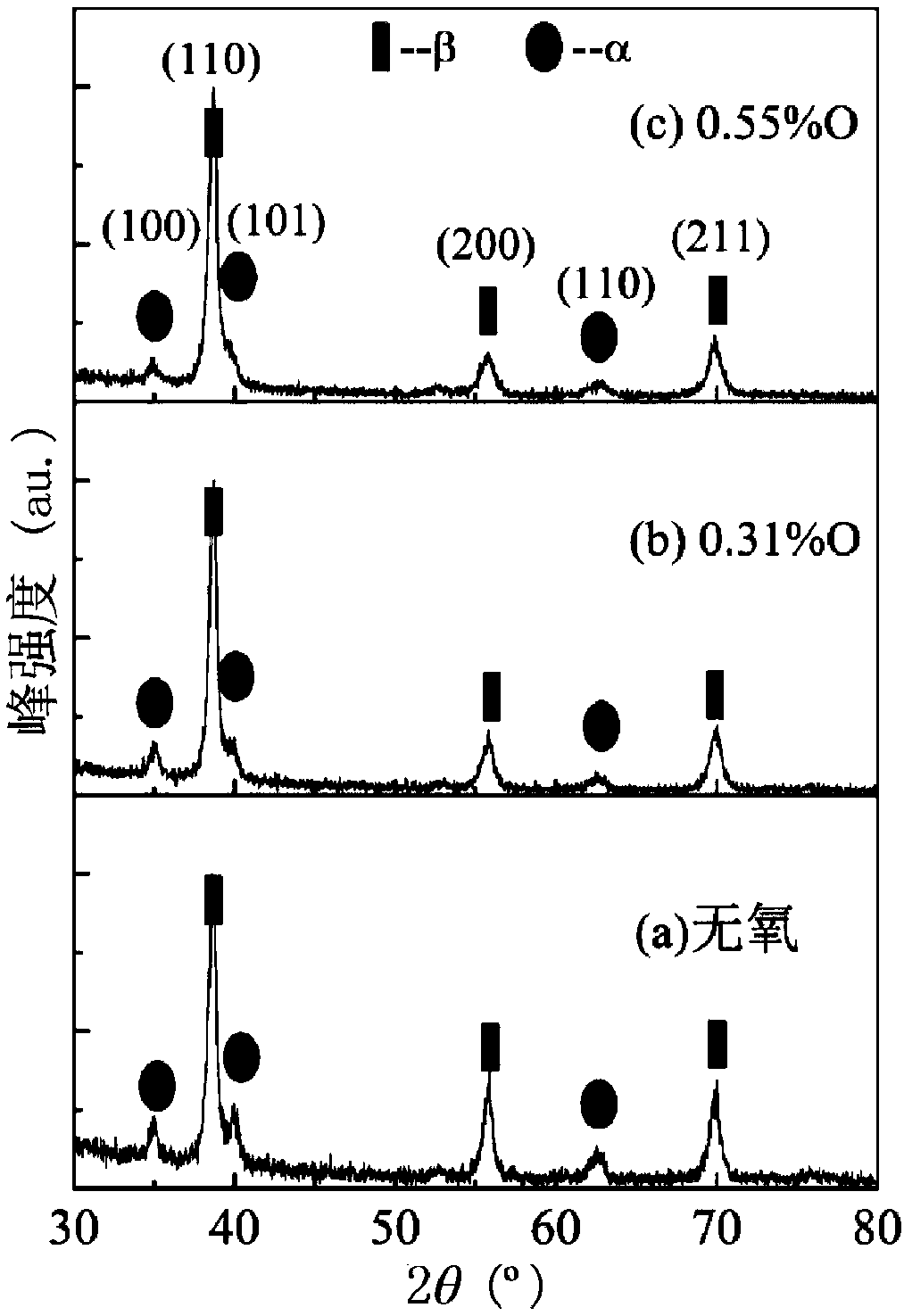
High strength high elasticity titanium alloy and preparation method
The invention relates to a high strength high elasticity titanium alloy and a preparation method. The alloy comprises the following components in percentages by weight: 31-33wt% of Nb, 4-8wt% of Zr, 2-4wt% of Sn, 0.30-0.55wt% of O (0.3wt% endpoint value is not contained) and the balance of Ti. The preparation method of the alloy comprises the follow specific steps: adopting a vacuum nonconsumableelectric-arc furnace to smelt to obtain a uniform alloy ingot, performing solution treatment at 850-950 DEG C after hot forging of a rod, and performing water cooling to room temperature; then performing cold rolling deformation processing, wherein the deformation is 80-90%; and finally, performing ageing thermal treatment, wherein the heating temperature is 400-500 DEG C and the insulating time is 1-24h. The titanium alloy provided by the invention has high strength and relatively low elasticity modulus. The elastic deformability is superior to those of various beta-titanium alloys high in elasticity. The titanium alloy is quite suitable for preparing ultralight small-sized elastic parts in the fields of aerospace, machinery and the like, and also can be applied to preparing biomedical implants.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Zn-Li-Mn-based zinc alloy and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN108315583AImprove mechanical propertiesHigh hardnessProsthesisZinc alloysMechanical property
The invention discloses a Zn-Li-Mn-based zinc alloy and a preparation method and application thereof. The Zn-Li-Mn-based zinc alloy comprises, by mass, greater than 0 and less than or equal to 1% of Li, greater than 0 and less than or equal to 1% of Mn and the balance of Zn. The Zn-Li-Mn-based zinc alloy has excellent mechanical properties, can provide long-term effective support in the human body, has excellent cell compatibility and blood compatibility and can be used for preparation of biomedical implants.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com