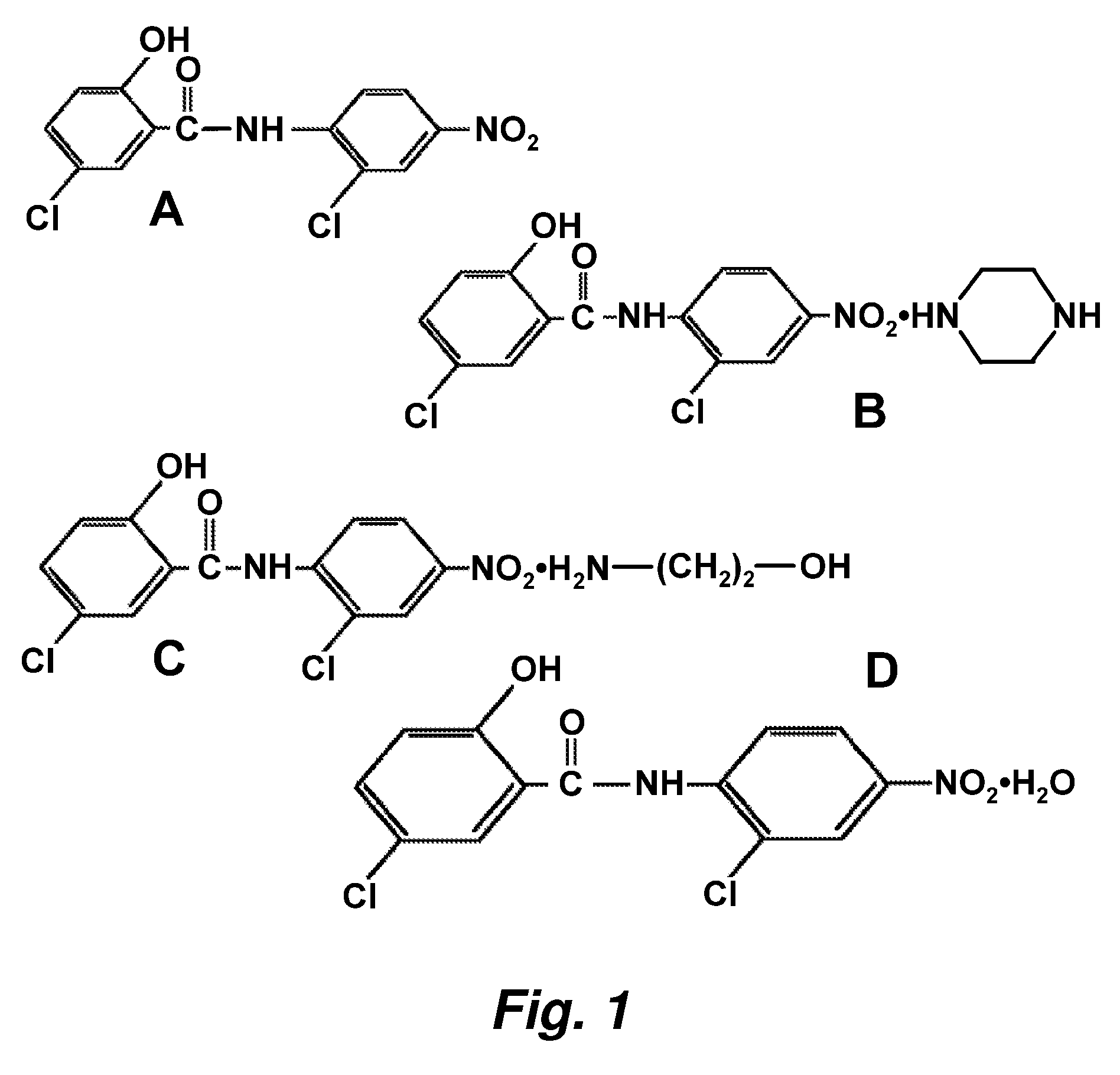
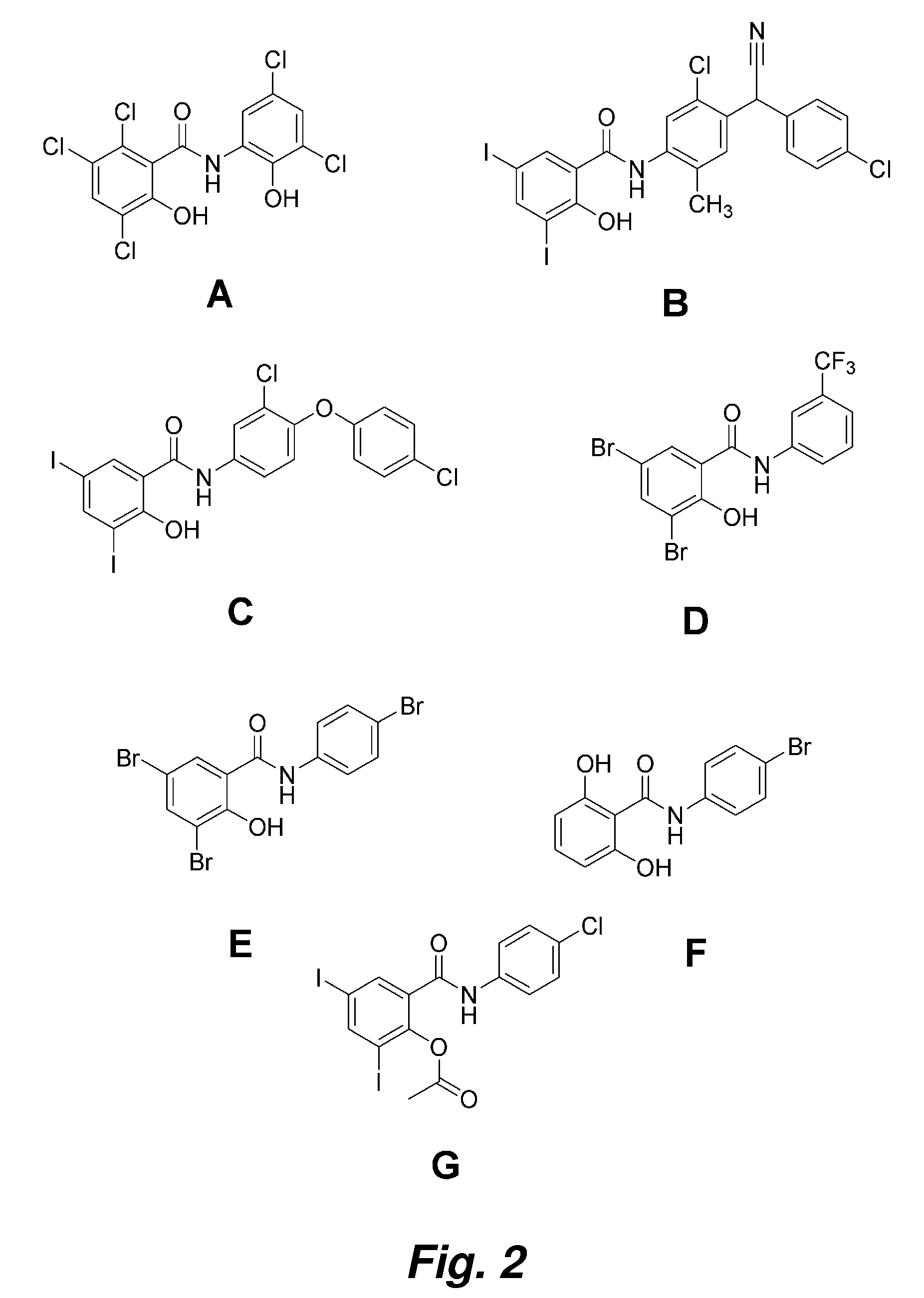
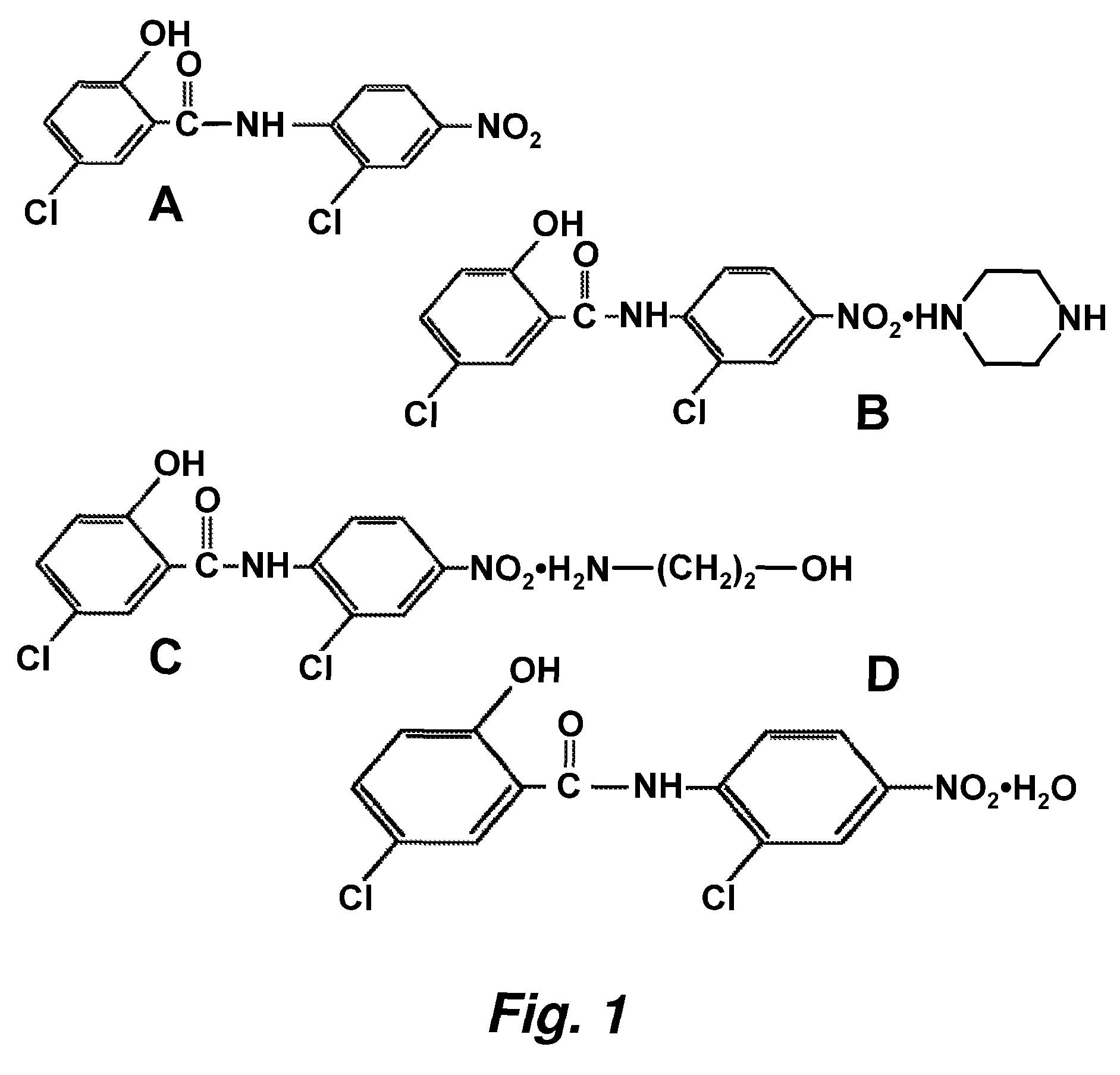
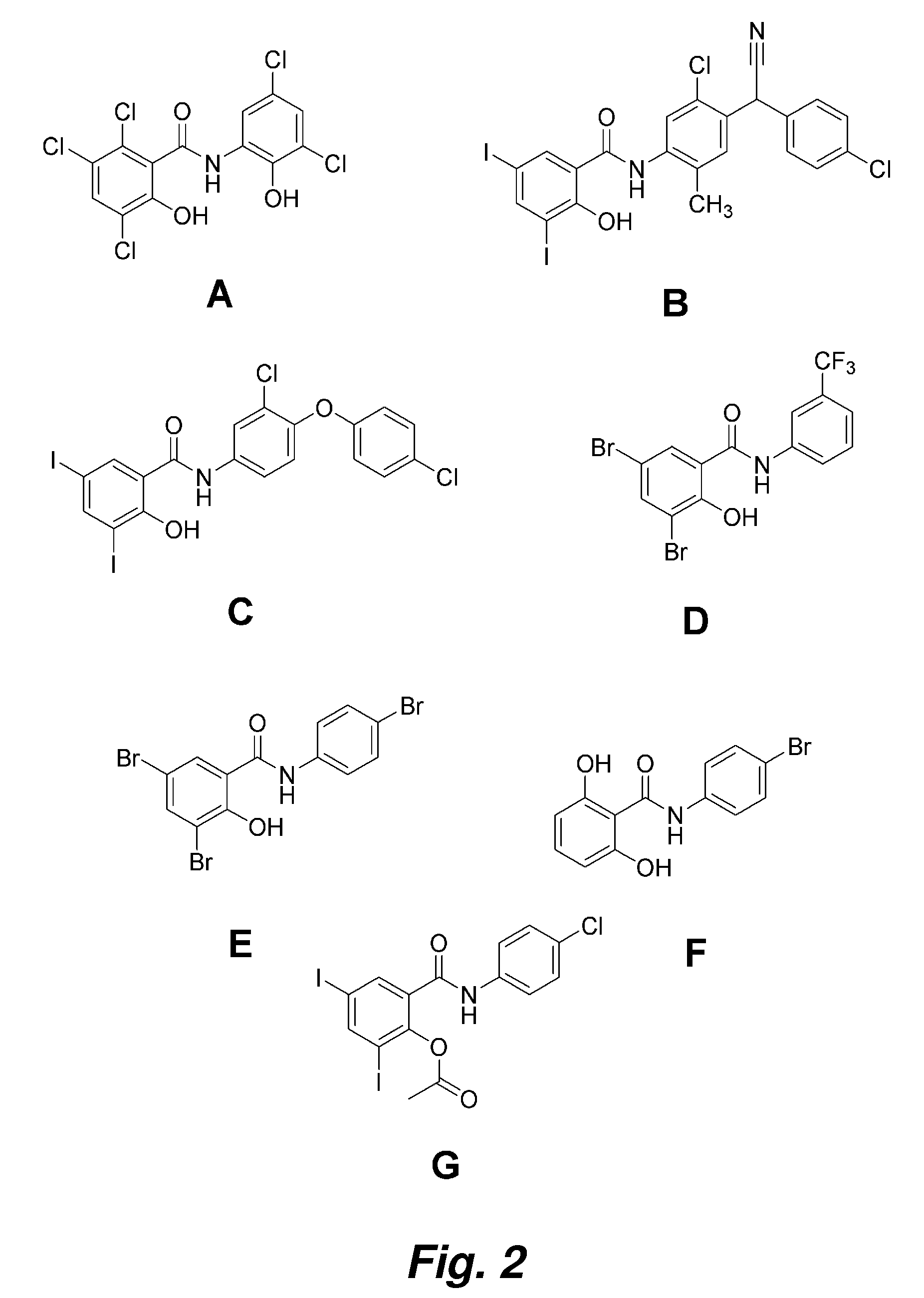
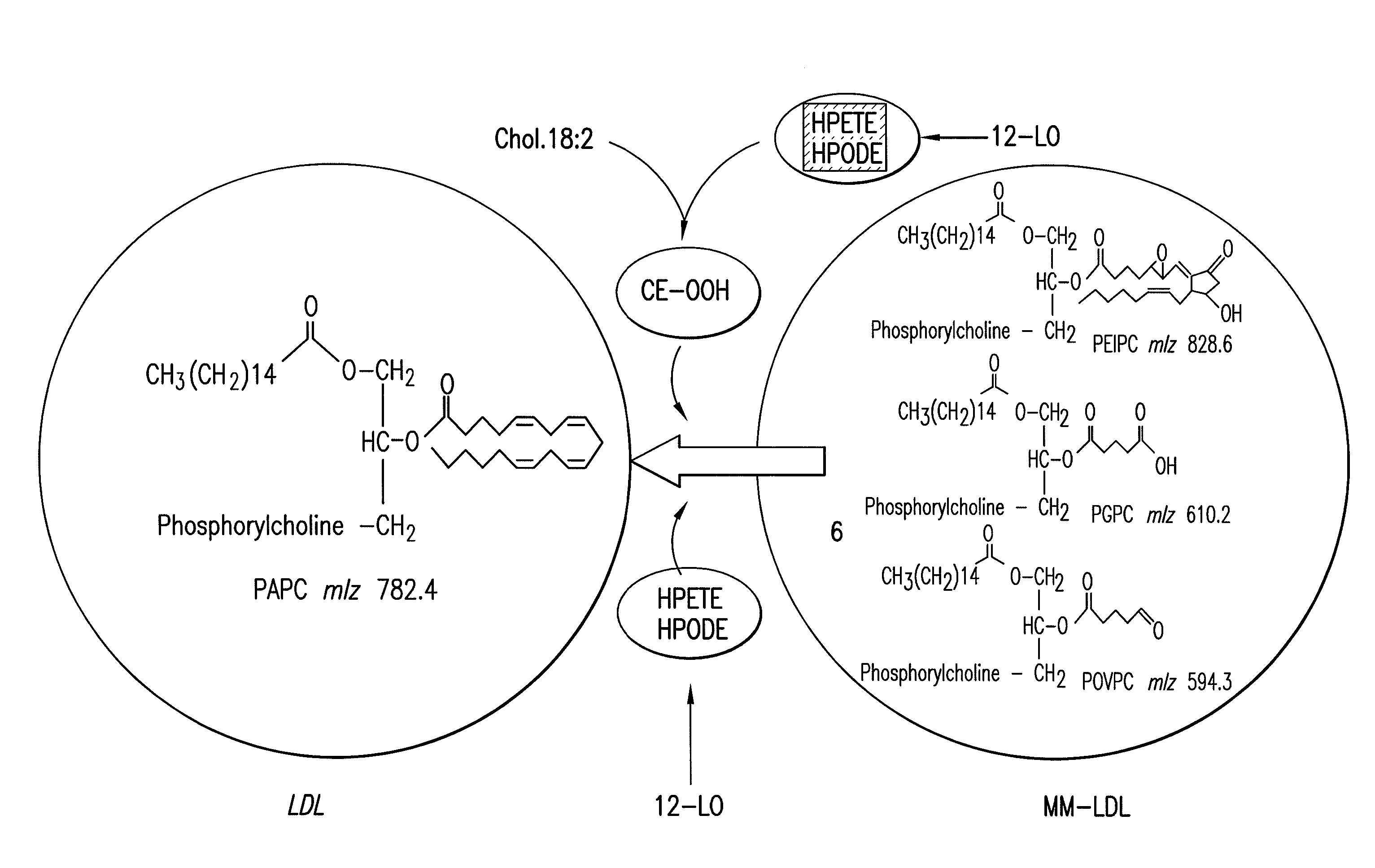
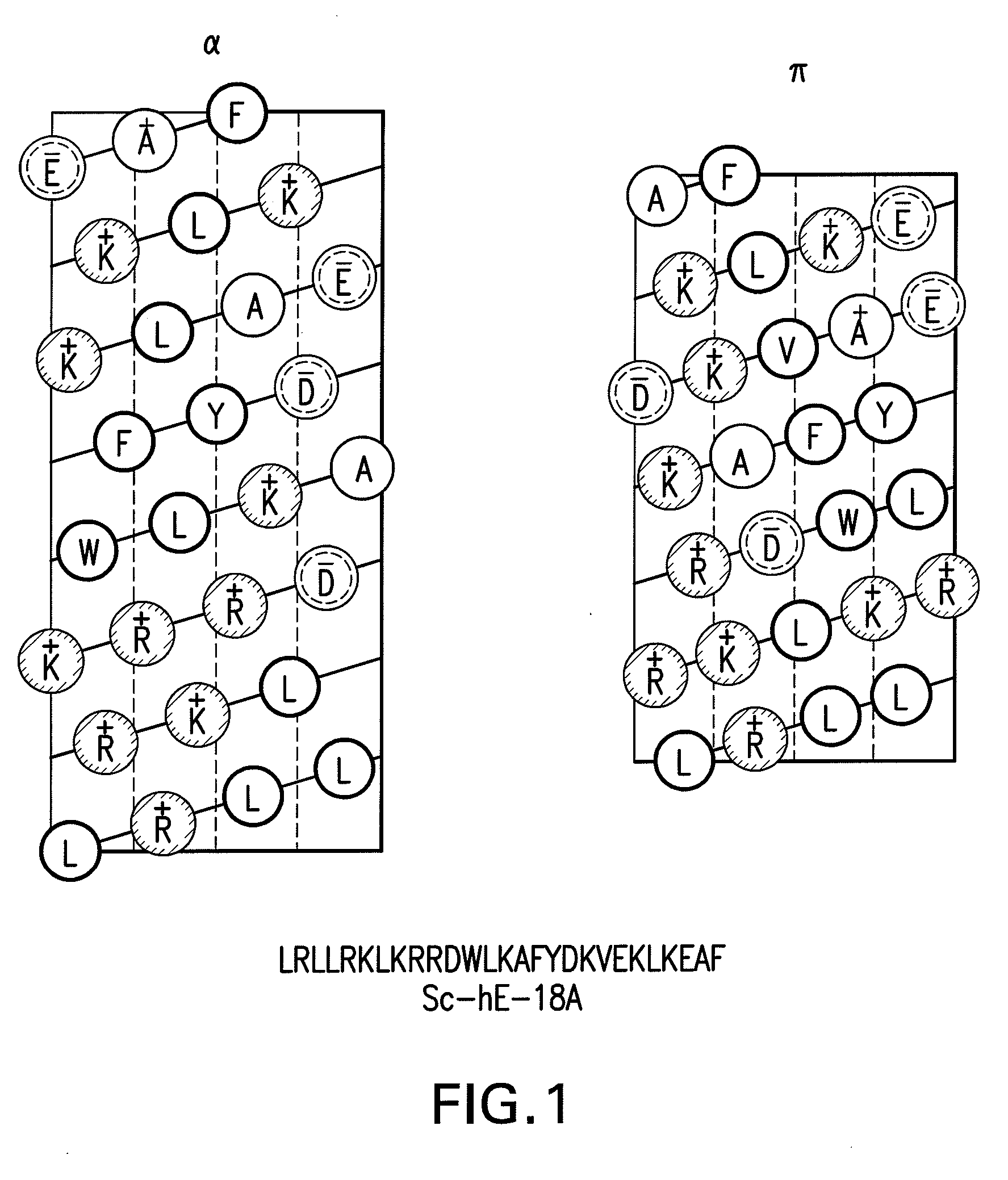
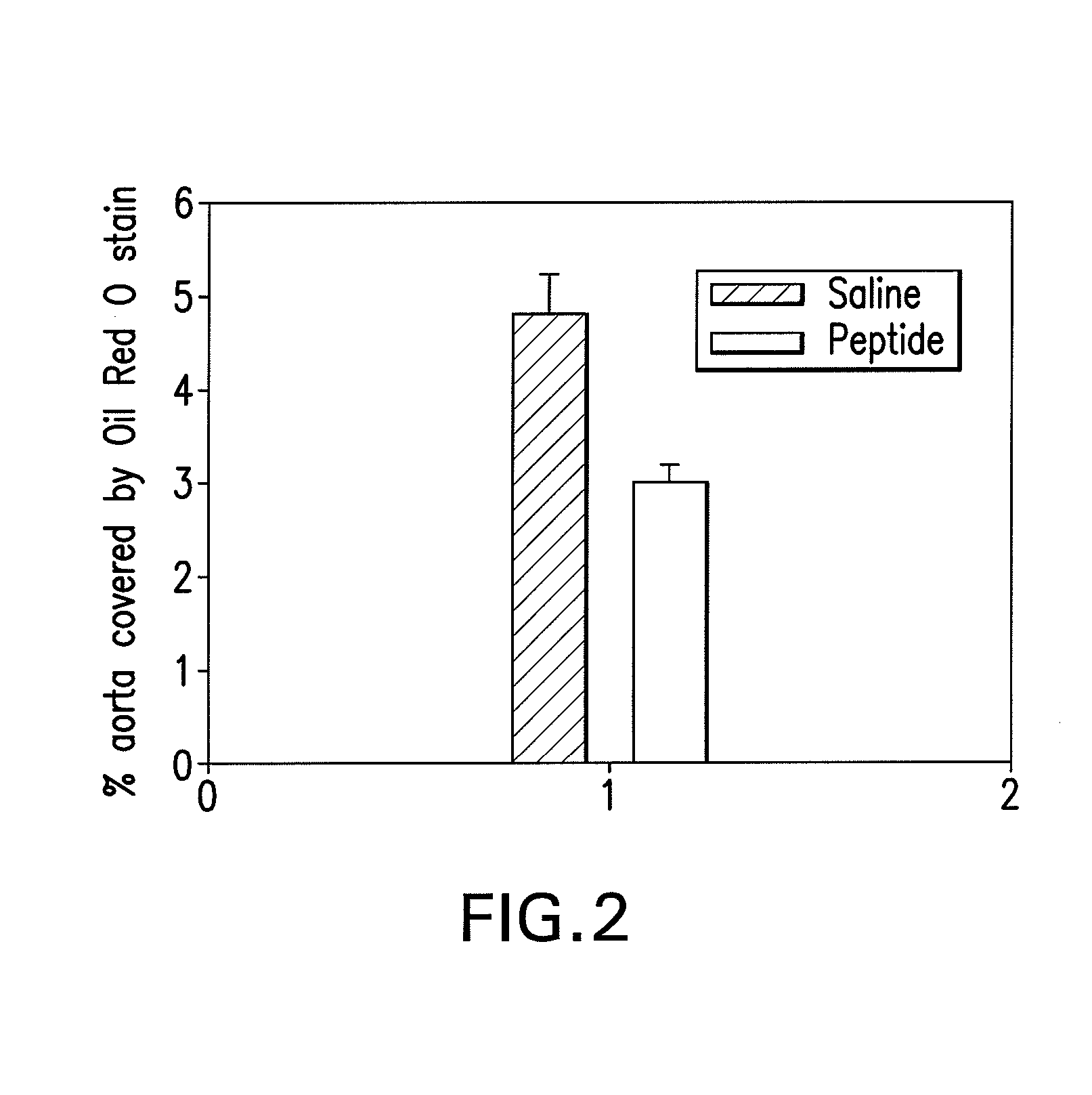
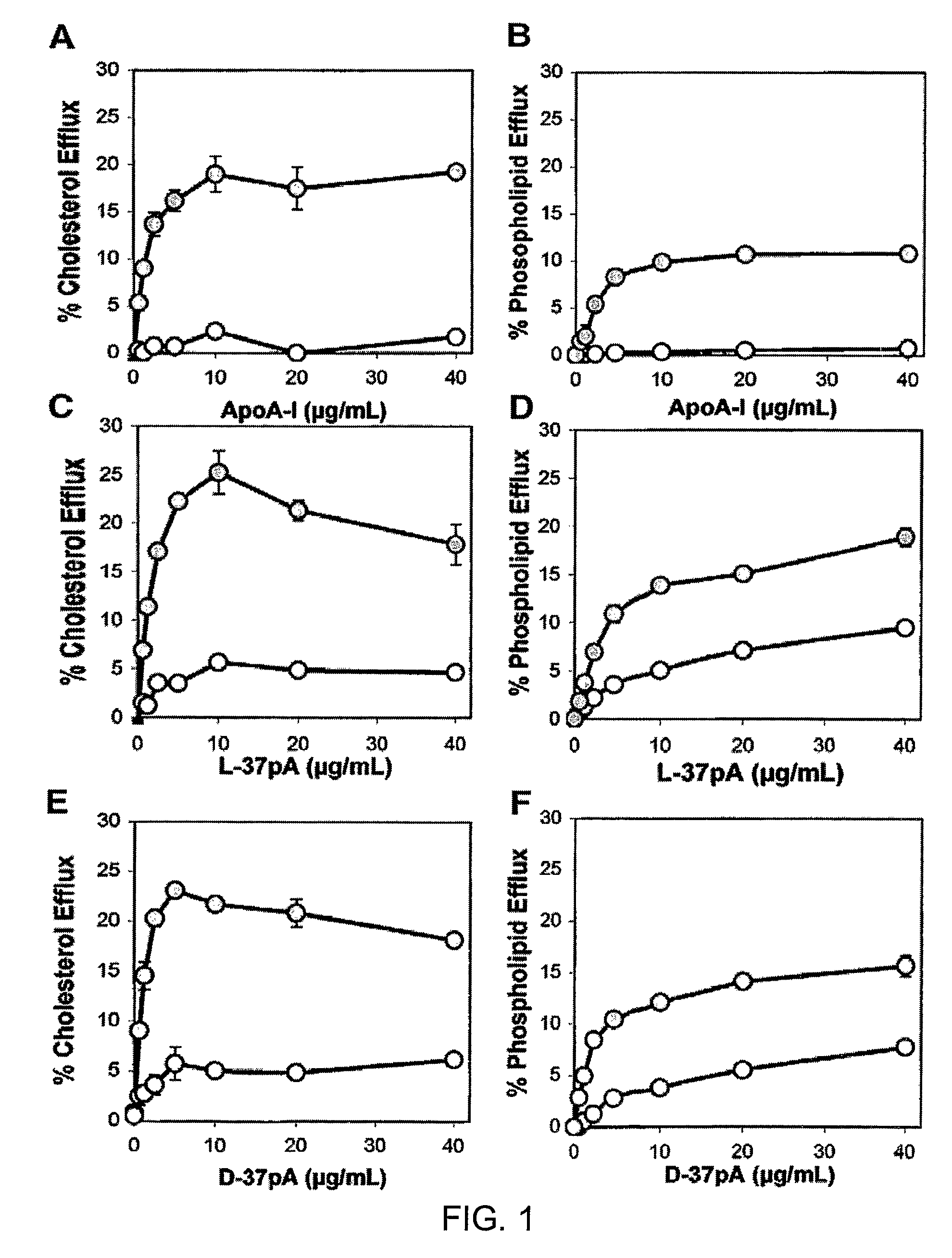
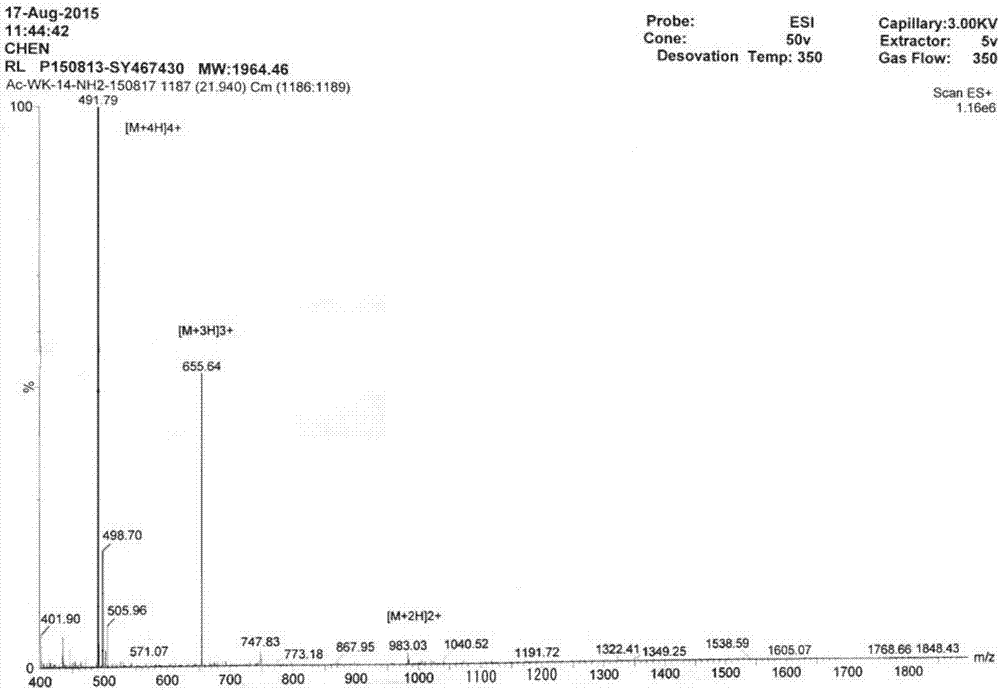
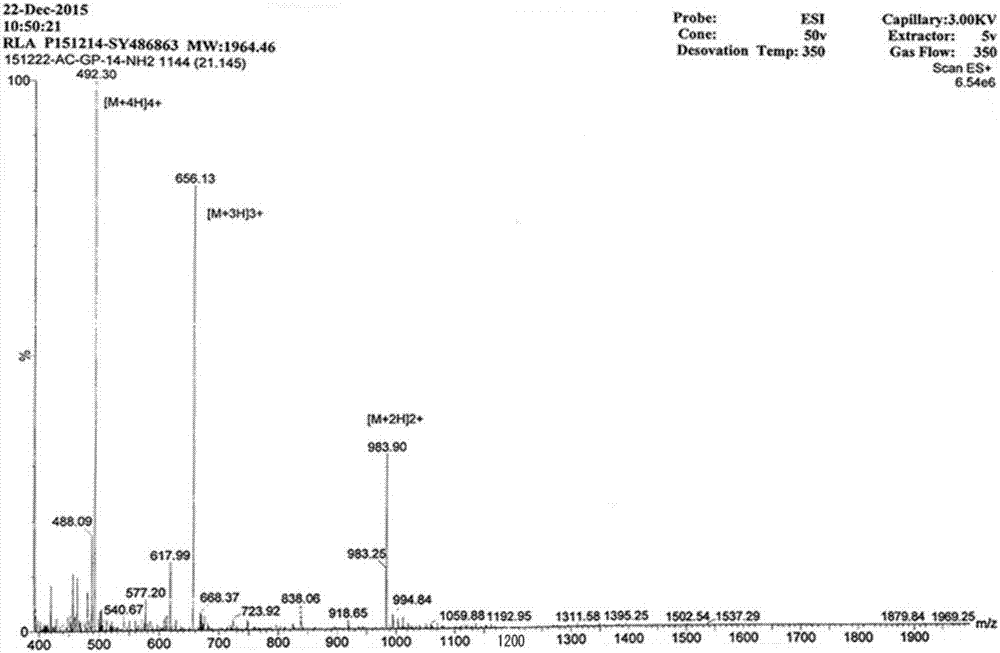
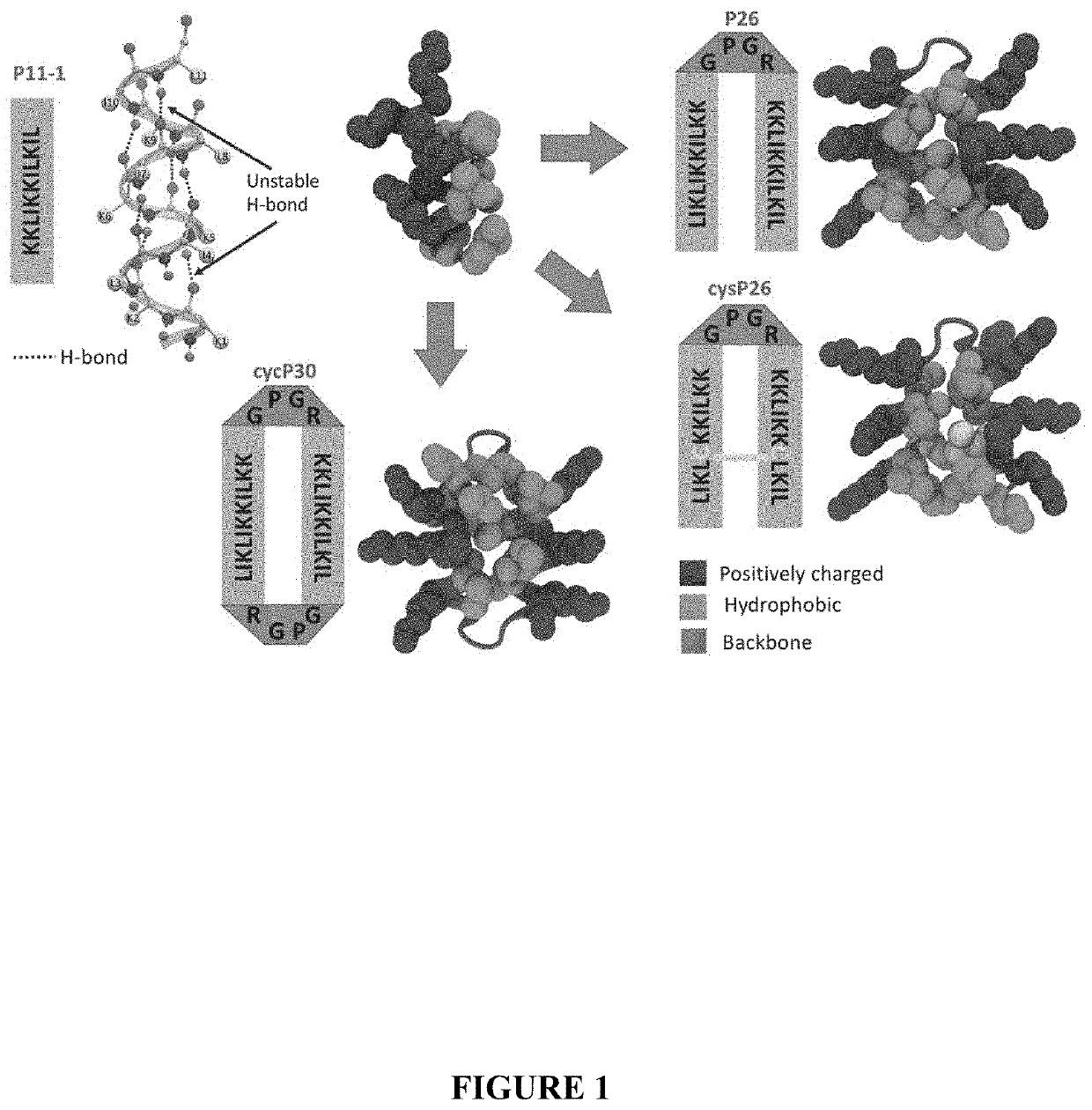
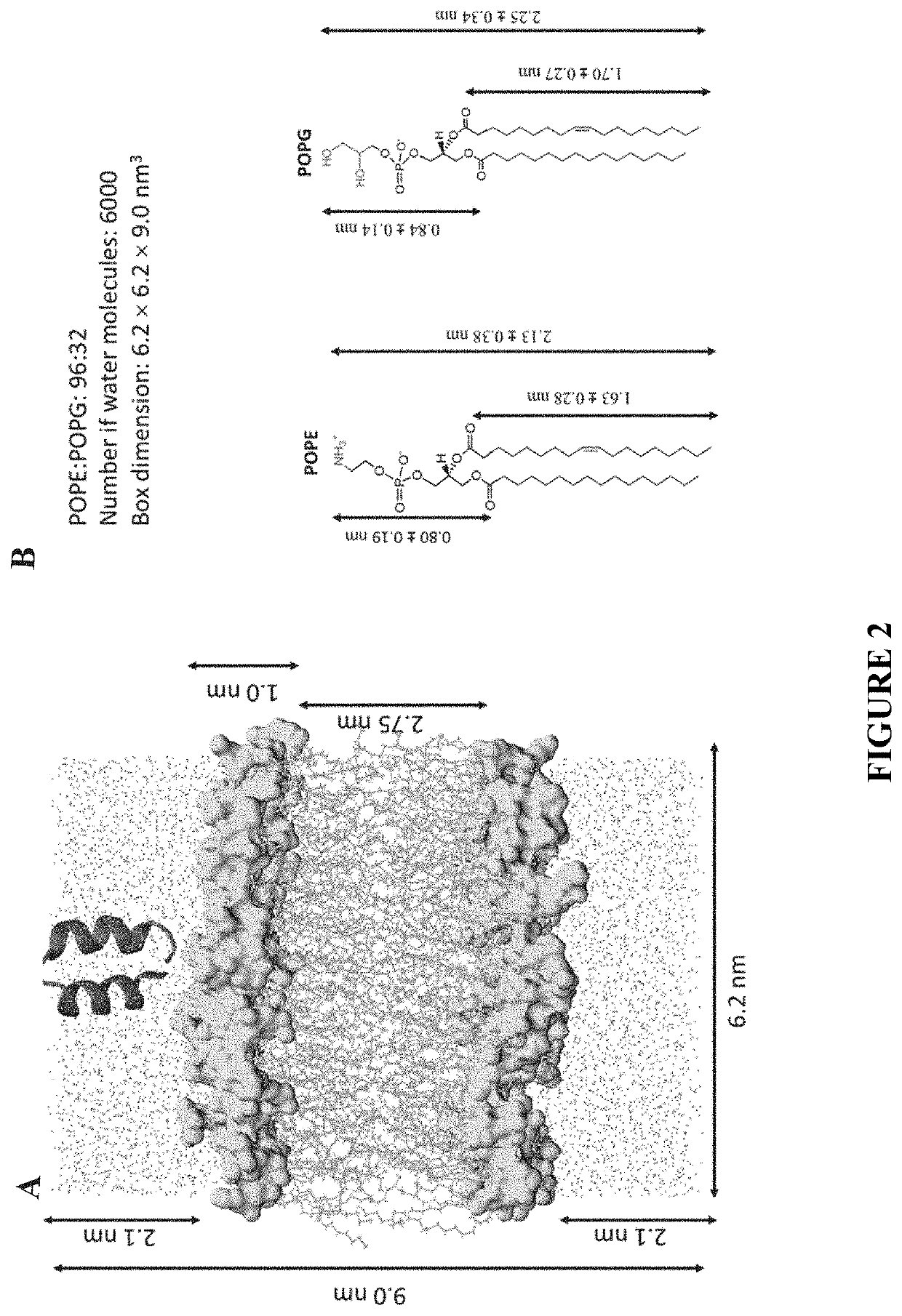
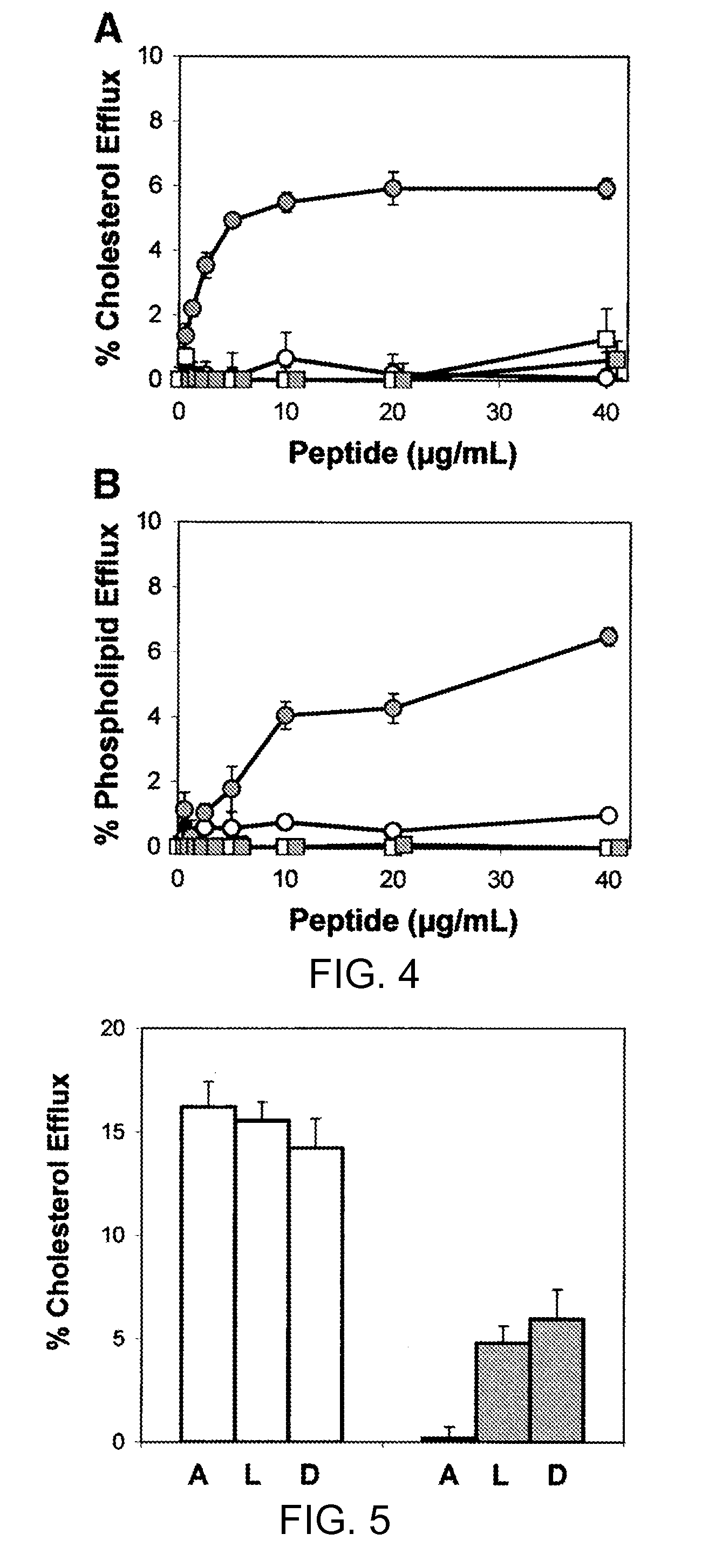
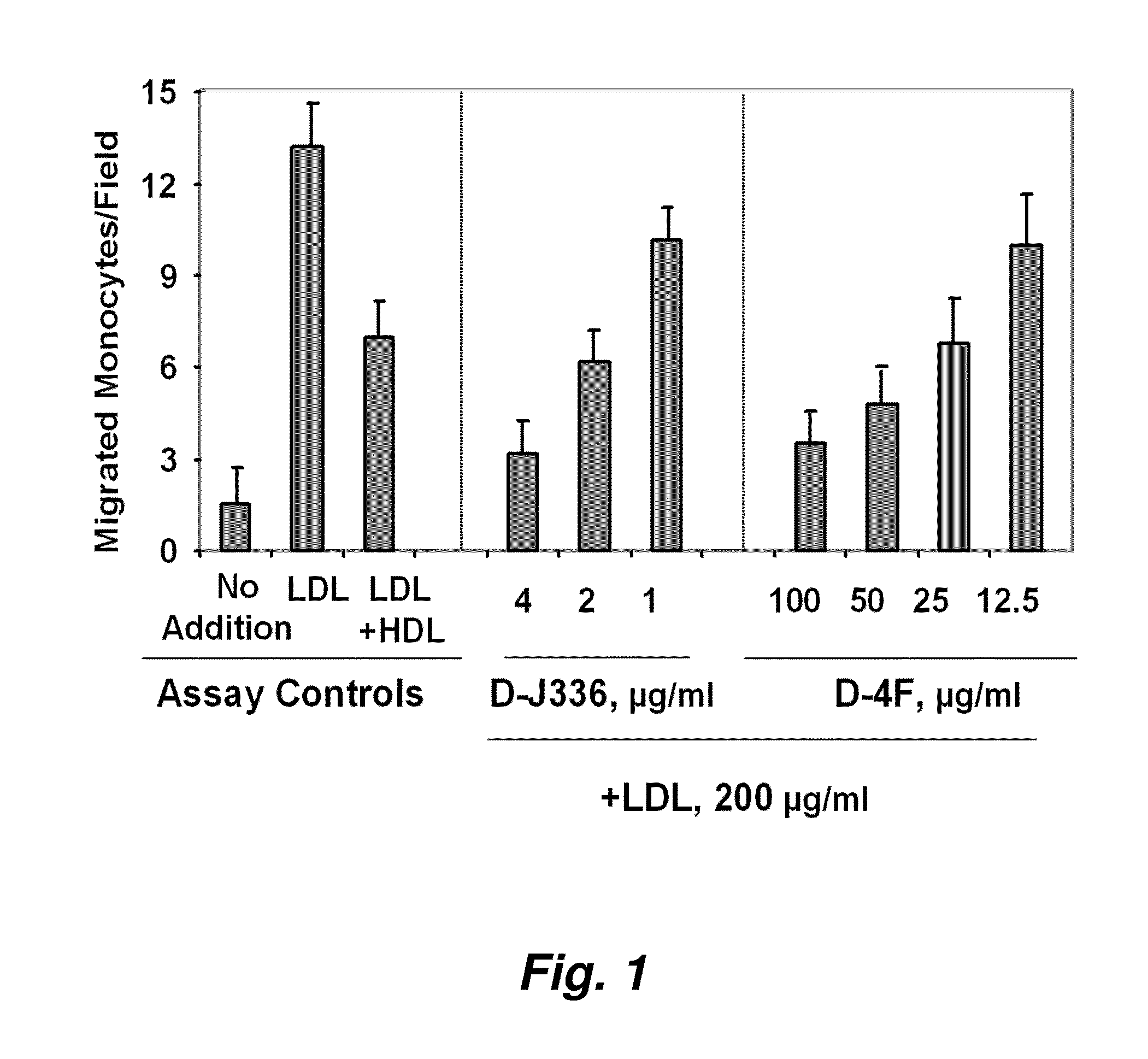
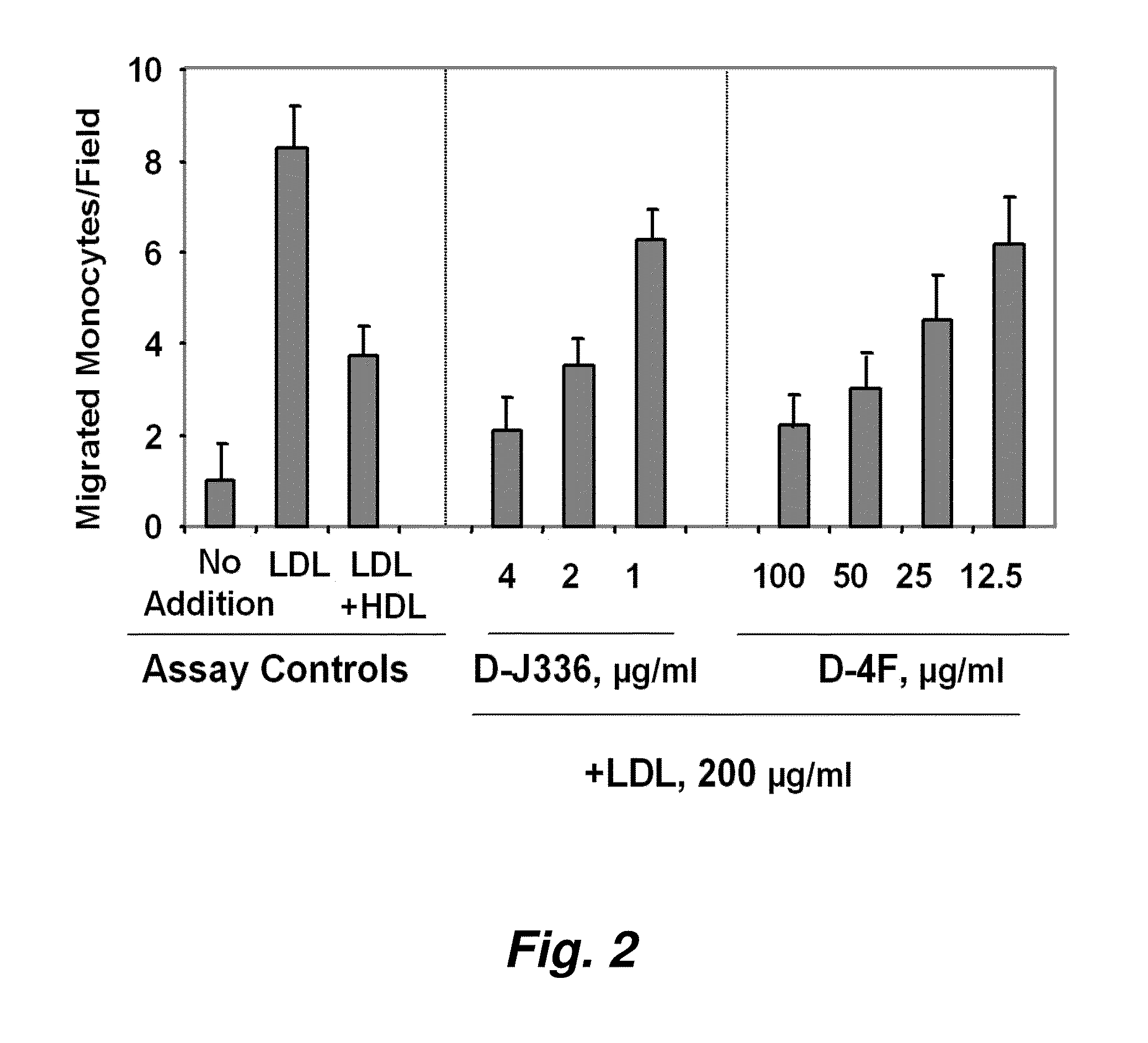
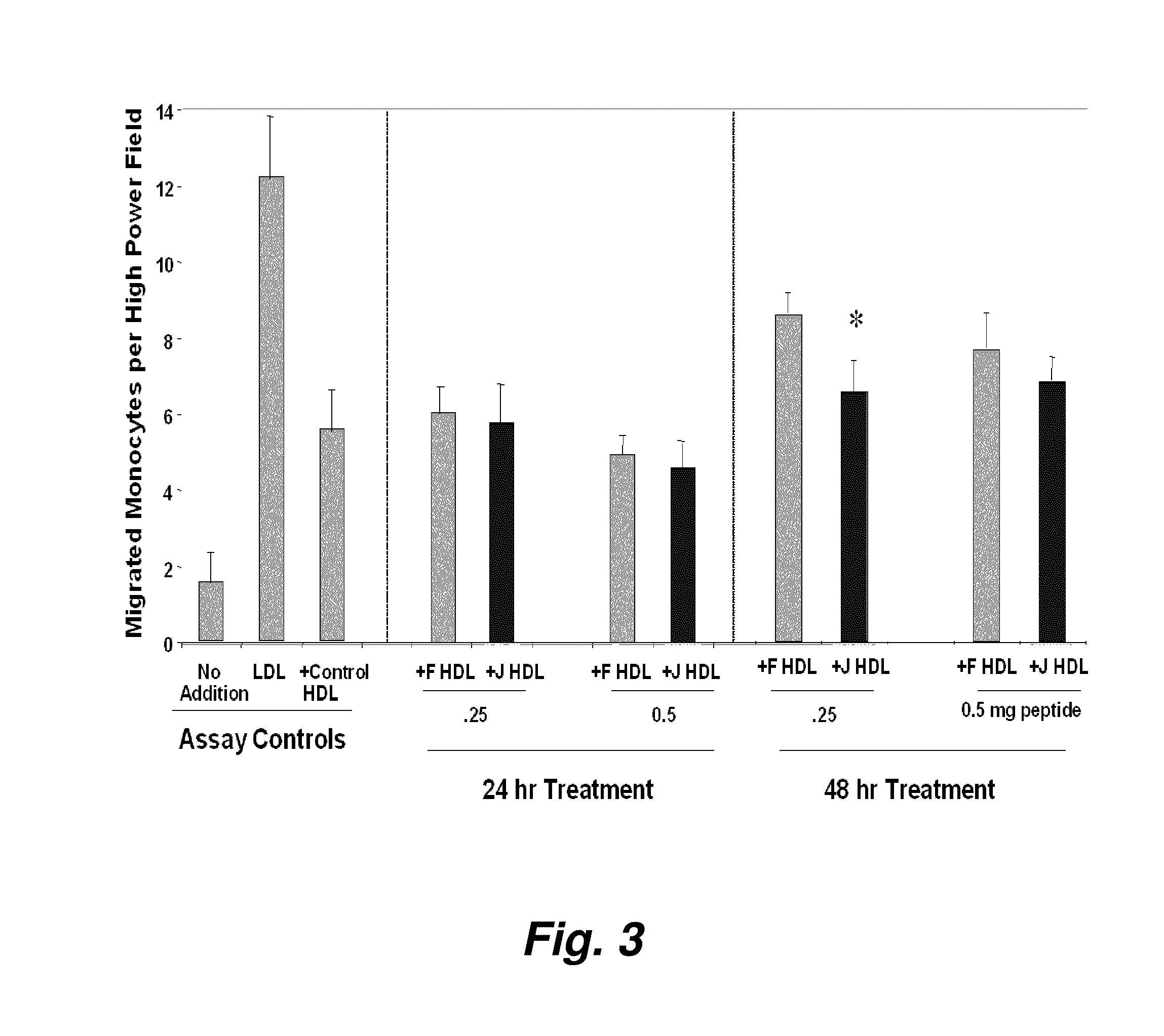
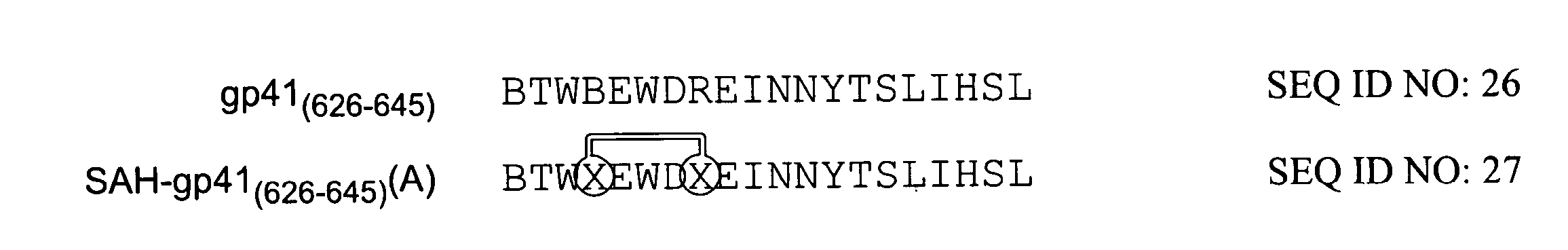Patents
Literature
62 results about "Helical peptide" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
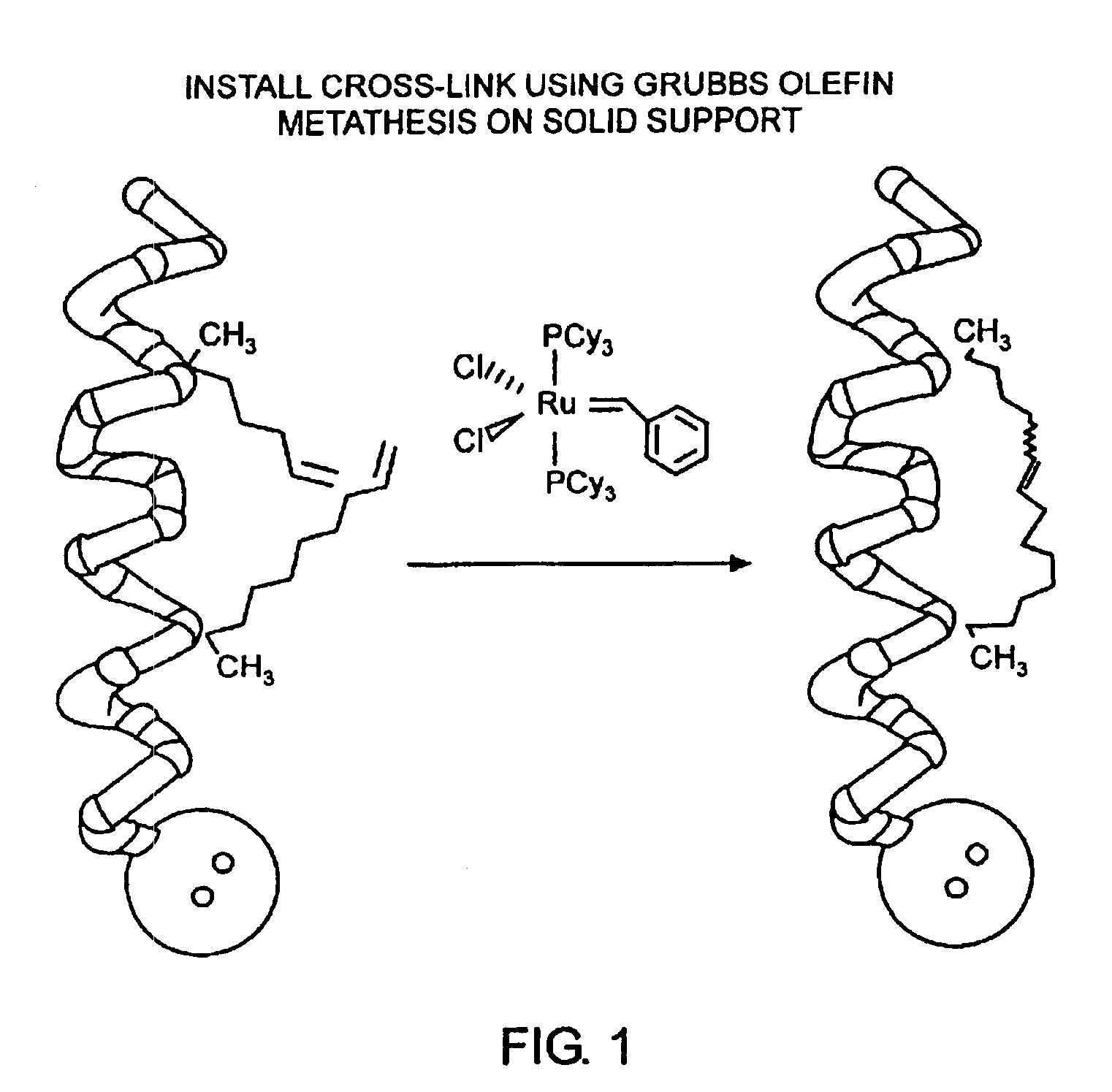
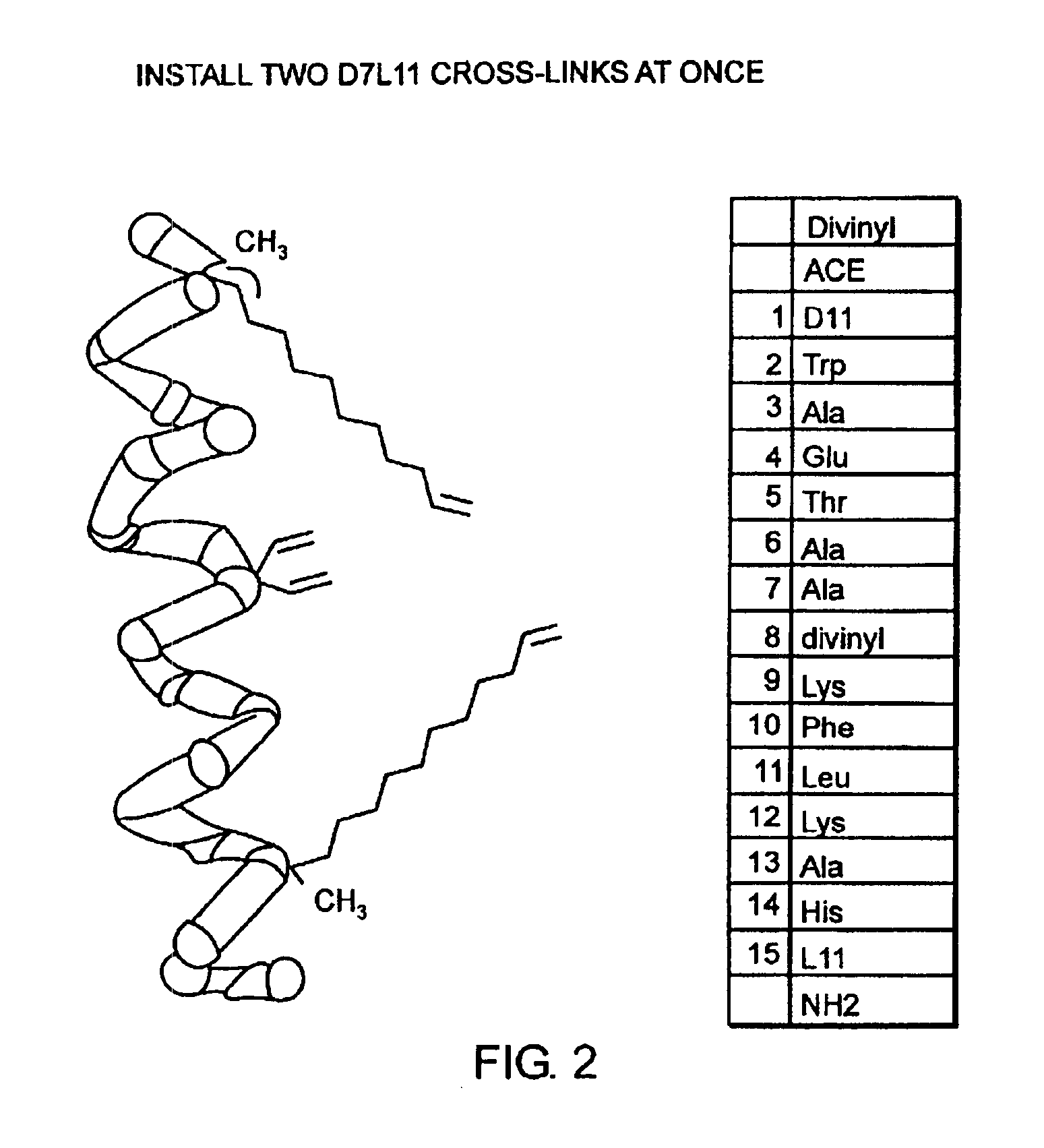
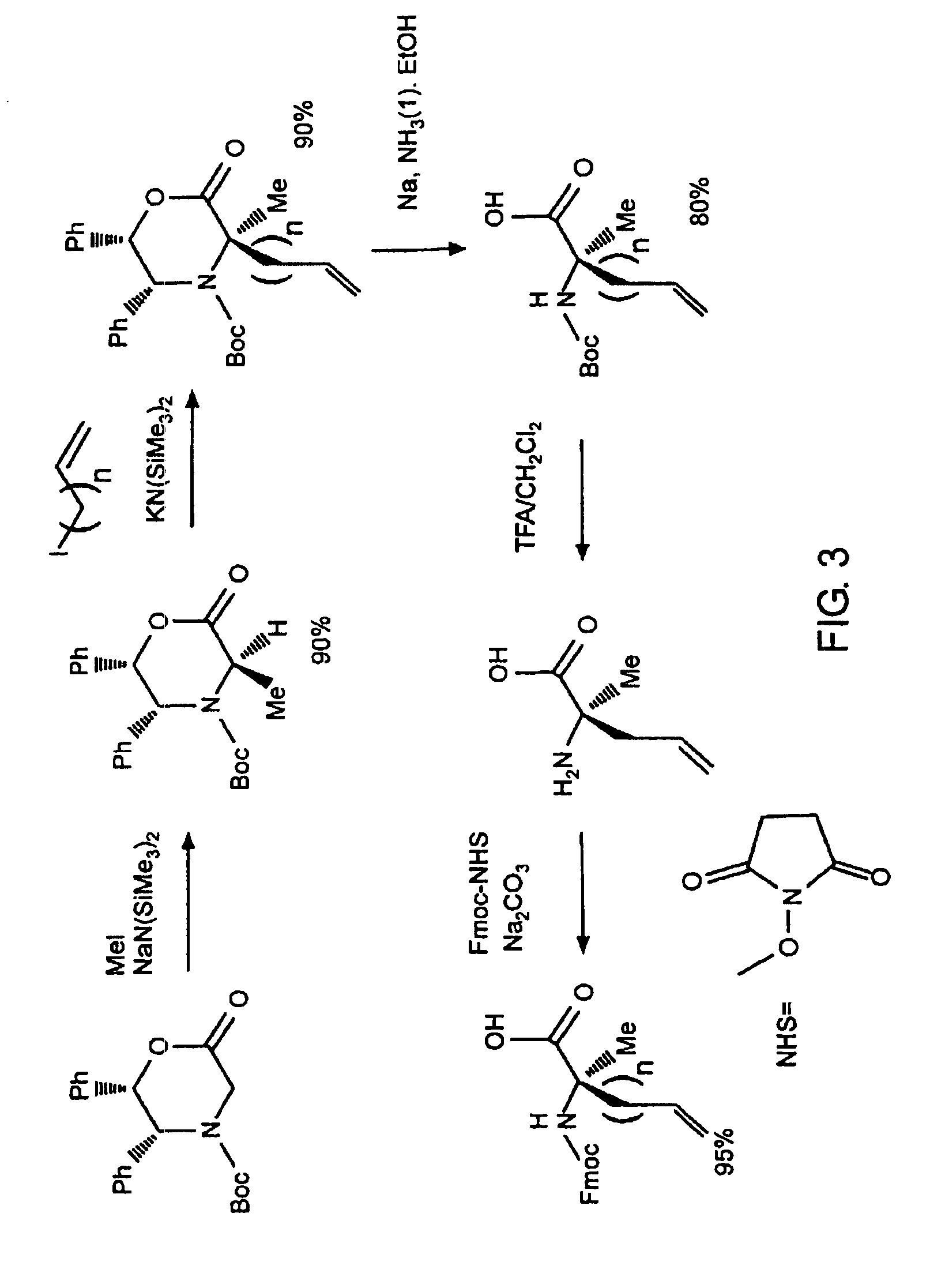
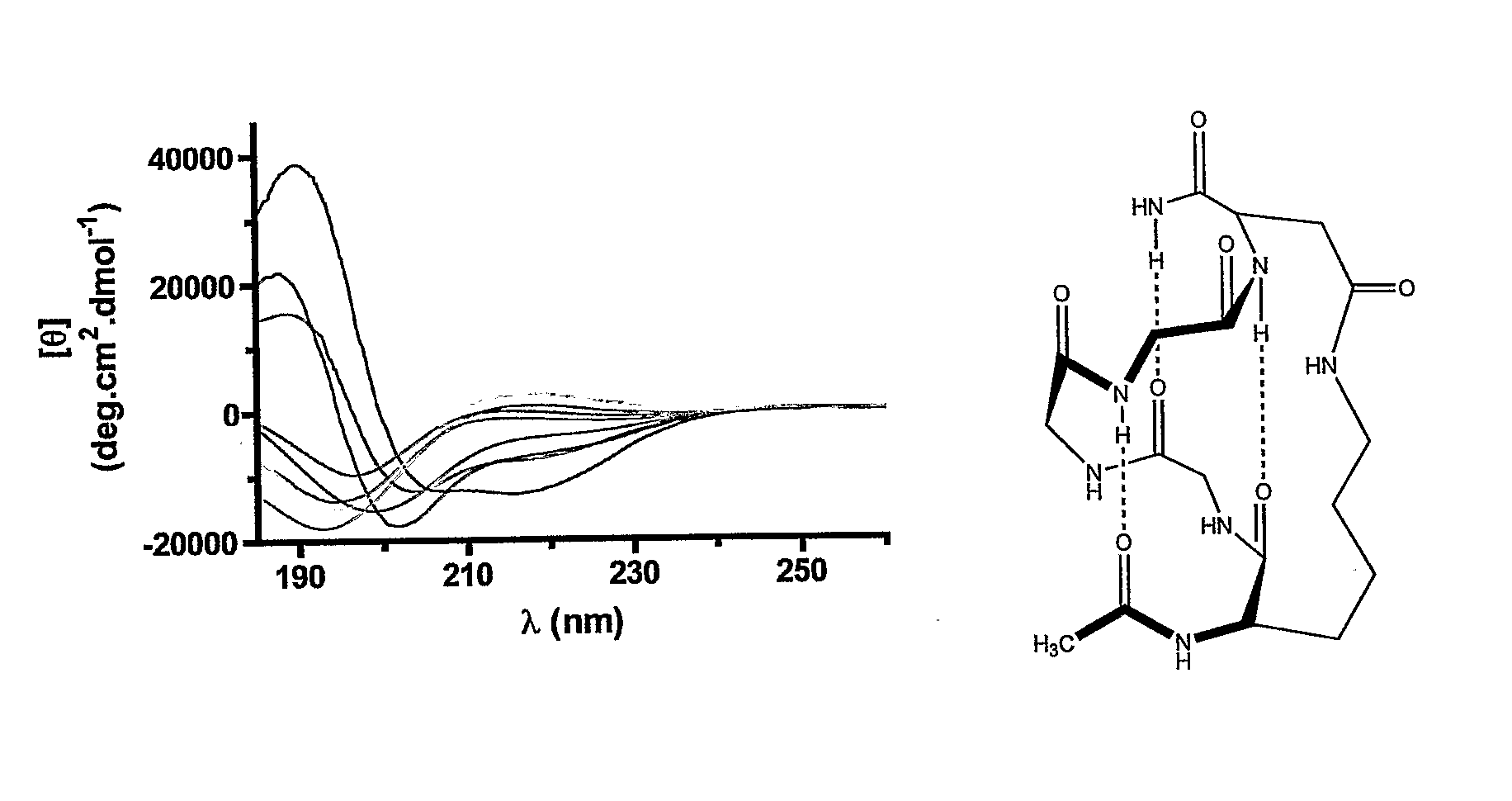
Stabilized compounds having secondary structure motifs
InactiveUS7192713B1Peptide-nucleic acidsGroup 8/9/10/18 element organic compoundsCrystallographyCarbon–carbon bond
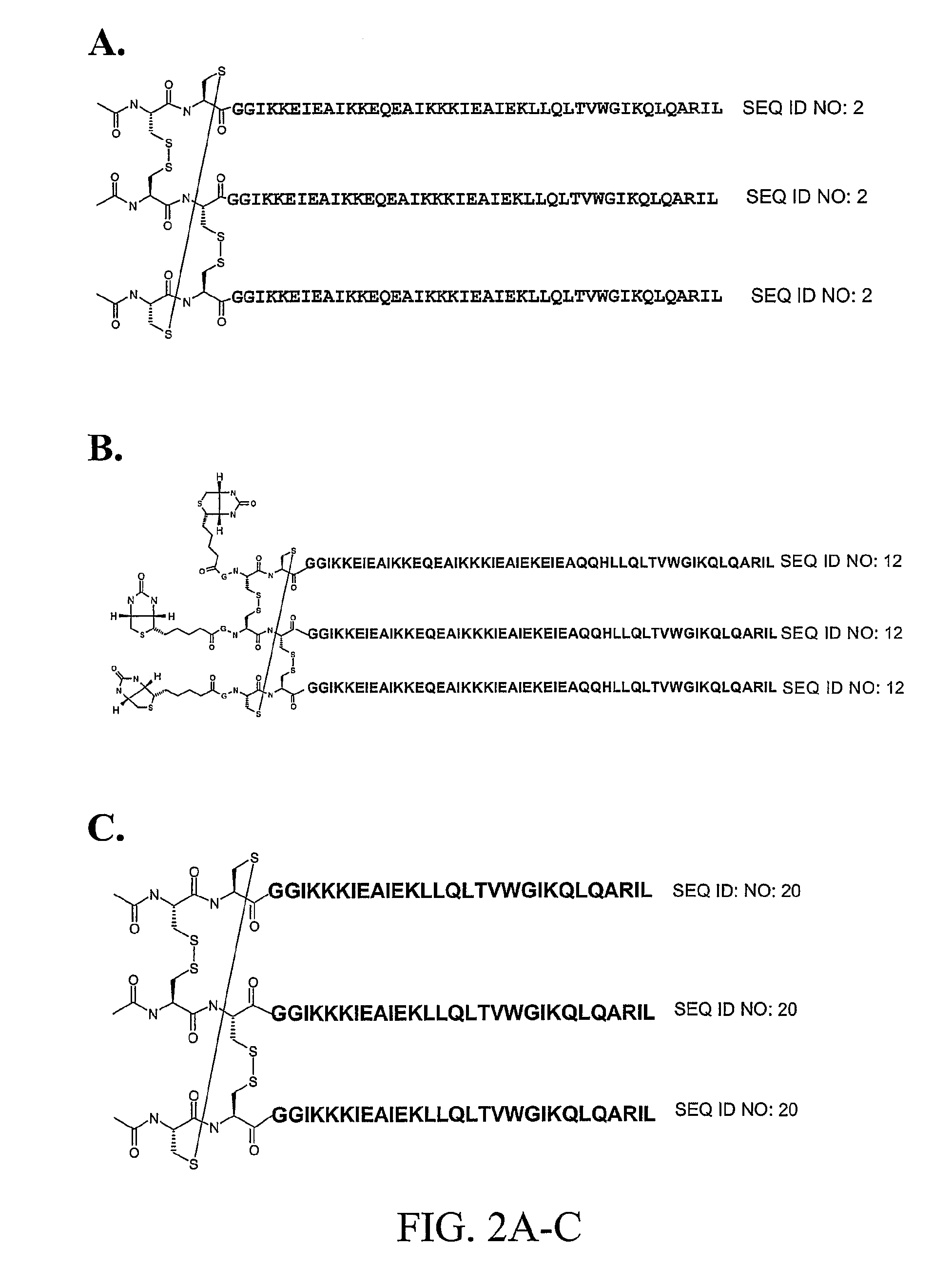
The present invention provides novel stabilized crosslinked compounds having secondary structure motifs, libraries of these novel compounds, and methods for the synthesis of these compounds libraries thereof. The synthesis of these novel stabilized compounds involves (1) synthesizing a peptide from a selected number of natural or non-natural amino acids, wherein said peptide comprises at least two moieties capable of undergoing reaction to promote carbon-carbon bond formation; and (2) contacting said peptide with a reagent to generate at least one crosslinker and to effect stabilization of a secondary structure motif. The present invention, in a preferred embodiment, provides stabilized p53 donor helical peptides. Additionally, the present invention provides methods for disrupting the p53 / MDM2 binding interaction comprising (1) providing a crosslinked stabilized α-helical structure; and (2) contacting said crosslinked stabilized α-helical structure with MDM2.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
Alpha Helical Mimics, Their Uses and Methods For Their Production
ActiveUS20080242598A1Enhance stability and bioavailability and activityImprove bioavailabilityNervous disorderDepsipeptidesMacrocyclic peptideAmino acid side chain
This invention discloses short chain peptides that have been constrained to adopt an alpha helical conformation and their use as alpha helical scaffolds for directing amino acid side chains into positions analogous to those found in longer chain alpha helical peptides and for attaching peptidic or non-peptidic appendages in order to mimic side chains of longer alpha helical peptides. More particularly the invention discloses alpha helical cyclic pentapeptides and their use as alpha helical scaffolds or macrocyclic alpha helical modules, either alone, or within longer chain peptides or attached to other macrocyclic peptides or attached to non-peptidic structures, for the purpose of mimicking naturally occurring peptides or proteins, and as agonists or antagonists of the biological activity of naturally-occurring peptides or proteins or for the preparation of new materials.
Owner:THE UNIV OF QUEENSLAND
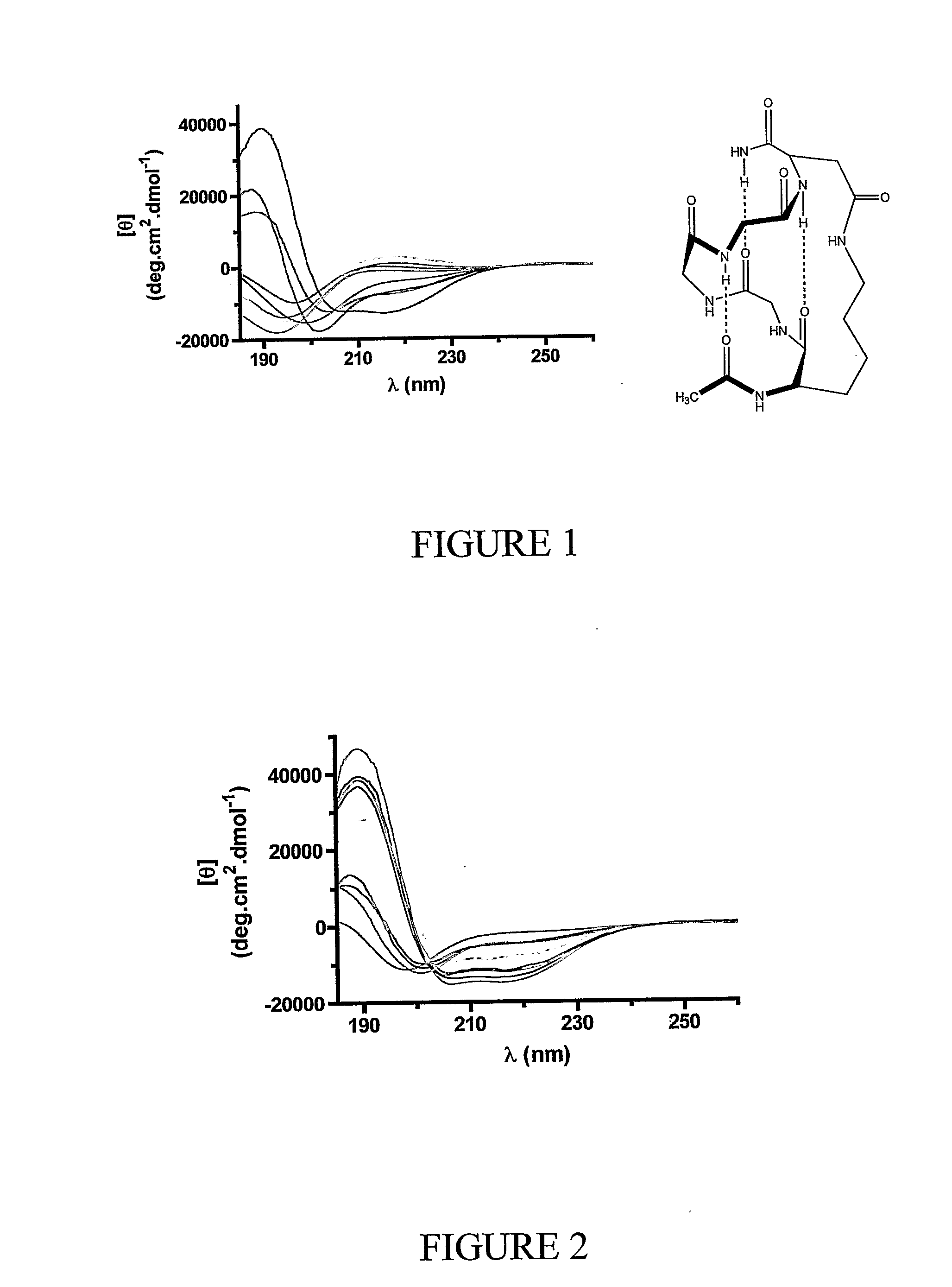
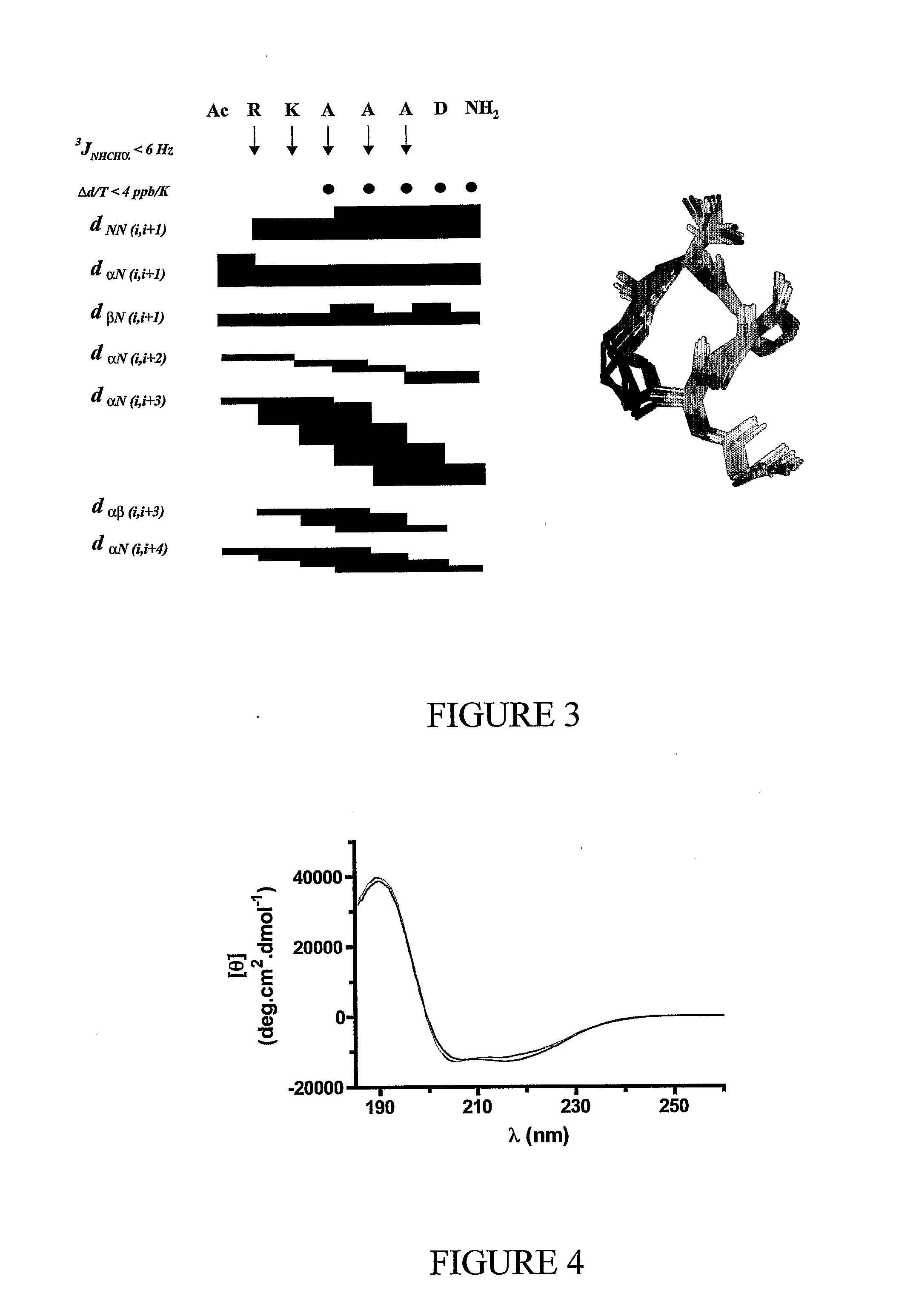
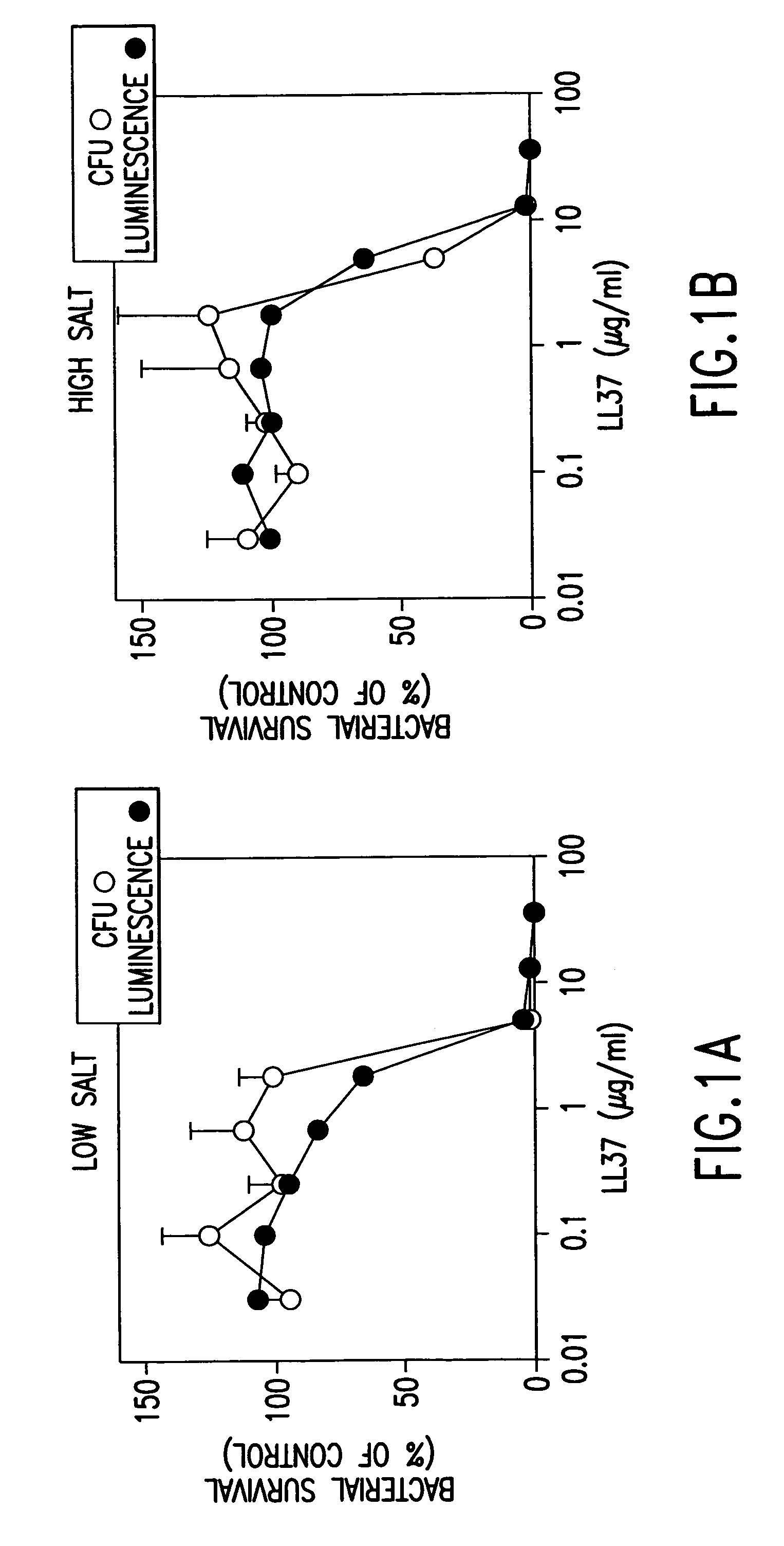
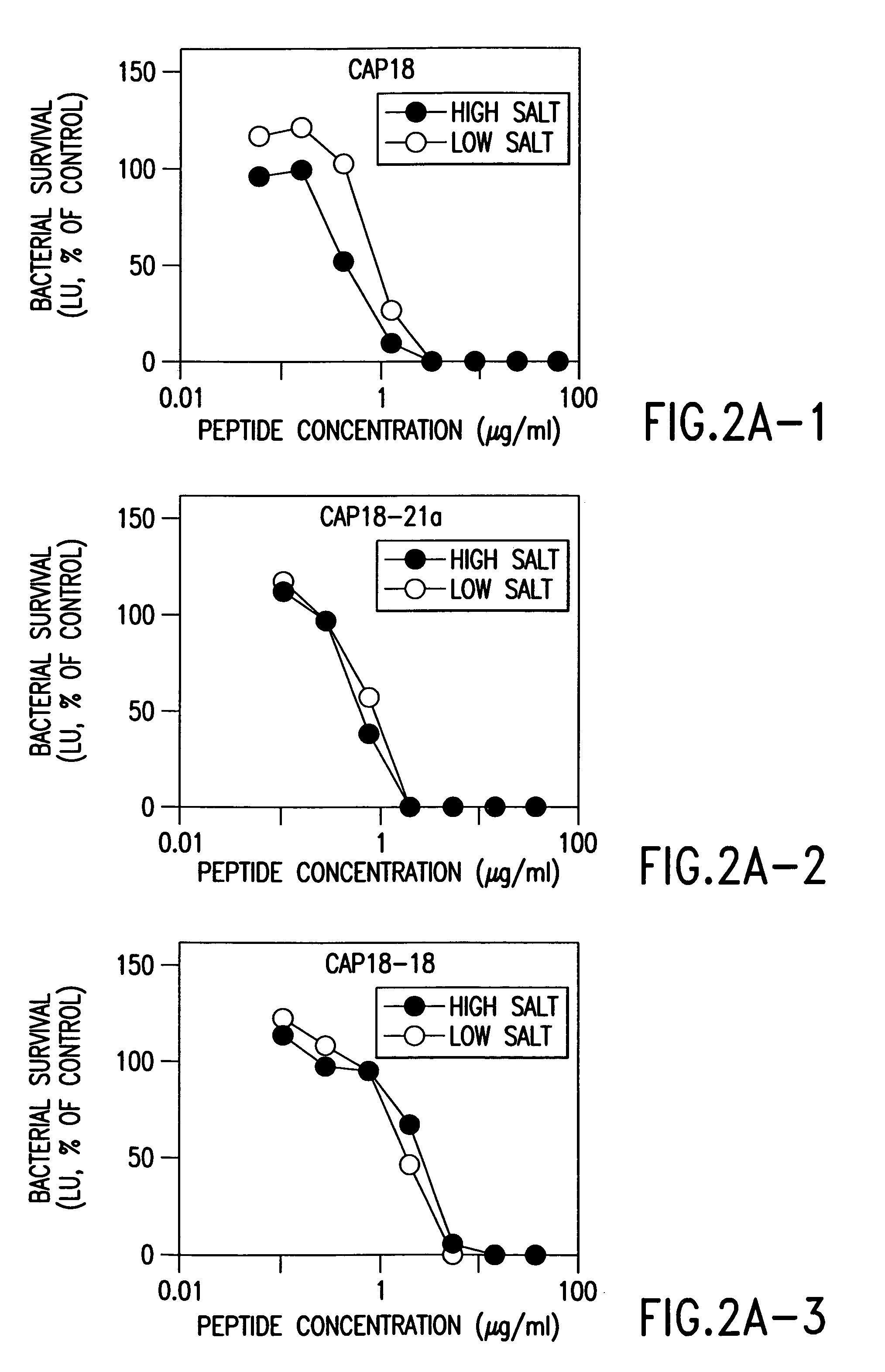
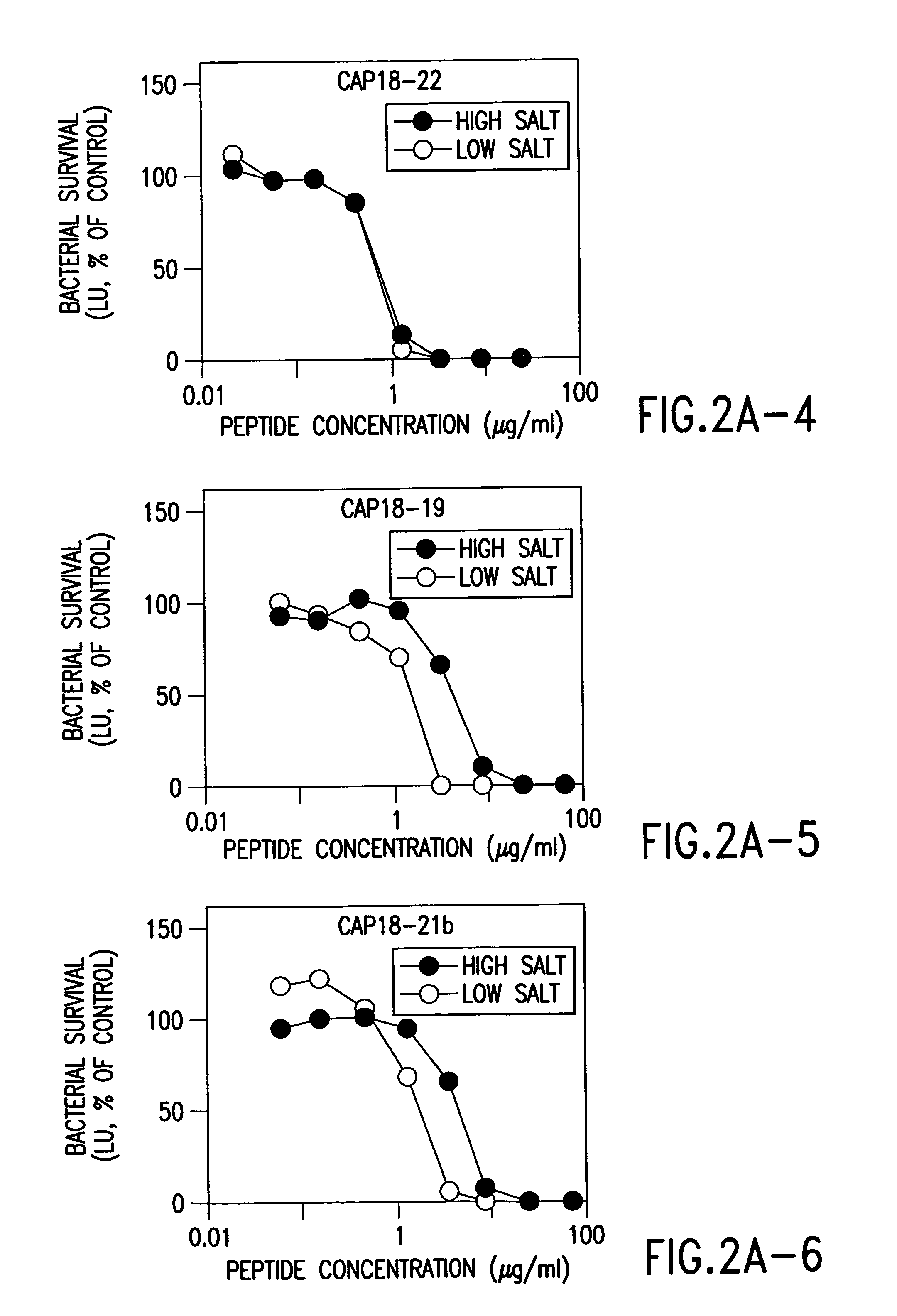
Alpha helical peptides with broad spectrum antimicrobial activity that are insensitive to salt
InactiveUS7071293B1Enhanced microbialEnhanced bacterial killingPeptide/protein ingredientsPeptide sourcesMicroorganismAntimicrobial peptides
The present invention relates to the use of antimicrobial peptides in the inhibition of microbial growth and proliferation. Novel antimicrobial truncated peptides are disclosed which are based upon SMAP 29 and RCAP 18, but which contain a lesser number of amino acid residues yet still retain bactericidal activity. In addition, synthetic peptides based upon the SMAP 29 protein are disclosed which have fewer amino acid residues and include substitutions yet retain substantial activity. The invention also relates to a method of inhibiting microbial growth by administering an effective amount of a peptide in accordance with the invention, or by combining the peptides with other antimicrobial agents or antibiotics.
Owner:UNIV OF IOWA RES FOUND +1
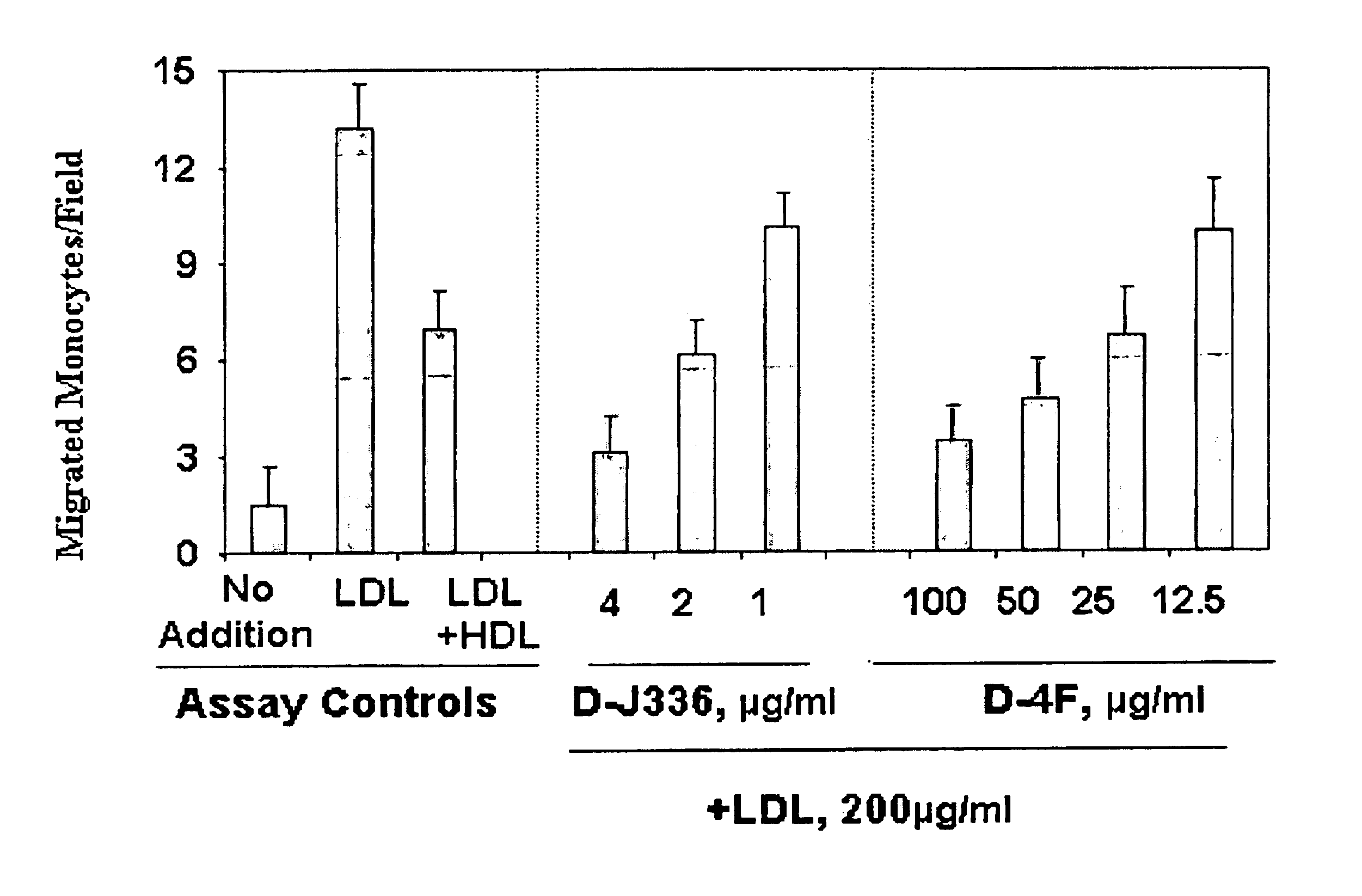
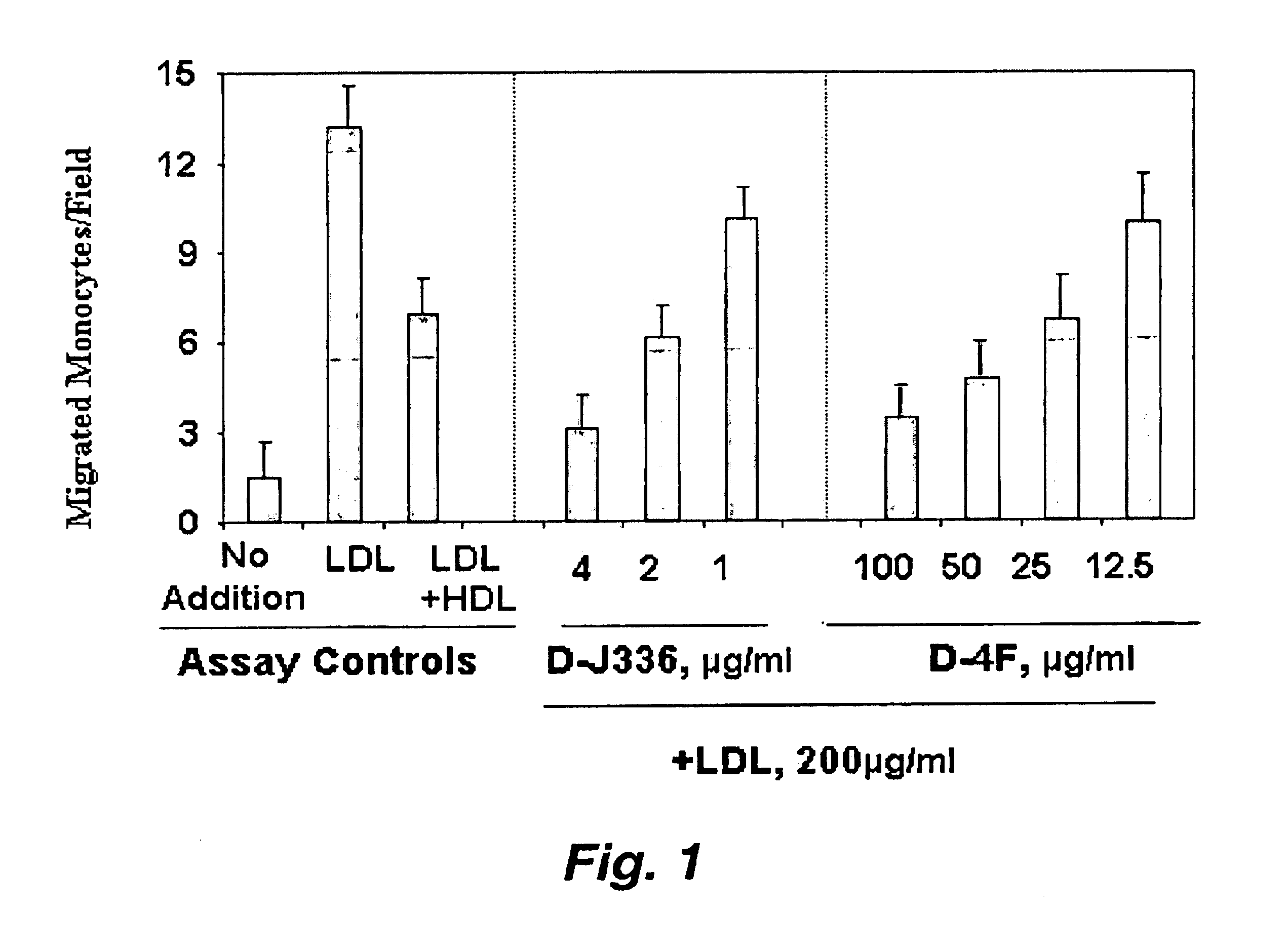
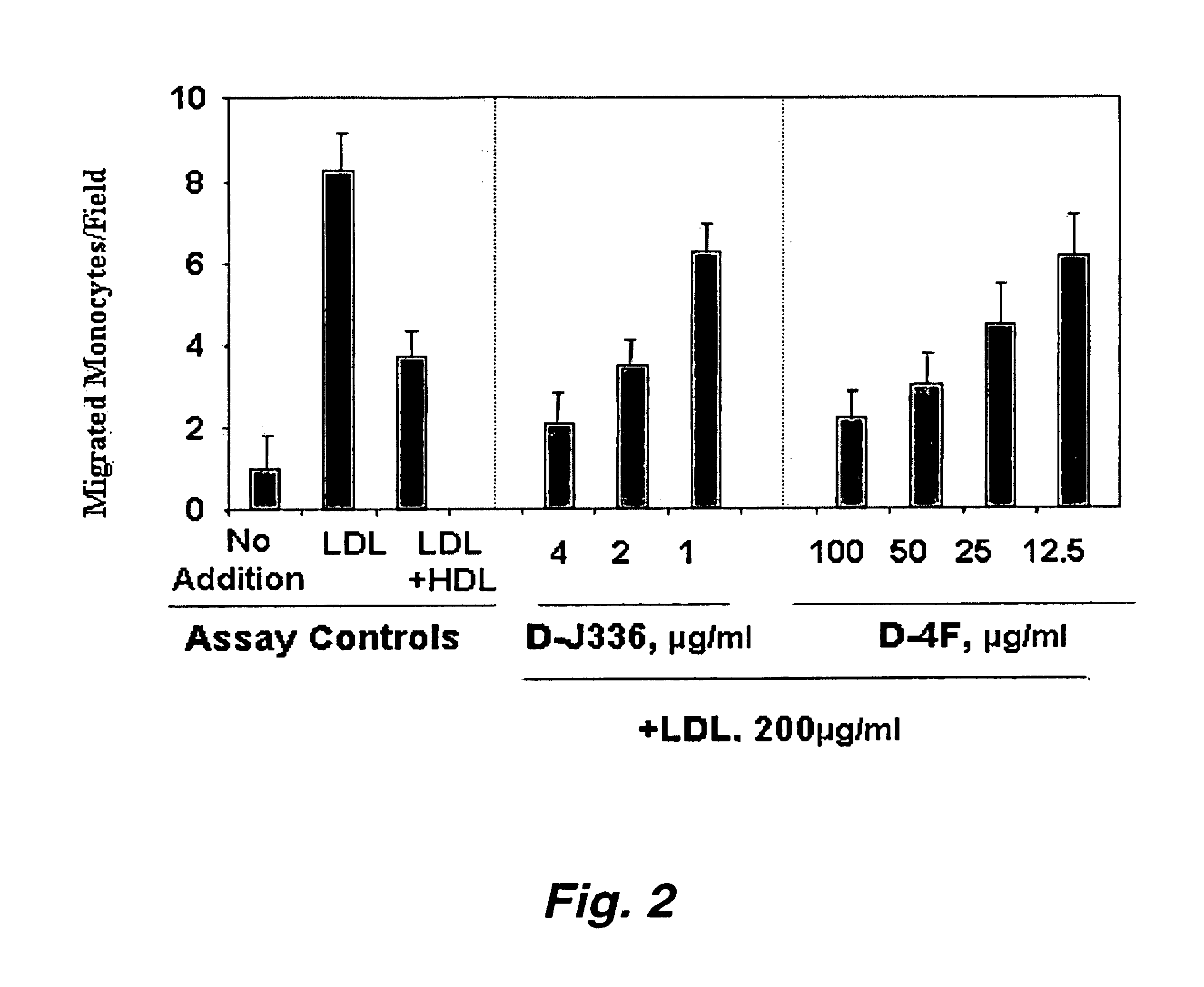
G-type peptides to ameliorate atherosclerosis
InactiveUS6930085B2Simplification of progressiveAlignment score can be increasedAntibacterial agentsAntimycoticsAmphipathic helixPeptide
This invention provides novel peptides that ameliorate one or more symptoms of atherosclerosis and / or other pathologies characterized by an inflammatory response. In certain embodiment, the peptides resemble a G* amphipathic helix of apolipoprotein J. The peptides are highly stable and readily administered via an oral route.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
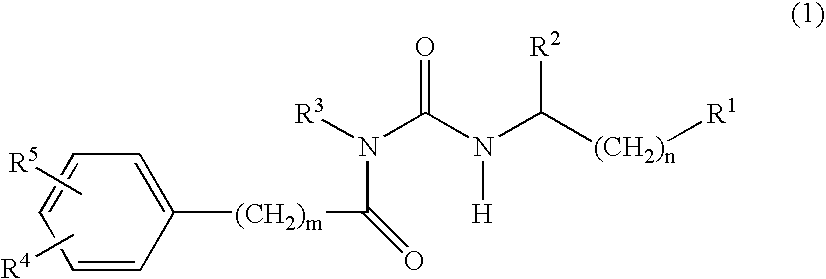
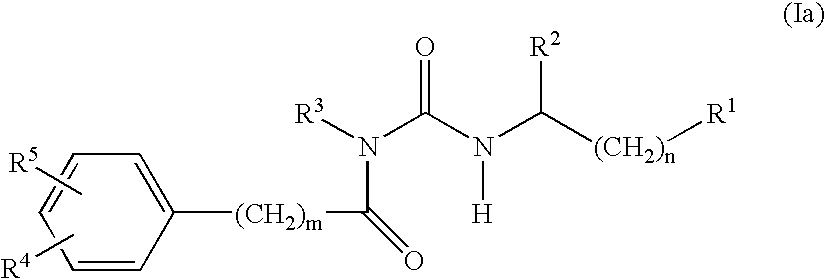
Alpha-helical mimetics
Benzoyl urea derivatives that are alpha helical peptides mimetics that mimic BH3-only proteins, compositions containing them, their conjugation to cell-targeting-moieties, and their use in the regulation of cell death are disclosed. The benzoyl urea derivatives are capable of binding to and neutralizing pro-survival Bcl-2 proteins. Use of benzoyl urea derivatives in the treatment and / or prophylaxis of diseases or conditions associated with deregulation of cell death are also described.
Owner:WALTER & ELIZA HALL INST OF MEDICAL RES
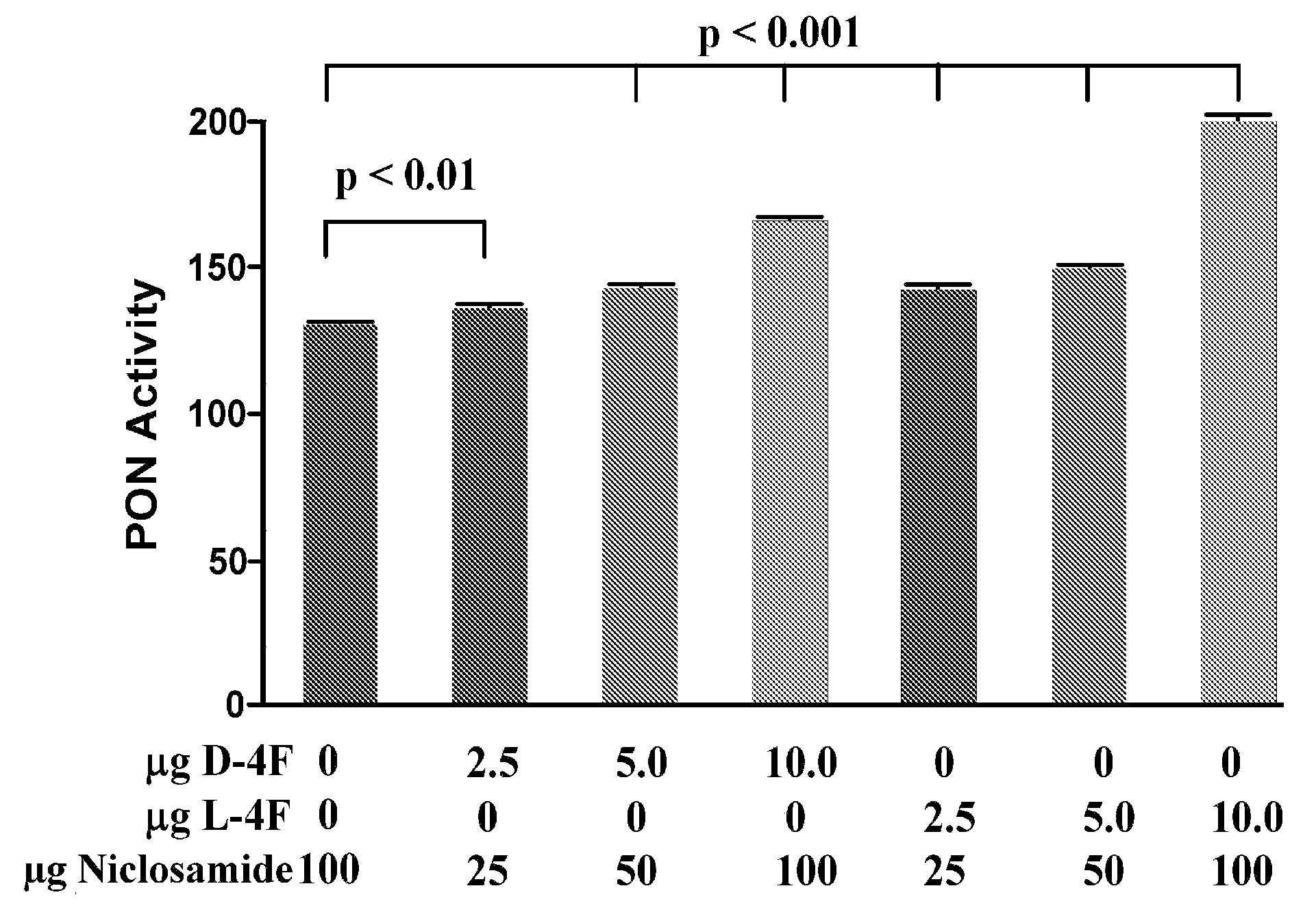
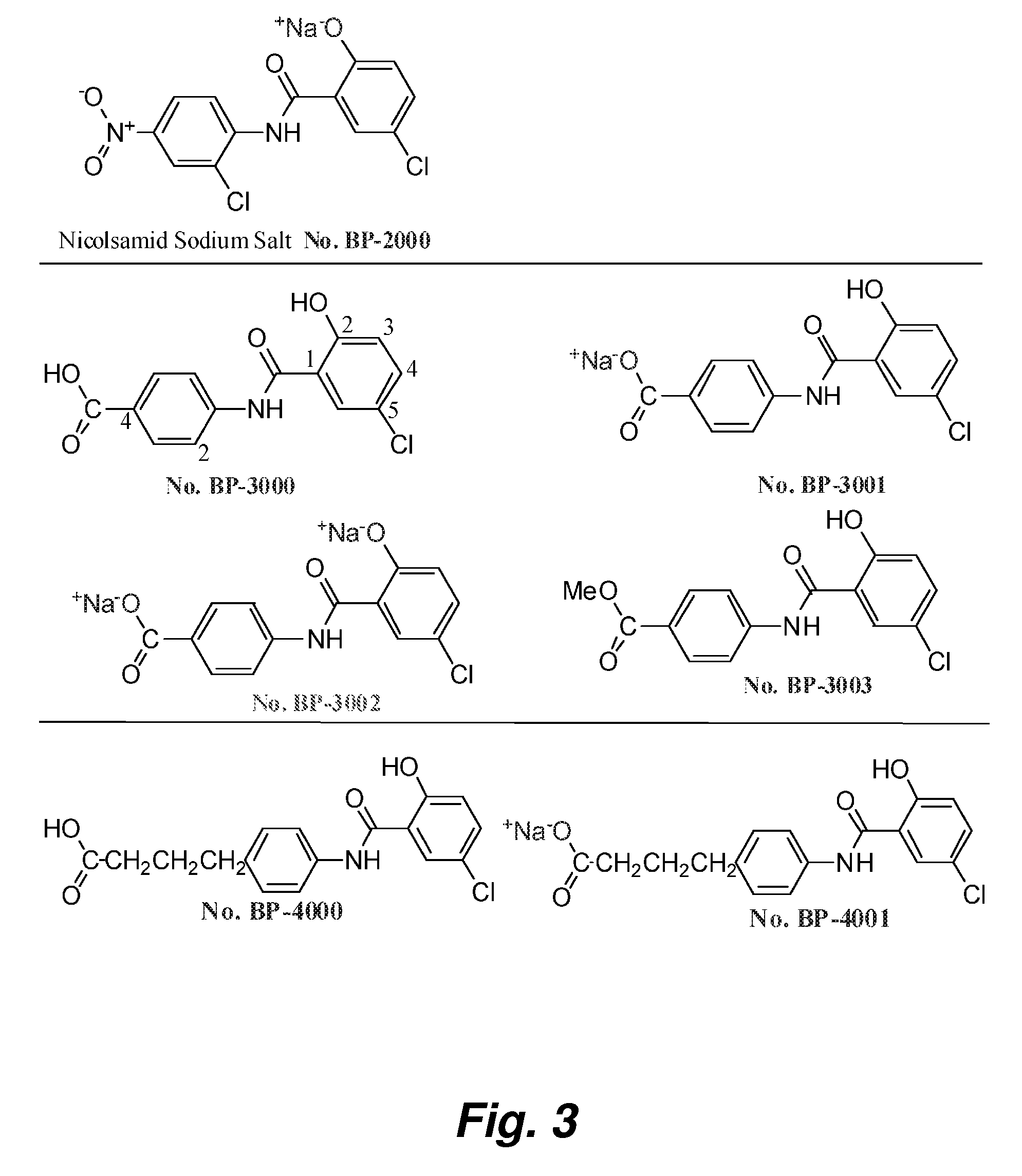
Salicylanilides enhance oral delivery of therapeutic peptides
This invention pertains to the surprising discovery that salicylanilides, e.g., niclosamide and / or niclosamide analogues when orally administered in conjunction with a peptide pharmaceutical (e.g., a class A amphipathic helical peptide as described herein) significantly increases the bioavailability of that peptide. Methods of peptide delivery using such “delivery agents” and pharmaceutical formulations are provided.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Salicylanilides enhance oral delivery of therapeutic peptides
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Synthetic apolipoprotein e mimicking polypeptides and methods of use
InactiveUS20100286025A1Antibacterial agentsSenses disorderAmphipathic helixVery low-density lipoprotein
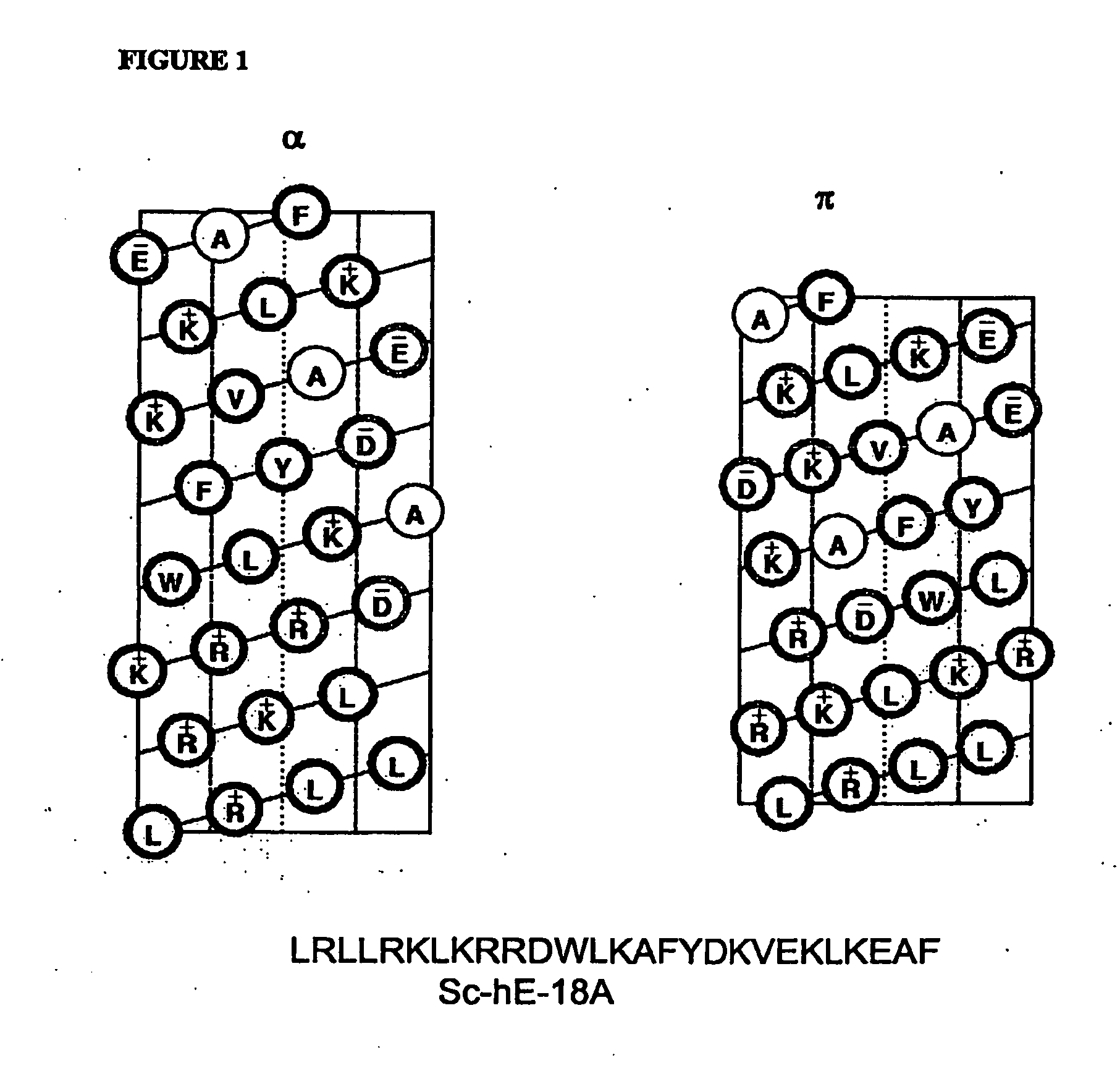
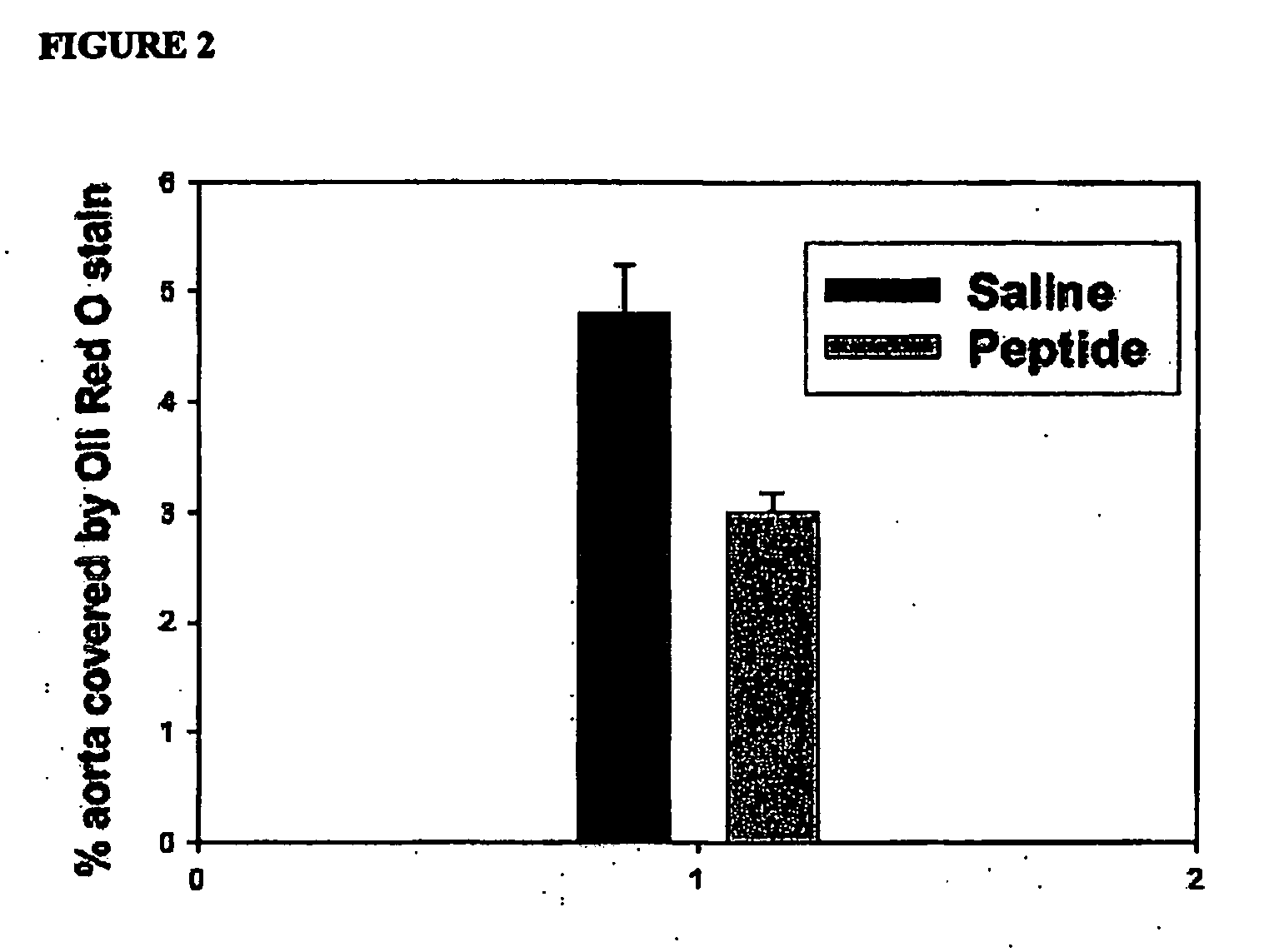
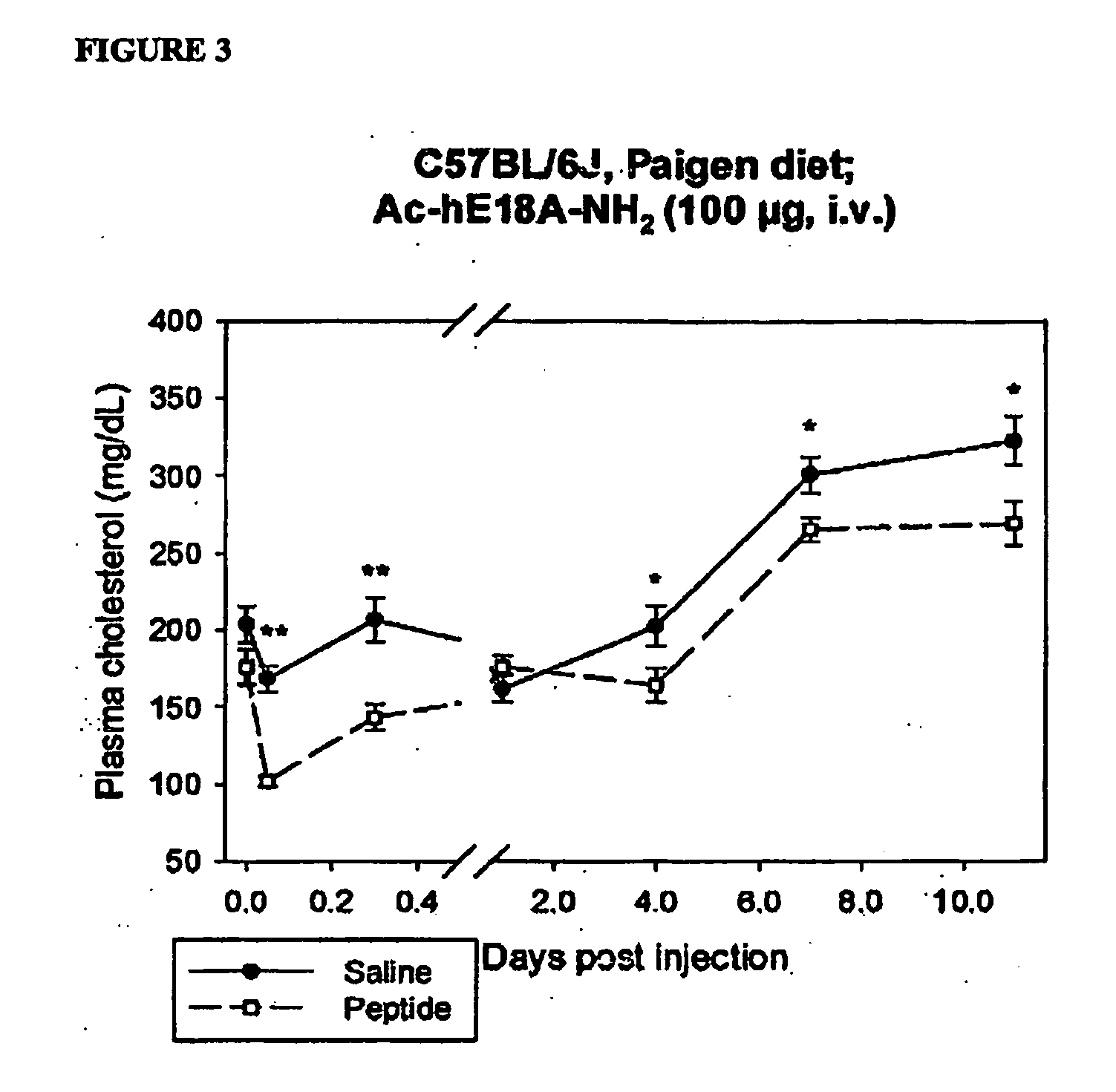
The present invention provides novel synthetic apolipoprotein E (ApoE)-mimicking peptides wherein the receptor binding domain of apolipoprotein E is covalently linked to 18A, the well characterized lipid-associating model class A amphipathic helical peptide, or a modified version thereof. Such peptides enhance low density lipoprotein (LDL) and very low density lipoprotein (VLDL) binding to and degradation by fibroblast or HepG2 cells. Also provided are possible applications of the synthetic peptides in lowering human plasma LDL / VLDL cholesterol levels, thus inhibiting atherosclerosis. The present invention also relates to synthetic peptides that can improve HDL function and / or exert anti-inflammatory properties.
Owner:UAB RES FOUND
G-type peptides and other agents to ameliorate atherosclerosis and other pathologies
InactiveUS20060205669A1Simplification of progressiveAlignment score can be increasedPeptide/protein ingredientsAntipyreticAmphipathic helixIntensive care medicine
This invention provides novel peptides, and other agents, that ameliorate one or more symptoms of atherosclerosis and / or other pathologies characterized by an inflammatory response. In certain embodiment, the peptides resemble a G* amphipathic helix of apolipoprotein J. The peptides are highly stable and readily administered via an oral route.
Owner:ALABAMA RES FOUND UNIV OF THE +1
Compositions and methods for the treatment of viral infections
ActiveUS20110318352A1Restore native alpha-helical structureImprove stabilitySsRNA viruses negative-senseBiocideViral infectionProteolysis
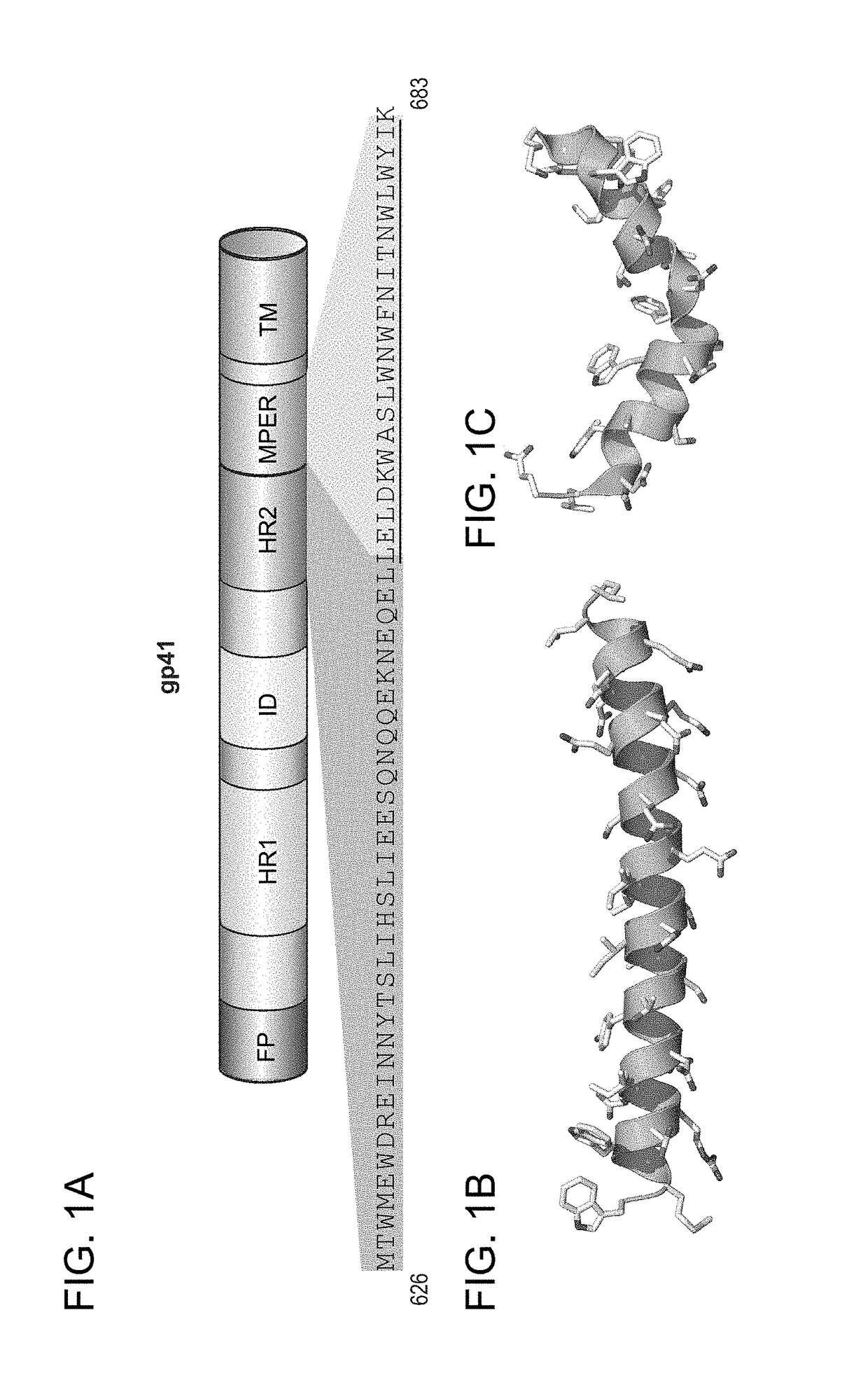
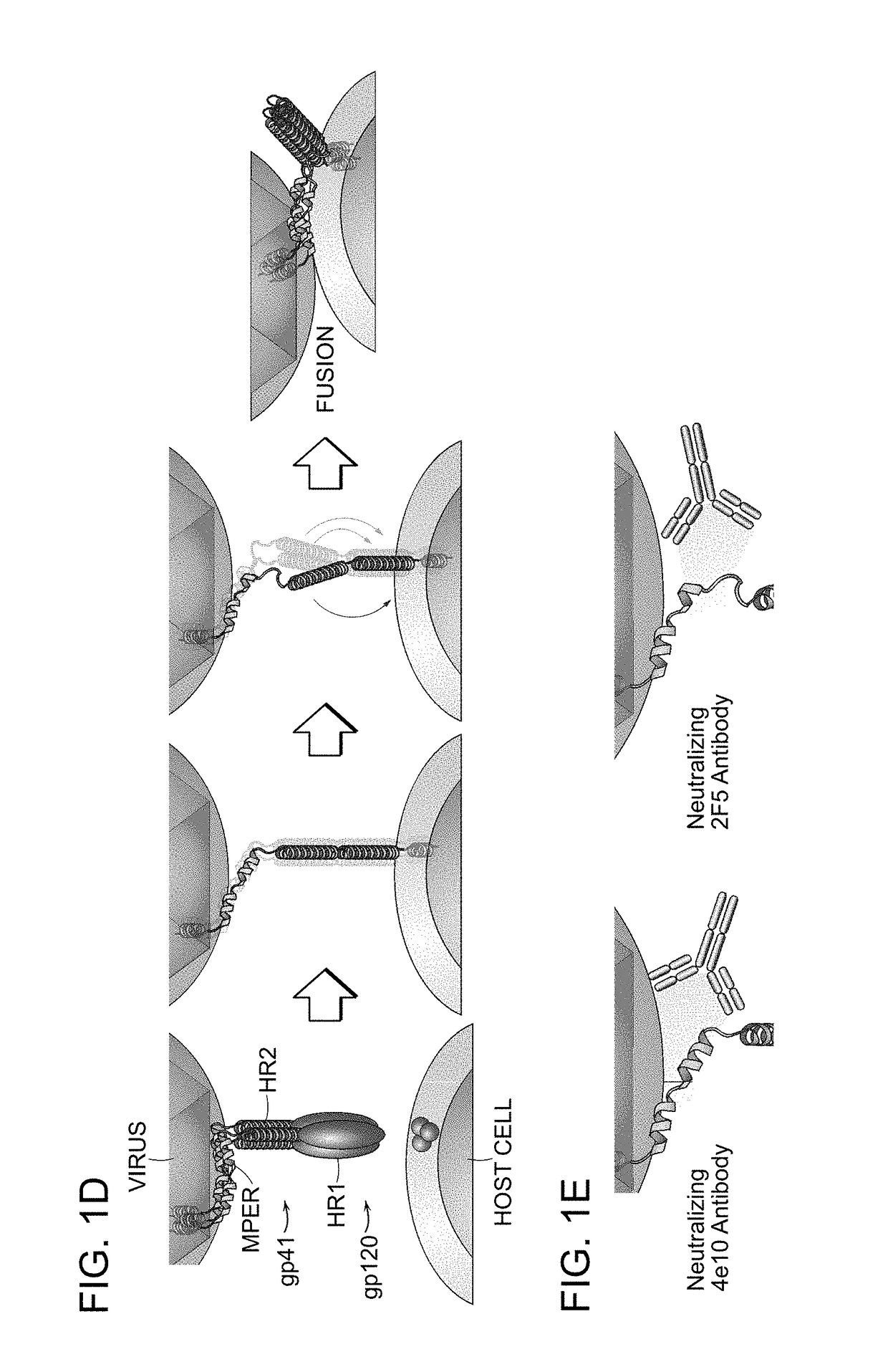
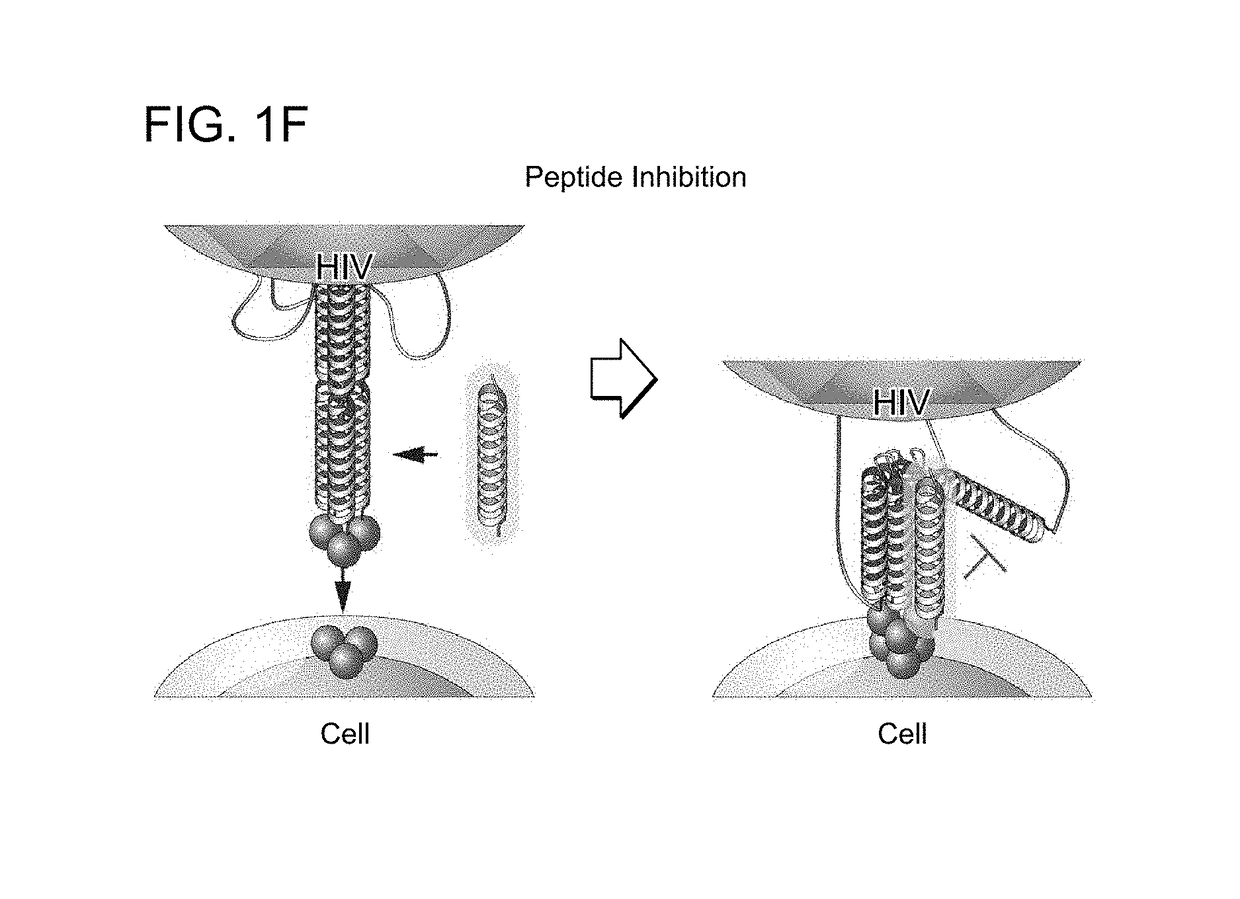
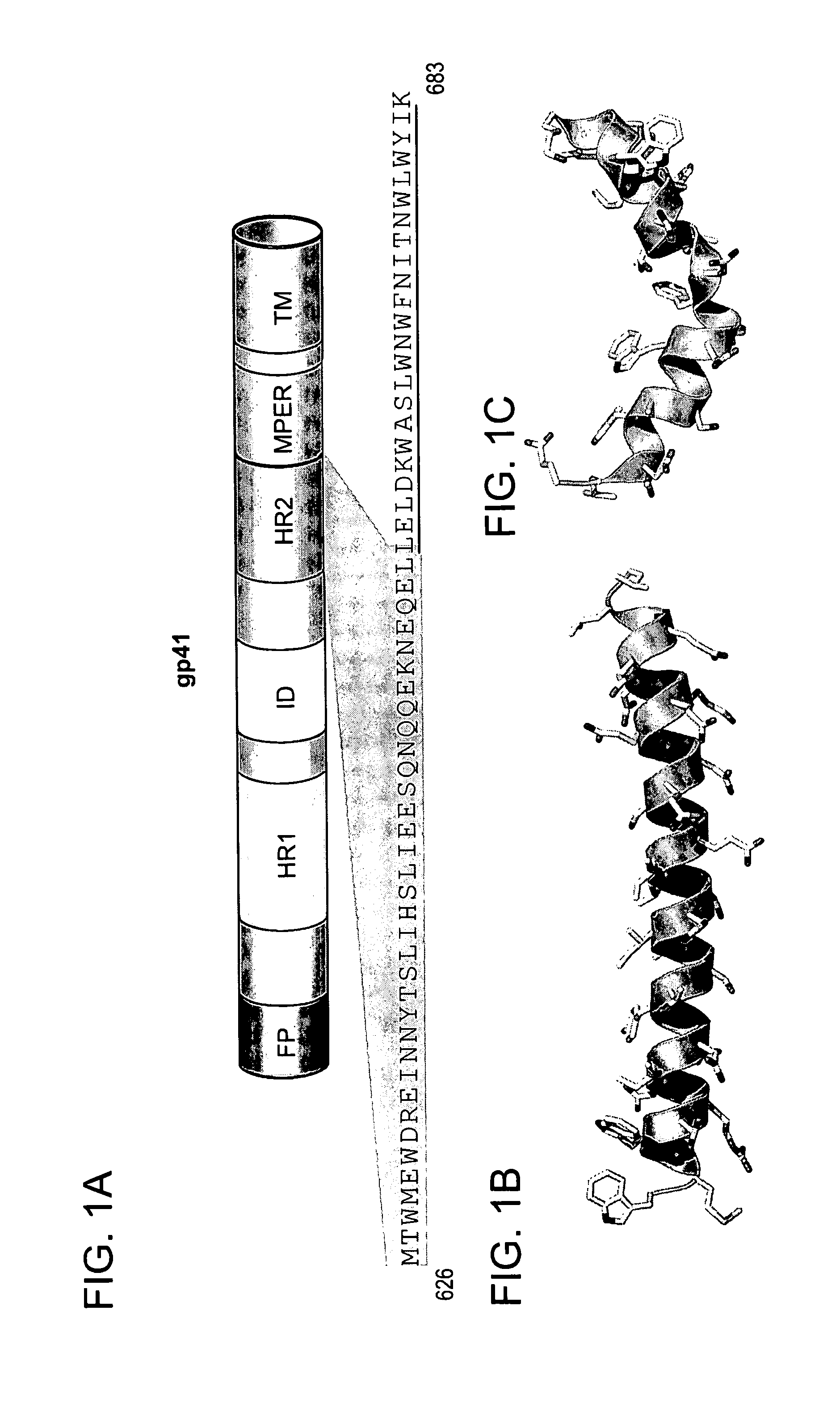
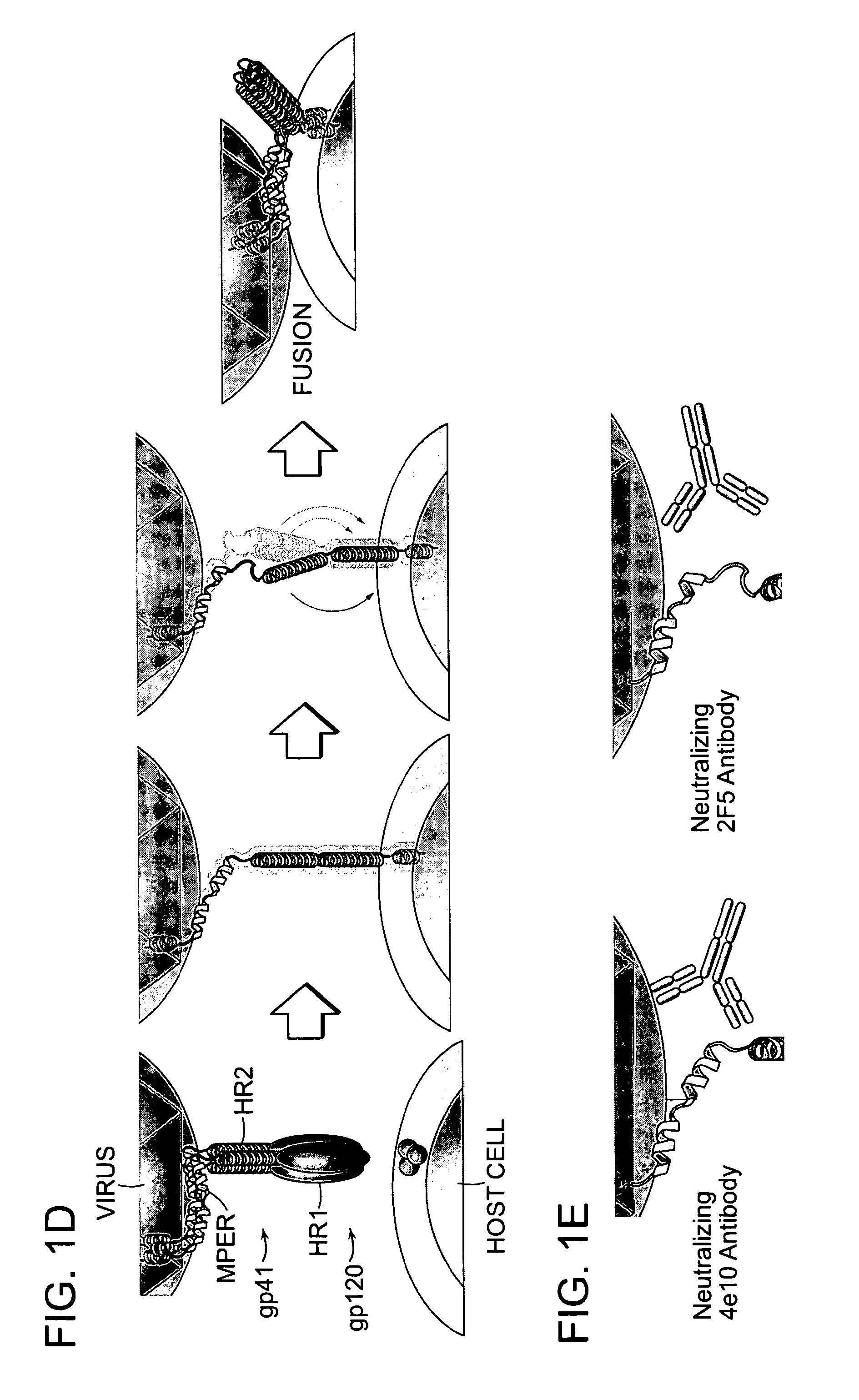
The invention provides compositions, kits and methods utilizing polypeptides having a viral alpha-helix heptad repeat domain in a stabilized a-helical structure (herein also referred to as SAH). The compositions are useful for treating and / or preventing viral infections. The invention is based, at least in part, on the result provided herein demonstrating that viral hydrocarbon stapled alpha helical peptides display excellent proteolytic, acid, and thermal stability, restore the native alpha-helical structure of the peptide, are highly effective in interfering with the viral fusogenic process, and possess superior pharmacokinetic properties compared to the corresponding unmodified peptides.
Owner:DANA FARBER CANCER INST INC
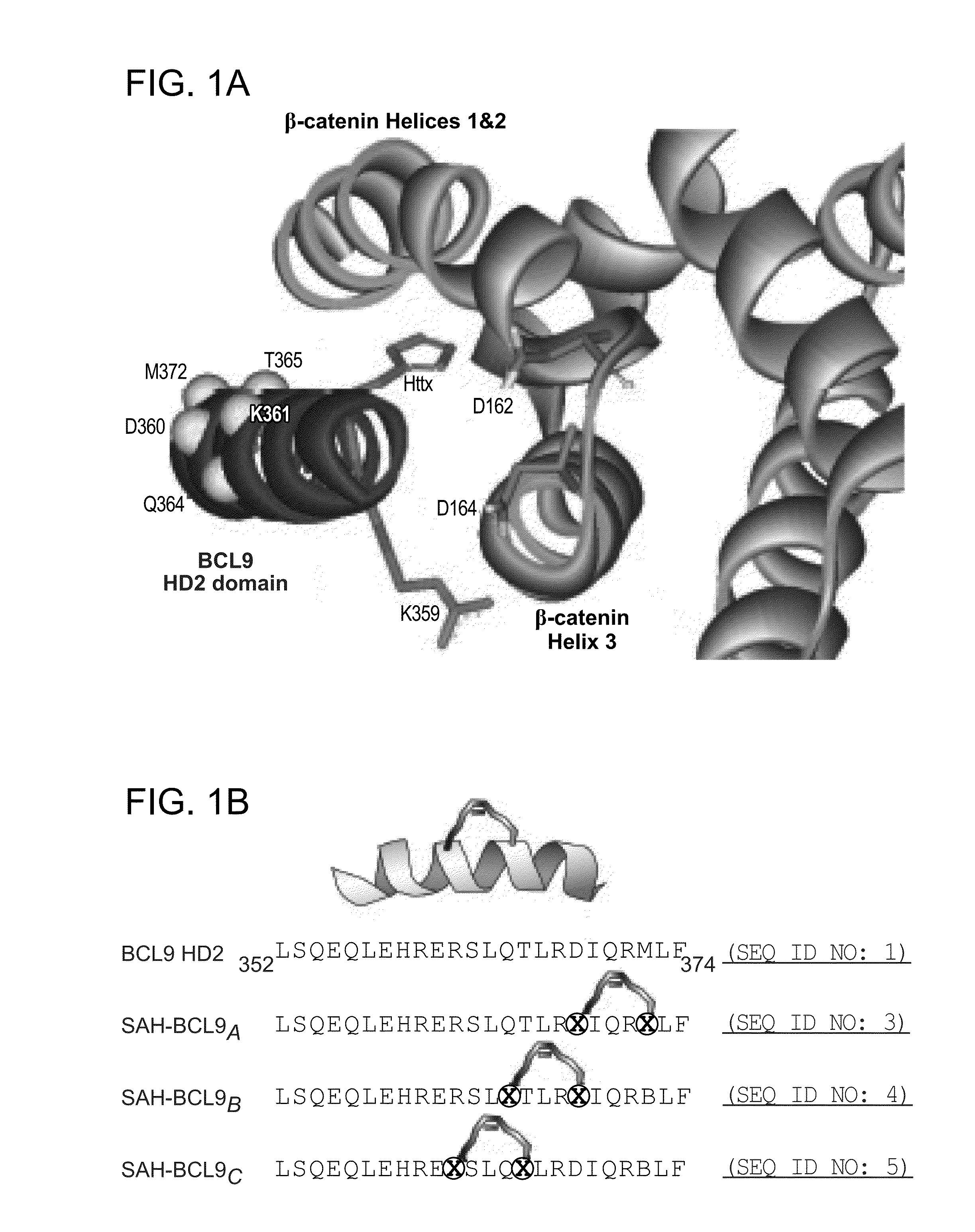
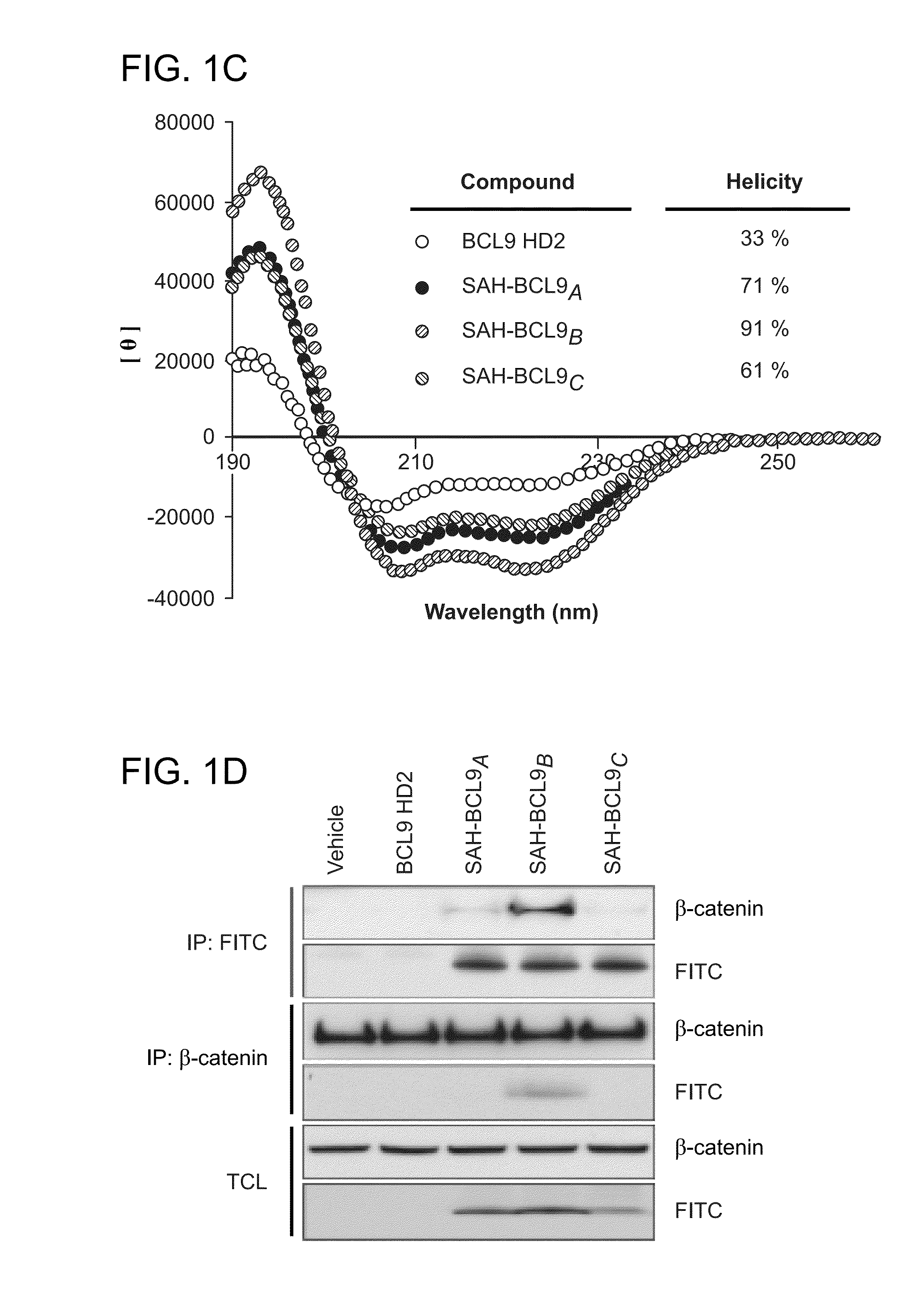
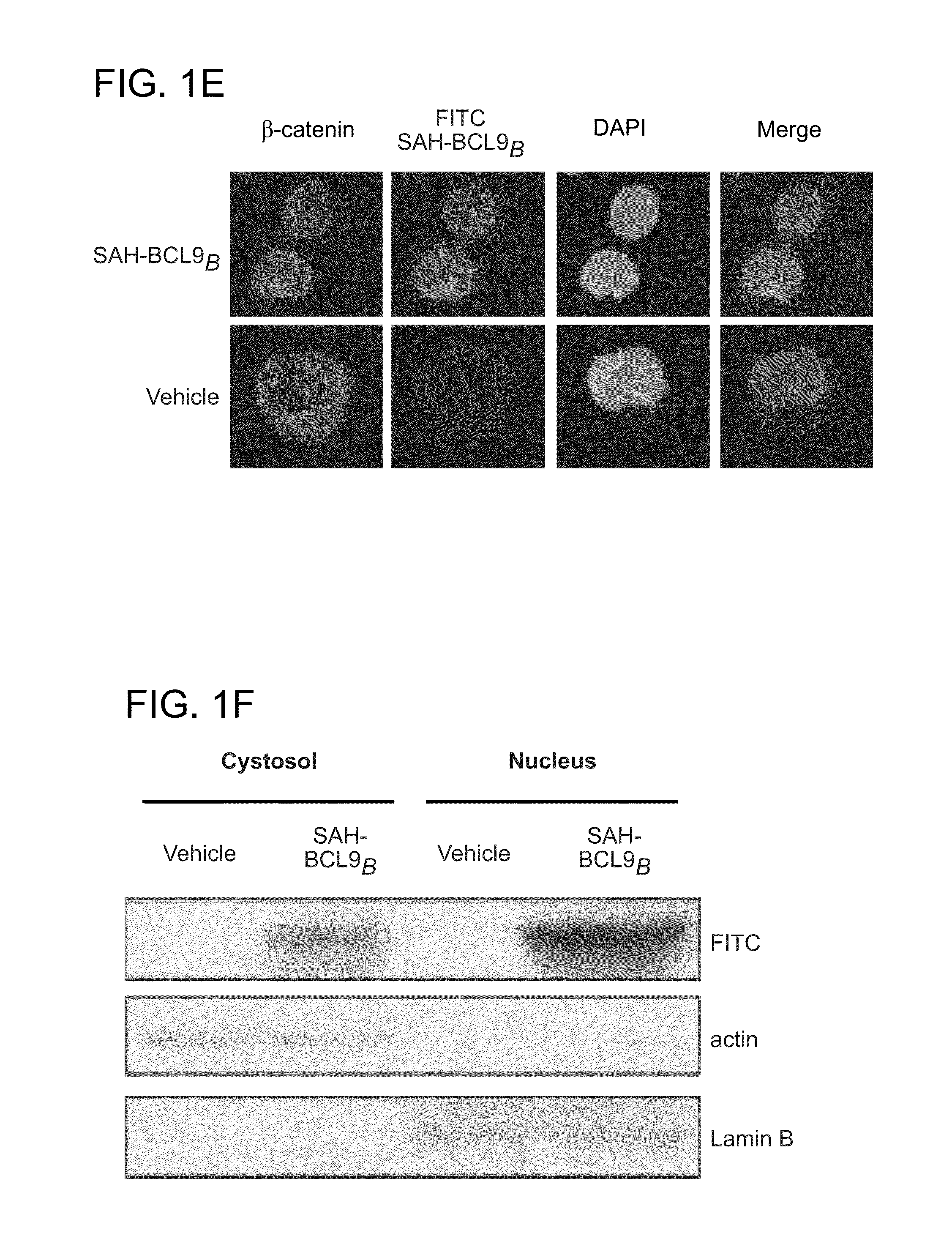
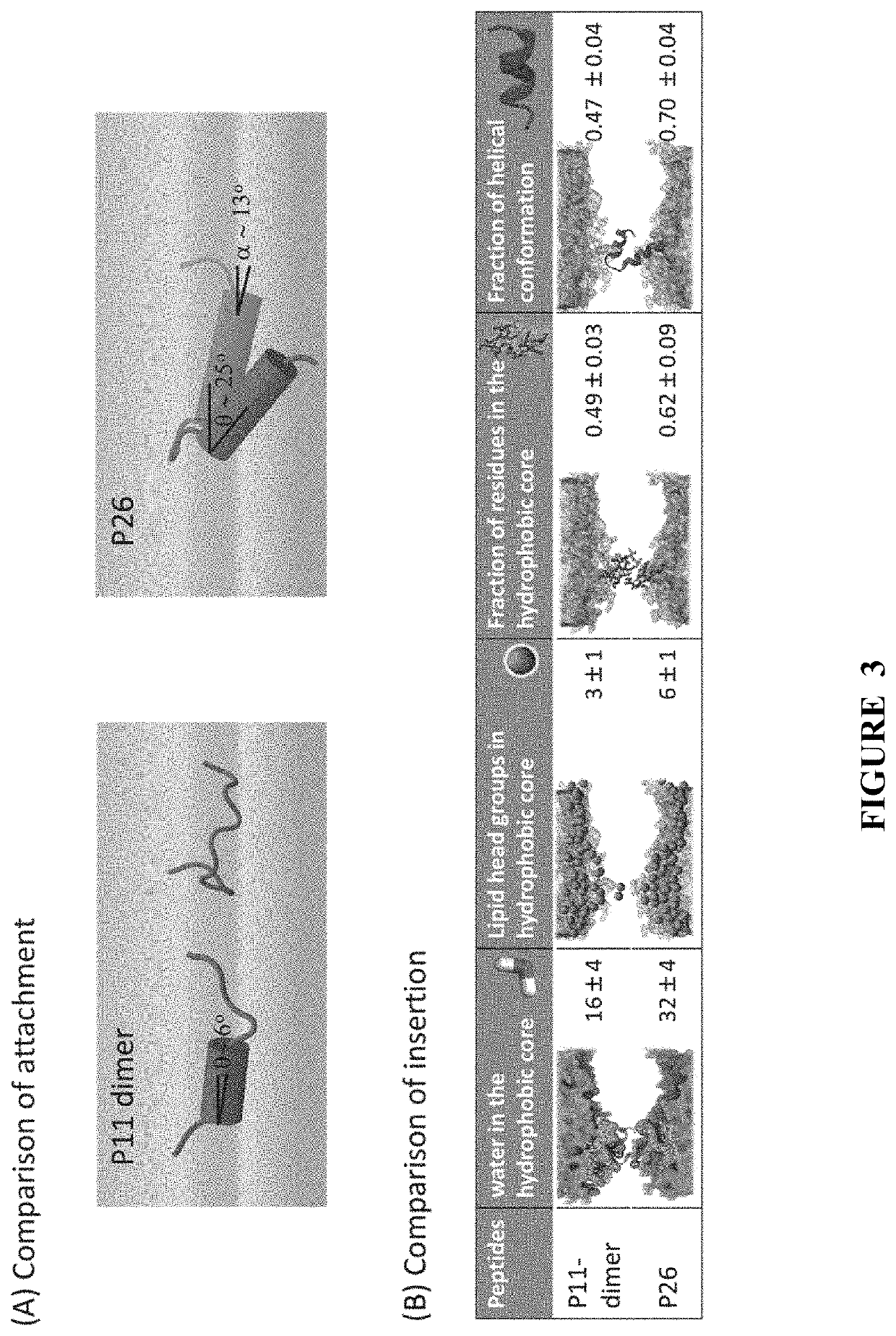
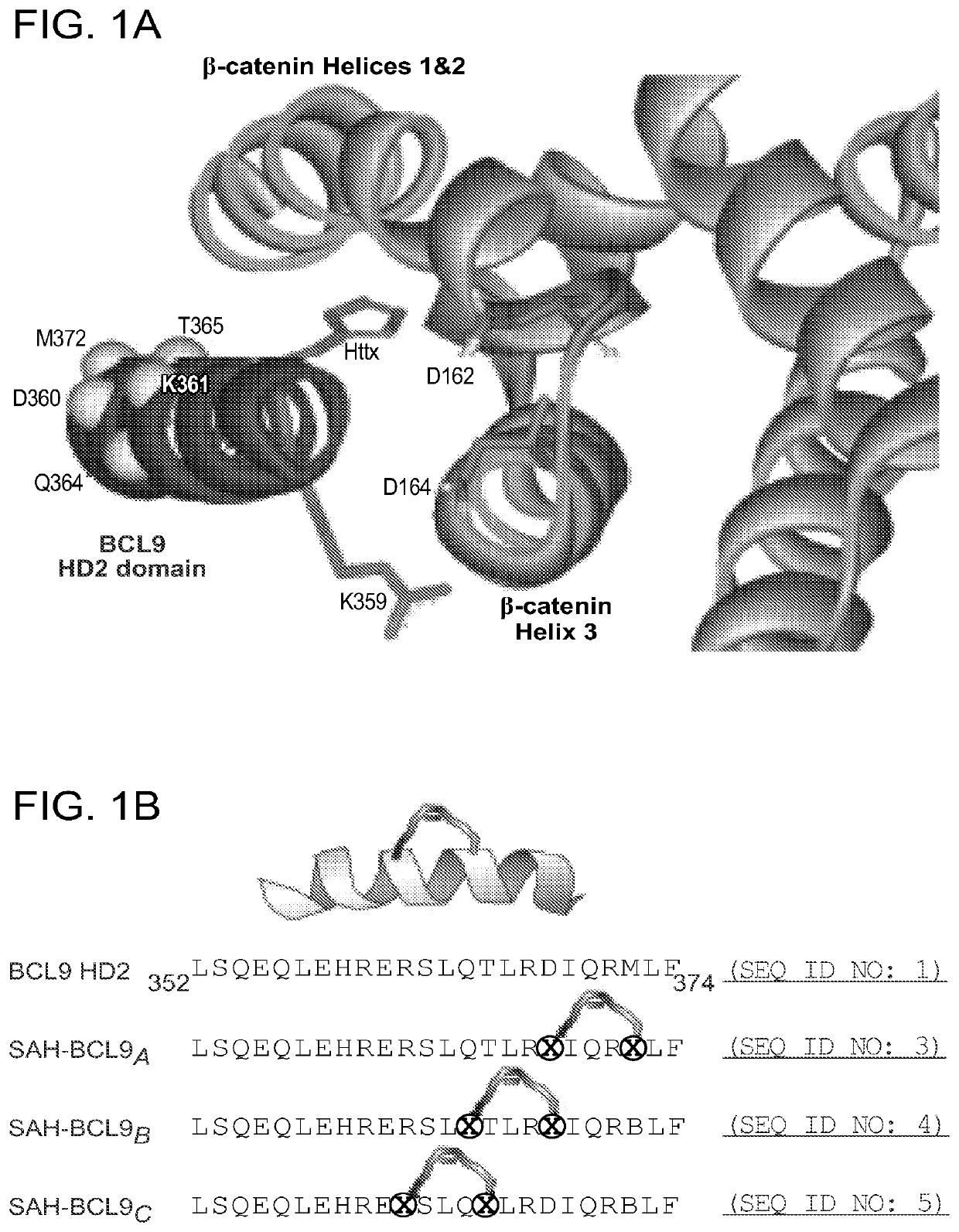
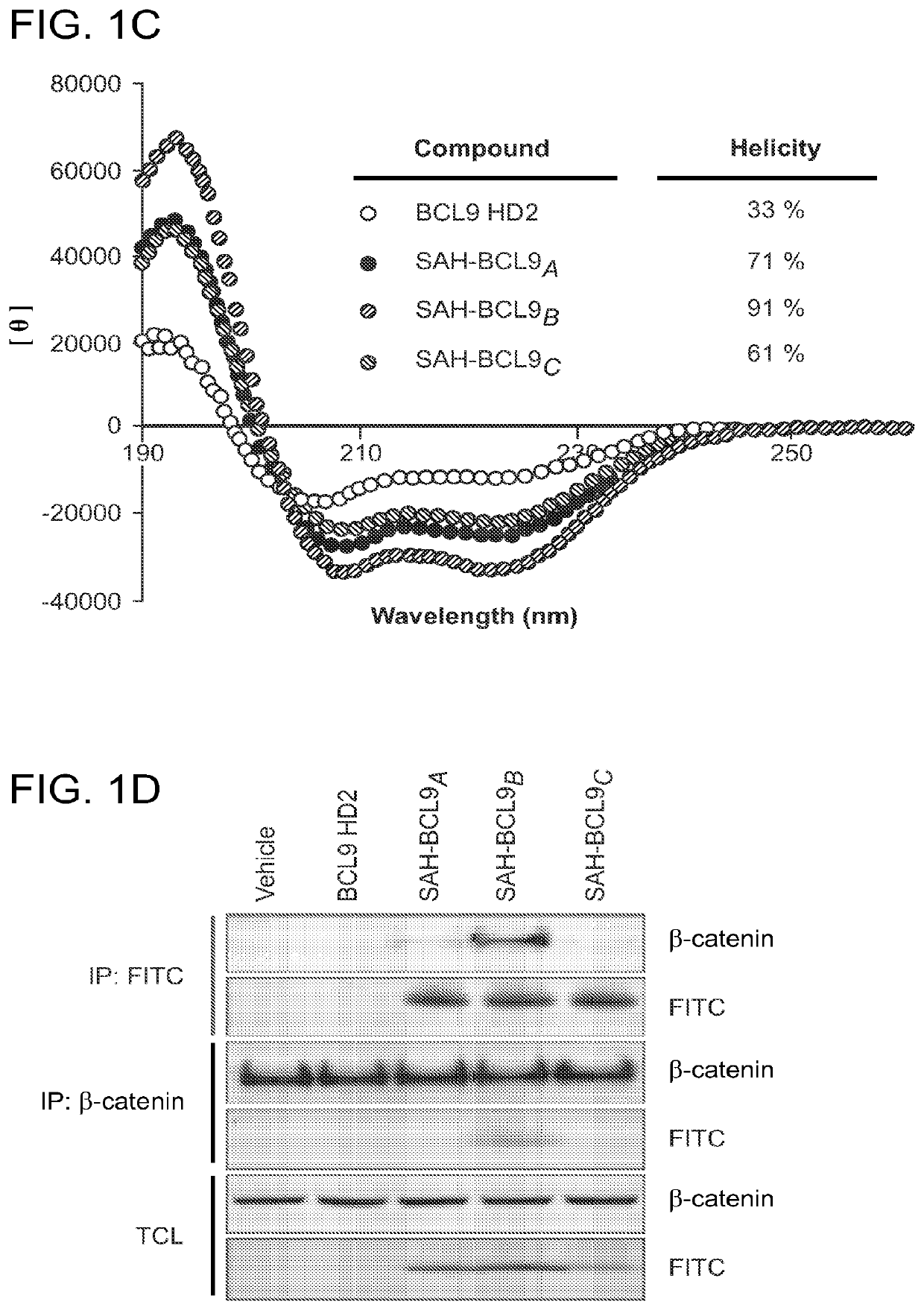
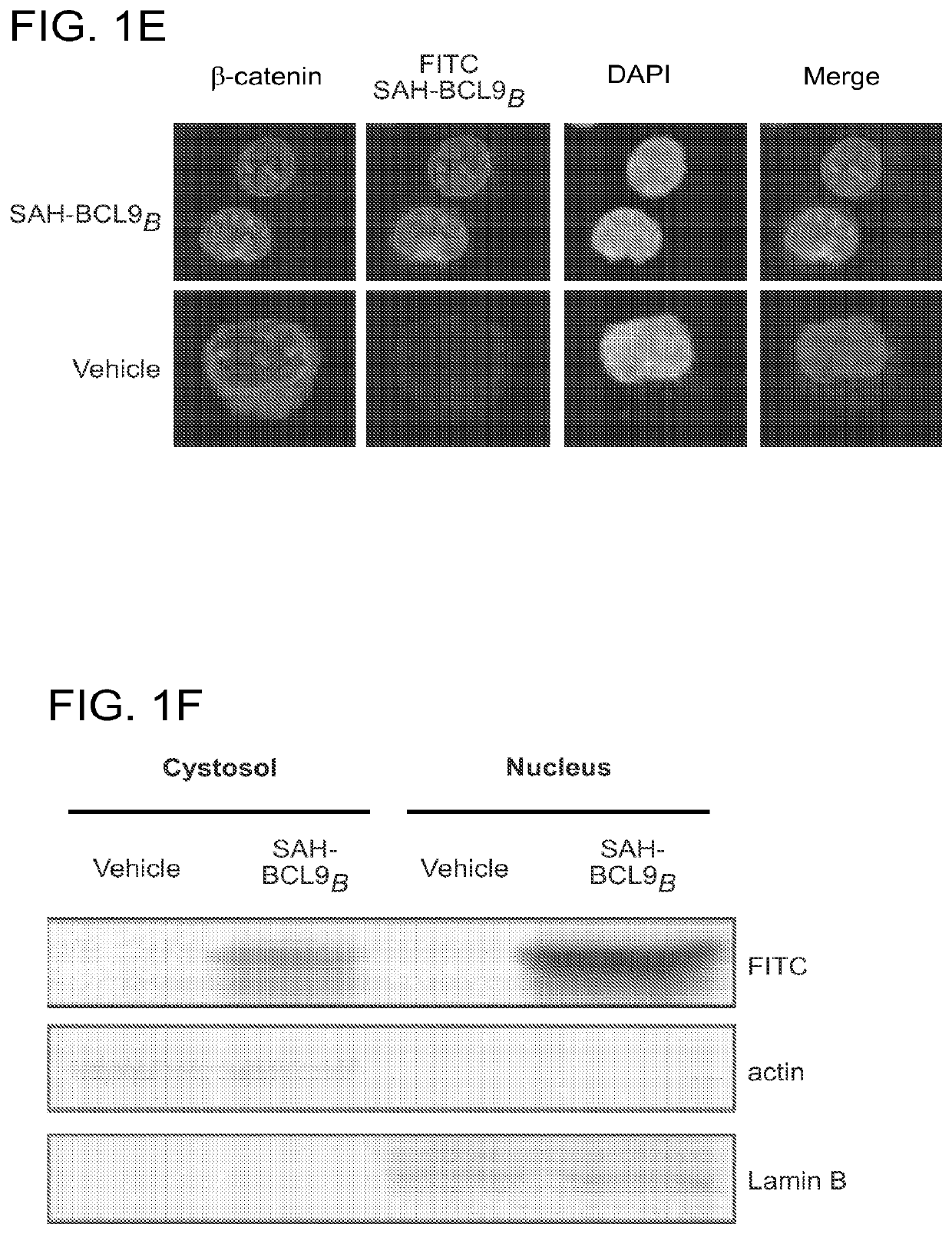
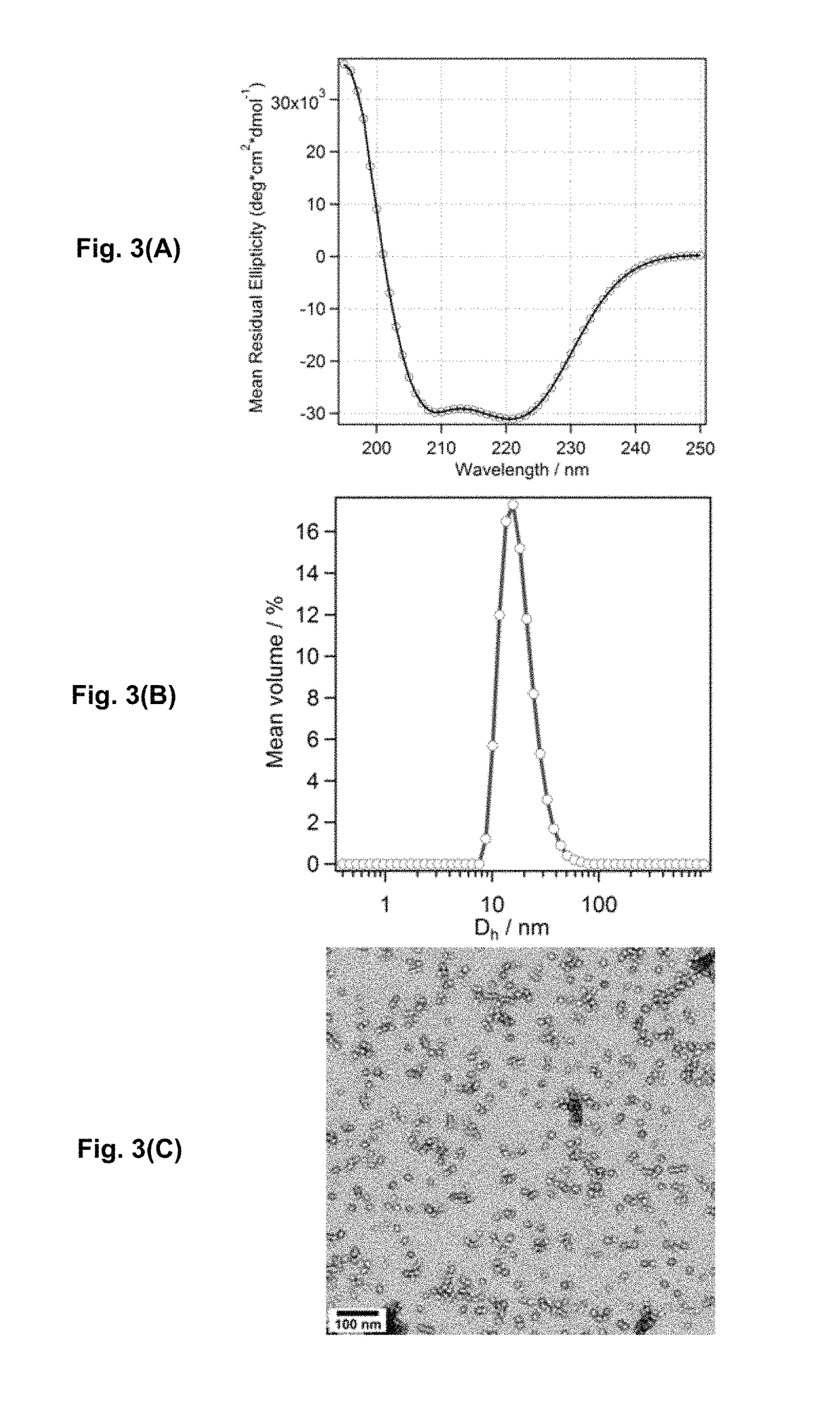
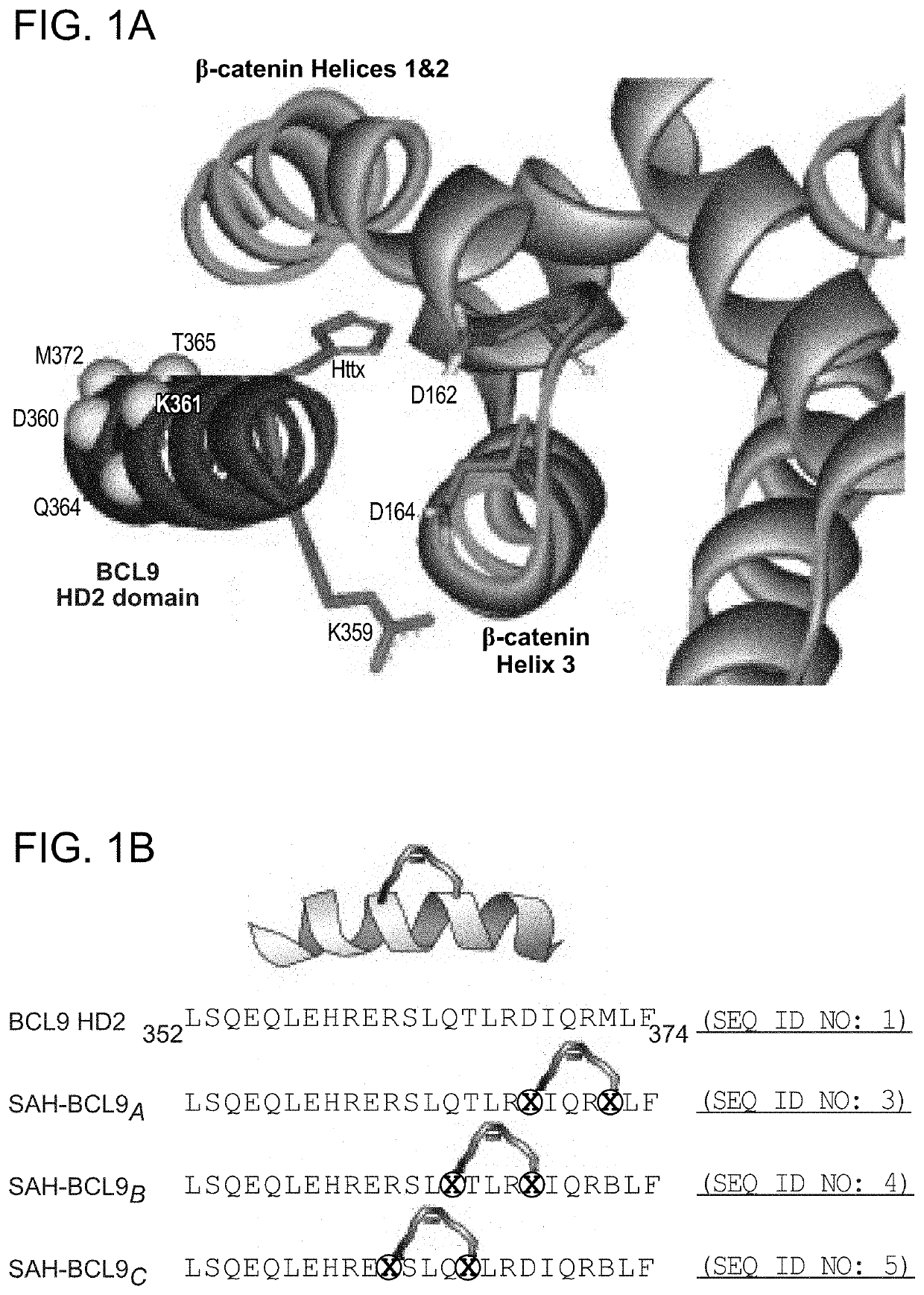
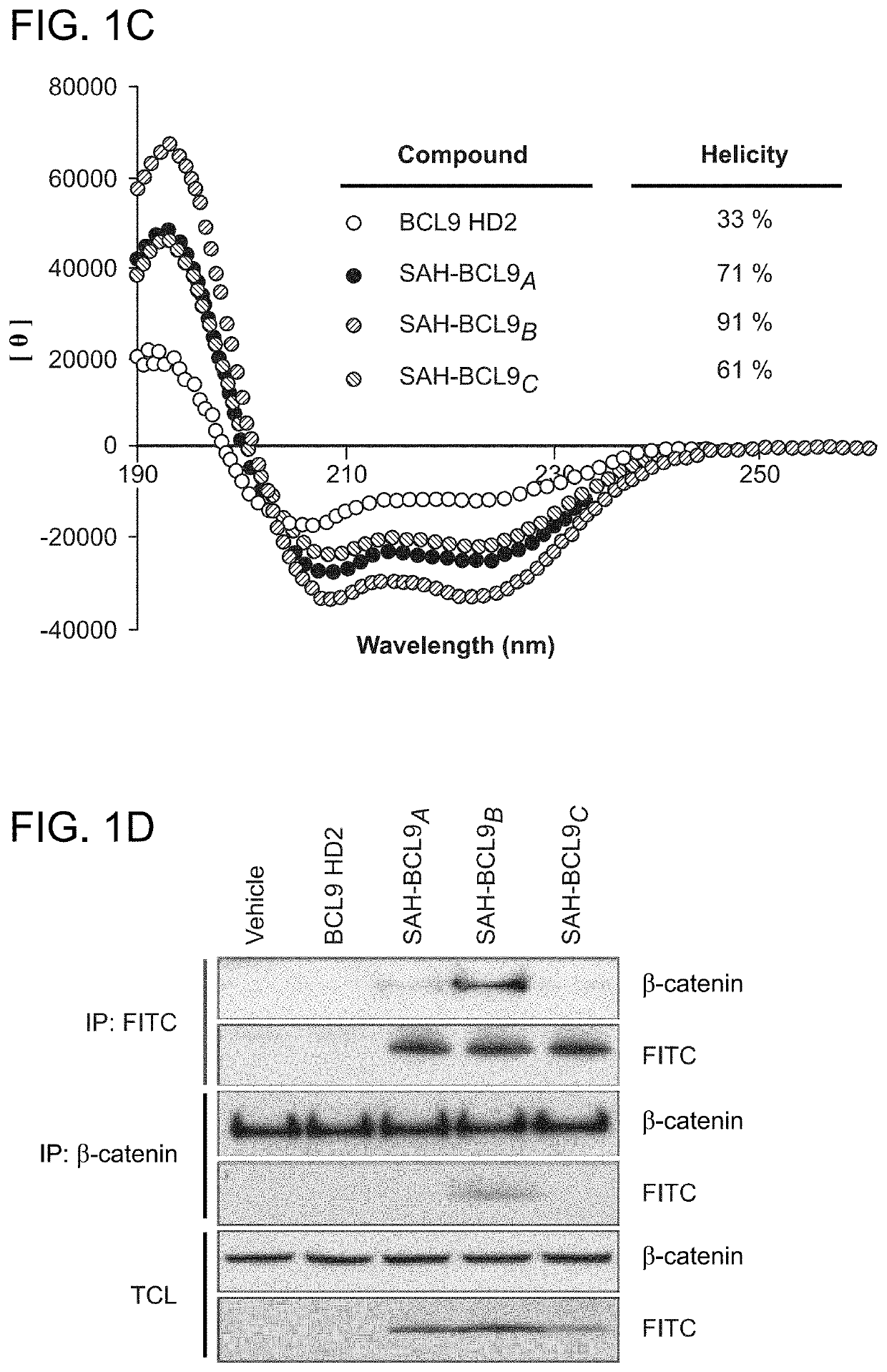
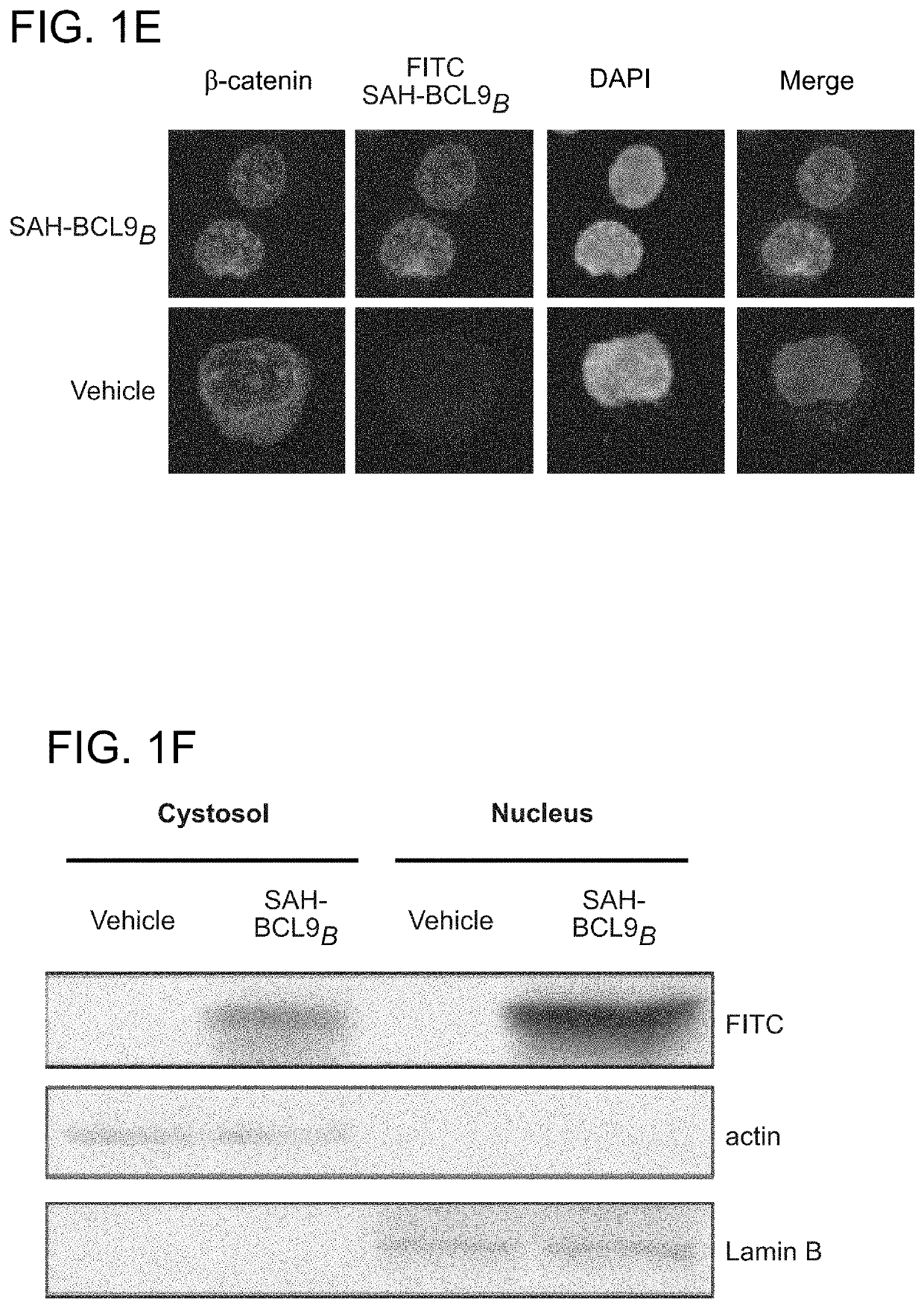
Targeting deregulated wnt signaling in cancer using stabilized alpha-helices of bcl-9
ActiveUS20140113857A1Improved pharmacokinetic propertiesGood acid stabilityPeptide/protein ingredientsImmunoglobulinsHuman cancerΒ catenin signaling
The invention provides structurally-constrained peptides by hydrocarbon stapling of a BCL9 HD2 helix for use as a therapeutic agent. The invention further provides methods and kits for use of the structurally-constrained peptide of the instant invention. The invention is based, at least in part, on the results provided herein demonstrating that hydrocarbon stapled helical peptides display excellent proteolytic, acid, and thermal stability, restore the native helical structure of the peptide, possess superior pharmacokinetic properties compared to the corresponding unmodified peptides, and are highly effective in binding to β-catenin in vitro, in cellulo, and in vivo, disrupting the BCL-9 / β-catenin interaction, and thereby interfering with deregulated Wnt / β-catenin signaling for therapeutic benefit in a variety of human diseases including human cancer.
Owner:DANA FARBER CANCER INST INC
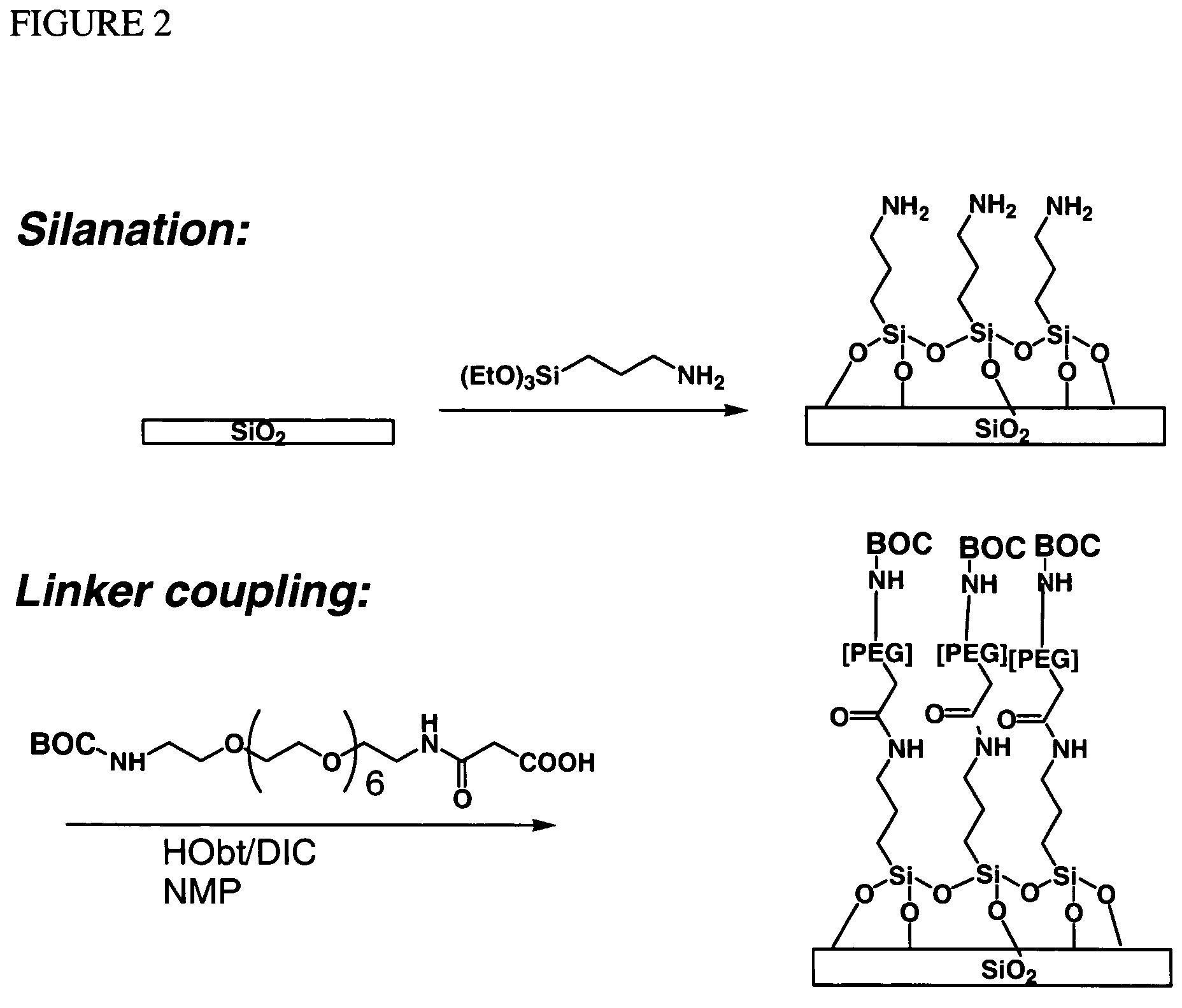
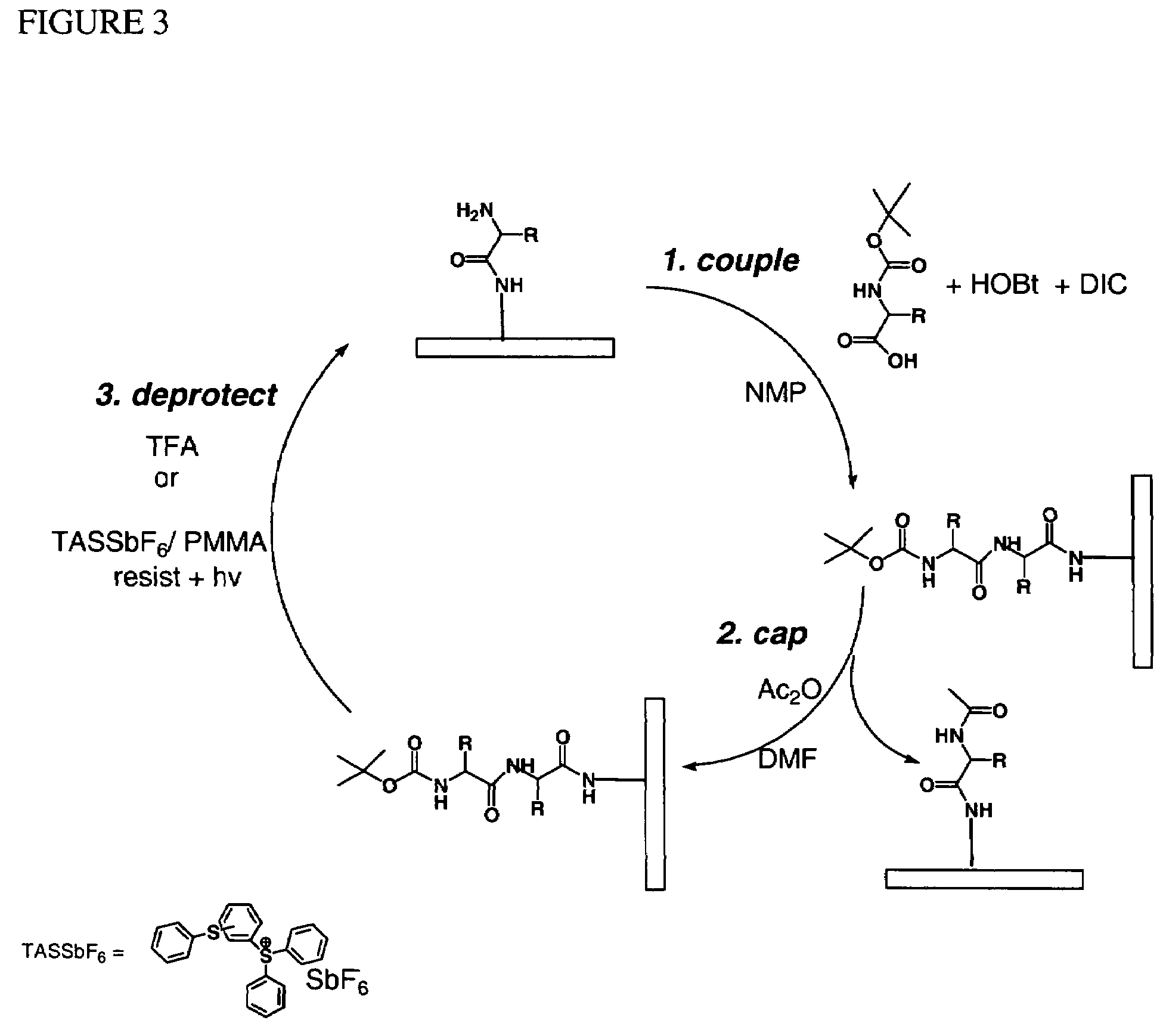
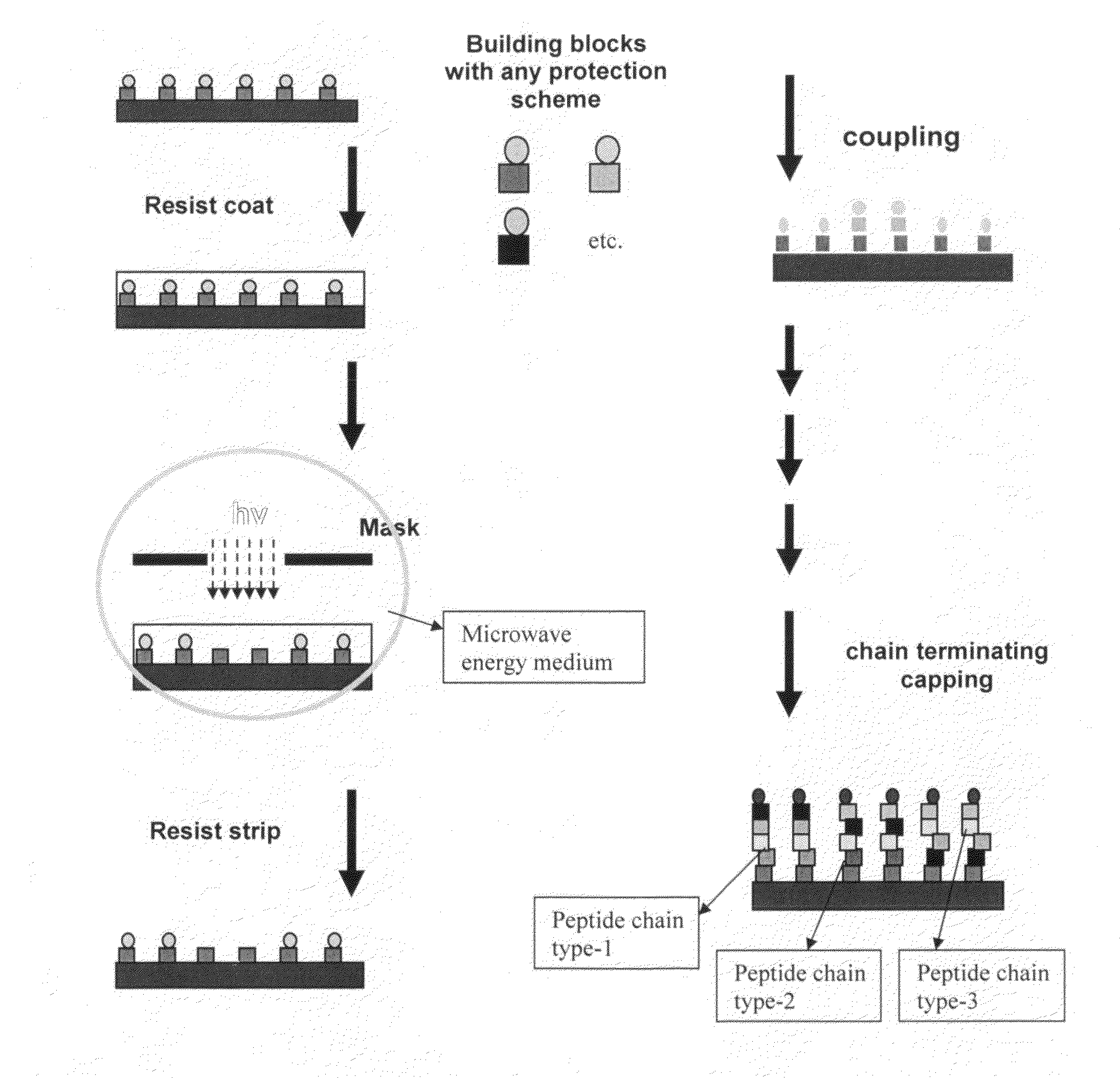
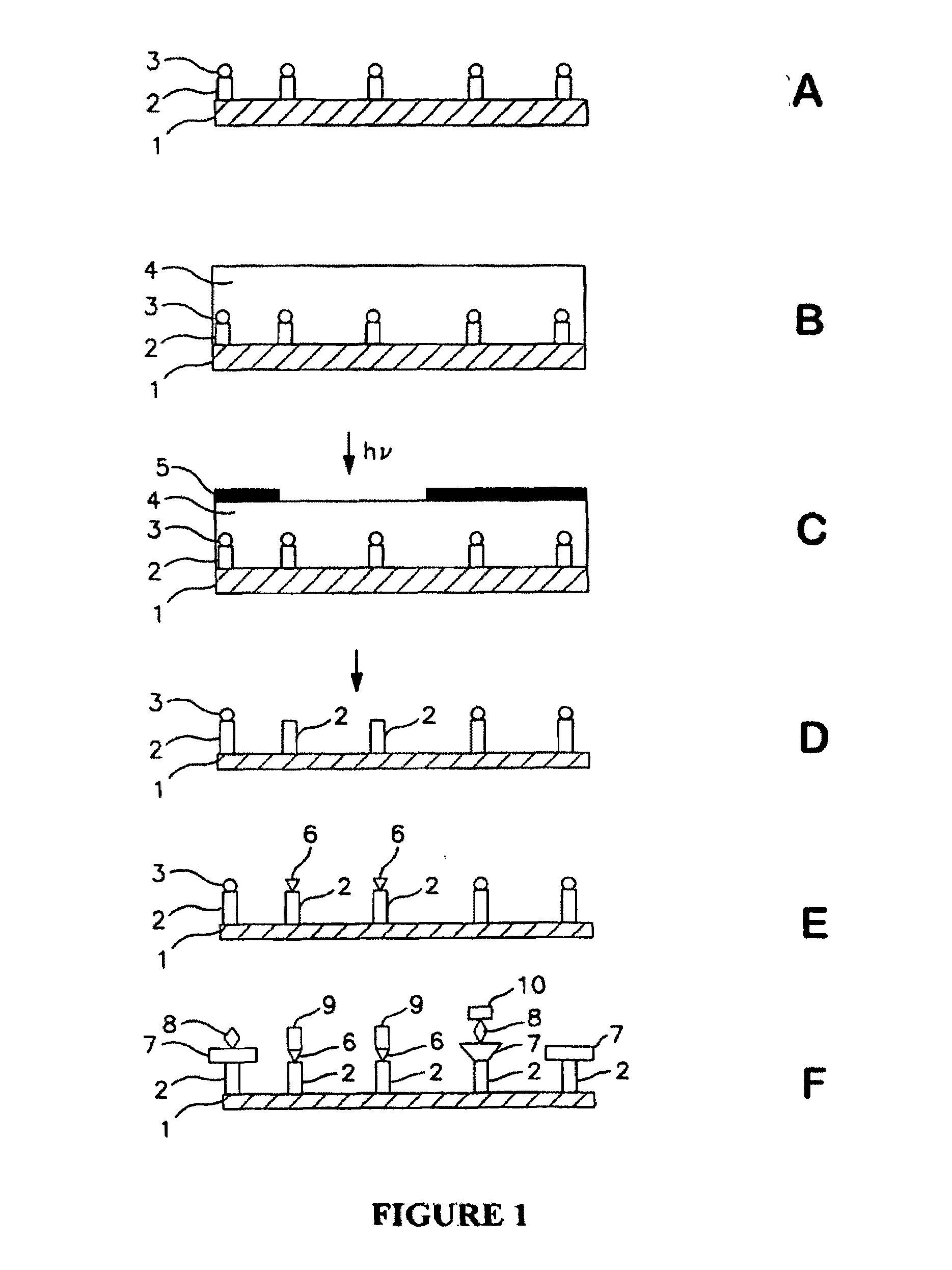
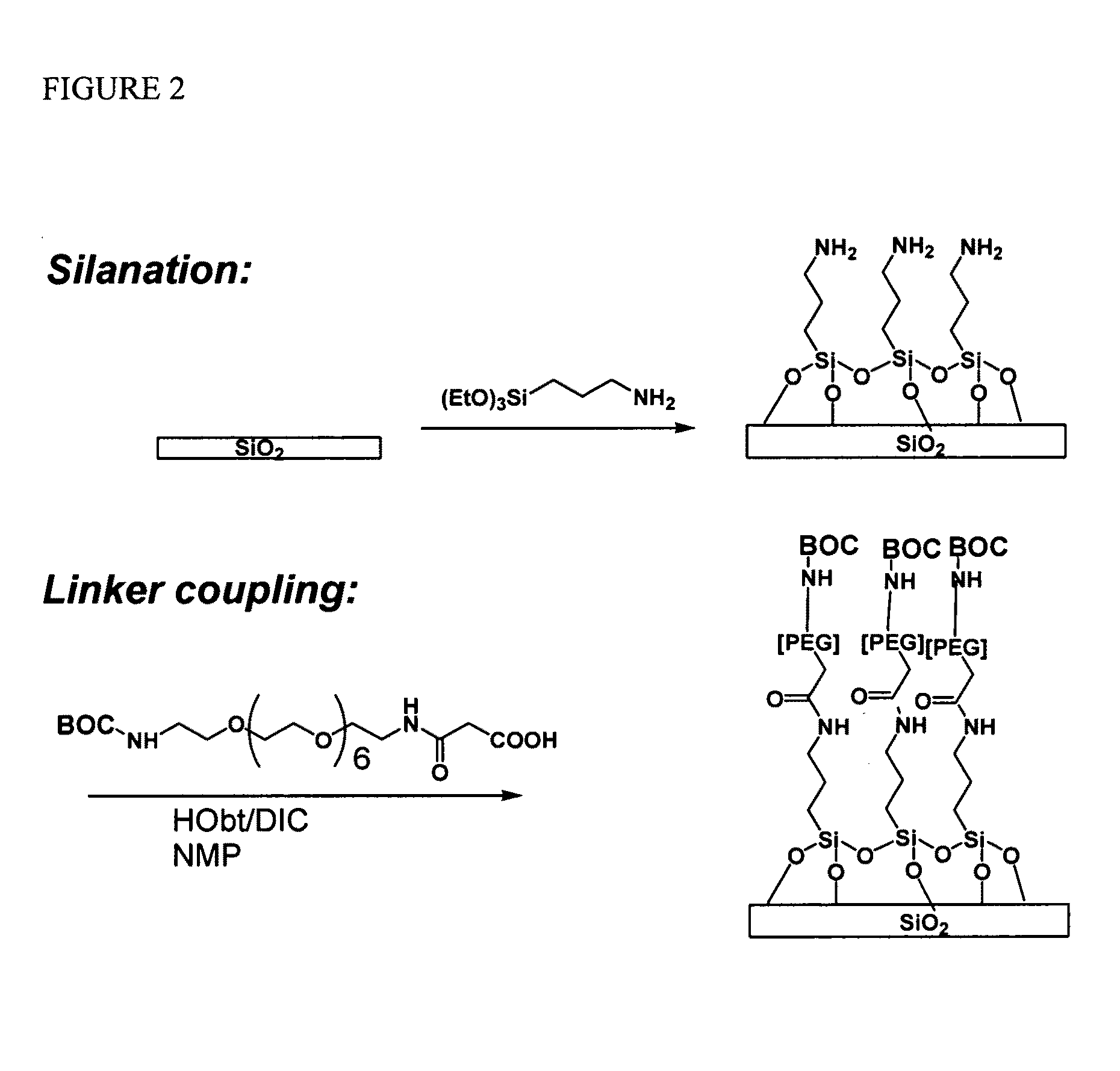
Molecular microarrays and helical peptides
InactiveUS7622295B2Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsSubstrate surfaceSemiconductor
Methods for fabricating dense arrays of polymeric molecules in a highly multiplexed manner are provided using semiconductor-processing-derived lithographic methods. Advantageously, the methods are adaptable to the synthesis of a variety of polymeric compounds. For example, arrays of branched peptides and polymers joined by peptide bonds may be fabricated in a highly multiplexed manner. Additionally, peptides that adopt helical structures are synthesized on a substrate surface and arrays are created having one or more features containing peptides capable of forming helixes.
Owner:INTEL CORP
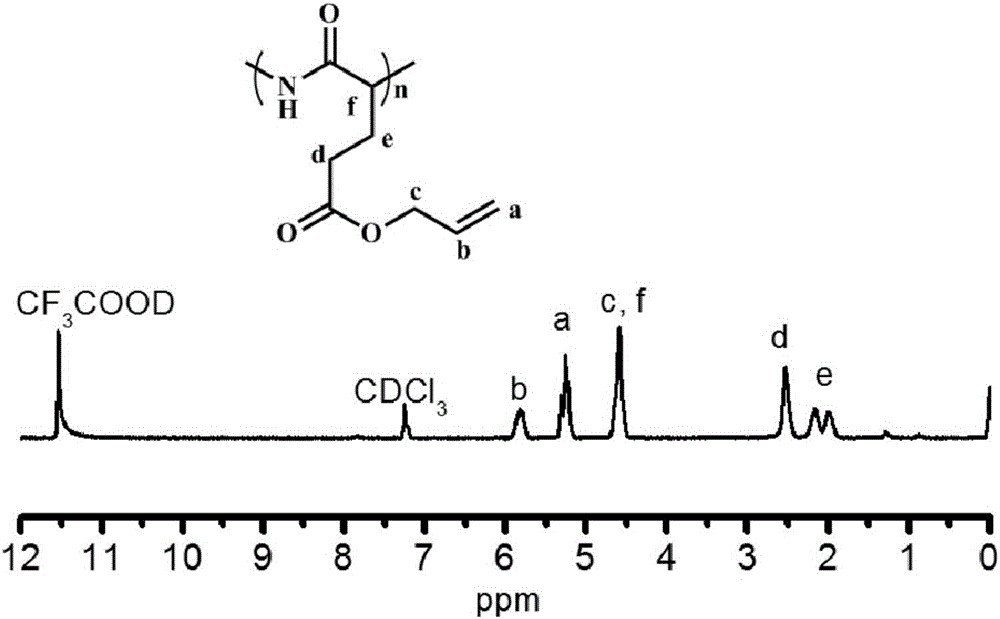
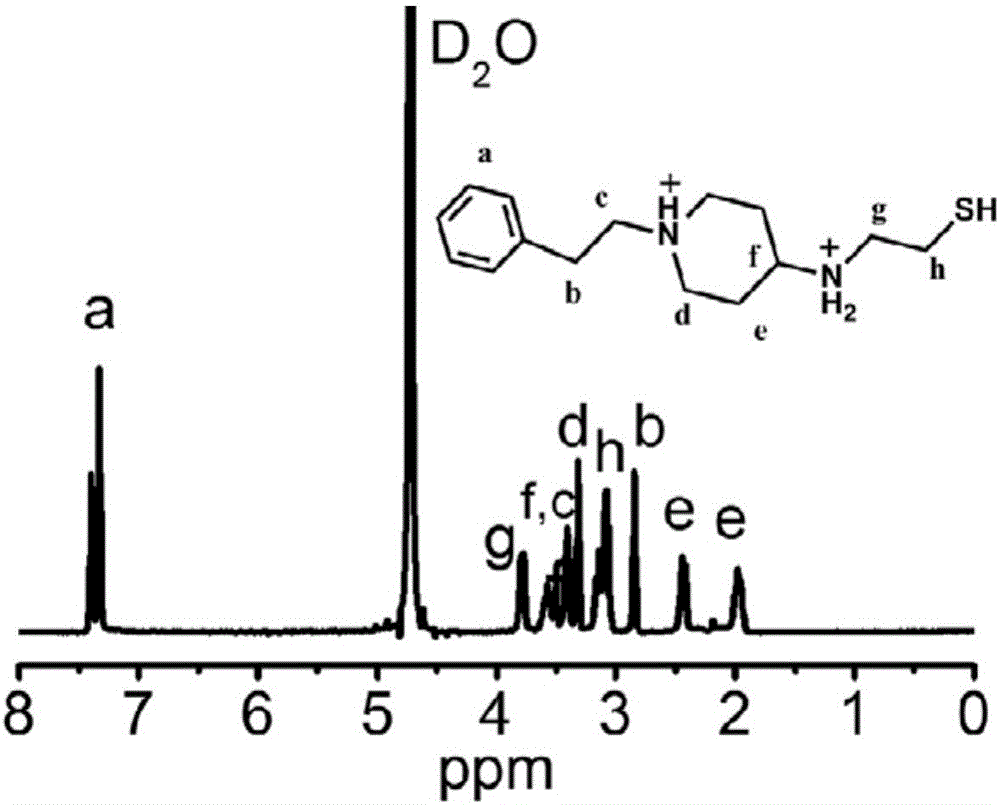
Non-viral gene transfection vector material based on cationic helical peptide
ActiveCN106589355ALow cytotoxicityHigh transfection efficiencyOrganic active ingredientsPeptidesSide chainPolypropylene
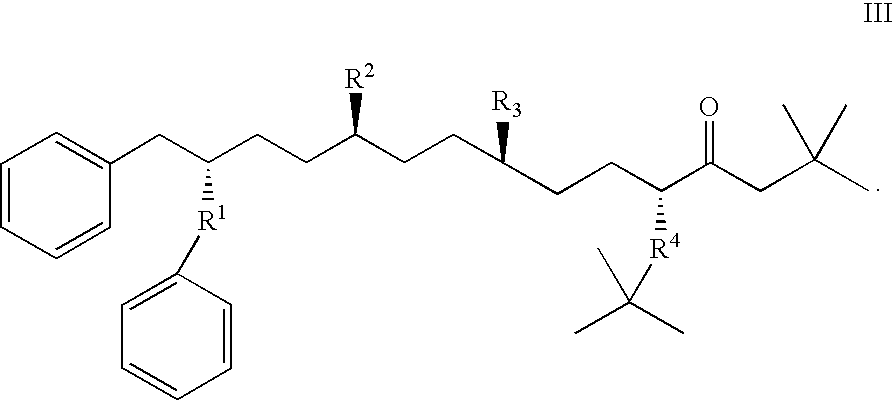
The invention belongs to the field of biomedical macromolecular materials and discloses a non-viral gene transfection vector material based on cationic helical peptide, and a preparation method and application thereof. The structure of the vector material is shown by general formulas (1) to (6) in the description, wherein R1 is C1-6 alkyl, benzyl, methoxypolyethylene glycol, polyethylene glycol or polypropylene oxide, R2 is C1-3 alkyl, benzyl or phenethyl, R3 is methyl or ethyl, R4 is hydroxy, and A is H, C1-3 alkyl, alkoxy, halogen or nitryl; in the general formulas (1) to (4), x represents polymerization degree of polypeptide and is not less than 5; in the general formulas (5) and (6), x represents the ratio of side chain repeating units, with 0<x<1. The cationic helical polypeptide main chain is of Alpha-helical conformation and effectively forms complex micelles with DNA and siRNA, and the material has good transfection efficiency, low cell toxicity and applicable to the transfer of pDNA and siRNA.
Owner:GUANGZHOU MEDICAL UNIV
Peptides promoting lipid efflux via abca1 and activating a lipoprotein lipase
ActiveUS20110033518A1Promote lipid effluxImprove lipophilicityOrganic active ingredientsApolipeptidesDiseaseA lipoprotein
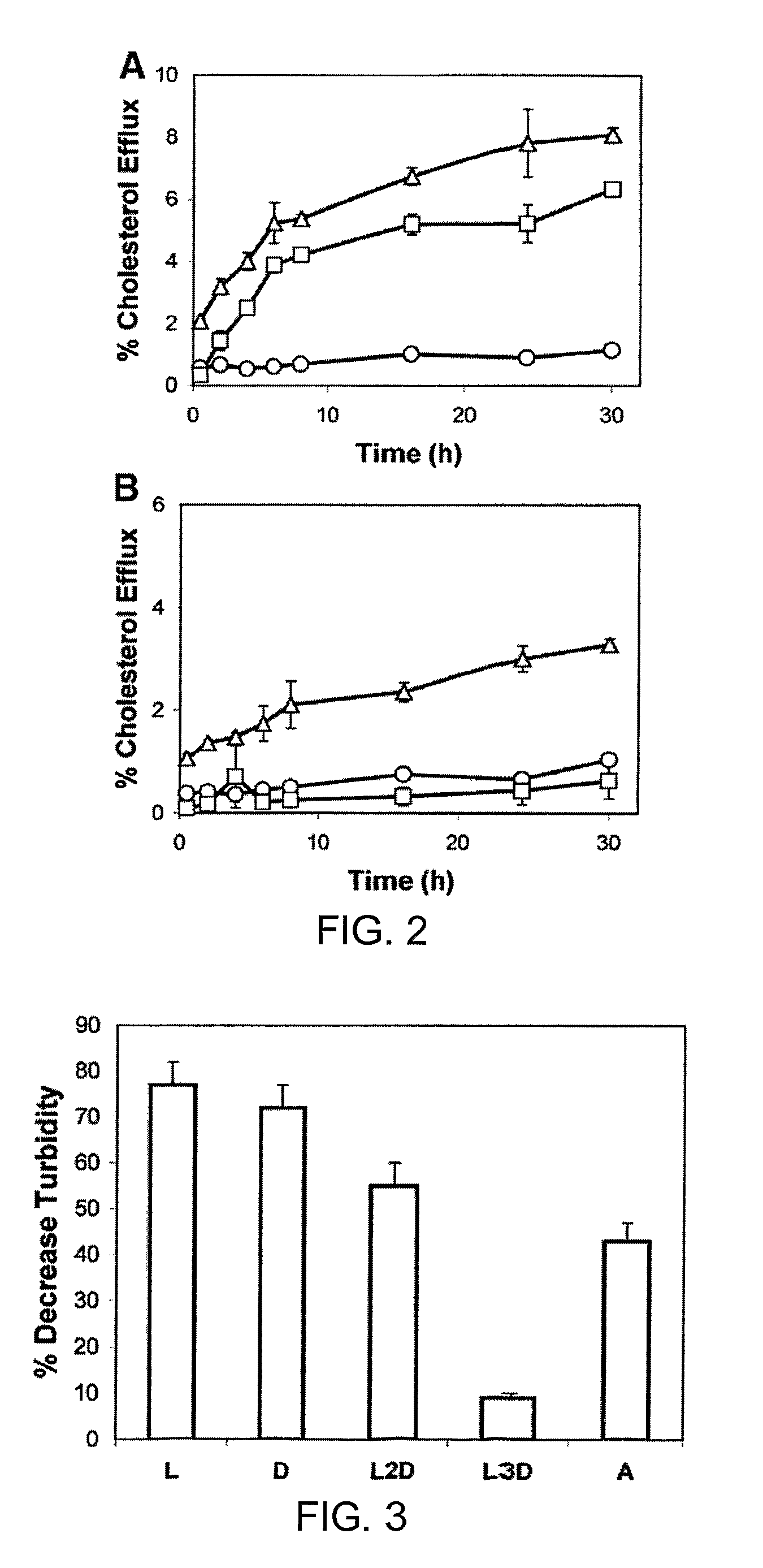
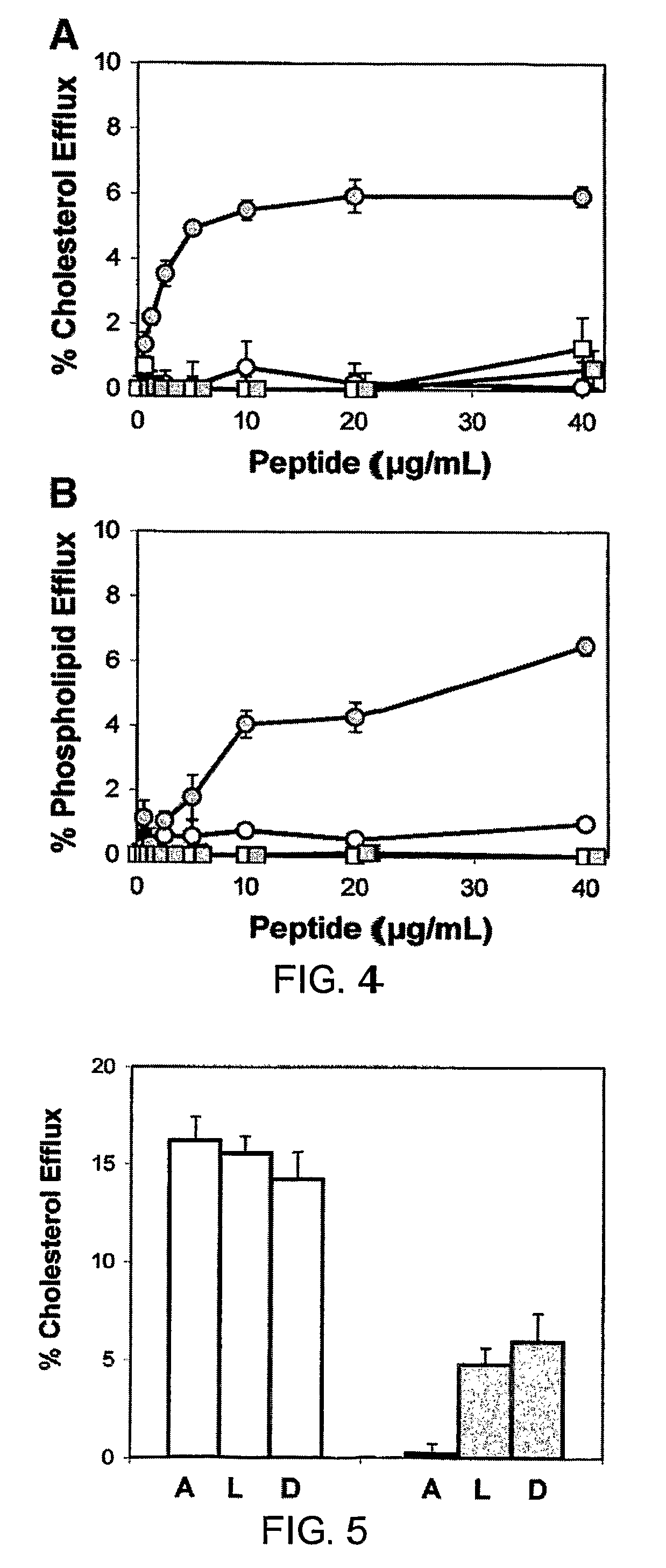
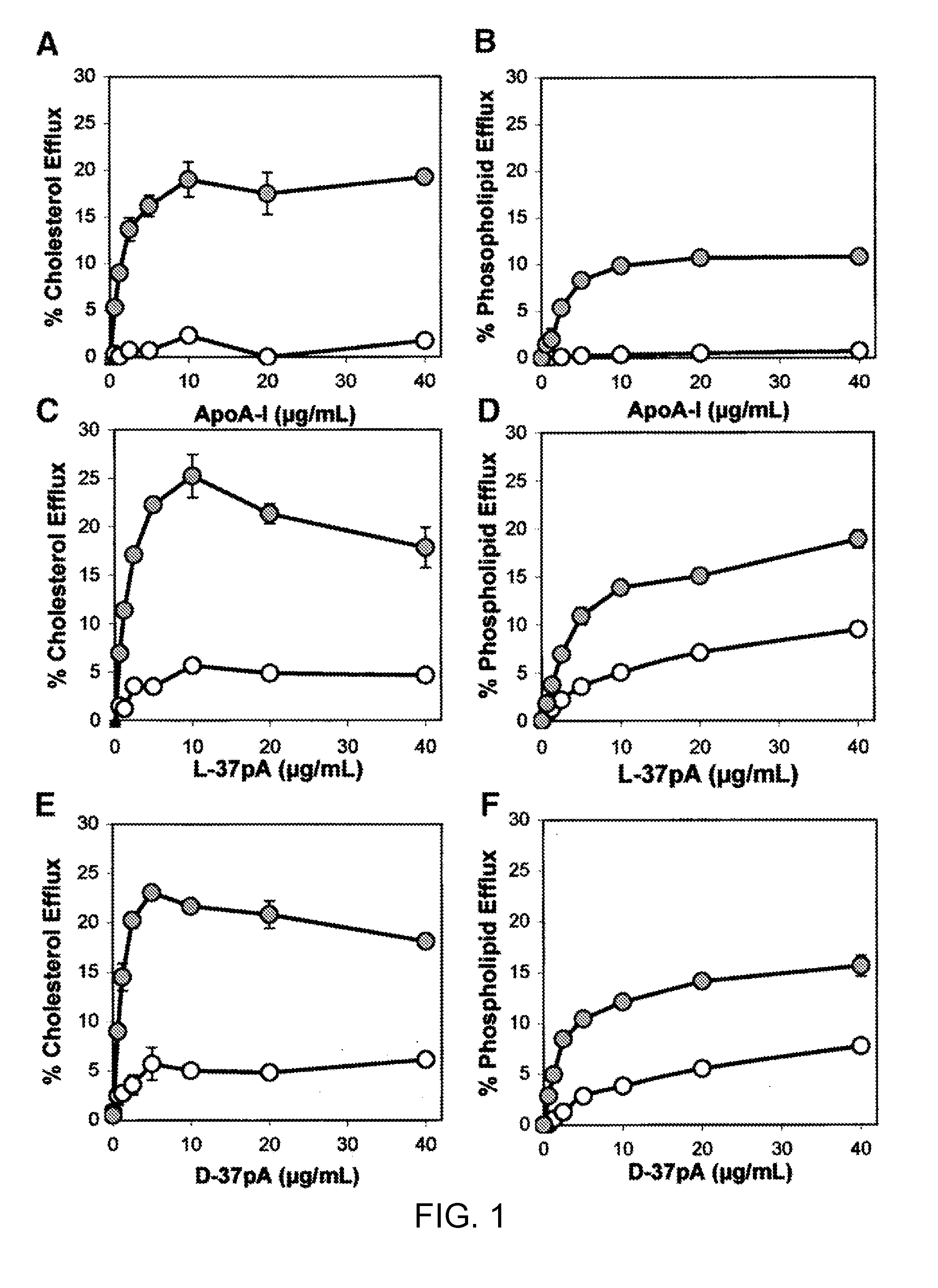
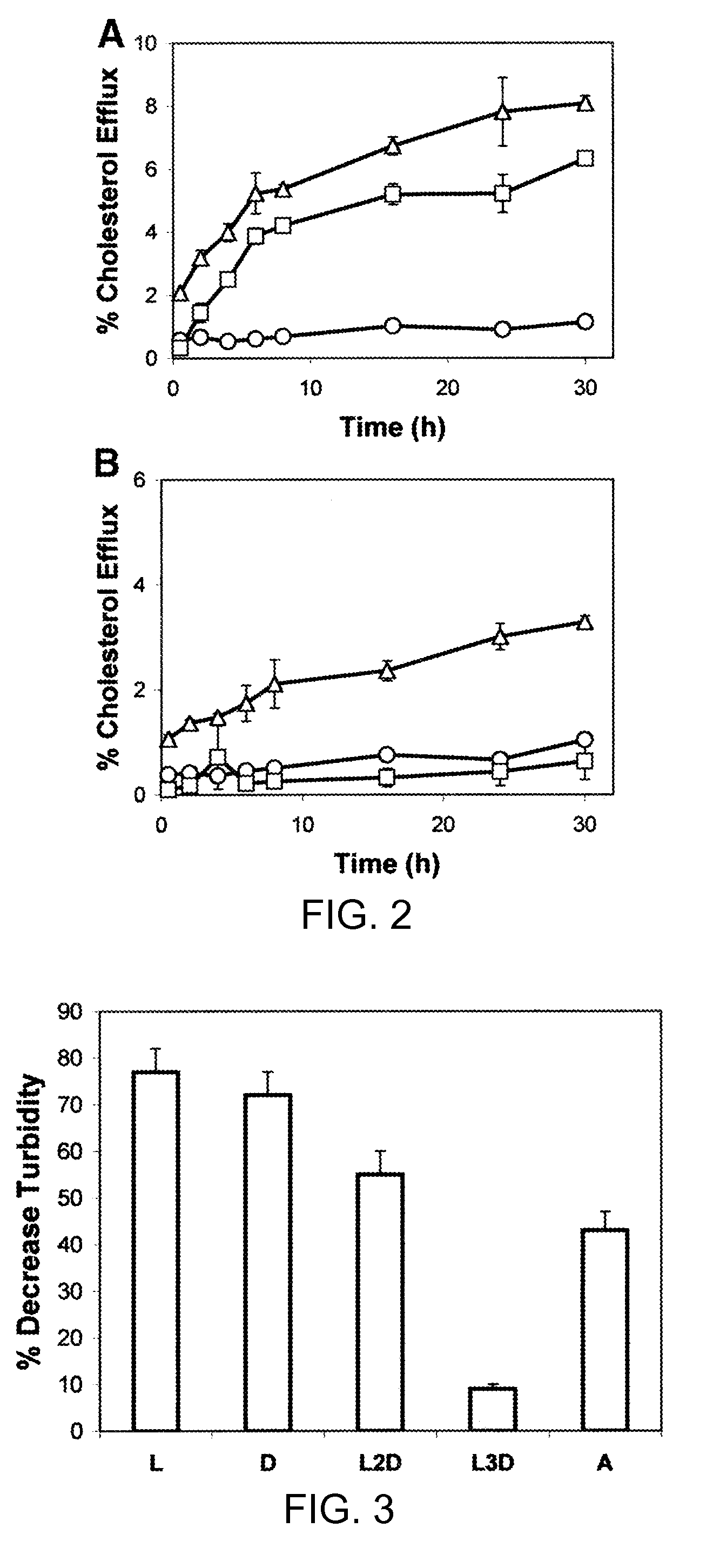
Disclosed herein are peptides and peptide analogs with multiple amphipathic α-helical domains that promote lipid efflux from cells via an ABCA1-dependent pathway, as well as peptides that activate lipoprotein lipase, and compositions comprising such peptides or combinations thereof. Also provided herein are methods of using multi-domain amphipathic α-helical peptides or peptide analogs to treat or inhibit dyslipidemic disorders. Methods for identifying non-cytotoxic peptides that promote ABCA1-dependent lipid efflux from cells and activate lipoprotein lipase within cells are also disclosed herein.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
Synthetic apolipoprotein e mimicking polypeptides and methods of use
InactiveUS20120245101A1Antibacterial agentsSenses disorderVery low-density lipoproteinAmphipathic helix
The present invention provides novel synthetic apolipoprotein E (ApoE)-mimicking peptides wherein the receptor binding domain of apolipoprotein E is covalently linked to 18A, the well characterized lipid-associating model class A amphipathic helical peptide, or a modified version thereof. Such peptides enhance low density lipoprotein (LDL) and very low density lipoprotein (VLDL) binding to and degradation by fibroblast or HepG2 cells. Also provided are possible applications of the synthetic peptides in lowering human plasma LDL / VLDL cholesterol levels, thus inhibiting atherosclerosis. The present invention also relates to synthetic peptides that can improve HDL function and / or exert anti-inflammatory properties.
Owner:UAB RES FOUND
Multi-domain amphipathic helical peptides and methods of their use
Disclosed herein are peptides or peptide analogs with multiple amphipathic α-helical domains that promote lipid efflux from cells via an ABCA1-dependent pathway. Also provided herein are methods of using multi-domain amphipathic α-helical peptides or peptide analogs to treat or inhibit dyslipidemic disorders. Methods for identifying non-cytotoxic peptides that promote ABCA1-dependent lipid efflux from cells are also disclosed herein.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
Covalently stabilized chimeric coiled-coil HIV gp41 N-peptides with improved antiviral activity
Owner:MSD ITAL +1
Multi-domain amphipathic helical peptides and methods of their use
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
Alpha helical antibacterial peptide RL as well as preparation method thereof and application thereof
ActiveCN107266533ALow hemolytic activityHigh inhibitory effectAntibacterial agentsPeptide/protein ingredientsEscherichia coliSalmonella Gallinarum
The invention provides alpha helical antibacterial peptide RL as well as a preparation method thereof and application thereof. The sequence of antibacterial peptide RL is as shown in SEQ ID No.1. The preparation method comprises the following step: designing an imperfect amphipathic alpha helical peptide template WXKYWXZZYKXWYK-NH2 containing a turn unit on the basis of imperfect amphipathic alpha helical multi-peptide folding principle, wherein X is positive charge amino acid, Y is hydrophobic amino acid, Z is the turn unit, and the antibacterial peptide is named as RL when X is equal to R, Y is equal to L and ZZ is equal to <D>PG. The preparation method is simple in technology, and antibacterial and hemolytic activity detection is performed on the obtained antibacterial peptide and proves that RL has efficient inhibiting effect on seven bacteria of escherichia coli, pseudomonas aeruginosa, staphylococcus aureus, staphylococcus epidermidis, salmonella typhimurium, salmonella gallinarum and bacillus subtilis, and has very low hemolytic activity.
Owner:NORTHEAST AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Compositions and Methods for the Treatment of Huanglongbing (HLB) aka Citrus Greening in Citrus Plants
PendingUS20200102356A1Improve the bactericidal effectReduce sensitivityAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsPlant peptidesAnti microbial peptideAmphipathic helix
The invention may include engineered antimicrobial peptides to treat HLB disease, preferably in citrus plants. Specifically, the invention may include novel antimicrobial peptide derived from amphipathic helical peptides that may further be used to treat HLB disease in citrus plants. In one embodiment, the invention may include an engineered antimicrobial peptide formed by coupling two amphipathic helical peptides. Specifically, a generalized antimicrobial peptide of the invitation may include a first amphipathic helical peptide coupled with a second amphipathic helical peptide by a linker domain forming a helix-turn-helix scaffold formation. Such amphipathic helical peptides may be endogenous to a target host, preferably a citrus plant.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA +1
Targeting deregulated wnt signaling in cancer using stabilized alpha-helices of bcl-9
ActiveUS20210002336A1Improved pharmacokinetic propertiesImprove stabilityPeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderHuman cancerIn vivo
The invention provides structurally-constrained peptides by hydrocarbon stapling of a BCL9 HD2 helix for use as a therapeutic agent. The invention further provides methods and kits for use of the structurally-constrained peptide of the instant invention. The invention is based, at least in part, on the results provided herein demonstrating that hydrocarbon stapled helical peptides display excellent proteolytic, acid, and thermal stability, restore the native helical structure of the peptide, possess superior pharmacokinetic properties compared to the corresponding unmodified peptides, and are highly effective in binding to β-catenin in vitro, in cellulo, and in vivo, disrupting the BCL-9 / β-catenin interaction, and thereby interfering with deregulated Wnt / β-catenin signaling for therapeutic benefit in a variety of human diseases including human cancer.
Owner:DANA FARBER CANCER INST INC
Hydrocarbon stapled stabilized alpha-helices of the HIV-1 GP41 membrane proximal external region
The invention provides structurally constrained viral peptides for use as therapeutic and vaccination agents, and for the production of antibodies for use in a number of applications including as therapeutic agents. The invention further provides methods and kits for use of the structurally constrained peptides and antibodies of the instant invention. The invention is based, at least in part, on the result provided herein demonstrating that viral hydrocarbon stapled helical peptides display excellent proteolytic, acid, and thermal stability, restore the native helical structure of the peptide, are highly effective in interfering with the viral fusogenic process, and possess superior pharmacokinetic properties compared to the corresponding unmodified peptides.
Owner:DANA FARBER CANCER INST INC
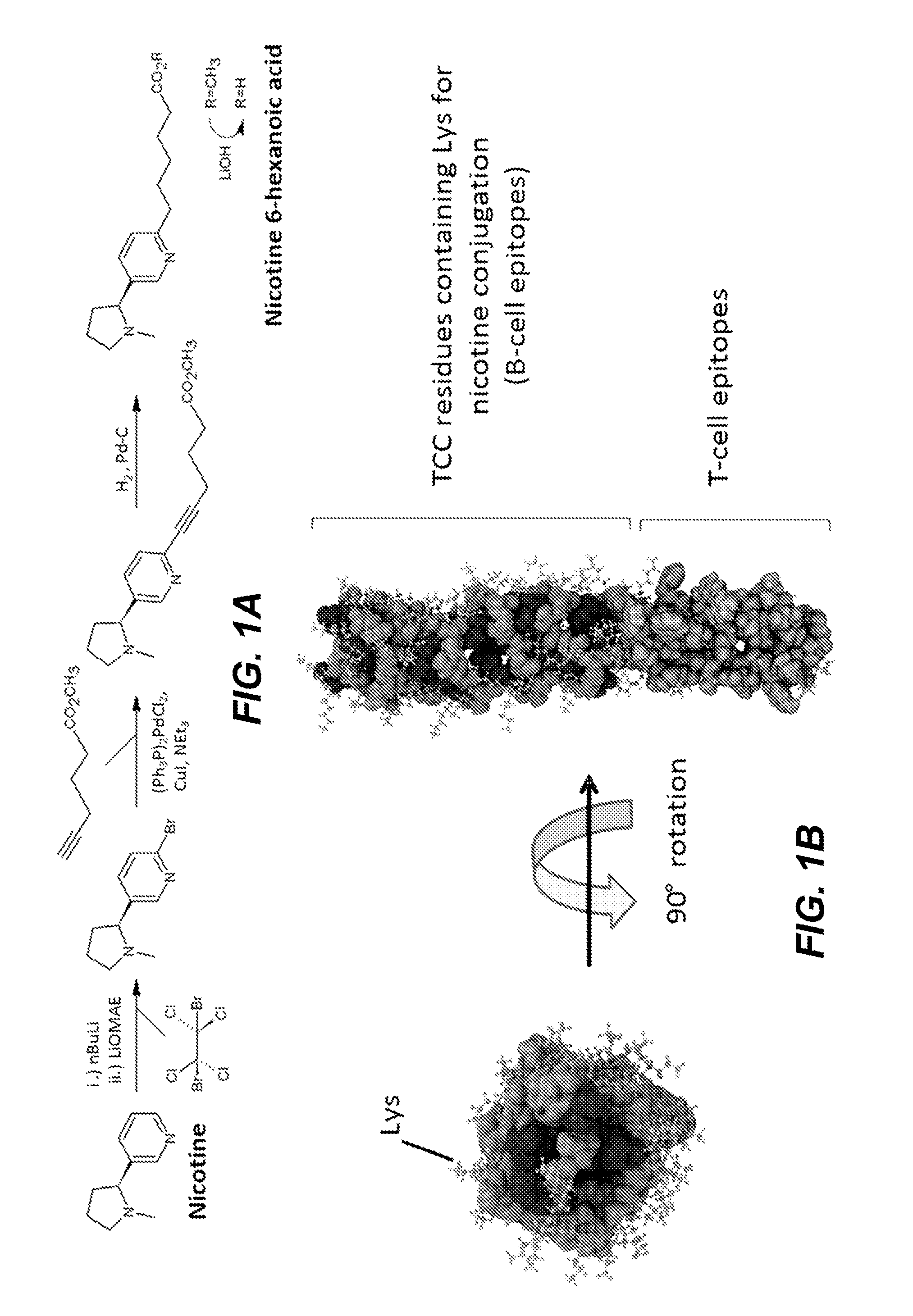
Synthetic hapten carrier compositions and methods
InactiveUS20170049883A1Thorough understandingSsRNA viruses negative-senseImmunoglobulin superfamilyVaccine deliveryAspartic acid residue
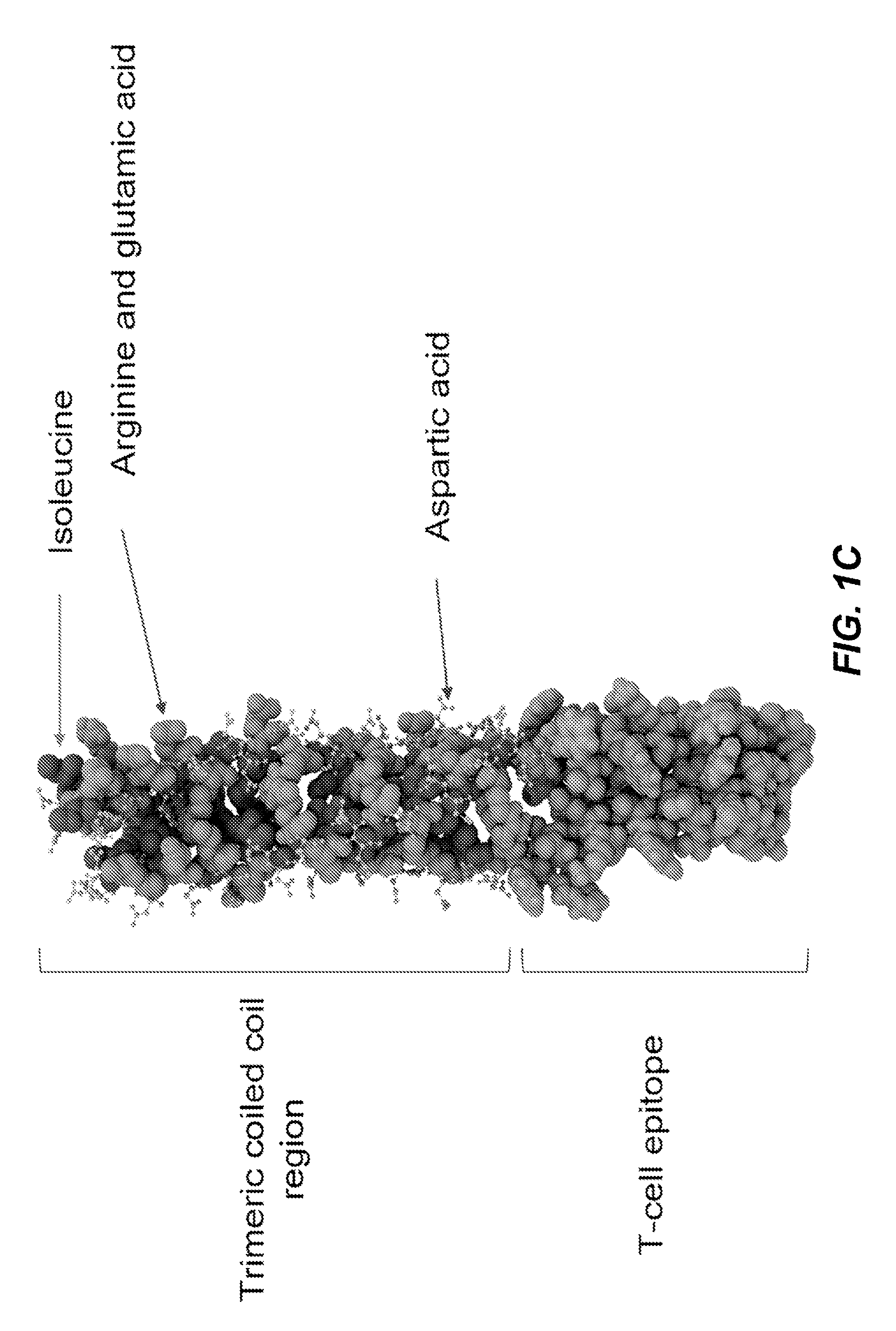
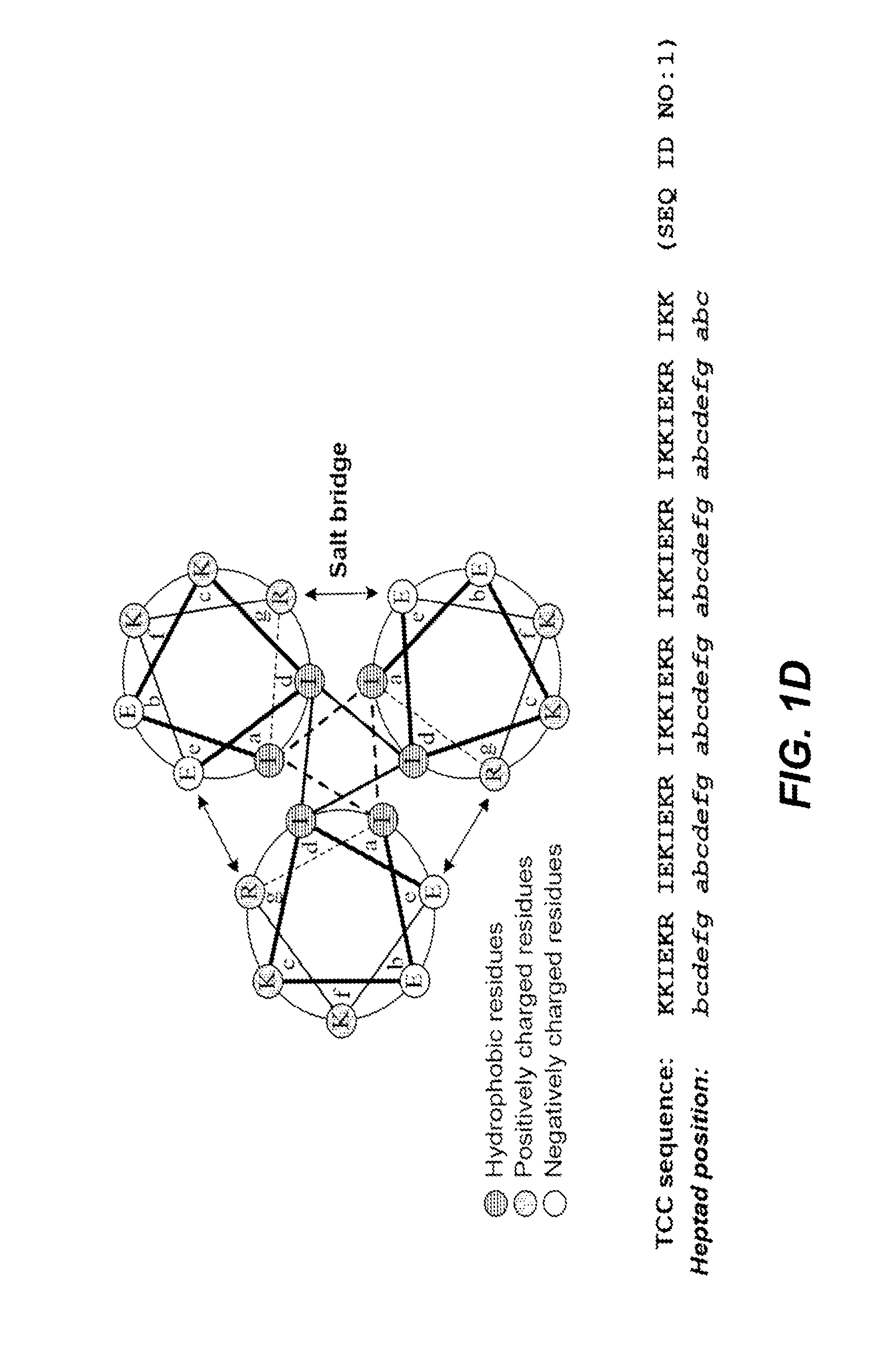
The present disclosure relates to peptide monomers comprising an amphipathic ?-helical peptide, and optionally, at least one T cell epitope peptide; and to dimers and trimers comprising the peptide monomers. The monomeric, dimeric, and trimeric peptides may be conjugated to at least one hapten, wherein the hapten is linked to a lysine or aspartic acid residue of the peptide monomer. These peptide conjugates are useful as vaccine delivery vehicles.
Owner:TRIA BIOSCI
Process for screening of a binding peptide specific for specific RNA and RNA binding peptides therefrom
InactiveUS20080318797A1Increase diversityImprove bindingCompound screeningPeptide librariesNucleotideBinding peptide
The present invention relates to a screening method for RNA specific binding peptide using alpha-helical peptides. The screening method for RNA specific binding peptide of the present invention using alpha-helical peptides enables the selection of a peptide having strong binding capacity to a specific RNA having particular morphology and nucleotide sequence and the investigation of functions of RNA using the selected peptides, and is very useful for the production of a new drug using synthetic peptide having more powerful and specific binding capacity to RNA than those of natural peptides.
Owner:SEOUL NAT UNIV R&DB FOUND
Multi-domain amphipathic helical peptides and methods of their use
Disclosed herein are peptides or peptide analogs with multiple amphipathic α-helical domains that promote lipid efflux from cells via an ABCA1-dependent pathway. Also provided herein are methods of using multi-domain amphipathic α-helical peptides or peptide analogs to treat or inhibit dyslipidemic disorders. Methods for identifying non-cytotoxic peptides that promote ABCA1-dependent lipid efflux from cells are also disclosed herein.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
Peptides and peptide mimetics to inhibit the onset and/or progression of fibrotic and/or pre-fibrotic pathologies
This invention provides methods of inhibiting the onset or progression of a fibrotic disease (or pre-fibrotic pathology) in a mammal. The method involves administering oen or more peptides (e.g., class A amphipathic helical peptides, G* peptides, etc.) as described herein to a mammal in need thereof, in an amount effective to inhibit the onset and / or progression of the fibrotic disease (or pre-fibrotic condition) in the mammal. In certain embodiments the fibrotic disease is selected from the group consisting of retroperitoneal fibrosis (RPF), hepatic fibrosis and / or chirrhosis, renal fibrosis, and pancreatic fibrosis
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Structured viral peptide compositions and methods of use
ActiveUS20120141527A1Stimulate immune responsePeptide/protein ingredientsViral antigen ingredientsVaccinationThermal stability
The invention provides structurally constrained viral peptides for use as therapeutic and vaccination agents, and for the production of antibodies for use in a number of applications including as therapeutic agents. The invention further provides methods and kits for use of the structurally constrained peptides and antibodies of the instant invention. The invention is based, at least in part, on the result provided herein demonstrating that viral hydrocarbon stapled helical peptides display excellent proteolytic, acid, and thermal stability, restore the native helical structure of the peptide, are highly effective in interfering with the viral fusogenic process, and possess superior pharmacokinetic properties compared to the corresponding unmodified peptides.
Owner:DANA FARBER CANCER INST INC
Molecular microarrays and helical peptides
Methods for fabricating dense arrays of polymeric molecules in a highly multiplexed manner are provided using semiconductor-processing-derived lithographic methods. Advantageously, the methods are adaptable to the synthesis of a variety of polymeric compounds. For example, arrays of branched peptides and polymers joined by peptide bonds may be fabricated in a highly multiplexed manner. Additionally, peptides that adopt helical structures are synthesized on a substrate surface and arrays are created having one or more features containing peptides capable of forming helixes.
Owner:CABEZAS EDELMIRA
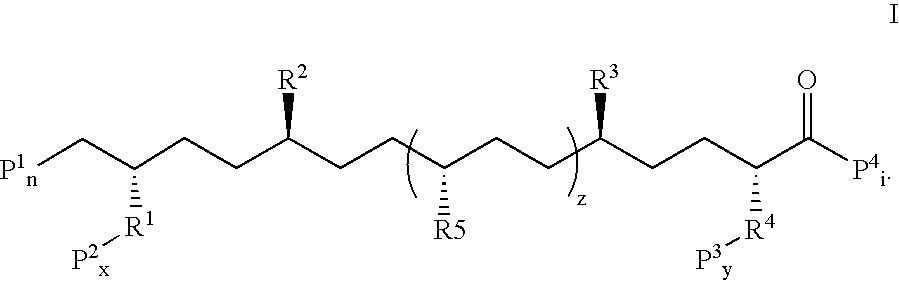
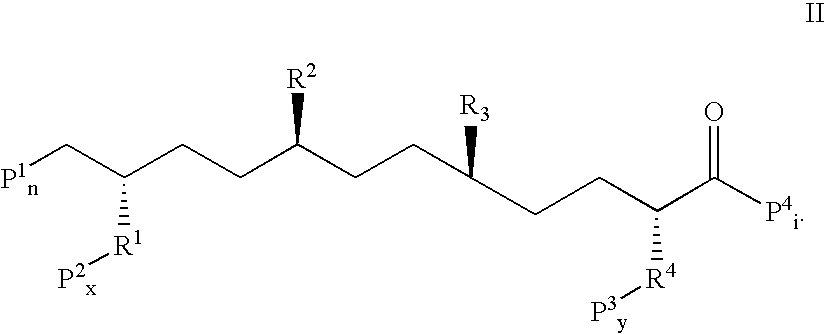
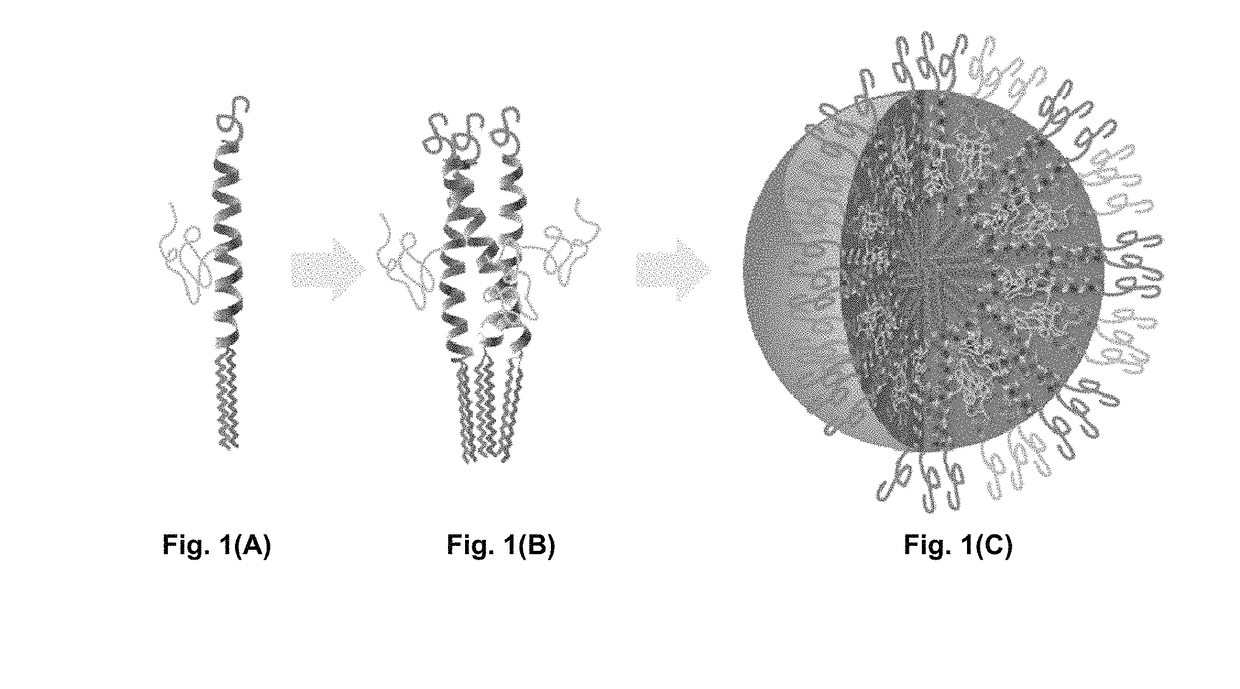
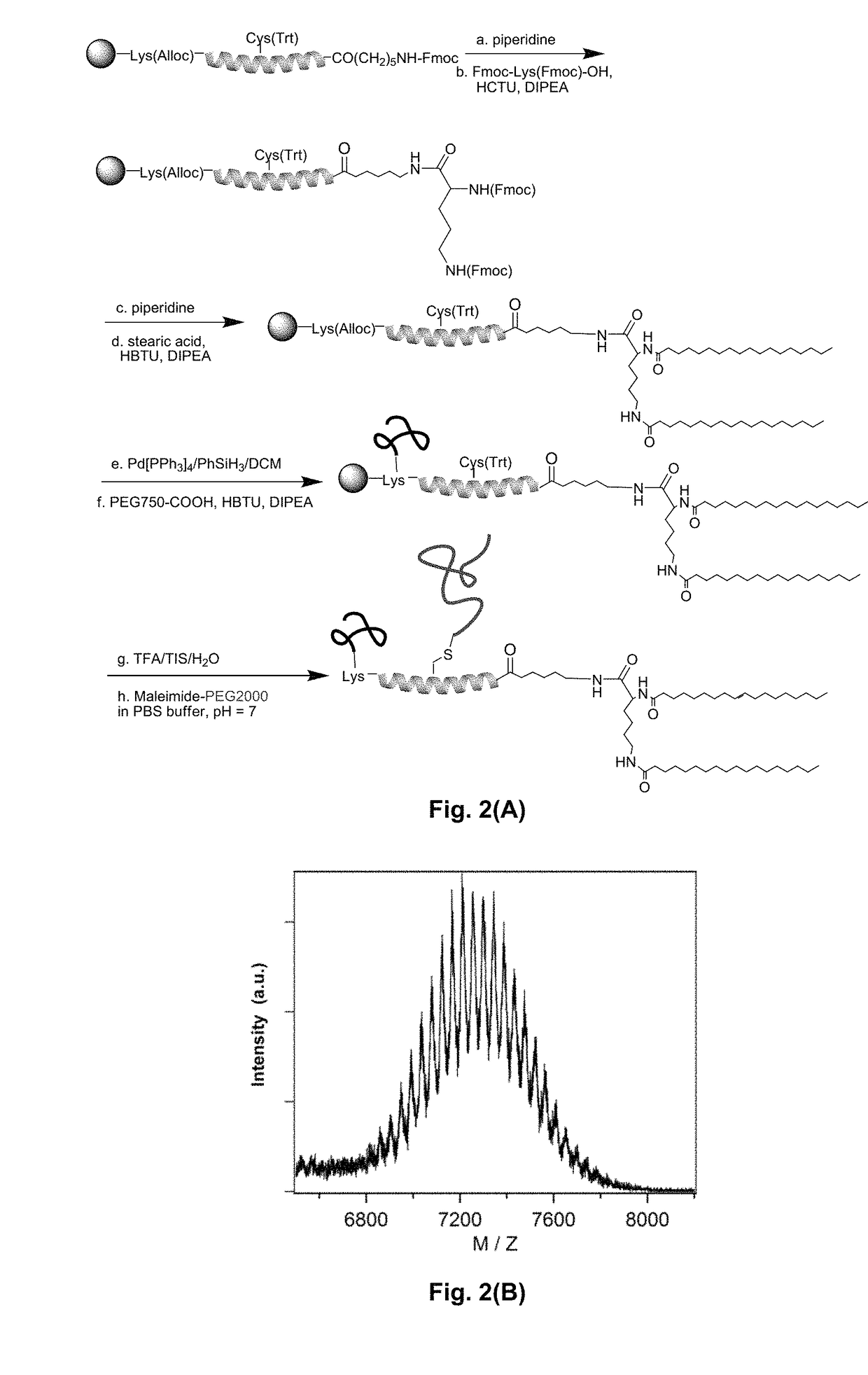
Bis-polymer lipid-peptide conjugates and nanoparticles thereof
The present invention provides bis-polymer lipid-peptide conjugates containing a hydrophobic block and headgroup containing a helical peptide and two polymer blocks. The conjugates can self-assemble to form helix bundle subunits, which in turn assemble to provide micellar nanocarriers for drug cargos and other agents. Particles containing the conjugates and methods for forming the particles are also disclosed.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Targeting deregulated Wnt signaling in cancer using stabilized alpha-helices of BCL-9
ActiveUS10703785B2Improved pharmacokinetic propertiesImprove stabilityPeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderHuman cancerIn vivo
The invention provides structurally-constrained peptides by hydrocarbon stapling of a BCL9 HD2 helix for use as a therapeutic agent. The invention further provides methods and kits for use of the structurally-constrained peptide of the instant invention. The invention is based, at least in part, on the results provided herein demonstrating that hydrocarbon stapled helical peptides display excellent proteolytic, acid, and thermal stability, restore the native helical structure of the peptide, possess superior pharmacokinetic properties compared to the corresponding unmodified peptides, and are highly effective in binding to β-catenin in vitro, in cellulo, and in vivo, disrupting the BCL-9 / β-catenin interaction, and thereby interfering with deregulated Wnt / β-catenin signaling for therapeutic benefit in a variety of human diseases including human cancer.
Owner:DANA FARBER CANCER INST INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com