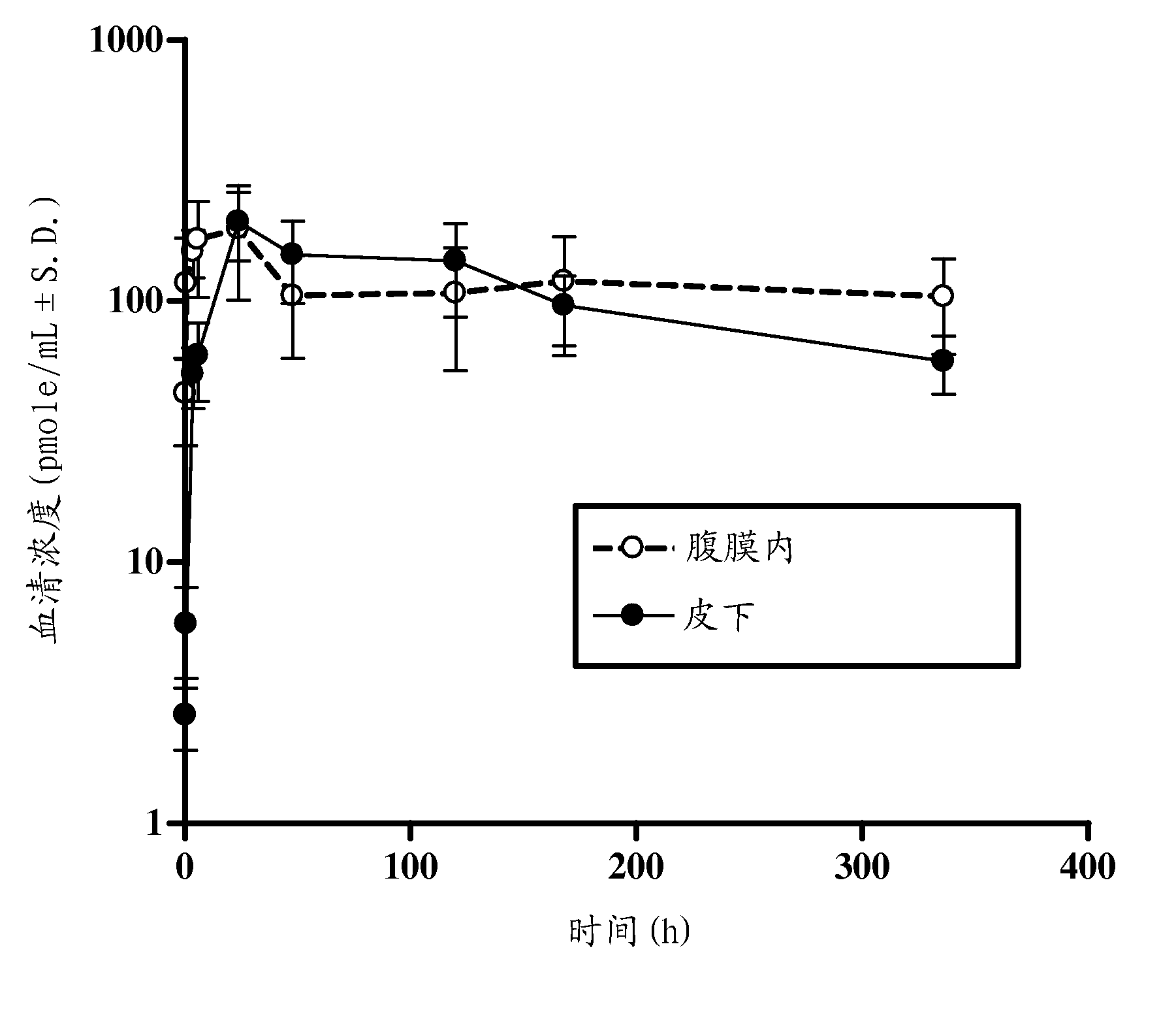
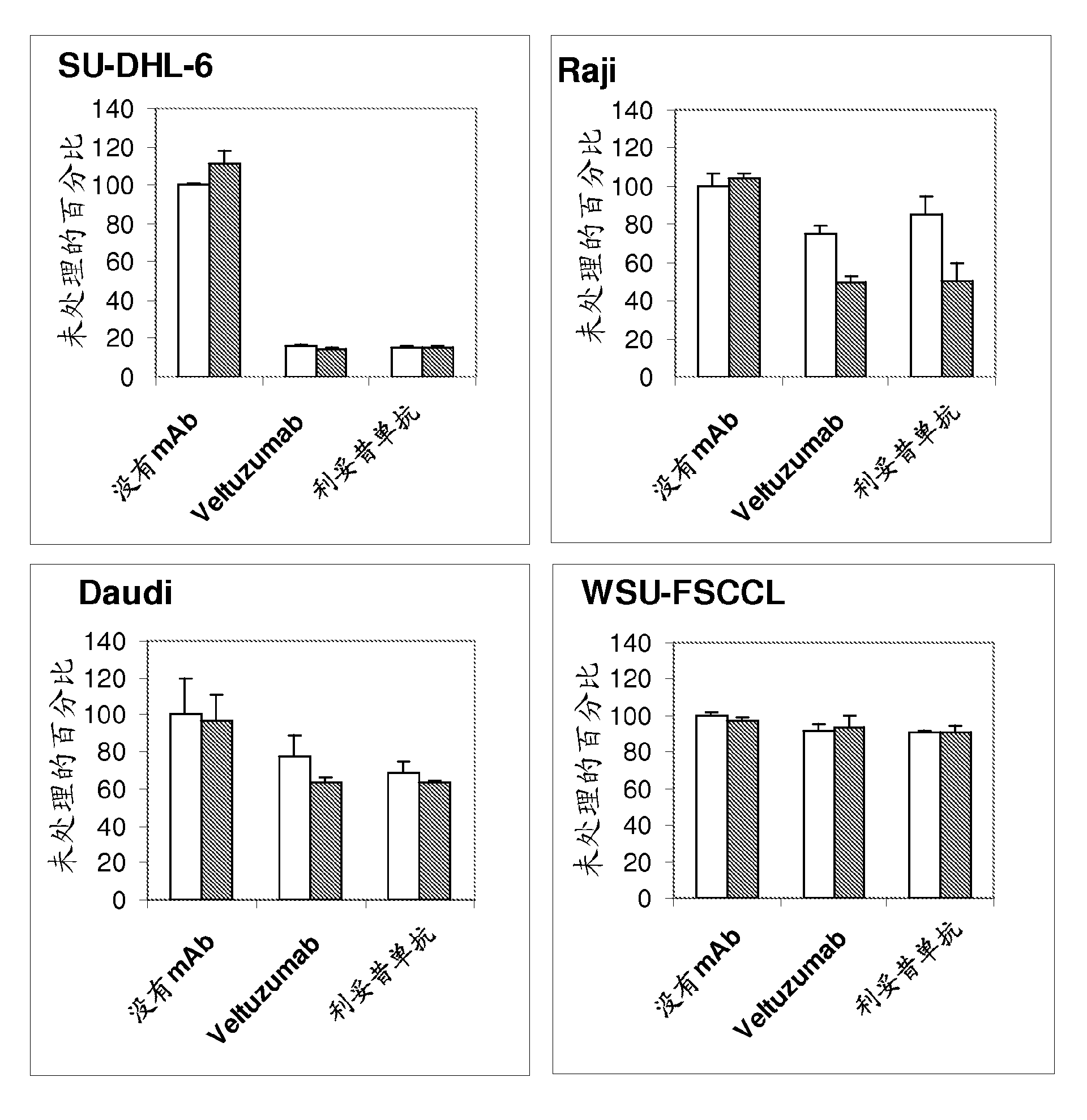
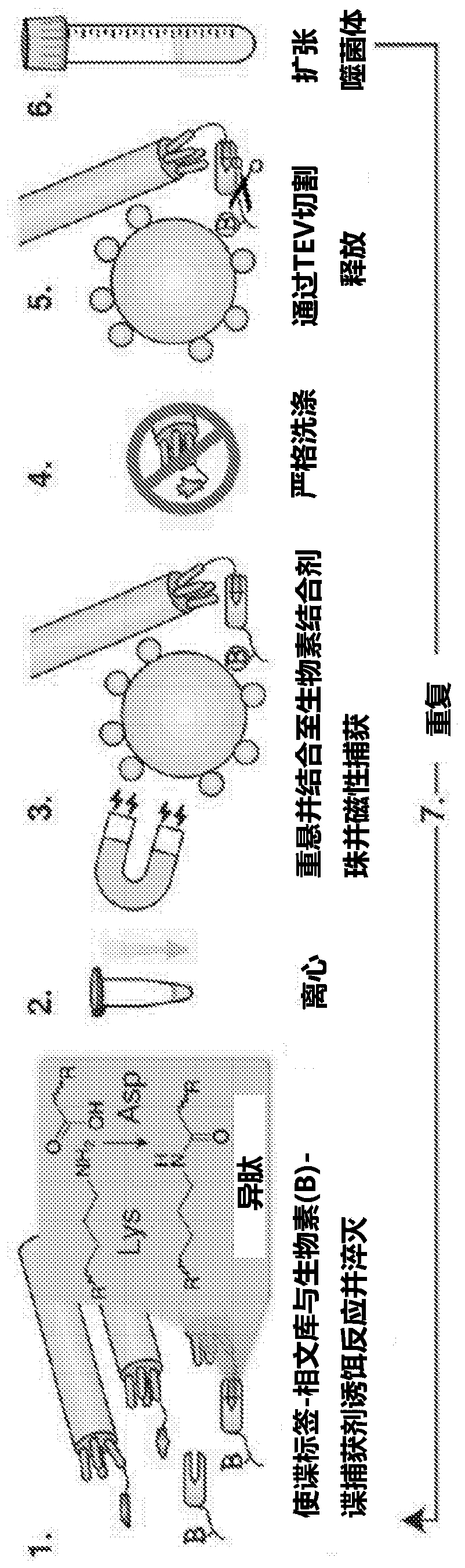
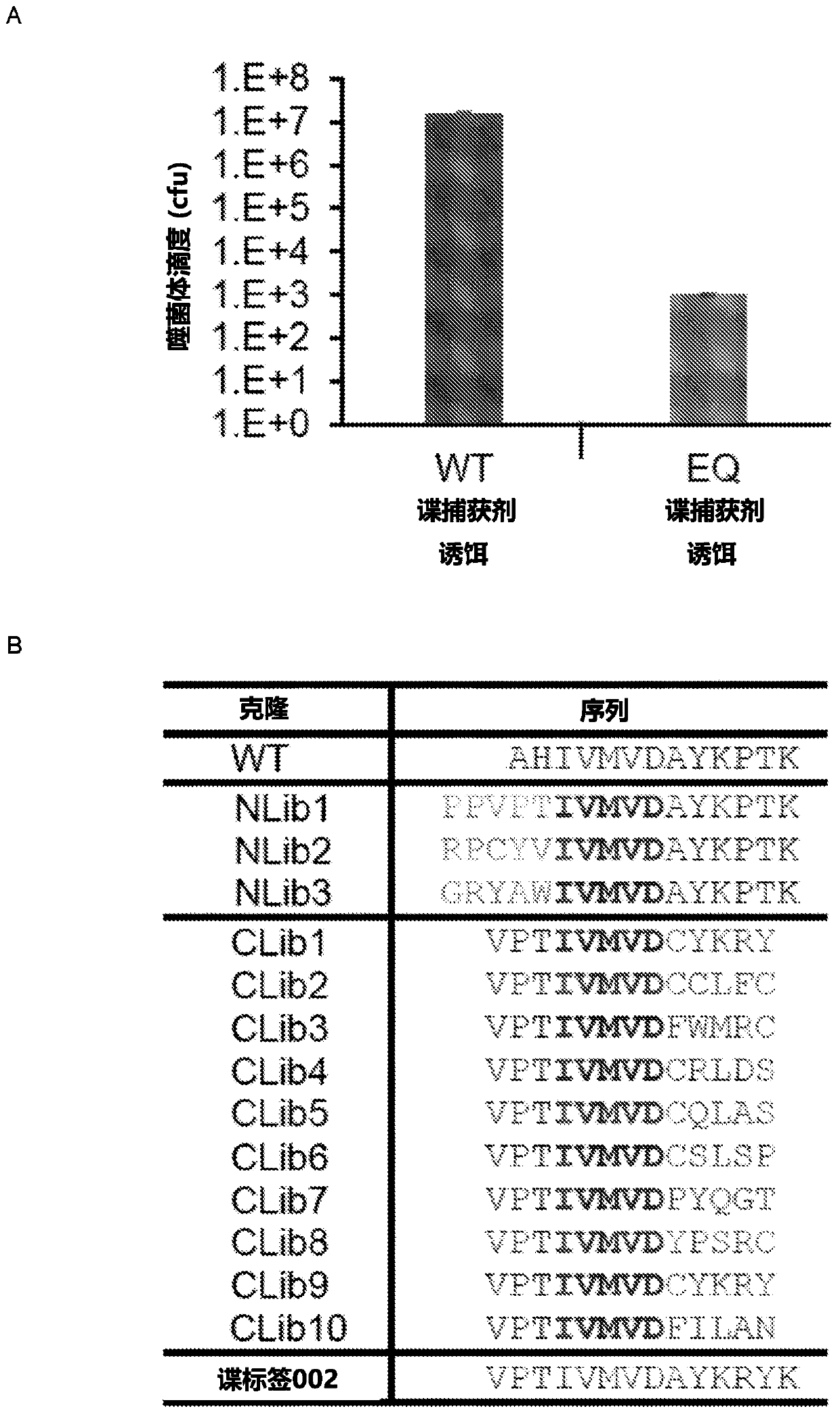
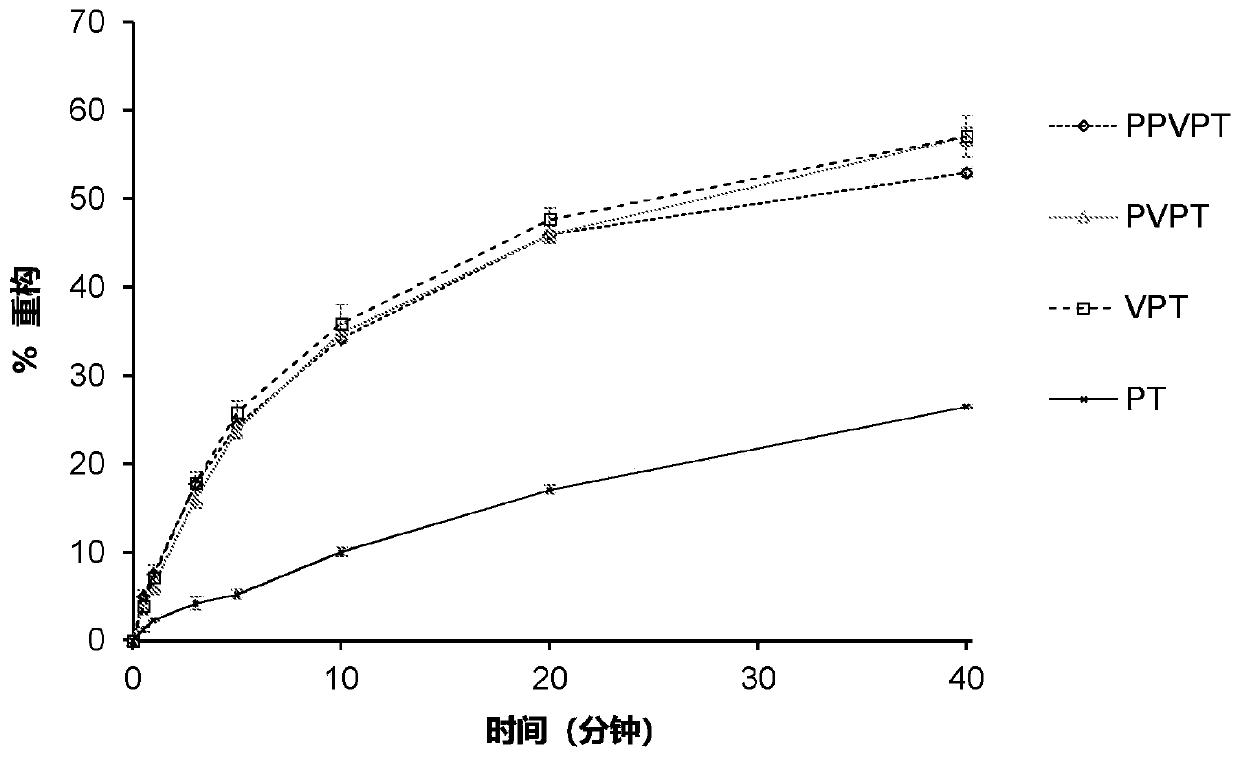
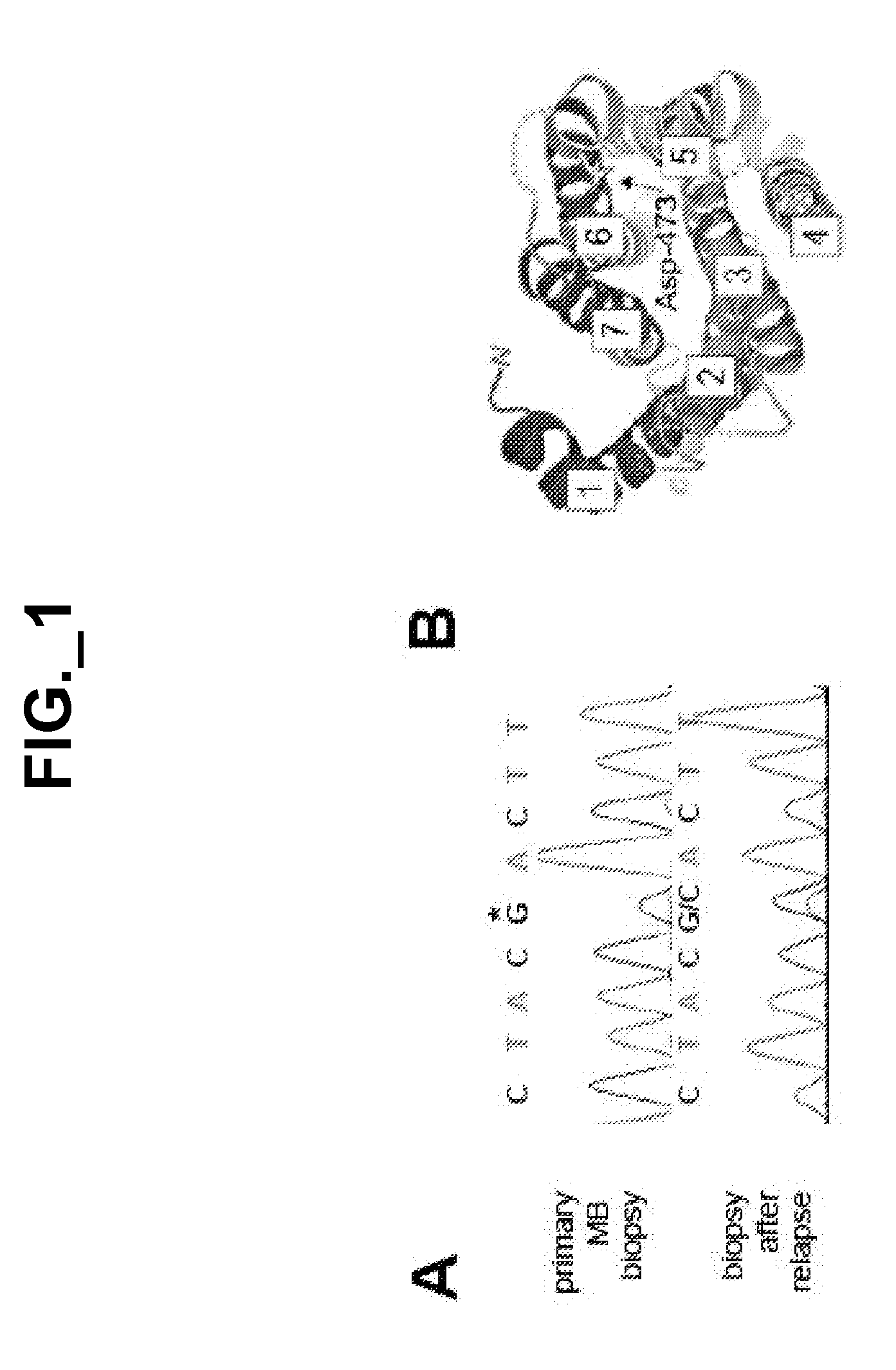
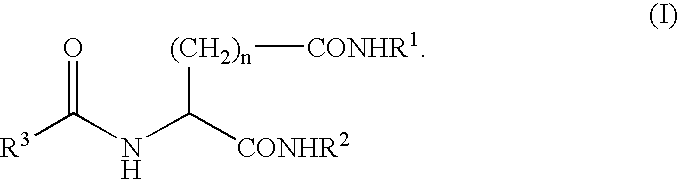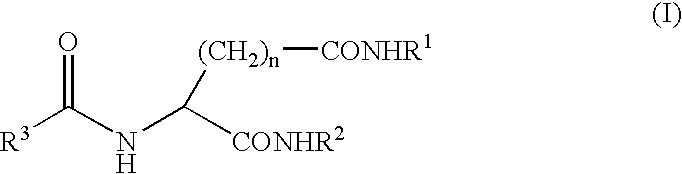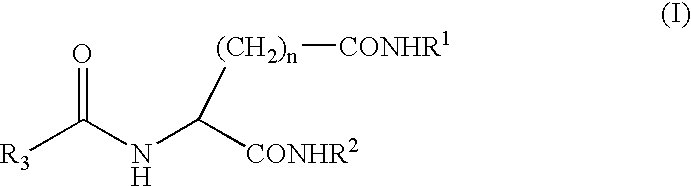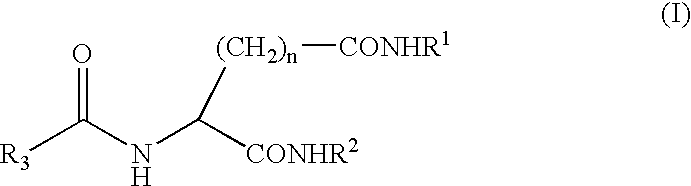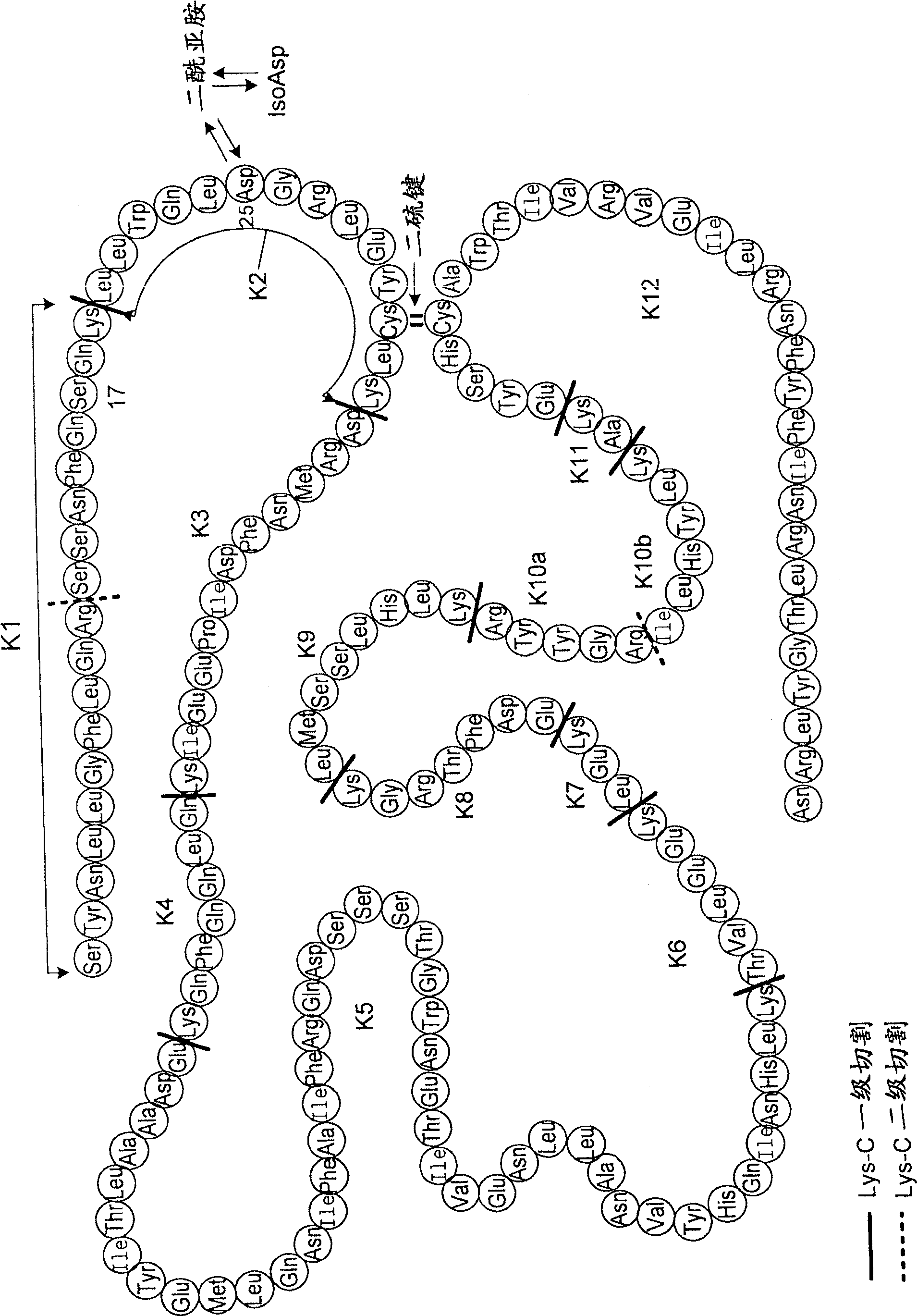Patents
Literature
79 results about "Aspartic acid residue" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
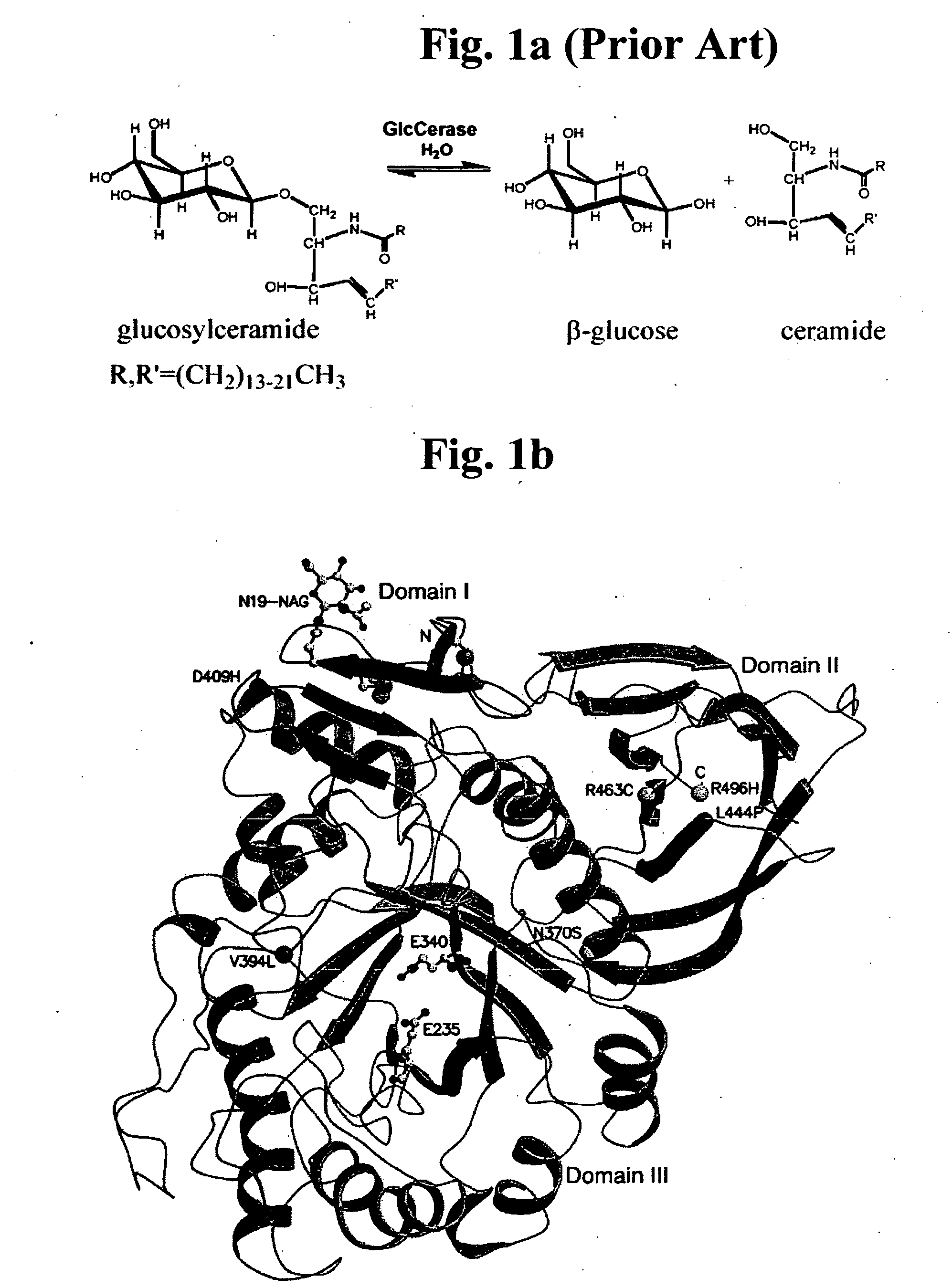
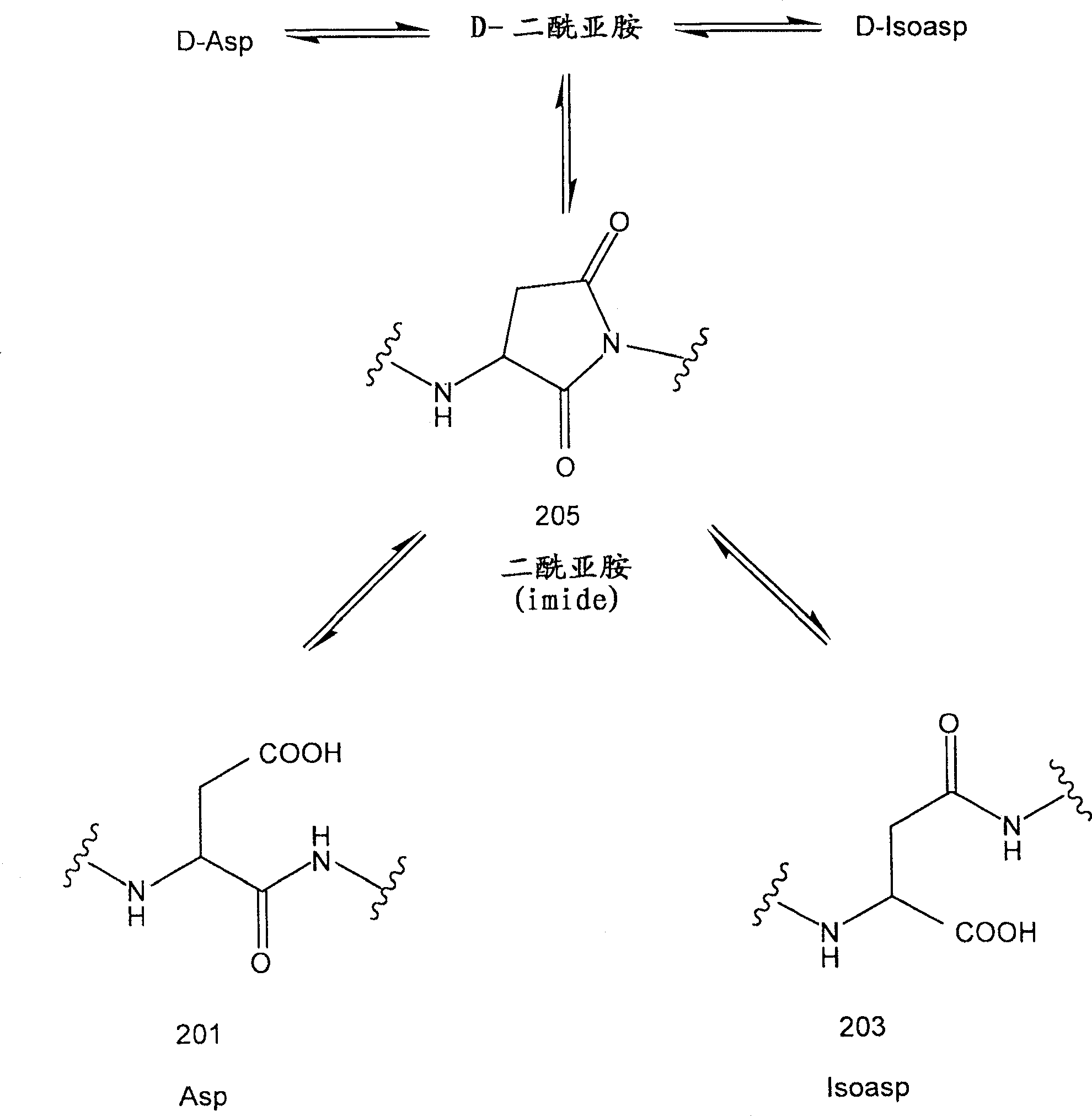
Aspartic acid (Asp) residues in peptides and proteins (l-Asp) are known to undergo spontaneous nonenzymatic reactions to form l-β-Asp, d-Asp, and d-β-Asp residues. The formation of these abnormal Asp residues in proteins may affect their three-dimensional structures and hence their properties and functions.
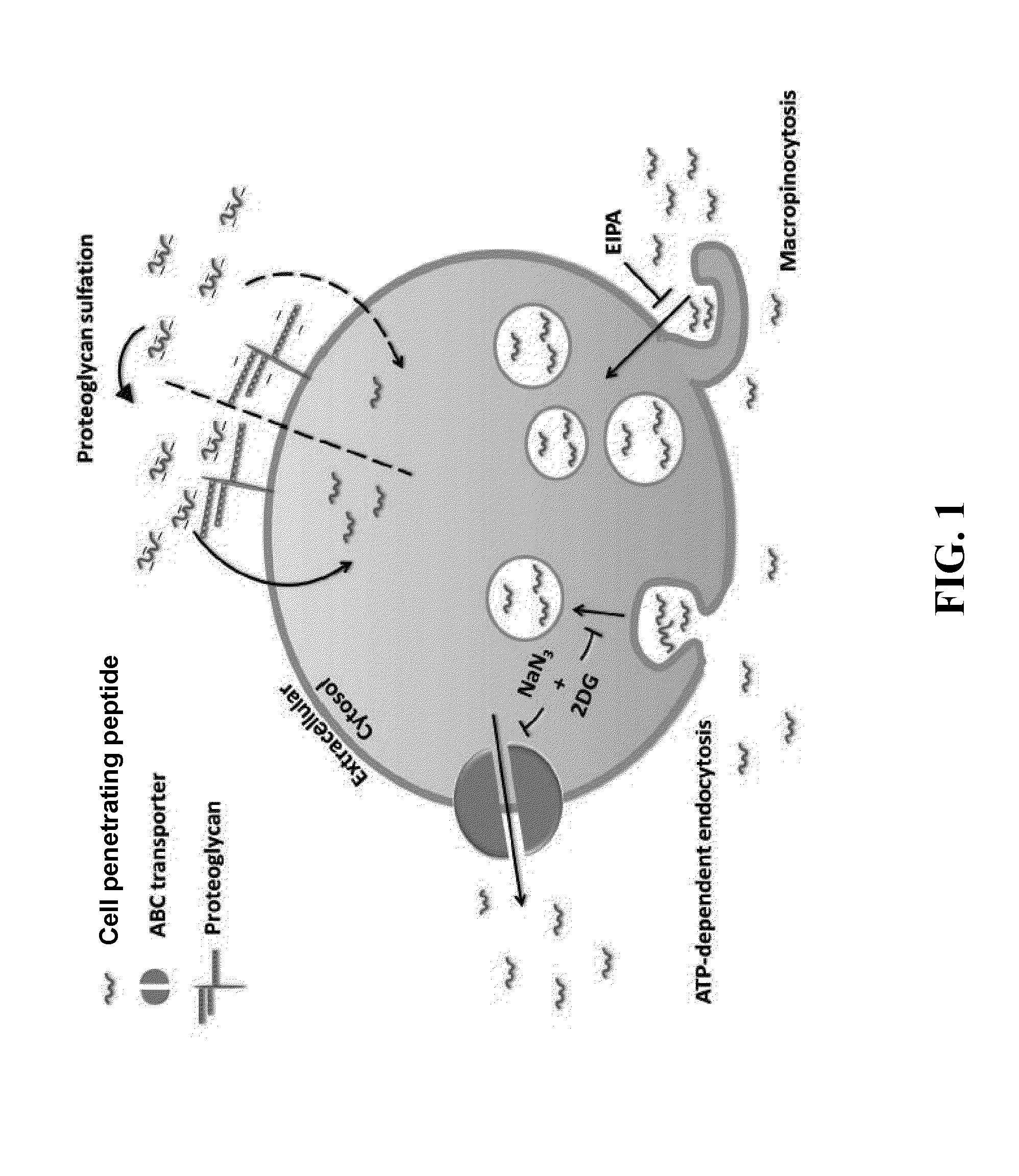
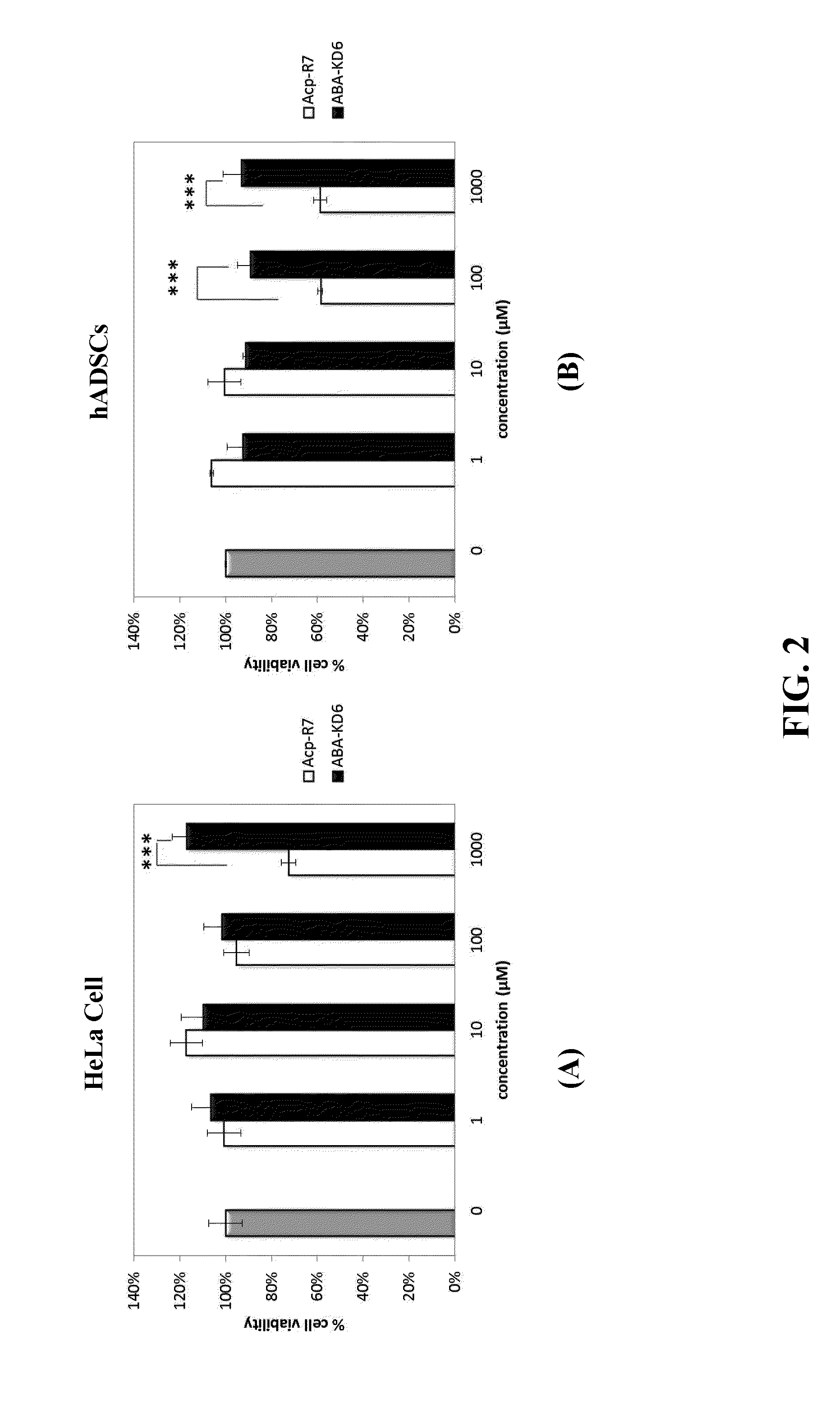
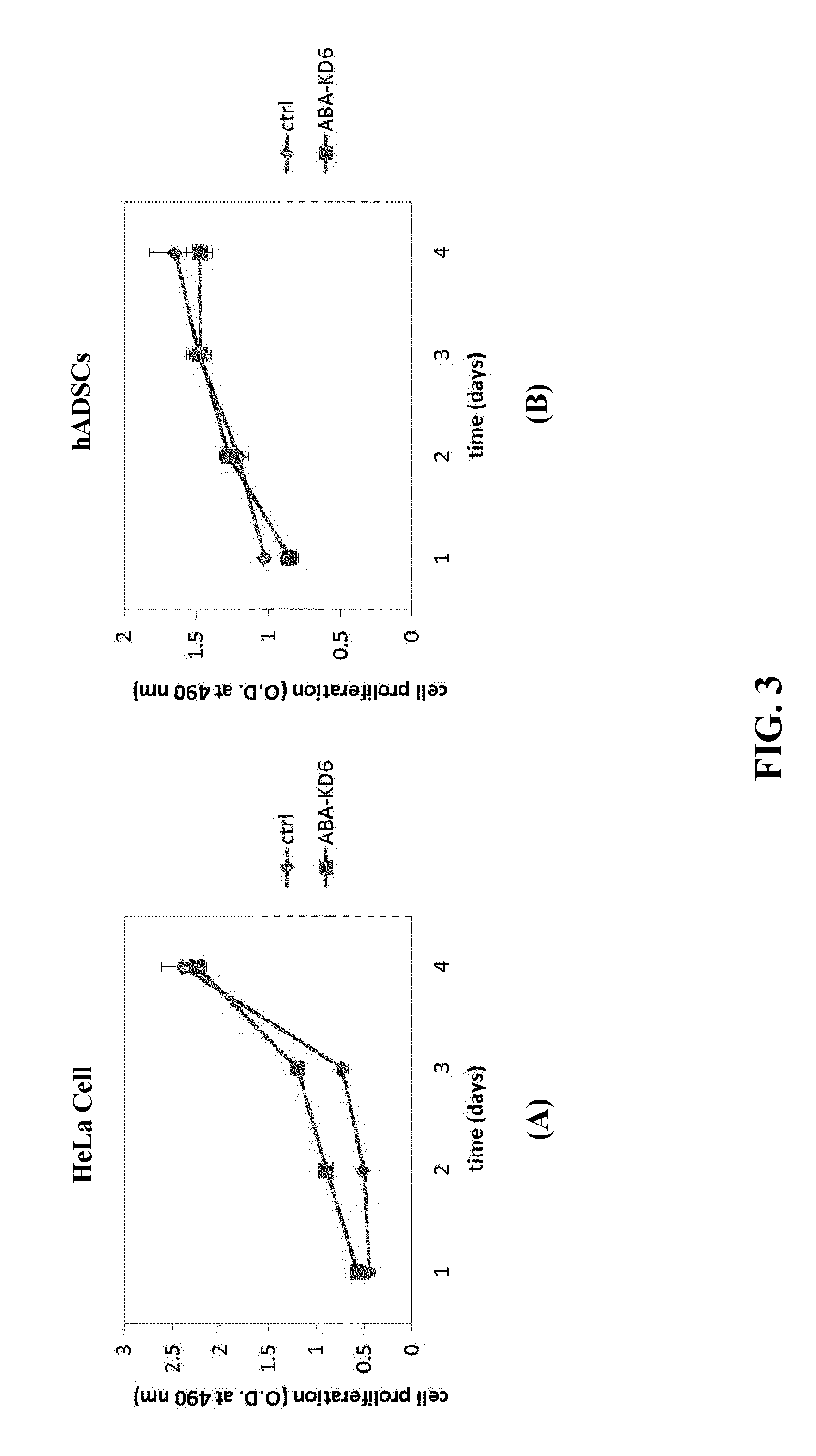
Anionic cell penetrating peptide and its use for intracellular delivery
The disclosure provides a cell penetrating peptide. The cell penetrating peptide includes an amino acid sequence of Dn, in which D represents an aspartate residue and 2≦n≦15.
Owner:KAOHSIUNG MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Gelling agent for oil
InactiveUS7244419B2Cosmetic preparationsFatty acid chemical modificationAspartic acid residueL-Aspartate
A compound represented by the following general formula (I), wherein R1 and R2 represent a hydrocarbon group having 1 to 26 carbon atoms, preferably a linear or branched alkyl group, R3 represents a hydrocarbon group having 7 to 10 carbon atoms, preferably a linear or branched alkyl group, n represents 1 or 2 provided that the acidic amino acid residue in the molecule is L-aspartic acid residue when n is 1 and said acidic amino acid residue is L-glutamic acid residue when n is 2, and a gelling agent for an oil comprising said compound
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
Iminochlorinaspartic acid derivatives
InactiveUS6063777AGood water solubilityImprove stabilityBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsAspartic acid residuePhotosensitizer
PCT No. PCT / JP97 / 03484 Sec. 371 Date Jun. 15, 1999 Sec. 102(e) Date Jun. 15, 1999 PCT Filed Sep. 30, 1997 PCT Pub. No. WO98 / 14753 PCT Pub. Date Apr. 9, 1998The present invention provides an iminochlorin aspartic acid derivative represented by the following formula (I): Wherein Asp represents an aspartic acid residue, or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof. The compound of the present invention is useful as a photosensitizer for photophysico-chemical diagnosis and therapy of cancer, because it has a high accumulability to cancerous cells, reactivity to external energy and a cancerous cell destroying effect which is effective even against cancers developing in deep site, while it is rapidly excreted from normal cells and therefore causes no damage thereto.
Owner:PFIZER JAPAN +1
Treatment of tauopathies
ActiveUS20120244146A1Shorten the progressMinimize and prevent neurofiblary tangle formationNervous disorderImmunoglobulins against animals/humansAspartic acid residueMedicine
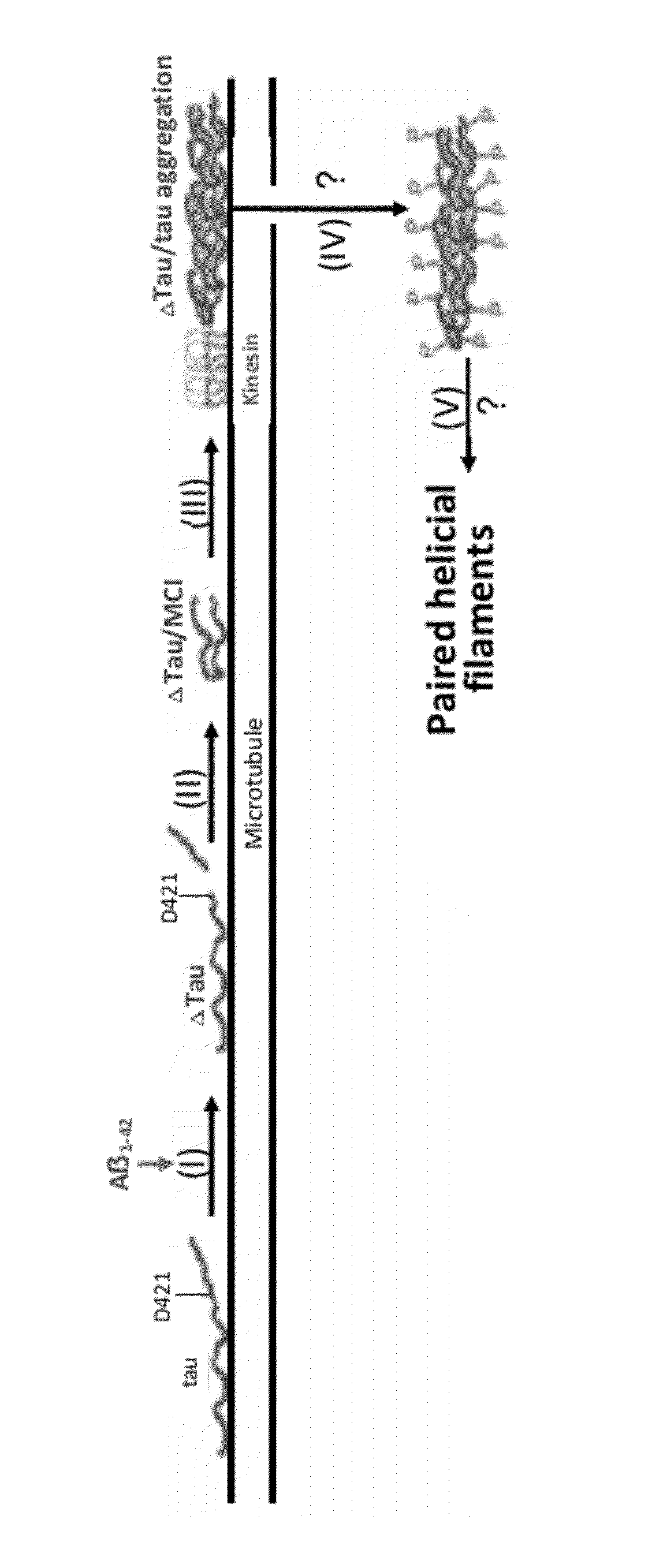
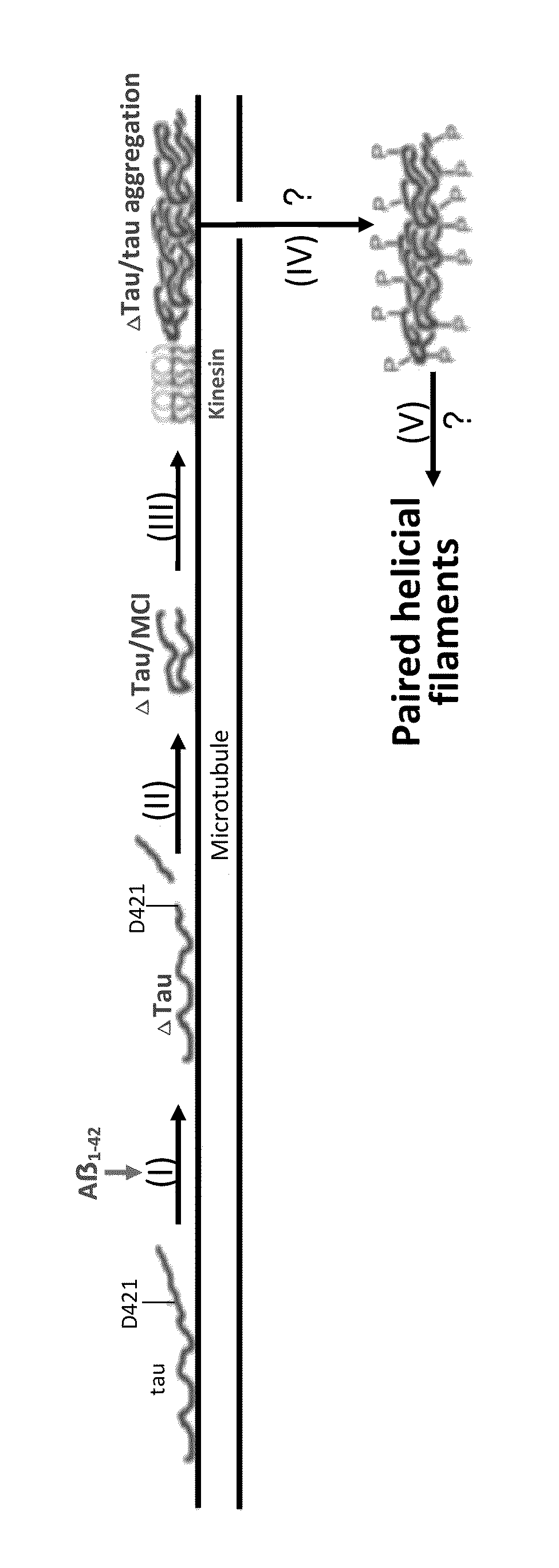
The invention is directed to methods of treatment of Alzheimer's disease and other tauopathies, via the administration of antibodies having specificity to abnormal forms of tau protein, the antibodies showing no binding and / or reactivity to a normal tau protein and being administered under conditions and in amounts effective to prevent or treat Alzheimer's disease or other tauopathies. In certain embodiments, the antibodies are selective for soluble truncated tau protein truncated at (i) its C-terminus after the glutamic acid residue Glu391, or (ii) at the aspartic acid residue Asp421, or (iii) at its N-terminus at the aspartic acid residue Asp13, or (iv) a combination of (i)-(iii). Further aspects of the invention are directed to the administration of an immunogen comprising an abnormal tau, preferably a soluble truncated tau.
Owner:TAUC3 BIOLOGICS LTD
Treatment of tauopathies
InactiveUS20120244174A1Shorten the progressMinimize and prevent neurofiblary tangle formationNervous disorderTripeptide ingredientsAspartic acid residueC-terminus
The invention is directed to methods of treatment of Alzheimer's disease and other tauopathies, via the administration of antibodies having specificity to abnormal forms of tau protein, the antibodies showing no binding and / or reactivity to a normal tau protein and being administered under conditions and in amounts effective to prevent or treat Alzheimer's disease or other tauopathies. In certain embodiments, the antibodies are selective for soluble truncated tau protein truncated at (i) its C-terminus after the glutamic acid residue Glu391, or (ii) at the aspartic acid residue Asp421, or (iii) at its N-terminus at the aspartic acid residue Asp13, or (iv) a combination of (i)-(iii). Further aspects of the invention are directed to the administration of an immunogen comprising an abnormal tau, preferably a soluble truncated tau.
Owner:TAU BIO LOGIC CORP
Polypeptide having the ability to form connections of glucosyl units in alpha-1,3 on an acceptor
InactiveUS20160136199A1Organic active ingredientsBiocideAspartic acid residueReceptor for activated C kinase 1
An isolated polypeptide having the ability to specifically form connections of glucosyl units in alpha 1,3 on an acceptor including at least one hydroxyl moiety. The polypeptide includes i) the pattern I of sequence SEQ ID NO: 1, ii) the pattern II of sequence SEQ ID NO: 2, iii) the pattern II of sequence SEQ ID NO: 3, iv) the pattern IV of sequence SEQ ID NO: 4 or derivates from one or several of said patterns. The polypeptide furthermore has the aspartic residue (D) in position 5 of the pattern II (SEQ ID NO: 2), the glutamic acid residue (E) at position 6 of the pattern III (SEQ ID NO: 3) and the aspartic acid residue (D) in position 6 of the pattern IV (SEQ ID NO: 4); and its uses.
Owner:INSTITUT NATIONAL DE LA RECHERCHE AGRONOMIQUE +2
Treatment of tauopathies
ActiveUS8703137B2Prevent and minimize formationInhibit caspase cleavageNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsAspartic acid residueAntiendomysial antibodies
The invention is directed to methods of treatment of Alzheimer's disease and other tauopathies, via the administration of antibodies having specificity to abnormal forms of tau protein, the antibodies showing no binding and / or reactivity to a normal tau protein and being administered under conditions and in amounts effective to prevent or treat Alzheimer's disease or other tauopathies. In certain embodiments, the antibodies are selective for soluble truncated tau protein truncated at (i) its C-terminus after the glutamic acid residue Glu391, or (ii) at the aspartic acid residue Asp421, or (iii) at its N-terminus at the aspartic acid residue Asp13, or (iv) a combination of (i)-(iii). Further aspects of the invention are directed to the administration of an immunogen comprising an abnormal tau, preferably a soluble truncated tau.
Owner:TAUC3 BIOLOGICS LTD
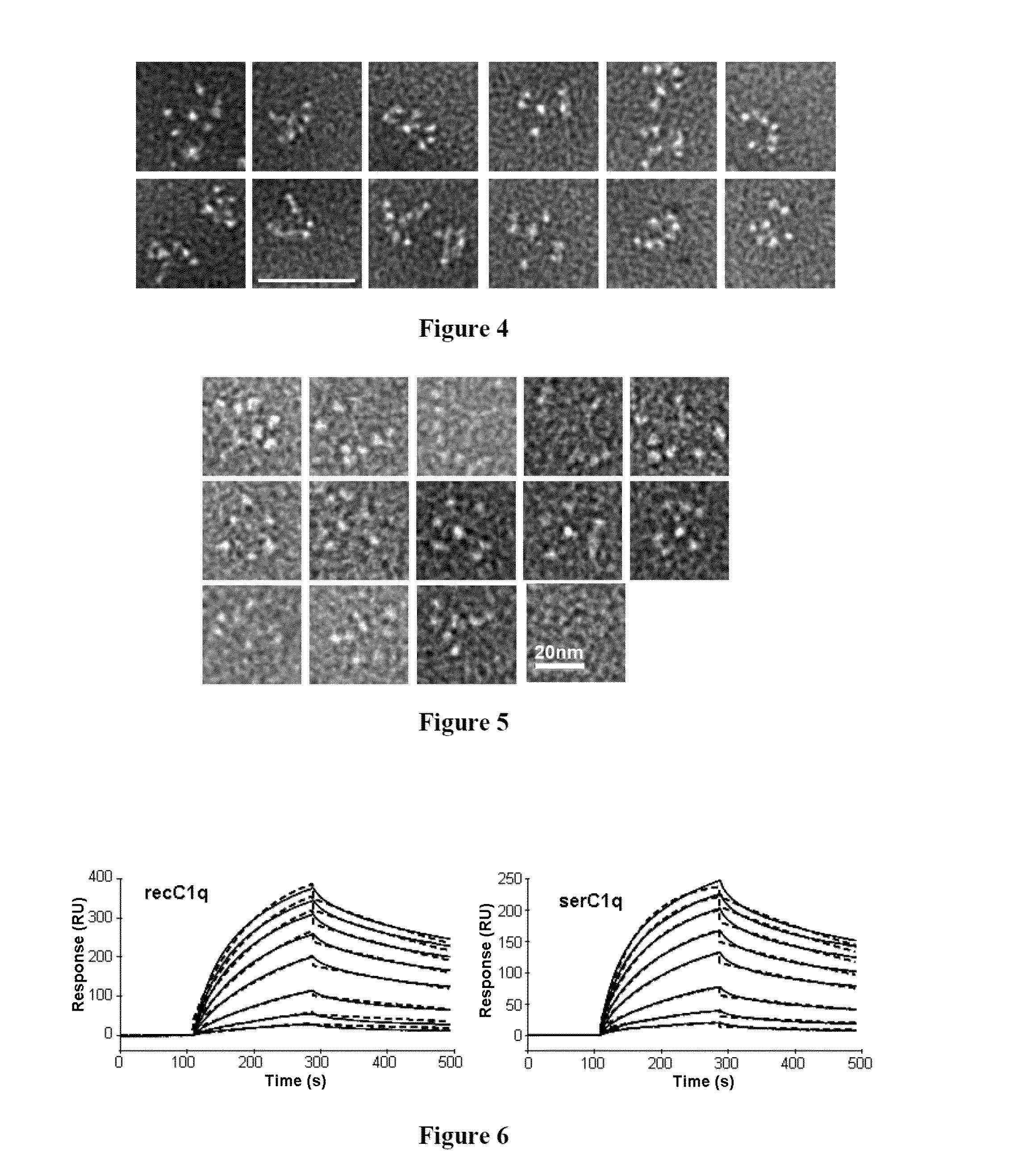
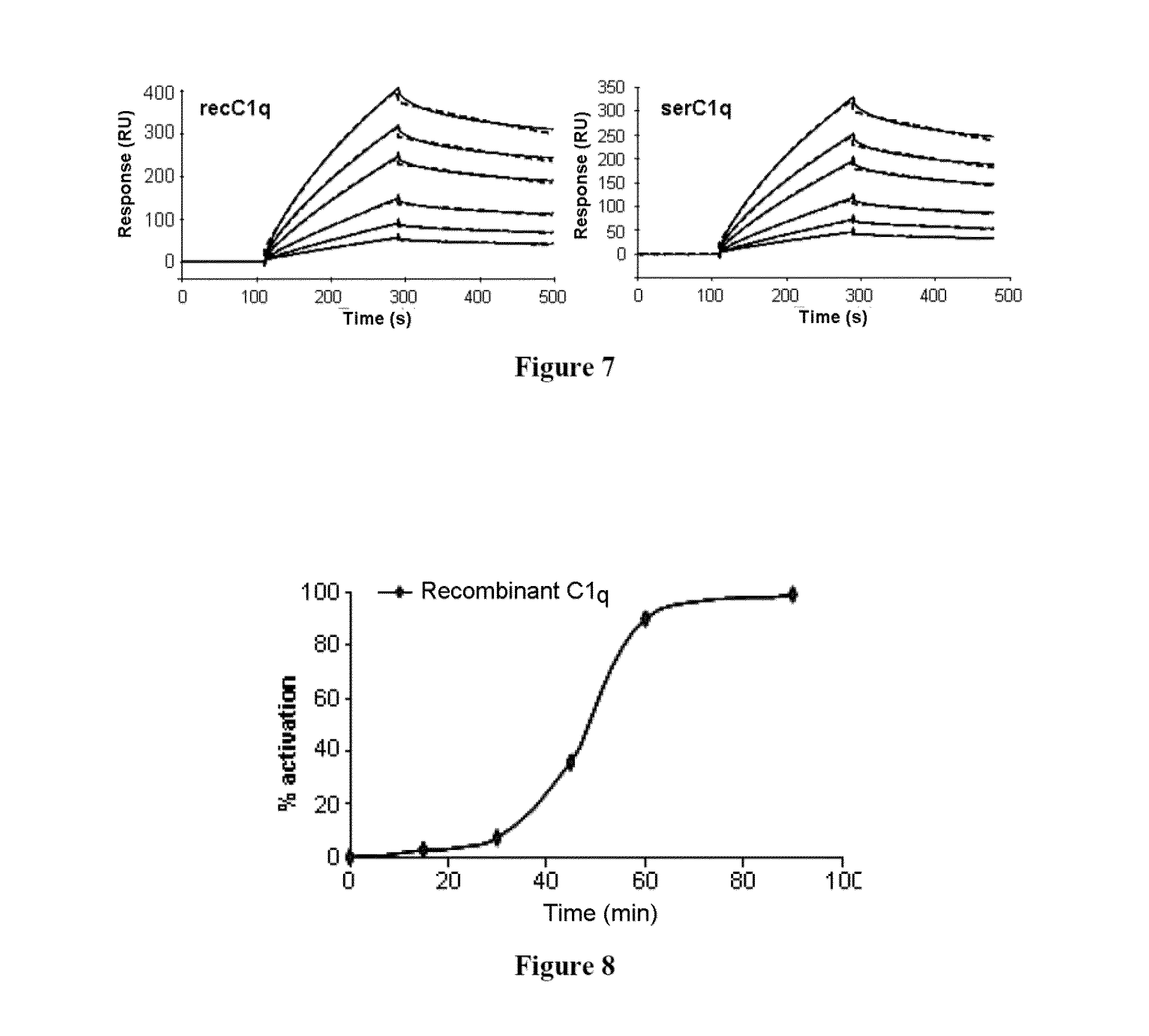
Method for preparing c1q recombinant protein
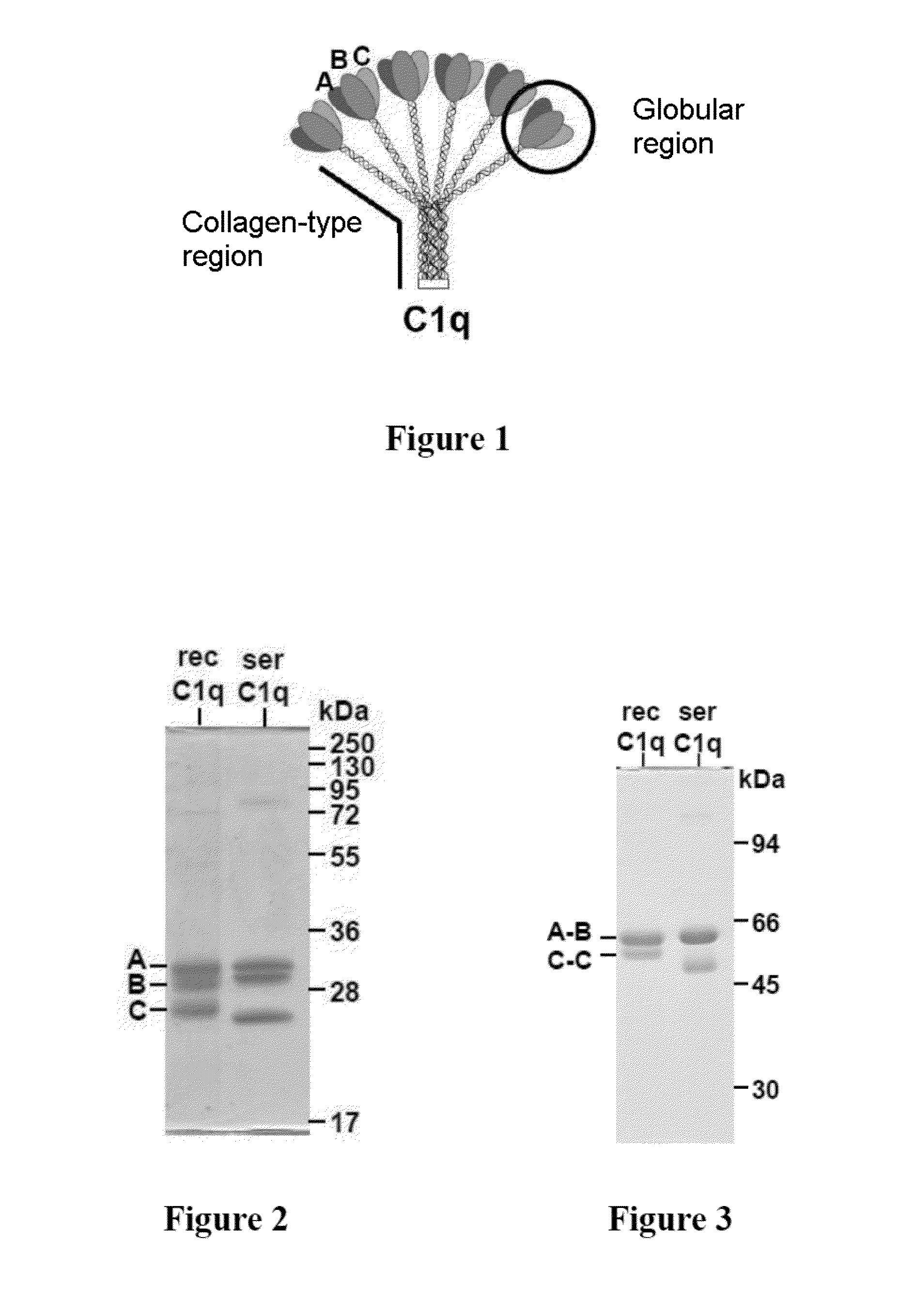
ActiveUS20150329606A1Possible formBacteriaAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsAspartic acid residueC-terminus
The present invention relates to a method for recombinant production of a C1q protein or a variant of the C1q protein, in which the protein is recovered from an in vitro culture of cells expressing a C1qA subunit or a variant of the C1qA subunit, a C1qB subunit or a variant of the C1qB subunit, and a C1qC subunit or a variant of the C1qC subunit, in which at least one of the subunits or subunit variants also has at the N-terminus or C-terminus a sequence of amino acids of at least six residues, at least 40% of which are glutamic acid and / or aspartic acid residues.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES +1
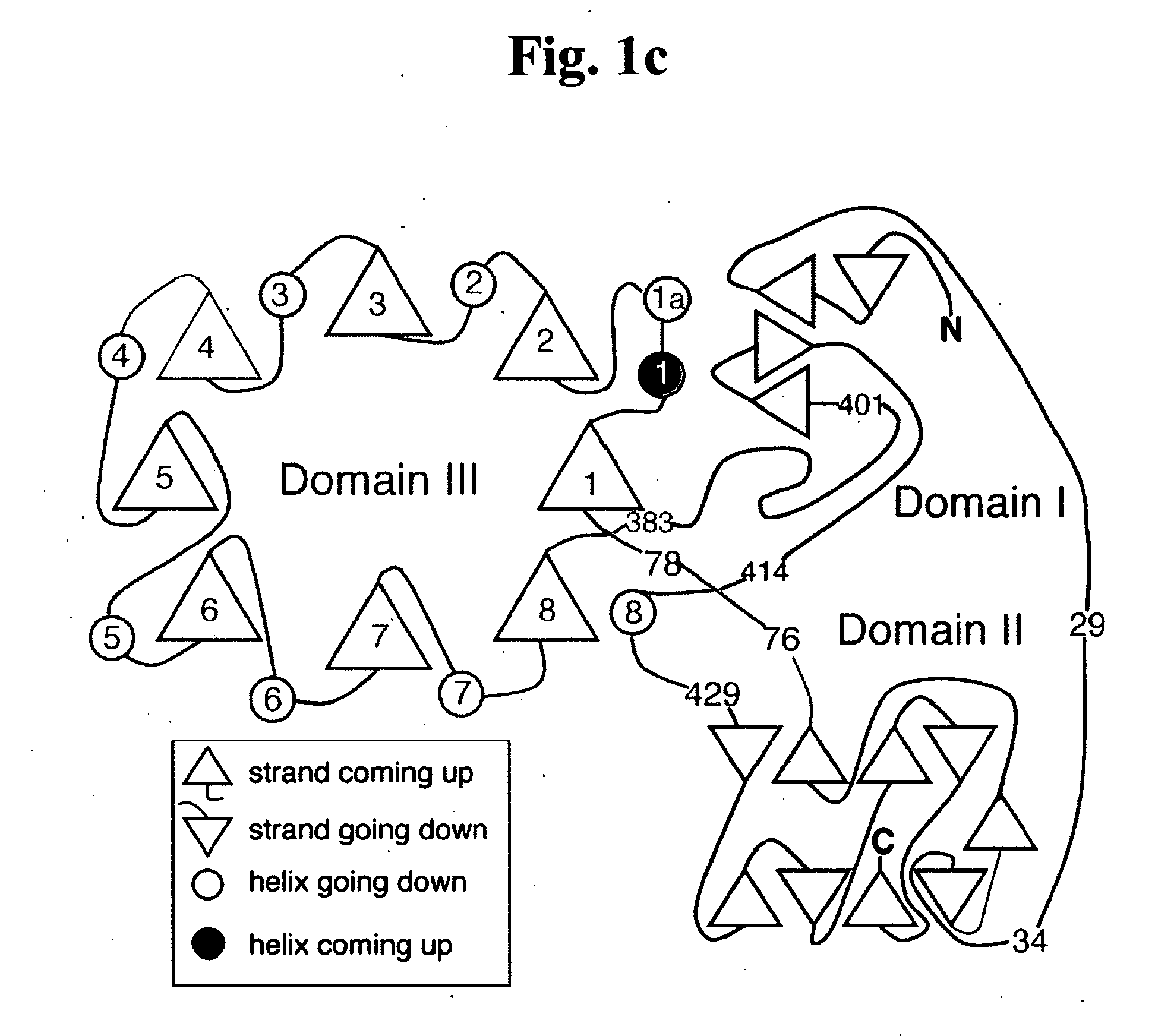
Gaucher disease drugs and methods of identifying same
InactiveUS20070166813A1High activitySubstantial glucocerebrosidase activityCompound screeningNervous disorderAspartic acid residueCrystallography
A method of identifying a compound capable of correcting an impaired enzymatic activity of a mutant glucocerebrosidase molecule, the method comprising: (a) obtaining a first set of structure coordinates, the first set of structure coordinates defining a 3D structure of a glucocerebrosidase molecule capable of displaying normal enzymatic activity or a portion thereof; (b) computationally generating using the first set of structure coordinates a second set of structure coordinates, the second set of structure coordinates defining a predicted 3D structure of the mutant glucocerebrosidase molecule or a portion thereof; and (c) computationally identifying, using the second set of structure coordinates, a compound capable of interacting with the mutant glucocerebrosidase molecule in such a way as to correct the impaired enzymatic activity thereof, thereby identifying the compound capable of correcting the impaired enzymatic activity of the mutant glucocerebrosidase molecule. A glucocerebrosidase preparation comprising a population of glucocerebrosidase molecules, wherein substantially each of said glucocerebrosidase molecules: (i) has an amino acid sequence at least 95 percent homologous to an amino acid sequence set forth by SEQ ID NO: 1 or 8; (ii) is glycosylated at, or has an aspartatic acid residue at, glycosylation residue 1 of said amino acid sequence; and (iii) is independently unglycosylated at one or more glycosylation residues selected from the group consisting of glycosylation residues 2, 3 and 4 of said amino acid sequence.
Owner:YEDA RES & DEV CO LTD
Systems and methods for the analysis of protein phosphorylation
The present invention relates to a method of applying mass spectrometry to analyzing peptides or proteins, especially in the proteome setting. More particularly, the invention relates to a mass spectrometry-based method for detection of protein / peptide phosphorylation wherein the side chains of glutamic acid and / or aspartic acid residues of said peptides or proteins are chemically modified as to improve the selectivity / efficiency of identification of the phosphorylated protein / peptide.
Owner:PROTANA +1
Structural variants of antibodies for improved therapeutic characteristics
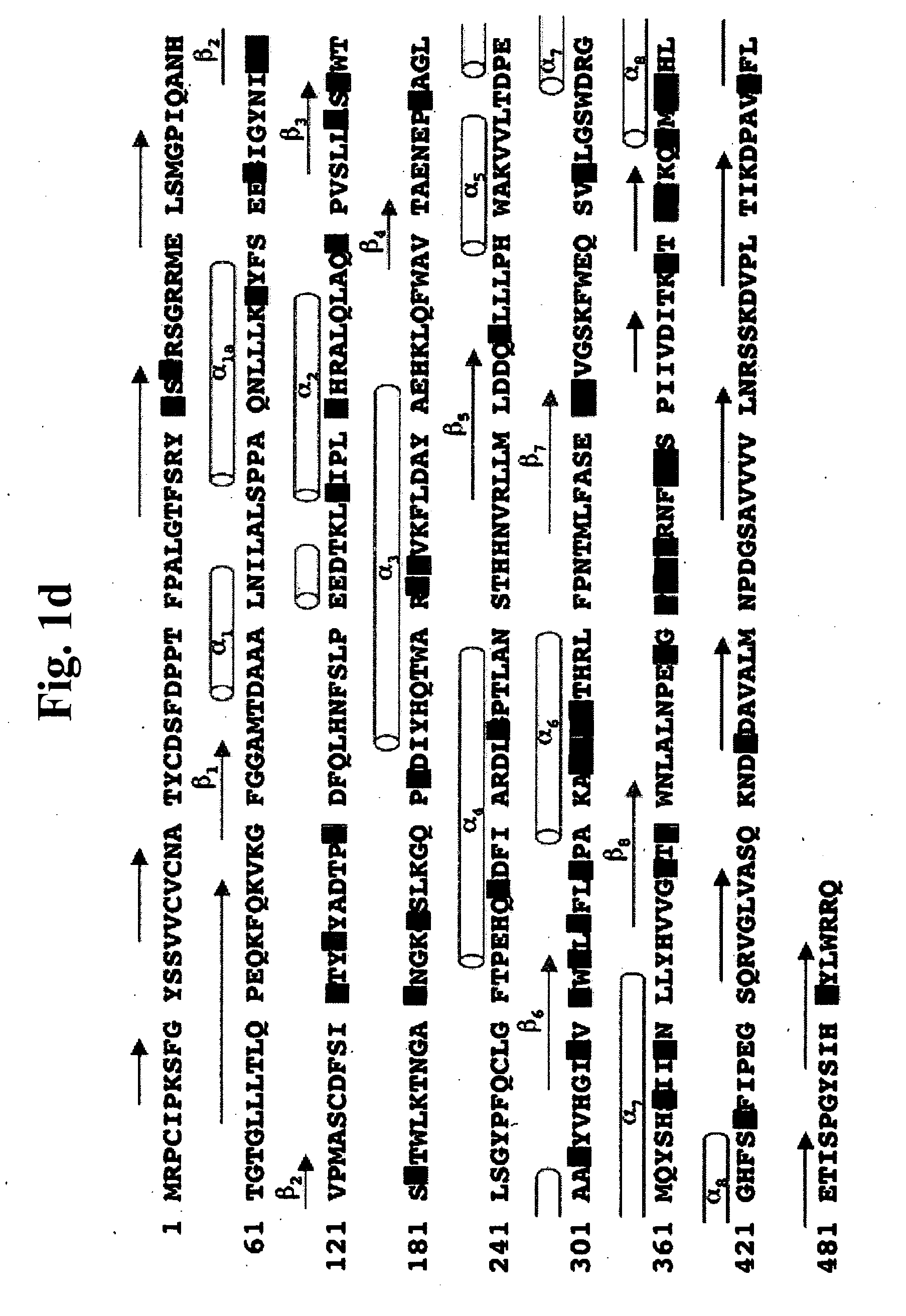
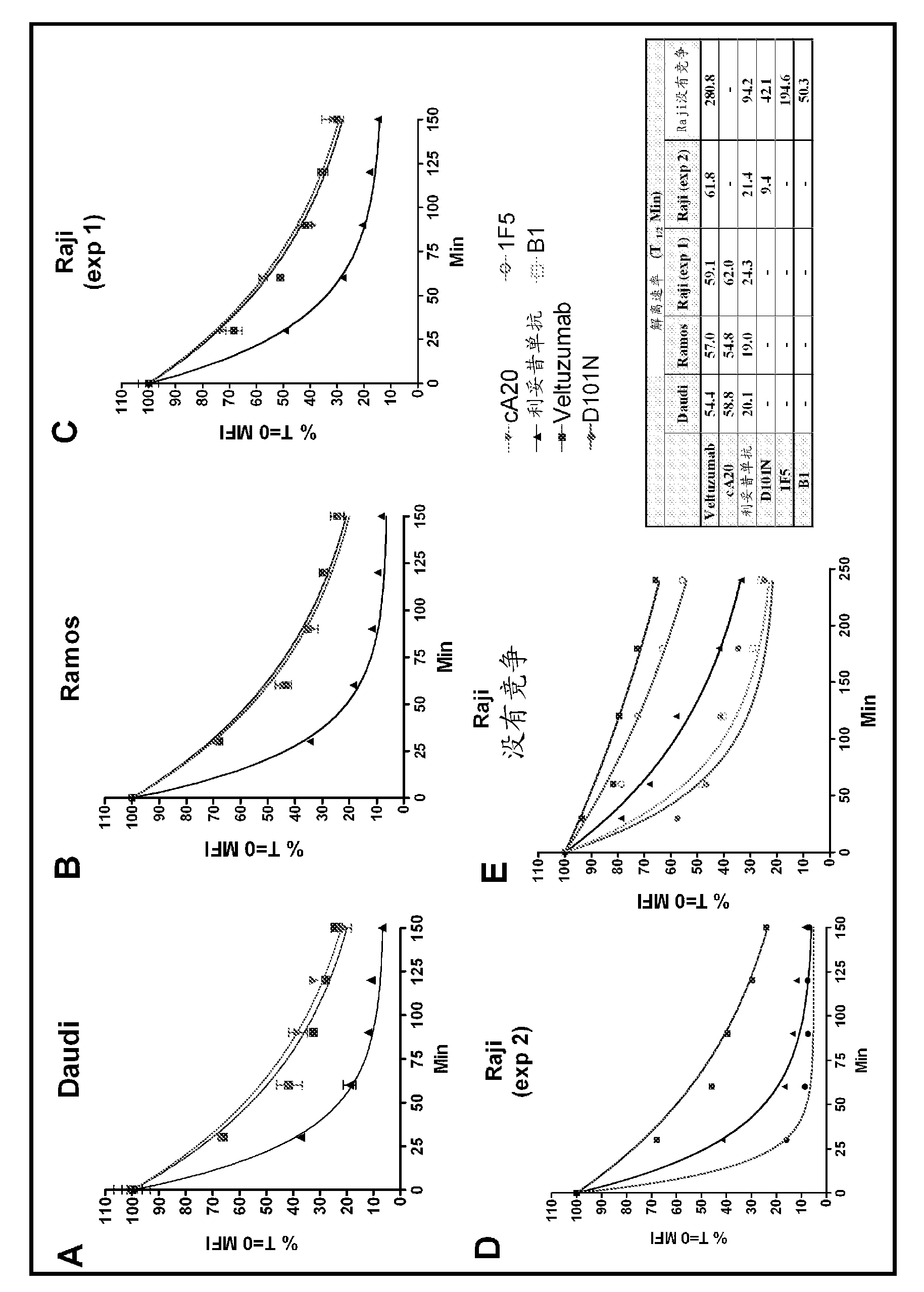
The present invention provides substituted humanized, chimeric or human anti-CD20 antibodies or antigen binding fragments thereof and bispecific antibodies or fusion proteins comprising the substituted antibodies or antigen binding fragments thereof. The antibodies, fusion proteins or fragments are useful for treatment of B-cell disorders, such as B-cell malignancies and autoimmune diseases, as well as GVHD, organ transplant rejection, and hemolytic anemia and cryoglobulinemia. Amino acid substitutions, particularly substitution of an aspartate residue at Kabat position 101 of CDR3 VH (CDRH3), result in improved therapeutic properties, such as decreased dissociation rates, improved CDC activity, improved apoptosis, improved B-cell depletion and improved therapeutic efficacy at very low dosages. Veltuzumab, a humanized anti-CD20 antibody that incorporates such sequence variations, exhibits improved therapeutic efficacy compared to similar antibodies of different CDRH3 sequence, allowing therapeutic effect at dosages as low as 200 mg or less, more preferably 100 mg or less, more preferably 80 mg or less, more preferably 50 mg or less, most preferably 30 mg or less of naked antibody when administered i.v. or s.c.
Owner:IMMUNOMEDICS INC
Variant enzyme of cytochrome P450BM-3D168R and method for preparing indirubin using the same
InactiveCN101333520AEasy to separateHigh utilization rate of raw materialsOxidoreductasesFermentationAspartic acid residueArginine
The invention discloses a cytochrome P450 BM-3 D168R mutant enzyme as well as a method applying the enzyme to prepare indirubin. The enzyme adopts the directed evolution technique, and takes P450 BM-3 (F87V / A74G / L188Q / E435T) as a male parent, and is obtained by implementing the fixed-point saturation and mutation at the codon for the aspartic acid residue in position 168 of the sequence in the male parent gene through screening. The base sequence is shown as SEQ ID NO.1 in the sequence table, the codon at the original point is mutated to CGG from GAT, and the corresponding amino acid residue is mutated to arginine from aspartic acid. The P450 BM-3 D168R mutant enzyme of the invention takes indirubin as main acquired product when catalyzing indole, and the product shows obvious red color.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Gelling agent for oil
InactiveUS20070237732A1Cosmetic preparationsOrganic chemistryAspartic acid residueCompound (substance)
A compound represented by the following general formula (I), wherein R1 and R2 represent a hydrocarbon group having 1 to 26 carbon atoms, preferably a linear or branched alkyl group, R3 represents a hydrocarbon group having 7 to 10 carbon atoms, preferably a linear or branched alkyl group, n represents 1 or 2 provided that the acidic amino acid residue in the molecule is L-aspartic acid residue when n is 1 and said acidic amino acid residue is L-glutamic acid residue when n is 2, and a gelling agent for an oil comprising said compound.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
Modified biotin-binding protein
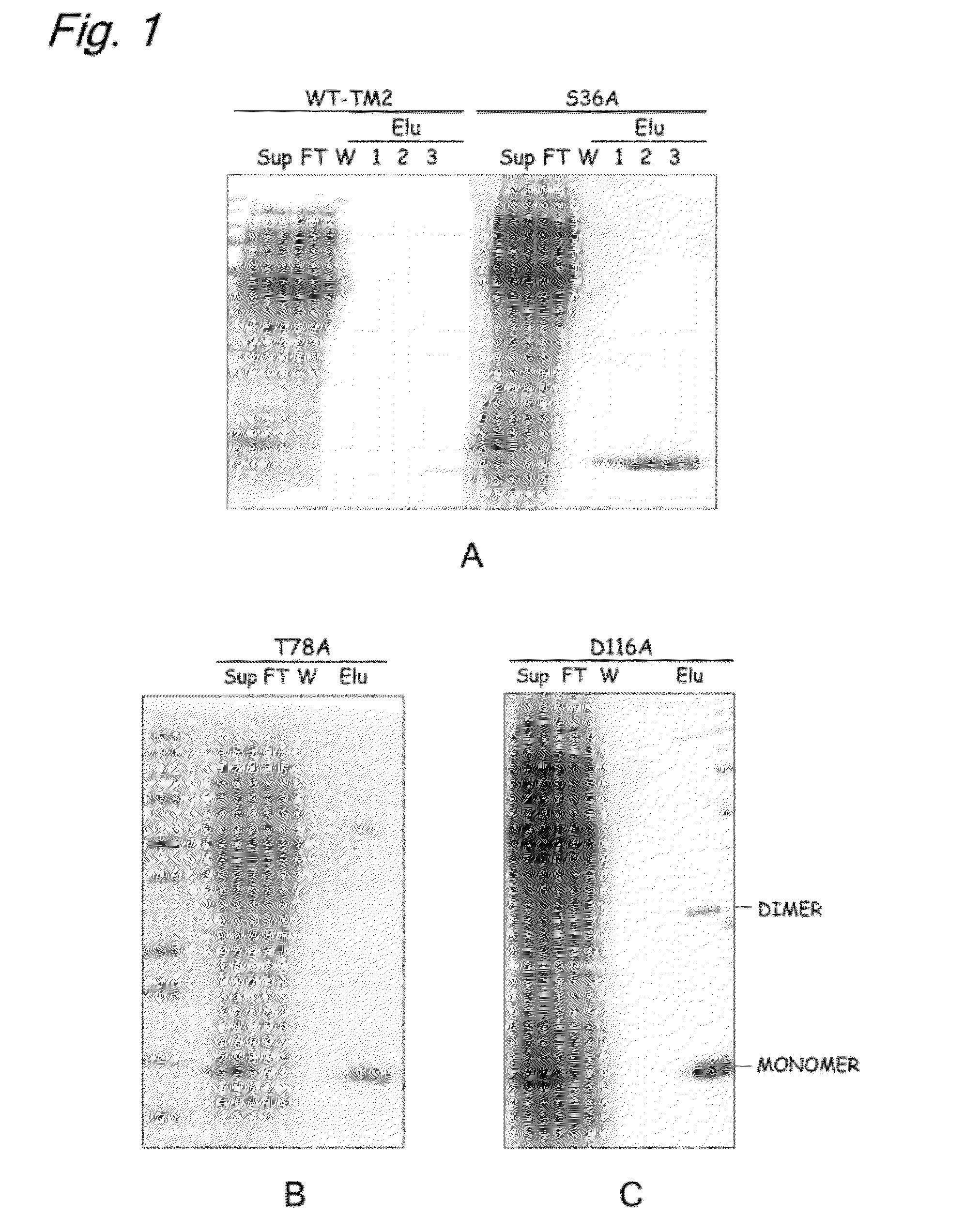
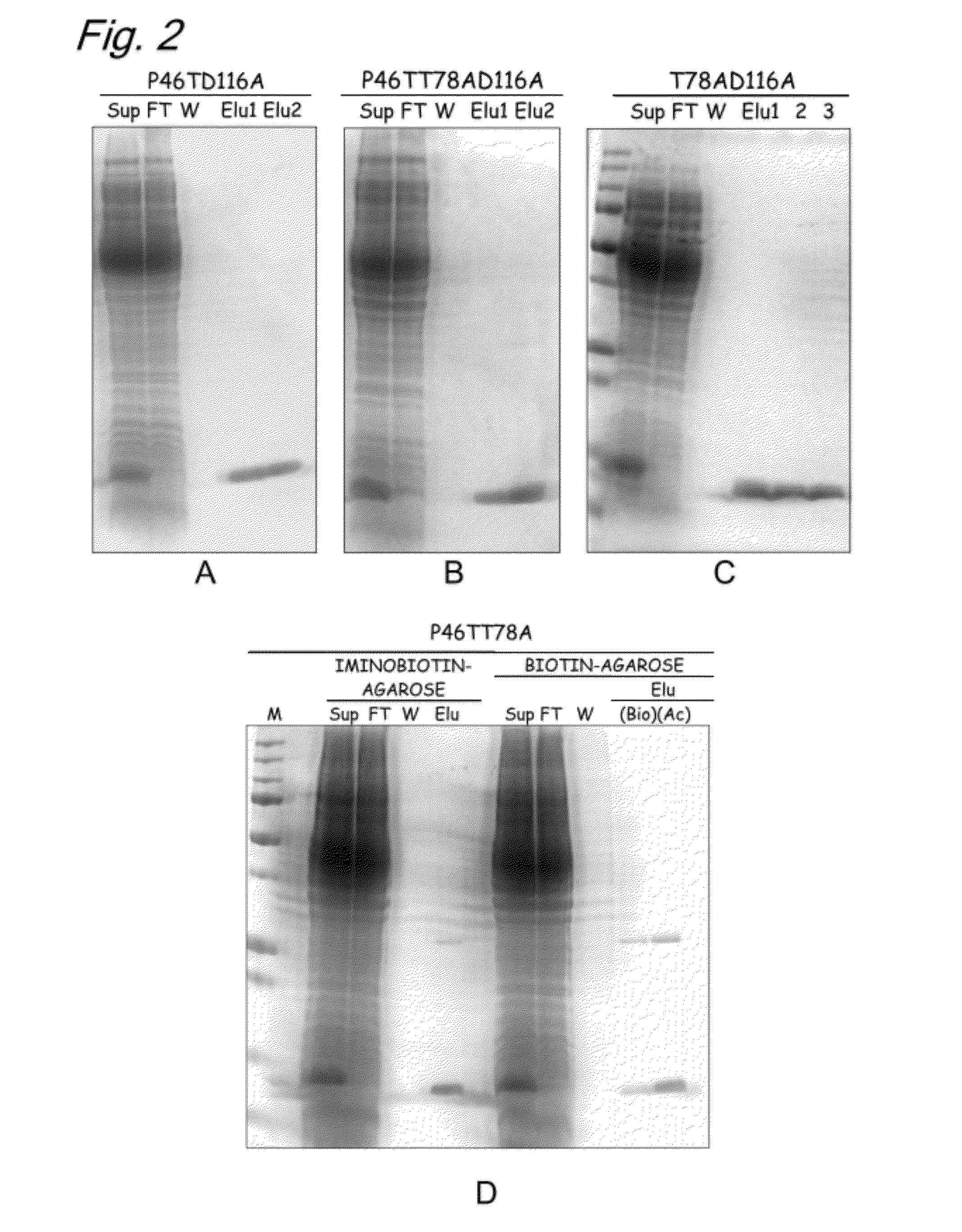
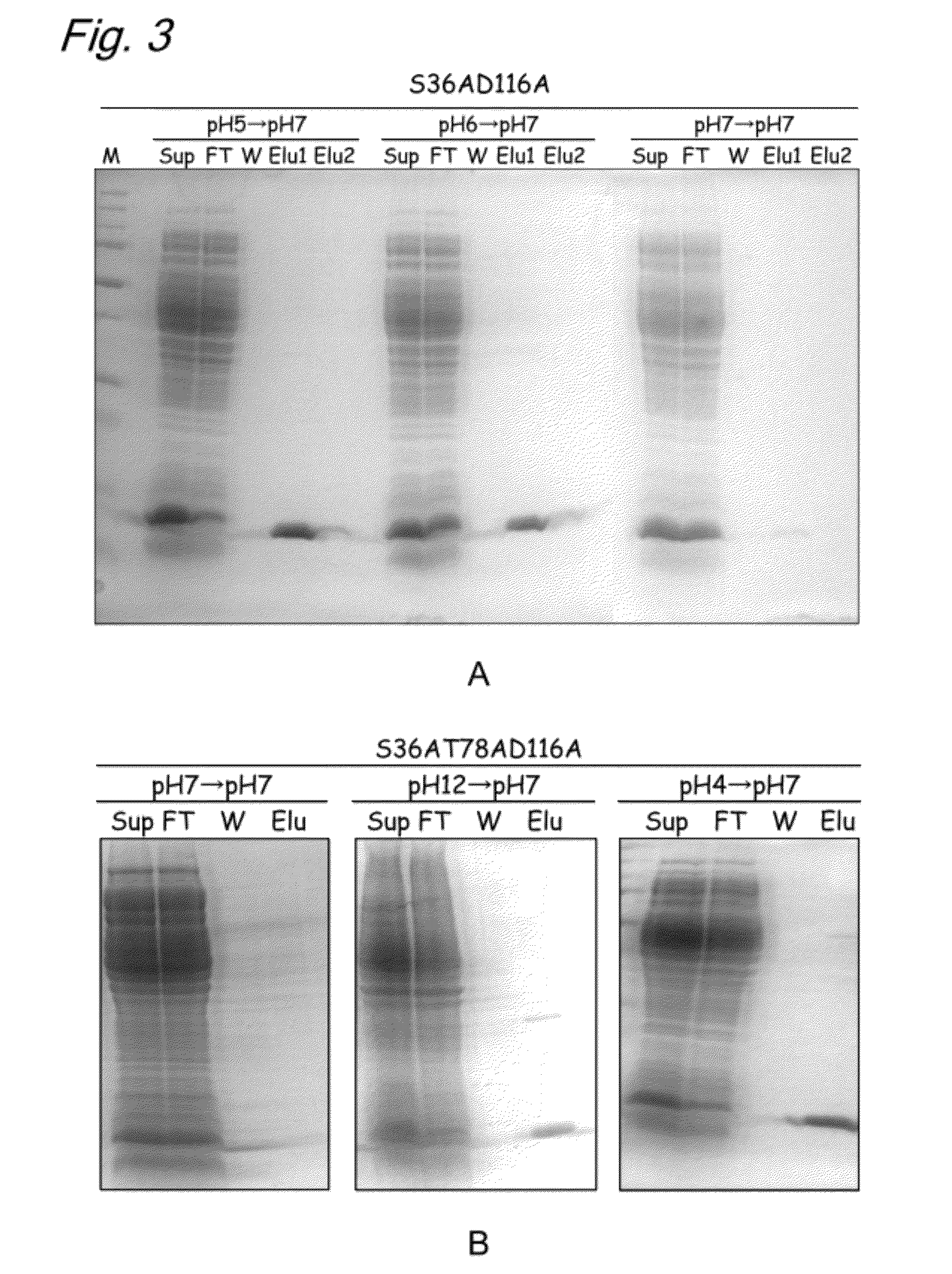
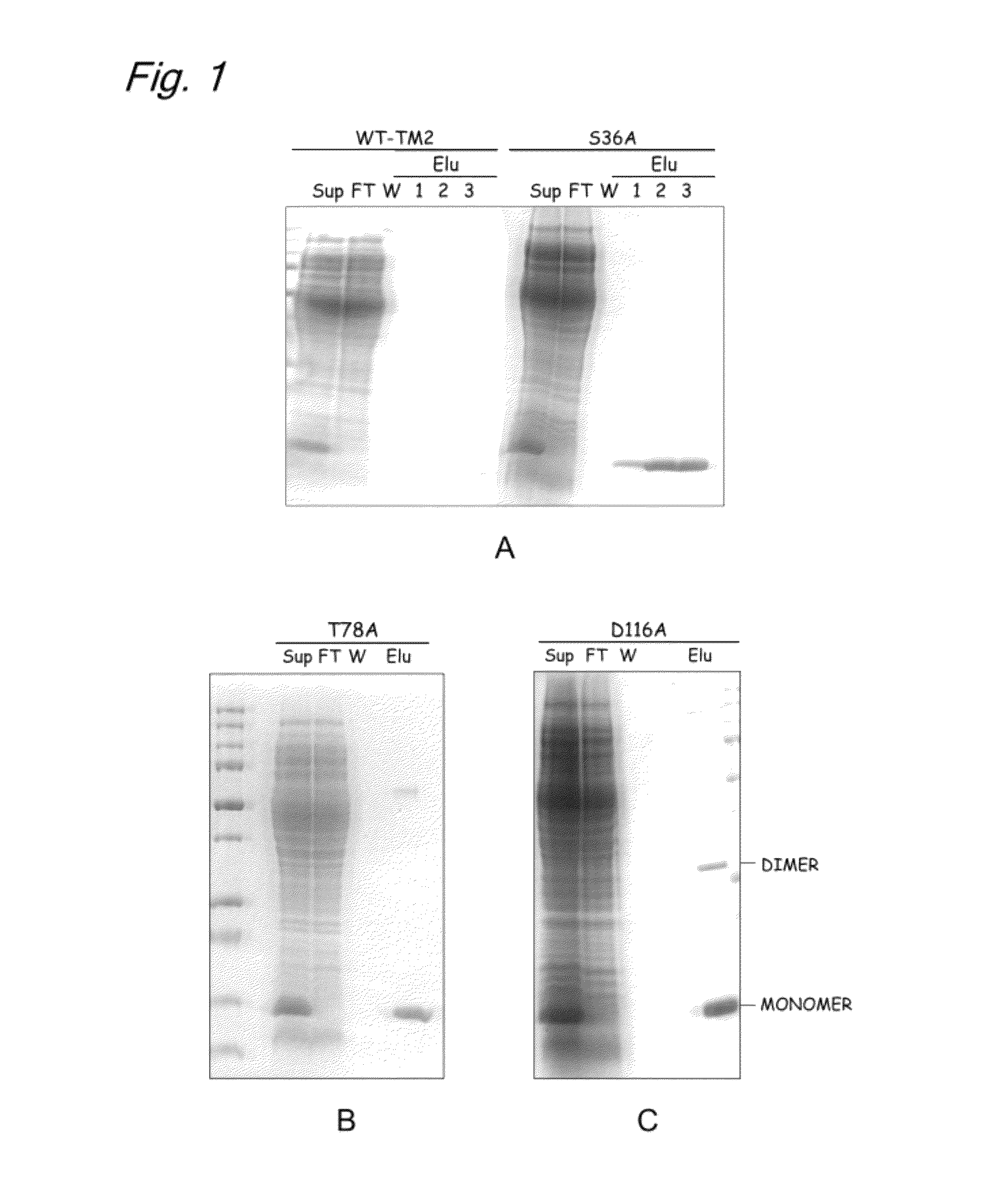
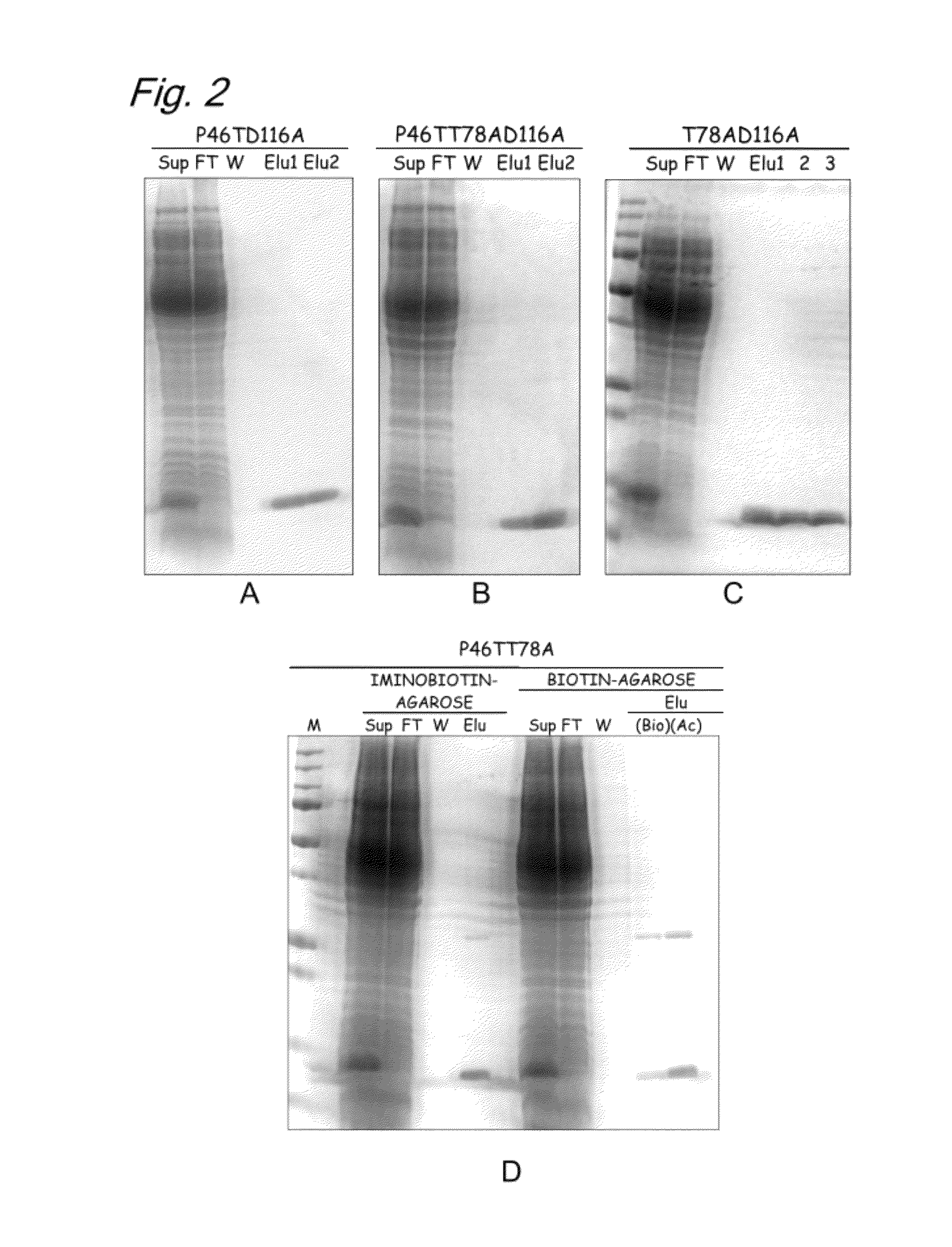
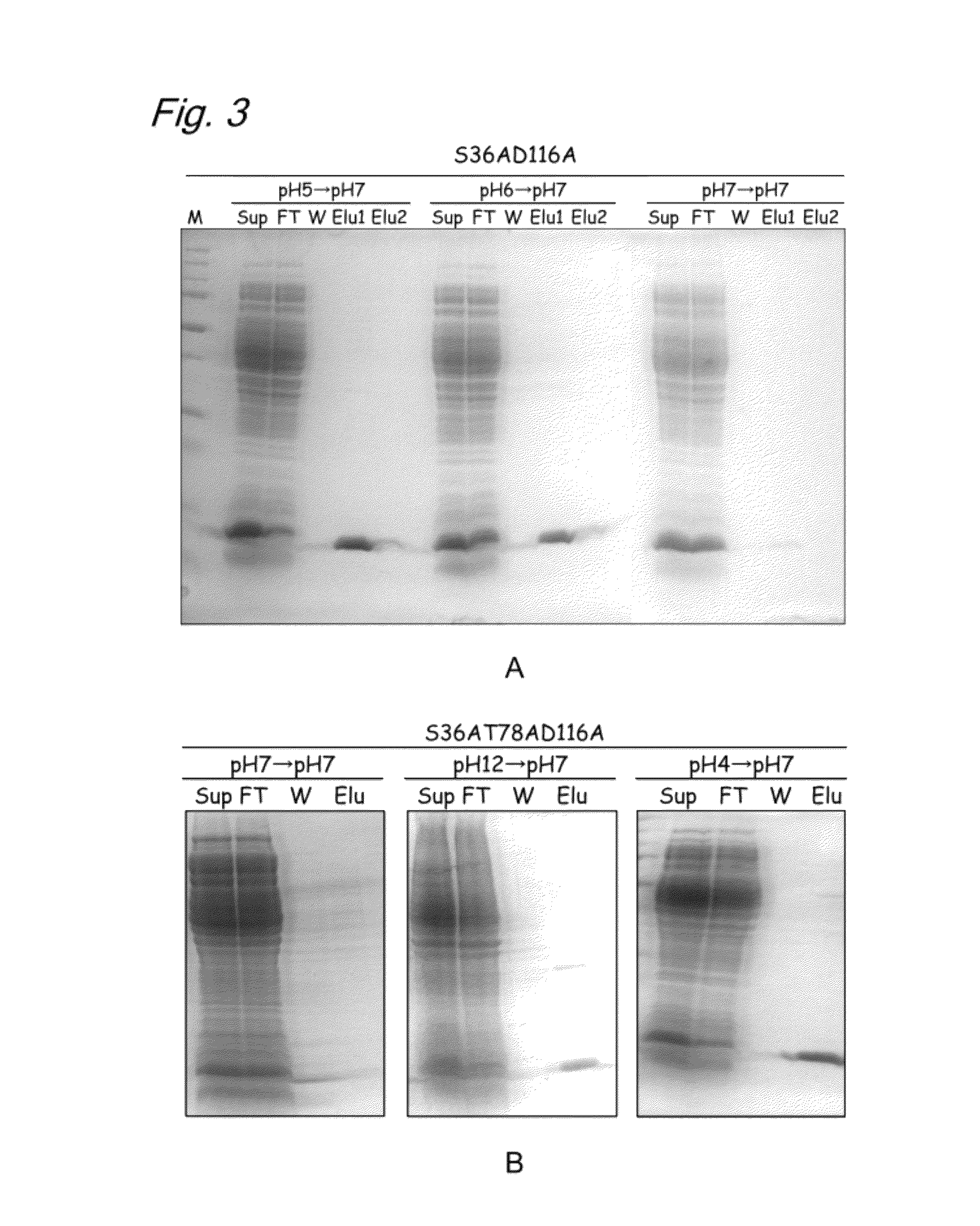
InactiveUS20120245331A1High expressionSugar derivativesBiological material analysisAspartic acid residueThreonine
The present invention provides a modified biotin-binding protein comprising an amino acid sequence represented by SEQ ID NO: 2 or its modified sequence and having a biotin-binding activity and replacement selected from the group consisting of:1) replacement of the 36th serine residue of SEQ ID NO: 2 with an amino acid residue that does not form a hydrogen bond;2) replacement of the 80th tryptophan residue of SEQ ID NO: 2 with a hydrophilic amino acid residue;3) replacement of the 116th aspartic acid residue of SEQ ID NO: 2 with an amino acid residue that does not form a hydrogen bond;4) replacement of the 46th proline residue of SEQ ID NO: 2 with a threonine, serine, or tyrosine residue and replacement of the 78th threonine residue of SEQ ID NO: 2 with an amino acid residue that does not form a hydrogen bond;5) replacement of the 46th proline residue of SEQ ID NO: 2 with a threonine, serine, or tyrosine residue and replacement of the 116th aspartic acid residue of SEQ ID NO: 2 with an amino acid that does not form a hydrogen bond; and6) replacement of the 46th proline residue of SEQ ID NO: 2 with a threonine, serine, or tyrosine residue, replacement of the 78th threonine residue of SEQ ID NO: 2 with an amino acid residue that does not form a hydrogen bond, and replacement of the 116th aspartic acid residue of SEQ ID NO: 2 with an amino acid that does not form a hydrogen bond.
Owner:JAPAN TOBACCO INC
Cyclo-polypeptides capable of combining with autocrine RNAIII activator protein of gold staphylococcus and its pharmaceutical use
The invention relates to a group of cyclo-polypeptides capable of combining with autocrine RNAIII activator protein of gold staphylococcus, Steroidal C#-[1]-X#-[1]-H#-[1]-A#-[2]-H#-[1]-A#-[2]-C#-[1], wherein C is natural L-type aminothiopropionic acid residue or its D-type isomer, X is any one of the four natural L-type amino acid residue or its D-type isomers, i.e. glutamine residue (Q), glutacid residue (E), aspartate residue (D), asparagines residue (N), H is L-type histidine residue or its D-type isomer, A is natural L-type aromatic residue or its D-type isomer. The polypeptides can be applied in preparing staphylococcus aureus resistant medicament.
Owner:INST OF BASIC MEDICAL SCI ACAD OF MILITARY MEDICAL SCI OF PLA +1
Synthetic hapten carrier compositions and methods
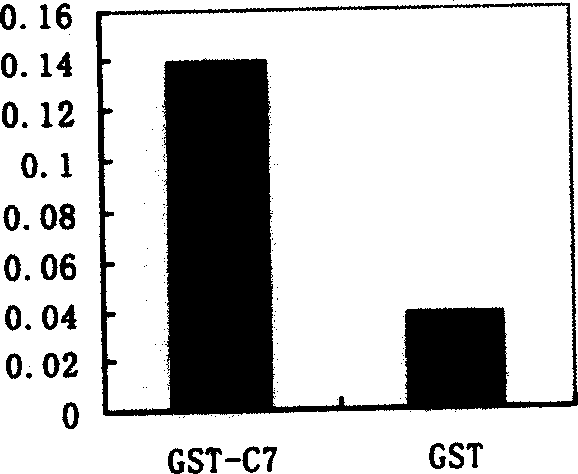
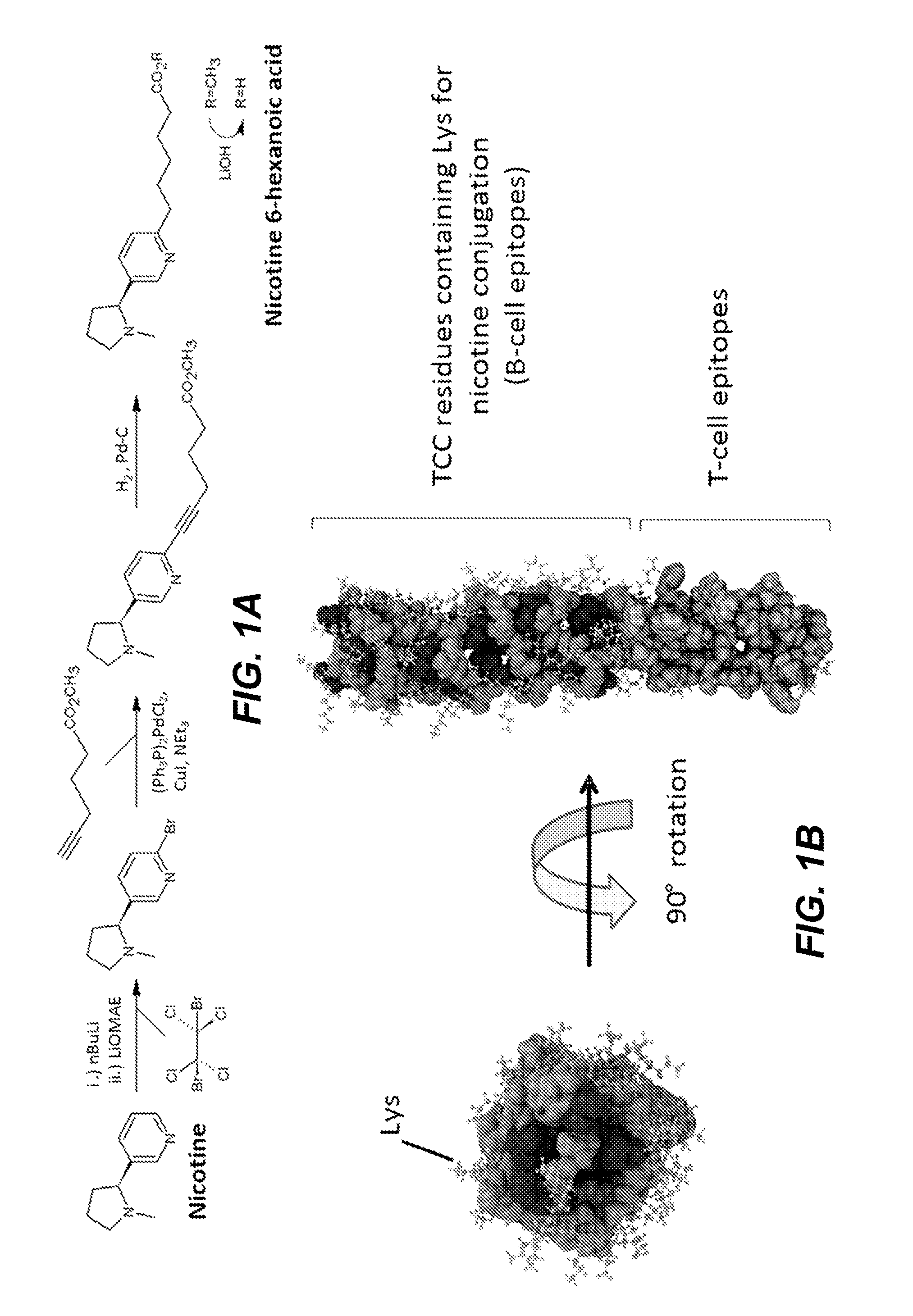
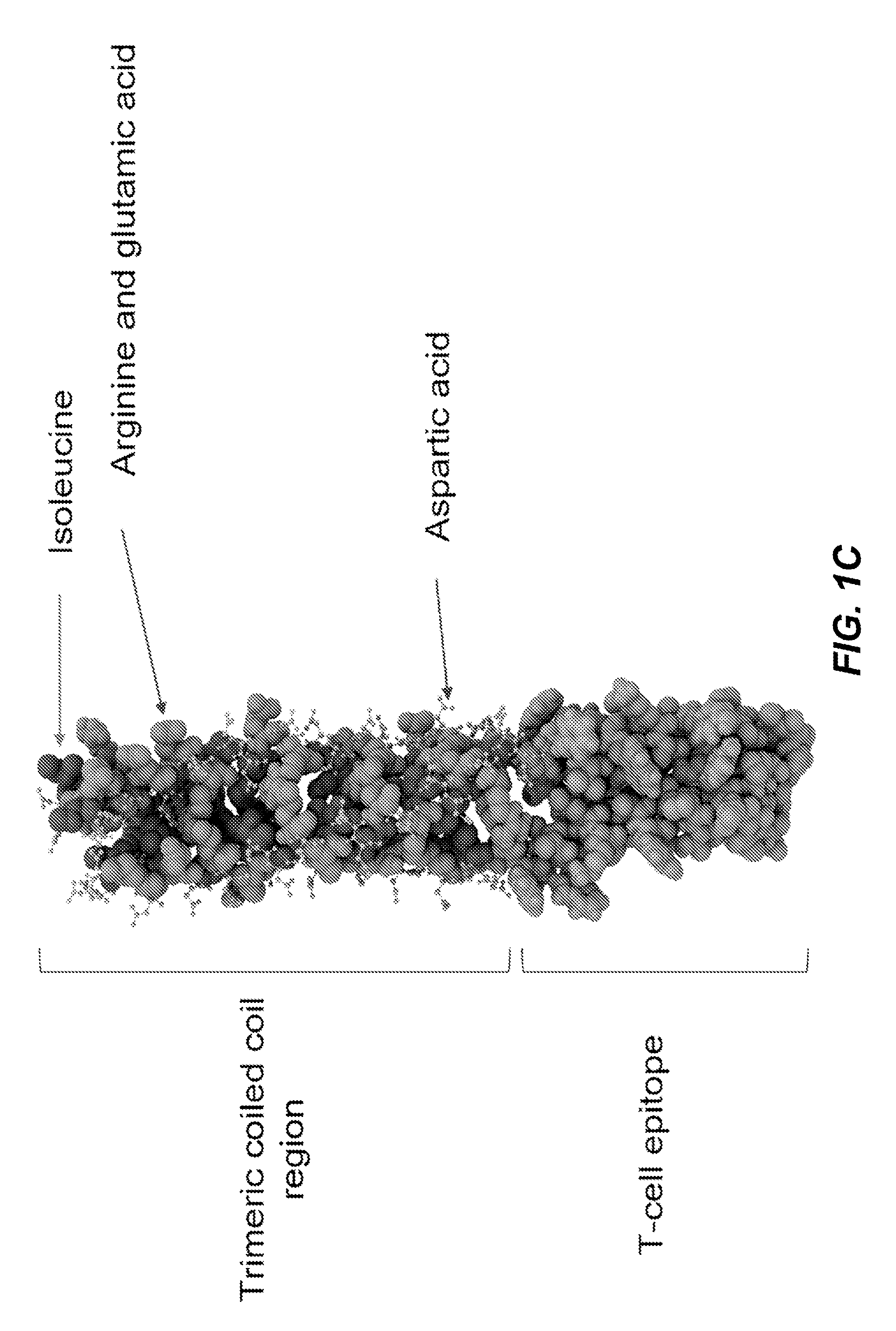
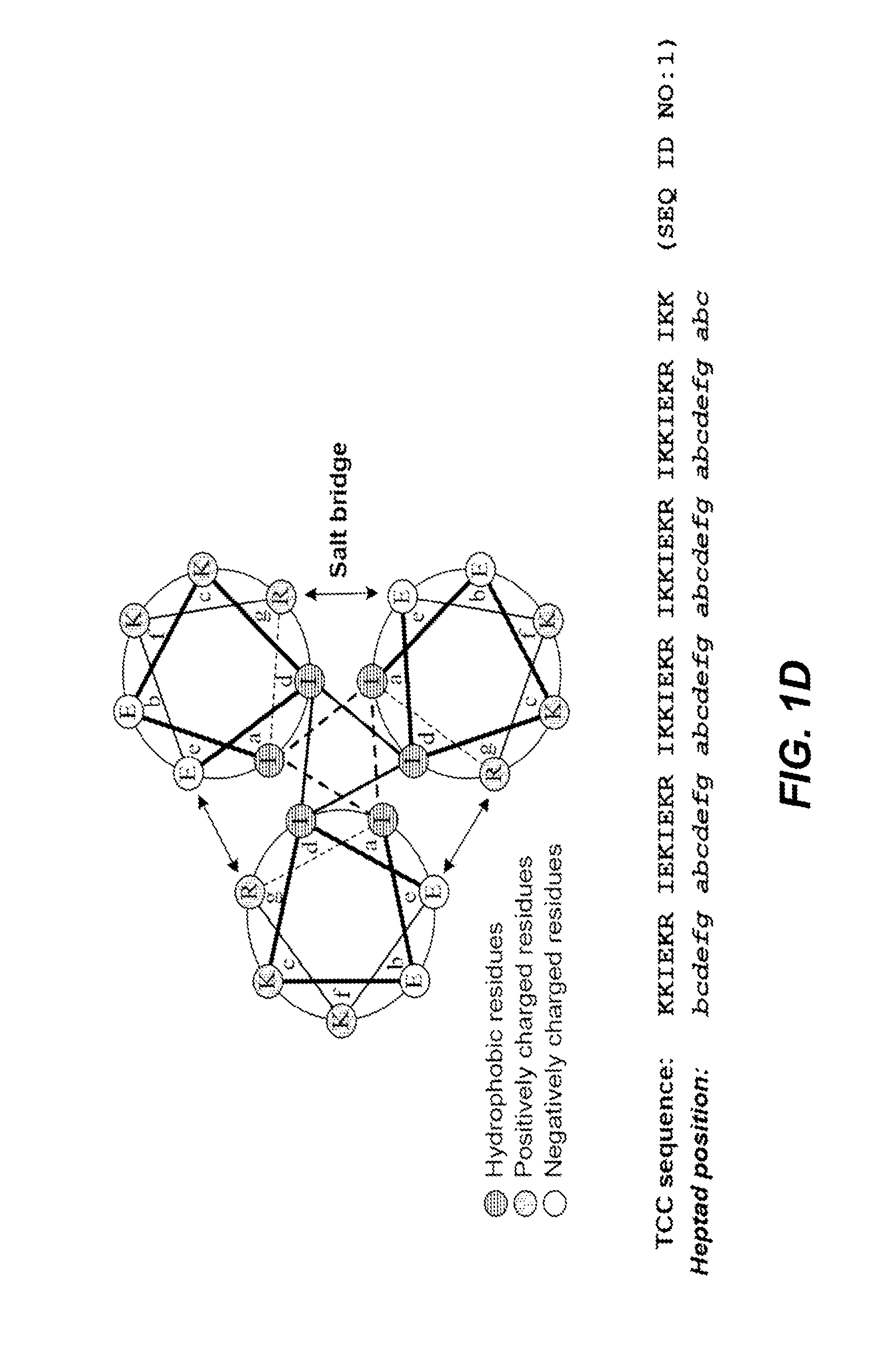
InactiveUS20170049883A1Thorough understandingSsRNA viruses negative-senseImmunoglobulin superfamilyVaccine deliveryAspartic acid residue
The present disclosure relates to peptide monomers comprising an amphipathic ?-helical peptide, and optionally, at least one T cell epitope peptide; and to dimers and trimers comprising the peptide monomers. The monomeric, dimeric, and trimeric peptides may be conjugated to at least one hapten, wherein the hapten is linked to a lysine or aspartic acid residue of the peptide monomer. These peptide conjugates are useful as vaccine delivery vehicles.
Owner:TRIA BIOSCI
Polymeric contrast agents for use in medical imaging
A contrast agent comprising a polypeptide is provided. The polypeptide contains lysine residues and optionally, one or more types of amino acid residues selected from the group consisting of glutamic acid residues and aspartic acid residues, wherein the lysine residues are substituted with a group derived from a steric hindrance molecule; and an image producing entity is present in a range between about 100 units and about 2000 units. Methods for administering the aforementioned contrast agent are also provided.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Double-chain polyethylene glycol-insulin compound and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101721712AHas a long-lasting functionHigh yieldPeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderInsulin activityAspartic acid residue
The invention relates to the field of biomedicine. A double-chain polyethylene glycol-insulin compound has a structural formula D-X-R2, wherein in the formula, R is CH3O-(CH2CH2O)n CH2CH2NH, and n is 50 to 250; X is L-glutamic acid residue or L-aspartic acid residue; and D is a product obtained by removing alanine residue of B30 site from natural porcine insulin or removing B30 threonine residue from human insulin. In PEG modification, the amino modification is changed into carboxyl modification, two polyethylene glycol chains are connected to two carboxyls of the B30 amino acid residue of the insulin, and the connection is high-yield and stable due to an amide bond. The synthesized double-chain polyethylene glycol-insulin compound with great application prospect in the long-acting effect is intrinsically chemical modified insulin. The double-chain polyethylene glycol-insulin compound has potential long-acting function.
Owner:何明磊
Variant enzyme of cytochrome P450BM-3D168S and method for preparing indirubin using the same
InactiveCN101333521AEasy to separateHigh utilization rate of raw materialsOxidoreductasesFermentationAspartic acid residueCytochrome P450
The invention discloses a cytochrome P450 BM-3 D168Smutant enzyme as well as a method applying the enzyme to prepare indirubin. The enzyme adopts the directed evolution technique, and takes P450 BM-3 (F87V / A74G / L188Q / E435T) as a male parent, and is obtained by implementing the fixed-point saturation and mutation at the codon for the aspartic acid residue in position 168 of the sequence in the male parent gene through screening. The base sequence is shown as SEQ ID NO.1 in the sequence table, the codon at the original point is mutated to TGG from GAT, and the corresponding amino acid residue is mutated to aspartic acid from serine. The P450 BM-3 D168Smutant enzyme of the invention takes indirubin as main acquired product when catalyzing indole, and the product shows obvious red color.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Compounds and methods for identifying compounds which inhibit a new class of aspartyl proteases
Compounds and methods for designing and identifying compounds which inhibit TFPP-like aspartyl protease enzymes by targeting the aspartic acid residues of the active site or mimicking peptides corresponding to the region surrounding the substrate's cleavage site are provided. Agents identified as inhibitors of TFPP-like aspartyl proteases such as type 4 prepilin peptidases are expected to be useful as anti-bacterial agents and in inhibiting development of drug resistant strains of bacteria.
Owner:TRUSTEES OF DARTMOUTH COLLEGE THE
Γ-glutamylcysteine producing yeast
A yeast which harbors a mutant glutathione synthetase having one or both of mutations selected from the group consisting of a mutation to replace a threonine residue at the position 47 with an isoleucine residue and a mutation to replace a glycine residue at the 387-position with an aspartic acid residue and produces γ-glutamylcysteine. The yeast is cultured under suitable conditions, the resultant culture or fractionation product thereof or the resultant culture or fractionation product thereof that had been heat-treated is mixed with food or beverage materials and processed into foods or beverage to produce γ-glutamylcysteine- or cysteine-containing foods or beverage.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
Proteins and peptide tags with enhanced rate of spontaneous isopeptide bond formation and uses thereof
PendingCN110709412APolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifDepsipeptidesAspartic acid residueArginine
The present invention relates to a two-part linker comprising a peptide tag (peptide) and a polypeptide (protein) that is capable of spontaneously forming an isopeptide bond, particularly wherein: a)said peptide comprises an amino acid sequence as set forth in SEQ ID NO: 1, wherein: (i) X at position 1 is arginine or no amino acid; (ii) X at position 2 is glycine or no amino acid; (iii) X at position 5 is histidine or threonine; (iv) X at position 11 is alanine, glycine or valine; and (v) X at position 14 is arginine or lysine, wherein when X at position 1 is no amino acid, X at position 2 isno amino acid; and b) said polypeptide comprises: i) an amino acid sequence as set forth in SEQ ID NO: 2; ii) a portion of (i) comprising an amino acid sequence as set forth in SEQ ID NO: 101; iii) an amino acid sequence with at least 80% sequence identity to a sequence as set forth in SEQ ID NO: 2, wherein said amino acid sequence comprises a lysine at position 34, a glutamic acid at position 80and one or more of the following: 1) threonine at position 5; 2) proline at position 16; 3) arginine at position 40; 4) histidine at position 65; 5) proline at position 92; 6) aspartic acid at position 100: 7) glutamic acid at position 108; and 8) threonine at position 116, wherein the specified amino acid residues are at positions equivalent to the positions in SEQ ID NO: 2; or iv) a portion of(iii) comprising an amino acid sequence with at least 80% sequence identity to a sequence as set forth in SEQ ID NO: 101, wherein the amino acid sequence comprises a lysine at position 10, a glutamicacid at position 56 and one or more of the following: 1) arginine at position 16; 2) histidine at position 41; 3) proline at position 68; and 4) aspartic acid at position 76, wherein the specified amino acid residues are at positions equivalent to the positions in SEQ ID NO: 101, and wherein said peptide and polypeptide are capable of spontaneously forming an isopeptide bond between the aspartic acid residue at position 10 of SEQ ID NO: 1 and the lysine residue at position 34 of SEQ ID NO: 2 or position 10 of SEQ ID NO: 101.
Owner:OXFORD UNIV INNOVATION LTD
Mutant smoothened and methods of using the same
ActiveUS20120282259A1Avoid signalingAvoid delayOrganic active ingredientsAnimal repellantsAspartic acid residueHh signaling
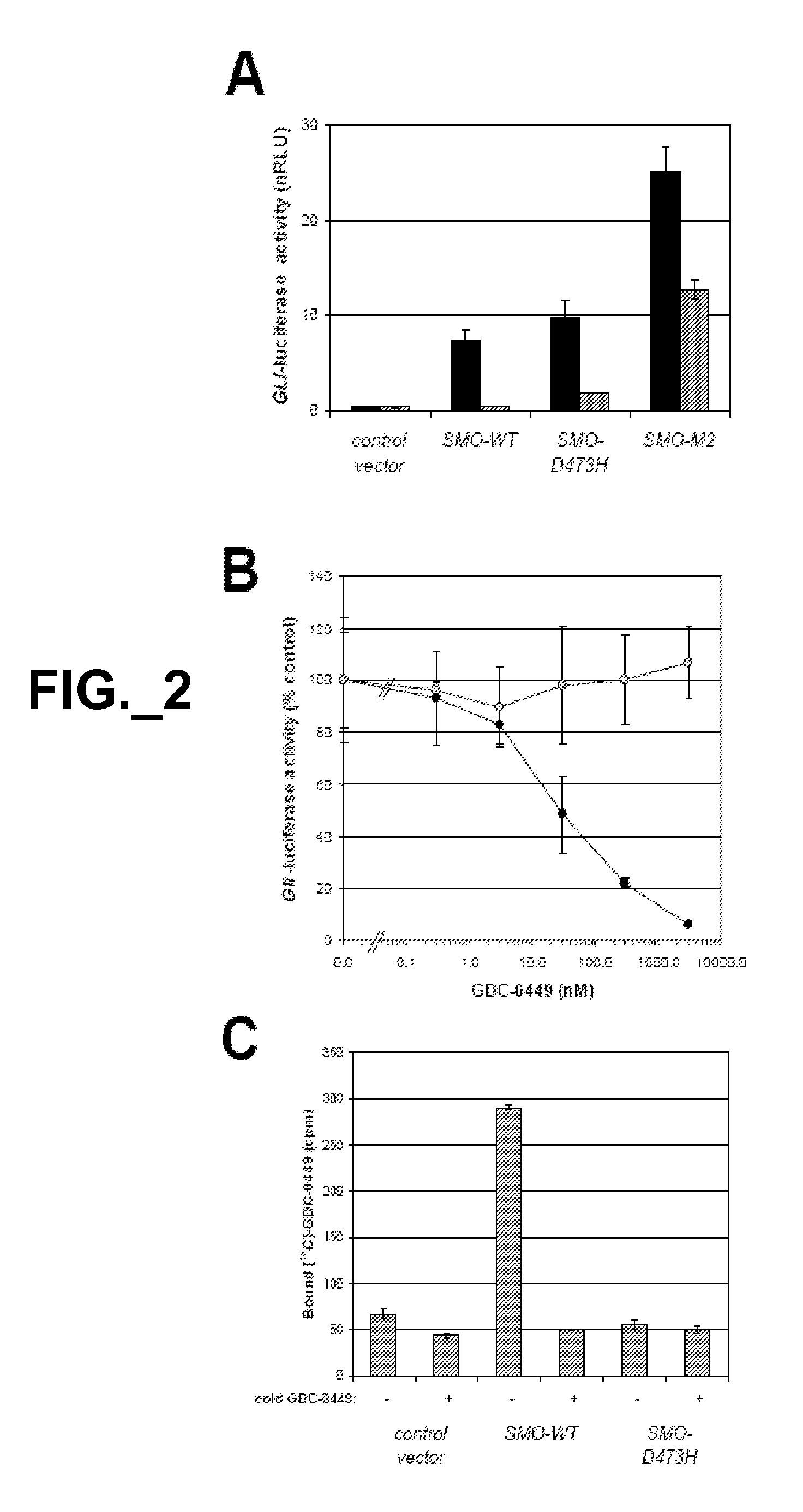
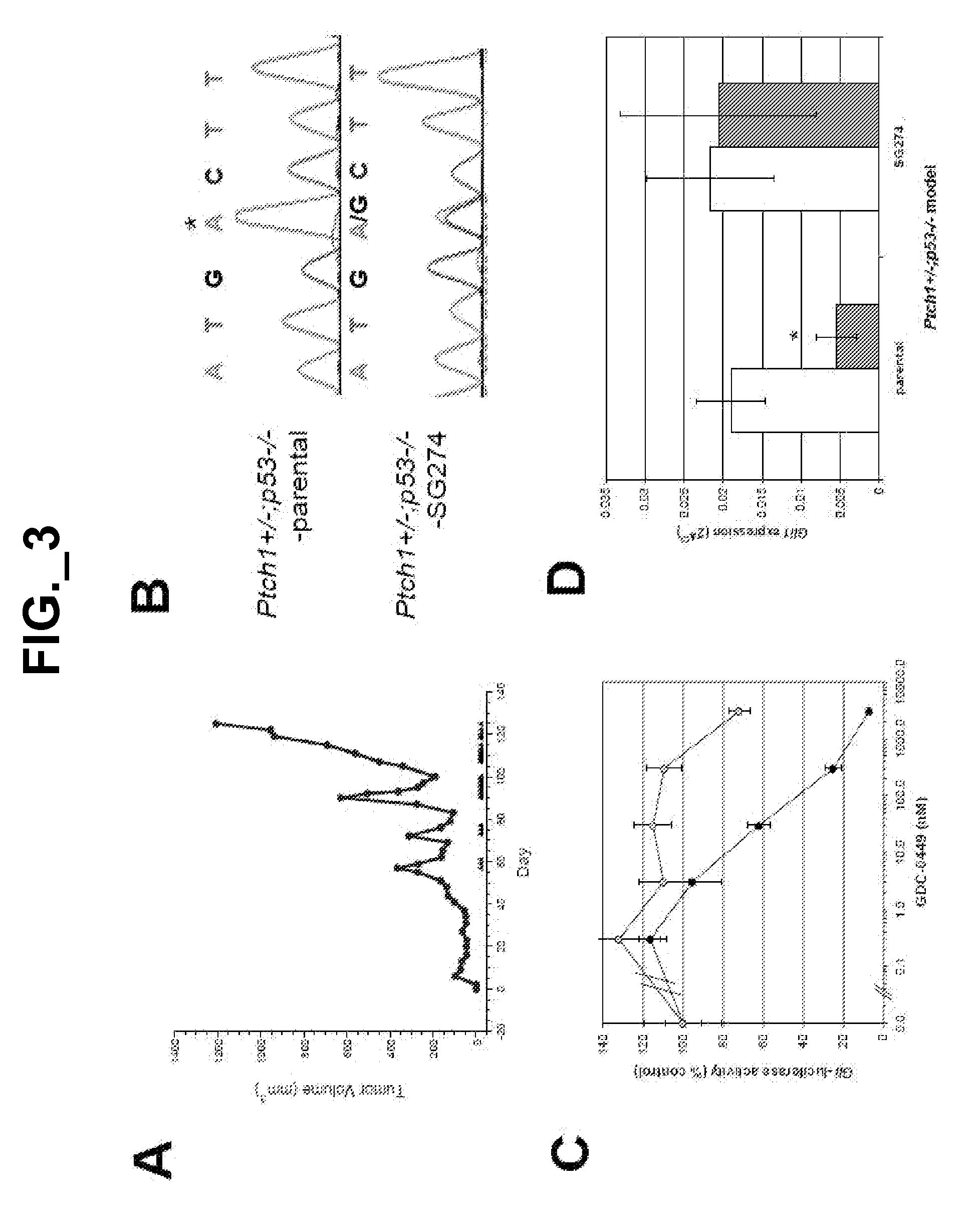
The emergence of mutations in tyrosine kinases following treatment of cancer patients with molecular-targeted therapy represents a major mechanism of acquired drug resistance. Here, we describe a mutation in the serpentine receptor, Smoothened (SMO), which results in resistance to a Hedgehog (Hh) pathway inhibitor in medulloblastoma. A single amino acid substitution in a conserved aspartic acid residue of SMO maintains Hh signaling, but results in the inability of the Hh pathway inhibitor, GDC-0449, to bind SMO and suppress the pathway. This mutation was not only acquired in a GDC-0449-resistant mouse model of medulloblastoma, but was identified in a Medulloblastoma patient following relapse on GDC-0449. The invention provides screening methods to detect SMO mutations and methods to screen for drugs that specifically modulate mutant SMO exhibiting drug resistance.
Owner:CURIS INC +1
VIP analog and its radioactive marker and their prepn process
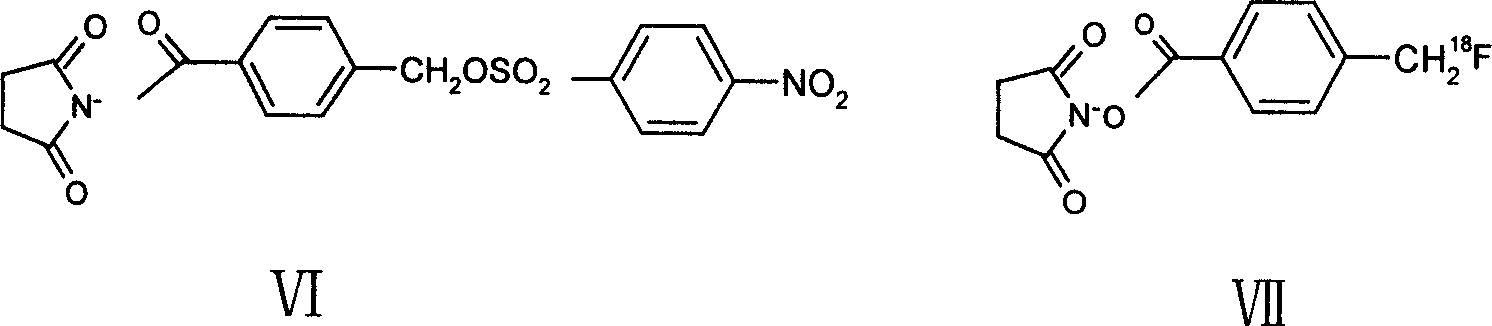
InactiveCN101089020ASuitable for diagnosisRadioactive preparation carriersAnimals/human peptidesVIP ReceptorsAspartic acid residue
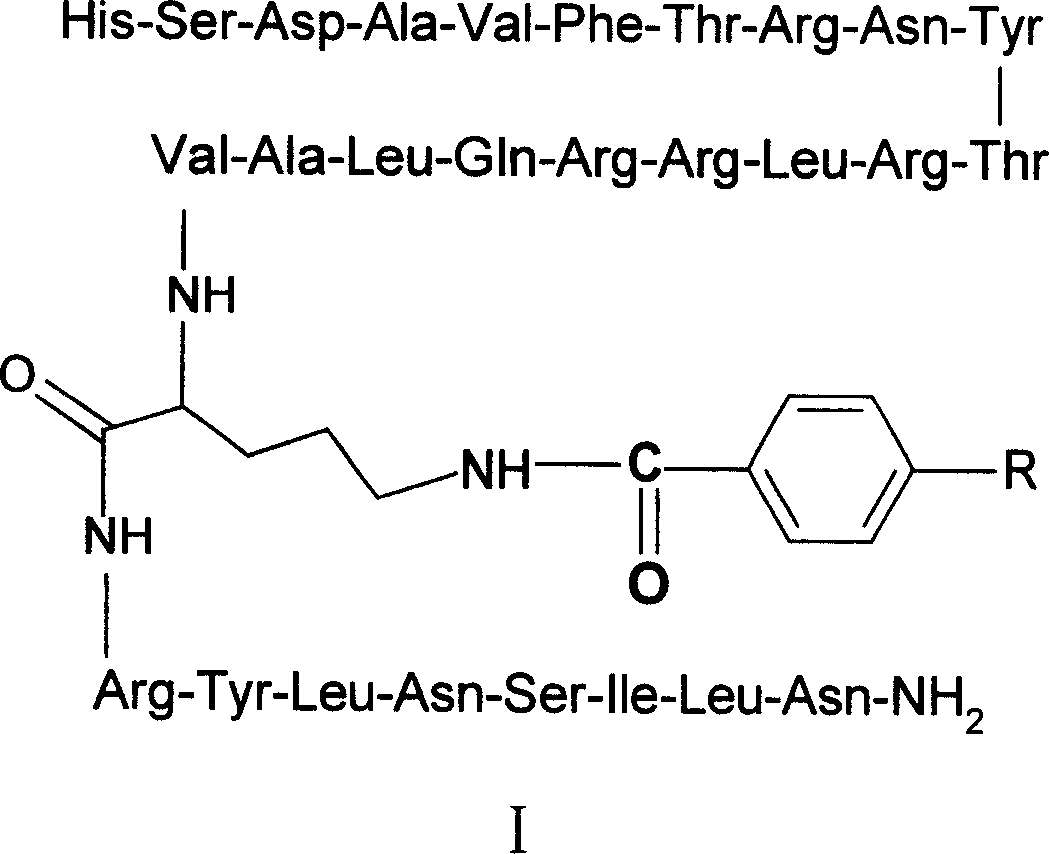
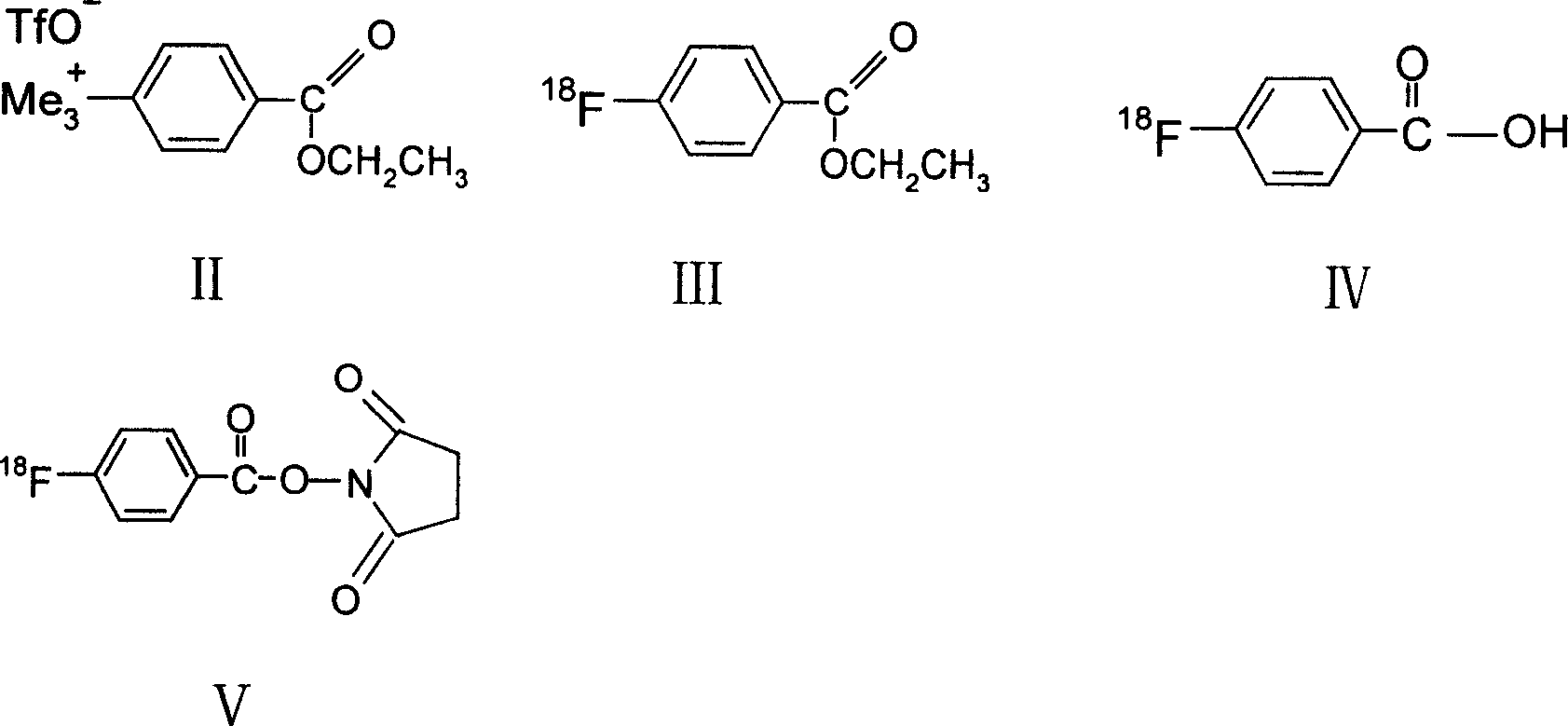
The present invention discloses one kind of VIP analog with the amino acid sequence as shown in SEQ ID No. 1, that is, the VIP analog has the VIP amino acid sequence with the arginine residue substituting the aspartic acid residue in the position 8, the arginine residues lysine residues in the positions 15 and 21, and the leucine residue substituting the methionine residue in the position 17. The present invention also discloses the radioactive marker, especially two 18F markers, of the VIP analog, and their preparation process. The VIP analog of the present invention has high metabolic stability and excellent receptor associativity, and the radioactive markers is suitable for use in preparing radioactive developing reagent for detecting in vivo VIP acceptor.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF APPLIED PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Antagonistic peptides for frizzled-1 and frizzled-2
InactiveUS8598122B2Increase volumeGood effectPeptide/protein ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementAspartic acid residueThreonine
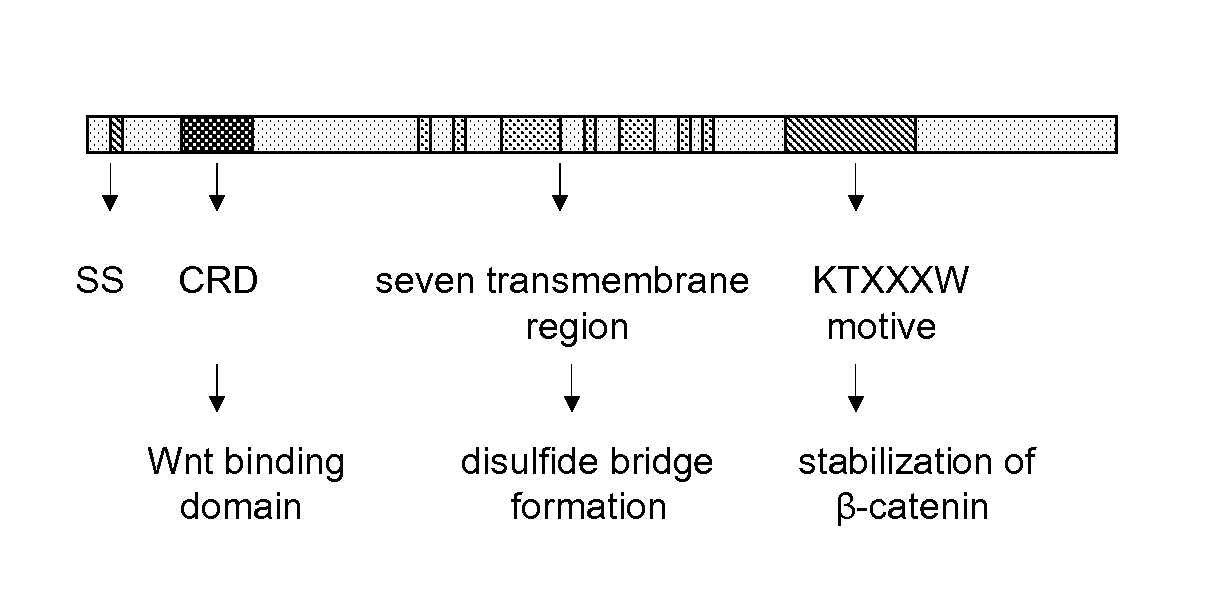
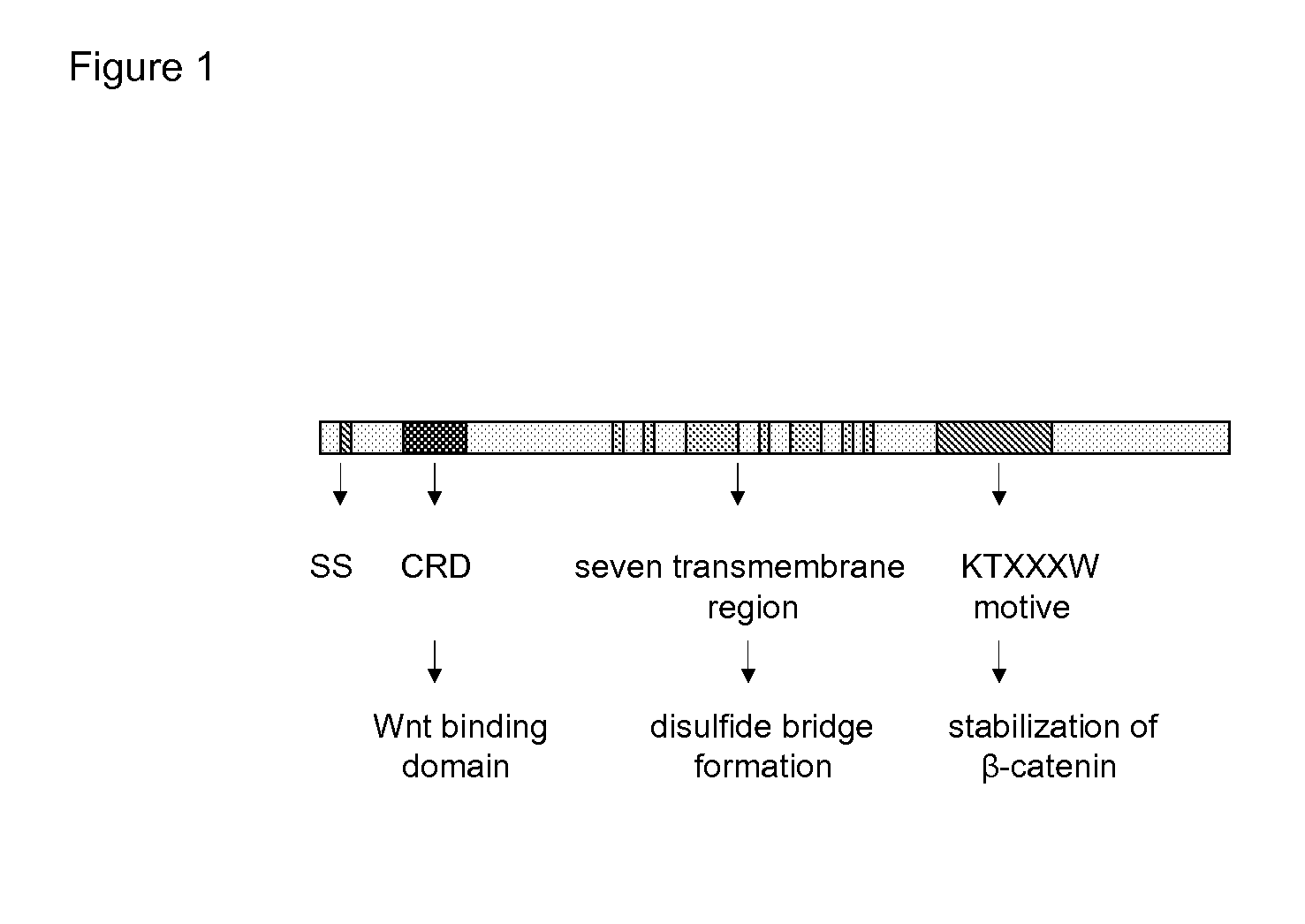
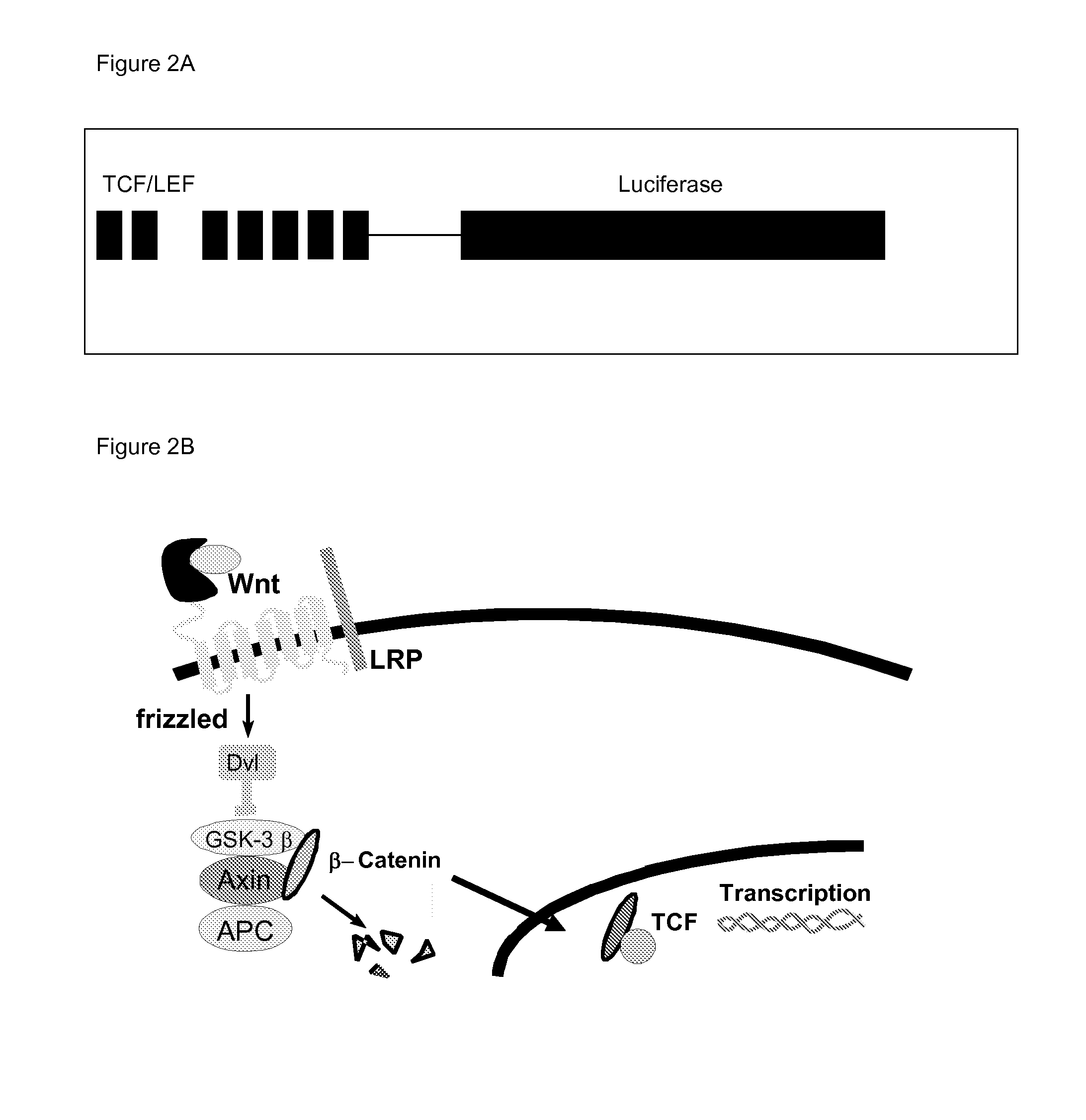
The invention is in the field of molecular medicine. It provides antagonistic compounds for frizzled 1 and / or frizzled-2 receptors, which may be useful in molecular imaging of the wound healing process after myocardial infarction and in therapeutic intervention into wound healing after remodeling of the heart, thereby ameliorating the consequences of myocardial infarction. The invention provides a method for antagonizing frizzled-1 or frizzled-2 receptors, wherein the receptor is contacted with a composition comprising a linear fragment of Wnt3(a) or Wnt5a or a functional analogue thereof, which comprises at least one cysteine residue, one threonine residue, one aspartic acid residue and one glycine residue.
Owner:MAASTRICHT UNIVERSITY +1
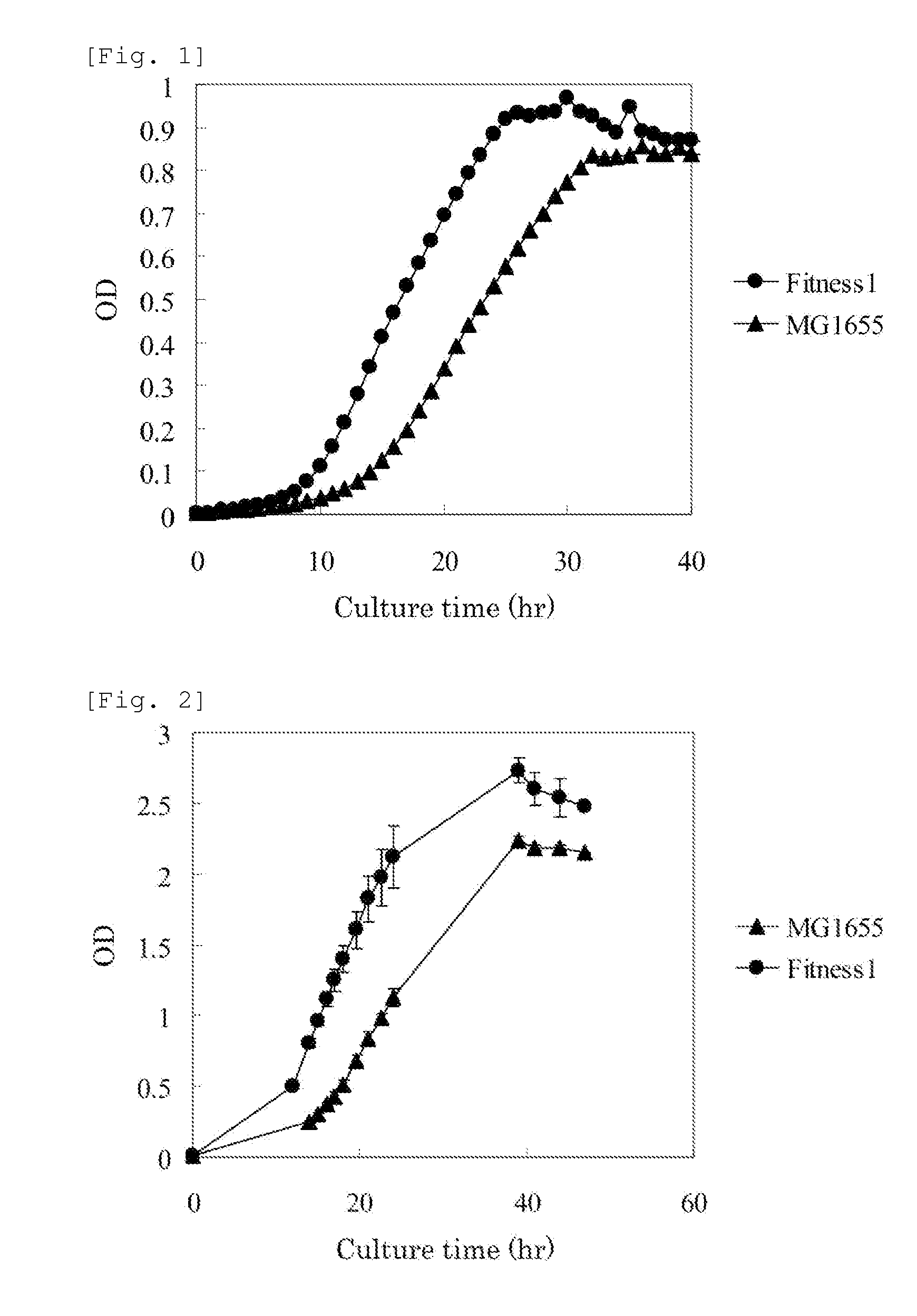
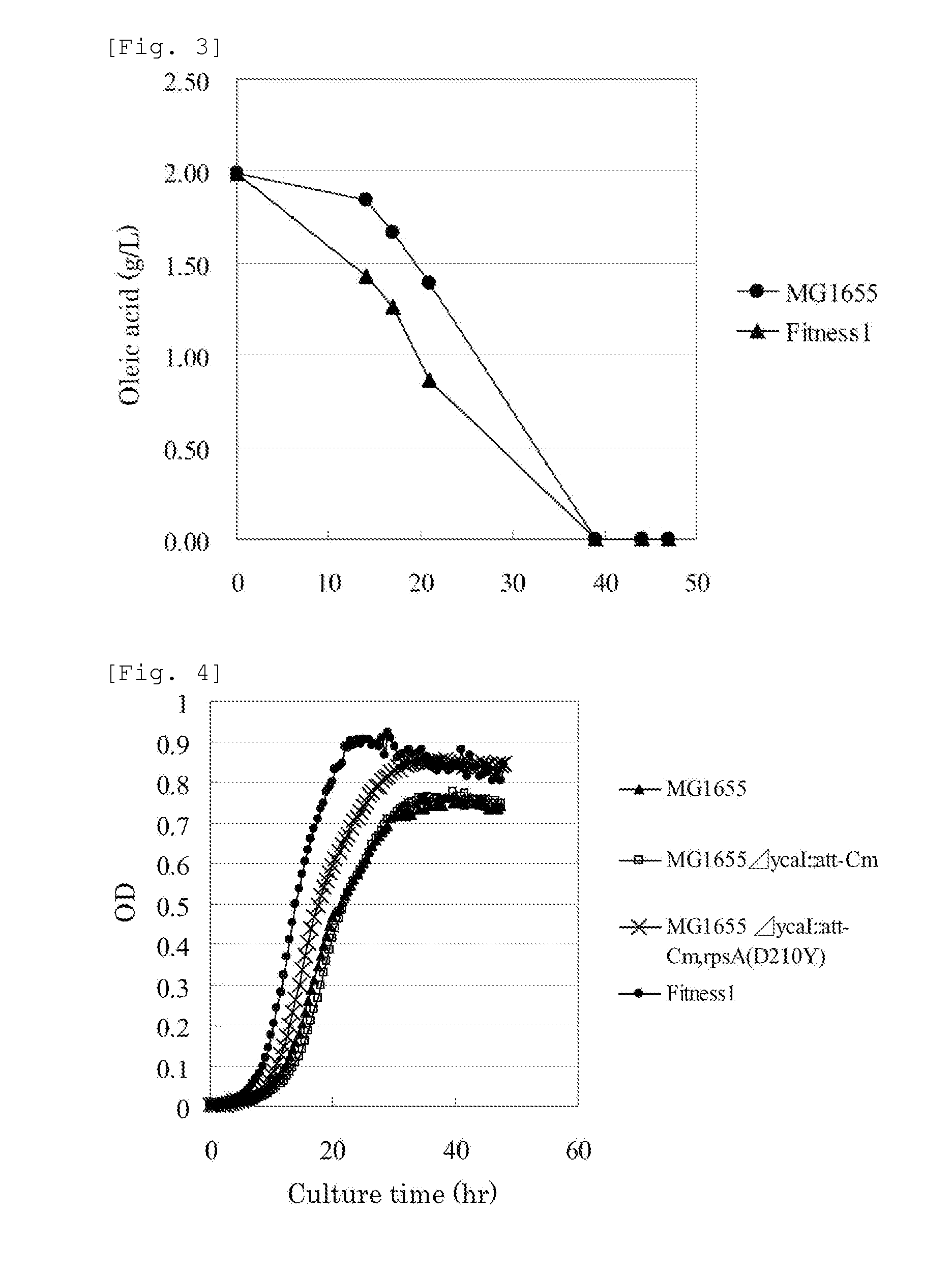
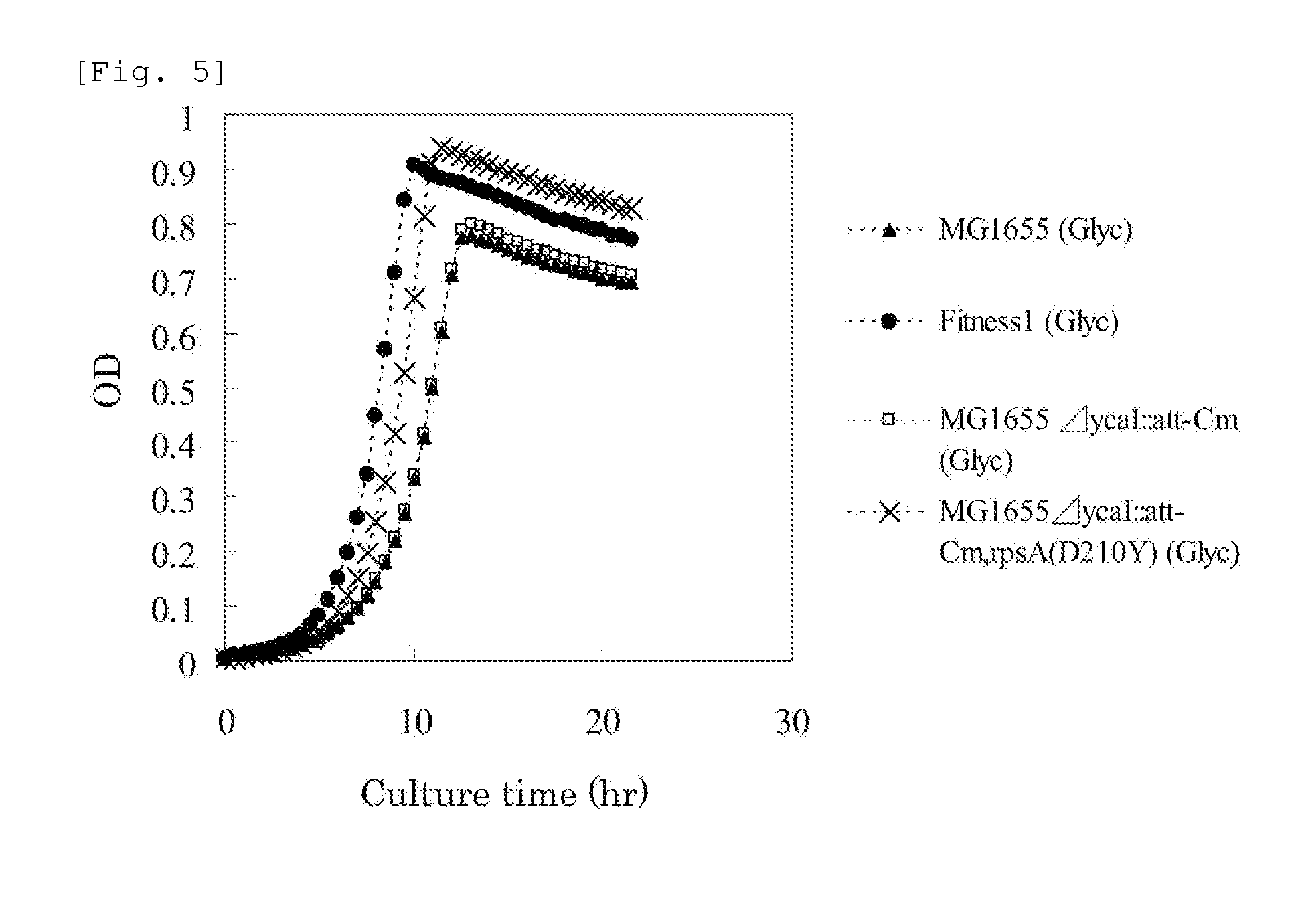
MUTANT rpsA GENE AND METHOD FOR PRODUCING L-AMINO ACID
InactiveUS20130005000A1Efficient productionImprove scalabilityBacteriaSugar derivativesAspartic acid residueGlycerol
A method for efficiently producing an L-amino acid utilizing a bacterium belonging to the family Enterobacteriaceae from a fatty acid or an alcohol such as glycerol as a raw material is provided. A bacterium belonging to the family Enterobacteriaceae which is able to produce L-amino acid and harbors an RpsA protein which has a mutation such that the native aspartic acid residue at position 210 is replaced with another amino acid residue is used. This bacterium is cultured in a medium containing a carbon source selected from a fatty acid and an alcohol, and the produced L-amino acid is collected from the medium.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
Mutational SHV beta-lactamase, gene order and uses thereof
The invention discloses a varied SHV type beta-lactamase, which comes from bacteria and comprises a variant from the following: the 79th alanine residue in amino-acid sequence shown in sequence 2 in the sequence table is substituted by threonine residue, or 101th aspartic acid residue is substituted by histidine residue, or 214th aspartic acid residue is substituted by alanine residue, or 203th serine is substituted by leucine residue. The invention also discloses the gene sequence of the varied SHV type beta-lactamase and the application of the beta-lactamase. The varied SHV type beta-lactamase of the invention is of activity from super-wide spectrum beta-lactamase, provides useful information for developing and preparing anti-medicine gene inspection chip of beta-lactamase, guides the research and development as well as preparation of anti-medicine bacteria antibiotic, and effectively improve the direction-targeting in the use of antibiotic.
Owner:SHANGHAI BIOCHIP
Recombinant interferon-beta with enhanced biological activity
Human interferon-ss protein analogs in which the asparagine at position 25, numbered in accordance with native human interferon-ss, is recombinantly replaced with an aspartate residue exhibit a biological activity of human interferon-ss (e.g. IFN-ss 1b) at an increased level relative to IFN-ss 1b. These analogs are obtained by introducing a gene coding for Asp25 IFN-ss into a cell and expressing the recombinant protein. The resulting IFN-ss protein analog is suitable for large scale manufacturing for incorporation in HA-containing or HA-free therapeutics for treatment of diseases including multiple sclerosis. A reduced Lys endoproteinase-C peptide map technique that produces a fingerprint profile for proteins using an enzymatic digest followed by RP-HPLC is also useful in quality control as an ID test for the IFN-ss protein analog products.
Owner:NOVARTIS AG
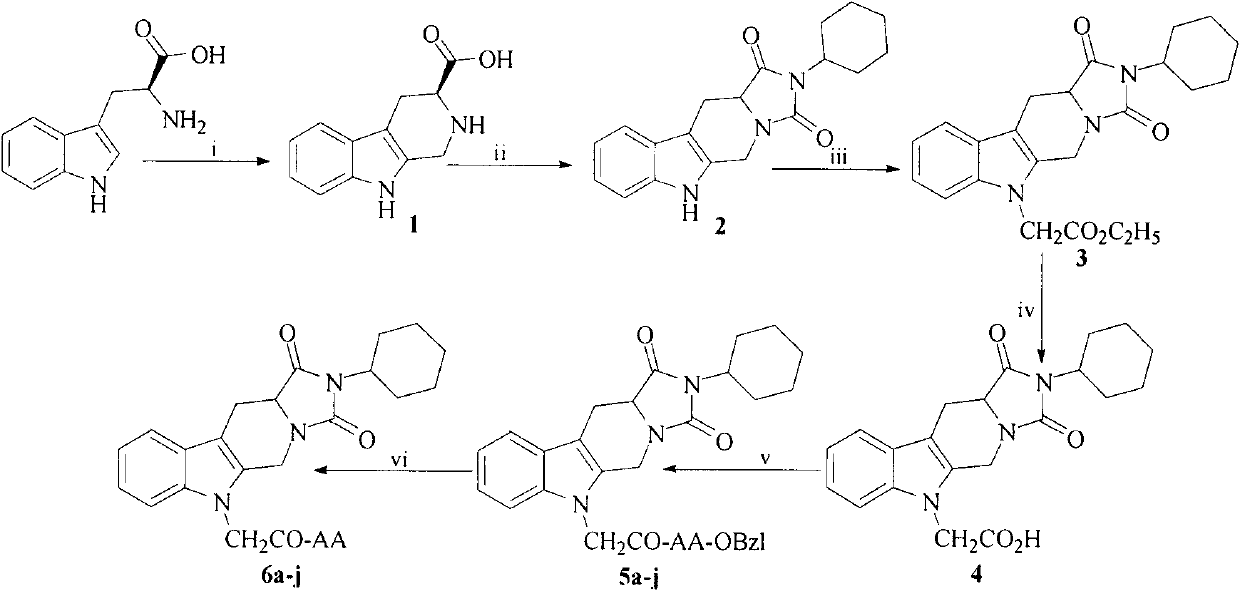
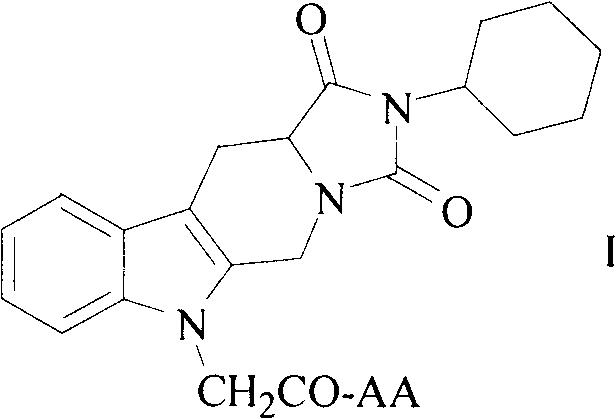
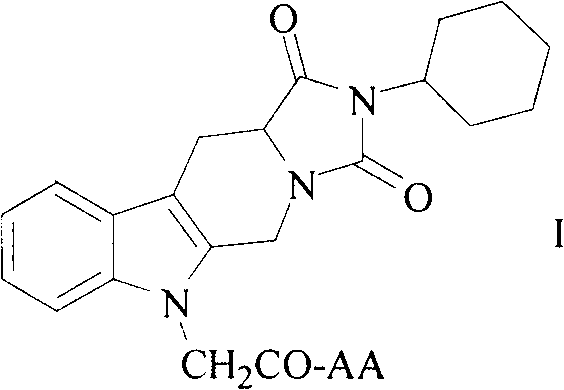
Cyclohexyl tetrahydro imidazo pyrido indole-diketone acetyl amino acids, and synthesis, antithrombotic effect and application thereof
InactiveCN103450197AOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryAntithrombotic AgentAspartic acid residue
The invention discloses 10 kinds of cyclohexyl tetrahydro imidazo pyrido indole-diketone acetyl amino acids represented by the general formula I (wherein AA represents a valine residue, a leucine residue, an isoleucine residue, a glycine residue, a glutamic acid residue, a tryptophan residue, a methionine residue, an aspartic acid residue, a phenylalanine residue and a tyrosine residue), discloses a synthesis method thereof, discloses in vitro platelet aggregation inhibition experiments thereof, further discloses an antithrombotic activity thereof in a rat arteriovenous bypass cannula thrombosis model, and thus discloses an application thereof in preparation of antithrombotic agents.
Owner:CAPITAL UNIVERSITY OF MEDICAL SCIENCES
Modified biotin-binding protein
The present invention provides a modified biotin-binding protein comprising an amino acid sequence represented by SEQ ID NO: 2 or its modified sequence and having a biotin-binding activity and replacement selected from the group consisting of:1) replacement of the 36th serine residue of SEQ ID NO: 2 with an amino acid residue that does not form a hydrogen bond;2) replacement of the 80th tryptophan residue of SEQ ID NO: 2 with a hydrophilic amino acid residue;3) replacement of the 116th aspartic acid residue of SEQ ID NO: 2 with an amino acid residue that does not form a hydrogen bond;4) replacement of the 46th proline residue of SEQ ID NO: 2 with a threonine, serine, or tyrosine residue and replacement of the 78th threonine residue of SEQ ID NO: 2 with an amino acid residue that does not form a hydrogen bond;5) replacement of the 46th proline residue of SEQ ID NO: 2 with a threonine, serine, or tyrosine residue and replacement of the 116th aspartic acid residue of SEQ ID NO: 2 with an amino acid that does not form a hydrogen bond; and6) replacement of the 46th proline residue of SEQ ID NO: 2 with a threonine, serine, or tyrosine residue, replacement of the 78th threonine residue of SEQ ID NO: 2 with an amino acid residue that does not form a hydrogen bond, and replacement of the 116th aspartic acid residue of SEQ ID NO: 2 with an amino acid that does not form a hydrogen bond.
Owner:JAPAN TOBACCO INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com