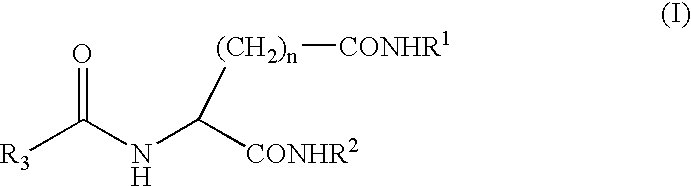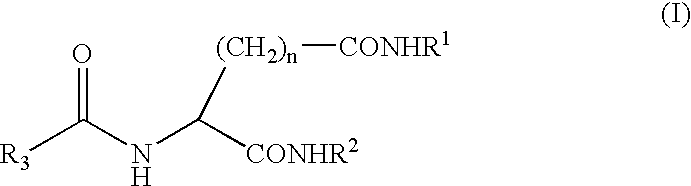Gelling agent for oil
a gelling agent and oil technology, applied in the direction of disinfection, make-up, candy, etc., can solve the problems of low solubility of oils, formation of heterogeneous gel compositions, and sometimes insufficient gel strength of gel compositions obtained
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Preparation of N-2-(R,S)-ethylhexanoyl-L-glutamic acid dibutylamide
[0035] 110 g of sodium glutamate monohydrate was dissolved in 140 g of water and 78 g of 27% aqueous sodium hydroxide and the solution was cooled to 10° C. The solution was added with 110 g of acetone and added dropwise with 87 g of 2-ethylhexanoyl chloride and 78 g of 27% aqueous sodium hydroxide. The reaction mixture for the acylation was diluted with 100 g of water and neutralized with 63 g of 95% sulfuric acid to separate an oil. The aqueous layer was removed, and the oil layer was concentrated under reduced pressure to obtain an oily substance. The resulting oily substance was dissolved in 742 g of methanol, and the solution was added with 6.2 g of 95% sulfuric acid and refluxed for 9 hours. The reaction mixture was left stand for cooling to 35° C. and neutralized with 8.8 g of n-butylamine, and then the methanol was evaporated to obtain an oily substance. The resulting oily substance was added with 643 g of to...
example 2
Preparation of N-octanoyl-L-glutamic acid dibutylamide
[0040] 110 g of sodium glutamate monohydrate was dissolved in 140 g of water and 78 g of 27% aqueous sodium hydroxide and cooled to 10° C. The solution was added with 110 g of acetone and added dropwise with 87 g of octanoyl chloride and 90 g of 27% aqueous sodium hydroxide. The reaction mixture for the acylation was diluted with 100 g of water and neutralized with 64 g of 95% sulfuric acid to separate an oil, The aqueous layer was removed, and the oil layer was concentrated under reduced pressure to obtain an oily substance. The resulting oily substance was dissolved in 742 g of methanol, and the solution was added with 6.2 g of 95% sulfuric acid and refluxed for 9 hours. The reaction mixture was left stand for cooling to 35° C. and neutralized with 10.5 g of n-butylamine, and then the methanol was evaporated to obtain an oily substance. The resulting oily substance was added with 630 g of toluene and 191 g of n-butylamine and ...
example 3
Preparation method of N-decanoyl-L-glutamic acid dibutylamide
[0045] In a manner similar to that of the aforementioned Example 1, N-decanoyl-L-glutamic acid dibutylamide was prepared.
[0046] (a) 13C-NMR peaks: 14.10, 14.47, 20.44, 20.48, 23.04, 26.07, 29.65, 29.67, 29.73, 29.83, 29.88, 31.92, 31.97, 32.24, 37.08, 39.70, 39.88, 52.90, 171.60, 173.33, 174.17 (ppm)
[0047] (b) 1H-NMR peaks (CDCl3) δ: 3.250 (m, 4H), 4.360 (m, 1H), 6.190 (brs, 1H), 6.980 (brs, 1H), 7.030 (brs, 1H)
[0048] (c) Wave number of infrared absorption spectrum: 3294.8, 2959.0, 2927.5, 1637.9, 1556.0, 1466.6 (cm−1)
[0049] (d) MS: 410.5 (M−H)−
[0050] Ethyloylglutamic acid dibutylamide, hexanoylglutamic acid dibutylamide, myristoylglutamic acid dibutylamide and palmitoylglutamic acid dibutylamide used in the following comparative examples were produced in a similar manner.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com