Polypeptide having the ability to form connections of glucosyl units in alpha-1,3 on an acceptor
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Screening of New Enzymes in L. citreum NRRL B-742
[0137]After sequencing of the genome of the strain L. citreum NRRL B-742, a gene proved particularly original. Indeed the corresponding putative protein was found to have a sequence having a maximum of only 54% identity with the putative glycoside hydrolase Leuconostoc fallax KCTC 3537 whose sequence is available in the database, and referenced by the NCBI under number ZP_08312597. Now, any other protein sequence with significant identity could be identified.
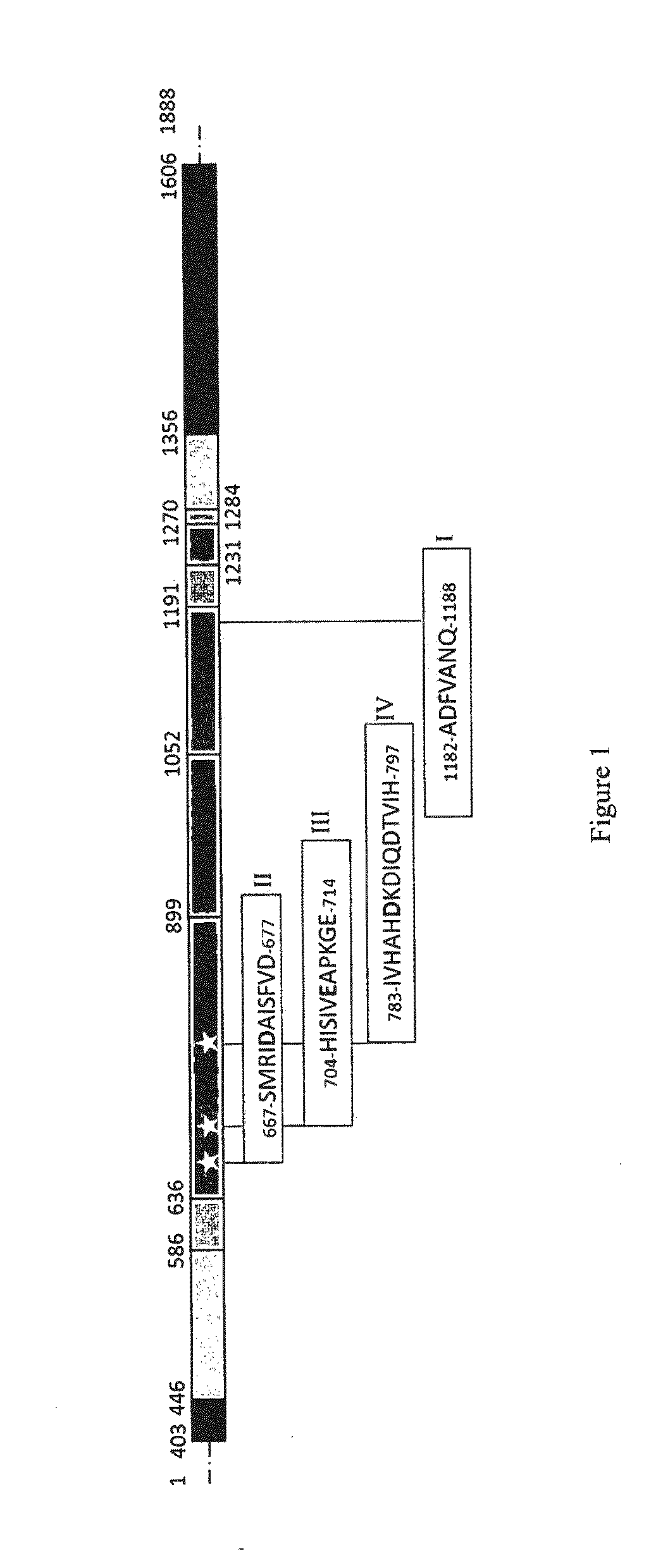
[0138]This gene encodes a putative transglucosylase of 1888 amino acids, having the characteristic catalytic triad DED and the 4 conserved regions usually described in transglucosylases of family 70. The schematic representation of the protein is shown in FIG. 1 (based on the alignment of protein sequences with GTF180) with 5 domains: i) domain V (403-446 and 1356 to 1800), ii) domain IV (446-586 and 1284-1356), iii) domain A (catalytic) (636-899, 1052-1191 and 1231-1270), iv) dom...
example 2
Production of a New Enzyme in E. coli
[0141]The gene encoding this enzyme has been cloned into several vectors (pET 53, 55, 49 and 60) commercially available from NOVAGEN or INVITROGEN, and expressed in different various of E. coli (TOP10, BL21AI, BL21 DE3 Star, Arctic Express DE3).
[0142]This cloning resulted in a consistent production of the protein. This production has helped initiate the experiments of biochemical characterisation to clarify the catalytic properties of the identified enzyme.
[0143]Simultaneously, a truncated form of the signal peptide and C-terminal, APS AC-1313 SEQ ID no 12 and SEQ ID no 13 for the nucleic and protein sequences, respectively) of the protein has been cloned and expressed in the strain of E. coli BL21 DE3 star, allowing again a significant expression of the protein; which expression has proved almost twice higher than that of the wild-type protein.
example 3
Reaction of a Polypeptide According to the Invention with Sucrose, a Dextran-Type Acceptor and the Enzyme Object of the Invention and Analysis of the Products of this Reaction
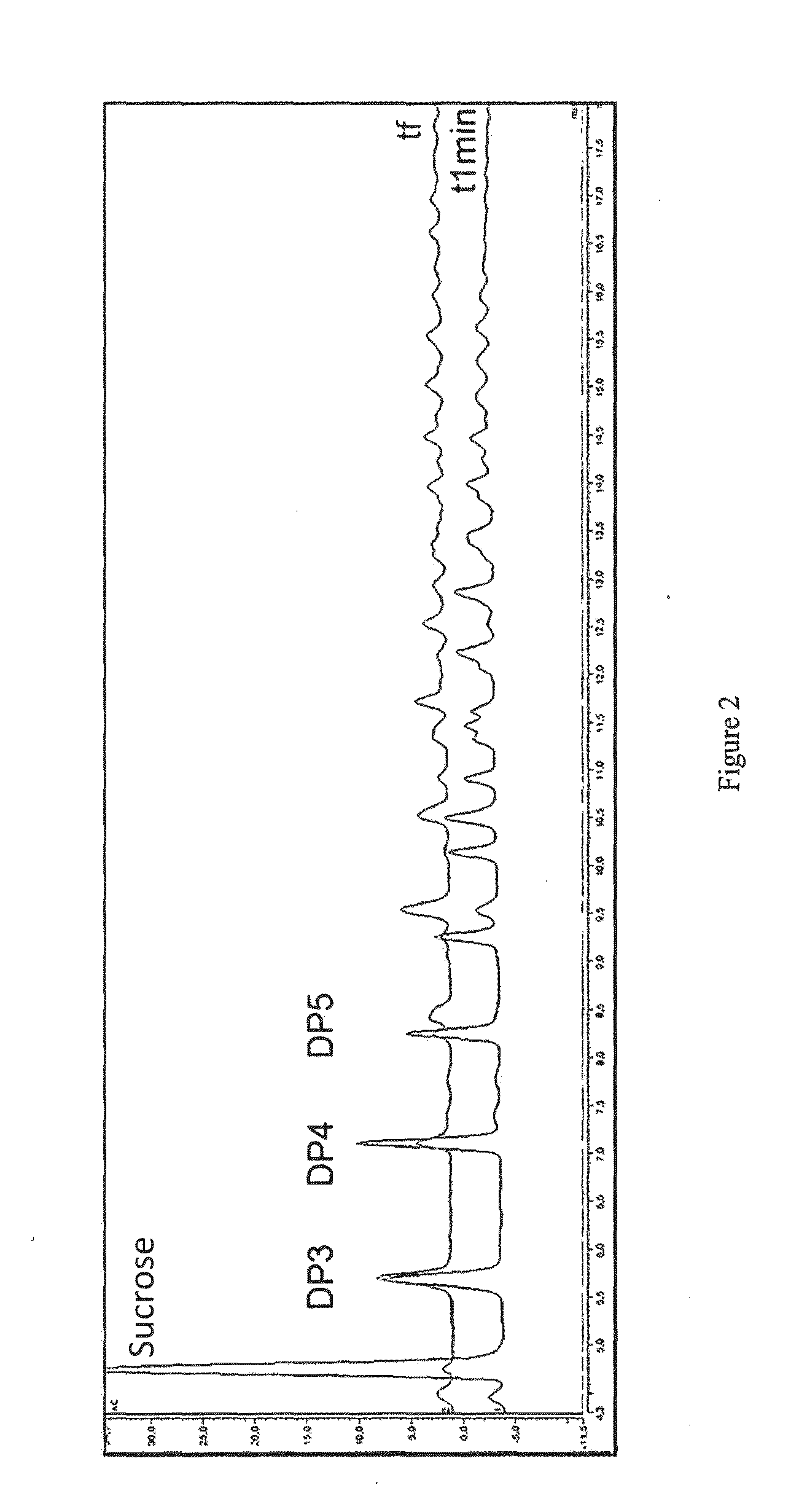
[0144]To characterise the functional properties of this putative transglucosylase, the enzyme was first implemented on sucrose alone, a natural substrate of enzymes of the GH70 family.
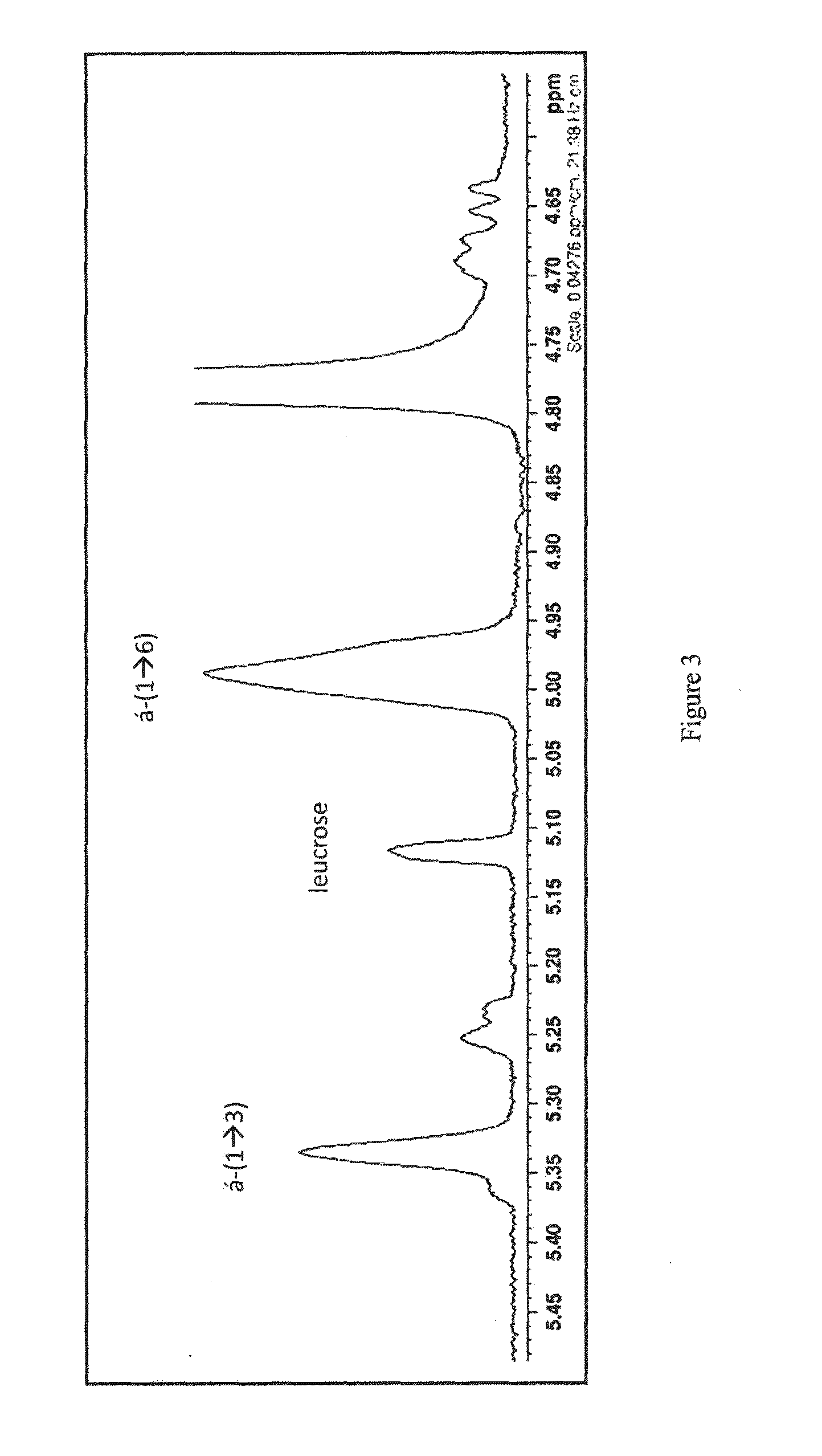
[0145]Unexpectedly, the chromatographic analyses (HPAEC-PAD, HPSEC) showed that the enzyme alone is only capable of hydrolysing the substrate in equimolar amounts of glucose and fructose. Now and from sucrose alone, this enzyme showed no ability to produce polymers of glucosyl units, as well as its truncated form.
[0146]It is interesting to note that to date, bioinformatic analyses on the primary structure of the GH of the family 70 would not predict this feature (structural determinants governing the ability—or not—of a transglucosylase polymerising are not yet known).
[0147]While nothing presaged that this protein had still an act...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pH | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com