Patents
Literature
54 results about "FAMILY ENTEROBACTERIACEAE" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
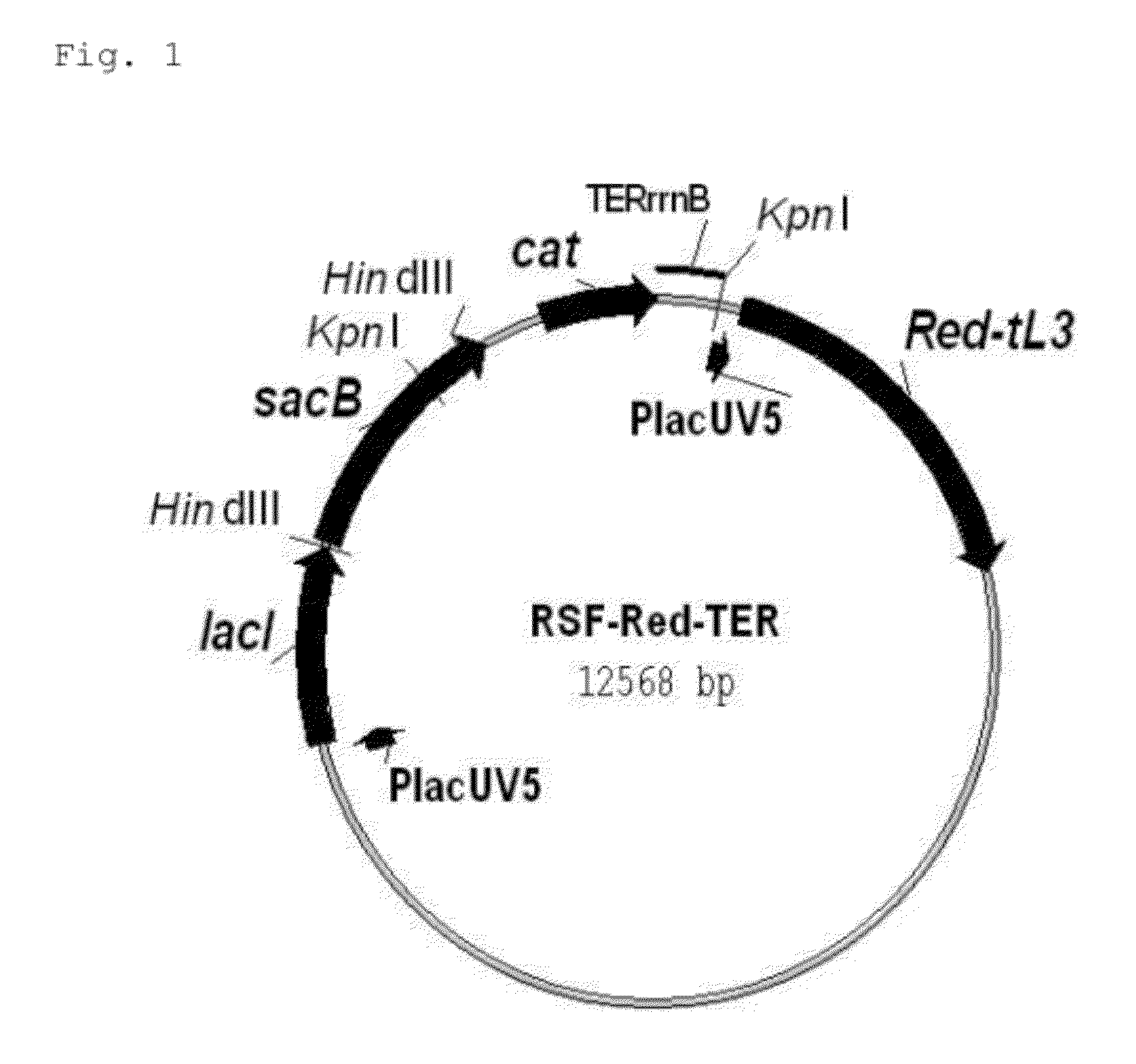
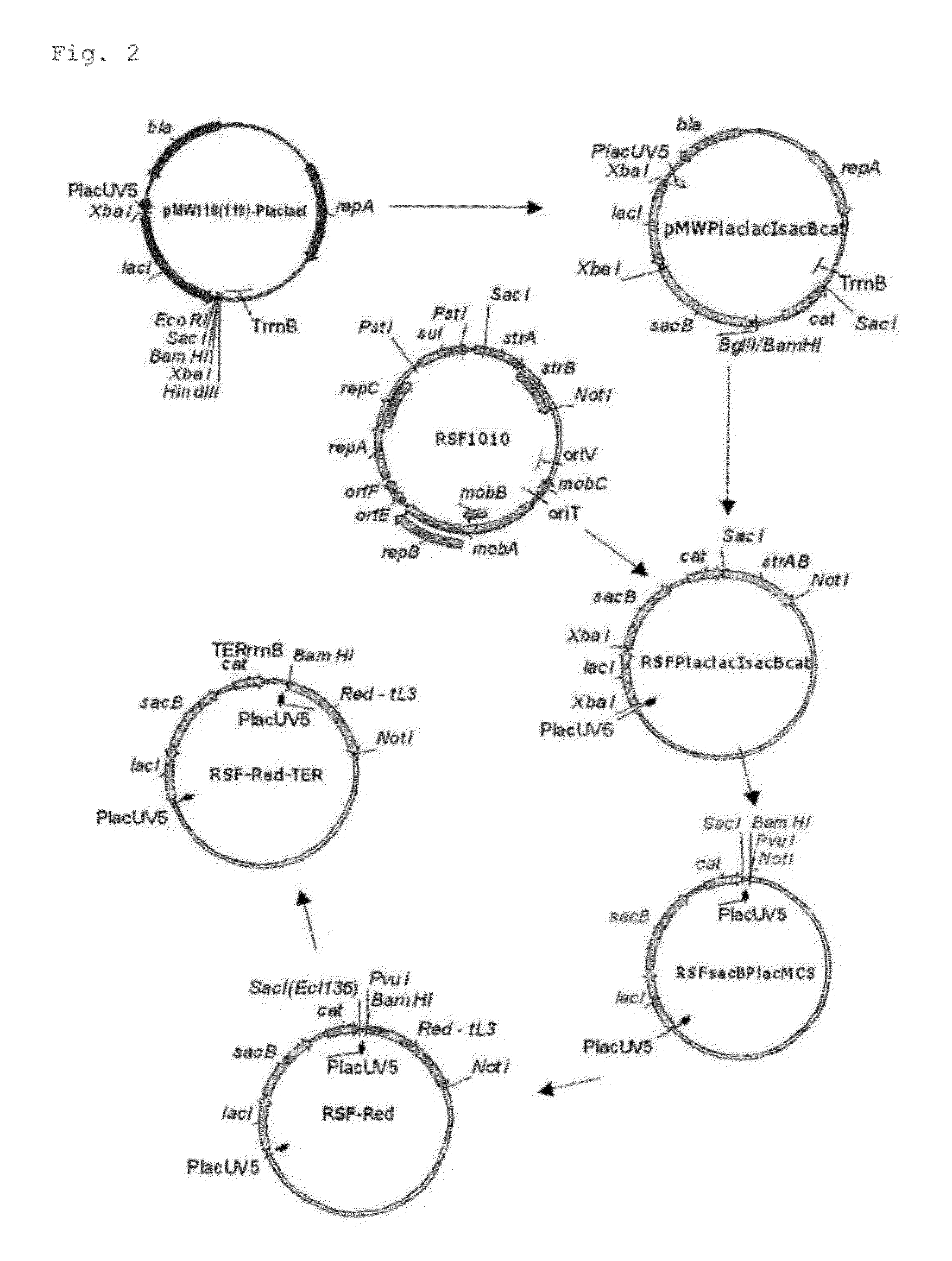
L-amino acid-producing microorganism and a method for producing an l-amino acid
ActiveUS20090104667A1Efficient productionHigh activityBacteriaUnicellular algaeMicroorganismOrotate phosphoribosyltransferase
An L-amino acid is produced by culturing a microorganism which belongs to the family Enterobacteriaceae and is able to produce an L-amino acid, wherein the bacterium has been modified to enhance orotate phosphoribosyltransferase activity is enhanced, in a medium to produce and cause accumulation of an L-amino acid in the medium or cells, and collecting the L-amino acid from the medium or the cells.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
Method of producing l-amino acid
InactiveUS20100047878A1Increase kinase activityHigh copy numberSugar derivativesBacteriaMicroorganismGlycerol
An L-amino acid is produced by culturing a microorganism belonging to the family Enterobacteriaceae having an L-amino acid-producing ability and modified so that glycerol dehydrogenase and dihydroxyacetone kinase activities are increased, in a medium containing glycerol as a carbon source to produce and accumulate an L-amino acid in the medium or cells, and collecting the L-amino acid from the medium or the cells.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
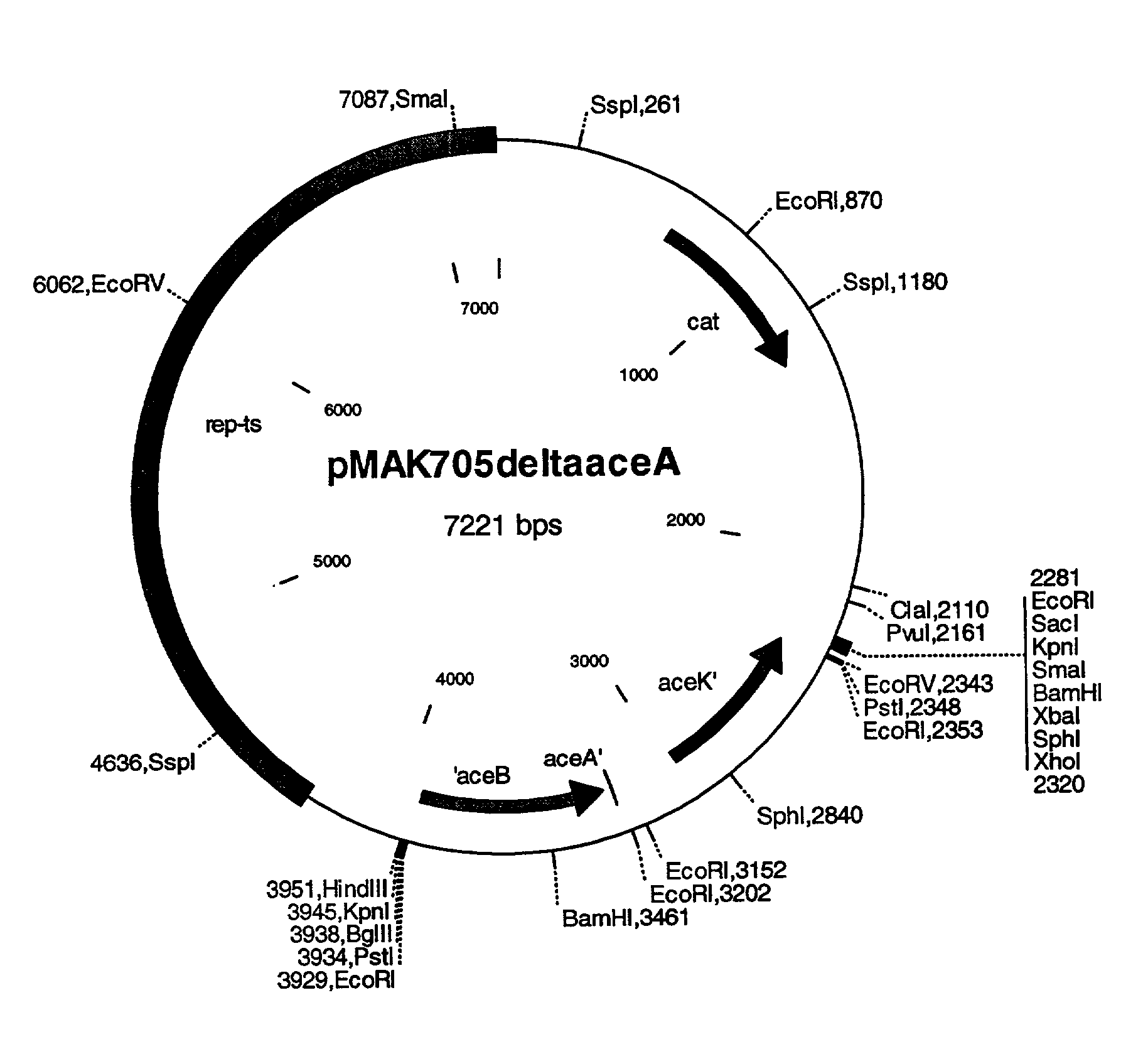
Process for the production of L-amino acids using strains of the family enterobacteriaceae that contain an attenuated aceA gene
A process for the production of L-amino acids, in particular L-threonine, in which the following steps are carried out: (a) fermentation of the microorganisms of the family Enterobacteriaceae producing the desired L-amino acid, in which the aceA gene or nucleotide sequences coding therefor are attenuated, in particular are switched off, (b) enrichment of the L-amino acid in the medium or in the cells of the bacteria, and (c) isolation of the L-amino acid.
Owner:DEGUSSA AG
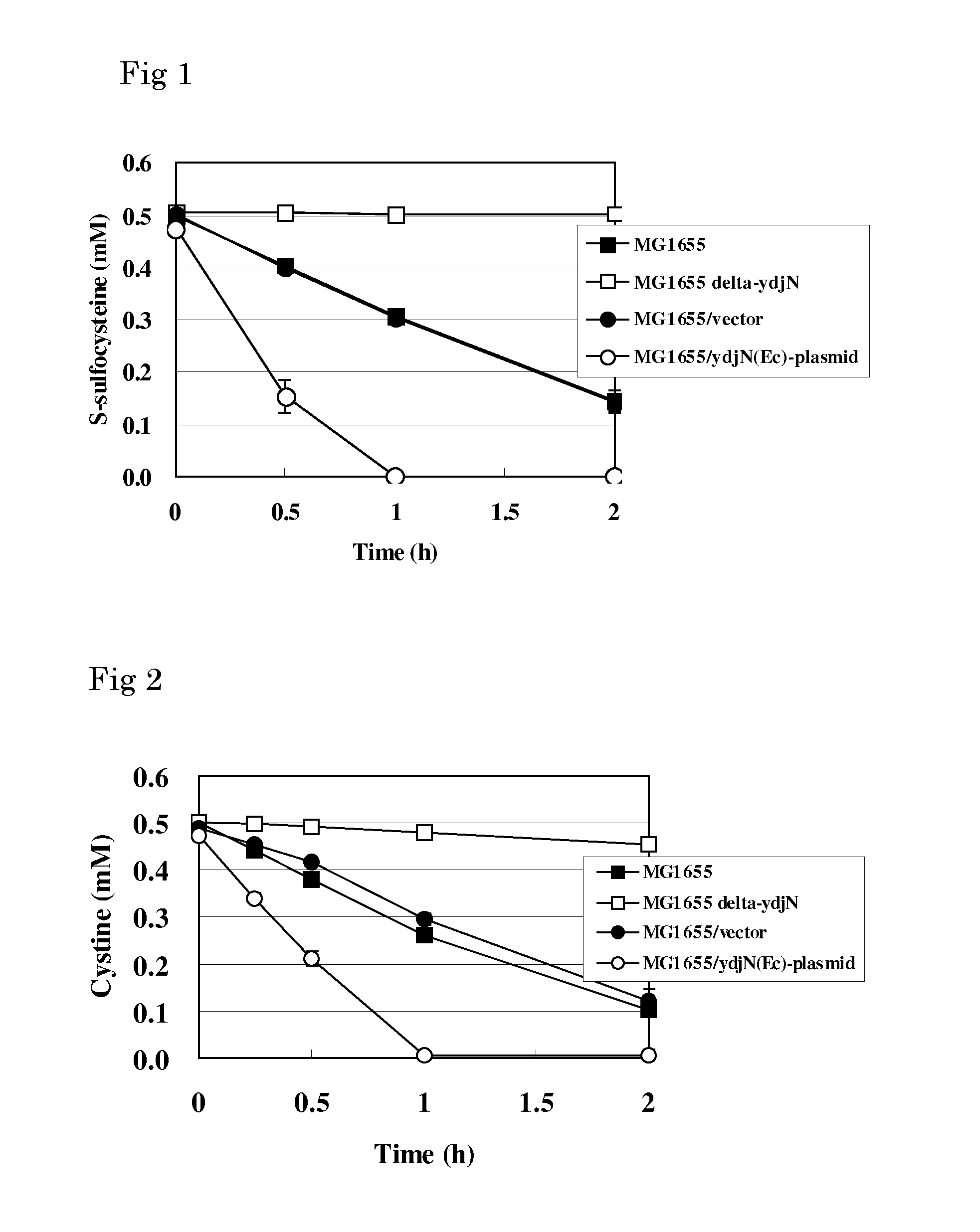
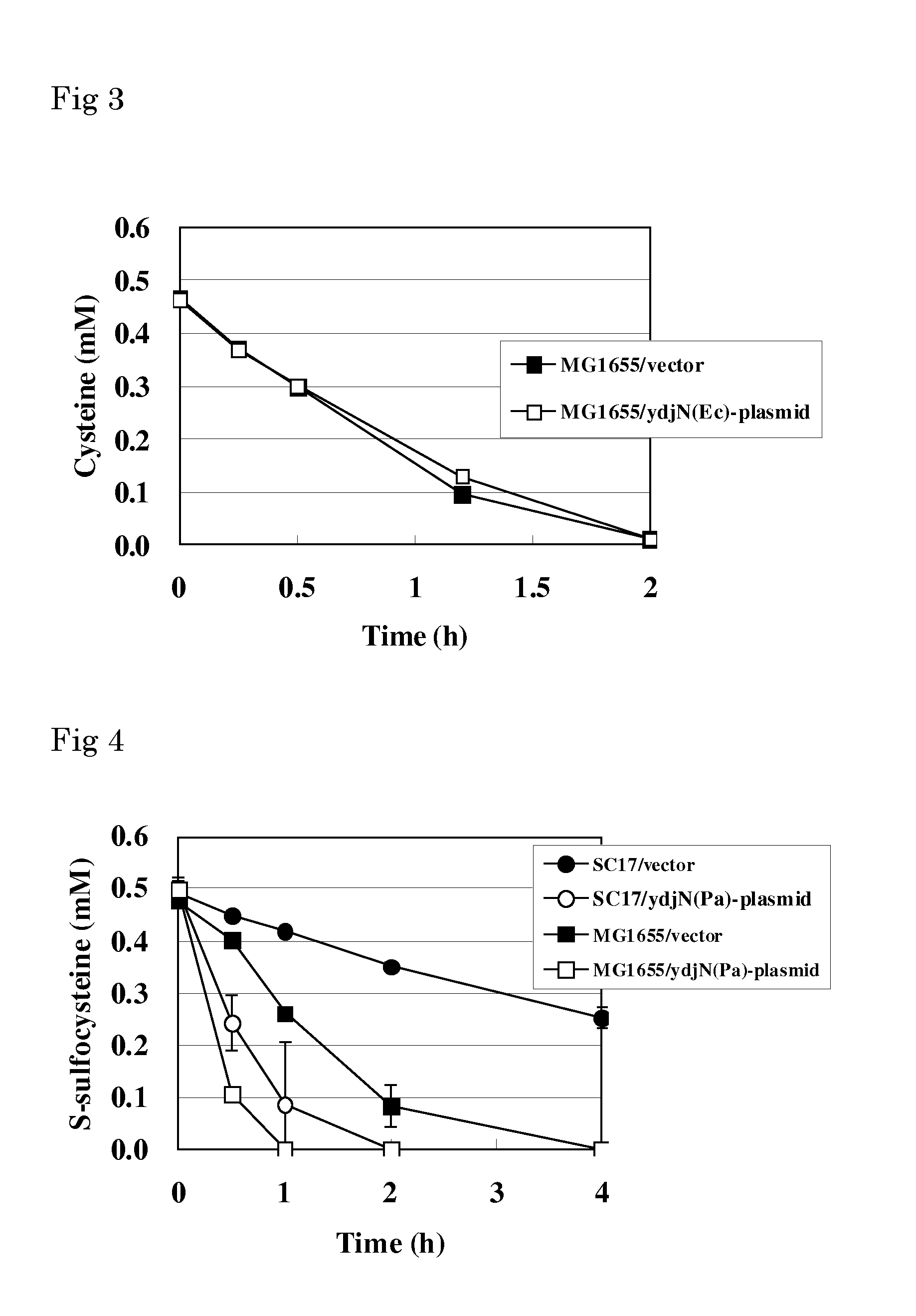
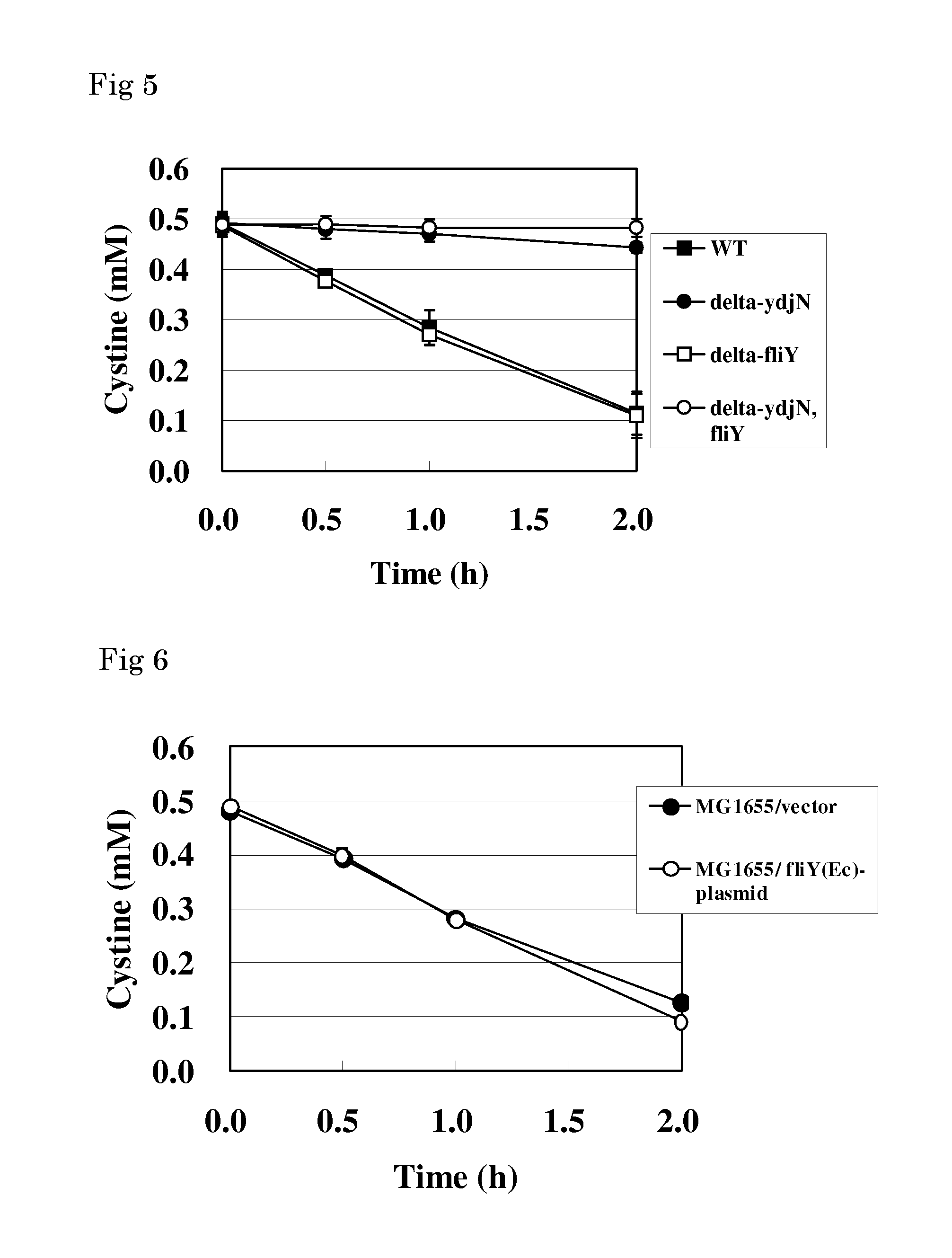
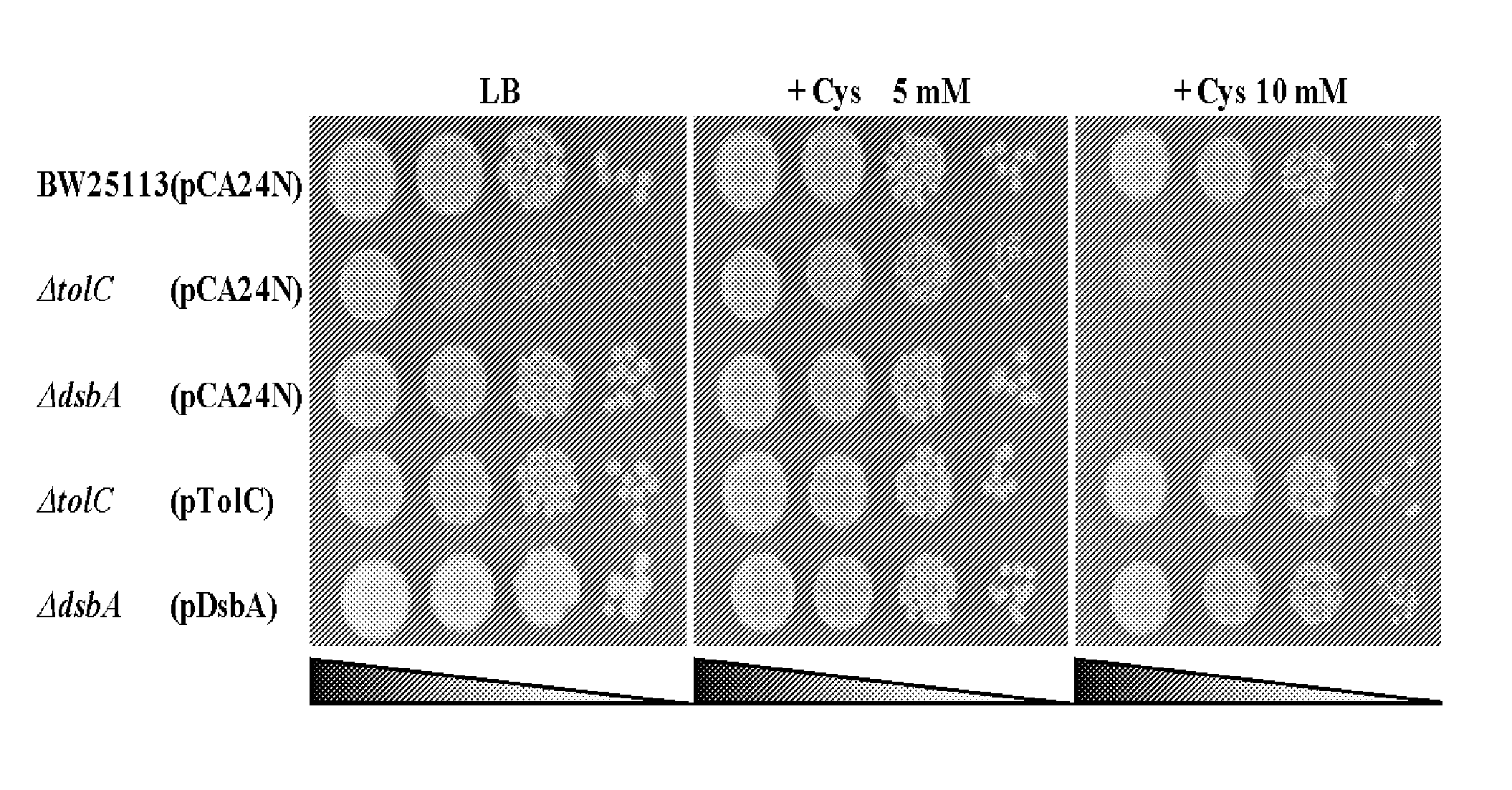
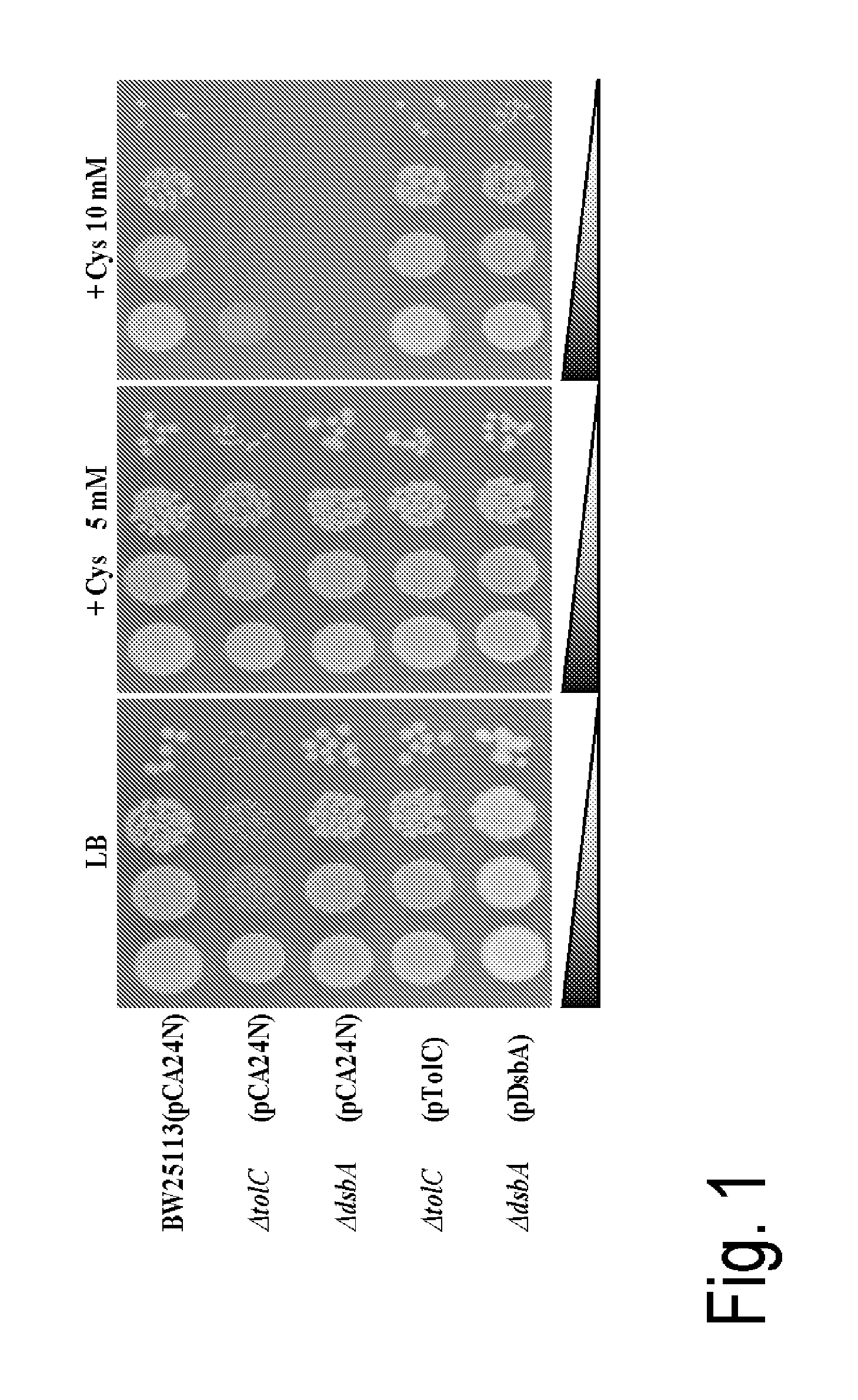
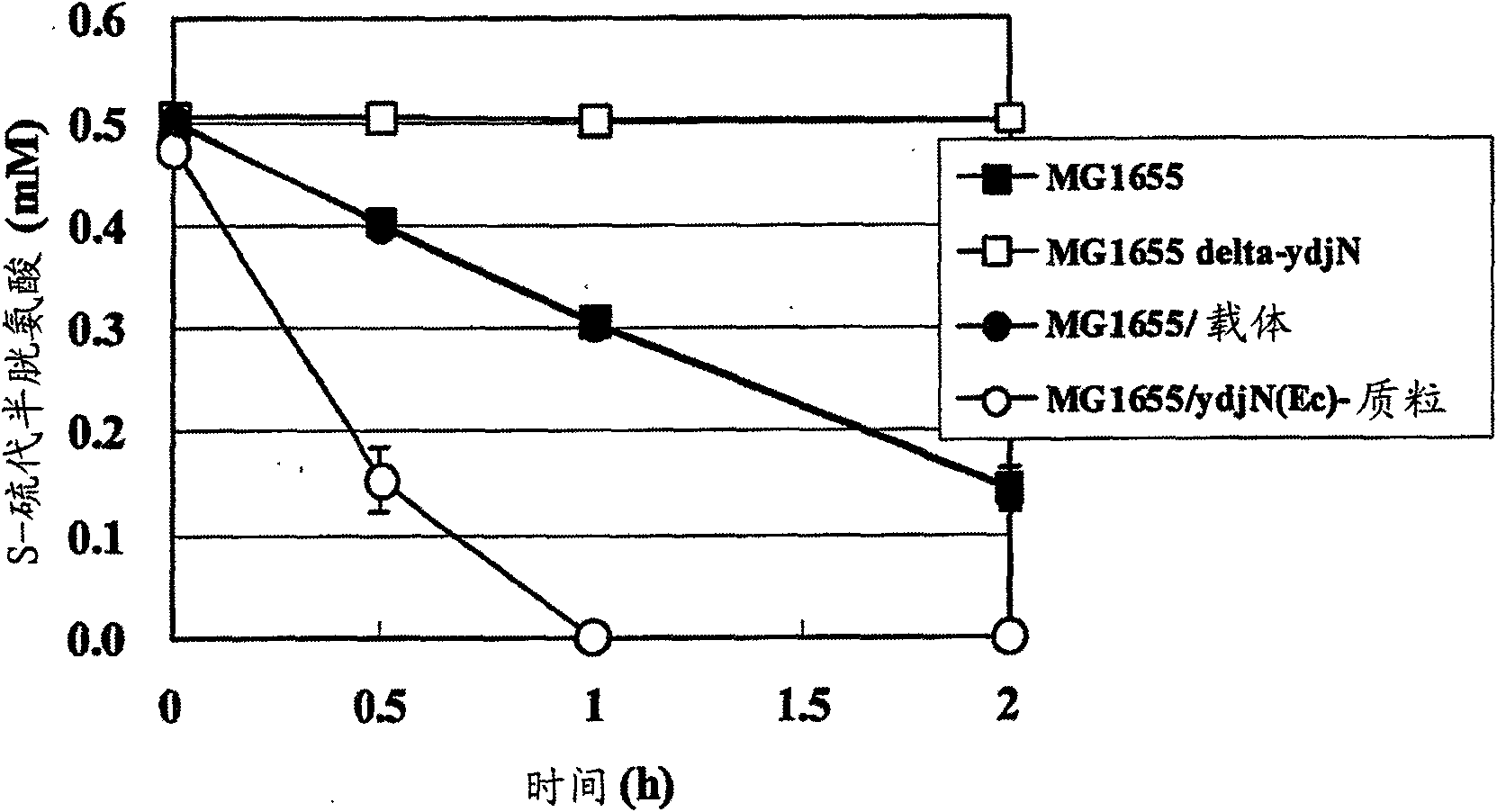
L-cysteine-producing bacterium and a method for producing l-cysteine
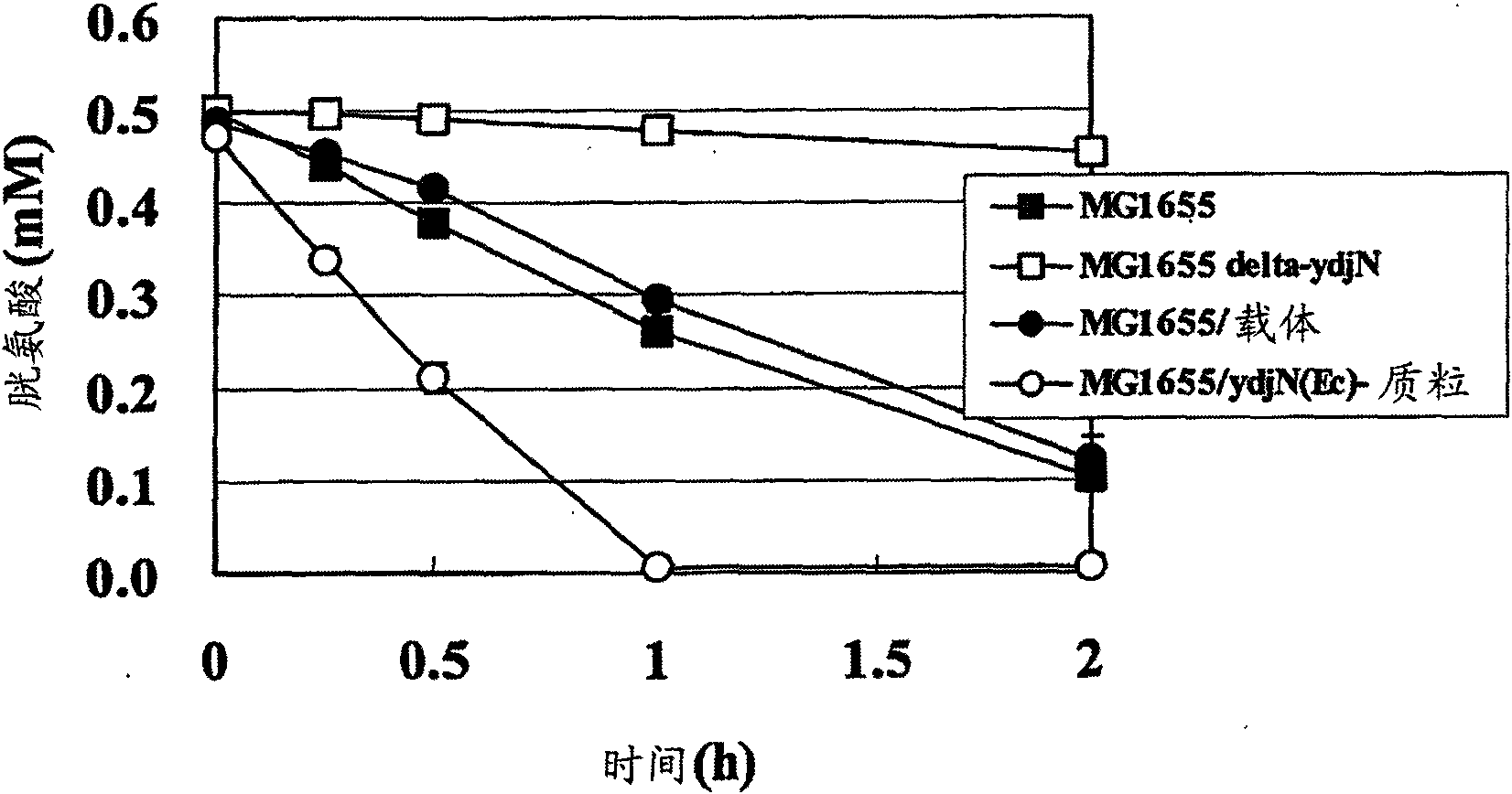
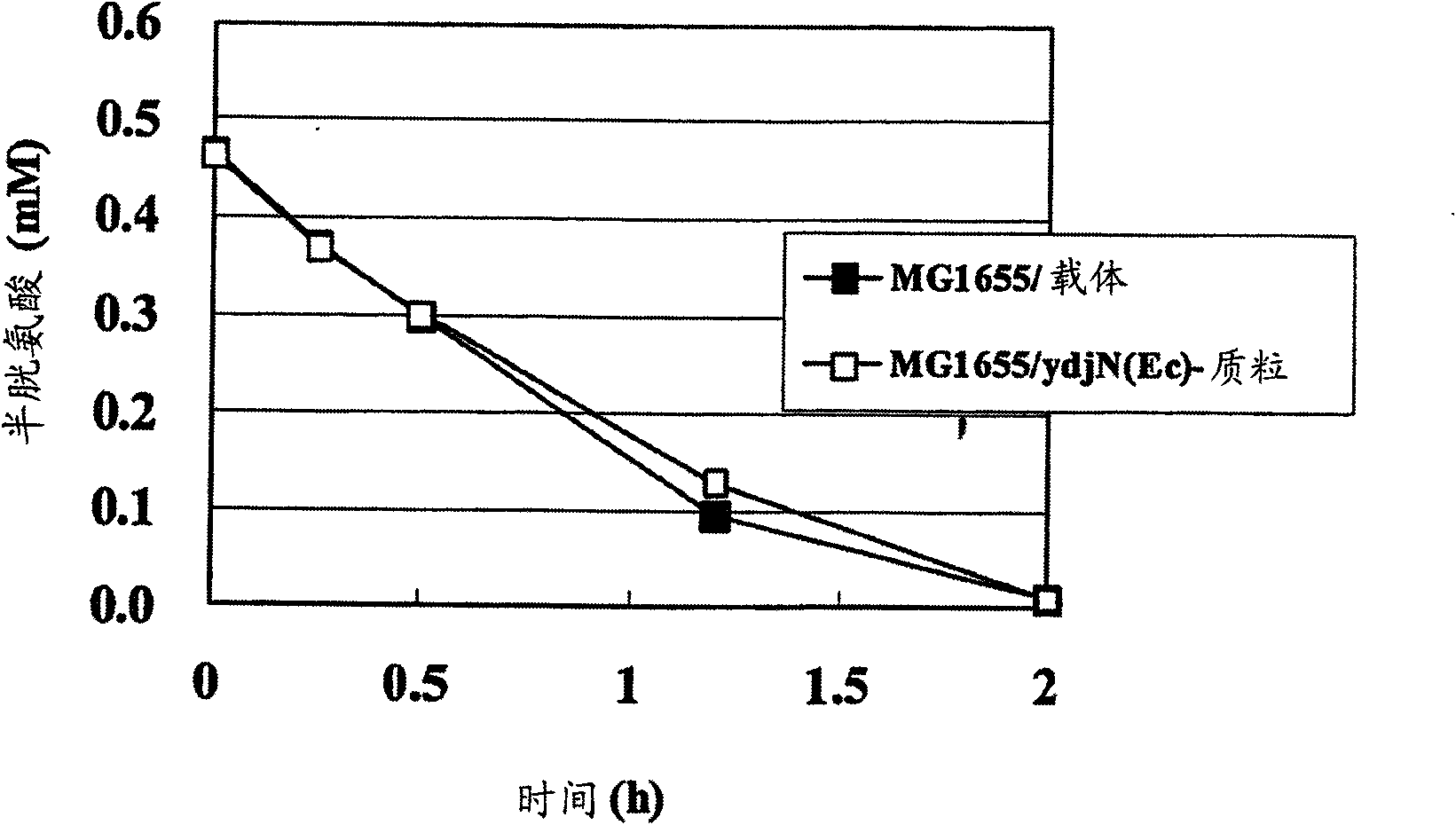
The present invention provides a bacterium belonging to the family Enterobacteriaceae, which is able to produce L-cysteine, and has been modified to decrease activity of the YdjN protein, or the activities of the YdjN and the FliY protein. This bacterium is cultured in a medium, and L-cysteine, L-cystine, a derivative or precursor thereof, or a mixture of these can be collected from the medium.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
Method for producing an organic acid
InactiveUS20100297716A1Improve production efficiencyImprove production yieldSugar derivativesGenetic engineeringOrganic acidEnterobacter
An organic acid is produced by allowing a bacterium belonging to the family Enterobacteriaceae, which has an ability to produce an organic acid and has been modified so that the phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase activity is enhanced, which is selected from Enterobacter, Pantoea, Erwinia, Klebsiella and Raoultella bacteria, or a product obtained by processing the bacterium, to act on an organic raw material in a reaction mixture containing carbonate ions, bicarbonate ions, or carbon dioxide gas to produce the organic acid, and collecting the organic acid.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
L-amino acid-producing microorganism and a method for producing an L-amino acid
ActiveUS8206954B2Efficient productionAbility to produceBacteriaOxidoreductasesMicroorganismPyrroloquinoline quinone
An L-amino acid is produced by culturing a bacterium belonging to the family Enterobacteriaceae, which has an L-amino acid-producing ability and inherently has a native activity of a glucose dehydrogenase that uses pyrroloquinoline quinone as a coenzyme, but has been modified so that the activity of the glucose dehydrogenase is reduced, in a medium, and collecting the L-amino acid from the medium.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
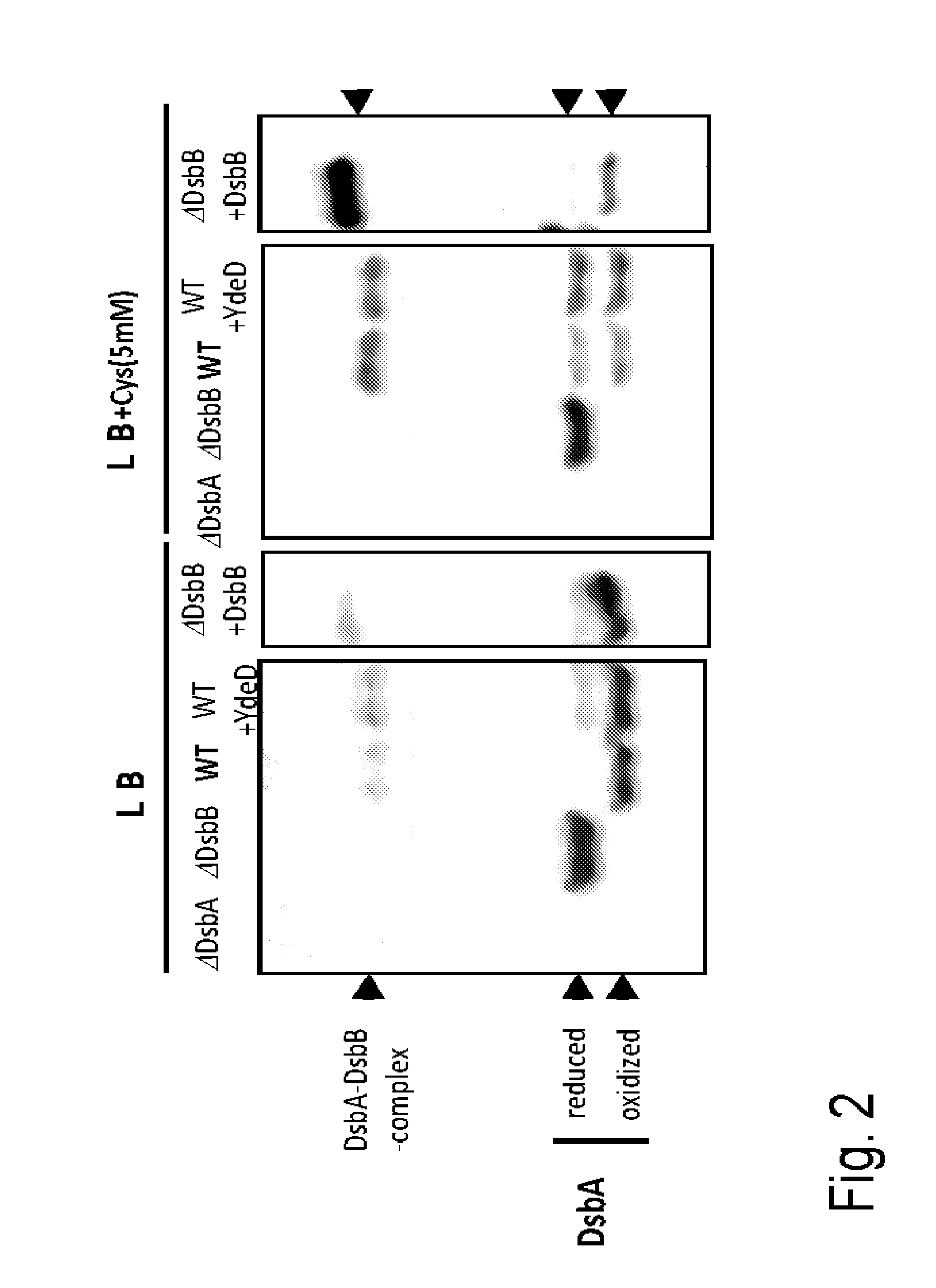
L-cysteine-producing bacterium and a method for producing l-cysteine
InactiveUS20100216196A1Improve abilitiesImproving bacterial production of L-cysteineBacteriaEnzymesCysteine thiolateDsbA
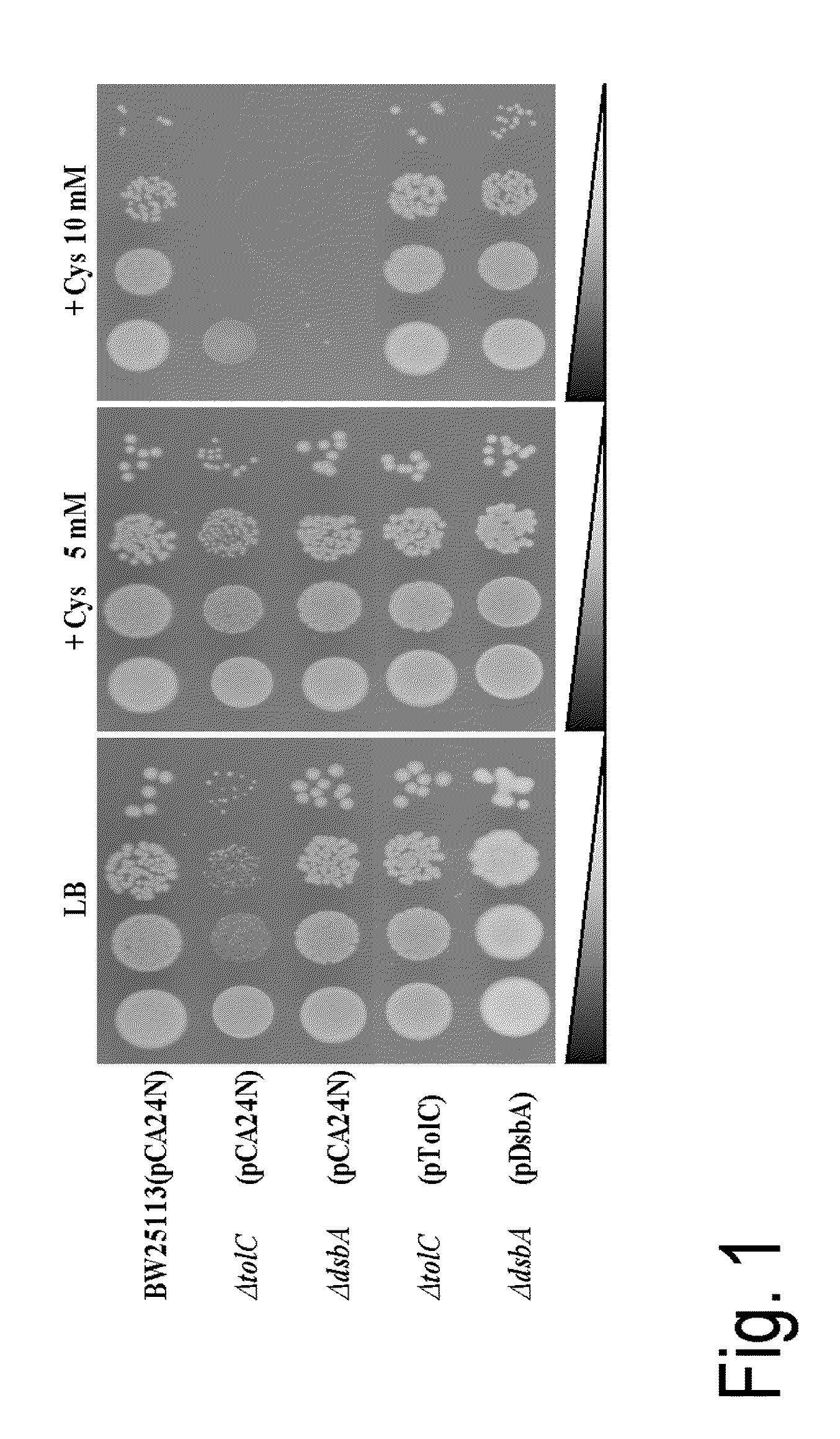
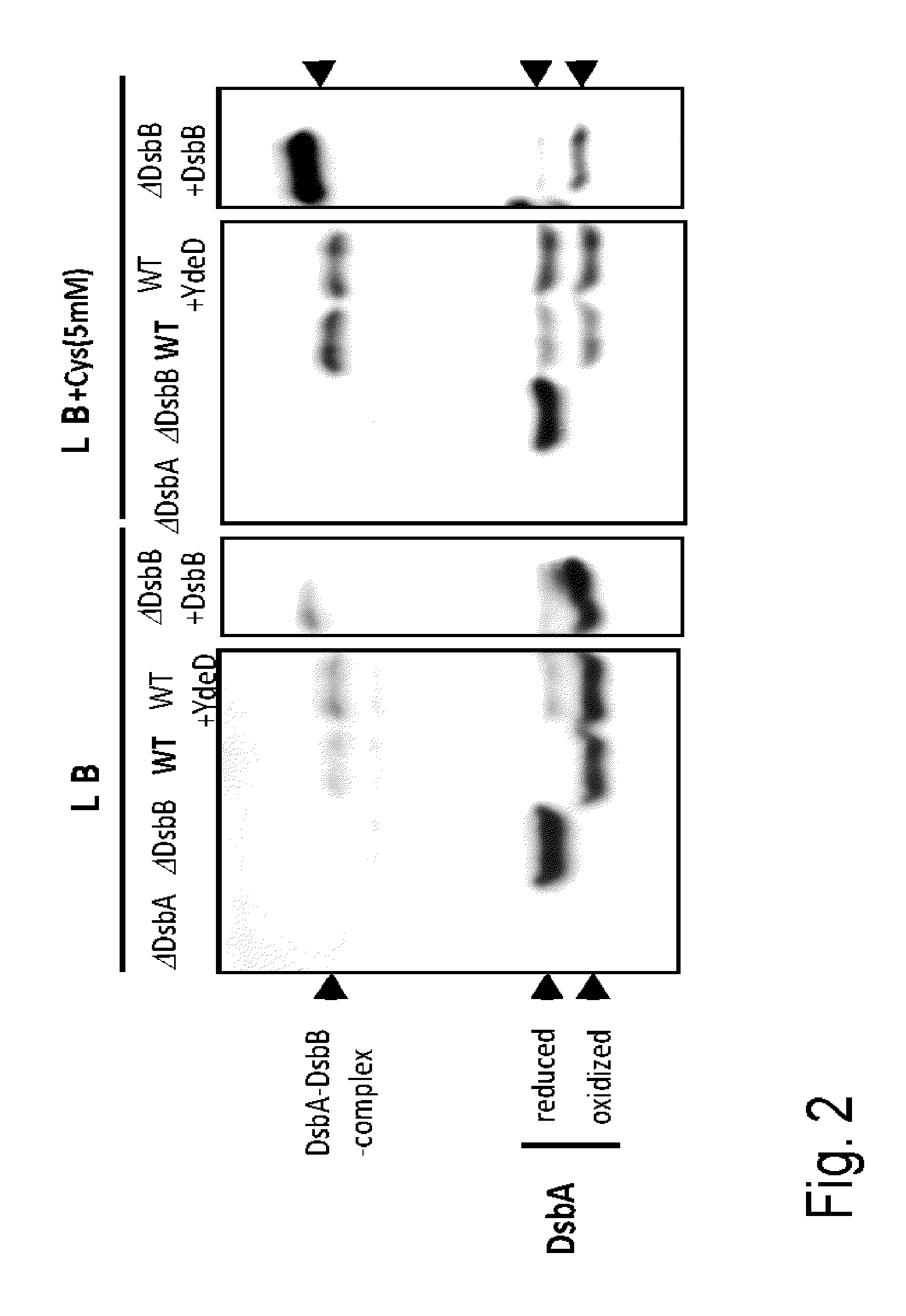
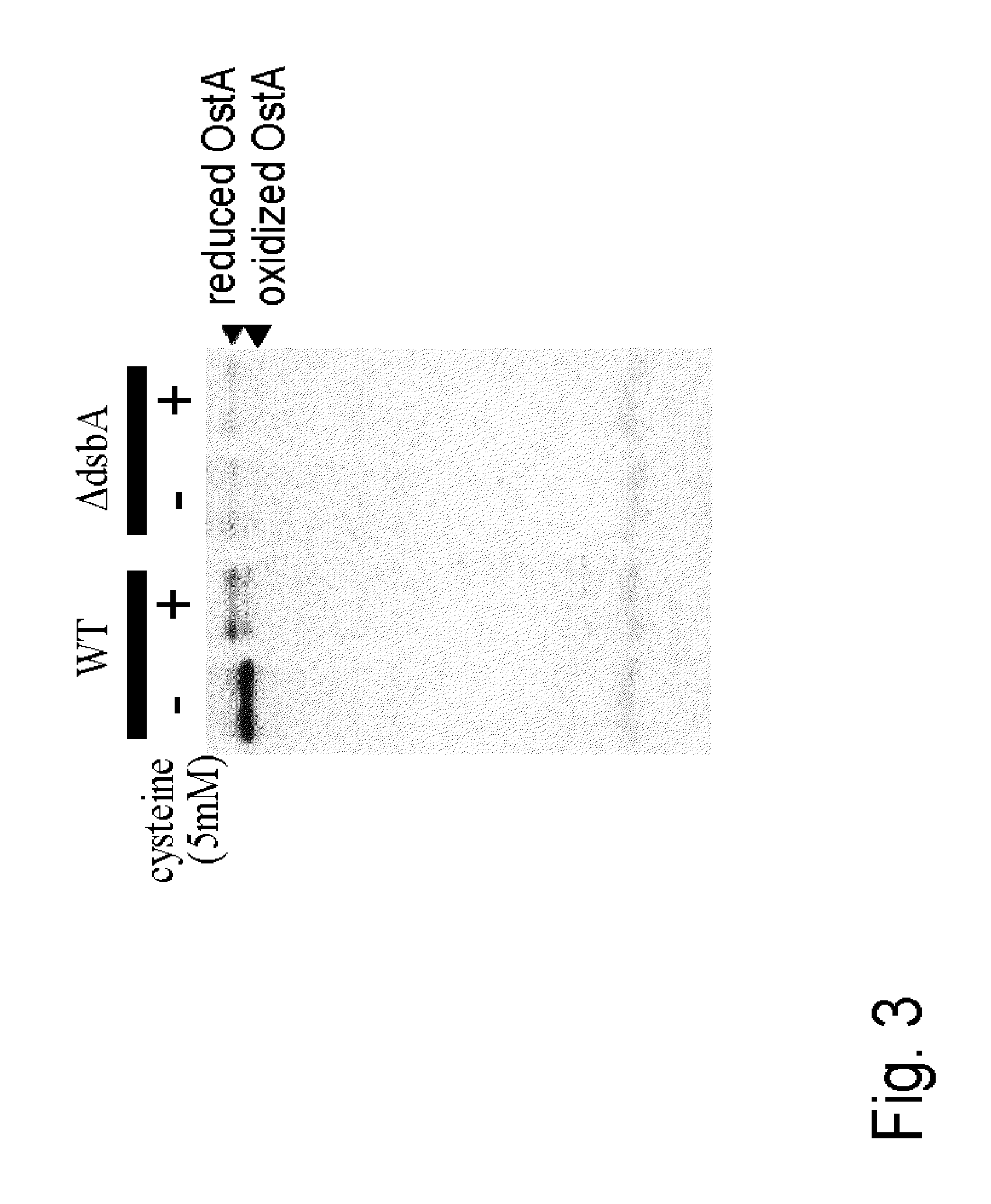
The present invention provides a bacterium belonging to the family Enterobacteriaceae, which is able to produce L-cysteine and has been modified to increase the activity of the protein encoded by the dsbA gene. This bacterium is cultured in a medium, and L-cysteine, L-cystine, a derivative or precursor thereof or a mixture thereof can be collected from the medium.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
L-amino acid-producing microorganism and a method for producing an l-amino acid
ActiveUS20110212496A1Efficient productionAbility to produceBacteriaOxidoreductasesMicroorganismPyrroloquinoline quinone
An L-amino acid is produced by culturing a bacterium belonging to the family Enterobacteriaceae, which has an L-amino acid-producing ability and inherently has a native activity of a glucose dehydrogenase that uses pyrroloquinoline quinone as a coenzyme, but has been modified so that the activity of the glucose dehydrogenase is reduced, in a medium, and collecting the L-amino acid from the medium.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
L-amino acid-producing microorganism and a method for producing an L-amino acid
ActiveUS8293505B2Efficient productionHigh activityBacteriaUnicellular algaeMicroorganismOrotate phosphoribosyltransferase
An L-amino acid is produced by culturing a microorganism which belongs to the family Enterobacteriaceae and is able to produce an L-amino acid, wherein the bacterium has been modified to enhance orotate phosphoribosyltransferase activity is enhanced, in a medium to produce and cause accumulation of an L-amino acid in the medium or cells, and collecting the L-amino acid from the medium or the cells.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
Method for producing l-amino acid
A bacterium which belongs to the family Enterobacteriaceae, and has an ability to produce L-lysine, L-threonine, L-asparagine, L-aspartic acid, L-methionine, L-alanine, L-isoleucine, and / or L-homoserine. The bacterium has been modified so that expression of the gltP and / or gltS genes is / are increased when cultured in a medium, resulting in the accumulation of the L-amino acid(s) in the medium or bacterial cells.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
Method of producing L-amino acid
InactiveUS8512987B2Increase productionEnhancing both glycerol dehydrogenaseSugar derivativesBacteriaMicroorganismGlycerol
An L-amino acid is produced by culturing a microorganism belonging to the family Enterobacteriaceae having an L-amino acid-producing ability and modified so that glycerol dehydrogenase and dihydroxyacetone kinase activities are increased, in a medium containing glycerol as a carbon source to produce and accumulate an L-amino acid in the medium or cells, and collecting the L-amino acid from the medium or the cells.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
L-amino acid producing microorganism and a method for producing an L-amino acid
ActiveUS7919284B2Efficient productionKdp system is enhancedSugar derivativesBacteriaMicroorganismMicrobiology
A microorganism belonging to the family Enterobacteriaceae, which has an L-amino acid-producing ability and has been modified so that the kdp system is enhanced, is cultured in a medium to produce and accumulate an L-amino acid in the medium or cells of the microorganism, and the L-amino acid is collected from the medium or cells to produce the L-amino acid.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
Method for producing L-isoleucine using a bacterium of the family Enterobacteriaceae having overexpressed the cycA gene
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
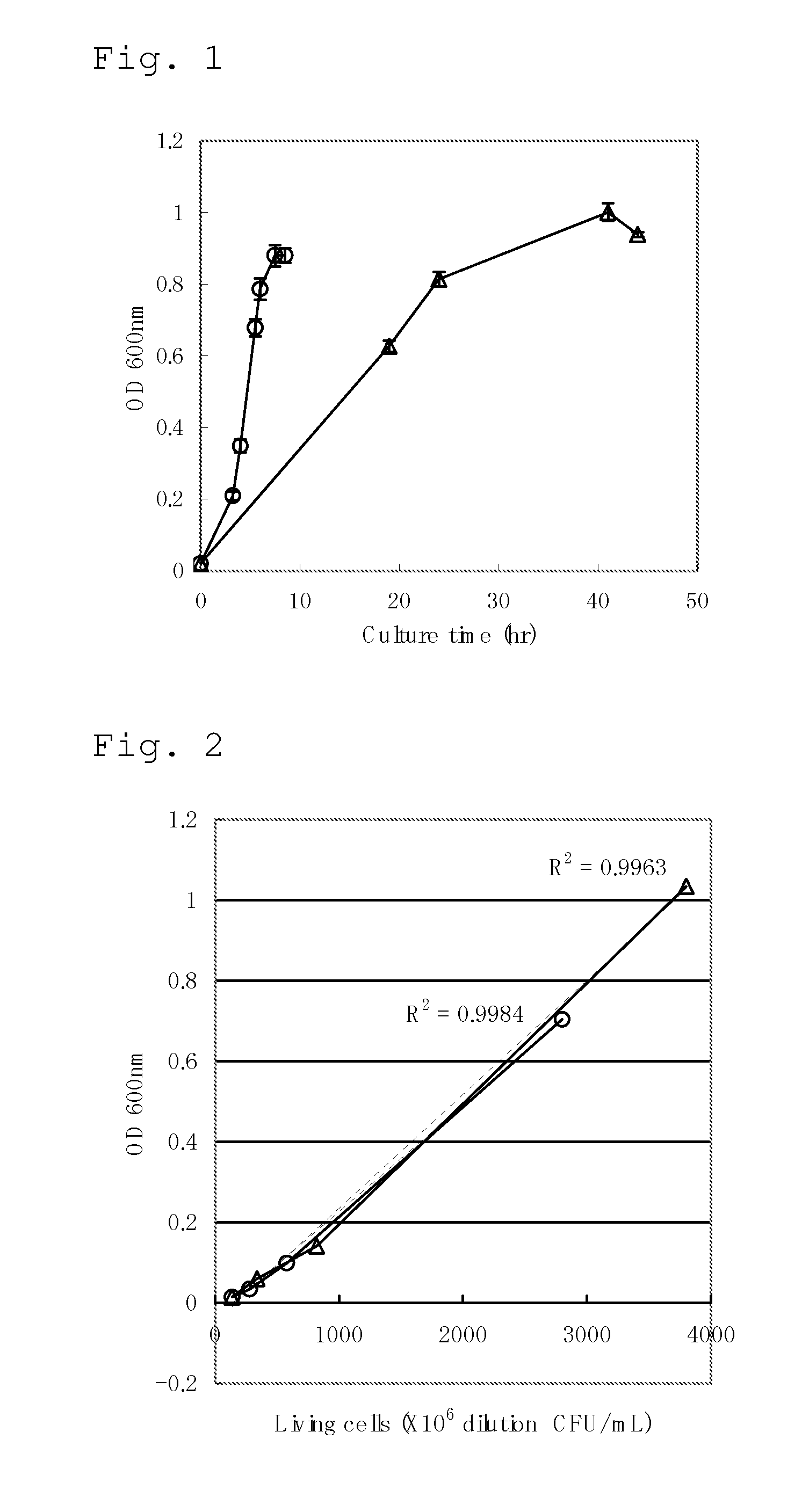
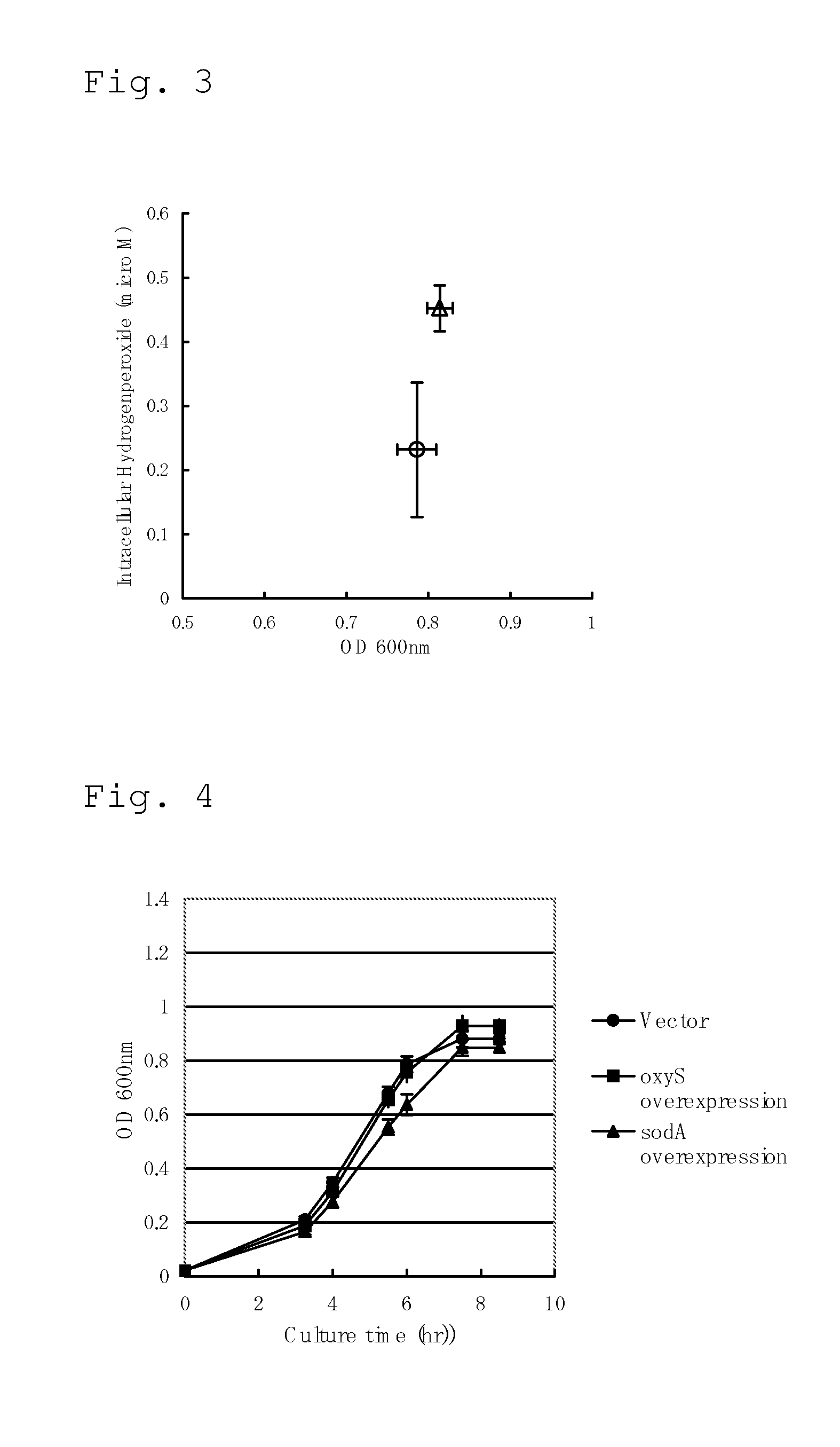
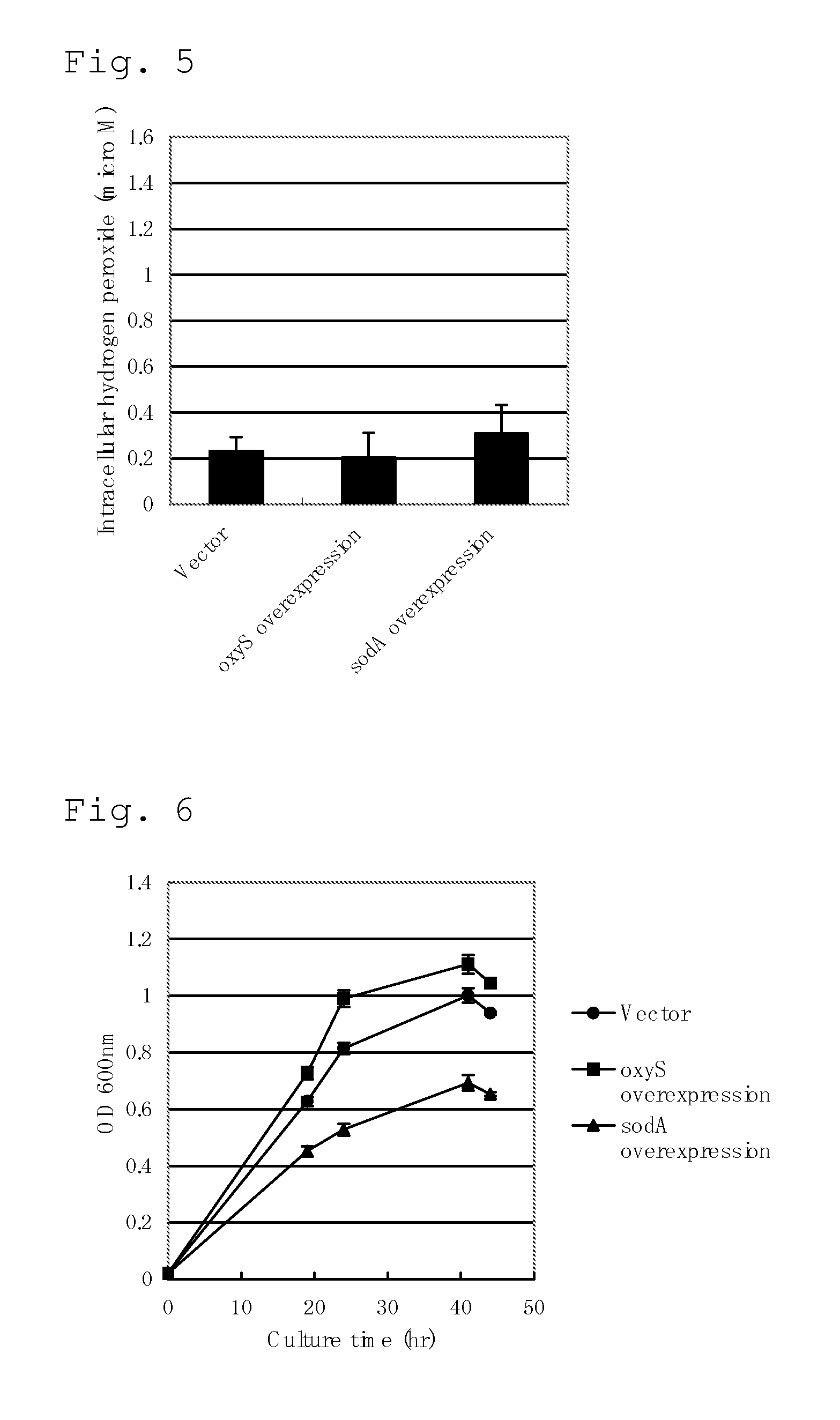
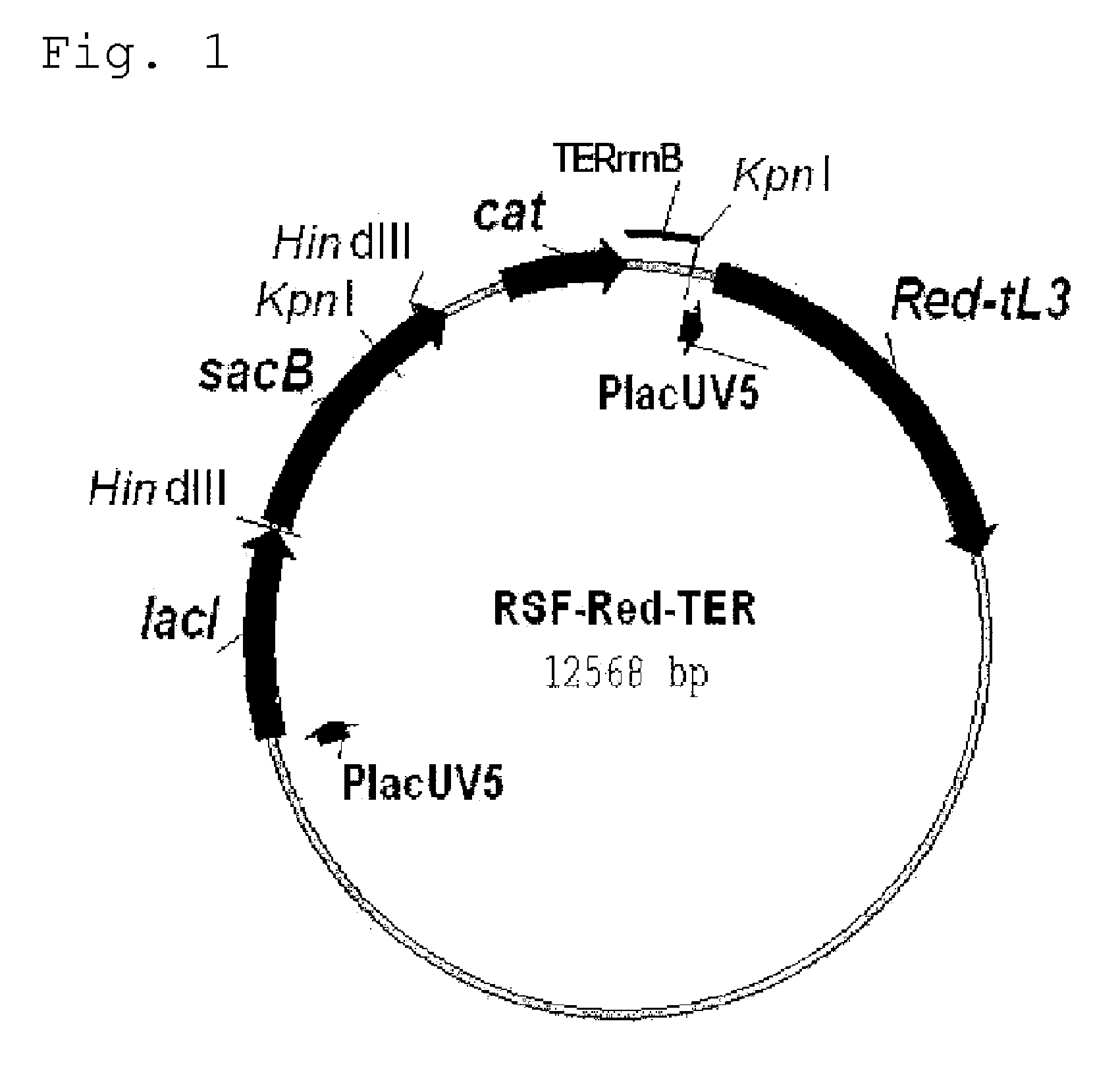
Method for Producing an L-Amino Acid
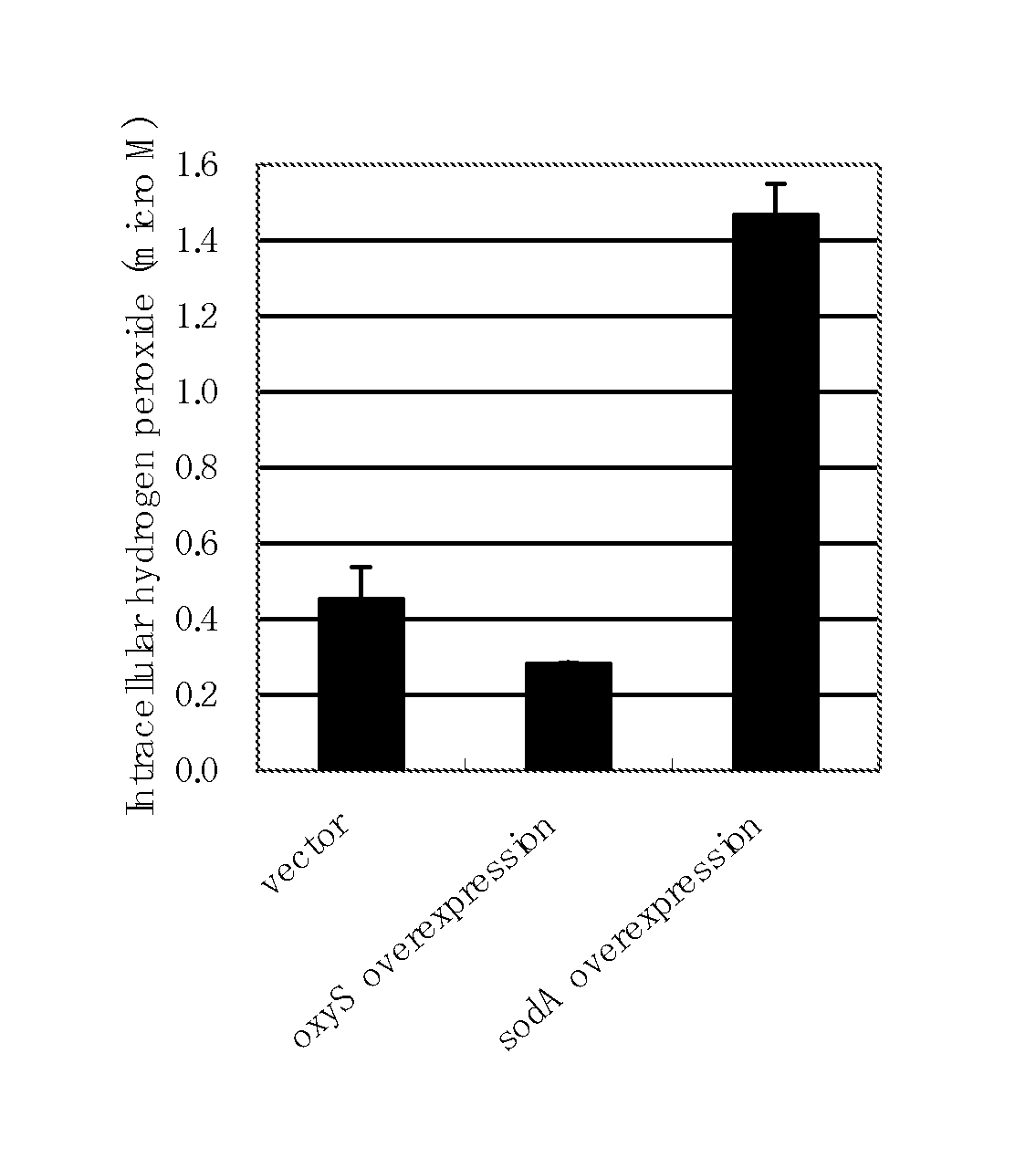
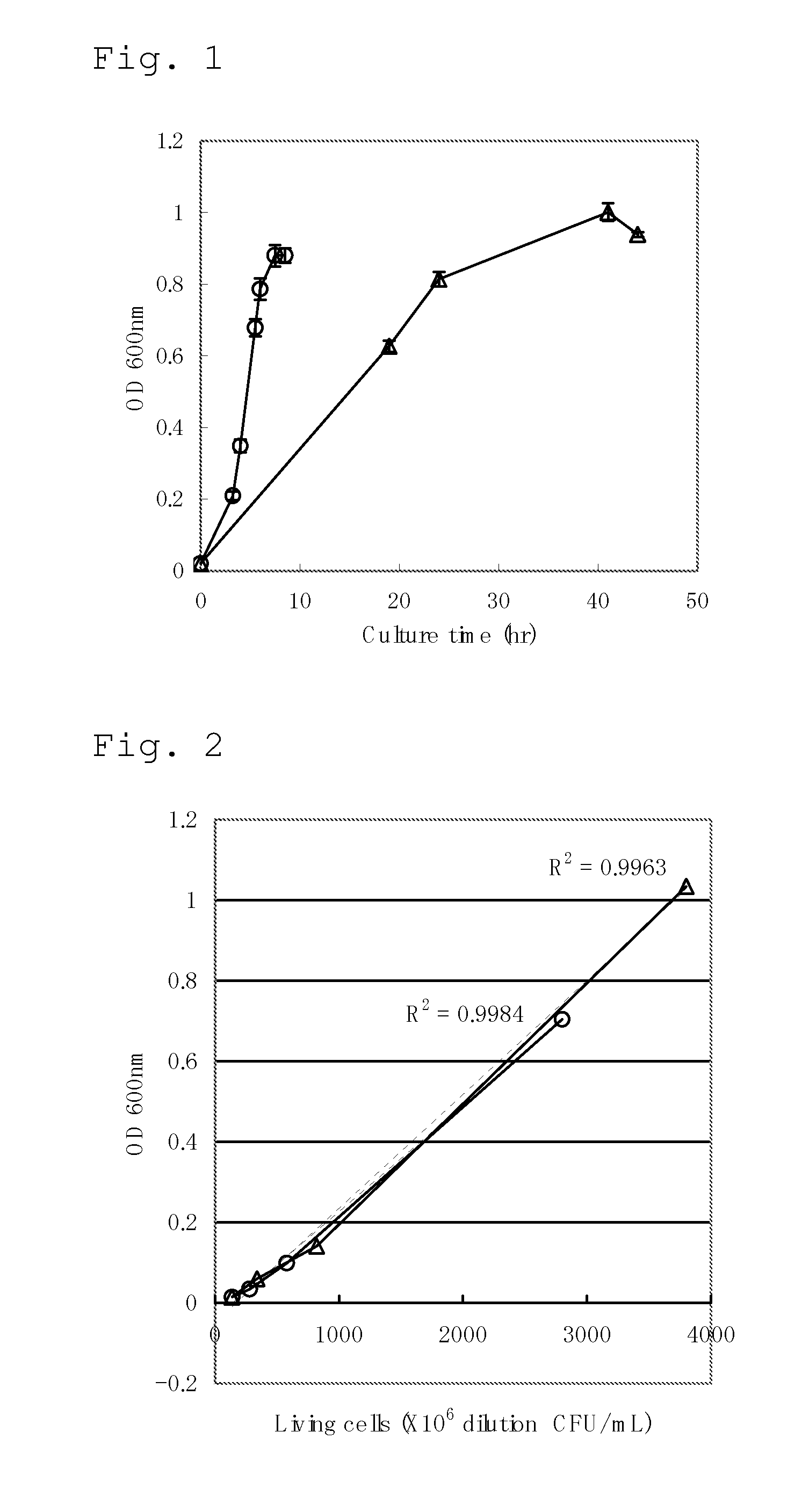
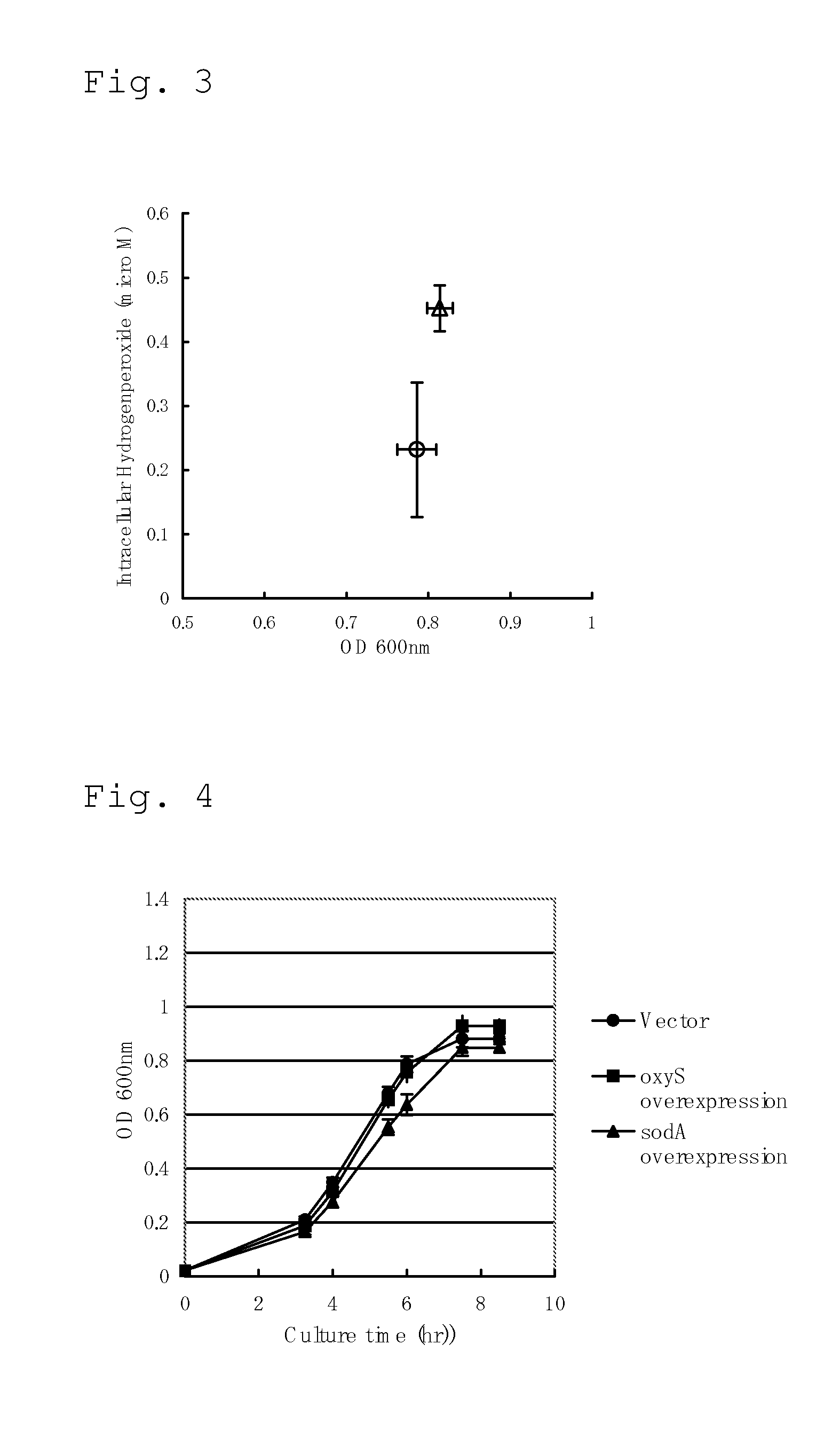
A method for producing an L-amino acid includes culturing a bacterium which belongs to the family Enterobacteriaceae and has an L-amino acid-producing ability in a medium containing a carbon source selected from a fatty acid and an alcohol, and collecting the L-amino acid from the medium. A bacterium which has been subjected to a modification including at least one of enhancement of oxyS gene expression, enhancement of fixABC gene expression, and combination thereof, is used as the bacterium, or a substance that reduces intracellular hydrogen peroxide concentration of the bacterium is added to the medium.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
Method for producing an organic acid
InactiveUS8247201B2Improve production efficiencyImprove production yieldSugar derivativesFermentationOrganic acidEnterobacter
An organic acid is produced by allowing a bacterium belonging to the family Enterobacteriaceae, which has an ability to produce an organic acid and has been modified so that the phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase activity is enhanced, which is selected from Enterobacter, Pantoea, Erwinia, Klebsiella and Raoultella bacteria, or a product obtained by processing the bacterium, to act on an organic raw material in a reaction mixture containing carbonate ions, bicarbonate ions, or carbon dioxide gas to produce the organic acid, and collecting the organic acid.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
Bacterium for fermenting L-tryptophan from mixed saccharum and fermentation method thereof
Owner:新疆梅花氨基酸有限责任公司
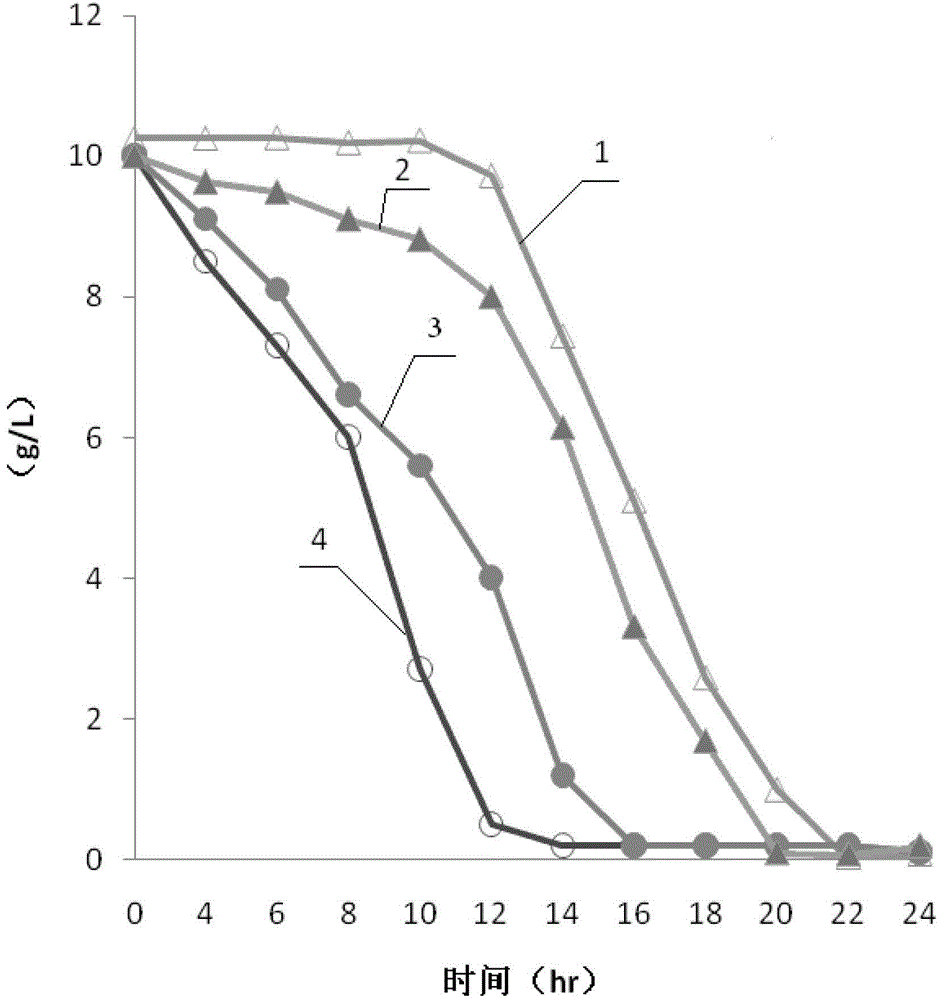
Process for the production of L-amino acids using strains of the family enterobacteriaceae that contain an attenuated dgsA gene
A process for the production of L-amino acids, in particular L-threonine, in which the following steps are carried out: (a) fermentation of the microorganisms of the family Enterobacteriaceae producing the desired L-amino acid, in which the dgsA gene or nucleotide sequences coding therefor are attenuated, in particular are switched off, (b) enrichment of the L-amino acid in the medium or in the cells of the bacteria, and (c) isolation of the L-amino acid.
Owner:EVONIK DEGUSSA GMBH
Microorganism capable of producing l-amino acid, and method for production of l-amino acid
An L-amino acid can be produced by: culturing, in a culture medium, a microorganism belonging to the family Enterobacteriaceae which is capable of producing the L-amino acid and is modified so that the kdp system can be potentiated, thereby producing and accumulating the L-amino acid in the culture medium or a cell of the microorganism; and collecting the L-amino acid from the culture medium or the cell.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
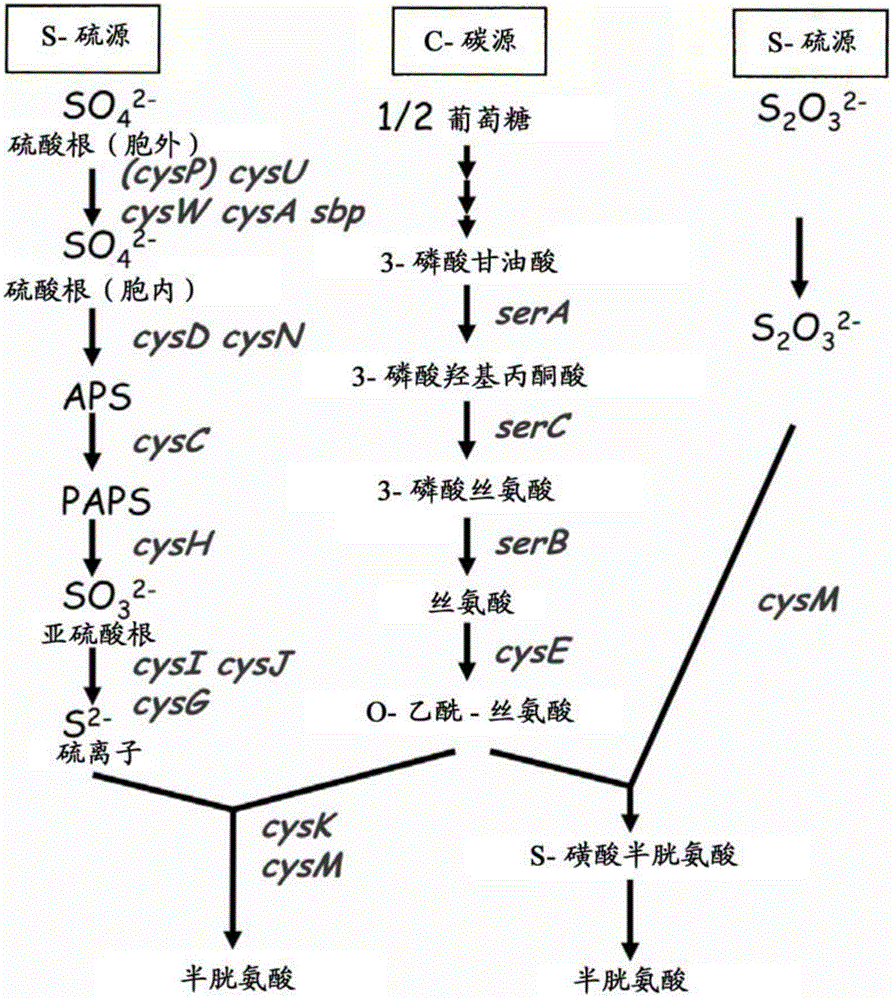
Method for producing l-cysteine
A method for producing L-cysteine and the like is provided by developing a novel technique for improving bacterial L-cysteine-producing ability. By culturing a bacterium belonging to the family Enterobacteriaceae and having L-cysteine-producing ability, of which expression of a gene involved in sulfite reduction is enhanced, in a medium containing thiosulfate and collecting L-cysteine, a related substance thereof, or a mixture thereof accumulated in the medium, these compounds are produced.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
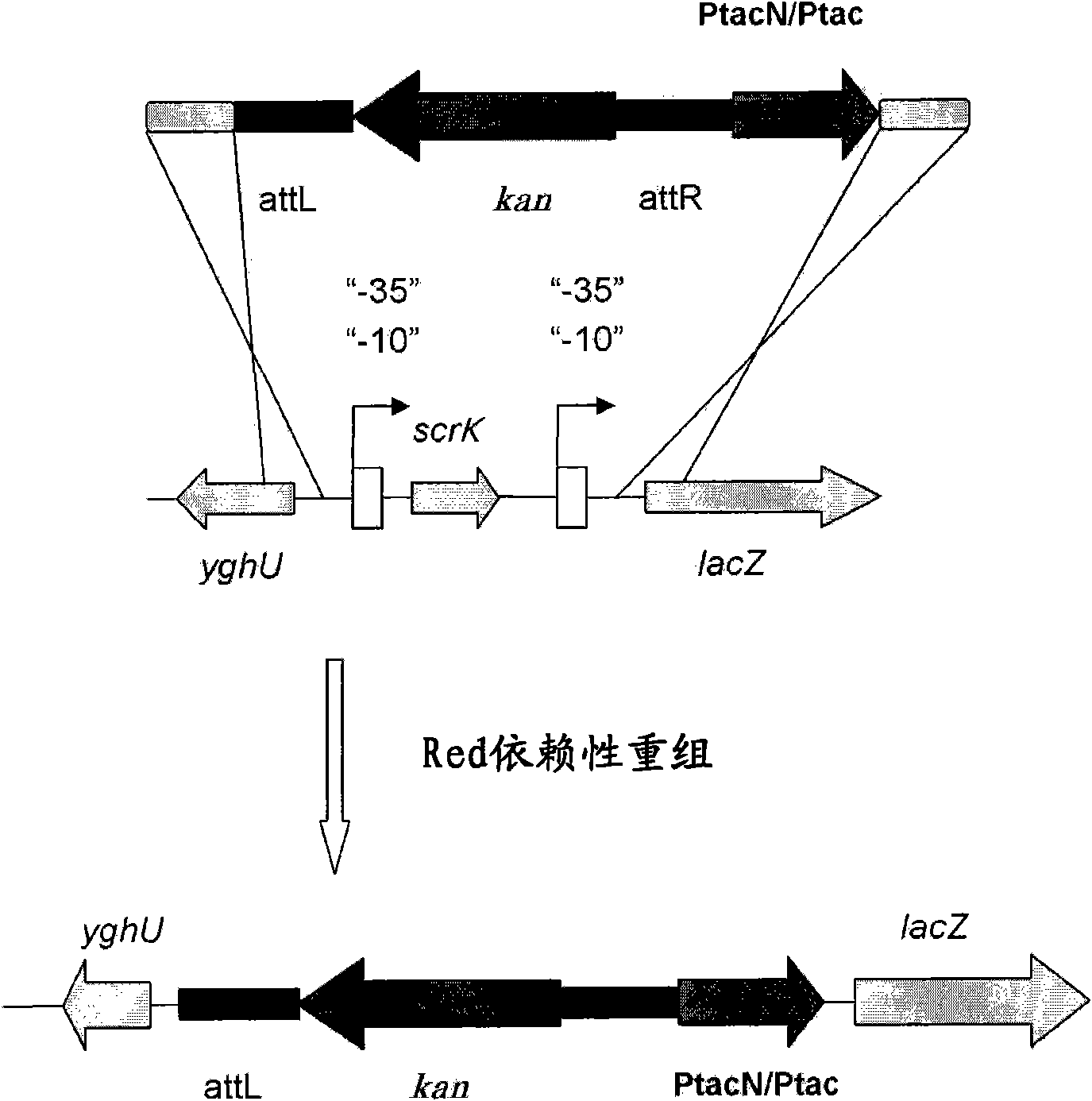
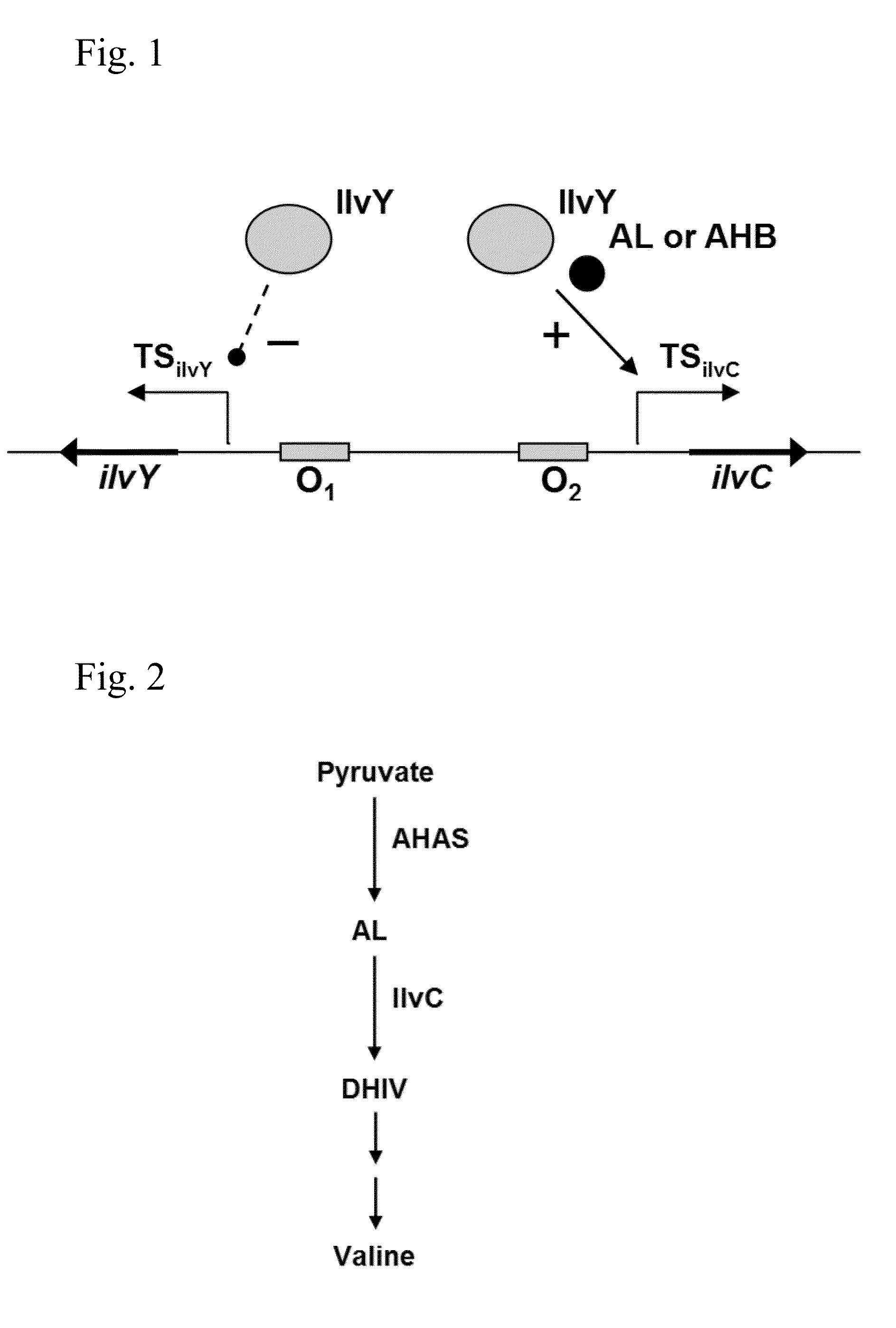
Auto-Indicible Expression System, and the Use Thereof for Producing Useful Metabolites Using a Bacterium of the Family Enterobacteriaceae
The present invention describes a method for producing a useful metabolite using a bacterium of the family Enterobacteriaceae, particularly a bacterium belonging to the genus Escherichia, which has been modified to contain a gene(s) expression system including elements of the LysR-type protein-regulated transcriptional machinery modified in such a way that auto-inducible positive feedback regulation of said system is mediated by a coinducer. The method is suitable for producing branched-chain L-amino acids, particularly L-valine, L-isoleucine and L-leucine; and D-pantothenic acid.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
METHOD FOR PRODUCING AN L-AMINO ACID USING A BACTERIUM OF THE FAMILY ENTEROBACTERIACEAE HAVING AN ATTENUATED EXPRESSION OF A gshA GENE
The present invention provides a method for producing an L-amino acid such as a branched-chain L-amino acid by fermentation using a bacterium of the family Enterobacteriaceae, particularly a bacterium belonging to the genus Escherichia, which has been modified to attenuate expression of the gshA gene.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
Method for producing an L-amino acid
A method for producing an L-amino acid includes culturing a bacterium which belongs to the family Enterobacteriaceae and has an L-amino acid-producing ability in a medium containing a carbon source selected from a fatty acid and an alcohol, and collecting the L-amino acid from the medium. A bacterium which has been subjected to a modification including at least one of enhancement of oxyS gene expression, enhancement of fixABC gene expression, and combination thereof, is used as the bacterium, or a substance that reduces intracellular hydrogen peroxide concentration of the bacterium is added to the medium.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
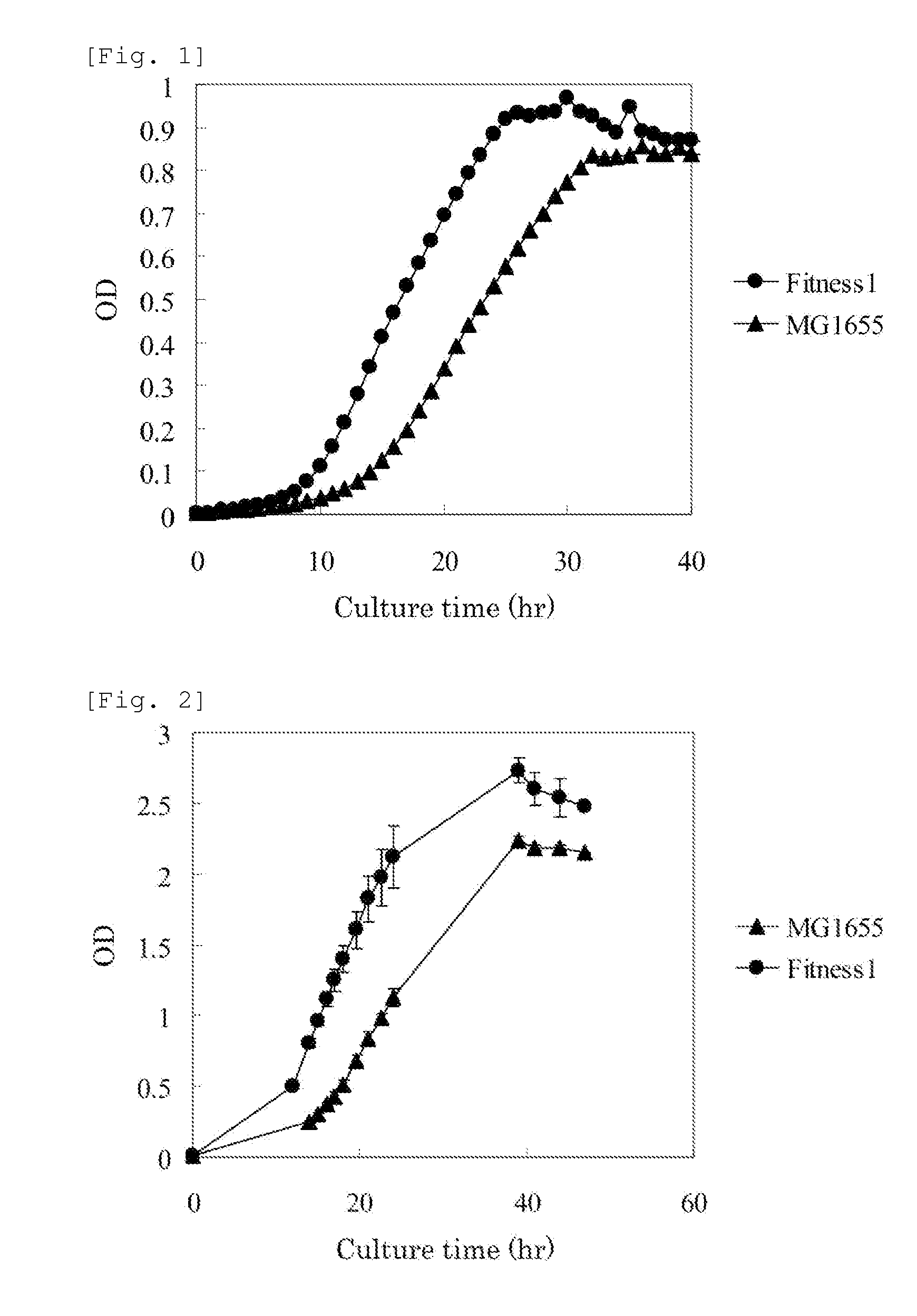
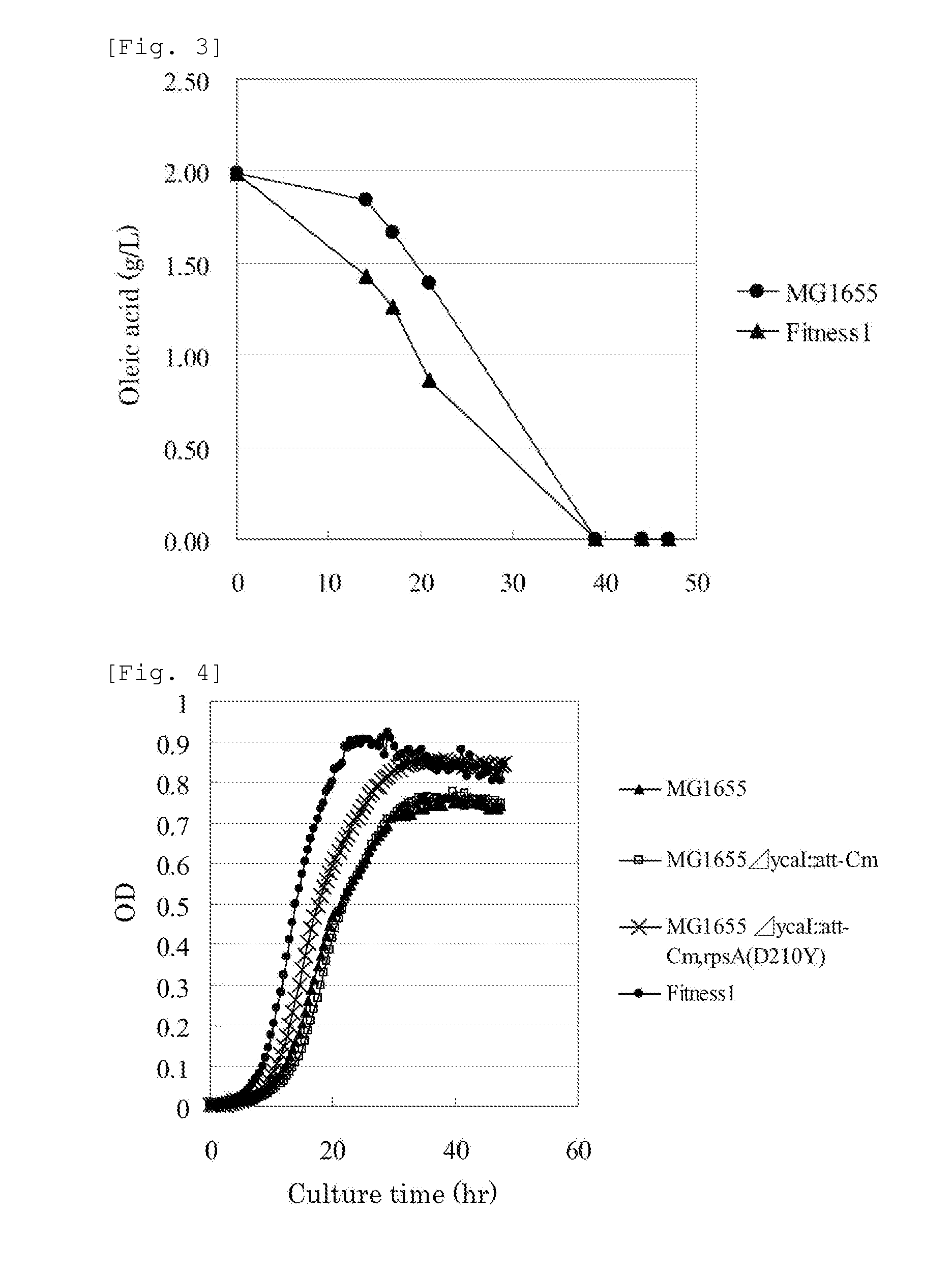
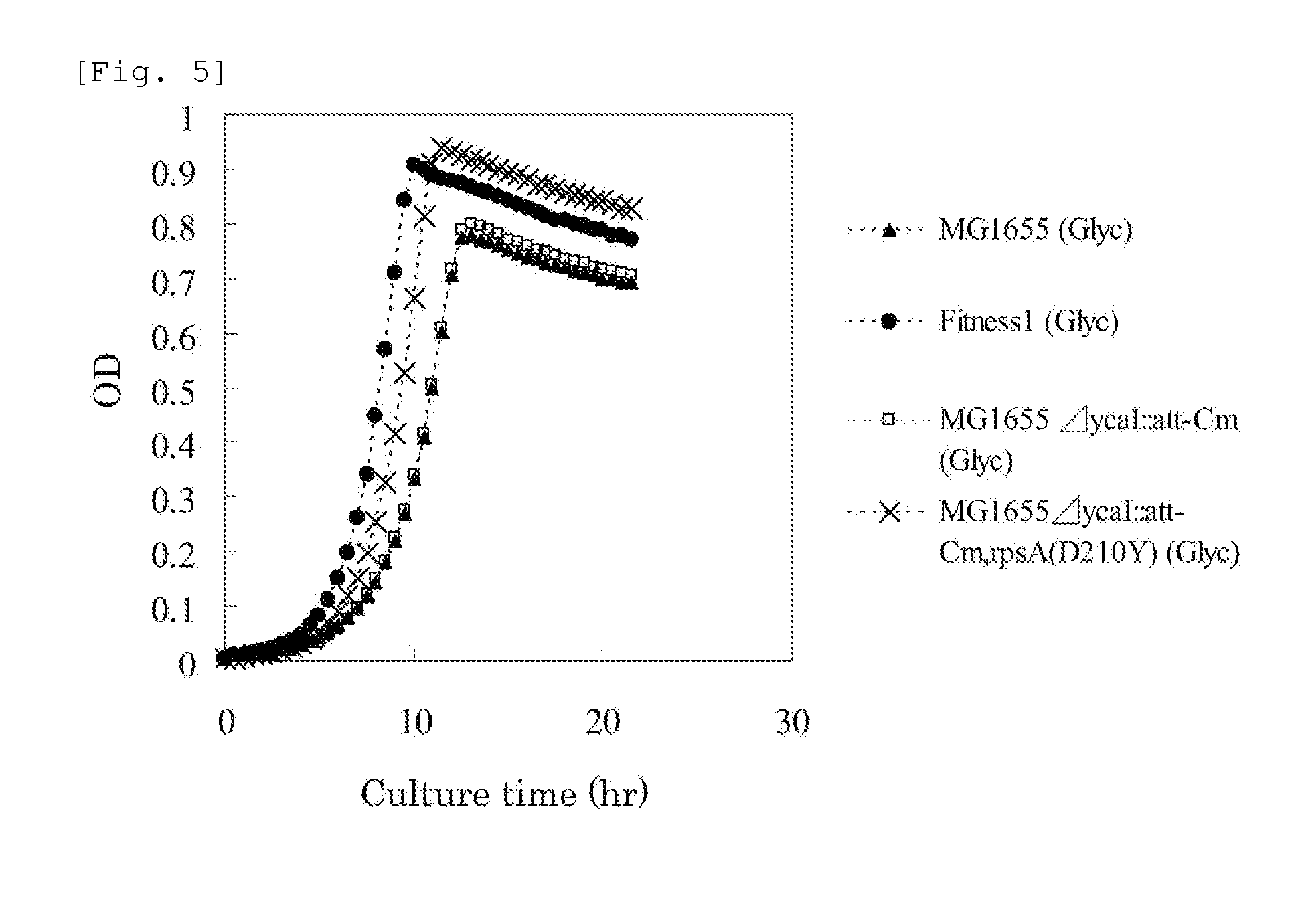
MUTANT rpsA GENE AND METHOD FOR PRODUCING L-AMINO ACID
InactiveUS20130005000A1Efficient productionImprove scalabilityBacteriaSugar derivativesAspartic acid residueGlycerol
A method for efficiently producing an L-amino acid utilizing a bacterium belonging to the family Enterobacteriaceae from a fatty acid or an alcohol such as glycerol as a raw material is provided. A bacterium belonging to the family Enterobacteriaceae which is able to produce L-amino acid and harbors an RpsA protein which has a mutation such that the native aspartic acid residue at position 210 is replaced with another amino acid residue is used. This bacterium is cultured in a medium containing a carbon source selected from a fatty acid and an alcohol, and the produced L-amino acid is collected from the medium.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
An l-cysteine-producing bacterium and a method for producing l-cysteine
InactiveCN102080062AIncrease production capacityEfficient productionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBacteroidesMicrobiology
The invention provides a novel method for producing L-cysteine. The method adopts the gene having the ingesting activity of L-cysteine in the bacterium belonging to the family Enterobacteriaceae. The present invention provides a bacterium belonging to the family Enterobacteriaceae, which is able to produce L-cysteine, and has been modified to decrease activity of the YdjN protein, or the activities of the YdjN and the FliY protein. This bacterium is cultured in a medium, and L-cysteine, L-cystine, a derivative or precursor thereof, or a mixture of these can be collected from the medium.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
An L-amino acid-producing bacterium and a method for producing an L-amino acid
ActiveCN101273054AImproved ability to produce L-amino acidsBacteria peptidesFermentationBacteroidesMicroorganism
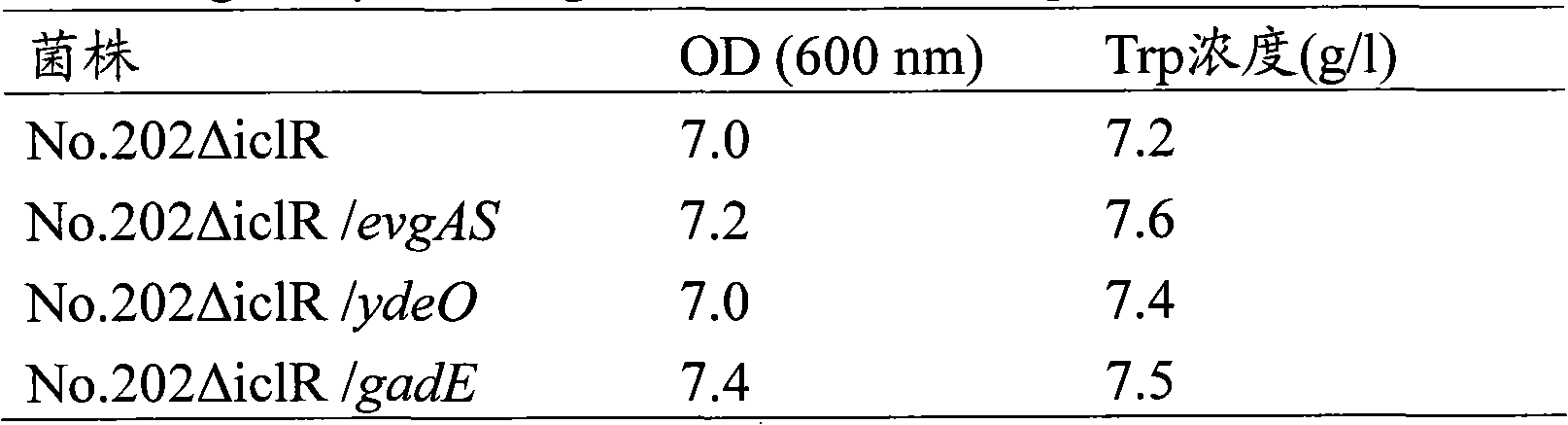
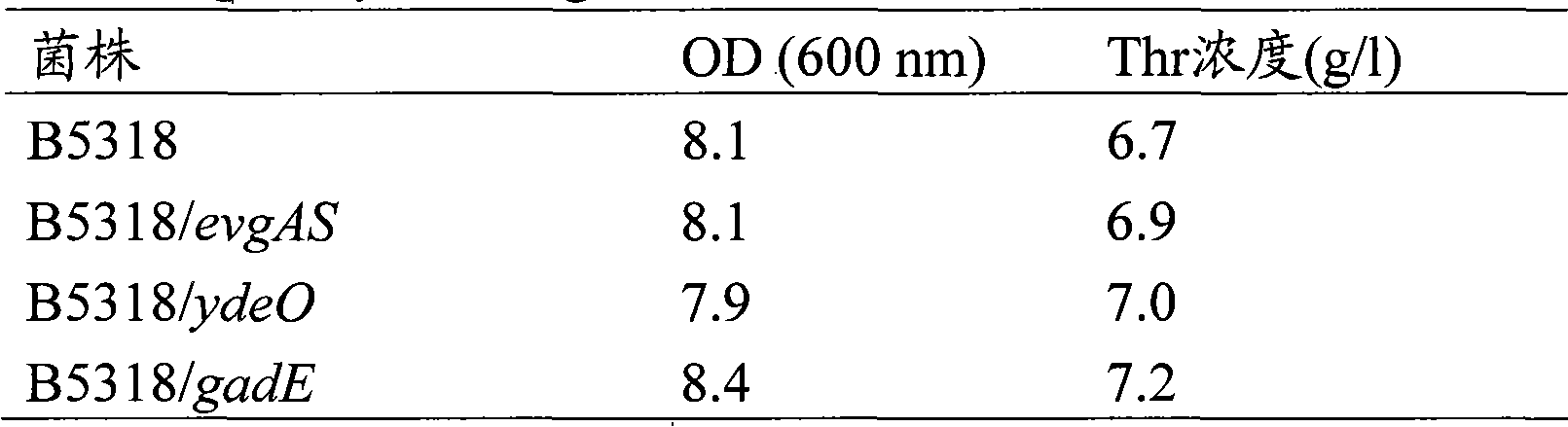
An L-amino acid is produced by culturing a microorganism of the family Enterobacteriaceae which has the ability to produce an L-amino acid and which has been modified so as to increase the amount of expression of one or more genes selected from the evgA gene, gadE gene, or ydeO gene that encodes a transcription factor involved in the EvgAS two-component system regulon in a medium to produce and accumulate an L-amino acid in the medium or in cells, and collecting the L-amino acid from the medium or cells.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
L-cysteine-producing bacterium and a method for producing L-cysteine
InactiveUS8293506B2Improving bacterial production of L-cysteineImprove abilitiesBacteriaEnzymesDsbAFAMILY ENTEROBACTERIACEAE
The present invention provides a bacterium belonging to the family Enterobacteriaceae, which is able to produce L-cysteine and has been modified to increase the activity of the protein encoded by the dsbA gene. This bacterium is cultured in a medium, and L-cysteine, L-cystine, a derivative or precursor thereof or a mixture thereof can be collected from the medium.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
Method for producing an organic acid
InactiveUS8497104B2Improve production efficiencyReduce the amount of solutionMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationEnterobacterPhosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase activity
An organic acid is produced by allowing a bacterium belonging to the family Enterobacteriaceae, which has an ability to produce an organic acid and has been modified so that the phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase activity is enhanced, and the glucose phosphotransferase activity is decreased, which is selected from Escherichia, Enterobacter, Pantoea, Erwinia, Klebsiella and Raoultella bacteria, or a product obtained by processing the bacterium, to act on an organic raw material in a reaction mixture containing carbonate ions, bicarbonate ions, or carbon dioxide gas to produce the organic acid.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
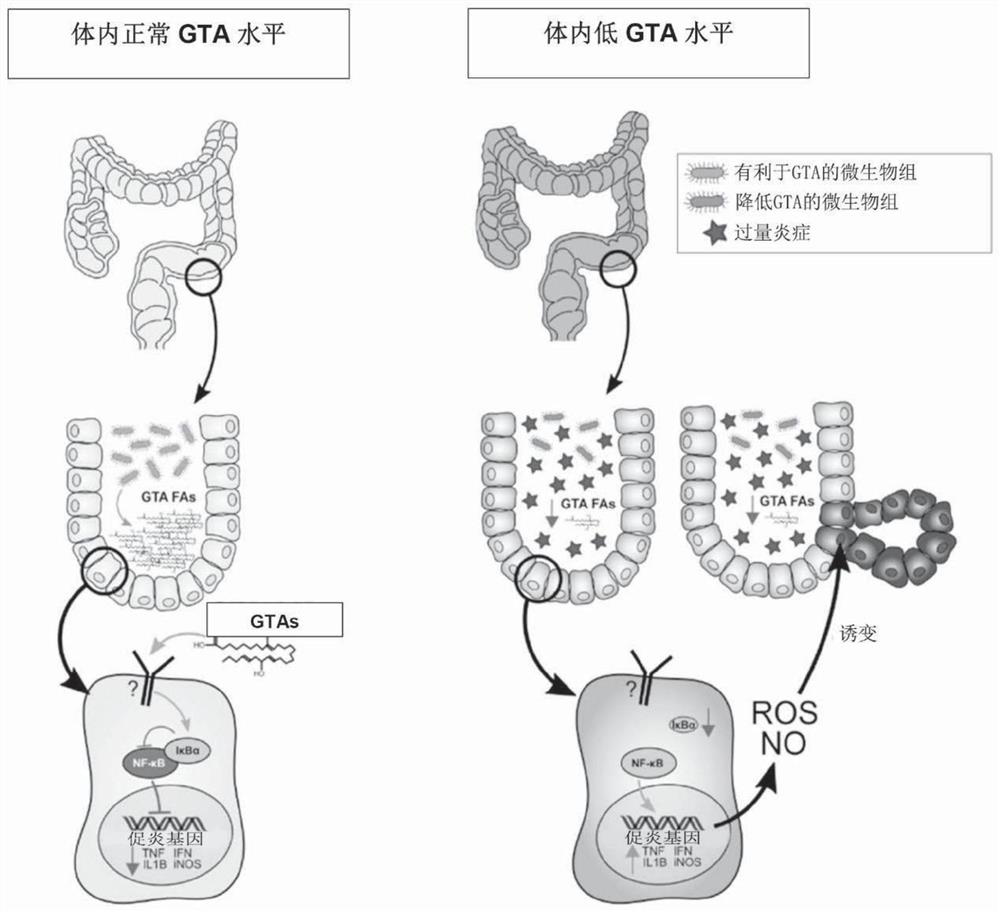
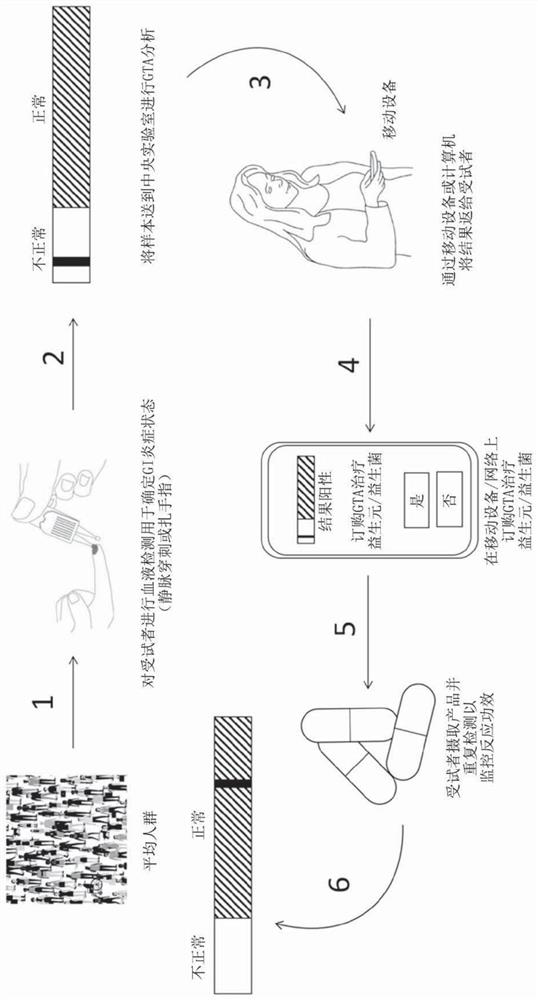
Long chain dicarboxylic fatty acid (LCDFA) producing microbes and uses thereof
A method for increasing gastric tract acid (GTA) production in a mammalian subject. The method comprises administering a therapeutically-effective amount of a composition comprising at least one liveor attenuated culture of a microbial species selected from the genus Blautia, species Faecalibacterium prausnitzii, genus Bacteroides, family Ruminococcaceae, family Lachnospiraceae, genus Coprococcus, genus Roseburia, genus Oscillospira, species Ruminococcus bromii, genus Ruminococcus, family Costridiaceae, species Dorea formicigenerans, species Bacteroides uniformis, genus Dorea, genus Streptococcus, order Clostridiales, genus Anaerostipes, genus Dialister, species Bifidobacterium adolescentis, family Coriobacteriaceae, genus Faecalibacterium, genus Sutterella, species Bacteroides ovatus, genus Parabacteroides, genus Ruminococcus, species Bacteroides faecis, species Eubacterium biforme, genus Phascolartobacterium, and family Enterobacteriaceae; or a prebiotic composition which increasesgrowth and / or viability of said microbial species in the gut. Administering the composition increases the synthesis of at least one GTA dicarboxylic fatty acid metabolite in said subject. Also described are method for determining gastrointestinal inflammation status and kits for detecting and treating a gastric tract acid (GTA) insufficiency.
Owner:医学生命探索有限公司
Bacterium capable of producing l-amino acid and method for producing l-amino acid
A bacterium is described which belongs to the Enterobacteriaceae family, and has an ability to produce an L-amino acid, such as L-glutamic acid, L-arginine and L-threonine. The bacterium is modified so that the activity of a protein encoded by ydcl gene is decreased, thereby producing and accumulating the L-amino acid selected from L-glutamic acid, L-arginine, and L-threonine in the culture medium or cells of the bacterium when cultured in a culture medium. Subsequently, the L-amino acid is collected from the culture medium or the bacterium.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
Method for Producing an L-Amino Acid Using a Bacterium of the Family Enterobacteriaceae Having Attenuated Expression of a Phosphate Transporter-Encoding Gene
The present invention provides a method for producing an L-amino acid by fermentation using a bacterium of the family Enterobacteriaceae. The bacterium can belong to the genus Escherichia, which has been modified to attenuate expression of a phosphate transporter-encoding gene, such as the pitA gene or pitB gene.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com