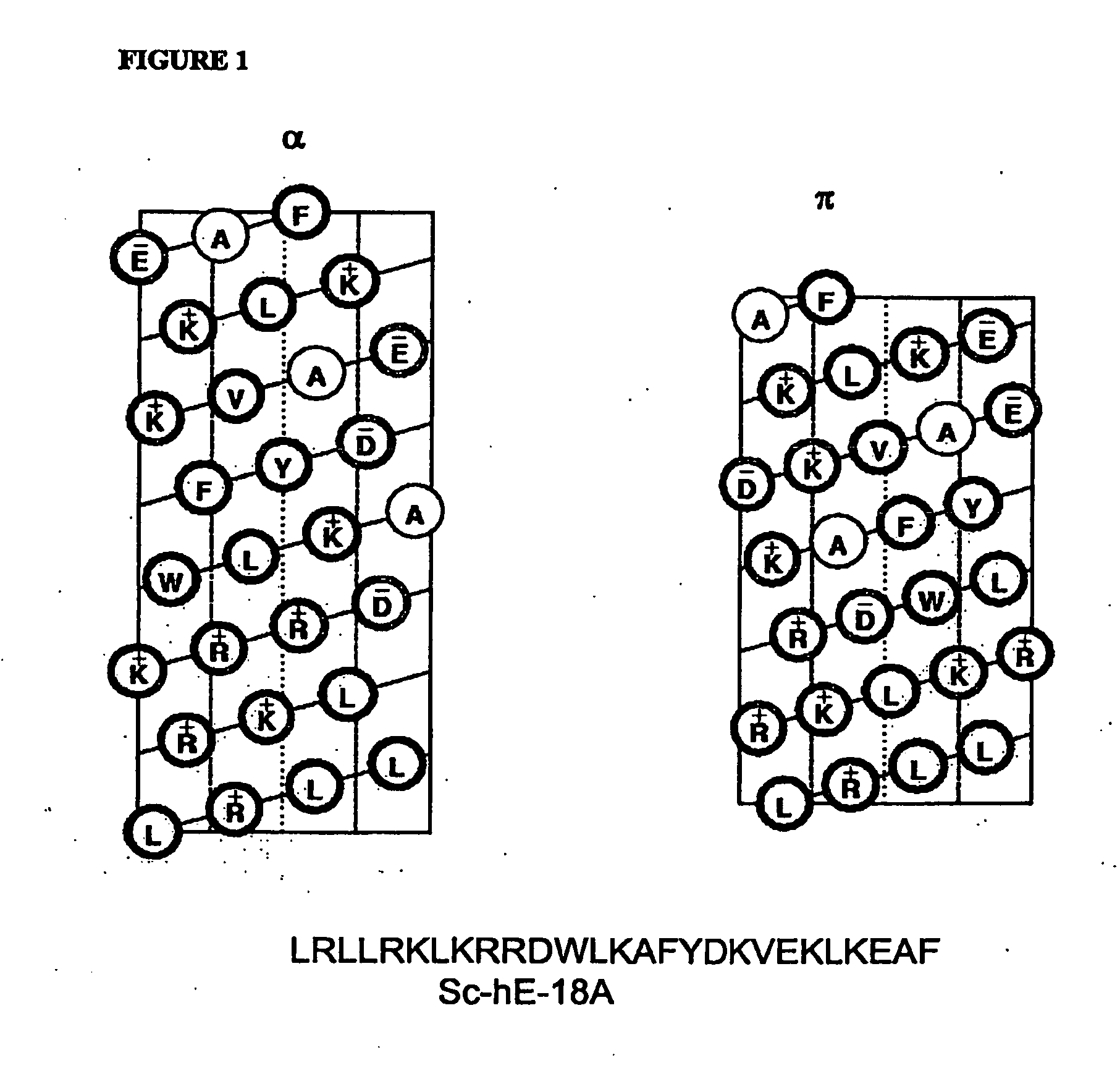
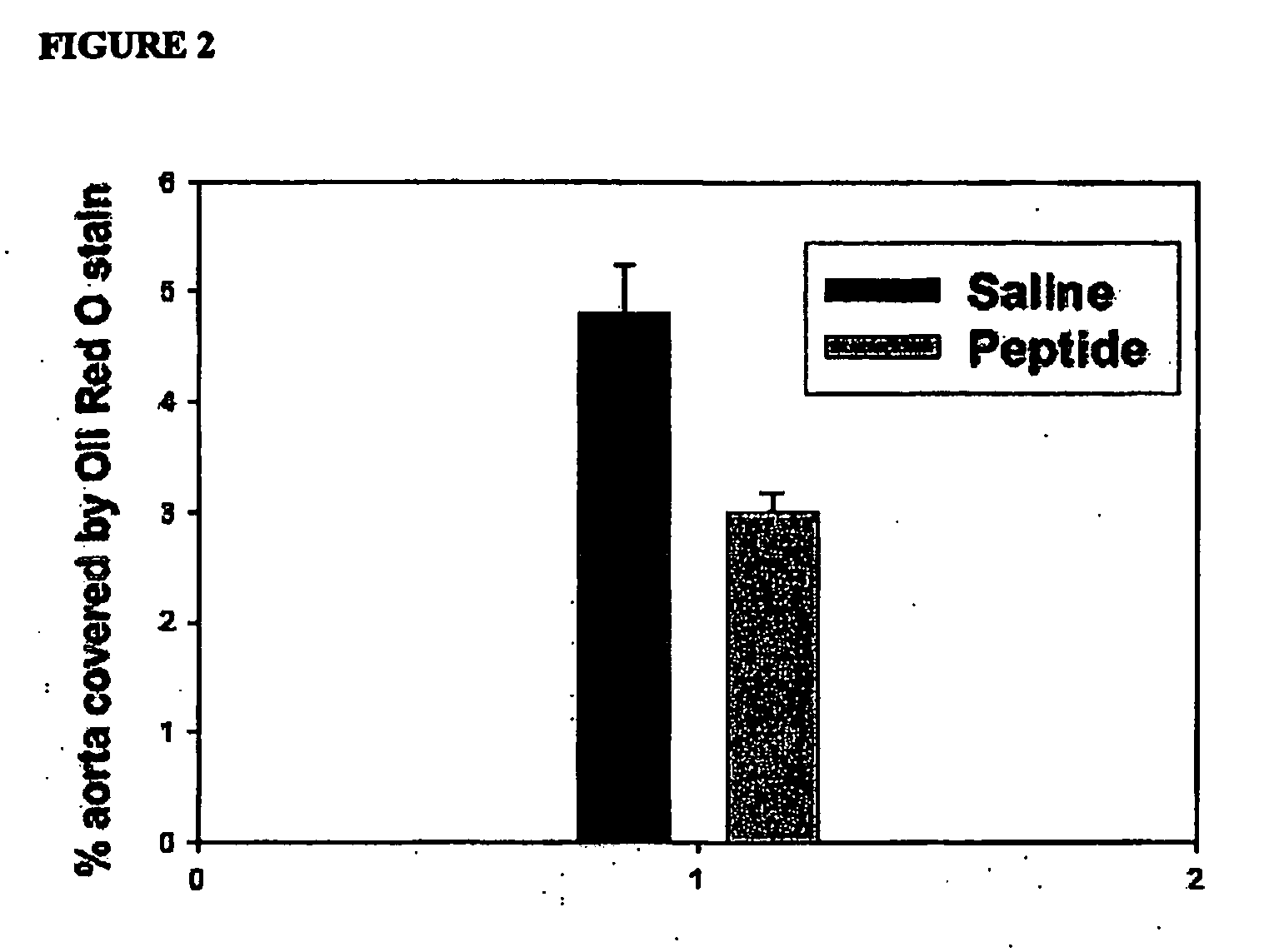
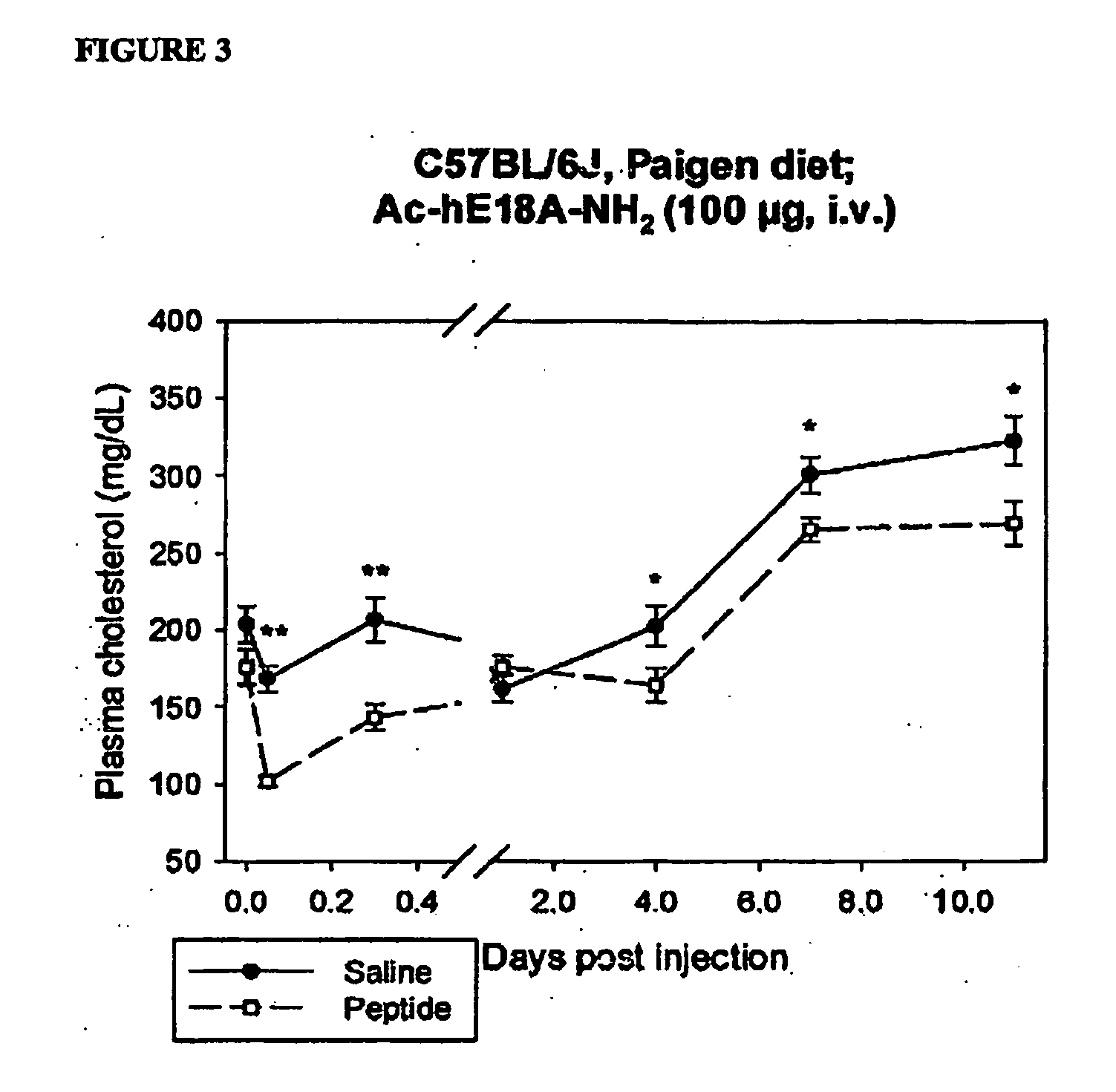
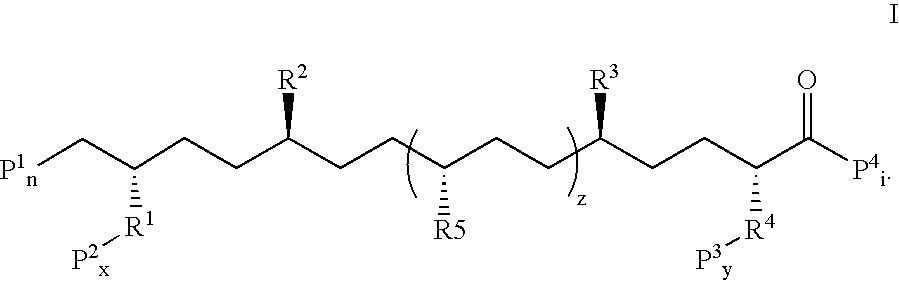
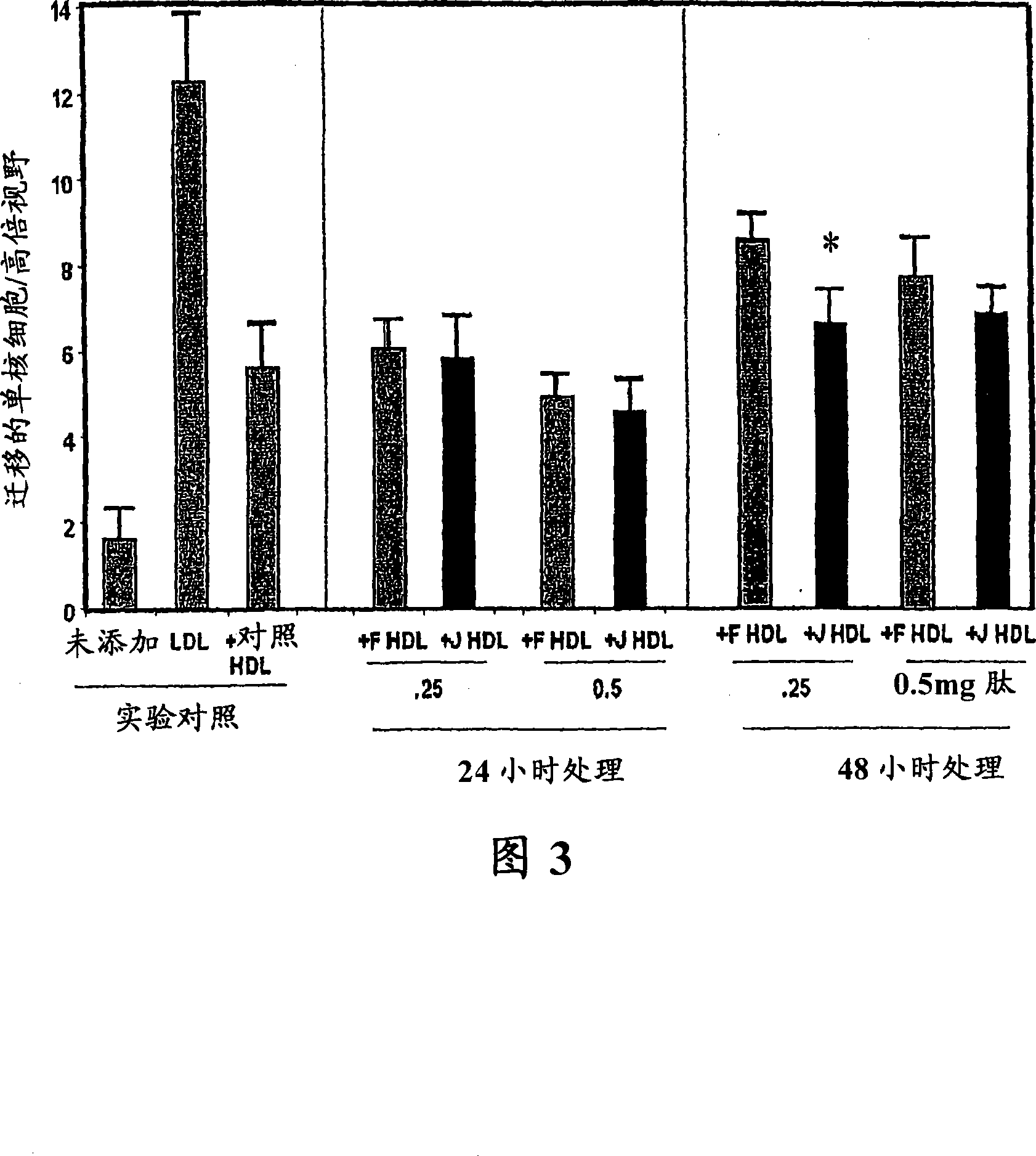
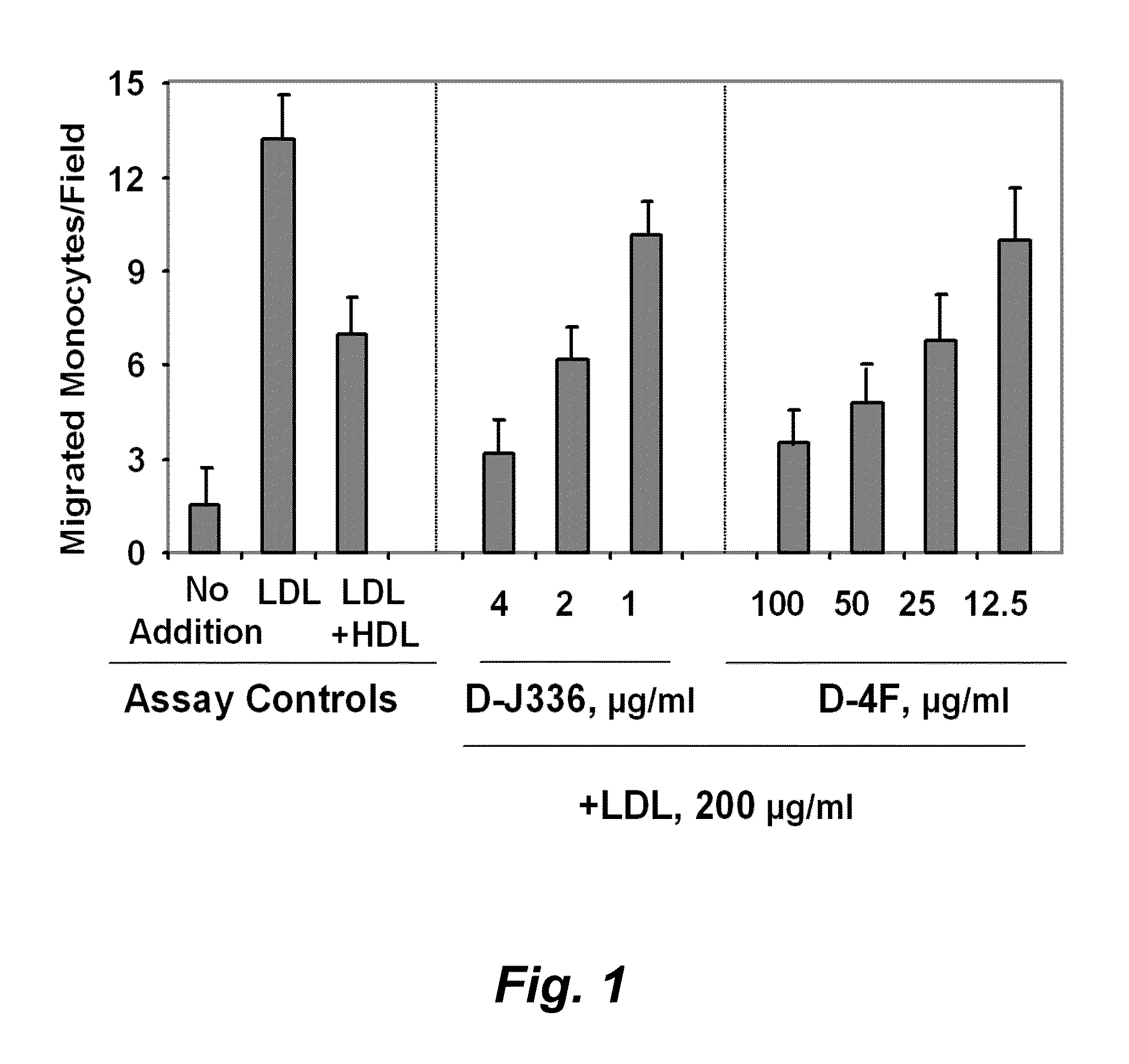
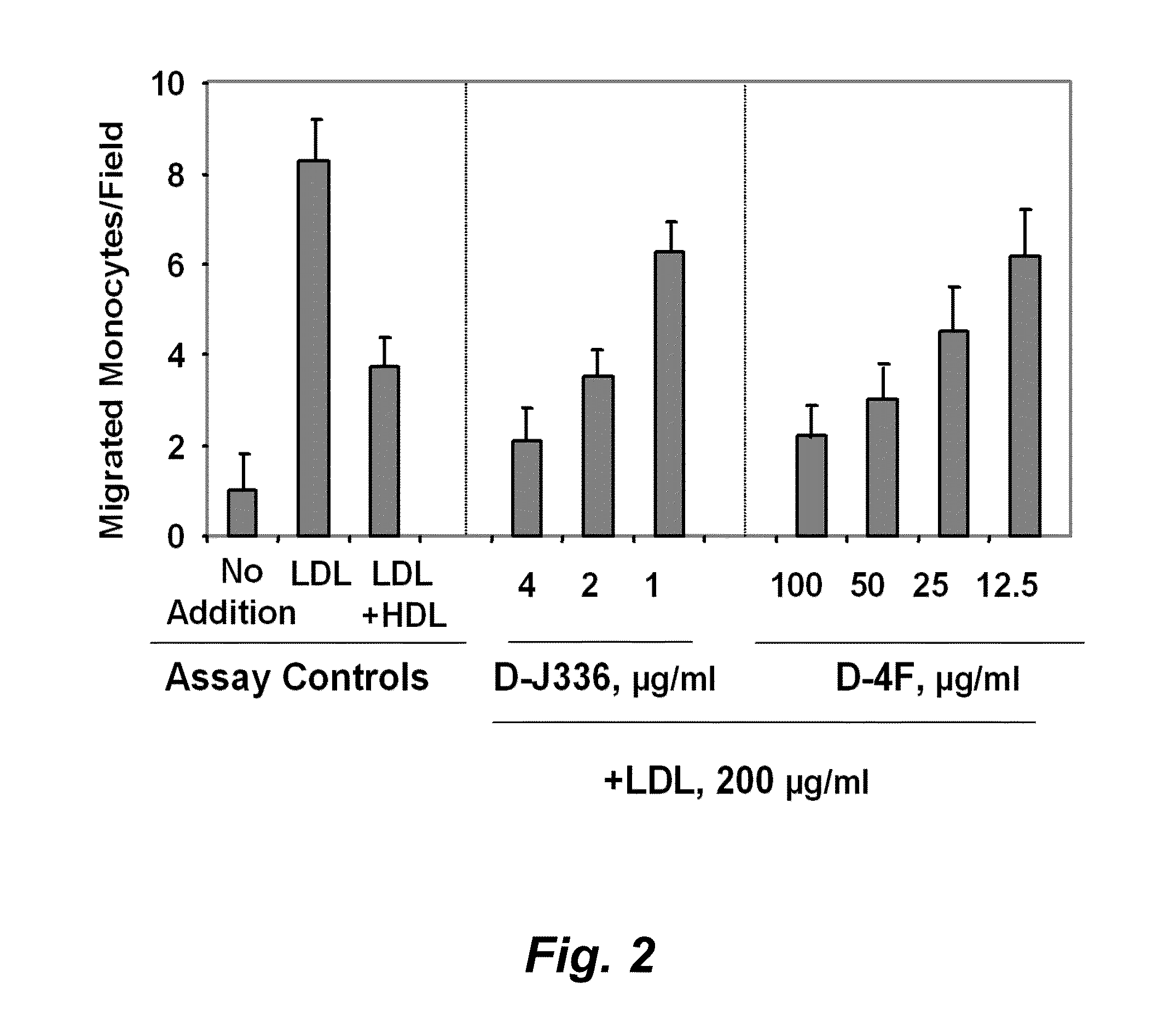
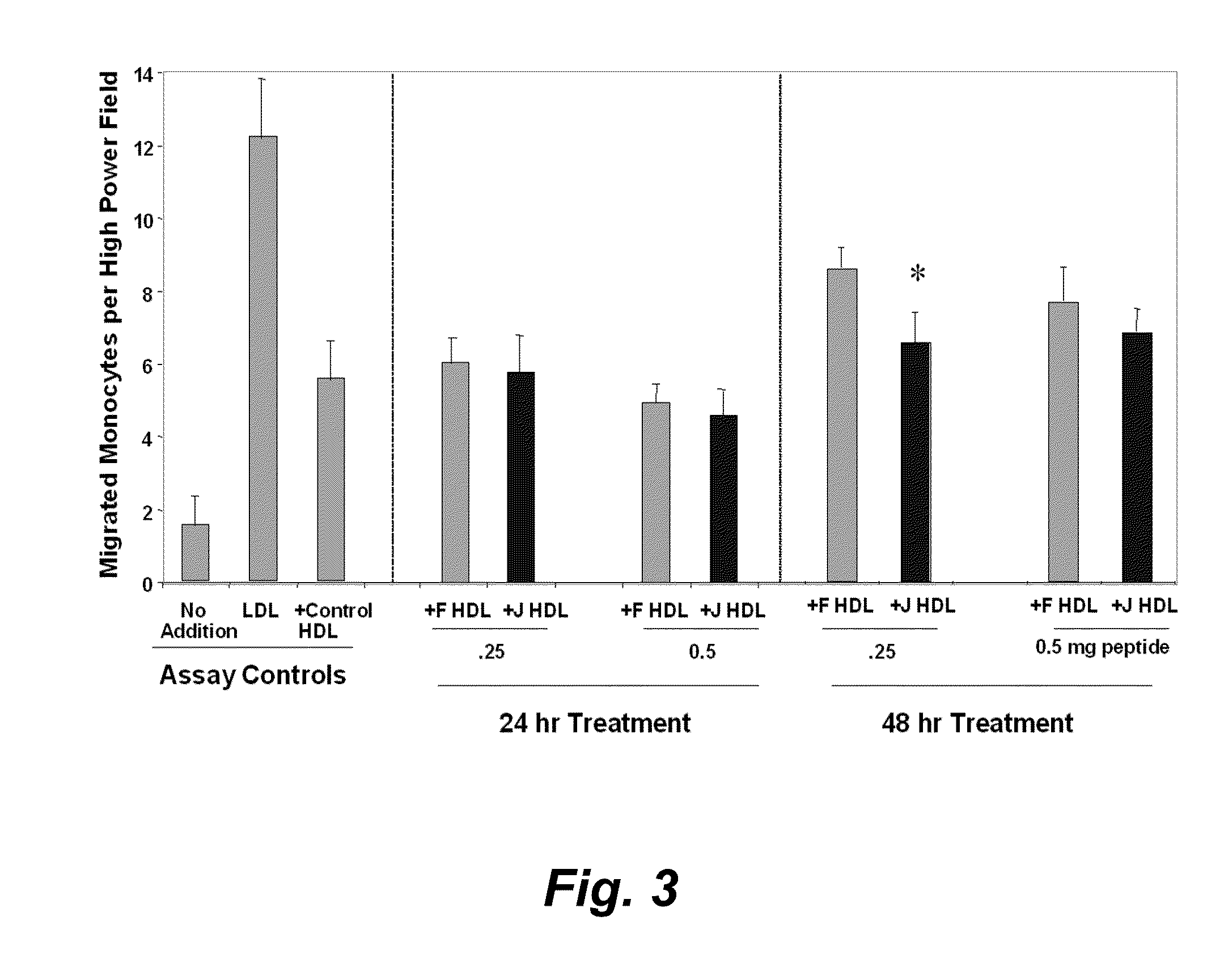
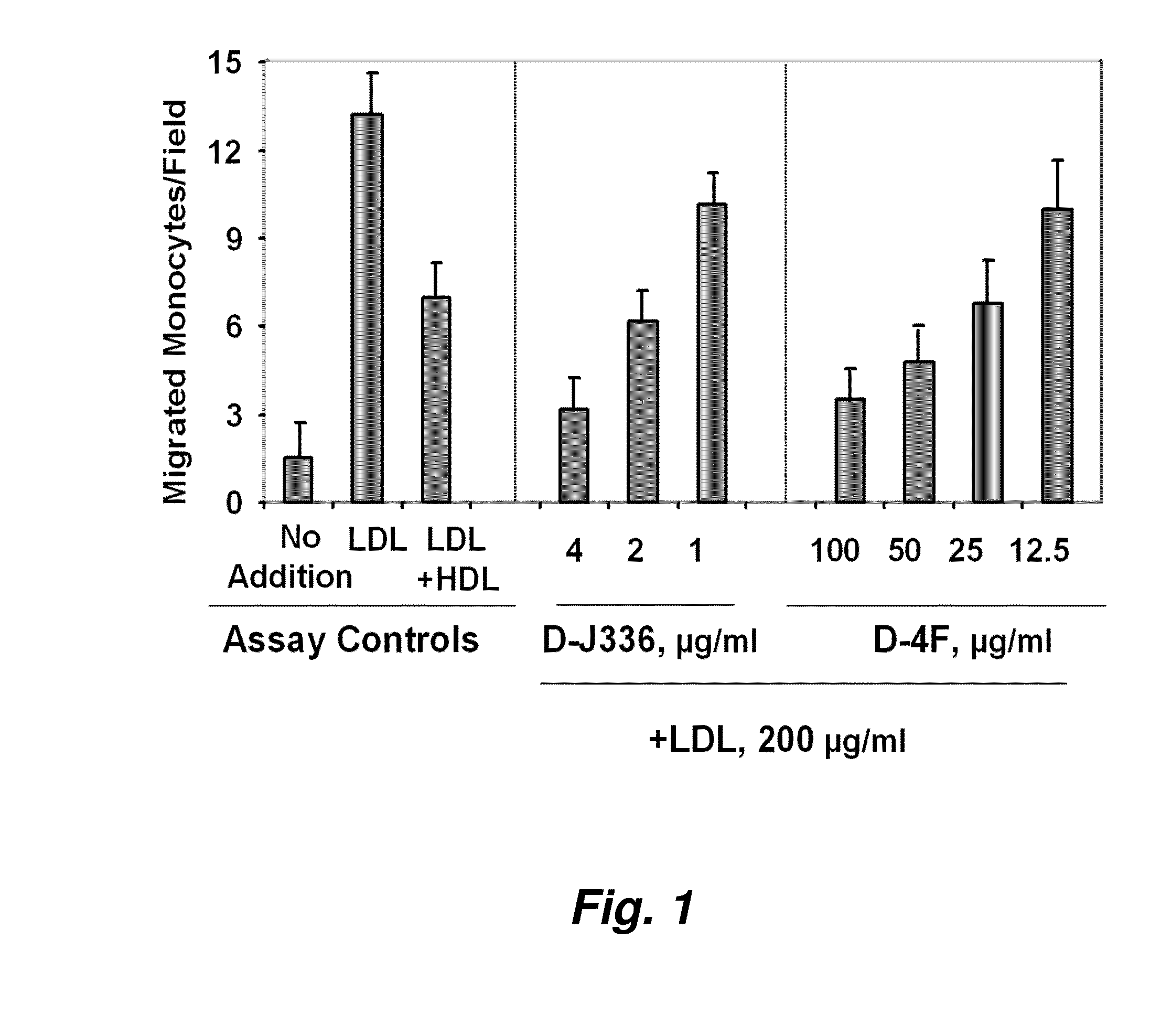
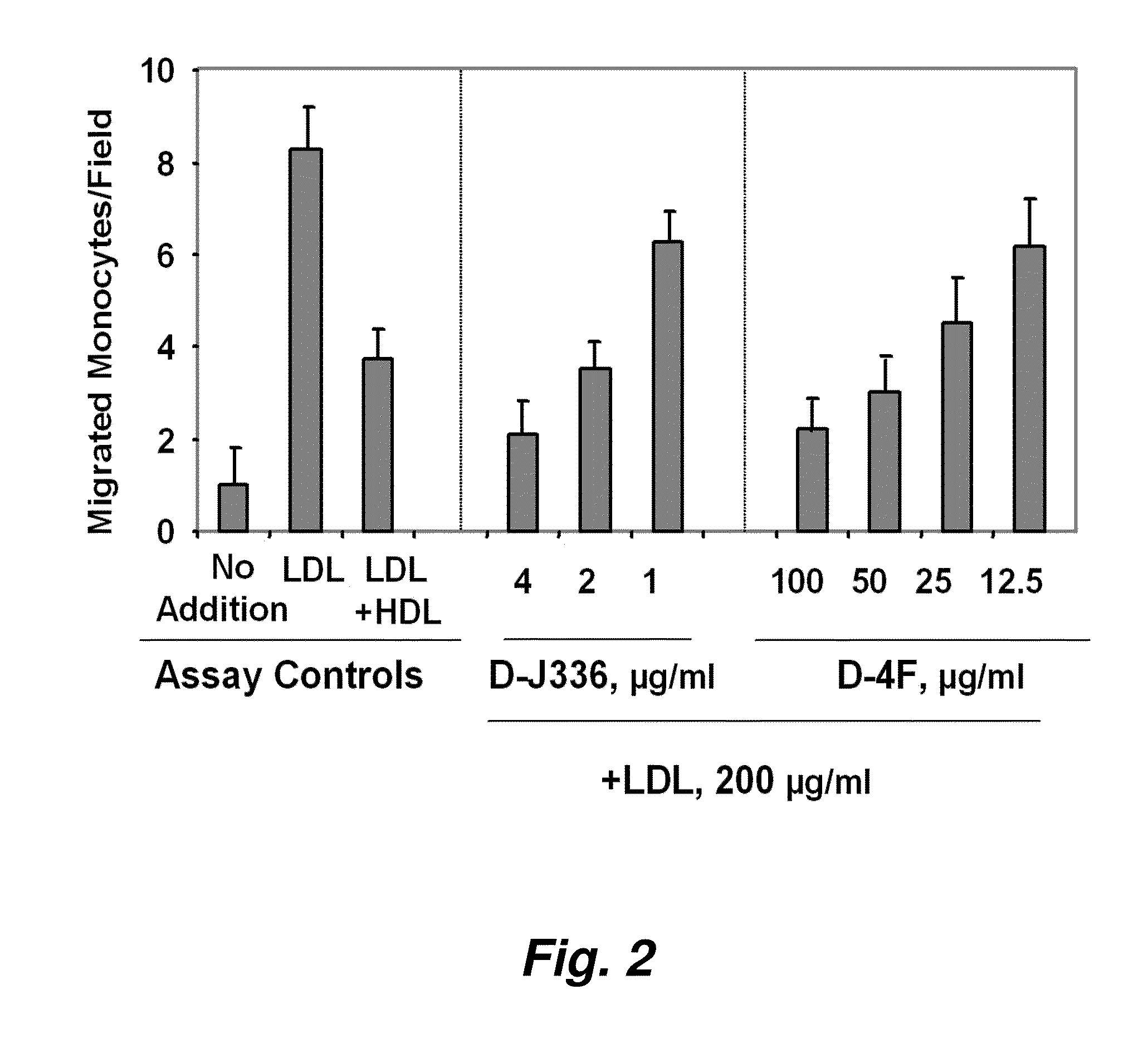
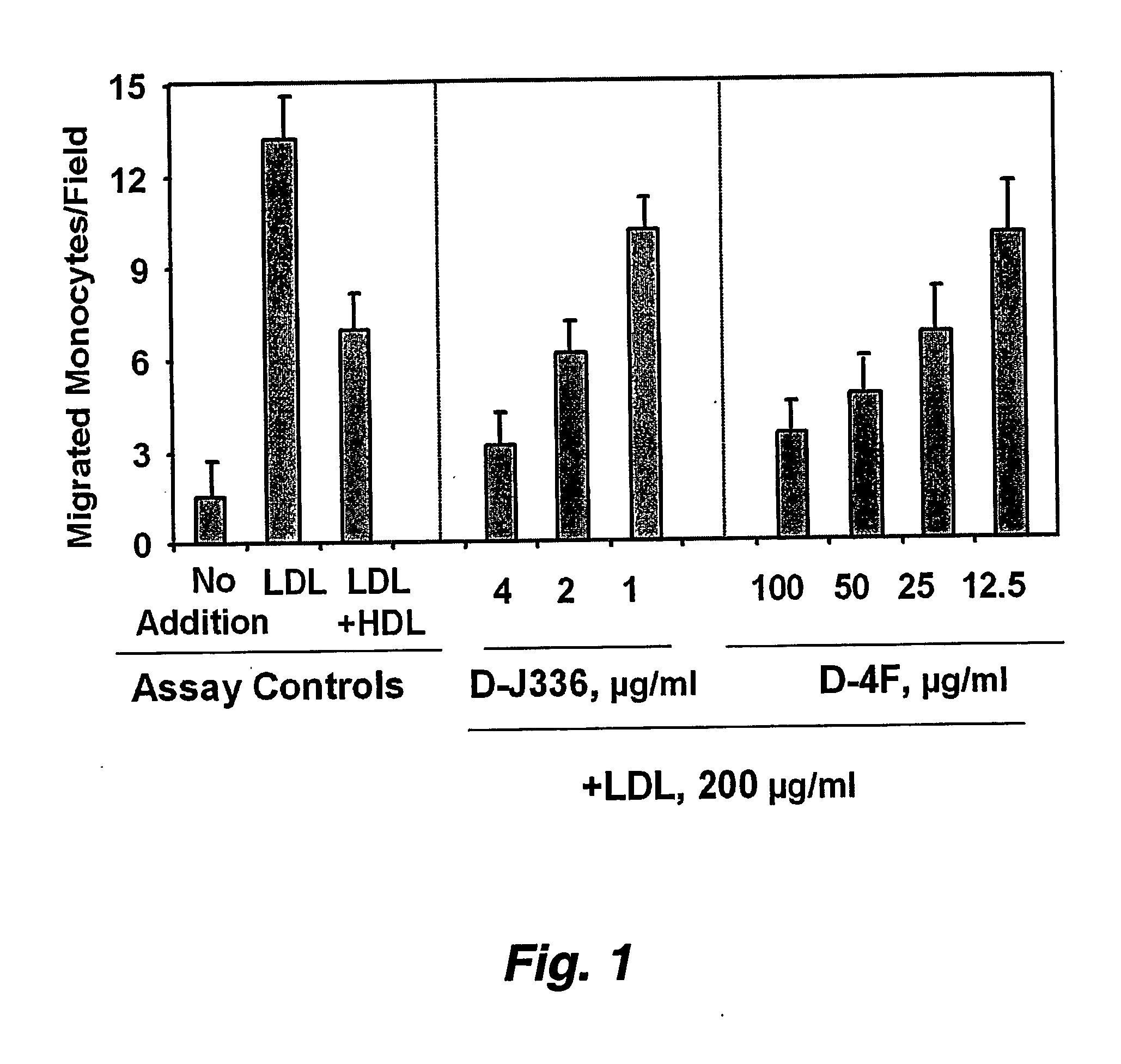
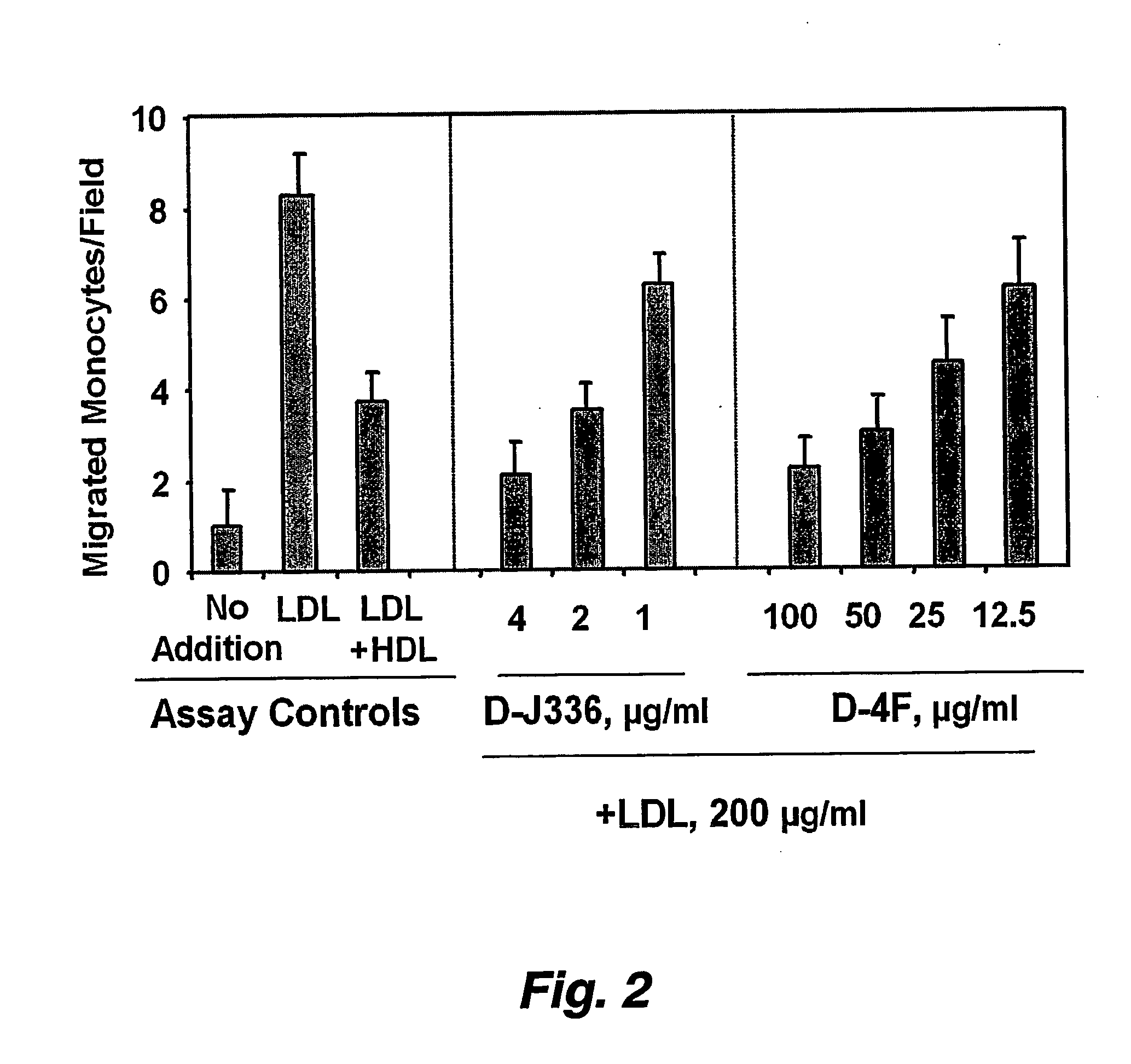
Patents
Literature
51 results about "Amphipathic helix" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
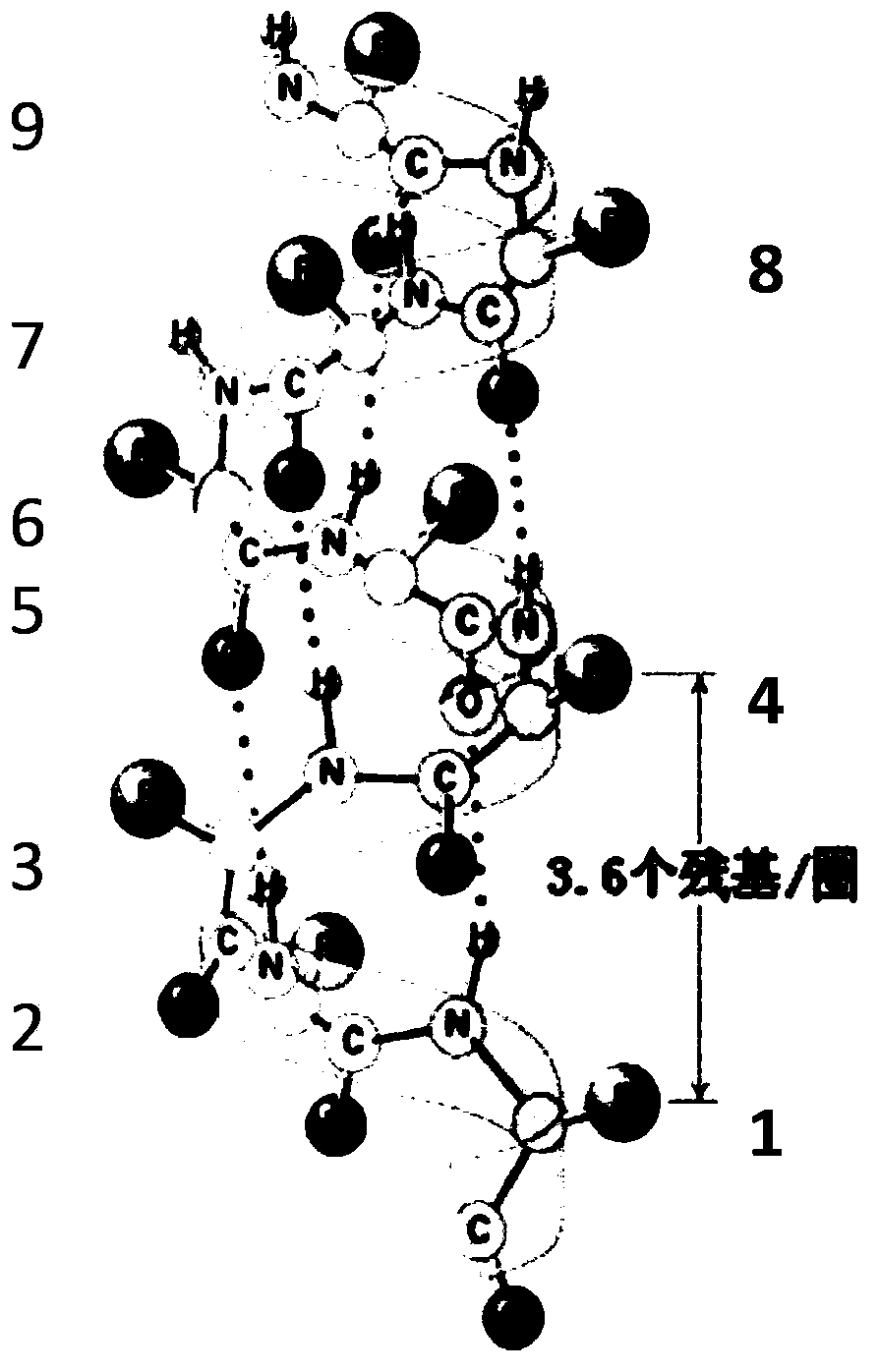
The Amphipathic Helix is a comprehensive volume discussing amphipathic helices in systems as diverse as serum lipoproteins, lung surfactant, cytotoxic peptides, ion channels, mitochondrial targeting, peptide hormones, G proteins, T-cell recognition, DNA binding proteins, and antifreeze proteins.
Peptides and peptide mimetics to treat pathologies characterized by an inflammatory response
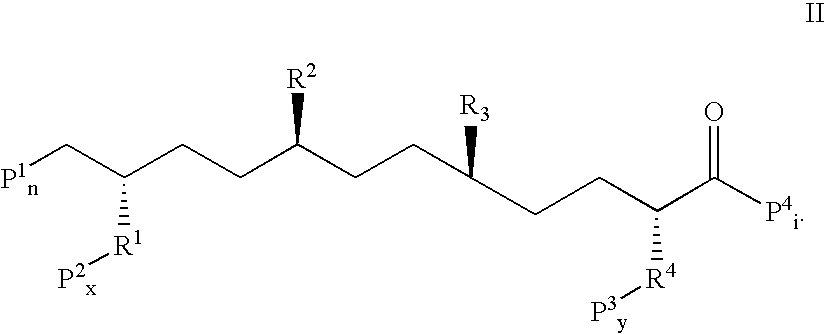
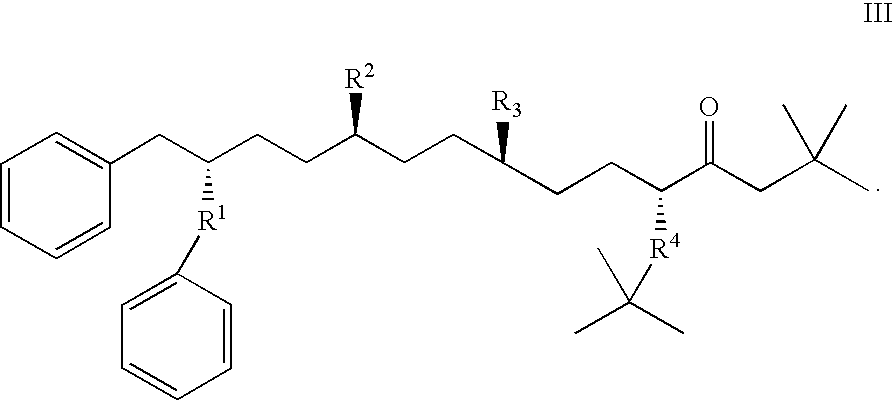
This invention provides novel active agents (e.g. peptides, small organic molecules, amino acid pairs, etc.) peptides that ameliorate one or more symptoms of atherosclerosis and / or other pathologies characterized by an inflammatory response. In certain embodiment, the peptides resemble a G* amphipathic helix of apolipoprotein J. The agents are highly stable and readily administered via an oral route.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA +1
Gene therapy approaches to supply apolipoprotein A-I agonists and their use to treat dyslipidemic disorders
InactiveUS6518412B1Improve the level ofIncrease productivityAntibacterial agentsBacteriaDyslipidemiaAmphipathic helix
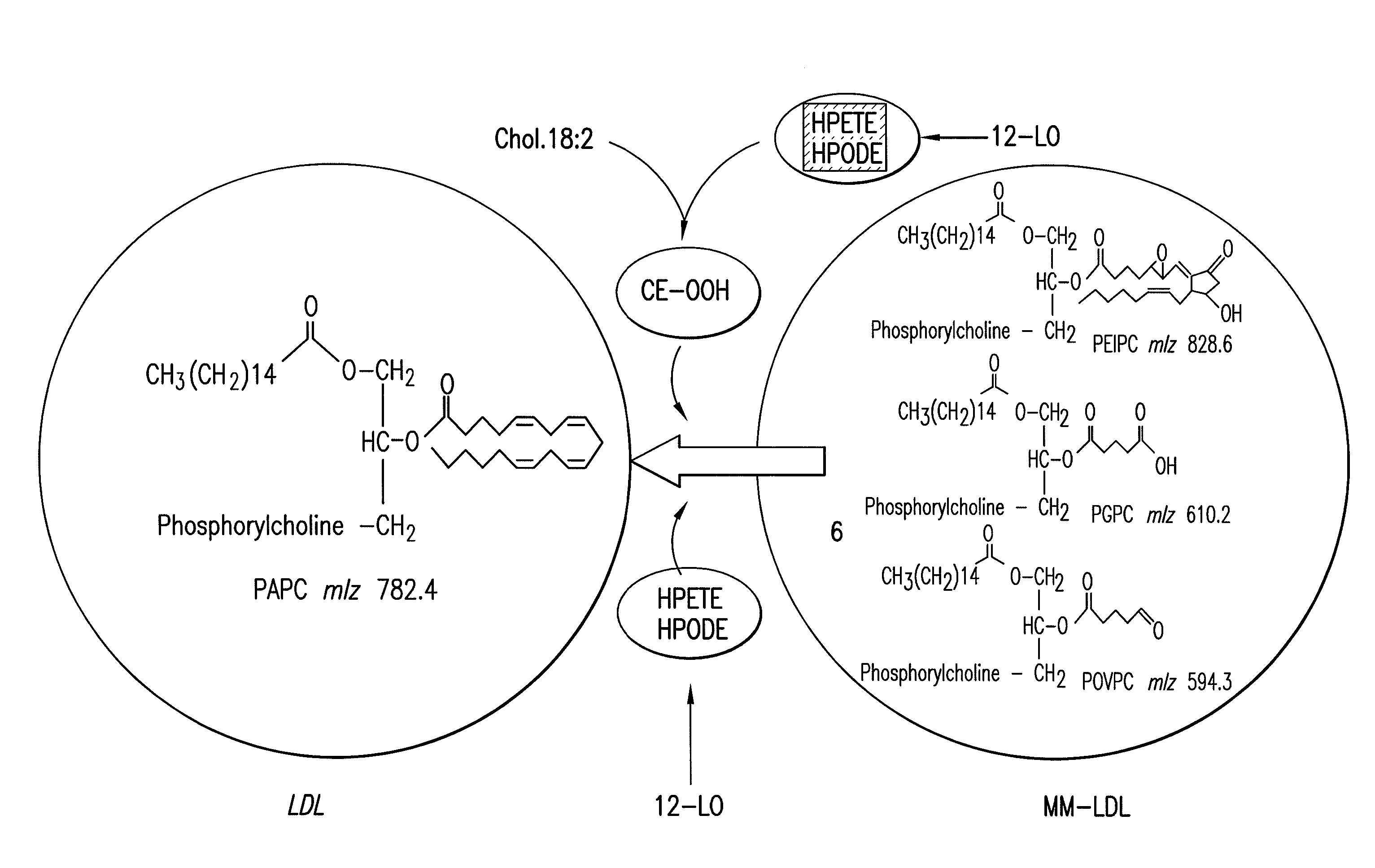
The invention relates to genetic approaches to supply nucleotide sequences encoding modified forms of the native forms of apolipoprotein A-I (ApoA-I): mature ApoA-I, preproApoA-I and proApoA-I; including native ApoA-I modified to contain ApoA-I agonists, peptides which mimic the activity of ApoA-I; ApoA-I superagonists, peptides which exceed the activity of native ApoA-I; and modified native ApoA-I having one or more amphipathic helices replaced by the nucleotide sequences of one or more ApoA-I agonists; for the treatment of disorders associated with dyslipoproteinemia, including cardiovascular disease, atherosclerosis, restenosis, hyperlipidemia, and other disorders such as septic shock.
Owner:DASSEUX JEAN LOUIS +5
Orally administered peptides to ameliorate atherosclerosis
InactiveUS7144862B2Readily taken up and deliveredMany symptomAntibacterial agentsBiocideAmphipathic helixMedicine
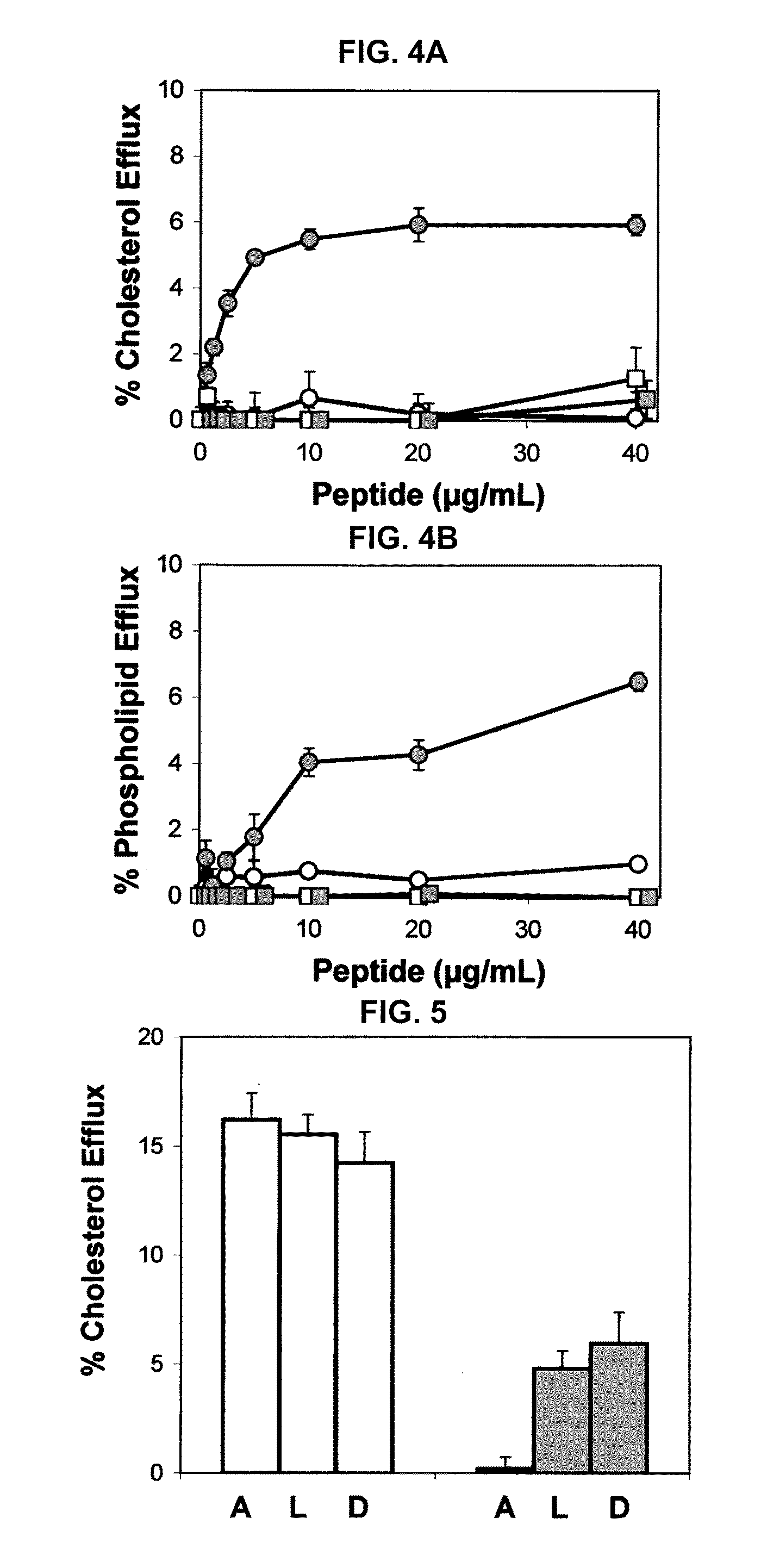
This invention provides novel peptides that ameliorate one or more symptoms of atherosclerosis. In certain embodiments, the peptide comprises an amino acid sequence that ranges in length from about 10 up to about 30 amino acids, that comprises at least one class A amphipathic helix, that bears at least one protecting group, that protects a phospholipid against oxidation by an oxidizing agent; and that is not the D-18A peptide. The peptides are highly stable and readily administered via an oral route.
Owner:UAB RES FOUND +1
Orally administered peptides synergize statin activity
InactiveUS7166578B2Many symptomReadily takenNervous disorderApolipeptidesAmphipathic helixPhospholipid
This invention provides novel peptides that ameliorate one or more symptoms of atherosclerosis. The peptides are highly stable and readily administered via an oral route. In addition, the peptides inhibit osteoporosis. When administered with a statin, the peptides enhance the activity of the statin permitting the statin to be used at significantly lower dosages. In certain embodiments, the peptides range in length from about 10 up to about 30 amino acids, comprise at least one class A amphipathic helix, and protect a phospholipid against oxidation by an oxidizing agent.
Owner:ALABAMA RESEARCG FOUND UNIV OF THE +1
Orally administered peptides synergize statin activity
InactiveUS7199102B2Many symptomEasy to useNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsAmphipathic helixLipid Transport
This invention provides novel peptides that ameliorate one or more symptoms of atherosclerosis. The peptides typically range in length up to about 30 amino acids, comprise at least one class A amphipathic helix, and protect a phospholipid against oxidation by an oxidizing agent. The peptides are highly stable and readily administered via an oral route. The peptides are effective to stimulate the formation and cycling of pre-beta high density lipoprotein-like particles and / or to promote lipid transport and detoxification. In addition, the peptides inhibit osteoporosis. When administered with a statin, the peptides enhance the activity of the statin permitting the statin to be used at significantly lower dosages and / or cause the statins to be significantly more anti-inflammatory at any given dose.
Owner:UAB RES FOUND +1
G-type peptides to ameliorate atherosclerosis
InactiveUS6930085B2Simplification of progressiveAlignment score can be increasedAntibacterial agentsAntimycoticsAmphipathic helixPeptide
This invention provides novel peptides that ameliorate one or more symptoms of atherosclerosis and / or other pathologies characterized by an inflammatory response. In certain embodiment, the peptides resemble a G* amphipathic helix of apolipoprotein J. The peptides are highly stable and readily administered via an oral route.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Peptides and peptide mimetics to treat pathologies characterized by an inflammatory response
Owner:UAB RES FOUND +1
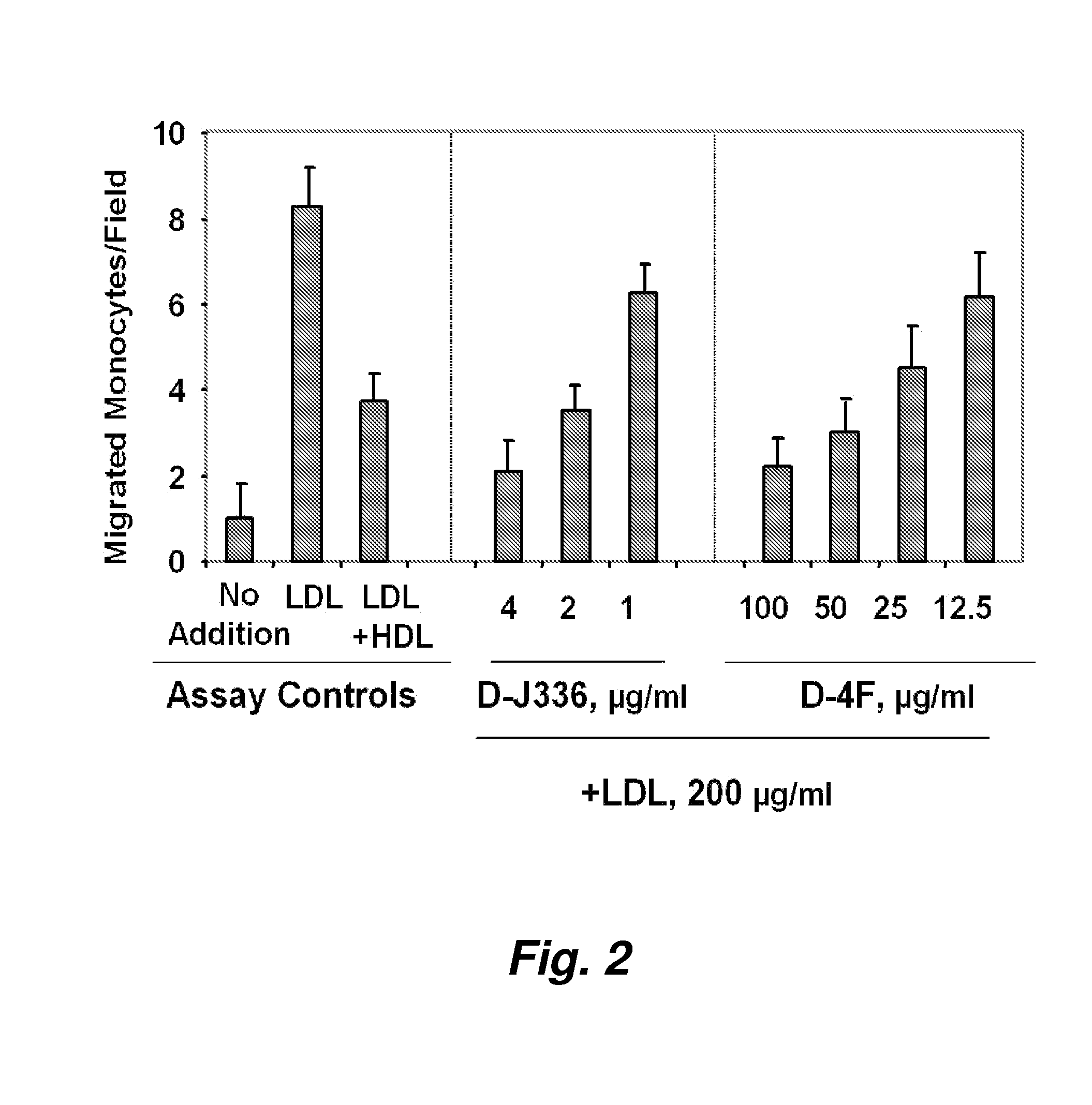
Salicylanilides enhance oral delivery of therapeutic peptides
This invention pertains to the surprising discovery that salicylanilides, e.g., niclosamide and / or niclosamide analogues when orally administered in conjunction with a peptide pharmaceutical (e.g., a class A amphipathic helical peptide as described herein) significantly increases the bioavailability of that peptide. Methods of peptide delivery using such “delivery agents” and pharmaceutical formulations are provided.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Peptides and peptide mimetics to treat pathologies characterized by an inflammatory response
InactiveUS20080293639A1Increase insulin sensitivityIncrease in adiponectinNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsAmphipathic helixActive agent
This invention provides novel active agents (e.g. peptides, small organic molecules, amino acid pairs, etc.) peptides that ameliorate one or more symptoms of atherosclerosis and / or other pathologies characterized by an inflammatory response. In certain embodiment, the peptides resemble a G* amphipathic helix of apolipoprotein J. The agents are highly stable and readily administered via an oral route.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Salicylanilides enhance oral delivery of therapeutic peptides
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Synthetic apolipoprotein e mimicking polypeptides and methods of use
InactiveUS20100286025A1Antibacterial agentsSenses disorderAmphipathic helixVery low-density lipoprotein
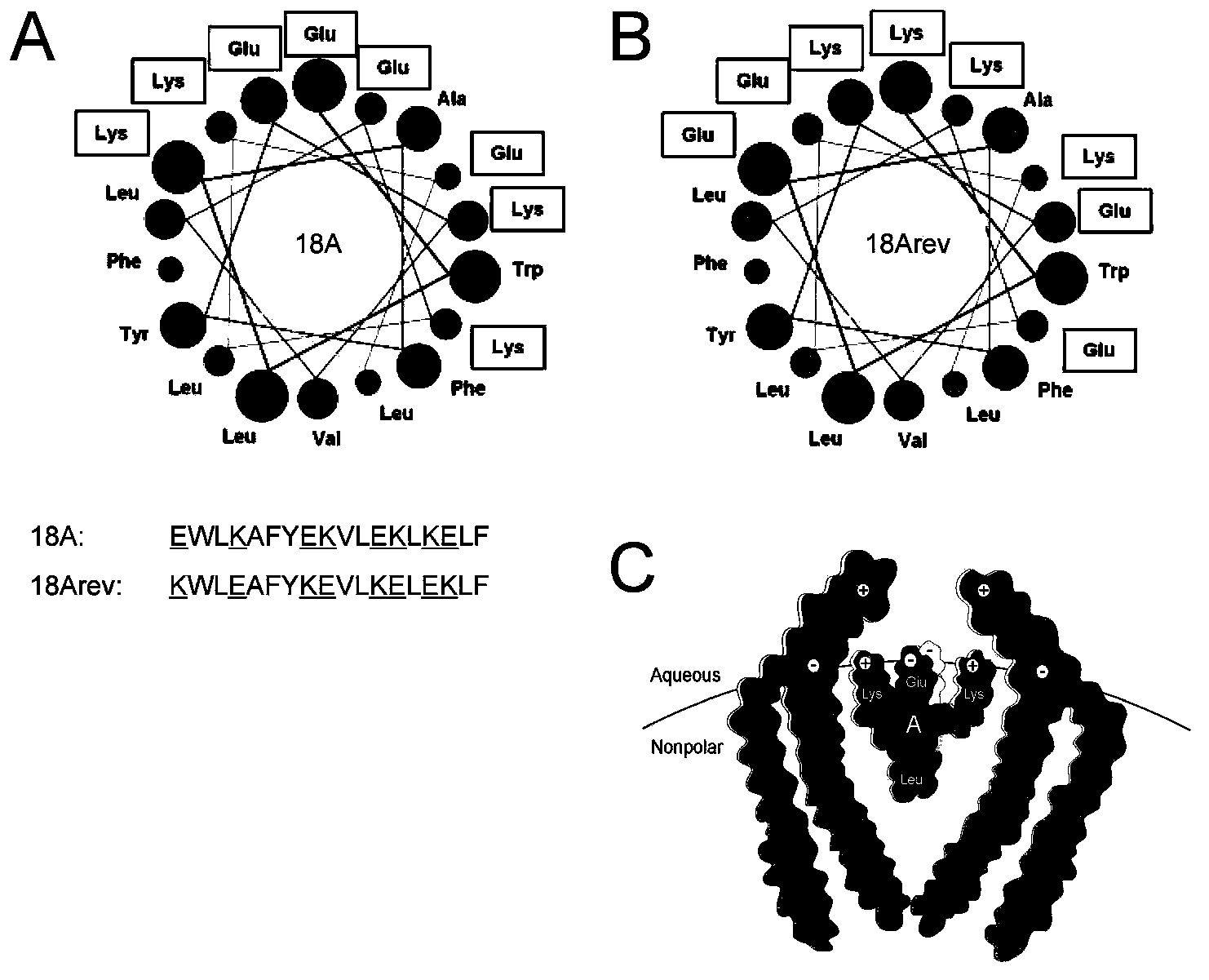
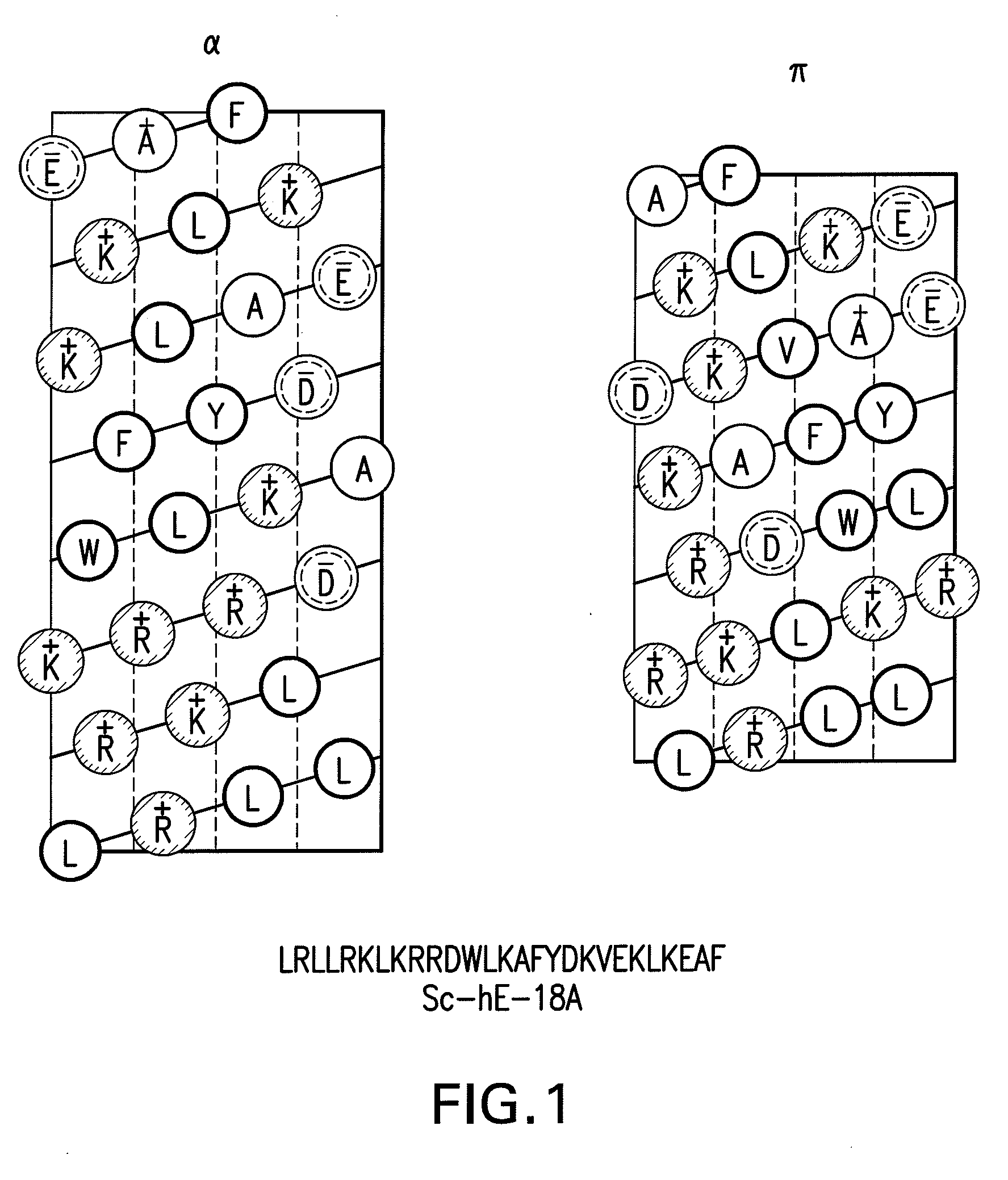
The present invention provides novel synthetic apolipoprotein E (ApoE)-mimicking peptides wherein the receptor binding domain of apolipoprotein E is covalently linked to 18A, the well characterized lipid-associating model class A amphipathic helical peptide, or a modified version thereof. Such peptides enhance low density lipoprotein (LDL) and very low density lipoprotein (VLDL) binding to and degradation by fibroblast or HepG2 cells. Also provided are possible applications of the synthetic peptides in lowering human plasma LDL / VLDL cholesterol levels, thus inhibiting atherosclerosis. The present invention also relates to synthetic peptides that can improve HDL function and / or exert anti-inflammatory properties.
Owner:UAB RES FOUND
G-type peptides and other agents to ameliorate atherosclerosis and other pathologies
InactiveUS20060205669A1Simplification of progressiveAlignment score can be increasedPeptide/protein ingredientsAntipyreticAmphipathic helixIntensive care medicine
This invention provides novel peptides, and other agents, that ameliorate one or more symptoms of atherosclerosis and / or other pathologies characterized by an inflammatory response. In certain embodiment, the peptides resemble a G* amphipathic helix of apolipoprotein J. The peptides are highly stable and readily administered via an oral route.
Owner:ALABAMA RES FOUND UNIV OF THE +1
Gene therapy approaches to supply apolipoprotein A-I agonists and their use to treat dyslipidemic disorders
InactiveUS6844327B2High activityImprove the level ofAntibacterial agentsBiocideDyslipidemiaAmphipathic helix
The invention relates to genetic approaches to supply nucleotide sequences encoding modified forms of the native forms of apolipoprotein A-I (ApoA-I): mature ApoA-I, preproApoA-I and proApoA-I; including native ApoA-I modified to contain ApoA-I agonists, peptides which mimic the activity of ApoA-I; ApoA-I superagonists, peptides which exceed the activity of native ApoA-I; and modified native ApoA-I having one or more amphipathic helices replaced by the nucleotide sequences of one or more ApoA-I agonists; for the treatment of disorders associated with dyslipoproteinemia, including cardiovascular disease, atherosclerosis, restenosis, hyperlipidemia, and other disorders such as septic shock.
Owner:DASSEUX JEAN LOUIS +5
Methods for improving the structure and function of arterioles
ActiveUS7579319B2Simple structureFunction increaseNervous disorderTetrapeptide ingredientsAmphipathic helixSmall artery
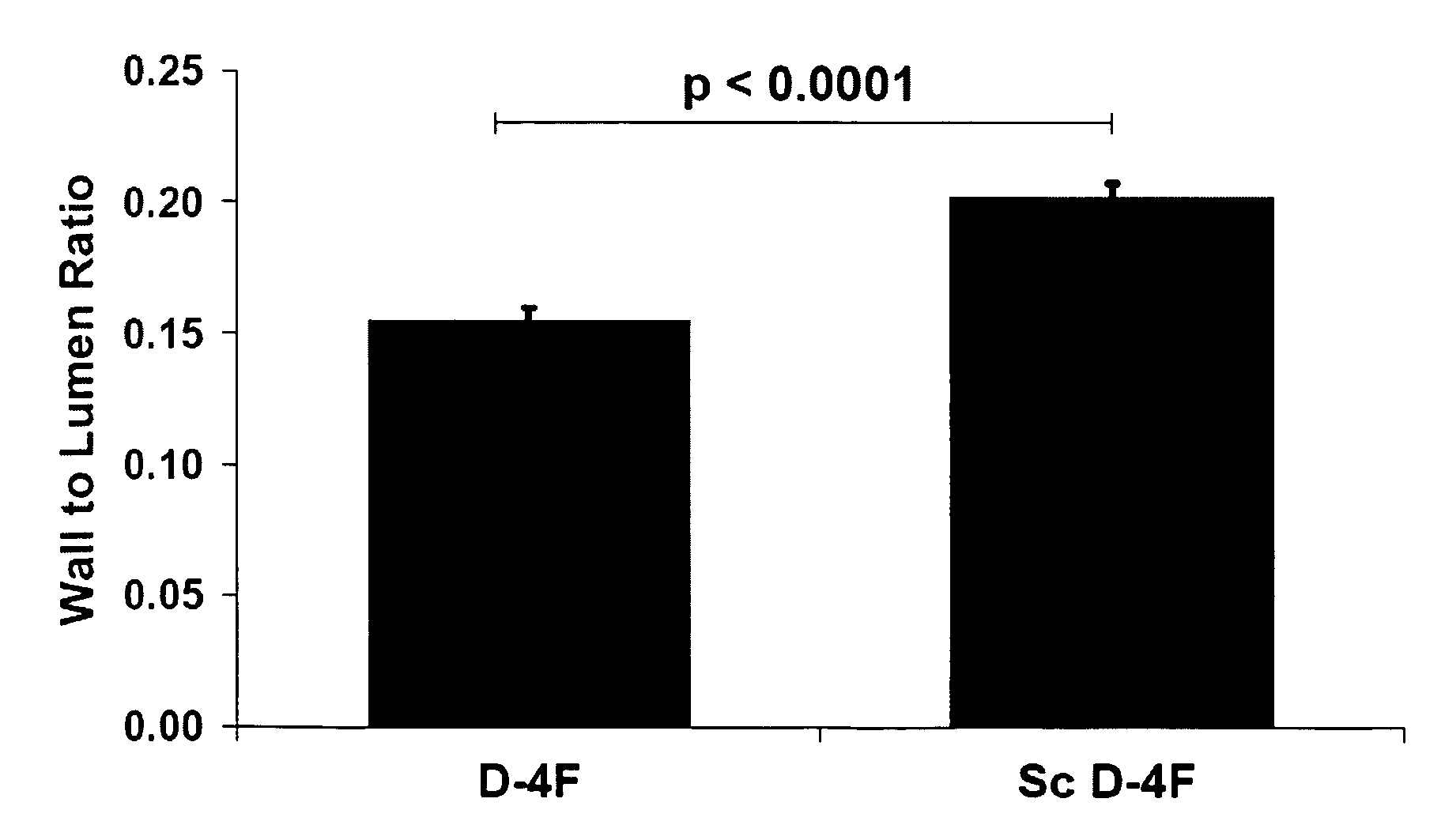
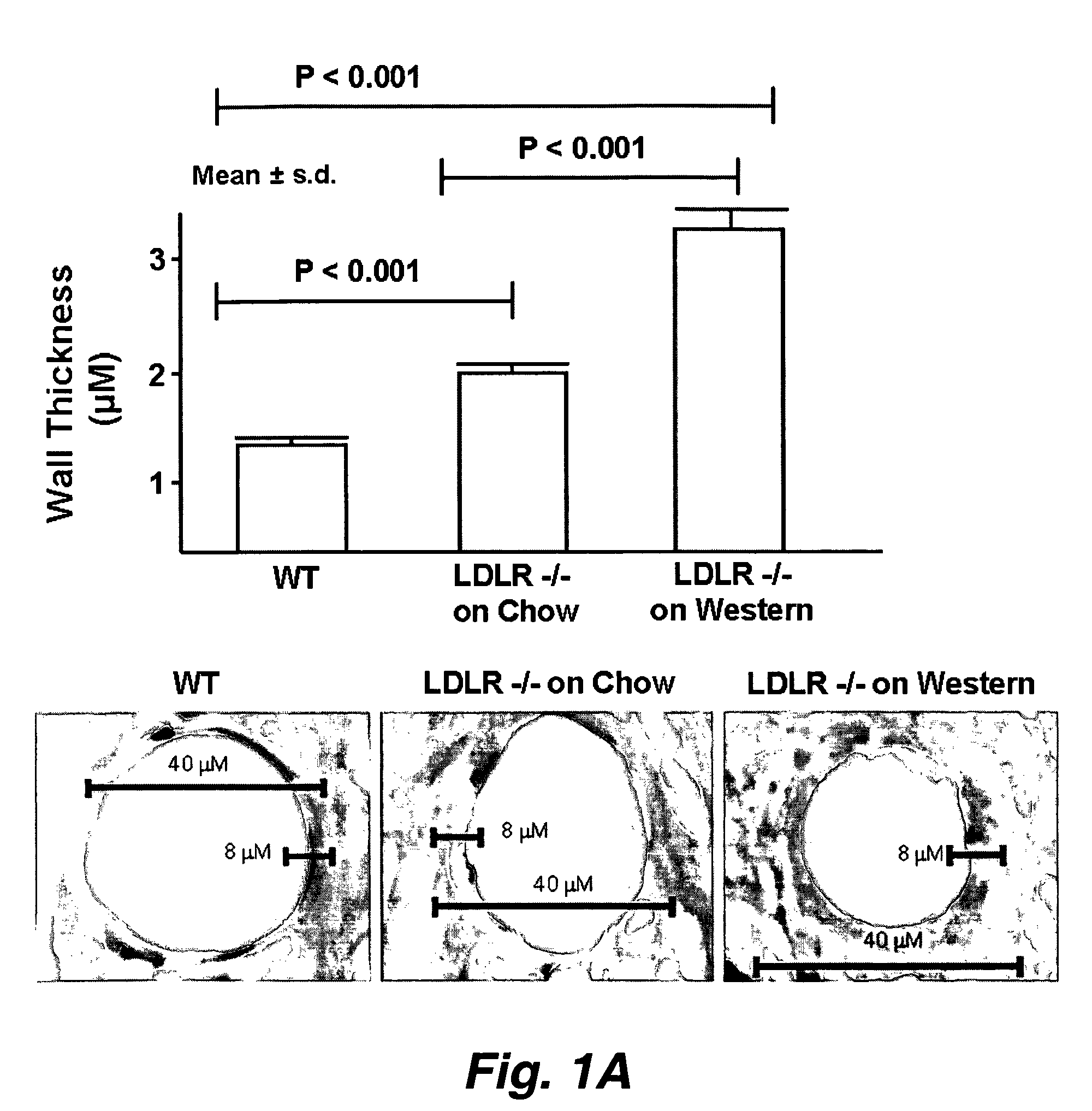
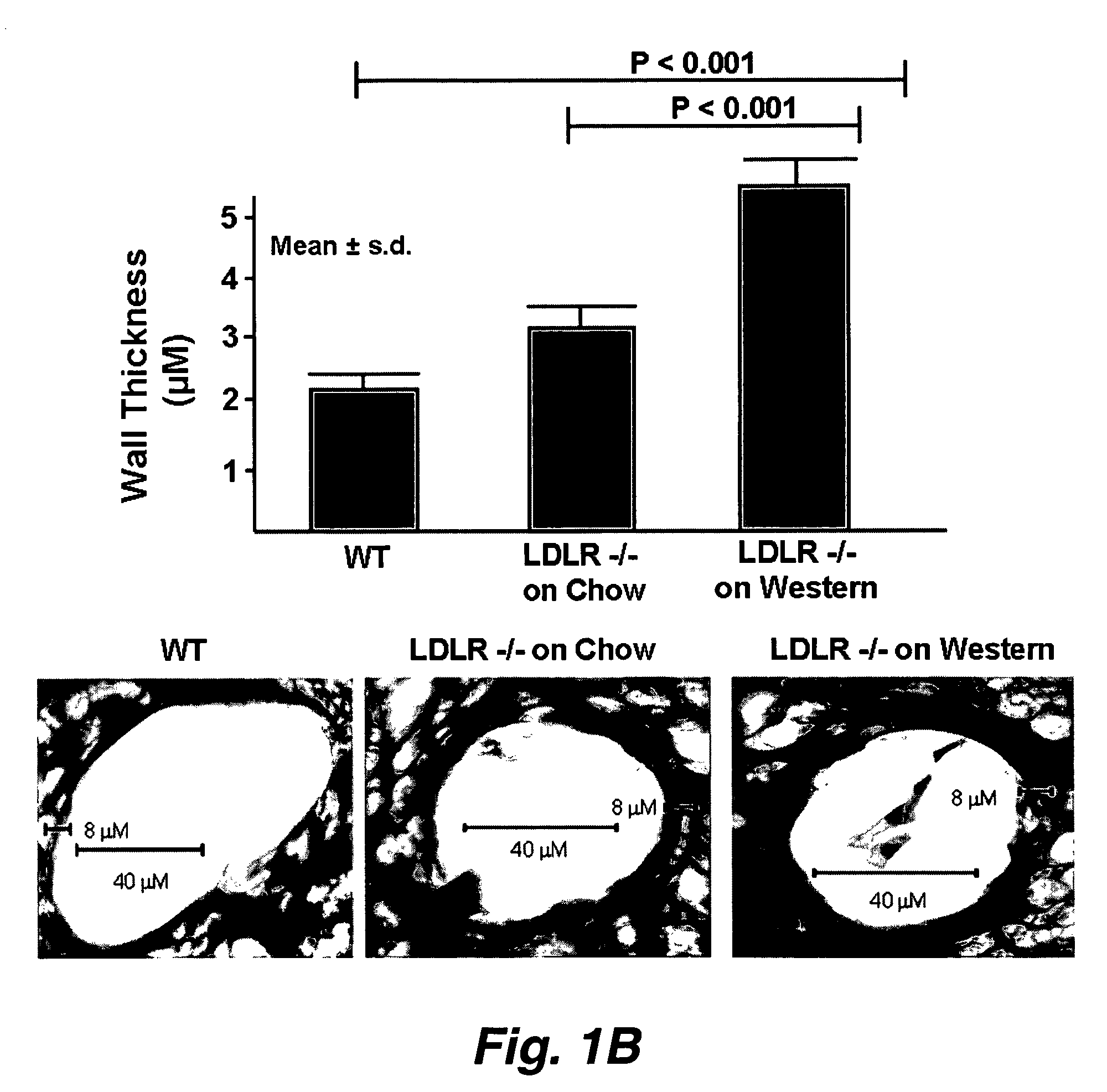
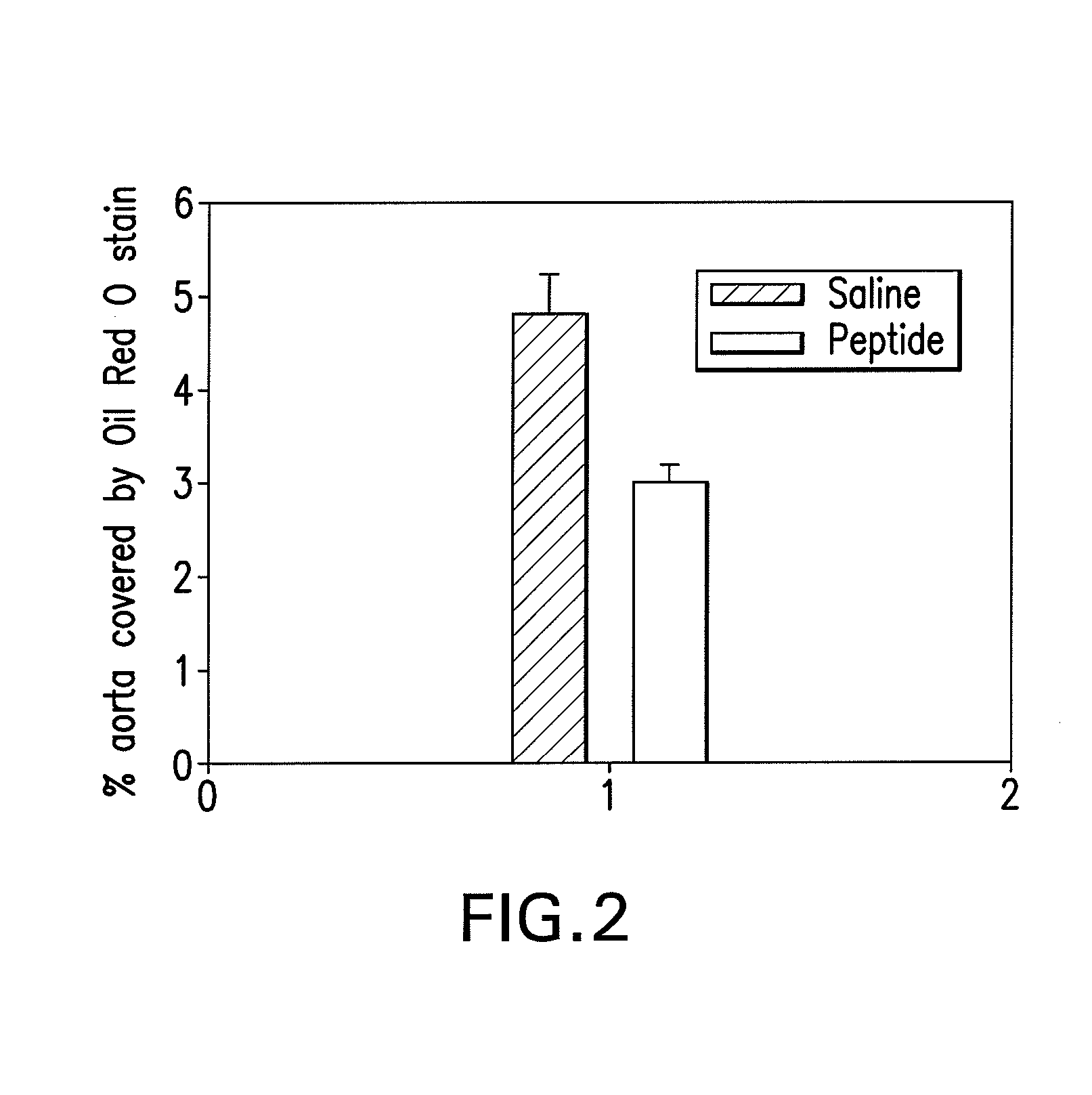
The present invention relates to the unexpected finding that vessels smaller than even the smallest arteries (i.e. arterioles) thicken, become dysfunctional and cause end organ damage to tissues as diverse as the brain and the kidney. This invention provides a method to improve the structure and function of arterioles and preserve the function of end organs such as the brain and kidney. In certain embodiments, the methods involve administering to a human having thickened arterioles in brain, kidney or alveoli a peptide that ranges in length up to 30 amino acids, and that comprises a class A amphipathic helix, and bears at least one protecting group.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Isolated phospholipid-protein particles
InactiveUS20080248565A1Speed up the processImprove solubilityPeptide preparation methodsDepsipeptidesADAMTS ProteinsApolipoproteins E
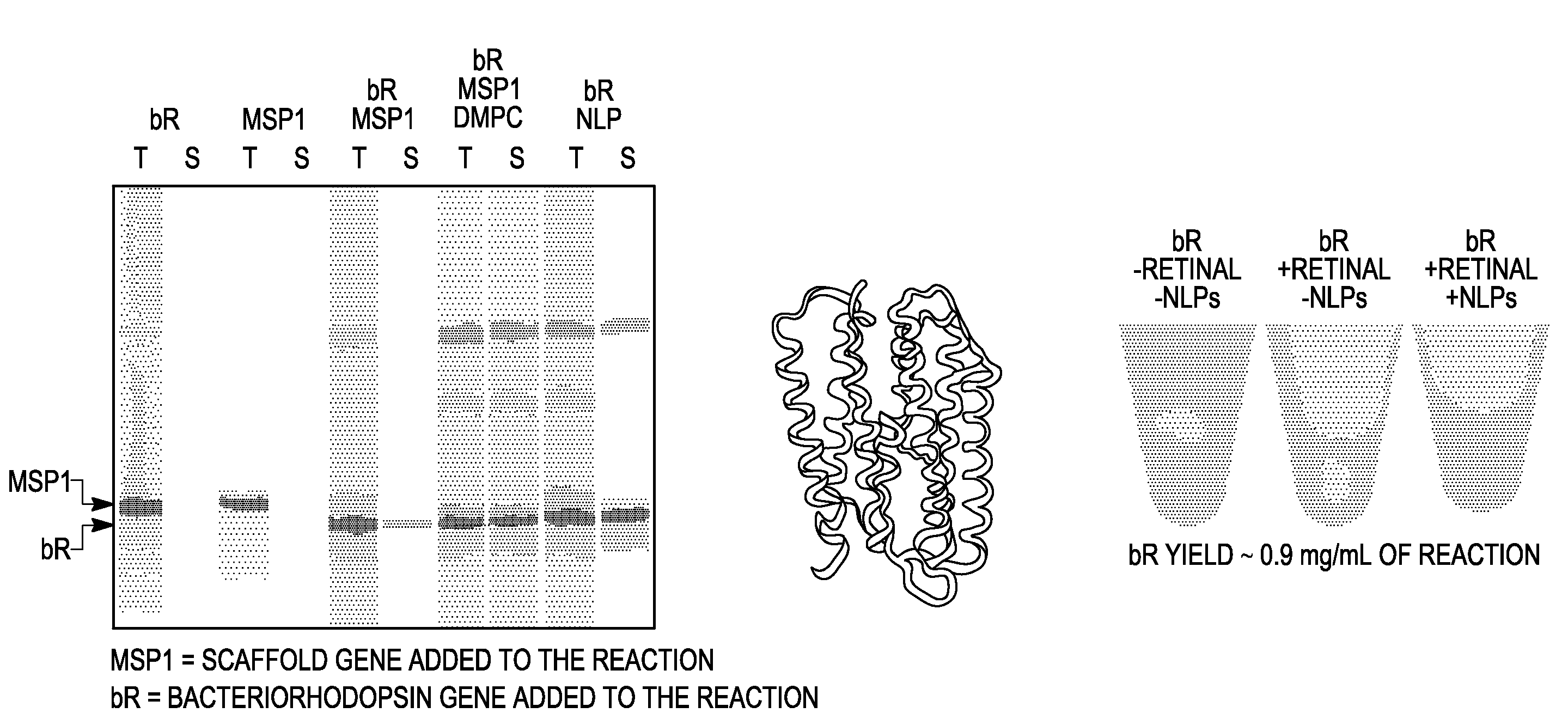
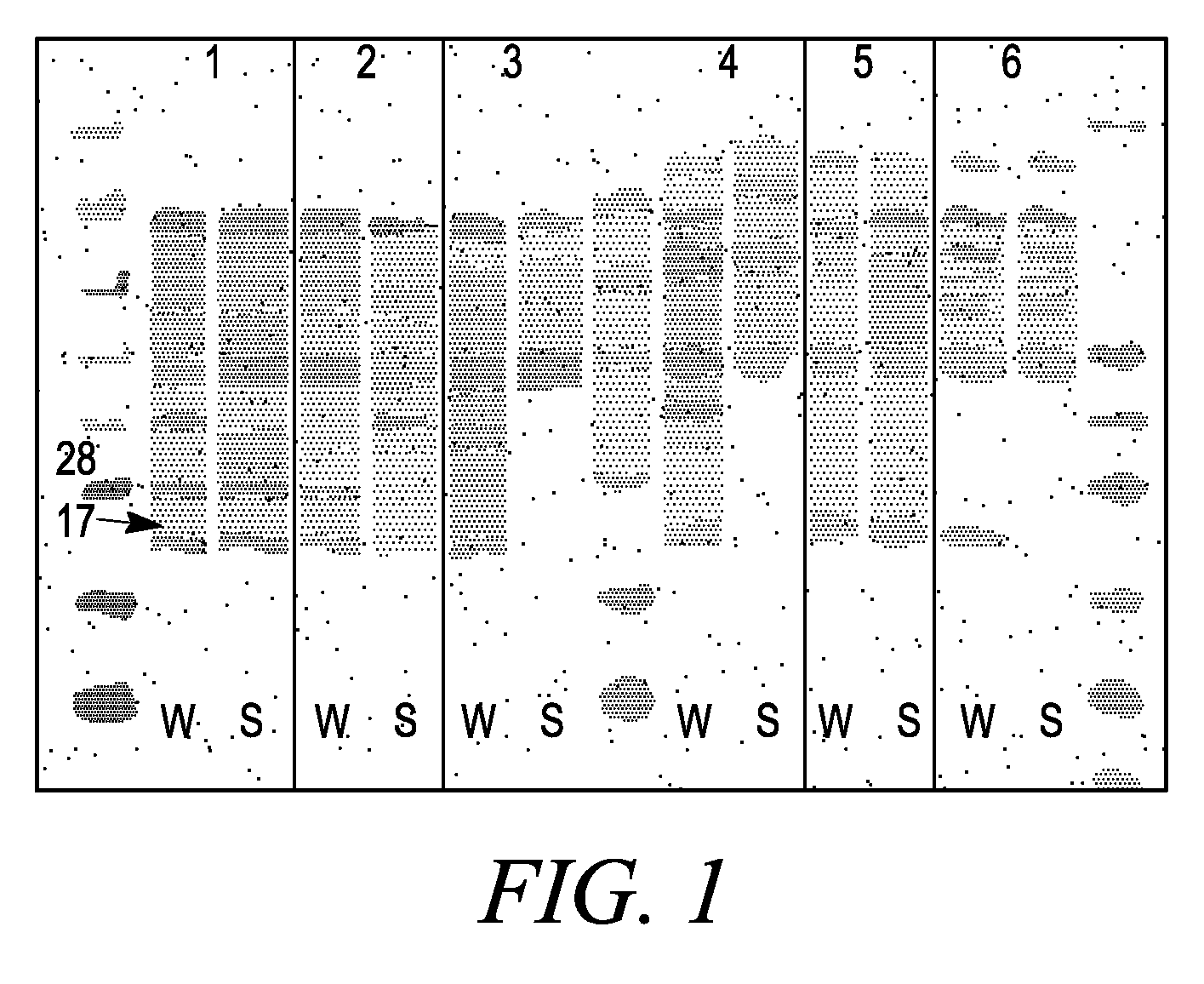
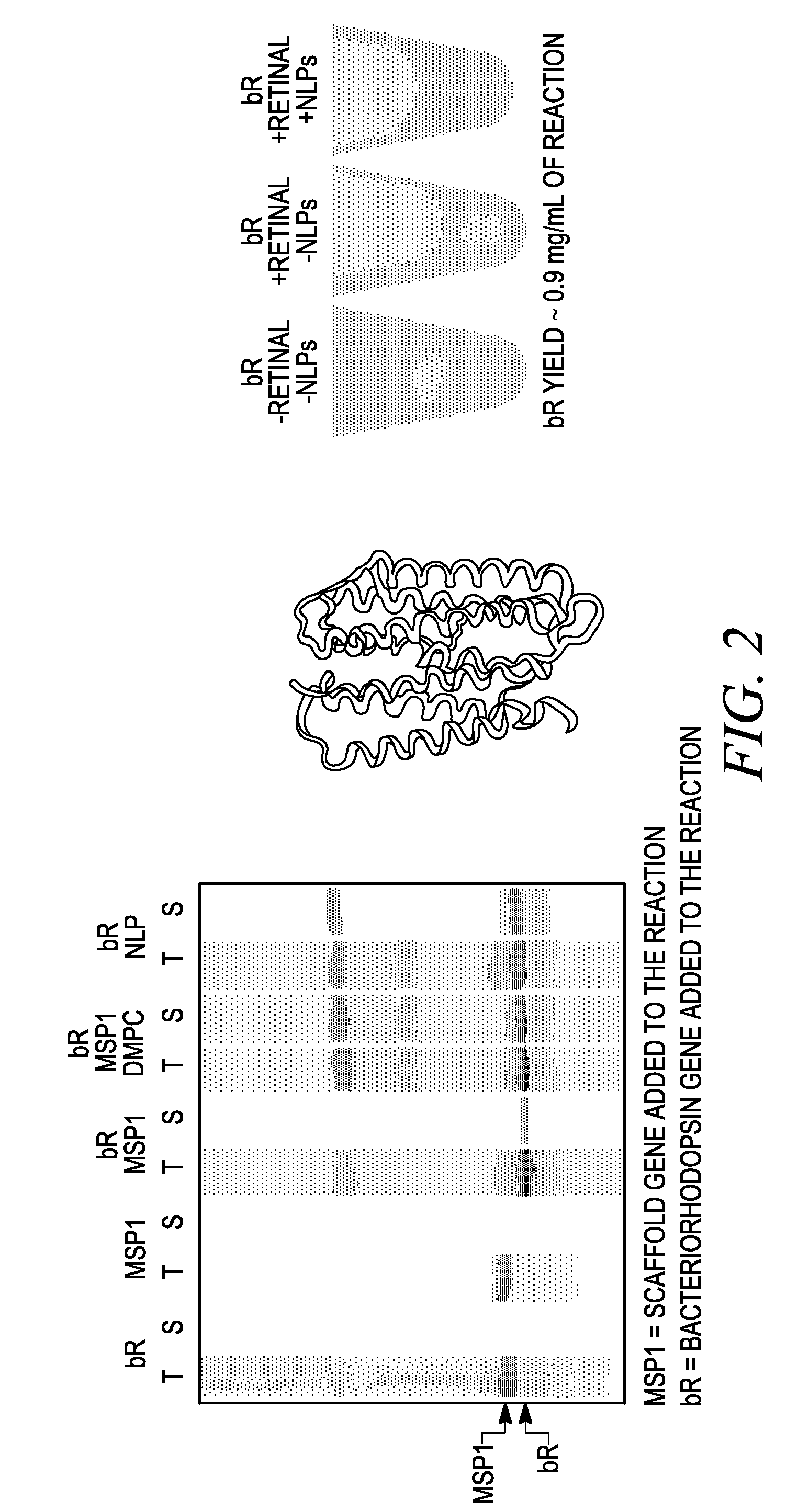
Systems and methods are provided for producing a protein of interest that is typically not amenable to expression in soluble form in in vitro expression systems. In some aspects, the invention provides methods of synthesizing proteins using in vitro protein synthesis systems that include a scaffold protein such as apolipoprotein or an amphipathic alpha helix containing (“AAHC”) protein, in which higher yields of soluble protein are produced than in the absence of the scaffold protein. The scaffold proteins may be provided in an in vitro protein synthesis system associated with lipid or not associated with lipid. The scaffold protein may be provided as a protein per se or may be encoded by a nucleic acid template and co-expressed with the protein of interest. The invention also provides compositions and kits for synthesis of proteins in soluble form, in which the compositions and kits include cell extracts for protein expression and isolation.
Owner:LIFE TECH CORP
Peptides and peptide mimetics to treat pathologies associated with eye disease
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Peptides and peptide simulacrums to treat pathologies characterized by an inflammatory response
InactiveCN101227918APeptide/protein ingredientsAgainst vector-borne diseasesAmphipathic helixActive agent
The present invention provides novel active agent (eg, peptides, small organic molecules, amino acid pairs, etc.) peptides that ameliorate one or more symptoms of atherosclerosis and / or other pathologies characterized by an inflammatory response. In certain embodiments, the peptide is similar to the G of apolipoprotein J * Amphipathic helix. The active agent is very stable and easy to administer by oral route.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
G-type peptides and other agents to ameliorate atherosclerosis and other pathologies
This invention provides novel peptides, and other agents, that ameliorate one or more symptoms of atherosclerosis and / or other pathologies characterized by an inflammatory response. In certain embodiment, the peptides resemble a G* amphipathic helix of apolipoprotein J. The peptides are highly stable and readily administered via an oral route.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA +1
High-density lipoprotein-like peptide-phospholipid scaffold (''HPPS'') nanoparticles
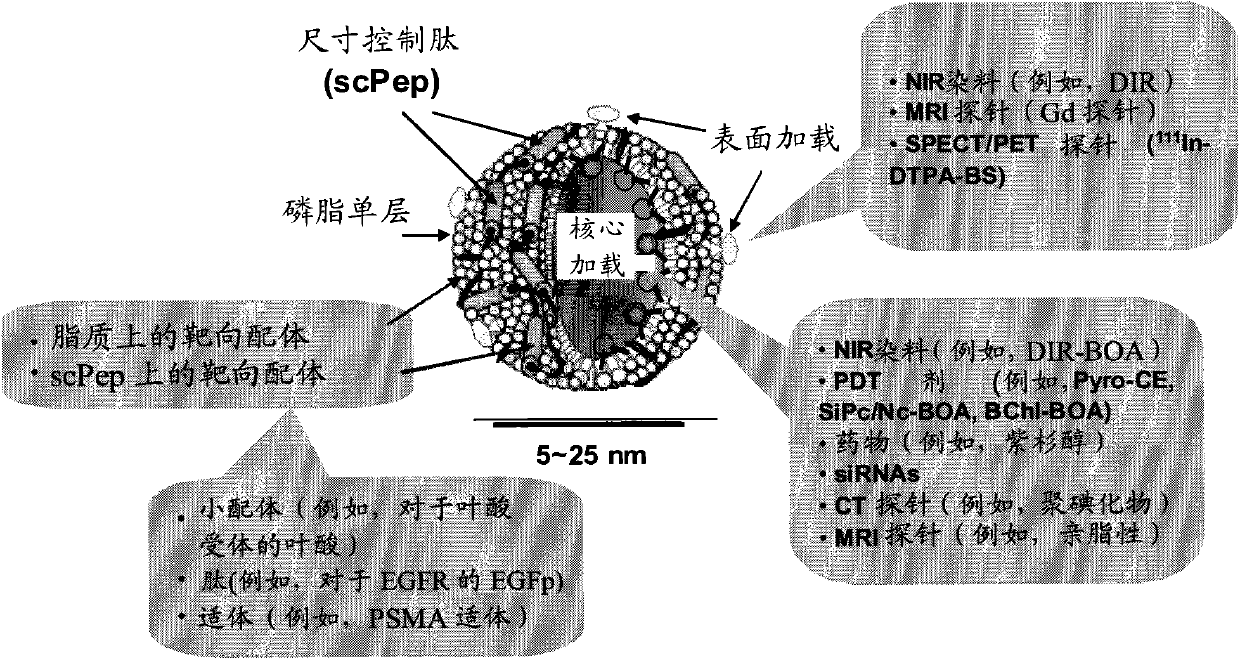
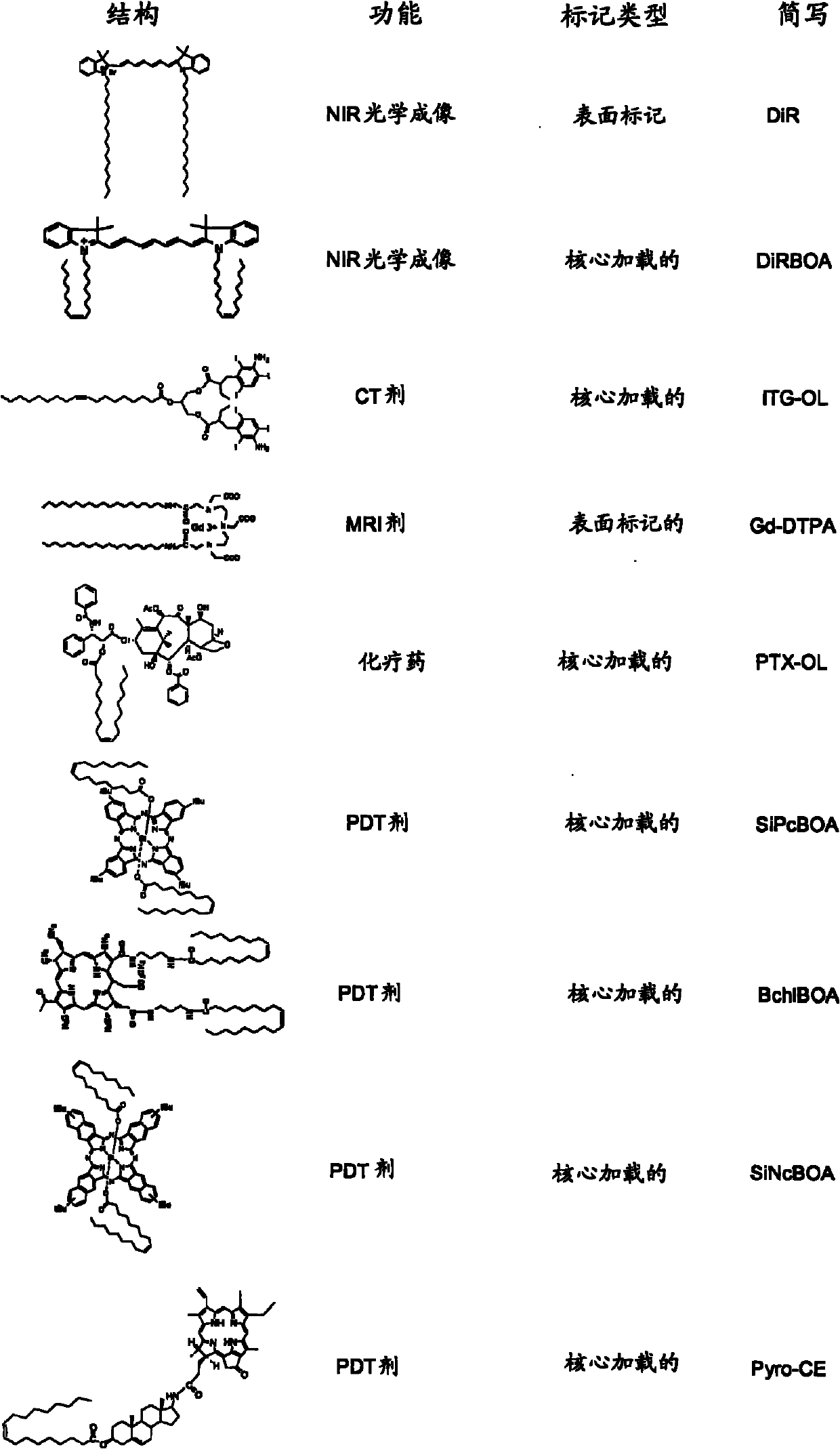
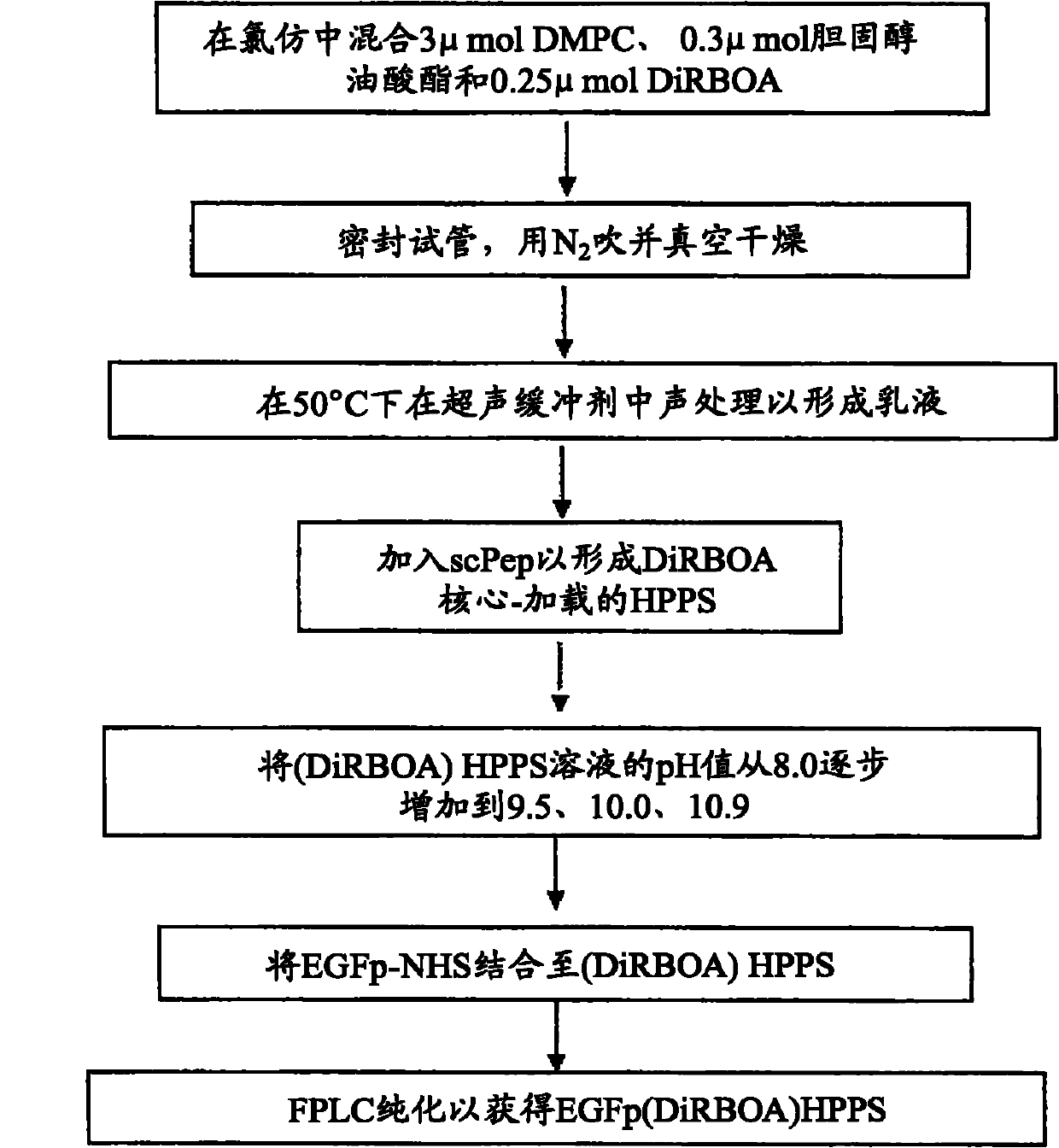
The present invention provides a non-naturally occurring High-Density Lipoprotein-like peptide-phospholipid scaffold (''HPPS'') nanoparticle. More particularly, the invention provides a non-naturally occurring peptide-lipid nanoscaffold comprising: (a) at least one phospholipid; (b) at least one unsaturated lipid, preferably an unsaturated sterol ester, further preferably an unsaturated cholesterol ester, further preferably cholsteryl oleate; and (c) at least one peptide, the peptide comprising an amino acid sequence capable of forming at least one amphipathic a- helix; wherein the components a), b) and c) associate to form the peptide-phospholipid nanoscaffold. In embodiments of the present invention, a cell surface receptor ligand is incorporated into the HPPS. In one embodiment, the cell surface receptor ligand is covalently bonded to the peptide scaffold of the HPPS nanoparticles. In other embodiments, a cell surface receptor ligand is coupled to a lipid anchor and is displayed on the surface of the HPPS nanoparticles by incorporation of the lipid anchor into the phospholipids monolayer of the HPPS nanoparticle. The present invention also provides pharmaceutical formulations comprising HPPS nanoparticles and methods of making the HPPS nanoparticles.
Owner:UNIV HEALTH NETWORK
Peptides and peptide mimetics to treat cancer
InactiveUS20100227825A1Symptoms improvedAntibacterial agentsSenses disorderAmphipathic helixActive agent
This invention provides novel active agents (e.g. peptides, small organic molecules, amino acid pairs, etc.) peptides that ameliorate one or more symptoms of atherosclerosis and / or other pathologies characterized by an inflammatory response. In certain embodiment, the peptides resemble a G* amphipathic helix of apolipoprotein J. The agents are highly stable and readily administered via an oral route.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
G-type peptides to ameliorate atherosclerosis
This invention provides novel peptides that ameliorate one or more symptoms of atherosclerosis and / or other pathologies characterized by an inflammatory response. In certain embodiment, the peptides resemble a G* amphipathic helix of apolipoprotein J. The peptides are highly stable and readily administered via an oral route.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
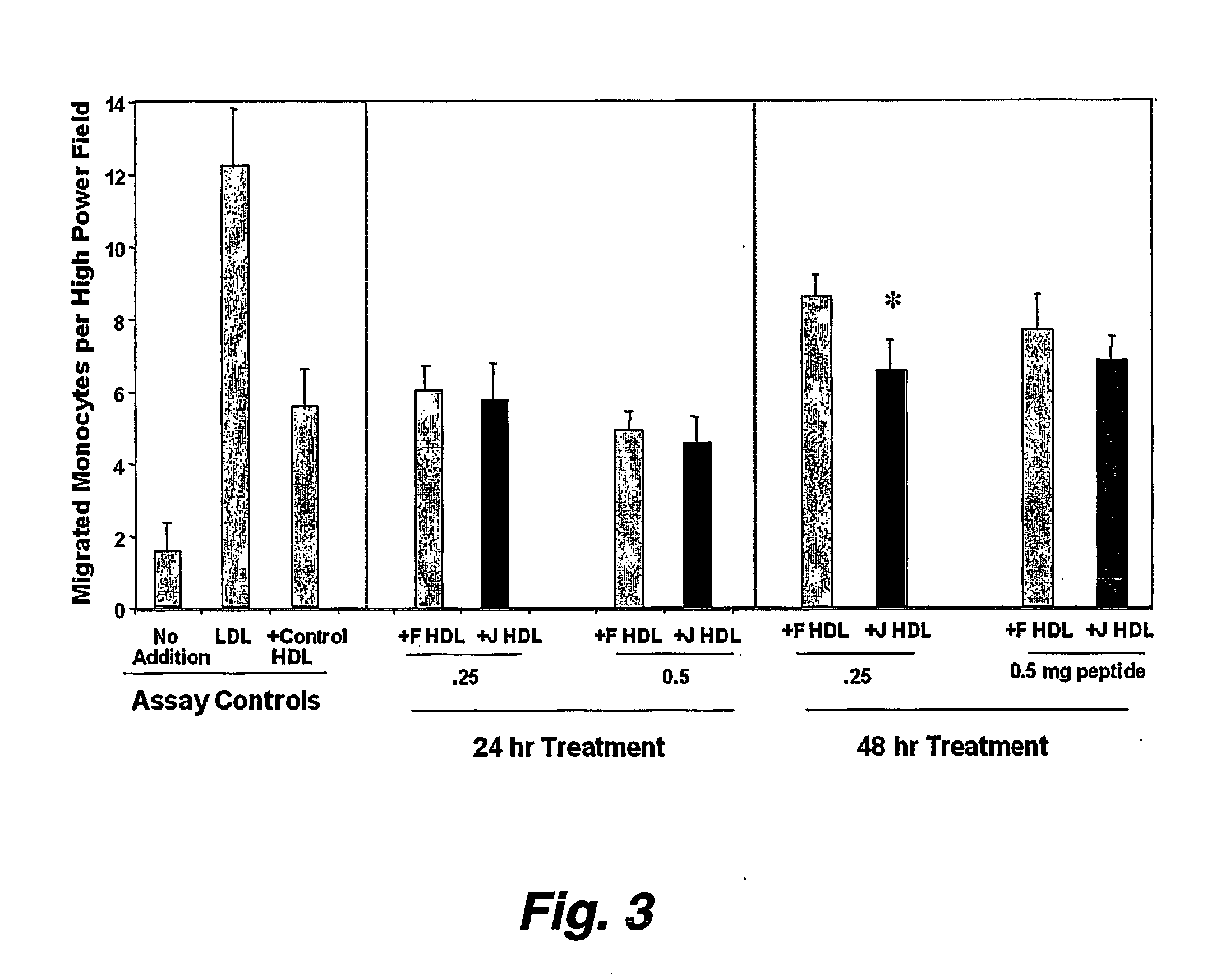
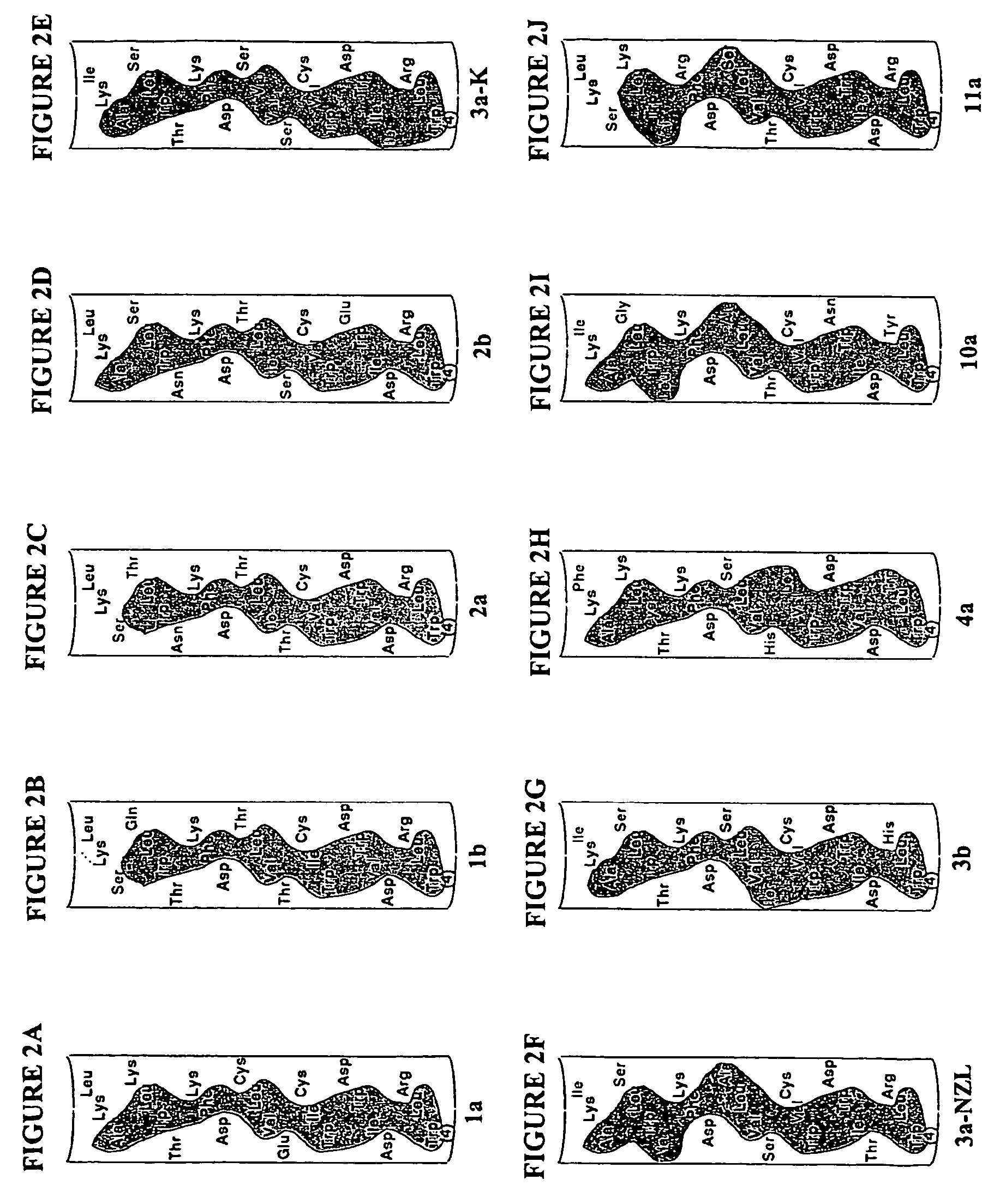
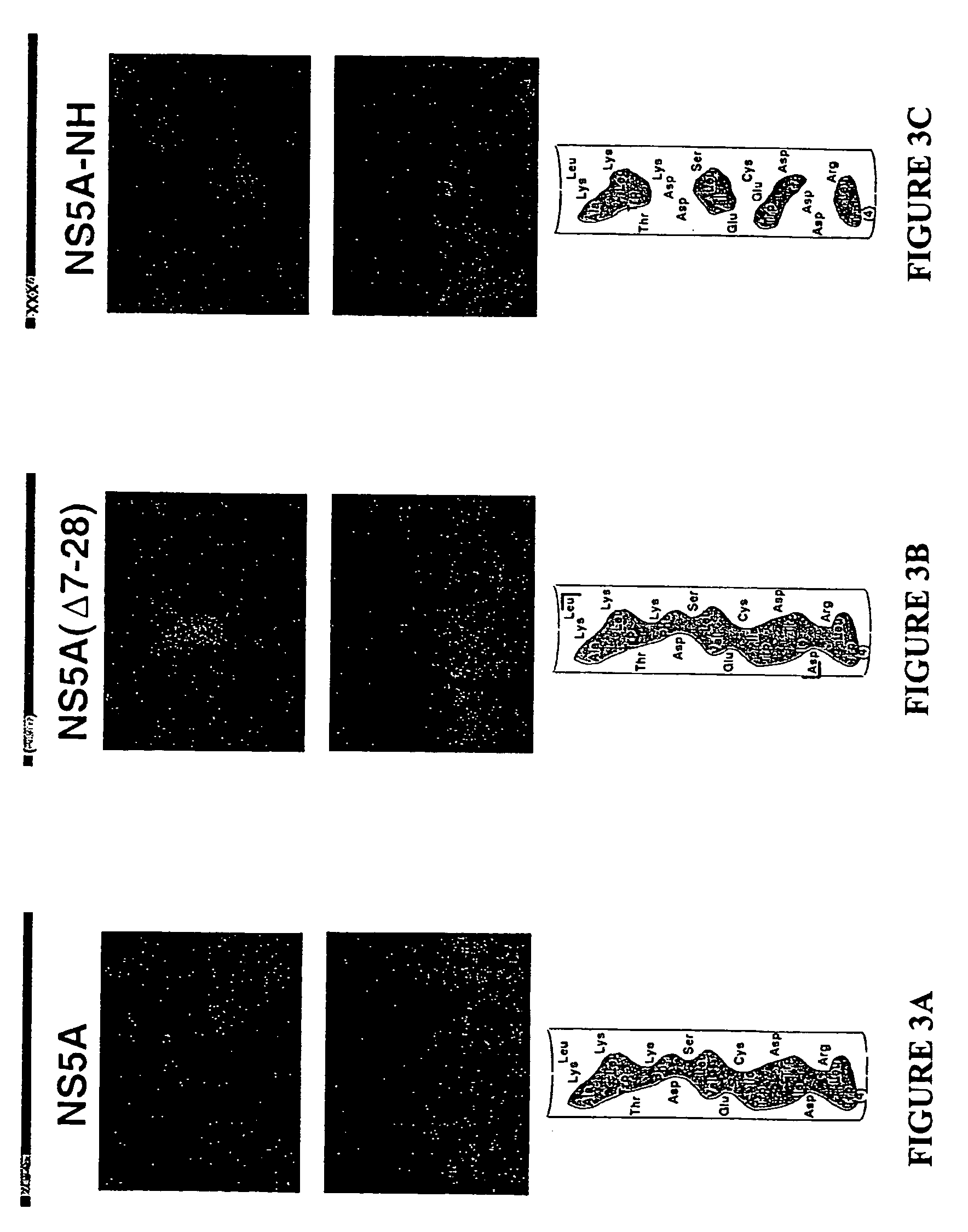
Agents for treatment of HCV and methods of use
InactiveUS7326536B2Interfere with abilityVirusesPeptide/protein ingredientsAmphipathic helixInfected cell
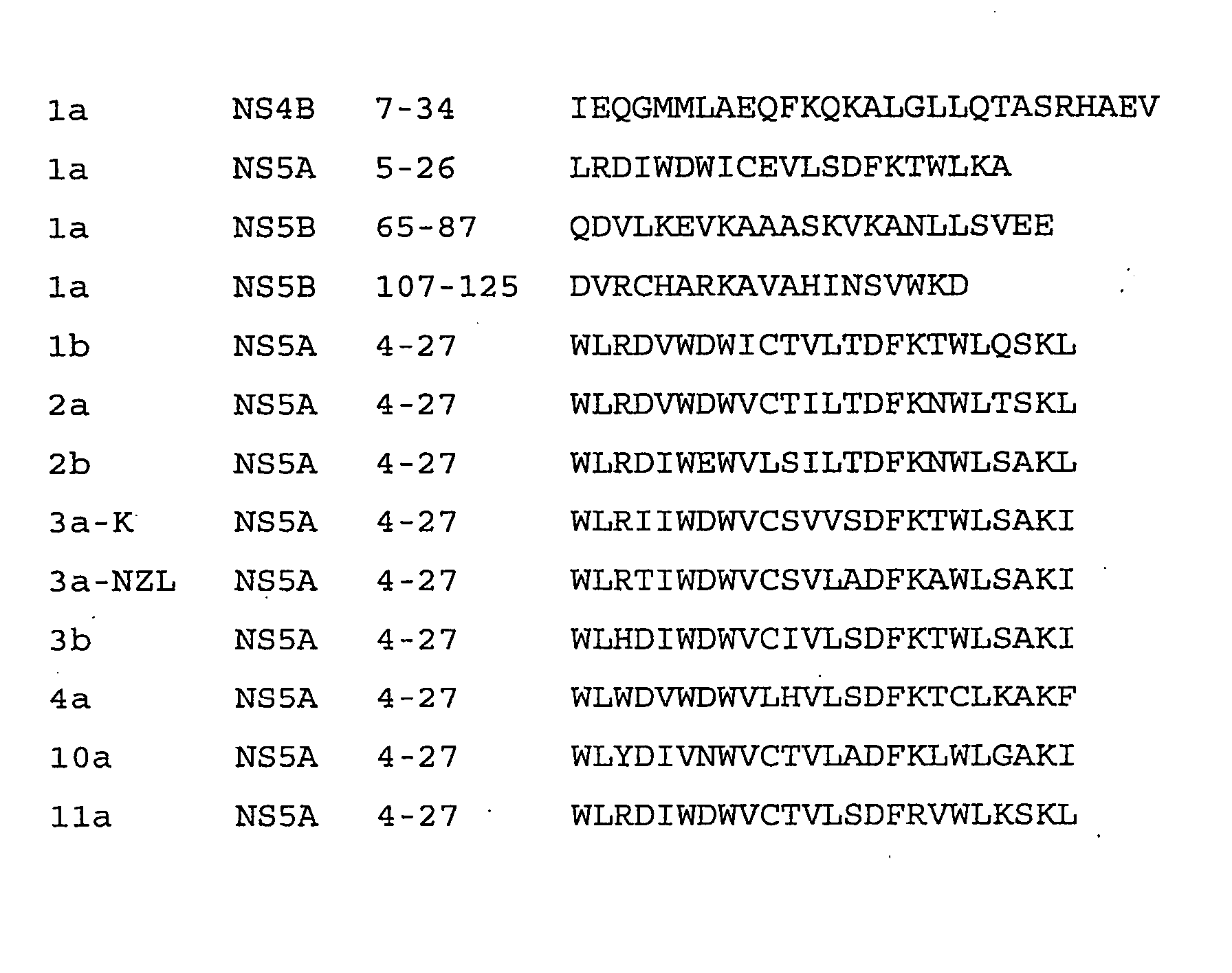
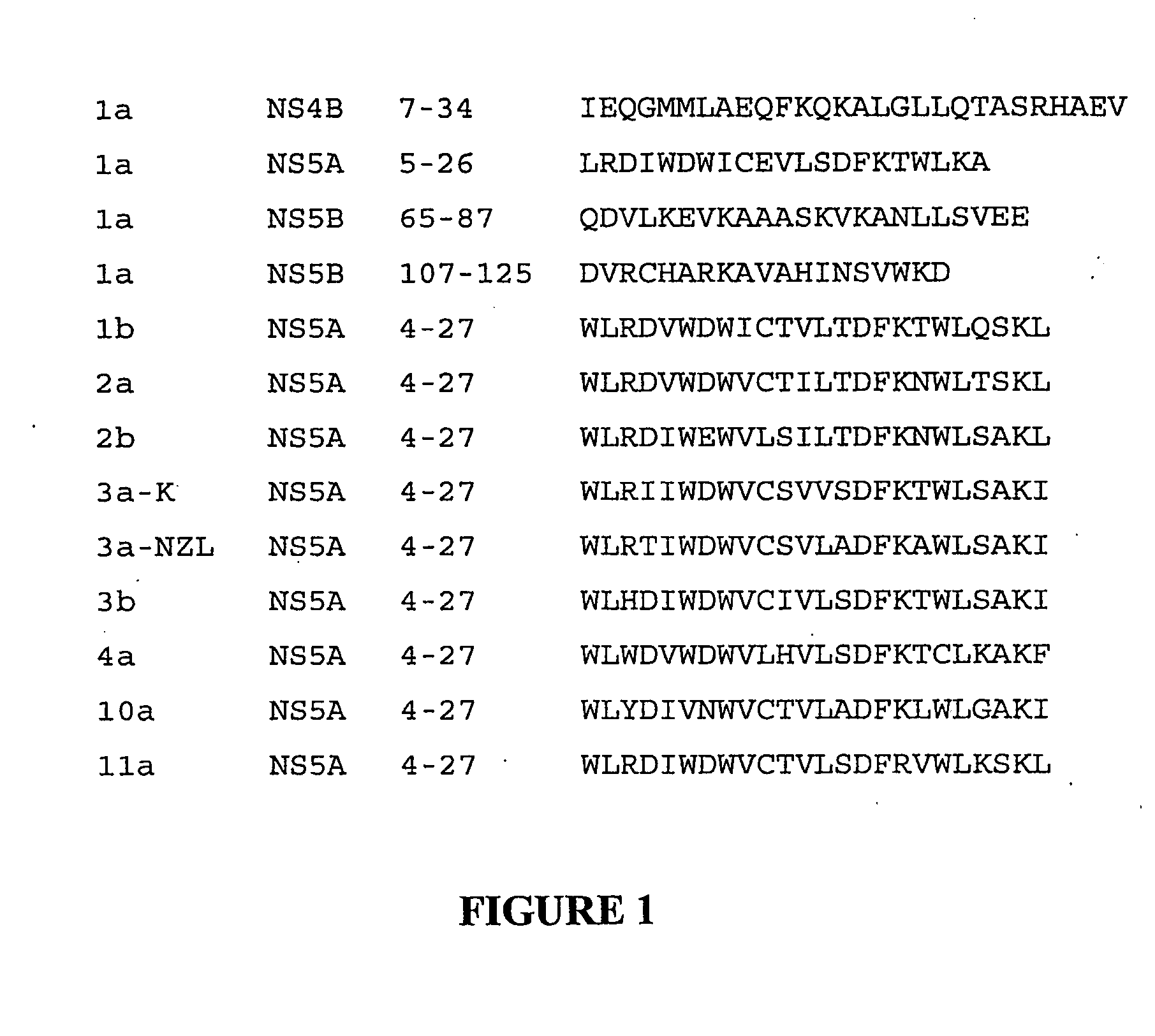
An amphipathic helix at the approximate N-terminus of Hepatitis C virus (HCV) nonstructural proteins mediates the association of these proteins with cytoplasmic membranes in infected cells. This association is essential for replication. Thus, assessing the ability of compounds or protocols to disrupt the association of such helices with cytoplasmic membranes permits identification of compounds and protocols which are useful in the treatment of HCV infection. Also useful in the invention are mimics, or function-disrupting ligands, of an amphipathic helix of the nonstructural proteins described herein and antibodies and fragments thereof immunoreactive with said helix.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV +1
Amphiphilic alpha helix self-assembling peptide and application thereof
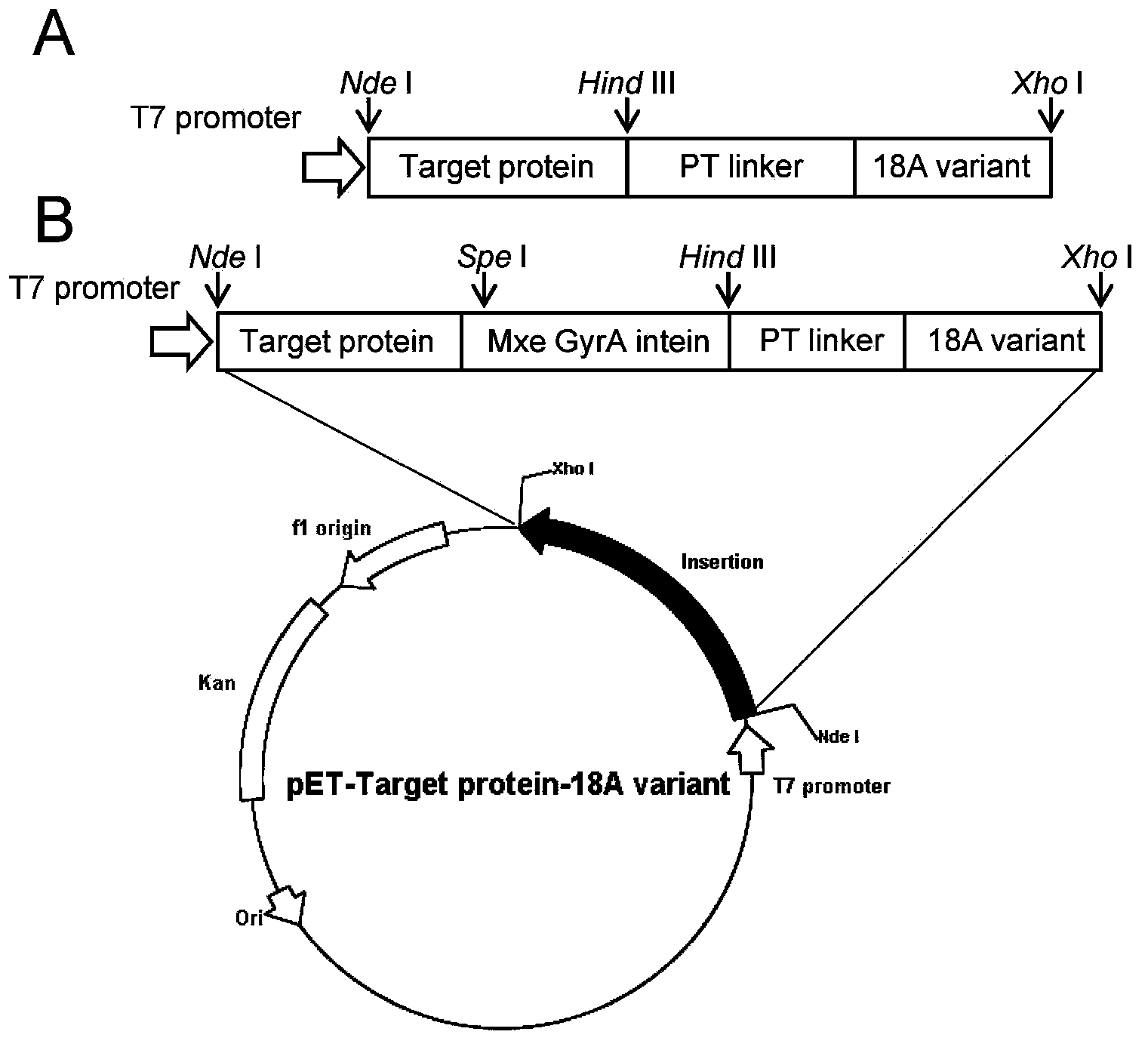
The invention relates to an amphiphilic alpha helix self-assembling peptide derived from SEQ ID NO:1 and an application of the amphiphilic alpha helix self-assembling peptide in protein production and purification. When the amphiphilic alpha helix self-assembling peptide and target protein are subjected to fusion expression, the amphiphilic alpha helix self-assembling peptide can induce the fusion protein to form active aggregate in cell, by comparing with polypeptide in SEQ ID NO: 1, the spatial distribution of the formed active aggregate in the cell is changed, a host cell growth state is improved, and fusion protein output is increased.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Peptides promoting lipid efflux via abca1 and activating a lipoprotein lipase
ActiveUS20110033518A1Promote lipid effluxImprove lipophilicityOrganic active ingredientsApolipeptidesDiseaseA lipoprotein
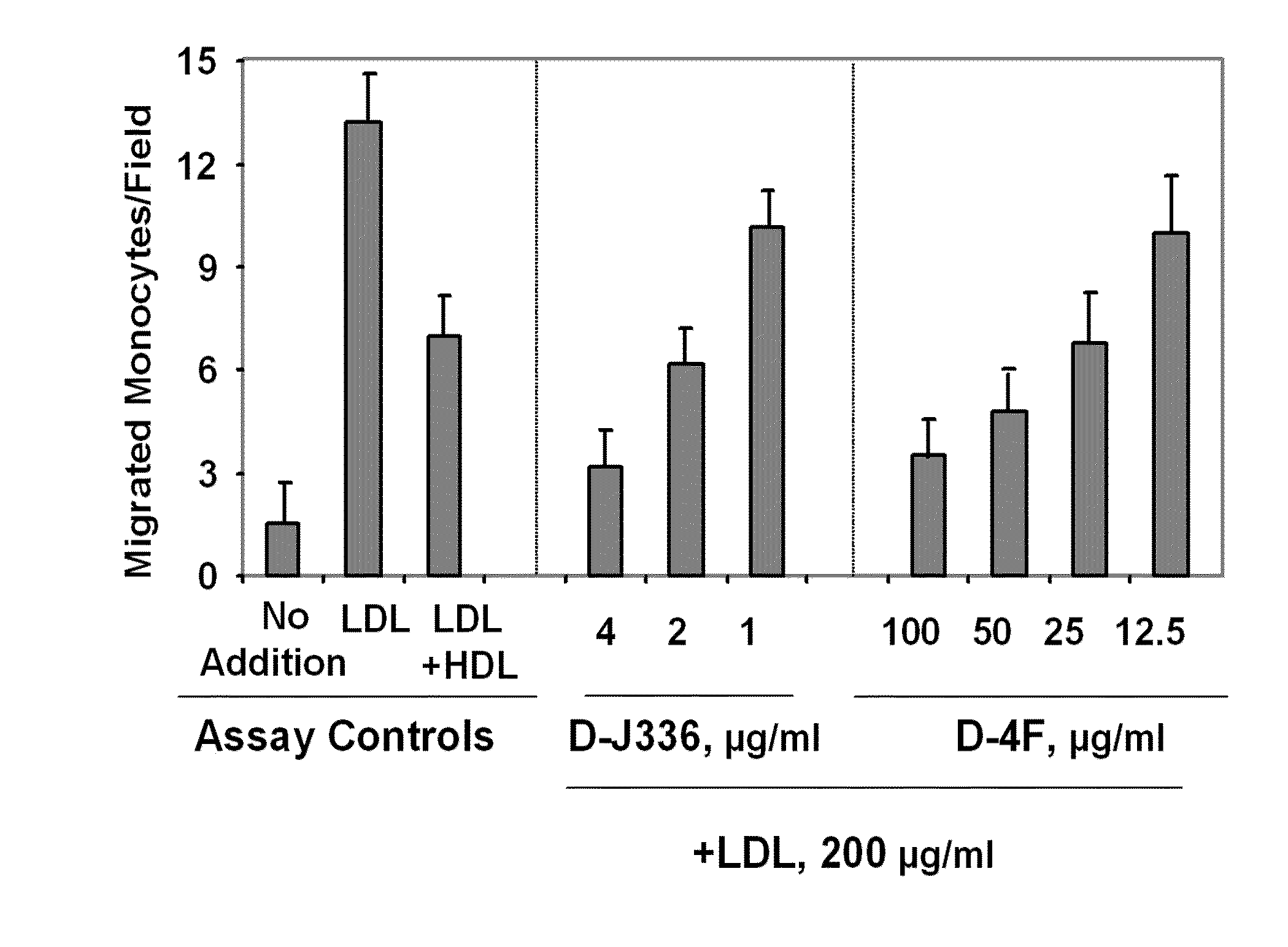
Disclosed herein are peptides and peptide analogs with multiple amphipathic α-helical domains that promote lipid efflux from cells via an ABCA1-dependent pathway, as well as peptides that activate lipoprotein lipase, and compositions comprising such peptides or combinations thereof. Also provided herein are methods of using multi-domain amphipathic α-helical peptides or peptide analogs to treat or inhibit dyslipidemic disorders. Methods for identifying non-cytotoxic peptides that promote ABCA1-dependent lipid efflux from cells and activate lipoprotein lipase within cells are also disclosed herein.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
Synthetic apolipoprotein e mimicking polypeptides and methods of use
InactiveUS20120245101A1Antibacterial agentsSenses disorderVery low-density lipoproteinAmphipathic helix
The present invention provides novel synthetic apolipoprotein E (ApoE)-mimicking peptides wherein the receptor binding domain of apolipoprotein E is covalently linked to 18A, the well characterized lipid-associating model class A amphipathic helical peptide, or a modified version thereof. Such peptides enhance low density lipoprotein (LDL) and very low density lipoprotein (VLDL) binding to and degradation by fibroblast or HepG2 cells. Also provided are possible applications of the synthetic peptides in lowering human plasma LDL / VLDL cholesterol levels, thus inhibiting atherosclerosis. The present invention also relates to synthetic peptides that can improve HDL function and / or exert anti-inflammatory properties.
Owner:UAB RES FOUND
Agents for treatment of HCV and methods of use
InactiveUS20080125367A1Interfere with abilityCompound screeningBiocideInfected cellAmphipathic helix
An amphipathic helix at the approximate N-terminus of Hepatitis C virus (HCV) nonstructural proteins mediates the association of these proteins with cytoplasmic membranes in infected cells. This association is essential for replication. Thus, assessing the ability of compounds or protocols to disrupt the association of such helices with cytoplasmic membranes permits identification of compounds and protocols which are useful in the treatment of HCV infection. Also useful in the invention are mimics, or function-disrupting ligands, of an amphipathic helix of the nonstructural proteins described herein and antibodies and fragments thereof immunoreactive with said helix.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV +1
Screening for Inhibitors of HCV Amphipathic Helix (AH) Function
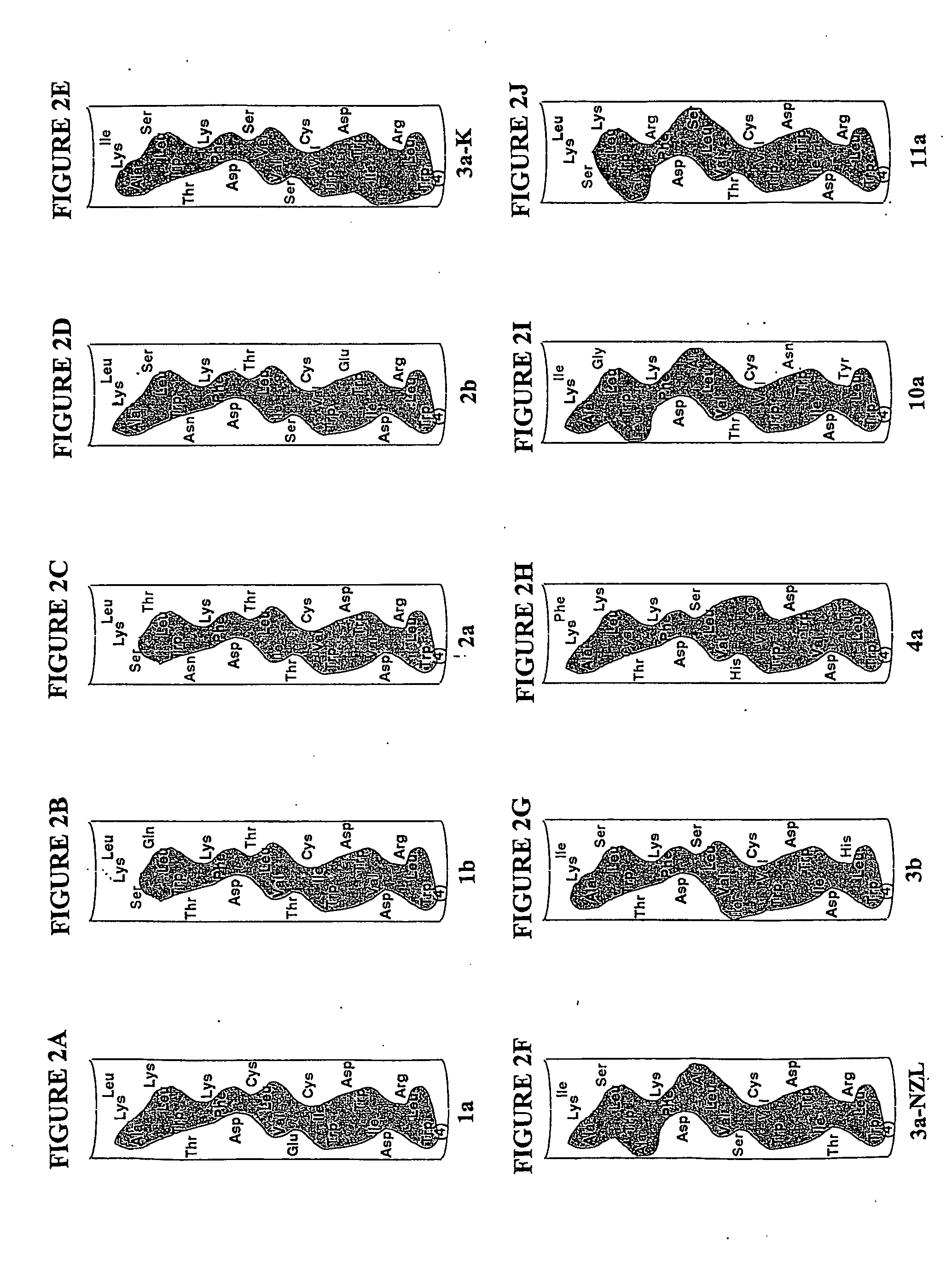
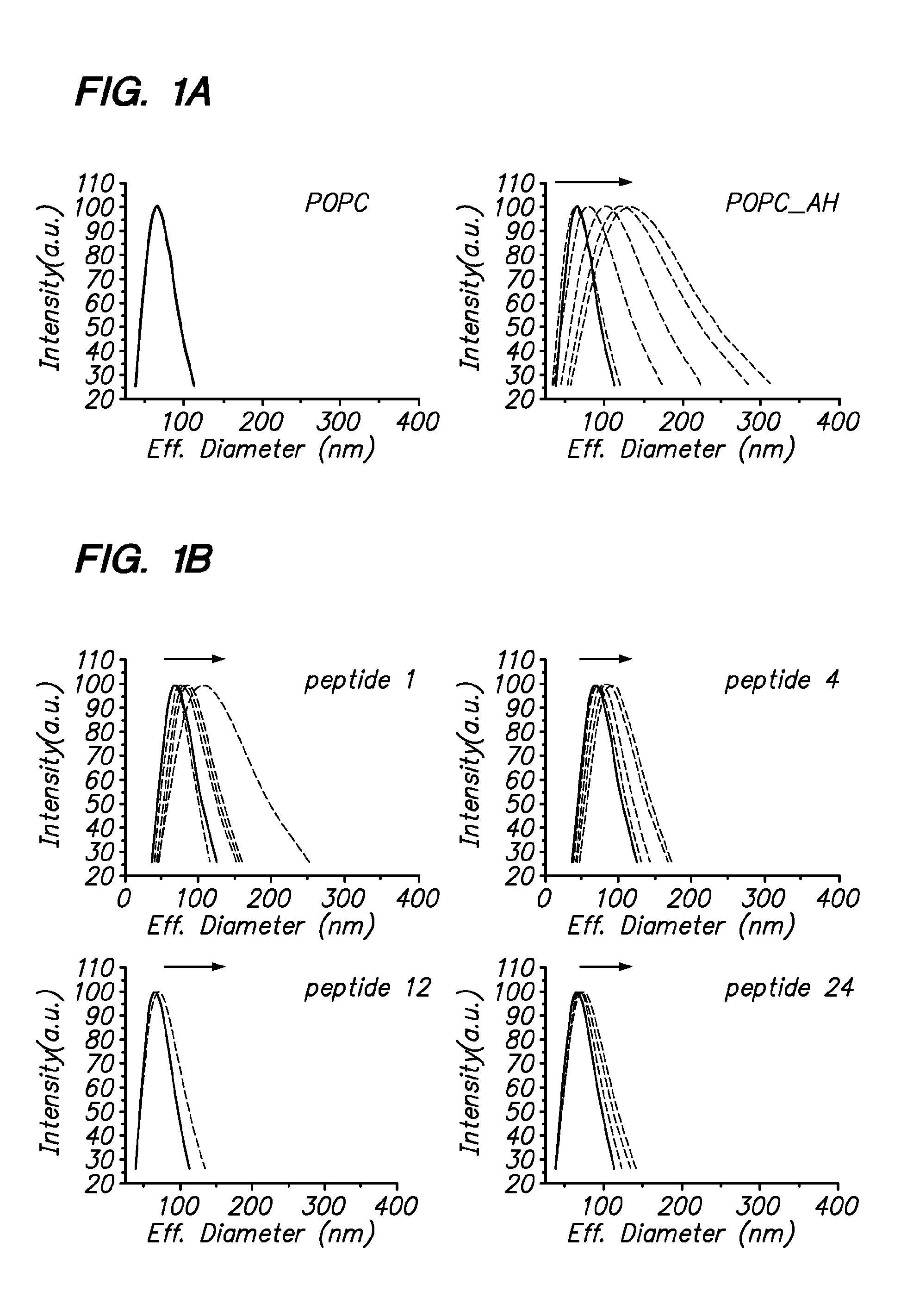
Screening methods are provided for identifying pharmacologic inhibitors of HCV amphipathic helix (AH) function, which inhibitors are useful in the prevention and treatment of HCV infection. Also provided are compounds useful in the inhibition of viral replication. The methods of the invention are based on the unexpected discovery that the presence of an AH, e.g. an AH of an HCV polypeptide, causes an increase in the apparent diameter of the vesicles. The methods of the invention provide for addition of AH peptides to lipid vesicles, for example in a high-throughput format; which addition may be performed in the absence or presence of a candidate pharmacologic agent. The change in apparent vesicle size is measured, and compared to control samples. An increase in vesicle size or aggregation is indicative of AH function being present; and a lack of increase is indicative that the AH function is absent or has been inhibited by a test agent.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Multi-domain amphipathic helical peptides and methods of their use
Disclosed herein are peptides or peptide analogs with multiple amphipathic α-helical domains that promote lipid efflux from cells via an ABCA1-dependent pathway. Also provided herein are methods of using multi-domain amphipathic α-helical peptides or peptide analogs to treat or inhibit dyslipidemic disorders. Methods for identifying non-cytotoxic peptides that promote ABCA1-dependent lipid efflux from cells are also disclosed herein.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
Multi-domain amphipathic helical peptides and methods of their use
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
Cysteine-containing peptides having antioxidant properties
InactiveUS20060286632A1Inhibit specific interactionReduced glutathioneApolipeptidesPeptide/protein ingredientsAmphipathic helixCysteine thiolate
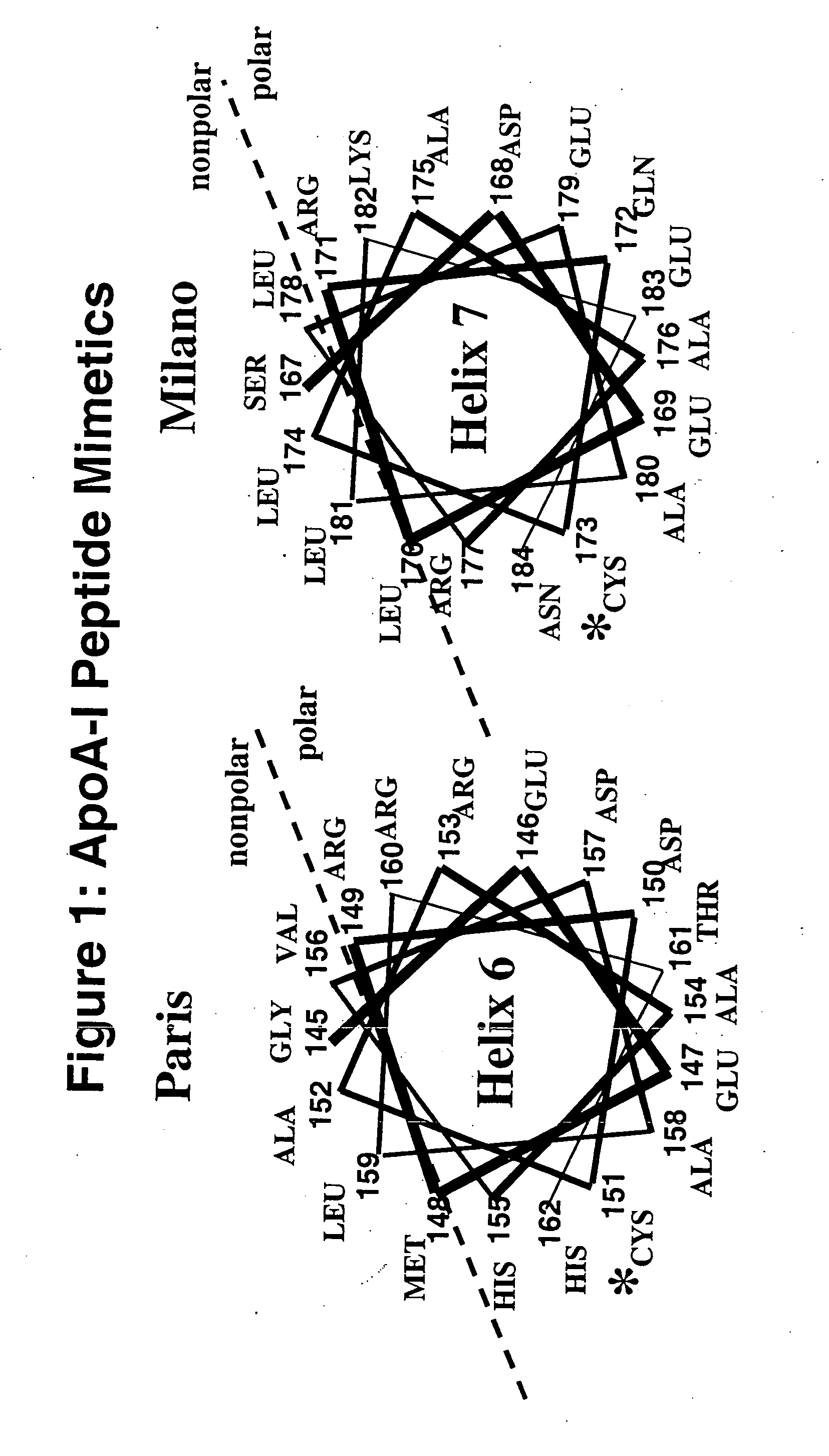
Cysteine containing amphipathic alpha helices of the exchangeable apolipoproteins, as exemplified by apolipoprotein (apo) A-IMilano (R173C) and apoA-IParis, (R151C) were found to exhibit potent antioxidant activity on phospholipid surfaces. The addition of a free thiol, at the hydrophobic / hydrophilic interface of an amphipathic alpha helix of synthetic peptides that mimic HDL-related proteins, imparts a unique antioxidant activity to these peptides which inhibits lipid peroxidation and protects phospholipids from water-soluble free radical initiators. These peptides can be used as therapeutic agents to combat cardiovascular disease, ischemia, bone disease and other inflammatory related diseases.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com