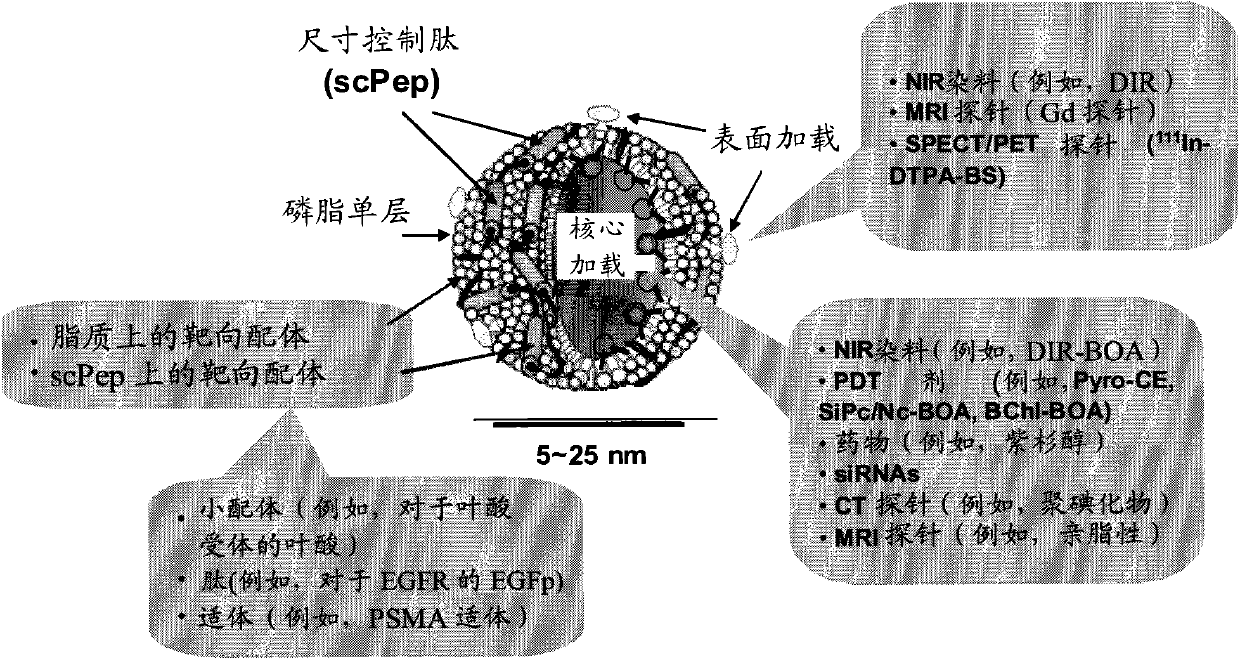
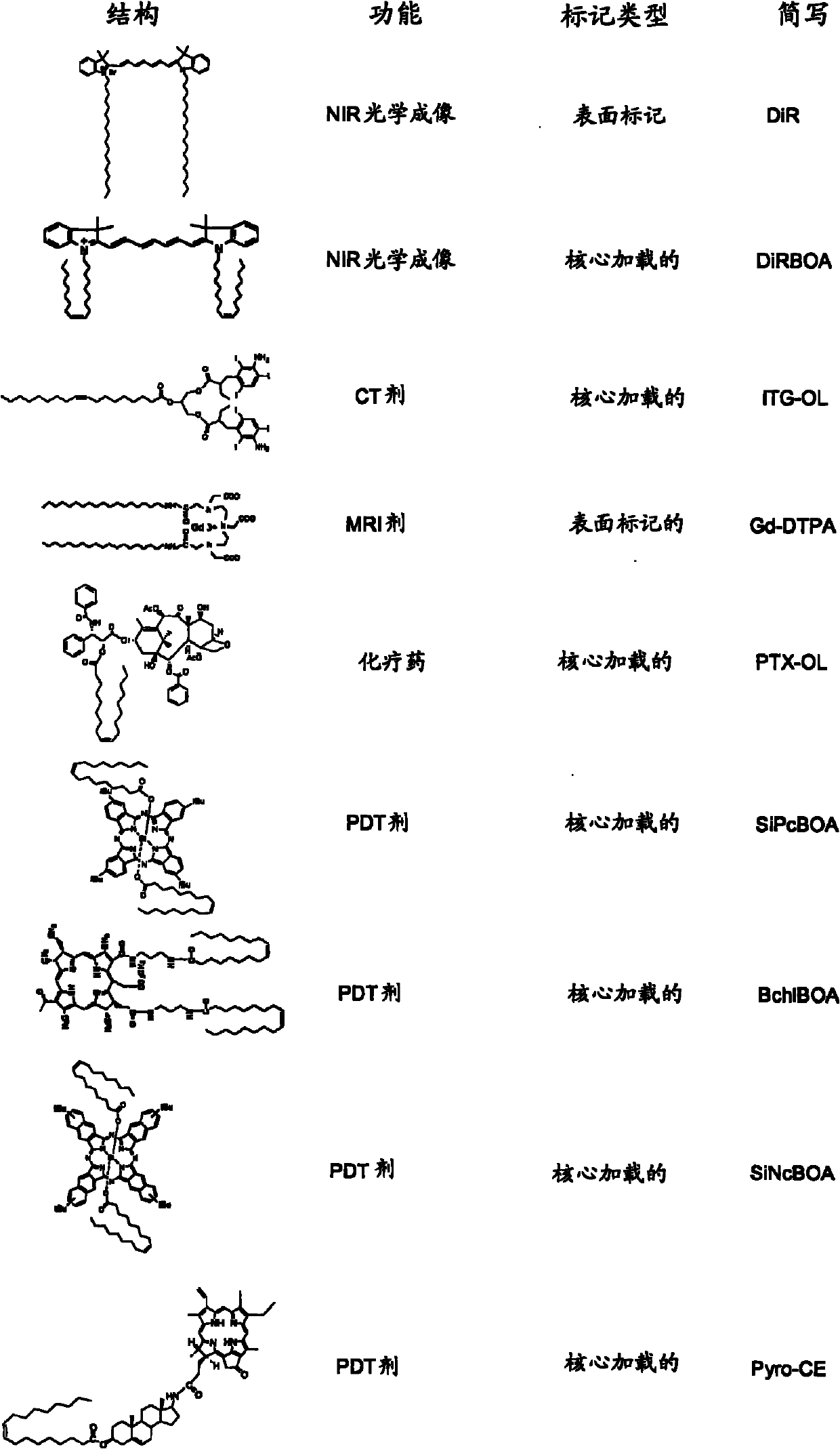
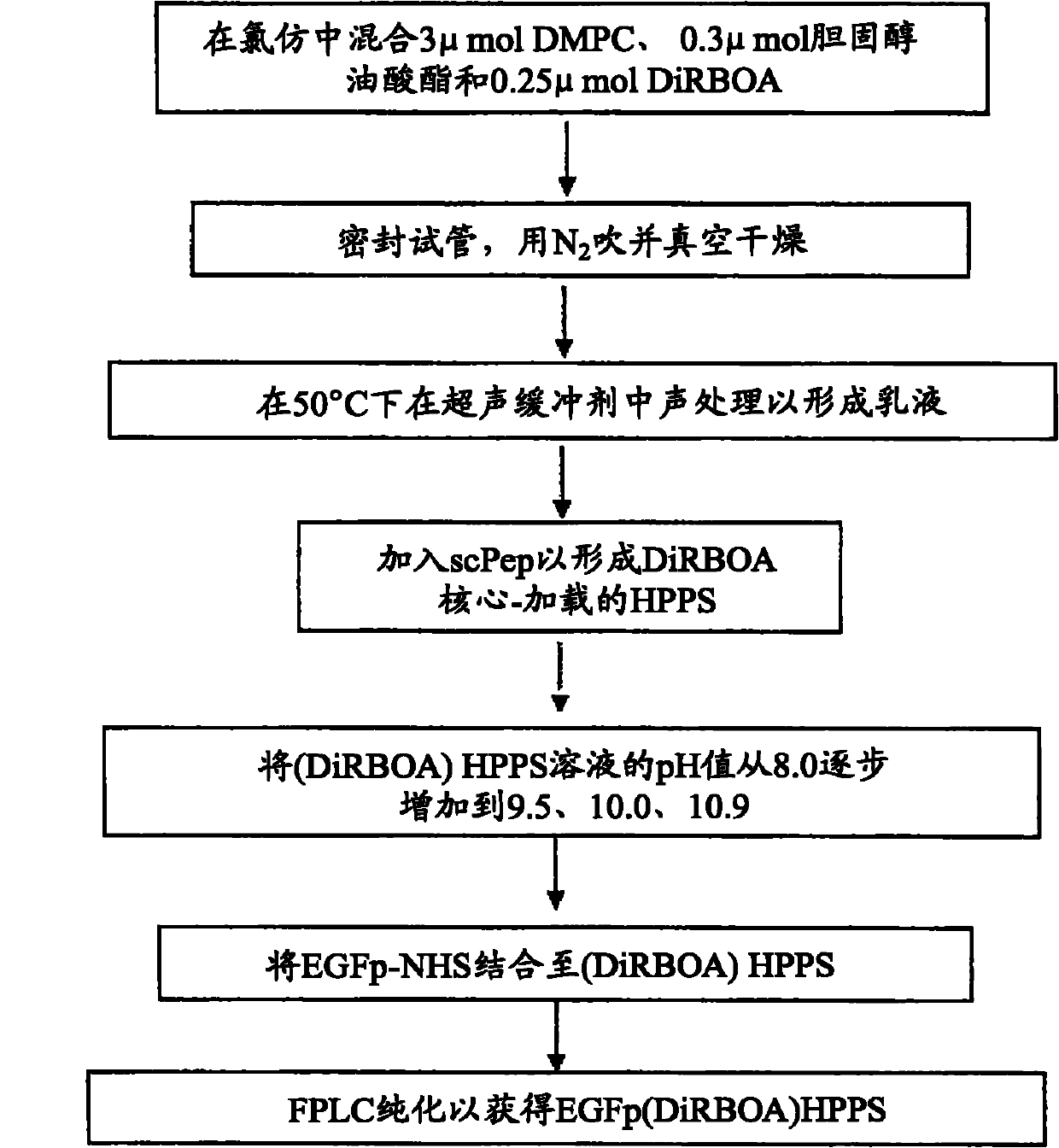
High-density lipoprotein-like peptide-phospholipid scaffold (''HPPS'') nanoparticles
A technology of lipid nanoparticles and phospholipids, applied in the fields of nano-drugs, specific peptides, general/multifunctional contrast agents, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0203] Preparation of starting materials
[0204] 1) Size control peptide (scPep)
[0205] Utilizing commercially available N-α-Fmoc-protected amino acids, Sieber amide resin as a solid support, and using HBTU / HOBt as a carboxyl activator, by utilizing the Fmoc solid-phase peptide synthesis (SPPS) protocol (Novabiochem, Resourceforpeptidesynthesis: http: / / www.emdbiosciences.com / g.asp?f=NBC / peptideres.htm), synthesize some short peptide analogs of amphipathic helices on the peptide synthesizer PS-3 (Protein Technologies, Inc.), such as Ac- DWLKAFYDKVAEKLKEAF ("2F"), AC-DWFKAFYDKVAEKFKEAF ("4F", also referred to herein as "+4F")), and Ac-FAEKFKEAVKDYFAKFWD (-4F). After synthesizing the protected sequence, the N-terminal Fmoc of the peptide-resin was removed with 20% piperidine in N,N-dimethylformamide (DMF) to expose the terminal amine. NH was subsequently capped with 10% pyridine in THF with 10% acetic anhydride 2 -peptide-resin. The Ac-peptide-resin was further treated wi...
Embodiment 2
[0214] Method for the preparation of HPPS nanoparticles
[0215] HPPS is a macromolecular complex that is completely soluble in an aqueous buffer, such as tris saline (10 mM tris-HCl, 150 mM NaCl, 1 mM EDTA, pH 7.5). Tris saline buffer was used as solvent for HPPS in all experiments outlined below.
[0216] 1) HPPS: 3 μmol of DMPC and 0.3 μmol of cholesterol oleate were dissolved in 0.5 mL of chloroform in a test tube. use N 2 The solvent was evaporated off slowly and further dried by high vacuum. Then 1 mL of buffer (10 mM Tris-HCl, pH 8.0, containing 0.1 M KCl, 1 mM EDTA) was added to the dry tube and sonicated at 50° C. for 1 hour to form an emulsion. ScPep 0.8 μmol was added to the solution to form HPPS particles. The particles were then purified by fast protein liquid chromatography (FPLC). The FPLC method will be described below.
[0217] 2) DiR-BOA core-loaded HPPS ((DiR-BOA)HPPS): 3 μmol of DMPC, 0.3 μmol of cholesterol oleate and 0.25 μmol of DiR-BOA were dissol...
Embodiment 3
[0225] Characterization of HPPS nanoparticles prepared by 4F
[0226] 1. Particle and payload stability: Particle and payload stability is important for all nanoparticle-based drug delivery systems. Conventional lipid-based nanocarriers (eg, liposomes and lipid emulsions) cannot maintain stability at ultra-small sizes (<25 nm). The HPPS nanocarrier system of the present invention exhibits remarkable stability. As shown in Table 4, HPPS maintained their size and DiR-BOA payload over a one-month period, as determined by dynamic light scattering (see below) and spectrofluorometry. After storage at 4 °C, no payload leakage was observed. It may be noted that the percentages in the table below indicate the proportion of the population of nanoparticles with the indicated size.
[0227] Table 4. Granule Stability
[0228]
[0229] Note: The table shows the average size, percent composition and DiR-BOA fluorescence intensity
[0230] Stability of all three dosage forms (formula...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com