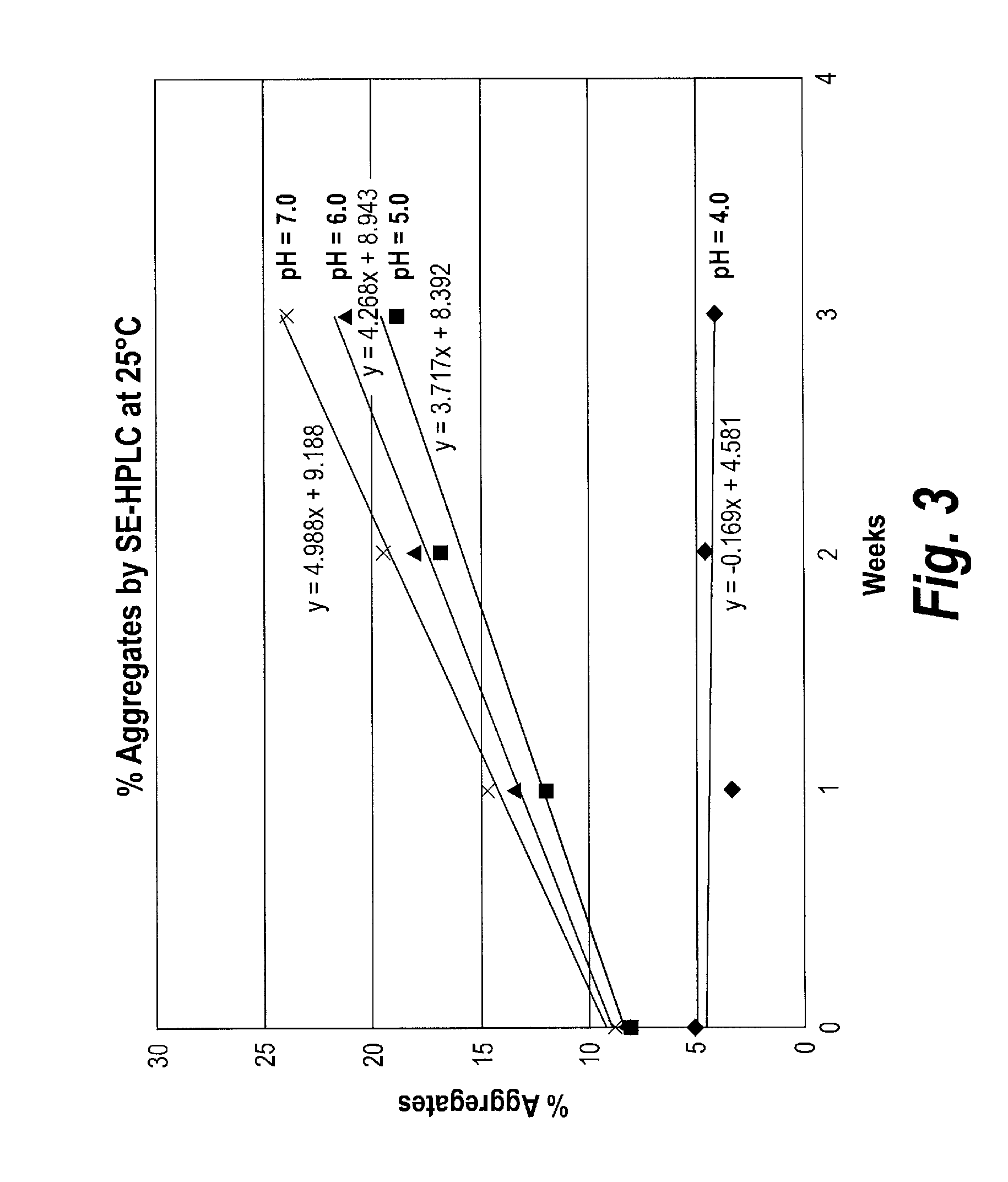
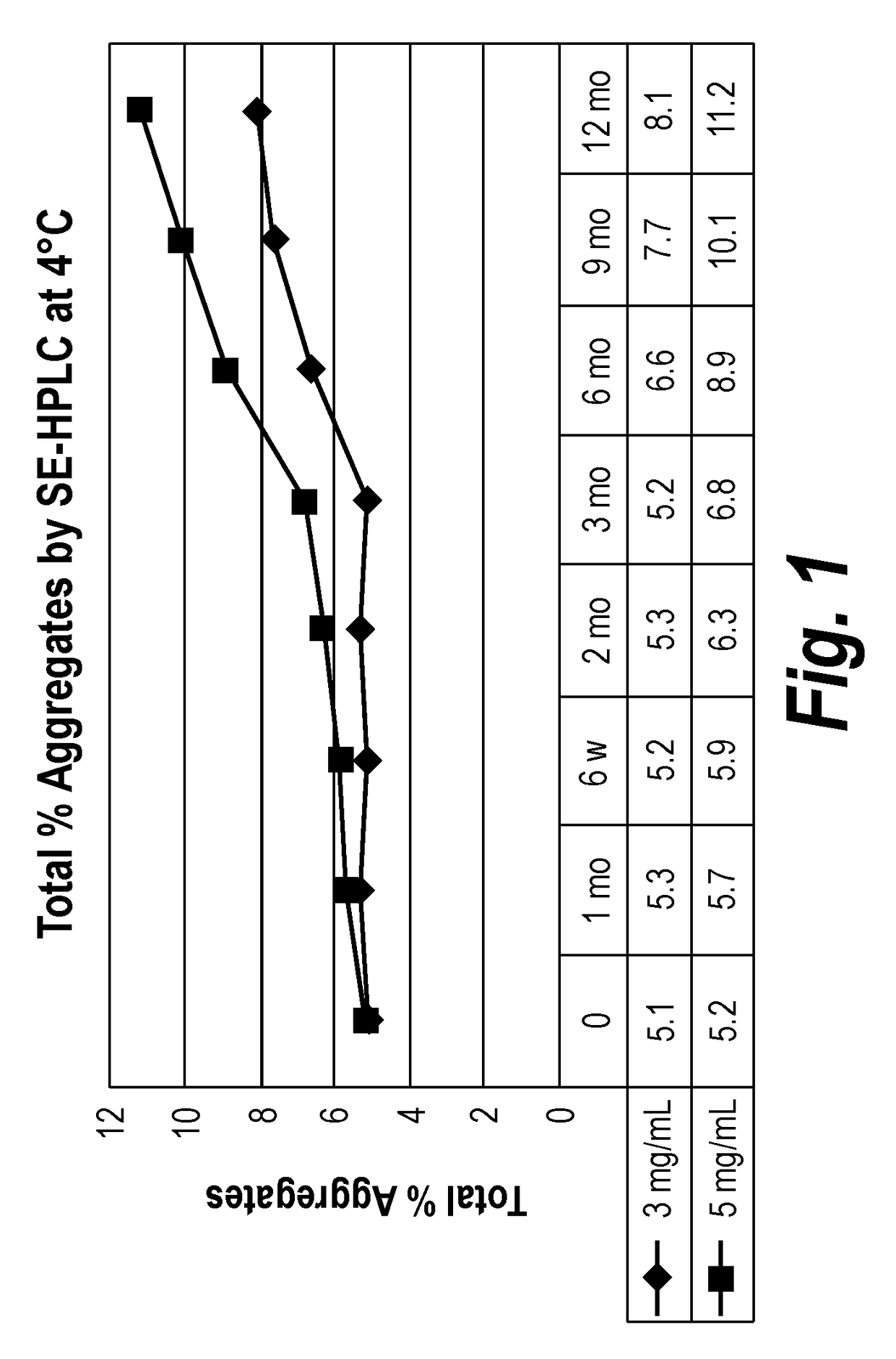
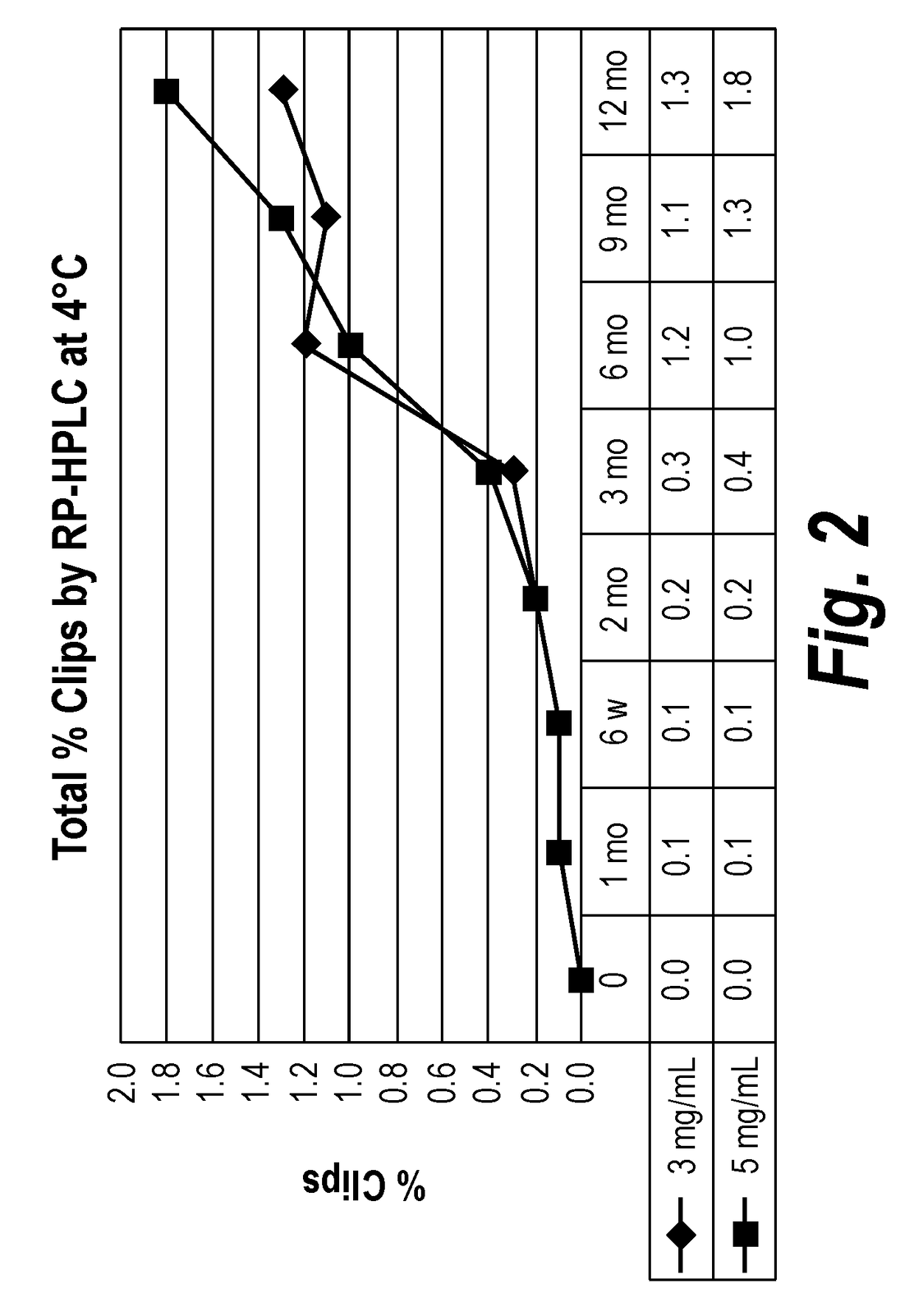
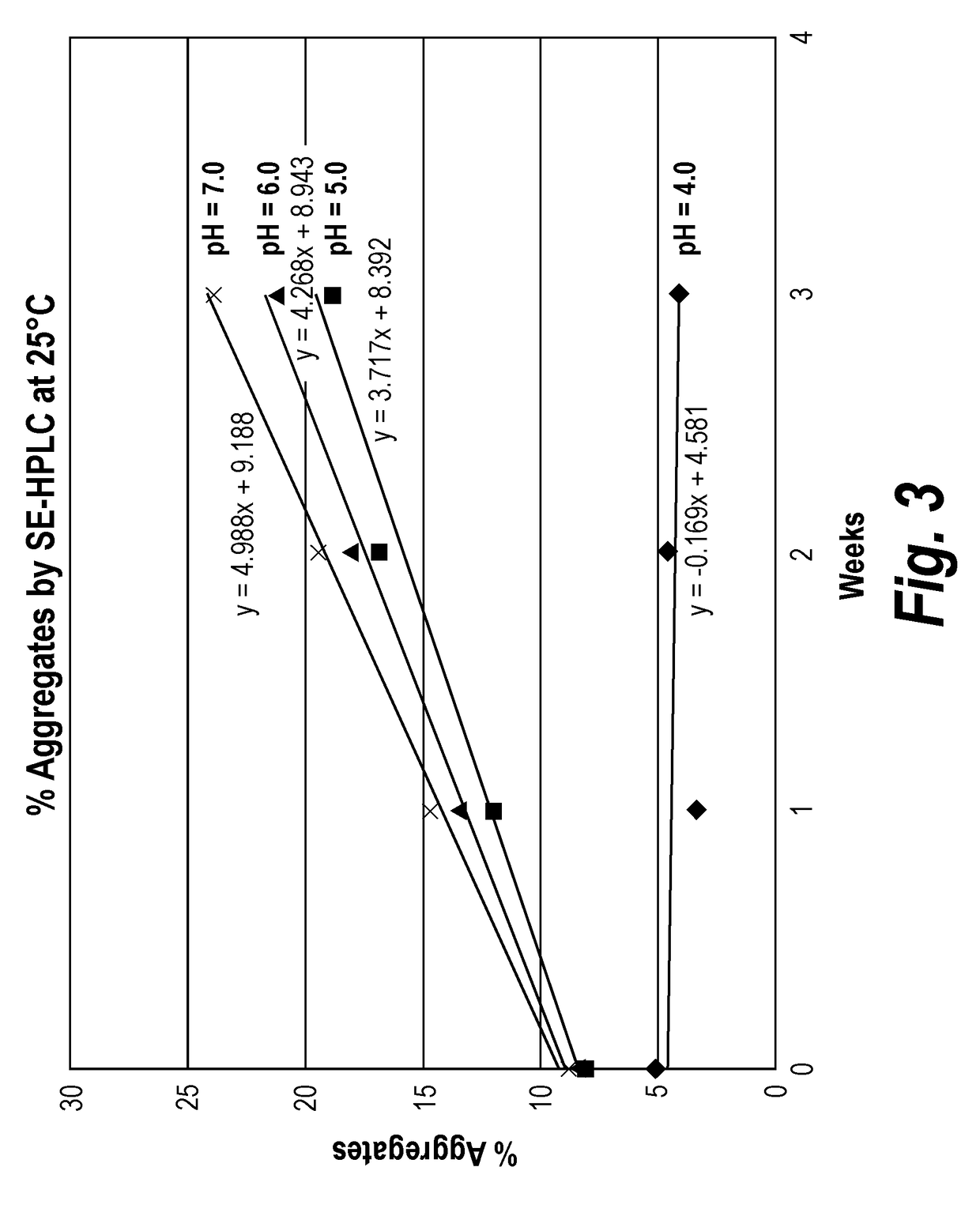
Patents
Literature
124 results about "Scaffold protein" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
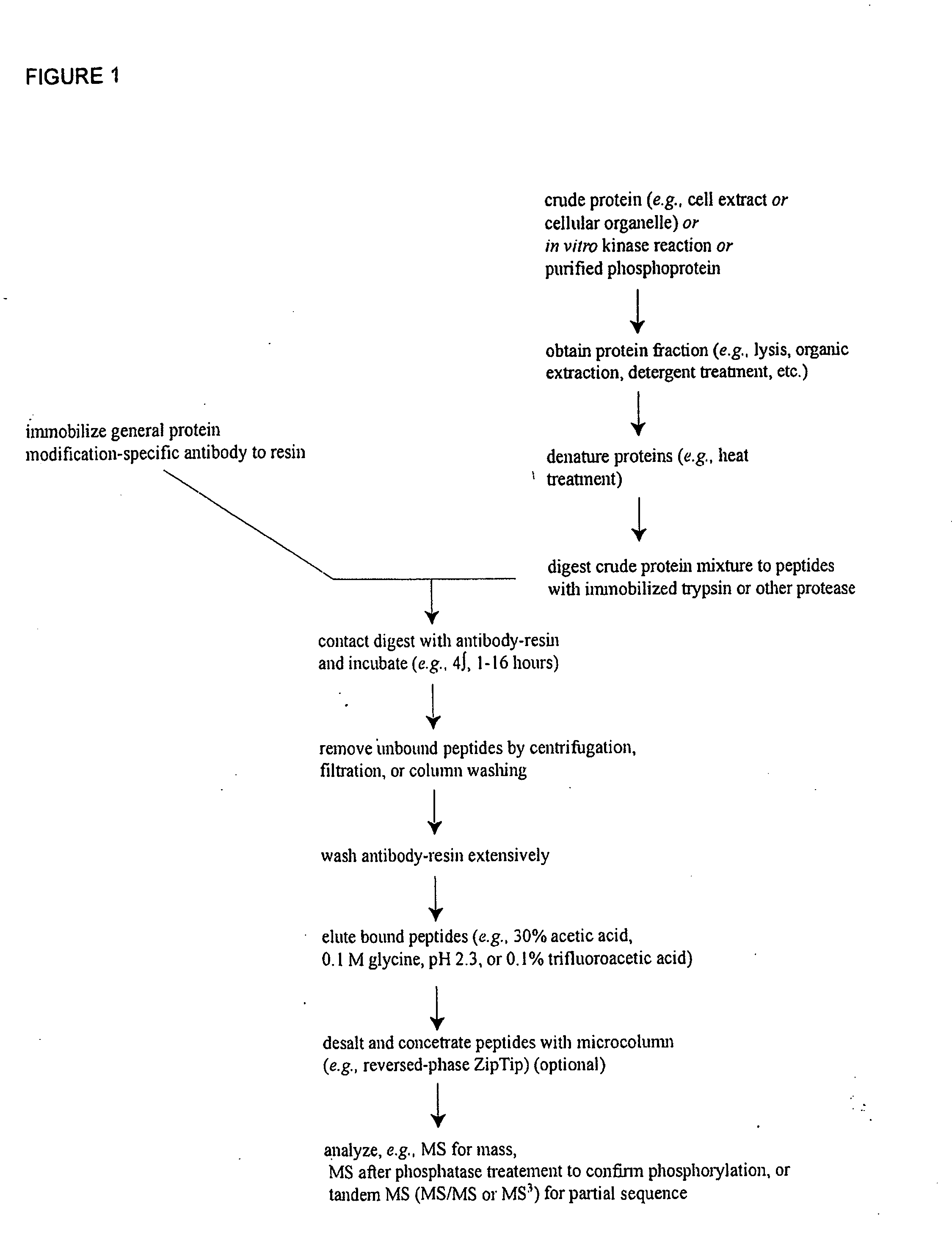
In biology, scaffold proteins are crucial regulators of many key signalling pathways. Although scaffolds are not strictly defined in function, they are known to interact and/or bind with multiple members of a signalling pathway, tethering them into complexes. In such pathways, they regulate signal transduction and help localize pathway components (organized in complexes) to specific areas of the cell such as the plasma membrane, the cytoplasm, the nucleus, the Golgi, endosomes, and the mitochondria.
Membrane scaffold proteins
InactiveUS7083958B2Improve stabilityGood monodispersityDepsipeptidesPeptide preparation methodsNative structurePhospholipid
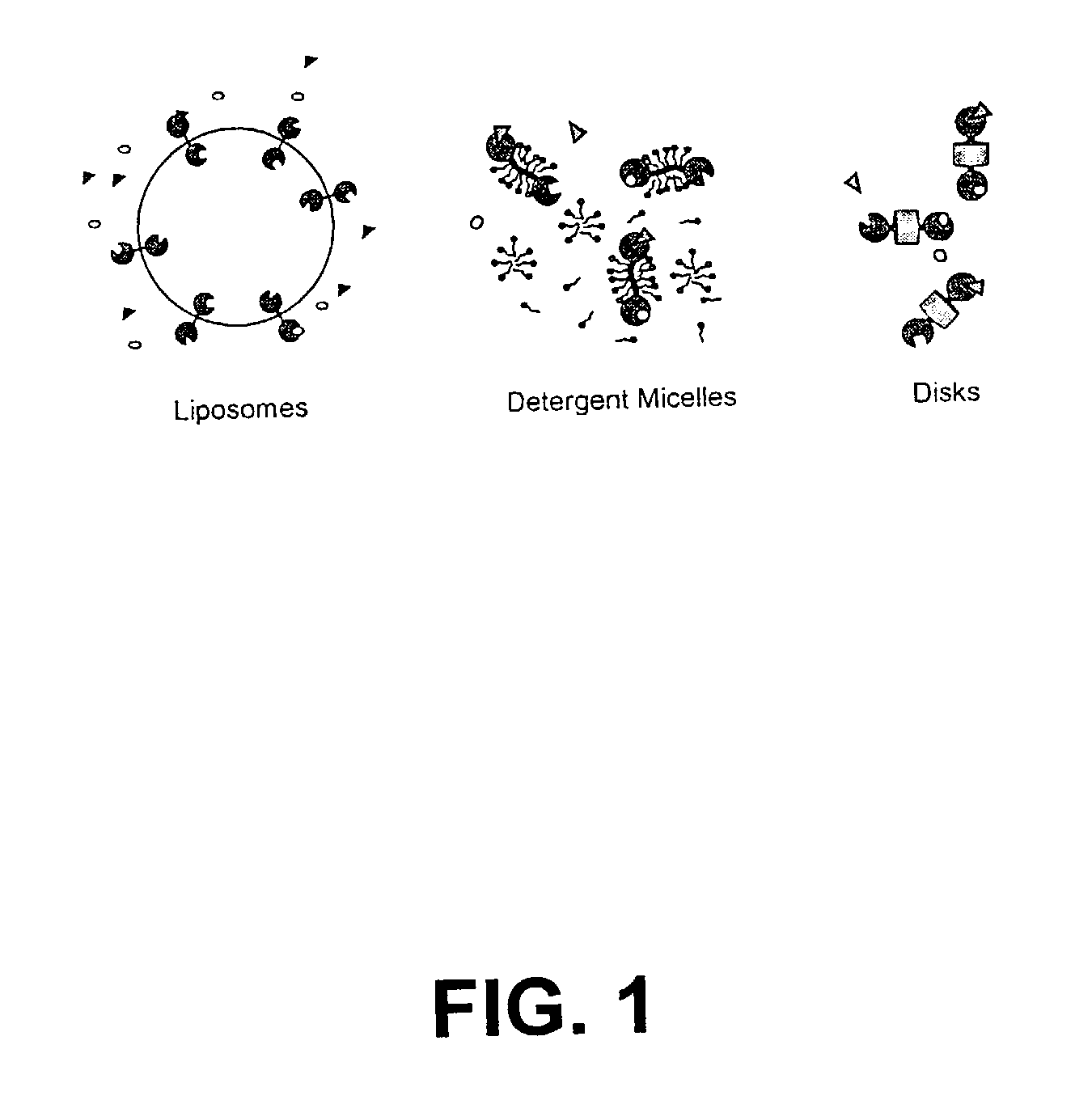
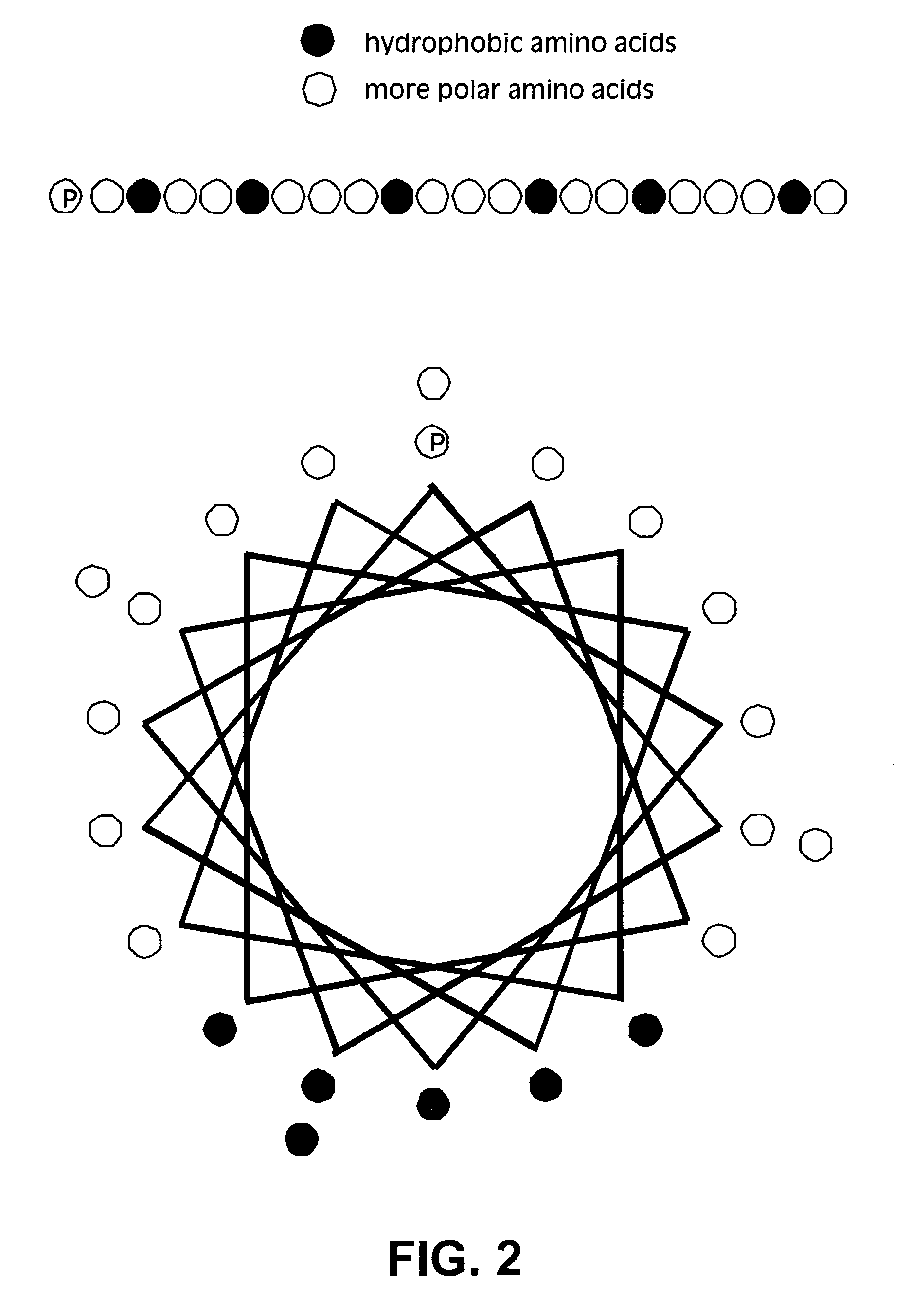
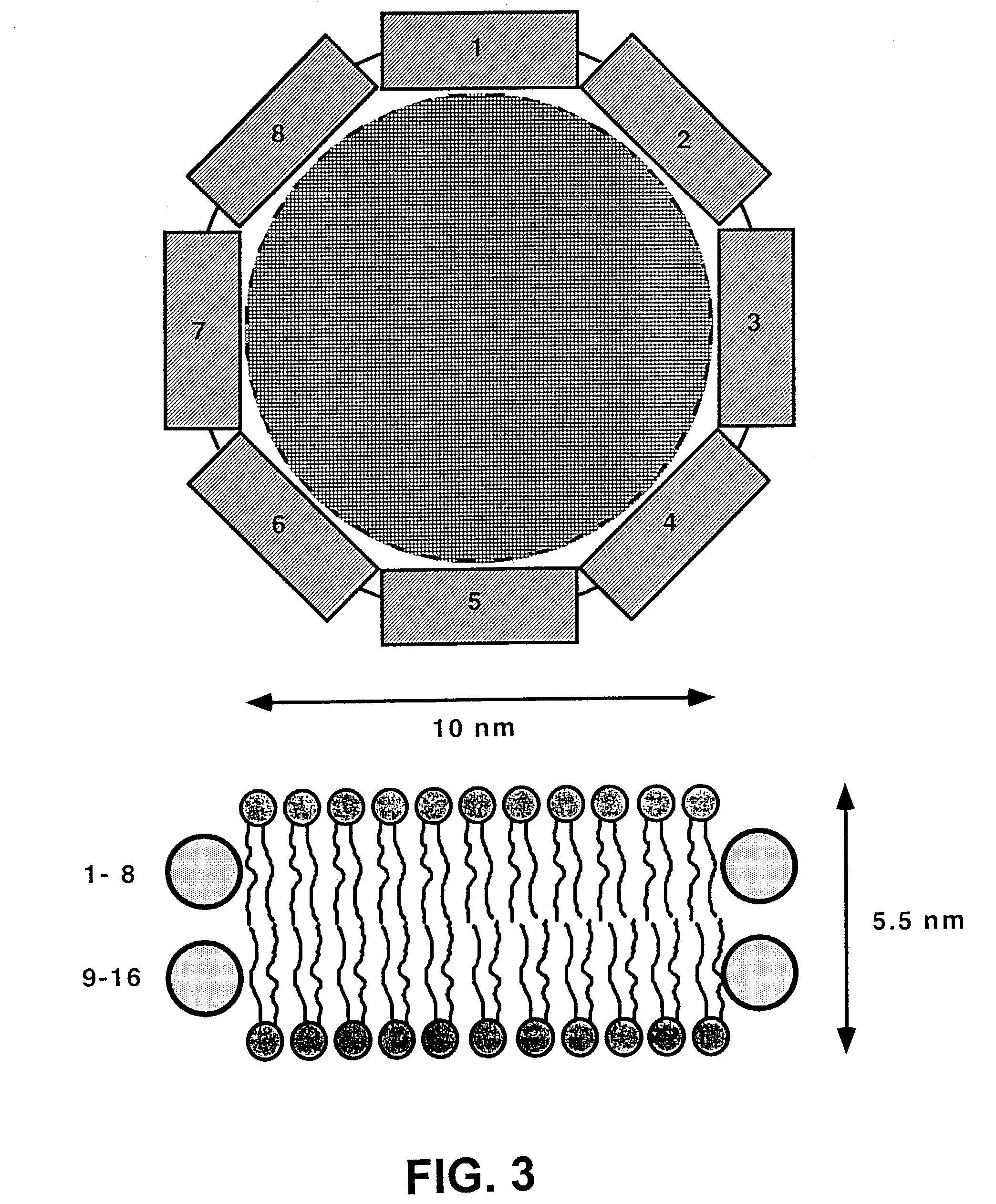
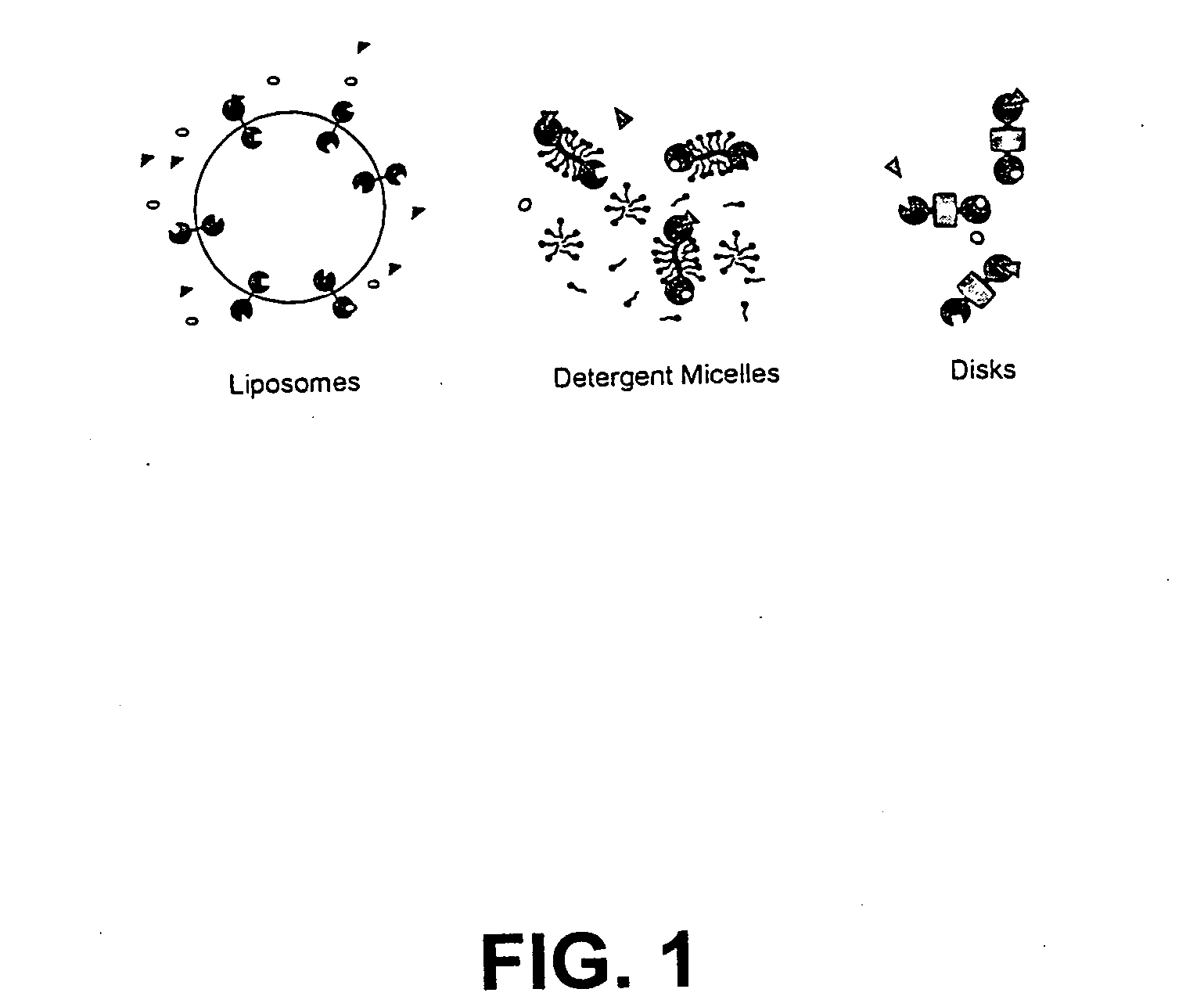
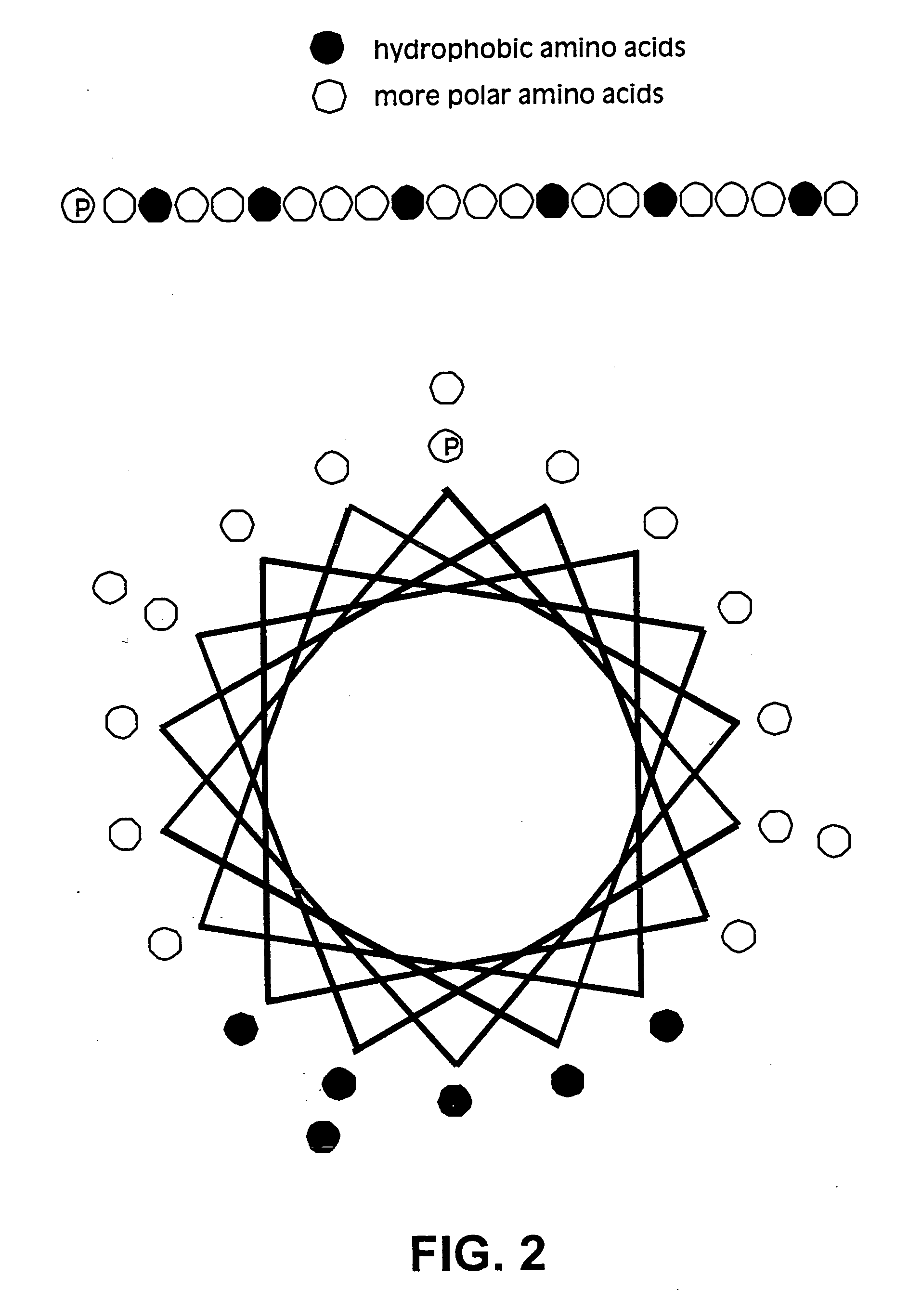
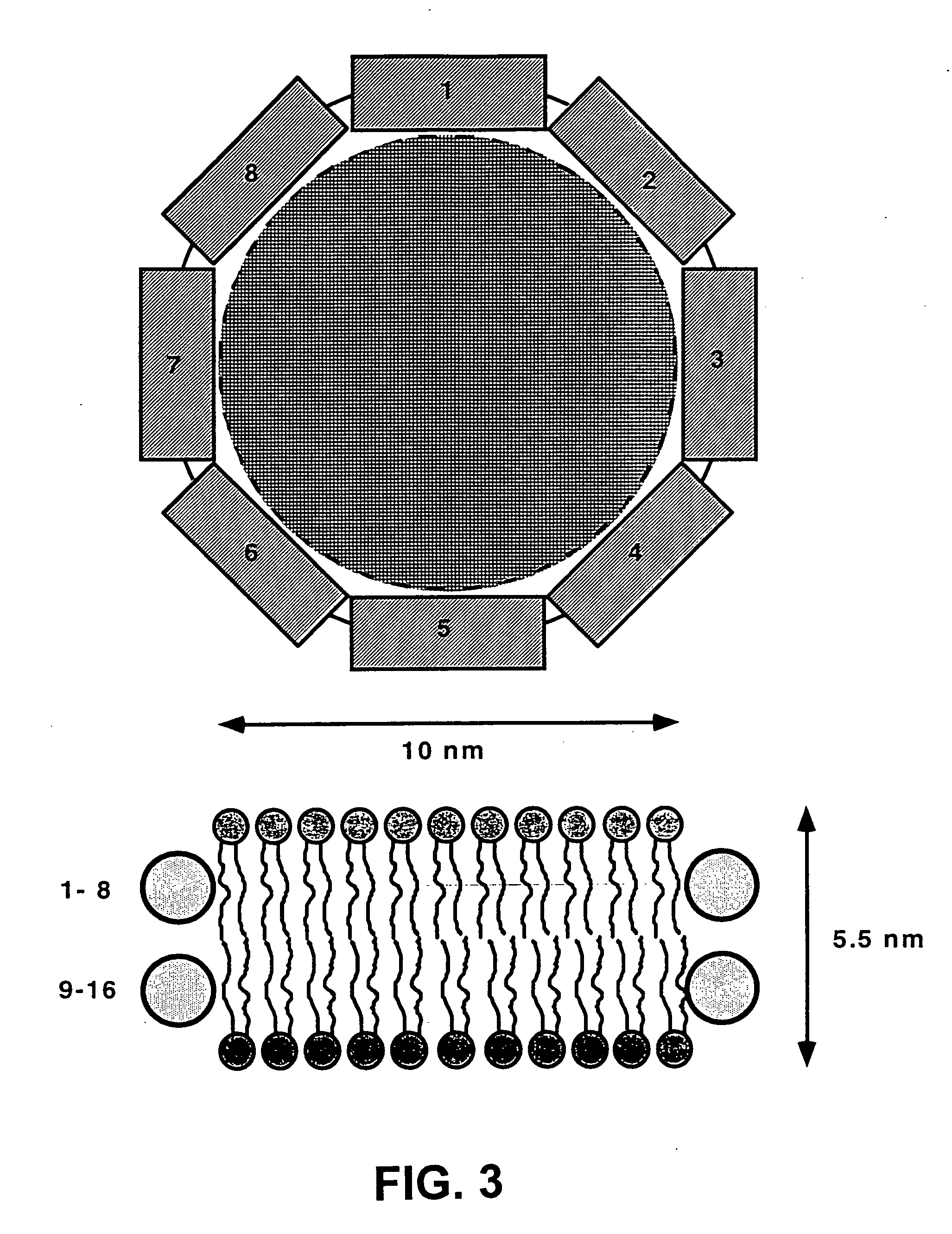
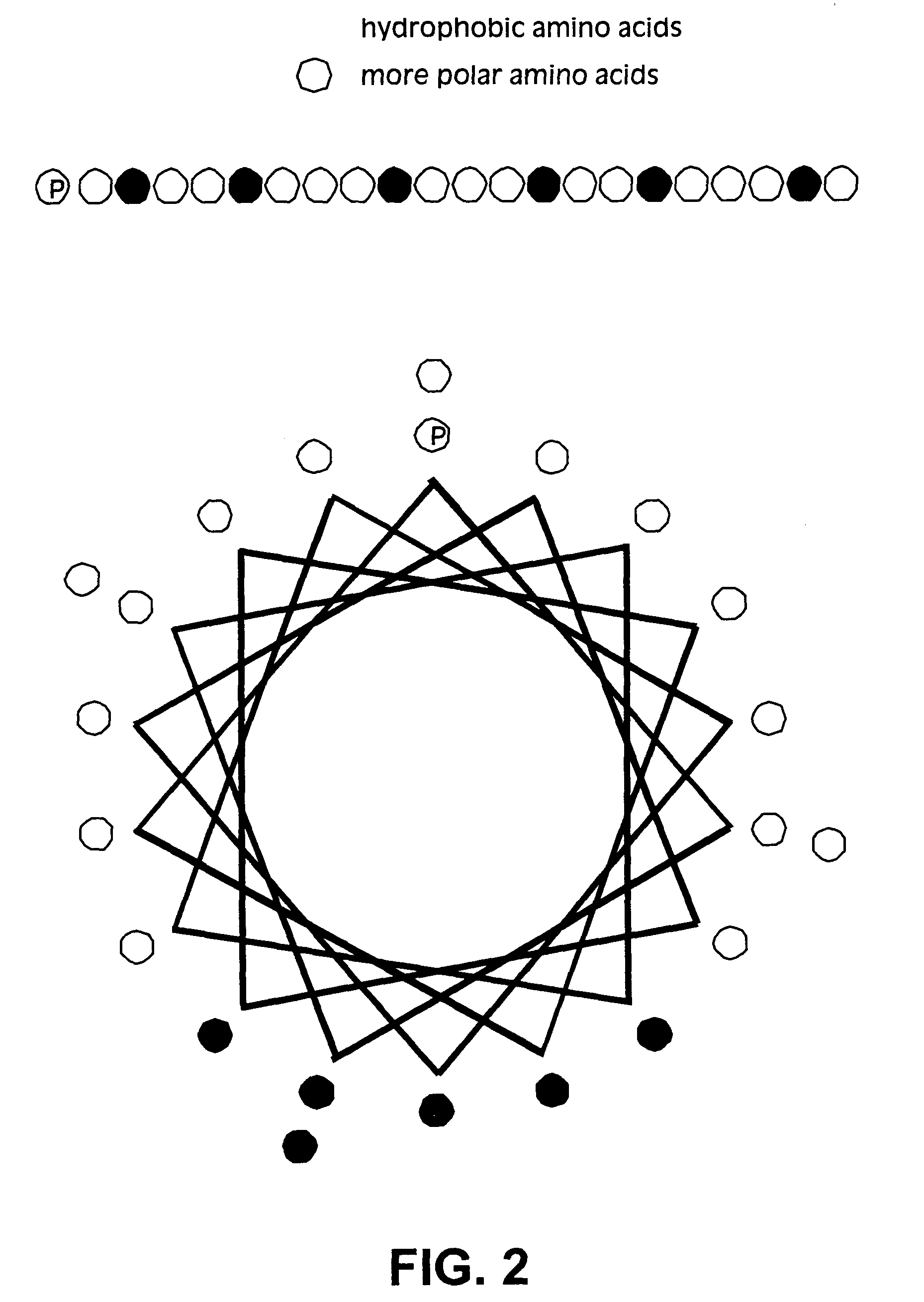
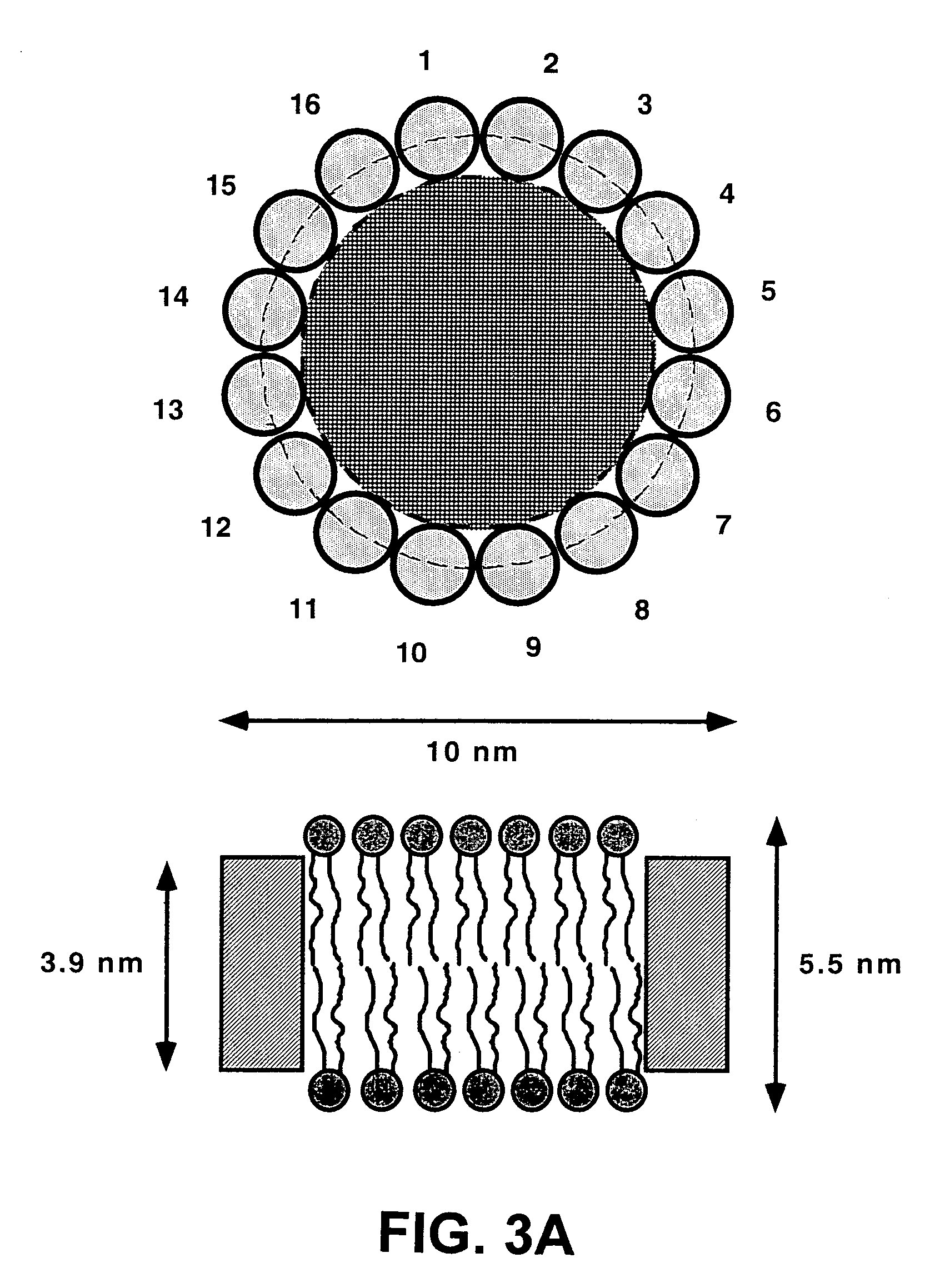
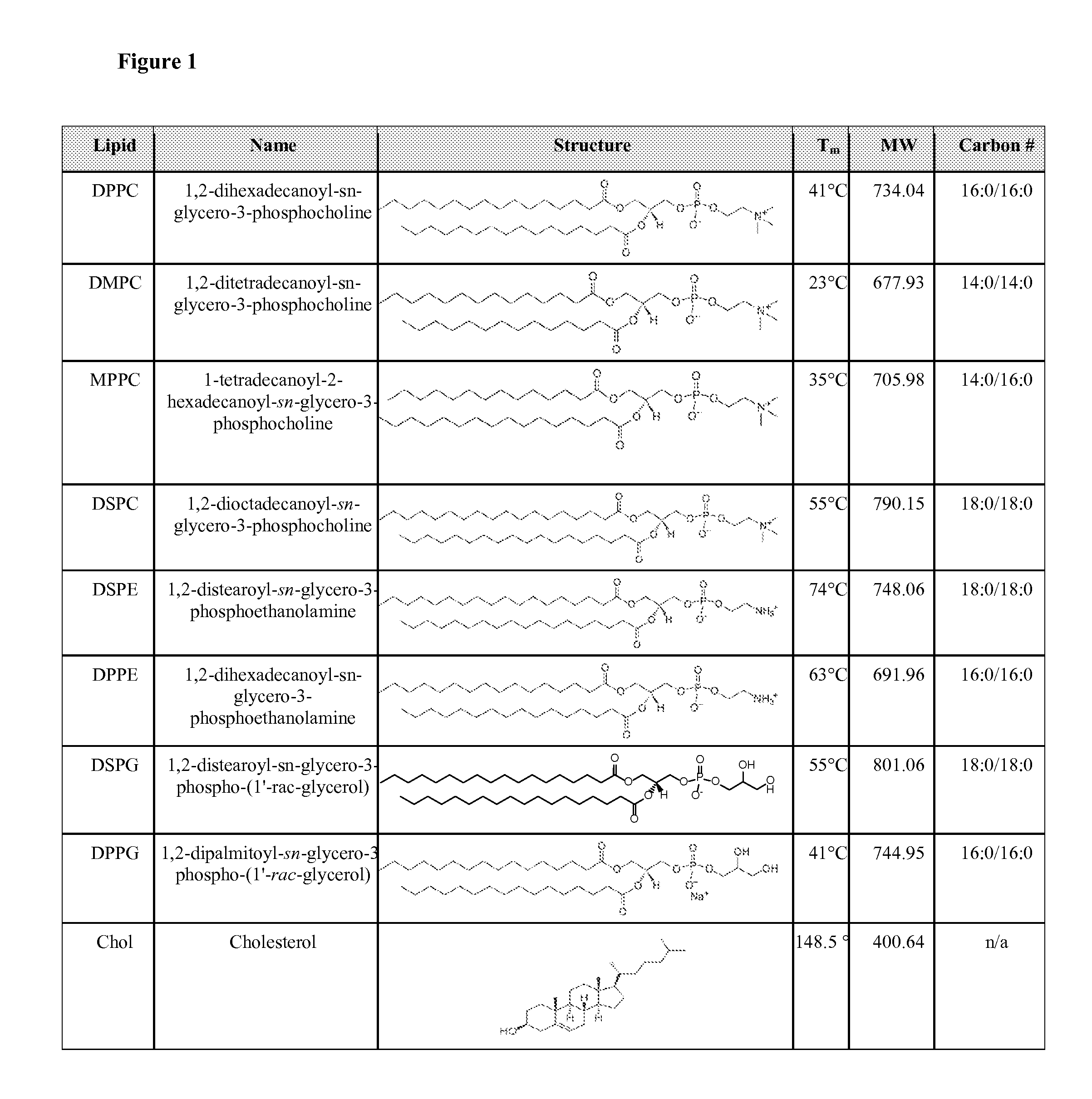
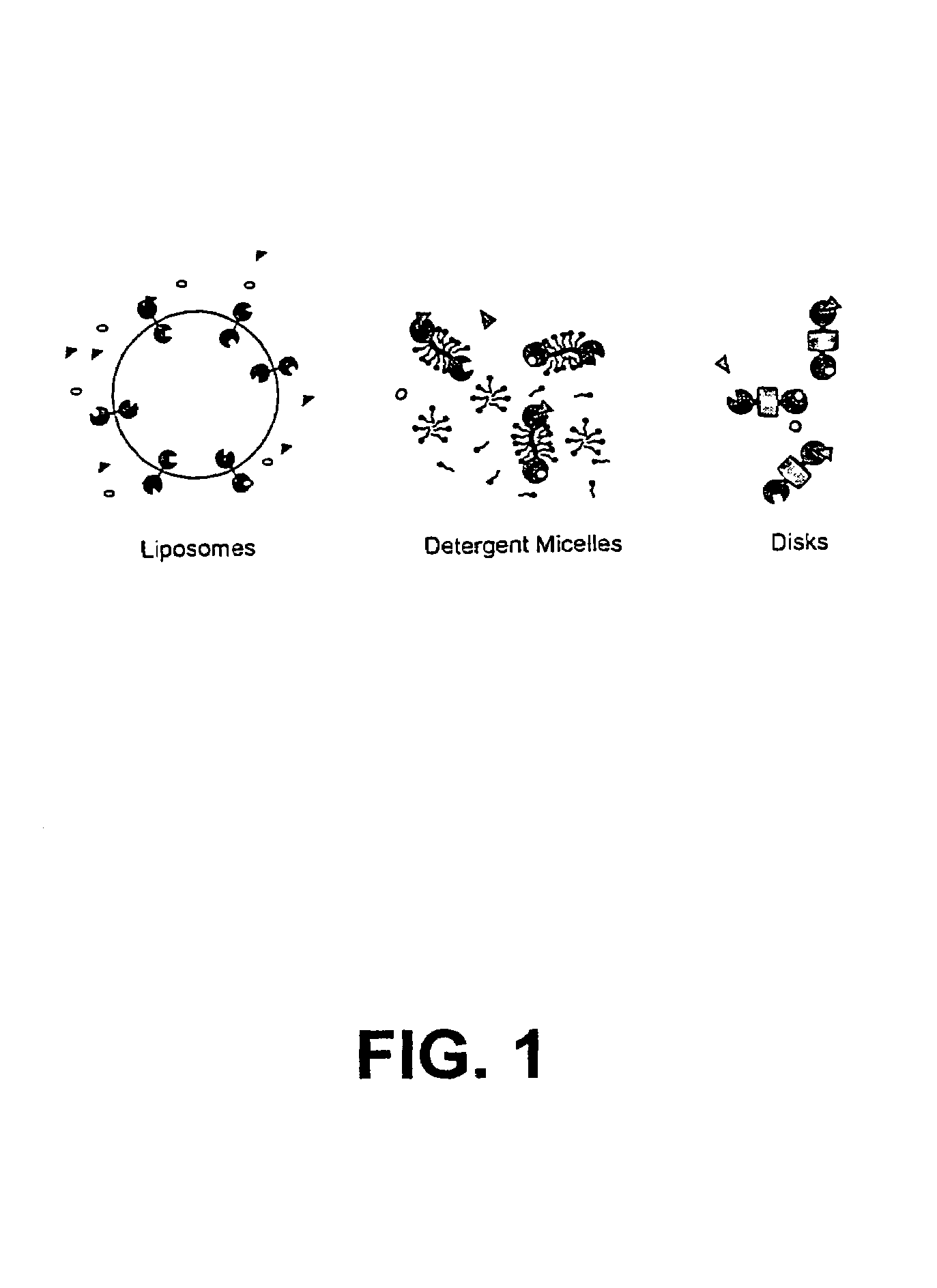
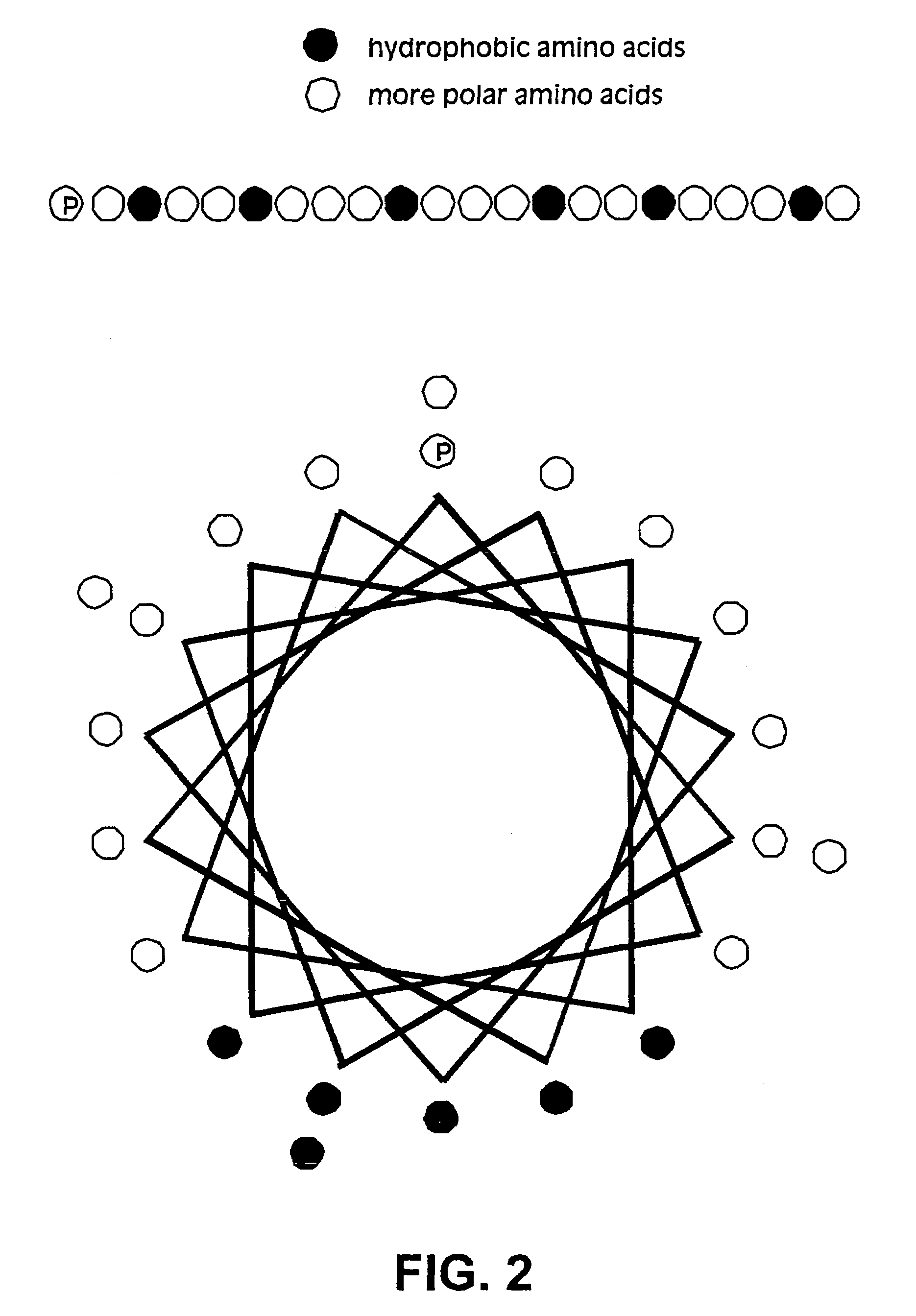
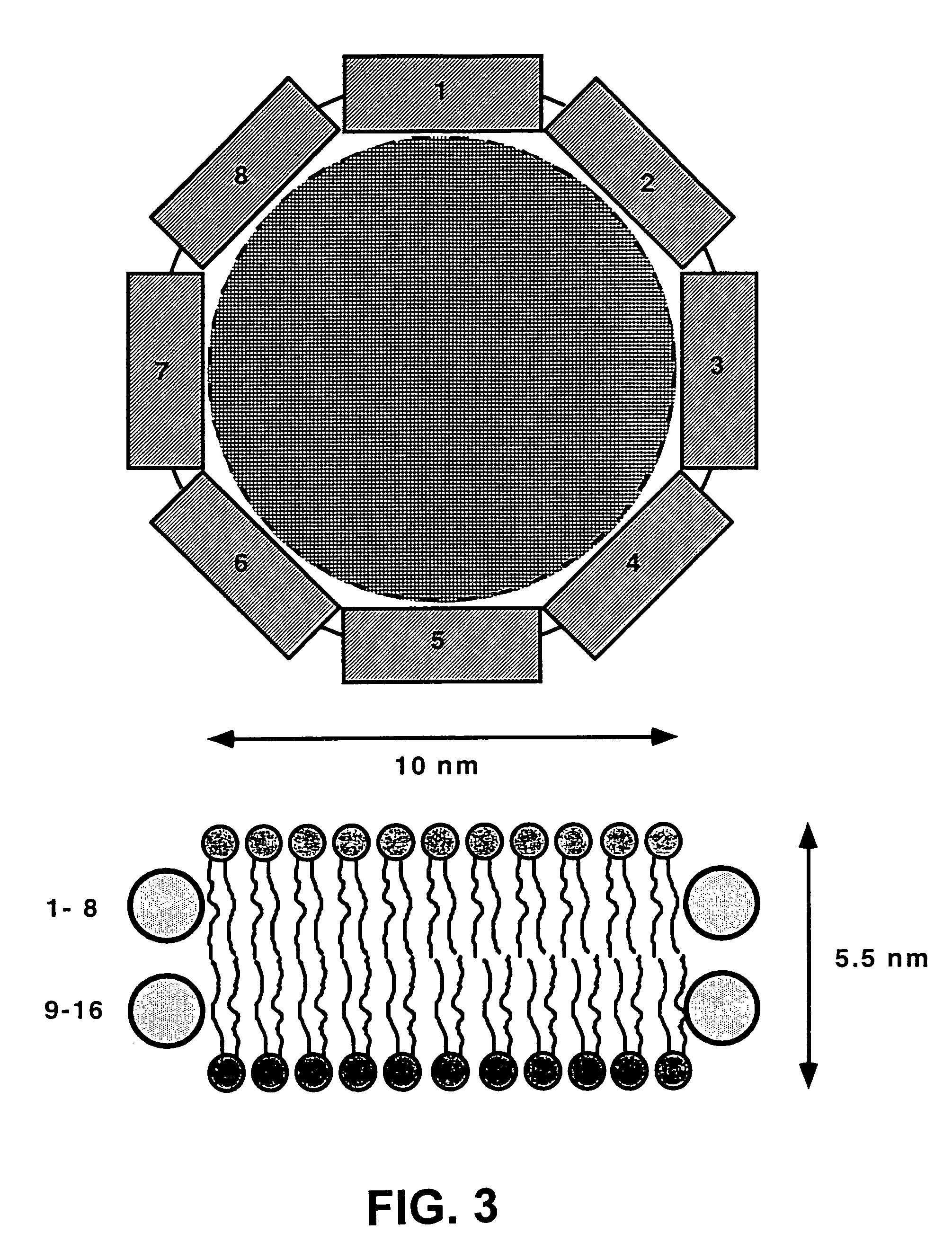
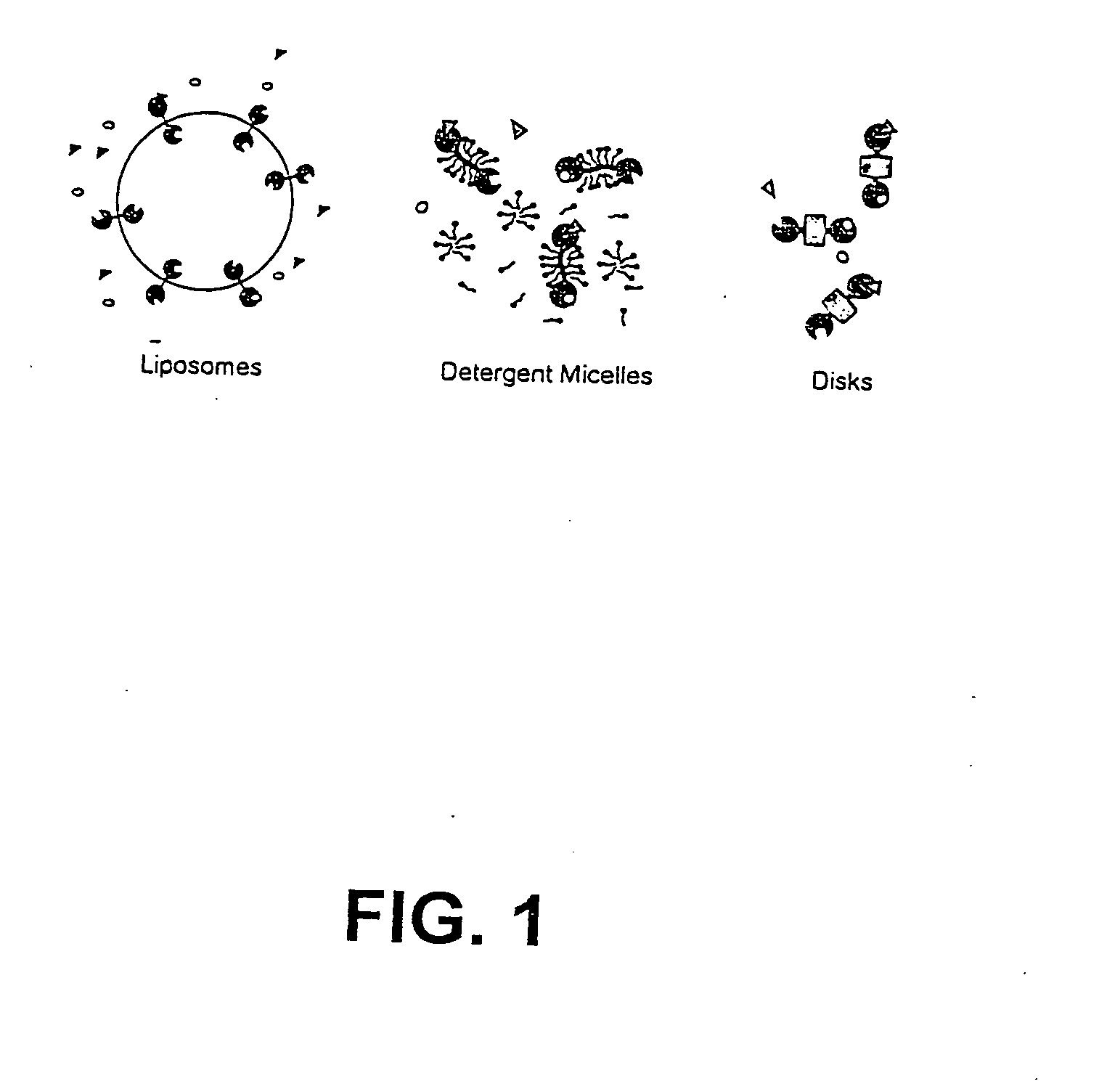
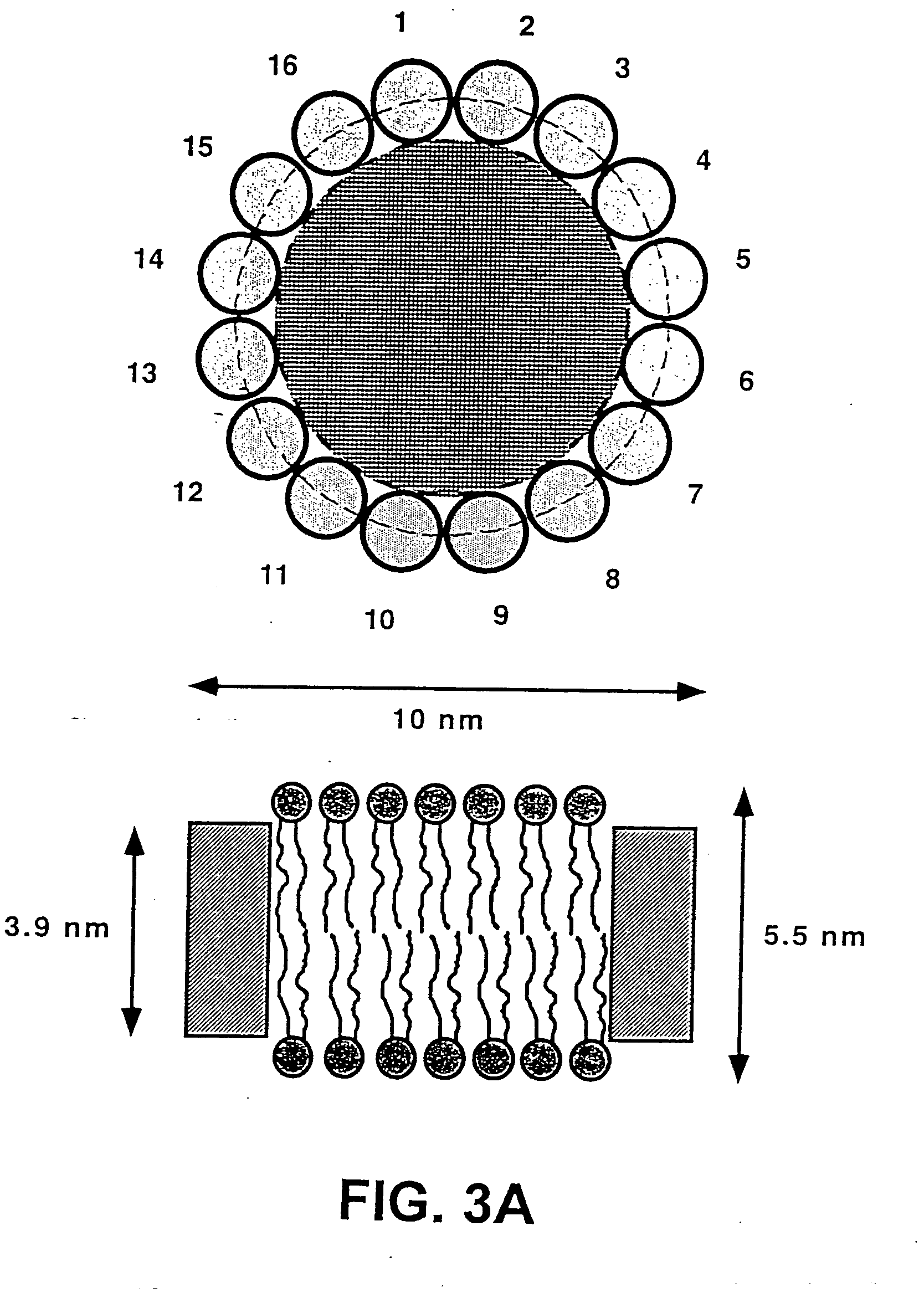
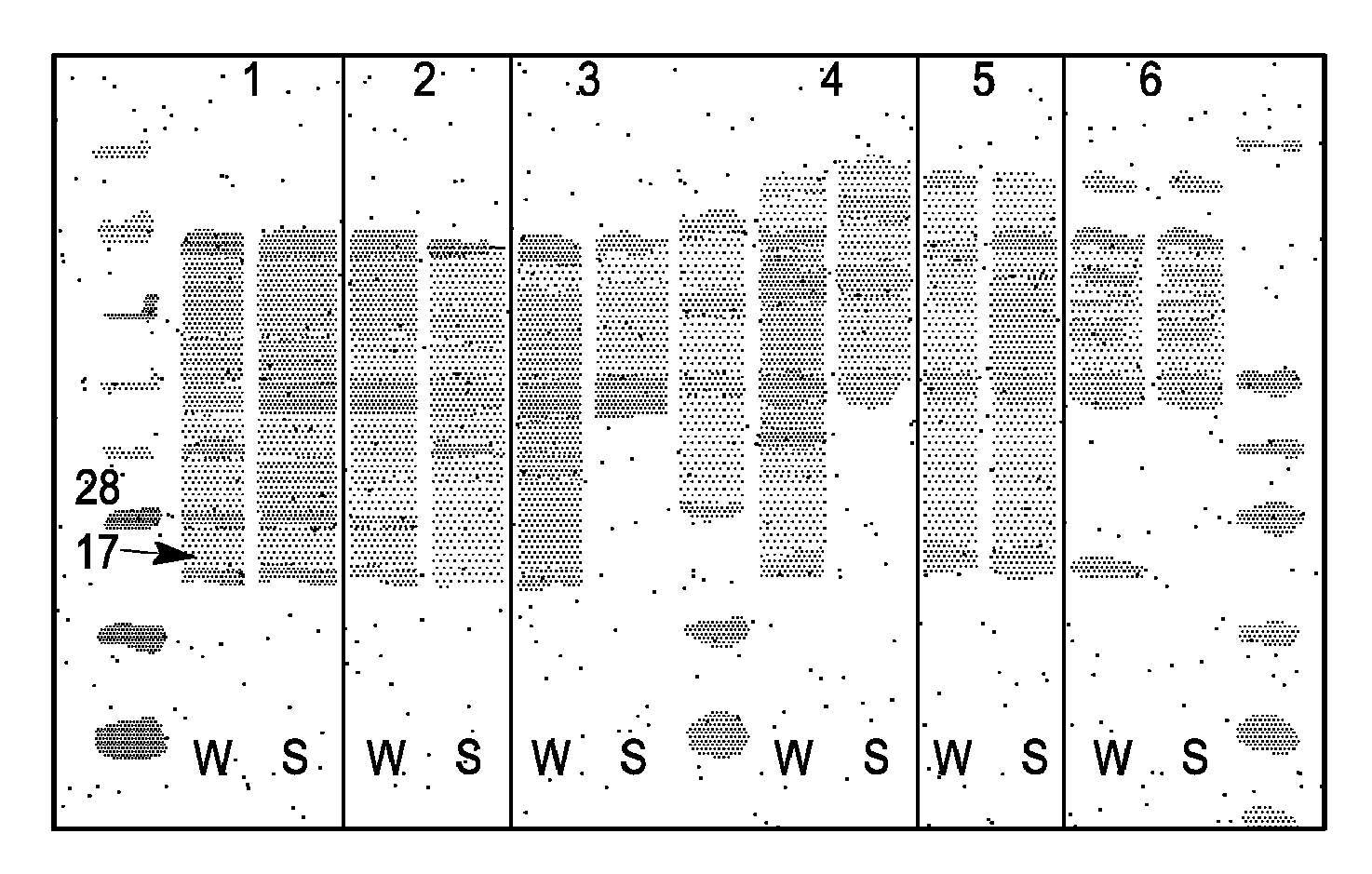
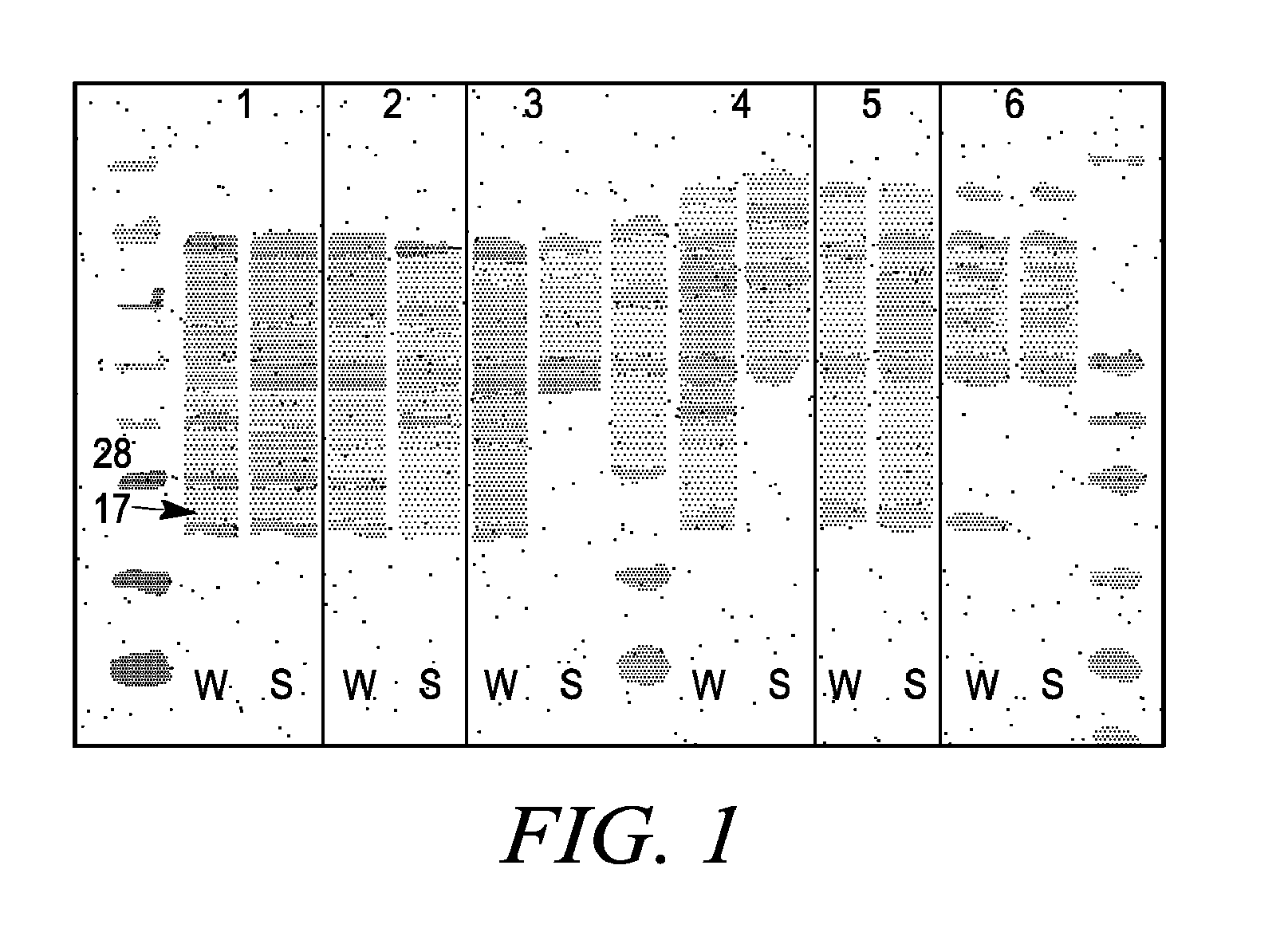
Membrane proteins are difficult to express in recombinant form, purify, and characterize, at least in part due to their hydrophobic or partially hydrophobic properties. The membrane scaffold proteins (MSP) of the present invention assemble with target membrane or other hydrophobic or partially hydrophobic proteins or membrane fragments to form soluble nanoscale particles which preserve their native structure and function; they are improved over liposomes and detergent micelles. In the presence of phospholipid, MSPs form nanoscopic phospholipid bilayer disks, with the MSP stabilizing the particle at the perimeter of the bilayer domain. The particle bilayer structure allows manipulation of incorporated proteins in solution or on solid supports, including for use with such surface-sensitive techniques as scanning probe microscopy or surface plasmon resonance. The nanoscale particles, which are robust in terms of integrity and maintenance of biological activity of incorporated proteins, facilitate pharmaceutical and biological research, structure / function correlation, structure determination, bioseparation, and drug discovery.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
Membrane scaffold proteins
InactiveUS20050182243A1Increase stability and monodispersityImprove purification effectBacterial antigen ingredientsProtozoa antigen ingredientsNative structurePhospholipid
The membrane scaffold proteins (MSP) of the present invention assemble with hydrophobic or partially hydrophobic proteins to form soluble nanoscale particles which preserve native structure and function; they are improved over liposomes and detergent micelles, in terms of stability and preservation of biological activity and native conformation. In the presence of phospholipid, MSPs form nanoscopic phospholipid bilayer disks, with the MSP stabilizing the particle at the perimeter of the bilayer domain. The particle bilayer structure allows manipulation of incorporated proteins in solution or on solid supports, including for use with such surface-sensitive techniques as scanning probe microscopy or surface plasmon resonance. The nanoscale particles, which are robust in terms of integrity and maintenance of biological activity of incorporated proteins, facilitate pharmaceutical and biological research, structure / function correlations, structure determinations, bioseparations, and drug discovery.
Owner:BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS THE A BODY & POLITIC OF THE STATE OF ILLINOIS
Membrane scaffold proteins
InactiveUS7048949B2Great stability and size homogeneity and useful functionalityEasy to understandPowder deliveryFungiNative structurePhospholipid
Membrane proteins are difficult to express in recombinant form, purify, and characterize, at least in part due to their hydrophobic or partially hydrophobic properties. Membrane scaffold proteins (MSP) assemble with target membrane or other hydrophobic or partially hydrophobic proteins or membrane fragments to form soluble nanoscale particles which preserve their native structure and function; they are improved over liposomes and detergent micelles. In the presence of phospholipid, MSPs form nanoscopic phospholipid bilayer disks, with the MSP stabilizing the particle at the perimeter of the bilayer domain. The particle bilayer structure allows manipulation of incorporated proteins in solution or on solid supports, including for use with such surface-sensitive techniques as scanning probe microscopy or surface plasmon resonance. The nanoscale particles facilitate pharmaceutical and biological research, structure / function correlation, structure determination, bioseparation, and drug discovery.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
Fibronectin based scaffold proteins having improved stability
ActiveUS20130184212A1Improve stabilityReduce fragmentationBacteriaPeptide/protein ingredientsScaffold proteinProteinoid
The present application provides fibronectin based scaffold proteins associated with improved stability. The application also relates to stable formulations of fibronectin based scaffold proteins and the use thereof in diagnostic, research and therapeutic applications. The application further relates to cells comprising such proteins, polynucleotides encoding such proteins or fragments thereof, and to vectors comprising such polynucleotides.
Owner:BRISTOL MYERS SQUIBB CO
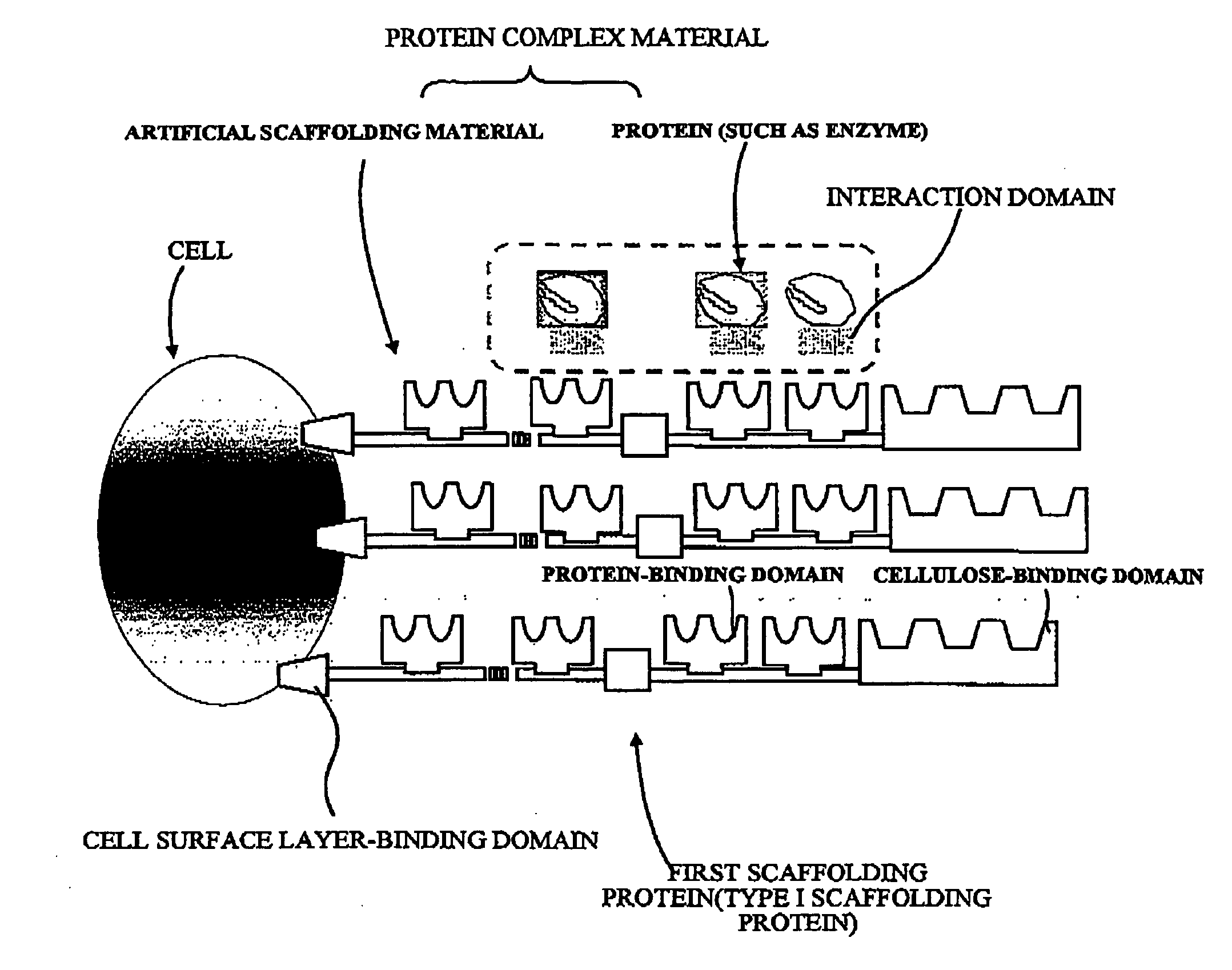
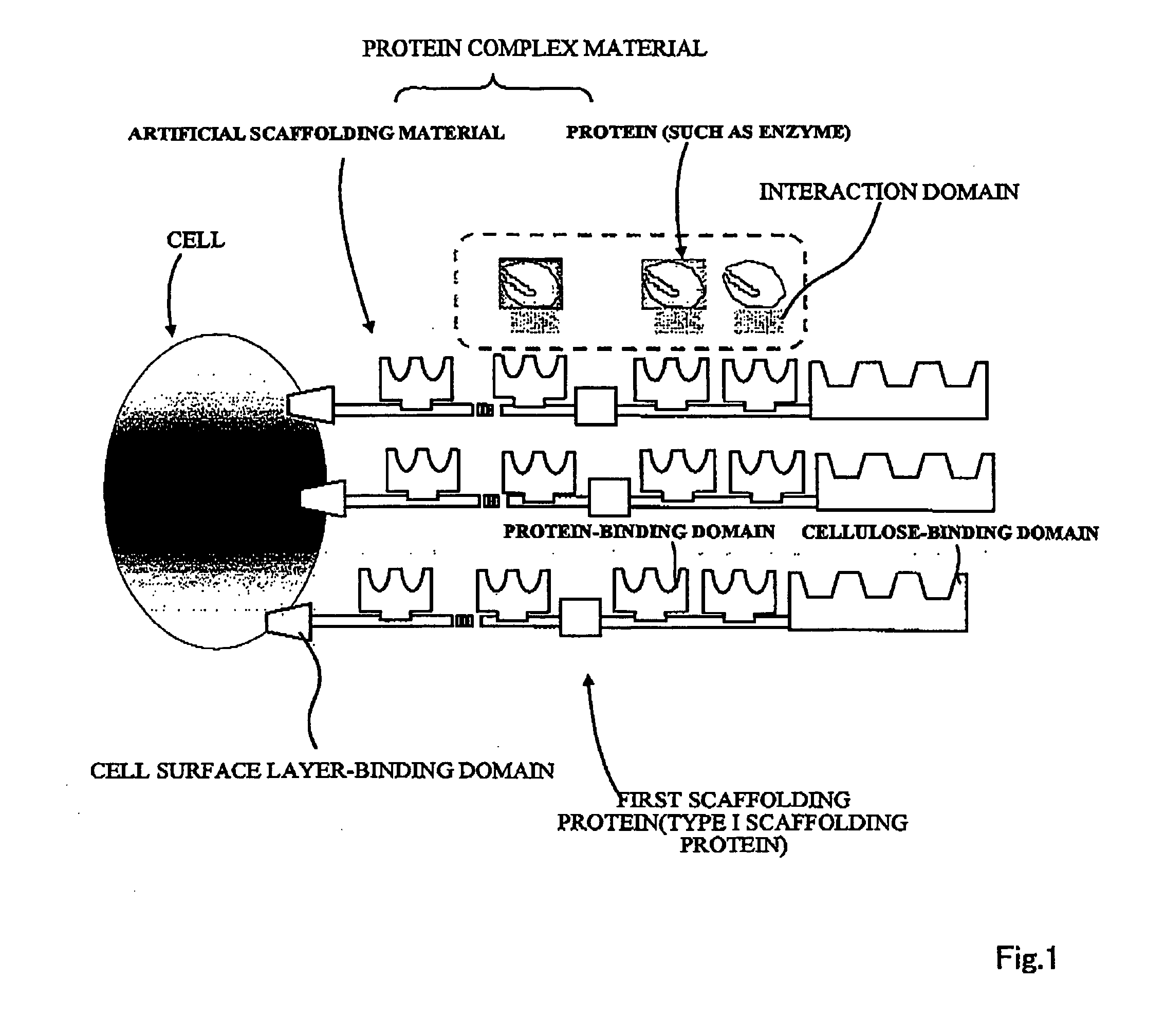
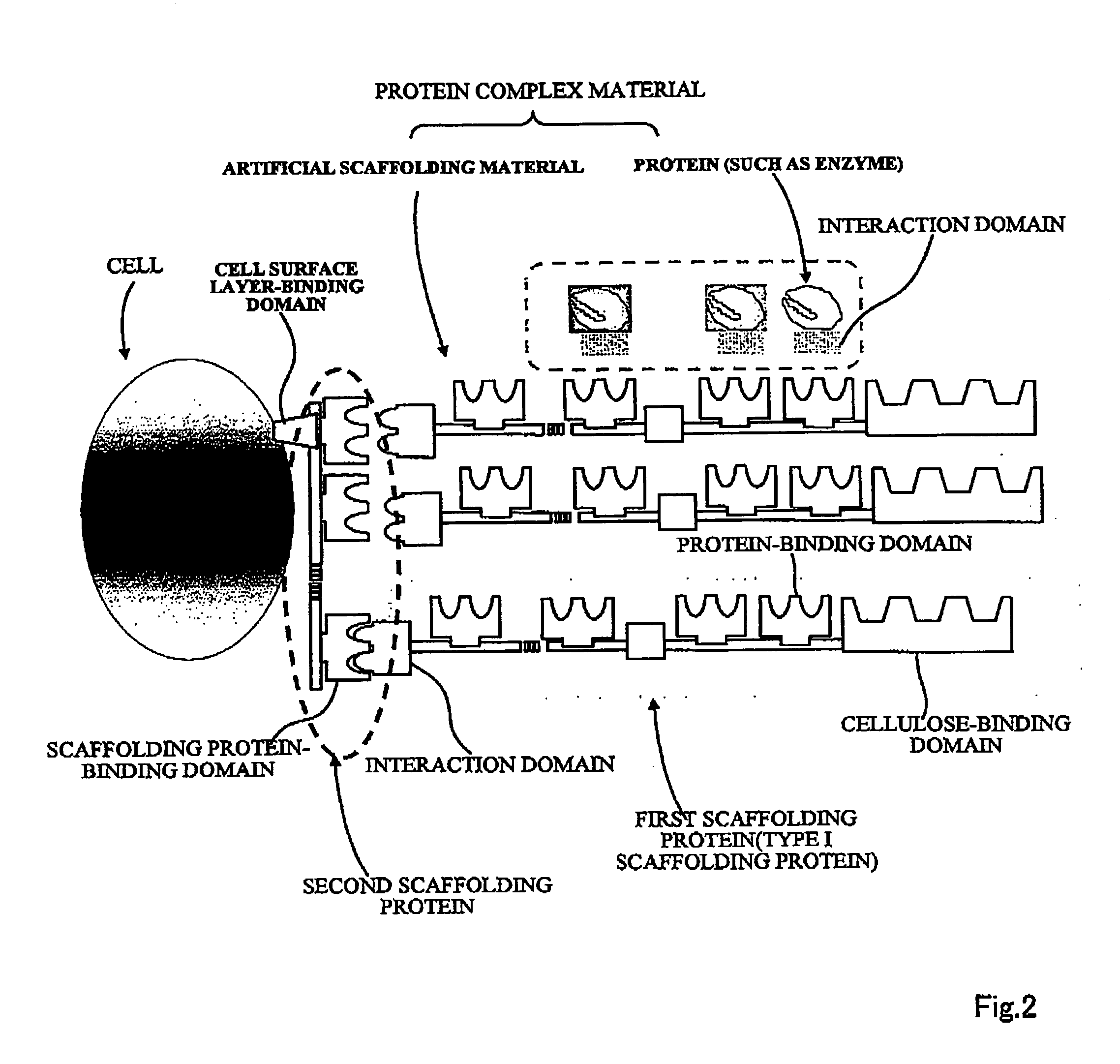
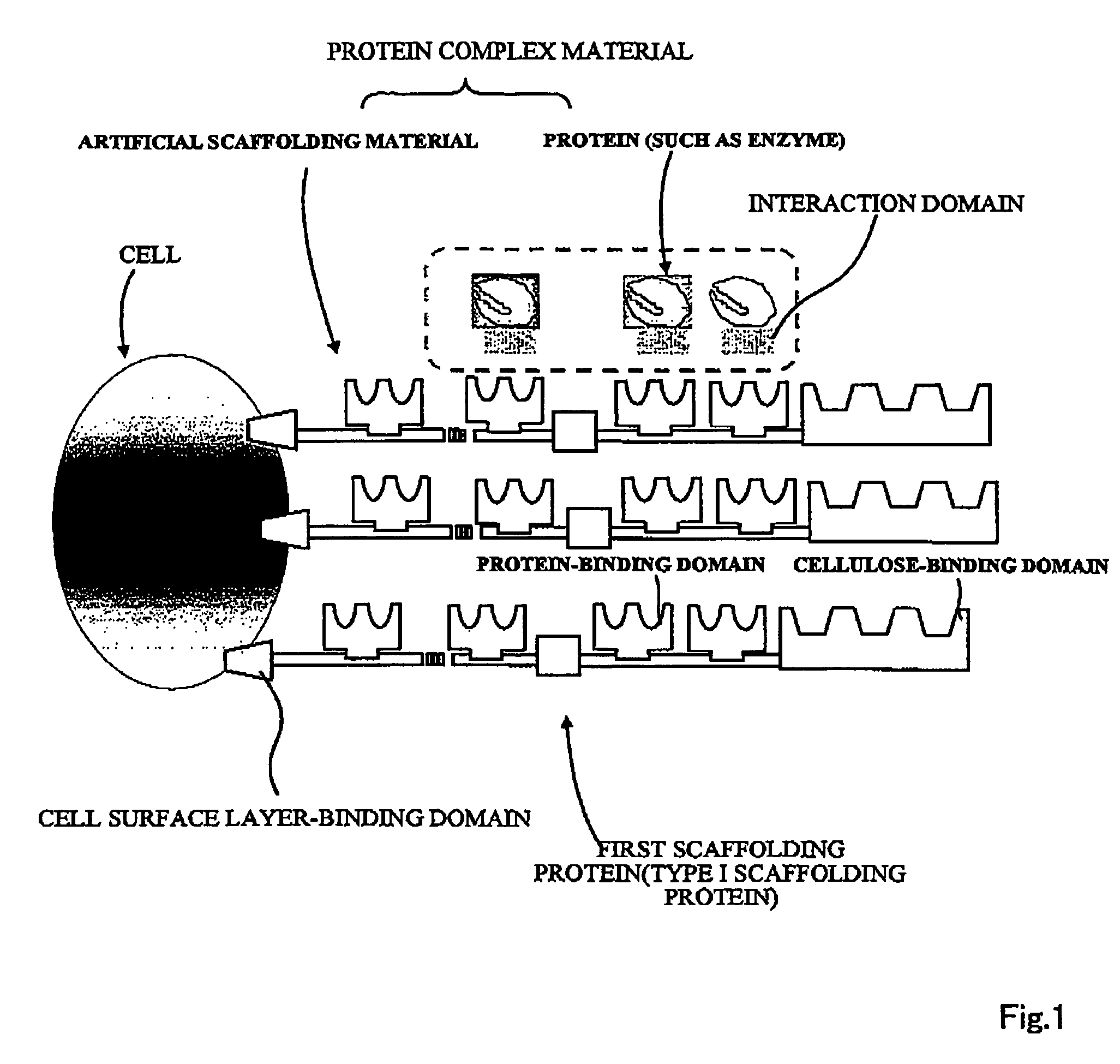
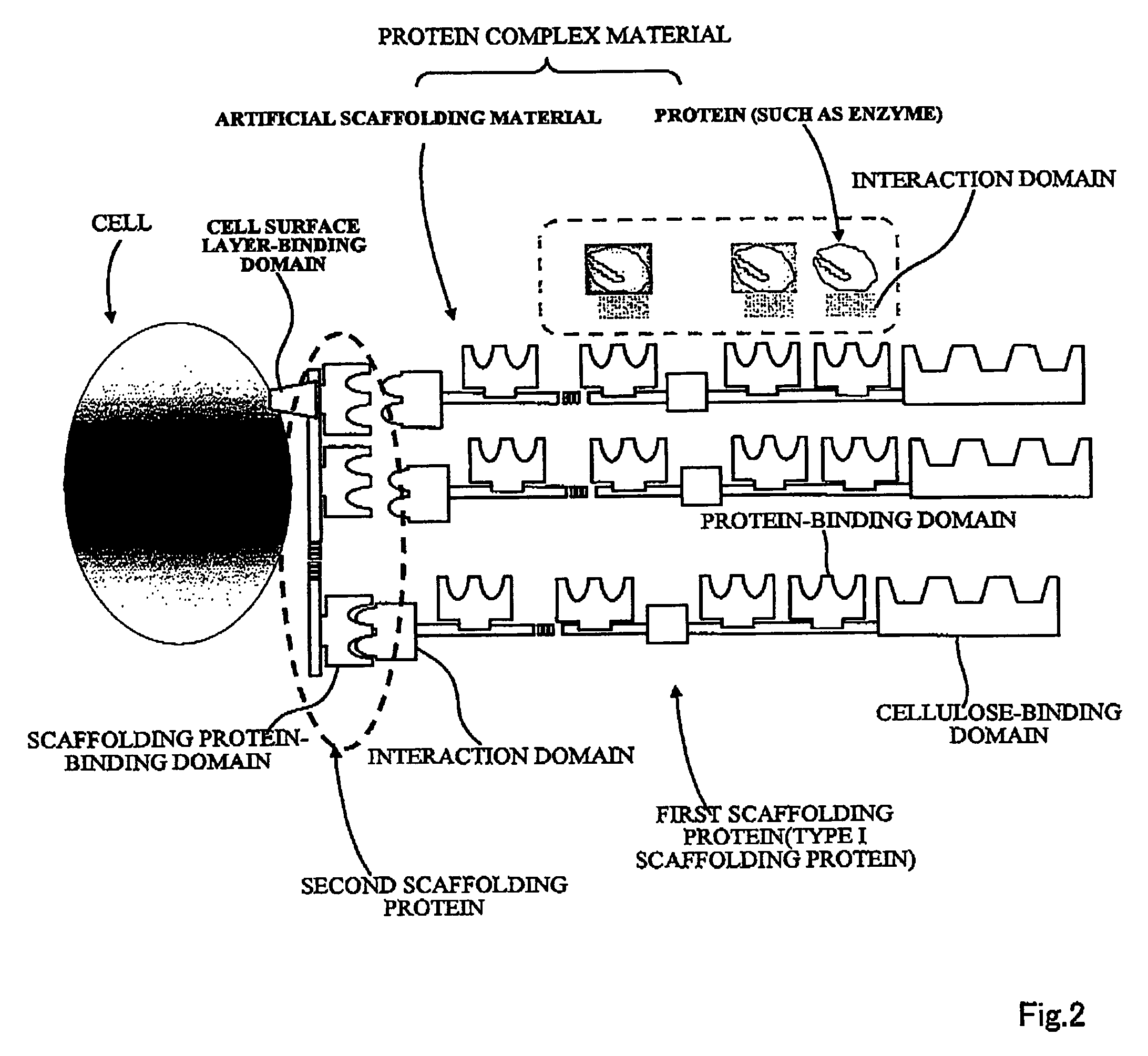
Artificial scaffolding material for protein retention and use of the same
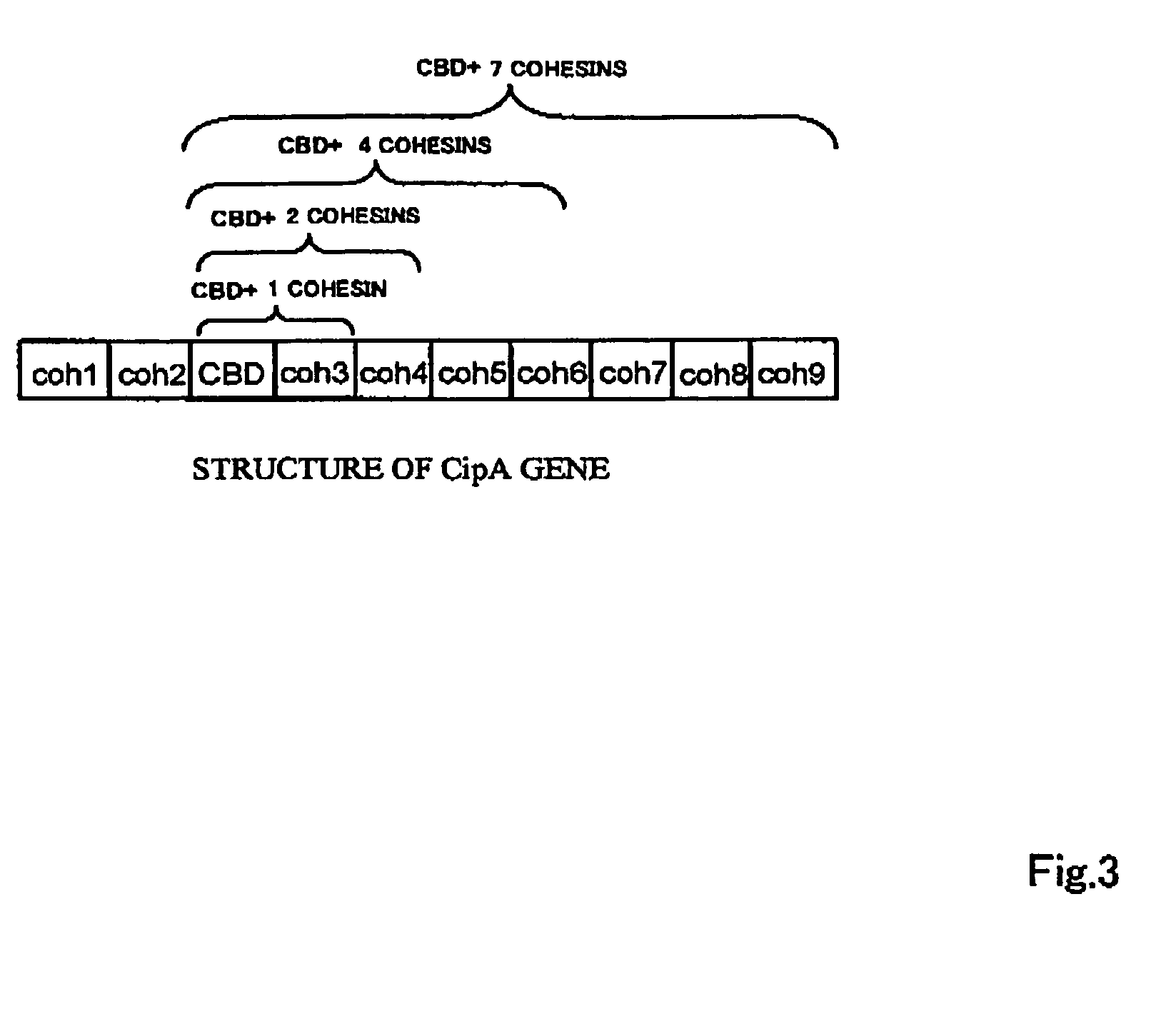
The present invention provides an artificial scaffolding material for retaining proteins suitable for placing contiguously one species or two or more species of proteins such as enzymes. To this end, the artificial scaffolding material for retaining proteins is provided with a cell and scaffolding proteins heterologous to the cell and placed on the surface layer side of the cell at an extent that allows aggregation properties to be conferred to the cell, and provided with a plurality of non-covalently binding protein-binding domains arranged in tandem.
Owner:TOYOTA CENT RES & DEV LAB INC +1
Personal Care Compositions and Methods for Their Use
InactiveUS20120014885A1Whitening skinReduce rednessCosmetic preparationsHair removalPersonal careDisease
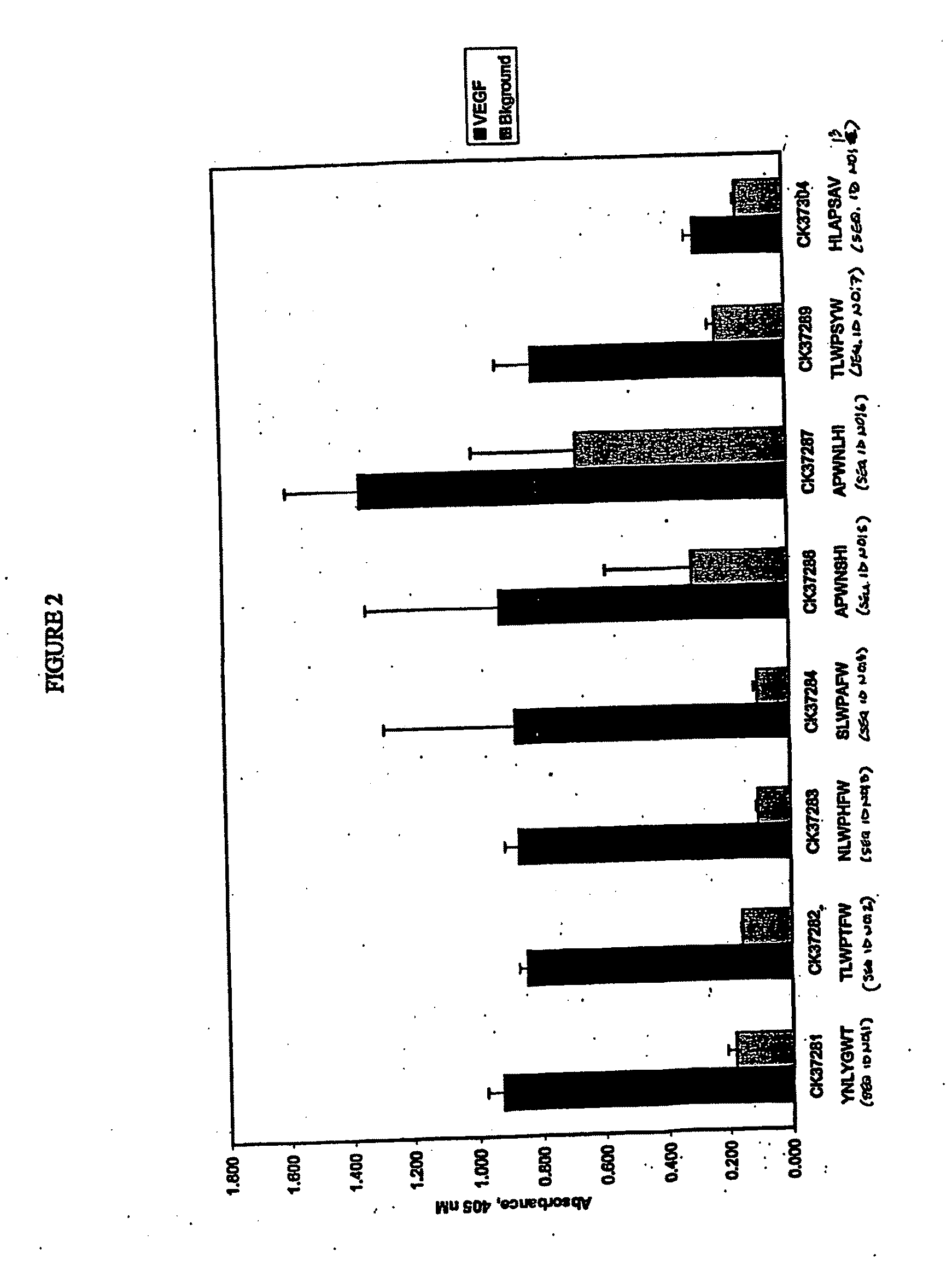
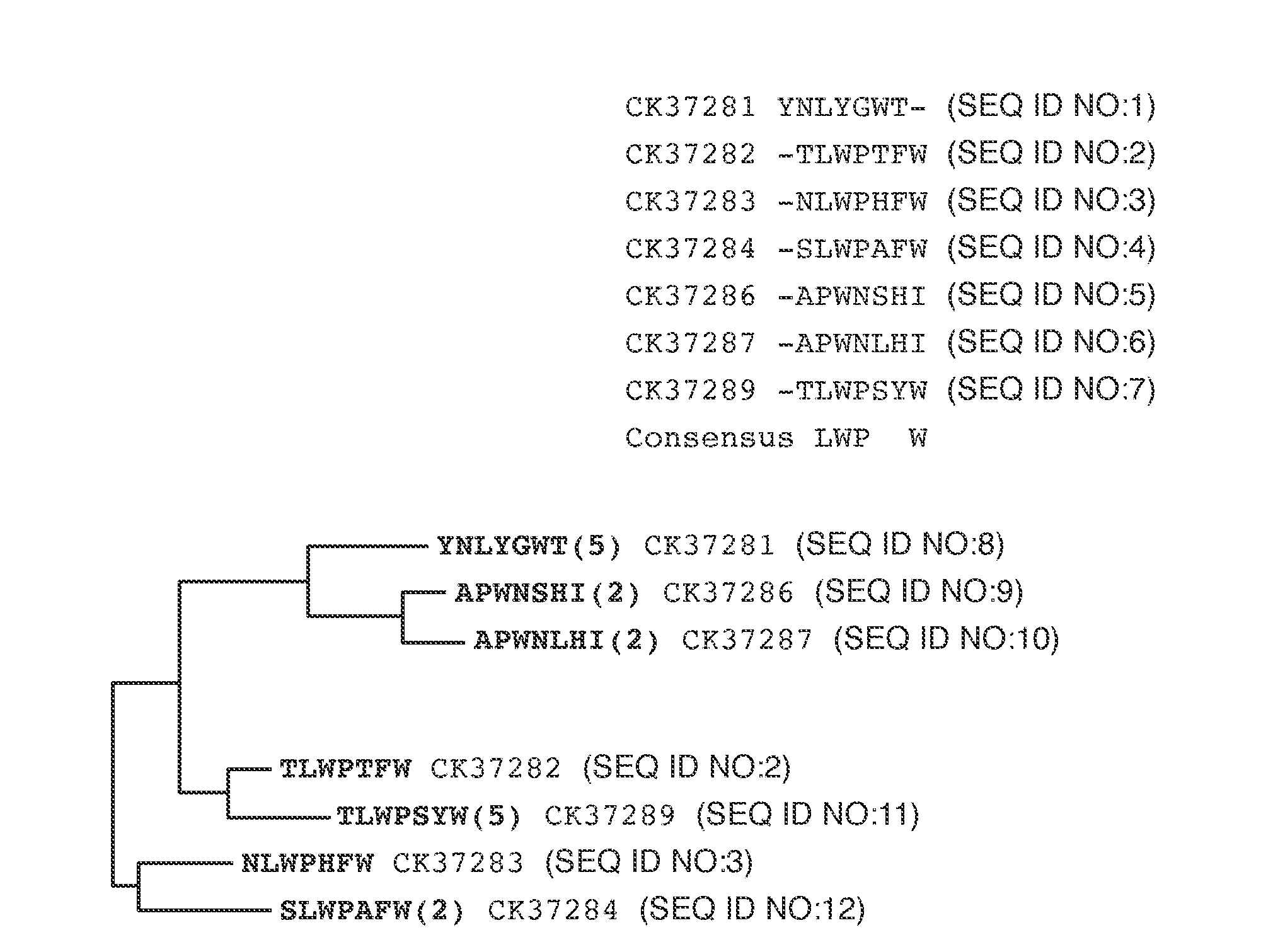
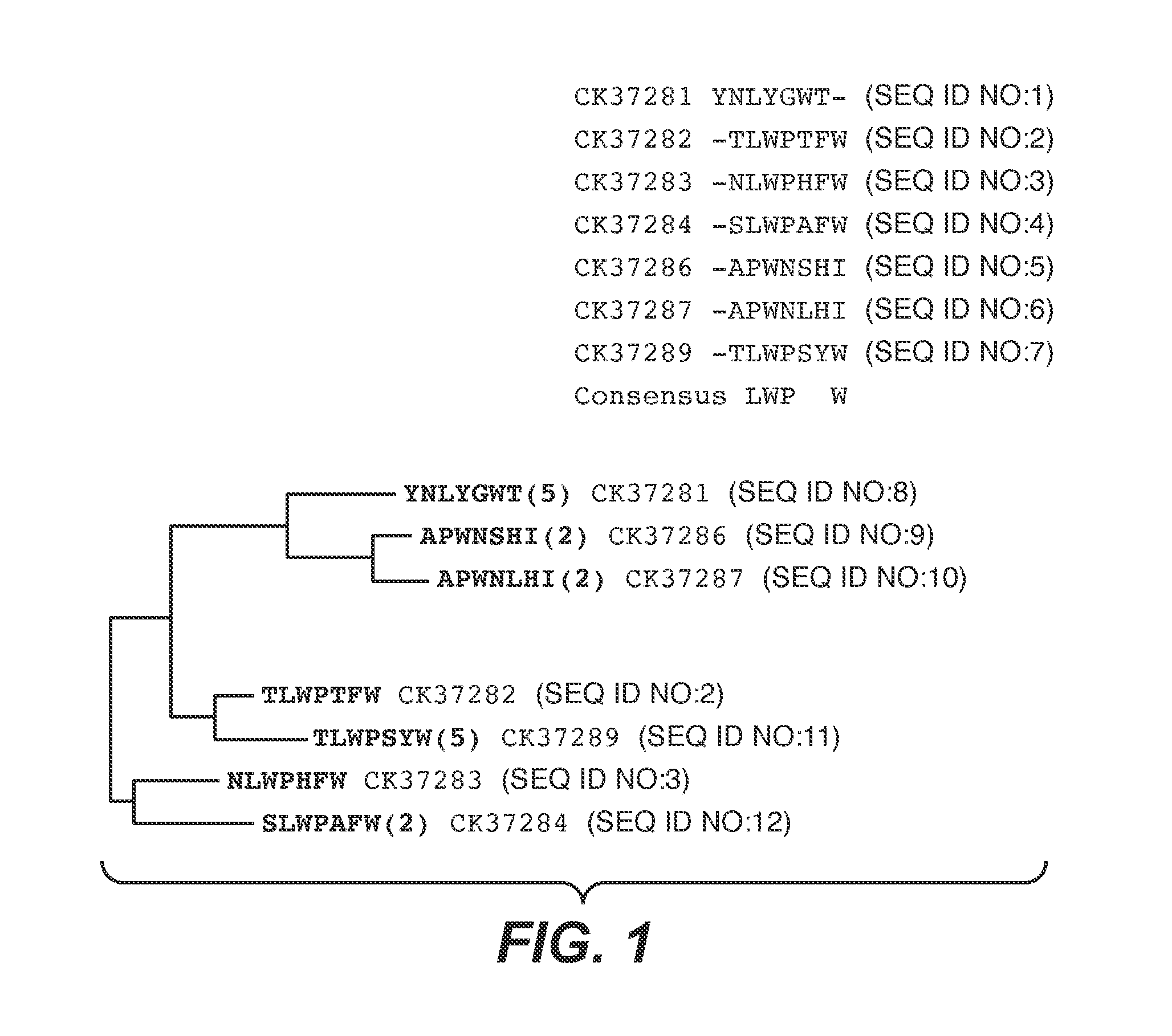
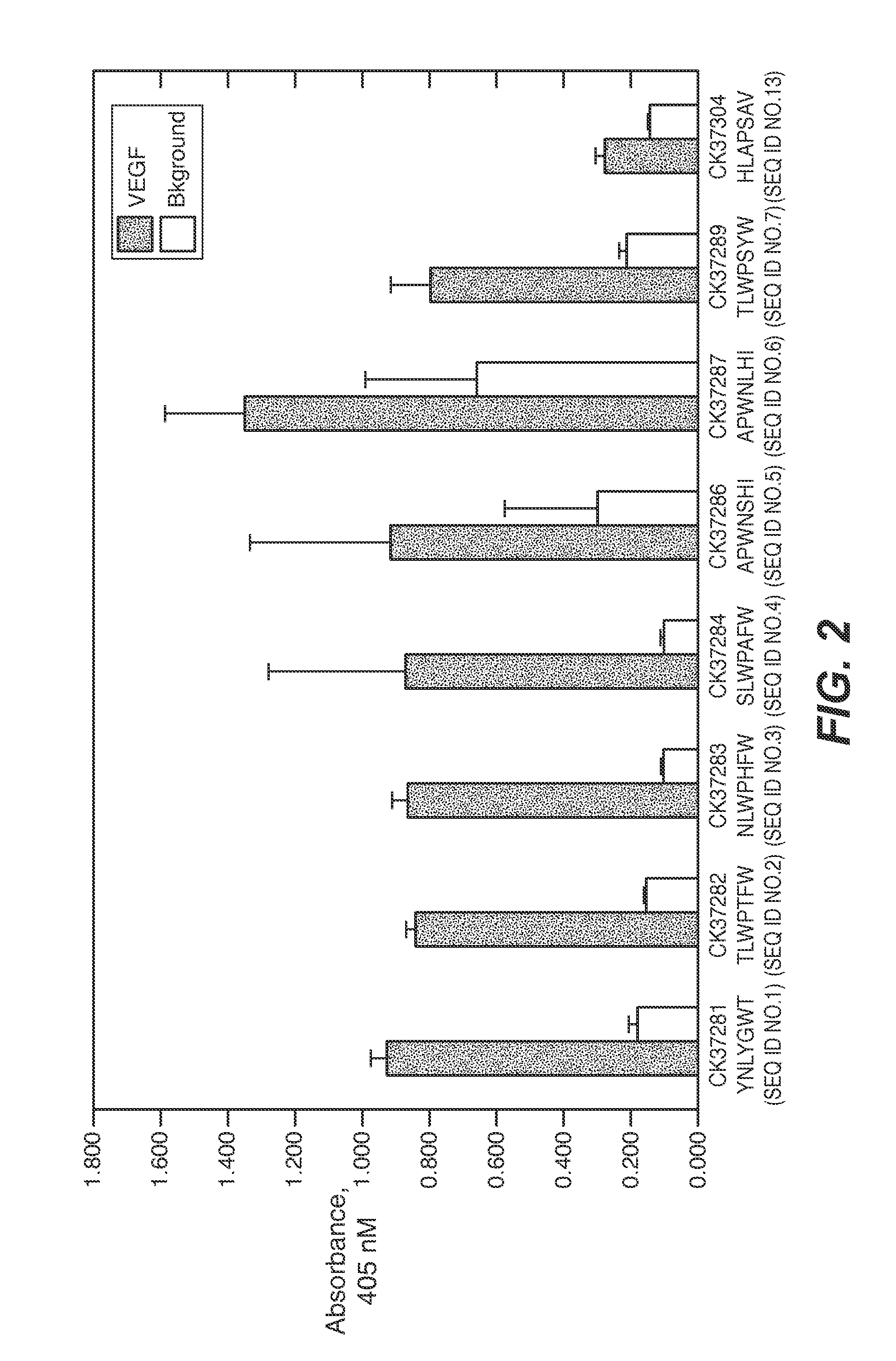
The present invention provides peptides and supported peptides for treating various diseases and conditions. In particularly preferred embodiments, the present invention provides compositions and methods for personal care. In some embodiments, the present invention provides compositions for use in skin and / or hair care, as well as cosmetic compositions. In alternative particularly preferred embodiments, the present invention provides peptides and supported peptides for treating diseases of the skin, such as rosacea. In some particularly preferred embodiments, the supported peptides of the present invention are anti-VEGF peptides. In alternative particularly preferred embodiments, the anti-VEGF peptides are expressed on a scaffold protein. In some most preferred embodiments, the scaffold protein comprises BBI.
Owner:DANISCO US INC
Scaffold product for human bone tissue engineering, methods for its preparation and uses thereof
InactiveUS20040191292A1Induced differentiationInduced proliferationBone implantSkeletal disorderOsteoblastCalcification
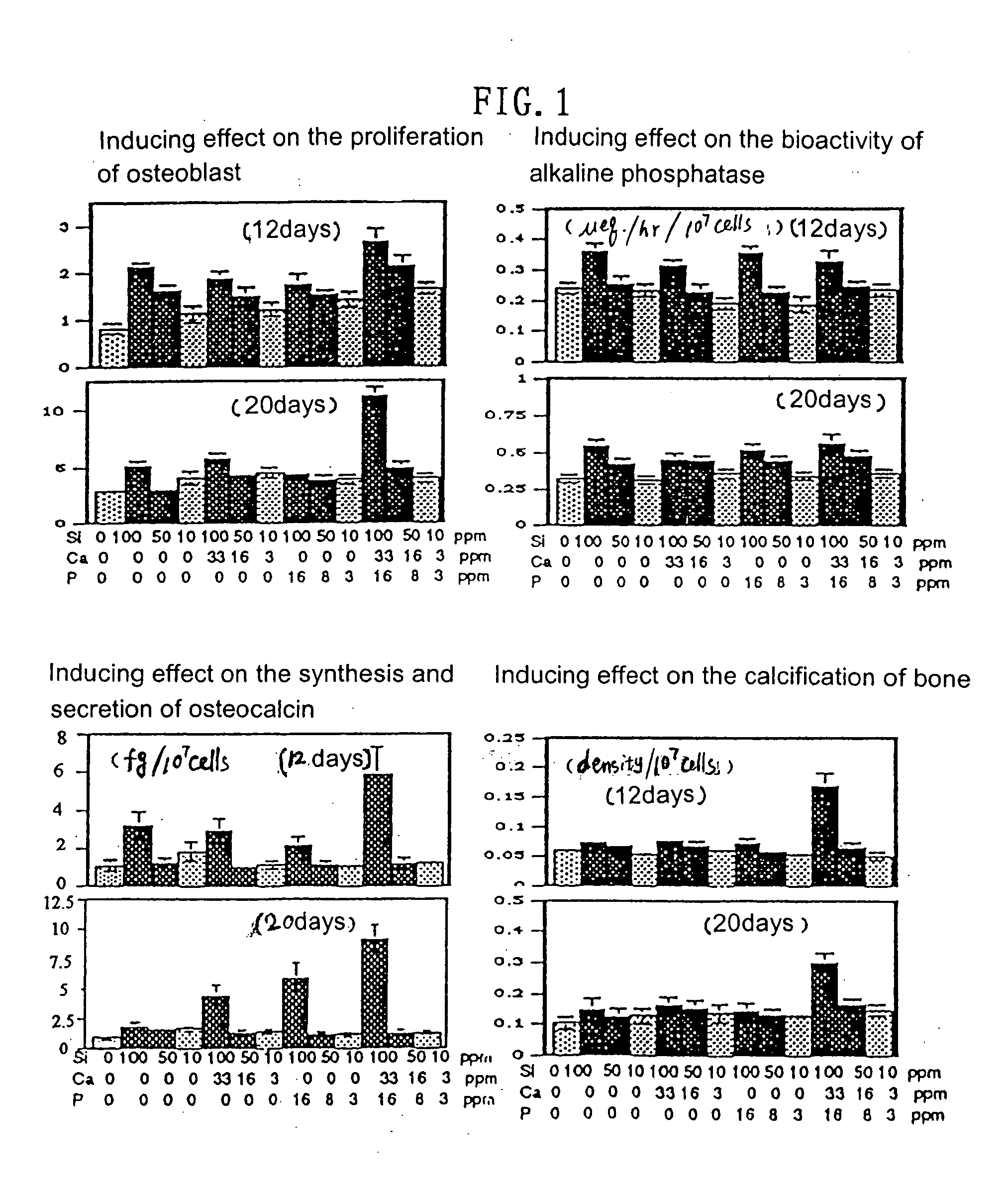
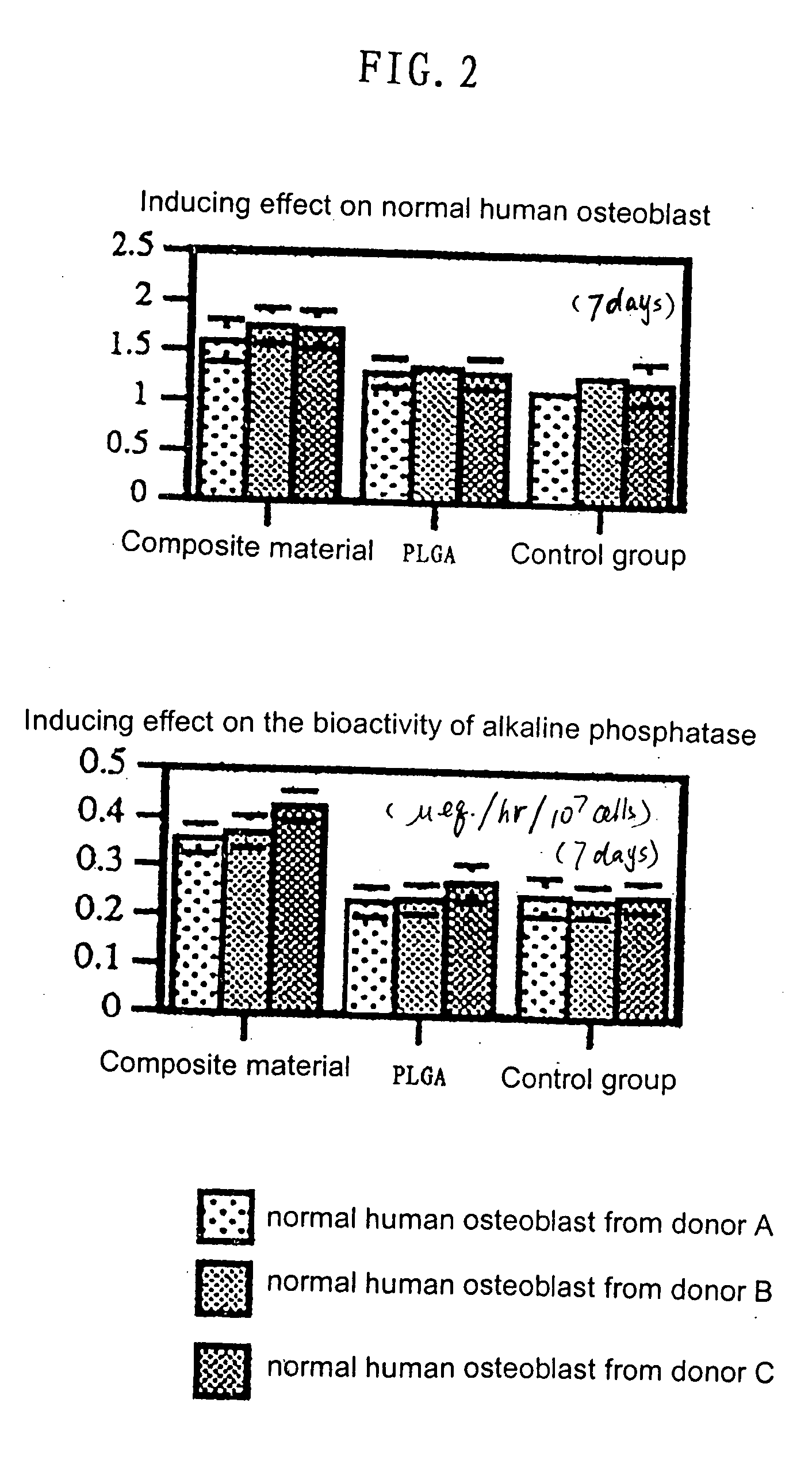
Scaffolds made of composite materials and uses thereof in the field of biomedical engineering are disclosed, wherein the composite materials comprise bioactive microparticles that could induce the human bone tissue to regenerate. The scaffolds uses the combination of silicon, calcium, and phosphorus microparticles as bioactive substance that could actively induce the human osteoblasts to proliferate and differentiate, promote the formation and calcification of new bone. Furthermore, the scaffolds employs organic polymer as carrier, takes a three-dimensional structure and external anatomical shape, and exhibits several characteristics compatible with the regeneration of bones and the neogenesis of blood vessels, thereby it could be used safely, economically and effectively for repairing the defect of bone tissue as well as in orthopedic operation of human bone. The present invention also discloses the methods for preparing the scaffolds.
Owner:YENSSEN BIOTECH
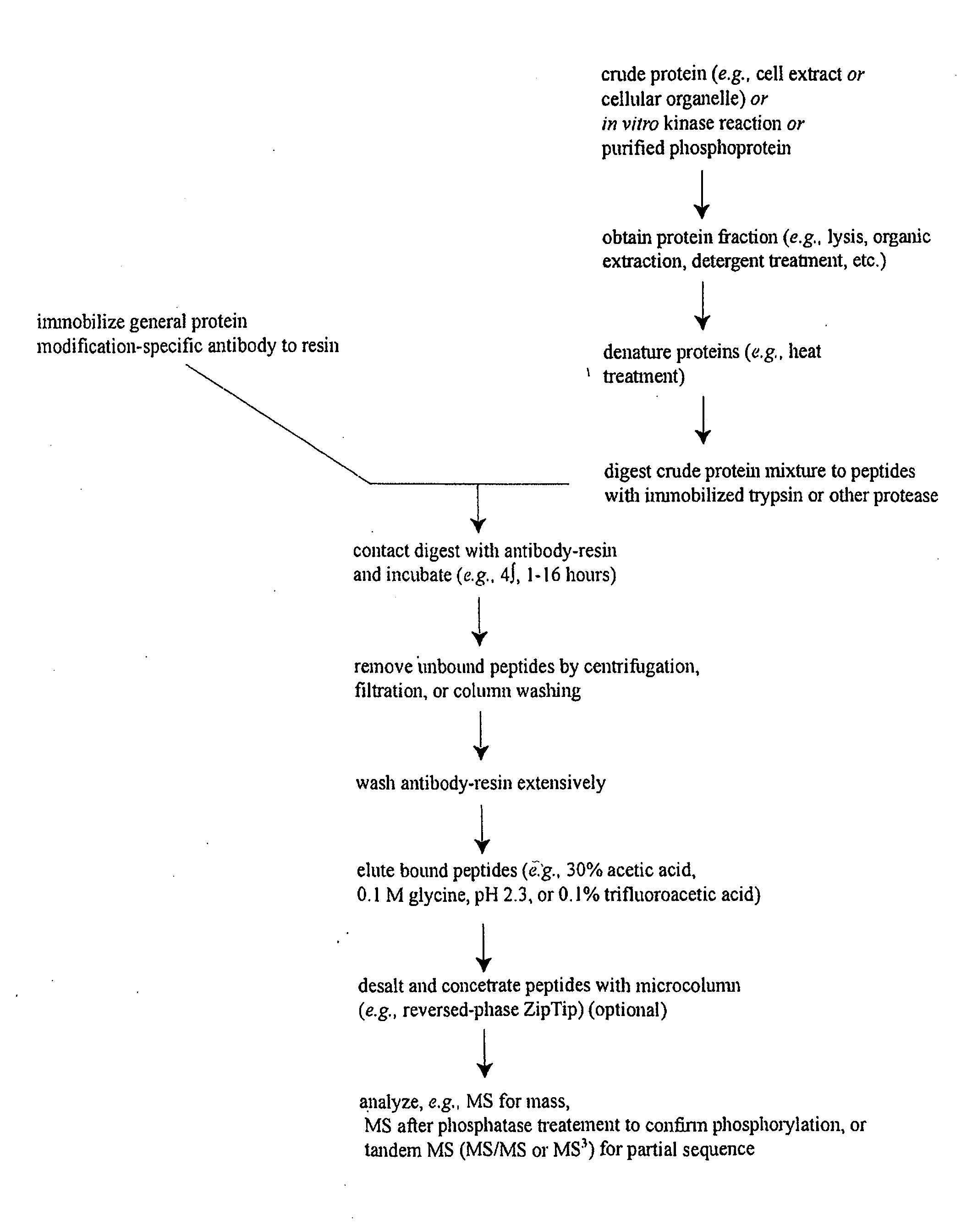
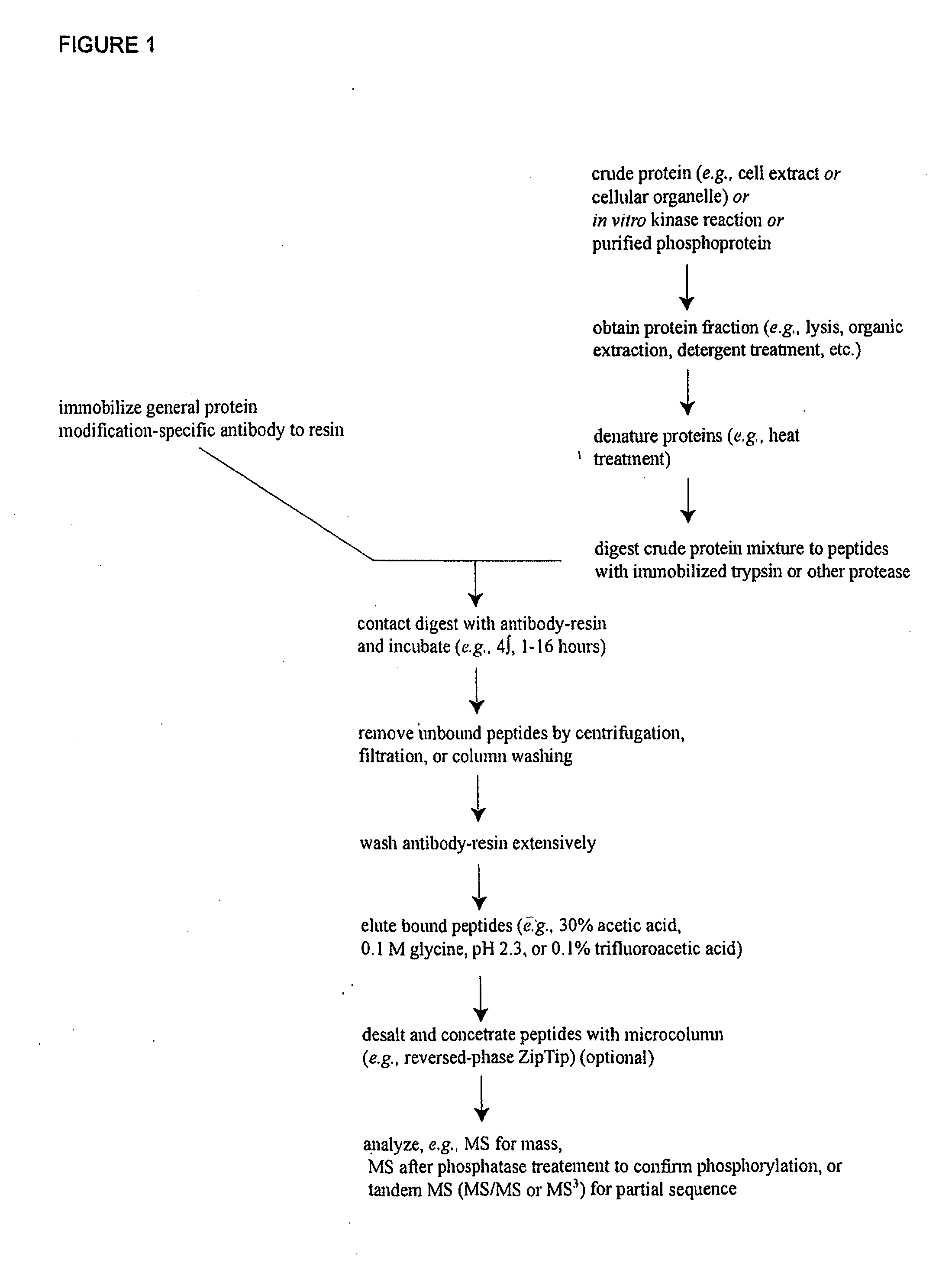
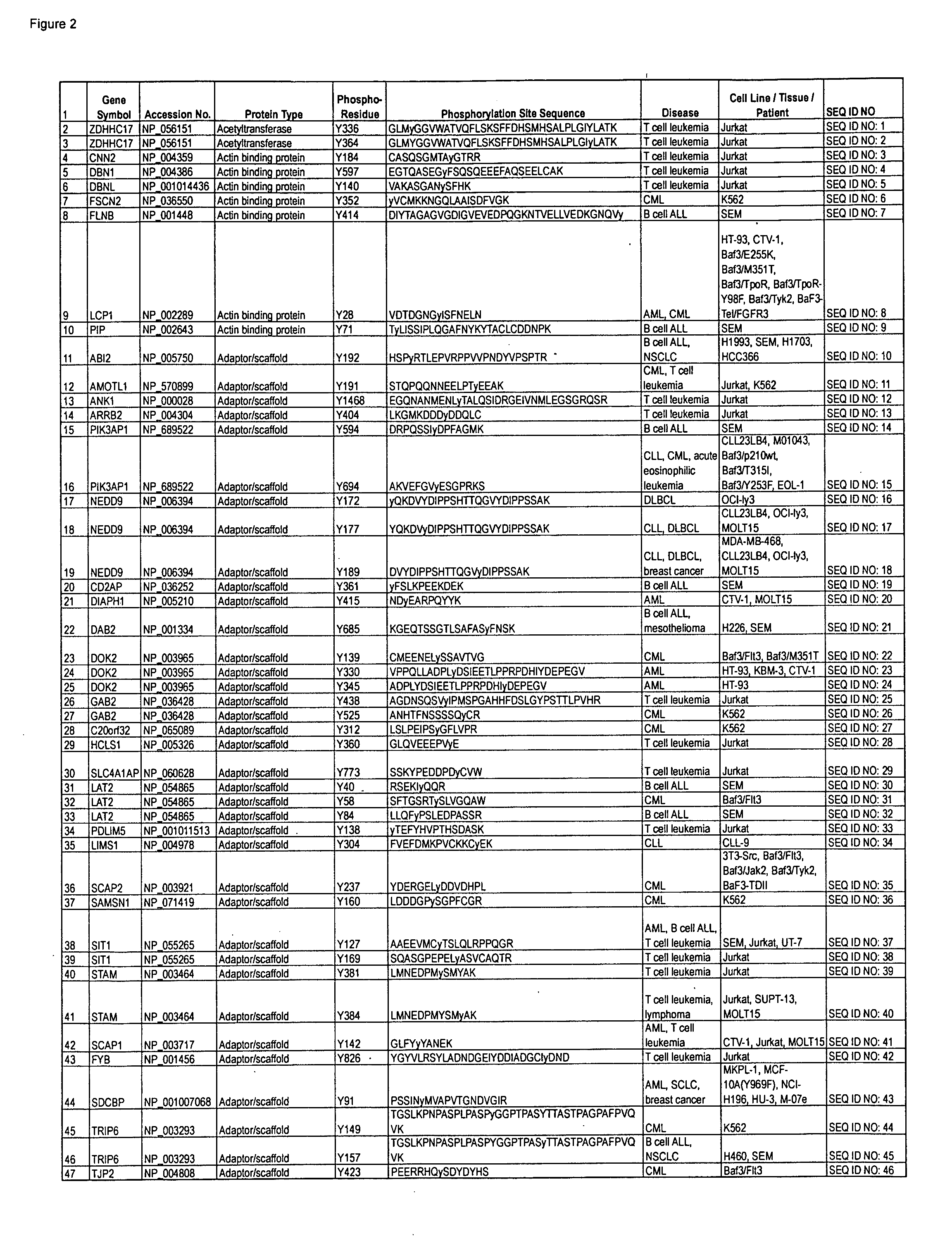
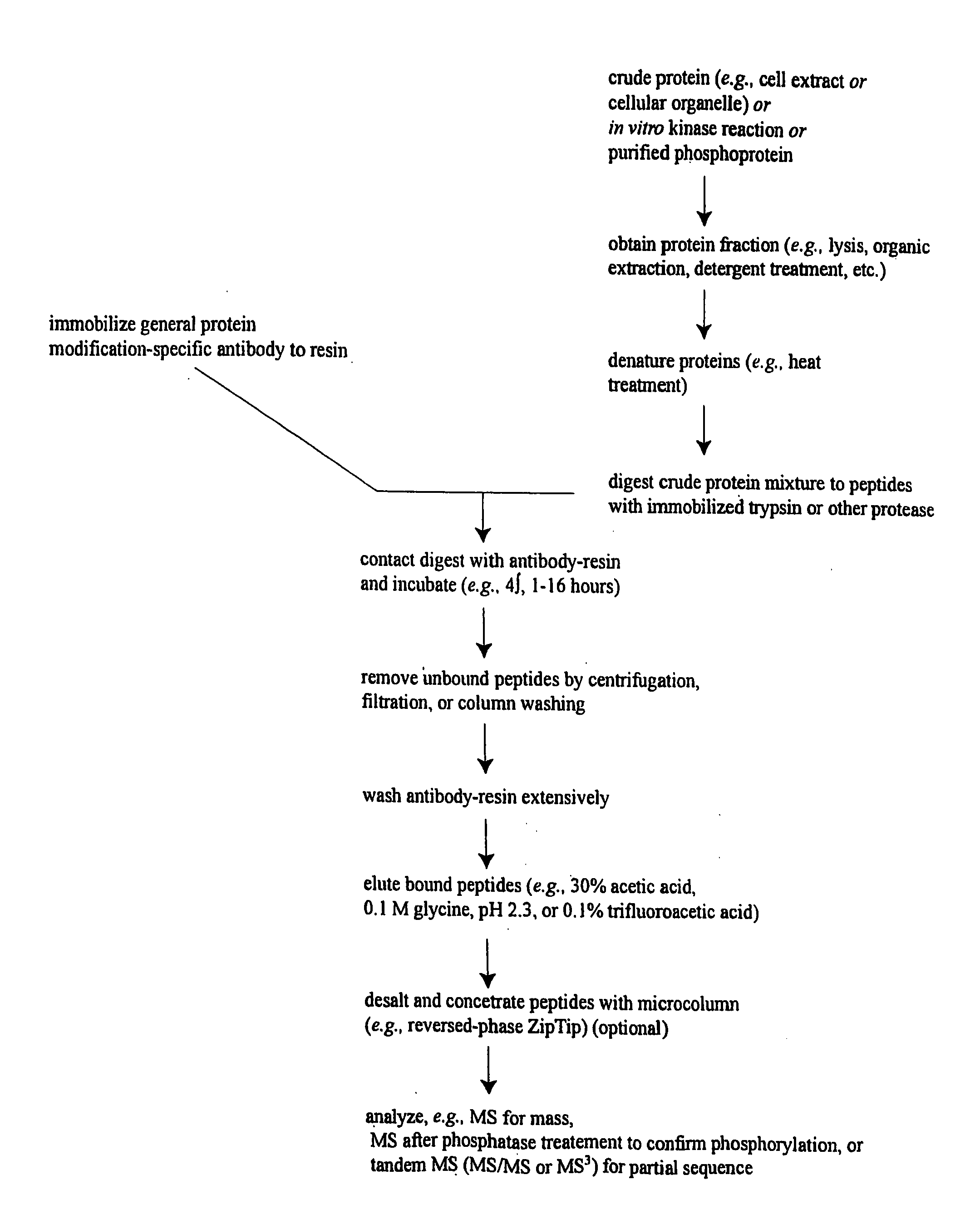
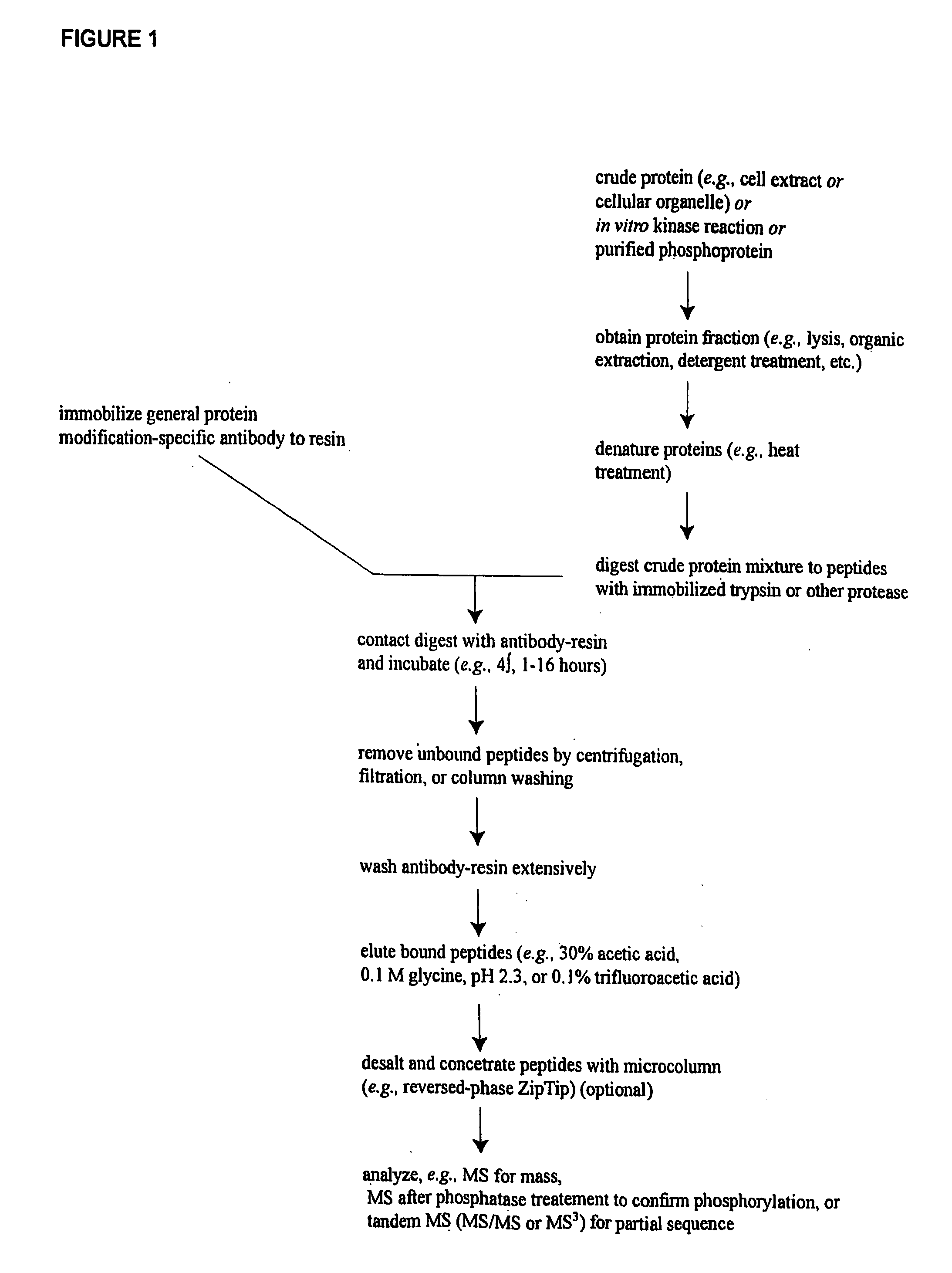
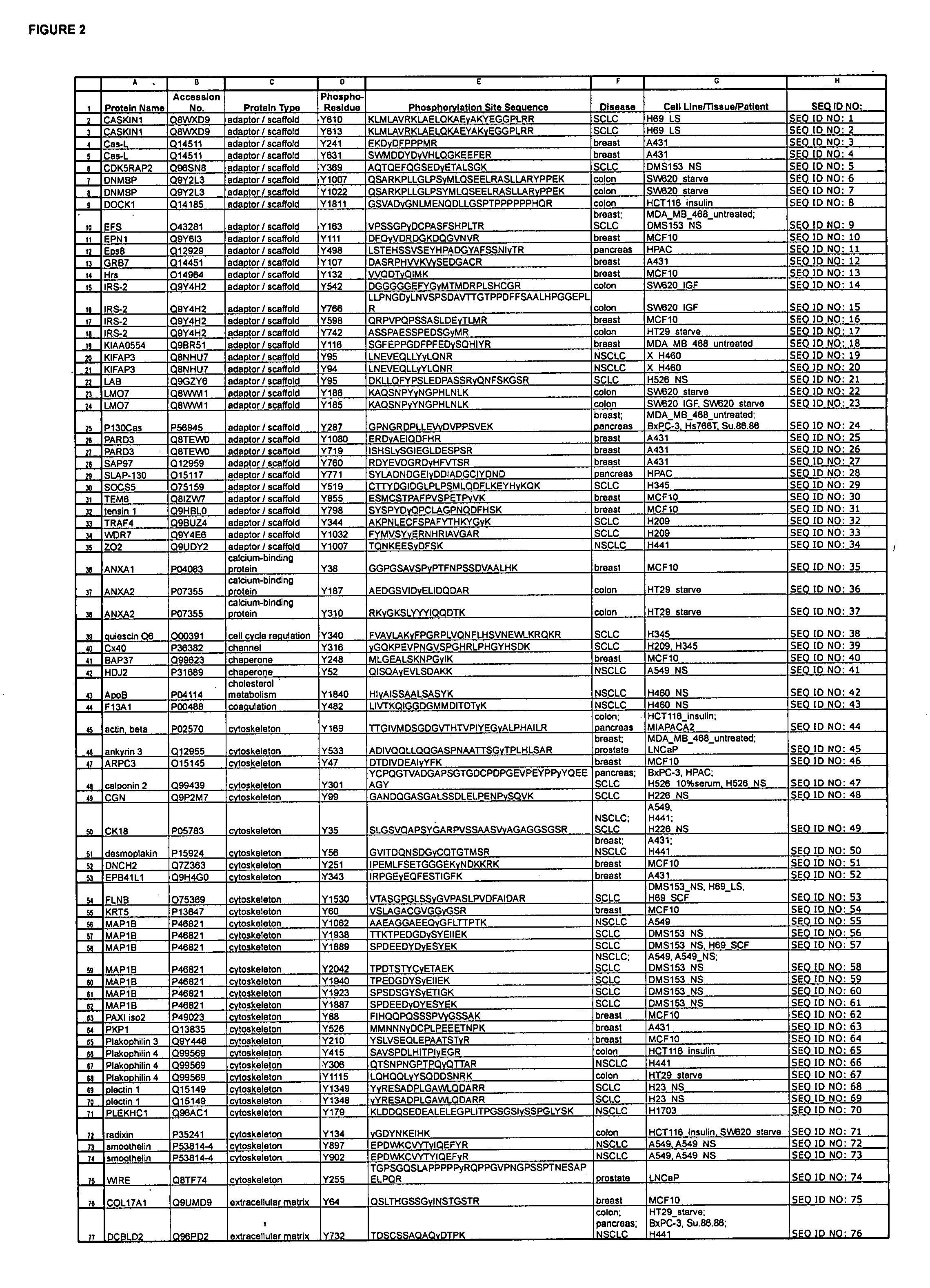
Reagents for the detection of protein phosphorylation in EGFR-signaling pathways
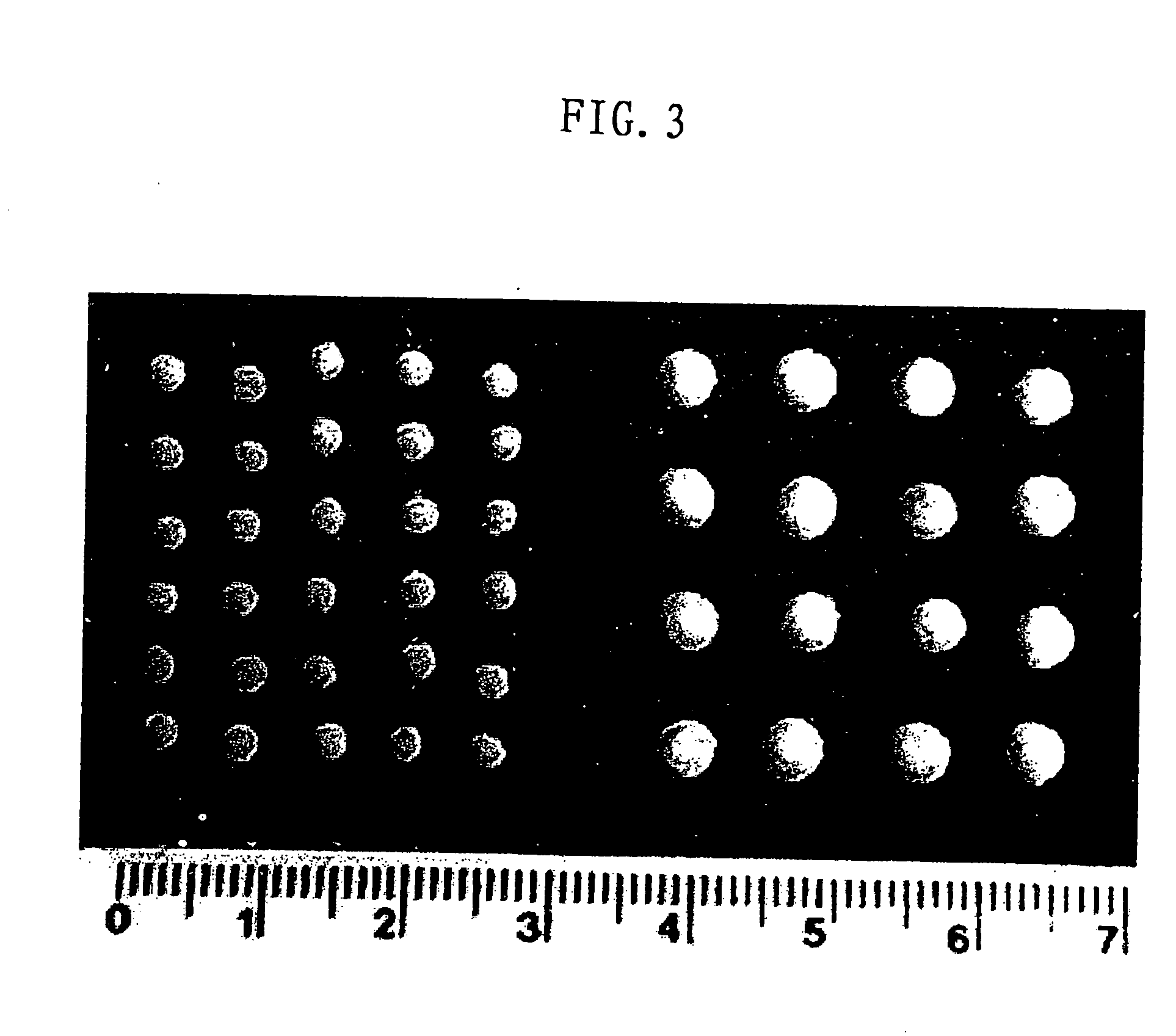
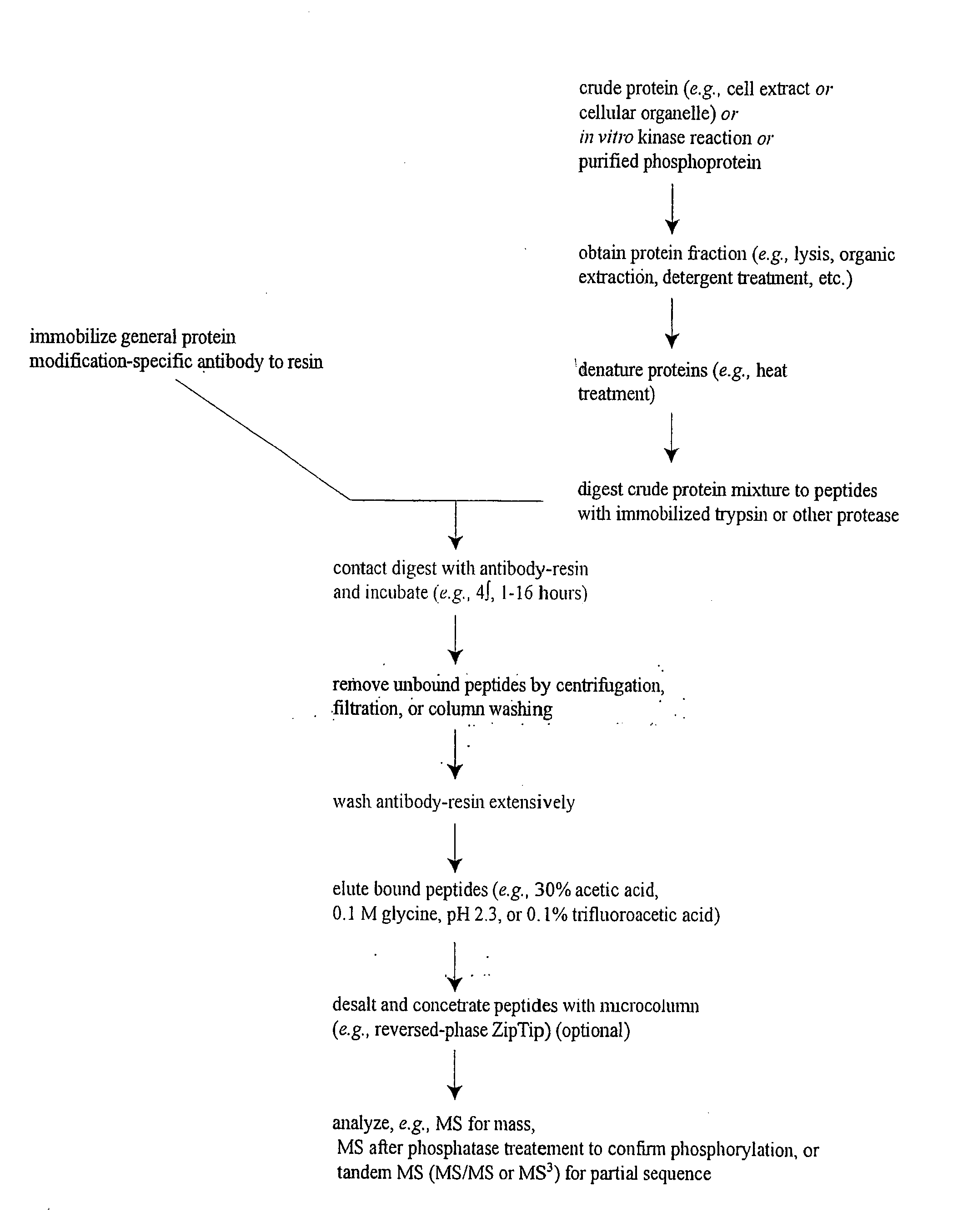
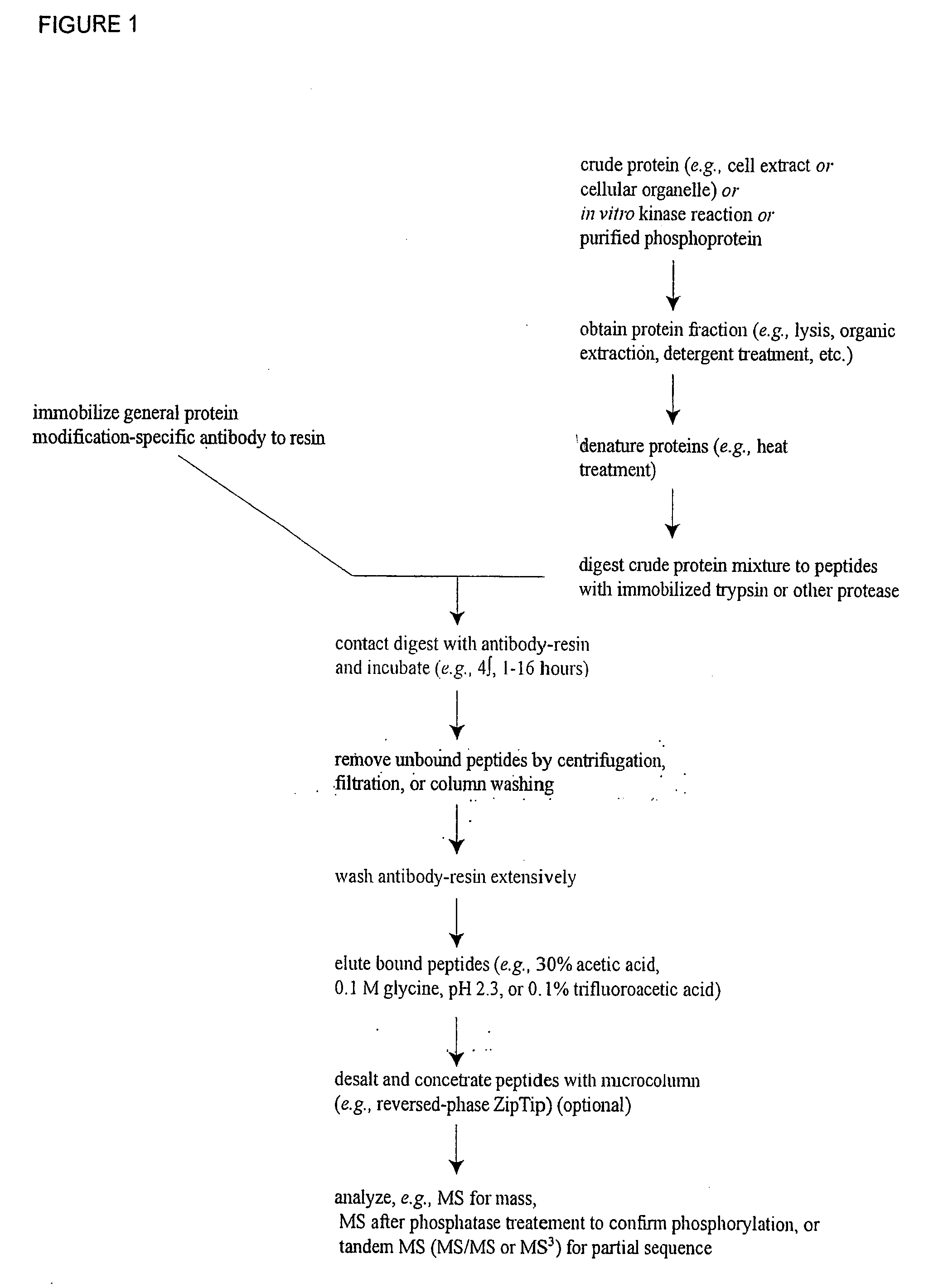
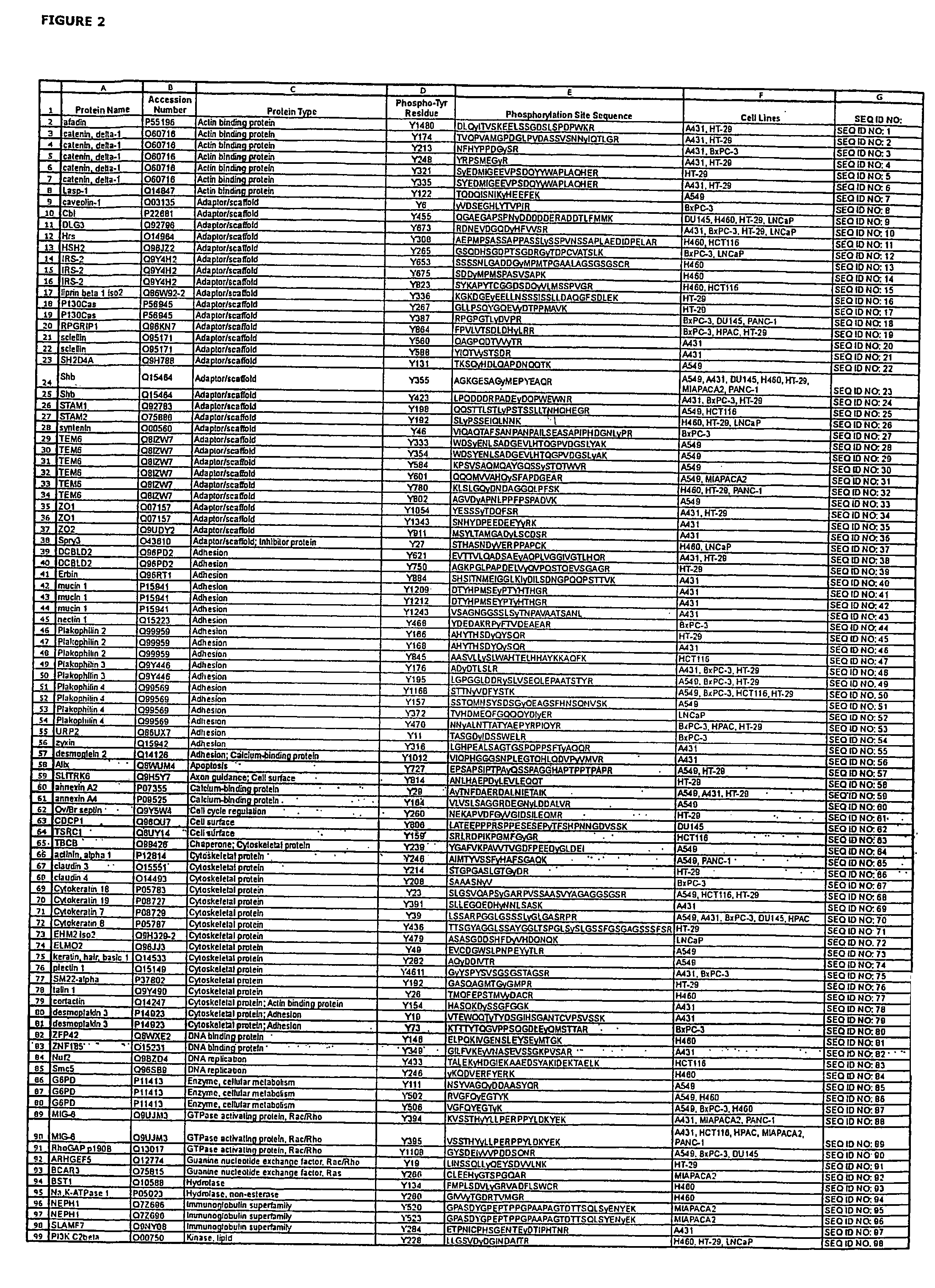
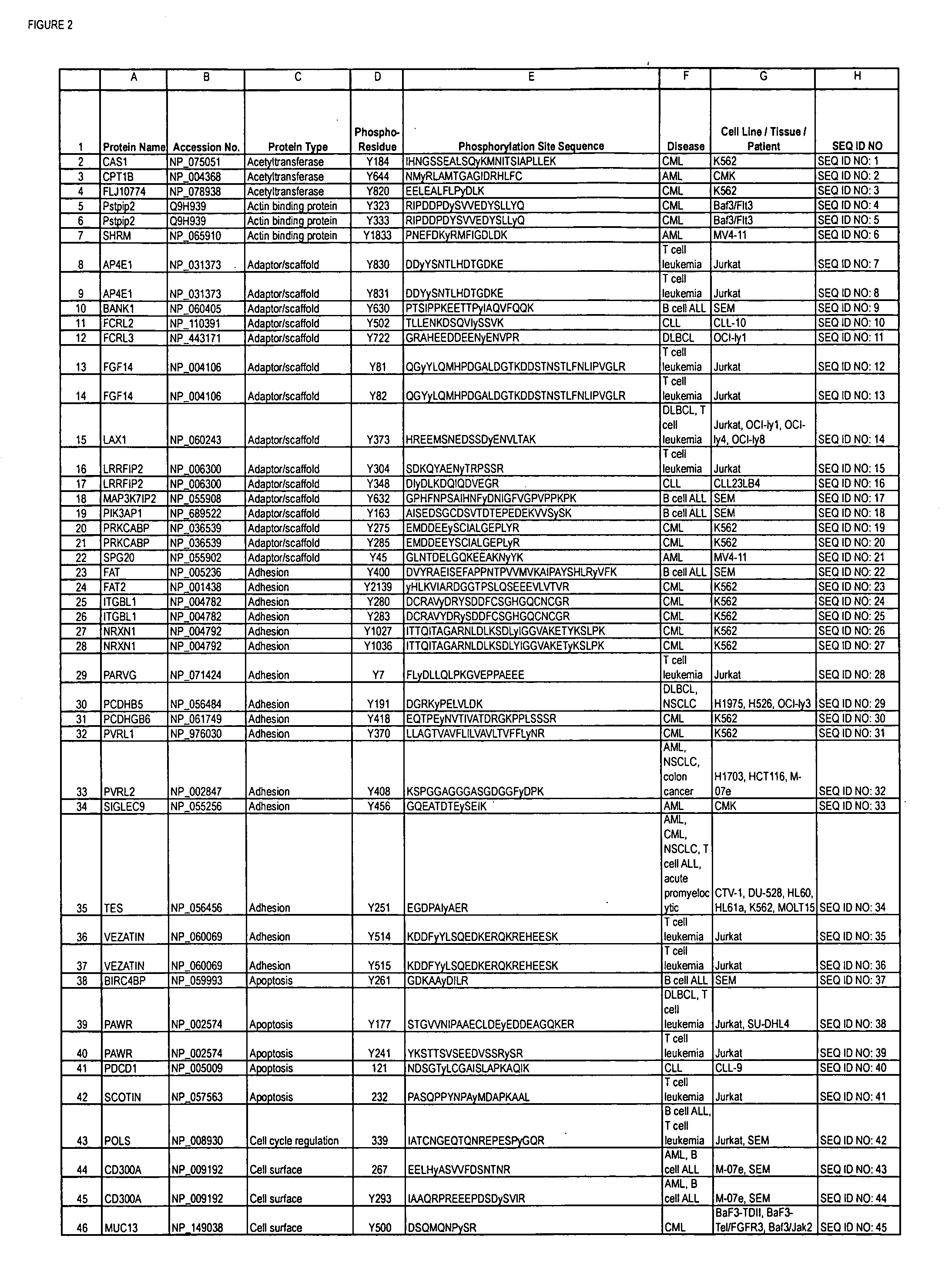
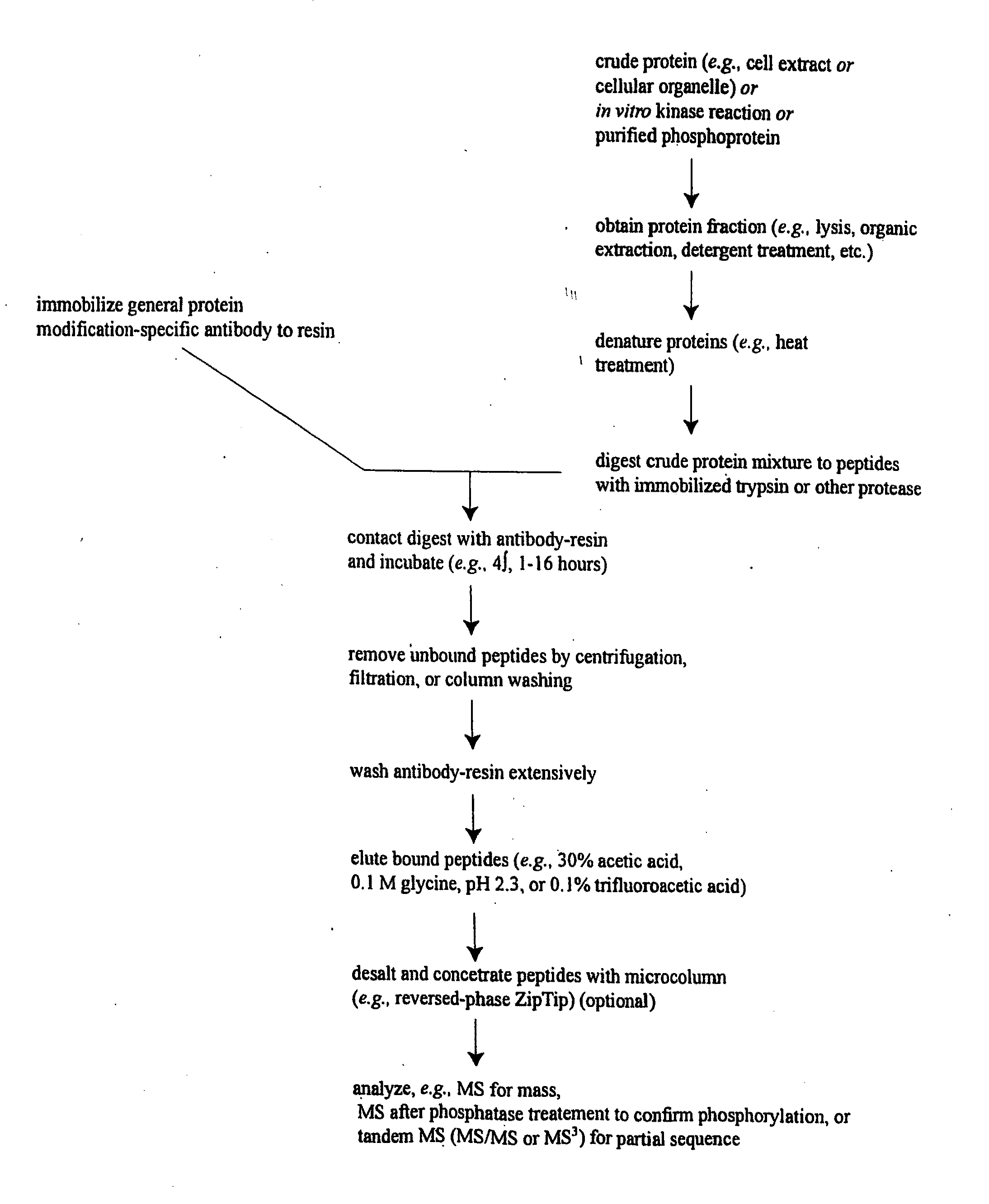
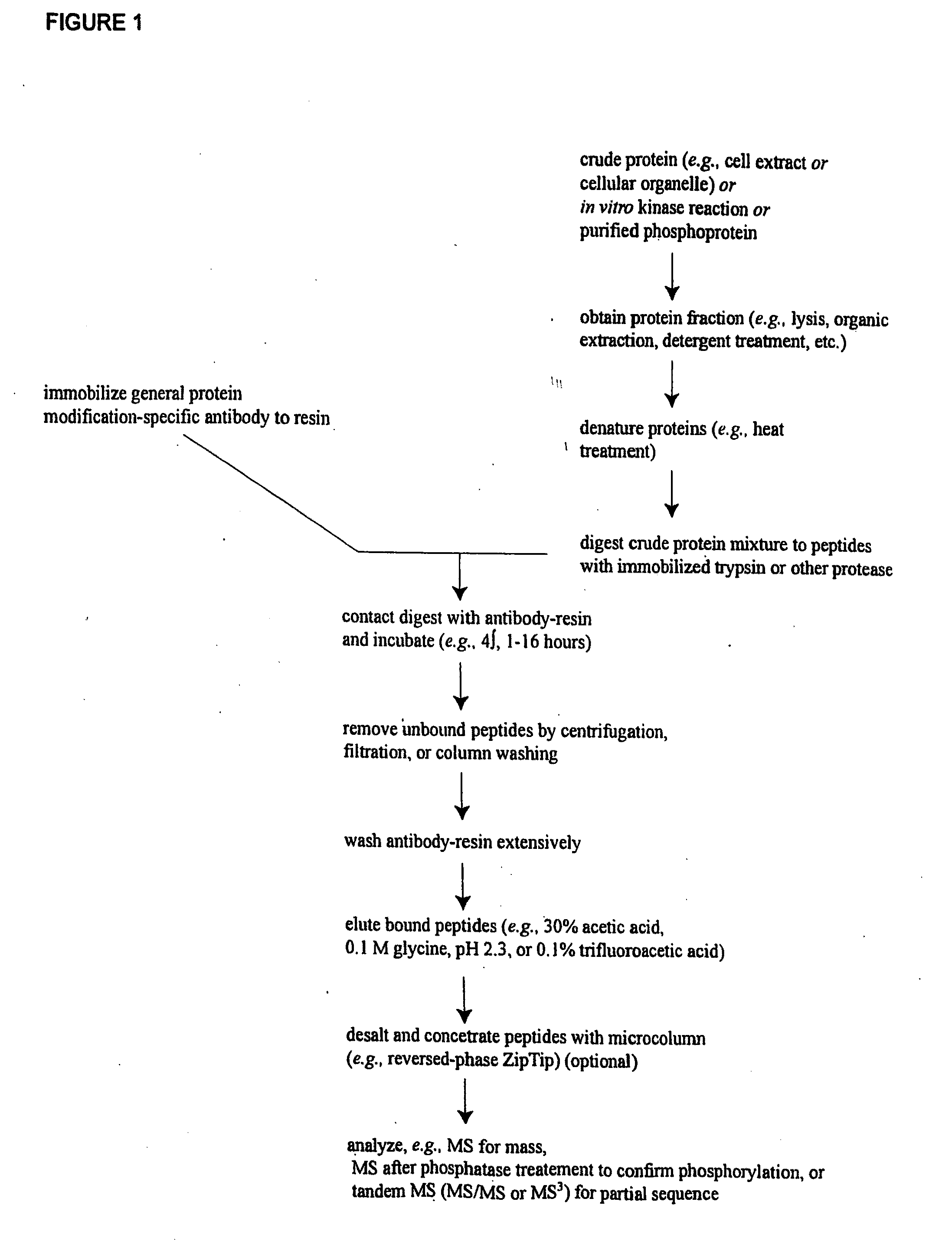
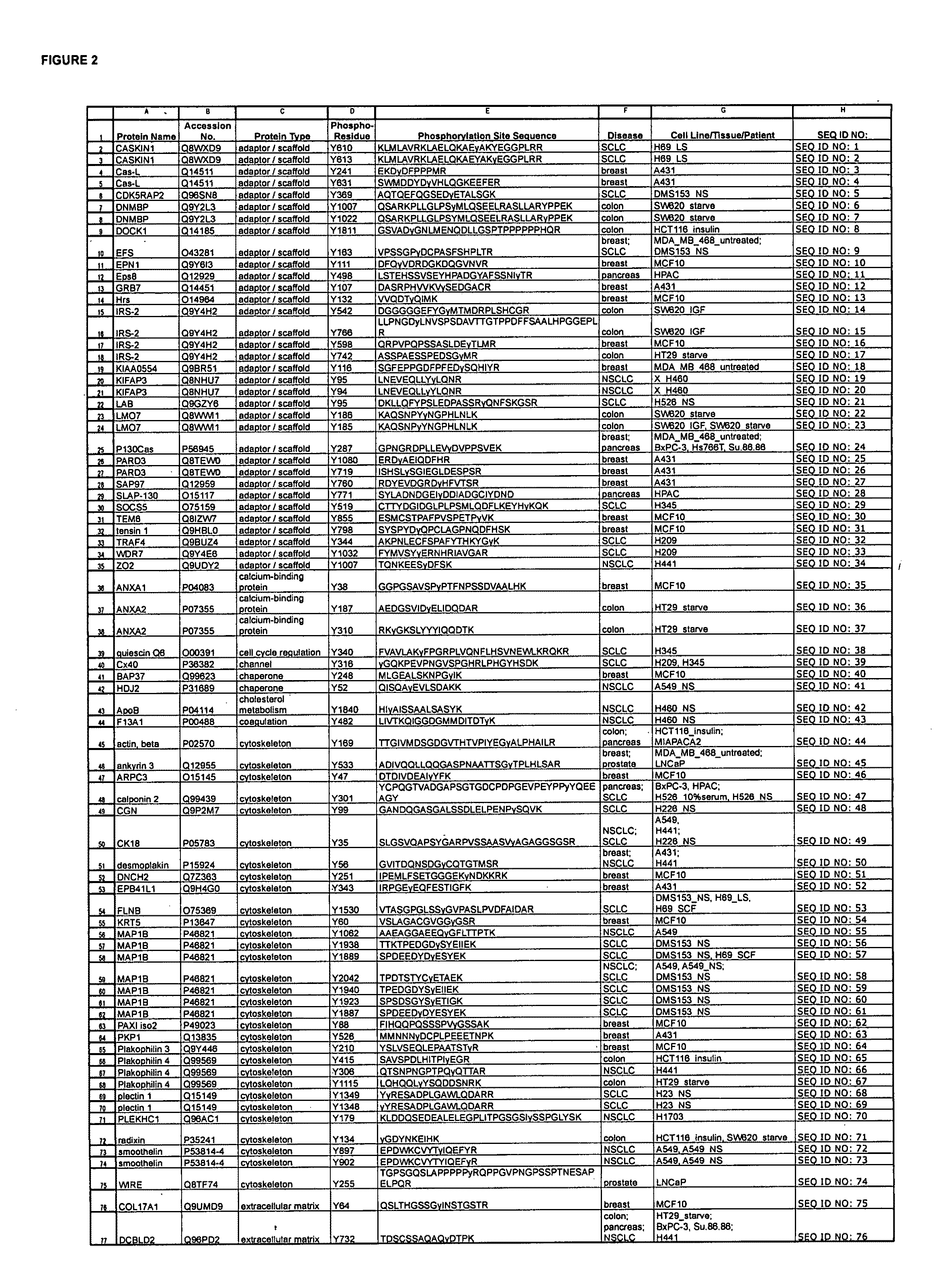
ActiveUS20080108795A1Isotope introduction to peptides/proteinsImmunoglobulins against animals/humansActin-binding proteinScaffold protein
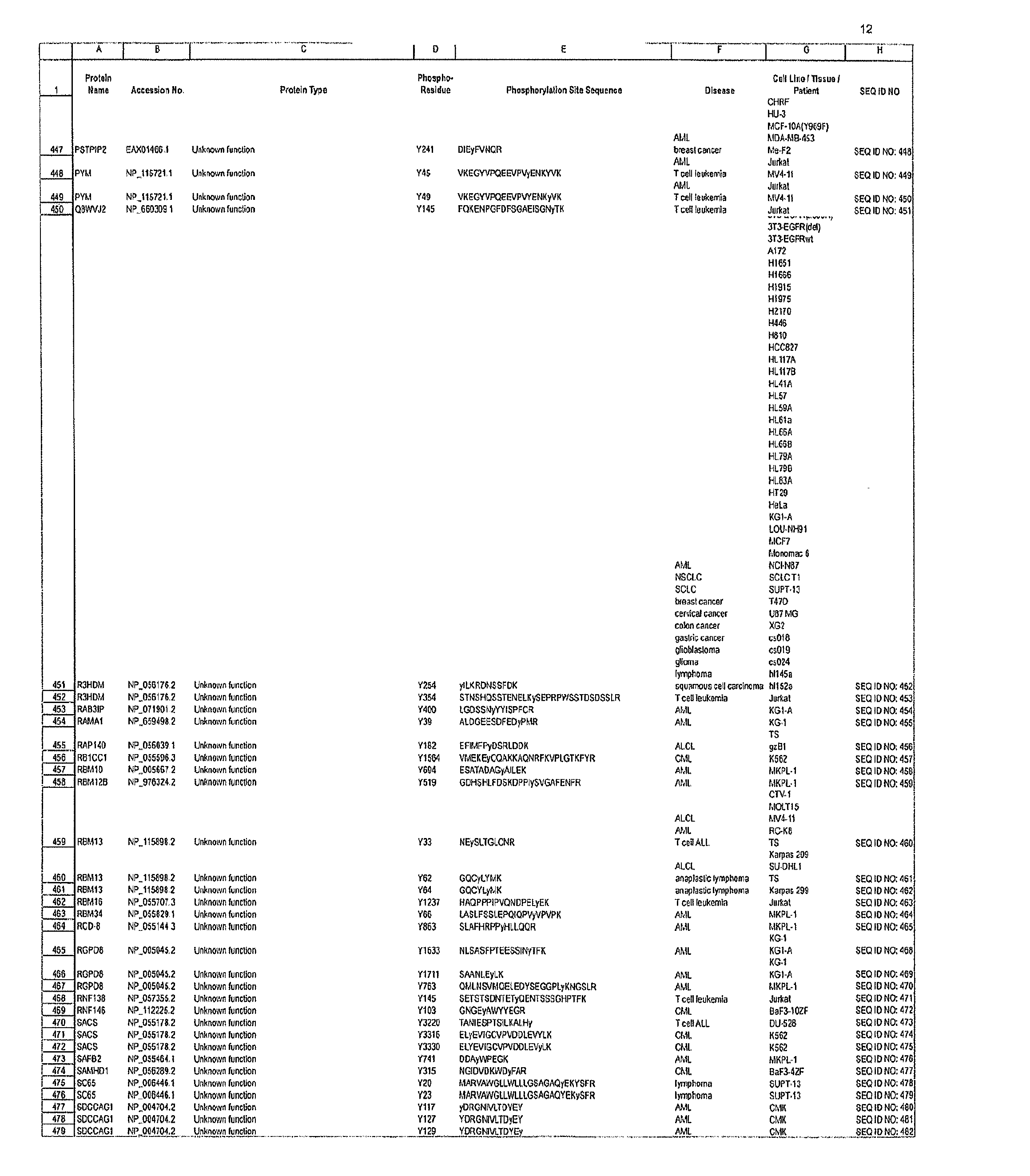
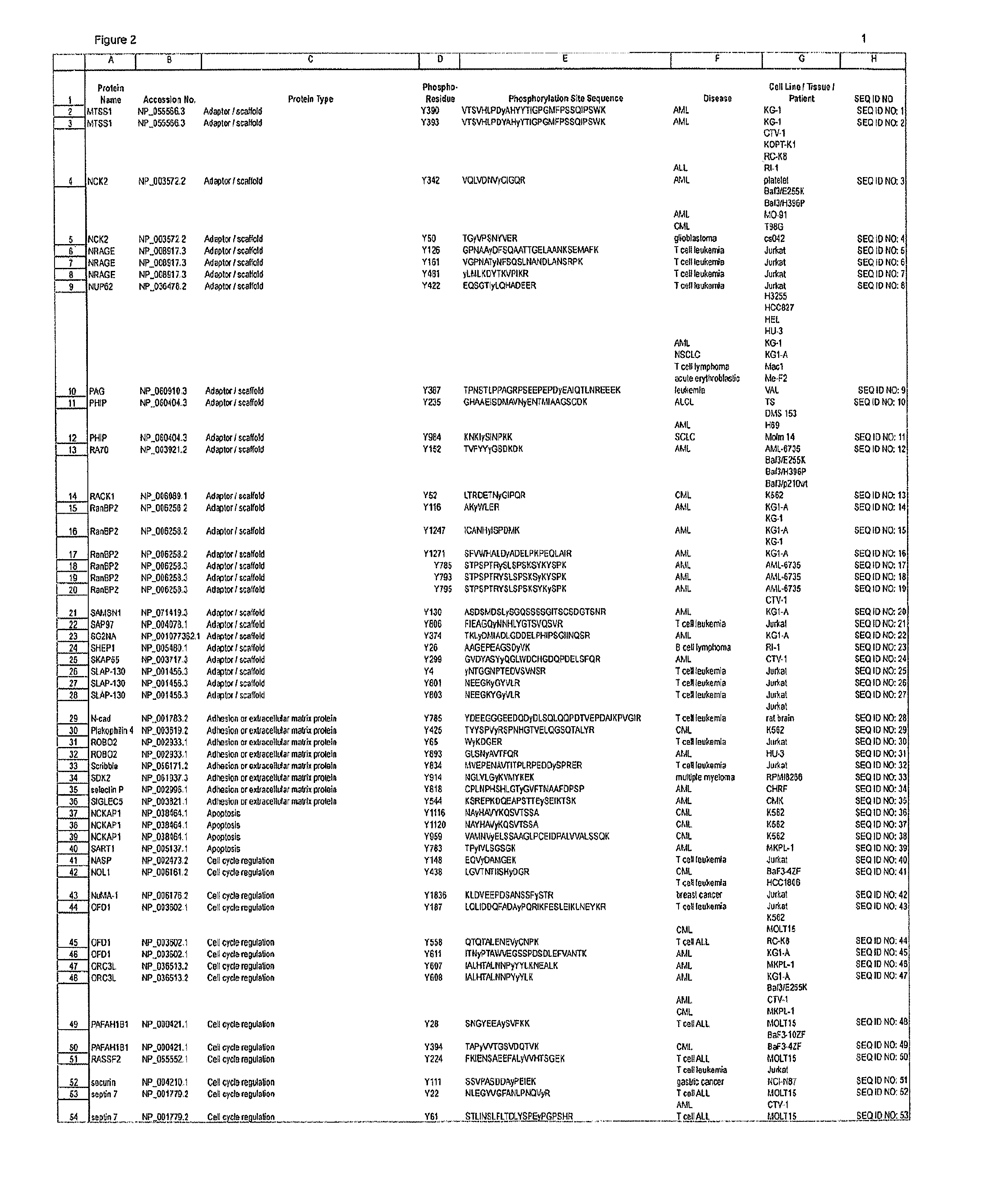
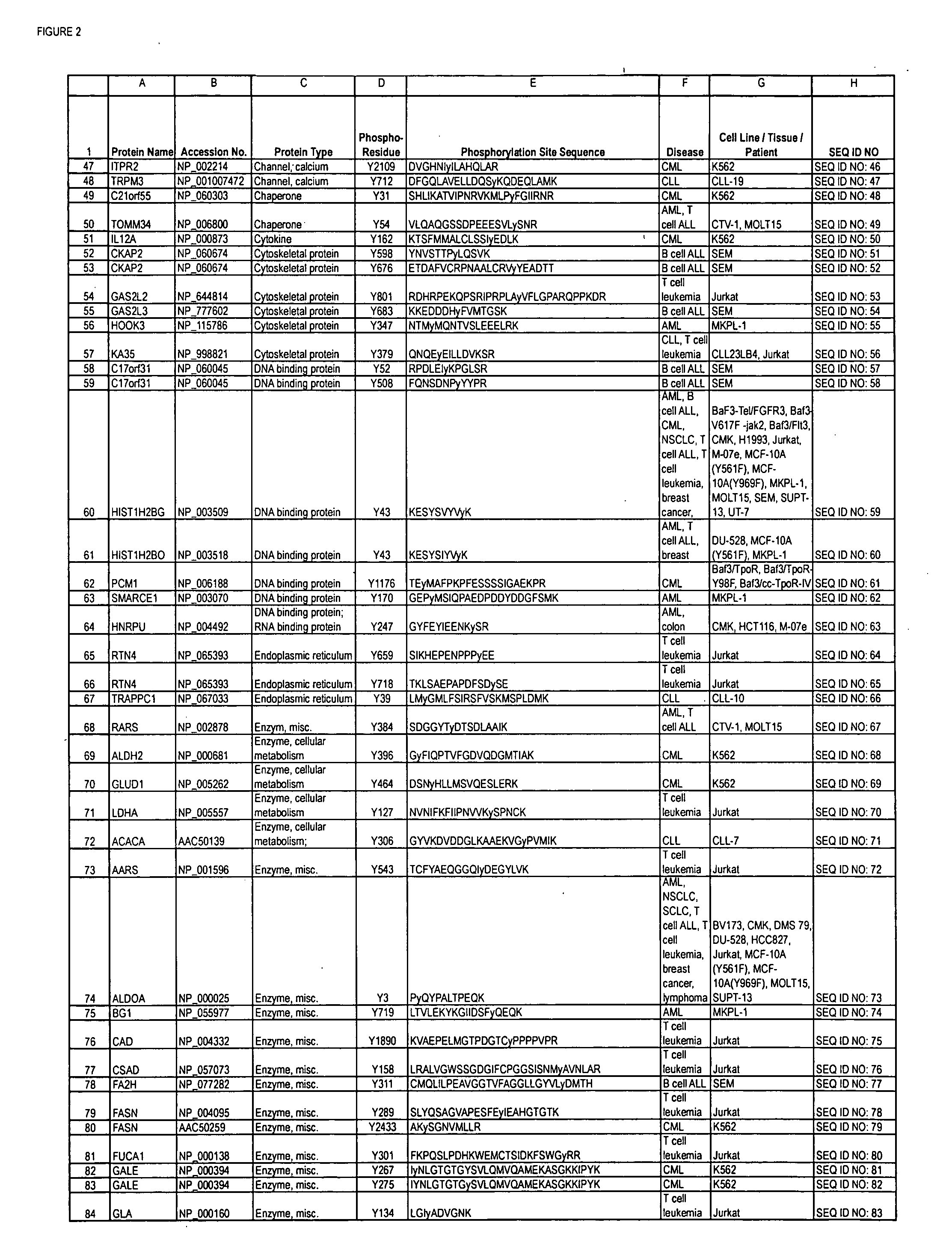
The invention discloses 168 novel phosphorylation sites identified in signal transduction proteins and pathways downstream of, and including, EGFR kinase, and provides phosphorylation-site specific antibodies and heavy-isotope labeled peptides (AQUA peptides) for the selective detection and quantification of these phosphorylated sites / proteins, as well as methods of using the reagents for such purpose. Among the phosphorylation sites identified are sites occurring in the following protein types: Actin Binding proteins, Adaptor / Scaffold proteins, Calcium-Binding Proteins, Cell Cycle Regulation proteins, Cytoskeletal proteins, DNA Binding and Replication Proteins, GTPase Activating proteins, Guanine Nucleotide Exchange Factor proteins, Lipid Kinases, Receptor Tyrosine Kinases, Receptor Tyrosine Kinase ligands, Protein Kinases, Receptor and Protein Phosphatases, Transcription Factor proteins, Tumor Suppressor proteins, and Vesicle proteins.
Owner:CELL SIGNALING TECHNOLOGY
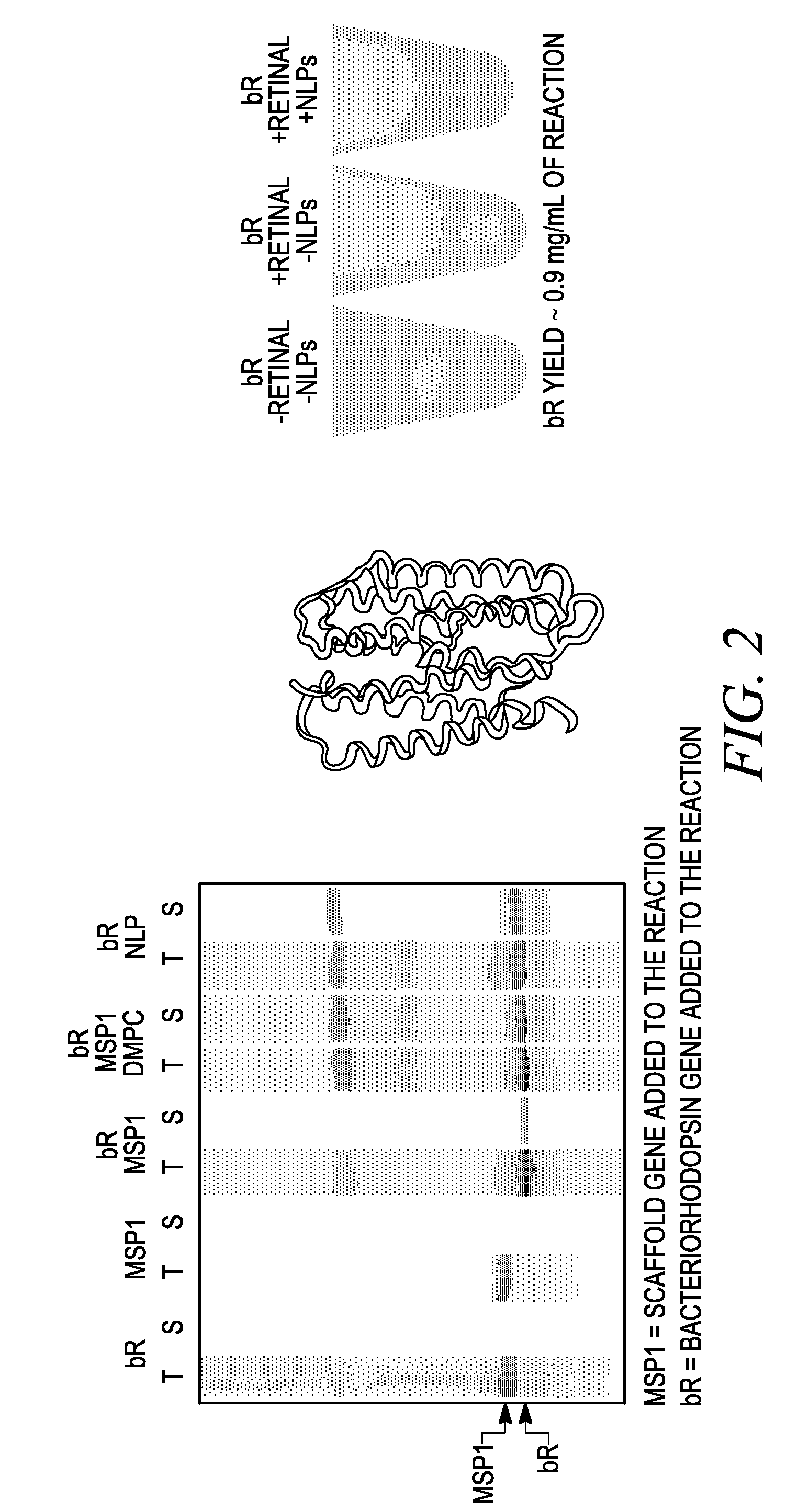
Methods and systems for monitoring production of a target protein in a nanolipoprotein particle
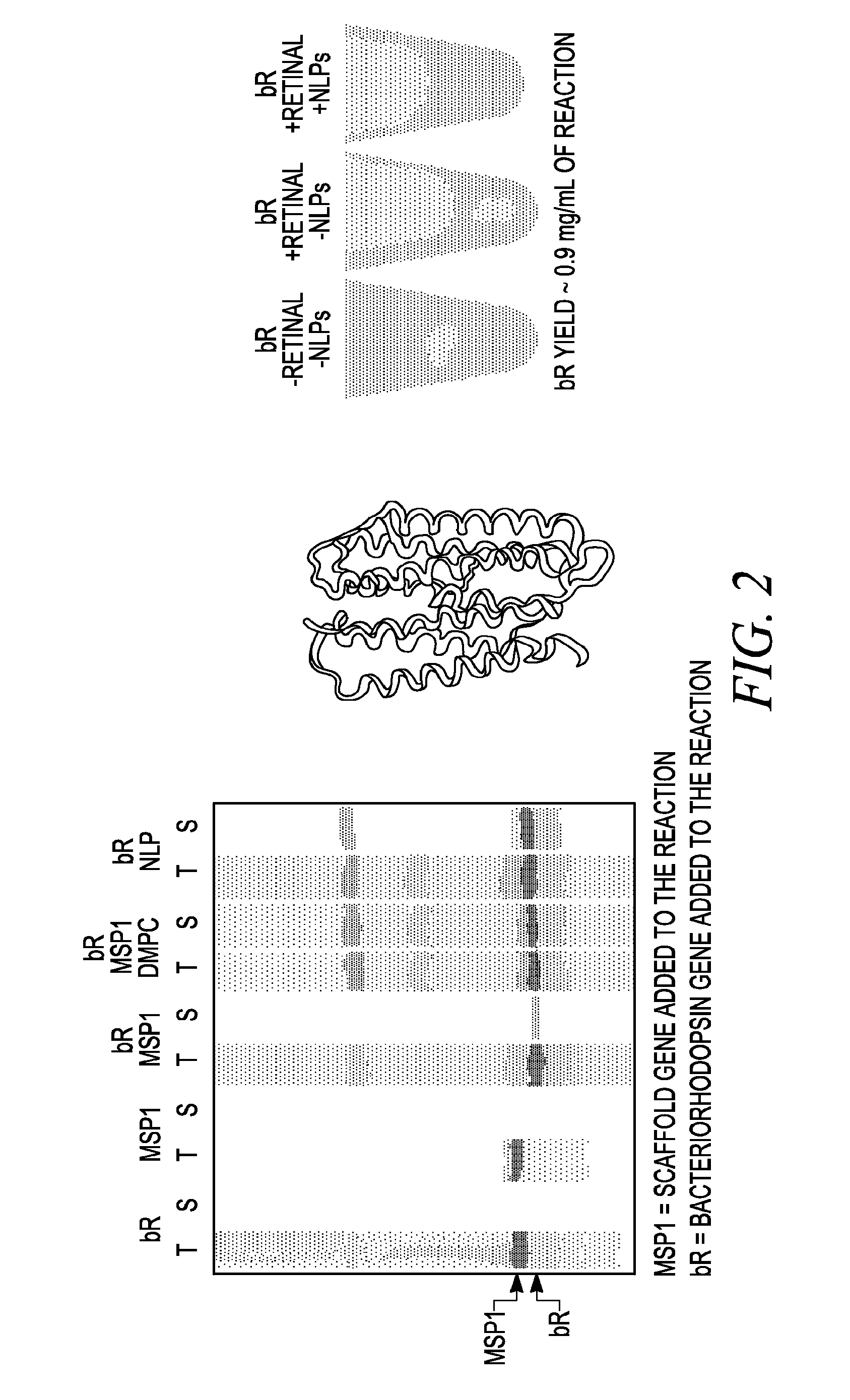
InactiveUS20090136937A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsLipid formationProtein target
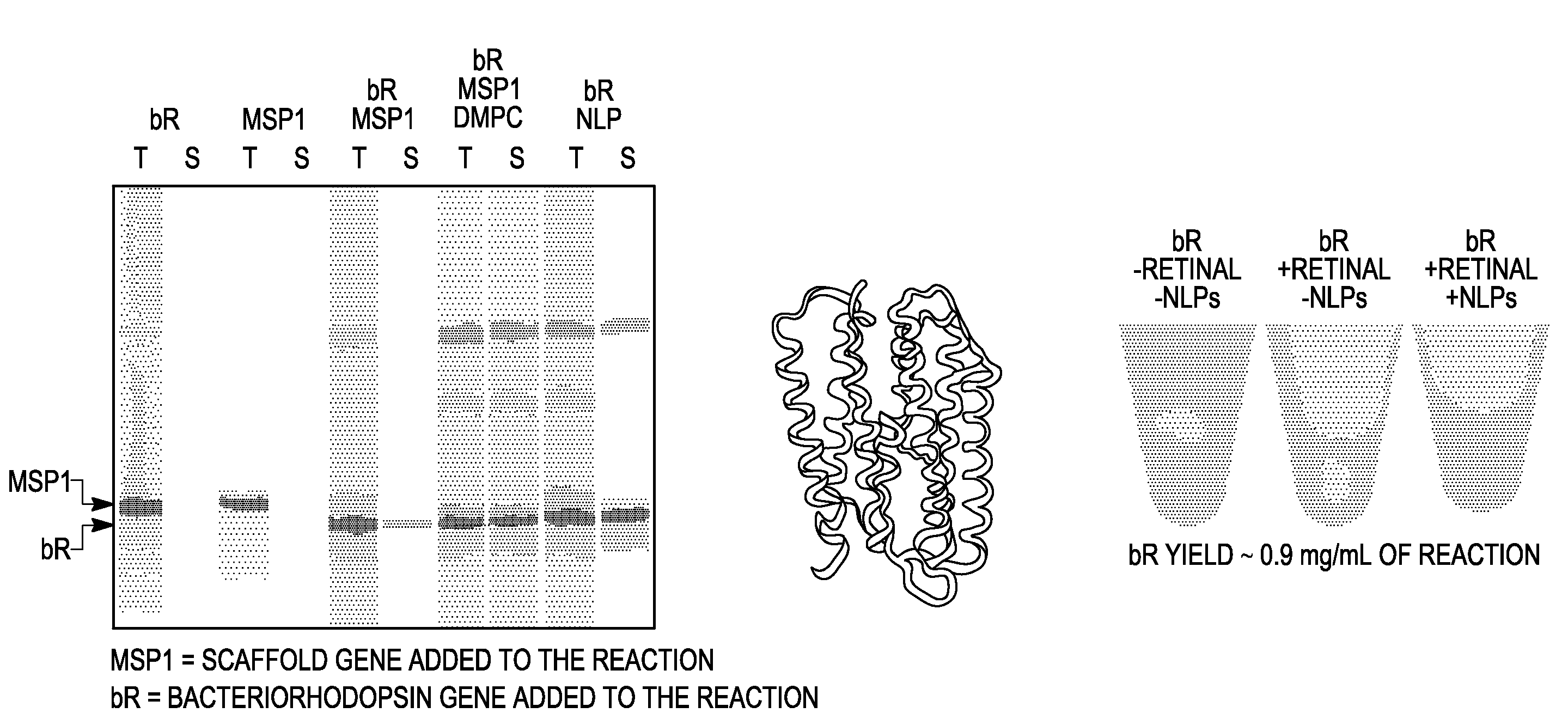
Provided herein are methods and systems for the monitoring production of a target protein in of a nanolipoprotein particle (NLP) that also includes a scaffold protein and a membrane forming lipid. The target protein is capable of assuming an active form and an inactive form. Monitoring is performed by an indicator protein that is capable of assuming an active form and an inactive form, the active form associated with a detectable activity of the indicator protein, the detectable activity further associated with the active form of the target protein.
Owner:LAWRENCE LIVERMORE NAT SECURITY LLC
Telodendrimer nanodiscs without apolipoprotein
The present invention provides a nanodisc without a membrane scaffold protein. The nanodisc includes a telodendrimer and a lipid; the nanodisc does not include a membrane scaffold protein. The telodendrimer has the general formula PEG-L-D-(R)n, wherein D is a dendritic polymer; L is a bond or a linker linked to the focal point group of the dendritic polymer; each PEG is a poly(ethylene glycol) polymer; each R is and end group of the dendritic polymer, or and end group with a covalently bound hydrophobic group, hydrophilic group, amphiphilic compound, or drug; and subscript n is an integer from 2 to 20. Methods of making the nanodiscs are also provided.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Fibronectin based scaffold proteins having improved stability
ActiveUS9562089B2Improve stabilityReduce fragmentationBacteriaPeptide/protein ingredientsScaffold proteinProteinoid
Owner:BRISTOL MYERS SQUIBB CO
Fibronectin based scaffold proteins having improved stability
ActiveUS20170166627A1Improve stabilityReduce fragmentationConnective tissue peptidesPeptide/protein ingredientsNucleotideScaffold protein
The present application provides fibronectin based scaffold proteins associated with improved stability. The application also relates to stable formulations of fibronectin based scaffold proteins and the use thereof in diagnostic, research and therapeutic applications. The application further relates to cells comprising such proteins, polynucleotides encoding such proteins or fragments thereof, and to vectors comprising such polynucleotides.
Owner:BRISTOL MYERS SQUIBB CO
Membrane scaffold proteins
InactiveUS7592008B2Increase stability and monodispersityImprove purification effectPeptide/protein ingredientsPharmaceutical delivery mechanismNative structurePhospholipid
The membrane scaffold proteins (MSP) of the present invention assemble with hydrophobic or partially hydrophobic proteins to form soluble nanoscale particles which preserve native structure and function; they are improved over liposomes and detergent micelles, in terms of stability and preservation of biological activity and native conformation. In the presence of phospholipid, MSPs form nanoscopic phospholipid bilayer disks, with the MSP stabilizing the particle at the perimeter of the bilayer domain. The particle bilayer structure allows manipulation of incorporated proteins in solution or on solid supports, including for use with such surface-sensitive techniques as scanning probe microscopy or surface plasmon resonance. The nanoscale particles, which are robust in terms of integrity and maintenance of biological activity of incorporated proteins, facilitate pharmaceutical and biological research, structure / function correlations, structure determinations, bioseparations, and drug discovery.
Owner:BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS THE A BODY & POLITIC OF THE STATE OF ILLINOIS
Isolated phospholipid-protein particles
InactiveUS20080248565A1Speed up the processImprove solubilityPeptide preparation methodsDepsipeptidesADAMTS ProteinsApolipoproteins E
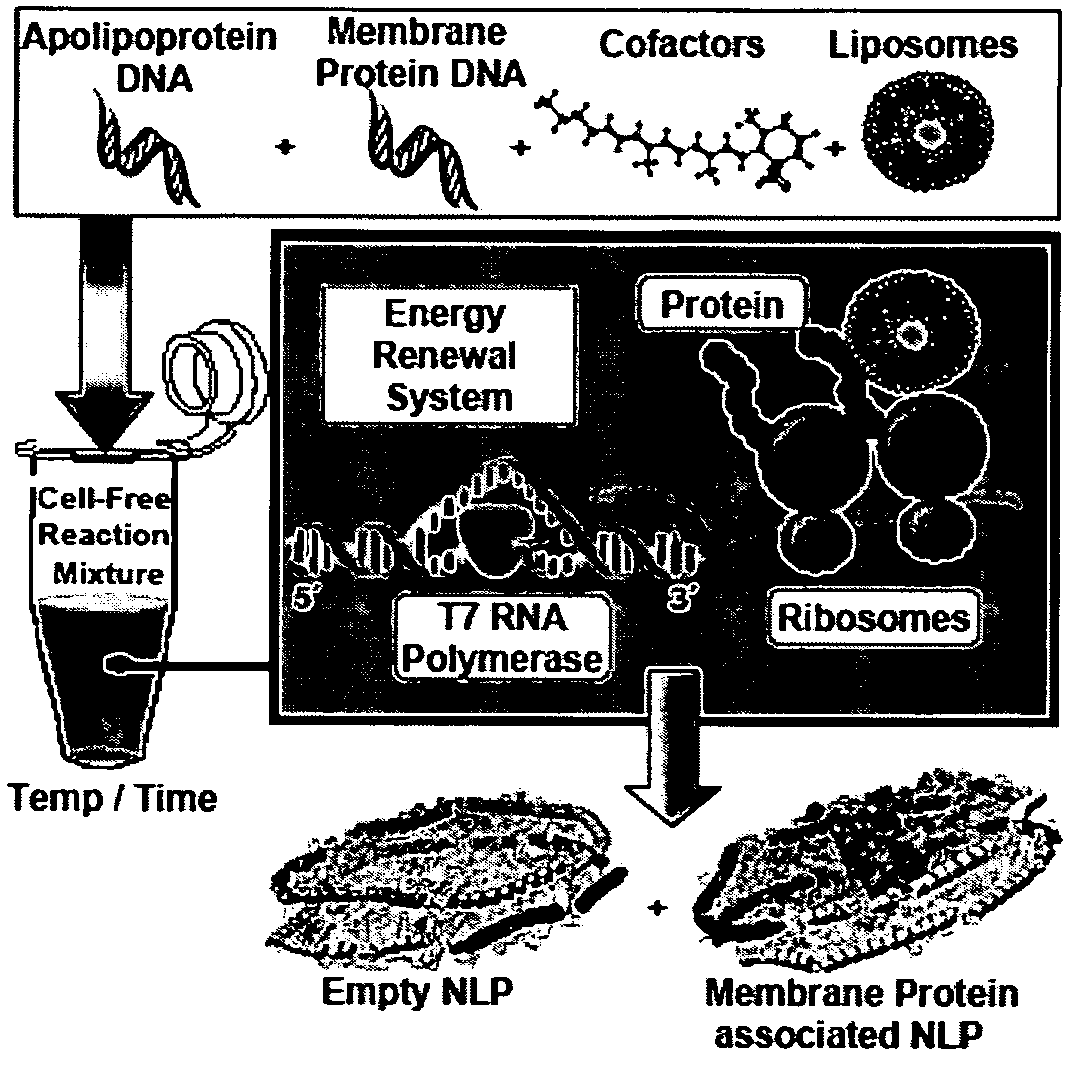
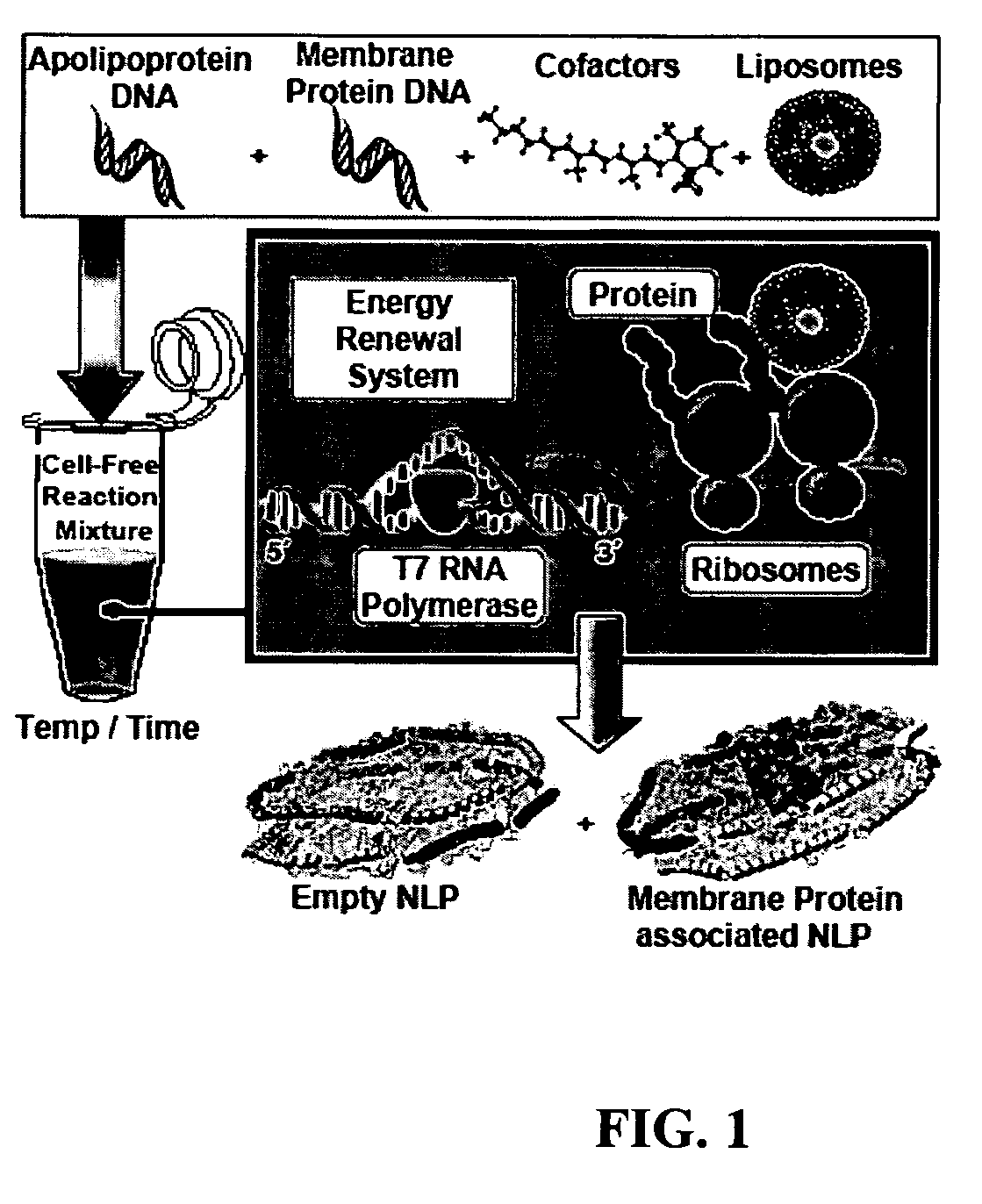
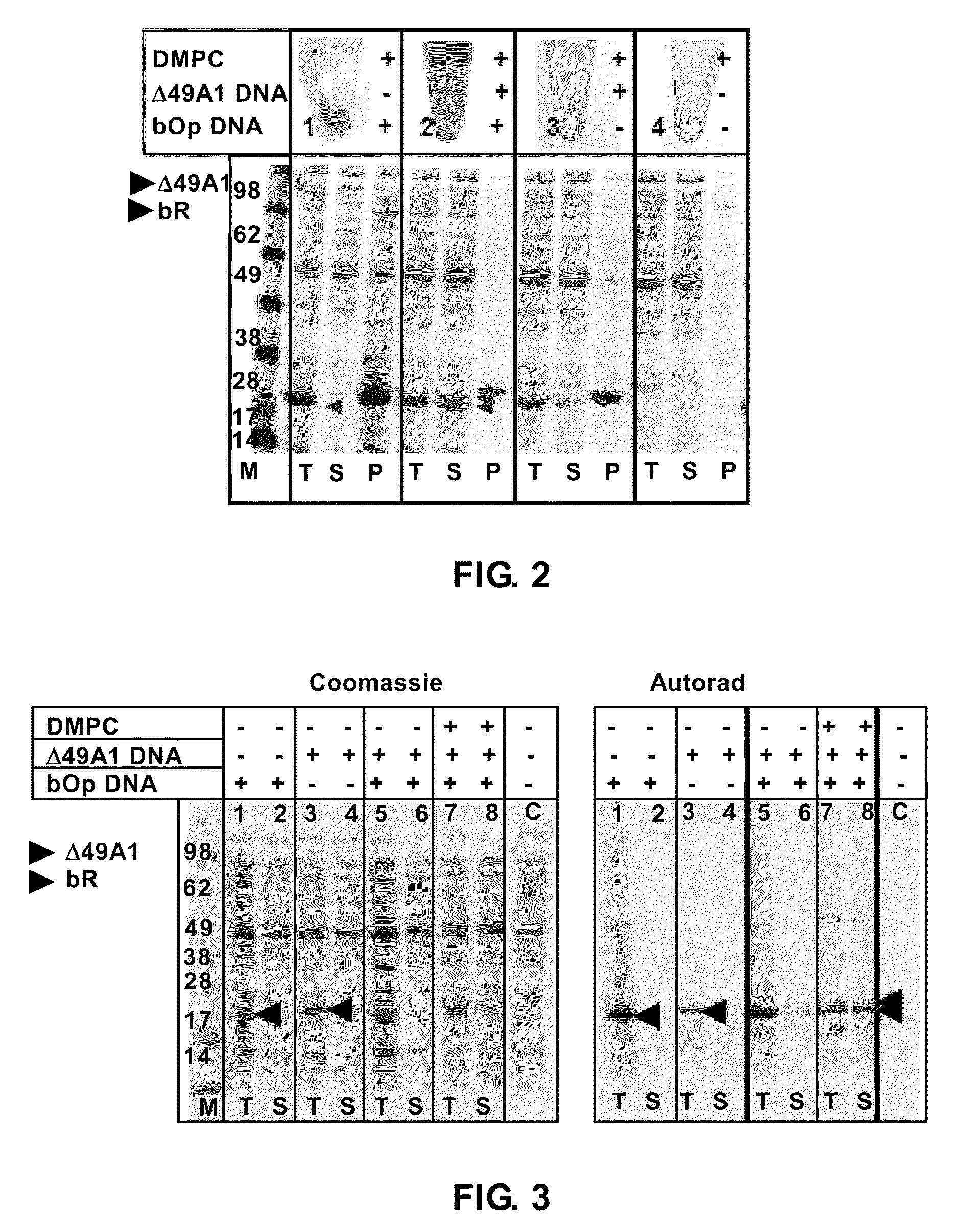
Systems and methods are provided for producing a protein of interest that is typically not amenable to expression in soluble form in in vitro expression systems. In some aspects, the invention provides methods of synthesizing proteins using in vitro protein synthesis systems that include a scaffold protein such as apolipoprotein or an amphipathic alpha helix containing (“AAHC”) protein, in which higher yields of soluble protein are produced than in the absence of the scaffold protein. The scaffold proteins may be provided in an in vitro protein synthesis system associated with lipid or not associated with lipid. The scaffold protein may be provided as a protein per se or may be encoded by a nucleic acid template and co-expressed with the protein of interest. The invention also provides compositions and kits for synthesis of proteins in soluble form, in which the compositions and kits include cell extracts for protein expression and isolation.
Owner:LIFE TECH CORP
Scaffold polypeptides for heterologous peptide display
The present invention relates to the use of Stefin A as a scaffold protein for the display of inserted peptides, particularly wherein the Stefin A is a human Stefin A. Several mutations are advantageously made in the wild type stefin A sequence to improve it as a scaffold; preferably the Stefin A comprises a heterologous peptide insertion at the Leu 73 site. Furthermore, preferably the scaffold protein comprises a V48D mutation; preferably the scaffold protein comprises a G4W mutation. Preferably the scaffold comprises Leu73, V48D and G4W mutations. The invention also relates to the scaffold proteins themselves, in particular a stefin A polypeptide having the Leu73, V48D and G4W mutations, such as shown as SEQ ID NO: 1. The invention also relates to a method for identifying binding proteins and to peptide A (RLNKPLPSLPV) and its use in treating yeast infections.
Owner:MEDICAL RESEARCH COUNCIL
Fibronectin based scaffold domain proteins that bind to myostatin
ActiveUS20140105896A1Inhibit myostatin activityIncreased muscle volumeBacteriaPeptide/protein ingredientsMyostatinFibrosis
The present invention relates to fibronectin-based scaffold domain proteins that bind to myostatin. The invention also relates to the use of these proteins in therapeutic applications to treat muscular dystrophy, cachexia, sarcopenia, osteoarthritis, osteoporosis, diabetes, obesity, COPD, chronic kidney disease, heart failure, myocardial infarction, and fibrosis. The invention further relates to cells comprising such proteins, polynucleotides encoding such proteins or fragments thereof, and to vectors comprising the polynucleotides encoding the proteins.
Owner:VERTIGO MEDIA INC +1
Reagents for the Detection of Protein Phosphorylation in Signaling Pathways
ActiveUS20090258436A1Microbiological testing/measurementImmunoglobulins against animals/humansEndoplasmic reticulumScaffold protein
The invention discloses novel phosphorylation sites identified in signal transduction proteins and pathways, and provides phosphorylation-site specific antibodies and heavy-isotope labeled peptides (AQUA peptides) for the selective detection and quantification of these phosphorylated sites / proteins, as well as methods of using the reagents for such purpose. Among the phosphorylation sites identified are sites occurring in the following protein types: adaptor / scaffold proteins, adhesion / extracellular matrix protein, apoptosis proteins, calcium binding proteins, cell cycle regulation proteins, chaperone proteins, chromatin, DNA binding / repair / replication proteins, cytoskeletal proteins, endoplasmic reticulum or golgi proteins, enzyme proteins, G / regulator proteins, inhibitor proteins, motor / contractile proteins, phosphatase, protease, Ser / Thr protein kinases, Protein kinase (Tyr)s, receptor / channel / cell surface proteins, RNA binding proteins, transcriptional regulators, tumor suppressor proteins, ubiquitan conjugating system proteins and proteins of unknown function.
Owner:CELL SIGNALING TECHNOLOGY
Reagents for the detection of protein phosphorylation in carcinoma signaling pathways
InactiveUS20090258442A1Immunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsFermentationPhospholipaseADAMTS Proteins
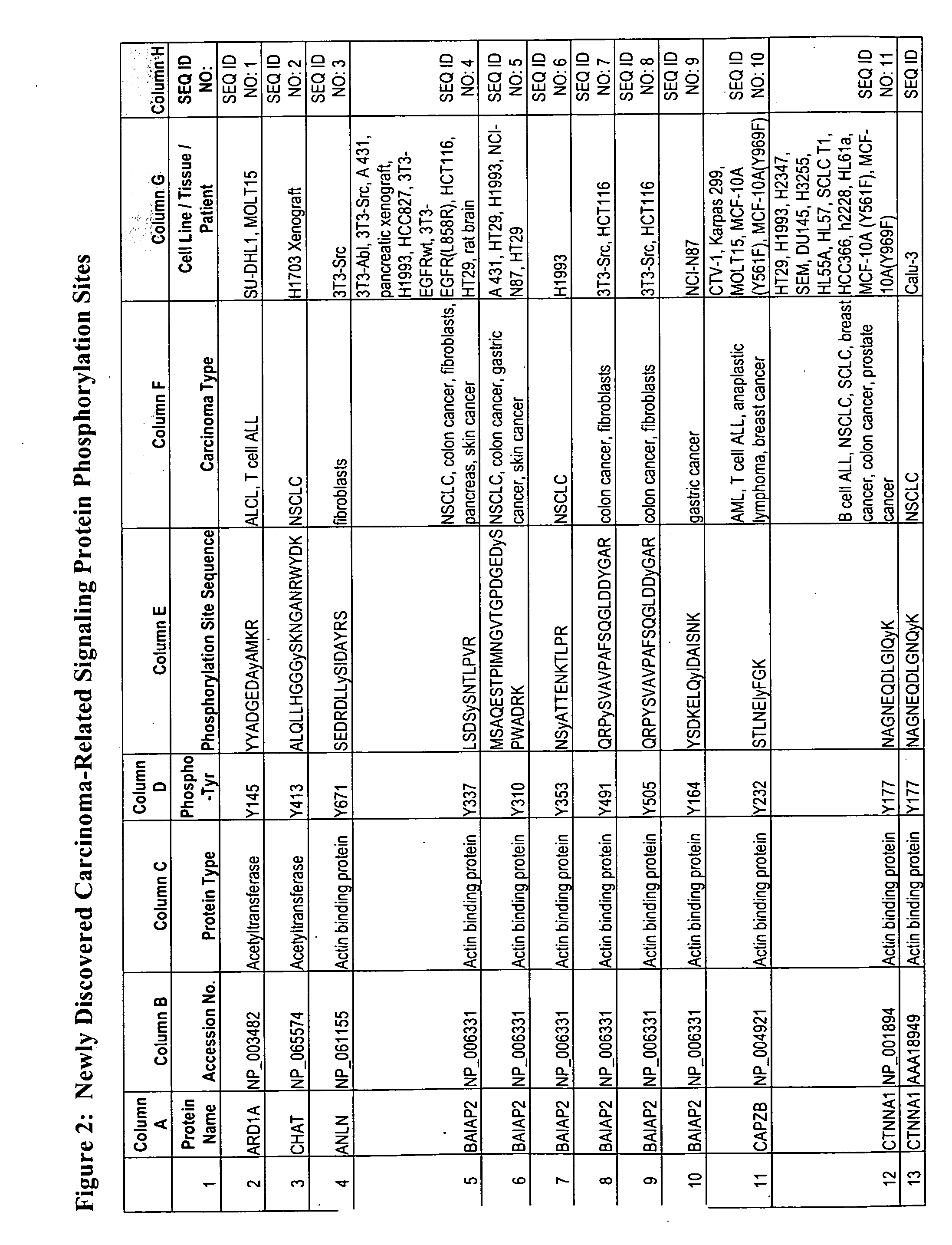
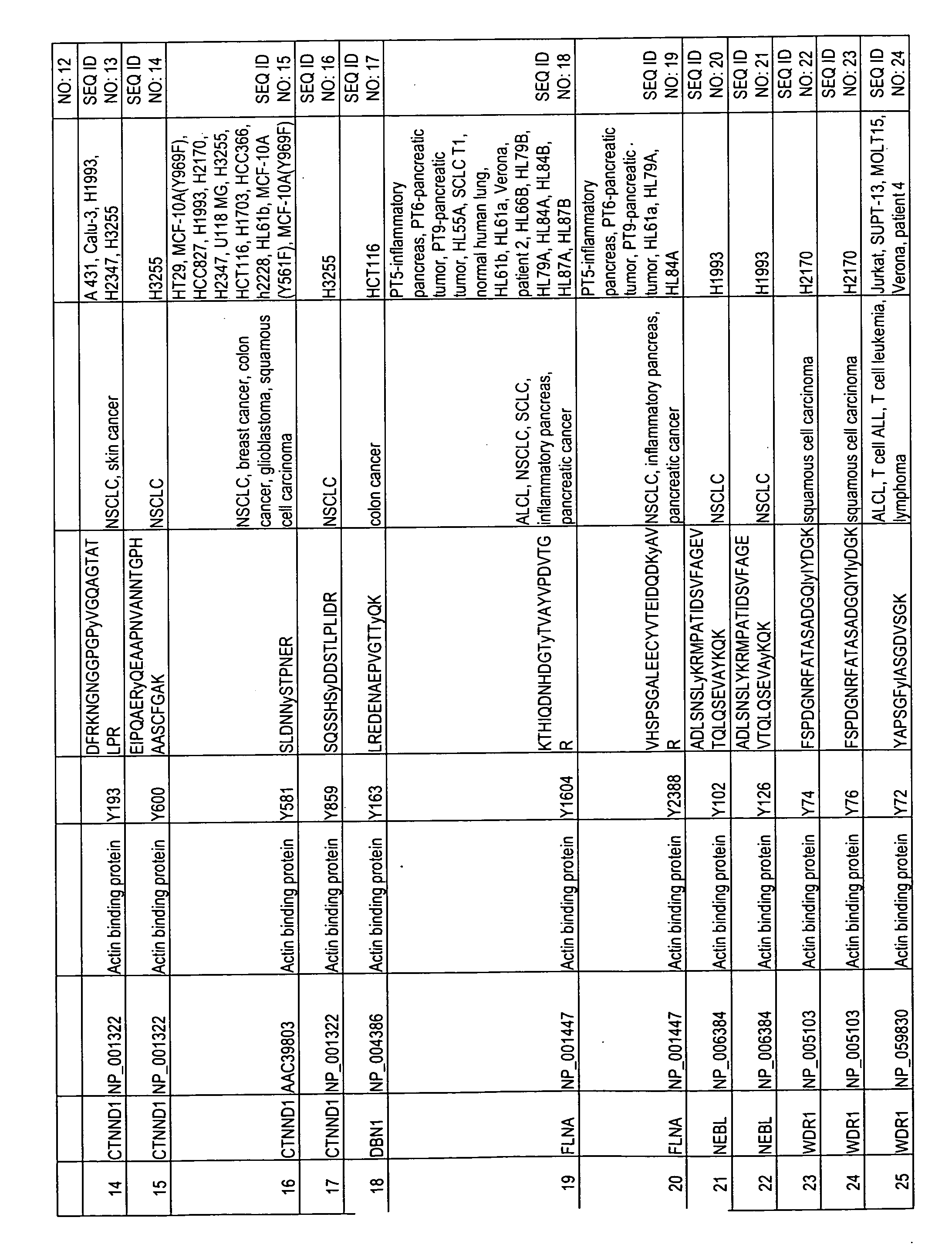
The invention discloses nearly 474 novel phosphorylation sites identified in signal transduction proteins and pathways underlying human carcinoma, and provides phosphorylation-site specific antibodies and heavy-isotope labeled peptides (AQUA peptides) for the selective detection and quantification of these phosphorylated sites / proteins, as well as methods of using the reagents for such purpose. Among the phosphorylation sites identified are sites occurring in the following protein types: Kinase, Adaptor / Scaffold proteins, Phosphatase, G protein Regulator / Guanine Nucleotide Exchange Factors / GTPase Activating Proteins, Cytoskeleton Proteins, DNA Binding Proteins, Phospholipase, Receptor Proteins, Enzymes, DNA Repair / Replication Proteins, Adhesion Proteins, and Proteases, as well as other protein types.
Owner:CELL SIGNALING TECHNOLOGY
Membrane scaffold proteins
Membrane proteins are difficult to express in recombinant form, purify, and characterize, at least in part due to their hydrophobic or partially hydrophobic properties. Membrane scaffold proteins (MSP) assemble with target membrane or other hydrophobic or partially hydrophobic proteins or membrane fragments to form soluble nanoscale particles which preserve their native structure and function; they are improved over liposomes and detergent micelles. In the presence of phospholipid, MSPs form nanoscopic phospholipid bilayer disks, with the MSP stabilizing the particle at the perimeter of the bilayer domain. The particle bilayer structure allows manipulation of incorporated proteins in solution or on solid supports, including for use with such surface-sensitive techniques as scanning probe microscopy or surface plasmon resonance. The nanoscale particles facilitate pharmaceutical and biological research, structure / function correlation, structure determination, bioseparation, and drug discovery.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
Structurally biased random peptide libraries based on different scaffolds
InactiveUS6936421B2BacteriaAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsGreen fluorescent proteinRandom Peptide Library
The invention relates to the use of scaffold proteins, particularly green fluorescent protein (GFP), in fusion constructs with random and defined peptides and peptide libraries, to increase the cellular expression levels, decrease the cellular catabolism, increase the conformational stability relative to linear peptides, and to increase the steady state concentrations of the library peptides and peptide library members expressed in cells for the purpose of detecting the presence of the peptides and screening peptide libraries. N-terminal, C-terminal, dual N- and C-terminal and one or more internal fusions are all contemplated. Novel fusions utilizing self-binding peptides to create a conformationally stabilized fusion domain are also contemplated.
Owner:RIGEL PHARMA
Reagents for the detection of protein phosphorylation in signaling pathways
InactiveUS20100009463A1Animal cellsIsotope introduction to peptides/proteinsCell Surface ProteinsPhosphorylation
The invention discloses novel phosphorylation sites identified in signal transduction proteins and pathways, and provides phosphorylation-site specific antibodies and heavy-isotope labeled peptides (AQUA peptides) for the selective detection and quantification of these phosphorylated sites / proteins, as well as methods of using the reagents for such purpose. Among the phosphorylation sites identified are sites occurring in the following protein types: adaptor / scaffold proteins, adhesion / extracellular matrix protein, apoptosis proteins, calcium binding proteins, cell cycle regulation proteins, chaperone proteins, chromatin, DNA binding / repair / replication proteins, cytoskeletal proteins, endoplasmic reticulum or golgi proteins, enzyme proteins, G / regulator proteins, inhibitor proteins, motor / contractile proteins, phosphatase, protease, Ser / Thr protein kinases, protein kinase (Tyr)s, receptor / channel / cell surface proteins, RNA binding proteins, transcriptional regulators, tumor suppressor proteins, ubiquitan conjugating system proteins and proteins of unknown function.
Owner:CELL SIGNALING TECHNOLOGY
Metamaterial Optical Elements Self-Assembled on Protein Scaffolds
InactiveUS20130181171A1Polarising elementsMaterial analysis by optical meansEngineeringCoat Proteins
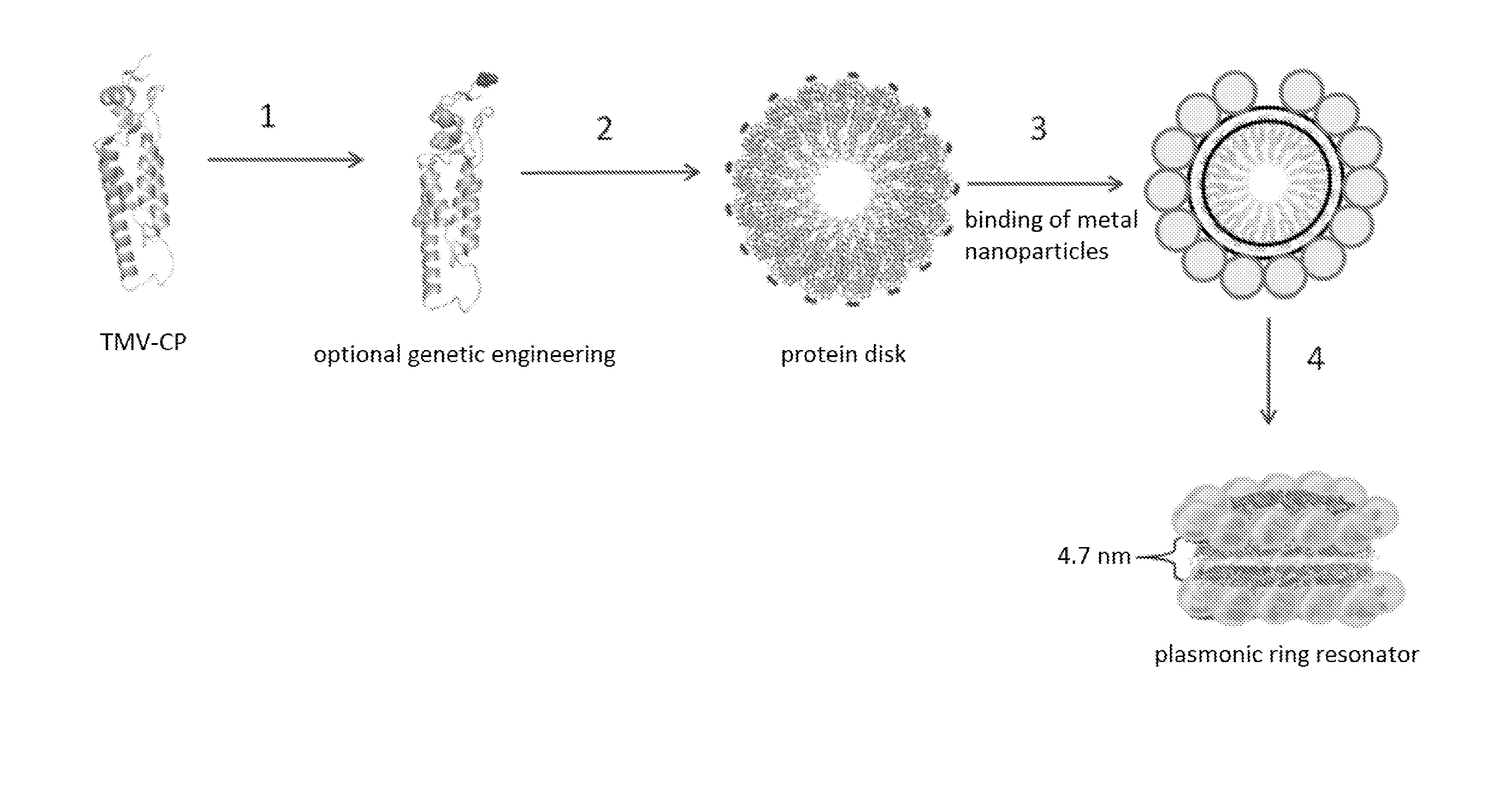
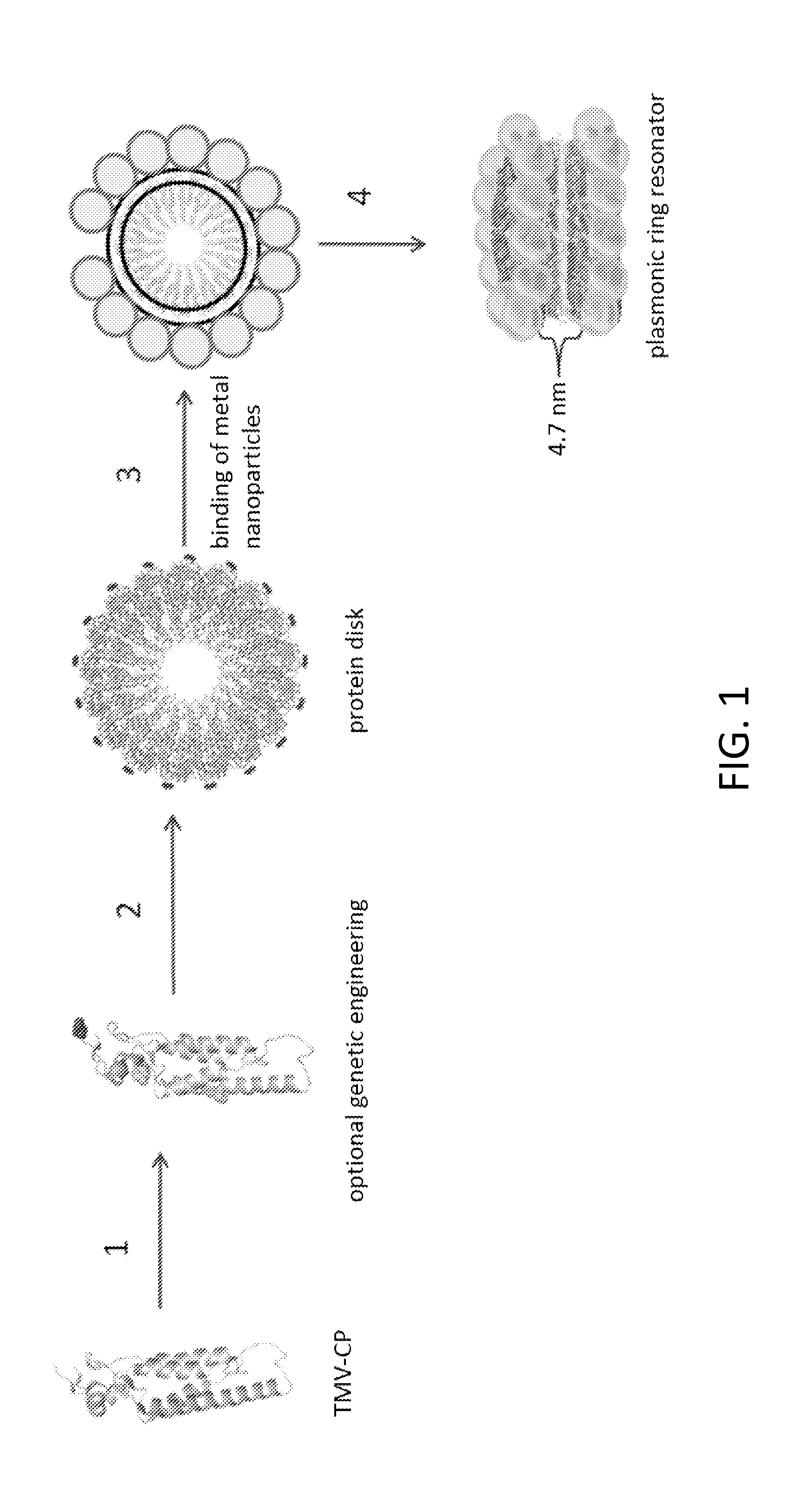
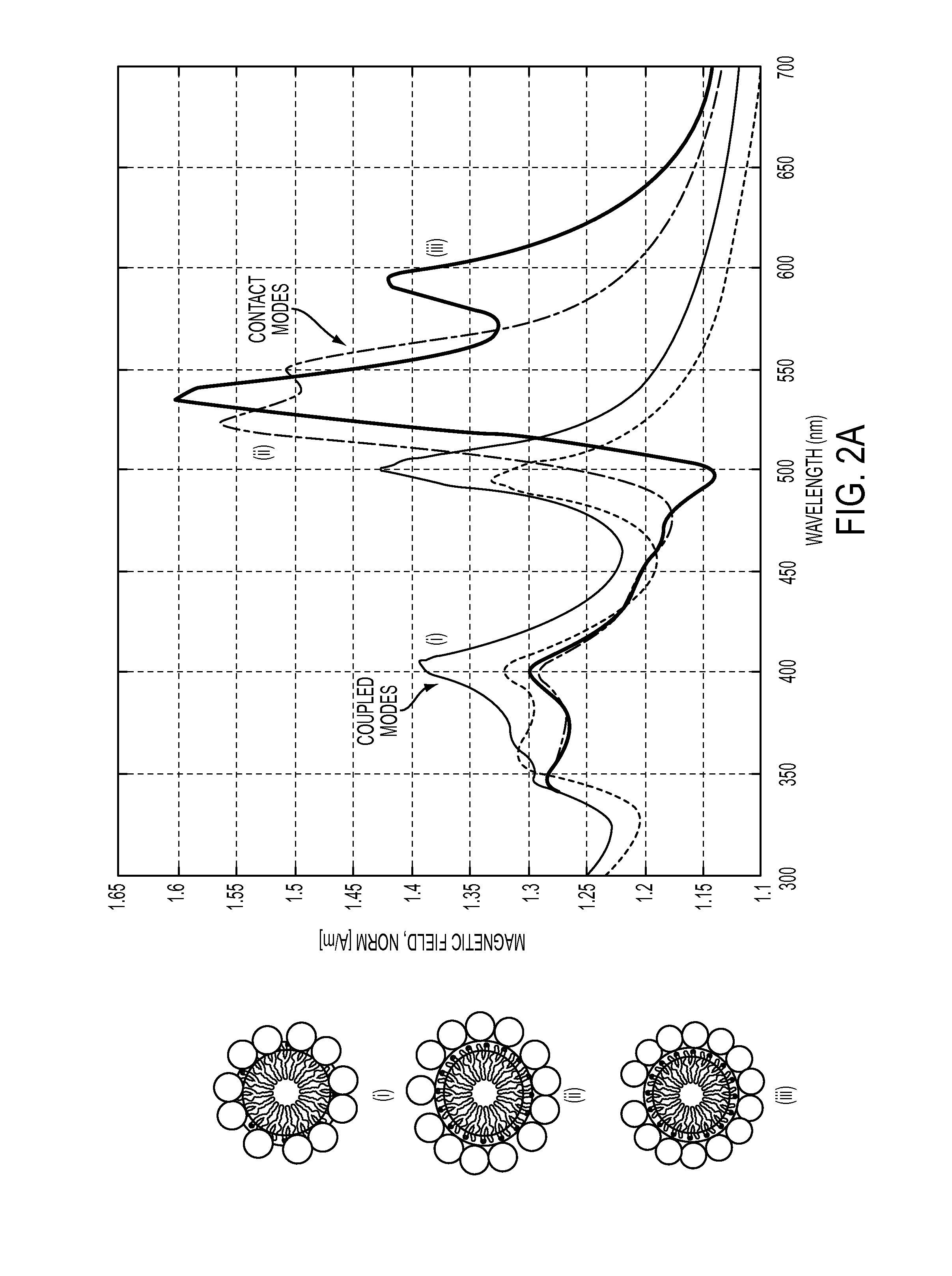
Protein scaffolds from tobacco mosaic virus coat protein modified to incorporate polyhistidine can bind to a metal or a dye while having improved self-assembly characteristics. The scaffold can take the form of tubes or disks, and can further be formed into dual plasmonic ring resonators. Such self-assembled structures provide useful optical properties.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
Telodendrimer nanodiscs without apolipoprotein
The present invention provides a nanodisc without a membrane scaffold protein. The nanodisc includes a telodendrimer and a lipid; the nanodisc does not include a membrane scaffold protein. The telodendrimer has the general formula PEG-L-D-(R)n, wherein D is a dendritic polymer; L is a bond or a linker linked to the focal point group of the dendritic polymer; each PEG is a poly(ethylene glycol) polymer; each R is and end group of the dendritic polymer, or and end group with a covalently bound hydrophobic group, hydrophilic group, amphiphilic compound, or drug; and subscript n is an integer from 2 to 20. Methods of making the nanodiscs are also provided.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Reagents for the detection of protein phosphorylation in Leukemia signaling pathways
ActiveUS20080248490A1Immunoglobulins against animals/humansBiological testingHuman leukemiaADAMTS Proteins
The invention discloses nearly 288 novel phosphorylation sites identified in signal transduction proteins and pathways underlying human Leukemia, and provides phosphorylation-site specific antibodies and heavy-isotope labeled peptides (AQUA peptides) for the selective detection and quantification of these phosphorylated sites / proteins, as well as methods of using the reagents for such purpose. Among the phosphorylation sites identified are sites occurring in the following protein types: Adaptor / Scaffold proteins, Cytoskeletal proteins, Cellular Metabolism enzymes, G Protein / GTPase Activating / Guanine Nucleotide Exchange Factor proteins, Immunoglobulin Superfamily proteins, Inhibitor proteins, Lipid Kinases, Nuclear DNA Repair / RNA Binding / Transcription proteins, Serine / Threonine Protein Kinases, Tyrosine Kinases, Protein Phosphatases, and Translation / Transporter proteins.
Owner:CELL SIGNALING TECHNOLOGY
Peptide personal care compositions and methods for their use
InactiveUS9084734B2Reduce rednessWhitening skinCosmetic preparationsHair removalDiseasePersonal care
Owner:DANISCO US INC
Isolated phospholipid-protein particles
InactiveUS20090161828A1Improve solubilitySpeed up the processMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationHydrolasesLipid formationADAMTS Proteins
Owner:LIFE TECH CORP
Reagents for the detection of protein phosphorylation in leukemia signaling pathways
InactiveUS20090220991A1Animal cellsImmunoglobulins against animals/humansPhosphodiesteraseLipid kinases
The invention discloses nearly 480 novel phosphorylation sites identified in signal transduction proteins and pathways underlying human Leukemia, and provides phosphorylation site specific antibodies and heavy-isotope labeled peptides (AQUA peptides) for the selective detection and quantification of these phosphorylated sites / proteins, as well as methods of using the reagents for such purpose. Among the phosphorylation sites identified are sites occurring in the following protein types: adaptor / scaffold proteins, acetyltransferases, actin binding proteins, adhesion proteins, apoptosis proteins, calcium-binding proteins, cell cycle regulation proteins, cell surface proteins, channel proteins, chaperone proteins, contractile proteins, cytokine proteins, cytoskeletal proteins, G protein regulators and GTPase activating proteins, guanine nucleotide exchange factors, helicase proteins, immunoglobulin superfamily proteins, inhibitor proteins, protein kinases, lipid kinases, ligases, lipid binding proteins, methytransferases, motor proteins, oxidoreductases, phosphotases, phosphodiesterases, phospholipases, proteases, receptor proteins, trascription factors, transferases, translation / transporter proteins, and ubiquitin conjugating system proteins.
Owner:CELL SIGNALING TECHNOLOGY
Artificial scaffolding material for protein retention and use of the same
The present invention provides an artificial scaffolding material for retaining proteins suitable for placing contiguously one species or two or more species of proteins such as enzymes. To this end, the artificial scaffolding material for retaining proteins is provided with a cell and scaffolding proteins heterologous to the cell and placed on the surface layer side of the cell at an extent that allows aggregation properties to be conferred to the cell, and provided with a plurality of non-covalently binding protein-binding domains arranged in tandem.
Owner:TOYOTA CENT RES & DEV LAB INC +1
Reagents for the Detection of Protein Phosphorylation in Carcinoma Signaling Pathways
InactiveUS20110105732A1Immunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsFermentationADAMTS ProteinsProtein phosphorylation
The invention discloses 214 novel phosphorylation sites identified in signal transduction proteins and pathways underlying human carcinoma, and provides phosphorylation-site specific antibodies and heavy-isotope labeled peptides (AQUA peptides) for the selective detection and quantification of these phosphorylated sites / proteins, as well as methods of using the reagents for such purpose. Among the phosphorylation sites identified are sites occurring in the following protein types: Adaptor / Scaffold proteins, Cytoskeleton proteins, GTP Signaling proteins, Kinases, Metabolism proteins, Phosphatases / Phospho-diesterases / Proteases, Receptor proteins, RNA Processing proteins, Transcription proteins, Translation proteins, Transporter proteins, and Ubitquitin proteins, as well as other protein types.
Owner:CELL SIGNALING TECHNOLOGY
Reagents for the detection of protein phosphorylation in carcinoma signaling pathways
InactiveUS20090099340A1Immunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsFermentationADAMTS ProteinsProtein phosphorylation
The invention discloses 214 novel phosphorylation sites identified in signal transduction proteins and pathways underlying human carcinoma, and provides phosphorylation-site specific antibodies and heavy-isotope labeled peptides (AQUA peptides) for the selective detection and quantification of these phosphorylated sites / proteins, as well as methods of using the reagents for such purpose. Among the phosphorylation sites identified are sites occurring in the following protein types: Adaptor / Scaffold proteins, Cytoskeleton proteins, GTP Signaling proteins, Kinases, Metabolism proteins, Phosphatases / Phospho-diesterases / Proteases, Receptor proteins, RNA Processing proteins, Transcription proteins, Translation proteins, Transporter proteins, and Ubitquitin proteins, as well as other protein types.
Owner:CELL SIGNALING TECHNOLOGY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com