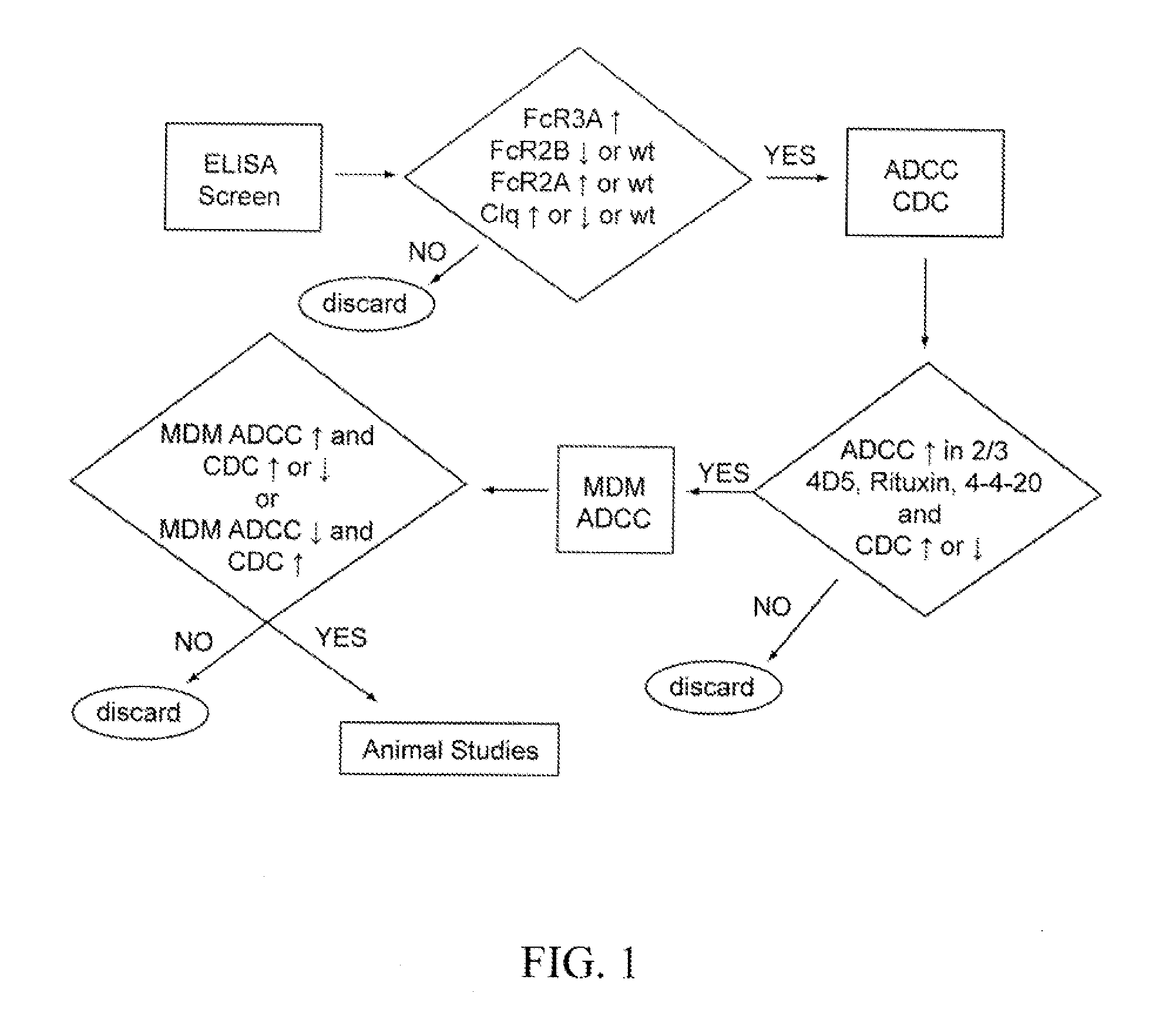
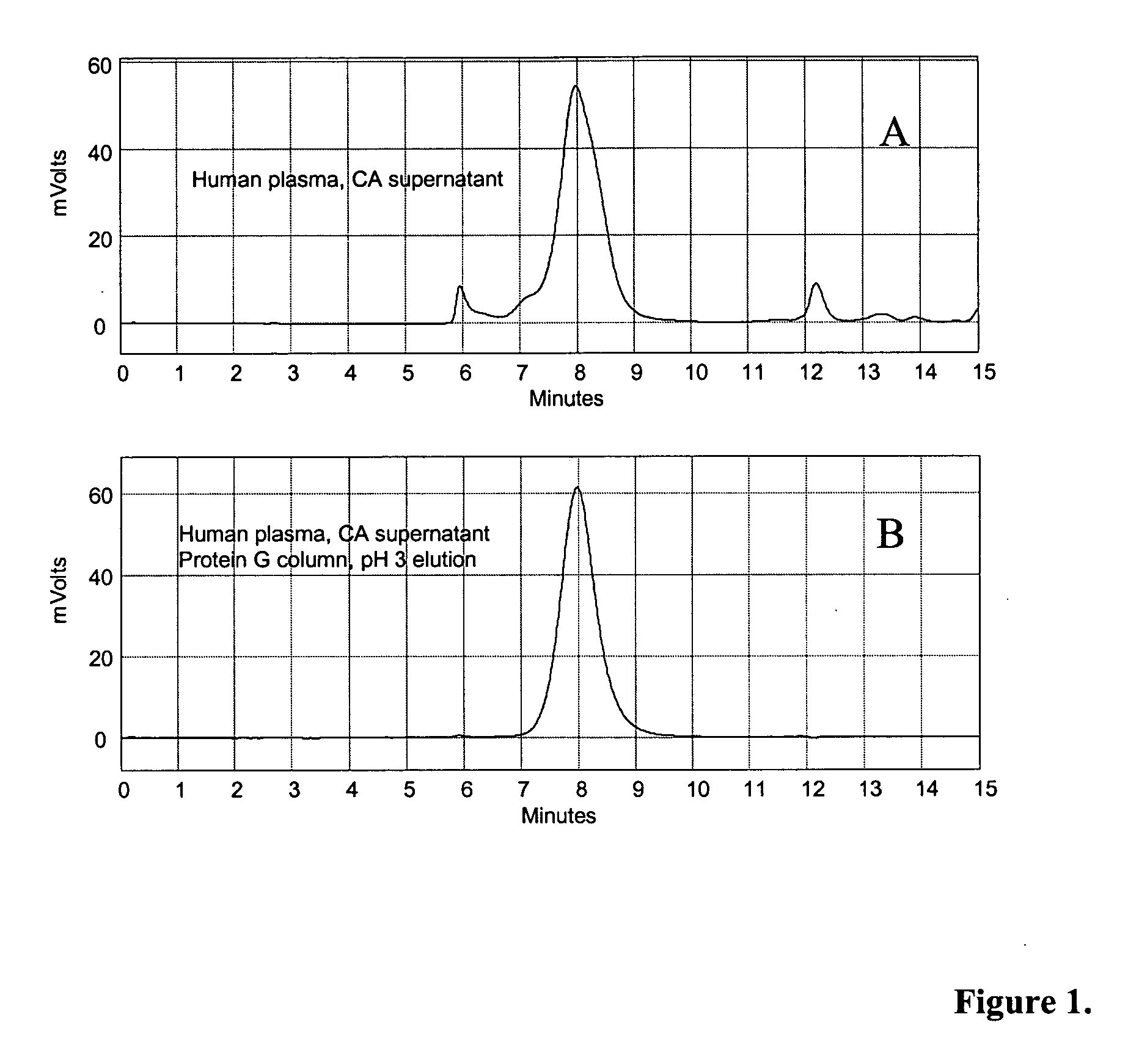
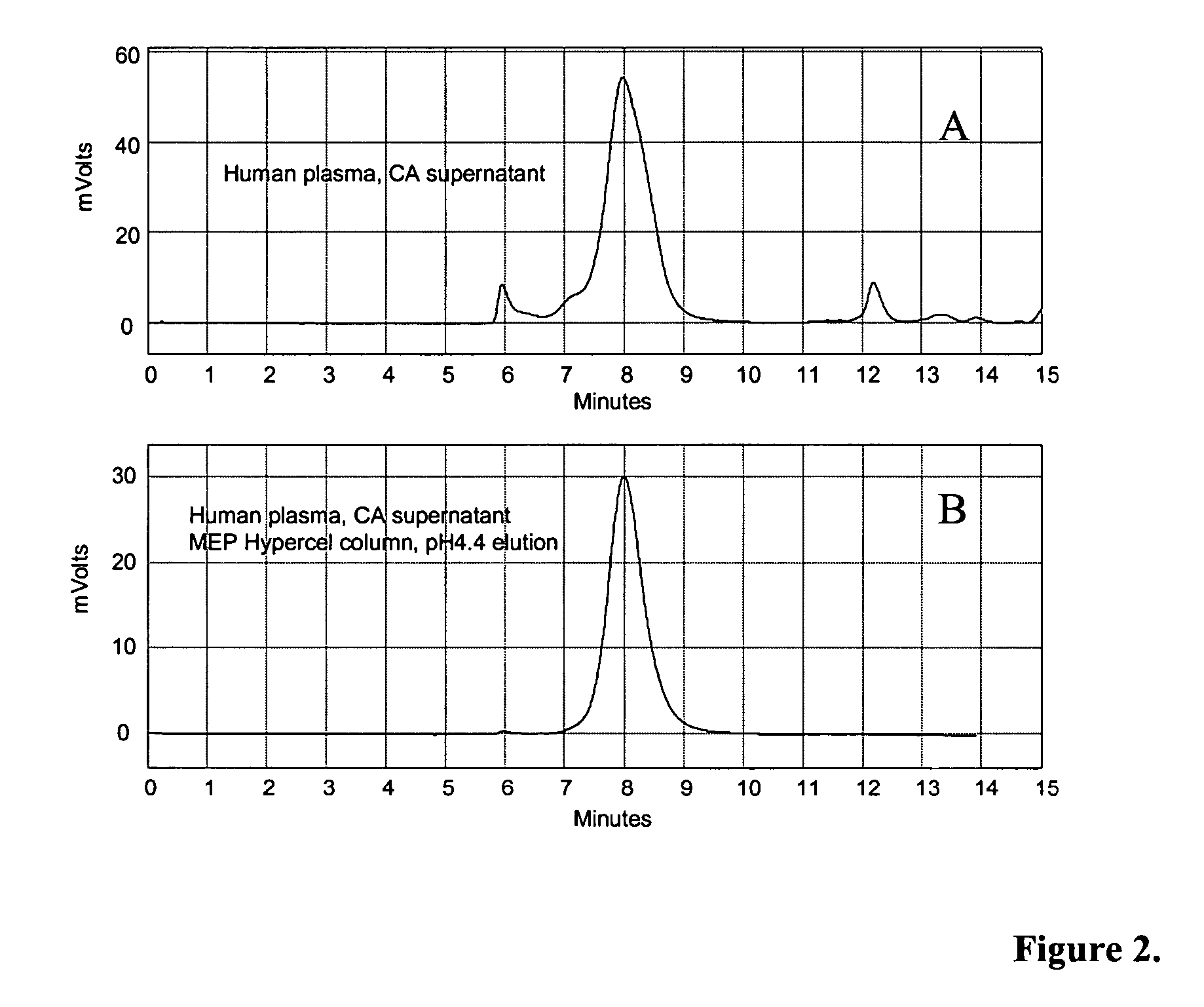
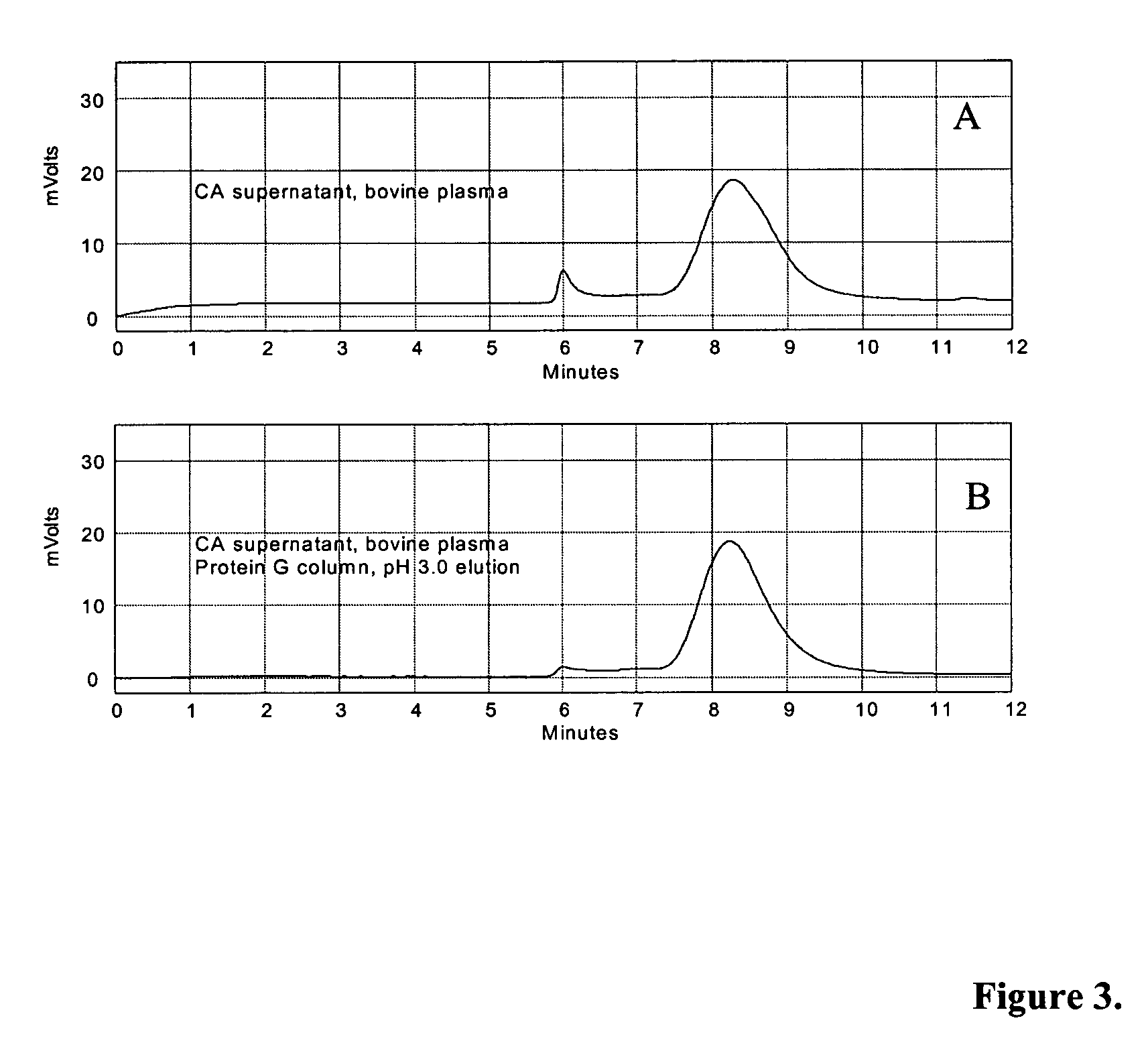
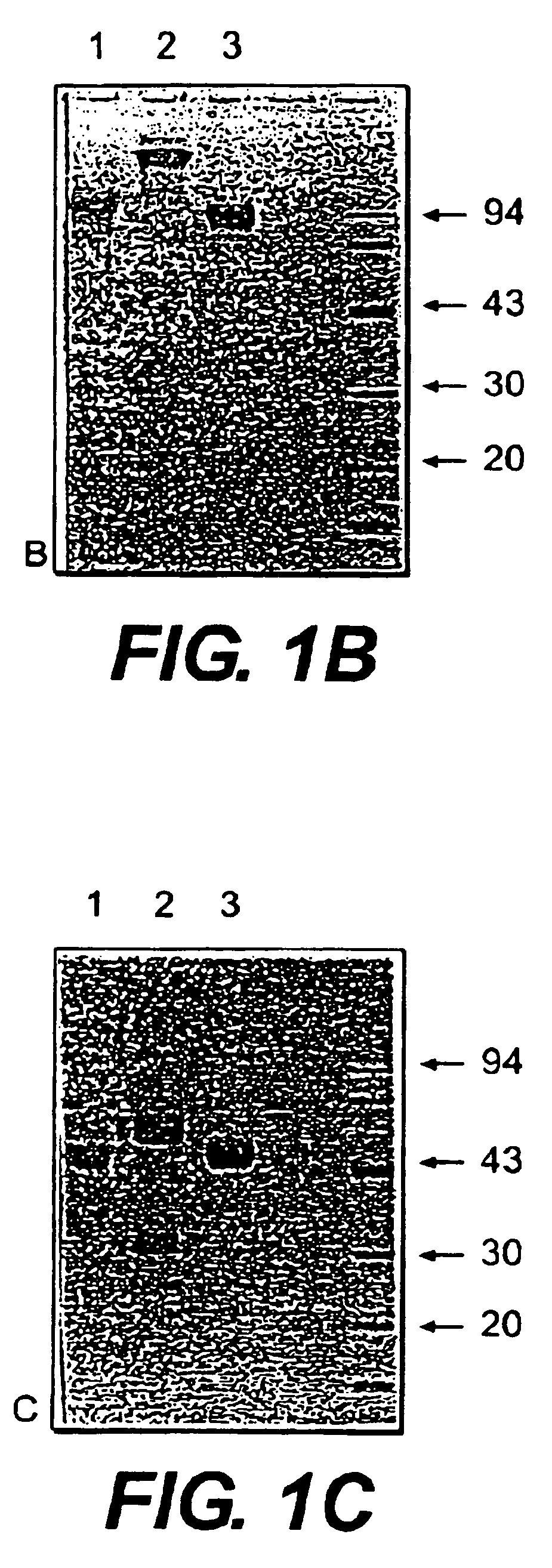
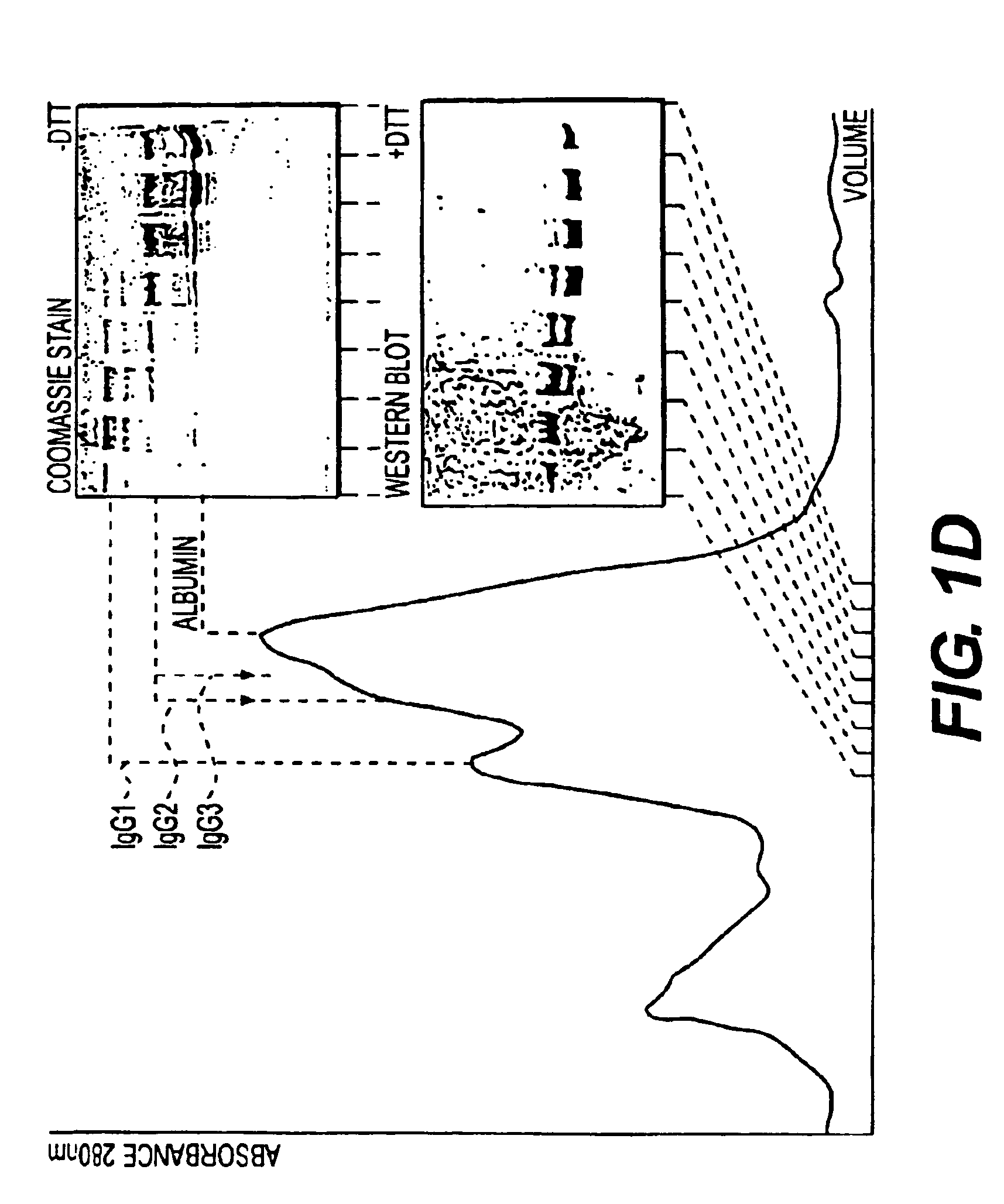
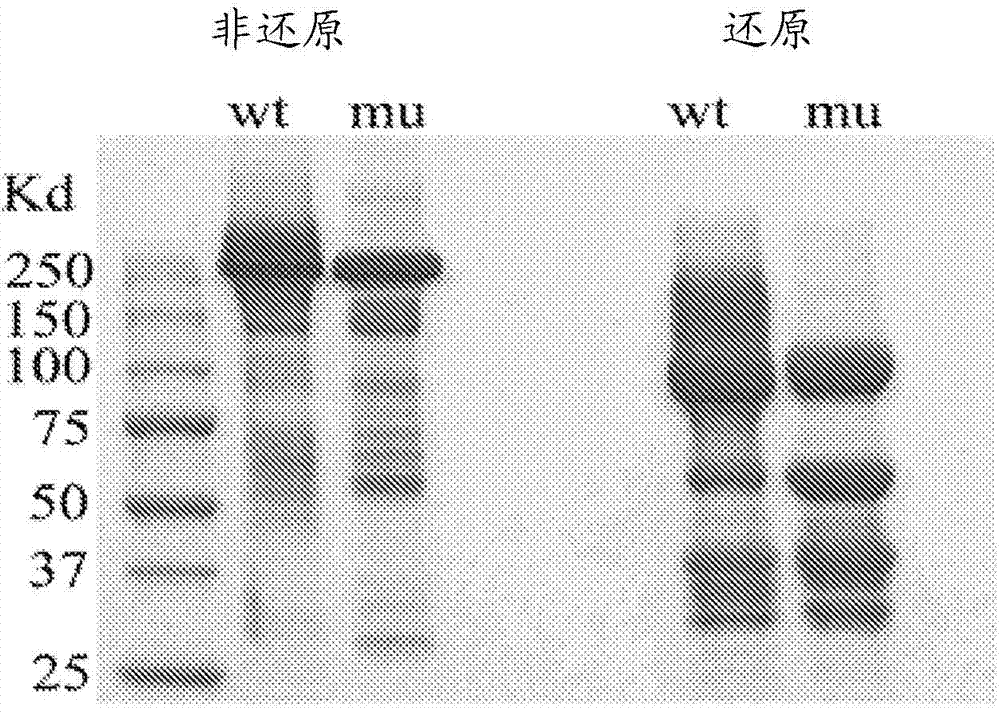
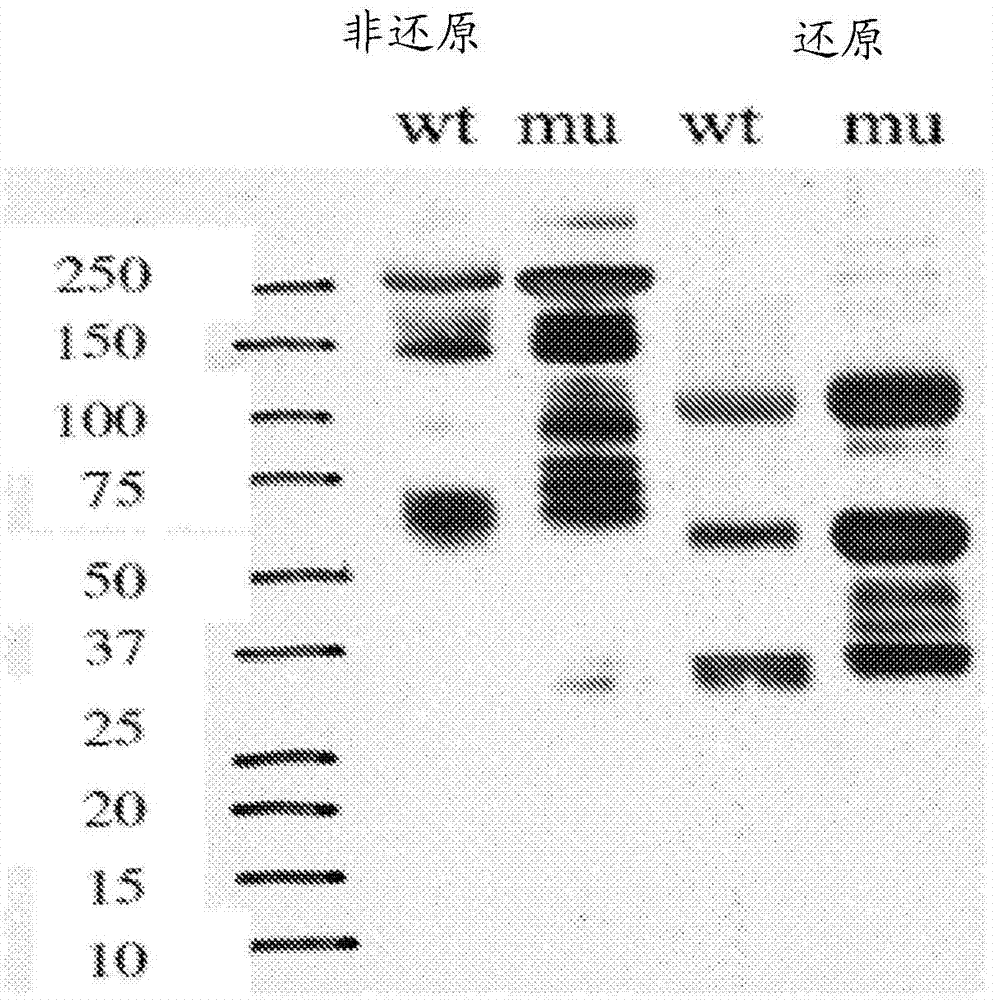
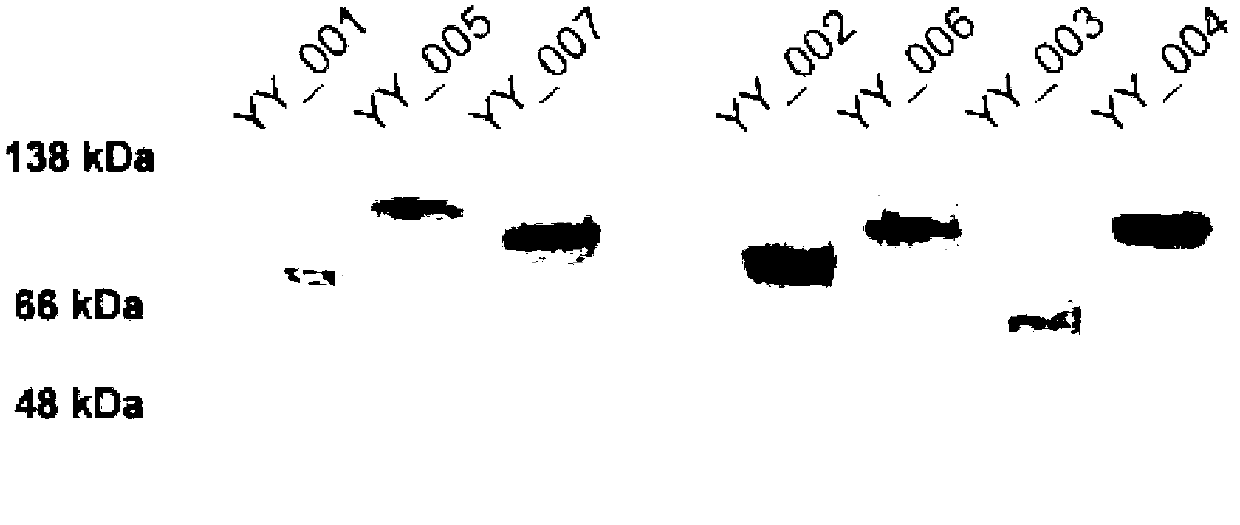Patents
Literature
60 results about "Immunglobulin e" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
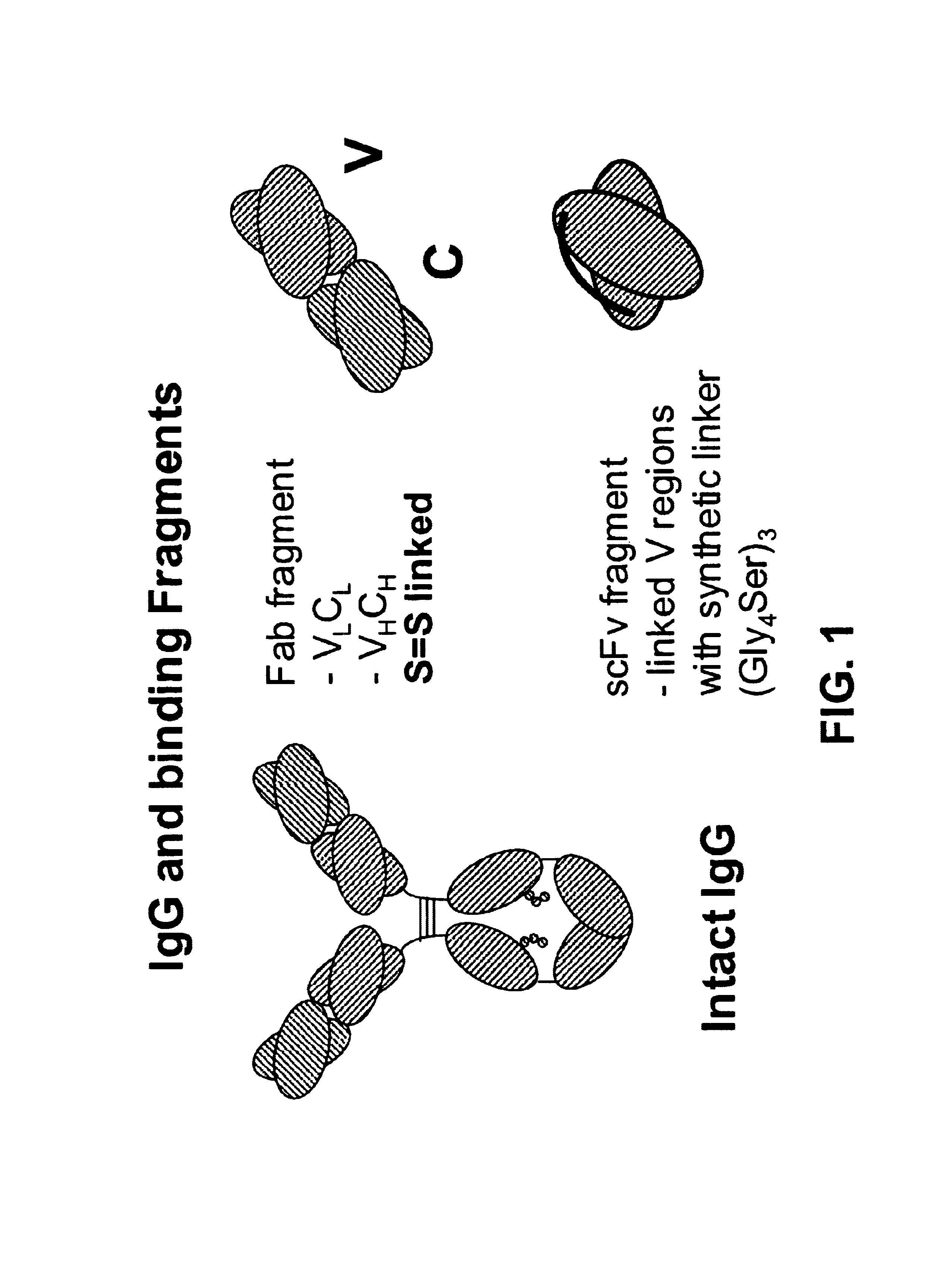
Immunoglobulin E (IgE) is the major mediator of asthma, urticaria, and rhinitis, which are classified as immediate allergic reactions. IgE is similar to IgG in structure, but IgE has two unique features: (1) The epsilon (ε) heavy chain has a high (12%) carbohydrate content and has an additional constant region (C H4).
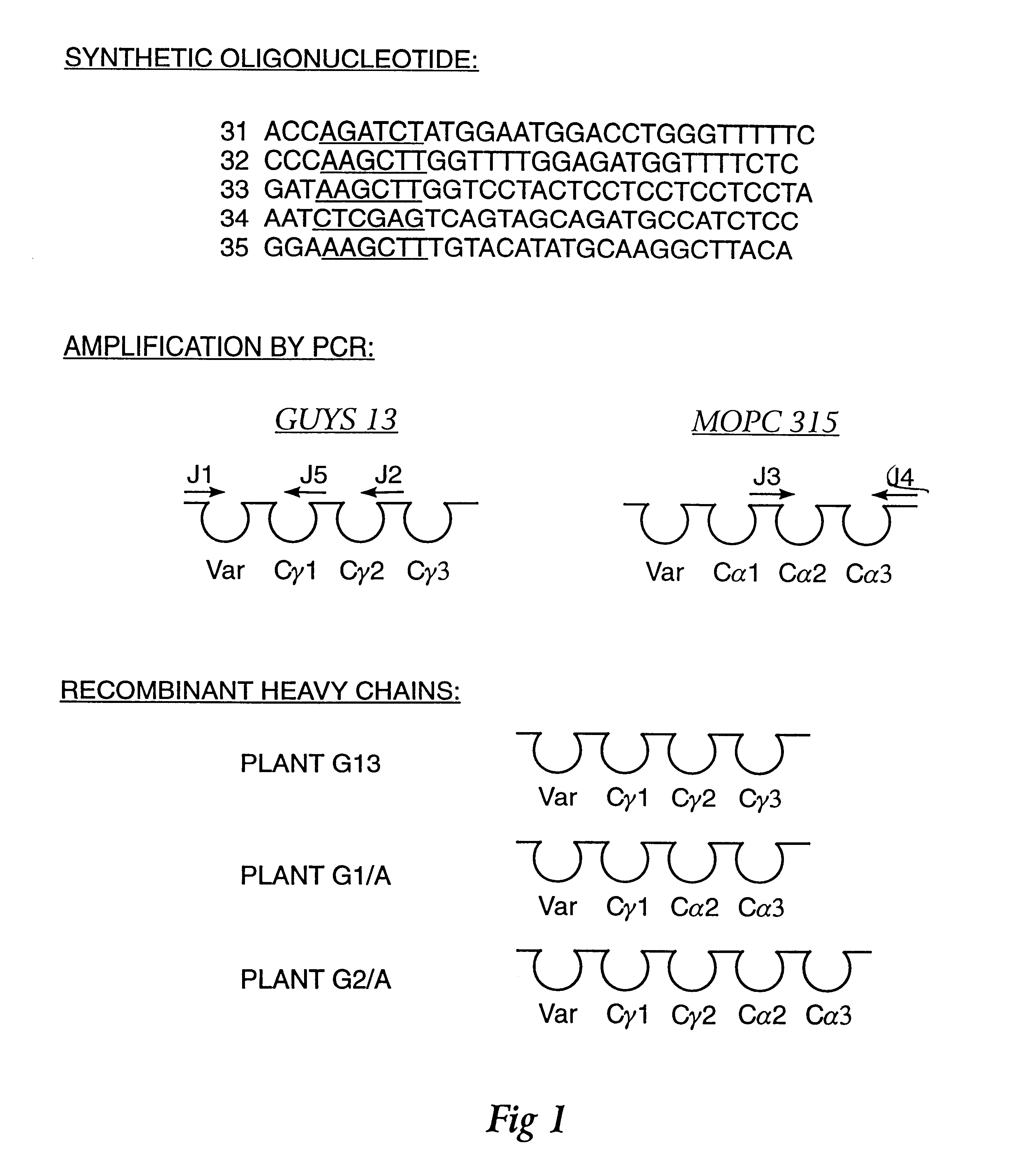
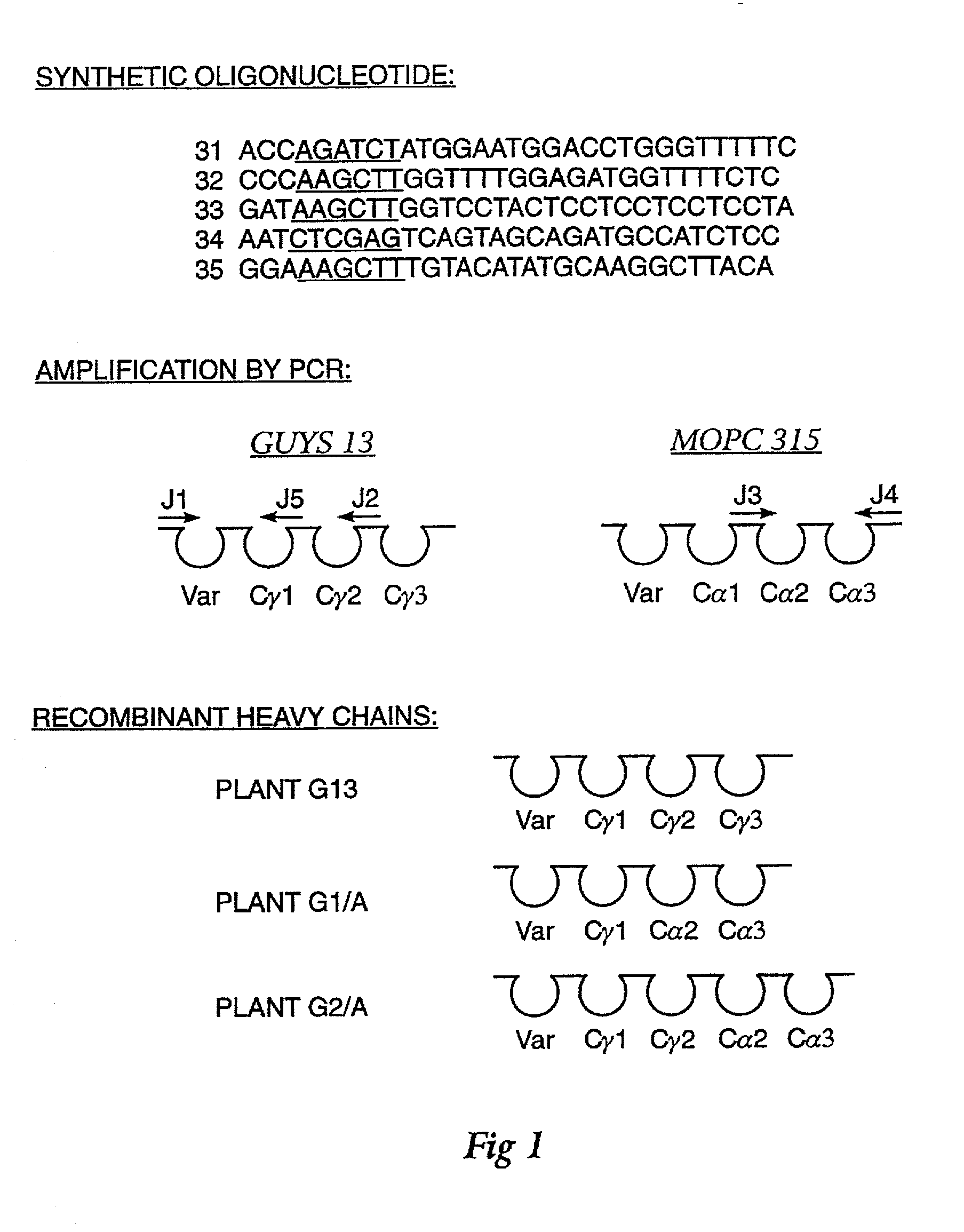
Method for producing immunoglobulins containing protection proteins in plants and their use
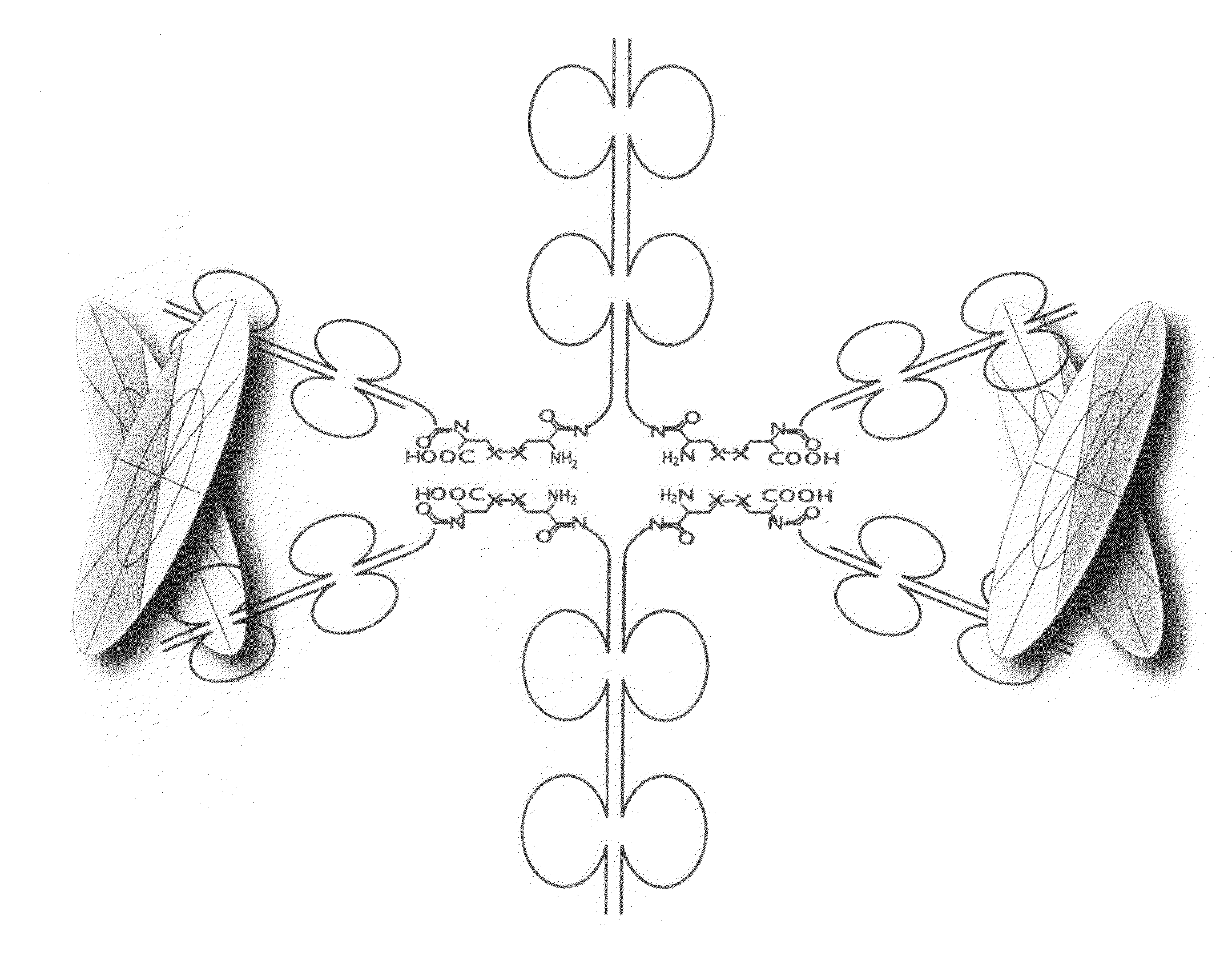
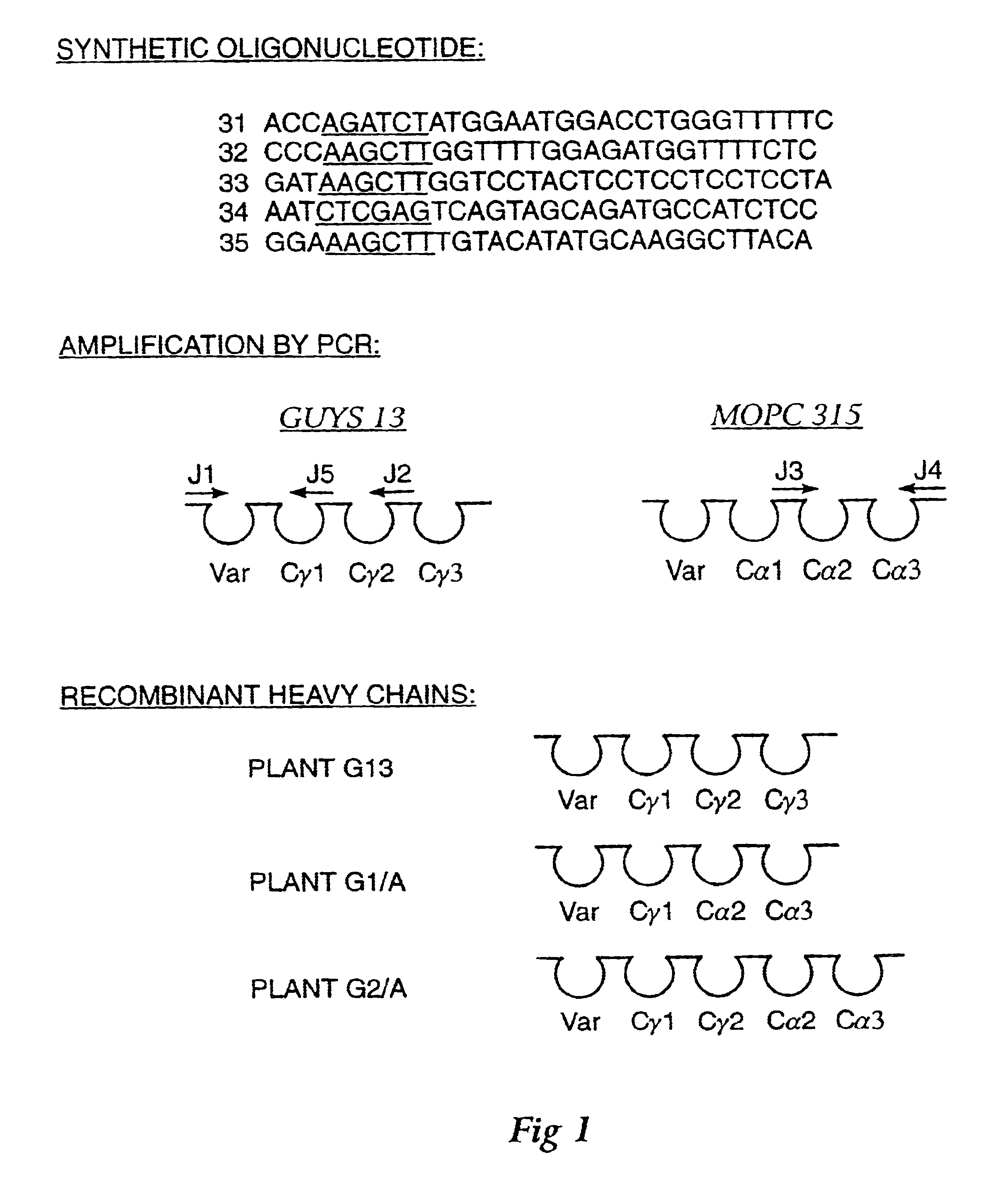
The immunoglobulins of the present invention are useful therapeutic immunoglobulins against mucosal pathogens such as S. mutans. The immunoglobulins contain a protection protein that protects the immunoglobulins in the mucosal environment. The invention also includes the greatly improved method of producing immunoglobulins in plants by producing the protection protein in the same cell as the other components of the immunoglobulins. The components of the immunoglobulin are assembled at a much improved efficiency. The method of the invention allows the assembly and high efficiency production of such complex molecules. The invention also contemplates the production of immunoglobulins containing protection proteins in a variety of cells, including plant cells, that can be selected for useful additional properties. The use of immunoglobulins containing protection proteins as therapeutic antibodies against mucosal and other pathogens is also contemplated.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA +2
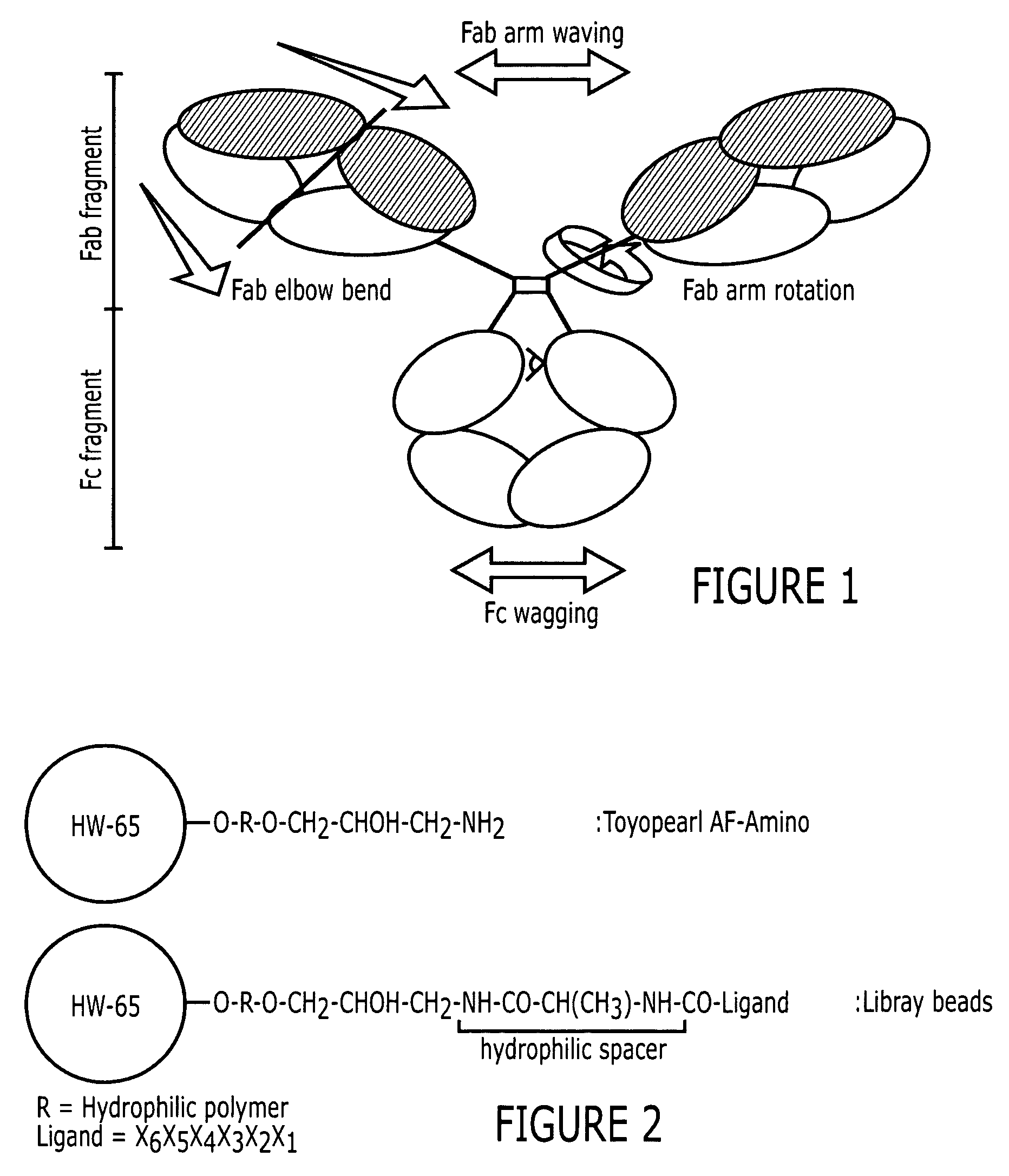
Hybrid immunoglobulins with moving parts
Hybrid immunoglobulins containing moving parts are provided as well as related compositions and methods of use and methods of production. In addition, analogous genetic devices are provided as well as related compositions and methods of use and methods of production.
Owner:BIOMOLECULAR HLDG LLC
Method for producing immunoglobulins containing protection proteins in plants and their use
The immunoglobulins of the present invention are useful therapeutic immunoglobulins against mucosal pathogens such as S. mutans. The immunoglobulins contain a protection protein that protects the immunoglobulins in the mucosal environment.The invention also includes the greatly improved method of producing immunoglobulins in plants by producing the protection protein in the same cell as the other components of the immunoglobulins. The components of the immunoglobulin are assembled at a much improved efficiency. The method of the invention allows the assembly and high efficiency production of such complex molecules.The invention also contemplates the production of immunoglobulins containing protection proteins in a variety of cells, including plant cells, that can be selected for useful additional properties. The use of immunoglobulins containing protection proteins as therapeutic antibodies against mucosal and other pathogens is also contemplated.
Owner:UNTD MED & DENT SCHLS OF GUYS & ST THOMASS HOSP
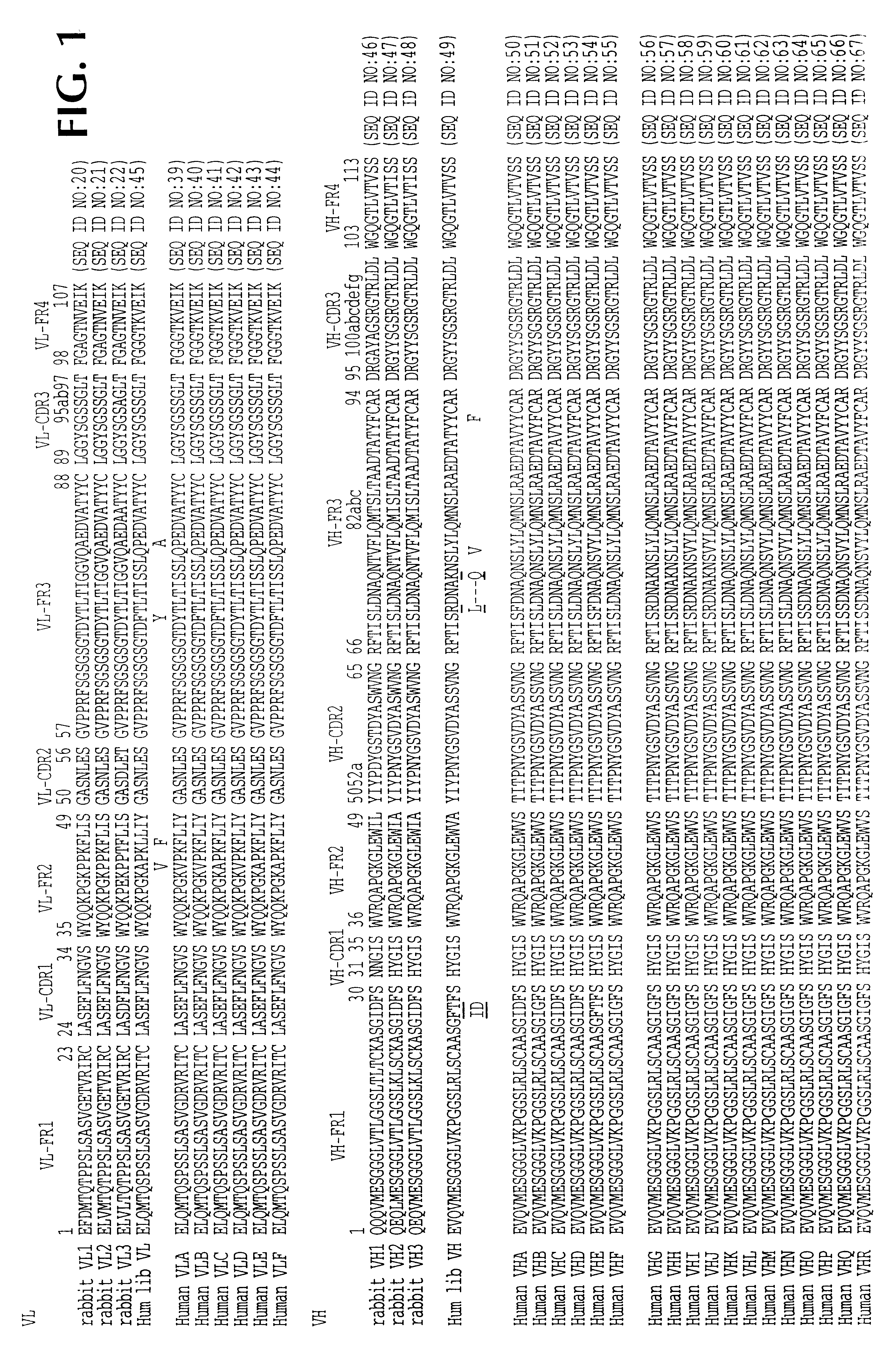
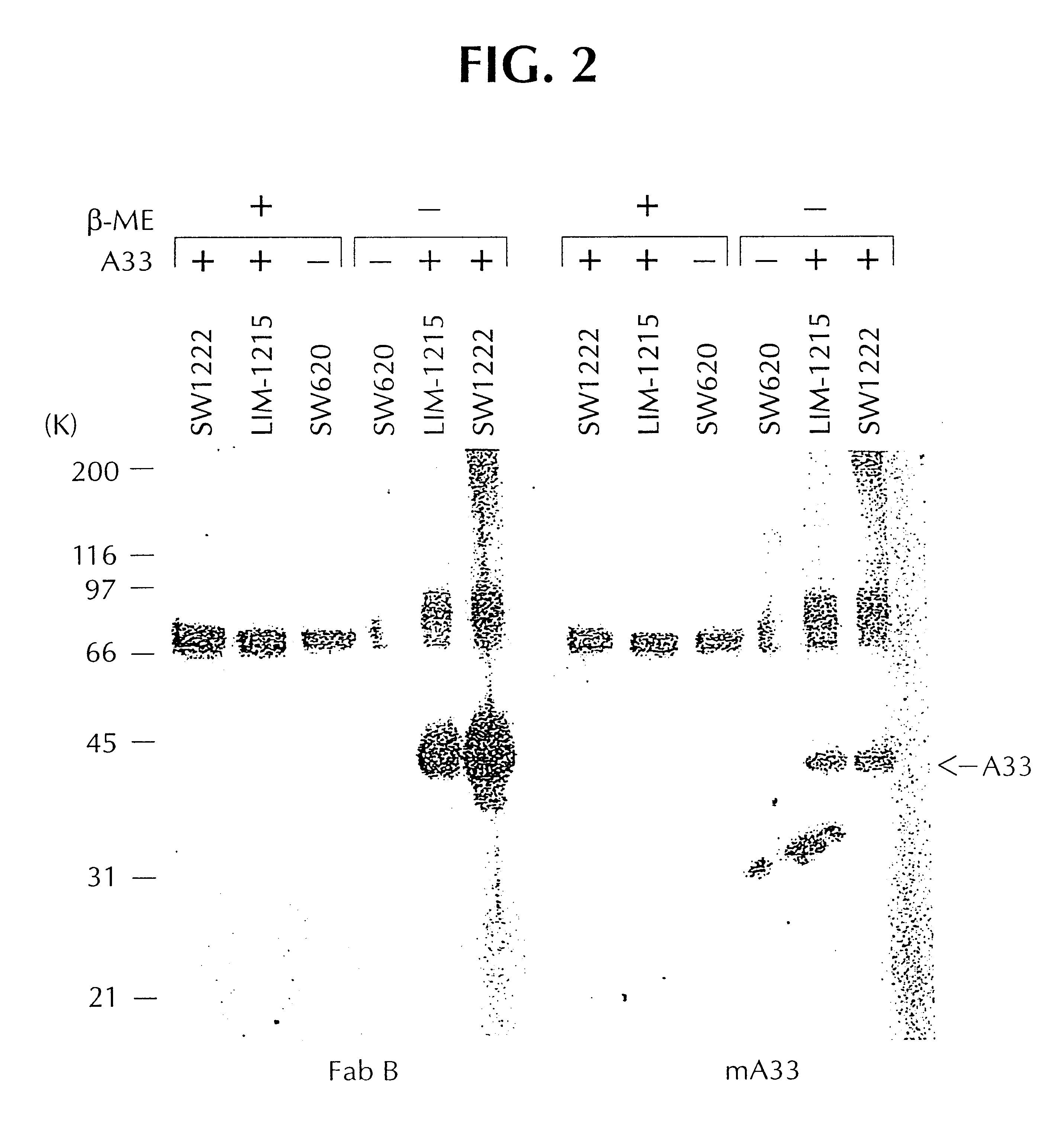
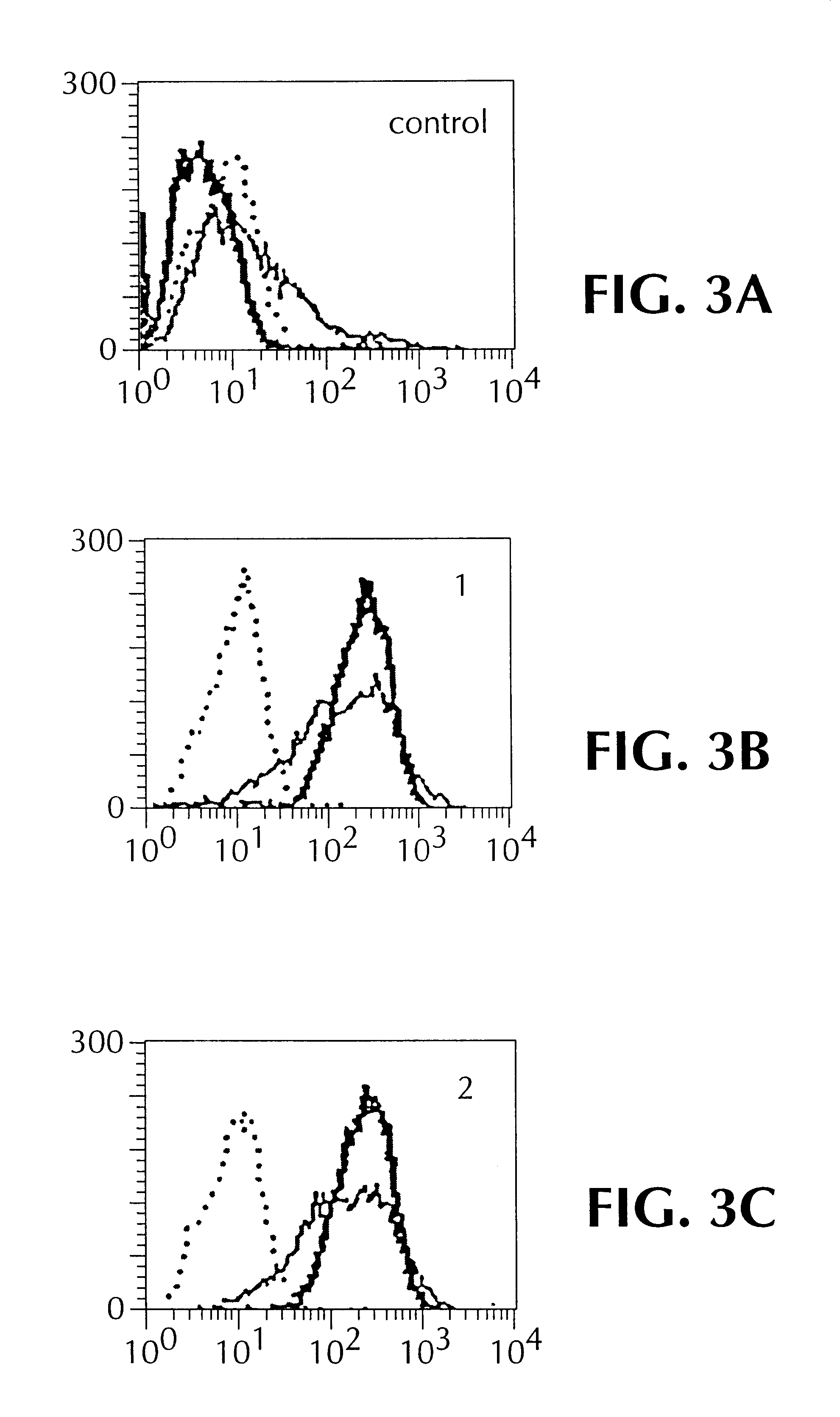
A33 antigen specific immunoglobulin products and uses thereof
InactiveUS6342587B1Immunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsAntibody ingredientsImmunglobulin eBacteriophage
The invention is directed to novel CDRs and immunoglobulin products that bind to A33 antigens and methods for their use. The invention also involves a method for making humanized antibodies, using a rabbit as a host animal, and phage display library methodologies, and the antibodies themselves. The methodology is useful, for example, in generating humanized antibodies against molecules associated with cancer, such as A33, which is associated with colon cancer.
Owner:LUDWIG INST FOR CANCER RES +2
Methods for the Treatment of Disease Using Immunoglobulins Having Fc Regions with Altered Affinities for FcgammaRactivating and FcgammaRinhibiting
ActiveUS20140134162A1Additive and synergistic and novel propertyImproved phenotypeSugar derivativesImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsImmunglobulin eWild type
The present invention relates to methods of treating or preventing cancer and other diseases using molecules, particularly polypeptides, more particularly immunoglobulins (e.g., antibodies), comprising a variant Fc region, wherein said variant Fc region comprises at least one amino acid modification relative to a wild-type Fc region, which variant Fc region binds an FcγR that activates a cellular effector (“FcγRActivating,” such as FcγRIIA or FcγRIIIA) and an FcγR that inhibits a cellular effector (“FcγRInhibiting,” such as FcγRIIA) with an altered Ratio of Affinities relative to the respective binding affinities of such FcγR for the Fc region of the wild-type immunoglobulin. The methods of the invention are particularly useful in preventing, treating, or ameliorating one or more symptoms associated with a disease, disorder, or infection where either an enhanced efficacy of effector cell function mediated by FcγR is desired (e.g., cancer, infectious disease) or an inhibited effector cell response mediated by FcγR is desired (e.g., inflammation, autoimmunde disease).
Owner:MACROGENICS INC
Methods for immunoglobulin purification
InactiveUS20050272917A1Serum immunoglobulinsImmunoglobulins against animals/humansImmunglobulin eBovine serum albumin
Disclosed herein are methods for purifying immunoglobulin G (IgG). The methods feature the use of particular buffers and reagents to isolate and purify human IgG or to remove host contaminating proteins, non-human or chimeric IgG, IgG dimers, IgG aggregates, bovine serum albumin, transmissible spongiform encephalopathy, DNA, viral DNA, or viral particles from a feedstock. IgG purified by the methods described herein can be used for research, diagnostic, or therapeutic purposes.
Owner:KYOWA HAKKO KIRIN CO LTD
Support for affinity chromatography and method for isolating immunoglobulin
InactiveUS9040661B2Peptide/protein ingredientsSerum immunoglobulinsImmunglobulin eImmobilized protein
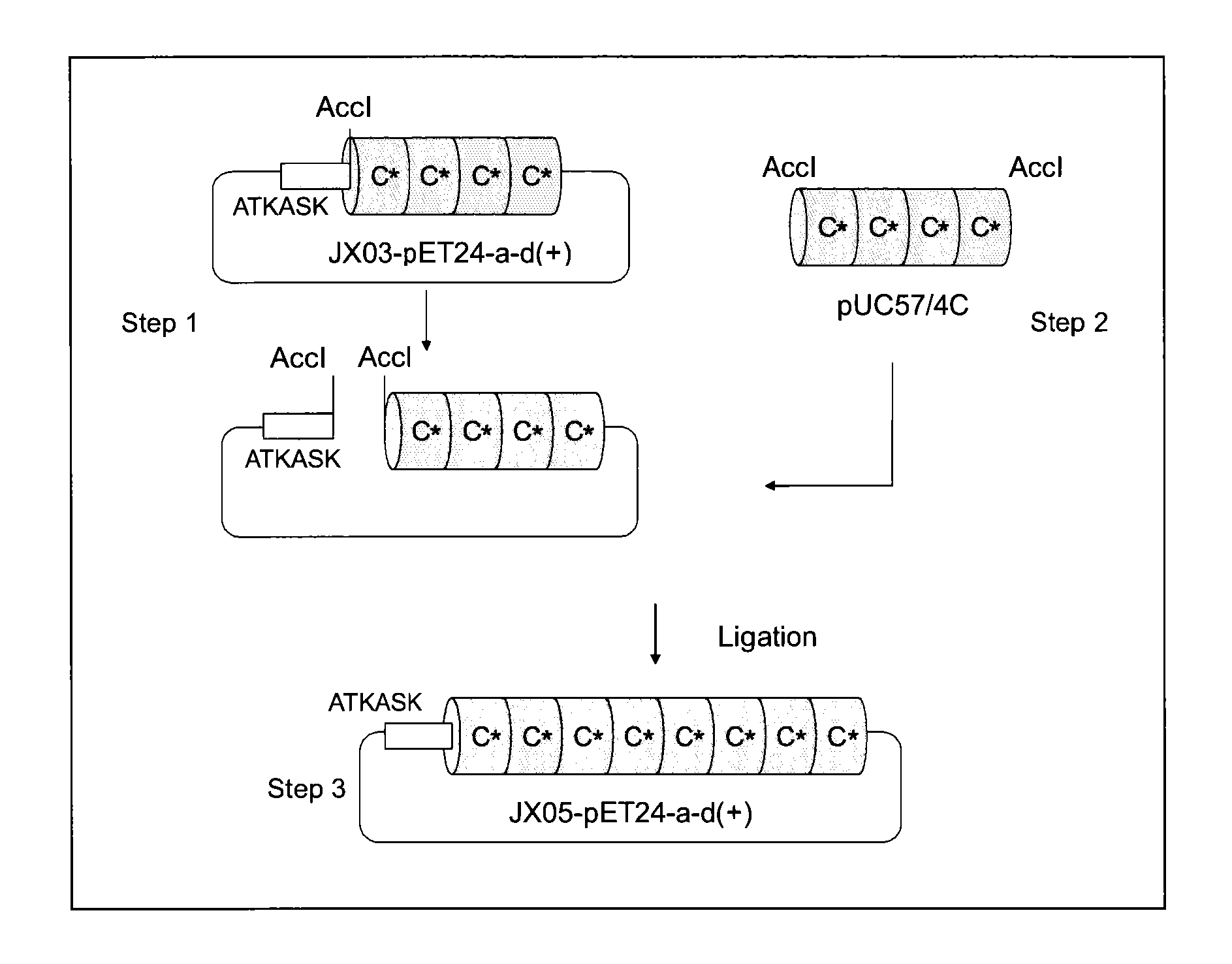
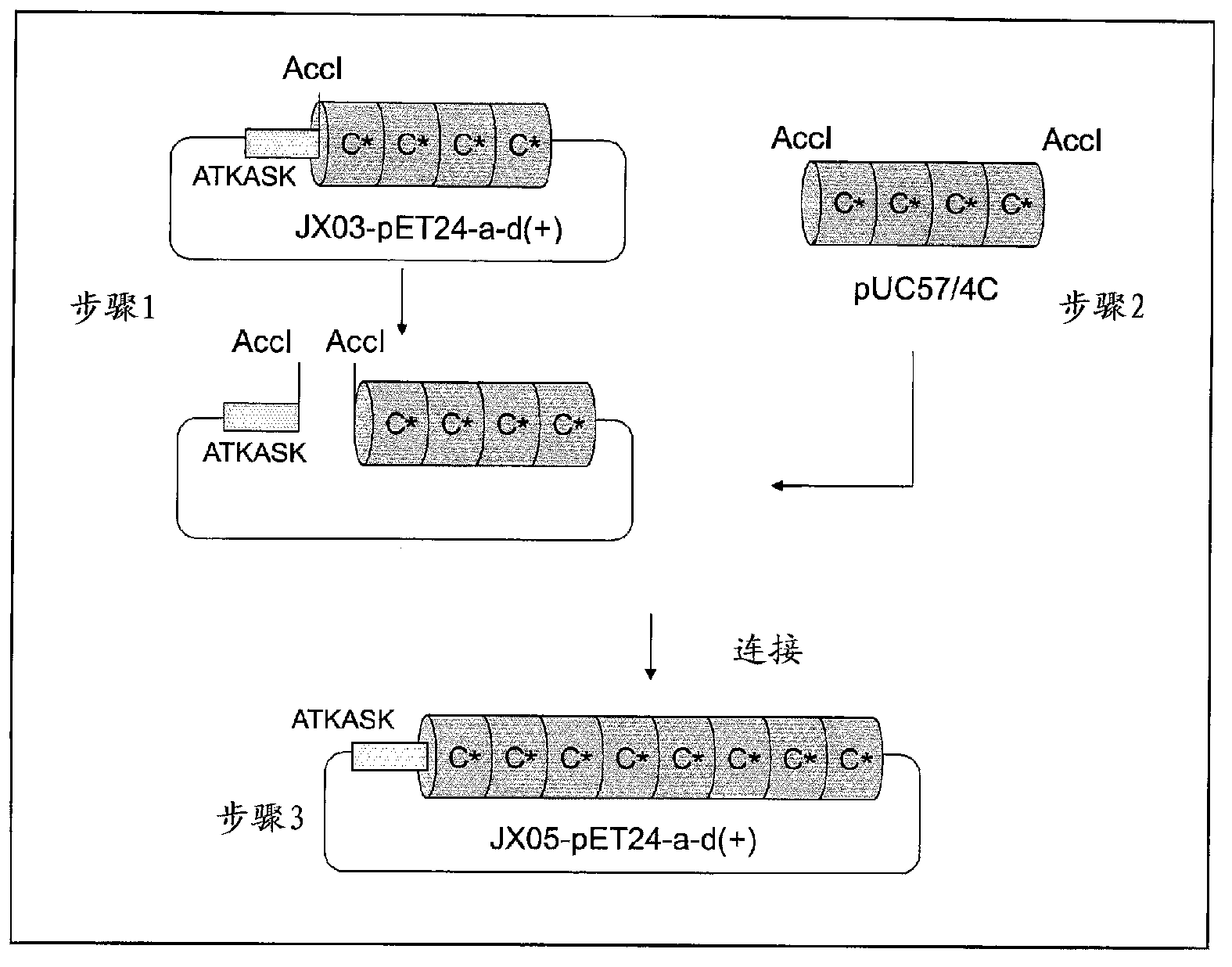
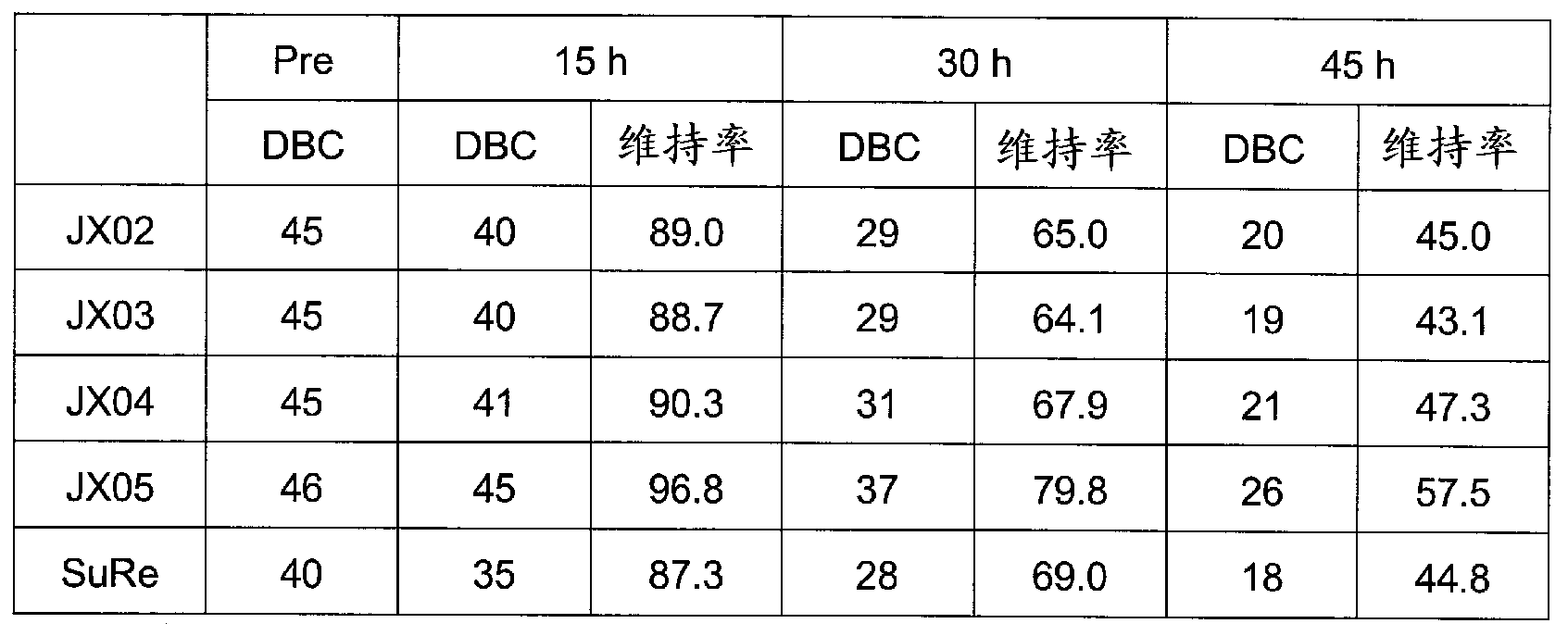
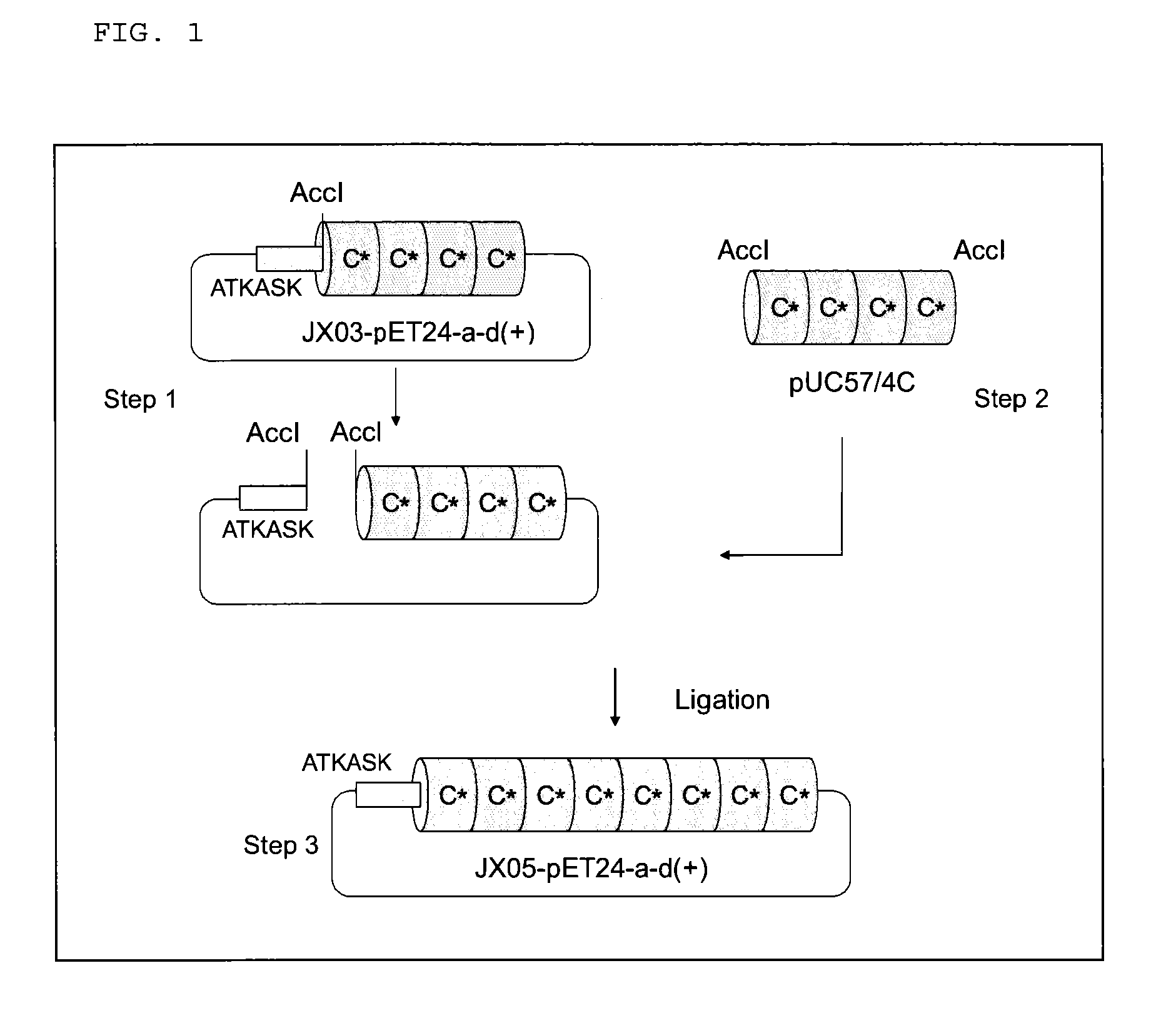
Provided are a support for affinity chromatography which has excellent alkali resistance, and a method for isolating immunoglobulin. A support for affinity chromatography, containing an immobilized protein ligand represented by the following formula (1):R—R2 (1)wherein R represents a polypeptide consisting of 4 to 30 amino acid residues that contains an amino acid sequence represented by ATK or ASK; and R2 represents a polypeptide consisting of 50 to 500 amino acid residues containing an immunoglobulin-binding domain consisting of an amino acid sequence represented by SEQ ID NO: 1 or SEQ ID NO: 2, the partial sequence thereof, or an amino acid sequence having 70% or more identity to these sequences; with the proviso that a terminus at which R2 binds to R is C-terminus or N-terminus of the immunoglobulin-binding domain.
Owner:JSR CORPORATIOON +1
Human monoclonal antibodies to activin receptor-like kinase-1
Owner:PFIZER INC +1
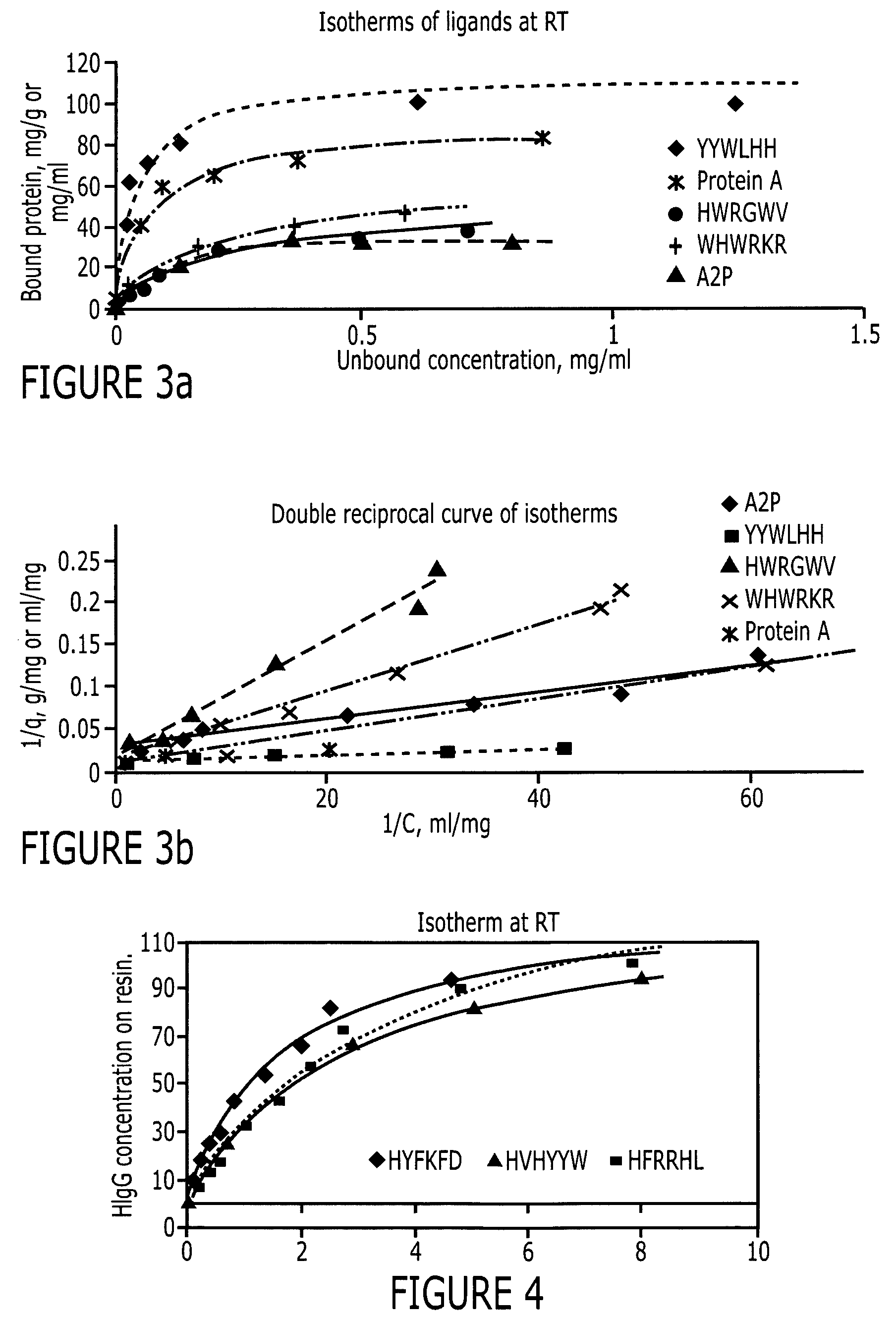
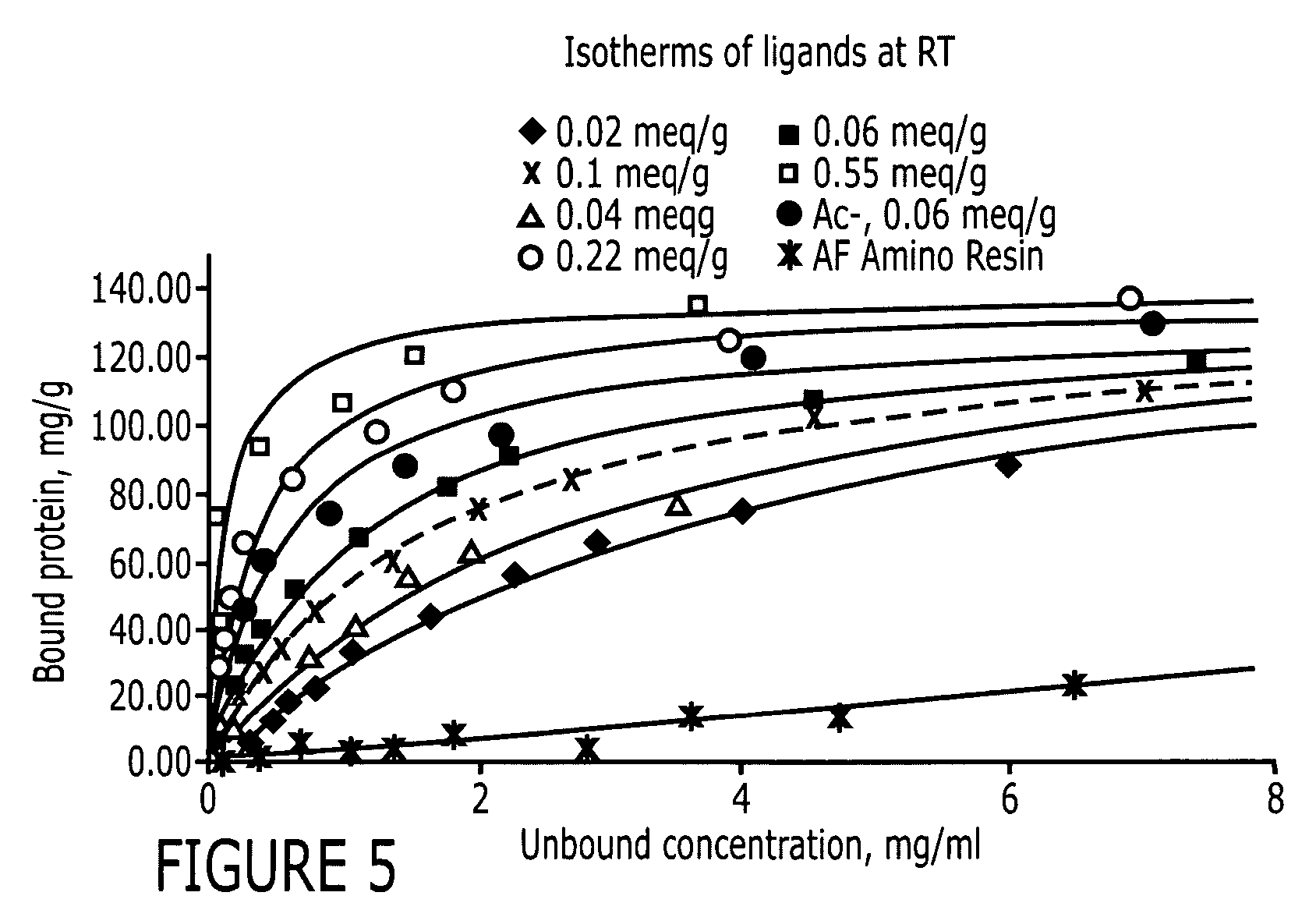
Purification of immunoglobulins using affinity chromatography and peptide ligands
ActiveUS7408030B2Peptide/protein ingredientsSolid sorbent liquid separationImmunglobulin ePeptide ligand
An immunoglobulin binding peptide having the general formula, from amino terminus to carboxy terminus, of Z-R1—R2—R3—R4—R5—R6—X, is described, wherein: R1 is H or Y; R2 is a hydrophobic, preferentially aromatic, amino acid (for example W, F, Y, V); R3 is a positively charged or aromatic amino acid (for example R, H, F, W); R4 is a hydrophobic or positively charged amino acid (for example G, Y, R, K, L); R5 is a positively charged or aromatic amino acid (for example W, F, R, H, Y); R6 a random amino acid but preferably hydrophobic or negatively charged (for example V, W, L, D, H); X is present or absent and when present is a linking group; and Z is present or absent and when present is a capping group bonded to the N terminus of R1; and wherein the amino acids of said peptide are in D form, L form, or a combination thereof. Methods of using such peptides for the purification of Immunoglobulins are also described.
Owner:NORTH CAROLINA STATE UNIV
Prosuction of antibodies or (functionalized) fragments thereof derived from heavy chain immunoglobulins of camelidae
InactiveUS7794981B2High catalytic activityImprove efficiencyPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsNatural antibodyComplementarity determining region
A process is provided for the production of an antibody or a fragment or functionalized fragment thereof using a transformed lower eukaryotic host containing an example DNA sequence encoding the antibody or (functionalized) fragment thereof, wherein the antibody or (functionalized) fragment thereof is derived from a heavy chain immunoglobulin of Camelidae and is devoid of light chains, and wherein the lower eukaryotic host is a mould, preferably belonging to the genera Aspergillus or Trichoderma, or a yeast, preferably belonging to the yeast genera Saccharomyces, Kluyveromyces, Hansenula, or Pichia. The heavy chain fragment can contain at least the whole variable domain. A complementary determining region (CDR) different from the CDR belonging to the natural antibody ex Camelidae can be grafted on the framework of the variable domain of the heavy chain immunoglobulin. The catalytic antibodies can be raised in Camelidae against transition state molecules. The functionalized antibody or fragment thereof can comprise a fusion protein of both a heavy chain immunoglobulin from Camelidae or a fragment thereof and another polypeptide, e.g., an enzyme, preferably an oxido-reductase. Also provided are new products obtainable by a process as described, and compositions containing a product produced by a process as described, which composition may contain a new product as provided.
Owner:BAC IP
Human monoclonal antibodies specific for glypican-3 and use thereof
ActiveCN103596985AAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsBiological material analysisLymphatic SpreadImmunglobulin e
Described herein is the identification of human monoclonal antibodies that bind GPC3 or heparan sulfate (HS) chains on GPC3 with high affinity. The antibodies described herein are capable of inhibiting HCC cell growth and migration. Provided are human monoclonal antibodies specific for GPC3 or HS chains on GPC3, including immunoglobulin molecules, such as IgG antibodies, as well as antibody fragments, such as single-domain VH antibodies or single chain variable fragments (scFv). Further provided are compositions including the antibodies that bind GPC3 or HS chains on GPC3, nucleic acid molecules encoding these antibodies, expression vectors comprising the nucleic acids, and isolated host cells that express the nucleic acids. Methods of treating cancer and / or inhibiting tumor growth or metastasis are also provided. Further provided are methods of detecting cancer in a subject and confirming a diagnosis of cancer in a subject.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
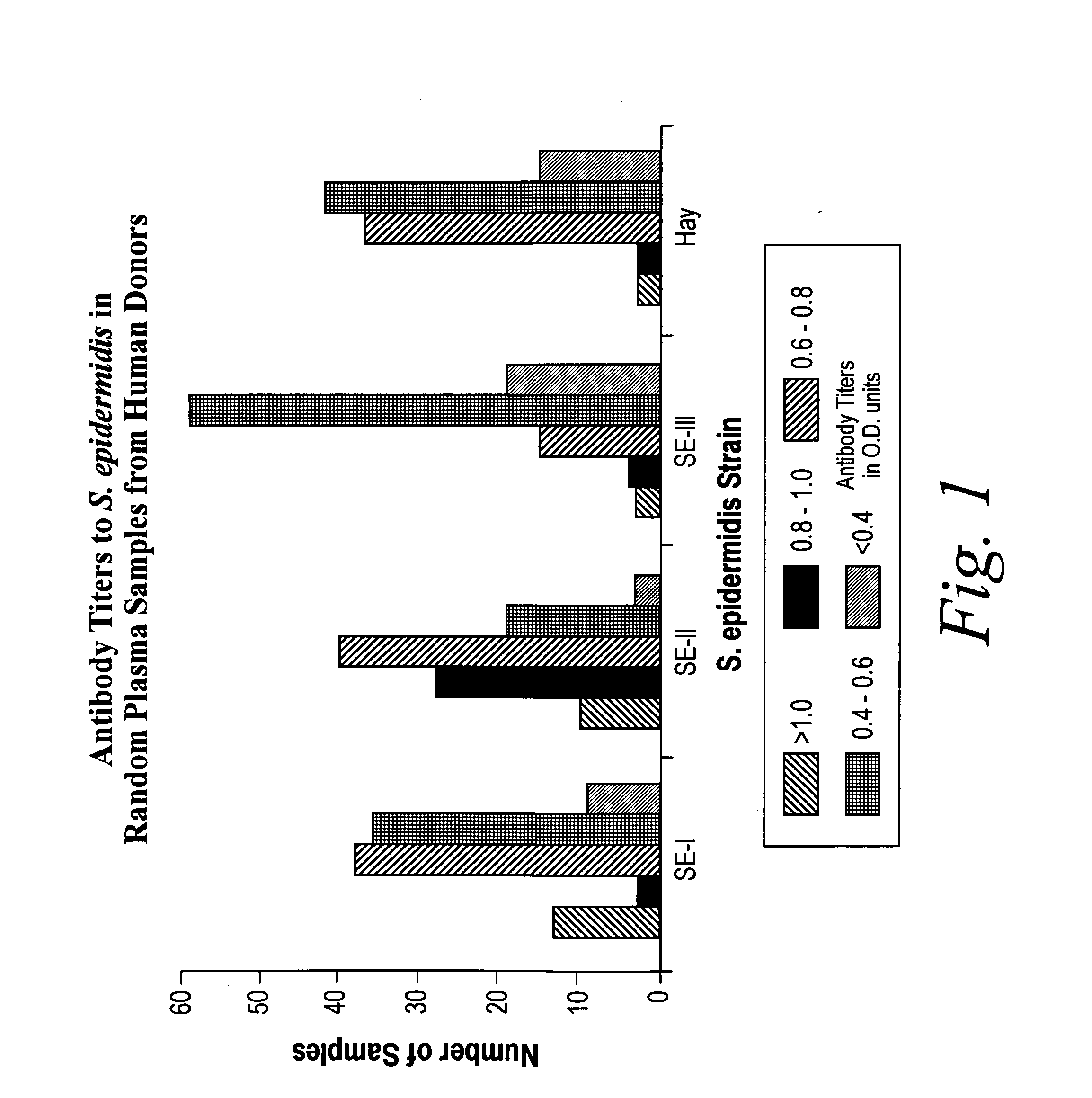
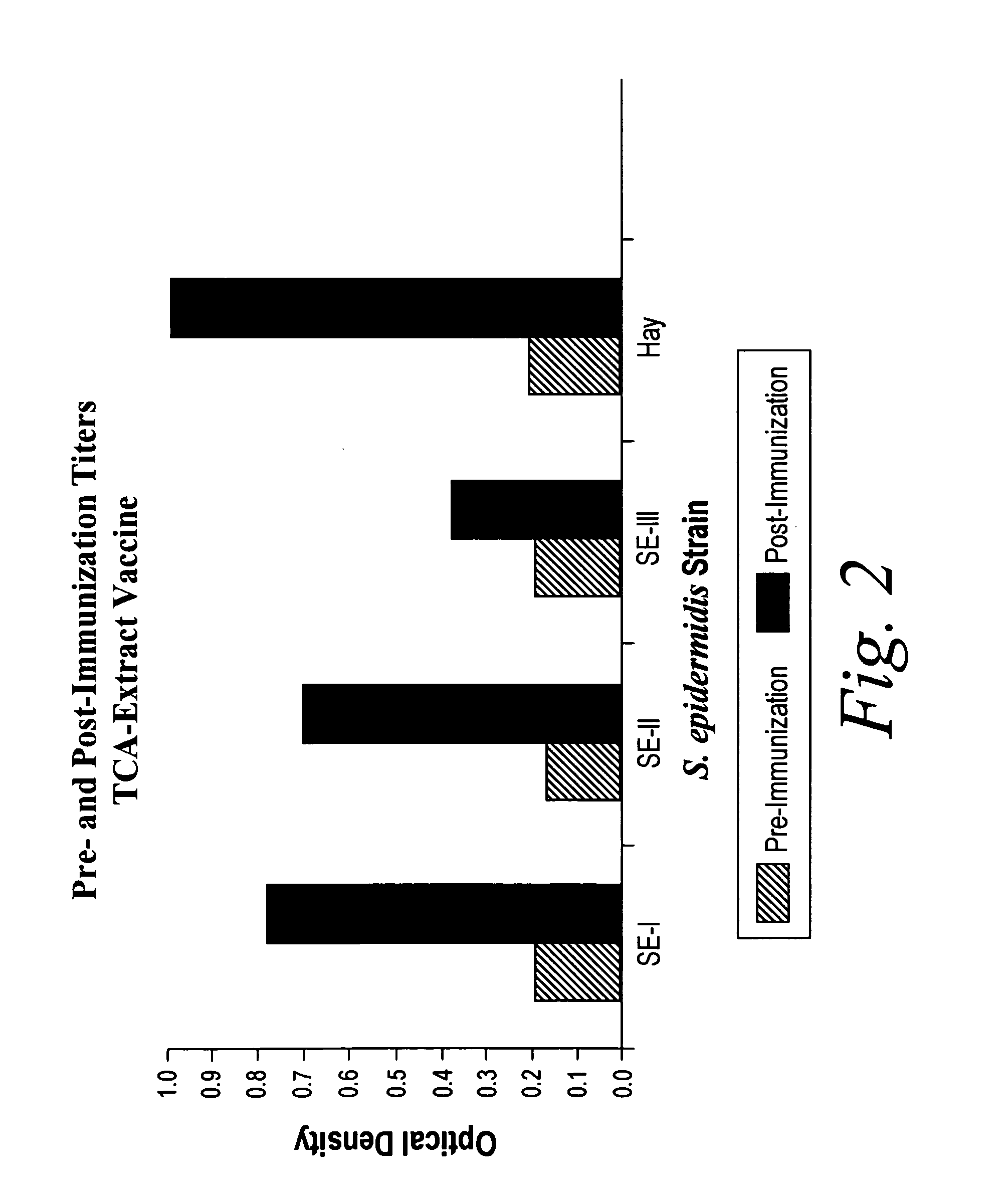
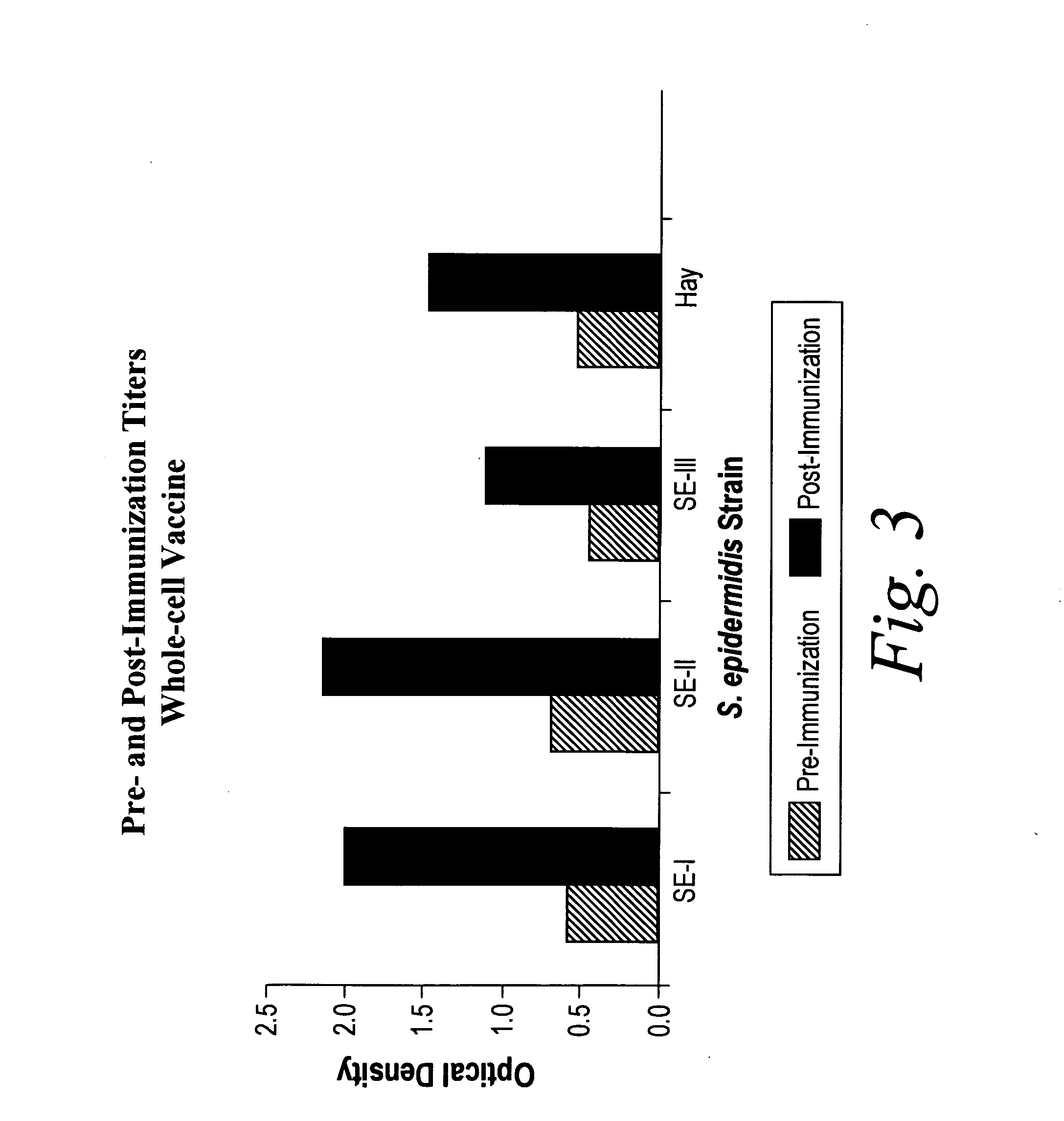
Isolated Broadly Reactive Opsonic Immunoglobulin for Treating a Pathogenic Coagulase-Negative Staphylococcus Infection
InactiveUS20080139789A1Immunoglobulins against animals/humansAntibody ingredientsAntigenImmunglobulin e
The invention describes the identification, making, and isolation of immunoglobulin and antigen useful for preventing, diagnosing, and treating staphylococcal infections. The invention further describes an in vivo animal model useful for testing the efficacy of pharmaceutical compositions, including pharmaceutical compositions of immunoglobulin and isolated antigen.
Owner:THE HENRY M JACKSON FOUND FOR THE ADVANCEMENT OF MILITARY MEDICINE INC
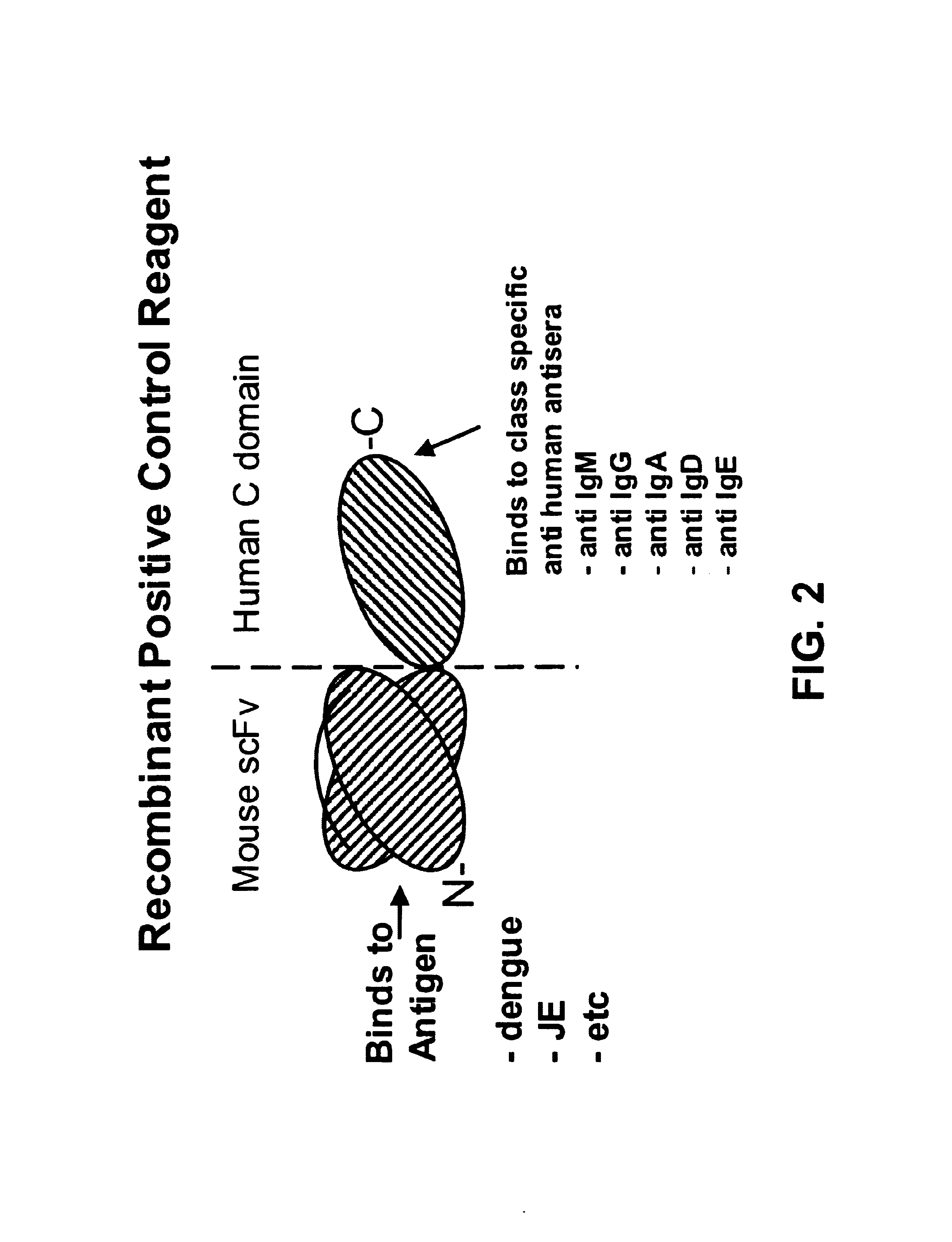
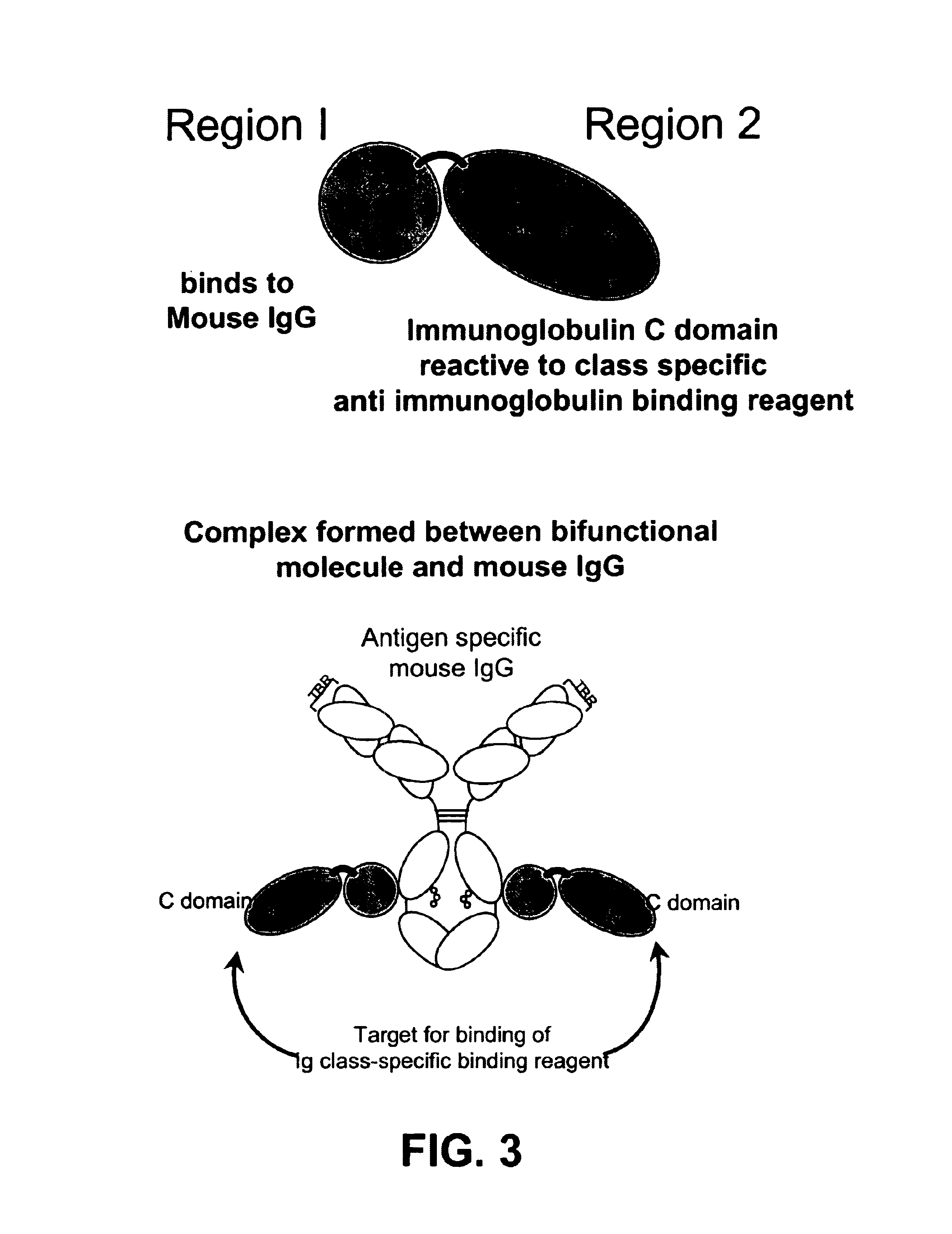
Bifunctional molecules
InactiveUS7026446B1Easy to produceAvoid inconvenienceAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsImmunoglobulins against bacteriaEpitopePositive control
The invention relates to a chimeric antibody conjugate comprising an antigen binding region of a non-human antibody and an immunoglobulin constant region which comprises at least one CH domain or epitope thereof, with the proviso that the constant region is not a naturally occurring FC fragment. A bifunctional molecule for use in labelling an antibody derived from a first species, the bifunctional molecule comprising a binding region which binds to the antibody of the first species or to one or more groups provided thereon, and a constant region derived from an antibody of a second species, the constant region comprising at least one CH domain or an epitope thereof. The present invention relates to bifunctional molecules and complexes which are useful as positive control reagents in antibody based diagnostic tests. The present invention also relates to polynucleotides encoding these bifunctional molecules, and to diagnostic assays involving the use of these molecules.
Owner:DIATECH PTY LTD
Method for extracting human immune globulin from component I+III or component III
ActiveCN101648998AAlleviate the tightness of plasma supplyAvoid pollutionImmunoglobulins against animals/humansPeptide preparation methodsSocial benefitsImmunglobulin e
The invention relates to a method for extracting human immune globulin from a component I+III or a component III, which can effectively extract human immune globulin from a component I+III or a component III so as to meet the demands of human immune globulin for people, and comprises the following steps: (1) dissolving the deposits of component I+III or component III; (2) removing the component I;(3) separating the component III; (4) separating a component II; (5) dissolving and filtering the component II; (6) ultrafiltering, dialyzing and concentrating; (7) purifying the component II; (8) purifying; and (9) ultrafiltering and dialyzing. The method is advanced, has simple process and can effectively separate the component II from the component I+III or the component III so as to further make the component II into a finished product of human immune globulin, and has very important realistic significance of relieving the short supply situation of domestic source plasma, not only sufficiently utilize raw materials but also prevent environmental pollution; therefore, the method has huge economic and social benefits.
Owner:BANGHE PHARMA CO LTD
Single variable domain antibodies against ox40l, constructs and therapeutic use
The present invention relates to immunoglobulin single variable domain sequences that are directed against (as de-fined herein) OX40L, as well as to compounds or constructs, and in particular proteins and polypeptides, that comprise or essentially consist of one or more such immunoglobulin single variable domain sequences. In particular these immunoglobulin single variable domain sequences can block binding of OX40L to OX40. The immunoglobulin single variable domains, compounds and constructs can be used for prophylactic, therapeutic or diagnostic purposes, such as for the treatment of inflammatory disease and / or disorder such as e.g. asthma, allergic asthma, chronic colitis, Crohn's disease, inflammatory bowel disease, and / or arthrosclerosis.
Owner:ABLYNX NV
Methods for producing immunoglobulins containing protection proteins in plants and their use
Owner:THE SCRIPPS RES INST
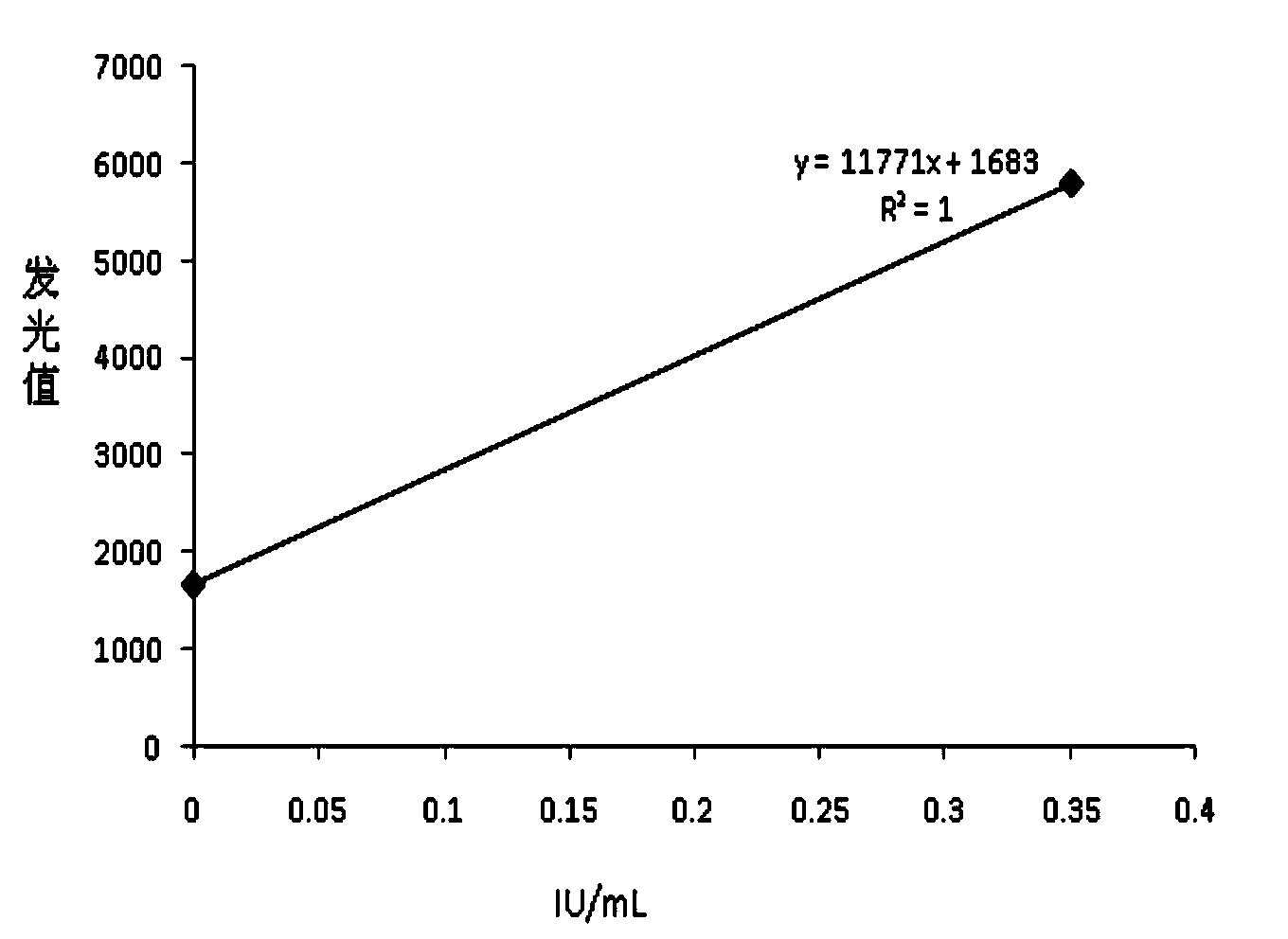
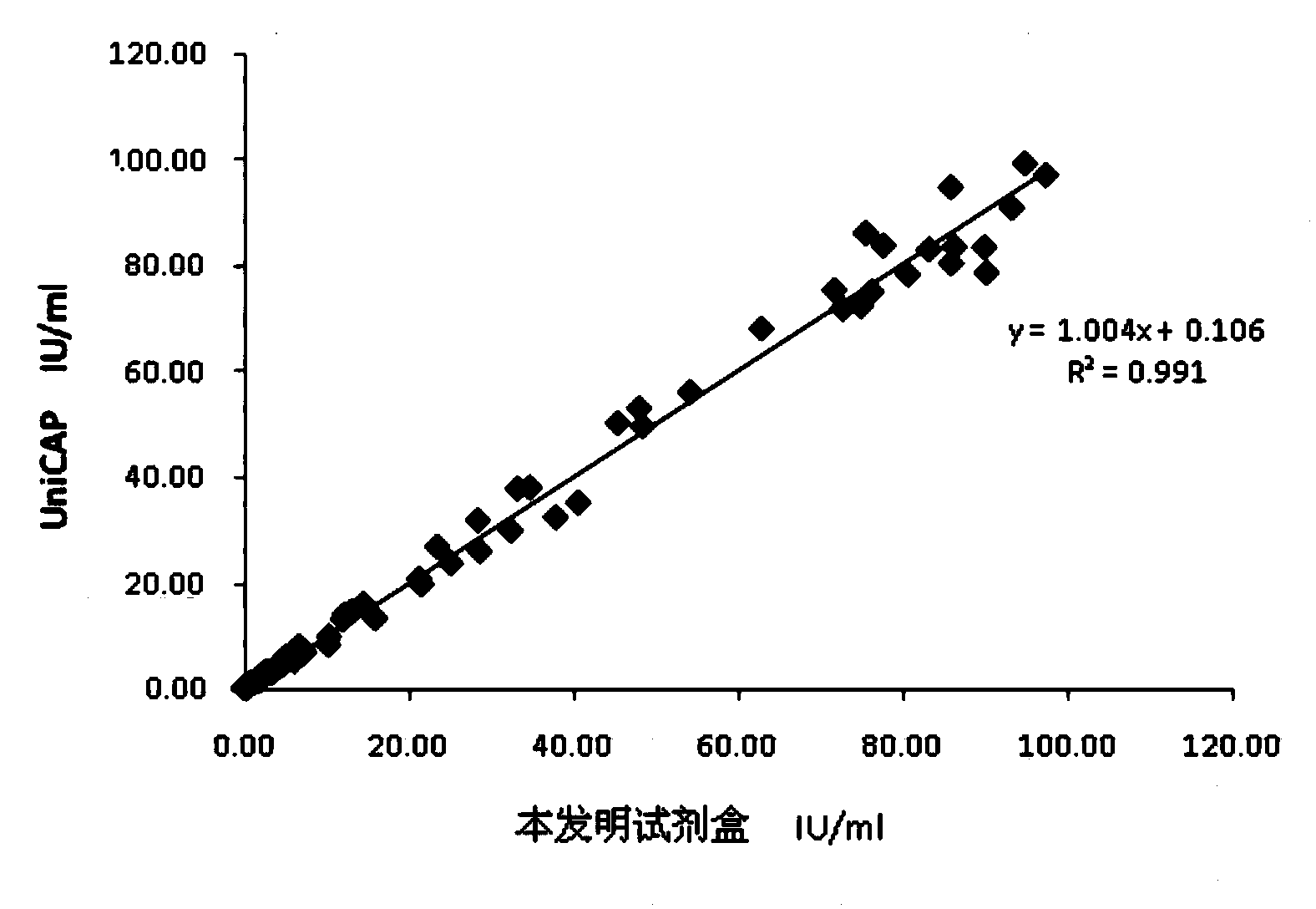
Chemiluminescence quantitative detection kit for food allergens, and preparation method and detection method thereof
ActiveCN103901215ANo pre-dilution requiredImprove accuracyDisease diagnosisBiological testingImmunglobulin eMicroparticle
Owner:SUZHOU HAOOUBO BIOPHARML
Methods of using immunoglobulin (Ig) compositions
InactiveUS20040241102A1Increase weightPromote effectivePowder deliverySerum immunoglobulinsDiseaseAntigen
The invention is directed to methods of using Ig compositions to prevent and / or treat humans, livestock and / or domesticated animals suffering from a variety of disorders. The Ig composition comprises a concentrated amount of one or more immunoglobulins selected from the group consisting of alpha, beta, and gamma globulins. Preferably, the Ig composition comprises other antibodies identified as providing an immune response and / or immune factors such as complement. The Ig composition preferably includes immunoglobulins specific to a variety of antigens.
Owner:CENT BIOMEDIA
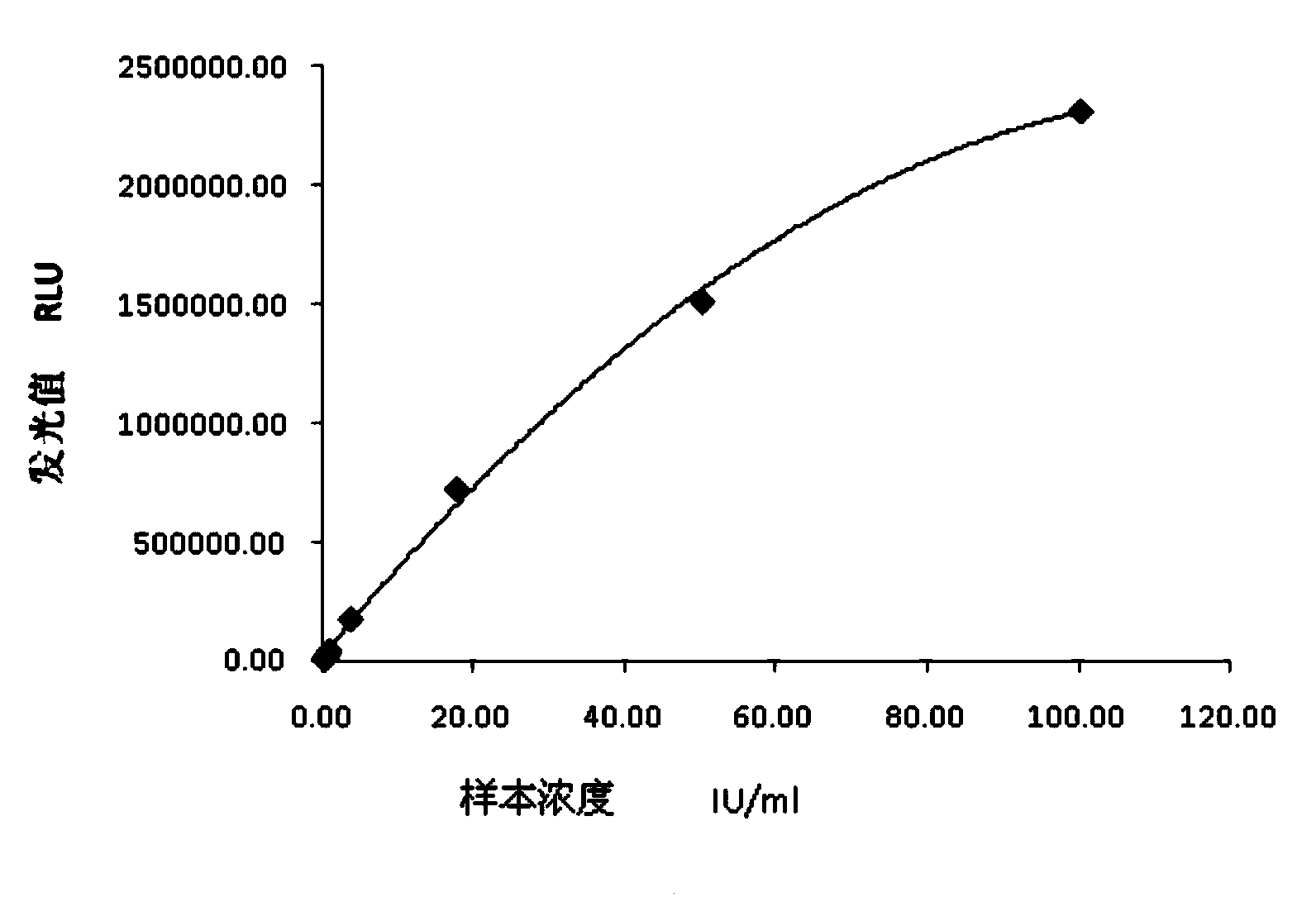
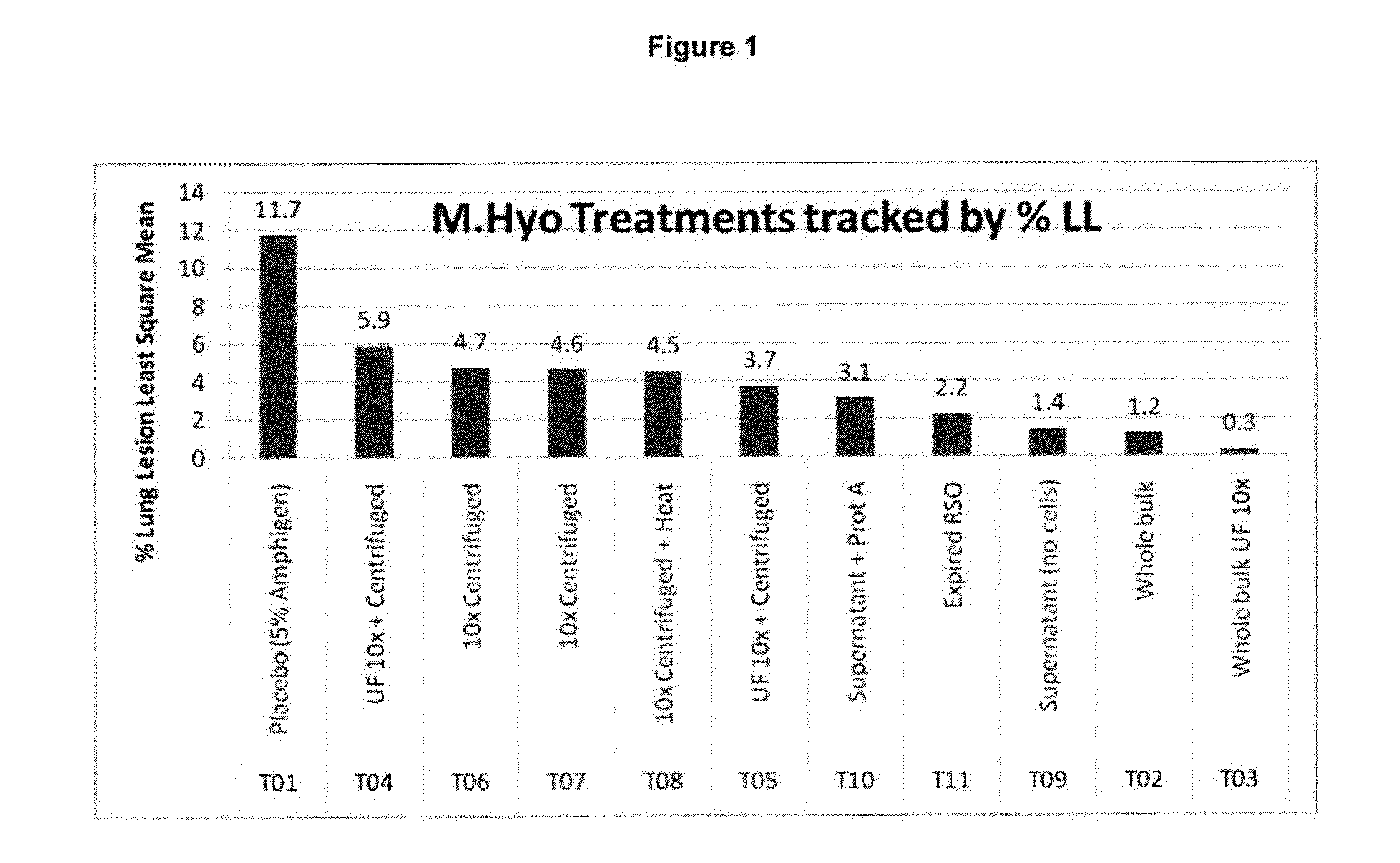
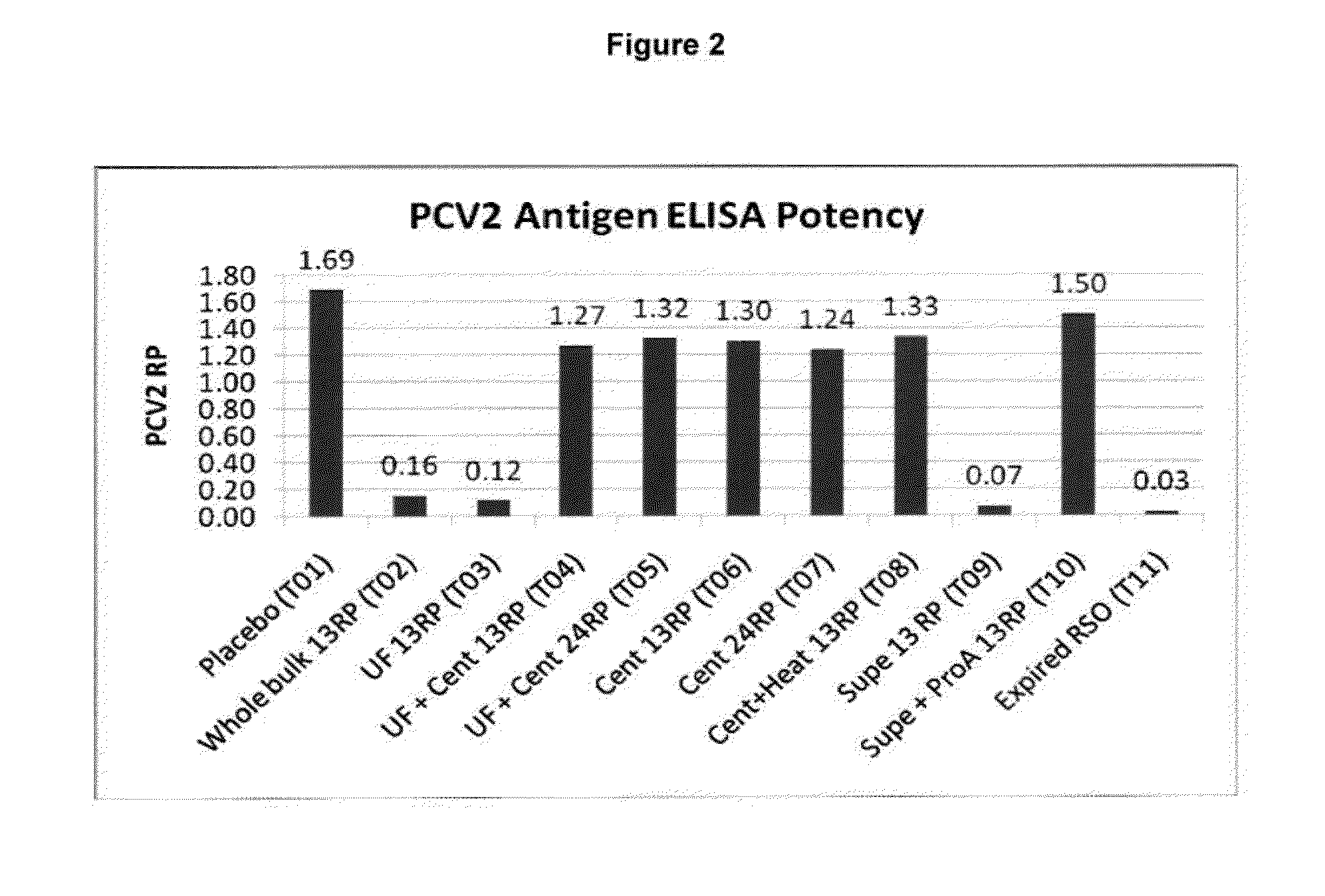
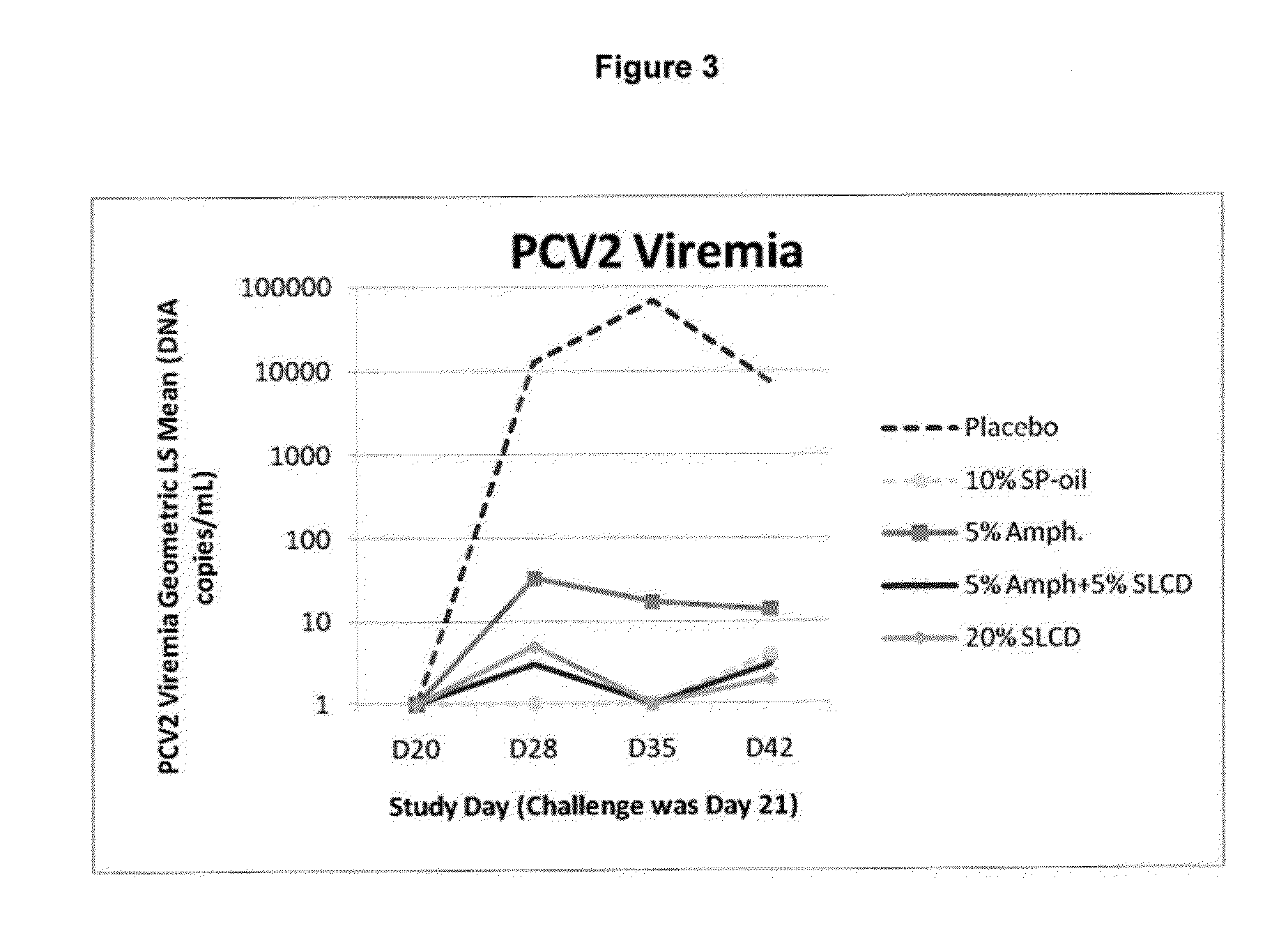
PCV/Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae combination vaccine
ActiveUS9125885B2Antibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsImmunglobulin eMycoplasma hyopneumoniae
This invention provides a multivalent immunogenic composition including a soluble portion of a Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae (M. hyo) whole cell preparation; and a porcine circovirus type 2 (PCV2) antigen, wherein the soluble portion of the M. hyo preparation is substantially free of both (i) IgG and (ii) immunocomplexes comprised of antigen bound to immunoglobulin.
Owner:ZOETIS SERVICE LLC
Fc-region variants with modified fcrn- and protein a-binding properties
ActiveUS20170342168A1Avoid systemic side effectsSenses disorderHybrid immunoglobulinsImmunglobulin eADAMTS Proteins
Herein is reported a heterodimeric polypeptide comprising a first polypeptide comprising in N-terminal to C-terminal direction at least a portion of an immunoglobulin hinge region, which comprises one or more cysteine residues, an immunoglobulin CH2-domain and an immunoglobulin CH3-domain, and a second polypeptide comprising in N-terminal to C-terminal direction at least a portion of an immunoglobulin hinge region, which comprises one or more cysteine residues, an immunoglobulin CH2-domain and an immunoglobulin CH3-domain, wherein the first polypeptide comprises the mutations Y349C, T366S, L368A and Y407V (hole-chain) and the second polypeptide comprises the mutations S354C and T366W (knob-chain), and wherein the first polypeptide (hole-chain) comprises the mutations i) I253A or I253G, and ii) L314A or L314G or L314D, and wherein the first polypeptide and the second polypeptide are connected by one or more disulfide bridges, and wherein the CH3-domain of the first polypeptide and the CH3-domain of the second polypeptide both bind or both do not bind to protein A (numbering according to the Kabat EU index).
Owner:F HOFFMANN LA ROCHE & CO AG
Support for affinity chromatography and method for isolating immunoglobulin
InactiveCN103270044ASolid sorbent liquid separationPeptide preparation methodsImmunglobulin eAntibody Affinity Chromatography
Provided are a support for affinity chromatography, which has excellent alkali resistance, and a method for isolating immunoglobulin. The support for affinity chromatography is a support, onto which a protein ligand represented by general formula (1): R-R2 has been immobilized. In general formula (1), R represents a polypeptide comprising 4 to 30 amino acid residues and containing an amino acid sequence represented by ATK or ASK, and R2 represents a polypeptide comprising 50 to 500 amino acid residues and containing an immunoglobulin-binding domain comprising an amino acid sequence represented by SEQ ID NO: 1 or 2, a partial sequence thereof, or an amino acid sequence having at least 70% homology therewith. (The end of R2 binding to R is the C- or N-terminus of the immunoglobulin-binding domain.)
Owner:JSR CORPORATIOON +1
Immunoadhesin comprising a glycorprotein v1 domain
ActiveUS20050079541A1Avoid stickingPrevents arterial thrombosisOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderImmunglobulin eFc domain
The present invention provides a fusion protein comprising (a) the extracellular domain of glycoprotein VI or a variant thereof that is functional for binding to collagen and (b) the Fc domain of an immunoglobulin or a function-conservative part thereof, characterised by a polypeptide chain having an amino acid sequence as shown in FIG. 7 and whereby the fusion protein is obtainable by a process which provides the fusion protein in the form of a specific dimer.
Owner:ADVANCECOR
Support for affinity chromatography and method for isolating immunoglobulin
InactiveUS20140005357A1Peptide/protein ingredientsSolid sorbent liquid separationImmunglobulin eImmobilized protein
Provided are a support for affinity chromatography which has excellent alkali resistance, and a method for isolating immunoglobulin. A support for affinity chromatography, containing an immobilized protein ligand represented by the following formula (1):R—R2 (1)wherein R represents a polypeptide consisting of 4 to 30 amino acid residues that contains an amino acid sequence represented by ATK or ASK; and R2 represents a polypeptide consisting of 50 to 500 amino acid residues containing an immunoglobulin-binding domain consisting of an amino acid sequence represented by SEQ ID NO: 1 or SEQ ID NO: 2, the partial sequence thereof, or an amino acid sequence having 70% or more identity to these sequences; with the proviso that a terminus at which R2 binds to R is C-terminus or N-terminus of the immunoglobulin-binding domain.
Owner:JSR CORPORATIOON +1
Functional humanization of complementarity determining regions (CDRS)
InactiveUS20100197896A1Maximizing numberAffecting specificityImmunoglobulinsFermentationComplementarity determining regionImmunglobulin e
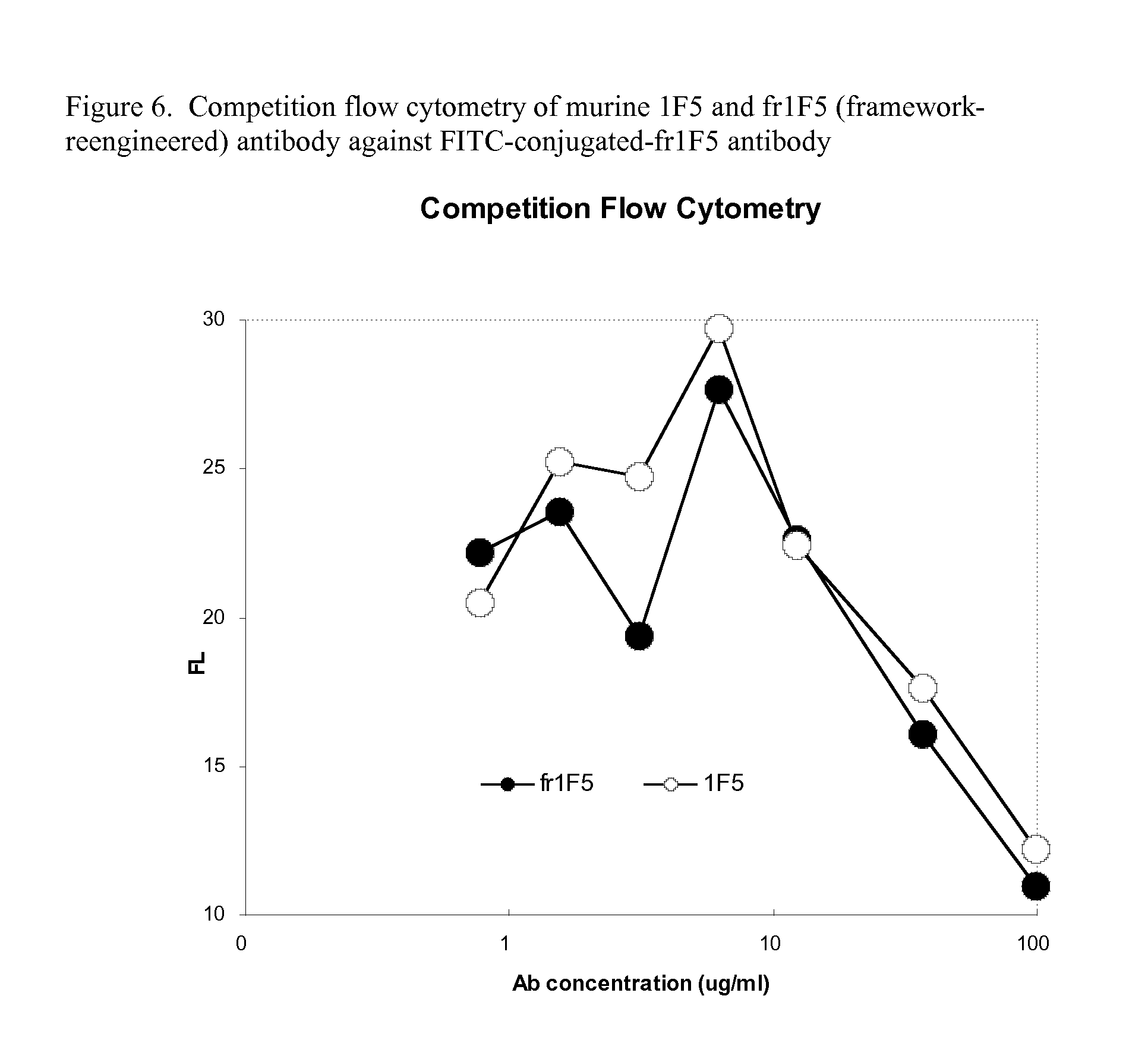
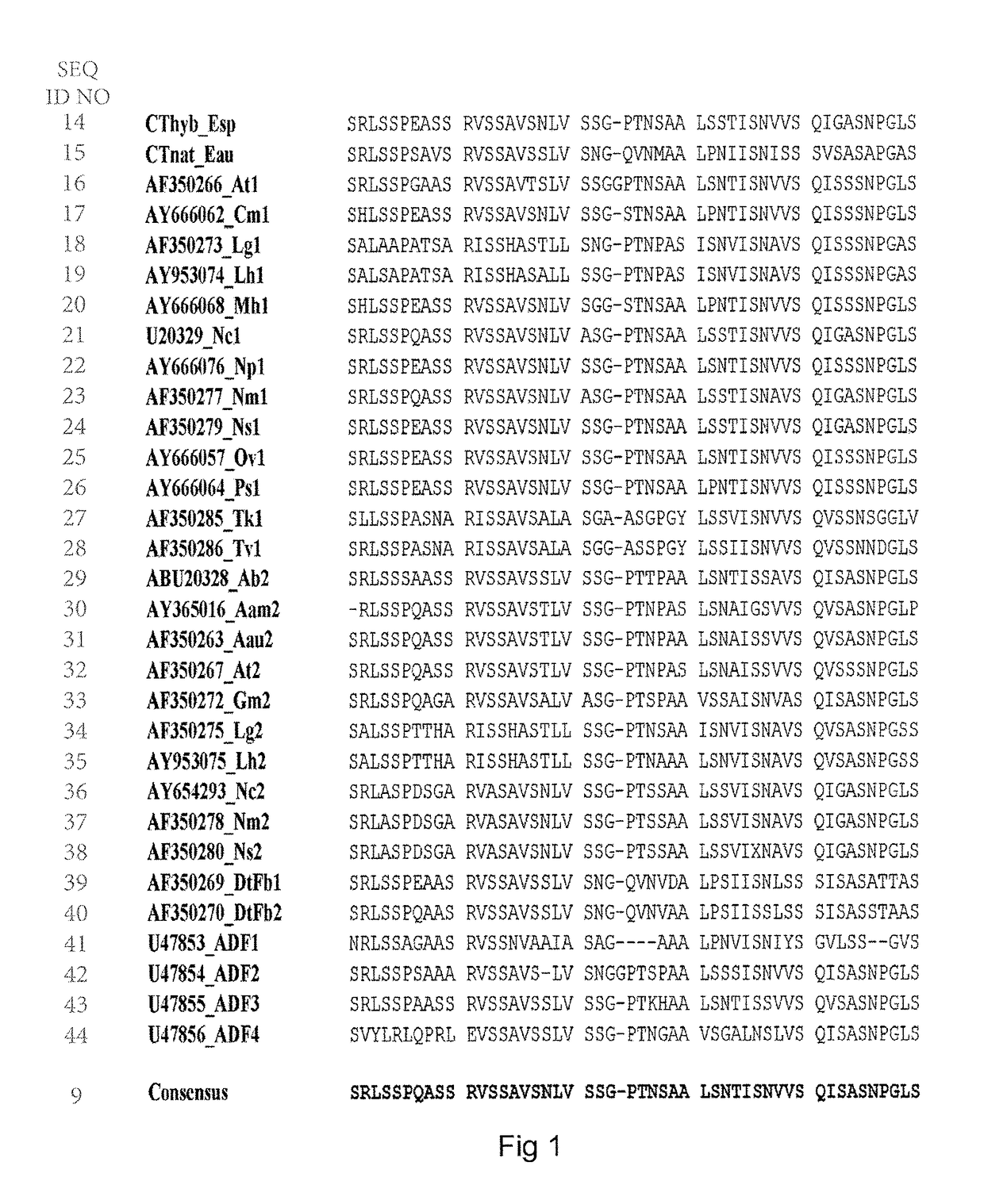
Current humanization approaches for immunoglobulins focus mostly on modifying the framework regions into human sequences. Herein is provided a method for humanizing antibody complementarity-determining regions (CDRs) through functional humanization to reduce the potential immunogenicity of non-human CDR-containing antibodies. CDRs with high sequence homology to the parent CDR are identified from a database of human CDR sequences. One or more human CDRs that are highly homologous to the parent CDR sequence can be used to replace the corresponding CDRs of murine immunoglobulins (or their humanized, or re-engineered versions). Human CDRs that improve or have minimal effects on the antigen binding affinity and specificity are adopted.
Owner:SINOMAB BIOSCI
Immunoglobulins containing protection proteins and their use
InactiveUS6808709B1Cell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsVaccinesTherapeutic antibodyImmunglobulin e
The immunoglobulins of the present invention are useful therapeutic immunoglobulins against mucosal pathogens such as S. mutans. The immunoglobulins contain a protection protein that protects the immunoglobulins in the mucosal environment. The invention also includes the greatly improved method of producing immunoglobulins in plants by producing the protection protein in the same cell as the other components of the immunoglobulins. The components of the immunoglobulin are assembled at a much improved efficiency. The method of the invention allows the assembly and high efficiency production of such complex molecules. The invention also contemplates he production of immunoglobulins containing protection proteins in a variety of cells, including plant cells, that can be selected for useful additional properties. The use of immunoglobulins containing protection proteins a therapeutic antibodies against mucosal and other pathogens is also contemplated.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Spider silk fusion protein structures incorporating immunoglobulin fragments as affinity ligands
ActiveUS9856308B2Promote regenerationStable structureConnective tissue peptidesAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsImmunglobulin eSpider Proteins
A recombinant fusion protein comprising the moieties Band CT, and optionally REP, wherein B is comprising at least one immunoglobulin fragment, which provides the capacity of selective interaction with an organic target; CT is a moiety of from 70 to 120 amino acid residues and is derived from the C-terminal fragment of a spider silk protein; and REP is a moiety of from 70 to 300 amino acid residues and is derived from the repetitive fragment of a spider silk protein.
Owner:SPIBER TECHNOLOGIES AB
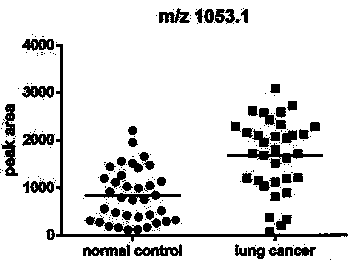
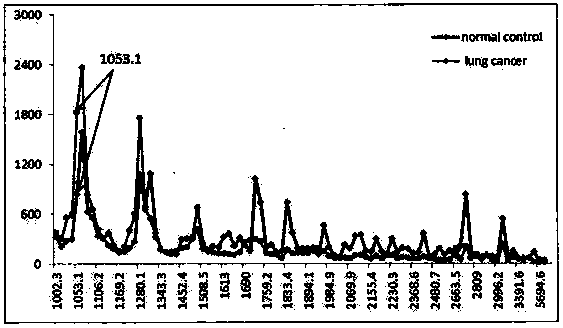
Application of urine immunoglobulin kappa chain C region protein and polypeptide fragments thereof in lung adenocarcinoma
The invention provides application of urine immunoglobulin kappa chain C region protein (Immunoglobulin Kappa Chain C Region, IGKC) and polypeptide fragments thereof in lung adenocarcinoma, and in particular relates to application of the urine immunoglobulin kappa chain C region protein and the polypeptide fragments thereof in preparation of a preparation for detecting and auxiliary diagnosis of the lung adenocarcinoma. Researches confirm that compared with a normal control and a lung adenocarcinoma patient group, specific expression of the urine immunoglobulin kappa chain C region protein inurine of a lung adenocarcinoma patient is up regulated, and the urine immunoglobulin kappa chain C region protein can be used for detection and auxiliary diagnosis of the lung adenocarcinoma. The advantages of non-invasive acquisition, large-scale repeated sampling, and convenient preservation of a urine specimen are played, and the urine specimen is used to detect the urine immunoglobulin kappa chain C region protein and the polypeptide fragments thereof.
Owner:张曼
Fused protein containing cFms extracellular fragments, preparation method and applications of fused protein with cFms extracellular fragments
InactiveCN103044555AReduce or inhibit the formation ofReduced and inhibited releaseNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsImmunologic disordersLymphatic Spread
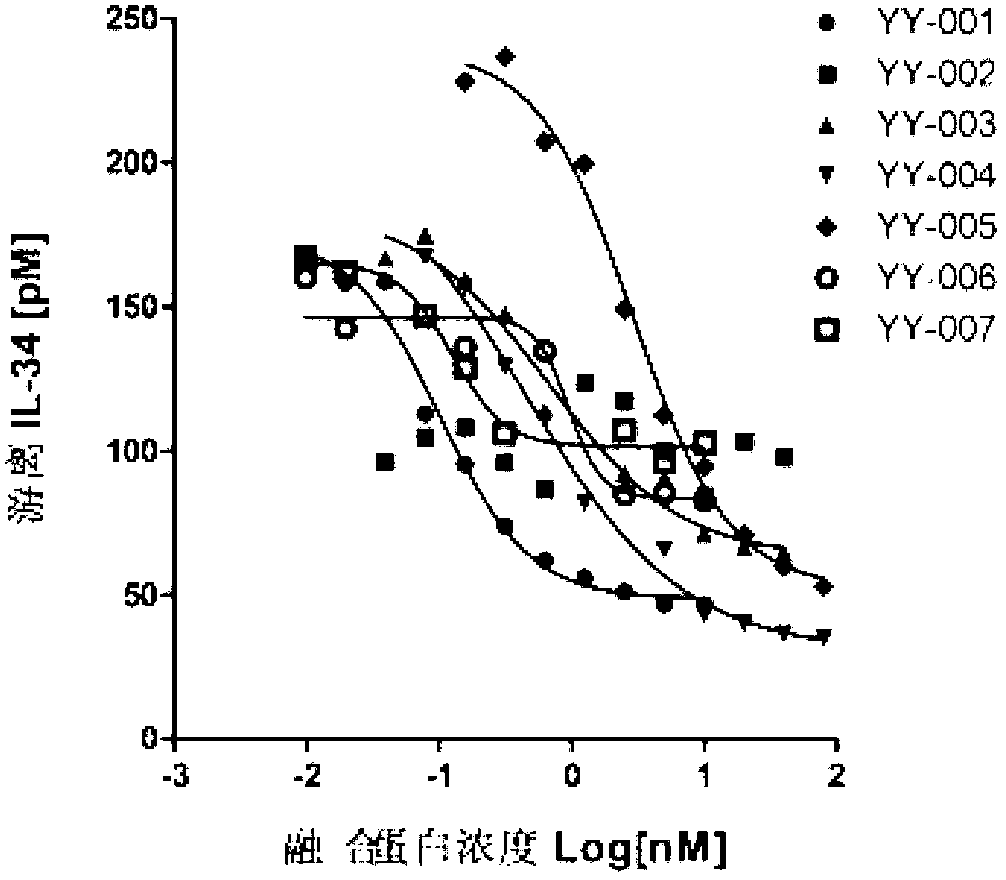
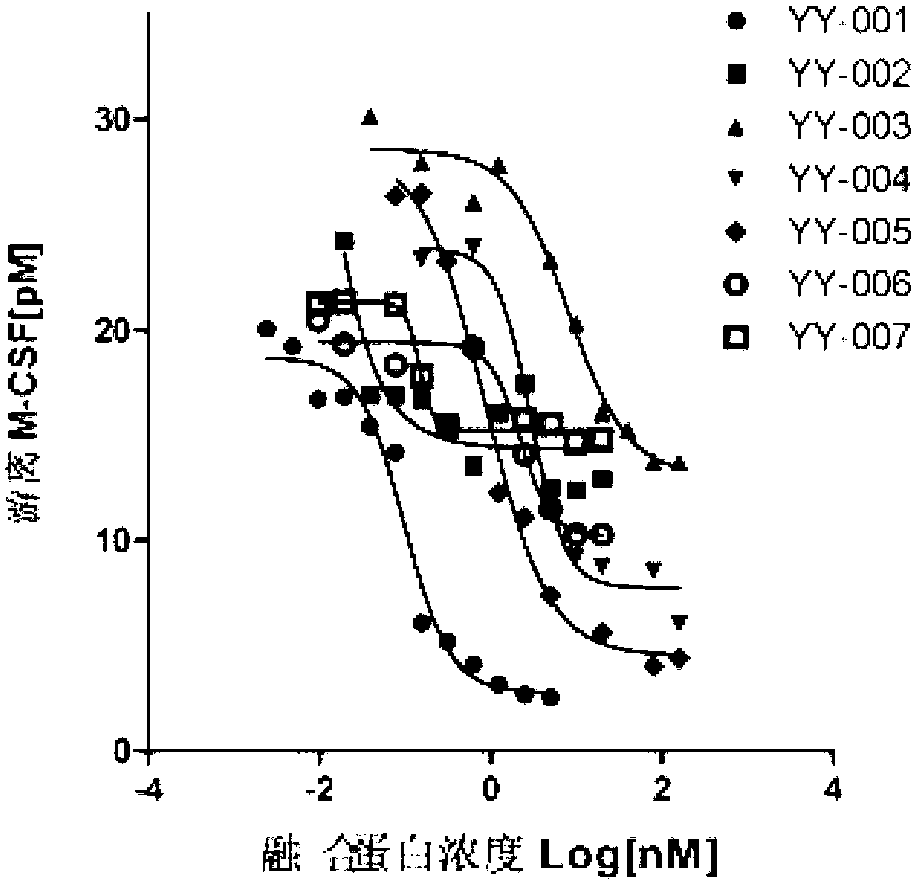
The invention provides a fused protein with extracellular fragments of a macrophage stimulating factor receptor (cFms). The fused protein is formed by connecting the cFms extracellular fragments and human immunoglobulin Fc by a connecting peptide and is named as cFmsECD-Fc. The cFms extracellular fragments are composed of at least two of five immunoglobulin (IgG) extracellular structure domains. The formed fused protein comprises YY-001, YY-002, YY-003, YY-004, YY-005, YY-006 and YY-007. The fused protein provided by the invention has functions of combining interleukin-34 (IL-34), combining the macrophage stimulating factor receptor (M-CSF) and blocking the combination of IL-34 / M-CSF ligand and common receptor cFms, and is suitable for treating diseases caused by the IL-34 / M-CSF under an abnormal condition. The fused protein is promising in the treatment on autoimmune diseases, inflammatory diseases, osteoporosis and tumor. And the fused protein is used for preparing medicines capable of inhibiting the inflammatory diseases, medicines capable of inhibiting the osteoporosis caused by osteoclast or medicines capable of inhibiting the growth and metastasis of the tumor.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
Treatment of mucositis with immunoglobulin
ActiveUS20150030613A1Relieve symptomsWound quicklyAntibacterial agentsAntimycoticsImmunglobulin eSecretory component
Owner:CSL BEHRING AG +1
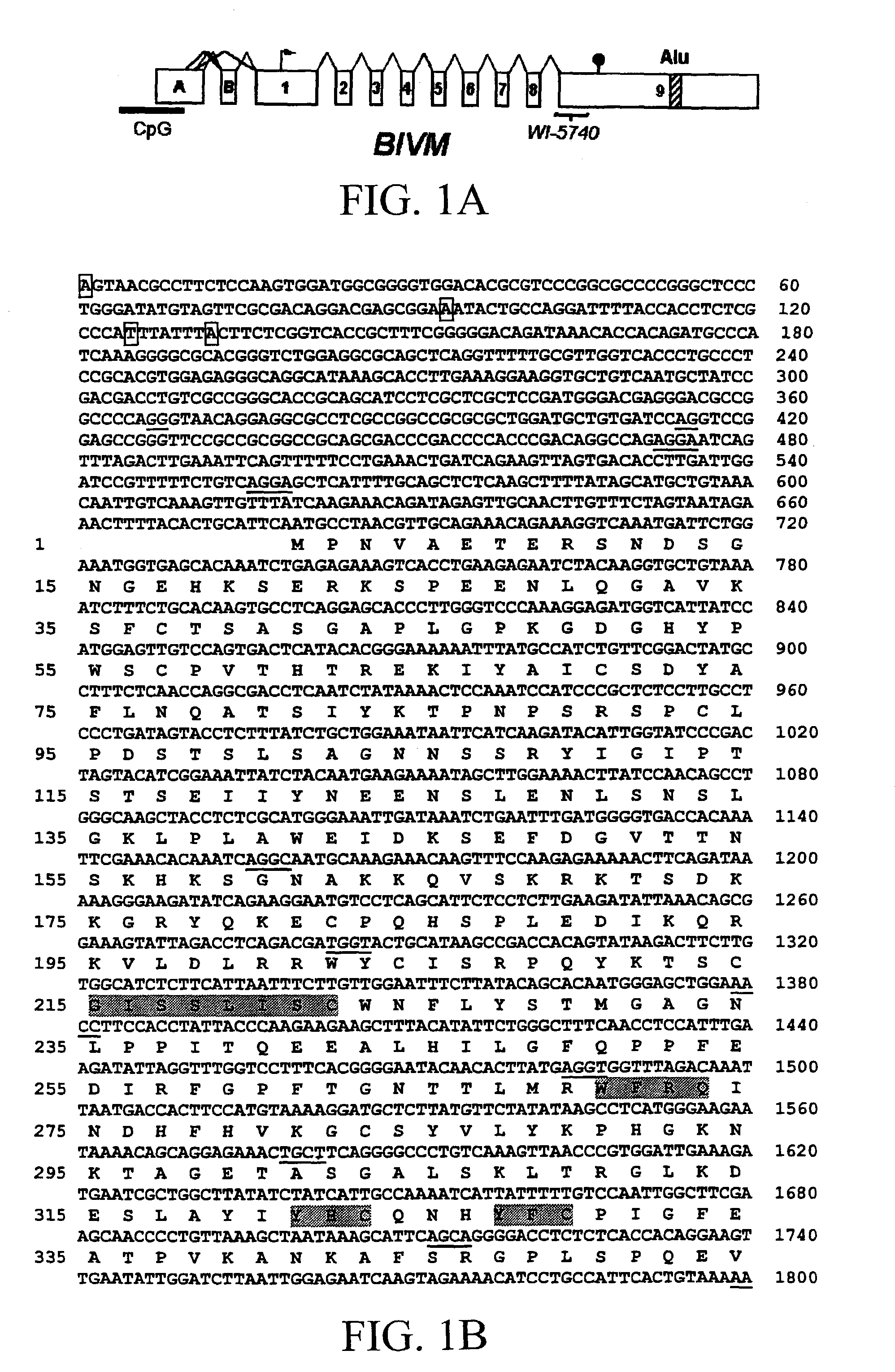
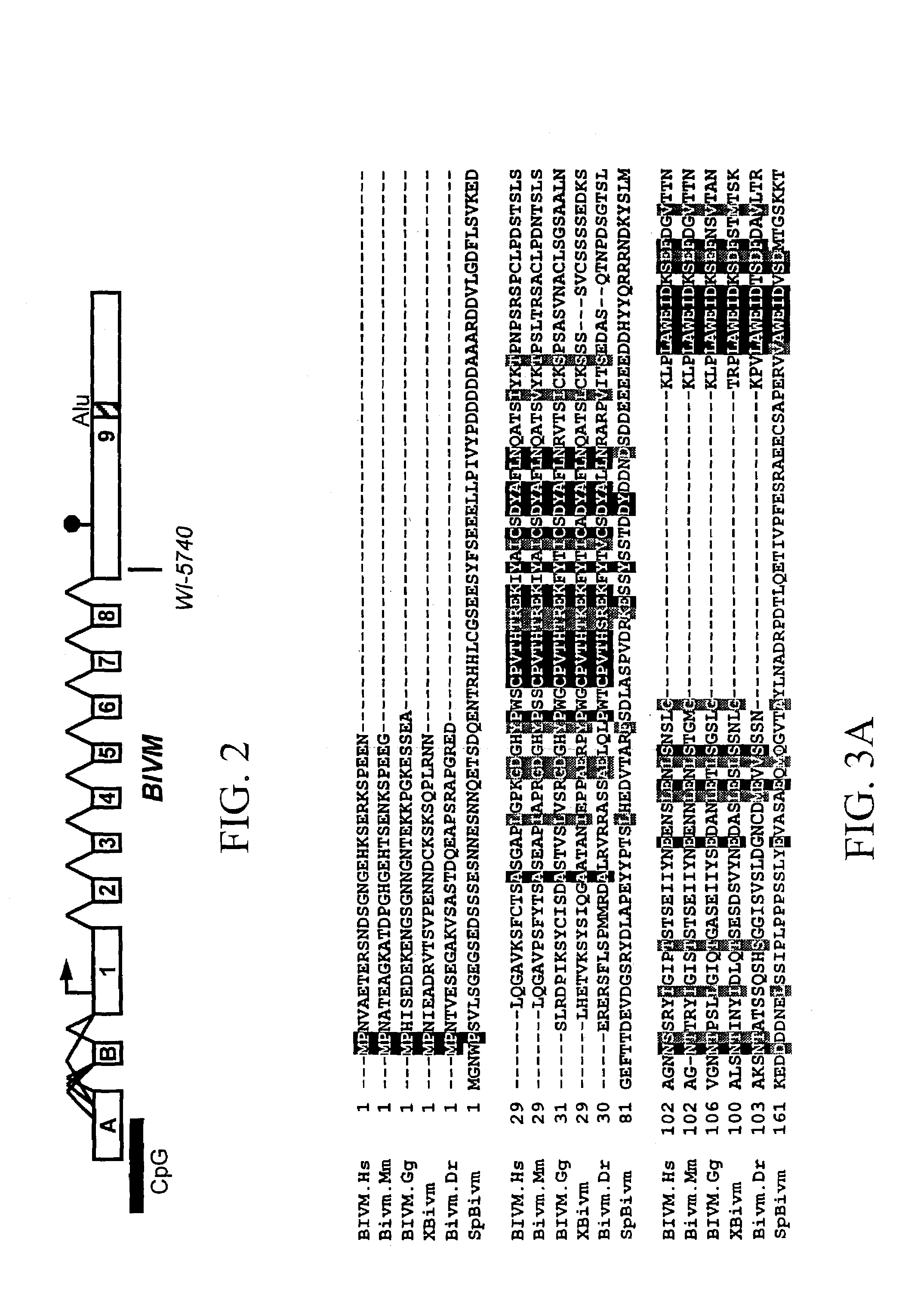
BIVM (basic, immunoglobulin-like variable motif-containing) gene, transcriptional products, and uses thereof
The subject invention provides polynucleotide sequences, designated BIVM, and transcriptional / translational products obtained from the polynucleotide sequences of the invention. The subject invention also provides polynucleotide and polypeptide sequences provided by SEQ ID NOs:1–28. Also provided are methods of detecting the presence of BIVM nucleic acids or polypeptides in samples suspected of containing BIVM genes, BIVM transcriptional products, or BIVM translational products. These methods are also useful for the detection of BIVM orthologs. Other embodiments provide polypeptide and / or nucleic acid vaccines for the induction of an immune response to in an individual. Kits for detecting the presence of BIVM genes, orthologs thereof, BIVM polypeptides, or BIVM transcriptional products are also provided.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTH FLORIDA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com